- 1School of Nursing, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China
- 2Department of Nursing, Beijing Sunshine Lu-Tong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China
- 4Department of Clinical Laboratory, Tianjin University Central Hospital, Tianjin, China
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common chronic liver condition globally, spanning a spectrum from simple steatosis to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and progressive fibrosis. Inflammation and metabolic dysregulation play key roles in its pathogenesis. Accordingly, inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers have gained increasing attention as potential tools for non-invasive diagnosis and disease staging.
Objective: This scoping review aimed to synthesize current evidence on the diagnostic performance of inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers for NAFLD, with a focus on their potential application in early screening and disease stratification.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed and CNKI databases for relevant peer-reviewed literature published up to August 2024. The search strategy combined MeSH terms and free-text keywords, and study selection was guided by the Population–Concept–Context (PCC) framework. Methodological quality was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale and AHRQ criteria.
Results: Fifteen eligible studies (11 case-control, 2 cohort, 1 cross-sectional, and 1 retrospective study) were included, yielding 18 candidate biomarkers. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index was commonly associated with early-stage NAFLD screening; cytokeratin-18 (CK18) was linked to NASH detection, while adiponectin and osteopontin (OPN) were related to liver fibrosis. Additionally, inflammatory indices such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), and systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) showed clinical promise due to their accessibility and low cost.
Conclusion: Inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers provide valuable non-invasive insights into the diagnosis and staging of NAFLD. The integration of multiple biomarkers may enhance diagnostic accuracy and support stratified management strategies. However, further validation is needed to establish standardized thresholds and confirm clinical utility across diverse populations.
1 Introduction
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a chronic liver condition characterized by diffuse hepatic steatosis in individuals without significant alcohol consumption or other identifiable causes of liver disease. It represents a continuous spectrum ranging from simple steatosis (NAFL) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In recent years, NAFLD has become one of the most common forms of chronic liver disease globally and is closely associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome (1, 2).
Currently, imaging modalities such as ultrasound, CT, and MRI are commonly employed for the initial assessment of NAFLD. However, their diagnostic performance is limited by suboptimal sensitivity and specificity. Liver biopsy remains the diagnostic gold standard but is constrained in large-scale applications due to its invasiveness, sampling variability, and risk of complications (3). Consequently, there is growing interest in developing sensitive, specific, non-invasive, and reproducible biomarkers for early detection(The term “non-invasive” used in this review follows the common definition in the field of hepatology. Although venous blood sampling involves a minor invasive procedure, it does not involve tissue extraction or imaging intervention, and is typically considered non-invasive compared to liver biopsy), disease classification, and fibrosis risk assessment in NAFLD.
The pathogenesis of NAFLD involves a complex interplay of inflammatory responses, lipid metabolism disorders, oxidative stress, immune dysregulation, and cellular injury (4). Biomarkers such as inflammatory cytokines, adipokines, liver injury indicators, immune cells, and their derived inflammatory ratios have shown potential clinical value in identifying disease severity and different stages of NAFLD (5, 6).
Although previous studies have preliminarily explored these aspects, the available evidence remains fragmented, inconsistently categorized, and often lacks standardized thresholds. There is a need for systematic integration, especially to identify the most promising biomarkers and define their stage-specific clinical value in practical diagnostic pathways.
This study adopts a scoping review approach to systematically identify and summarize recent evidence on inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers related to the non-invasive diagnosis of NAFLD. The aim is to pinpoint key molecules, categorize their potential roles in early screening, disease classification, and fibrosis prediction, and provide a theoretical basis for establishing a multi-biomarker screening system to advance the precision identification and personalized management of NAFLD.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design
This study was designed as a scoping review following the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines (7), The protocol of this study was registered on Open Science Framework (OSF)(https://osf.io/u4nw7). The methodological framework proposed by Daudt et al. was adopted to comprehensively examine the current status and characteristics of research on inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers in the non-invasive diagnosis of NAFLD.
2.2 Research questions
This review focuses on two core questions:
1. Do inflammatory or metabolic biomarkers hold diagnostic value for NAFLD?
2. Which biomarkers have shown notable performance in NAFLD screening, classification, or fibrosis risk assessment in current studies?
2.3 Information sources and search strategy
A comprehensive literature search was conducted across multiple databases, with tailored search terms for each platform: Chinese databases included CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP; English databases included PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Embase. The strategy combined subject headings and free-text terms using Boolean operators. Reference lists were also manually searched using snowballing techniques to identify additional systematic reviews. The search covered publications up to August 31, 2024. For example, the PubMed search strategy is detailed in Table 1. The search strategies for other databases can be found in Supplementary Material 1.
2.4 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Based on the PCC framework for scoping reviews (8)—Participants, Concept, and Context—the inclusion criteria were:
1. Participants: Patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
2. Concept: Studies involving inflammatory or metabolic biomarkers.
3. Context: Clinical practice or studies with original data.
Exclusion criteria were:
1. Non-original research (e.g., narrative reviews, systematic reviews, editorials, letters without original data, conference abstracts, study protocols).
2. Non-English and non-Chinese articles.
3. Duplicate publications.
4. Full text not available.
2.5 Study selection and data extraction
All retrieved records were imported into EndNote for deduplication. A two-stage screening process was then conducted. In the first round, two reviewers independently screened titles and abstracts. In the second round, full texts were reviewed. Disagreements were resolved through discussion or consultation with a third reviewer. Data extracted included author, publication year, country/region, study design, participant characteristics, sample size, type of biomarker, and its association with NAFLD.
2.6 Quality assessment
Two reviewers independently assessed the methodological quality of included studies. The Cohen’s Kappa (κ) between the reviewers was 0.80, indicating almost perfect agreement (9).Cohort and case-control studies were evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (10), which includes three domains: selection, comparability, and exposure assessment, with a maximum score of 9. Scores of 0–3, 4–6, and 7–9 were interpreted as indicative of low, moderate, and high methodological quality, respectively.
Cross-sectional studies were evaluated using the quality assessment tool developed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) (11), comprising 11 items. Total scores of 0-3, 4-7, and 8–11 indicated low, medium, and high quality, respectively (12). Any disagreements were resolved through discussion or by a third reviewer.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search and selection
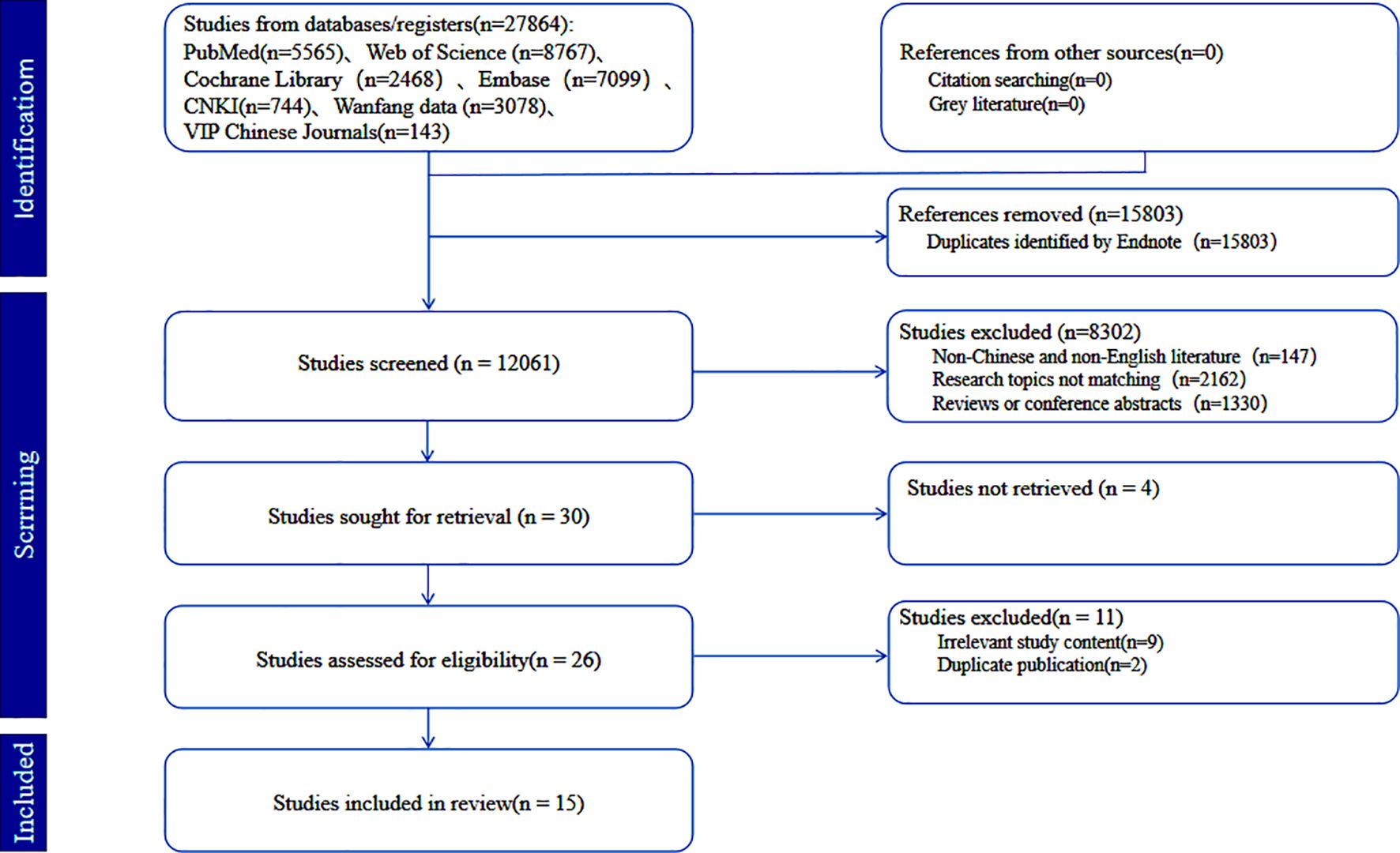
A total of 27,864 studies were retrieved from seven databases: CNKI (n=744), Wanfang (n=3,078), VIP (n=143), PubMed (n=5,565), Web of Science (n = 8,767), Cochrane Library (n=2,468), and Embase (n=7,099). After removing duplicates, 12,061 articles remained for screening. Based on pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria, 15 studies were finally included (6 in Chinese and 9 in English). The study selection process is shown in the PRISMA flow diagram (13) (Figure 1).
3.2 Basic characteristics of included studies
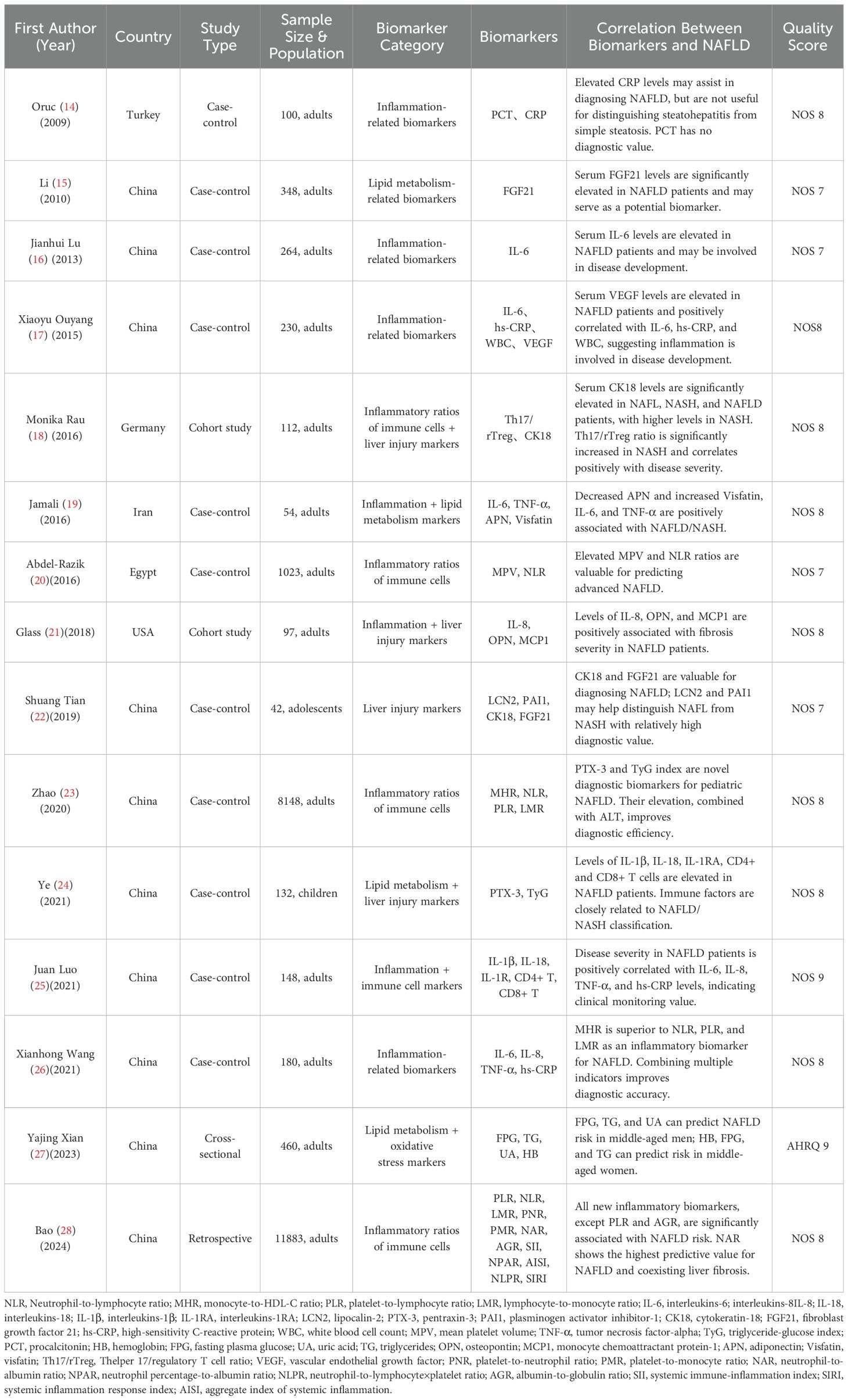
The 15 studies were published between 2009 and 2024 and conducted in China (n =10), Turkey (n=1), Germany (n=1), Iran (n=1), Egypt (n=1), and the United States (n= 1). Most were case-control studies (n=11), with additional cohort studies (n=2), one cross-sectional study, and one retrospective study. Sample sizes ranged from 42 to 11,883 participants, including both adults and children. All included studies scored ≥7 in methodological quality assessments, indicating generally high quality. To unify the analytical logic, biomarkers were categorized into five functional groups: Inflammatory markers: CRP, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-18;Immune cell-derived ratios: NLR, MHR, SII, AISI, Th17/Treg;Metabolic markers: TyG index, FGF21, adiponectin, visfatin;Liver injury/inflammatory markers: CK18, OPN, PTX3, LCN2;Oxidative stress markers: Serum uric acid, hemoglobin.Detailed information is presented in Table 2.
3.3 Summary of biomarker types and diagnostic associations
Findings from the included studies suggest that inflammatory, metabolic, and liver injury biomarkers—as well as derived immune-inflammatory ratios—have potential clinical utility in identifying and stratifying different stages of NAFLD.
Inflammatory biomarkers such as IL-6, IL-1β, IL-18, TNF-α, and CRP were positively correlated with NAFLD severity, particularly IL-6 and TNF-α, which demonstrated value in disease stratification and phenotype identification.
Immune cell-derived inflammatory ratios (e.g., Th17/Treg, NLR, MHR) are accessible through routine blood tests, making them cost-effective and convenient indicators of systemic or cellular immune inflammation. Several studies found that combining these markers in predictive models enhanced diagnostic accuracy for NASH and fibrosis progression compared to traditional single biomarkers.
Metabolic biomarkers such as FGF21, TyG index, and adiponectin were closely linked to insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis, indicating their suitability for early diagnosis and high-risk population screening.
Liver injury/inflammatory biomarkers such as CK18, LCN2, PTX3, and OPN showed good performance in disease classification and fibrosis risk prediction. CK18 and LCN2 reflect hepatocellular apoptosis and tissue damage, while OPN and PTX3 are involved in inflammation-mediated fibrogenesis, aiding in the identification of NASH and advanced high-risk patients.
Oxidative stress-related biomarkers, including elevated serum uric acid and hemoglobin levels, were independently associated with NAFLD, possibly reflecting oxidative stress and metabolic burden. These may serve as useful tools for early detection in high-risk individuals.
4 Discussion
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a complex, multifactorial metabolic liver disorder. Its pathological progression typically evolves from simple steatosis (NAFL) to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (29, 30). With the emergence of the “multiple-hit” hypothesis (31–33), it is now recognized that the development of NAFLD involves not only lipid accumulation (34, 35), but also a combination of mechanisms such as inflammation (36–38), insulin resistance (39, 40), genetic susceptibility (41–43) (40–42), and gut microbiota dysbiosis (44, 45). Among these, lipid metabolism disorders and subsequent cellular inflammatory responses are considered central mechanisms of NAFLD pathogenesis (46), with inflammation playing a critical role in hepatocellular injury, immune cell recruitment, and fibrosis progression (47, 48) , as illustrated in Figure 2.
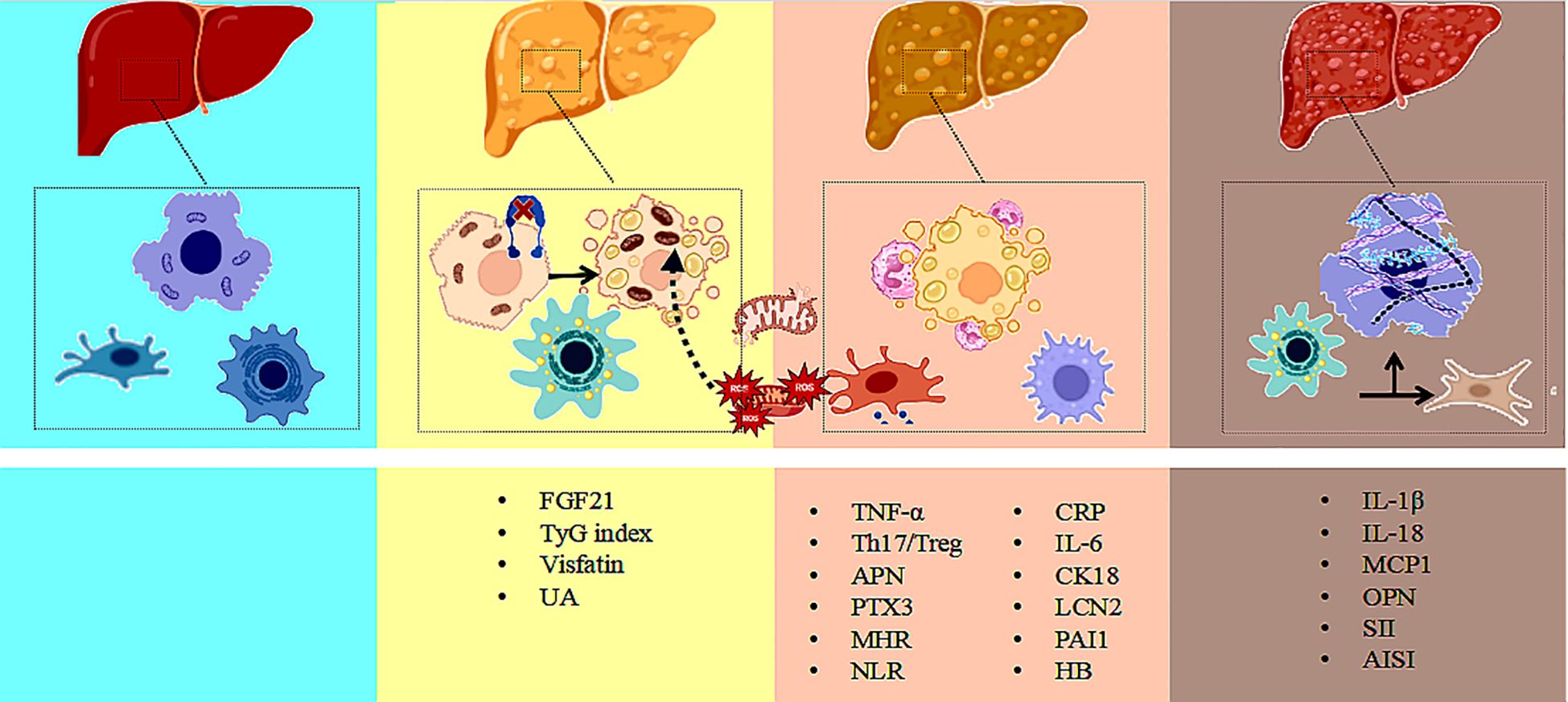
Figure 2. Multi-biomarker interaction network in NAFLD progression: integrating metabolic and inflammatory pathways. Illustrate the dynamic interaction network of metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers during the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, covering key biomarkers and their diagnostic applications across the NAFL, NASH, and fibrosis stages.
4.1 Inflammation-related biomarkers
Inflammatory responses play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), exacerbating lipid metabolic disturbances and insulin resistance while directly promoting hepatic fat accumulation and chronic disease progression. Current evidence highlights the diagnostic significance of classical acute-phase proteins, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and immune cell-derived inflammatory ratios in disease stratification, staging assessment, and fibrosis risk prediction in NAFLD.
4.1.1 Acute phase proteins
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase protein synthesized by hepatocytes in response to inflammatory stimuli and is highly sensitive to liver inflammation in NAFLD. Studies have shown that CRP levels rise rapidly within 6–8 hours of onset and peak at 24–48 hours, correlating positively with the severity of inflammation (OR: 1.41, 95% CI: 1.31–1.51, P < 0.001) (49). High-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP), in particular, has been significantly associated with the occurrence of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) (OR: 1.60, 95% CI: 1.17–2.19, P = 0.003), serving as an indirect indicator of hepatic inflammatory activity (49). Although CRP lacks organ specificity, it has demonstrated strong predictive synergy in several composite diagnostic models.
4.1.2 Pro-inflammatory cytokines
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), primarily secreted by activated macrophages, T lymphocytes, and natural killer (NK) cells, is abundantly expressed in hepatic immune cells of patients with NAFLD (50–53). By activating the NF-κB signaling pathway, TNF-α induces hepatocyte apoptosis, promotes reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and disrupts insulin signaling, serving as a central mediator in the inflammatory progression of NAFLD (54).Existing studies have shown that serum TNF-α levels are positively correlated with intrahepatic triglyceride levels (r = 0.28, P < 0.04) (55), suggesting potential for early screening and targeted therapy research.
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pivotal cytokine regulating hepatic inflammation and metabolic dysregulation. Elevated IL-6 levels activate hepatic stellate cells via the JAK/STAT pathway, promote lipid droplet accumulation, and stimulate Kupffer cell responses, playing a key role in the transition from NAFL to NASH (56). Studies have shown that serum IL-6 levels in NAFLD patients are significantly higher than those in healthy controls(P =0.0179), and serum IL-6 levels in patients with liver fibrosis (S1, S2-3) are higher than those in non-fibrotic patients(P< 0.05) (57). Notably, IL-6 also drives Th17 cell polarization, indicating its dual role in inflammatory and immune regulation (58–60).This suggests that IL-6 levels are positively correlated with the severity of NAFLD and have the potential to serve as an early predictor of disease progression.
IL-1β and IL-18 are essential pro-inflammatory cytokines mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. IL-1β amplifies inflammatory cascades by inducing TNF-α and IL-6 production, while IL-18 promotes liver injury through T cell–mediated immune responses (61). Both cytokines are markedly elevated in NASH and advanced fibrosis and are closely associated with distinct NAFLD subtypes (62, 63).Furthermore, their natural antagonist, IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), is significantly decreased in NAFLD(P< 0.05), suggesting a dysregulated inflammatory balance during disease progression (64).
4.1.3 Chemokines
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) recruits macrophages and monocytes into liver tissue during inflammation, contributing to chronic inflammation maintenance (65). MCP-1 levels positively correlate with fibrosis severity in NAFLD and may serve as a surrogate marker of hepatic fibrosis (66, 67). However, its specific role and diagnostic value in NAFLD require further evaluation.
4.2 Immune cells and derived inflammatory ratios
An imbalance between Th17 and Treg cells is a hallmark of immune dysregulation in NAFLD. Th17 cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, contributing to hepatic inflammation and lipid accumulation, whereas Treg cells release IL-10 and exert immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects (68, 69). Studies have shown that the Th17/Treg ratio is significantly elevated in patients with NAFLD and is closely associated with insulin resistance and liver injury, indicating its potential as an early warning signal for NASH risk (18).
Peripheral counts of neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes, as well as their derived ratios, serve as accessible indicators of systemic inflammation and have demonstrated potential in early NAFLD screening (68, 70). Neutrophil infiltration is a characteristic feature of NASH, and elevated neutrophil counts have been identified as an independent risk factor for NAFLD (71). As key components of innate immunity, intermediate monocyte subsets (CD14++CD16+) are significantly increased in NAFLD and may serve as potential predictive markers (72).
CD4+ T lymphocytes play a central role in adaptive immune regulation and can differentiate into Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg subsets, coordinating both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in liver tissue (73). Impaired proliferation and activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells may compromise immune surveillance, thereby facilitating NAFLD progression (74). Lymphocyte aggregation correlates positively with lobular inflammation and fibrosis staging, suggesting a potential bridging role in the transition from NAFL to NASH (75).
Composite inflammatory indices derived from routine hematological and biochemical parameters have gained attention for their simplicity, low cost, and applicability in large-scale non-invasive screening of NAFLD. These indices reflect subclinical systemic inflammation and include the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte-to-HDL ratio (MHR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), and aggregate index of systemic inflammation (AISI). NLR is markedly elevated in patients with moderate-to-severe NAFLD and NASH (76); MHR reflects the balance between immune activation and anti-inflammatory capacity (77); and SII and AISI, as integrative markers, have demonstrated strong discriminatory power in disease stratification and fibrosis prediction (78). These scoring systems help reduce the bias of single biomarkers and support early risk stratification and individualized therapeutic decision-making.
4.3 Lipid metabolism-related biomarkers
The liver plays a central role in lipid metabolism, encompassing fatty acid synthesis, transport, and oxidation. Disruptions in lipid metabolic homeostasis constitute a foundational mechanism in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and interact bidirectionally with insulin resistance and oxidative stress, leading to lipotoxicity and chronic inflammation (79). Accordingly, lipid metabolism–related biomarkers hold potential clinical value in early screening and identification of high-risk individuals.
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), primarily secreted by hepatocytes, regulates lipogenesis, energy metabolism, and insulin sensitivity (80). In patients with NAFLD, elevated FGF21 levels are thought to represent a compensatory response to metabolic stress, particularly endoplasmic reticulum stress (81). A recent study demonstrated promising diagnostic performance of FGF21 for NAFLD, with an AUC of 0.832 (95% CI: 0.77–0.886, P < 0.001), suggesting its potential utility as an adjunctive biomarker (82).
Adiponectin, an adipokine with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic properties, is markedly reduced during the progression from NAFLD to NASH (83). Hypoadiponectinemia is closely linked to insulin resistance and increased cardiovascular risk (84). In a comparative analysis, adiponectin outperformed several metabolic markers in differentiating NAFLD subtypes, with an AUC of 0.643–0.644 (95% CI: 0.089–0.345, P < 0.001) (85).
Visfatin, secreted primarily by visceral adipose tissue, exhibits insulin-mimetic properties by modulating glucose metabolism and insulin signaling pathways (86). Reduced visfatin levels may exacerbate insulin resistance and contribute to NAFLD progression, underscoring its potential as an indicator of metabolic dysregulation (87).
The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, derived from fasting plasma glucose and triglyceride levels, was initially developed to evaluate insulin resistance (88, 89). Multiple studies have demonstrated its superior diagnostic accuracy for NAFLD compared with traditional predictors (90, 91). The TyG index reflects underlying mechanisms of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity that drive insulin resistance and hepatic fat accumulation (92). It has shown robust predictive capability for NAFLD, with an AUC of 0.782 (95% CI: 0.773–0.790), sensitivity of 72.2%, and specificity of 70.5% (93).
4.4 Combined markers of liver injury and inflammation
The progression of NAFLD involves hepatocellular apoptosis, tissue remodeling, and persistent inflammation. Certain serum biomarkers reflect both hepatic injury and systemic inflammation, thereby offering dual diagnostic value for disease classification and fibrosis risk prediction.
Cytokeratin-18 (CK-18) is a specific marker of hepatocyte apoptosis, released into circulation upon membrane disruption (94). Elevated serum CK-18 levels help distinguish NAFL from NASH, with the M30 fragment showing good diagnostic performance (AUC = 0.750, 95% CI: 0.714-0.787). When the CK-18 concentration exceeds 375 U/L, the diagnostic performance improves (AUC = 0.79), with a sensitivity of 81.5%, specificity of 65.0%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 80.8%, and negative predictive value (NPV) of 43.1% (P < 0.0001) (95).
Lipocalin-2 (LCN2), a glycoprotein secreted primarily by neutrophils, is upregulated in hepatic injury and inflammatory states. Induced by endotoxins, IL-6, and IL-1β, LCN2 contributes to neutrophil infiltration and upregulation of chemokine receptor CXCR2 (96–98). Its serum levels are significantly elevated in NASH and exhibit high diagnostic accuracy: for NAFLD, a cutoff of >57.57 ng/mL yields 76.47% sensitivity and 100% specificity; for NASH, a cutoff of >84.485 ng/mL yields 84.62% sensitivity and 80.95% specificity. The corresponding AUC values are 0.882 (95% CI: 0.745–0.961) and 0.868 (95% CI: 0.708–0.959), respectively (22).
Pentraxin 3 (PTX3), an acute-phase protein with immunomodulatory properties, is structurally similar to C-reactive protein (CRP) but exhibits higher specificity. Elevated PTX3 levels in NAFLD are associated with steatosis severity and hepatic enzyme abnormalities (99) (100). In pediatric NAFLD, PTX3 has a diagnostic cutoff of 3.03 U/L for NASH (sensitivity: 89%, specificity: 86%) (100). In adults, plasma PTX3 levels correlate significantly with NAFLD activity score, fibrosis stage, and steatosis grade (r = 0.659, P < 0.001; r = 0.354, P < 0.01; r = 0.455, P < 0.001). A cutoff of 2.45 ng/mL yields 91.1% sensitivity and 71.4% specificity for diagnosing NASH in adults (101).
Osteopontin (OPN), a glycoprotein secreted by adipose tissue macrophages, is closely associated with advanced hepatic fibrosis. OPN expression increases with fibrosis severity and is significantly elevated in patients with stage ≥F3 NAFLD (P < 0.001), supporting its potential use as a biomarker for progressive disease (102, 103).
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), synthesized by hepatocytes and visceral adipose tissue, contributes to extracellular matrix accumulation and hepatic stellate cell activation. Elevated PAI-1 levels are associated with obesity, dyslipidemia, and inflammation, and promote fibrogenic progression in NAFLD (104, 105). Notably, PAI-1 demonstrates high diagnostic accuracy for NASH (106); a serum level >11.60 ng/mL yields an AUC of 0.954 (95% CI: 0.884–0.988), with 100% sensitivity and 90% specificity (107).
4.5 Oxidative stress-related biomarkers
Oxidative stress is one of the key mechanisms driving the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) from metabolic dysfunction to tissue damage and liver fibrosis. The excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), induced by metabolic toxicity, fatty acid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, activates Kupffer cells, disrupts hepatocyte membrane integrity, and triggers chronic inflammation (108). Therefore, oxidative stress-related biomarkers serve as intermediate indicators of the pathogenesis of NAFLD, with potential diagnostic and prognostic value.
Uric acid has a dual biological role: at low concentrations, it acts as an antioxidant, while at higher concentrations, it becomes a pro-oxidative and pro-inflammatory mediator (109). Hyperuricemia is closely associated with the onset and progression of NAFLD, contributing to liver damage by activating immune responses, promoting insulin resistance, and exacerbating oxidative stress (110). Studies have shown that even within the normal range, uric acid levels are an independent risk factor for NAFLD (OR (95% CI): 1.46 (1.17-1.82) to 2.13 (1.42-3.18)) (111). Uric acid is not only related to the severity of liver damage in NAFLD but also holds potential as a predictive biomarker for disease progression. A study in Korea found a positive correlation between serum uric acid levels and the five-year incidence of NAFLD, suggesting its potential as an early diagnostic marker (112). Furthermore, a meta-analysis showed that the SUA threshold for NAFLD was 308 μmol/L, with a sensitivity of 94.12% (71.3-99.9) and a specificity of 70.6% (44.0-89.7) (113). However, the diagnostic performance of uric acid may vary among different populations, and further analysis of its cut-off value variability is needed to ensure its accuracy and reliability in broad clinical applications.
The role of iron metabolism biomarkers in NAFLD is also significant, particularly with hemoglobin (Hb) and ferritin. Ferritin catalyzes the production of free radicals, which may exacerbate oxidative stress (114). Animal studies have demonstrated that iron overload in NASH models significantly affects the progression of NAFLD, and iron-reducing treatment has shown protective effects against NASH (115). In NAFLD patients, Hb is considered an important predictor of liver fibrosis, especially in lean NAFLD (BMI < 25 kg/m²), where Hb is the only independent predictor (116). Thus, Hb can serve as a serum biomarker for NAFLD patients with normal weight, assisting in diagnosis and disease progression assessment.
5 Conclusions and limitations
With the rising global prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), there is an increasing clinical demand for noninvasive diagnostic tools capable of early detection and progression stratification. Inflammation and metabolic dysregulation, as core mechanisms underlying NAFLD, have prompted extensive research into related biomarkers for noninvasive assessment. Based on a systematic scoping review approach, this study summarizes the diagnostic potential and strength of evidence for various inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers across different clinical stages of NAFLD—including early screening, NASH differentiation, fibrosis evaluation, and complication prediction.
From the integrated findings, multiple biomarkers exhibit distinct advantages at specific diagnostic stages. For example, the TyG index shows superior performance in early screening; CK18 is highly specific for NASH diagnosis; and OPN demonstrates significant value in fibrosis assessment. Composite inflammatory ratios (e.g., NLR, MLR, AISI, SII) have shown strong translational potential due to their simplicity and accessibility. Meanwhile, metabolic markers such as adiponectin and FGF21 exhibit dynamic correlations with disease severity, supporting their potential role in disease monitoring and intervention evaluation.
Overall, the clinical value of inflammation- and metabolism-related biomarkers in the noninvasive diagnosis of NAFLD is becoming increasingly evident, particularly in the development of predictive models and risk scoring systems. However, limitations persist in current studies, including sample heterogeneity, inconsistency in diagnostic criteria, and a lack of prospective validation. Future research should focus on large-scale, multicenter studies and mechanistic investigations to facilitate the transition of high-value biomarkers from “research indicators” to “clinical tools,” ultimately advancing precision diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD.
Among the 15 studies included in this scoping review, 10 were conducted in China. This geographical concentration may introduce regional bias and limit the generalizability of the findings to Western or multi-ethnic populations. It reflects the active research landscape in East Asia, particularly in China, where hospital-based studies on non-invasive biomarkers for NAFLD are prominent. Although several key biomarkers showed consistent diagnostic trends across studies, supporting their potential clinical value, the evidence drawn mainly from a single region should be interpreted with caution. Further validation in multi-center cohorts with geographic and ethnic diversity is needed to assess the global applicability of these biomarkers. In addition, this review did not systematically search grey literature databases or clinical trial registries, which may lead to a risk of publication bias. Future reviews should broaden information sources and incorporate grey literature and registered trial data to improve the comprehensiveness and representativeness of the findings.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://osf.io/u4nw7.
Author contributions
HL: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Investigation. DZ: Writing – original draft, Data curation. NW: Methodology, Writing – original draft. PX: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Formal analysis. HH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Scientific Research Project of Tianjin Education Commission (grant number 2021kj261).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Biorender for the assistance in image creation for this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1652996/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Wong VW, Ekstedt M, Wong GL, and Hagström H. Changing epidemiology, global trends and implications for outcomes of NAFLD. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:842–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.04.036
2. Bedossa P. Pathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. (2017) 37 Suppl 1:85–9. doi: 10.1111/liv.13301
3. Boursier J, Hagström H, Ekstedt M, Moreau C, Bonacci M, Cure S, et al. Non-invasive tests accurately stratify patients with NAFLD based on their risk of liver-related events. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:1013–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.031
4. Zambrano-Vásquez OR, Cortés-Camacho F, Castañeda-Sánchez JI, Aréchaga-Ocampo E, Valle-Velázquez E, Cabrera-Angeles JC, et al. Update in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease management: role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Life Sci. (2025) 372:123638. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123638
5. Ajmera V, Perito ER, Bass NM, Terrault NA, Yates KP, Gill R, et al. Novel plasma biomarkers associated with liver disease severity in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. (2017) 65:65–77. doi: 10.1002/hep.28776
6. Perito ER, Ajmera V, Bass NM, Rosenthal P, Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB, et al. Association between cytokines and liver histology in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Commun. (2017) 1:609–22. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1068
7. Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. (2018) 169:467–73. doi: 10.7326/m18-0850
8. Peters MDJ, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Khalil H, Larsen P, Marnie C, et al. Best practice guidance and reporting items for the development of scoping review protocols. JBI Evid Synth. (2022) 20:953–68. doi: 10.11124/jbies-21-00242
9. McHugh ML. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb). (2012) 22:276–82. doi: 10.11613/BM.2012.031
10. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
11. Caio G, Volta U, Sapone A, Leffler DA, De Giorgio R, Catassi C, et al. Celiac disease: a comprehensive current review. BMC Med. (2019) 17:142. doi: 10.1186/s12916-019-1380-z
12. Hu J, Dong Y, Chen X, Liu Y, Ma D, Liu X, et al. Prevalence of suicide attempts among Chinese adolescents: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Compr Psychiatry. (2015) 61:78–89. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2015.05.001
13. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
14. Oruc N, Ozutemiz O, Yuce G, Akarca US, Ersoz G, Gunsar F, et al. Serum procalcitonin and CRP levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a case control study. BMC Gastroenterol. (2009) 9:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-230x-9-16
15. Li H, Fang Q, Gao F, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang X, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 levels are increased in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients and are correlated with hepatic triglyceride. J Hepatol. (2010) 53:934–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.018
16. Lu J, Chen J, Peng X, Wu K, Wu C, and Zhao Y. Detection and significance of serum interleukin-6 in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. China J Modern Med. (2013) 23:45–9.
17. Ouyang X, Chen J, Yang Y, and Liu S. Correlation analysis of serum VEGF levels with IL-6 and hs-CRP in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Med Theory Pract. (2015) 28:2589–2590, 2609. doi: 10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2015.19.006
18. Rau M, Schilling AK, Meertens J, Hering I, Weiss J, Jurowich C, et al. Progression from nonalcoholic fatty liver to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is marked by a higher frequency of Th17 cells in the liver and an increased Th17/resting regulatory T cell ratio in peripheral blood and in the liver. J Immunol. (2016) 196:97–105. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501175
19. Jamali R, Arj A, Razavizade M, and Aarabi MH. Prediction of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via a novel panel of serum adipokines. Med (Baltimore). (2016) 95:e2630. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000002630
20. Abdel-Razik A, Mousa N, Shabana W, Refaey M, ElMahdy Y, Elhelaly R, et al. A novel model using mean platelet volume and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a marker of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in NAFLD patients: multicentric study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2016) 28:e1–9. doi: 10.1097/meg.0000000000000486
21. Glass O, Henao R, Patel K, Guy CD, Gruss HJ, Syn WK, et al. Serum interleukin-8, osteopontin, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 are associated with hepatic fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Commun. (2018) 2:1344–55. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1237
22. Tian S. Diagnostic value of serum biomarkers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2019). doi: 10.27307/d.cnki.gsjtu.2019.002794
23. Zhao Y, Xia J, He H, Liang S, Zhang H, and Gan W. Diagnostic performance of novel inflammatory biomarkers based on ratios of laboratory indicators for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:981196. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.981196
24. Ye X, Li J, Wang H, and Wu J. Pentraxin 3 and the TyG index as two novel markers to diagnose NAFLD in children. Dis Markers. (2021) 2021:8833287. doi: 10.1155/2021/8833287
25. Luo J, Yan Z, and Guo W. Levels and clinical significance of serum inflammatory factors and T-cell subsets in patients with NAFLD. Digestive and Interventional Diagnosis and Therapy. (2021) 26:243–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2021.02.020
26. Wang X and Gao Z. Association between disease severity and inflammatory factors in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Exp Lab Med. (2021) 39:1159–1160, 1171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1129.2021.05.034
27. Xian Y, Wang R, Cai W, Ma L, and Lin S. Analysis of influencing factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in middle-aged populations based on serum biochemical biomarkers. J Xinjiang Med Univ. (2023) 46:254–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2023.02.020
28. Bao B, Xu S, Sun P, and Zheng L. Neutrophil to albumin ratio: a biomarker in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and with liver fibrosis. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1368459. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1368459
29. Rinella ME. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. JAMA. (2015) 313:2263–73. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.5370
30. Diehl AM and Day C. Cause, pathogenesis, and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:2063–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1503519
31. Peng C, Stewart AG, Woodman OL, Ritchie RH, and Qin CX. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A review of its mechanism, models and medical treatments. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:603926. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.603926
32. Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, and Sanyal AJ. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. (2018) 24:908–22. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
33. Pierantonelli I and Svegliati-Baroni G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: basic pathogenetic mechanisms in the progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation. (2019) 103:e1–e13. doi: 10.1097/tp.0000000000002480
34. Vacca M, Allison M, Griffin JL, and Vidal-Puig A. Fatty acid and glucose sensors in hepatic lipid metabolism: implications in NAFLD. Semin Liver Dis. (2015) 35:250–61. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1562945
35. Perla FM, Prelati M, Lavorato M, Visicchio D, and Anania C. The role of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Children (Basel). (2017) 4:46. doi: 10.3390/children4060046
36. Arrese M, Cabrera D, Kalergis AM, and Feldstein AE. Innate immunity and inflammation in NAFLD/NASH. Dig Dis Sci. (2016) 61:1294–303. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4049-x
37. Farzanegi P, Dana A, Ebrahimpoor Z, Asadi M, and Azarbayjani MA. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur J Sport Sci. (2019) 19:994–1003. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2019.1571114
38. Schuster S, Cabrera D, Arrese M, and Feldstein AE. Triggering and resolution of inflammation in NASH. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 15:349–64. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0009-6
39. Kitade H, Chen G, Ni Y, and Ota T. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance: new insights and potential new treatments. Nutrients. (2017) 9:387. doi: 10.3390/nu9040387
40. Rosso C, Mezzabotta L, Gaggini M, Salomone F, Gambino R, Marengo A, et al. Peripheral insulin resistance predicts liver damage in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. (2016) 63:107–16. doi: 10.1002/hep.28287
41. Umano GR, Martino M, and Santoro N. The association between pediatric NAFLD and common genetic variants. Children (Basel). (2017) 4:49. doi: 10.3390/children4060049
42. Marzuillo P, Grandone A, Perrone L, and Miraglia Del Giudice E. Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms in the pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of genetics. World J Hepatol. (2015) 7:1439–43. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i11.1439
43. Marzuillo P, Miraglia del Giudice E, and Santoro N. Pediatric fatty liver disease: role of ethnicity and genetics. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:7347–55. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7347
44. Compare D, Coccoli P, Rocco A, Nardone OM, De Maria S, Cartenì M, et al. Gut–liver axis: the impact of gut microbiota on non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2012) 22:471–6. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2012.02.007
45. Pinzone MR, Celesia BM, Di Rosa M, Cacopardo B, and Nunnari G. Microbial translocation in chronic liver diseases. Int J Microbiol. (2012) 2012:694629. doi: 10.1155/2012/694629
46. Takahashi Y and Fukusato T. Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: overview with emphasis on histology. World J Gastroenterol. (2010) 16:5280–5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5280
47. Zhang TS, Qin HL, Wang T, Li HT, Li H, Xia SH, et al. Global publication trends and research hotspots of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a bibliometric analysis and systematic review. Springerplus. (2015) 4:776. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1542-1
48. Henao-Mejia J, Elinav E, Jin C, Hao L, Mehal WZ, Strowig T, et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature. (2012) 482:179–85. doi: 10.1038/nature10809
49. Duan Y, Pan X, Luo J, Xiao X, Li J, Bestman PL, et al. Association of inflammatory cytokines with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:880298. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.880298
50. Mounika N, Mungase SB, Verma S, Kaur S, Deka UJ, Ghosh TS, et al. Inflammatory protein signatures as predictive disease-specific markers for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Inflammation. (2025) 48:25–41. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02035-0
51. McGeehan GM, Becherer JD, Bast RC Jr., Boyer CM, Champion B, Connolly KM, et al. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha processing by a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Nature. (1994) 370:558–61. doi: 10.1038/370558a0
52. Loman BR, Hernández-Saavedra D, An R, and Rector RS. Prebiotic and probiotic treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. (2018) 76:822–39. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy031
53. Ajmal MR, Yaccha M, Malik MA, Rabbani MU, Ahmad I, Isalm N, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in patients of cardiovascular diseases and its association with hs-CRP and TNF-α. Indian Heart J. (2014) 66:574–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2014.08.006
54. Nagai H, Matsumaru K, Feng G, and Kaplowitz N. Reduced glutathione depletion causes necrosis and sensitization to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in cultured mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology. (2002) 36:55–64. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.33995
55. Martin-Rodriguez JL, Gonzalez-Cantero J, Gonzalez-Cantero A, Martí-Bonmatí L, Alberich-Bayarri Á, Gonzalez-Cejudo T, et al. Insulin resistance and NAFLD: Relationship with intrahepatic iron and serum TNF-α using 1H MR spectroscopy and MRI. Diabetes Metab. (2019) 45:473–9. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2019.01.005
56. Yang F, Li H, Li Y, Hao Y, Wang C, Jia P, et al. Crosstalk between hepatic stellate cells and surrounding cells in hepatic fibrosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 99:108051. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108051
57. Hou X, Yin S, Ren R, Liu S, Yong L, Liu Y, et al. Myeloid-cell-specific IL-6 signaling promotes microRNA-223-enriched exosome production to attenuate NAFLD-associated fibrosis. Hepatology. (2021) 74:116–32. doi: 10.1002/hep.31658
58. Song X, Gao H, and Qian Y. Th17 differentiation and their pro-inflammation function. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2014) 841:99–151. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-9487-9_5
59. Zhang F, Jiang WW, Li X, Qiu XY, Wu Z, Chi YJ, et al. Role of intrahepatic B cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines and regulating intrahepatic T cells. J Dig Dis. (2016) 17:464–74. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12362
60. Olteanu S, Kandel-Kfir M, Shaish A, Almog T, Shemesh S, Barshack I, et al. Lack of interleukin-1α in Kupffer cells attenuates liver inflammation and expression of inflammatory cytokines in hypercholesterolaemic mice. Dig Liver Dis. (2014) 46:433–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2014.01.156
61. Geng Y, Ma Q, Liu YN, Peng N, Yuan FF, Li XG, et al. Heatstroke induces liver injury via IL-1β and HMGB1-induced pyroptosis. J Hepatol. (2015) 63:622–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.010
62. Mehal WZ. The inflammasome in liver injury and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis. (2014) 32:507–15. doi: 10.1159/000360495
63. Yamanishi K, Maeda S, Kuwahara-Otani S, Hashimoto T, Ikubo K, Mukai K, et al. Deficiency in interleukin-18 promotes differentiation of brown adipose tissue resulting in fat accumulation despite dyslipidemia. J Transl Med. (2018) 16:314. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1684-3
64. Italiani P, Manca ML, Angelotti F, Melillo D, Pratesi F, Puxeddu I, et al. IL-1 family cytokines and soluble receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. (2018) 20:27. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1525-z
65. Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S, and Sawaya BE. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): an overview. J Interferon Cytokine Res. (2009) 29:313–26. doi: 10.1089/jir.2008.0027
66. Kirovski G, Dorn C, Huber H, Moleda L, Niessen C, Wobser H, et al. Elevated systemic monocyte chemoattractrant protein-1 in hepatic steatosis without significant hepatic inflammation. Exp Mol Pathol. (2011) 91:780–3. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2011.08.001
67. Kassel KM, Guo GL, Tawfik O, and Luyendyk JP. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 deficiency does not affect steatosis or inflammation in livers of mice fed a methionine-choline-deficient diet. Lab Invest. (2010) 90:1794–804. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.143
68. Moayedfard Z, Sani F, Alizadeh A, Bagheri Lankarani K, Zarei M, and Azarpira N. The role of the immune system in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and potential therapeutic impacts of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:242. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02929-6
69. Zhang X, Zhang Z, Lin W, Lin K, and Zhang Z. Expression of Th1/Th2 cytokines in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Liver. (2013) 18:30–2. doi: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2013.01.011
70. Wang S, Zhang C, Zhang G, Yuan Z, Liu Y, Ding L, et al. Association between white blood cell count and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in urban Han Chinese: a prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. (2016) 6:e010342. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010342
71. Wu L, Gao X, Guo Q, Li J, Yao J, Yan K, et al. The role of neutrophils in innate immunity-driven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: lessons learned and future promise. Hepatol Int. (2020) 14:652–66. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10081-7
72. Zhang J, Chen W, Fang L, Li Q, Zhang X, Zhang H, et al. Increased intermediate monocyte fraction in peripheral blood is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Wien Klin Wochenschr. (2018) 130:390–7. doi: 10.1007/s00508-018-1348-6
73. Van Herck MA, Weyler J, Kwanten WJ, Dirinck EL, De Winter BY, Francque SM, et al. The differential roles of T cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:82. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00082
74. Ma C, Kesarwala AH, Eggert T, Medina-Echeverz J, Kleiner DE, Jin P, et al. NAFLD causes selective CD4(+) T lymphocyte loss and promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Nature. (2016) 531:253–7. doi: 10.1038/nature16969
75. Bruzzì S, Sutti S, Giudici G, Burlone ME, Ramavath NN, Toscani A, et al. B2-Lymphocyte responses to oxidative stress-derived antigens contribute to the evolution of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 124:249–59. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.06.015
76. Peng Y, Li Y, He Y, Wei Q, Xie Q, Zhang L, et al. The role of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for the assessment of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis: a systematic review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 12:503–13. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2018.1463158
77. Canpolat U, Çetin EH, Cetin S, Aydin S, Akboga MK, Yayla C, et al. Association of monocyte-to-HDL cholesterol ratio with slow coronary flow is linked to systemic inflammation. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. (2016) 22:476–82. doi: 10.1177/1076029615594002
78. Toosi AE. Liver fibrosis: causes and methods of assessment, A review. Rom J Intern Med. (2015) 53:304–14. doi: 10.1515/rjim-2015-0039
79. Rector RS, Thyfault JP, Wei Y, and Ibdah JA. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome: an update. World J Gastroenterol. (2008) 14:185–92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.185
80. Flippo KH and Potthoff MJ. Metabolic messengers: FGF21. Nat Metab. (2021) 3:309–17. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00354-2
81. Spann RA, Morrison CD, and den Hartigh LJ. The nuanced metabolic functions of endogenous FGF21 depend on the nature of the stimulus, tissue source, and experimental model. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:802541. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.802541
82. Xu K, He BW, Yu JL, Kang HM, Zheng TT, Chen ZY, et al. Clinical significance of serum FGF21 levels in diagnosing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease early. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:25191. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76585-6
83. Polyzos SA, Toulis KA, Goulis DG, Zavos C, and Kountouras J. Serum total adiponectin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism. (2011) 60:313–26. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2010.09.003
84. Zheng Bo, Xiaerpuhazi H, and Tan Li. Changes in serum levels of hypoxia- inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α), high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), and adiponectin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and their correlation with carotid atherosclerosis. J Pract Hepatol. (2024) 27:198–201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2024.02.010
85. Chen H, Chen S, Liu D, Liang Y, Li H, Bao Y, et al. Associations between multiple metabolic biomarkers with steatotic liver disease subcategories: A 5-year Chinese cohort study. Cell Rep Med. (2025) 6:101884. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101884
86. Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K, et al. Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science. (2005) 307:426–30. doi: 10.1126/science.1097243
87. Zhu C, Chen D, Ai Z, Yang Li, and Min M. Relationship between serum visfatin, adiponectin and clinicopathological features of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Hepatol. (2011) 27:735–737 + 748.
88. Watt MJ, Miotto PM, De Nardo W, and Montgomery MK. The liver as an endocrine organ-linking NAFLD and insulin resistance. Endocr Rev. (2019) 40:1367–93. doi: 10.1210/er.2019-00034
89. Simental-Mendía LE, Simental-Mendía E, Rodríguez-Hernández H, Rodríguez-Morán M, and Guerrero-Romero F. The product of triglycerides and glucose as biomarker for screening simple steatosis and NASH in asymptomatic women. Ann Hepatol. (2016) 15:715–20. doi: 10.5604/16652681.1212431
90. Fedchuk L, Nascimbeni F, Pais R, Charlotte F, Housset C, and Ratziu V. Performance and limitations of steatosis biomarkers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2014) 40:1209–22. doi: 10.1111/apt.12963
91. Kitae A, Hashimoto Y, Hamaguchi M, Obora A, Kojima T, and Fukui M. The triglyceride and glucose index is a predictor of incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based cohort study. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 2019:5121574. doi: 10.1155/2019/5121574
92. Gutierrez-Grobe Y, Ponciano-Rodríguez G, Ramos MH, Uribe M, and Méndez-Sánchez N. Prevalence of non alcoholic fatty liver disease in premenopausal, posmenopausal and polycystic ovary syndrome women. role estrogens Ann Hepatol. (2010) 9:402–9. doi: 10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31616-3
93. Zhang S, Du T, Zhang J, Lu H, Lin X, Xie J, et al. The triglyceride and glucose index (TyG) is an effective biomarker to identify nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. (2017) 16:15. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0409-6
94. Zhang H, Rios RS, Boursier J, Anty R, Chan WK, George J, et al. Hepatocyte apoptosis fragment product cytokeratin-18 M30 level and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis risk diagnosis: an international registry study. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:341–50. doi: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000002603
95. Kawanaka M, Nishino K, Nakamura J, Urata N, Oka T, Goto D, et al. Correlation between serum cytokeratin-18 and the progression or regression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann Hepatol. (2015) 14:837–44. doi: 10.5604/16652681.1171767
96. Borkham-Kamphorst E, van de Leur E, Zimmermann HW, Karlmark KR, Tihaa L, Haas U, et al. Protective effects of lipocalin-2 (LCN2) in acute liver injury suggest a novel function in liver homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2013) 1832:660–73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.01.014
97. Sultan S, Pascucci M, Ahmad S, Malik IA, Bianchi A, Ramadori P, et al. LIPOCALIN-2 is a major acute-phase protein in a rat and mouse model of sterile abscess. Shock. (2012) 37:191–6. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31823918c2
98. Ding M, Qi X, Huang W, Lin Y, and Yan H. Resident CD24 (+)LCN2 (+) LPCs aggravate fibrosis and inflammatory progression via the recruitment of TPPP3 (+)COL10A1 (+) macrophages in NASH. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2025) 57:1–14. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2025081
99. Ye D, Yang K, Zang S, Lin Z, Chau HT, Wang Y, et al. Corrigendum to “Lipocalin-2 mediates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by promoting neutrophil-macrophage crosstalk via the induction of CXCR2. J Hepatol. (2017) 66:669. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.12.006
100. Hamza RT, Elfaramawy AA, and Mahmoud NH. Serum pentraxin 3 fragment as a noninvasive marker of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children and adolescents. Horm Res Paediatr. (2016) 86:11–20. doi: 10.1159/000446566
101. Boga S, Koksal AR, Alkim H, Yilmaz Ozguven MB, Bayram M, Ergun M, et al. Plasma pentraxin 3 differentiates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) from non-NASH. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. (2015) 13:393–9. doi: 10.1089/met.2015.0046
102. Syn WK, Choi SS, Liaskou E, Karaca GF, Agboola KM, Oo YH, et al. Osteopontin is induced by hedgehog pathway activation and promotes fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. (2011) 53:106–15. doi: 10.1002/hep.23998
103. Song Z, Chen W, Athavale D, Ge X, Desert R, Das S, et al. Osteopontin takes center stage in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. (2021) 73:1594–608. doi: 10.1002/hep.31582
104. Thuy S, Ladurner R, Volynets V, Wagner S, Strahl S, Königsrainer A, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in humans is associated with increased plasma endotoxin and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 concentrations and with fructose intake. J Nutr. (2008) 138:1452–5. doi: 10.1093/jn/138.8.1452
105. Jiang X and Sun M. Changes and clinical significance of serum PAI-1 in non- alcoholic fatty liver disease. Chin J Exp Diagnostics. (2020) 24:953–5.
106. Alsharoh H, Ismaiel A, Leucuta DC, Popa SL, and Dumitrascu DL. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. (2022) 31:206–14. doi: 10.15403/jgld-4091
107. Piazzolla VA and Mangia A. Noninvasive diagnosis of NAFLD and NASH. Cells. (2020) 9:1005. doi: 10.3390/cells9041005
108. Ipsen DH, Lykkesfeldt J, and Tveden-Nyborg P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2018) 75:3313–27. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2860-6
109. Gherghina ME, Peride I, Tiglis M, Neagu TP, Niculae A, and Checherita IA. Uric acid and oxidative stress-relationship with cardiovascular, metabolic, and renal impairment. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:3188. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063188
110. Crane JK and Mongiardo KM. Pro-inflammatory effects of uric acid in the gastrointestinal tract. Immunol Invest. (2014) 43:255–66. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2013.864667
111. Hwang IC, Suh SY, Suh AR, and Ahn HY. The relationship between normal serum uric acid and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Korean Med Sci. (2011) 26:386–91. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.3.386
112. Lee JW, Cho YK, Ryan M, Kim H, Lee SW, Chang E, et al. Serum uric Acid as a predictor for the development of nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease in apparently healthy subjects: a 5-year retrospective cohort study. Gut Liver. (2010) 4:378–83. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2010.4.3.378
113. Huang F, Liu A, Fang H, and Geng X. Serum uric acid levels in non-alcoholic steatosis patients: a meta-analysis. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2017) 26:334–42. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.092016.04
114. Valenzuela R, Rincón-Cervera M, Echeverría F, Barrera C, Espinosa A, Hernández-Rodas MC, et al. Iron-induced pro-oxidant and pro-lipogenic responses in relation to impaired synthesis and accretion of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in rat hepatic and extrahepatic tissues. Nutrition. (2018) 45:49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2017.07.007
115. Cai JM, Shen J, Cao Y, Sun MY, and Zhao Y. Effects of iron overload on lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rats. Carcinogenesis Teratogenesis Mutagenesis. (2017) 29:179–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-616x.2017.03.004
Keywords: non-alchoholic fatty liver disease, inflammatory cyotokines, biomarkers, non-invasive diagnosis, scoping review
Citation: Liang H, Zhang D, Wei N, Xi P, Ge H and Zhang Y (2025) A new perspective on non-invasive diagnosis of non- alcoholic fatty liver disease: evidence integration of inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers based on a scoping review. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1652996. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1652996
Received: 24 June 2025; Accepted: 12 August 2025;
Published: 28 August 2025.
Edited by:
Rashu Barua, New York University, United StatesReviewed by:
Md Hasif Sinha, University of Louisville, United StatesSarath Chandra Ponnada, Great Eastern Medical School & Hospital, India
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Zhang, Wei, Xi, Ge and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haize Ge, Z2VoYWl6ZUAxNjMuY29t; Yan Zhang, Wmhhbmd5YW43NjY4QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
 Huimin Liang
Huimin Liang Deyuan Zhang1†
Deyuan Zhang1†