- 1The First Clinical College of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2Orthopedics Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
As individuals age, bone density declines and the likelihood of fractures increases, particularly in women experiencing menopause. Hip fractures, the most severe consequence of osteoporosis, are becoming more common due to the aging global population and a 1-3% annual increase in hip fractures in most regions. The specific epigenetic mechanisms underlying the onset of osteoporosis and its related fractures remain predominantly unexamined. Research indicates that epigenetic modifications can elevate the risk of osteoarthritis, osteoporosis and bone fractures, especially hip fractures, by linking genetic predispositions with environmental factors. Essential regulatory components in these factors encompass microRNAs, lncRNAs, and circular RNAs. This review examines the function of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in the advancement of osteoporosis, with an emphasis on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. The objective is to enhance comprehension of RNA classes in osteoporotic hip fractures, which may facilitate early detection and prognosis, as well as clarify cellular interactions, potentially resulting in innovative diagnostic techniques and targeted therapies.
1 Introduction
Human bone metabolism encompasses resorption and formation, regulated by osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Osteoporosis, a metabolic disorder, is characterized by diminished bone density and increased resorption, thereby elevating the risk of fractures (1). Osteoporotic fractures predominantly occur in specific anatomical sites such as the hip, pelvis, spine, wrist, and forearm, with hip fractures being especially severe and debilitating. Hip fractures are a common source of disability, with annual mortality rates reaching 30%. Immutable risk factors encompass lower socioeconomic status, advanced age, female gender, previous fractures, metabolic bone disorders, and osseous malignancies. Alterable risk factors encompass low body mass index, osteoporosis, heightened fall risk, medications influencing fall risk or bone mineral density, and substance abuse (2–4). Postmenopausal women are predominantly susceptible to osteoporotic hip fractures, and existing diagnostic tools exhibit limitations, underscoring the necessity for novel early diagnostic methods and treatment protocols for osteoporosis (5, 6).
One common joint degenerative disease that affects adults and causes pain and disability is osteoarthritis (OA). Age, obesity, joint damage, and heredity are some of the factors that lead to its development. OA results in abnormalities of the meniscus, synovial tissue, subchondral bone, and articular cartilage. Degradation of cartilage, development of osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, and hyperplasia of synovial tissue are important characteristics. Numerous molecules and pathways play a role in the pathophysiology of OA, with the NF-κB pathway being activated by systemic inflammation and secreted cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β. Current research emphasizes how non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), such as circular RNAs, microRNAs, and long ncRNAs, regulate the development of OA (7). Furthermore, studies indicate that the advancement of osteoporosis is affected by epigenetic elements, exhibiting variations in miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA expression in postmenopausal individuals relative to healthy controls (8, 9). This has resulted in heightened attention on miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs as prospective therapeutic targets or biomarkers. They can encode functional peptides that influence the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts by modulating cellular signaling, regulating gene expression, and participating in various biological processes via their small open reading frames (10–12). This review examines the functions of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in the progression of osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, their impacts on osteoblasts and osteoclasts, and their prospective uses as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
2 The association between noncoding RNAs and osteoporosis
2.1 Noncoding RNAs
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNA molecules generated during genome transcription, encompassing miRNA, siRNA, circRNA, sncRNA, and lncRNA, which do not encode proteins. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), exceeding 200 nucleotides in length, modulate cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, influencing gene expression, protein translation, and stability, while serving as decoys, scaffolds, or competing endogenous RNAs, which may contribute to disease pathogenesis (13). MicroRNAs, measuring 18–25 nucleotides in length, modulate post-transcriptional gene expression. Primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) represent the most rudimentary form, which is processed by RNA endonuclease III (Drosha) and DGCR8/Pasha to yield pre-miRNAs, a precursor of microRNAs, contributing to disease. MicroRNAs, which regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and apoptosis, are essential for sustaining or determining cell survival following cleavage by the enzyme Dicer (14). CircRNAs are non-coding RNAs characterized by a closed-loop structure, varying in length from 100 to several thousand nucleotides, generated via reverse splicing. They function as miRNA sponges or competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs), vying for miRNA binding and affecting transcription within the nucleus. CircRNAs are additionally associated with protein factors. Small non-coding RNAs, such as tRNA-derived small RNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, and PIWI-interacting RNAs, are predominantly examined in tumors, presenting a novel research opportunity concerning osteoporosis (Figure 1) (15).
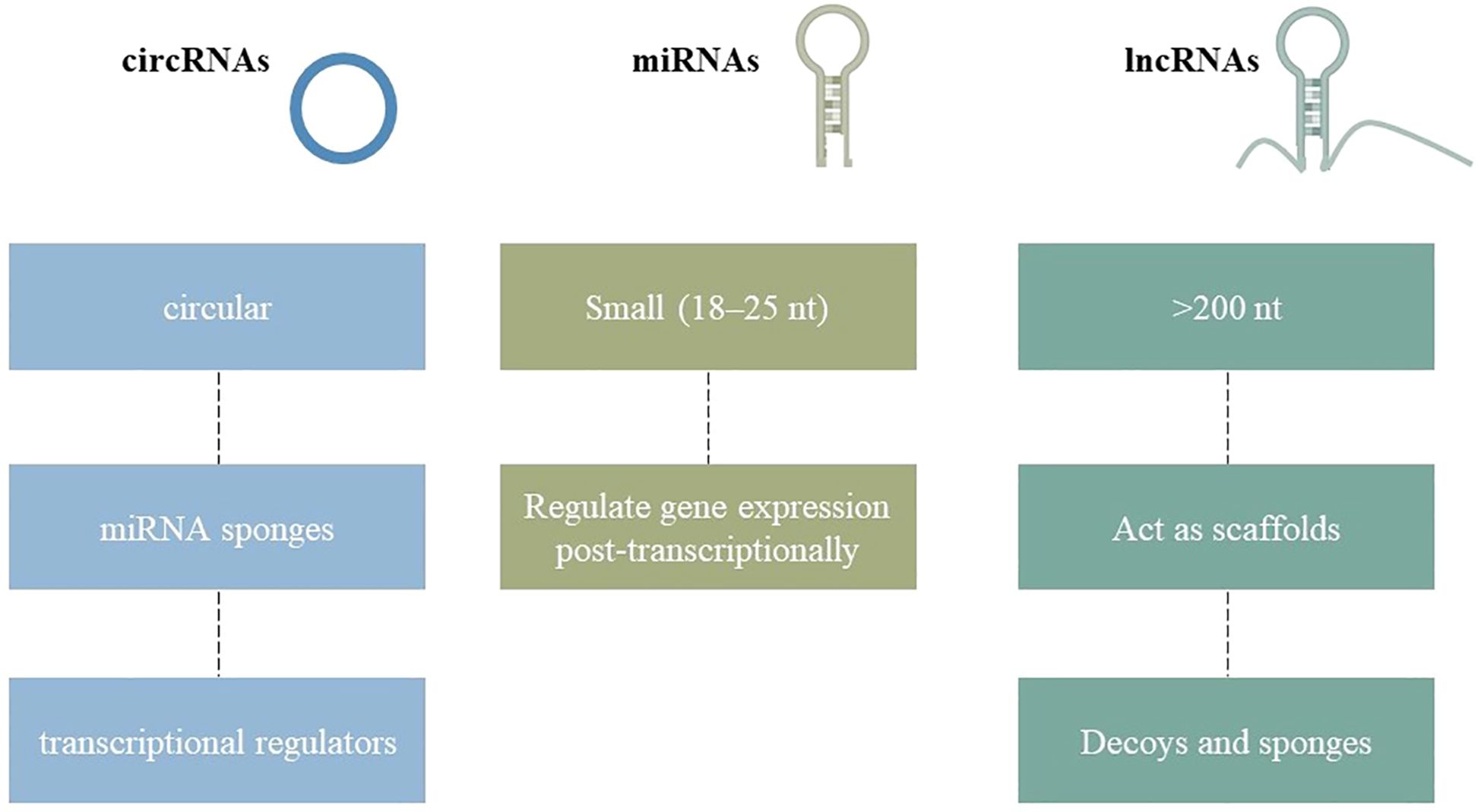
Figure 1. Structural diversity of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) relevant to osteoporosis. MicroRNAs are short linear sequences, long non-coding RNAs are extended transcripts with diverse regulatory functions, and circular RNAs form closed loops that often act as molecular sponges. These RNA classes collectively influence osteoblast and osteoclast activity, shaping bone health.
2.2 The regulatory function of ncRNAs in osteoporosis
Bone metabolism encompasses both anabolism and catabolism, with osteoblasts and osteoclasts being essential for bone formation and resorption. Osteoporosis, defined by diminished formation and heightened absorption, elevates the risk of fractures (16). Recent studies have shown that ncRNAs play a pivotal role in osteoporosis, with over 300 dysregulated ncRNAs identified in postmenopausal individuals. Modulating these associated ncRNAs may be advantageous in the treatment of osteoporosis, with critical functions confirmed via genetic animal models (Figure 2) (17, 18). The research identifies functional bone ncRNAs associated with fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women, delineating specific subsets in weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing skeletal locations. Seventy-five iliac bone ncRNAs and ninety-four femoral bone ncRNAs were identified as being associated with total hip bone mineral density (BMD), with five ncRNAs exhibiting a positive correlation with BMD in femoral bone (19).
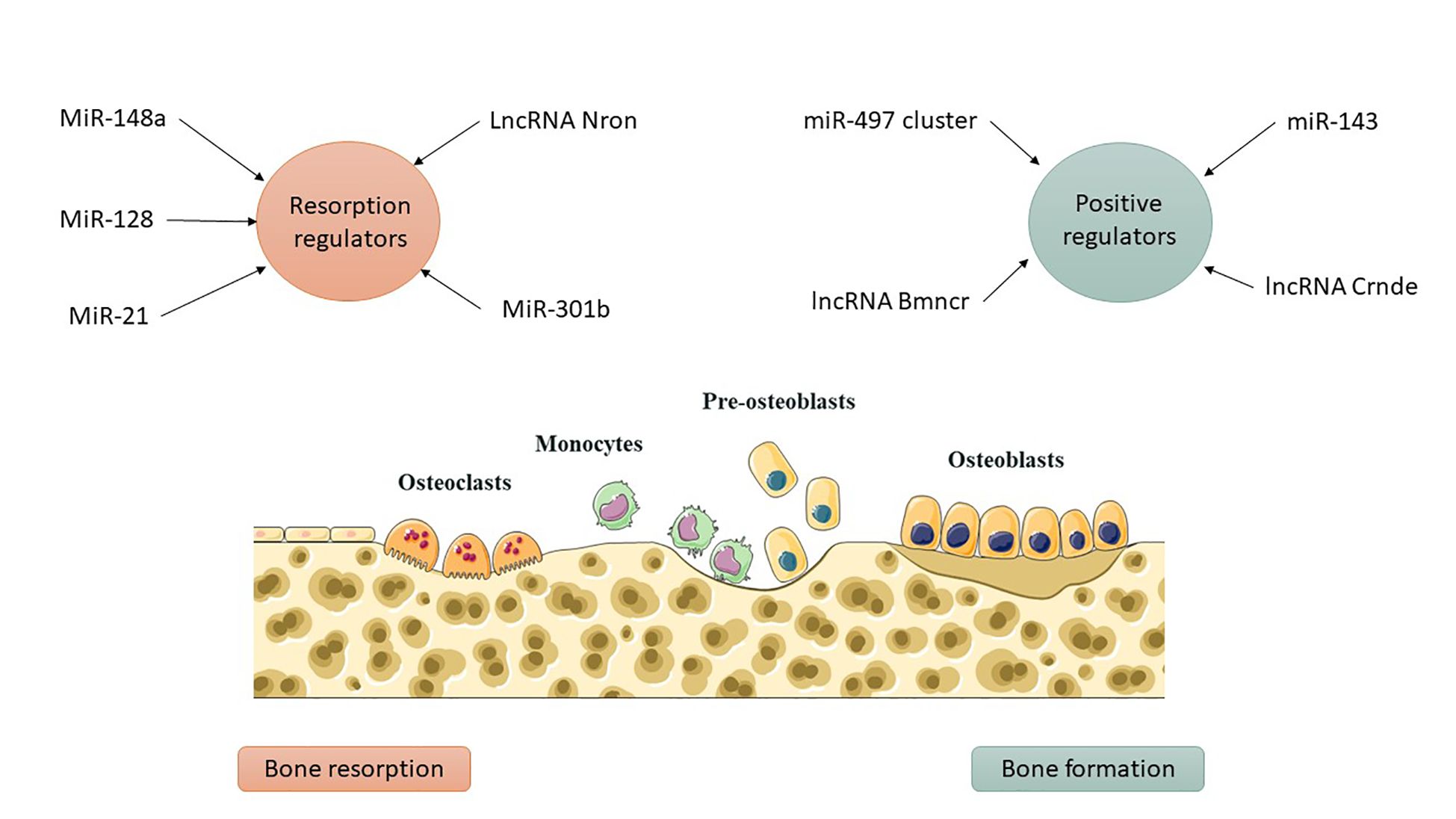
Figure 2. ncRNAs as regulators of bone remodeling. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts normally maintain a balance between bone formation and resorption. Dysregulated ncRNAs disrupt this balance, tipping it toward bone loss and increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
A novel molecular mechanism implicated in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis has been elucidated by the identification of the LINC00339-PARP1-CDC42 regulatory axis. This finding raises the possibility that the LINC00339-PARP1 interaction could be a promising therapeutic target for altering osteoblast dysfunction, as well as expanding our understanding of how epigenetic regulation impacts bone remodeling. Importantly, these findings offer a conceptual framework for lncRNA-driven therapies in skeletal disorders and demonstrate the translational potential of RNA-protein complex targeting to restore bone homeostasis. A study employing high-throughput transcriptome sequencing and bioinformatics identified differentially expressed mRNAs and ncRNAs in bone mesenchymal stem cells from individuals with senile osteoporosis. The research identified substantial changes in 415 mRNAs, 30 lncRNAs, 6 circRNAs, and 27 miRNAs, with the proposed network possibly functioning as a therapeutic target (20).
Postmenopausal women frequently encounter osteoporosis as a result of estrogen deficiency, calcium depletion, and the aging process. A study identified a circRNA-associated ceRNA network in the bone marrow stem cells of ovariectomized mice, demonstrating diminished bone mass and heightened osteogenesis in OVX-induced osteoporotic mice. The research examined mRNAs within the circRNA-associated ceRNA network, possibly associated with osteoporosis pathology. Variably expressed mRNAs were identified as participating in extracellular matrix-receptor interactions, fatty acid metabolism, and PPAR signaling (21). The study identifies PPARγ, PI3K-Akt, and MiR-216a as modulators of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation (22). It also identifies potential ceRNAs implicated in osteoporosis, concentrating on circRNA-associated networks that regulate OP-related genes and pathogenesis. The data improves comprehension of circRNA-associated ceRNA networks in osteoporotic conditions (21).
Innovative circRNA networks, such as circRNA 0020 and circRNA 3832, represent prospective biomarkers for osteoporosis research. Non-coding RNA and Wnt signaling pathways are essential for the pathogenesis of osteoporosis, with miR-23b-3p suppressing conditions in murine models and miR-146a promoting differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells (23). Comprehending these pathways will guide precise molecular therapy. Investigations into the CircRNA/Wnt axis are concentrating on its involvement in osteoporosis, facilitating osteogenic differentiation via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and augmenting osteogenesis through CircStag1. lncRNAs are pivotal in epigenetic modifications during mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation and degenerative bone diseases, modulating gene expression and possibly serving as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis (24). Nonetheless, obstacles such as off-target effects and intricate secondary structures necessitate advanced bioinformatic tools for precise interaction prediction and sequencing technologies.
3 Bone formation
3.1 Positive regulators
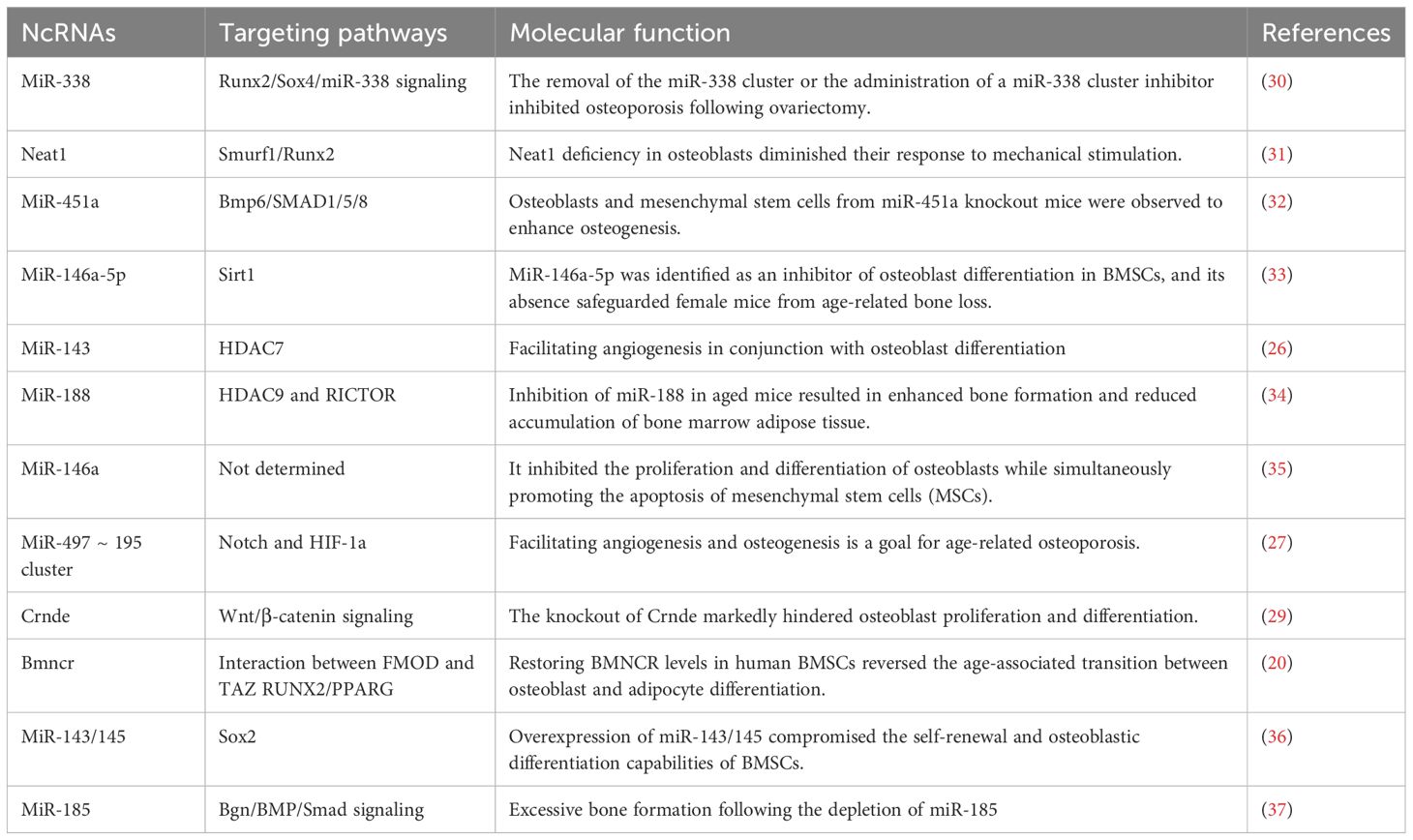
Osteoblasts, derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells, regulate bone homeostasis by facilitating bone formation. Research has demonstrated that MiR-143, a gene predominantly expressed in osteoblasts, is crucial for promoting osteoblast differentiation in osteoporosis (25). The overexpression of this factor was observed to impede osteoblastic differentiation in miR-143-deficient mice. The research employed mRNA sequencing, target prediction, and luciferase reporter assays. Injection of HDAC7-siRNA into miR-143 knockout mice resulted in substantial alleviation of symptoms. Administration of AgammiR-143 expedited osteogenesis and mitigated bone loss in a mouse model of aging-induced osteoporosis (26). The miR-497 cluster, which targets F-box and WD-40 domain proteins, sustains Notch activity and HIF-1α stability in endothelial cells (27). LncRNA Bmncr affects the fate of aging bone marrow stem cells, resulting in osteopenia in mice. Overexpression enhances bone density and stimulates bone formation via TAZ-ABL interaction (28). Knockout mice exhibit diminished osteoblast proliferation and bone mass attributed to decreased expression of Alp, Runx2, and Osx, highlighting the significance of Crnde in osteoblast proliferation and differentiation (29) (Table 1).
3.2 Negative regulators
Certain non-coding RNAs have been identified as negative regulators of osteogenesis. Li and colleagues performed a miRNA microarray analysis to compare bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) in young and aged mice, discovering that miR-188 expression was markedly elevated in aged mice. The global knockout of miR-188 or the application of aptamer-antagomiR-188 in bone marrow diminished age-related bone loss and enhanced adipogenesis, whereas its overexpression in osterix+ osteoprogenitors or bone marrow-derived stem cells exacerbated bone loss and adipogenesis (34). MiR-188 targets HDAC9 and RICTOR, thereby augmenting osteoblastic activity and bone formation in murine models (34). Expression of MiR-146a-5p is elevated in the bone tissue of aging female mice and patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP). MiR-146a−/− mice exhibited mitigated bone loss, expedited MSC proliferation, and diminished apoptosis, as indicated by elevated osteoblastic markers (38). Zheng et al. discovered that Sirt1 can interact with miR-146a-5p in its 3'-UTR, indicating its potential role in enhancing bone health. The protein expression of Sirt1 was markedly increased in miR-146a global knockout mice, indicating a correlation with aging and a possible role in osteoporosis prevention (33). LncRNA Neat1 was essential for osteoblastic differentiation, and its depletion compromised bone structure and resulted in loss in mice exposed to mechanical loading. Depletion of Neat1 impeded bone formation and mitigated unloading-induced bone loss. Paraspeckles enhance the nuclear retention of Smurf1 and inhibit translation, resulting in the degradation of Runx2 (39). PMOP is a prevalent bone disorder, with miR-143 and miR-145 identified as potential therapeutic targets. The overexpression of miR-143/145 impedes osteoblastic differentiation in bone marrow stem cells, whereas the knockout or use of antagomiR-143/145 enhances estrogen-deficient osteoporosis in female mice (40). Cytoplasmic miR-143/145 and lncRNA MIR143HG, regulated by ERβ, modulate the translation of pluripotency genes through the canonical ceRNA pathway. MIR143HG collaborates with miR-143 to jointly activate SOX2 transcription (40). Knockout of miR-185 diminishes bone loss in estrogen-deficient osteoporosis models, whereas miR-185 agomir reinstates bone formation. The enrichment of the MiR-338 cluster in PMOP patients and OVX-induced mice indicates that MiR-338-3p or miR-3065-5p may alleviate osteoporotic symptoms (37).
4 Bone resorption
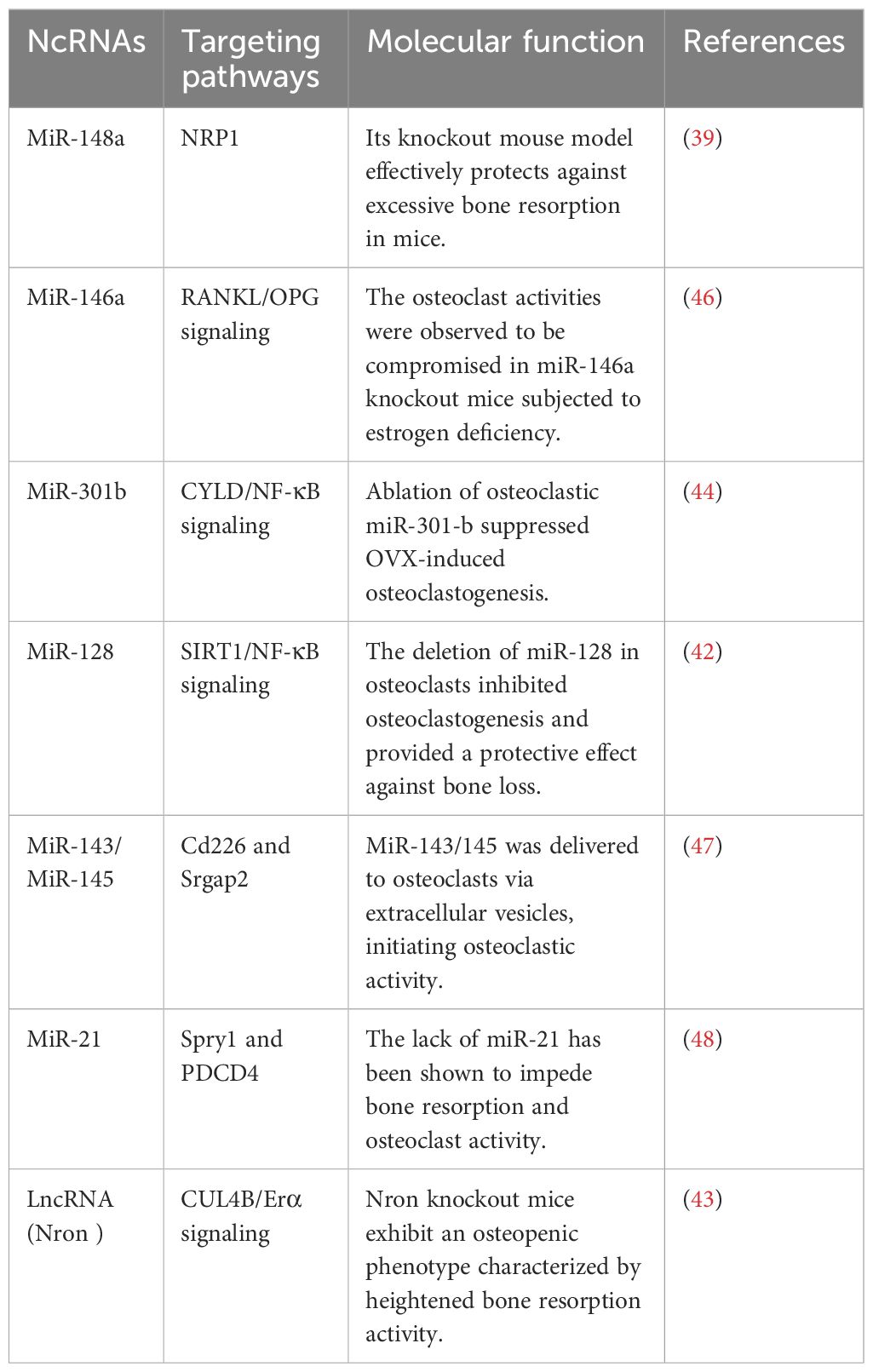
Comprehending the aberrant bone resorption by osteoclasts is essential for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of osteoporosis, given their distinction from macrophage/monocyte precursor cells affected by RANKL and other osteoclastogenic factors (37). Mir-21, an RNA molecule, modulates bone resorption in mice by inhibiting osteoclast formation, preserving skeletal structure, and alleviating osteoporosis, with its target PDCD4 influencing osteoclast differentiation (41). Mir-128, a crucial RNA in aging and inflammatory disorders such as osteoporosis, facilitates osteoclastogenesis in postmenopausal individuals and ovariectomized mice. It specifically targets Sirt1 and activates NF-κB signaling pathways (42). Xu et al. identified increased levels of miR-143/145 in the serum, saliva, and BMSCs of postmenopausal women, which impede self-renewal and differentiation. Depletion or inhibition of antagomiR-143/145 mitigated bone loss and impaired regeneration in estrogen-deficient osteoporosis (43). MiR-301b, miR-146a, and miR-148a represent prospective therapeutic targets for osteoporosis resulting from estrogen deficiency. MiR-146a safeguards against bone resorption, whereas global knockout impairs osteoclast activity (35). MiR-148a-/− mice exhibited augmented bone mass and diminished resorption in osteoporosis models, whereas depletion curtailed excessive resorption; conversely, agomiR-148a or AAV-shNRP1 accelerated the progression of osteoporosis (39). β-CTX secretion in PMOP patients correlates with miR-148a expression, whereas miR-301b is upregulated in bone tissue. The osteoclastic conditional knockout diminishes osteoclastogenesis and the quantity of osteoclasts, thereby offering substantial bone protection (39). MiR-301-b directly targets CYLD, an anti-inflammatory factor. CYLD modulates osteoclastogenesis through the activation of NF-κB signaling. In vivo investigations regarding osteoporosis related to lncRNA or circRNA are scarce (44). LncRNA Nron is prevalent in bone tissue and diminished in OVX mice. Osteoclasts exhibit diminished Nron expression alongside increased bone resorption. Transgenic mice or pharmaceutical overexpression of Nron resulted in increased bone mass due to inhibited osteoclastogenesis, involving Nron's interaction with CUL4B and its NCM2 motif, which regulates the Erα pathway (45)(Figure 3). To summarize, multiple studies have recognized ncRNAs as crucial regulators of osteoporosis. Investigations into lncRNAs and miRNAs are essential for osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis; however, there is a paucity of studies regarding circRNA functionality in transgenic animals, which is necessary to elucidate the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Comprehending the regulation of ncRNAs will facilitate the identification of specific targets for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis. Table 2 delineates the function of select ncRNAs in osteoporosis and their mechanisms in bone resorption.
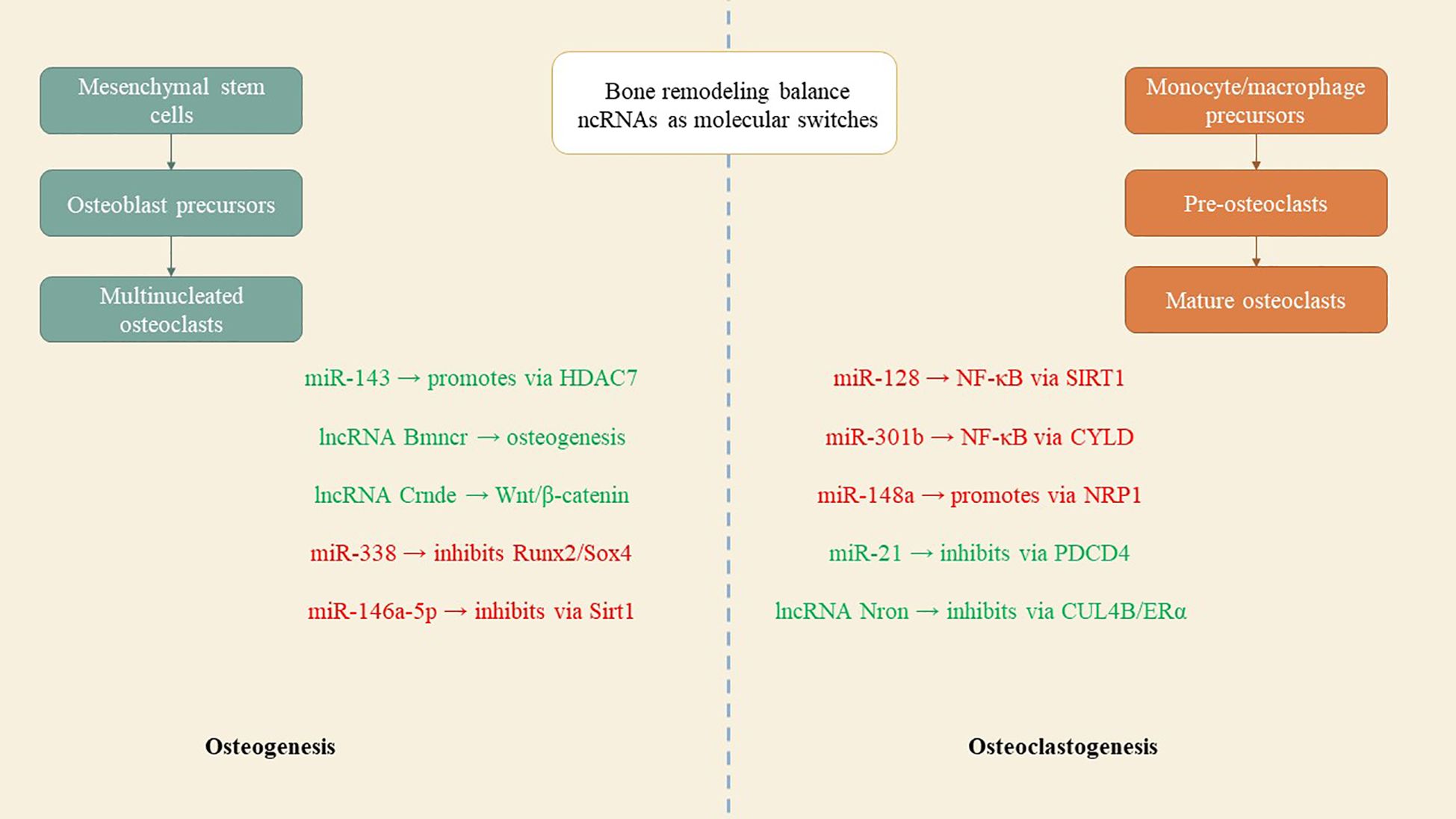
Figure 3. ncRNAs as molecular switches in bone metabolism. Positive regulators such as miR-143, lncRNA Bmncr, and lncRNA Crnde promote osteoblast differentiation, while inhibitory ncRNAs like miR-338 and miR-146a-5p suppress bone formation. On the resorption side, ncRNAs such as miR-128, miR-148a, and miR-301b enhance osteoclast activity, whereas miR-21 and lncRNA Nron counteract bone loss. Their interplay determines whether bone is preserved or degraded.
5 The regulatory function of ncRNAs in osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common condition that induces pain and disability, adversely affecting quality of life and imposing a socio-economic burden worldwide. The condition impacts the hip, knee, and finger joints, resulting in cartilage deterioration, subchondral bone alteration, and osteophyte formation, affecting more than 25% of individuals aged 18 and above (49). The majority of osteoarthritis patients have not received sufficient treatment, resulting in merely symptomatic relief. The identification of biomarkers for early diagnosis, subgroup classification, staging, and disease prognosis is imperative. Comprehending the mechanisms of pathogenic osteoarthritis will facilitate the identification of novel biomarkers to avert or postpone disease progression (50). NcRNAs are essential in cartilage development and maintenance by regulating chondrocyte proliferation, differentiation, and extracellular matrix biosynthesis. Aberrant ncRNA expression can result in ECM degradation, hypertrophy, and apoptosis, contributing to osteoarthritis. In vivo studies underscore the essential roles of ncRNAs in preserving cartilage homeostasis (51).
Monocytes can differentiate into two types of macrophages: M1 recruits immune cells during inflammation, while M2 suppresses immune cell secretion, promoting angiogenesis and tissue repair. The production of M1 and M2 macrophages must be balanced in order to prevent tissue damage. While M2 promotes tissue repair and inhibits the release of immune cells, cytokines such as LPS and TNF-α promote the accumulation of M1. Research indicates that PPARβ/δ agonists and pseudolactulic acid B prevent osteoporosis, while BMSC-Exo can improve osteoarthritis by regulating inflammation and macrophage polarization (52).
5.1 Beneficial miRNA modulators for the maintenance of articular cartilage homeostasis
Recent studies indicate that Sox9 is essential in cartilage development and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. MiR-140, a cartilage-specific non-coding RNA, is modulated by Sox9. MiR-140 knockout mice exhibit reduced stature and diminished body weight, yet manifest osteoarthritis-like pathology after 12 months. MiR-140-/− mice exhibit diminished articular cartilage damage in surgical arthritis models and exhibit milder osteoarthritis symptoms in antigen-induced arthritis models, highlighting its involvement in the progression of osteoarthritis (53, 54). MiR-455, an abundantly expressed RNA in chondrocytes, modulates cartilage homeostasis in both human and murine chondrocytes; however, in mice, it precipitates accelerated cartilage degeneration (55). Studies indicate that miR-455-deficient mice display osteoarthritis-like pathology at six months, whereas miR-455-3p and 5p mimics substantially hinder cartilage degeneration in mice subjected to DMM surgery. MiR-455-5p and -3p suppressed HIF-2α, a modulator of cartilage homeostasis, and siRNA-mediated silencing of HIF-2α mitigated cartilage degeneration in vivo (55). Runx2 modulates chondrocyte hypertrophy and the advancement of osteoarthritis, whereas miR-204 and miR-211 are microRNAs that preserve joint homeostasis by inhibiting osteoarthritis development. The global knockout of miR-204/211 induces spontaneous osteoarthritis by 15 weeks, while conditional knockout in mesenchymal progenitors displays aging-like phenotypes, and its reduction results in Runx2 accumulation and cartilage degradation. The research indicated that mesenchymal progenitor cells in dKO mice generated an overabundance of mesenchymal cells, resulting in synovial hyperplasia. Nonetheless, these osteoarthritis phenotypes may be enhanced through intra-articular administration of AAV5-miR-204 or by silencing Runx2 (46). The study also highlighted the role of certain ncRNAs in osteoarthritis. A novel lncRNA, AC005165.1, is dysregulated in osteoarthritis articular cartilage and subchondral bone, influencing the expression of the osteoarthritis risk gene FRZB, indicating potential therapeutic targets (56).
5.2 Negative miRNA regulators of cartilage homeostasis
Wang and associates identified the upregulation of miR-21-5p in osteoarthritis patients, resulting in the creation of cartilage-specific knockout mice that inhibit spontaneous osteoarthritis in mice at 12 months (57). The research indicated that intra-articular administration of antagomiR-21-5p mitigated articular cartilage degeneration in a murine DMM model, whereas agomiR-21-5p exacerbated the condition. FGF18 was identified as a direct target of miR-21-5p, and its protein expression was elevated in cKO mice. Mir-21-5p is associated with temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. The study revealed that miR-21-5p−/− mice exhibited diminished TMJOA progression by expressing fewer inflammatory genes and proteins (57). MiRNA target databases identified Spry1 as a target gene of miR-21-5p, and miR-141/200c was elevated in osteoarthritis patients. The research indicated that miR-141/200c, a gene associated with cartilage repair, can mitigate OA in murine models, and its delivery via nanoparticles can impede OA progression by targeting SIRT1, a deacetylase (47). MiR-146a, a biomarker for OA, was identified in early OA patients and mice subjected to destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) surgery. Furthermore, in mice deficient in MiR-146a, both spontaneous OA and OA induced by knee destabilization were inhibited. Lenti-miR-146a-mimic suppressed the expression of Sox9 and Col2a1 in murine articular cartilage cells, whereas Lenti-miR-146a-inhibitor counteracted this effect, suggesting potential therapeutic advantages in osteoarthritis management (48). MiR-146a modulates cartilage anabolism by targeting genes such as Tgif1, Camk2d, and Ppp3r via NF-κB-dependent signaling. It also elevates miR-483-5p expression in the articular cartilage of osteoarthritis patients and mice with DMM-induced osteoarthritis (48). The Bai group (58) created doxycycline-inducible miR-483 transgenic mice to examine its crucial function in osteoarthritis. The research revealed that miR-483-5p, an RNA regulated by p53, modulated mTORC1, a transcription factor, and its interaction with Matn3 and Timp2 in mice promoted chondrocyte hypertrophy and cartilage angiogenesis. MiR-34a-5p, a protein associated with obesity, was observed to be elevated in the plasma, cartilage, and synovium of osteoarthritis patients and mice with DMM-induced osteoarthritis. The intra-articular delivery of miR-34a-5p or its complete knockout safeguarded cartilage from damage induced by DMM (59).
5.3 Circular RNAs in osteoarthritis
Recent advancements in high-throughput RNA sequencing have resulted in the identification of more than 30,000 circRNAs, with ongoing research on circRNAs in osteoarthritis continually progressing. RNA sequencing has demonstrated the upregulation of circNFKB1 and circGCN1L1 in human chondrocytes (60–62). The research indicated that the knockdown of circNFKB1 suppressed ECM catabolism and accelerated osteoarthritis progression in mice. Injection of ad-circNFKB1 into mice with DMM-induced osteoarthritis resulted in cartilage degradation and osteophyte development. CircGCN1L1 promoted chondrocyte apoptosis, and inflammation, and reduced ECM anabolism in TMJ OA by sequestering miR-330-3p and targeting TNF-α (61). CircRNAs, including circSERPINE2, circPDE4B, and circFOXO3, can mitigate osteoarthritis progression by downregulating miR-1271 and E26 transformation-specific-related genes, thereby promoting cartilage protection (63–65). The research indicated that adeno-associated virus overexpressing circSERPINE2 mitigated the osteoarthritis phenotype in rabbits by modulating chondrocyte proliferation and extracellular matrix metabolism, with the circPDE4B-RIC8A axis being pivotal in the regulation of p38 MAPK signaling (65, 66). CircFOXO3 induces autophagy, mitigates chondrocyte apoptosis, and enhances ECM anabolism. The in vivo anti-OA effect was confirmed, demonstrating that it downregulates CircPARD3B in synovial tissues, thereby inhibiting synovial angiogenesis through miR-326 and SIRT1 (64, 67). The research investigates the capacity of small non-coding RNAs, such as tRNA-derived fragments, as novel instruments for assessing fracture healing and tissue regeneration. Following the fracture, levels of miR-451a diminished, whereas miR-328-3p, miR-133a-3p, miR-375-3p, miR-423-5p, and miR-150-5p exhibited an increase, indicating that fracture healing may induce systemic metabolic alterations (68). Functional studies will confirm their potential in therapeutic applications aimed at fracture healing processes or as biomarker tools, utilizing circulating small non-coding RNAs as indicators.
5.4 LncRNAs in osteoarthritis
lncRNAs, which do not translate into polypeptides, are essential in the regulation of gene expression. They are frequently dysregulated in cartilage or synovial fluid during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Recent studies indicate that HOTAIR and LINC02288 are upregulated in human osteoarthritic cartilage, with LINC02288 facilitating chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation through the modulation of the miR-347a-3p/RTN axis (69, 70). HOTAIR, a protein, interacts with miR-17-5p and enhances FUT2 expression, resulting in chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation. This axis facilitates the progression of osteoarthritis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Intra-articular injections cause significant cartilage deterioration (71). HOTAIR suppressed chondrocyte proliferation, facilitating apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation via the miR-20b/PTEN pathway, whereas MM2P safeguarded chondrocyte differentiation, augmented Colla2 and Acan expression, and stimulated proteoglycan and type II collagen secretion in chondrocytes by inducing M2 macrophage polarization and enhancing the transfer of M2-derived exosomal SOX9 (72). Linc-ROR, a long non-coding RNA, enhances chondrogenesis and cartilage formation in mesenchymal stem cells by modulating SOX9 expression. It additionally acts as a sponge for miR-138 and miR-145, inhibiting the chondrogenic activity of BMSCs and the expression of SOX9. The co-expression of linc-ROR demonstrates a restorative effect. These ncRNAs have been validated in transgenic murine models (73) (Figure 4).
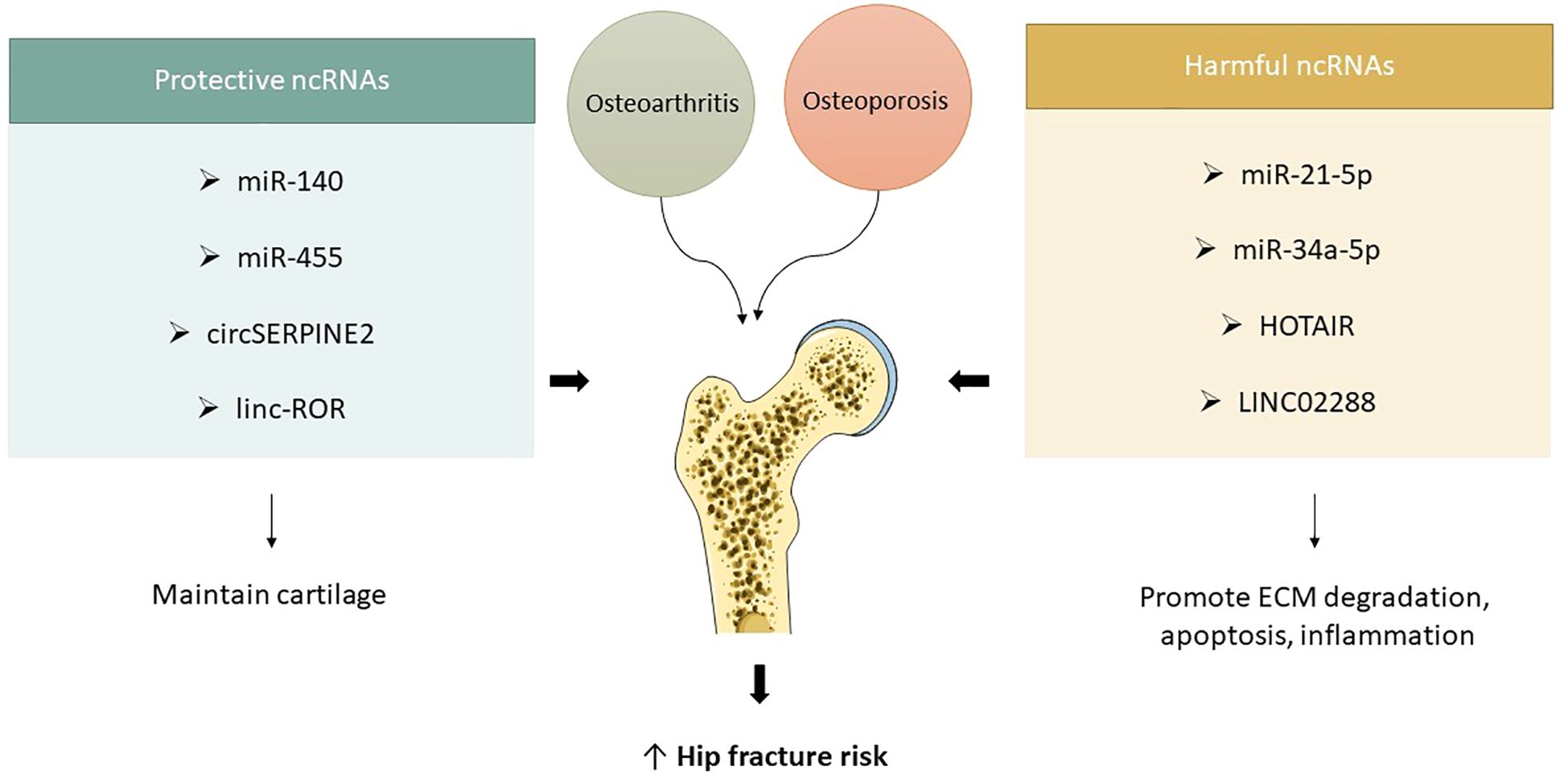
Figure 4. ncRNAs in osteoarthritis and hip fracture vulnerability. Protective ncRNAs (e.g., miR-140, miR-455, circSERPINE2, linc-ROR) help maintain cartilage structure and joint integrity, while harmful ncRNAs (e.g., miR-21-5p, miR-34a-5p, HOTAIR, LINC02288) promote cartilage breakdown, inflammation, and apoptosis. Their dysregulation links osteoarthritis progression with increased fracture risk in osteoporotic hips.
5.5 LncRNAs in hip fracture
An orthopedic condition that is frequently caused by trauma, tumor excision, and other abnormalities is skeletal fracture. Local soft tissue, vascular damage, and a loss of bone mechanical integrity are all involved. A sophisticated network of cells and cytokines works to repair broken bones and restore skeletal function during fracture healing. In order to sustain osteoblast differentiation and activity, hormones, growth factors, and cytokines that control gene expression are essential. Due to high-energy traffic injuries, femoral neck fractures are more common in young or middle-aged people. Although lncRNAs play a significant role in carcinogenesis, their function in osteogenic differentiation has not received much attention (74, 75). According to a study, SNHG7 may function as a biomarker because it is down-regulated in femoral neck fracture tissues and correlated with fracture type. Osteoblast cell migration and proliferation were inhibited by SNHG7 knockout, while cell apoptosis was increased and osteoblastic activity was reduced when SNHG7 was silenced. This emphasizes how crucial it is to comprehend lncRNAs in relation to skeletal fractures. Potential targets for microRNAs binding with SNHG7 were predicted by a bioinformatics analysis, and studies indicate that lncRNAs can modulate miRNA (76). SNHG7 was found to target miR-9, which may be involved in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Fractured tissues had higher levels of miR-9, indicating that miR-9 inhibitors may be able to inhibit the growth of si-SNHG7 cells. LncRNAs are involved in lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA crosstalk and ceRNA networks. By attaching itself to the 3'-UTR, MiR-9 has been shown to suppress the expression of TGFBR2. Inhibition of TGFβ signaling can hinder osteoblast migration and differentiation during fracture healing, as TGFβ is essential for the regulation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts (77). According to the study, TGFBR2 expression was downregulated in MC3T3-E1 cells when miR-9 was overexpressed, and TGFBR2 levels were lower in fractured tissues. The expression of TGFBR2, p-smad2, and p-smad3 in cells was markedly reduced by SNHG7 knockout. The complicated process of fracture healing controls the activation, growth, and differentiation of progenitor cells, also known as local mesenchymal stem cells. However, delayed healing or nonunion occurs in 5–10% of fracture patients. The goal of research is to prevent fracture nonunion and increase fracture healing rates. With HAGLR downregulated in fractured femoraneck tissues and linked to the type of bone fracture, lncRNAs are essential for fracture healing (78, 79). Inhibition of HAGLR resulted in decreased osteoblast activity, apoptosis, migratory capacity, and viability. The inhibitory effects of miRNA on downstream genes are lessened by lncRNA, which sponges’ miRNA to suppress its expression. H19 sponges use the Wnt pathway to speed up osteogenesis in hMSCs by upregulating RUNX2 through miRNA-141 and miR-22. In tissues from fractured femoral necks, miRNA-19a-3p is upregulated and may be a target of HAGLR (79). Cell division, embryogenesis, and bone remodeling are all inhibited by TGF-β signaling. TGFBR2 is downregulated in femur bone fractures, and MC3T3-E1 cells' TGFBR2 level is inhibited by miRNA-19a-3p overexpression. TGFBR2, p-smad2, p-smad3, and RUNX2 were all downregulated in MC3T3-E1 cells through HAGLR knockdown. The TGF-β pathway is inhibited by downregulating HAGLR, which speeds up the healing of femur neck fractures. The research examines the function of LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 in osteogenic differentiation, employing an in vitro model and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR to identify osteogenic differentiation markers. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were evaluated using DLR assay, RIP, and ELISA, validating gene interactions and measuring alkaline phosphatase activity. Bioinformatics methodologies forecasted genes and pathways, indicating that OS augments osteogenic differentiation markers and NR2F1-AS1 expression, whereas the suppression of miR-423-5p promotes osteoblast differentiation, stimulates proliferation, activates ALP activity, and inhibits apoptosis (78, 80, 81).
6 The application of lncRNAs and cirRNAs in osteoporosis diagnosis and prognosis
The application of circRNAs and lncRNAs in the prediction and diagnosis of osteoporosis is constrained by a paucity of studies involving human subjects. Chen et al. (82) discovered elevated levels of lncRNA XIST in the peripheral blood monocytes of osteoporosis patients, whereas Fei et al. identified a significant downregulation of 51 lncRNA transcripts in this population. The mRNAs of postmenopausal women were associated with inflammatory response, osteoclast differentiation, and cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction (83). ALP, which is downregulated in postmenopausal women, was located within 100 kb of lncRNAs, suggesting a cis-regulatory influence of lncRNAs on mRNAs associated with bone metabolism. The study comprised three women and two healthy controls. Tong et al. discovered that monocytes in postmenopausal women exhibit elevated levels of lncRNA DANCR, indicating its potential as a biomarker for osteoporosis, particularly as monocytes from women with diminished bone mineral density show increased expression of this RNA (84). Monocytes that are overexpressed exhibit elevated levels of TNF-α and IL-6, which are associated with osteoporosis. DANCR expression correlates with low bone mineral density osteoporosis. Anti-IL-6 or anti-TNF-α therapies may mitigate elevated bone-resorbing activity in murine bone cultures. The association between DANCR, IL-6, and TNF-α in osteoporosis therapies remains under examination. The limited concentration of lncRNAs in plasma/serum may impede their analysis, potentially postponing their application as cell-free biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis (85, 86). A study identified XIST upregulation in patients' serum, underscoring the difficulties in diagnosing osteoporosis through lncRNAs in plasma or serum. The increased expression of CASC11, a crucial diagnostic marker for osteoporosis, was associated with an extended treatment duration and a high recurrence rate. Plasma SNHG1, a downregulated lncRNA in postmenopausal women, exhibited significant downregulation, especially in those with PMOP, positioning it as a potential biomarker for PMOP diagnosis (87). CircRNAs are non-coding RNA molecules comprising hundreds of nucleotides, categorized into exon circular RNAs, intronic circRNAs (ciRNAs), and exon-intron circular RNAs (EIciRNAs). They employ mechanisms such as peptide transformation, protein interaction, and miRNA sponges for physiological and pathological processes. Research indicates that the highly expressed circRNA Circ_0002060 may function as a diagnostic biomarker for osteoporosis, exhibiting 78% sensitivity and 69% specificity in clinical samples. Its concentration is associated with diminished bone mineral density and T-score, but not with weight, height, or age. Circ_0006393, conversely, exhibits low expression levels and facilitates bone remodeling (88).
7 The application of lncRNAs and cirRNAs in osteoporosis treatment
lncRNAs, which regulate bone metabolism, are being investigated as potential target molecules for novel osteoporosis therapies. Nonetheless, their implementation in clinical settings remains nascent. Only 25 clinical trials are registered, primarily concentrating on validating lncRNAs as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis, rather than as therapeutic agents. These trials primarily concentrate on cancer and cardiovascular patients, with no assessments conducted on individuals with musculoskeletal disorders. The therapeutic utilization of lncRNAs is impeded by insufficient understanding of their biological functions and the limitations of conventional gene therapies. These factors encompass low efficacy of in vivo transgene transfection, repeated utilization of immunogenic gene delivery vehicles, and erratic transgene behavior, frequently resulting in malignancies (89, 90). Innovative strategies to modulate lncRNA expression in vivo are being developed to address these challenges, with potential applicability to other conditions such as osteoporosis. Sidi et al. (91) employed the BC-819 plasmid to treat bladder cancer patients by overexpressing the H19 promoter and regulating a toxin, thereby enhancing transfection and administering it into the bladder. The research demonstrated that a hybrid system combining a sleeping beauty transposon and baculovirus, which induces cell apoptosis and suppresses proliferation, effectively hinders cell proliferation in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma. A system for the overexpression of MEG3 lncRNA was established utilizing MS2 bacteriophage virus-like particles cross-linked with the GE11 polypeptide. This approach successfully suppressed tumor proliferation in a murine model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hu et al. (92) employed liposome-based invivofectamine® to diminish MALAT1 expression in chemoresistant prostate cancer. They employed functionalized carbon nanotubes to administer anti-MALAT1 antisense oligonucleotides, thereby diminishing tumor burden. A study demonstrated the downregulation of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 in murine models, emphasizing cardiotoxicity. Lentiviruses incorporating shRNA diminished lncRNA levels, influencing cardiotoxicity. Strategies for LncRNA knockdown are contingent upon localization, the efficacy of synthetic nucleic acids, and the duration of effect. Single-stranded oligonucleotides are favored (93).
Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) are double-stranded DNA entities delivered as double-stranded DNA constructs within plasmids. They are transcribed and processed within target cells, yielding small RNA molecules with a defined secondary structure. ShRNAs can be continuously transcribed, yielding an extended therapeutic effect and minimizing off-target gene effects. The overexpression of lncRNA poses technical challenges and controversies; however, advancements in siRNA and miRNA facilitate this process (94, 95). Overexpression necessitates vectors and delivery systems with enhanced transfection efficiency. In vitro transfection serves as an alternative to in vivo cell transfection, and lncRNAs are found within extracellular vesicles. EVs can be directed towards particular cell types and modified to incorporate specific molecules, rendering them as targeted delivery vehicles for tissues (96). Mesenchymal stem cells and osteoclasts can internalize extracellular vesicles from various sources, influencing osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis, indicating that extracellular vesicles may serve as carriers for long non-coding RNAs implicated in the regulation of bone metabolism. The overexpression or downregulation of lncRNA in vivo can be mitigated by the capacity of lncRNAs to recruit and bind proteins such as PCR2189 and PUMILIO190 (97, 98). This implies that their activity may be modulated by compounds capable of binding to target lncRNAs in a similar manner. Research should concentrate on identifying pharmaceuticals that can target lncRNAs, including small molecules or structurally analogous decoy proteins. The inherent interaction of lncRNAs with proteins and ligands may be investigated as carrier-like entities for drugs and proteins, including those for osteoporosis therapy (98). Advancements in genome editing, especially CRISPR/Cas9 technology, have facilitated the permanent regulation of lncRNA expression in human cells at the genetic level. This method broadens the potential for modulating lncRNA expression through strategies primarily aimed at RNA. The inaugural clinical trial in human subjects to assess the safety and efficacy of this method has commenced, with the initial trial registered under USA approval in August 2018. Chen et al. (99) investigated LncRNA gene editing via CRISPR/Cas9 in vitro to elucidate the enhancer role of the genomic locus rs6426749 concerning lncRNA LINC00339. The complex structure of lncRNAs may promote RNAi-based therapeutic approaches for lncRNAs, owing to enhanced specificity and diminished risk of gene disruption (100).
8 The role of ncRNAs in osteoporosis in relation to hip fractures
Peptidoglycan recognition protein 1 (PGLYRP1) is a crucial mRNA in osteoporosis, a condition characterized by the dysregulation of innate immunity and bacteriostatic activity. It contributes to the negative regulation of interferon-gamma production and the innate immune response. The differentiation of osteoclasts is stimulated by reduced expression of solute carrier family 11 member 1 (SLC11A1), which also plays a role in the positive regulation of interferon-gamma production and the homeostasis of cellular cadmium ions. PGLYRP1 and SLC11A1 may influence the advancement of osteoporosis by regulating various biological processes. The C-C type chemokine (CCR3) significantly contributes to osteoporosis by interacting with various chemokines and elevating intracellular calcium ion levels. CCR3 may promote osteoclast migration and is elevated during osteoclastogenesis. Osteoporosis is associated with sarcopenia, a condition predominantly connected to metabolic disorders including diabetes, obesity, and cachexia. These conditions demonstrate analogous biological pathways and risk factors, increasing bone vulnerability to osteoporosis and augmenting the probability of falls attributable to sarcopenia (101). A study aimed to clarify the RNA sequencing profile of sarcopenia in elderly female patients with osteoporosis and hip fractures, identifying a significant genetic candidate implicated in the etiology of hip fractures. The research indicates that miR-23b-3p and miR-140-3p, in conjunction with miR-21-5p, miR-122-5p, and miR-125b-5p, are associated with osteoporotic hip fractures. These miRNAs are involved in bone metabolism by suppressing osteoblast expression and facilitating osteoclastogenesis. MiR-21-5p and miR-125b-5p are associated with osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis, whereas miR-122-5p is downregulated in osteoporosis. The function of these miRNAs in bone metabolism is still ambiguous. Peripheral blood samples were collected from healthy controls, osteoporosis patients without vertebral fractures, and patients with vertebral fractures (102–105). Data were consolidated to identify differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs. Protein-protein interaction networks were established, and enrichment analyses were conducted. The Cytoscape-cytoHubba plug-in was employed to identify essential differentially expressed mRNAs. A total of 3,378 lncRNA-mRNA pairs were identified, with co-expressed mRNA predominantly enriched in immune-related pathways. This study indicates that miR-23b-3p and miR-140-3p, in conjunction with miR-21-5p, miR-122-5p, and miR-125b-5p, are associated with osteoporotic hip fractures. These miRNAs are involved in bone metabolism by suppressing osteoblast expression and facilitating osteoclastogenesis. MiR-21-5p and miR-125b-5p are associated with osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis, whereas miR-122-5p is downregulated in osteoporosis. The function of these miRNAs in bone metabolism is still ambiguous (105, 106).
9 Conclusion and future outlooks
Multiple in vivo studies have demonstrated that ncRNAs are essential in skeletal development and disorders through the regulation of gene expression. Identifying essential ncRNAs among the myriad of ncRNAs present in skeletal tissues poses a challenge in elucidating their interactions. Tissue-specific ncRNAs are essential in vivo, while in vitro investigations have elucidated their direct targets and roles in particular cell types. In vivo, functional validation can elucidate the roles of these ncRNAs within the physiological system. However, the investigation of ncRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for osteoporotic hip fractures remains nascent, necessitating further research on biological mechanisms, detection methodologies, and in vivo therapeutic administration. Nonetheless, recent findings and technological innovations are encouraging for the treatment of osteoarthritis, osteoporosis and related hip fractures.
Author contributions
JZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Stromsnes K, Fajardo CM, Soto-Rodriguez S, Kajander ERU, Lupu R-I, Pozo-Rodriguez M, et al. Osteoporosis: causes, mechanisms, treatment and prevention: role of dietary compounds. Pharmaceuticals. (2024) 17:1697. doi: 10.3390/ph17121697
2. Martiniakova M, Biro R, Kovacova V, Babikova M, Zemanova N, Mondockova V, et al. Current knowledge of bone-derived factor osteocalcin: its role in the management and treatment of diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, osteopetrosis and inflammatory joint diseases. J Mol Med. (2024) 102:435–52. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02418-8
3. Mi B, Xiong Y, Knoedler S, Alfertshofer M, Panayi AC, Wang H, et al. Ageing-related bone and immunity changes: insights into the complex interplay between the skeleton and the immune system. Bone Res. (2024) 12:42. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00346-4
4. Liang B, Burley G, Lin S, and Shi Y-C. Osteoporosis pathogenesis and treatment: existing and emerging avenues. Cell Mol Biol Letters. (2022) 27:72. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00371-3
5. Harinarayan C, Marwah R, Sahay R, Kalra S, and Babhulkar S. Clinical practice guidelines on postmenopausal osteoporosis:* An executive summary and recommendations. J mid-life Health. (2013) 4:107–26.
6. Tella SH and Gallagher JC. Prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2014) 142:155–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.09.008
7. He Y, Li Z, Alexander PG, Ocasio-Nieves BD, Yocum L, Lin H, et al. Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: risk factors, regulatory pathways in chondrocytes, and experimental models. Biology. (2020) 9:194. doi: 10.3390/biology9080194
8. Baniasadi M, Talebi S, Mokhtari K, Zabolian AH, Khosroshahi EM, Entezari M, et al. Role of non-coding RNAs in osteoporosis. Pathology-Research Practice. (2024) 253:155036. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.155036
9. Li Z, Xue H, Tan G, and Xu Z. Effects of miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs on osteoporosis as regulatory factors of bone homeostasis (Review). Mol Med Rep. (2021) 24. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12428
10. Chen Y, Sun Y, Xue X, and Ma H. Comprehensive analysis of epigenetics mechanisms in osteoporosis. Front Genet. (2023) 14:1153585. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1153585
11. Ismail SM, Abd-Elmawla MA, Shabayek MI, Darwish HA, and El-Sawalhi MM. The role of LncRNAs and CircRNAs in osteoporosis: a focus on osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis signaling pathways. Future J Pharm Sci. (2024) 10:64. doi: 10.1186/s43094-024-00640-2
12. Trojniak J, Sendera A, Banaś-Ząbczyk A, and Kopańska M. The microRNAs in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6240. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116240
13. Mattick JS, Amaral PP, Carninci P, Carpenter S, Chang HY, Chen L-L, et al. Long non-coding RNAs: definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 24:430–47. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00566-8
14. Dexheimer PJ and Cochella L. MicroRNAs: from mechanism to organism. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:409. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00409
15. Zhao X, Zhong Y, Wang X, Shen J, and An W. Advances in circular RNA and its applications. Int J Med Sci. (2022) 19:975. doi: 10.7150/ijms.71840
16. Lee WC, Guntur AR, Long F, and Rosen CJ. Energy metabolism of the osteoblast: implications for osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. (2017) 38:255–66. doi: 10.1210/er.2017-00064
17. Loganathan T and Doss C GP. Non-coding RNAs in human health and disease: potential function as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Funct Integr Genomics. (2023) 23:33. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00947-4
18. Li C, Ni Y-Q, Xu H, Xiang Q-Y, Zhao Y, Zhan J-K, et al. Roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2021) 6:383. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00779-x
19. Gautvik KM, Günther CC, Prijatelj V, Medina-Gomez C, Shevroja E, Rad LH, et al. Distinct subsets of noncoding RNAs are strongly associated with BMD and fracture, studied in weight-bearing and non–weight-bearing human bone. J Bone Mineral Res. (2020) 35:1065–76. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3974
20. Zhu D-L, Zhang Y, Zhang X-Y, Qiu Z-H, Li K, Zhou X-R, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00339 promotes osteoporosis development via modulating of regulator CDC42 by binding PARP1. Non-coding RNA Res. (2025) 15:18–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.06.004
21. Wang H, Zhou K, Xiao F, Huang Z, Xu J, Chen G, et al. Identification of circRNA-associated ceRNA network in BMSCs of OVX models for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:10896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67750-8
22. Li H, Li T, Fan J, Li T, Fan L, Wang S, et al. miR-216a rescues dexamethasone suppression of osteogenesis, promotes osteoblast differentiation and enhances bone formation, by regulating c-Cbl-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death differentiation. (2015) 22:1935–45. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.99
23. Gao M, Zhang Z, Sun J, Li B, and Li Y. The roles of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks in the development and treatment of osteoporosis. Front endocrinology. (2022) 13:945310. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.945310
24. Cai Y, Sun H, Song X, Zhao J, Xu D, and Liu M. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway inhibits osteoporosis by regulating the expression of TERT: an in vivo and in vitro study. Aging. (2023) 15:11471–88. doi: 10.18632/aging.205136
25. Zhu S, Chen W, Masson A, and Li Y-P. Cell signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis. Cell Discov. (2024) 10:71. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00689-6
26. Wang R, Zhang H, Ding W, Fan Z, Ji B, Ding C, et al. miR-143 promotes angiogenesis and osteoblast differentiation by targeting HDAC7. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:179. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2377-4
27. Yang M, Li CJ, Sun X, Guo Q, Xiao Y, Su T, et al. MiR-497∼195 cluster regulates angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis by maintaining endothelial Notch and HIF-1α activity. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:16003. doi: 10.1038/ncomms16003
28. Li CJ, Xiao Y, Yang M, Su T, Sun X, Guo Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA Bmncr regulates mesenchymal stem cell fate during skeletal aging. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:5251–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI99044.
29. Mulati M, Kobayashi Y, Takahashi A, Numata H, Saito M, Hiraoka Y, et al. The long noncoding RNA Crnde regulates osteoblast proliferation through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in mice. Bone. (2020) 130:115076. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.115076
30. Lin C, Yu S, Jin R, Xiao Y, Pan M, Pei F, et al. Circulating miR-338 cluster activities on osteoblast differentiation: potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Theranostics. (2019) 9:3780. doi: 10.7150/thno.34493
31. Liu C, Gao X, Li Y, Sun W, Xu Y, Tan Y, et al. The mechanosensitive lncRNA Neat1 promotes osteoblast function through paraspeckle-dependent Smurf1 mRNA retention. Bone Res. (2022) 10:18. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00191-3
32. Lu X-D, Han W-X, and Liu Y-X. Suppression of miR-451a accelerates osteogenic differentiation and inhibits bone loss via Bmp6 signaling during osteoporosis. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2019) 120:109378. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109378
33. Zheng M, Tan J, Liu X, Jin F, Lai R, and Wang X. miR-146a-5p targets Sirt1 to regulate bone mass. Bone Rep. (2021) 14:101013. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2021.101013
34. Li C-J, Cheng P, Liang M-K, Chen Y-S, Lu Q, Wang J-Y, et al. MicroRNA-188 regulates age-related switch between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:1509–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI77716
35. Zhao J, Huang M, Zhang X, Xu J, Hu G, Zhao X, et al. MiR-146a deletion protects from bone loss in OVX mice by suppressing RANKL/OPG and M-CSF in bone microenvironment. J Bone Mineral Res. (2019) 34:2149–61. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3832
36. Xu R, Shen X, Xie H, Zhang H, Liu D, Chen X, et al. Identification of the canonical and noncanonical role of miR-143/145 in estrogen-deficient bone loss. Theranostics. (2021) 11:5491. doi: 10.7150/thno.55041
37. Cui Q, Xing J, Yu M, Wang Y, Xu J, Gu Y, et al. Mmu-miR-185 depletion promotes osteogenic differentiation and suppresses bone loss in osteoporosis through the Bgn-mediated BMP/Smad pathway. Cell Death disease. (2019) 10:172. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1428-1
38. Saferding V, Hofmann M, Brunner JS, Niederreiter B, Timmen M, Magilnick N, et al. microRNA-146a controls age-related bone loss. Aging Cell. (2020) 19:e13244. doi: 10.1111/acel.13244
39. Pan B, Zheng L, Liu S, Fang J, Lou C, Hu X, et al. MiR-148a deletion protects from bone loss in physiological and estrogen-deficient mice by targeting NRP1. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:470. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01261-5
40. Yao Q, He T, Liao JY, Liao R, Wu X, Lin L, et al. Noncoding RNAs in skeletal development and disorders. Biol Res. (2024) 57:16. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00497-y
41. Hu CH, Sui BD, Du FY, Shuai Y, Zheng CX, Zhao P, et al. miR-21 deficiency inhibits osteoclast function and prevents bone loss in mice. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:43191. doi: 10.1038/srep43191
42. Shen G, Ren H, Shang Q, Zhang Z, Zhao W, Yu X, et al. miR-128 plays a critical role in murine osteoclastogenesis and estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss. Theranostics. (2020) 10:4334–48. doi: 10.7150/thno.42982
43. Jin F, Li J, Zhang Y-B, Liu X, Cai M, Liu M, et al. A functional motif of long noncoding RNA Nron against osteoporosis. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3319. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23642-7
44. Zhu J, Wang H, and Liu H. Osteoclastic miR-301-b knockout reduces ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss by regulating CYDR/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 529:35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.111
45. Li J, Jin F, Cai M, Lin T, Wang X, and Sun Y. LncRNA nron inhibits bone resorption in periodontitis. J Dent Res. (2022) 101:187–95. doi: 10.1177/00220345211019689
46. Huang J, Zhao L, Fan Y, Liao L, Ma PX, Xiao G, et al. The microRNAs miR-204 and miR-211 maintain joint homeostasis and protect against osteoarthritis progression. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:2876. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10753-5
47. Ji ML, Jiang H, Wu F, Geng R, Ya LK, Lin YC, et al. Precise targeting of miR-141/200c cluster in chondrocytes attenuates osteoarthritis development. Ann Rheum Dis. (2021) 80:356–66. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218469
48. Zhang X, Wang C, Zhao J, Xu J, Geng Y, Dai L, et al. miR-146a facilitates osteoarthritis by regulating cartilage homeostasis via targeting Camk2d and Ppp3r2. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:e2734. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.146
49. Litwic A, Edwards MH, Dennison EM, and Cooper C. Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull. (2013) 105:185–99. doi: 10.1093/bmb/lds038
50. Attur M, Krasnokutsky-Samuels S, Samuels J, and Abramson SB. Prognostic biomarkers in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2013) 25:136–44. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835a9381
51. Gu J, Rao W, Huo S, Fan T, Qiu M, Zhu H, et al. MicroRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:1092776. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1092776
52. Italiani P and Boraschi D. From monocytes to M1/M2 macrophages: phenotypical vs. Funct Differentiation. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:514. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00514
53. Nakamura Y, He X, Kato H, Wakitani S, Kobayashi T, Watanabe S, et al. Sox9 is upstream of microRNA-140 in cartilage. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. (2012) 166:64–71. doi: 10.1007/s12010-011-9404-y
54. Miyaki S, Sato T, Inoue A, Otsuki S, Ito Y, Yokoyama S, et al. MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and homeostasis. Genes Dev. (2010) 24:1173–85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1915510
55. Ito Y, Matsuzaki T, Ayabe F, Mokuda S, Kurimoto R, Matsushima T, et al. Both microRNA-455-5p and -3p repress hypoxia-inducible factor-2α expression and coordinately regulate cartilage homeostasis. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:4148. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24460-7
56. Tuerlings M, van Hoolwerff M, van Bokkum JM, Suchiman HED, Lakenberg N, Broekhuis D, et al. Long non-coding RNA expression profiling of subchondral bone reveals AC005165. 1 modifying FRZB Expression during osteoarthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2022) 61:3023–32. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab826
57. Wang XB, Zhao FC, Yi LH, Tang JL, Zhu ZY, Pang Y, et al. MicroRNA-21-5p as a novel therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2019). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez102
58. Wang H, Zhang H, Sun Q, Wang Y, Yang J, Yang J, et al. Intra-articular delivery of antago-miR-483-5p inhibits osteoarthritis by modulating matrilin 3 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2. Mol Ther. (2017) 25:715–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.12.020
59. Endisha H, Datta P, Sharma A, Nakamura S, Rossomacha E, Younan C, et al. MicroRNA-34a-5p promotes joint destruction during osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2021) 73:426–39. doi: 10.1002/art.41552
60. Liu D, Liang YH, Yang YT, He M, Cai ZJ, Xiao WF, et al. Circular RNA in osteoarthritis: an updated insight into the pathophysiology and therapeutics. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13:11–23.
61. Tang S, Nie X, Ruan J, Cao Y, Kang J, and Ding C. Circular RNA circNFKB1 promotes osteoarthritis progression through interacting with ENO1 and sustaining NF-κB signaling. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:695. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05148-2
62. Zhu H, Hu Y, Wang C, Zhang X, and He D. CircGCN1L1 promotes synoviocyte proliferation and chondrocyte apoptosis by targeting miR-330-3p and TNF-α in TMJ osteoarthritis. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:284. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2447-7
63. Shen S, Wu Y, Chen J, Xie Z, Huang K, Wang G, et al. CircSERPINE2 protects against osteoarthritis by targeting miR-1271 and ETS-related gene. Ann Rheum Dis. (2019) 78:826–36. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214786
64. Zhao C, Li X, Sun G, Liu P, Kong K, Chen X, et al. CircFOXO3 protects against osteoarthritis by targeting its parental gene FOXO3 and activating PI3K/AKT-mediated autophagy. Cell Death Disease. (2022) 13:932. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05390-8
65. Shen S, Yang Y, Shen P, Ma J, Fang B, Wang Q, et al. circPDE4B prevents articular cartilage degeneration and promotes repair by acting as a scaffold for RIC8A and MID1. Ann Rheumatic Diseases. (2021) 80:1209–19. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-219969
66. Zhang Q, Qiao X, and Xia W. CircSERPINE2 weakens IL-1β-caused apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of chondrocytes by regulating miR-495/TGFBR2 axis. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201601
67. Lin Z, Ma Y, Zhu X, Dai S, Sun W, Li W, et al. Potential predictive and therapeutic applications of small extracellular vesicles-derived circPARD3B in osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:968776. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.968776
68. Bourgery M, Ekholm E, Hiltunen A, Heino TJ, Pursiheimo JP, Bendre A, et al. Signature of circulating small non-coding RNAs during early fracture healing in mice. Bone Rep. (2022) 17:101627. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2022.101627
69. Wang B, Sun Y, Liu N, and Liu H. LncRNA HOTAIR modulates chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-1277-5p/SGTB axis. Wound Repair Regen. (2021) 29:495–504. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12908
70. Fu Q, Zhu J, Wang B, Wu J, Li H, Han Y, et al. LINC02288 promotes chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation through miR-374a-3p targeting RTN3. J Gene Med. (2021) 23:e3314. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3314
71. Hu J, Wang Z, Shan Y, Pan Y, Ma J, and Jia L. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes osteoarthritis progression via miR-17-5p/FUT2/β-catenin axis. Cell Death disease. (2018) 9:711. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0746-z
72. Chen Y, Zhang L, Li E, Zhang G, Hou Y, Yuan W, et al. Long-chain non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes the progression of osteoarthritis via sponging miR-20b/PTEN axis. Life Sci. (2020) 253:117685. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117685
73. Feng L, Yang ZM, Li YC, Wang HX, Lo JHT, Zhang XT, et al. Linc-ROR promotes mesenchymal stem cells chondrogenesis and cartilage formation via regulating SOX9 expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. (2021) 29:568–78. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.12.020
74. Loi F, Córdova LA, Pajarinen J, Lin TH, Yao Z, and Goodman SB. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair. Bone. (2016) 86:119–30. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.02.020
75. Zheng XQ, Huang J, Lin JL, and Song CL. Pathophysiological mechanism of acute bone loss after fracture. J advanced Res. (2023) 49:63–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.019
76. Chen Z, Liu Z, Shen L, and Jiang H. Long non-coding RNA SNHG7 promotes the fracture repair through negative modulation of miR-9. Am J Transl Res. (2019) 11:974–82.
77. Tan A-Q and Zheng Y-F. The roles of SNHG family in osteoblast differentiation. Genes. (2022) 13:2268. doi: 10.3390/genes13122268.
78. Yao J, Xin R, Zhao C, and Yu C. MicroRNAs in osteoblast differentiation and fracture healing: From pathogenesis to therapeutic implication. Injury. (2024) 55:111410. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2024.111410
79. Pan L and Ding W. LncRNA HAGLR accelerates femoral neck fracture healing through negatively regulating miRNA-19a-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:4080–7. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_20984
80. Sun X, Xie Z, Ma Y, Pan X, Wang J, Chen Z, et al. TGF-β inhibits osteogenesis by upregulating the expression of ubiquitin ligase SMURF1 via MAPK-ERK signaling. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:596–606. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25920
81. Chen Y, Huang K, Ji W, Huang M, Sima J, Li J, et al. LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 is involved in osteogenic differentiation in fracture healing via miR-423-5p. Cytotechnology. (2025) 77:135. doi: 10.1007/s10616-025-00786-8
82. Chen X, Yang L, Ge D, Wang W, Yin Z, Yan J, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes osteoporosis through inhibiting bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Exp Ther Med. (2019) 17:803–11. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7033
83. Fei Q, Bai X, Lin J, Meng H, Yang Y, and Guo A. Identification of aberrantly expressed long non-coding RNAs in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Int J Mol Med. (2018) 41:3537–50. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3575
84. Huang S, Zhu X, Xiao D, Zhuang J, Liang G, Liang C, et al. LncRNA SNHG1 was down-regulated after menopause and participates in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Biosci Rep. (2019) 39. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190445
85. Luo J, Li L, Shi W, Xu K, Shen Y, and Dai B. Oxidative stress and inflammation: roles in osteoporosis. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1611932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1611932
86. Wang T and He C. TNF-α and IL-6: the link between immune and bone system. Curr Drug targets. (2020) 21:213–27. doi: 10.2174/1389450120666190821161259
87. Yu H, Zhou W, Yan W, Xu Z, Xie Y, and Zhang P. LncRNA CASC11 is upregulated in postmenopausal osteoporosis and is correlated with TNF-α. Clin Interventions aging. (2019) 14:1663–9. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S205796
88. Huang Y, Xie J, and Li E. Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals circ_0002060 as a potential diagnostic biomarkers for osteoporosis. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:15688–94. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28838
89. Patil S, Dang K, Zhao X, Gao Y, and Qian A. Role of lncRNAs and circRNAs in bone metabolism and osteoporosis. Front Genet. (2020) 11:584118. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.584118
90. Jiménez-Ortega RF, Aparicio-Bautista DI, Becerra-Cervera A, Ortega-Meléndez AI, Patiño N, Rivera-Paredez B, et al. The regulatory role of long non-coding RNAs in the development and progression of osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:4273. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094273
91. Sidi AA, Ohana P, Benjamin S, Shalev M, Ransom JH, Lamm D, et al. Phase I/II marker lesion study of intravesical BC-819 DNA plasmid in H19 over expressing superficial bladder cancer refractory to bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J urology. (2008) 180:2379–83. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.08.006
92. Hou J, Zhang G, Wang X, Wang Y, and Wang K. Functions and mechanisms of lncRNA MALAT1 in cancer chemotherapy resistance. biomark Res. (2023) 11:23. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00467-8
93. Li X, Dai Y, Yan S, Shi Y, Han B, Li J, et al. Down-regulation of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury following acute myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 491:1026–33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.08.005
94. Moore CB, Guthrie EH, Huang MT, and Taxman DJ. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA): design, delivery, and assessment of gene knockdown. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton NJ). (2010) 629:141–58. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-657-3_10
95. Sliva K and Schnierle BS. Selective gene silencing by viral delivery of short hairpin RNA. Virol J. (2010) 7:248. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-248
96. Payandeh Z, Tangruksa B, Synnergren J, Heydarkhan-Hagvall S, Nordin JZ, Andaloussi SEL, et al. Extracellular vesicles transport RNA between cells: Unraveling their dual role in diagnostics and therapeutics. Mol Aspects Med. (2024) 99:101302. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2024.101302
97. Geng Z, Sun T, Yuan L, and Zhao Y. The existing evidence for the use of extracellular vesicles in the treatment of osteoporosis: a review. Int J Surg (London England). (2025) 111:3414–29. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002339
98. Silva AM, Moura SR, Teixeira JH, Barbosa MA, Santos SG, and Almeida MI. Long noncoding RNAs: a missing link in osteoporosis. Bone Res. (2019) 7:10. doi: 10.1038/s41413-019-0048-9
99. Chen XF, Zhu DL, Yang M, Hu WX, Duan YY, Lu BJ, et al. An Osteoporosis Risk SNP at 1p36.12 Acts as an Allele-Specific Enhancer to Modulate LINC00339 Expression via Long-Range Loop Formation. Am J Hum Genet. (2018) 102:776–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.03.001
100. You L, Tong R, Li M, Liu Y, Xue J, and Lu Y. Advancements and obstacles of CRISPR-cas9 technology in translational research. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. (2019) 13:359–70. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2019.02.008
101. Sun R, Duan D, and Li R. Transcriptome Sequencing Identifies Abnormal lncRNAs and mRNAs and Reveals Potentially Hub Immune-Related mRNA in Osteoporosis with Vertebral Fracture. Clin Interventions aging. (2024) 19:203–17. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S441251
102. Kang YJ, Yoo JI, and Baek KW. Differential gene expression profile by RNA sequencing study of elderly osteoporotic hip fracture patients with sarcopenia. J orthopaedic translation. (2021) 29:10–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2021.04.009
103. Jones TL, Esa MS, Li KC, Krishnan SG, Elgallab GM, Pearce MS, et al. Osteoporosis, fracture, osteoarthritis & sarcopenia: A systematic review of circulating microRNA association. Bone. (2021) 152:116068. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.116068
104. Wu Y-Z, Huang H-T, Cheng T-L, Lu Y-M, Lin S-Y, Ho C-J, et al. Application of microRNA in human osteoporosis and fragility fracture: A systemic review of literatures. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:5232. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105232
105. Garg B, Malhotra R, Mittal S, Kumar A, Mehta N, Malik G, et al. Differential miRNA expression in osteoporotic elderly patients with hip fractures compared to young patients. Indian J orthopaedics. (2022) 56:399–411. doi: 10.1007/s43465-021-00561-9
106. Ramírez-Salazar EG, Carrillo-Patiño S, Hidalgo-Bravo A, Rivera-Paredez B, Quiterio M, Ramírez-Palacios P, et al. Serum miRNAs miR-140-3p and miR-23b-3p as potential biomarkers for osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture in postmenopausal Mexican-Mestizo women. Gene. (2018) 679:19–27. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.074
Keywords: hip fracture, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, non-coding RNAs, biomarkers, diagnostics
Citation: Zhang C, Chen Y and Zhang J (2025) Non-coding RNAs in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis-related hip fractures: molecular biomarkers for precision diagnosis and prognosis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1653831. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1653831
Received: 26 June 2025; Accepted: 16 September 2025;
Published: 13 October 2025.
Edited by:
Giacomina Brunetti, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian Zhang, WmhhbmdqaWFuQGhvc3BpdGFsLmNxbXUuZWR1LmNu
 Chengxuan Zhang1
Chengxuan Zhang1 Jian Zhang
Jian Zhang