- 1Department of Endocrinology, Longyan First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Longyan, China
- 2Department of Physical Examination, Longyan First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Longyan, China
- 3The School of Clinical Medicine, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
By Zhong L, Lin R, Cao B, Zhong W, Tu M and Wei W (2025). Front. Endocrinol. 16:1591108. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1591108
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2D as published. We found that the figure in Figure 2C and Figure 2D are duplicated, and the x-axis of Figure 2D should be TFQI. The corrected Figure 2D and its caption appear below.
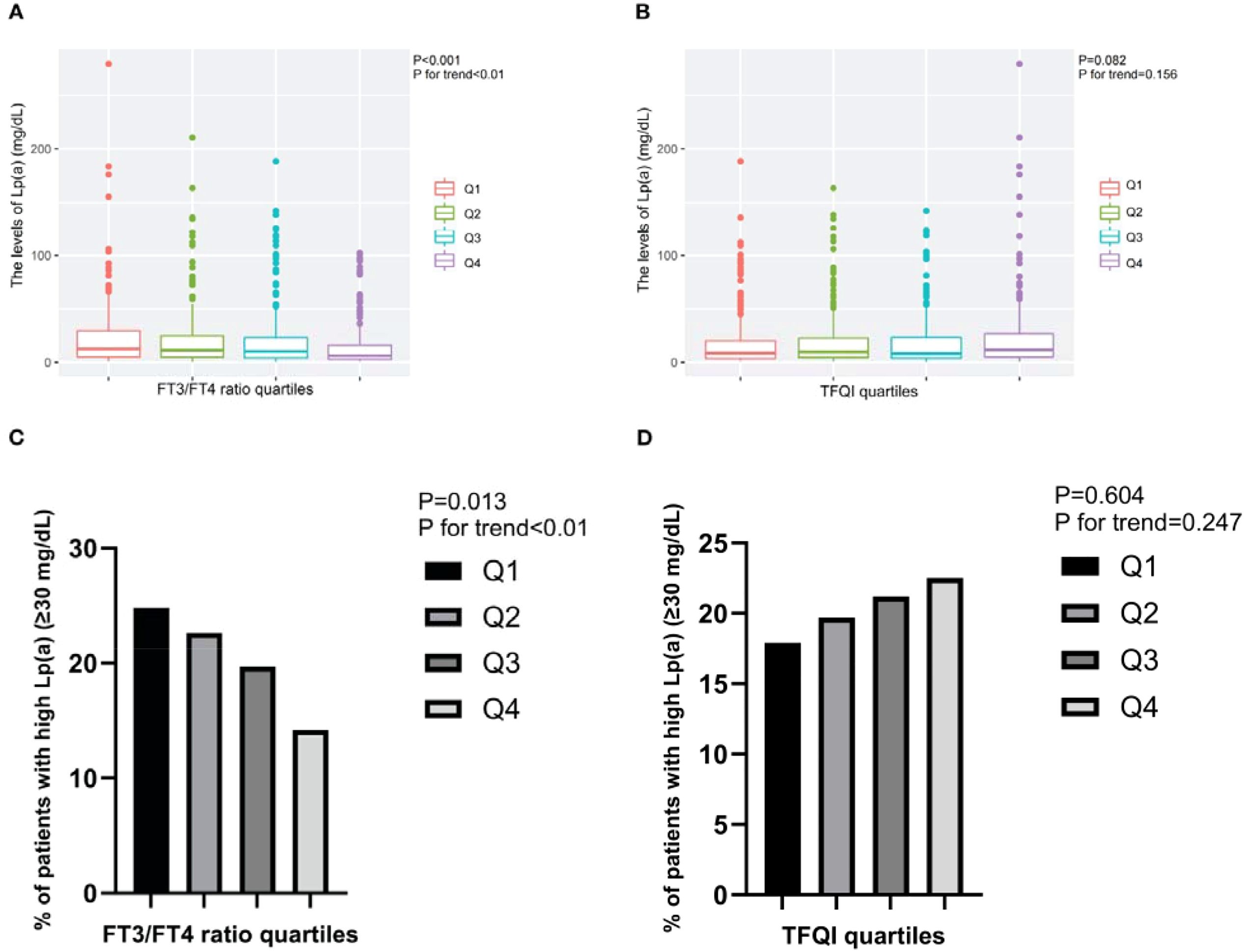
Figure 2. The levels of Lp(a) and the prevalence of T2DM patients with high Lp(a) level across the quartiles of thyroid parameters. (A) The levels of Lp(a) across the FT3/FT4 ratio quartiles. (B) The levels of Lp(a) across the TFQI quartiles. (C) The prevalence of T2DM patients with high Lp(a) level across the FT3/FT4 ratio quartiles. (D) The prevalence of T2DM patients with high Lp(a) level across the TFQI quartiles. Q1, the 1st quartiles; Q2, the 2nd quartiles; Q3, the 3rd quartiles; Q4, the 4th quartiles; Lp(a), lipoprotein(a); NS, P>0.05; FT3, Free Triiodothyronine; FT4, Free Thyroxine; TFQI, Thyroid feedback quantile-based index; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The original version of this article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: lipoprotein(a), sensitivity to thyroid hormones, type 2 diabetes mellitus, thyroid feedback quantile-based index, free triiodothyronine/free thyroxine ratio
Citation: Zhong L, Lin R, Cao B, Zhong W, Tu M and Wei W (2025) Correction: Impaired sensitivity to thyroid hormones is associated with high lipoprotein(a) level in euthyroid patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1654047. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1654047
Received: 25 June 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Davide Gnocchi, University of Bari Medical School, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Zhong, Lin, Cao, Zhong, Tu and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wen Wei, MTgxMzkwOTg5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Mei Tu, dG0xMzg1OTU5NjYyOEAxNjMuY29t
 Luojing Zhong
Luojing Zhong Ruiyu Lin
Ruiyu Lin Baozhen Cao1
Baozhen Cao1 Wen Wei
Wen Wei