- 1Department of Endocrinology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is increasingly recognized as a risk factor for cognitive impairment, ranging from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to dementia. The underlying mechanisms involve a complex interplay of hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, vascular dysfunction, and amyloid pathology. Effective management strategies remain an area of active investigation. This review explores the pathophysiological mechanisms linking T2D to cognitive dysfunction and evaluates current and emerging therapeutic strategies to preserve cognitive function in diabetic patients. Chronic hyperglycemia and insulin resistance impair neuronal function and synaptic plasticity, while microvascular complications contribute to cerebral hypoperfusion and white matter lesions. Additionally, metabolic disturbances exacerbate neurodegenerative processes, further compromising cognitive health. Effective management strategies for cognitive impairment in T2D include regular cognitive screening, stringent glycemic control, lifestyle modifications, comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, patient education and pharmacological interventions such as metformin, GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1RAs), and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which may offer neuroprotective benefits. In this review, we conclude that cognitive impairment in T2D results from complex, interrelated mechanisms requiring early intervention and personalized strategies. While current therapies focus on metabolic and vascular risk reduction, future research should prioritize biomarker discovery, mechanism-driven treatments, and long-term clinical trials to optimize outcomes. A proactive, integrated care model is essential to mitigate cognitive decline in this high-risk population.
1 Introduction
A growing body of literature has demonstrated that type 2 diabetes (T2D) is increasingly recognized as a significant risk factor for cognitive impairment, including mild cognitive impairment (MCI), dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease (AD), particularly in domains of memory, executive function, and processing speed (1, 2). All cognitive impairment could lead to reduced treatment compliance, medication management, and self-care ability in T2D patients. Cognitive impairment in T2D manifests through a characteristic pattern of deficits that primarily affect memory, executive function, and processing speed (3). Patients often experience gradual declines in episodic memory, struggling to recall recent events or retain new information, alongside noticeable difficulties in complex tasks requiring planning, decision-making, and mental flexibility (4). Executive dysfunction is particularly prominent, leading to impaired problem-solving abilities and reduced capacity to multitask (5, 6). Additionally, slowed information processing results in delayed responses during cognitive tasks and conversations (7). Many patients also report increased distractibility and working memory challenges, while visuospatial difficulties may emerge in later stages (8). These cognitive changes frequently co-occur with mood disturbances, such as depression, and often correlate with longer diabetes duration, poor glycemic control, and the presence of microvascular complications (9). Hence, early recognition of these manifestations is critical for timely intervention to preserve cognitive function in diabetic patients (10).
The growing prevalence of T2D worldwide is expected to contribute to a significant increase in dementia cases (9). Cognitive impairment in T2D patients not only diminishes personal autonomy—increasing reliance on caregivers for daily activities—but also exacerbates socioeconomic burdens through lost productivity and higher medical costs associated with dementia care. Early intervention can preserve functional abilities, allowing individuals to maintain meaningful social roles, employment, and community engagement for longer periods. Furthermore, mitigating cognitive decline reduces caregiver strain, which disproportionately affects families and healthcare systems in aging populations. Public health initiatives targeting diabetes-related cognitive risks could yield substantial societal benefits by delaying disability onset, reducing long-term care needs, and promoting healthier aging. Given the rising global prevalence of T2D, addressing its cognitive consequences is not just a medical imperative but a societal necessity to foster resilient communities and sustainable healthcare systems for future generations.
Chronic hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and microvascular dysfunction drive pathological processes such as neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and amyloid deposition, which collectively impair synaptic plasticity and cognitive function (4). While glycemic control remains a cornerstone of diabetes management, certain antidiabetic agents may offer additional neuroprotective benefits beyond glucose-lowering effects (11). Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, a newer class of glucose-lowering drugs, have emerged as promising candidates for mitigating diabetes-associated cognitive decline (12, 13). Beyond their renal and cardiovascular benefits, preclinical and clinical evidence suggests that SGLT2 inhibitors may improve cognitive outcomes through multifaceted mechanisms, including enhanced cerebral metabolism, reduced neuroinflammation, improved endothelial function, and direct neuroprotective effects (14). This review explores the pathophysiological links between T2D and cognitive impairment, examines the potential mechanisms by which early intervention and personalized strategies confer cognitive benefits, and discusses the clinical implications of these findings for diabetes management and dementia prevention.
2 Evidence of cognitive impairment associated with T2D
Cognitive impairment is a well-documented complication of T2D, affecting memory, executive function, attention, and processing speed (15). Additionally, the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia is approximately twice as high in individuals with T2D (16). Moreover, the rate of progression from MCI to dementia is 1.5 to 3.0 times higher in patients with T2D than in those without T2D (17). The Rotterdam Study and the Framingham Heart Study have demonstrated that T2D is associated with a 50-100% increased risk of dementia (18, 19). The Health and Retirement Study provided evidence that individuals with T2D had a 1.66-fold higher likelihood of cognitive impairment without dementia, as compared to those with normal cognition, among participants of European ancestry (20). In the rural China, the prevalence of MCI in older individuals with T2D was 53.48% (21). A systematic evaluation showed that incidence of cognitive impairment in elderly patients with T2D in China was 48%, with a higher incidence in population who were female, with a lower education level, a low income, no spouse, and living alone (22). A meta-analysis of T2D cases twelve years ago reported an increase of 73% in the risk of all types of cognitive impairment and 56% in the risk of AD in diabetic patients (23). Biomarkers of AD and AD-related dementias (ADRD) play a crucial role in the accurate diagnosis of AD and ADRD. In longitudinal cohort of the Look AHEAD–Continuation study, which included overweight or obese elderly with T2D, increasing plasma levels of neurofilament light chain (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) were found to be associated with impaired cognitive function, but Aβ42/40 or pTau-181 were not associated with cognitive decline (24).
3 Cause and risk factors linking T2D to cognitive impairment
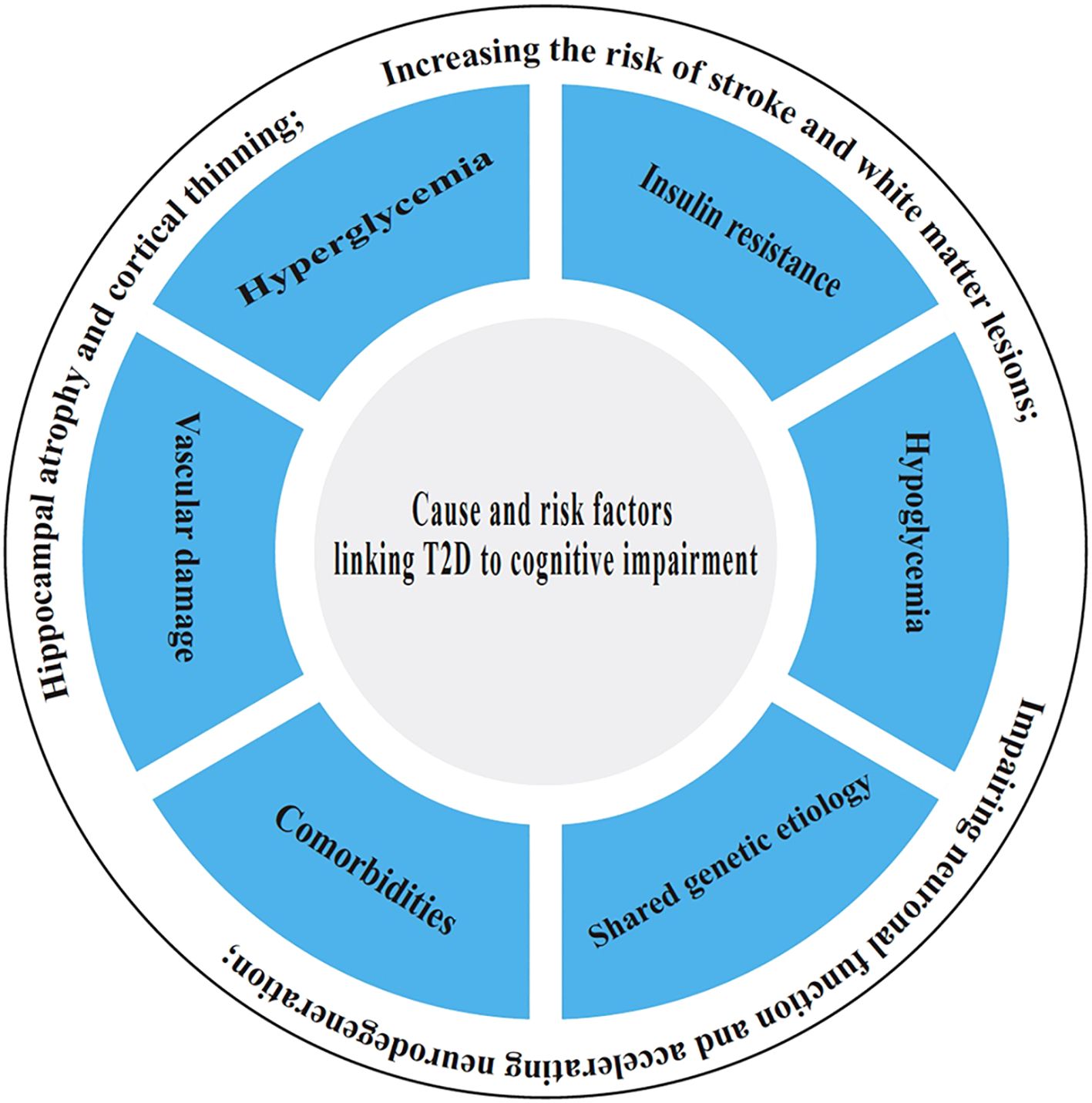
The underlying causes and risk factors linking T2D to cognitive impairment involve a complex interplay of metabolic disturbances, including chronic hyperglycemia and insulin resistance, which collectively lead to vascular damage, reduced cerebral blood flow, and microvascular complications, increasing the risk of stroke and white matter lesions (25). Additionally, prolonged high blood sugar levels promote oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and the accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which impair neuronal function and accelerate neurodegeneration. Other risk factors include obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, which are common in T2D and further exacerbate cognitive decline (26). Poor glycemic control, longer diabetes duration, and recurrent hypoglycemic episodes also contribute to structural brain changes, such as hippocampal atrophy and cortical thinning. Genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors like physical inactivity and poor diet may further amplify the risk, highlighting the complex interplay between metabolic dysfunction and cognitive deterioration in T2D. It is as reflected by Figure 1.
3.1 Hyperglycemia
Chronically elevated blood glucose is a key factor linking T2D to MCI, dementia, and AD (27). Data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) indicate that elevated long-term mean HbA1c levels are significantly linked to an increased risk of cognitive impairment (CI), particularly in the domains of global cognition and episodic memory (28). Prolonged exposure to high blood glucose levels induces oxidative stress, triggers inflammatory responses, and facilitates the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which cross-link proteins and lipids, thereby impairing neuronal function, exacerbating inflammation, and accelerating neurodegenerative processes (29). Persistent hyperglycemia also disrupts Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) integrity, allowing harmful substances to enter the brain and trigger neuroinflammation (30). Chronic hyperglycemia in T2D damages small blood vessels, which reduces cerebral blood flow and leads to white matter hyperintensities, impairing connectivity between brain regions (31). Hyperglycemia may alter gene expression related to synaptic plasticity and neurodegeneration (32).
3.2 Insulin resistance
Insulin crosses the BBB and binds to receptors in neurons, supporting synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and glucose metabolism. Insulin resistance is a hallmark of T2D and plays a central role in cognitive decline (33). Insulin resistance in the brain reduces glucose uptake and energy deficits, and then neurons become energy-deprived due to impaired glucose utilization and synaptic plasticity (34). Neuronal insulin resistance disrupts long-term potentiation (LTP) which is critical for learning and memory, and decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) resulting in neurodegeneration (35). Moreover, insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) is the key molecular to clear both insulin and amyloid-β (Aβ). Hyperinsulinemia from insulin resistance competes for IDE, which may contribute to reduce Aβ clearance leading to increasing amyloid plaques (36). Insulin resistance also activates glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), promoting tau phosphorylation and neurofibrillary tangles (37). Furthermore, loss of insulin signal in microglia leads to mitochondrial dysfunction, diminishes the autophagy process, and promotes neuroinflammation. This cascade of events contributes to the accumulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-6, TNF-a), impaired Aβ clearance, and accelerates the progression of AD (38–40). A case-control study demonstrated that serum levels of IL-6 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) were significantly associated with the risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among Chinese patients with T2D (41). Additionally, chronic insulin resistance impairs endothelial function resulting in decreasing cerebral blood flow and breakdown of the BBB, allowing toxins and inflammatory molecules into the brain (42).
3.3 Vascular damage
Vascular damage is a critical pathway linking T2D to cognitive impairment and dementia. Chronic hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in T2D lead to endothelial dysfunction, BBB disruption, and micro- and macrovascular damage, impairing cerebral blood flow and promoting ischemia (43). Small vessel disease manifests as white matter hyperintensities, microinfarcts, and microbleeds, disrupting neural connectivity and accelerating cognitive decline (44). Additionally, diabetes exacerbates cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and atherosclerosis, increasing stroke risk and compounding neurodegeneration (45). Neuroimaging studies show that individuals with T2D exhibit greater white matter lesions and brain atrophy, correlating with poorer memory and executive function (46). Thus, vascular damage serves as a key mediator between T2D and dementia, highlighting the importance of early vascular risk factor management in diabetic patients.
3.4 Hypoglycemia
Severe or recurrent hypoglycemic episodes, often a side effect of diabetes treatment, contributes to cognitive impairment in T2D through multiple mechanisms (47). Data from the CHARLS cohort also suggest that excessively low HbA1c levels, as well as greater fluctuations in HbA1c, are associated with an increased risk of CI (28). Severe hypoglycemic episodes can lead to acute neuronal damage by depriving the brain of glucose, its primary energy source, resulting in synaptic dysfunction, oxidative stress, and even selective neuronal death, particularly in memory-related regions like the hippocampus (48). Recurrent hypoglycemia may also impair cognitive reserve over time, accelerating neurodegeneration and increasing dementia risk (49, 50). Additionally, hypoglycemia-induced inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption further exacerbate cognitive decline. Epidemiological studies show that individuals with T2D who experience severe hypoglycemia have a higher risk of developing dementia, suggesting a bidirectional relationship between poor glycemic control and cognitive dysfunction (51–53). Therefore, balancing glycemic targets to avoid both hyper- and hypoglycemia is crucial for preserving brain health in diabetes management.
3.5 Comorbidities
Comorbidities of T2D significantly contribute to cognitive impairment through interconnected metabolic, vascular, and inflammatory pathways. Hypertension, commonly coexisting with T2D, exacerbates cerebrovascular damage by promoting small vessel disease, white matter lesions, and microinfarcts, which impair cognitive function (54, 55). Obesity and dyslipidemia drive systemic inflammation and insulin resistance, further compromising brain metabolism and increasing Aβ deposition (28, 56–59). Diabetic nephropathy reduces toxin clearance and promotes uremic encephalopathy, while peripheral neuropathy may limit physical activity, worsening cerebral blood flow (60). Sleep apnea, prevalent in T2D, induces chronic intermittent hypoxia and oxidative stress, accelerating hippocampal atrophy (61, 62). Depression, another frequent comorbidity, not only diminishes cognitive reserve but also shares underlying mechanisms with neurodegeneration, including hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction (63, 64). Several studies have suggested a causal relationship between depression and an increased risk of developing T2D, with both major depressive disorder and depressive symptoms showing a positive association with T2D. However, the causal relationship between depression and cognitive disorders in individuals with T2D remains to be further investigated (65–67). Insulin resistance plays an important role in the development of depressive symptom and cognitive decline in individuals with T2D (68). Together, these comorbidities create a synergistic assault on brain health, amplifying T2D’s direct neurotoxic effects and substantially elevating dementia risk. This highlights the importance of comprehensive, multi-system management in preserving cognitive function in diabetic patients.
3.6 Shared genetic etiology underlying AD and T2D
Emerging evidence reveals a shared genetic etiology between AD and T2D, suggesting common biological pathways drive both conditions (69). Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified overlapping risk loci, including APOE-ϵ4 (which influences lipid metabolism and amyloid clearance), CLU (involved in synaptic maintenance and glucose homeostasis), and IDE (insulin-degrading enzyme, which clears both insulin and amyloid-beta) (70, 71). Bioinformatics analysis of effective biomarkers in type 2 diabetes with cognitive impairment and aging indicates that the genes TP53 and IL1B may play a potential role in influencing the progression of type 2 diabetes associated with cognitive impairment and aging through the Lipid and atherosclerosis, MAPK signaling, and fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis signaling pathways (72). Polygenic risk scores for T2D correlate with higher AD incidence, while Mendelian randomization studies support a causal link between insulin resistance and neurodegeneration (73). Shared mechanisms include impaired insulin signaling in the brain, mitochondrial dysfunction, and chronic inflammation, which exacerbate amyloid and tau pathology. These findings highlight the role of metabolic dysregulation in AD pathogenesis and suggest that T2D and AD may represent different manifestations of a broader “metabolic-cognitive syndrome,” opening avenues for targeted therapies that address both conditions.
3.7 Gut microbiota and AD in T2D
Microbial balance plays a crucial role in maintaining glucose homeostasis and safeguarding cognitive function. Growing evidence has shown that an imbalance in gut microbiota is linked to the pathogenesis of T2D (74–76). Furthermore, it suggests that gut microbiota affects cognitive impairment associated with T2D via the gut-brain axis (77, 78). In the Hong study, it was reported that patients with diabetic cognitive dysfunction exhibited a reduced abundance of Bifidobacterium and unnamed bacteria RF39, along with an increased abundance of Peptidococcus and Leucococcus (79). In the cognitive impairment db/db diabetic mouse model, fecal microbiota analysis revealed that species abundance and diversity in db/db mice were significantly higher compared to those in the control group (80). The microbiota-gut-brain axis includes neural, immune, endocrine, and metabolic pathways, but the communication system is not fully understood. Recent studies suggest that microbiota dysbiosis and T2D caused by long-term high-fat diet (HFD) increase permeability of the gut and blood-brain barrier mediated neurodegenerative disorders (81–83). In addition, diabetic cognitive impairment is associated with neuroinflammation induced by imbalance of the gut microbiota (84, 85).
4 Molecular mechanisms underlying cognitive impairment in T2D
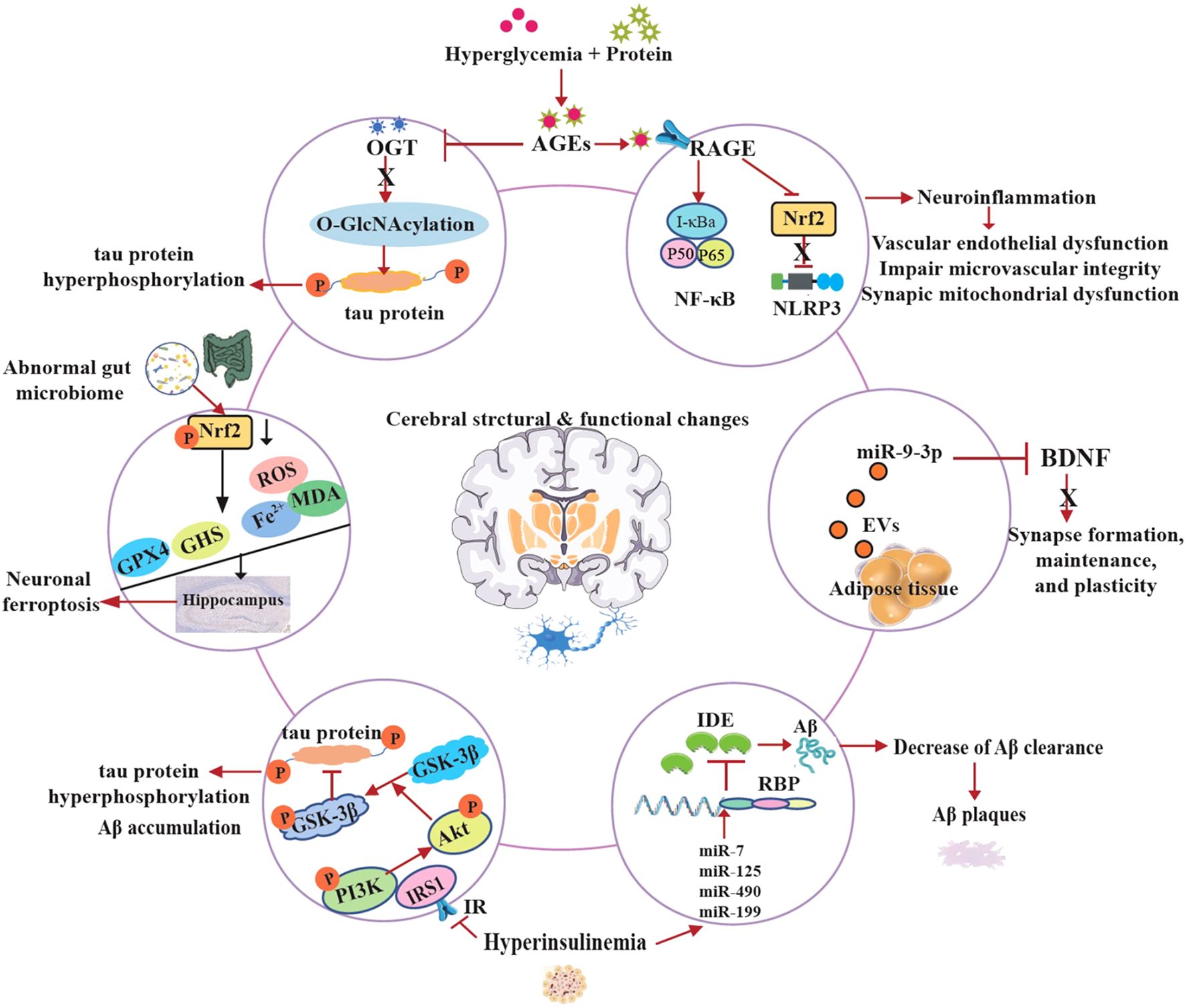
The pathogenesis of cognitive decline in T2D is unclear and the exact molecular mechanisms are complex and multifactorial. Emerging research reveals that T2D-induced cognitive dysfunction involves intricate molecular pathways that disrupt neuronal homeostasis and synaptic plasticity (86). At the cellular level, chronic hyperglycemia activates the polyol pathway leading to advanced glycation end products (AGEs) formation. On the one hand, AGEs reduced the levels of O-Linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase (OGT), thereby downregulating O-GlcNAcylation and inducing tau protein hyperphosphorylation, which is implicated in diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction (87). On the other hand, AGEs crosslink with the receptor of AGEs (RAGE), activating NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasomes, perpetuating a vicious cycle of neuroinflammation (88). Moreover, this process impairs cerebral microvascular integrity and induces synaptic mitochondrial dysfunction (89, 90).
IDE is an atypical zinc-metalloprotease that plays a key role in regulating insulin and Aβ levels in the brain and peripheral tissues. It degrades both insulin and Aβ. Hyperinsulinemia refers to excess insulin levels in the blood due to insulin resistance. High insulin levels and insulin resistance are suggested to be associated with reduction of IDE (91). The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the relationship between hyperinsulinemia and IDE expression remain poorly understood. The novel insights into the regulation of IDE reveal that miR-7, miR-125, miR-490 and miR-199 downregulate IDE expression at the post-transcriptional level in response to high insulin levels. In addition, the authors found that IDE contains multiple potential binding sites for several RNA binding proteins (RBP) (92, 93). Furthermore, insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) proteins become less active due to the development of hyperinsulinemia, which arises from insulin resistance as a result of the reduced expression of insulin receptors (IR). The inactive of IRS1 leads to the down-regulation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway and the up-regulation of GSK-3β activity, and promotes tau hyperphosphorylation and Aβ accumulation in the brain (37, 94, 95).
The dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus is a crucial brain region involved in memory encoding. Tang et al. found that neuronal ferroptosis in the hippocampus contributes to the initiation and development of learning impairment and memory processes in T2D mice (96, 97). Recent studies indicate that diabetes causes hippocampal neuronal damage and loss due to increased iron concentrations, MDA, and ROS levels, along with decreased GSH and GPX4. Furthermore, the underlying mechanism of neuronal ferroptosis is associated with the inhibition of Nrf2 in the hippocampus induced by T2D (88, 98). In recent years, a growing research interest in microbiota-gut-brain with T2D has been demonstrated that the gut microbiota plays an important role in the development of metabolic disorders. Specially, in the central nervous system (CNS), suggested by preclinical studies indicate that the restoration of intestinal microbiota may enhance cognitive function impaired by diabetes and ameliorate hippocampal neuron ferroptosis (77, 99).
In the latest study, authors identified that the miR-9-3p cargo in adipose tissue-derived extracellular vesicle (EVs) obtained from high-fat diet-fed mice or patients with T2D significantly suppressed BDNF levels in primary neurons, thereby inducing synaptic damage associated with obesity-related insulin resistance (33).
The large-scale proteomic analysis conducted as part of the UK Biobank Pharma Proteomics Project demonstrated that a 51-protein model exhibited excellent accuracy in predicting the 15-year risk of dementia among individuals with T2D. Furthermore, elevated levels of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 12 (ARHGEF12) was specifically linked to an increased risk of dementia. Pathway analysis revealed that elevation of IL6-JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway was involved in the development of dementia in T2D patients. Additionally, dysregulation of fatty acid was identified as a specific mechanism associated with the pathogenesis of AD in the context of T2D (100). These results may have potential applications in early risk stratification and targeted interventions, and may indicate possible therapeutic targets.
Overall, these evidences provide these molecular perturbations collectively drive synaptotoxicity, white matter degeneration, and accelerated amyloidogenesis, positioning T2D as a potent modifier of Alzheimer’s pathology (Figure 2). Therapeutic targeting of these pathways may offer neuroprotection in diabetic cognitive decline.
5 Evidence from intervention of cognitive impairment in T2D
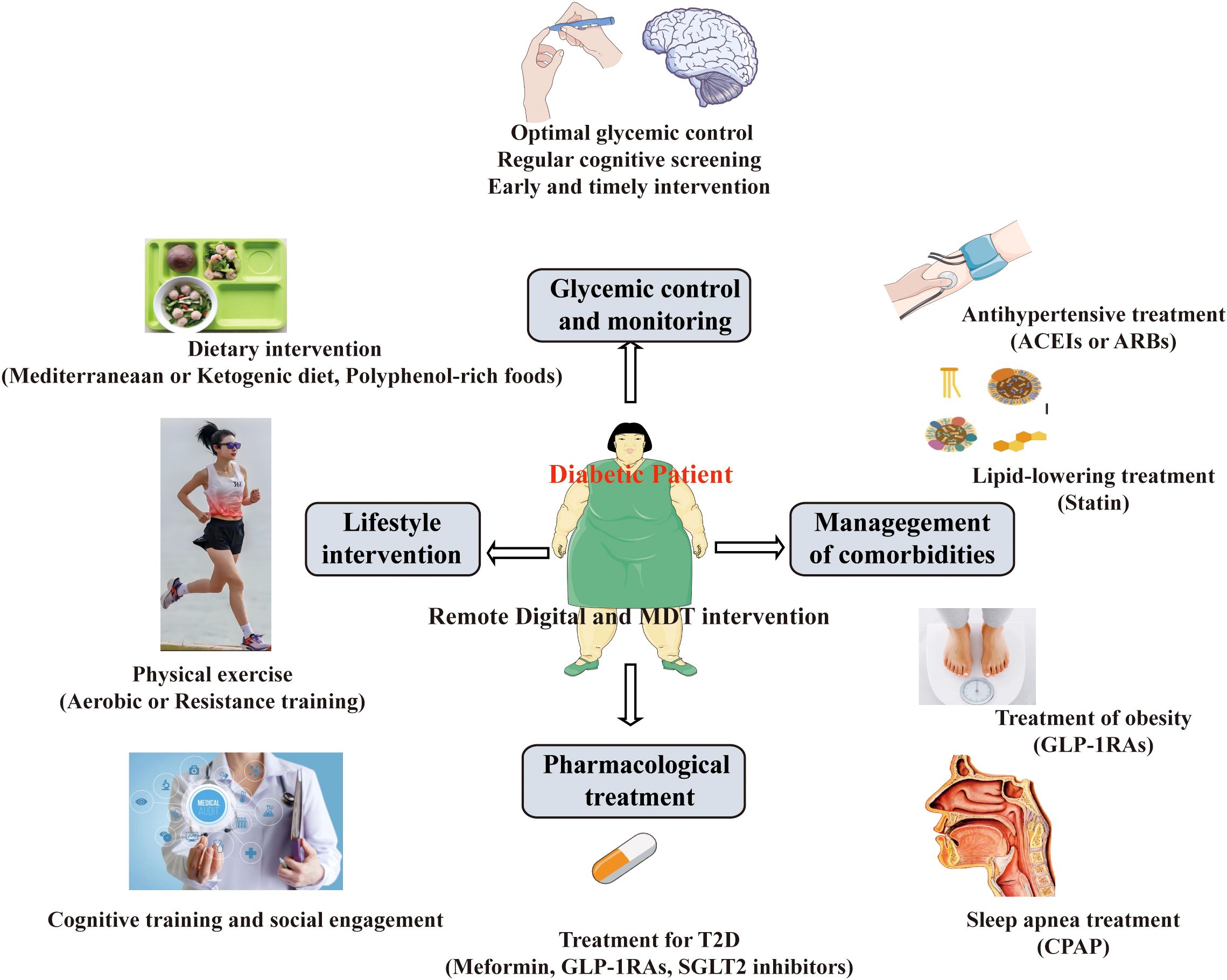
Cognitive dysfunction is often unrecognized in individuals with T2D. Cognitive dysfunction in T2D can have significant consequences on an individual’s overall health, quality of life, and disease management. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find effective therapeutic strategies to improve cognitive function among patients with T2D (Figure 3).
5.1 Glycemic control and monitoring
A growing body of clinical and experimental evidence demonstrates that optimal glycemic control may help prevent or delay cognitive decline in T2D, though the relationship is complex and influenced by treatment strategies (101–103). Longitudinal studies show a U-shaped association, where both hyperglycemia (HbA1c>8%) and recurrent severe hypoglycemia accelerate cognitive impairment (104, 105). The ACCORD MIND trial found that intensive glycemic control (HbA1c <6.0%) did not significantly improve cognition but increased hypoglycemia risk (106). Meta-analyses suggest HbA1c variability (fluctuations) is an independent predictor of dementia risk, possibly due to oxidative stress (107). The Look AHEAD trial (focused on weight loss + glycemic control) showed no significant cognitive benefit, possibly due to limited follow-up (108). The DCCT-EDIC study (Type 1 diabetes) found that tight glycemic control initiated early in the disease course has been associated with better long-term cognitive outcomes, where early intensive glucose management reduced later cognitive decline by 30-40% (109). Some RCTs suggest metformin may reduce dementia risk, while insulin therapy in older adults may worsen cognition if hypoglycemia occurs (110, 111).
Strong evidence indicates that proactive monitoring and early intervention in patients with T2D can significantly delay or mitigate cognitive impairment (112, 113). Longitudinal studies demonstrate that regular cognitive screening in diabetic populations enables earlier detection of subtle deficits, allowing for timely interventions before significant neurodegeneration occurs (114, 115).
The 2025 American Diabetes Association (ADA) clinical guidelines recommend that cognitive capacity should be monitored throughout the life span for all diabetic patients (116). The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) are the two most widely used assessing tools for cognitive function, and recommended by the guideline (117). Nonetheless, the MMSE and MoCA tests exhibit low sensitivity and specificity in detecting early stages of MCI. In recent years, retinal microperimetry has emerged as a valuable tool for monitoring cognitive function in diabetic patients (118, 119). Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technologies have proven particularly valuable, as they minimize glycemic variability - an independent risk factor for cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive dysfunction (120, 121). These findings underscore the importance of incorporating cognitive assessments into standard diabetes care protocols and implementing preventive strategies at the earliest detectable stage of metabolic dysfunction to optimally preserve brain health.
5.2 Lifestyle intervention
A robust body of research demonstrates that structured lifestyle interventions can significantly mitigate cognitive decline in individuals with T2D. These interventions primarily target diet, physical activity, weight management, and cognitive training, working through metabolic, vascular, and neuroprotective pathways (122, 123).
Emerging research highlights that targeted dietary interventions can significantly influence cognitive outcomes in individuals with T2D by modulating metabolic, vascular, and neurodegenerative pathways (124). Adherence to a Mediterranean diet, rich in polyphenols and omega-3 fatty acids, has been associated with improved memory and slower hippocampal atrophy, likely due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (125, 126). Ketogenic diets and intermittent fasting enhance neuronal energy metabolism through ketone bodies and autophagy, improving cognitive performance in insulin-resistant individuals (78, 127, 128). Polyphenol-rich foods, such as berries and cocoa, further protect against neurodegeneration by modulating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation (129). Clinical trials, including PREDIMED and COSMOS, underscore the cognitive benefits of these dietary strategies, particularly in at-risk populations like APOE-ϵ4 carriers (130, 131). Together, these findings advocate for personalized, nutrient-dense dietary interventions as a viable approach to delay or prevent cognitive decline in T2D.
Emerging evidence demonstrates that physical exercise significantly attenuates cognitive impairment in T2D through multifaceted physiological mechanisms (132). Both aerobic and resistance training have been shown to improve memory, executive function, and processing speed in T2D patients, with neuroimaging studies revealing increased hippocampal volume and enhanced cerebral blood flow following regular exercise. Aerobic activities like brisk walking and cycling elevate brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels, promoting neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity, while resistance training reduces systemic inflammation and improves insulin sensitivity in brain tissue (133, 134). Combined exercise regimens appear particularly effective, as demonstrated in clinical trials such as Look AHEAD, where greater physical activity was associated with slower cognitive decline over time (108). Exercise also mitigates key pathological processes in T2D-related cognitive impairment, including reducing oxidative stress, improving cerebrovascular function, and decreasing Aβ accumulation (135, 136). In a Chinese randomized clinical trial found that Tai Chi Chuan improved global cognitive function more effectively than fitness walking in older adults with type 2 diabetes and MCI (137). These neuroprotective effects appear dose-dependent, with current guidelines recommending at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly for optimal cognitive benefits (138). The findings underscore structured physical activity as a potent, non-pharmacological intervention to preserve brain health in diabetic populations.
Growing evidence suggests that cognitive training and social engagement interventions can help mitigate cognitive impairment in individuals with T2D by enhancing neural resilience and compensatory mechanisms (139). Computerized cognitive training programs targeting memory, attention, and executive function have demonstrated efficacy in improving processing speed and working memory in T2D patients, with neuroimaging studies showing increased functional connectivity in prefrontal and parietal regions (140, 141). Social engagement, including group activities and interactive cognitive stimulation, appears to provide additional benefits by reducing stress-related cortisol exposure while promoting cognitive reserve through complex social interactions (142). The Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study (FINGER) demonstrated that multidomain interventions combining cognitive training, social engagement, and lifestyle modifications significantly reduced dementia risk in at-risk populations, including those with metabolic disorders (143, 144). These approaches may be particularly valuable for T2D patients as they address both the direct neurological consequences of hyperglycemia and the psychosocial factors that often accompany chronic disease. While optimal protocols remain under investigation, current evidence supports incorporating structured cognitive exercises and social activities into comprehensive care plans for diabetes-related cognitive protection.
5.3 Pharmacological treatment
Emerging evidence suggests that certain pharmacological treatments for T2D may also help prevent or mitigate cognitive impairment, though findings remain nuanced. Metformin, the first-line antidiabetic medication, has demonstrated neuroprotective properties in observational studies, with some evidence linking its use to reduced dementia risk, potentially through AMPK activation and reduced neuroinflammation (145, 146). A case-control study of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) from the Memory Clinic at Hebei General Hospital indicates that long-term use of metformin is associated with reduced rates of cognitive impairment and a decreased burden of cerebral small vessel disease among patients with T2D (147). Data analysis from the global AD Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) study indicated that metformin treatment in T2D patients was associated with a positive effect on cognitive performance (148).
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs, e.g., liraglutide, semaglutide) show promising candidates for dual glycemic and cognitive management, with preclinical studies demonstrating their ability to reduce Aβ accumulation, enhance synaptic plasticity, BDNF modulation, and improve cerebral blood flow (77, 149, 150). While not currently approved for cognitive outcomes in T2D, in a post hoc analysis of three cardiovascular outcome trials (LEADER, SUSTAIN 6, and PIONEER 6), patients with GLP-1RAs treatment represented a statistically significant 53% lower risk of all-cause dementia diagnosis compared to patients with placebo (149). In an exploratory analysis of the REWIND trail, patients with long-term treatment with the GLP-1RA dulaglutide also demonstrated reduction of cognitive decline (151). In the ELAD study, patients on liraglutide maintained greater temporal lobe and total cortical volume compared to those on placebo, along with better cognitive function preservation (152). The ongoing evoke and evoke+ are the first trials investigating the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of oral semaglutide in early-stage symptomatic AD (153). If both trails are successful, semaglutide may be considered for future treatment of AD. Conversely, insulin therapy in elderly patients with T2D requires careful consideration, as it may increase hypoglycemia-related cognitive risks.
SGLT2 inhibitors are medications used to manage T2D by preventing glucose absorption in renal tubules. They may provide cerebrovascular protection by reducing oxidative stress and improving endothelial function, although direct cognitive benefits remain under investigation (154, 155). The latest evidence demonstrates that SGLT2 inhibitors may offer cognitive benefits in patients with T2D through multiple protective mechanisms (12, 154, 156). Clinical observational studies report a 10-30% lower incidence of dementia among SGLT2 inhibitor users compared to other antidiabetic medications, with particular benefits seen for vascular cognitive impairment (157–159). The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial’s subanalysis found empagliflozin-treated patients had slower progression of cognitive decline, potentially linked to its hemodynamic effects and ketone-mediated neuroprotection (160). While dedicated cognitive endpoint trials are ongoing, current evidence positions SGLT2 inhibitors as promising dual-purpose agents for both glycemic control and potential cerebrovascular protection in T2D, though their precise neurocognitive effects require further validation through randomized controlled trials with comprehensive cognitive assessments.
SGLT2 inhibitors may exert cognitive benefits in T2D through multiple interconnected molecular mechanisms. By inducing mild ketosis, these agents provide alternative cerebral energy substrates (β-hydroxybutyrate) that bypass insulin-resistant glucose metabolism, supporting neuronal function during metabolic stress (161). Their systemic metabolic effects including activation of AMPK, enhanced cerebral ketone metabolism, a shift in microglial activation from the pro-inflammatory phenotype to the anti-inflammatory phenotype, and reduced oxidative stress, contribute to the mitigation of neuroinflammation through the suppression of the NLRP3 inflammasome and AGE-RAGE signaling pathways (162, 163). At the cellular level, SGLT2 inhibitors may exert neuroprotective effects through increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression, ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction, while inhibiting-mediated tau phosphorylation (pTau) (164–167). Emerging evidence also suggests gut microbiome modulation, with increased production of neuroprotective short-chain fatty acids (168, 169). Additionally, SGLT2 inhibitors attenuated pTau accumulation by modulating brain insulin signaling through the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin (1–7)/mitochondrial assembly receptor axis in a T2D-AD mouse model (170). These pleiotropic effects position SGLT2 inhibitors as promising multitarget therapeutic agents for addressing diabetes-related cognitive impairment; however, additional clinical validation is required to confirm their efficacy and safety.
5.4 Management of comorbidities
The bulk of the evidence proves that comprehensive management of T2D comorbidities significantly improves cognitive outcomes by addressing multiple interconnected pathological pathways. Tight glycemic control and concurrent management of hypertension with ACE inhibitors or ARBs preserves cerebrovascular integrity, while statin therapy may mitigate both vascular cognitive impairment and neurodegenerative pathology through pleiotropic effects (171–173). Treatment of obesity with lifestyle interventions or GLP-1RAs not only improves metabolic parameters but also enhances neurogenesis and reduces neuroinflammation (174, 175). Additionally, addressing sleep apnea with CPAP therapy improves cerebral oxygenation, and antidepressant treatment for comorbid depression helps restore neurotrophic factor signaling (176). Multidomain interventions that simultaneously target glycemic control, vascular risk factors, and lifestyle modifications - as demonstrated in trials like the FINGER study - show particularly robust cognitive benefits, suggesting that a holistic approach to T2D management may be more effective than isolated therapies for preserving brain health in diabetic patients (177).
5.5 Remote digital technologies for interventions
Remote digital technologies, often referred to as “Digital Health” or “eHealth”, provide scalable, accessible, and cost-effective solution for addressing cognitive decline in patients with diabetes (178). These technologies utilize smartphones, tablets, wearable devices, and web-based platforms to provide cognitive assessment, training, monitoring, and comprehensive interventions directly to patients in their home environments (179–184). Remote digital technology for diabetic cognitive care intervenes at multiple levels.
To facilitate the early identification of subtle cognitive changes and to monitor their progression over time without the necessity for frequent, in-person neuropsychological assessments, Computerized Cognitive Tests and Digital Biomarkers are employed to evaluate and track cognitive alterations (185, 186). Computerized Cognitive Tests are validated, game-like assessments conducted on tablets or computers that evaluate memory, attention, executive function, and processing speed (187). These tests often demonstrate greater sensitivity to change compared to traditional paper-and-pencil assessments (188). Digital biomarkers assess cognitive states by utilizing passive data gathered from smartphones and wearable devices (189). This includes metrics such as keystroke dynamics, voice analysis, and gait analysis.
To enhance or maintain cognitive function, structured and repetitive exercises that promote neuroplasticity are utilized. This includes Brain Training Apps, Serious Games (Gamification), and Virtual Reality (VR) for cognitive training and rehabilitation (Cognitive Therapeutics) (190, 191). Brain training apps like BrainHQ, CogniFit, and Lumosity provide games for specific cognitive areas that can be prescribed and monitored remotely by clinicians (192–194). Serious Games (Gamification) enhance patient engagement, leading to better adherence to cognitive exercises.
To provide human support, guidance, and accountability, video conferencing, secure messaging platforms, and remote patient monitoring (RPM) platforms are integrated into telehealth and remote coaching care planning (195, 196). Patients can have virtual consultations with endocrinologists, neurologists, diabetes educators, or neuropsychologists via video conferencing. Secure Messaging Platforms provide asynchronous communication for patients and clinician (197). Clinicians aggregate data from CGMs, wearables, and cognitive apps via RPM platforms, enabling care teams to monitor a patient’s overall health and intervene proactively.
In summary, Remote digital technologies signify a paradigm shift in the management of diabetes-associated cognitive decline. These technologies facilitate a transition from a reactive, clinic-centric approach to a proactive, continuous, and patient-centered care model. By integrating cognitive training, glycemic monitoring, and lifestyle coaching into a unified remote platform, we gain a powerful means to not only enhance diabetes management but also safeguard brain health and preserve patients’ quality of life. The next step involves validating these tools and embedding them seamlessly into standard clinical practice.
5.6 A multidisciplinary team intervention
Diabetes-associated cognitive decline results from a complex interplay of metabolic, vascular, inflammatory, and comorbid factors. Therefore, no single healthcare professional can effectively address all these domains. A multidisciplinary team (MDT) intervention and collaborative care model are crucial components in effectively addressing the issue (198–200). An effective MDT for this population includes an endocrinologist, a neurologist, a certified diabetes educator, a registered dietitian nutritionist, a pharmacist, a psychologist, a care manager, a physical therapist, and a family member, all working within an integrated system of care. An endocrinologist initiates annual cognitive screening (using tools like MoCA or Mini-Cog) in high-risk T2D patients. When abnormal results are identified, a referral to neurology for formal diagnostic evaluation is initiated, and the rest of care team is alerted. The MDT then convenes to review the patient’s case and develops a unified, patient-centered care plan. The nurse care manager routinely monitors patient outcomes, such as HbA1c levels and hypoglycemic events, through a shared electronic health record system and conducts follow-ups to ensure the effectiveness of the care plan. The social worker and psychologist actively collaborate with caregivers, offering comprehensive training, essential resources, and emotional support to enhance their capacity in providing care.
In summary, managing cognitive impairment in T2D exemplifies the success of collaborative care. An MDT model effectively addresses the biological, psychological, and social complexities of the disease, breaking the cycle and enabling patients to live safer, higher-quality lives. It represents the standard that healthcare systems should aim for.
6 Conclusion
Cognitive impairment in T2D is driven by multiple interrelated mechanisms, including chronic hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction, which collectively contribute to neurodegeneration and cognitive decline. Addressing these impairments requires a comprehensive management strategy that combines optimal glycemic control (prioritizing medications with potential neuroprotective benefits, such as GLP-1RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors), lifestyle modifications (e.g., aerobic exercise, Mediterranean diet, and cognitive training), and aggressive management of cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, dyslipidemia). Emerging therapies targeting neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and insulin signaling in the brain hold promise but require further clinical validation. Artificial intelligence (AI) will be utilized to personalize cognitive training programs, predict cognitive decline through digital biomarkers, and deliver adaptive coaching. Socially Assistive Robots will provide companionship to older adults with more advanced impairments and remind them to engage in cognitive exercises or take their medication. Future research should focus on identifying early biomarkers, developing personalized interventions, and conducting long-term trials to establish evidence-based approaches for preventing and treating diabetes-related cognitive decline. A proactive, multidisciplinary approach is essential to mitigate cognitive deterioration and improve quality of life in T2D patients.
Author contributions
XC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YH: Writing – review & editing. XX: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Srikanth V, Sinclair AJ, Hill-Briggs F, Moran C, and Biessels GJ. Type 2 diabetes and cognitive dysfunction-towards effective management of both comorbidities. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2020) 8:535–45. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30118-2
2. Jia L, Du Y, Chu L, Zhang Z, Li F, Lyu D, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health. (2020) 5:e661–e71. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30185-7
3. Yu JH, Kim REY, Park SY, Lee DY, Cho HJ, Kim NH, et al. Association of long-term hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance with brain atrophy and cognitive decline: A longitudinal cohort study. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2023) 25:1091–100. doi: 10.1111/dom.14958
4. Yu X, He H, Wen J, Xu X, Ruan Z, Hu R, et al. Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments. Open Med (Wars). (2025) 20:20241091. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1091
5. Antal B, McMahon LP, Sultan SF, Lithen A, Wexler DJ, Dickerson B, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus accelerates brain aging and cognitive decline: Complementary findings from UK Biobank and meta-analyses. Elife. (2022) 11:1–24. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73138
6. Kim MJ, Bronas UG, Quinn L, Sharp LK, Park C, Gruss V, et al. Cognitive function and self-management behaviors in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Nurs Res. (2023) 72:38–48. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0000000000000624
7. Sadanand S, Balachandar R, and Bharath S. Memory and executive functions in persons with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2016) 32:132–42. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2664
8. Low S, Ng TP, Lim CL, Moh A, Ang SF, Wang J, et al. Association between lower extremity skeletal muscle mass and impaired cognitive function in type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:2956. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59914-3
9. McCrimmon RJ, Ryan CM, and Frier BM. Diabetes and cognitive dysfunction. Lancet. (2012) 379:2291–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60360-2
10. Kim MJ and Fritschi C. Relationships between cognitive impairment and self-management in older adults with type 2 diabetes: an integrative review. Res Gerontol Nurs. (2021) 14:104–12. doi: 10.3928/19404921-20201117-01
11. Hong B, Bea S, Ko HY, Kim WJ, Cho YM, and Shin JY. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, dulaglutide, and risk for dementia: A population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med. (2024) 177:1319–29. doi: 10.7326/M23-3220
12. Mone P, Lombardi A, Gambardella J, Pansini A, Macina G, Morgante M, et al. Empagliflozin improves cognitive impairment in frail older adults with type 2 diabetes and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:1247–51. doi: 10.2337/dc21-2434
13. Wu CY, Iskander C, Wang C, Xiong LY, Shah BR, Edwards JD, et al. Association of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors with time to dementia: A population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:297–304. doi: 10.2337/dc22-1705
14. Refardt J, Imber C, Nobbenhuis R, Sailer CO, Haslbauer A, Monnerat S, et al. Treatment effect of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin on chronic syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2023) 34:322–32. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022050623
15. You Y, Liu Z, Chen Y, Xu Y, Qin J, Guo S, et al. The prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. (2021) 58:671–85. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01648-9
16. Ehtewish H, Arredouani A, and El-Agnaf O. Diagnostic, prognostic, and mechanistic biomarkers of diabetes mellitus-associated cognitive decline. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1–32. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116144
17. Koekkoek PS, Kappelle LJ, van den Berg E, Rutten GE, and Biessels GJ. Cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: guidance for daily care. Lancet Neurol. (2015) 14:329–40. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70249-2
18. Li J, Liu C, Ang TFA, and Au R. Associations of mid- and late-life fasting blood glucose levels with dementia risk among patients with diabetes: framingham heart study. Eur J Neurol. (2025) 32:e70062. doi: 10.1111/ene.70062
19. Ott A, Stolk RP, van Harskamp F, Pols HA, Hofman A, and Breteler MM. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of dementia: The Rotterdam Study. Neurology. (1999) 53:1937–42. doi: 10.1212/wnl.53.9.1937
20. Ware EB, Morataya C, Fu M, and Bakulski KM. Type 2 diabetes and cognitive status in the health and retirement study: A mendelian randomization approach. Front Genet. (2021) 12:634767. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.634767
21. Liu X and Cao Y. The mediating effect of physical performance on physical activity and mild cognitive impairment among older adults with type 2 diabetes in rural China. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2024) 39:e70001. doi: 10.1002/gps.70001
22. Chen JF, Zhang YP, Han JX, Wang YD, and Fu GF. Systematic evaluation of the prevalence of cognitive impairment in elderly patients with diabetes in China. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2023) 225:107557. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107557
23. Gudala K, Bansal D, Schifano F, and Bhansali A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of dementia: A meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. J Diabetes Investig. (2013) 4:640–50. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12087
24. Mielke MM, Evans JK, Neiberg RH, Molina-Henry DP, Marcovina SM, Johnson KC, et al. Alzheimer disease blood biomarkers and cognition among individuals with diabetes and overweight or obesity. JAMA Netw Open. (2025) 8:e2458149. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.58149
25. Biessels GJ and Despa F. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2018) 14:591–604. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0048-7
26. Little K, Llorian-Salvador M, Scullion S, Hernandez C, Simo-Servat O, Del Marco A, et al. Common pathways in dementia and diabetic retinopathy: understanding the mechanisms of diabetes-related cognitive decline. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 33:50–71. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.10.008
27. Zheng F, Yan L, Yang Z, Zhong B, and Xie W. HbA(1c), diabetes and cognitive decline: the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Diabetologia. (2018) 61:839–48. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4541-7
28. Feng J, Teng Z, and Chen S. Associations of obesity-related indices with mild cognitive impairment in adults 60 years and older with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective study. PeerJ. (2025) 13:e19442. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19442
29. Pignalosa FC, Desiderio A, Mirra P, Nigro C, Perruolo G, Ulianich L, et al. Diabetes and cognitive impairment: A role for glucotoxicity and dopaminergic dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:1–20. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212366
30. Klug NR, Chechneva OV, Hung BY, and O’Donnell ME. High glucose-induced effects on Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransport and Na(+)/H(+) exchange of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells: involvement of SGK1, PKCbetaII, and SPAK/OSR1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2021) 320:C619–C34. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00177.2019
31. Kaufman CS, Bai SX, Eickmeyer SM, and Billinger SA. Chronic hyperglycemia before acute ischemic stroke impairs the bilateral cerebrovascular response to exercise during the subacute recovery period. Brain Behav. (2021) 11:e01990. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1990
32. Gao X, Wei Y, Sun H, Hao S, Ma M, Sun H, et al. Role of bmal1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus-related glycolipid metabolic disorder and neuropsychiatric injury: involved in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and circadian rhythms. Mol Neurobiol. (2023) 60:4595–617. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03360-5
33. Wang J, Li L, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Zhang C, et al. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:1264–79 e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.08.004
34. Zhang S, Zhang Y, Wen Z, Yang Y, Bu T, Bu X, et al. Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes: abnormal glucose metabolic regulation in the brain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1192602. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1192602
35. Stranahan AM, Norman ED, Lee K, Cutler RG, Telljohann RS, Egan JM, et al. Diet-induced insulin resistance impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognition in middle-aged rats. Hippocampus. (2008) 18:1085–8. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20470
36. Hefner M, Baliga V, Amphay K, Ramos D, and Hegde V. Cardiometabolic modification of amyloid beta in alzheimer’s disease pathology. Front Aging Neurosci. (2021) 13:721858. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.721858
37. Jo D, Choi SY, Ahn SY, and Song J. IGF1 enhances memory function in obese mice and stabilizes the neural structure under insulin resistance via AKT-GSK3beta-BDNF signaling. BioMed Pharmacother. (2025) 183:117846. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.117846
38. Barone E and Butterfield DA. Insulin signaling in microglia: A metabolic switch controlling neuroinflammation and amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Metab. (2025) 37:1630–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.06.005
39. Sun M and Mi W. Microglial insulin resistance drives neurodegeneration. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2025) 36:696–98. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2025.06.006
40. Chen W, Liu X, Munoz VR, and Kahn CR. Loss of insulin signaling in microglia impairs cellular uptake of Abeta and neuroinflammatory response exacerbating AD-like neuropathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2025) 122:e2501527122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2501527122
41. Zheng M, Chang B, Tian L, Shan C, Chen H, Gao Y, et al. Relationship between inflammatory markers and mild cognitive impairment in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: a case-control study. BMC Endocr Disord. (2019) 19:73. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0402-3
42. Padovani A, Galli A, Bazzoli E, Tolassi C, Caratozzolo S, Gumina B, et al. The role of insulin resistance and APOE genotype on blood-brain barrier integrity in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. (2025) 21:e14556. doi: 10.1002/alz.14556
43. Wang S, Tang C, Liu Y, Border JJ, Roman RJ, and Fan F. Impact of impaired cerebral blood flow autoregulation on cognitive impairment. Front Aging. (2022) 3:1077302. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.1077302
44. Filler J, Georgakis MK, and Dichgans M. Risk factors for cognitive impairment and dementia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. (2024) 5:e31–44. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(23)00217-9
45. Chau ACM, Cheung EYW, Chan KH, Chow WS, Shea YF, Chiu PKC, et al. Impaired cerebral blood flow in type 2 diabetes mellitus - A comparative study with subjective cognitive decline, vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease subjects. NeuroImage Clin. (2020) 27:102302. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102302
46. Inoue C, Kusunoki Y, Ohigashi M, Osugi K, Kitajima K, Takagi A, et al. Association between brain imaging biomarkers and continuous glucose monitoring-derived glycemic control indices in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2024) 12:1–10. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2023-003744
47. Wu K, Xie W, Chen Z, Zhou L, Wang L, Zhou Y, et al. Disturbed hippocampal histidine metabolism contributes to cognitive impairment induced by recurrent nonsevere hypoglycemia in diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 682:325–34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.10.036
48. McCrimmon RJ. Consequences of recurrent hypoglycaemia on brain function in diabetes. Diabetologia. (2021) 64:971–77. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05369-0
49. Nikpendar M, Javanbakht M, Moosavian H, Sajjadi S, Nilipour Y, Moosavian T, et al. Effect of recurrent severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia on the cognitive function and brain oxidative status in the rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2024) 16:161. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01410-z
50. Zhou Y, Huang L, Zheng W, An J, Zhan Z, Wang L, et al. Recurrent nonsevere hypoglycemia exacerbates imbalance of mitochondrial homeostasis leading to synapse injury and cognitive deficit in diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 315:E973–E86. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00133.2018
51. Cukierman-Yaffe T, Bosch J, Jung H, Punthakee Z, and Gerstein HC. Hypoglycemia and incident cognitive dysfunction: A post hoc analysis from the ORIGIN trial. Diabetes Care. (2019) 42:142–47. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0690
52. Lee AK, Rawlings AM, Lee CJ, Gross AL, Huang ES, Sharrett AR, et al. Severe hypoglycaemia, mild cognitive impairment, dementia and brain volumes in older adults with type 2 diabetes: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) cohort study. Diabetologia. (2018) 61:1956–65. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4668-1
53. Liu S, Lu Y, Cai X, Cong R, Li J, Jiang H, et al. Glycemic control is related to cognitive dysfunction in elderly people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rural chinese population. Curr Alzheimer Res. (2019) 16:950–62. doi: 10.2174/1567205016666191023110712
54. Zhuo X, Huang M, and Wu M. Analysis of cognitive dysfunction and its risk factors in patients with hypertension. Med (Baltimore). (2022) 101:e28934. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028934
55. Iwai K, Ushigome E, Matsumoto S, Kitagawa N, Ushigome H, Yokota I, et al. Home blood pressure is associated with cognitive impairment among elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: KAMOGAWA-HBP study. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. (2019) 16:506–12. doi: 10.1177/1479164119847479
56. Liu P, Wang ZH, Kang SS, Liu X, Xia Y, Chan CB, et al. High-fat diet-induced diabetes couples to Alzheimer’s disease through inflammation-activated C/EBPbeta/AEP pathway. Mol Psychiatry. (2022) 27:3396–409. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01600-z
57. Shippy DC and Ulland TK. Lipid metabolism transcriptomics of murine microglia in Alzheimer’s disease and neuroinflammation. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:14800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41897-6
58. Liu Y, Qiu H, Zhang M, and Lin J. Sex-specific association between body roundness index and cognitive impairment among hospitalized middle-aged and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes in China: a cross-sectional analysis. Eur J Med Res. (2025) 30:570. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02849-0
59. Zhang W, Fu L, Bi Y, Liu J, Li X, Zhang X, et al. Large-scale functional network connectivity mediates the associations between lipids metabolism and cognition in type 2 diabetes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2024) 44:384–96. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231204426
60. Li J, Pan J, Li B, Tian H, Zhu Y, Liao Z, et al. Positive correlation between cognitive impairment and renal microangiopathy in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a multicenter retrospective study. J Int Med Res. (2018) 46:5040–51. doi: 10.1177/0300060518789299
61. He Q, Ji L, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang H, Wang J, et al. Acetate enables metabolic fitness and cognitive performance during sleep disruption. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:1998–2014 e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.019
62. Brzecka A, Madetko N, Nikolenko VN, Ashraf GM, Ejma M, Leszek J, et al. Sleep disturbances and cognitive impairment in the course of type 2 diabetes-A possible link. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2021) 19:78–91. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200309101750
63. Chow YY, Verdonschot M, McEvoy CT, and Peeters G. Associations between depression and cognition, mild cognitive impairment and dementia in persons with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 185:109227. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109227
64. Rosado AF, Rosa PB, Platt N, Pierone BC, Neis VB, Severo Rodrigues AL, et al. Glibenclamide treatment prevents depressive-like behavior and memory impairment induced by chronic unpredictable stress in female mice. Behav Pharmacol. (2021) 32:170–81. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000599
65. Liu K, Zhou D, Chen L, and Hao S. Depression and type 2 diabetes risk: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1436411. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1436411
66. Su MH, Shih YH, Lin YF, Chen PC, Chen CY, Hsiao PC, et al. Familial aggregation and shared genetic loading for major psychiatric disorders and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. (2022) 65:800–10. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05665-x
67. Possidente C, Fanelli G, Serretti A, and Fabbri C. Clinical insights into the cross-link between mood disorders and type 2 diabetes: A review of longitudinal studies and Mendelian randomisation analyses. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2023) 152:105298. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105298
68. Yao J, Zhu CQ, Sun Y, Huang YW, Li QH, Liao HM, et al. Insulin resistance: The role in comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2025) 175:106218. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2025.106218
69. Chung SJ, Kim MJ, Kim J, Ryu HS, Kim YJ, Kim SY, et al. Association of type 2 diabetes GWAS loci and the risk of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. (2015) 21:1435–40. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.10.010
70. Gao L, Cui Z, Shen L, and Ji HF. Shared genetic etiology between type 2 diabetes and alzheimer’s disease identified by bioinformatics analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. (2016) 50:13–7. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150580
71. Camargo LM, Zhang XD, Loerch P, Caceres RM, Marine SD, Uva P, et al. Pathway-based analysis of genome-wide siRNA screens reveals the regulatory landscape of APP processing. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0115369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115369
72. Wang Q and Yang Y. Bioinformatics analysis of effective biomarkers and immune infiltration in type 2 diabetes with cognitive impairment and aging. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:23279. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74480-8
73. Xu F, Wu S, Gao S, Li X, Huang C, Chen Y, et al. Causal association between insulin sensitivity index and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. (2025) 169:e16254. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16254
74. Baars DP, Fondevila MF, Meijnikman AS, and Nieuwdorp M. The central role of the gut microbiota in the pathophysiology and management of type 2 diabetes. Cell Host Microbe. (2024) 32:1280–300. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.07.017
75. Zhang Y, Xu D, Cai X, Xing X, Shao X, Yin A, et al. Gut commensal barnesiella intestinihominis ameliorates hyperglycemia and liver metabolic disorders. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2025) 12:e2411181. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411181
76. Sun Y, Nie Q, Zhang S, He H, Zuo S, Chen C, et al. Parabacteroides distasonis ameliorates insulin resistance via activation of intestinal GPR109a. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:7740. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43622-3
77. de Paiva IHR, da Silva RS, Mendonca IP, de Souza JRB, and Peixoto CA. Semaglutide attenuates anxious and depressive-like behaviors and reverses the cognitive impairment in a type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse model via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. (2024) 19:36. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10142-w
78. Liu Z, Dai X, Zhang H, Shi R, Hui Y, Jin X, et al. Gut microbiota mediates intermittent-fasting alleviation of diabetes-induced cognitive impairment. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:855. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14676-4
79. Zhang Y, Lu S, Yang Y, Wang Z, Wang B, Zhang B, et al. The diversity of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes with or without cognitive impairment. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2021) 33:589–601. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01553-9
80. Song X, Zhu Z, Qian X, Liu X, Chen S, and Tang H. Multi-omics characterization of type 2 diabetes mellitus-induced cognitive impairment in the db/db mouse model. Molecules. (2022) 27:1–23. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061904
81. Zhang W, Yi C, Song Z, Yu B, Jiang X, Guo L, et al. Reshaping the gut microbiota: Tangliping decoction and its core blood-absorbed component quercetin improve diabetic cognitive impairment. Phytomedicine. (2025) 140:156560. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156560
82. Huang S, Wang X, Wang M, Lin J, Ren J, Lu C, et al. S-9-PAHSA protects against high-fat diet-induced diabetes-associated cognitive impairment via gut microbiota regulation. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2025) 31:e70417. doi: 10.1111/cns.70417
83. Hussein HM, Elyamany MF, Rashed LA, and Sallam NA. Vitamin D mitigates diabetes-associated metabolic and cognitive dysfunction by modulating gut microbiota and colonic cannabinoid receptor 1. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2022) 170:106105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2021.106105
84. Luo Y, Zhu J, Hu Z, Luo W, Du X, Hu H, et al. Progress in the pathogenesis of diabetic encephalopathy: the key role of neuroinflammation. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2024) 40:e3841. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3841
85. Huang Z, Liu J, Li H, Ai Y, and Zhou D. Network pharmacology-based prediction and “gut microbiota-inflammation-brain axis” validation of the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of Plantagins Herba for treating diabetes-related cognitive dysfunction. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1601689. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601689
86. Kassab S, Begley P, Church SJ, Rotariu SM, Chevalier-Riffard C, Dowsey AW, et al. Cognitive dysfunction in diabetic rats is prevented by pyridoxamine treatment. A multidisciplinary investigation. Mol Metab. (2019) 28:107–19. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.08.003
87. Huang R, Tian S, Zhang H, Zhu W, and Wang S. Chronic hyperglycemia induces tau hyperphosphorylation by downregulating OGT-involved O-GlcNAcylation in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res Bull. (2020) 156:76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.01.006
88. Zheng Y, Wang C, Liu W, Chen J, Sun Y, Chang D, et al. Upregulation of Nrf2 signaling: A key molecular mechanism of Baicalin’s neuroprotective action against diabetes-induced cognitive impairment. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 174:116579. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116579
89. Wang T, Fu F, Han B, Zhang L, and Zhang X. Danshensu ameliorates the cognitive decline in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by attenuating advanced glycation end product-mediated neuroinflammation. J Neuroimmunol. (2012) 245:79–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.02.008
90. Samanta S, Akhter F, Xue R, Sosunov AA, Wu L, Chen D, et al. Synaptic mitochondria glycation contributes to mitochondrial stress and cognitive dysfunction. Brain. (2025) 148:262–75. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae229
91. Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, et al. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2003) 100:4162–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0230450100
92. Martin-Martin Y, Perez-Garcia A, Torrecilla-Parra M, Fernandez-de Frutos M, Pardo-Marques V, Casarejos MJ, et al. New insights on the regulation of the insulin-degrading enzyme: role of microRNAs and RBPs. Cells. (2022) 11:1–16. doi: 10.3390/cells11162538
93. Fernandez-de Frutos M, Galan-Chilet I, Goedeke L, Kim B, Pardo-Marques V, Perez-Garcia A, et al. MicroRNA 7 impairs insulin signaling and regulates abeta levels through posttranscriptional regulation of the insulin receptor substrate 2, insulin receptor, insulin-degrading enzyme, and liver X receptor pathway. Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 39:1–19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00170-19
94. Foda AM, Ibrahim SS, Ibrahim SM, and Elbaz EM. Pterostilbene Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Rat Model through Improving Insulin Resistance via the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta Pathway: A Comparative Study with Metformin. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2024) 15:3064–77. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00352
95. Xiong R, Wang XL, Wu JM, Tang Y, Qiu WQ, Shen X, et al. Polyphenols isolated from lychee seed inhibit Alzheimer’s disease-associated Tau through improving insulin resistance via the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2020) 251:112548. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112548
96. Tang W, Li Y, He S, Jiang T, Wang N, Du M, et al. Caveolin-1 alleviates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction through modulating neuronal ferroptosis-mediated mitochondrial homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2022) 37:867–86. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0233
97. Ma M, Jing G, Tian Y, Yin R, and Zhang M. Ferroptosis in cognitive impairment associated with diabetes and alzheimer’s disease: mechanistic insights and new therapeutic opportunities. Mol Neurobiol. (2025) 62:2435–49. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04417-9
98. Wang B, Zhu S, Guo M, Ma RD, Tang YL, Nie YX, et al. Artemisinin ameliorates cognitive decline by inhibiting hippocampal neuronal ferroptosis via Nrf2 activation in T2DM mice. Mol Med. (2024) 30:35. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00797-9
99. Chen J, Guo P, Han M, Chen K, Qin J, and Yang F. Cognitive protection of sinomenine in type 2 diabetes mellitus through regulating the EGF/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling, the microbiota-gut-brain axis, and hippocampal neuron ferroptosis. Phytother Res. (2023) 37:3323–41. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7807
100. Wang Z, Ning Y, Gao P, Xu L, Cao S, Li Y, et al. Proteomic signature of dementia risk in type 2 diabetes. J Adv Res. (2025). doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2025.08.012
101. Rovner BW, Casten RJ, Piersol CV, White N, Kelley M, and Leiby BE. Improving glycemic control in african americans with diabetes and mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2020) 68:1015–22. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16339
102. Koh DH, Rho YJ, Lee SY, Kim KN, and Ju YJ. Association between blood glucose control and subjective cognitive decline in korean patients with diabetes aged over 50 years. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:1–10. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127267
103. Lin Y, Gong Z, Ma C, Wang Z, and Wang K. Relationship between glycemic control and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. (2023) 15:1126183. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1126183
104. Yu J, Hua H, and Yin M. U-shaped association between HbA1c and all-cause mortality in CVD patients with diabetes. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:28386. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80116-8
105. Xiao Y, Hong X, Neelagar R, and Mo H. Association between glycated hemoglobin A1c levels, control status, and cognitive function in type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:5011. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89374-6
106. Abbatecola AM and Paolisso G. Relationship between baseline glycemic control and cognitive function in individuals with type 2 diabetes and other cardiovascular risk factors: the action to control cardiovascular risk in diabetes-memory in diabetes (ACCORD-MIND) trial: response to Cukierman-Yaffe et al. Diabetes Care. (2009) 32:e102; author reply e03. doi: 10.2337/dc09-0658
107. Song J, Bai H, Xu H, Xing Y, and Chen S. HbA1c variability and the risk of dementia in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. (2022) 2022:7706330. doi: 10.1155/2022/7706330
108. Carmichael OT, Neiberg RH, Dutton GR, Hayden KM, Horton E, Pi-Sunyer FX, et al. Long-term change in physiological markers and cognitive performance in type 2 diabetes: the look AHEAD study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 105:e4778–91. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa591
109. Jacobson AM, Ryan CM, Braffett BH, Gubitosi-Klug RA, Lorenzi GM, Luchsinger JA, et al. Cognitive performance declines in older adults with type 1 diabetes: results from 32 years of follow-up in the DCCT and EDIC Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2021) 9:436–45. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00086-3
110. Chen PC, Hong CT, Chen WT, Chan L, and Chien LN. Metformin adherence reduces the risk of dementia in patients with diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Endocr Pract. (2023) 29:247–53. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2023.01.007
111. Chen NC, Chen CL, and Shen FC. The risk factors of severe hypoglycemia in older patients with dementia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pers Med. (2022) 12:1–12. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010067
112. Nguyen B, Deardorff WJ, Shi Y, Jing B, Lee AK, and Lee SJ. Fingerstick glucose monitoring by cognitive impairment status in Veterans Affairs nursing home residents with diabetes. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2022) 70:3176–84. doi: 10.1111/jgs.17962
113. Xu W, Hu X, Zhang X, Ling C, Wang C, and Gao L. Cognitive impairment and related factors among middle-aged and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes from a bio-psycho-social perspective. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2021) 14:4361–69. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S333373
114. Chen Q, Zhu S, Shang J, Fang Q, Xue Q, and Hua J. Corrections to preprint server information. Neurology. (2024) 103:e209573. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209573
115. Callisaya ML, Beare R, Moran C, Phan T, Wang W, and Srikanth VK. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, brain atrophy and cognitive decline in older people: a longitudinal study. Diabetologia. (2019) 62:448–58. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4778-9
116. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice C. 5. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of care in diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. (2025) 48:S86–S127. doi: 10.2337/dc25-S005
117. Chu CS, Lee IC, Hung CC, Lee IC, Hung CF, and Chen NC. Comparison of the mini-mental state examination and computerized brief cognitive screening test as cognitive screening tools in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Curr Alzheimer Res. (2021) 18:1111–17. doi: 10.2174/1567205018666211215151418
118. Ortiz-Zuniga AM, Simo-Servat O, Rojano-Toimil A, Vazquez-de Sebastian J, Castellano-Tejedor C, Hernandez C, et al. The gaze fixation assessed by microperimetry: A useful tool for the monitoring of the cognitive function in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Pers Med. (2021) 11:1–9. doi: 10.3390/jpm11080698
119. Ciudin A, Ortiz AM, Fidilio E, Romero D, Sanchez M, Comas M, et al. Retinal microperimetry: A useful tool for detecting insulin resistance-related cognitive impairment in morbid obesity. J Clin Med. (2019) 8:1–11. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122181
120. Dong S, Wang L, Zhao C, Zhang R, Gao Z, Jiang L, et al. Relationship between key continuous glucose monitoring-derived metrics and specific cognitive domains in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Neurol. (2023) 23:200. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03242-2
121. Savoy A, Holden RJ, de Groot M, Clark DO, Sachs GA, Klonoff D, et al. Improving care for people living with dementia and diabetes: applying the human-centered design process to continuous glucose monitoring. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2024) 18:201–06. doi: 10.1177/19322968221137907
122. Sawyer RP, Blair J, Shatz R, Manly JJ, and Judd SE. Association of adherence to a MIND-style diet with the risk of cognitive impairment and decline in the REGARDS cohort. Neurology. (2024) 103:e209817. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209817
123. Gadde KM, Yin X, Goldberg RB, Orchard TJ, Schlogl M, Dabelea D, et al. Coronary artery calcium and cognitive decline in the diabetes prevention program outcomes study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2023) 12:e029671. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.029671
124. Pu S, Xu Y, Tong X, Zhang Y, Sun X, and Gao X. Correlation of dietary inflammation index and dietary pattern with mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). (2024) 71:152–62. doi: 10.1016/j.endien.2024.01.008
125. Soldevila-Domenech N, Cuenca-Royo A, Babio N, Forcano L, Nishi S, Vintro-Alcaraz C, et al. Metformin use and cognitive function in older adults with type 2 diabetes following a mediterranean diet intervention. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:742586. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.742586
126. Lotan R, Ravona-Springer R, Shakked J, Lin HM, Ouyang Y, Shahar DR, et al. Greater intake of the MEDI diet is associated with better cognitive trajectory in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 190:109989. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109989
127. Horner S, Berger L, and Gibas K. Nutritional Ketosis and photobiomodulation remediate mitochondria warding off Alzheimer’s disease in a diabetic, ApoE4+ patient with mild cognitive impairment: A case report. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2020) 30:101777. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.101777
128. Lee J, An HS, Shin HJ, Jang HM, Im CO, Jeong Y, et al. Intermittent fasting reduces neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in high-fat diet-fed mice by downregulating lipocalin-2 and galectin-3. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1–16. doi: 10.3390/nu16010159
129. Gomaa AA, Makboul RM, Al-Mokhtar MA, and Nicola MA. Polyphenol-rich Boswellia serrata gum prevents cognitive impairment and insulin resistance of diabetic rats through inhibition of GSK3beta activity, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokines. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 109:281–92. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.056
130. Ni J, Nishi SK, Babio N, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Corella D, Castaner O, et al. Dairy product consumption and changes in cognitive performance: two-year analysis of the PREDIMED-plus cohort. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2022) 66:e2101058. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202101058
131. Vyas CM, Manson JE, Sesso HD, Cook NR, Rist PM, Weinberg A, et al. Effect of multivitamin-mineral supplementation versus placebo on cognitive function: results from the clinic subcohort of the COcoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS) randomized clinical trial and meta-analysis of 3 cognitive studies within COSMOS. Am J Clin Nutr. (2024) 119:692–701. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.12.011
132. Ghahfarrokhi MM, Shirvani H, Rahimi M, Bazgir B, Shamsadini A, and Sobhani V. Feasibility and preliminary efficacy of different intensities of functional training in elderly type 2 diabetes patients with cognitive impairment: a pilot randomised controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. (2024) 24:71. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04698-8
133. Wang M, Xie K, Zhao S, Jia N, Zong Y, Gu W, et al. Aerobic exercise improves cognitive impairment in mice with type 2 diabetes by regulating the MALAT1/miR-382-3p/BDNF signaling pathway in serum-exosomes. Mol Med. (2023) 29:130. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00727-1
134. Shekarchian M, Peeri M, and Azarbayjani MA. Physical activity in a swimming pool attenuates memory impairment by reducing glutamate and inflammatory cytokines and increasing BDNF in the brain of mice with type 2 diabetes. Brain Res Bull. (2023) 201:110725. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.110725
135. Zhou Z, Wang M, Huang C, Li Y, Gao L, Zhu Y, et al. Treadmill exercise training alleviates diabetes-induced depressive-like behavior and cognitive impairment by improving hippocampal CA1 neurons injury in db/db mice. Brain Res Bull. (2022) 190:84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.09.018
136. Guo Y, Huang L, Kuang J, Sun T, Zhang X, Tian H, et al. Physical function is associated with cognitive status, brain amyloid-beta deposition, and blood biomarkers in Chinese Han population. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2024) 30:e14921. doi: 10.1111/cns.14921
137. Chen Y, Qin J, Tao L, Liu Z, Huang J, Liu W, et al. Effects of tai chi chuan on cognitive function in adults 60 years or older with type 2 diabetes and mild cognitive impairment in China: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e237004. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.7004
138. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice C. 5. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. (2024) 47:S77–S110. doi: 10.2337/dc24-S005
139. Uchendu C and Blake H. Effectiveness of cognitive-behavioural therapy on glycaemic control and psychological outcomes in adults with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Med. (2017) 34:328–39. doi: 10.1111/dme.13195
140. Bahar-Fuchs A, Barendse MEA, Bloom R, Ravona-Springer R, Heymann A, Dabush H, et al. Computerized Cognitive Training for Older Adults at Higher Dementia Risk due to Diabetes: Findings From a Randomized Controlled Trial. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2020) 75:747–54. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glz073
141. Bloom R, Schnaider-Beeri M, Ravona-Springer R, Heymann A, Dabush H, Bar L, et al. Computerized cognitive training for older diabetic adults at risk of dementia: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). (2017) 3:636–50. doi: 10.1016/j.trci.2017.10.003
142. Joseph NT, Santos TL, and Amaro L. Naturalistic social cognitive and emotional reactions to technology-mediated social exposures and cortisol in daily life. Biol Psychol. (2022) 173:108402. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2022.108402
143. Stephen R, Liu Y, Ngandu T, Antikainen R, Hulkkonen J, Koikkalainen J, et al. Brain volumes and cortical thickness on MRI in the Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability (FINGER). Alzheimers Res Ther. (2019) 11:53. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0506-z
144. Saaskilahti M, Kulmala J, Nurhonen M, Lehtisalo J, Peltonen M, Mangialasche F, et al. The effect of multidomain lifestyle intervention on health care service use and costs - secondary analyses from the Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability (FINGER): a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing. (2024) 53:1–9. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afae249
145. Zheng J, Xu M, Walker V, Yuan J, Korologou-Linden R, Robinson J, et al. Evaluating the efficacy and mechanism of metformin targets on reducing Alzheimer’s disease risk in the general population: a Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia. (2022) 65:1664–75. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05743-0
146. Campbell JM, Stephenson MD, de Courten B, Chapman I, Bellman SM, and Aromataris E. Metformin use associated with reduced risk of dementia in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. (2018) 65:1225–36. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180263
147. Teng Z, Feng J, Qi Q, Dong Y, Xiao Y, Xie X, et al. Long-term use of metformin is associated with reduced risk of cognitive impairment with alleviation of cerebral small vessel disease burden in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front Aging Neurosci. (2021) 13:773797. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.773797
148. Pomilio C, Perez NG, Calandri I, Crivelli L, Allegri R, AAsDN I, et al. Diabetic patients treated with metformin during early stages of Alzheimer’s disease show a better integral performance: data from ADNI study. Geroscience. (2022) 44:1791–805. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00568-6
149. Norgaard CH, Friedrich S, Hansen CT, Gerds T, Ballard C, Moller DV, et al. Treatment with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and incidence of dementia: Data from pooled double-blind randomized controlled trials and nationwide disease and prescription registers. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). (2022) 8:e12268. doi: 10.1002/trc2.12268
150. Lai S, Kang Z, Sun J, Wang Z, Xu Y, Xing S, et al. Semaglutide and high-intensity interval exercise attenuate cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetic mice via BDNF modulation. Brain Sci. (2025) 15:1–18. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15050480
151. Cukierman-Yaffe T, Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Diaz R, Garcia-Perez LE, Lakshmanan M, et al. Effect of dulaglutide on cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes: an exploratory analysis of the REWIND trial. Lancet Neurol. (2020) 19:582–90. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30173-3
152. Femminella GD, Frangou E, Love SB, Busza G, Holmes C, Ritchie C, et al. Evaluating the effects of the novel GLP-1 analogue liraglutide in Alzheimer’s disease: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (ELAD study). Trials. (2019) 20:191. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3259-x
153. Cummings JL, Atri A, Feldman HH, Hansson O, Sano M, Knop FK, et al. evoke and evoke+: design of two large-scale, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies evaluating efficacy, safety, and tolerability of semaglutide in early-stage symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. (2025) 17:14. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01666-7
154. Youn YJ, Kim S, Jeong HJ, Ah YM, and Yu YM. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and their potential role in dementia onset and cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neuroendocrinol. (2024) 73:101131. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2024.101131
155. Nakhal MM, Aburuz S, Sadek B, and Akour A. Repurposing SGLT2 inhibitors for neurological disorders: A focus on the autism spectrum disorder. Molecules. (2022) 27:1–17. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217174
156. Tang H, Donahoo WT, Svensson M, Shaaban CE, Smith G, Jaffee MS, et al. Heterogeneous treatment effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on risk of dementia in people with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Alzheimers Dement. (2024) 20:5528–39. doi: 10.1002/alz.14048
157. Shin A, Koo BK, Lee JY, and Kang EH. Risk of dementia after initiation of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in adults aged 40–69 years with type 2 diabetes: population based cohort study. BMJ. (2024) 386:q1911. doi: 10.1136/bmj.q1911
158. Sun M, Wang X, Lu Z, Yang Y, Lv S, Miao M, et al. Comparative effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in preventing Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and other dementia types among patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. (2025) 51:101623. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2025.101623
159. Pai YW, Chen IC, Lin JF, Chen XH, Chen HH, Chang MH, et al. Association of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors with risk of incident dementia and all-cause mortality in older patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX US collaborative networks. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2024) 26:5420–30. doi: 10.1111/dom.15918
160. Liang B, Gu N, Comment on Mone, et al. Empagliflozin improves cognitive impairment in frail older adults with type 2 diabetes and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:1247–51. doi: 10.2337/dc22-0778
161. Avgerinos KI, Mullins RJ, Vreones M, Mustapic M, Chen Q, Melvin D, et al. Empagliflozin induced ketosis, upregulated IGF-1/insulin receptors and the canonical insulin signaling pathway in neurons, and decreased the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate in the brain of non-diabetics. Cells. (2022) 11:1–18. doi: 10.3390/cells11213372
162. Muhammad RN, Albahairy MA, Abd El Fattah MA, and Ibrahim WW. Empagliflozin-activated AMPK elicits neuroprotective properties in reserpine-induced depression via regulating dynamics of hippocampal autophagy/inflammation and PKCzeta-mediated neurogenesis. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2024) 241:2565–84. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06663-0
163. Sim AY, Kim JY, Lee YH, and Lee JE. Neuroprotective roles of SGLT2 and DPP4 inhibitors: Modulating ketone metabolism and suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome in T2D induced Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol. (2025) 390:115271. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2025.115271
164. Lin B, Koibuchi N, Hasegawa Y, Sueta D, Toyama K, Uekawa K, et al. Glycemic control with empagliflozin, a novel selective SGLT2 inhibitor, ameliorates cardiovascular injury and cognitive dysfunction in obese and type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2014) 13:148. doi: 10.1186/s12933-014-0148-1
165. Abdelaziz HA, Hamed MF, Ghoniem HA, Nader MA, and Suddek GM. Empagliflozin mitigates PTZ-induced seizures in rats: modulating npas4 and CREB-BDNF signaling pathway. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. (2025) 20:5. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10162-6
166. Borikar SP, Chitode GV, Tapre DN, Lokwani DK, and Jain SP. Empagliflozin ameliorates olfactory bulbectomy-induced depression by mitigating oxidative stress and possible involvement of brain derived neurotrophic factor in diabetic rats. Int J Neurosci. (2024), 1–17. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2024.2414270
167. Gamal NM, Bakly WE, Saad SST, Waseef D, El-Shal AS, Ezzat W, et al. Dapagliflozin mitigates cognitive deficits in a rat model of chronic restrained stress by addressing insulin resistance and mitochondrial dysfunction. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04136-5
168. Huang Q, Liu L, Tan X, Wang S, Wang S, Luo J, et al. Empagliflozin alleviates neuroinflammation by inhibiting astrocyte activation in the brain and regulating gut microbiota of high-fat diet mice. J Affect Disord. (2024) 360:229–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.05.150
169. Zhang XY, Chen J, Yi K, Peng L, Xie J, Gou X, et al. Phlorizin ameliorates obesity-associated endotoxemia and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed mice by targeting the gut microbiota and intestinal barrier integrity. Gut Microbes. (2020) 12:1–18. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1842990
170. Sim AY, Choi DH, Kim JY, Kim ER, Goh AR, Lee YH, et al. SGLT2 and DPP4 inhibitors improve Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive function through distinct mechanisms in a T2D-AD mouse model. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115755. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115755
171. Kuan YC, Huang KW, Yen DJ, Hu CJ, Lin CL, and Kao CH. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers reduced dementia risk in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Int J Cardiol. (2016) 220:462–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.06.215
172. D’Silva E, Meor Azlan NF, and Zhang J. Angiotensin II receptor blockers in the management of hypertension in preventing cognitive impairment and dementia-A systematic review. Pharmaceutics. (2022) 14:1–17. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102123
173. Lee YB, Kim MY, Han K, Kim B, Park J, Kim G, et al. Association between cholesterol levels and dementia risk according to the presence of diabetes and statin use: a nationwide cohort study. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:19383. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24153-1
174. Rajendra A, Bondonno NP, Zhong L, Radavelli-Bagatini S, Murray K, Rainey-Smith SR, et al. Plant but not animal sourced nitrate intake is associated with lower dementia-related mortality in the Australian Diabetes, Obesity, and Lifestyle Study. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1327042. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1327042
175. Nassar M, Nassar O, Abosheaishaa H, and Misra A. Comparative outcomes of systemic diseases in people with type 2 diabetes, or obesity alone treated with and without GLP-1 receptor agonists: a retrospective cohort study from the Global Collaborative Network: Author list. J Endocrinol Invest. (2025) 48:483–97. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02466-4
176. Abud R, Salgueiro M, Drake L, Reyes T, Jorquera J, and Labarca G. Efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) preventing type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) and insulin resistance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. (2019) 62:14–21. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2018.12.017
177. Ngandu T, Lehtisalo J, Solomon A, Levalahti E, Ahtiluoto S, Antikainen R, et al. A 2 year multidomain intervention of diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring versus control to prevent cognitive decline in at-risk elderly people (FINGER): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2015) 385:2255–63. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60461-5
178. DuBord AY, Paolillo EW, and Staffaroni AM. Remote digital technologies for the early detection and monitoring of cognitive decline in patients with type 2 diabetes: insights from studies of neurodegenerative diseases. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2024) 18:1489–99. doi: 10.1177/19322968231171399
179. Canonico ME, Hsia J, Guthrie NL, Simmons M, Mehta P, Lupinacci P, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy delivered via digital mobile application for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of a randomized, controlled trial. Clin Cardiol. (2022) 45:850–56. doi: 10.1002/clc.23853
180. Lockwood J, Williams L, Martin JL, Rathee M, and Hill C. Effectiveness, user engagement and experience, and safety of a mobile app (Lumi nova) delivering exposure-based cognitive behavioral therapy strategies to manage anxiety in children via immersive gaming technology: preliminary evaluation study. JMIR Ment Health. (2022) 9:e29008. doi: 10.2196/29008
181. Ghosh A, Cherian RJ, Wagle S, Sharma P, Kannan KR, Bajpai A, et al. An unguided, computerized cognitive behavioral therapy intervention (TreadWill) in a lower middle-income country: pragmatic randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e41005. doi: 10.2196/41005
182. Dissanayaka N, Brooks D, Worthy P, Mitchell L, Pachana NA, Byrne G, et al. A single-blind, parallel-group randomised trial of a Technology-assisted and remotely delivered Cognitive Behavioural Therapy intervention (Tech-CBT) versus usual care to reduce anxiety in people with mild cognitive impairment and dementia: study protocol for a randomised trial. Trials. (2023) 24:420. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07381-2
183. Ford CT, Galler JA, He Y, Young C, Simpson BGK, Wu CY, et al. Using apple watches to monitor health and behaviors of individuals with cognitive impairment: A case series study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2025) 80:glae250. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glae250
184. Rykov YG, Patterson MD, Gangwar BA, Jabar SB, Leonardo J, Ng KP, et al. Predicting cognitive scores from wearable-based digital physiological features using machine learning: data from a clinical trial in mild cognitive impairment. BMC Med. (2024) 22:36. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03252-y
185. Sarrias-Arrabal E, Izquierdo-Ayuso G, and Vazquez-Marrufo M. Attentional networks in neurodegenerative diseases: anatomical and functional evidence from the Attention Network Test. Neurol (Engl Ed). (2023) 38:206–17. doi: 10.1016/j.nrleng.2020.05.022
186. Chudzik A, Sledzianowski A, and Przybyszewski AW. Machine learning and digital biomarkers can detect early stages of neurodegenerative diseases. Sensors (Basel). (2024) 24:1–31. doi: 10.3390/s24051572
187. Schultebraucks K, Yadav V, and Galatzer-Levy IR. Utilization of machine learning-based computer vision and voice analysis to derive digital biomarkers of cognitive functioning in trauma survivors. Digit biomark. (2021) 5:16–23. doi: 10.1159/000512394
188. Chan JYC, Kwong JSW, Wong A, Kwok TCY, and Tsoi KKF. Comparison of computerized and paper-and-pencil memory tests in detection of mild cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic studies. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2018) 19:748–56 e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2018.05.010
189. Brasier N, Wang J, Dincer C, Guder F, Schauwecker I, Schaffarczyk D, et al. Next-generation digital biomarkers: continuous molecular health monitoring using wearable devices. Trends Biotechnol. (2024) 42:255–57. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.12.001
190. Duff K, Ying J, Suhrie KR, Dalley BCA, Atkinson TJ, Porter SM, et al. Computerized cognitive training in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A randomized clinical trial. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. (2022) 35:400–09. doi: 10.1177/08919887211006472
191. Bonnechere B. Evaluation of processing speed of different cognitive functions across the life span using cognitive mobile games. Games Health J. (2022) 11:132–40. doi: 10.1089/g4h.2021.0144
192. Sanchez-Castaneda C, Luis-Ruiz S, Ramon-Krauel M, Lerin C, Sanchez C, Miro N, et al. Executive function training in childhood obesity: food choice, quality of life, and brain connectivity (TOuCH): A randomized control trial protocol. Front Pediatr. (2021) 9:551869. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.551869
193. Meltzer JA, Kates Rose M, Le AY, Spencer KA, Goldstein L, Gubanova A, et al. Improvement in executive function for older adults through smartphone apps: a randomized clinical trial comparing language learning and brain training. Neuropsychol Dev Cognit B Aging Neuropsychol Cognit. (2023) 30:150–71. doi: 10.1080/13825585.2021.1991262
194. Torous J, Staples P, Fenstermacher E, Dean J, and Keshavan M. Barriers, benefits, and beliefs of brain training smartphone apps: an internet survey of younger US consumers. Front Hum Neurosci. (2016) 10:180. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00180
195. Chen PV, Helm A, Caloudas SG, Ecker A, Day G, Hogan J, et al. Evidence of phone vs video-conferencing for mental health treatments: A review of the literature. Curr Psychiatry Rep. (2022) 24:529–39. doi: 10.1007/s11920-022-01359-8
196. Bouabida K, Chaves BG, Anane E, and Jagram N. Navigating the landscape of remote patient monitoring in Canada: trends, challenges, and future directions. Front Digit Health. (2025) 7:1523401. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1523401
197. Flickinger TE, Waselewski M, Tabackman A, Huynh J, Hodges J, Otero K, et al. Communication between patients, peers, and care providers through a mobile health intervention supporting medication-assisted treatment for opioid use disorder. Patient Educ Couns. (2022) 105:2110–15. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2022.02.014
198. Neeland IJ, Al-Kindi SG, Tashtish N, Eaton E, Friswold J, Rahmani S, et al. Lessons learned from a patient-centered, team-based intervention for patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: year 1 results from the CINEMA program. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11:e024482. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.024482
199. Alshowair A, Altamimi S, Alruhaimi FA, Alshahrani S, Alsuwailem F, Alkhaldi M, et al. Cost-savings associated with multi-disciplinary team approach for reducing macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: A predictive model. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. (2024) 16:211–23. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S451739
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, cognitive impairment, insulin resistance, neuroinflammation, glycemic control, neuroprotection
Citation: Chen X, Huang Y and Xiong X (2025) Mechanisms underlying cognitive impairment and management strategies in type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1655768. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1655768
Received: 28 June 2025; Accepted: 29 September 2025;
Published: 15 October 2025.
Edited by:
Lei Sha, China Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xiu-Jun Liu, Wuhan Mental Health Center, ChinaZarin Nudar Rodoshi, Mymensingh Medical College, Bangladesh
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Huang and Xiong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaolin Chen, eGlhb2xpbmNoZW5Ad2h1LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiaoxing Xiong, eGlhb3hpbmd4aW9uZ0B3aHUuZWR1LmNu
†ORCID: Xiaolin Chen, orcid.org/0000-0001-5087-2964
 Xiaolin Chen
Xiaolin Chen Yan Huang1
Yan Huang1 Xiaoxing Xiong
Xiaoxing Xiong