- 1Center for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 2Jiangxi Provincial Cardiovascular Disease Clinical Medical Research Center, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 4School of Pharmacy, Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 5Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
Background: Existing evidences regarding the association between the ratio of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and first stroke in hypertensive patients remains limited. This study aims to assess the role of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio in the risk of first stroke in Chinese hypertensive patients.
Methods and results: This prospective cohort study encompassed 12, 893 hypertensive patients from the Chinese Hypertension Registry. Cox proportional hazards regression, restricted cubic spline (RCS), and subgroup analysis were applied to evaluate the association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke. The hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to estimate the strength of the association. The mean age of all participants was 63.7 ± 9.5 years, and 531 cases of first stroke occurred, with an average follow-up time of 3.9 years. In the fully adjusted model, each 1-unit increase of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio raised the risk of first stroke by 43% (HR=1.43, 95% CI: 1.22–1.67). Compared with patients in the Q1 of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, the adjusted HRs of stroke for those in Q2, Q3, and Q4 were respectively 1.32 (95% CI: 1.03,1.70), 1.49 (95% CI: 1.14, 1.96), and 1.94 (95% CI: 1.45, 2.59), with a statistically significant trend (P for trend < 0.001). Analyses using restricted cubic spline confirmed the linear association between the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke. Subgroup analysis revealed a stronger association between the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke in drinkers (P for interaction=0.024).
Conclusion: A high LDL-C/HDL-C ratio may increase the risk of first stroke in hypertensive patients, especially among current drinkers.
Introduction
Stroke is the leading cause of disability and death worldwide (1). Between 1990 and 2019 (2), global stroke prevalence cases, incidence cases, and deaths increased significantly by 85%, 70%, and 43%, respectively. The incidence and prevalence of stroke in China continue to rise (3–6), making it a major public health challenge. According to the latest epidemiologic survey data (7), China has 2.4 million new stroke cases and 1.1 million stroke-related deaths each year. Globally, hypertension is not only one of the most important risk factors for stroke (8, 9) but also a primary risk factor for ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke (10). Given that traditional risk factors do not fully explain stroke risk, identifying and intervening with modifiable risk factors, especially in hypertensive patients, is essential to optimize stroke prevention and reduce the burden of disease and the risk of recurrence.
Growing evidence suggests that the ratio of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is a new indicator of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk (11, 12). This ratio not only reflects the state of lipoprotein homeostasis (13), but also is significantly associated with the risk of cardiovascular events (14, 15). Specifically, elevated LDL-C levels are a clear risk factor for ischemic stroke and further increase the risk of subsequent major cardiovascular events, especially in patients with a history of stroke (16, 17). Low HDL-C levels, on the other hand, independently affect the prognosis of cerebrovascular disease (18–20), and studies have confirmed that HDL-C is negatively associated with the risk or severity of ischemic stroke (21, 22).
Nevertheless, existing evidence regarding the association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and stroke risk in hypertensive populations remains limited, and stroke etiology involves multifactorial mechanisms. This study was therefore conducted to examine the relationship between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and stroke in Chinese hypertensive patients, aiming to provide evidence for stroke prevention strategies, therapeutic approaches, and comprehensive clinical management.
Methods
Participants
All data used in this study were obtained from the Chinese Hypertension Registry Study (registration number: ChiCTR1800017274), which was a real-world, multicenter, observational study. The study was initiated in March 2018 in Wuyuan County, Jiangxi Province, China, and the inclusion criteria were (1) aged ≥18 years and (2) having hypertension, defined as sitting resting blood pressure ≥140/90 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive drugs. The study aimed to assess the current treatment status, associated risk factors, and prognosis of local hypertensive patients. Specific inclusion and exclusion criteria have been detailed previously (23). This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Anhui Medical University (NO. CH1059), and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University (NO. 2018019). All patients signed an informed consent before enrollment.
A total of 14,234 hypertensive patients were enrolled in this study. Patients with a previous history of stroke (n = 984), using lipid-lowering drugs (n = 343), missing data on HDL-C/LDL-C (n = 7), missing data on waist circumference (WC) (n = 2), missing data on smoking history (n = 4), and being lost to follow-up (n = 1) were excluded. Finally, 12,893 subjects were analyzed (Figure 1).
Data collection
All participants underwent baseline and follow-up health assessments by trained researchers following standard operating procedures to determine their demographic characteristics, including age, sex, smoking history, alcohol consumption, medical history, and medications. Anthropometric indicators include height, weight, and waist circumference. Body mass index (BMI) is defined as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m²). Trained medical personnel assessed blood pressure (BP) to control for measurement differences between different observers. After the participants were allowed to rest for 5 min, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and heart rate (HR) were measured three times consecutively with an Omron electronic sphygmomanometer. The interval between consecutive readings was 1 minute, and three measurements were taken on the right arm and averaged. With respect to alcohol drinking, subjects were classified as never, former or current drinkers, and according to alcohol consumption (none, ≤2 drinks per week, ≥2 drinks per week) (24). Smoking status was defined as never (smoked <100 cigarettes in lifetime), former (smoked ≥100 cigarettes in lifetime but had not reported smoking at baseline), or current smoking (smoked cigarettes in the past 30 days) (25).
Subjects were informed in advance of the need to fast overnight for 8–12 hours before blood samples were collected. The samples were quickly processed to obtain serum, which was stored at -80 °C for testing (Bioengineering, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China). All tests were performed using a fully automated clinical analyzer (Beckman Coulter, USA) to measure fasting blood glucose (FPG), homocysteine (Hcy), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), HDL-C and LDL-C. The estimate glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation (26). Chronic kidney disease (CKD) was defined as eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (27). Dyslipidemia was defined as TC greater than or equal to 5.2mmol/L, TG greater than or equal to 1.7 mmol/L, LDL-C greater than or equal to 3.4 mmol/L,or HDL-C less than 1.0 mmol/L, or self-reported dyslipidemia (28).
Diabetes mellitus was defined as a self-reported physician diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, FPG concentration ≥ 7.0 mmol/L, or use of hypoglycemic medications. The history of coronary heart disease (CHD) was primarily self-reported by participants through a questionnaire. Each participant was asked about the presence of symptoms, the type of treatment received, and the availability of medical records (including discharge summaries, biochemical test data, and imaging data) during episodes of coronary heart disease or stroke atrial fibrillation (AF) was defined as the presence of AF on a standard 12-lead electrocardiogram or a history of AF.
Outcome assessments
The primary outcome of follow-up was the first occurrence of a nonfatal or fatal symptomatic stroke, excluding subarachnoid hemorrhage and subclinical stroke. Outcome information was initially collected through face-to-face questionnaire surveys, home visits, or telephone interviews, and subsequently verified using hospital information systems (HIS), the National Health Information Platform, or the National Basic Medical Insurance System to ensure complete ascertainment of stroke events across the entire cohort. Final adjudication of all suspected stroke cases was conducted by the End Point Adjudication Committee, which comprised experts in neurology, neurosurgery, cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, and public health, applying predefined diagnostic criteria.
Statistical analyses
Baseline characteristics were described using mean (standard deviation, SD) for continuous variables. Categorical variables were described as frequency (%). One-way analysis of variance or chi-square tests were used to compare the characteristics of populations grouped by LDL-C/HDL-C ratio quartiles and to explore the distribution of the intervals.
Cox proportional hazard regression was used to estimate hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for the association between the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and the first stroke. Three models were constructed with sequential adjustments: Model 1 was adjusted no covariates. Model 2 was adjusted for sex and age. Model 3 was adjusted for sex, age, BMI, WC, SBP, DBP, FPG, TC, TG, eGFR, Hcy, smoking, drinking, diabetes, dyslipidemia, CKD, CHD, AF, antiplatelet drugs, glucose-lowering drugs. In the regression analyses model, covariates were selected based on clinical importance, statistical significance in univariable analysis, and the potential confounders effect estimates individually changed by at least 10%. Multiple collinearity screening between covariates showed that all variance inflation factors (VIF) were less than 5. The proportional hazards assumption was verified using Schoenfeld residual tests. A generalized additive model with restricted cubic spline smoothing was employed to evaluate the dose-response relationship between the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke. Subgroup analyses were performed to assess potential effect modifications in the association between the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and stroke. To control the overall type I error, the Bonferroni method was applied for multiple testing correction: the adjusted significance level α for the interaction tests in stratified subgroups was set at 0.05/7 = 0.007.
All statistical analyses were performed using R software (version 3.3.1 version; http://www.R-project.org) and Empower version 2.17.8 (www.empowerstats.com) for statistical analysis. All statistical tests were performed using a two-sided test and were statistically significant with a P value < 0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics of study participants
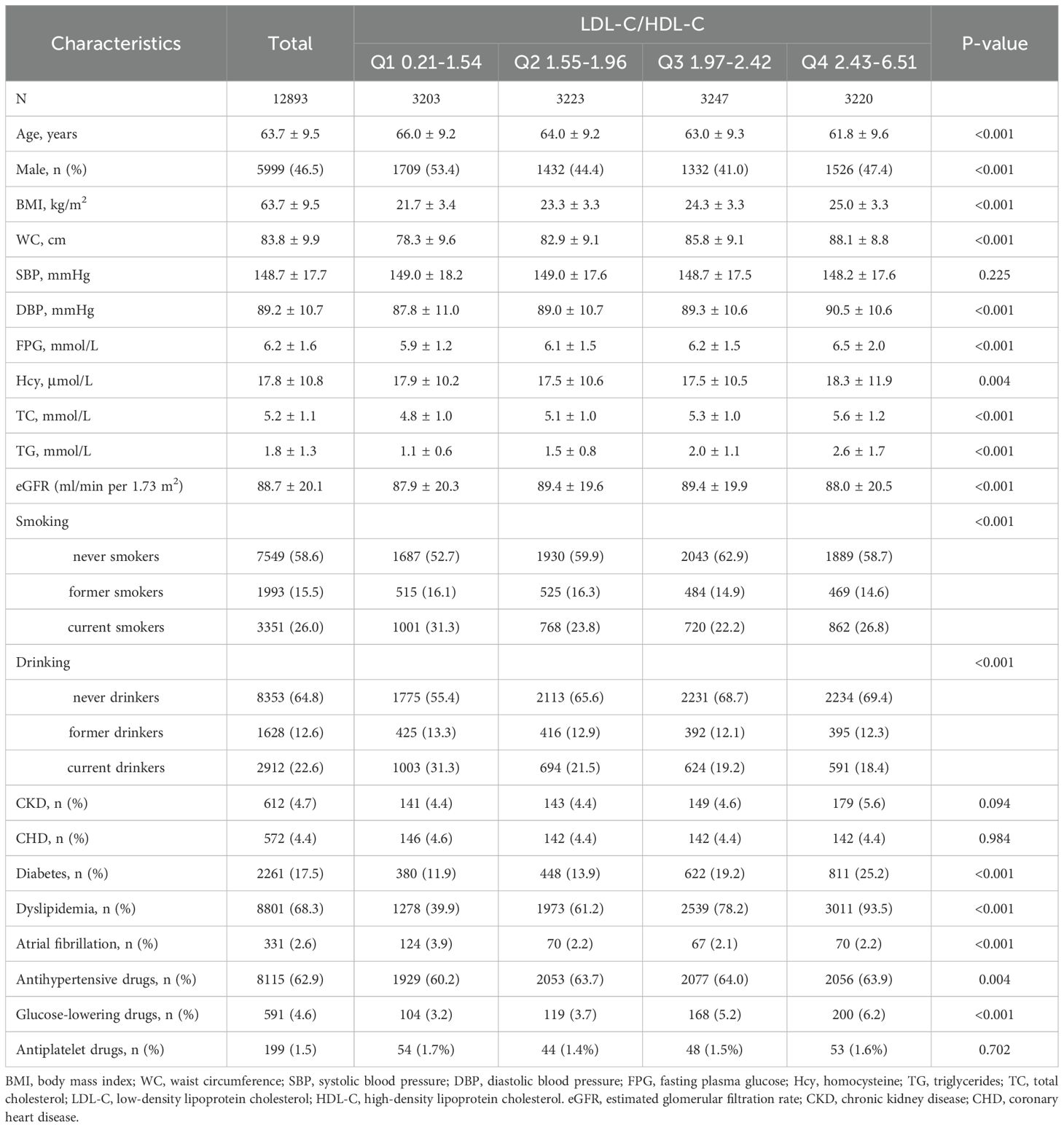
A total of 12, 893 hypertensive patients (mean age 63.7 ± 9.5 years; 46.5% males) were finally enrolled for the final analysis. Baseline characteristics of the patients grouped by LDL-C/HDL-C quartiles were presented in Table 1. Participants with higher LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were more likely to be younger, females, have higher BMI, WC, DBP, FPG, Hcy, TC, TG, higher rates of current smoking, diabetes, use of antihypertensive drugs and glucose-lowering drugs, have lower eGFR, and lower rates of current drinking and AF. SBP, CKD, CHD, use of antiplatelet drugs did not differ statistically between LDL-C/HDL-C quartiles.
Association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and stroke
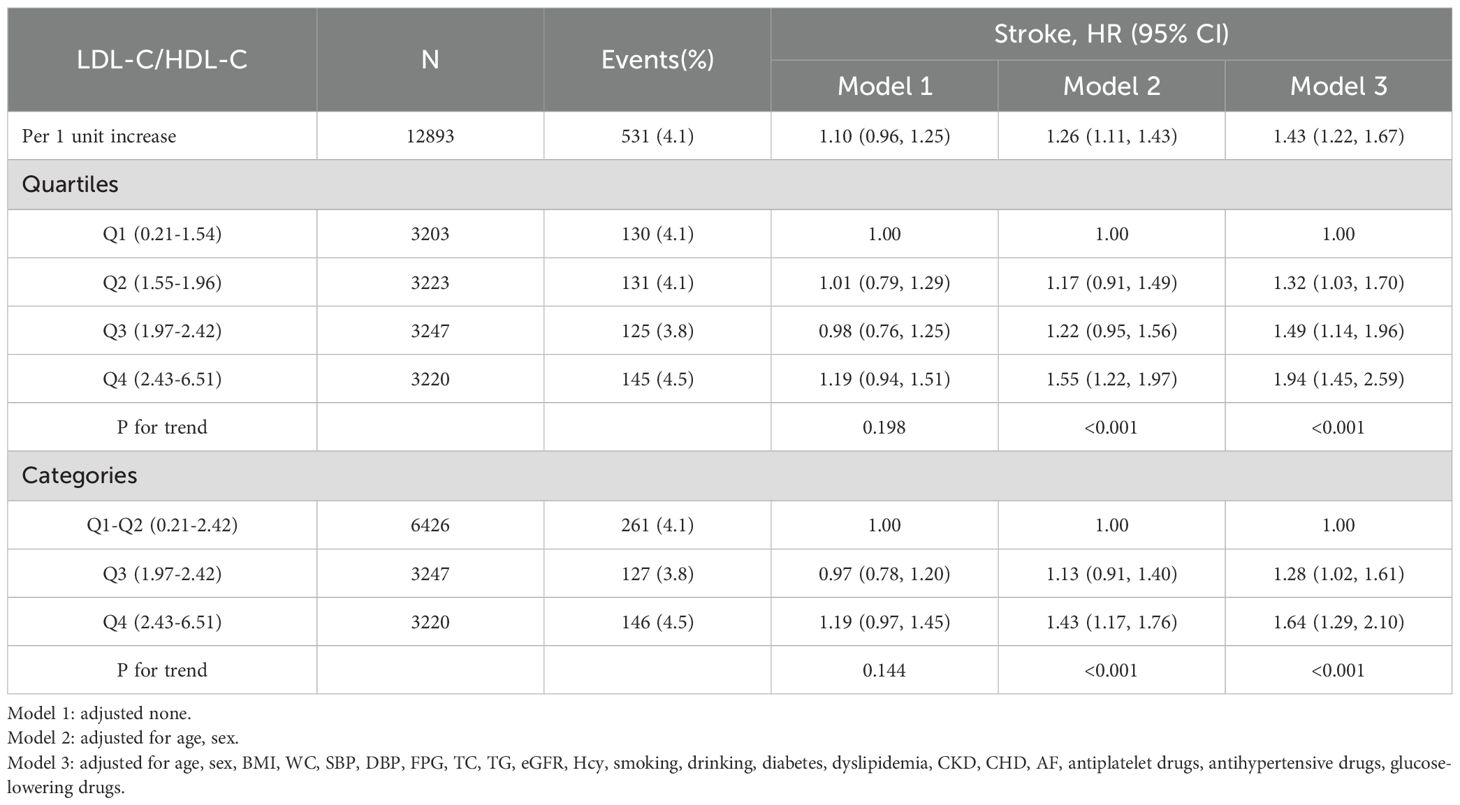
After an average follow-up of 3.9 years, 531 cases of first stroke occurred. In Figure 2, the results of the dose-response relationship analysis revealed a positive linear association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke. HRs and 95% CIs of first stroke according to quartiles of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were summarized in Table 2. In the fully adjusted model (Model 3), each 1-unit increment in LDL-C/HDL-C ratio was associated with a 43% increase in the risk of first stroke (HR, 1.43; 95%CI: 1.22, 1.67). When LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were grouped by quartiles, full adjusted HRs of first stroke for patients in quartile 2, quartiles 3 and quartile 4 of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were 1.32 (95%CI: 1.03,1.70), 1.49 (95%CI: 1.14, 1.96) and 1.94 (95% CI: 1.45, 2.59), compared with those in the quartile 1 (P for trend <0.001). Compared with patients in the combined group of quartile 1 and quartile 2, full adjusted HRs of first stroke for patients in quartiles 3 and quartile 4 of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were respectively 1.28 (95%CI: 1.02,1.61) and 1.64 (95%CI: 1.29, 2.10).
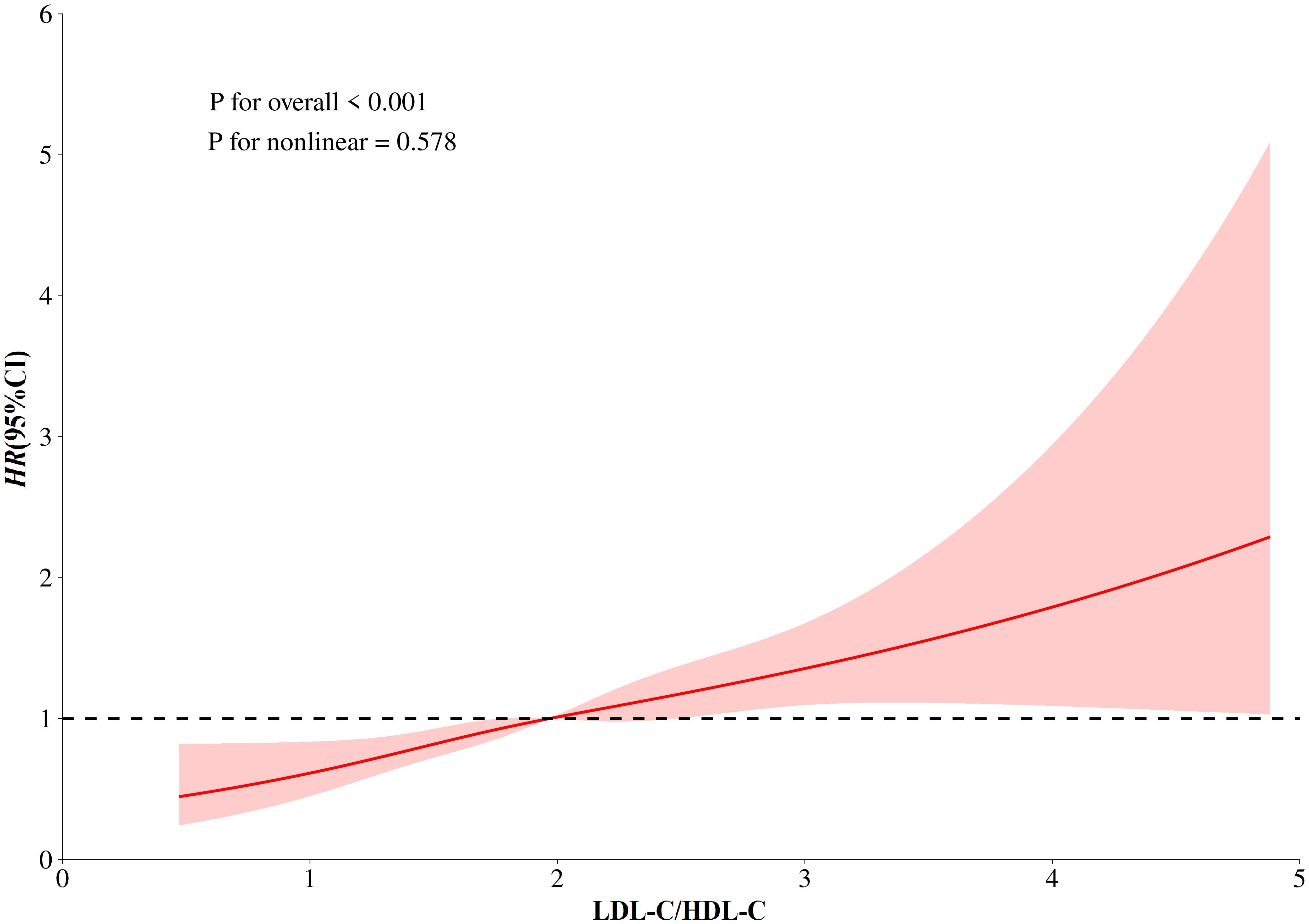
Figure 2. Dose-response relationship between LDL-C/HDL-C Ratio and Stroke. Models were adjusted for sex, age, BMI, WC, SBP, DBP, FPG, TC, TG, eGFR, Hcy, smoking, drinking, diabetes, dyslipidemia, CKD, CHD, AF, antiplatelet drugs, anti-hypertensive drugs, glucose-lowering drugs.
Subgroup analysis
We further performed stratified analyses to assess the effect of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio (per 1 unit increment) on first stroke in various subgroups (Table 3). The association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke were consistent in the following subgroups: sex (male vs. female; P-interaction=0.547), age (<65 vs. ≥65 y; P-interaction=0.556), BMI(<24, ≥24 kg/m2; P-interaction=0.668), smoking (never smokers vs. former smokers vs. current smokers; P-interaction=0.473), diabetes (no vs. yes; P-interaction=0.401), and dyslipidemia (no vs. yes; P-interaction=0.906). However, there was a significant interaction between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and drinking on first stroke. A stronger positive association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke was found in former drinkers (HR, 1.56; 95%CI: 1.11, 2.19) and current drinkers (HR, 1.76; 95%CI: 1.38, 2.25) compared with never drinkers (HR, 1.28; 95%CI: 1.06, 1.55; P-interaction=0.024).
Discussion
In this prospective cohort study of 12,893 hypertensive patients free of prior stroke, we demonstrated that an elevated LDL-C/HDL-C ratio was independently associated with a 43% increased risk of first stroke per 1-unit increment after comprehensive adjustment for cardiovascular risk factors. Notably, this association exhibited a linear dose-response relationship, was significantly potentiated among current drinkers.
This result is consistent with previous findings on lipid ratios and cardiovascular risk, as Zhang et al (29). found in a study of 3469 participants that the risk of stroke in the highest quartile of the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio was 23.45 times higher than in the lowest quartile (OR = 24.45, 95% CI: 17.18-34.79), and the risk increased by the increment of quartile of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio. Liu et al. (30) further revealed the “time-dependent” role of LDL-C/HDL-C ratios in stroke prognosis in a study of 3410 participants, suggesting that acute lipid modulation may improve short-term outcomes, but that long-term high LDL-C/HDL-C ratios remain an important target for intervention in stroke prevention. A large number of evidence supports (11, 12, 31) that the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio has significant predictive value in the assessment of cardiovascular disease risk. In a prospective cohort study of 5099 Chinese rural hypertensive patients, Zheng et al (32) found that the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio was significantly associated with the risk of ischemic stroke, with a predictive efficacy that exceeded that of traditional lipid markers. A prospective cohort study investigating the interaction between dyslipidemia and hypertension in ischemic stroke reported that when stratifying participants into two groups according to LDL-C/HDL-C (≥2 vs. <2), and adjusting for age, sex, BMI, smoking, alcohol consumption, and other questionnaire-based covariates, the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio was significantly associated with ischemic stroke risk (HR = 1.414, 95% CI: 1.034–1.933) (33). By contrast, our study provides the first evidence of a continuous, linear association between this ratio and incident stroke in a strictly stroke-naïve cohort. Although our group previously published an analysis of mortality outcomes using the same registry (34), the present investigation focuses specifically on first stroke events with extended follow-up, thereby offering novel pathophysiological insights into primary prevention. Furthermore, based on a large longitudinal study of 384,093 participants from the UK Biobank database, with a median of 11.9 years follow-up, Yuan (35) et al. reported a nonlinear relationship between the reciprocal of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and stroke: compared with LDL-C/HDL-C=1.67-2.50, LDL-C/HDL-C > 2.5 was correlated with a higher ischemic stroke risk, and LDL-C/HDL-C <1.67 was correlated with a higher hemorrhagic stroke risk after full multivariate adjustment. The conclusion of this study differed from ours, which might be due to the fact that this research was conducted among the British healthy population.
The current academic opinion on the association between alcohol consumption and stroke risk remains controversial, and this association shows significant differences depending on the type of stroke (36). Previous studies have shown (37) that heavy drinking and alcohol abuse are independent risk factors for ischemic stroke, especially in young men. The Meta-analysis system of Patra et al. (38) assessed the dose-effect relationship between alcohol consumption and stroke risk: the risk of ischemic stroke showed a J-shaped curve (small amounts of alcohol may be protective, whereas large amounts increase the risk), whereas the risk of hemorrhagic stroke showed a monotonically increasing trend with increasing alcohol consumption. This finding is partially consistent with the observations of the present study, but no protective effect of alcohol on stroke was found in the present study, and this discrepancy may be related to the higher prevalence of hypertension in the study population. Although the study by Yang (39) et al. reported that small amounts of low-frequency alcohol consumption (≤30 g/day, <5 days/week) were associated with a reduced risk of ischemic stroke at short-term follow-up (≤7 years), this protective effect disappeared at long-term follow-up (>7 years), and the risk of stroke was significantly higher in high-frequency drinkers. This finding suggests that in the long term, alcohol consumption does not reduce stroke risk, regardless of the drinking pattern. Existing studies (40–43) have shown that alcohol consumption may be associated with increased levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and decreased levels of fibrinogen, which may explain the potential association between mild-to-moderate alcohol consumption and a reduced risk of ischemic stroke, but this association does not apply to hemorrhagic stroke. For hemorrhagic stroke (44), alcohol may increase risk by affecting blood pressure. The findings of Kiyohara et al. in the Kuyama-cho study (45) in Japan further support the idea that there is a significant synergistic effect between hypertension and heavy alcohol consumption. Individuals with hypertension combined with heavy alcohol consumption had a significantly increased risk of cerebral hemorrhage compared with nondrinkers; at the same time, the risk of cerebral infarction was twice as high in hypertensive heavy drinkers as in light drinkers. These results show that alcohol consumption may amplify the effects of hypertension on stroke (46). Therefore, the coexistence of alcohol consumption and hypertension warrants special consideration in stroke prevention strategies. Current evidence suggests that hypertensive patients should avoid alcohol consumption to mitigate stroke risk.
Our investigation provides the first evidence of a continuous, linear association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and incident stroke in a strictly stroke-naive hypertensive cohort, with comprehensive adjustment for cardiometabolic confounders. This analysis benefits from long-term follow-up in a large cohort, ensuring robust statistical power. Some potential limitations of our study should be noted. First, our study relied on baseline lipid measurements without dynamic monitoring, potentially affecting long-term risk estimation. Second, despite comprehensive adjustment for known confounders, residual confounding from unmeasured variables cannot be entirely ruled out. Finally, Restricted generalizability due to exclusive focus on rural hypertensive populations in Jiangxi Province—extrapolation to urban settings, other regions. Nevertheless, these findings offer clinically actionable guidance for stroke prevention through lipid ratio management in hypertensive patients, warranting validation via future multicenter urban-rural comparative studies.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that an elevated LDL-C/HDL-C ratio—a superior marker of atherogenic/antiatherogenic lipoprotein balance compared to isolated LDL-C or HDL-C measurements—independently associates with increased first stroke risk in hypertensive patients, persisting after adjustment for traditional cardiovascular risk factors and other potential confounders. These findings support the potential clinical utility of the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio as a stroke risk biomarker. Furthermore, our results highlight the importance of incorporating both lipid ratio management and blood pressure control in hypertension treatment strategies. Future research should further validate the predictive value of the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio for stroke prevention and elucidate its underlying biological mechanisms.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
CY: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Supervision. MW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. LZ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Writing – original draft. TW: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WFZ: Writing – review & editing, Validation. WZ: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HB: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology. XC: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Cultivation of backup projects for the National Science and Technology Awards (20223AEI91007), Jiangxi Science and Technology Innovation Base Plan -Jiangxi Clinical Medical Research Center (20223BCG74012), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (grant number: 20232BAB206140), Jiangxi Provincial Drug Administration Science and Technology Project (2023JS26).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the contributions of all the staff involved in in the China Hypertension Registry Study, as well as the research participants who have dedicated their time to collaborate with us.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
BMI, Body mass index; WC, Waist circumference; BP, Blood pressure; SBP, Systolic blood pressure; DBP, Diastolic blood pressure; FPG,Fasting plasma glucose; Hcy, Homocysteine; TG, Triglycerides; TC,Total cholesterol; LDL-C, Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; eGFR, Estimated glomerular filtration rate; CKD, Chronic kidney disease; CKD-EPI, Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration; CHD, Coronary heart disease; AF, Atrial fibrillation; SD,Standard deviation; HR, Hazard ratio; CI, Confidence interval.
References
1. Krishnamurthi RV, Ikeda T, and Feigin VL. Global, regional and country-specific burden of ischaemic stroke, intracerebral haemorrhage and subarachnoid haemorrhage: A systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Neuroepidemiology. (2020) 54:171–79. doi: 10.1159/000506396
2. GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:795–820. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
3. Wang Y, Zhou L, Guo J, Wang Y, Yang Y, Peng Q, et al. Secular trends of stroke incidence and mortality in China, 1990 to 2016: The Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2020) 29:104959. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104959
4. Wang W, Jiang B, Sun H, Ru X, Sun D, Wang L, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480 687 adults. Circulation. (2017) 135:759–71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025250
5. Zhao Y, Hua X, Ren X, Ouyang M, Chen C, Li Y, et al. Increasing burden of stroke in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence, incidence, mortality, and case fatality. Int J Stroke. (2023) 18:259–67. doi: 10.1177/17474930221135983
6. Guan T, Ma J, Li M, Xue T, Lan Z, Guo J, et al. Rapid transitions in the epidemiology of stroke and its risk factors in China from 2002 to 2013. Neurology. (2017) 89:53–61. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004056
7. Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, Chen Z, Wang W, Anderson CS, et al. Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:394–405. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30500-3
8. Qin X, Li Y, Sun N, He M, Tang G, Yin D, et al. Impact of achieved blood pressure on first stroke in uncomplicated grade 1 hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e005247. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005247
9. Li Y, Liang M, Jiang C, Wang G, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Impact of achieved blood pressure on renal function decline and first stroke in hypertensive patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2018) 33:409–17. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx267
10. Pandian JD, Sylaja PN, Lackland DT, Babu V, Kumar Paramasivan N, Sebastian I, et al. World Stroke Organization and World Hypertension League position statement on hypertension control strategies in prevention and management of stroke. Int J Stroke. (2025) 20:151–65. doi: 10.1177/17474930241309276
11. Packard CJ, Ford I, Robertson M, Shepherd J, Blauw GJ, Murphy MB, et al. Plasma lipoproteins and apolipoproteins as predictors of cardiovascular risk and treatment benefit in the PROspective Study of Pravastatin in the Elderly at Risk (PROSPER). Circulation. (2005) 112:3058–65. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.526848
12. Endo A, Yoshida Y, Kageshima K, Sato H, Suga T, Nasu H, et al. Contributors to newly developed coronary artery disease in patients with a previous history of percutaneous coronary intervention beyond the early phase of restenosis. Intern Med. (2014) 53:819–28. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.53.1438
13. Lee M, Cheng CY, Wu YL, Lee JD, Hsu CY, and Ovbiagele B. Association between intensity of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction with statin-based therapies and secondary stroke prevention: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Neurol. (2022) 79:349–58. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.5578
14. Yokokawa H, Yasumura S, Tanno K, Ohsawa M, Onoda T, Itai K, et al. Serum low-density lipoprotein to high-density lipoprotein ratio as a predictor of future acute myocardial infarction among men in a 2.7-year cohort study of a Japanese northern rural population. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2011) 18:89–98. doi: 10.5551/jat.5215
15. Zhong Z, Hou J, Zhang Q, Zhong W, Li B, Li C, et al. Assessment of the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio as a predictor of one year clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes after percutaneous coronary intervention and drug-eluting stent implantation. Lipids Health Dis. (2019) 18:40. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-0979-6
16. Yaghi S and Elkind MS. Lipids and cerebrovascular disease: research and practice. Stroke. (2015) 46:3322–8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.011164
17. Lau KK, Chua BJ, Ng A, Leung IY, Wong YK, Chan AH, et al. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of recurrent vascular events in chinese patients with ischemic stroke with and without significant atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10:e021855. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.021855
18. Rizos E and Mikhailidis DP. Are high density lipoprotein (HDL) and triglyceride levels relevant in stroke prevention? Cardiovasc Res. (2001) 52:199–207. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00383-2
19. Ridker PM, Genest J, Boekholdt SM, Libby P, Gotto AM, Nordestgaard BG, et al. HDL cholesterol and residual risk of first cardiovascular events after treatment with potent statin therapy: an analysis from the JUPITER trial. Lancet. (2010) 376:333–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60713-1
20. Yeh PS, Yang CM, Lin SH, Wang WM, Chen PS, Chao TH, et al. Low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with atherosclerotic stroke: a prospective cohort study. Atherosclerosis. (2013) 228:472–7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.03.015
21. Tziomalos K, Giampatzis V, Bouziana SD, Spanou M, Kostaki S, Papadopoulou M, et al. Prognostic significance of major lipids in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis. (2017) 32:395–400. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9924-9
22. Zhang Y, Tuomilehto J, Jousilahti P, Wang Y, Antikainen R, and Hu G. Total and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and stroke risk. Stroke. (2012) 43:1768–74. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.646778
23. Yu Y, Hu L, Huang X, Zhou W, Bao H, and Cheng X. BMI modifies the association between serum HDL cholesterol and stroke in a hypertensive population without atrial fibrillation. J Endocrinol Invest. (2021) 44:173–81. doi: 10.1007/s40618-020-01288-4
24. Giraldi L, Leoncini E, Pastorino R, Wünsch-Filho V, de Carvalho M, Lopez R, et al. Alcohol and cigarette consumption predict mortality in patients with head and neck cancer: a pooled analysis within the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology (INHANCE) Consortium. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:2843–51. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx486
25. Mackey RH, Mora S, Bertoni AG, Wassel CL, Carnethon MR, Sibley CT, et al. Lipoprotein particles and incident type 2 diabetes in the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:628–36. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0645
26. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. (2009) 150:604–12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006
27. Xiong Y, Zhong Q, Zhang Y, Liu Z, and Wang X. The association between circadian syndrome and chronic kidney disease in an aging population: a 4-year follow-up study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1338110. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1338110
28. Lu Y, Zhang H, Lu J, Ding Q, Li X, Wang X, et al. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and availability of lipid-lowering medications among primary health care settings in China. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4:e2127573. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27573
29. Zhang XX, Wei M, Shang LX, Lu YM, Zhang L, Li YD, et al. LDL-C/HDL-C is associated with ischaemic stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19:217. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01392-7
30. Liu L, Yin P, Lu C, Li J, Zang Z, Liu Y, et al. Association of LDL-C/HDL-C ratio with stroke outcomes within 1 year after onset: A hospital-based follow-up study. Front Neurol. (2020) 11:408. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00408
31. Kunutsor SK, Zaccardi F, Karppi J, Kurl S, and Laukkanen JA. Is high serum LDL/HDL cholesterol ratio an emerging risk factor for sudden cardiac death? Findings from the KIHD study. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2017) 24:600–8. doi: 10.5551/jat.37184
32. Zheng J, Sun Z, Zhang X, Li Z, Guo X, Xie Y, et al. Non-traditional lipid profiles associated with ischemic stroke not hemorrhagic stroke in hypertensive patients: results from an 8.4 years follow-up study. Lipids Health Dis. (2019) 18:9. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-0958-y
33. Wei L, Sun J, Xie H, Zhuang Q, Wei P, Zhao X, et al. Interaction analysis of abnormal lipid indices and hypertension for ischemic stroke: A 10-year prospective cohort study. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:819274. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.819274
34. Yu Y, Li M, Huang X, Zhou W, Wang T, Zhu L, et al. A U-shaped association between the LDL-cholesterol to HDL-cholesterol ratio and all-cause mortality in elderly hypertensive patients: a prospective cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19:238. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01413-5
35. Yuan S, Huang X, Ma W, Yang R, Xu F, Han D, et al. Associations of HDL-C/LDL-C with myocardial infarction, all-cause mortality, haemorrhagic stroke and ischaemic stroke: a longitudinal study based on 384–093 participants from the UK Biobank. Stroke Vasc Neurol. (2023) 8:119–26. doi: 10.1136/svn-2022-001668
36. Larsson SC, Wallin A, Wolk A, and Markus HS. Differing association of alcohol consumption with different stroke types: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. (2016) 14:178. doi: 10.1186/s12916-016-0721-4
37. Reynolds K, Lewis B, Nolen JD, Kinney GL, Sathya B, and He J. Alcohol consumption and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis. JAMA. (2003) 289:579–88. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.5.579
38. Patra J, Taylor B, Irving H, Roerecke M, Baliunas D, Mohapatra S, et al. Alcohol consumption and the risk of morbidity and mortality for different stroke types–a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. (2010) 10:258. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-258
39. Yang W, Kang DW, Ha SY, and Lee SH. Drinking patterns and risk of ischemic stroke in middle-aged adults: do beneficial drinking habits indeed exist? Stroke. (2021) 52:164–71. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032144
40. Mukamal KJ and Rimm EB. Alcohol consumption: risks and benefits. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2008) 10:536–43. doi: 10.1007/s11883-008-0083-2
41. O’Keefe JH, Bybee KA, and Lavie CJ. Alcohol and cardiovascular health: the razor-sharp double-edged sword. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2007) 50:1009–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.04.089
42. Agarwal DP. Cardioprotective effects of light-moderate consumption of alcohol: a review of putative mechanisms. Alcohol Alcohol. (2002) 37:409–15. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/37.5.409
43. Brien SE, Ronksley PE, Turner BJ, Mukamal KJ, and Ghali WA. Effect of alcohol consumption on biological markers associated with risk of coronary heart disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies. BMJ. (2011) 342:d636. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d636
44. Puddey IB, Beilin LJ, and Rakic V. Alcohol, hypertension and the cardiovascular system: a critical appraisal. Addict Biol. (1997) 2:159–70. doi: 10.1080/13556219772705
45. Kiyohara Y, Kato I, Iwamoto H, Nakayama K, and Fujishima M. The impact of alcohol and hypertension on stroke incidence in a general Japanese population. Hisayama Study. Stroke. (1995) 26:368–72. doi: 10.1161/01.str.26.3.368
Keywords: hypertension, LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, first stroke, cohort study, alcohol drinking
Citation: Yu C, Wu M, Zhu L, Wang T, Zhang W, Zhou W, Bao H and Cheng X (2025) Association between LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and first stroke in hypertensive patients: a prospective cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1657213. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1657213
Received: 01 July 2025; Accepted: 25 August 2025;
Published: 11 September 2025.
Edited by:
Nina Japundzic-Zigon, University of Belgrade, SerbiaReviewed by:
Arianna Toscano, University Hospital of Policlinico G. Martino, ItalyHiroya Ohta, Hokkaido University of Science, Japan
Mohamed Hany, Alexandria University, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Wu, Zhu, Wang, Zhang, Zhou, Bao and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weifang Zhang, el93ZWlmYW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Wei Zhou, ei13Njc3QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to the work
 Chao Yu
Chao Yu Meihui Wu
Meihui Wu Lingjuan Zhu
Lingjuan Zhu Tao Wang
Tao Wang Weifang Zhang
Weifang Zhang Wei Zhou
Wei Zhou Huihui Bao
Huihui Bao Xiaoshu Cheng
Xiaoshu Cheng