- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine and Neurology, Tenth People’s Hospital of Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Yangpu Hospital of Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Background: The main determinant of skeletal fragility in postmenopausal patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) and osteopenia is thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) suppressive therapy. Evidence for the use of bisphosphonates, including technetium-99 methylene diphosphonate (99Tc-MDP), in this clinical setting remains limited.
Objective: To investigate the effects of 99Tc-MDP on osteopenia (T-score <-1.0≥-2.5 SD for the lumbar spine by DXA) in postmenopausal women with DTC under TSH suppression therapy compared with routine calcium/vitamin D supplementation.
Methods: A total of 102 postmenopausal patients with DTC and osteopenia under TSH suppression therapy were enrolled in this open-label, prospective study. Patients were divided into two groups: calcium/vitamin D supplements (groupCa) and calcium/vitamin D plus 99Tc-MDP (groupmdp) groups. Lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD) by DXA was measured before and 12 months after treatment. Bone turnover markers were evaluated at baseline, 6 months, and 12 months.
Results: The combined 99Tc-MDP treatment significantly increased the mean percentage change of lumbar BMD at month 12 compared with groupCa (t=2.156, p=0.035). A significant decrease in BMD of the lumber spine from 0.9148 ± 0.08 to 0.8726 ± 0.08 (t=3.81, p=0.001) at month 12 was observed in groupCa. The mean percentage change from baseline in the levels of serum β-isomer of C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX), procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (P1NP) showed that 99Tc-MDP combined treatment significantly increased PINP at month 6 (t=2.37, p = 0.02) and 12 (t=2.224, p = 0.029), and significantly decreased β-CTX at month 12 (t=-2.746, p = 0.008) compared with groupCa. No severe adverse events were reported in either group.
Conclusions: 99Tc-MDP is safe and could maintain lumbar BMD in postmenopausal women with DTC and osteopenia under TSH suppression therapy during a 1-year follow-up. Calcium/vitamin D supplementation alone did not effectively prevent bone loss in these patients.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR2200064170
Introduction
Differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) has become the most common endocrine malignancy. Papillary and follicular thyroid cancer are the two main histological types. According to the American Thyroid Association (ATA) and Chinese Thyroid Association (CTA), most patients with DTC undergo total or near-total thyroidectomy, radioiodine ablation, and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) suppression (1, 2). TSH suppression therapy is necessary in DTC because tumor cells express TSH receptors on cell membranes and respond to TSH stimulation by increasing the expression of several proteins and the rate of cell growth (3, 4). However, our previous study found that excessive intake of levothyroxine (L-T4) contributed to a negative balance of bone formation and resorption resulting in bone loss (5). Postmenopausal women with DTC receiving TSH suppression therapy are particularly vulnerable to osteopenia (OP) (6–11).
99Tc-methylene diphosphonate (99Tc-MDP), a chemical compound of technetium-99 conjugated with methylene diphosphonate ([99Tc-MDP], or Yunke, Chengdu Yunke Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chengdu, Sichuan, China), is an anti–bone destruction drug patented in China. It has been widely used with good efficacy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (patent No. ZL94113006.1) (12) and osteoporosis (patent No. ZL00100083.7) in China since 2000. Therefore, it is mainly indicated for RA and osteoporosis as described in its drug instructions. Our previous study showed that 99Tc-MDP was as efficacious as alendronate in improving lumbar bone mineral density (BMD) in DTC patients with osteoporosis under TSH suppression therapy (13). In clinical practice, we routinely encourage postmenopausal DTC patients under TSH suppression therapy to take oral calcium/vitamin D supplements. The BMD maintenance effect of the 99Tc-MDP was supposed in the current clinical study.
Patients and methods
Study design
This was part of an open-label, non-randomized clinical study (ChiCTR2200064170).
Primary endpoint
Lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD) before and 12 months after treatment.
Secondary endpoints
Bone turnover markers, including serum β--isomerized of C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX) and procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (P1NP), and adverse events were evaluated at baseline, 6 months, and 12 months after treatment.
Setting and participants
Postmenopausal DTC patients with OP under TSH suppression therapy from March 2022 to December 2022 were enrolled if they fulfilled all the following criteria. (1) They were pathologically diagnosed with DTC, including papillary or follicular carcinoma; (2) received a near-total thyroidectomy and radioiodine treatment; (3) bone mineral density (BMD) of the lumbar spine was tested by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) at baseline and at 12 months; (4) TSH suppression therapy was defined as a TSH level between 0.1–0.5 μIU/mL and had lasted for at least 1 year before the study; (5) they had osteopenia, namely, a T-score <-1.0≥-2.5 SD for the lumbar spine. They were followed up for at least 1 year.
We excluded patients who met the following criteria: (1) they had received medications for OP before TSH suppression treatment; (2) had secondary OP owing to parathyroid gland or kidney disease; (3) had severe liver or kidney disease; (4) had long-term use of an immunosuppressive agent, estrogen, or estrogen receptor modulators.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Research Ethics of Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital. All patients were fully informed about their treatment and consented to participate in the clinical trial.
TSH suppression therapy
TSH suppression treatment was based on the risk stratification of DTC using L-thyroxine (L-T4) as recommended (1, 2): (1) For patients with persistent disease, TSH suppression below 0.1 μIU/mL is recommended. (2) For patients free of disease but originally presenting with high-risk disease, TSH suppression from 0.1 to 0.5 μIU/mL is recommended. (3) For patients with low risk of recurrence, TSH suppression from 0.3 to 2 μIU/mL is recommended. The dose of L-T4 was maintained stable during the study period. Free T3, free T4, and TSH were measured using a time-resolved immunofluorometric assay (Anytest, Sym-Bio Lifescience Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
Treatment protocol
Patients were divided into two groups: calcium/vitamin D supplements (groupCa) and calcium/vitamin D combined 99Tc-MDP (groupmdp) groups.
1. groupCa: Calcium carbonate 1200mg and vitamin D (afalciferol) 0.25μg once a day were orally administered.
2. groupmdp: Calcium carbonate 1200mg and vitamin D (afalciferol) 0.25μg once a day were orally administered. In addition, 99Tc-MDP 10 mg was intravenously administered weekly for 10 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for 22 weeks, and monthly for another 5 months.
BMD in spine lumbar
DXA (v.13.20; enCORETM 2009, GE Healthcare) was used to measure BMD at the L1–4 vertebral regions. Precision errors, established with a local normal population, were less than 1.5% for all locations at baseline and at 12 months.
Serum bone turnover markers
Serum β-CTX, P1NP, and bone alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Modular E170, Hoffmann-La Roche, Basel, Switzerland) with intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation (CVs) of 2.7% and 3.4%, respectively.
Adverse reaction
Laboratory assays for routine blood tests, liver, and renal function were measured at baseline and 12 months. A treating physician reviewed the clinical results and any discomfort at each visit.
Study size
The predetermined primary endpoint was the difference in the change in BMD of the lumbar spine between the two groups. Group samples of 46 and 46 achieved 80% power to detect superiority using a one-sided two-sample t-test. The margin of superiority was 0.036. The significance level (alpha) of the one-sided test was 0.025. The standard deviations of the two groups were 0.05 and 0.07, respectively. Considering a 10% loss to follow-up, the group sample size was 51 patients per group.
Statistical methods
Continuous data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. The independent-sample t-test and Fisher’s exact chi-square test in SPSS 22 were used to compare baseline information and clinical characteristics within groups, and to determine differences in BMD values between baseline and 12 months after treatment. Differences in bone turnover markers and other laboratory results were determined using a two-sided t-test.
Results
Clinical characteristics
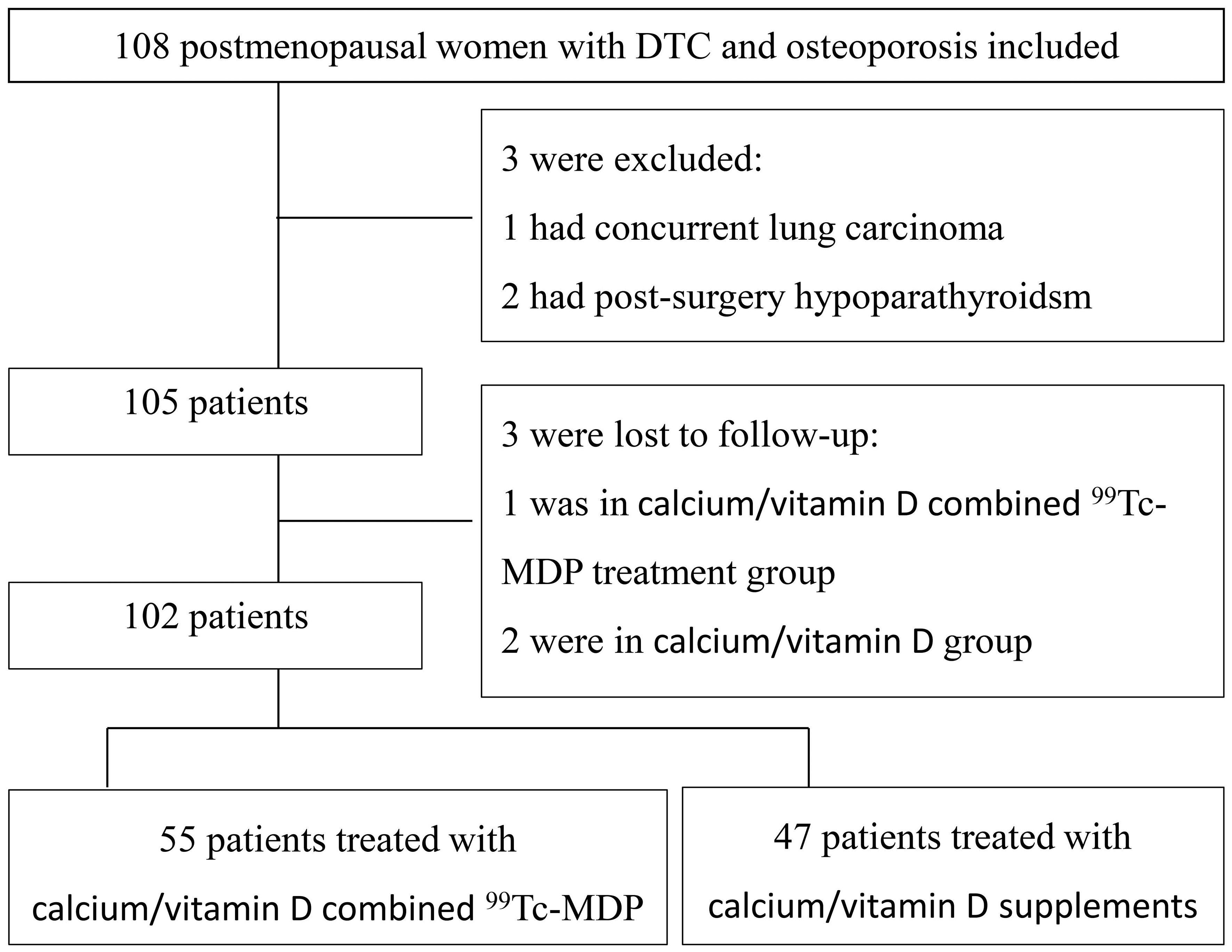
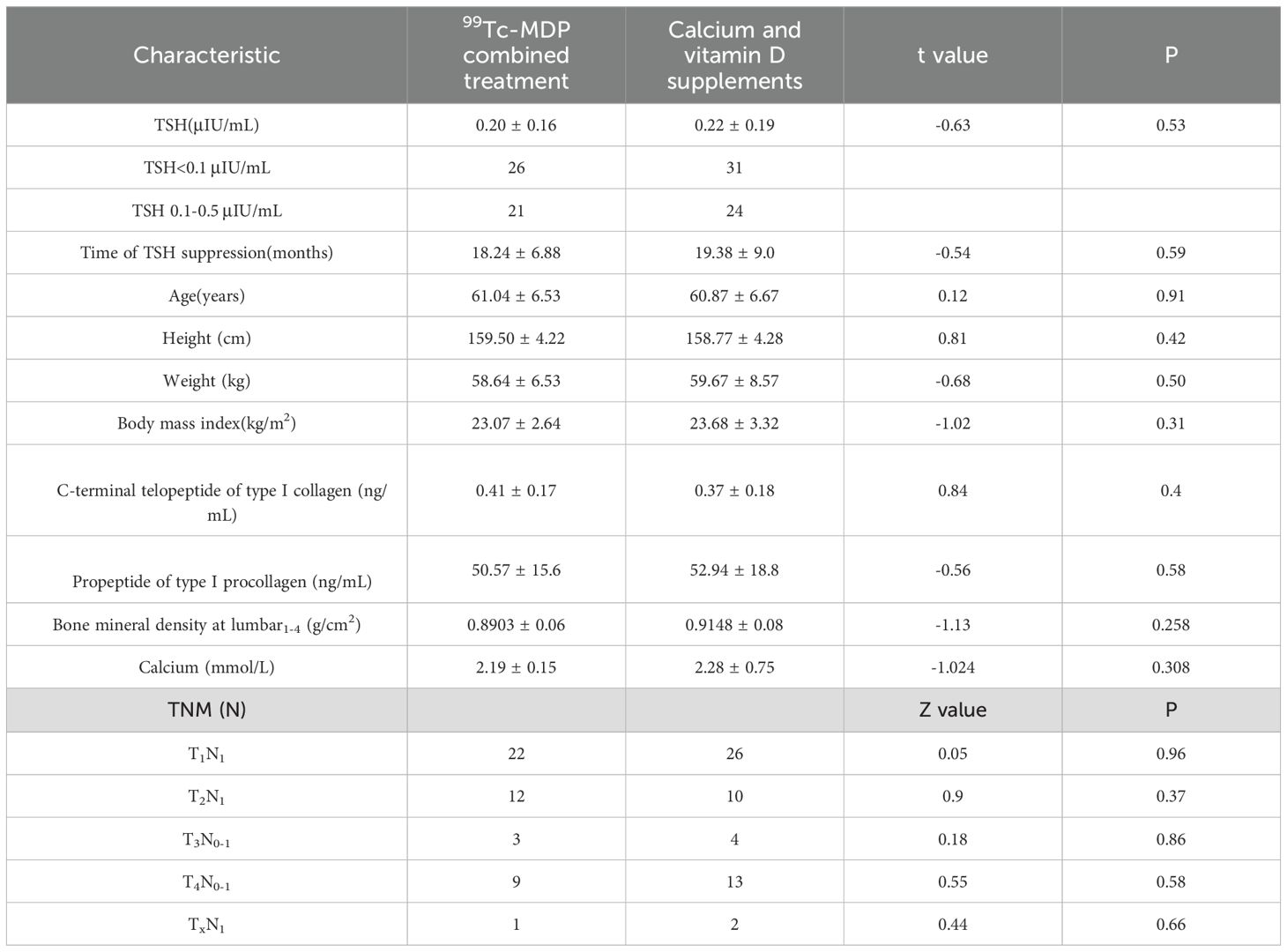
A total of 108 postmenopausal DTC patients with OP under TSH suppression therapy were enrolled. Three patients were excluded and three more were lost during follow-up. Out of the 102 included patients, 55 were in groupCa and 47 were in groupmdp (Figure 1). Age, weight, BMI, TSH values, duration of TSH suppression therapy, and BMD at baseline are listed in Table 1 and showed no significant differences (p > 0.05). In groupmdp, 26 and 21 patients had TSH<0.1 μIU/mL and TSH between 0.1-0.5 μIU/mL, respectively, while in groupCa, 31 and 24 patients had TSH < 0.1 μIU/mL and TSH between 0.1–0.5 μIU/mL.
Lumbar BMD
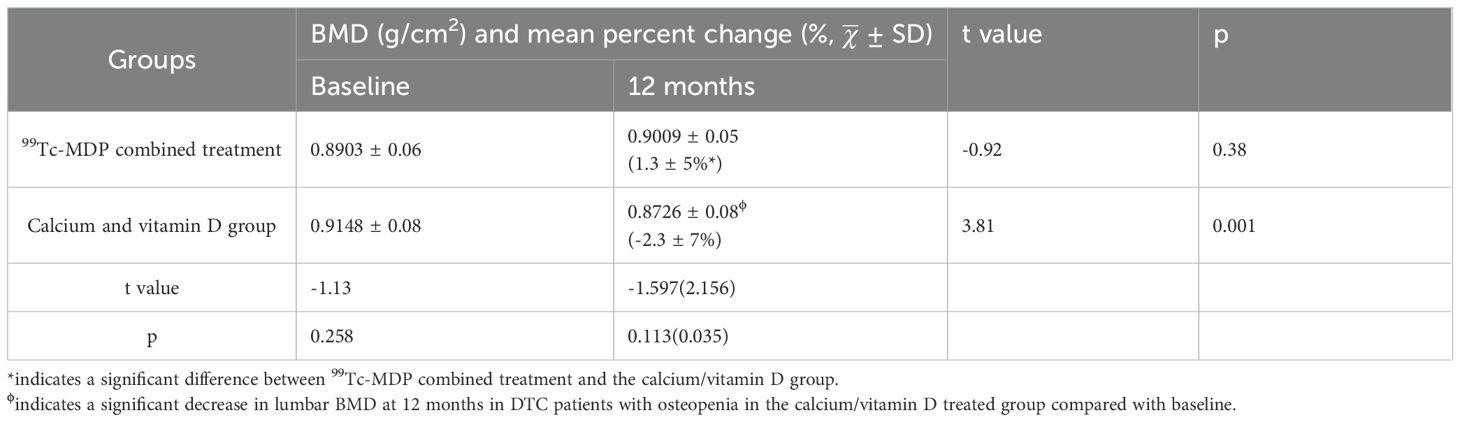
The combined 99Tc-MDP treatment showed a significant increase in the mean percentage change of lumbar BMD at month 12 compared with groupCa (t=2.156, p=0.035), see Table 2. Within-group comparisons showed no significant difference in lumbar BMD in groupmdp at month 12 compared with baseline (t=-0.92, p= 0.38). However, a significant decrease in BMD of the lumbar spine from 0.9148 ± 0.08 to 0.8726 ± 0.08 (t=3.81, p=0.001) at month 12 was observed in groupCa (Table 2).
99Tc-MDP treatment showed no significant difference in the subgroup analysis of lumbar BMD in patients with a TSH level <0.1μIU/mL and between 0.1-0.5μIU/mL, The baseline lumbar BMD(g/cm2) and the mean percent changes (%, ± SD) were 0.8943 ± 0.06 and 0.908 ± 0.07(t=0.54, p= 0.59), 0.0088 ± 0.06 and 0.1834 ± 0.05(t=0.45, p= 0.65), in patients with a suppressed TSH level <0.1μIU/mL and between 0.1-0.5μIU/mL, respectively (Table 3).
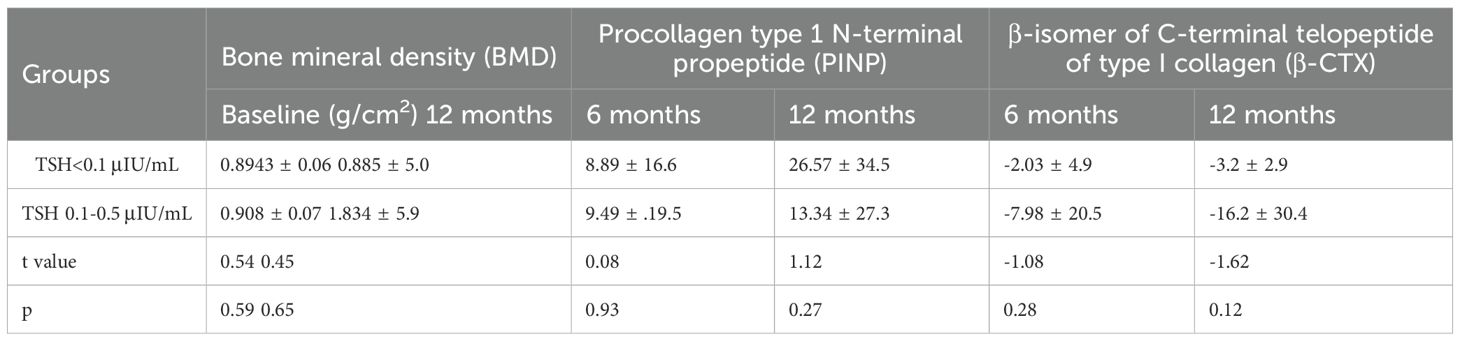
Table 3. Mean percent change (%, ± SD) of lumbar spine bone mineral density and bone metabolism markers in patients with different suppressed TSH levels treated with 99Tc-MDP.
Bone turnover markers
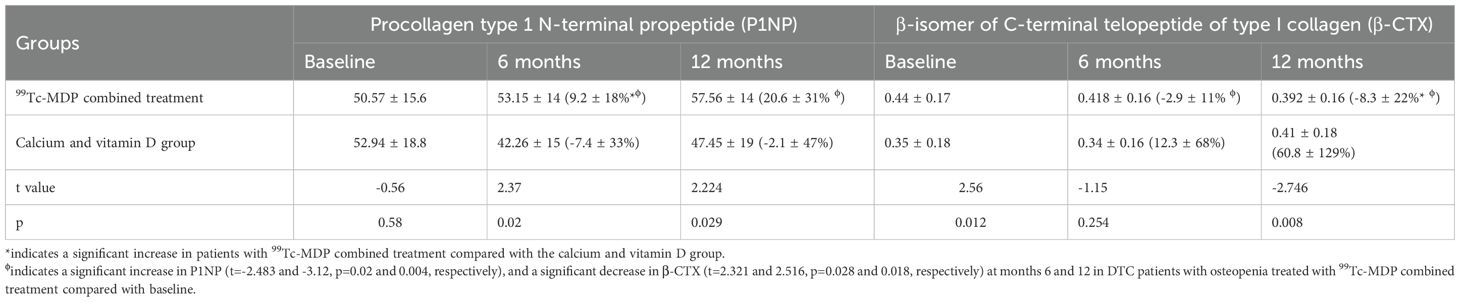
99Tc-MDP combined treatment significantly increased P1NP at month 6 (t=2.37, p = 0.02) and 12 (t=2.777, p = 0.007), and significantly decreased β-CTX at month 12 (t=-2.746, p = 0.008) compared with groupCa. Significant increases in P1NP (t=-2.483 and -3.12, p=0.02 and 0.004, respectively) and decreases in β-CTX (t=2.321 and 2.516, p=0.028 and 0.018, respectively) were found at months 6 and 12 in groupmdp compared with baseline (Figure 2, Table 4).
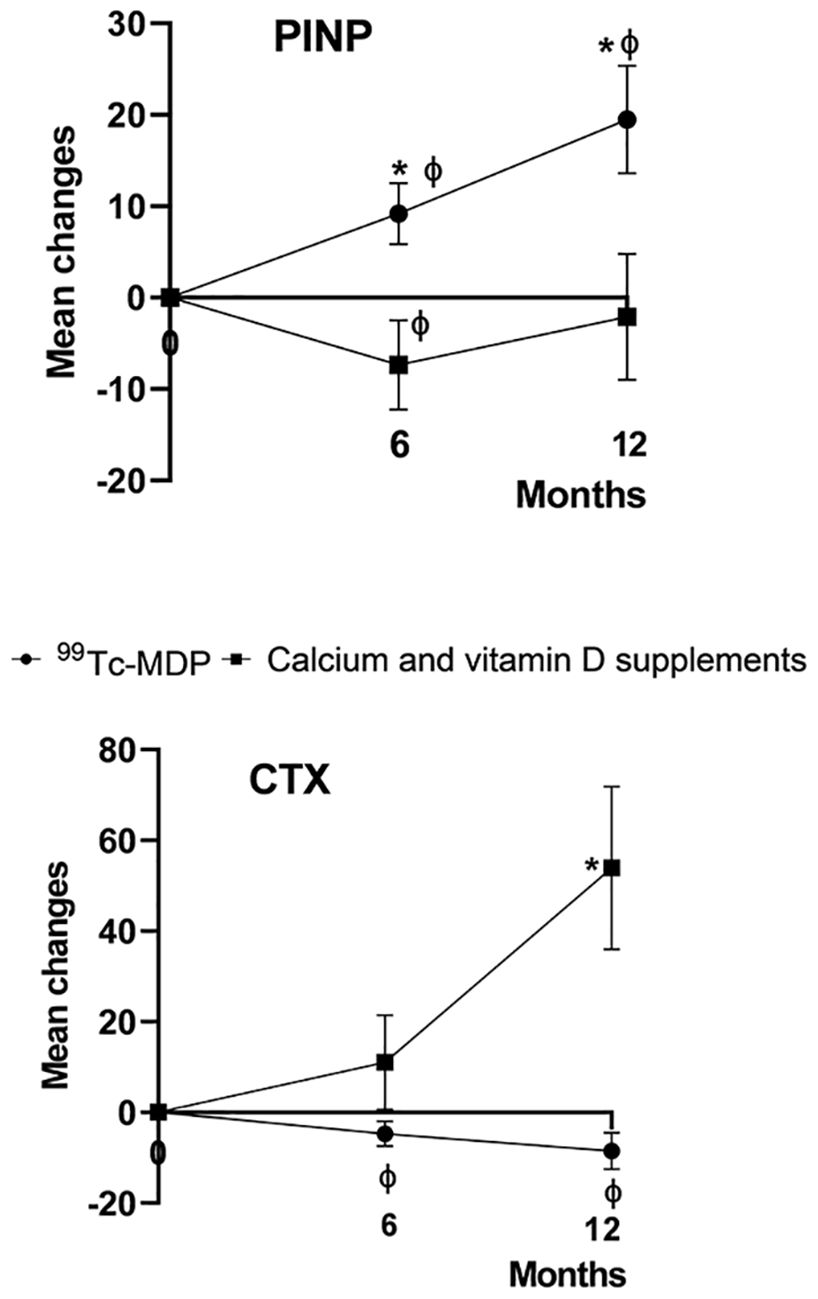
Figure 2. Percentage change from baseline in levels of bone turnover markers. The mean percentage change from baseline in the levels of serum β-isomer of C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX) and procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (P1NP) are shown at 6 and 12 months after the baseline visit. An asterisk (*) indicates p < 0.05 for comparisons between 99Tc-MDP combined treatment and calcium/vitamin D supplement groups. 99Tc-MDP combined treatment significantly increased P1NP at month 6 (t=2.37, p = 0.02) and month 12 (t =2.224, p = 0.029), and significantly decreased β-CTX at month 12 (t=-2.746, p = 0.008) compared with the calcium/vitamin D supplement group. The vertical lines represent the 95% confidence intervals at each time point. A ‘ϕ’ indicates p < 0.05 for within-group comparisons with baseline.
99Tc-MDP treatment showed no significant difference in the subgroup analysis of P1NP and β-CTX in patients with a TSH level <0.1μIU/mL and between 0.1-0.5μIU/mL. The mean percent changes (%, ± SD) were 0.0889 ± 0.26 and 0.0949 ± 0.19 (t=0.08, p=0.93), 0.2657 ± 0.34 and 0.1334 ± 0.27 (t=1.12, p= 0.27) at months 6 and 12, respectively (Table 3).
Safety
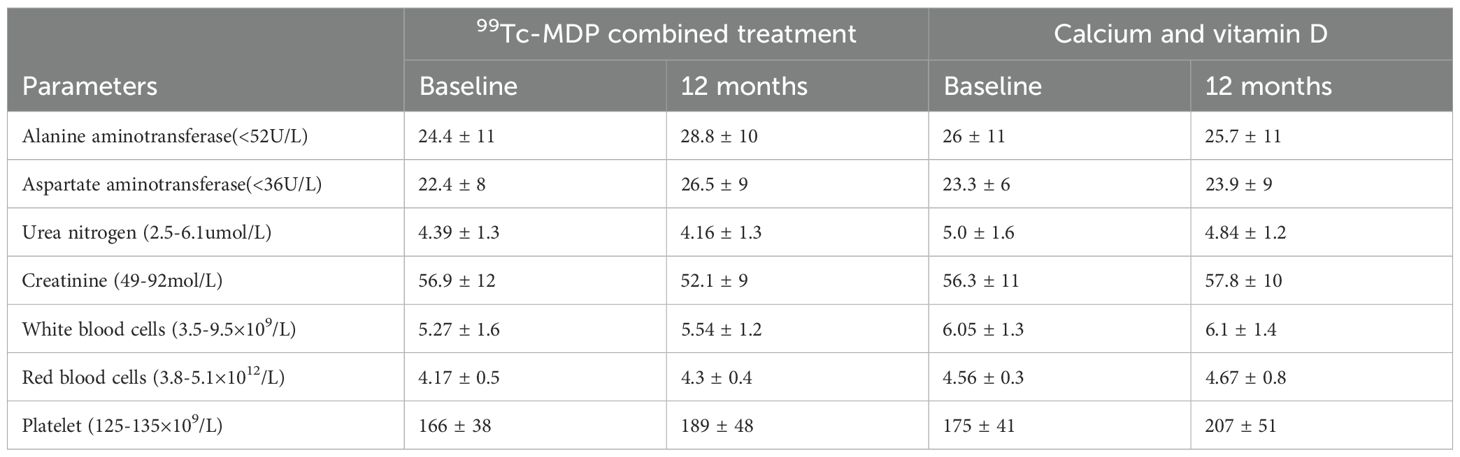
No severe adverse events were found in either group. When comparing blood counts and liver and renal function indices at baseline with those at the 12-month follow-up, no significant differences were found (p>0.05) in the groupmdp (Table 5).
Discussion
DTC has become one of the most common endocrine malignancies with a good prognosis. TSH suppression treatment is necessary as tumor cells express TSH receptors on the cell membrane and respond to TSH stimulation by increasing the expression of several proteins and the rate of cell growth (3, 4, 14). However, studies, including ours, have found that excessive intake of L-T4 results in a negative balance of bone formation and resorption, leading to bone loss (5). Therefore, skeletal health should be an important issue in the therapeutic decision-making of patients with DTC. The 2015 ATA guidelines recommend the use of calcium and vitamin D supplementation (1) to correct the negative calcium balance induced by mild thyroid hormone excess and possibly to improve the effectiveness of bone-active agents such as bisphosphonates (15). In addition, a recent study reported that calcium plus vitamin D had important clinical significance in adjusting bone metabolism and delaying the progression of osteoporosis in patients with hyperthyroidism (16). However, the effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on bone loss in DTC patients with osteopenia under TSH suppression therapy remained unclear. Our results indicated that calcium plus vitamin D supplements alone cannot effectively prevent further bone loss in postmenopausal women with DTC under TSH suppression treatment. The reason may be the difference between endogenous and exogenous hyperthyroidism.
99Tc-MDP is a novel bisphosphonate derivative without radioactivity and has been used for osteoarthritis, necrosis of the talus, ankylosing spondylitis, and rheumatoid arthritis in China for many years (17–20). We further studied the preventive effects of 99Tc-MDP on bone loss in postmenopausal women with DTC under TSH suppression therapy. The study found that 99Tc-MDP is effective in preventing BMD loss in patients with OP. The BMD maintenance effect of 99Tc-MDP demonstrated in the present clinical study is, as far as we know, the first to compare outcomes with calcium/vitamin D supplements in this patient population. The possible mechanisms accounting for the improvement in BMD with 99Tc-MDP may include elevation of the osteogenic capacity of mesenchymal stem cells and decreased adipogenic differentiation capacity (21), induction of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, and inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and activation by regulatory effects on the osteoprotegerin (OPG)/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa‐B ligand (RANKL)/receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK) system (22–24). However, for patients with certain bone remodeling disorders such as osteopathia striata with cranial sclerosis (25), 99Tc-MDP is not recommended because its osteogenesis promoting effect. Anti-osteopenia treatment may be recommended at the diagnosis of low BMD (T-score > –2.0) and for those at risk of fractures in patients requiring TSH suppression therapy.
Reduced serum TSH levels may themselves be an individual factor associated with decreased BMD and, consequently, with a greater risk of bone fracture (26). In this study, we subdivided DTC patients into groups with suppressed TSH<0.1 level and 0.1-0.5 μIU/mL. The subgroup analysis in the 99Tc-MDP treatment group showed no significant differences in the mean percentage change of lumbar BMD and bone metabolism biomarkers, which may be due to the limited number of patients and the short-term follow-up. Interestingly, a systematic review and meta-analysis reported significantly higher levels of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio among postmenopausal women with osteoporosis compared with postmenopausal women without osteoporosis (27). In our study, we included patients with DXA-confirmed osteopenia. Further research will be valuable for postmenopausal patients with DTC.
The potential safety issues should be considered when bisphosphonates are used (15) because nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates (N-BPs) can cause rare but serious side effects, such as atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw (28–31). Intravenous zoledronic acid has been shown to induce atrial fibrillation (32, 33), and this risk may be relatively increased in patients with subclinical hyperthyroidism (34). Animal experiments (21) and our clinical study showed that 99Tc-MDP treatment does not cause osteonecrosis of the jaw, and no other side effects were observed.
There were several limitations to our study, such as its non-randomized nature. The effects of 99Tc-MDP on OP should be observed with long-term follow-up. A systematic review reported low BMD at the total hip of postmenopausal women undergoing TSH-suppressive therapy, whereas the effects on BMD at the lumbar spine and femoral neck were variable (15). Another limitation of our study was the lack of data on the total hip or femoral neck.
In conclusion, 99Tc-MDP is safe and could maintain lumbar BMD in postmenopausal patients with DTC and osteopenia under TSH suppression therapy during a 1-year follow-up. Calcium/vitamin D supplementation alone could not effectively prevent bone loss in these patients. Additionally, bone health management for postmenopausal patients with DTC undergoing TSH suppression therapy is summarized in Figure 3.
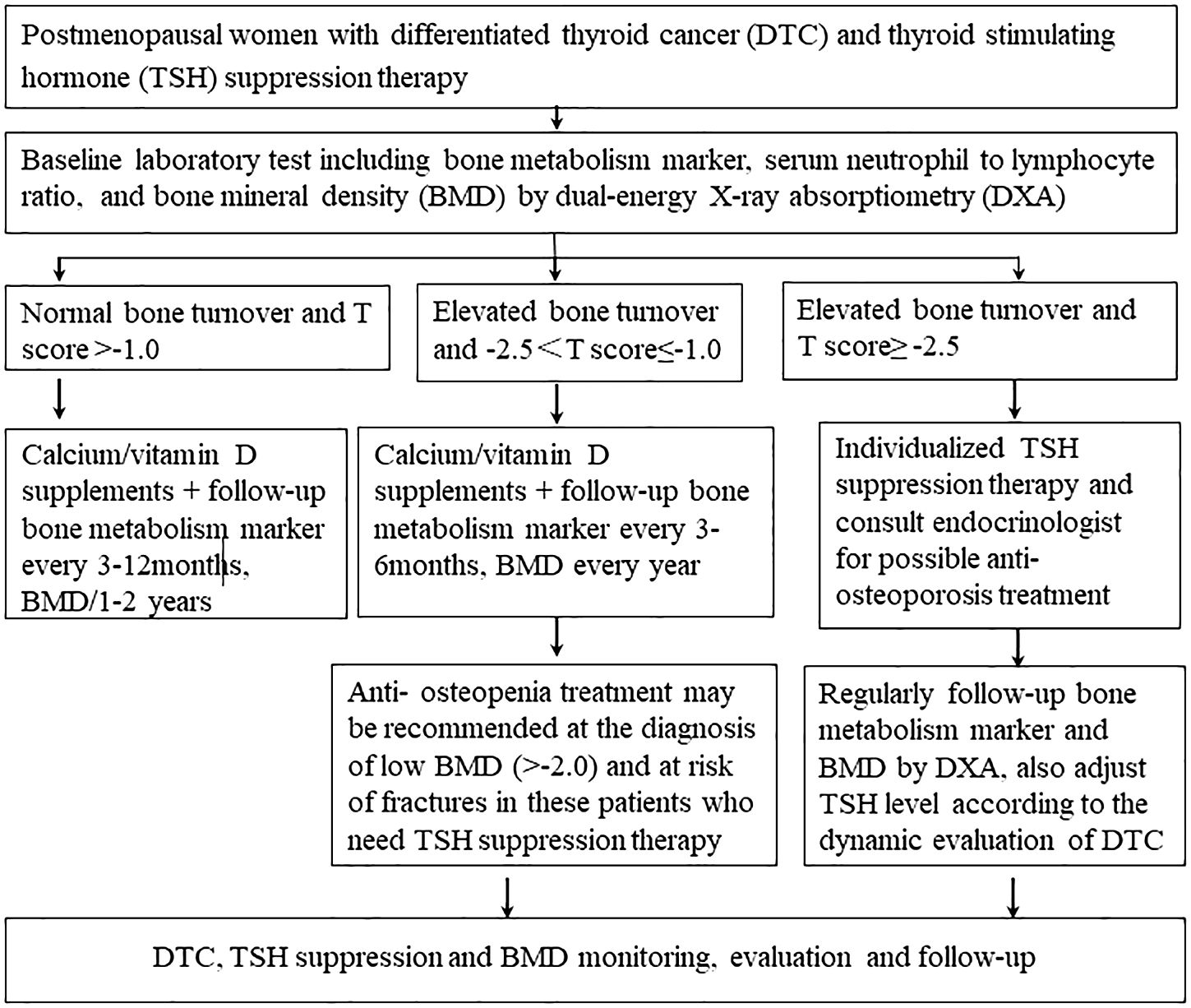
Figure 3. Bone health management for postmenopausal patients with differentiated thyroid cancer under thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression therapy.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Research Ethics in Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital (approval number SHSY-IEC-5.0/22K101/P01). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YZ: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. YW: Software, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. DS: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Project administration. CM: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fund (grant number 82171974), Ten People’s Hospital Clinical Study Fund (grant number YNCR2A007).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American thyroid association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. (2016) 26:1–133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020
2. Gao M. Diagnosis and treatment guideline for thyroid nodules and differentiated cancer. Chin J Endocrino Metab. (2024) 39:181–226. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20221023-00589
3. Biondi B and Cooper DS. Benefits of thyrotropin suppression versus the risks of adverse effects in differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. (2010) 20:135–46. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0311
4. Brabant G. Thyrotropin suppressive therapy in thyroid carcinoma: what are the targets? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2008) 93:1167–9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2228
5. Huo Y, Wang D, Wu S, Wang H, and Ma C. The impact of TSH supression treatment on bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Chin J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2017) 37:212–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-2848.2017.04.005
6. Diamond T, Nery L, and Hales I. A therapeutic dilemma: suppressive doses of thyroxine significantly reduce bone mineral measurements in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women with thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1991) 72:1184–8. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-6-1184
7. Heemstra KA, Hamdy NA, Romijn JA, and Smit JW. The effects of thyrotropin-suppressive therapy on bone metabolism in patients with well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. (2006) 16:583–91. doi: 10.1089/thy.2006.16.583
8. Karner I, Hrgović Z, Sijanović S, Buković D, Klobucar A, Usadel KH, et al. Bone mineral density changes and bone turnover in thyroid carcinoma patients treated with supraphysiologic doses of thyroxine. Eur J Med Res. (2005) 10:480–8.
9. Kim MK, Yun KJ, Kim MH, Lim DJ, Kwon HS, Song KH, et al. The effects of thyrotropin-suppressing therapy on bone metabolism in patients with well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Bone. (2015) 71:101–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2014.10.009
10. Kung AW, Lorentz T, and Tam SC. Thyroxine suppressive therapy decreases bone mineral density in post-menopausal women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (1993) 39:535–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1993.tb02405.x
11. Sugitani I and Fujimoto Y. Effect of postoperative thyrotropin suppressive therapy on bone mineral density in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: a prospective controlled study. Surgery. (2011) 150:1250–7. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.09.013
12. Fu Q, Feng P, Sun LY, Zuo XX, Zhao DB, He DY, et al. A double-blind, double-dummy, randomized controlled, multicenter trial of 99Tc-methylene diphosphonate in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Chin Med J. (2021) 134:1457–64. doi: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000001527
13. Xie J, Yuan X, Mao W, Cai H, Gao K, Lv Z, et al. (99)Tc-methylene diphosphonate treatment is safe and efficacious for osteoporosis in postmenopausal differentiated thyroid cancer patients undergoing TSH suppression: A three-center non-randomized clinical study. Cancer Manag Res. (2022) 14:995–1005. doi: 10.2147/cmar.S354471
14. McGriff NJ, Csako G, Gourgiotis L, Lori CG, Pucino F, and Sarlis NJ. Effects of thyroid hormone suppression therapy on adverse clinical outcomes in thyroid cancer. Ann Med. (2002) 34:554–64. doi: 10.1080/078538902321117760
15. Cellini M, Rotondi M, Tanda ML, Piantanida E, Chiovato L, Beck-Peccoz P, et al. Skeletal health in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J endocrinological Invest. (2020) 44:431–42. doi: 10.1007/s40618-020-01359-6
16. Liu H, Ma Q, Han X, and Huang W. Bone mineral density and its correlation with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in patients with hyperthyroidism. J Int Med Res. (2020) 48:300060520903666. doi: 10.1177/0300060520903666
17. Liu H, Guo H, Guo S, Wang J, Ye Y, and Ma C. Novel treatment of 99Tc-MDP improves clinical and radiographic results for patients with osteochondral lesions of the talus. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2019) 63:199–206. doi: 10.23736/s1824-4785.16.02872-7
18. Su D, Shen M, Gu B, Wang X, Wang D, Li X, et al. (99) Tc-methylene diphosphonate improves rheumatoid arthritis disease activity by increasing the frequency of peripheral γδ T cells and CD4(+) CD25(+) Foxp3(+) Tregs. Int J rheumatic diseases. (2016) 19:586–93. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.12292
19. Wu Q, Ni Y, Yang Q, and Sun H. (99)Tc-MDP treatment for the therapy of rheumatoid arthritis, choroidal neovascularisation and Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Biomed Rep. (2016) 4:400–2. doi: 10.3892/br.2016.609
20. Sun X, Chen M, and Yuan S. Clinical application of 99Tc-MDP in the treatment of osteonecrosis of femoral head. Labeled Immunoassays Clin Med. (2011) 18:320–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1703.2011.05.011
21. Zhao Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Akiyama K, Chen C, Atsuta I, et al. Technetium-99 conjugated with methylene diphosphonate ameliorates ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic phenotype without causing osteonecrosis in the jaw. Calcified Tissue Int. (2012) 91:400–8. doi: 10.1007/s00223-012-9649-7
22. Chen J, Lan Y, He Y, He C, Xu F, Zhang Y, et al. 99Tc-MDP-induced human osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and expression of osteoprotegerin. Mol Med Rep. (2017) 16:1801–9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6839
23. Gong W, Dou H, Liu X, Sun L, and Hou Y. Technetium-99 conjugated with methylene diphosphonate inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2012) 39:886–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2012.12006.x
24. Shi L, Ning Y, Xu L, Li J, and Zhang X. Technetium-99 conjugated with methylene diphosphonate ameliorates glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis. BioMed Res Int. (2018) 2018:7902760. doi: 10.1155/2018/7902760
25. Katsevman GA, Turner RC, Lucke-Wold BP, Sedney CL, and Bhatia S. Osteopathia striata with cranial sclerosis (OSCS): review of the literature and case report demonstrating challenges of spinal fusion after trauma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). (2016) 158:1115–20. doi: 10.1007/s00701-016-2794-4
26. Dziedzic M, Bonczar M, Ostrowski P, Stachera B, Plutecki D, Buziak-Bereza M, et al. Association between serum TSH concentration and bone mineral density: an umbrella review. Hormones (Athens). (2024) 23:547–65. doi: 10.1007/s42000-024-00555-w
27. Salimi M, Khanzadeh M, Nabipoorashrafi SA, Seyedi SA, Yaghoobpoor S, Brismée JM, et al. Association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with bone mineral density in post-menopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Womens Health. (2024) 24:169. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-03006-1
28. Watts NB and Diab DL. Long-term use of bisphosphonates in osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 95:1555–65. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1947
29. Favus MJ. Bisphosphonates for osteoporosis. New Engl J Med. (2010) 363:2027–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMct1004903
30. Bi Y, Gao Y, Ehirchiou D, Cao C, Kikuiri T, Le A, et al. Bisphosphonates cause osteonecrosis of the jaw-like disease in mice. Am J pathology. (2010) 177:280–90. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090592
31. Khosla S, Cauley JA, Compston J, Kiel DP, Rosen C, Saag KG, et al. Addressing the crisis in the treatment of osteoporosis: A path forward. J Bone mineral Res. (2017) 32:424–30. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3074
32. Black DM, Delmas PD, Eastell R, Reid IR, Boonen S, Cauley JA, et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. New Engl J Med. (2007) 356:1809–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa067312
33. Papapetrou PD. Bisphosphonate-associated adverse events. Hormones (Athens Greece). (2009) 8:96–110. doi: 10.14310/horm.2002.1226
Keywords: differentiated thyroid cancer, 99Tc-MDP, thyroid stimulating hormone suppression, bone mineral density, osteopenia
Citation: Zhang Y, Wang Y, Sun D and Ma C (2025) 99Tc-MDP maintains bone mineral density for postmenopausal differentiated thyroid cancer patients with osteopenia under thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1657617. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1657617
Received: 01 July 2025; Accepted: 10 September 2025;
Published: 02 October 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Antonelli, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Brandon Peter Lucke-Wold, University of Florida, United StatesMara Carsote, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Sun and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chao Ma, bWNfNzQxOUBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yuanfang Zhang1†
Yuanfang Zhang1† Yingqiu Wang
Yingqiu Wang Chao Ma
Chao Ma