- 1Department of Pharmacy, Nanjing Luhe People’s Hospital, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Nanjing Luhe People’s Hospital, Yangzhou University, Nanjing, China
- 3Public Experimental Platform, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China
- 4Department of General Surgery, Nanjing Luhe People’s Hospital, Yangzhou University, Nanjing, China
- 5Department of Central Laboratory, Nanjing Luhe People’s Hospital, Yangzhou University, Nanjing, China
- 6Department of Endocrinology, Nanjing Luhe People’s Hospital, Yangzhou University, Nanjing, China
Aim: This cross-sectional study investigated the relationship between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG: A surrogate marker for assessing insulin resistance.) index and hyperuricemia (HUA: Metabolic diseases caused by purine metabolism disorders.) risk in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: From January 2021 to December 2023, T2DM patients were enrolled from Luhe District People’s Hospital in Nanjing. Participants were stratified by TyG index quartiles. Logistic regression and restricted cubic spline (RCS) analyses assessed the TyG-HUA association.
Results: This study included 996 participants with type 2 diabetes, with a male predominance of 54.82%, a mean age of 60.39 years, and a median TyG index of 7.63. Compared to the lowest TyG quartile, the highest quartile exhibited a 4.23-fold (95% CI: 1.46 ~ 12.24, P value = 0.008) increased HUA risk. Restricted cubic spline analysis revealed a nonlinear relationship between the TyG index and HUA (nonlinear P value = 0.044). As the TyG level increased, the risk of HUA initially rose and then showed a downward trend (P for TyG = 0.008).
Conclusions: Elevated TyG index independently predicts HUA risk in T2DM patients. Early metabolic intervention may mitigate HUA-related cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Introduction
Hyperuricemia (HUA) is a prevalent metabolic disorder worldwide, recognized as the “fourth major metabolic abnormality” alongside hypertension, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia (1, 2). Its comorbidity with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is particularly pronounced, with a 19% HUA prevalence among T2DM patients, driven by shared pathophysiological mechanisms including insulin resistance (IR), obesity, and dyslipidemia (3–5).
The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, calculated as ln[fasting triglycerides (TG, mg/dL) × fasting blood glucose (FBG, mg/dL)/2], is a validated surrogate marker of IR and systemic metabolic dysregulation (6, 7). In T2DM populations, elevated TyG index not only predicts diabetic nephropathy risk but also correlates with aberrant uric acid metabolism (8, 9). Mechanistically (10, 11), TyG-reflected IR promotes hepatic purine metabolism (increasing uric acid production) and inhibits renal tubular uric acid excretion, leading to serum uric acid accumulation (12–14). Clinical evidence confirms a strong positive correlation between TyG index and serum uric acid levels (15, 16).For example: Luo Y et al. found a positive correlation between the TyG index and SUA levels in non-obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, TyG may outperform HOMA-IR in predicting HUA in this population (17). Among patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), every 0.1-unit increase in TyG corresponded to a 1.53-unit elevation in SUA levels. Further, the TyG index was identified as an independent risk factor for HUA development in NAFLD patients. As a readily available metric, TyG can help identify high-risk individuals for NAFLD progression, potentially reducing the incidence of HUA and related complications (18). In a study of a physical examination cohort in Xinjiang, China, TyG index demonstrated stronger correlation with HUA than nine obesity indices and showed superior performance over these indices in detecting HUA (19).
Thus, the TyG-HUA association in T2DM epitomizes the insulin resistance–lipotoxicity–end-organ damage cascade. This study aims to elucidate this relationship in a Chinese T2DM cohort to facilitate early risk stratification and integrated metabolic comorbidity management.
Materials and methods
Study participants
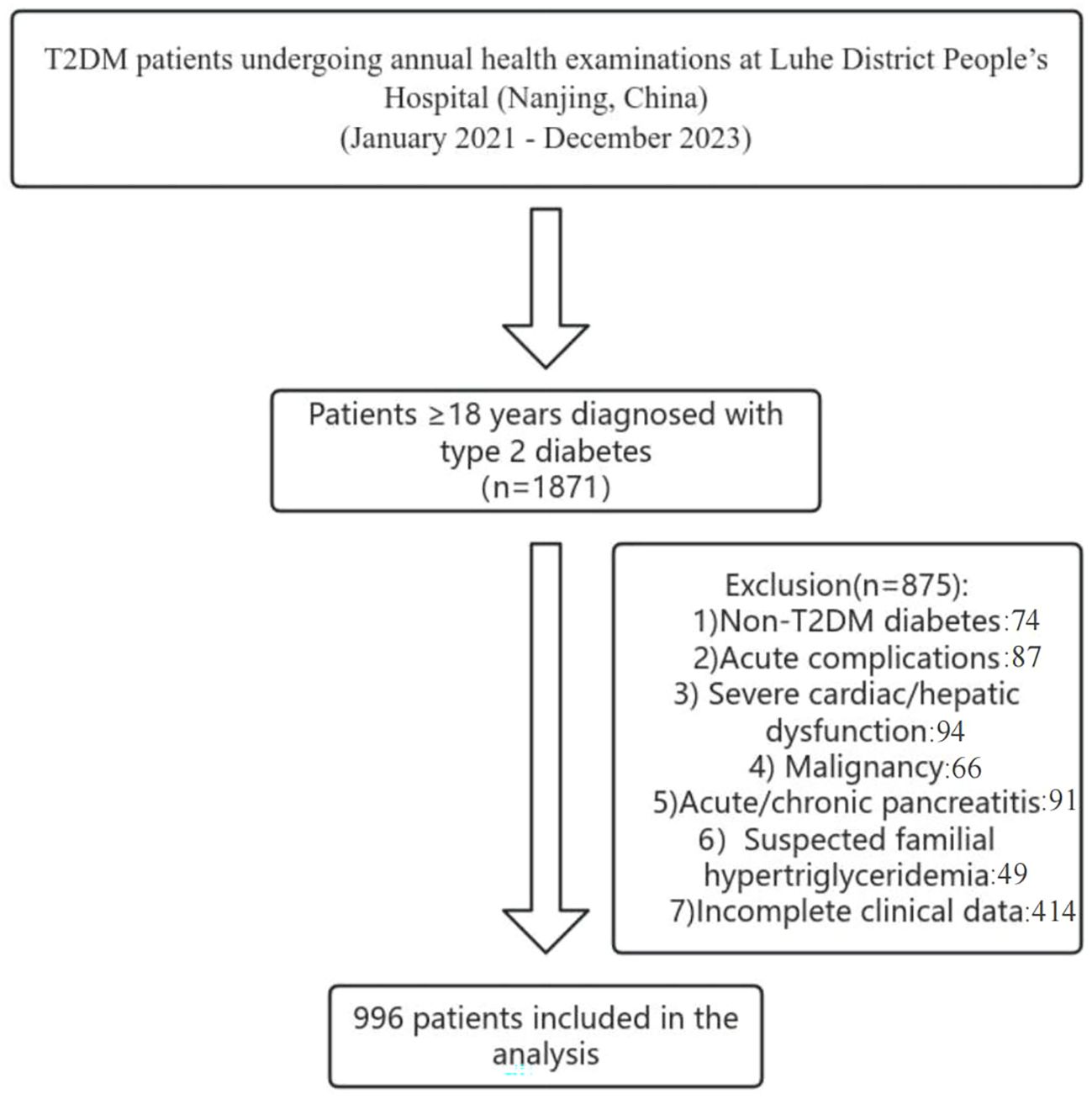
We conducted a cross-sectional study of T2DM patients undergoing annual health examinations at Liuhe District People’s Hospital (Nanjing, China) between January 2021 and December 2023. Inclusion criteria: Adults ≥18 years meeting WHO T2DM diagnostic criteria or previously diagnosed T2DM (20). Exclusion criteria: Non-T2DM diabetes; acute complications (e.g., ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma); severe cardiac/hepatic dysfunction(Severe cardiac dysfunction refers to a state of severely reduced cardiac pumping capacity, leading to inadequate systemic organ perfusion and a substantially increased risk of multi-organ failure;Severe hepatic dysfunction denotes a critical loss of the liver’s synthetic, metabolic, and detoxification functions, often accompanied by portal hypertension and high-risk stratification in end-stage liver disease scoring systems); malignancy; acute/chronic pancreatitis; suspected familial hypertriglyceridemia; incomplete clinical data. From 1,871 initially screened, 996 patients were included(As shown in the following Figure 1). All eligible patients were consecutively screened and enrolled.
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
The research protocol was developed in accordance with the relevant requirements of the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki. The research protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Liuhe District People’s Hospital, Jiangsu Province (Ethics Number: LHLL0029), and all participants signed the informed consent form. This process ensures compliance with ethical regulations (Supplementary Figure S1).
Data definitions
TyG Index (21): In[TG (mg/dL) × FBG (mg/dL)/2] (conversion: TG: 1 mmol/L = 88.57 mg/dL; FBG: 1 mmol/L = 18 mg/dL).
T2DM (22): (1) Classic symptoms + random glucose ≥11.1 mmol/L or FBG ≥7.0 mmol/L or 2-h OGTT ≥11.1 mmol/L; (2) Asymptomatic patients required confirmatory testing.
HUA (23): the diagnosis of hyperuricemia (HUA) strictly follows the recommended criteria in the “Multidisciplinary Expert Consensus on Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperuricemia-related Diseases (2023 Edition)” in China, which is: in a normal purine diet state, fasting blood uric acid levels > 420 μmol/L on two separate days. This standard is gender-neutral and uniformly applicable to all adult patients. Regarding the time interval of “not on the same day”, we follow clinical practice and define it as two independent tests at least one week apart.
25-hydroxyvitamin D standard: serum 25(OH)D levels (24): sufficient (≥30 ng/mL [75 nmol/L]), insufficient (20–29 ng/mL [50–74 nmol/L]), and deficient (<20 ng/mL [50 nmol/L]).Covariates:The covariates that may influence the association between the TyG index and kidney disease include age (Age, years), gender (Sex, male/female), hypertension (Hypertension, yes/no), body mass index (BMI, kg/m2), systolic blood pressure (SBP, mmHg), diastolic blood pressure (DBP, mmHg), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c,%), total cholesterol (TC, mmol/L), triglycerides (TG, mmol/L), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C, mmol/L), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C, mmol/L), lipoprotein a (Lp(a), mg/dL), alanine aminotransferase (ALT, IU/L), aspartate aminotransferase (AST, IU/L), fasting blood glucose (FBG, mmol/L), urea (UREA, mmol/L), serum creatinine (Scr, mmol/L), serum uric acid (SUA, μmol/L), glomerular filtration rate (eGFR,mL/min/1.73m2), urine albumin creatinine ratio (UACR, mg/g), blood calcium (Ca, mmol/L), blood phosphorus (P, mmol/L), parathyroid hormone (PTH, ng/L), and 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D, ng/mL).
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 and R 4.2.2. Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD or median (IQR); categorical variables as frequencies (%). Group differences were assessed via ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis, or χ² tests (25). Multivariable logistic regression estimated OR and 95% CI for TyG-HUA associations across three models:Model 1: Adjusted for age, sex;Model 2: Model 1 + BMI, SBP, DBP, HbA1c, lipids, liver enzymes, renal markers, minerals, 25(OH)D;Model 3: Model 2 + eGFR.Multicollinearity was excluded (VIF < 5). Restricted cubic splines (RCS) evaluated nonlinearity. Subgroup (sex, hypertension) and sensitivity (vitamin D deficiency) analyses were performed. Significance: two-tailed P < 0.05.Furthermore, subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were conducted among individuals lacking vitamin D to further confirm the aforementioned relationship. In summary, this section provides a detailed account of the statistical methods employed in the study, from the description and comparison of variables to the construction of regression models and the assessment of multicollinearity. It offers a comprehensive and systematic exploration of the relationship between the TyG index and HUA, providing robust statistical support for the research conclusions.
Results
Baseline characteristics
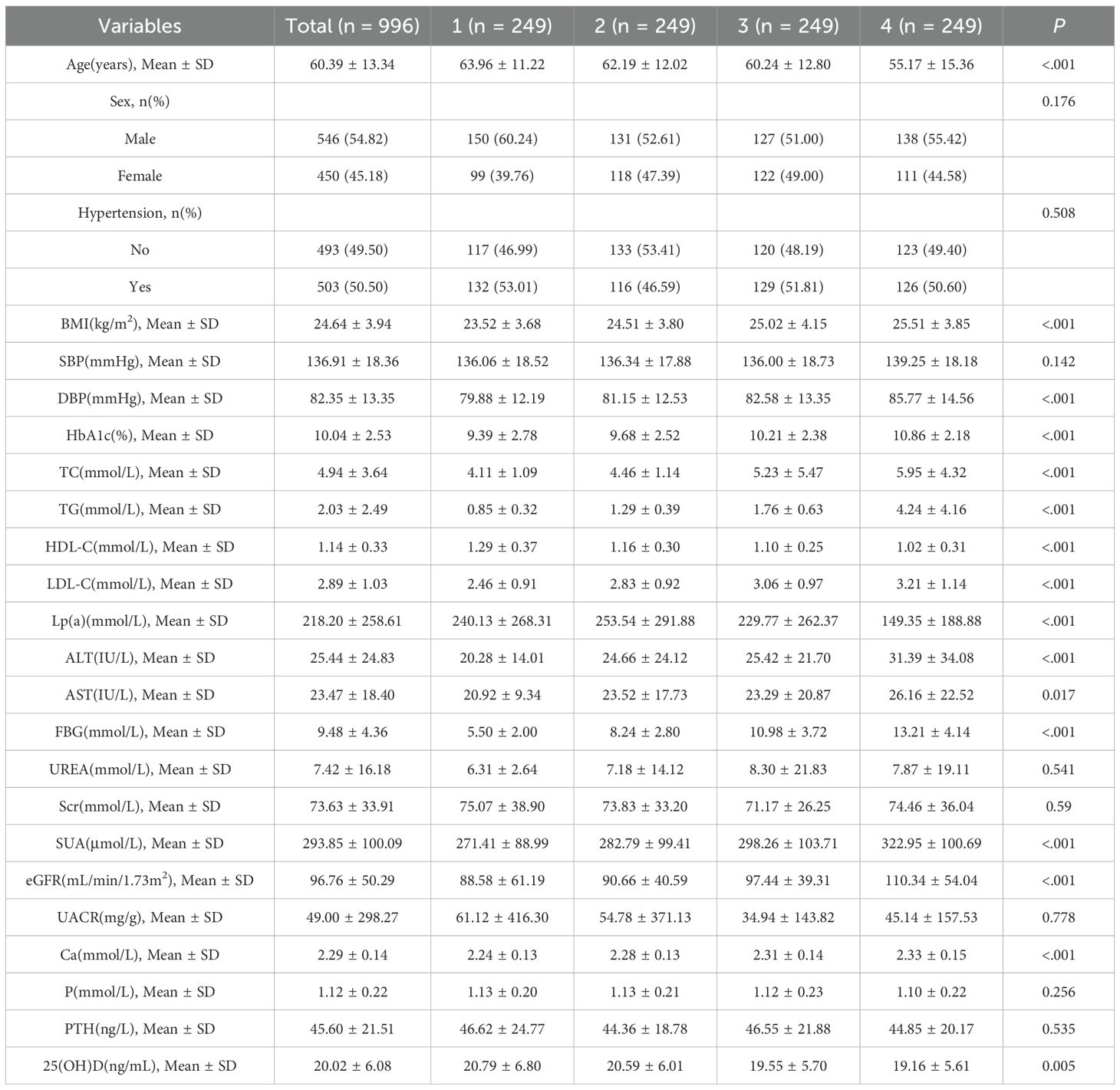
The cohort (*n* = 996) had a mean age of 60.39 ± 13.34 years; 54.82% were male. Higher TyG quartiles were associated with younger age, elevated BMI, blood pressure, HbA1c, LDL-C, liver enzymes, FBG, uric acid, eGFR, and calcium, but lower HDL-C and 25(OH)D (P < 0.05; Table 1).
Collinearity assessment and logistic regression results
Collinearity diagnostics revealed no significant multicollinearity among covariates, with all variance inflation factors (VIF) < 5 (Supplementary Table S1).
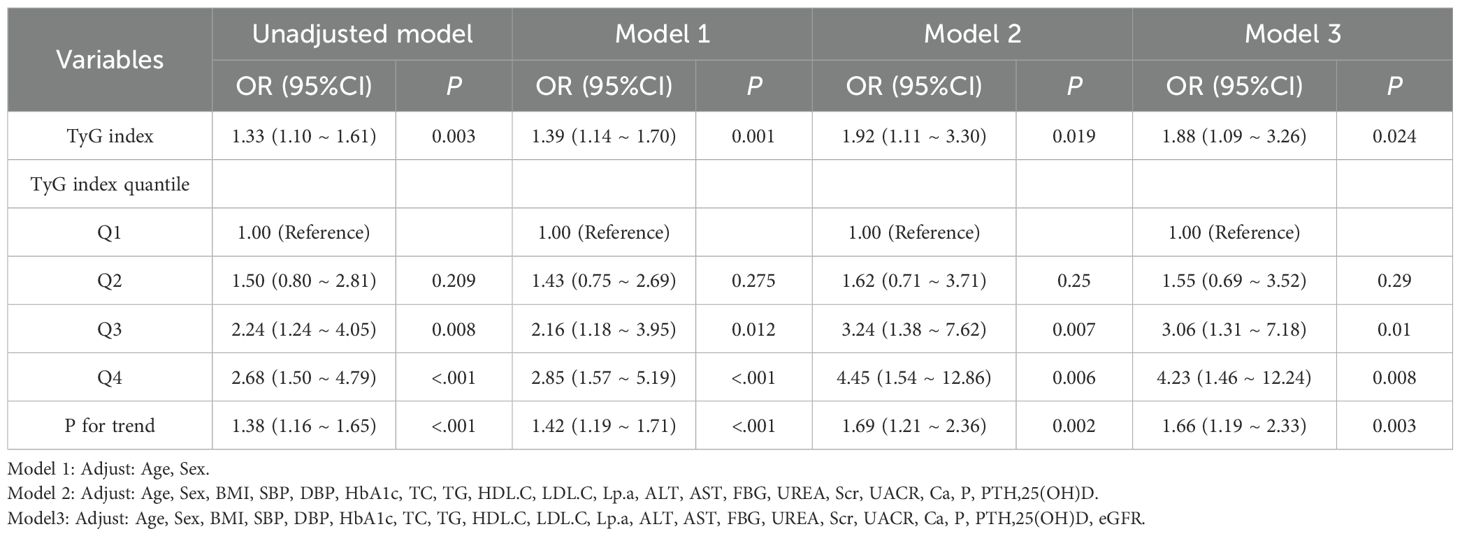
Logistic regression results are presented in Table 2. Logistic regression analyses(Crude model) demonstrated a consistent positive association between the TyG index and HUA: Each unit increase in TyG index was associated with a 33% elevated risk of HUA (OR = 1.33, 95% CI: (1.10 ~ 1.61)). Adjusted models:Model 1 (adjusted for age and sex): Higher TyG index significantly increased HUA risk (OR = 2.85, 95% CI: 1.57–5.19; P < 0.001).Model 2 (Model 1 + BMI, SBP, DBP, HbA1c, lipids, liver enzymes, renal markers, minerals, 25(OH)D): Participants in the highest TyG quartile had a 4.45-fold higher HUA risk versus the lowest quartile (OR = 4.45, 95% CI: 1.54–12.86; P = 0.006).Model 3 (Model 2 + eGFR): The association persisted (Q4 vs. Q1: OR = 4.23, 95% CI: 1.46–12.24; P = 0.008).Key conclusion: The TyG index remained an independent predictor of HUA risk after multivariable adjustment, with progressively increasing risk across ascending TyG quartiles.
Nonlinear Relationship Analysis: Restricted cubic splines (RCS) confirmed a nonlinear relationship between the TyG index and HUA risk (The nonlinear P value was 0.044; Figure 2). The number of knots used in the RCS analysis is 4, and the inflection point value is 7.6.The dose-response curve exhibited an inverted U-shape: HUA risk initially rose with increasing TyG levels but declined at higher values (The P value of TyG was 0.008).
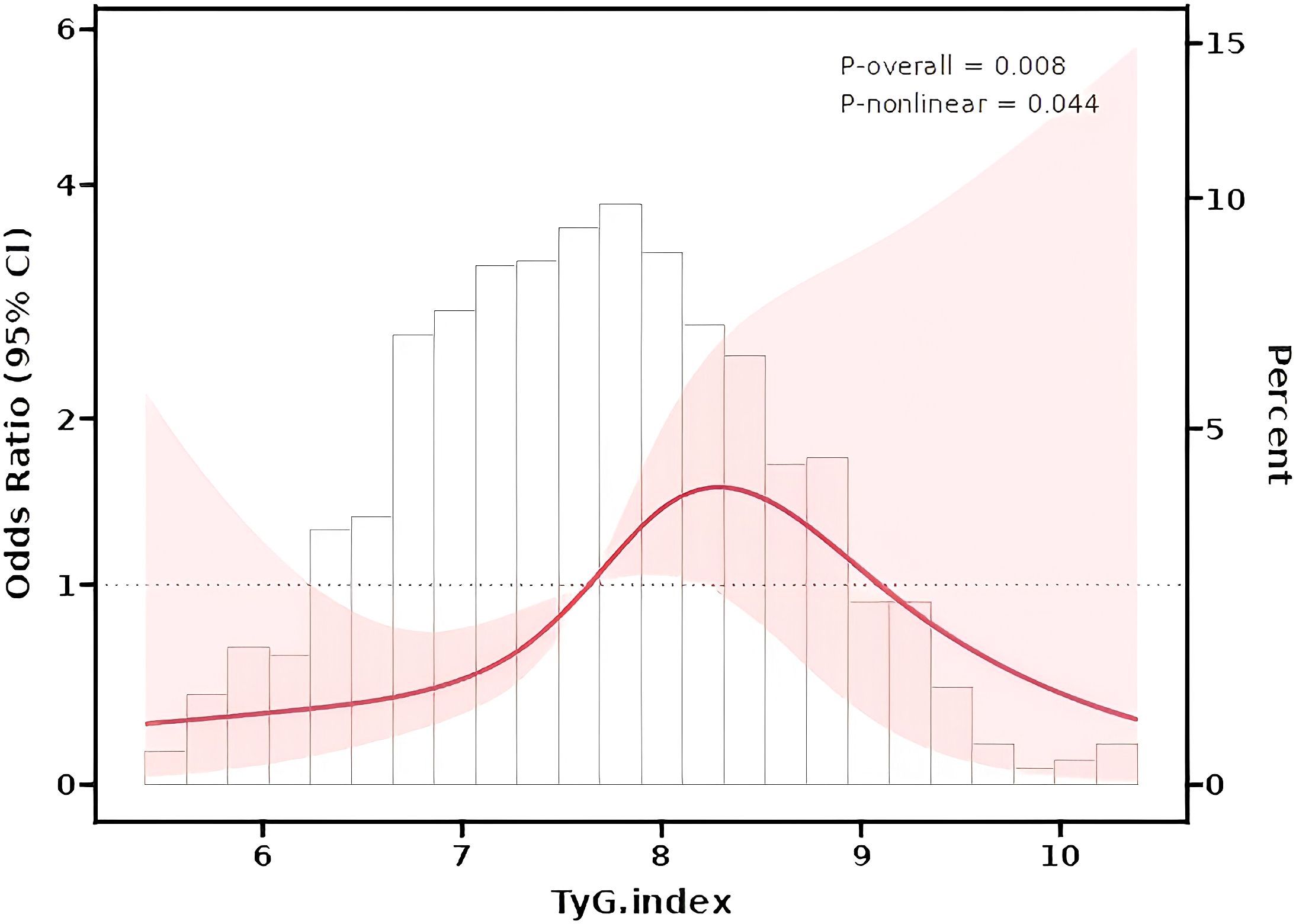
Figure 2. Restrcited cubic splines (RCS) for the shape of the association of TyG index and HUA risk.
Subgroup and sensitivity analyses
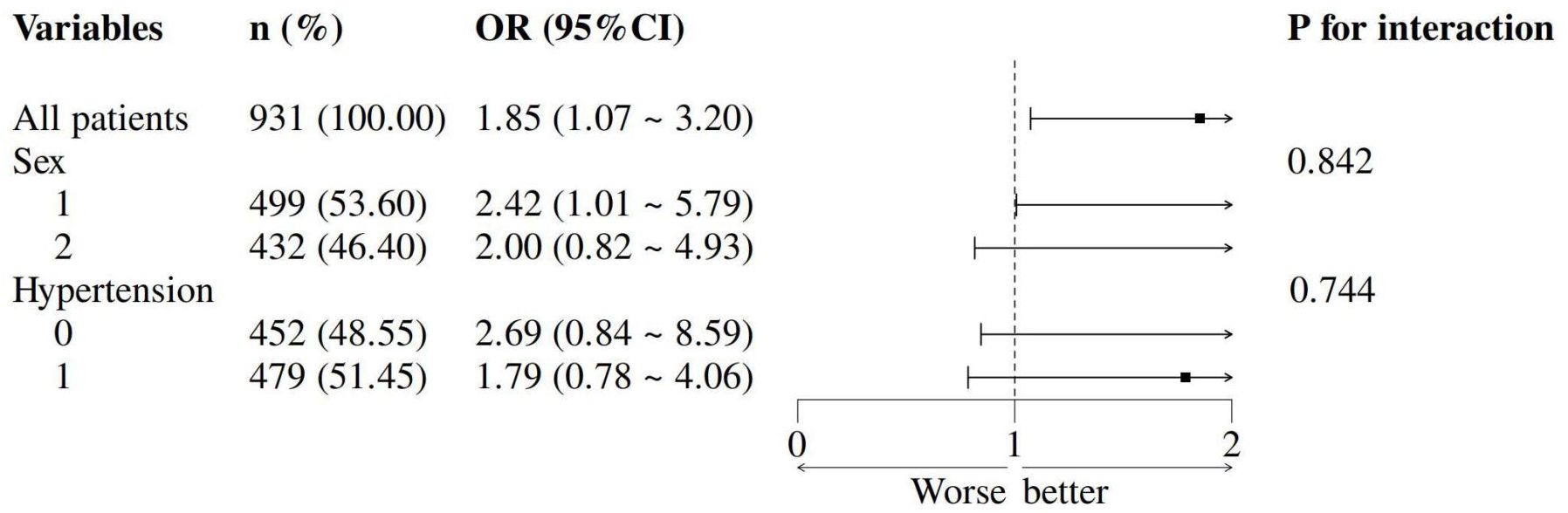
The TyG-HUA association remained consistent across sex and hypertension subgroups (all Pinteraction > 0.05; Figure 3). Sensitivity analysis in vitamin D-deficient patients yielded stable results (Supplementary Table S2).
Discussion
This study establishes an independent and nonlinear association between elevated TyG index and HUA risk in T2DM patients, persisting after rigorous adjustment for confounders and across analytical methods (quartile/continuous TyG).
Additionally, the relationship between the TyG index and the risk of HUA is nonlinear, where HUA first increases and then decreases as the TyG index rises. This phenomenon primarily stems from the transition of metabolic compensation mechanisms and stage-specific organ dysfunction. Early Stage: HUA Increases with Rising TyG Index. Increased uric acid production (26, 27): A higher TyG index indicates insulin resistance and glycolipid metabolic disorders, leading to increased free fatty acid release. This enhances hepatic triglyceride synthesis and purine metabolism, elevating uric acid production (10). Reduced uric acid excretion: Insulin resistance inhibits renal uric acid excretion, while hyperinsulinemia promotes renal reabsorption of sodium and uric acid, further raising serum uric acid levels (28–30). The TyG index often correlates with visceral obesity (increased waist circumference). Adipose tissue releases inflammatory cytokines and free fatty acids (31), which not only worsen insulin resistance but also enhance uric acid production by activating purine metabolic pathways. Hypertriglyceridemia causes accumulation of ketone bodies and lactate, competitively inhibiting uric acid excretion in renal tubules while promoting hepatic uric acid synthase activity (32). Late Stage: HUA decreases with sustained high TyG Index. Prolonged HUA induces urate crystal deposition in renal tubules, leading to chronic kidney disease (33). As glomerular filtration rate declines, total uric acid excretion decreases. Advanced metabolic syndrome patients often develop complications like diabetic nephropathy and cardiac insufficiency, with significantly reduced systemic metabolic function. This weakens hepatic uric acid synthesis capacity (34). Although the TyG index remains high, uric acid production decreases due to overall metabolic failure.
The experimental findings of this study align with the majority of relevant literature regarding the positive correlation between the TyG index and serum uric acid levels. However, our research incorporated a wider range of covariates in analyzing the TyG-uric acid relationship, thereby enhancing the accuracy of risk prediction models and significantly strengthening the scientific rigor and clinical relevance of the study. Notably, this investigation has limitations. The study sample was exclusively drawn from Nanjing, introducing geographical constraints. Nevertheless, given the relatively homogeneous nature of the study population, the conclusions should maintain validity.
The results of this cross-sectional study provide an important hypothesis for future prospective cohort studies and randomized controlled trials: whether reducing the TyG index through lifestyle changes can effectively prevent or delay the occurrence of hyperuricemia in T2DM patients. If this hypothesis is confirmed, the TyG index is expected to become a practical biomarker for HUA risk stratification and intervention effect evaluation.
Conclusions
Higher TyG index independently predicts HUA risk in type 2 diabetics, exhibiting a nonlinear trajectory. Integrating TyG assessment into T2DM management may optimize metabolic control and reduce HUA-related complications. Further studies should validate its clinical utility in diverse populations.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because this is a retrospective analysis of anonymized data. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XS: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZQ: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. XL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. XC: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. XYL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the participants for their contribution to the current study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1666563/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Ethical approval and consent to participate.
References
1. Li L, Zhang Y, and Zeng C. Update on the epidemiology, genetics, and therapeutic options of hyperuricemia. Am J Transl Res. (2020) 12:3167–81.
2. Zhou H, Yang J, Yuan X, Song X, Zhang X, Cao T, et al. Hyperuricemia research progress in model construction and traditional Chinese medicine interventions. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1294755. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1294755
3. Li C, Hsieh MC, and Chang SJ. Metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and hyperuricemia. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2013) 25:210–6. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835d951e
4. Yang H, Ying J, Zu T, Meng XM, and Jin J. Insights into renal damage in hyperuricemia: Focus on renal protection (Review). Mol Med Rep. (2025) 31:59. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13424
5. Choi HK, McCormick N, and Yokose C. Excess comorbidities in gout: the causal paradigm and pleiotropic approaches to care. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:97–111. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00725-9
6. Li C, Zhang Z, Luo X, Xiao Y, Tu T, Liu C, et al. The triglyceride-glucose index and its obesity-related derivatives as predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients: insights from NHANES data with machine learning analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2025) 24:47. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02591-1
7. Li HF, Miao X, and Li Y. The triglyceride glucose (TyG) index as a sensible marker for identifying insulin resistance and predicting diabetic kidney disease. Med Sci Monit. (2023) 29:e939482. doi: 10.12659/MSM.939482
8. Shi W, Xing L, Jing L, Tian Y, and Liu S. Usefulness of Triglyceride-glucose Index for estimating Hyperuricemia risk: Insights from a general Population. Postgrad Med. (2019) 131:348–56. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2019.1624581
9. Gou R, Dou D, Tian M, Chang X, Zhao Y, Meng X, et al. Association between triglyceride glucose index and hyperuricemia: a new evidence from China and the United States. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1403858. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1403858
10. Li Q, Shao X, Zhou S, Cui Z, Liu H, Wang T, et al. Triglyceride-glucose index is significantly associated with the risk of hyperuricemia in patients with diabetic kidney disease. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:19988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23478-1
11. Zhang R, Peng J, Wu Q, Zhu H, Zhang Z, Feng Y, et al. Association between the combination of the triglyceride-glucose index and obesity-related indices with hyperuricemia among children and adolescents in China. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:150. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02547-0
12. Zhang C, Li L, Zhang Y, and Zeng C. Recent advances in fructose intake and risk of hyperuricemia. BioMed Pharmacother. (2020) 131:110795. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110795
13. Li X, Wang L, Zhou H, and Xu H. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and chronic kidney disease: results from NHANES 1999-2020. Int Urol Nephrol. (2024) 56:3605–16. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04103-8
14. Dong J, Yang H, Zhang Y, and Hu Q. Triglyceride-glucose index is a predictive index of hyperuricemia events in elderly patients with hypertension: a cross-sectional study. Clin Exp Hypertens. (2022) 44:34–9. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2021.1984499
15. Lertsakulbunlue S, Sangkool T, Bhuriveth V, Mungthin M, Rangsin R, Kantiwong A, et al. Associations of triglyceride-glucose index with hyperuricemia among Royal Thai Army personnel. BMC Endocr Disord. (2024) 24:17. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01542-3
16. Wang J, He Q, Sun W, Li W, Yang Y, Cui W, et al. The association between the triglyceride glucose index and hyperuricemia: A dose-response meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2025) 17:1462. doi: 10.3390/nu17091462
17. Luo Y, Hao J, He X, et al. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and serum uric acid levels: a biochemical study on anthropometry in non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. DMSO. (2022) 15:3447–58. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S387961
18. Qi J, Ren X, Hou Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Tan E, et al. Triglyceride-glucose index is significantly associated with the risk of hyperuricemia in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2023) 16:1323–34. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S408075
19. Kahaer M, Zhang B, Chen W, Liang M, He Y, Chen M, et al. Triglyceride glucose index is more closely related to hyperuricemia than obesity indices in the medical checkup population in Xinjiang, China. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 2:861760. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.861760
20. Xu L, Ran J, Shao H, Chen M, Tang H, Li Y, et al. Incidence and risk factors of diagnosed young-adult-onset type 2 diabetes in the U.S.: the national health interview survey 2016-2022. Diabetes Care. (2025) 48:371–80. doi: 10.2337/dc24-1699
21. Liu D, Ren B, Tian Y, Chang Z, and Zou T. Association of the TyG index with prognosis in surgical intensive care patients: data from the MIMIC-IV. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:193. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02293-0
22. American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. (2021) 44:S15–33. doi: 10.2337/dc21-S002
23. Kjaergaard AD, Smith GD, and Stewart P. Mendelian randomization studies in endocrinology: raising the quality bar for submissions and publications in the journal of clinical endocrinology & Metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2023) 109:1–3. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad569
24. Wang R, Xu F, Xia X, Xiong A, Dai D, Ling Y, et al. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on primary depression: A meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2024) 344:653–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.10.021
25. Li M, Lian B, Xu X, Zhao P, Tang B, Hu C, et al. Collaborative relationships in translational medical research among Chinese clinicians: an internet-based cross-sectional survey. J Transl Med. (2021) 19:247. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02911-5
26. Yanai H, Adachi H, Hakoshima M, and Katsuyama H. Molecular biological and clinical understanding of the pathophysiology and treatments of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:9221. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179221
27. Washio KW, Kusunoki Y, Murase T, Nakamura T, Osugi K, Ohigashi M, et al. Xanthine oxidoreductase activity is correlated with insulin resistance and subclinical inflammation in young humans. Metabolism. (2017) 70:51–6. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.01.031
28. Ponticelli C, Podestà MA, and Moroni G. Hyperuricemia as a trigger of immune response in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2020) 98:1149–59. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.056
29. Kang DH, Nakagawa T, Feng L, Watanabe S, Han L, Mazzali M, et al. A role for uric acid in the progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2002) 13:2888–97. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000034910.58454.fd
30. Vidal-Ostos F, Ramos-Lopez O, Blaak EE, Astrup A, and Martinez JA. The triglyceride-glucose index as an adiposity marker and a predictor of fat loss induced by a low-calorie diet. Eur J Clin Invest. (2022) 52:e13674. doi: 10.1111/eci.13674
31. Yu P, Yuan H, Li X, and Chen H. Impact of cortisol on liver fat and metabolic health in adrenal incidentalomas and Cushing’s syndrome. Endocrine. (2025) 87:334–43. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-04043-4
32. Mei Y, Dong B, Geng Z, and Xu L. Excess uric acid induces gouty nephropathy through crystal formation: A review of recent insights. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:911968. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.911968
33. Cui D, Liu S, Tang M, Lu Y, Zhao M, Mao R, et al. Phloretin ameliorates hyperuricemia-induced chronic renal dysfunction through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and uric acid reabsorption. Phytomedicine. (2020) 66:153111. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153111
Keywords: TyG index, hyperuricemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, statistical analysis, RCS
Citation: Sun X, Li X, Qian Z, Chen X, Zhang J, Zhao C and Liu X (2025) Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and hyperuricemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1666563. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1666563
Received: 15 July 2025; Accepted: 25 September 2025;
Published: 17 October 2025.
Edited by:
Khalid Siddiqui, Kuwait University, KuwaitReviewed by:
Yue-Ming Gao, Peking University Third Hospital, ChinaGuangda He, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, China
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Li, Qian, Chen, Zhang, Zhao and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xu Sun, c3VueHUxMjdAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Xu Sun
Xu Sun Xin Li1,2†
Xin Li1,2†