- 1Department of Orthodontics, Beijing Stomatological Hospital and School of Stomatology,Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Endocrinology, First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 3Department of Endocrinology, Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 4Clinical Research Center for Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Shijiazhuang, China
Objective: To evaluate the effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on systemic and local levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and their relationship with glycolipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and periodontitis.
Methods: In this prospective cohort study, 234 patients with T2DM and periodontitis underwent standardized non-surgical periodontal therapy, including scaling and root planing, supplemented with systemic antibiotics. Clinical parameters (gingival bleeding index, periodontitis staging and grading), serum levels of TNF-α, HbA1c, leptin, adiponectin, resistin, free fatty acids (FFA), and levels of TNF-α, leptin, adiponectin, and resistin in gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) were assessed at baseline, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks post-treatment. Correlations were analyzed using Spearman’s rank correlation with false discovery rate correction.
Results: Periodontal therapy resulted in significant improvements in all clinical periodontal parameters (P<0.01). Systemic and local GCF levels of TNF-α, leptin, resistin, and FFA demonstrated significant and progressive reductions, while adiponectin levels increased significantly at 4 and 8 weeks (P<0.01). HbA1c and FBG levels were also significantly improved by week 8 (P<0.01). TNF-α dynamics were strongly correlated with adipokine levels and clinical indices, with the most robust correlations observed within the GCF microenvironment.
Conclusion: Systematic periodontal therapy effectively reduces local and systemic inflammation, improves glycemic control, and ameliorates glycolipid metabolic disorders in patients with T2DM and periodontitis. The strong interrelationships observed, particularly within the GCF, underscore the potential role of TNF-α as a key mediator in the mouth-systemic metabolic interplay.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis are both highly prevalent chronic diseases with a strong bidirectional relationship (1). The long-term hyperglycemic state in diabetic patients reduces their resistance to infection and ability to heal, making them prone to various complications—with periodontitis being one of the most common oral manifestations (2). Research indicates that periodontitis occurs more frequently in diabetic patients than in non-diabetic populations, with its severity directly correlating to glycemic control levels (3). As a chronic infectious condition, periodontitis damages periodontal tissues (gingiva, periodontal ligament, dentin and alveolar bone). Its pathogenic bacteria and inflammatory mediators can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream, elevating the risk of diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease (4–6). Furthermore, periodontitis impacts glycemic control in diabetic patients and may increase their risk of other complications (7). Understanding the mechanisms of interaction between diabetes and periodontitis is therefore crucial for early intervention and comprehensive patient management.
In recent years, periodontitis has been considered a localized inflammatory disease of the oral periodontal tissues (8). However, growing research shows that diabetes and periodontitis share a common pathogenic mechanism—both involve pro-inflammatory mediators in the inflammatory response (9, 10). Periodontitis has strong associations with several systemic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, blood disorders, chronic liver disease, osteoporosis, and autoimmune diseases (11). It has also emerged as the sixth most common complication of diabetes mellitus (12). The oral microbiome plays a crucial role in how both periodontitis and diabetes mellitus develop and progress by modulating the innate and adaptive immune systems (13, 14). Additionally, the buildup of cytokines, chemokines, prostaglandins, and late glycosylation end products is central to the disease’s pathogenesis and progression (15, 16). Treatment of periodontitis has shown notable benefits—it significantly improves glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in diabetes patients with poor glycemic control (17). These findings indicate that the interaction between periodontitis and diabetes mellitus extends beyond oral health, significantly affecting systemic metabolic status. This highlights the critical role of oral health in managing chronic diseases.
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), a major inflammatory factor, plays a dual role in both the inflammatory response of periodontitis and glycolipid metabolism (18). Studies have shown that TNF-α induces insulin resistance and disrupts lipid metabolism, leading to glucose and lipid abnormalities (19). However, TNF-α’s mechanism of action in patients with diabetes mellitus and periodontitis remains unclear, particularly regarding its relationship with glycolipid metabolism indices before and after periodontal treatment. Prolonged TNF-α expression may represent a pathway through which bacteria cause significant inflammatory damage, a process sometimes enhanced by immunodeficiency from lymphocyte subset mobilization (20). Hyperglycemia can worsen periodontal disease in diabetic patients by affecting TNF-α levels (21). The systemic nature of this inflammatory response is evidenced by elevated serum TNF-α levels in patients with acute apical abscesses (22). Additionally, adipokines—including lipocalin and resistin—secreted by adipocytes have emerged as prognostic markers of oral disease (23). In this study, we hypothesized that periodontal treatment could significantly reduce TNF-α levels and thereby improve glycolipid metabolism. By analyzing the correlation between TNF-α and glycolipid metabolism indicators, this study aims to provide a scientific basis for clinical treatment and further clarify the interaction between diabetes and periodontitis.
Information and methods
Case selection
This cross-sectional cohort study aimed to examine the correlation between TNF-α and glycolipid metabolic indices in patients aged 18–75 years with diabetes mellitus complicated by periodontitis. Data of 234 patients with diabetes mellitus and periodontitis were collected from March 2022 to April 2024 in our hospital. Patients underwent basic therapies, including scaling, root planing, and conventional medication. The study followed the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines and was approved by our hospital’s medical ethics committee.
Inclusion criteria: (1) Diagnosed with type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 2022 criteria (24). Patients were required to have a documented disease duration of ≥1 year and stable glycemic control, defined as no change in hypoglycemic medication regimen for at least 3 months prior to enrollment. Based on baseline HbA1c levels, diabetic control was categorized as: inadequate control (HbA1c 7.5%–9.0%) and moderate control (HbA1c <7.5%) (25). The majority of the cohort fell into the inadequate control category to investigate the metabolic effects of periodontal therapy in this challenging population. (2) ≥15 natural teeth present (excluding third molars and retained roots). (3) & (4) A diagnosis of periodontitis was established according to the 2018 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions (26). Periodontitis Staging: All enrolled patients were classified as either Stage III (severe periodontitis with potential for tooth loss due to periodontitis) or Stage IV (advanced periodontitis with extensive tooth loss and complex rehabilitation needs), based on interdental CAL (≥5 mm at the maximum site), radiographic bone loss extending to the mid-third of the root or beyond, and probing depth (PD) ≥6 mm at the maximum site. Periodontitis Grading: The grade of periodontitis was determined primarily based on the evidence of progression, calculated as the percentage of bone loss divided by the patient’s age (BL/A) (26). Since all subjects were diagnosed with diabetes mellitus—a well-established risk factor for periodontitis progression—the grade was directly modified to Grade B (moderate progression rate) or Grade C (rapid progression rate), as per the classification guidelines. (5) Age 18–75 years; (6) complete clinical data.
Exclusion criteria were rigorously applied to minimize confounding variables and ensure the internal validity of the study. These criteria were as follows: (1) Receipt of any periodontal therapy, including scaling and root planing, surgical procedures, or antibiotic treatment specifically for periodontal conditions, within the 6 months preceding the study baseline (27); (2) Chronic use (defined as >3 months) of medications known to affect periodontal tissues, such as phenytoin, calcium channel blockers, or cyclosporine, which can induce gingival enlargement (28); (3) Use of immunosuppressants or systemic corticosteroids within the 3 months prior to enrollment; (4) Presence of severe diabetic complications, including advanced retinopathy (confirmed by fundoscopy or OCT), nephropathy (defined as an eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m² or albuminuria >30 mg/g creatinine), or established neuropathy (Toronto Clinical Scoring System score ≥5), as these conditions can independently modulate systemic inflammation (29); (5) Concurrent active infections (e.g., pneumonia, urinary tract infection) or any malignancy; (6) Diagnosis of other systemic inflammatory or autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn’s disease; (7) Poorly controlled hypertension (resting blood pressure ≥160/100 mmHg) or hyperlipidemia (LDL cholesterol ≥190 mg/dL) (29); (8) Significant smoking history, defined as ≥10 pack-years or current smoking status confirmed by a positive cotinine test, as smoking is a primary risk factor for periodontal disease progression (26); (9) Unstable glycemic control that necessitated frequent adjustments to medication.
The sample size was calculated using the standard formula for cross-sectional studies (30). As in Equation 1:
Where n is the sample size, take α=0.05, check the Z-value table to get Z1-α/2 = 1.96, δ is the allowable error, control the allowable error at 6%, p denotes the prevalence of diabetes mellitus with periodontitis, according to the reference, the prevalence of diabetes mellitus with periodontitis is 73.14%, so the minimum total sample content is 218, and the sample size of the present study is 234 in accordance with the requirements.
Intervening method
The periodontal treatment cycle lasted 4 weeks and included full-mouth cleaning, subgingival scaling, root planing, occlusal adjustment, and extraction of non-retainable affected teeth. During treatment, patients received oral tetracycline (1 g/d) for 2 weeks. The systematic basic periodontal treatment was delivered in 4 sessions at 1-week intervals, comprising supragingival scaling, subgingival scaling, and root planing. Patients received instruction in oral hygiene practices, including proper brushing techniques, flossing, and interproximal brushing. Throughout the study, patients maintained their usual diabetes medications. Along with dietary control and exercise, patients continued their prescribed medications: metformin (25 mg after meals, thrice daily or 50 mg, twice daily), glibenclamide (2.5 mg before meals, thrice daily), or thirst-quenching pills (10 capsules before meals, thrice daily), based on their individual conditions.
Data collection
Tests for serological indices
Blood samples were collected at baseline (before treatment) and at 4 and 8 weeks post-treatment to assess systemic changes. All procedures were standardized to minimize pre-analytical variability, which is critical for the reliability of biomarker measurements (31). (1) Serum Sampling and Processing: A 2 mL sample of peripheral venous blood was drawn into an Eppendorf tube. The sample was allowed to clot at room temperature for 30 minutes before being centrifuged at 1,500 x g for 15 minutes at 4°C. The resulting serum was aliquoted and stored at -20°C until analysis. (2) Serum Metabolic and Adipokine Assays: A separate 10 mL sample of fasting venous blood was collected for metabolic panels. Fasting blood glucose (FBG) was measured using the glucose oxidase method, and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) was measured via immunosuppressive turbidimetry (Roche Diagnostics). Serum concentrations of leptin were determined by an immunoscattering turbidimetric assay (Shanghai Debo Biotechnology Co.). Adiponectin and resistin levels were quantified using commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits (Shenzhen Jingmei Biological Co., Ltd. and Shenzhen Xinbosheng Biotechnology Co., respectively). All assays were performed according to the manufacturers’ detailed instructions. (3) Serum Free Fatty Acids (FFA): FFA levels were measured using a photometric colorimetric method on a fully automated spectrophotometer (TAS-990, Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co., Ltd.).
Gingival crevicular fluid sampling and analysis
To assess the local periodontal inflammatory and metabolic milieu, gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) was collected at baseline, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks post-treatment, coinciding with the serum sampling time points. The sampling protocol was adapted from established methods (32). Briefly, GCF was obtained from the four sites with the deepest probing depths (one site per quadrant) using standardized periopaper strips (OraFlow Inc., USA). Sites were isolated with cotton rolls, supragingival plaque was carefully removed, and the area was gently air-dried. Paper strips were inserted into the gingival sulcus until mild resistance was felt and left in place for 30 seconds. Strips contaminated with blood or saliva were discarded. The GCF volume was immediately measured using a pre-calibrated electronic periotrometer (Periotron 8000, OraFlow Inc., USA). Each strip was then eluted into 200 μL of phosphate-buffered saline and stored at -80 °C until batch analysis. Levels of TNF-α, leptin, adiponectin, and resistin in the GCF eluent were determined using commercially available, high-sensitivity ELISA kits (R&D Systems, USA), following the manufacturers’ instructions. The total amount of each analyte (pg) was normalized to the GCF volume (μL) and expressed as concentration (pg/μL) for statistical analysis.
Gingival bleeding index
The gingival bleeding index was assessed to quantify gingival inflammation (33). All clinical examiners underwent standardized training and calibration exercises before the study commenced to ensure high inter-rater reliability. Agreement was assessed using the Cohen’s kappa statistic, with a target value of κ > 0.8 indicating almost perfect agreement (34).
(1) Examination Procedure: A blunt-ended periodontal probe with a tip diameter of 0.5 mm was gently guided into the gingival sulcus, parallel to the long axis of the tooth. The probe was then swept from the distal to the mesial aspect along the sulcus base on both the buccal/labial and lingual/palatal surfaces of each tooth. After probing each tooth, the examiner waited for 10–15 seconds to observe any bleeding.
(2) Scoring Criteria: The following 0–5 scale was used to score bleeding for each tooth surface: 0 points: Healthy gingival margin and papilla; no bleeding after probing. 1 point: Apparently healthy gingiva, but bleeding appears from the sulcus upon probing. 2 points: Bleeding on probing with an accompanying change in gingival color. No swelling is observed. 3 points: Bleeding on probing, color change, and mild gingival edema. 4 points: Bleeding on probing, obvious color change, and significant edema. 5 points: Spontaneous bleeding or severe bleeding upon probing, accompanied by significant edema and color change, potentially with ulceration.
Periodontitis staging and grading
As detailed in the inclusion criteria, all patients were diagnosed, staged, and graded according to the 2018 International Classification of Periodontal Diseases (26). Staging (I-IV) defined the severity and complexity of the disease, while grading (A-C) estimated the rate of progression. The presence of diabetes mellitus was used as a modifier to upgrade the grade, reflecting the patient’s heightened risk for disease progression. All staging and grading assessments were conducted by calibrated periodontists based on full-mouth clinical and radiographic examinations.
Examiners were similarly trained and calibrated for periodontitis grading based on the 2018 International Classification of Periodontal Diseases. Inter-rater reliability was assessed with kappa statistics, showing good agreement (kappa > 0.8).
Statistical methods
Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0. The normality of continuous variables was assessed via the Shapiro–Wilk test (alpha=0.05), and homogeneity of variances was evaluated using Levene’s test. For longitudinal comparisons of normally distributed data that met the sphericity assumption (Mauchly’s test, p > 0.05), repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied, followed by Bonferroni-adjusted pairwise comparisons for post hoc testing. When the sphericity assumption was violated (p ≤ 0.05), the Greenhouse–Geisser correction was used. For non-normally distributed longitudinal data, the Friedman test was employed, with Dunn–Bonferroni tests for subsequent pairwise comparisons when overall significance was detected. Normally distributed data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), and non-normally distributed data as the median (interquartile range, IQR). Categorical variables were analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. Bivariate correlations were examined using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (ρ), with the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure applied to control the false discovery rate (FDR).
Results
Basic data of the patients
The baseline characteristics of the 234 enrolled patients are summarized in Table 1. The cohort comprised 130 males (55.6%) and 104 females (44.4%), with a mean age of 68.4 ± 6.1 years. According to the predefined glycemic control categories, the majority of patients (n=178, 76.1%) were classified as having inadequate diabetic control (HbA1c 7.5%–9.0%), while 56 patients (23.9%) were in the moderate control group (HbA1c <7.5%). Regarding periodontal status, all patients were diagnosed with severe or advanced periodontitis as per the 2018 classification, with 151 patients (64.5%) classified as Stage III and 83 patients (35.5%) as Stage IV. In terms of disease progression rate (Grading), 162 patients (69.2%) were graded as Grade C (rapid progression) and 72 (30.8%) as Grade B (moderate progression). The detailed clinical periodontal parameters at baseline, including mean CAL and PD, are provided in the Table 1.
Gingival bleeding index and periodontitis grading before and after treatment
In this study, we evaluated the effect of the treatment program on the improvement of periodontal health by comparing the changes in gingival bleeding index (GBI) and periodontitis grading before and after treatment. As can be seen in Figure 1, Prior to treatment, the subjects exhibited high GBI and periodontitis grading, indicative of poor periodontal health. After 4 weeks of treatment, both GBI and periodontitis grading significantly decreased, demonstrating a notable improvement in periodontal health. Further improvement was observed by 8 weeks post-treatment, with continued reductions in both GBI and periodontitis grading. These results highlight the efficacy of the treatment in improving gingival bleeding and reducing periodontitis grading over time.
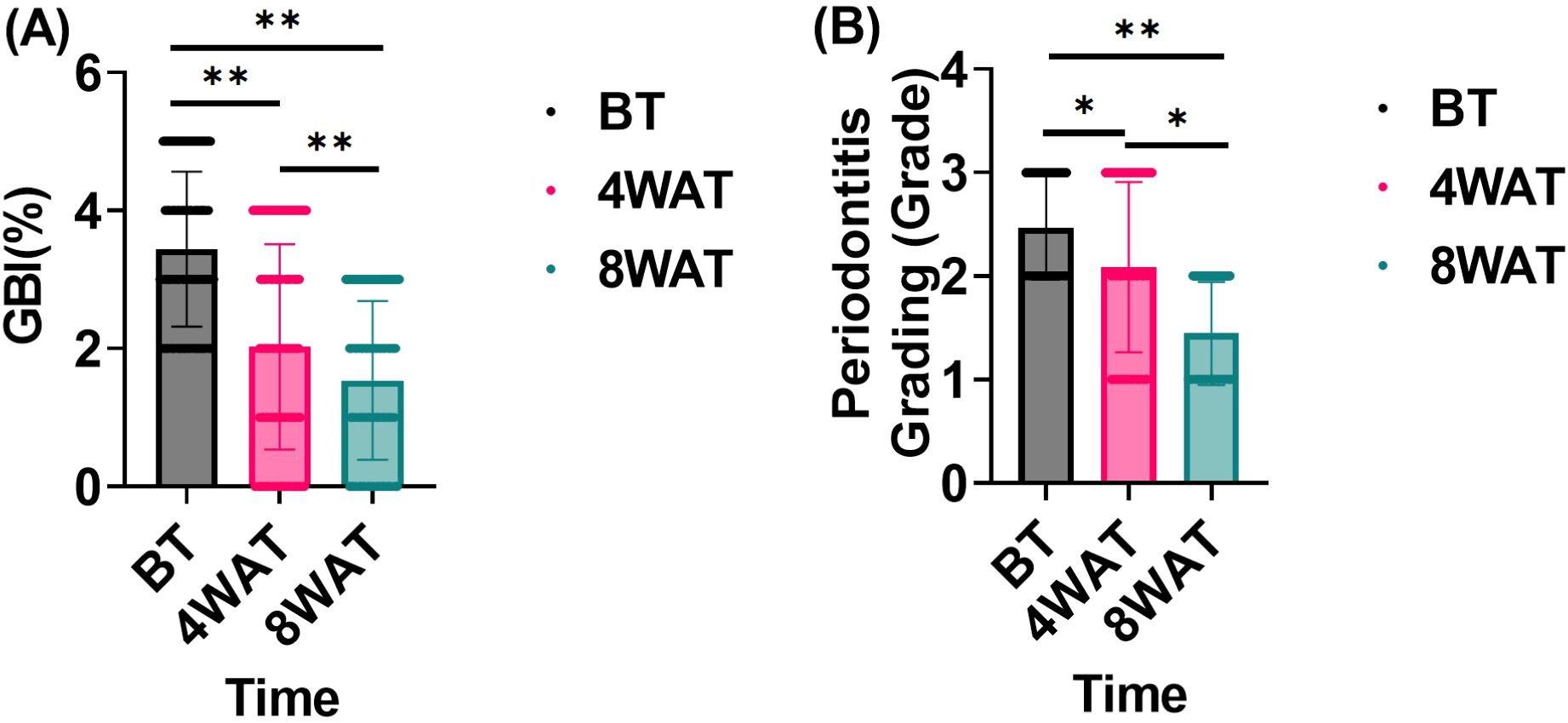
Figure 1. Gingival bleeding index and periodontitis grading before and after treatment. BT is Before Treatment,4WAT is 4 Weeks After Treatment,8WAT is 8 Weeks After Treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (A) GBI levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4 Weeks After Treatment (4WAT), and blue dots represent 8WAT. (B) Periodontitis Grading at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT.
FBG and HbA1c levels before and after treatment
This study evaluated the effect of the treatment regimen on FBG and HbA1c levels in diabetic patients. As shown in Figure 2, These findings underscore the time-dependent efficacy of the treatment in enhancing glycemic control. The initial lack of significant change in FBG, despite a notable reduction in HbA1c at 4 weeks, suggests that the treatment’s impact on fasting blood glucose may require a longer duration to manifest fully. By 8 weeks, the significant decrease in both FBG and HbA1c indicates that the treatment not only sustained the initial improvement in HbA1c but also extended its beneficial effects to FBG, leading to a more comprehensive improvement in glycemic control. This progressive enhancement over time highlights the importance of continued treatment for optimal outcomes in managing glycemic parameters.
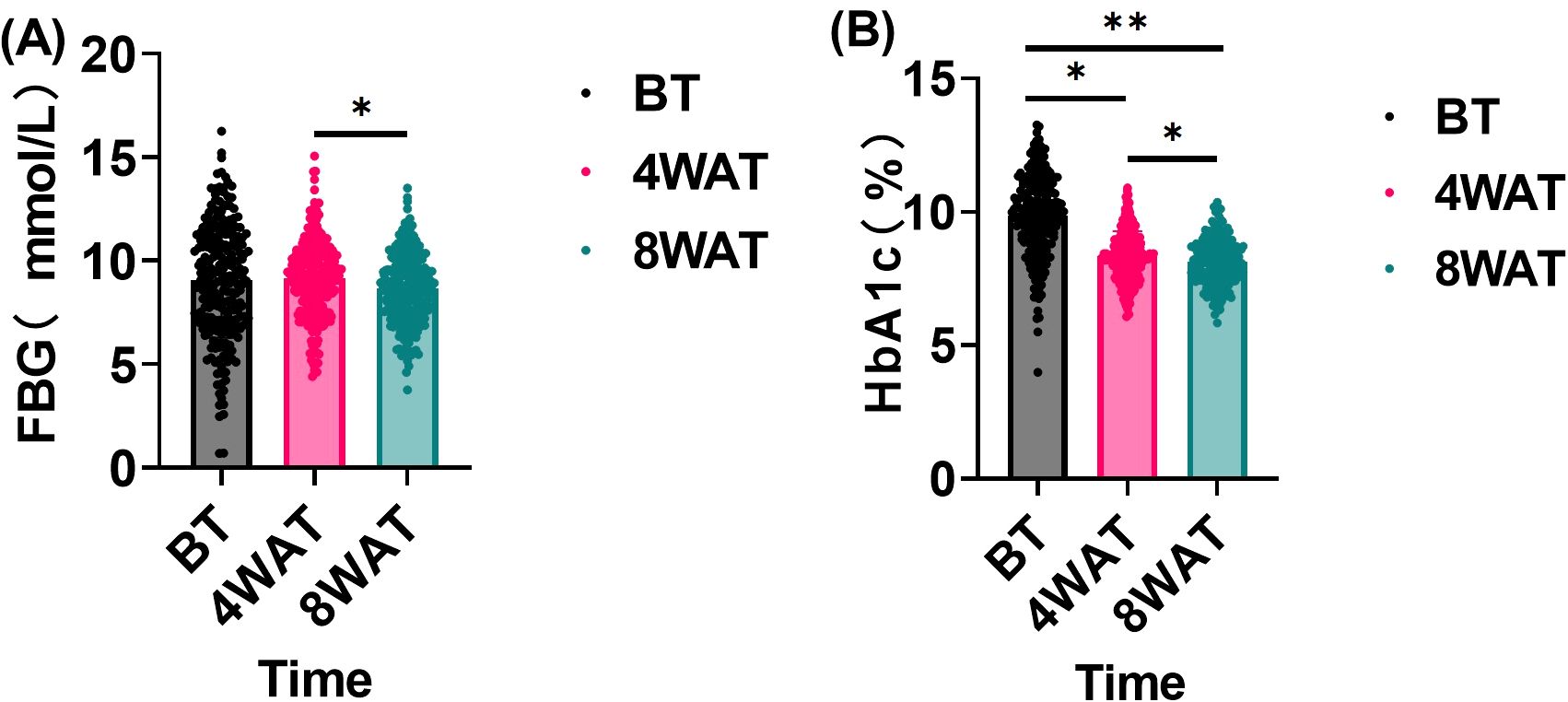
Figure 2. FBG and HbA1c levels before and after treatment(n = 234, `x ± s). BT is Before Treatment, 4WAT is 4 Weeks After Treatment, 8WAT is 8 Weeks After Treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (A) FBG levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT. (B) HbA1c levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT.
Serum leptin, adiponectin and resistin levels before and after treatment
This study further investigated the effects of the treatment regimen on leptin, adiponectin, and resistin levels in diabetic patients. As shown in Figure 3, The sustained and progressive changes in leptin, adiponectin, and resistin levels over the 8-week treatment period highlight the long-term efficacy of the treatment in modulating inflammatory and metabolic profiles. The initial significant reductions in leptin and resistin, coupled with the increase in adiponectin after 4 weeks, suggest a rapid onset of the treatment’s anti-inflammatory and metabolic regulatory effects. The further improvements observed at 8 weeks indicate that these effects are not only maintained but also enhanced with continued treatment. These results imply that the treatment has a cumulative impact on reducing inflammation and improving metabolic health, which is crucial for addressing underlying inflammatory and metabolic disorders.
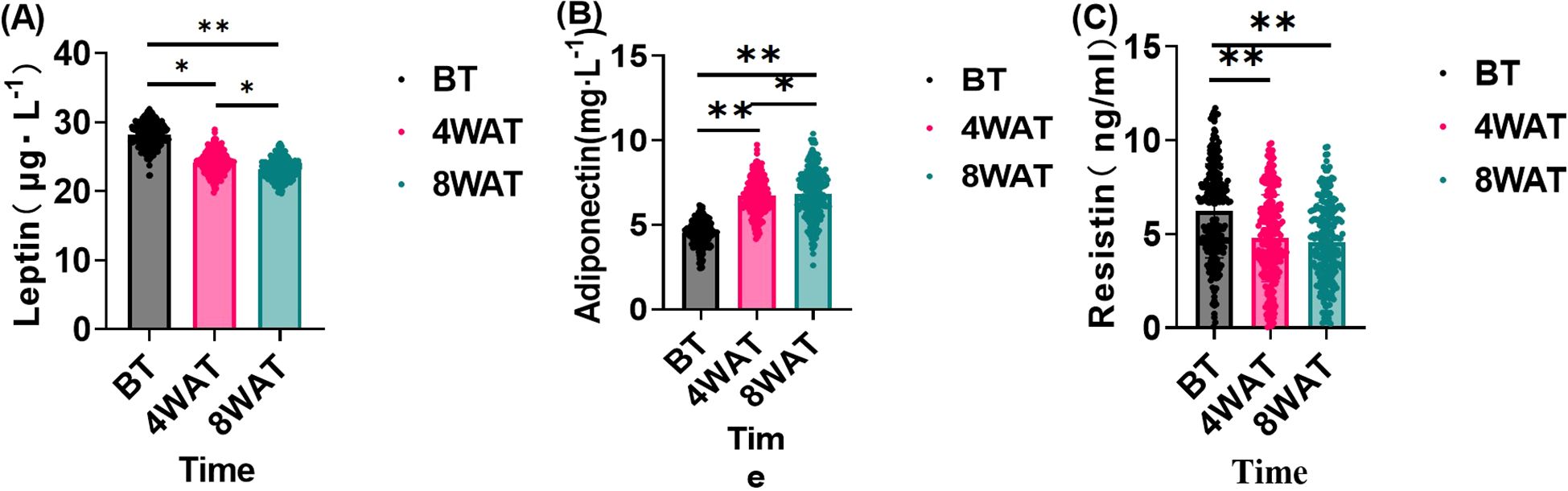
Figure 3. Changes in serum leptin, lipocalin and resistin before and after treatment. BT is Before Treatment, 4WAT is 4 Weeks After Treatment, 8WAT is 8 Weeks After Treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (A) Leptin levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT. (B) Adiponectin levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT. (C) Resistin levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT.
TNF-α and free fatty acid levels before and after treatment
This study investigated the effect of treatment regimen on TNF-α and FFA levels in diabetic patients. These indicators, which are closely related to inflammatory response and metabolic state, may impact periodontal health. As shown in Figure 4, At baseline, patients exhibited elevated levels of TNF-α and FFA, indicative of significant inflammatory responses and metabolic disorders. After 4 weeks of treatment, both TNF-α and FFA levels significantly decreased, demonstrating the treatment’s efficacy in modulating these markers in the short term. By 8 weeks, further reductions were observed, highlighting sustained and progressive improvements in inflammatory and metabolic status throughout the treatment period.
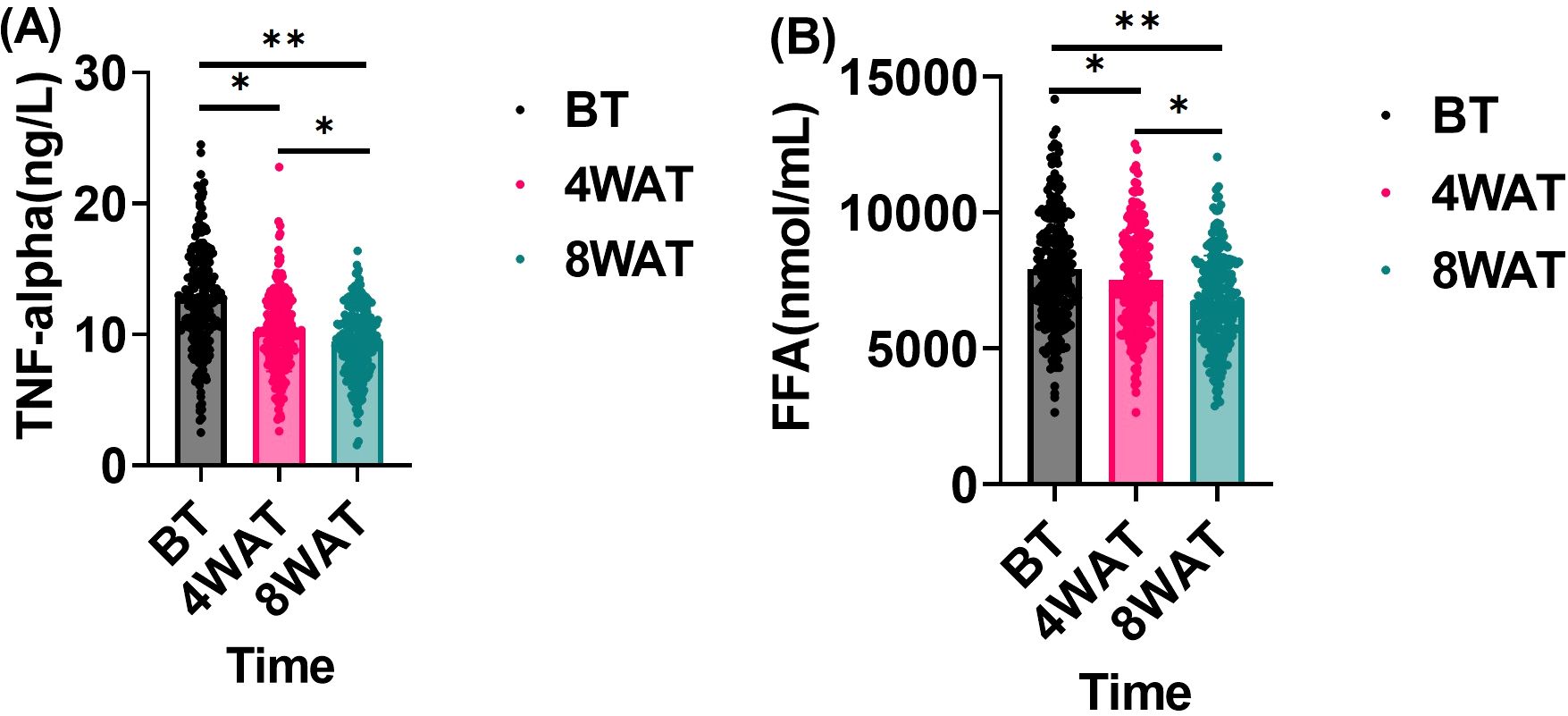
Figure 4. Changes in TNF-α and FFA before and after treatment. BT is Before Treatment, 4WAT is 4 Weeks After Treatment, 8WAT is 8 Weeks After Treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (A) TNF-α levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT. (B) FFA levels at different time points. Black dots represent BT, pink dots represent 4WAT, and blue dots represent 8WAT.
Changes in inflammatory and metabolic indices within gingival crevicular fluid
Analysis of GCF provided insights into the local periodontal changes paralleling systemic effects. As detailed in Table 2, GCF levels of TNF-α, leptin, and resistin exhibited a significant and progressive decrease from baseline to 4 and 8 weeks post-treatment (all P < 0.01). Conversely, adiponectin levels in GCF showed a significant and sustained increase following therapy (P < 0.01). These local changes mirrored the systemic trends observed in serum, indicating that periodontal therapy effectively modulated the inflammatory and metabolic profile directly at the disease site. Furthermore, the reduction in GCF TNF-α at 8 weeks was strongly correlated with the concomitant reduction in serum TNF-α (ρ = 0.512, P < 0.01), reinforcing the link between local periodontal inflammation and systemic inflammatory burden.
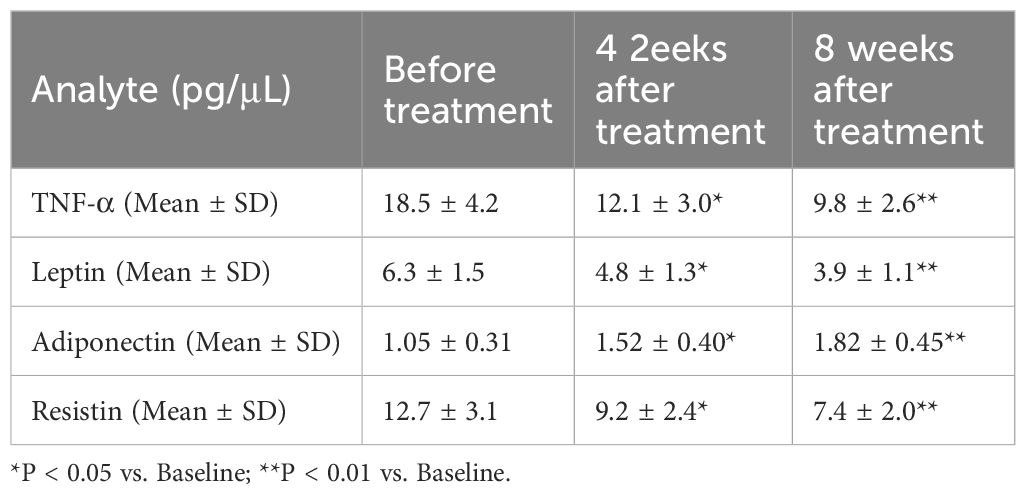
Table 2. Dynamics of inflammatory and metabolic mediators in gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) following periodontal therapy.
Results of correlation analysis of indicators
The temporal dynamics of TNF-α correlations with glycolipid metabolic and periodontal indices are summarized in Table 3. At baseline, TNF-α exhibited moderate positive associations with resistin (ρ = 0.327, P < 0.01) and HbA1c (ρ = 0.213, P < 0.01), while showing an inverse relationship with adiponectin (ρ = -0.229, P < 0.01). Following 4 weeks of therapy, TNF-α correlations intensified markedly with leptin (ρ = 0.671, P < 0.01), resistin (ρ = 0.619, P < 0.01), and periodontal indices (gingival bleeding index: ρ = 0.245; periodontitis grading: ρ = 0.331; P < 0.01). By 8 weeks, while associations with leptin (ρ = 0.165, P < 0.05) and adiponectin (ρ = -0.179, P < 0.01) attenuated, correlations with free fatty acids (FFA: ρ = 0.472) and periodontal severity (ρ = 0.446) became predominant (P < 0.01). Notably, resistin maintained the strongest persistent linkage to TNF-α across all phases (ρ > 0.323, P < 0.01), suggesting its potential role as a coregulated inflammatory mediator, as detailed in Figure 5.
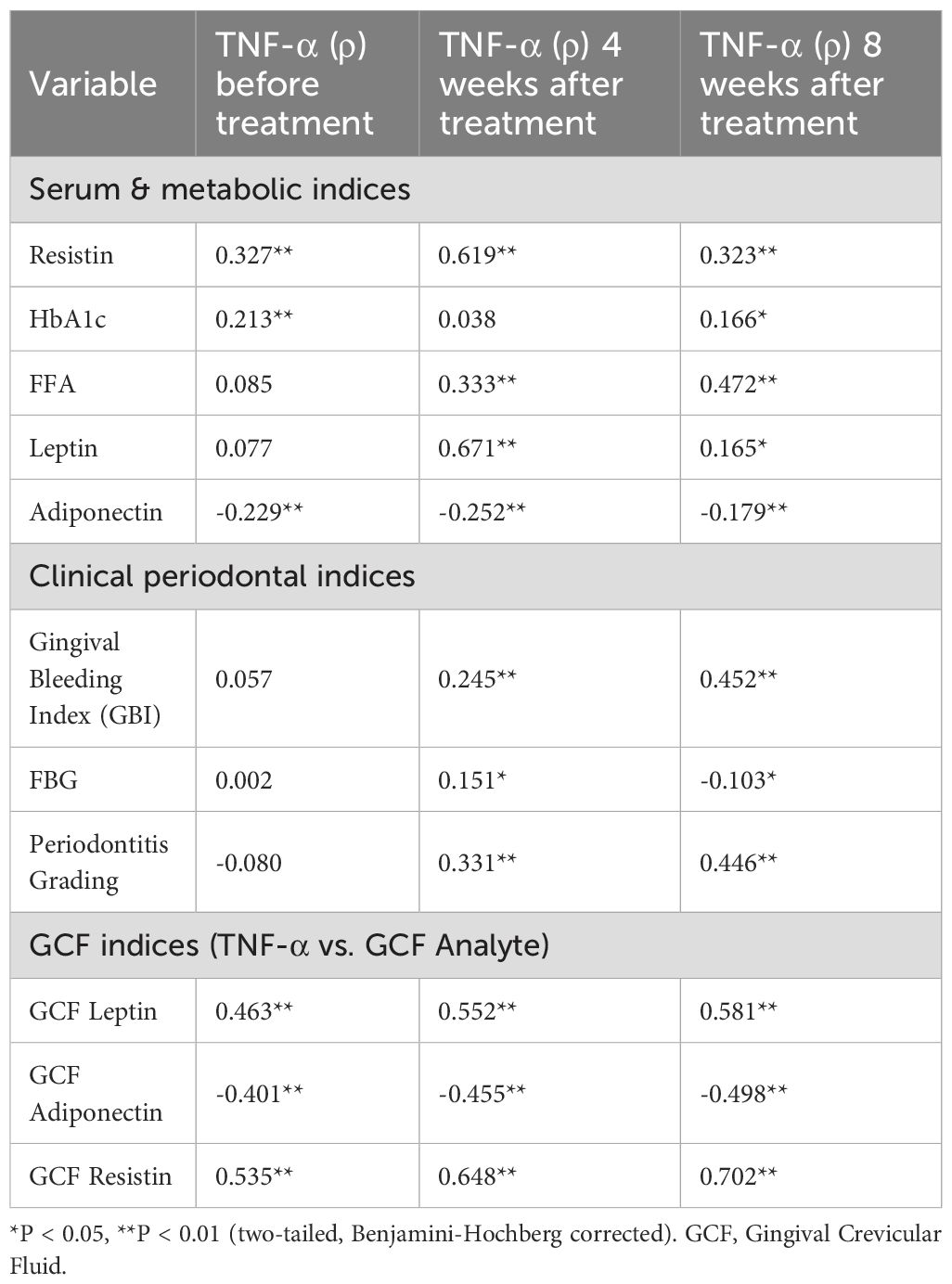
Table 3. Spearman’s correlation coefficients (ρ) between TNF-α and glycolipid metabolic/periodontal/GCF indices across treatment phases.
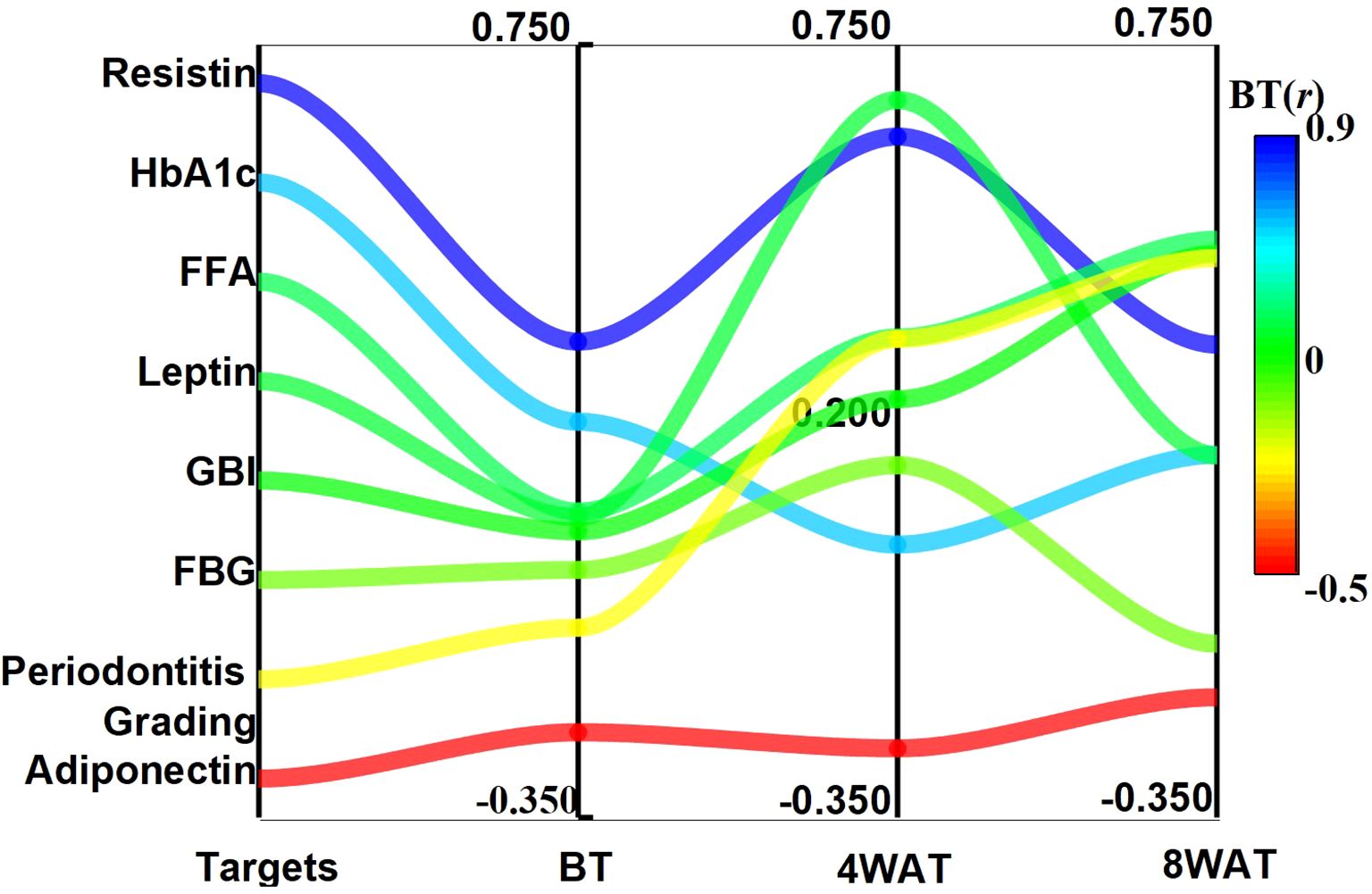
Figure 5. Trends of correlation coefficients between TNF-α and glycolipid metabolism and clinical indicators at different time points. BT is Before Treatment, 4WAT is 4 Weeks After Treatment, 8WAT is 8 Weeks After Treatment.
The correlation analysis was extended to the local periodontal microenvironment by examining the relationships between TNF-α and adipokines within the GCF (Table 3). Strong and persistent correlations were observed throughout the study period. At baseline, GCF TNF-α was already positively correlated with GCF leptin (ρ = 0.463) and GCF resistin (ρ = 0.535), and negatively correlated with GCF adiponectin (ρ = -0.401) (all P < 0.01). These associations intensified at the 4-week follow-up and remained the strongest of all measured correlations at the 8-week time point (GCF leptin: ρ = 0.581; GCF resistin: ρ = 0.702; GCF adiponectin: ρ = -0.498; all P < 0.01). The stability and magnitude of these relationships within the GCF highlight a tightly coupled network of inflammation and metabolism operating directly within the periodontal pocket.
Discussion
An epidemiological survey indicates that from 2011 to 2020, the prevalence of dentate periodontitis among adults was approximately 62%, with severe periodontitis affecting 23.6% (35). In this study, through cross-sectional cohort research, we observed changes in periodontal health and metabolic indicators of patients with diabetes-associated periodontitis after systematic periodontal treatment. After 4-week and 8-week basic periodontal treatment, patients showed significant decreases in GBI and periodontitis grading. This demonstrates the treatment plan’s remarkable effectiveness in improving periodontal health. Our finding aligns with Menezes’s previous research (36), which suggests that systematic periodontitis treatment can effectively control periodontal inflammation and improve periodontal tissue health. Moreover, the treatment led to significant changes in metabolic indicators: decreased serum leptin levels, increased serum adiponectin levels, and decreased resistin levels (P < 0.05). These improvements persisted through the 8-week post-treatment period. This indicates that periodontal treatment enhances periodontal health and positively affects patients’ metabolic state. The research results suggest that periodontitis patients experience endoplasmic reticulum stress in their visceral fat cells, leading to hypoadiponectinemia (37). Adiponectin is an adipocytokine with anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects. Higher adiponectin levels may improve insulin resistance and disorders of glucose and lipid metabolism (38). In patients with type 2 diabetes, the local inflammation of periodontitis leads to enhanced systemic inflammation, decreased adiponectin levels, and lipid metabolism disorders, creating an imbalance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects (39). This decrease in adiponectin levels in patients with diabetes and periodontitis strengthens the connection between these two conditions (40). Leptin, a peptide hormone, regulates energy balance, immune-inflammatory responses, and bone metabolism. Periodontitis progressively weakens tooth-supporting structures, ultimately causing tooth loss (41). Research with ob/ob mice has shown that leptin-deficient obesity increases the risk of periodontitis (42). Elevated levels of leptin and resistin may decrease inflammatory response and metabolic disorders, indicating how periodontal treatment helps regulate systemic metabolism. Consequently, periodontal therapy has been shown to enhance periodontal metabolism and reduce systemic inflammation and metabolic disorders in diabetic patients with periodontal disease.
Periodontal diseases arise from immune responses that trigger gingivitis, periodontitis, and their systemic effects (43). TNF-α, a key inflammatory cytokine, is strongly linked to insulin resistance, glucose metabolism disorders, and abnormal lipid metabolism. In our study, TNF-α levels decreased significantly after periodontal treatment (P < 0.05), suggesting that the treatment was associated with a reduction in inflammation. Both adipocytokines and oxidative stress play roles in periodontitis development (44, 45). The observation that demographic factors exclusively predict baseline TNF-α levels is noteworthy and can be contextualized within the framework of social determinants of health. These demographic variables often serve as proxies for cumulative life-course exposures, which shape an individual’s foundational inflammatory state. For instance, factors such as race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic environment are linked to disparities in baseline inflammatory profiles (46, 47). Research indicates that community-level disadvantages can drive increases in systemic inflammation over time (47). Furthermore, the influence of socioeconomic status on periodontal health may be mediated more by income and health behaviors than directly through inflammatory pathways (48). Therefore, it is plausible that chronic exposure to varying social and environmental stressors sets a distinct immunological tone, reflected in our baseline TNF-α measurements, before the acute effects of the intervention homogenize the inflammatory response.
The analysis of gingival crevicular fluid offers a unique window into the local periodontal biochemical milieu. Our findings demonstrate that non-surgical periodontal therapy induces a profound and progressive shift in the GCF profile, characterized by a significant reduction in pro-inflammatory (TNF-α) and metabolism-disrupting mediators (leptin, resistin), alongside an increase in the insulin-sensitizing adipokine adiponectin. These local changes, which temporally paralleled the systemic improvements in serum biomarkers, strongly suggest that the periodontal pocket is an active site of metabolic crosstalk. The significant correlation between the reduction of TNF-α in GCF and serum further solidifies the pathophysiological link between local periodontal inflammation and the systemic inflammatory state (49). This local modulation likely constitutes a pivotal initial step in the mechanistic pathway through which periodontal therapy confers its salutary systemic effects on glycolipid metabolism in diabetic patients.
Correlation analysis revealed that the relationships between TNF-α and indicators of glucose and lipid metabolism and related clinical indicators changed significantly during the treatment process. Four weeks after treatment, the correlations between TNF-α and leptin, adiponectin, resistin, FFA, the gingival bleeding index, and periodontitis grade were significantly greater (P < 0.05). These findings are consistent with TNF-α being involved in fat metabolism in the early treatment stages, likely because of its dual role in inflammation and metabolic regulation. Specifically, TNF-α is known to participate in inflammatory responses and influence metabolism by controlling adipocytokine expression. By eight weeks post-treatment, while some TNF-α correlations had weakened, their relationships with free fatty acids, the gingival bleeding index, and periodontitis grading strengthened. Correlation analysis revealed that the strengths of the associations between TNF-α and indicators of glucose/lipid metabolism and periodontal health changed during the treatment process. These observed shifts in correlation coefficients over time describe a pattern of changing associations, which may reflect the complex interplay between systemic inflammation and metabolism following periodontal intervention. However, as these are population-level correlations, they cannot be used to infer individual causal pathways. Notably, a significant correlation between TNF-α and resistin was observed, which persisted throughout the study period. This finding aligns with previous research by Zhang et al. (50). Resistin, an adipocyte-secreted hormone, is implicated in insulin resistance and inflammatory processes (51). The consistent association observed in our study invites the hypothesis that resistin and TNF-α may be interact within the shared inflammatory pathway of periodontitis and diabetes. This potential interaction warrants further investigation in future mechanistic studies designed to test causal relationships. Furthermore, the correlation analysis within GCF revealed a tightly interconnected network at the local disease site. The strong positive correlations of GCF TNF-α with GCF leptin and resistin, and its negative correlation with adiponectin, which were more pronounced than the systemic correlations, suggest a potent, localized interplay between inflammation and metabolism in the periodontium of diabetic patients. This reinforces the concept of the periodontal pocket as a significant site of pathophysiological crosstalk (52).
The results of this study indicate that periodontal treatment can significantly improve the periodontal health of diabetic patients and positively impact glucose and lipid metabolism by reducing TNF-α levels. This finding is closely related to the body’s inflammatory response, the regulatory role of adipocytokines, and the systemic metabolic state. For example, carriers of the TNF-α -308 G > A allele are more susceptible to apical periodontitis (53), leading to persistent periodontitis and maintaining the body in a state of chronic inflammation. The overexpression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α can trigger a systemic inflammatory response, further exacerbating insulin resistance and metabolic disorders (54). Periodontal treatment may contribute to the reduction of this systemic inflammatory response and to improvements in glucose and lipid metabolism by removing periodontal inflammatory foci and decreasing TNF-α levels. Periodontal treatment also affects the serum levels of leptin, adiponectin, and resistin. These adipocytokines play crucial roles in insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. The increased adiponectin and decreased leptin and resistin levels may benefit glucose and lipid metabolism by enhancing insulin signaling and lipid metabolism pathways. Moreover, periodontal health is closely linked to the systemic metabolic state. Periodontitis influences metabolic processes through the inflammatory response and immune regulation. When periodontal treatment improves oral health, it may disrupt this harmful interaction, potentially promoting better metabolic function.
The selection of 4-week and 8-week post-treatment timepoints in our study was guided by a strategic consideration of inflammatory marker kinetics and established precedents in periodontal research involving patients with type 2 diabetes. We acknowledge that these intervals may not capture the most immediate transient peaks or very long-term effects; however, they are strategically positioned to assess the establishment of a new systemic inflammatory steady state. Following interventions such as non-surgical periodontal therapy, the initial response involves rapid fluctuations in upstream cytokines like TNF-α, which have a very short half-life (55). In contrast, more sustained systemic repercussions, reflected by downstream markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), require several weeks to stabilize at a new, lower baseline, which genuinely signifies a shift in the patient’s inflammatory status (56). This intermediate observation window is consistent with high-quality evidence in the field. For instance, a randomized controlled trial by Yarahmadi et al. (2024) successfully demonstrated significant reductions in TNF-α and IL-6 at 8 weeks in diabetic patients with periodontal disease (57). Similarly, studies on other chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, commonly employ intervals of 4 to 12 weeks to assess the efficacy of anti-inflammatory interventions (58). Furthermore, while significant improvements in long-term glycemic control as measured by HbA1c may take several months to manifest (58), the early modulation of inflammation observed at 4 and 8 weeks serves as a crucial prognostic indicator for these ultimate metabolic benefits. Therefore, our chosen timepoints provide a scientifically grounded framework for evaluating the substantive impact of periodontal therapy on systemic inflammation.
This study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. The most significant limitation is the absence of a non-treatment or placebo control group. This design precludes us from definitively ruling out the possibility that the observed improvements reflect regression to the mean, natural fluctuation of the disease, or the effects of unmeasured confounders. However, several aspects of our data suggest that the changes are likely attributable to the treatment effect. First, the improvements were progressive and sustained over the 8-week observation period across a wide array of distinct biomarkers (from systemic cytokines to local GCF mediators) and clinical indices, a pattern less consistent with random fluctuation. Second, the observed temporal dynamics, particularly the intensification and subsequent evolution of correlations between TNF-α and metabolic markers, align with a biologically plausible sequence of events following the reduction of a key inflammatory driver (18–20). Finally, the magnitude and consistency of the metabolic improvements are in line with previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs that have demonstrated the beneficial effect of periodontal therapy on glycemic control in diabetic patients (59, 60). Nonetheless, future randomized controlled trials with longer follow-up are warranted to conclusively confirm our findings. The 8-week follow-up period is relatively short, and the long-term sustainability of the observed metabolic and inflammatory improvements remains to be determined. Furthermore, potential confounders such as diet and physical activity were not systematically controlled or documented, and the influence of adjunctive tetracycline treatment cannot be excluded. Additionally, our study focused specifically on TNF-α as a primary mediator based on its well-established central role in the pathogenesis of both periodontitis and insulin resistance (61–66); however, we did not assess other pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6), which also participate in these processes. This focus, while providing depth to our understanding of TNF-α, means that the contributions of other inflammatory pathways remain unexplored in this cohort. Although the sample size was adequate, patient heterogeneity may exist. Finally, the specific mechanisms of action of TNF-α were not explored. Future studies with longer follow-up, randomized controlled designs, detailed monitoring of lifestyle factors, broader cytokine profiling, and integrated mechanistic investigations are warranted to validate and extend our findings.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that systematic periodontal treatment in diabetic patients significantly improves their periodontal health, blood glucose control, and glucose and lipid metabolism by reducing TNF-α levels. These findings provide an important foundation for treating patients with diabetes-complicated periodontitis. Future research should explore TNF-α’s mechanism in these patients to optimize treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University (Approval No.: 20210502). Informed consent was obtained from all the participants. All methods were carried out in accordance with Declaration of Helsinki. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YMG: Project administration, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Resources, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. AY: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology, Software. YQG: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. SD: Writing – review & editing, Software, Methodology, Data curation. LW: Formal analysis, Project administration, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. NZ: Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Young Scientist Program of Beijing Stomatological Hospital, Capital Medical University (Nos. YSP202203); and the Government-funded Outstanding Talents Training Program in Clinical Medicine (Project Number: ZF2025125).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lee H, Joo JY, Song JM, Kim HJ, Kim YH, and Park HR. Immunological link between periodontitis and type 2 diabetes deciphered by single-cell RNA analysis. Clin Transl Med. (2023) 13:e1503. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1503
2. Li S, Li H, Kong H, Wu SY, Cheng CK, and Xu J. Endogenous and microbial biomarkers for periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1292596. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1292596
3. Chung YL, Lee JJ, Chien HH, Chang MC, and Jeng JH. Interplay between diabetes mellitus and periodontal/pulpal-periapical diseases. J Dent Sci. (2024) 19:1338–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.03.021
4. Aizenbud I, Wilensky A, and Almoznino G. Periodontal disease and its association with metabolic syndrome-A comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:13011. doi: 10.3390/ijms241613011
5. Deng Y, Xiao J, Ma L, Wang C, Wang X, Huang X, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in periodontitis and associated systemic diseases: implications for pathomechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:1024. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021024
6. Herrera D, Sanz M, Shapira L, Brotons C, Chapple I, Frese T, et al. Periodontal diseases and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and respiratory diseases: Summary of the consensus report by the European Federation of Periodontology and WONCA Europe. Eur J Gen Pract. (2024) 30:2320120. doi: 10.1080/13814788.2024.2320120
7. Zhao X, Yang Y, Yu J, Ding R, Pei D, Zhang Y, et al. Injectable hydrogels with high drug loading through B-N coordination and ROS-triggered drug release for efficient treatment of chronic periodontitis in diabetic rats. Biomaterials. (2022) 282:121387. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121387
8. Villoria G, Fischer RG, Tinoco E, Meyle J, and Loos BG. Periodontal disease: A systemic condition. Periodontol. (2000) 2024. 96:7–19. doi: 10.1111/prd.12616
9. Park MS, Jeon J, Song TJ, and Kim J. Association of periodontitis with microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus: A nationwide cohort study. J Diabetes Complications. (2022) 36:108107. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.108107
10. Costa R, Ríos-Carrasco B, Monteiro L, López-Jarana P, Carneiro F, and Relvas M. Association between type 1 diabetes mellitus and periodontal diseases. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1147. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031147
11. Pinto KP, Serrão G, Alves Ferreira CM, Sassone LM, Fidalgo T, and Silva E. Association between apical periodontitis and chronic diseases: an umbrella review. Iran Endod J. (2023) 18:134–44. doi: 10.22037/iej.v18i3.42560
12. Qin H, Li G, Xu X, Zhang C, Zhong W, Xu S, et al. The role of oral microbiome in periodontitis under diabetes mellitus. J Oral Microbiol. (2022) 14:2078031. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2022.2078031
13. Tang B, Yan C, Shen X, and Li Y. The bidirectional biological interplay between microbiome and viruses in periodontitis and type-2 diabetes mellitus. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:885029. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.885029
14. Păunică I, Giurgiu M, Dumitriu AS, Păunică S, Pantea Stoian AM, Martu MA, et al. The bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus-A review. Diagnostics (Basel). (2023) 13:681. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13040681
15. Li LL, Xie XT, Wu Y, and Yan FH. Advances in research on the mechanism of association between periodontitis and diabetes mellitus. Sichuan Da Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2023) 54:71–6. doi: 10.12182/20230160203
16. Yang Y, Sun X, Yang Y, and Qie Y. Insight of the interrelationship and association mechanism between periodontitis and diabetes mellitus. Regener Ther. (2024) 26:1159–67. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.11.001
17. Elnour M and Mirghani HO. Periodontitis treatment (surgical and nonsurgical) effects on glycemic control: A review and meta-analysis. Ann Afr Med. (2023) 22:131–5. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_53_22
18. Prasetyo EP, Sampoerno G, Juniarti DE, Cahyani F, Saraswati W, Kuntjoro M, et al. Effect of lipopolysaccharide-induced apical periodontitis in diabetes mellitus rats on periapical inflammation. Eur J Dent. (2023) 17:1146–52. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1758790
19. Akash M, Rehman K, and Liaqat A. Tumor necrosis factor-α: role in development of insulin resistance and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:105–10. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26174
20. Marigo L, Cerreto R, Giuliani M, Somma F, Lajolo C, and Cordaro M. Diabetes mellitus: biochemical, histological and microbiological aspects in periodontal disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2011) 15:751–8.
21. Bakshi D, Kaur G, Singh D, Sahota J, Thakur A, and Grover S. Estimation of plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-a, interleukin-4 and 6 in patients with chronic periodontitis and type II diabetes mellitus. J Contemp Dent Pract. (2018) 19:166–9. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2231
22. Palafox-Sánchez CA, Cruz A, Salazar-Camarena DC, Gascón LG, Cintra LTA, Muñoz-Valle JF, et al. Evaluation of serum levels of cytokines in acute apical abscess: A longitudinal observational study. J Endod. (2023) 49:1090–8. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2023.07.001
23. Chaudhry SZ and Ghafoor S. Adipokines: Diagnostic and prognostic markers for oral diseases. J Pak Med Assoc. (2023) 73:858–62. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.4737
24. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:S17–38. doi: 10.2337/dc22-S002
25. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:S83–96. doi: 10.2337/dc22-S006
26. Tonetti MS, Greenwell H, and Kornman KS. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J Periodontol. (2018) 89 Suppl 1:S159–72. doi: 10.1002/JPER.18-0006
27. Giannobile WV, Burt BA, and Genco RJ eds. Design of randomized controlled trials. In: Clinical research in oral health. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons (2010). 119–36.
28. Muramatsu T, Yokoyama Y, Yatani H, Kado T, Koso K, and Hanioka T. Team medical approach for drug-induced gingival overgrowth. J Jpn Soc Periodontol. (2019) 61:37–43. doi: 10.1155/crid/8318894
29. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care. (2024) 47:S179–218. doi: 10.2337/dc24-S010
30. Wu SX. Sample size calculation basics for clinical research. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House (2008) p. 24–6.
31. Narayanan S. Preanalytical variables in biological monitoring. Pure Appl Chem. (2000) 72:1487–510. doi: 10.1351/pac200072081487
32. Griffiths GS. Formation, collection and significance of gingival crevice fluid. Periodontol. (2000) 2003:31:32–42. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0757.2003.03103.x
33. Abrahamian L, Pascual-LaRocca A, Barallat L, Valles C, Herrera D, Sanz M, et al. Intra- and inter-examiner reliability in classifying periodontitis according to the 2018 classification of periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. (2022) 49:457–64. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13604
34. Mühlemann HR and Son S. Gingival sulcus bleeding–a leading symptom in initial gingivitis. Helv Odontol Acta. (1971) 15:107–13.
35. Trindade D, Carvalho R, MaChado V, Chambrone L, Mendes JJ, and Botelho J. Prevalence of periodontitis in dentate people between 2011 and 2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. J Clin Periodontol. (2023) 50:604–26. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13769
36. Menezes CC, Barbirato D, Fogacci MF, Marañón-Vásquez GA, Carneiro JRI, Maia LC, et al. Systemic benefits of periodontal therapy in patients with obesity and periodontitis: a systematic review. Braz Oral Res. (2024) 38:e031. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2024.vol38.0031
37. Wu Q, Yan L, Wu X, Chen Y, Ye L, Lv Y, et al. Experimental periodontitis induced hypoadiponectinemia by IRE1α-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress in adipocytes. BMC Oral Health. (2023) 23:1032. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03758-6
38. Sun Y, Yin Y, Yang S, Ai D, Qin H, Xia X, et al. Lipotoxicity: The missing link between diabetes and periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. (2024) 59:431–45. doi: 10.1111/jre.13242
39. Cheng R, Xu X, Yang S, Mi Z, Zhao Y, Wang C, et al. The effect of APN, hs-CRP and APN/hs-CRP in periodontitis with DAA. BMC Oral Health. (2023) 23:85. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02765-x
40. Mahendra J, Mahendra L, Divya D, Ilango P, Devarajan N, and Thanigaimalai A. Association of Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus and lipocalin with periodontitis in type 2 diabetic subjects. Oral Dis. (2023) 29:1163–71. doi: 10.1111/odi.14091
41. Guo Z, Peng Y, Hu Q, Liu N, and Liu Q. The relationship between leptin and periodontitis: a literature review. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e16633. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16633
42. Li Z, Zheng Z, Pathak JL, Li H, Wu G, Xu S, et al. Leptin-deficient ob/ob mice exhibit periodontitis phenotype and altered oral microbiome. J Periodontal Res. (2023) 58:392–402. doi: 10.1111/jre.13099
43. Zhang M, Liu Y, Afzali H, and Graves DT. An update on periodontal inflammation and bone loss. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1385436. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1385436
44. Iniesta M, Chamorro C, Ambrosio N, Marín MJ, Sanz M, and Herrera D. Subgingival microbiome in periodontal health, gingivitis and different stages of periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. (2023) 50:905–20. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13793
45. Sabbagh S, Adatorwovor R, Kirakodu S, Rojas-Ramirez MV, Al-Sabbagh M, Dawson D, et al. Periodontal inflammatory and microbial profiles in healthy young African Americans and Caucasians. J Clin Periodontol. (2024) 51:905–14. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13989
46. Gogniat MA, Khan OA, Ratangee B, Bolton CJ, Zhang P, Liu D, et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations of neighborhood disadvantage with fluid biomarkers of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Neurology. (2025) 105:e214280. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000213770
47. Chen Y, Wang L, Mo S, Zhao D, and Fan Y. Mediators of the association between education and periodontitis: Mendelian randomization study. BMC Oral Health. (2025) 25:159. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06006-1
48. Toy VE, Ataoglu T, Eltas A, Otlu HG, and Karabulut AB. Obesity as a modifying factor of periodontal therapy outcomes: local and systemic adipocytokines and oxidative stress markers. Clin Oral Investig. (2023) 27:2763–73. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04854-7
49. Hajishengallis G and Chavakis T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21:426–40. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-00488-6
50. Zhang Y, Jia R, Zhang Y, Sun X, Mei Y, Zou R, et al. Effect of nonsurgical periodontal treatment on cytokines/adipocytokines levels among periodontitis patients with or without obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. (2023) 23:717. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03383-3
51. Kamil MA, Peeran SW, Basheer SN, Elhassan A, Alam MN, and Thiruneervannan M. Role of resistin in various diseases with special emphasis on periodontal and periapical inflammation - A review. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. (2023) 15:S31–5. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_655_22
52. Fischer RG, Lira Junior R, Retamal-Valdes B, Figueiredo LC, Malheiros Z, Stewart B, et al. Periodontal disease and its impact on general health in Latin America. Section V: Treatment of periodontitis. Braz Oral Res. (2020) 34:e026. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2020.vol34.0026
53. Jakovljevic A, Jacimovic J, Georgiou AC, Nikolic N, Aminoshariae A, van der Waal SV, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms as a predisposing factor for the development of apical periodontitis-An umbrella review. Int Endod J. (2022) 55:700–13. doi: 10.1111/iej.13756
54. Kandaswamy E, Lee CT, Gururaj SB, Shivanaikar S, and Joshi VM. Association of adipokine levels with obesity in periodontal health and disease: A systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression. J Periodontal Res. (2024) 59:623–35. doi: 10.1111/jre.13263
55. Cavaillon JM, Adib-Conquy M, Fitting C, Adrie C, and Monchi M. Cytokine cascade in sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis. (2003) 35:535–44. doi: 10.1080/00365540310015935
56. Aispure O, Ivanov D, Smirnov A, Lazko F, Ryabykh S, and Guz A. Dynamics of C-reactive protein level after orthopedic surgeries. Int J Surg. (2024) 11:7.
57. Yarahmadi M, Zeynali N, Zadeh F, Yousefimanesh HA, Nejatian T, Gravand E, et al. The effects of synbiotic supplementation along with non-surgical periodontal therapy in improving metabolic status and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with periodontal disease: A double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Educ Health Promot. (2024) 13:430. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1382_23
58. D'Aiuto F, Gkranias N, Bhowruth D, Horváth Á, Szentpéteri A, Hamar A, et al. Systemic effects of periodontitis treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 12 month randomised controlled clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2018) 6:954–65. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30038-X
59. Sanz M, Ceriello A, Buysschaert M, Khan T, Orlandi M, Suvan J, et al. Scientific evidence on the links between periodontal diseases and diabetes: Consensus report and guidelines of the joint workshop on periodontal diseases and diabetes by the International diabetes Federation and the European Federation of Periodontology. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2018) 137:231–41. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.12.001
60. Teshome A and Yitayeh A. The effect of periodontal therapy on glycemic control and fasting plasma glucose level in type 2 diabetic patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. (2016) 17:31. doi: 10.1186/s12903-016-0249-1
61. Graves DT and Cochran D. The contribution of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor to periodontal tissue destruction. J Periodontol. (2003) 74:391–401. doi: 10.1902/jop.2003.74.3.391
62. Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, and Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. (1993) 259:87–91. doi: 10.1126/science.7678183
63. Krogh-Madsen R, Plomgaard P, Møller K, Mittendorfer B, and Pedersen BK. Influence of TNF-alpha and IL-6 infusions on insulin sensitivity and expression of IL-18 in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2006) 291:E108–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00471.2005
64. Ding C, Ji X, Chen X, Xu Y, and Zhong L. TNF-α gene promoter polymorphisms contribute to periodontitis susceptibility: evidence from 46 studies. J Clin Periodontol. (2014) 41:748–59. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12279
65. Li Y, Yang J, Wu X, and Sun W. TNF-α polymorphisms might influence predisposition to periodontitis: A meta-analysis. Microb Pathog. (2020) 143:104113. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104113
66. Czókolyová M, Pusztai A, Végh E, Horváth Á, Szentpéteri A, Hamar A, et al. Changes of metabolic biomarker levels upon one-year anti-TNF-α Therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: associations with vascular pathophysiology. Biomolecules. (2021) 11:1535. doi: 10.3390/biom11101535
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, periodontitis, tumor necrosis factor α, glycosylated hemoglobin, resistin
Citation: Guo Y, Zhang X, Yang A, Guo Y, Dong S, Wang L, Zhang N and Zhou H (2025) Periodontal therapy mitigates inflammation via TNF-α reduction and improves glycolipid metabolism in diabetic patients: a cross-sectional cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1668695. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1668695
Received: 18 July 2025; Accepted: 16 October 2025;
Published: 30 October 2025.
Edited by:
Zoe Zhu, Tufts University, United StatesReviewed by:
Zhenting Xiang, Temple University, United StatesJinmei Zhang, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, China
Copyright © 2025 Guo, Zhang, Yang, Guo, Dong, Wang, Zhang and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ning Zhang, ZGVudGlzdHpoYW5nMTEyQDE2My5jb20=; Huimin Zhou, MTY2MDEyNTlAaGVibXUuZWR1LmNu
 Yiman Guo1
Yiman Guo1 Xincheng Zhang
Xincheng Zhang Aige Yang
Aige Yang Ning Zhang
Ning Zhang Huimin Zhou
Huimin Zhou