- 1Department of Ophthalmology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Harbin Second Hospital, Harbin, China
Purpose: This study aims to assess the effects of heavy silicone oil (HSO) tamponade in patients with diabetic tractional retinal detachment (TRD) treated with pars plana vitrectomy (PPV), and to evaluate the role of extended-release hormone implantation in controlling inflammation and mitigating postoperative complications.
Methods: A prospective, randomized, controlled design was used in this study. This study included 96 eyes from 96 patients diagnosed with diabetic TRD, all of whom were treated at our institution between March 2024 and March 2025. Group 1 consisted of 54 eyes from 54 patients (PPV + HSO + dexamethasone implant), while Group 2 included 42 eyes from 42 patients (PPV + HSO). The primary outcomes included best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), intraocular pressure (IOP), retinal reattachment rate, anterior chamber (AC) fibrin exudation, anterior proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR), and posterior iris synechiae during the 3-month postoperative follow-up period.
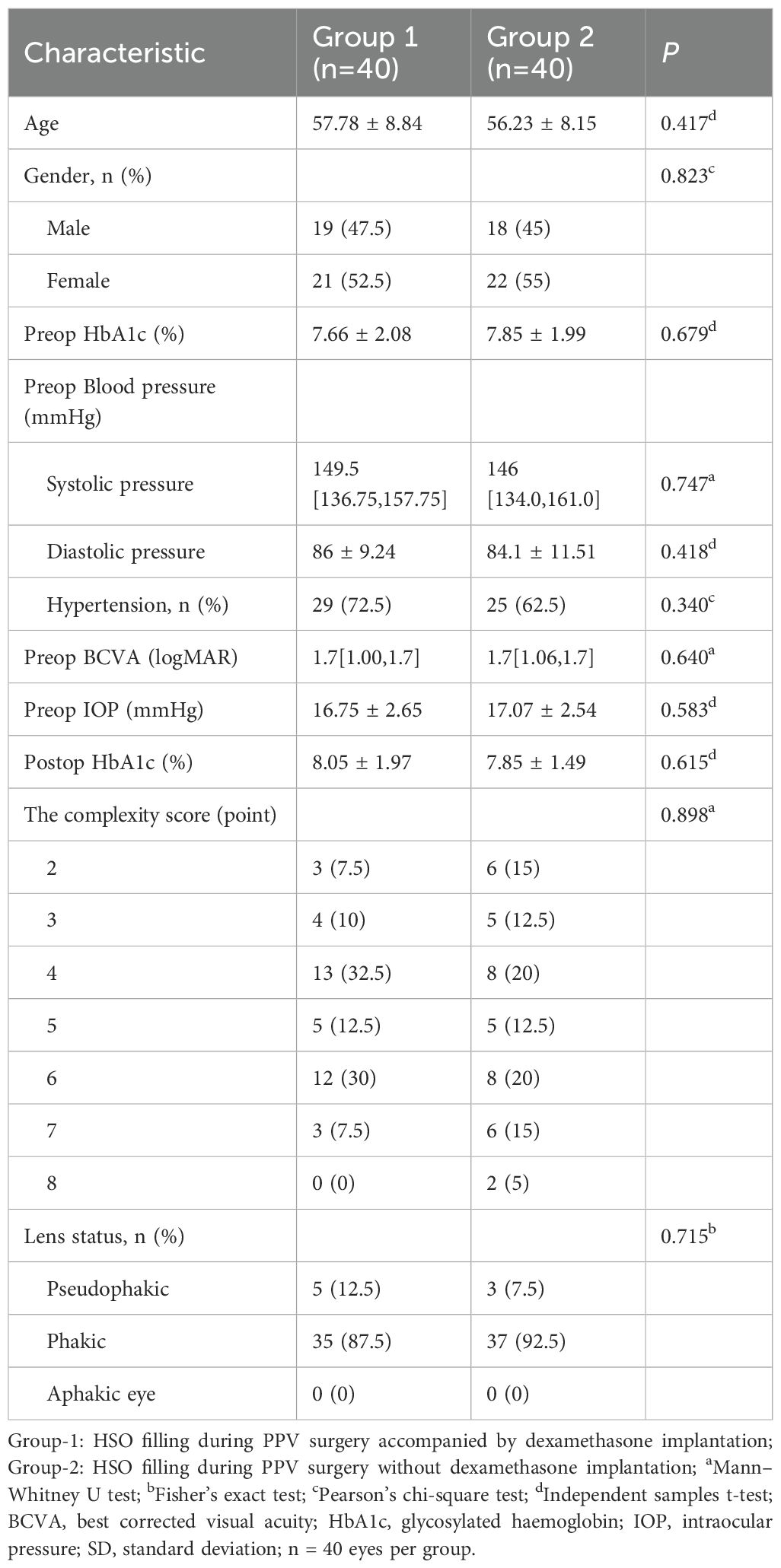
Results: Eighty eyes from 80 patients were ultimately included in the study, with 40 eyes assigned to each group. Patient characteristics, including age, sex, preoperative HbA1c levels and preoperative blood pressure,DR severity were similar (P >0.05). Both groups demonstrated improvements in BCVA postoperatively compared to baseline (P <0.05,Bonferroni adjusted). Group 1 demonstrated a improvement in BCVA compared to Group 2 at 1 month and 3 months postoperatively,but P >0.05 after adjusted. At 3 months postoperatively, IOP did not differ significantly between the groups (P > 0.05). At 1 week postoperatively, AC fibrin exudation was decreased in Group 1(P = 0.007, P = 0.07 Bonferroni adjusted). At 3 months postoperatively,compared with Group 2, Group 1 had significantly lower postoperative anterior PVR (P = 0.010 Bonferroni adjusted), Group 1 had lower rates of retinal reattachment and posterior iris synechiae (P = 0.032 and P = 0.008, all P>0.05 Bonferroni adjusted).
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this first study of dexamethasone implants with HSO in PDR suggests intraoperative DEX may be a safe, potentially beneficial adjunct for diabetic TRD undergoing phacoemulsification plus vitrectomy with HSO, reducing inflammation and number of anti-VEGF injections over 3 months, and offering useful directions for future research in this preliminary prospective evaluation overall.
1 Introduction
Diabetes is one of the primary contributors to vision impairment in adults within the working-age group (1). The progression of diabetes can lead to a wide range of irreversible complications; for example, one-third of diabetic patients suffer from diabetic retinopathy (DR) (2). VEGF plays a crucial role in this process. Neovascularization can occur when VEGF levels are elevated, which is a sign of proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). PDR is among the most serious complications of diabetes, often resulting in permanent vision loss (3, 4). Additionally, numerous studies have shown that increased levels of inflammatory factors promote angiogenesis and neuronal degeneration, leading to retinal damage; therefore, inflammatory factors are crucial in the early development of DR (5). As the DR progresses, patients may develop diabetic macular oedema (DME), vitreous hemorrhage (VH), and TRD and even progress to neovascular glaucoma. Pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) is an important method for treating complications of PDR and refractory macular oedema (6, 7). During surgery, different types of tamponade (e.g., gas, silicone oil) are chosen based on the presence of retinal tears and tractional retinal attachment. However, according to the literature, silicone oil can induce an intraocular inflammatory response, which tends to intensify over time (8). Increased intraocular inflammatory factor levels are strongly associated with the onset and progression of PVR (9, 10). Although the fibrovascular membranes are removed and the detached retina is reattached during PPV, postoperative complications such as haemorrhage, retinal detachment (RD), PVR, and macular oedema may still occur. Anti-VEGF therapy may still be required in some patients after PPV to alleviate DME (11), however, there is currently no effective method to prevent the onset of retinal proliferation.
The application of intravitreal extended-release hormones to treat diabetic macular oedema primarily offers anti-neovascularization, anti-inflammatory, and anti-osmotic effects. Compared with other anti-VEGF drugs, intravitreal extended-release hormones can provide sustained release for up to 6 months after intravitreal administration (12, 13). Clinical studies have shown that the implantation of extended-release hormones can significantly reduce the recurrence rate of RD, minimize the severity of PVR, and decrease the need for anti-VEGF treatments in DME patients during PPV (14–16). However, there are no clinical studies examining the combination of HSO tamponade with extended-release hormone implantation during PPV in patients with PDR. The primary objective of this study was to assess the effects of HSO tamponade in patients with diabetic TRD undergoing PPV and to evaluate the role of extended-release hormone implantation in controlling inflammation and mitigating postoperative complications. This study will observe these contents.Although dexamethasone implants are widely used in patients with diabetic retinopathy, this study will provide a new treatment option for diabetic retinopathy patients who require heavy silicone oil filling during surgery.
2 Materials and methods
The study was conducted as a randomized, prospective, controlled design at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, with ethical compliance ensured through Helsinki Declaration adherence.The Institutional Review Board of Harbin Medical University granted ethical approval for this study (Study No. YJSKY2024-334). All enrolled subjects voluntarily provided signed informed consent documents in compliance with ethical requirements. This study included 96 eyes from 96 patients diagnosed with diabetic TRD, all of whom were treated at our institution between March 2024 and March 2025. A computer-based randomization system (Research Randomizer) was used to randomly assign numbers to the subjects. We placed the generated randomization sequence into sequentially numbered, sealed, opaque envelopes. Subsequently, personnel not involved in subject screening opened these envelopes in sequential order to implement the group assignment. These patients received a 25G three-port PPV under retrobulbar anaesthesia. Group 1 received PPV with HSO and dexamethasone implantation, whereas Group 2 underwent PPV with HSO only.
2.1 Patient eligibility
Inclusion criteria comprised the following: (1) diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus, (2) participants aged 40 years or older, (3) TRD due to PDR requiring HSO tamponade, with concurrent cataracts or intraocular lenses (IOLs), and (4) at least 3 months of postoperative follow-up.
Exclusion criteria comprised: (1) incomplete clinical follow-up (<3 months); (2) TRD not caused by PDR; (3) patients presenting with exudative retinal detachment or rhegmatogenous retinal detachment; (4) the presence of glaucoma and an IOP more than 21 mmHg; (5) patients with other retinal pathologies that could affect macular structure and vision; (6) patients who had undergone vitreoretinal surgery; (7) cases exhibiting iris neovascularization; (8) patients with uncontrolled diabetes (glycosylated haemoglobin [HbA1c] >12%); and (9) patients with bleeding disorders, active ocular infections, a history of recent myocardial infarction, or pregnancy.
2.2 Sample size estimation
The primary endpoint of this study is the incidence of PVR (binary outcome). We will use a two-sample comparison of proportions (superiority, two-sided design). The significance level is set at α = 0.05 (two-sided) with Power = 0.80, and the allocation ratio is 1:1. Based on prior studies of dexamethasone in PDR patients undergoing silicone oil tamponade, we assume a PVR incidence of 28.6% in the control group (no dexamethasone implant) and 0% in the treatment group, with an anticipated loss to follow-up rate of 10%. The required sample size was calculated to be 50 participants.
2.3 Examinations
A detailed patient history, including sex, age, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, was collected preoperatively. The complete ophthalmologic examinations were performed on all participants, which included measurement of BCVA (logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution [logMAR]), dilated fundus examination using a slit-lamp biomicroscope, IOP measurement via a noncontact tonometer, and measurement of central macular thickness (CMT) in the central 1-mm-diameter region using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT). Additionally, B-scan ultrasound and scanning laser ophthalmoscopy were performed to assess retinal.
Referenced severity assessment for PDR,the complexity score (CS) was calculated as the sum of five items:1. Extent of FVP: number of involved quadrants (1–4), awarding 1 point per quadrant;2. FVP location: involvement limited to anterior or limited to posterior to the equator scored 0; combined anterior + posterior involvement scored +1;3. TRD: +1 point when present;4. Traction-rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (TRRD): +2 points when present;5. Posterior vitreous detachment: absence of PVD contributed +1 point (17).
2.4 Surgical technique
All procedures were performed by the same experienced vitreoretinal surgeon using identical instruments throughout.A total of 96 patients participated and were randomly divided into two groups. Eyes in Group 1 (n=54) with significant cataracts initially underwent phacoemulsification of the crystalline lens plus the intraocular lens (IOL). A 25-gauge instrument was used to carry out anterior and central vitrectomy in all eyes. Additionally, an intravitreal injection of 0.1 mL of triamcinolone (Kenacort-A, DEVA,40 mg/mL) was administered to facilitate visualization and complete adherent posterior cortical vitreous detachment. All fibrovascular membranes were peeled to the greatest extent possible. The internal limiting membrane was not peeled in any of the eyes. After a thorough examination of the entire retina, retinal tears and lesion areas were treated with laser photocoagulation, followed by 360° panretinal laser photocoagulation. Total air-fluid exchange was performed, followed by the implantation of a dexamethasone implant into all eyes after the retina was fully reattached. Finally, HSO was injected into the eyes. Eyes in Group 2 (n=42) underwent the same procedure, except without intraoperative dexamethasone implantation (patients with severe fundus conditions underwent posterior capsulotomy and iridectomy). Silicone oil was removed from all the eyes after 3 months. In eyes with significant posterior lens capsule opacification, an intraoperative excision of the optical zone (approximately 5 mm in diameter) was performed. Postoperatively, the two groups of patients both received eyedrops postoperatively.
2.5 Subsequent visits
IOP was evaluated on the day after surgery, as well as at one week, one month, and three months postoperatively. Slit-lamp biomicroscopy was performed to evaluate the anterior chamber reaction. BCVA was evaluated at the first week, first month, and third month following the surgery, while CMT was measured using OCT at the same time point. B-scan ultrasonography and laser scanning fundus photography were performed to observe whether retinal redetachment occurred after surgery. Simultaneously, a slit-lamp biomicroscope was used to observe whether posterior iris synechia and posterior capsular opacification had occurred. Intraoperatively, the extent of the anterior PVR and other complications were observed under the wide-field retinal viewing system. Patients may have received anti-VEGF therapy if macular oedema developed during the observation period or received appropriate medication if the IOP was >21mmHg.
2.6 Outcome measures
To minimize the risk of assessment bias related to subjective outcome measures, all outcome assessors in this study were blinded. Assessors were not involved in patient group assignment and, blinded to allocation, conducted evaluations according to standardized procedures.The main outcome measures consisted of BCVA and IOP at the first, third month; anterior PVR; posterior iris synechia; the retinal reattachment rate at the third month; and the occurrence of anterior chamber fibrin exudation at the first week. The secondary outcome measures included changes in CMT, the number of anti-VEGF agents administered within 3 months postoperatively, and the degree of posterior capsule opacification (PCO). Adverse events such as AC haemorrhage, silicone microemulsion in the AC, and vitreous rehaemorrhage were also analysedanalyzed.
2.7 Statistical analyses
Data analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). In this study, according to the types of data, the data are presented as the means, medians [IQR], standard deviations, and percentages. The analysis was conducted using the chi-square test, Shapiro-Wilk test, Fisher’s exact test, independent samples t-test, and nonparametric tests such as the Mann-Whitney U test or the Wilcoxon test. Kruskal–Wallis and Spearman. Statistical significance was defined as a P < 0.05. Difference Δ (Group 1 − Group 2) with 95% CIs is shown as the absolute difference in proportions (Newcombe method) for binary outcomes and as the Hodges–Lehmann median difference for continuous outcomes. P values are Bonferroni-adjusted (two-sided α = 0.05). We prespecified subgroup analyses by HbA1c (≤7.0%, 7.0–<9.0%, ≥9.0%) and age (≤51, 52–57, 58–63, >63 years). Three-month postoperative treatment effects on BCVA and anterior PVR were then estimated.
3 Results
3.1 Basic characteristics
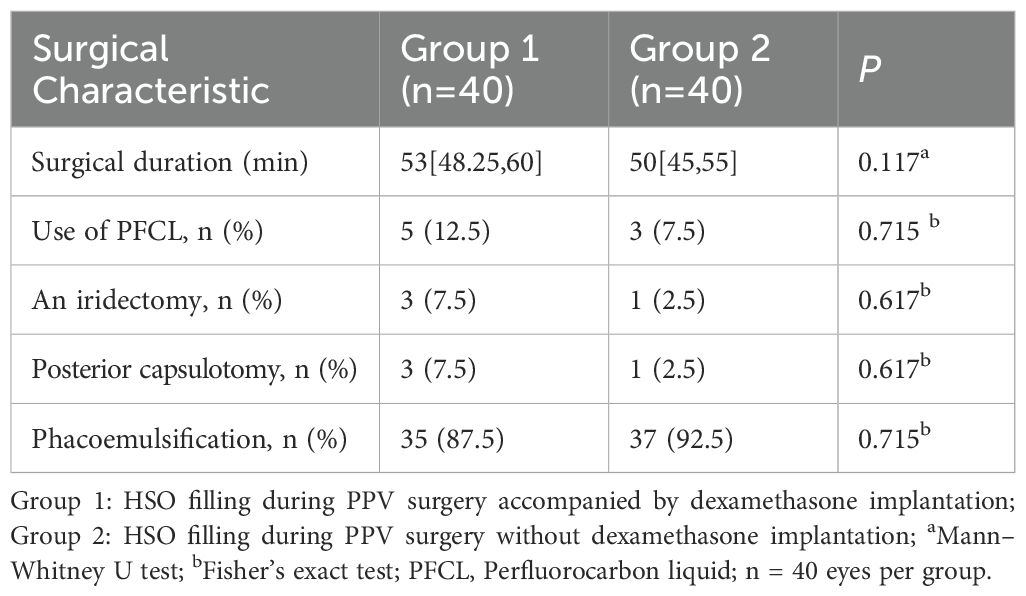
This prospective study comprised 96 eyes from 96 patients:54 eyes (54 patients) in Group 1 (PPV + HSO + dexamethasone implant,Figure 1) and 42 eyes (42 patients) in Group 2 (PPV + HSO). Ten patients were excluded from the final analysis because of failure to follow up on time, and six eyes were excluded because of dependence on silicone oil. The demographic and baseline characteristics are detailed in Table 1. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in age, sex, preoperative HbA1c levels, preoperative hypertension (P = 0.417, P = 0.823, P = 0.679, P = 0.340, respectively). The average preoperative BCVA was 1.70 [1.00, 1.70] in group 1 and 1.70 [1.06, 1.70] in group 2,P = 0.640.In group 1, the mean preoperative IOP was 16.75 ± 2.65 mmHg, while in group 2, it was 17.07 ± 2.54 mmHg, this difference was not significant (P = 0.583). Statistical analysis showed no statistically significant difference in the baseline CS scores between Group 1 and Group 2 (P = 0.898). Five patients in group 1 had IOLs, while three in group 2 had IOLs. The study included only patients who were above 40 years of age and had diabetes mellitus. The remaining 72 patients had cataracts and underwent phacoemulsification during vitrectomy. The surgical details between the two groups showed no significant difference (Table 2). The surgical duration was not significantly different between the two groups (P = 0.117). Due to the severity of their condition, 5 patients in Group 1 received perfluorocarbon liquid (PFCL) during surgery, 3 of whom underwent posterior capsulotomy and iridectomy. In Group 2, 3 patients also received PFCL during surgery, with 1 patient undergoing posterior capsulotomy and iridectomy.
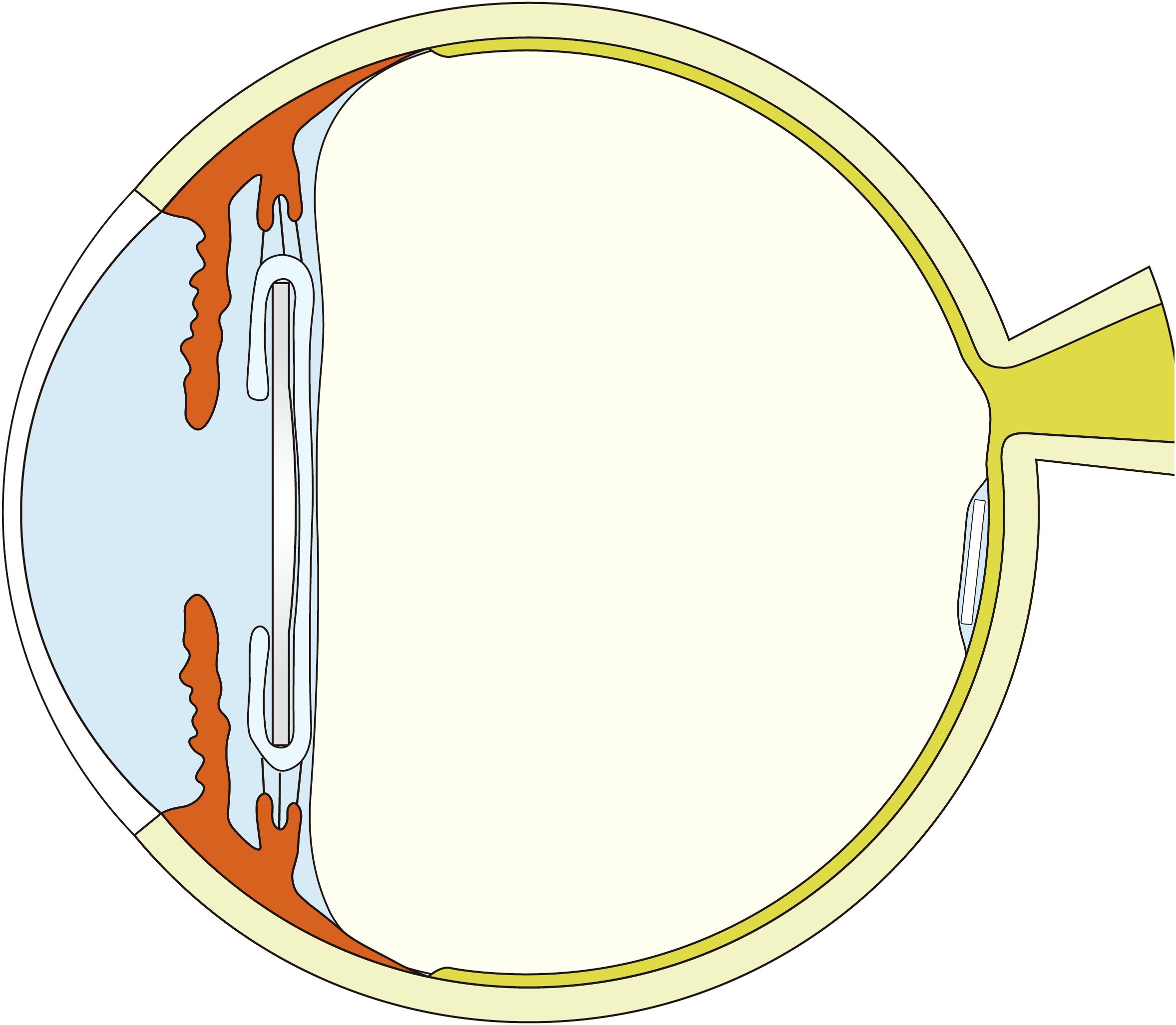
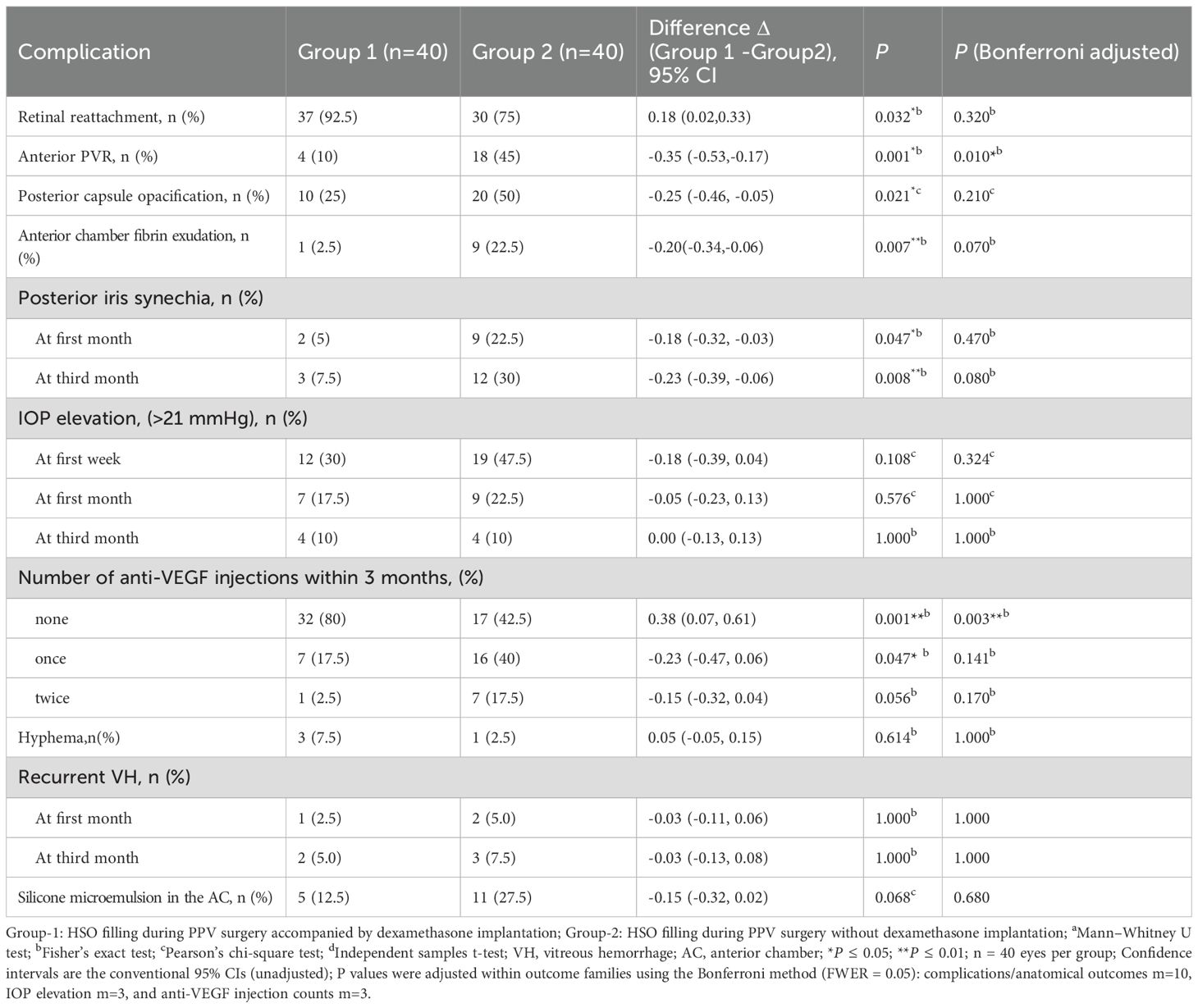
Figure 1. A schematic diagram: dexamethasone implant in a vitreous cavity filled with heavy silicone oil.
3.2 Visual acuity measurements
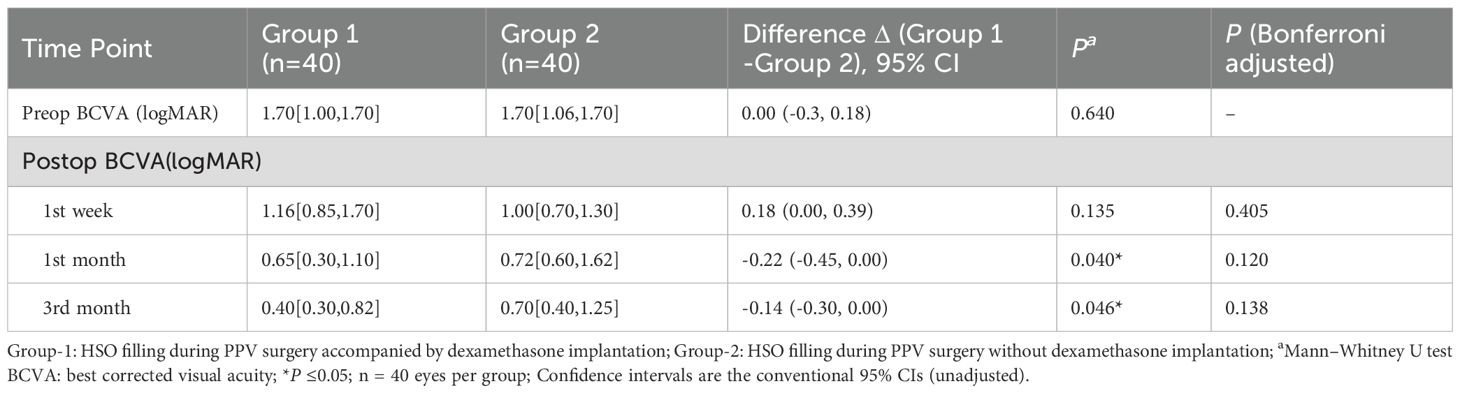
Both groups of patients showed improvement in vision postoperatively, with Group 1 experiencing a greater improvement in vision (Table 3, Figure 2). Group 1 had a mean preoperative LogMAR BCVA of 1.70 [1.00, 1.70], with significant improvements at the 1st week, 1st month, and 3rd month compared to baseline (all P <0.05,Bonferroni adjusted). Similarly, Group 2 had a mean preoperative BCVA of 1.70 [1.06, 1.70] LogMAR, with significant improvements in BCVA at the 1st week, 1st month, and 3rd month compared to baseline (P <0.001,Bonferroni adjusted). No significant difference in BCVA was observed between the two groups at baseline or 1 week postoperatively (P = 0.640, P = 0.135). However, at the first month, Group 1 showed a significantly greater improvement in BCVA than Group 2 (Group 1: 0.65 [0.30, 1.10], Group 2: 0.72 [0.60, 1.62], P = 0.040). At the third month, Group 1 demonstrated significantly BCVA compared to Group 2 (P = 0.046). However, after Bonferroni correction, neither the 1-month nor the 3-month postoperative comparisons were significant. In Group 1, 3-month BCVA differed across age strata (Kruskal–Wallis H = 9.902, P = 0.019), whereas treating age as a continuous variable showed no significant correlation with BCVA (Spearman ρ=−0.155, P = 0.339). In Group 2, 3-month postoperative BCVA differed across preoperative HbA1c strata (Kruskal–Wallis P = 0.039), whereas the overall correlation was not significant (Spearman ρ=−0.151, P = 0.354).
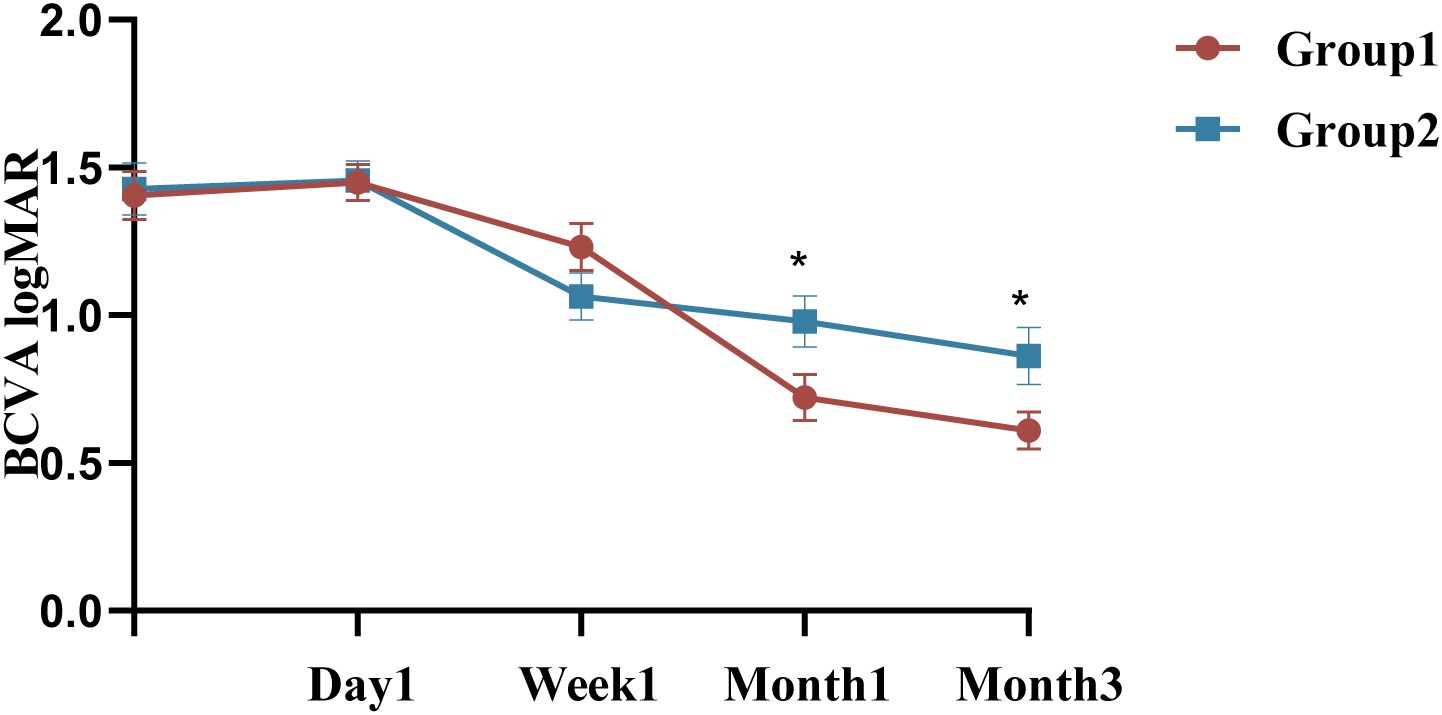
Figure 2. Changes and differences in BCVA between the two groups. BCVA: best corrected visual acuity; *P ≤ 0.05 (unadjusted); n = 40 eyes per group.
3.3 Intraocular pressure measurements
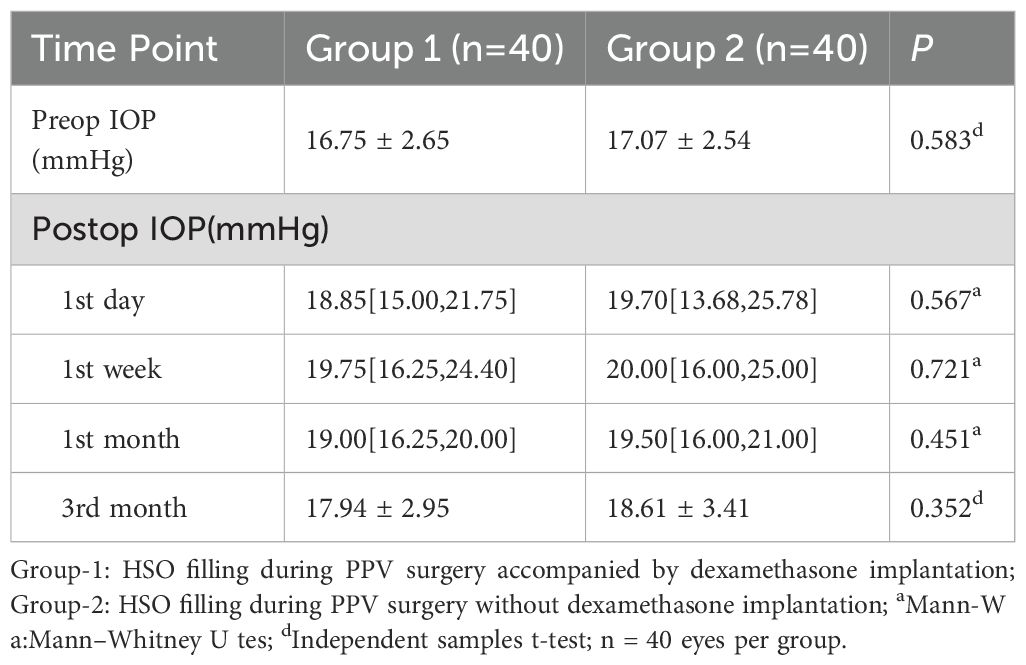
Group 1 had a mean preoperative IOP of 16.75 ± 2.65mmHg, with no significant variation in IOP at the 1st day, 1st month, or third month compared to baseline, P >0.05 (Figure 3). However, at the 1st week, the IOP in Group 1 was 19.75 [16.25, 24.40] mmHg, with a significant difference compared to baseline (P <0.05, Bonferroni adjusted). In contrast, the mean preoperative IOP in Group 2 was 17.07 ± 2.54 mmHg, with significant changes observed at all follow-up visits (P <0.05, Bonferroni adjusted). IOP measurements showed no statistically significant between Group 1 and 2 at any follow-up visit (P = 0.567, P = 0.721, P = 0.451, and P = 0.352, respectively), detailed summary is provided in Table 4. All patients with elevated IOP were treated with topical eye drops, and anterior chamber puncture was performed in a very small number of patients.
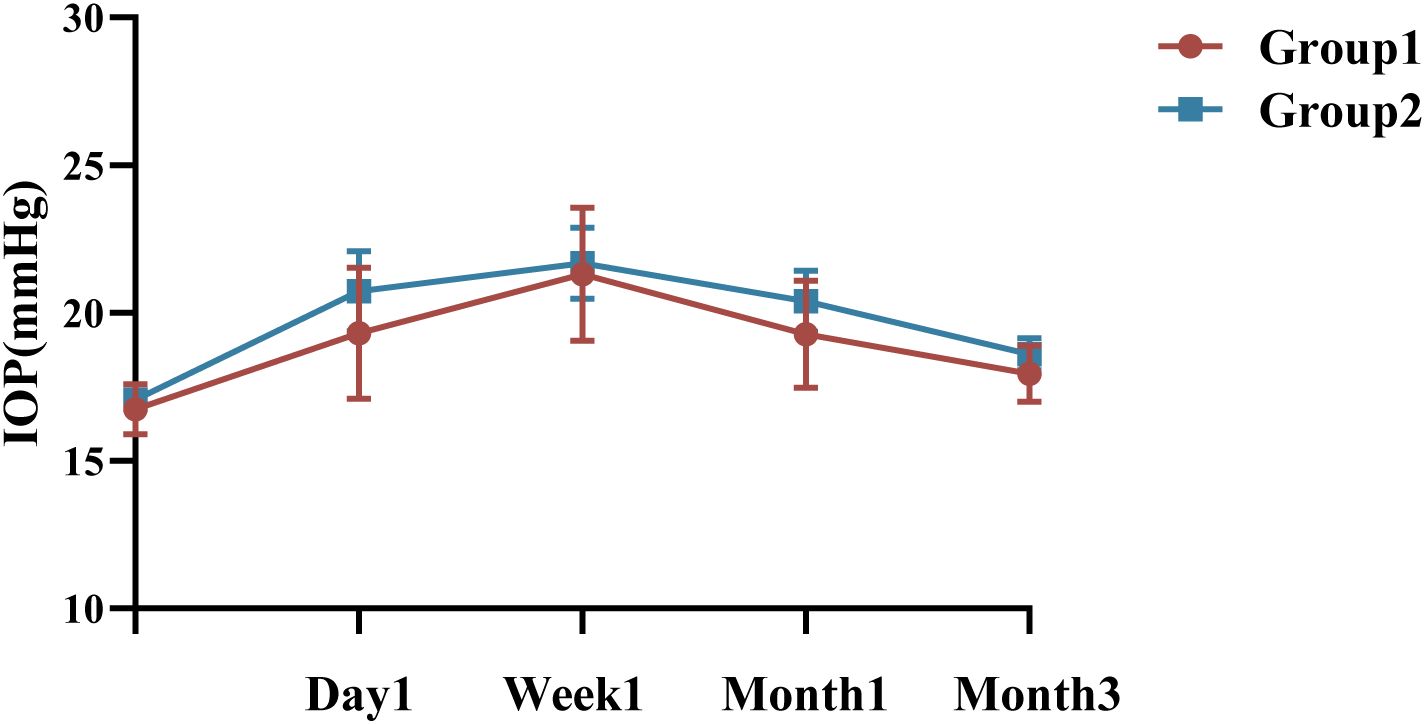
Figure 3. Changes and differences in IOP between the two groups. IOP, intraocular pressure; n = 40 eyes per group.
3.4 Variables and safety related to treatment
The rate of retinal reattachment at the third month was 92.5% in Group 1 and 75% in Group 2 (P = 0.032)(Figure 4). After three months, the incidence of anterior PVR differed significantly between the two groups (P = 0.001), with a significant surgical effect in group 1 (Figure 5). Additionally, Group 1 presented significantly lower rates of anterior chamber fibrin exudation at the 1st week, as well as reduced posterior iris synechia at months 1 and 3 (P = 0.047, P =0.008). However, after Bonferroni correction, only anterior PVR remained statistically significant (P = 0.010). Additionally, in the postoperative IOP observations, no statistically significant difference was observed in the proportion of patients exhibiting IOP >21 mmHg between groups at the 1st day, 1st week, 1st month, or 3rd month (P = 0.228, P = 0.108, P = 0.576, P = 1.000, respectively). At 1 week postoperatively, patients in Group 1 who required 1, 2, or 3 types of glaucoma medications numbered 8 (20%), 3 (7.5%), and 2 (5%), respectively; in addition, 1 patient (2.5%) underwent AC paracentesis. In Group 2, the corresponding numbers were 4 (10%), 3 (7.5%), and 3 (7.5%), with no patients requiring AC paracentesis. Although the proportion of patients requiring glaucoma medications and invasive intervention was slightly higher in Group 1, the differences between groups were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). At 1 month postoperatively, intraocular pressure control showed a marked improvement compared to the 1-week postoperative period. In Group 1, 2 (5%), 3 (7.5%), and 1 (2.5%) patients required 1, 2, or 3 medications, respectively. In Group 2, the corresponding numbers were 2 (5%), 2 (5%), and 1 (2.5%). No patients in either group required AC paracentesis. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups (P > 0.05). At 3 months postoperatively, only 2 patients (5%) in each group continued to require a single glaucoma medication, while all other patients achieved stable IOP without any treatment. At the third month, there was a significant difference in the number of anti-VEGF injections between the two groups.Especially among patients who received zero anti-VEGF injections, Group 1 had significantly more patients than Group 2, P = 0.003, after Bonferroni correction). (Figure 6). Other surgical complications did not differ significantly between the two groups, such as hyphema at the 1st month (P = 0.614), vitreous hemorrhage at the 1st month, 3rd month(P = 1.000,P = 1.000), and silicone microemulsion in the AC(P = 0.068). Detailed summary is provided in Table 5.
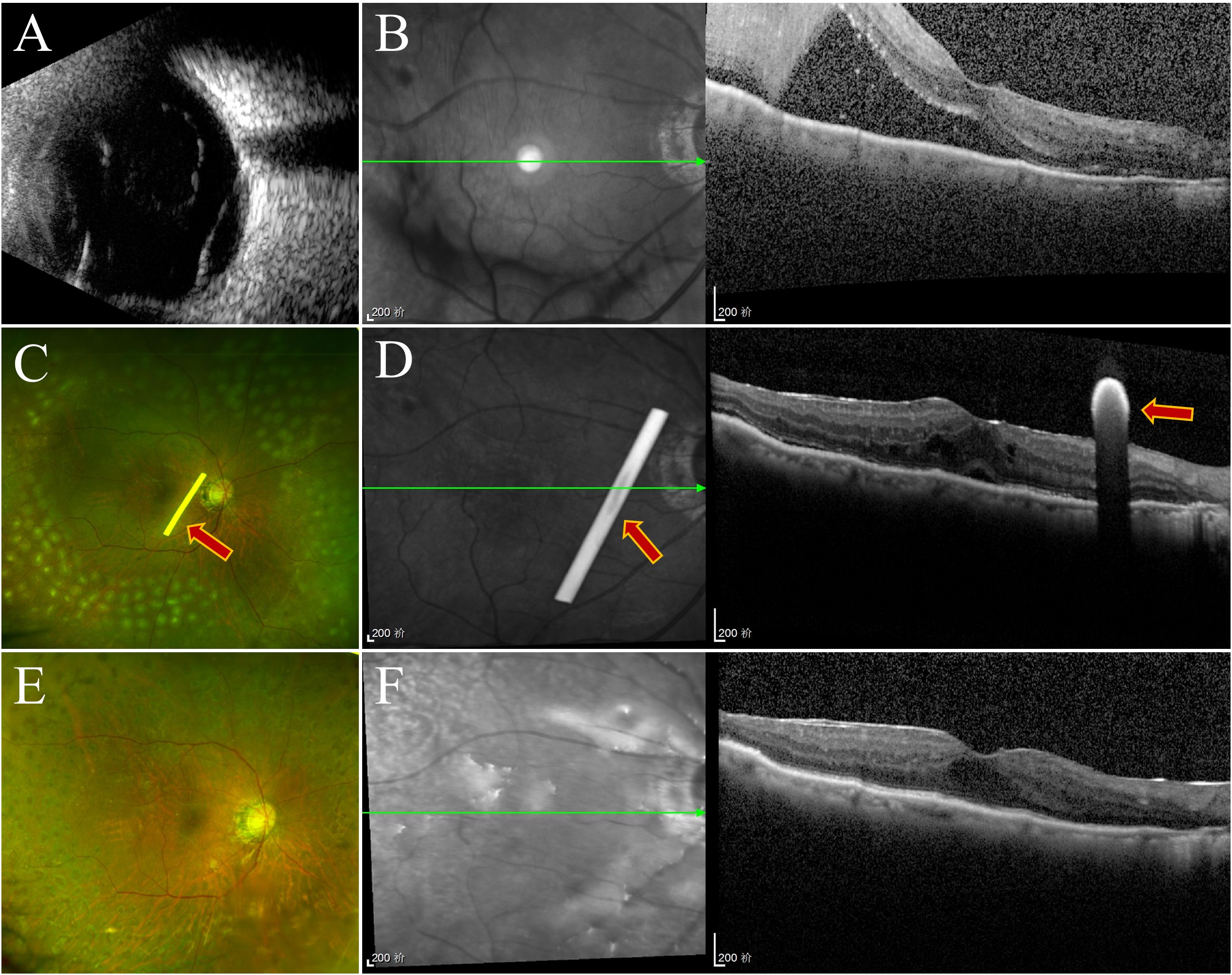
Figure 4. Follow-up examination of one patient in group 1. (A) Ultrasonography of the oculus dexter shows inferior retinal detachment. (B) Before surgery, OCT revealed retinal detachment. (C) SLO revealed silicone oil within the vitreous cavity, residual laser markings across the retina, and a white dexamethasone implant rod (marked with arrows). (D) OCT revealed that the retina was repositioned at the first week, and the dexamethasone implant was placed near the macular area (marked with arrows). (E, F) Three months later, the retina was repositioned, and the implant had been completely absorbed.
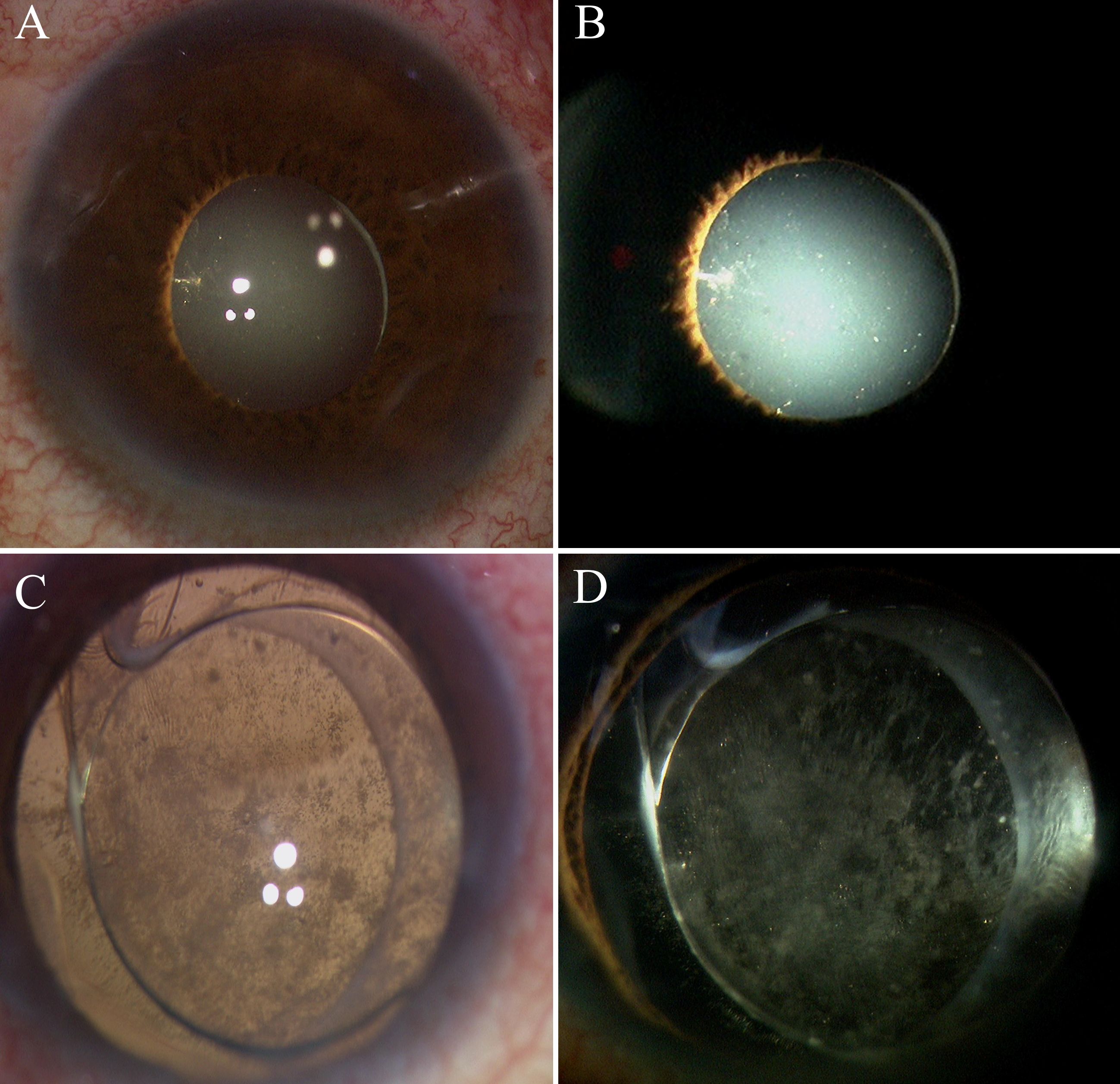
Figure 5. Intraoperative anterior segment observation in group 1 and group 2. (A, B) are from Group 1, and (C, D) are from Group 2. (A, B) No anterior proliferation was visible under the microscope during surgery. (C, D) Posterior capsule opacification and extensive anterior proliferative membranes were visible.
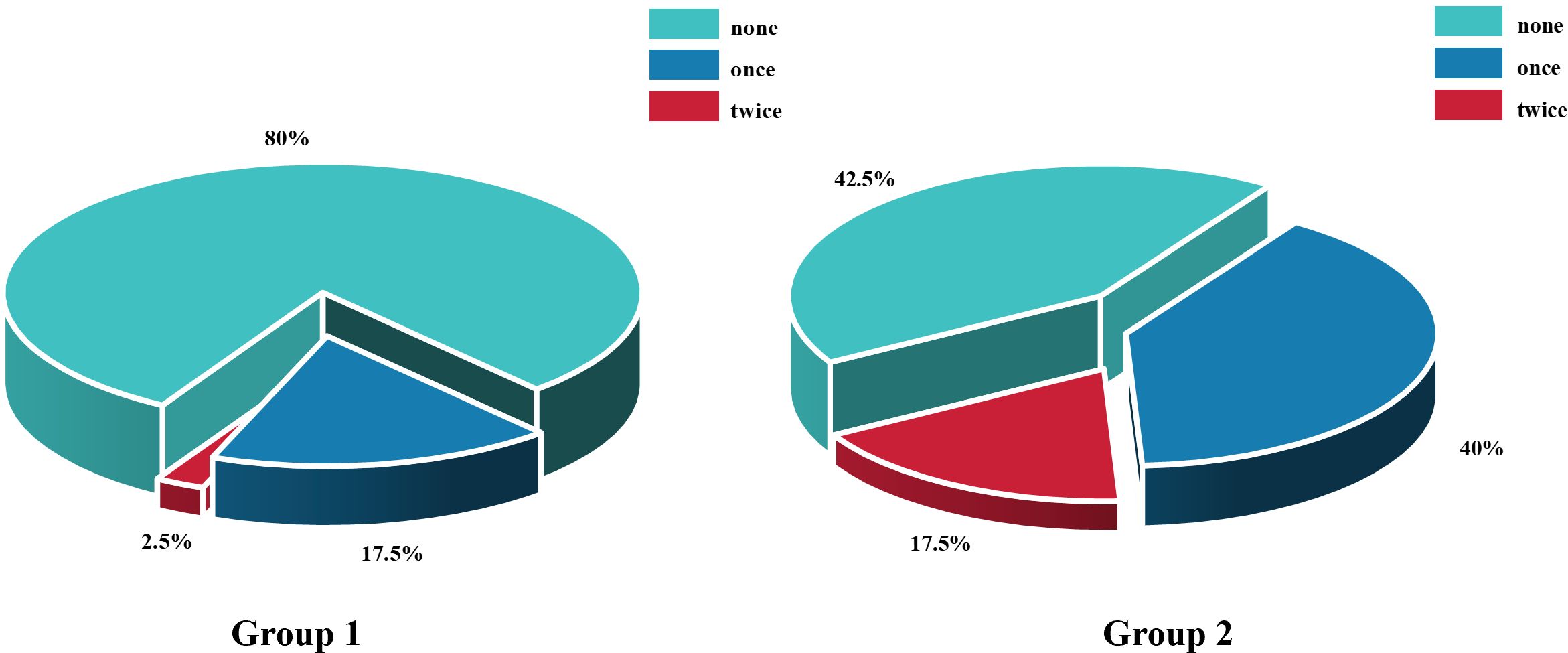
Figure 6. Comparison of the number of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injections between Group 1 and Group 2 within 3 months postoperatively. n = 40 eyes per group.
4 Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first clinical trial investigating surgical HSO filling combined with intravitreal DEX implantation in PDR patients undergoing PPV. This study prospectively evaluated the effects of HSO tamponade in patients with diabetic TRD undergoing PPV and to evaluate the role of extended-release hormone implantation in controlling inflammation and mitigating postoperative complications. Our results suggested that the implantation of dexamethasone following intravitreal HSO filling in diabetic TRD patients undergoing PPV led to markedly reduce the incidence of anterior PVR and lower the number of anti-VEGF injections within 3 months postoperatively. It was also associated with improved postoperative visual acuity and higher retinal reattachment rates, as well as lower rates of AC fibrin exudation, posterior iris synechiae, and PCO.
Animal studies have demonstrated that oxygen and antioxidant gradients in the eye change following vitrectomy, affecting the circulation of inflammatory cells (18). Furthermore, complex ocular surgery and increased risk factors for inflammation can result in increased levels of inflammatory factors (19, 20). Moreover, blood glucose level also plays an important role in the development of DR. In diabetic patients, elevated blood glucose can disorder the blood-aqueous barrier after surgery, leading to increased vascular permeability, elevated inflammatory mediators (21). But we only observed that in Group 2, 3-month postoperative BCVA differed across preoperative HbA1c, whereas the overall correlation was not significant. We think the short duration of follow-up and insufficient sample size limited our observations. Silicone oil is increasingly commonly utilized in patients with diabetes, RD, and PVR. Silicone oil can help PDR patients prevent recurrent haemorrhage, reset detached retinas, and suppress the development of PVR (22–24). Additionally, during the surgery, the operator will select light silicone oil (LSO) or HSO filling on the basis of the location of the retinal rupture and detached surface, the existence of PVR, and the patient’s overall health (25). Although silicone oils can help with disease recovery, they also increase the levels of vascular permeability-related inflammatory factors, which promote the development of ME (26). HSO is more prone to emulsification and irritation than regular silicone oil (27). Some investigations reported mild to moderate AC reactions, including fibrous membranes, keratic precipitates, pseudohypopyon, and hyphaema, with HSO filling for three months (28), Li W et al. observed that HSO can induce posterior chamber inflammatory reactions, such as the production of cataracts and deposits on the lens surface (29, 30). Morescalchi F proposed that HSO induces an inflammatory response by increasing cytokine levels in the vitreous cavity and that the cytokines involved are similar to those involved in PVR (31). The primary cause of recurrent RD in patients with diabetic TRD combined with cataracts is PVR and high levels of inflammatory factors. M. Sherif et al. retrospectively evaluated five cases of recurrent RD with stage C PVR and concluded that dexamethasone could be a therapeutic option for PVR (32). In this study, it was observed that 45% of patients who underwent HSO tamponade had anterior PVR at 3rd month. Utku Limoni et al. reported that implanting dexamethasone combined phacoemulsification and PPV in patients with diabetic TRD had a stable effect, confirming the importance of long-acting steroid dexamethasone implants (16). This research also confirmed that compared to Group 2, patients who received dexamethasone implantation had better postoperative outcomes in controlling anterior segment inflammation, reducing the probability of PVR and RD. PVR most commonly occurs within one month after RD surgery (77%) and by approximately 45 days in 95% of cases—indicating a relatively acute process (33). And anterior PVR can be identified and evaluated more effectively at the time of silicone oil removal. However, as some PVR and RD may arise over extended follow-up, our study has inherent limitations in evaluating long-term outcomes. Compared to LSO, HSO exhibits a greater tendency to emulsify due to its lower viscosity (27). This leads to a significantly increased accumulation of oil globules in the AC, on the iris surface, and along the posterior surface of the cornea. Similarly, in our study, numerous silicone oil globules were observed on the posterior surface of the lens capsule in many patients during HSO removal surgery. These globules not only exacerbated intraocular inflammation but also contributed to the development of anterior PVR and PCO, as well as elevated IOP. The incidence of HSO microemulsions in the AC was 12.5% in patients who received dexamethasone implants, compared to 27.5% in those without the implant. This difference is presumed to be associated with the anti-inflammatory properties of dexamethasone. In addition, no detailed assessment was conducted in this study, and further improvements are needed moving forward.
Clinical studies have shown that the use of Ozurdex® after vitrectomy is safe and effective in reducing DME (34–36). Hsu and Cherng-Ru reviewed 12 eyes and confirmed that the DEX implant could help manage recurrent macular oedema (ME) in patients who had undergone vitrectomy with silicone oil filling (37). Additionally, Altun reported that administering a dexamethasone implant and silicone oil filling during vitrectomy in individuals with proliferative PDR not only reduced recurrent DME but also decreased the number of anti-VEGF agents (38). The majority of patients in this study had VH and TRD preoperatively; thus, we were unable to collect preoperative CMT values. However, by comparing the number of anti-VEGF injections administered three months postoperatively, we found a significant difference between the two groups (P <0.001). Additionally, we observed that the CMTs of some patients in Group 1 remained lower than their values from the first week.The per-treatment cost of the dexamethasone implant is comparable to that of other anti-VEGF agents. However, due to its sustained-release properties, the implant may reduce the need for frequent injections, thereby decreasing overall treatment burden and associated costs. Furthermore, it provides a valuable option for patients with low follow-up adherence.
Dexamethasone implants are known to cause an increase in IOP and accelerate cataract progression. Therefore, all patients included in this study underwent phacoemulsification with vitrectomy, with postoperative IOP monitoring. The results revealed a statistically significant difference in IOP at the first week between Group 1 and the baseline level (P <0.001). Compared with the baseline IOP, Group 2 showed a marked statistical difference at different time points (P < 0.05). The IOP reached its peak at the first week in both groups, which may be attributed to the higher rate of retinectomy. The disruption of the blood–ocular barrier during surgery likely led to an increase in inflammatory factors, which are consistent with those reported by Wong D et al. (39). However, IOP did not differ significantly between two groups at the first day, first week, or months 1 or 3. Patients with IOP >21 mmHg were counted separately, and no significant differences were observed between the two groups at any of the time points. The majority of patients in this study with elevated IOP were treated with topical eye drops, and their IOP was effectively controlled. Moreover, our results show that, over time, the number of patients requiring pharmacologic therapy and AC paracentesis gradually decreased. The 3-month postoperative follow-up indicates that the dexamethasone implant appears to be safe.This result is consistent with the findings of the Ozurdex PLACID study group and a 12-month multicentre prospective clinical trial, which demonstrated that dexamethasone implants cause transient IOP increases that can be managed with medication (40, 41). Silicone oil is not only toxic to the retina but also increases the risk of postoperative complications with prolonged filling time (42). Before surgery, the doctor examines the peripheral retina and vitreous. For patients with a favourable recovery, silicone oil is generally removed after three months. The development of PCO is influenced by multiple factors, including blood glucose levels, inflammatory mediators, IOL types, and the effect of silicone oil. Considering that anterior PVR may interfere with the assessment of the posterior capsule, we believe that although a difference in the incidence of PCO was observed between the two groups in this study, it cannot be conclusively attributed to the anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone.
Based on the above discussion, the occurrence of complications such as anterior PVR, PCO, and SO emulsification is influenced by many complex factors (21, 43). Compared with HSO, LSO tamponade may be associated with a lower incidence of anterior PVR and silicone oil emulsification.Considering the factors outlined above,we plan to include a LSO control group in future studies to systematically investigate the effects of dexamethasone implants on key outcomes.This will allow for a more in-depth exploration of whether dexamethasone can effectively suppress the inflammatory responses potentially triggered by HSO itself. Furthermore, in view of the potential for late postoperative PVR and recurrent RD, we have planned a multicenter, prospective clinical trial with 12-month follow-up that includes a LSO control group.
5 Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the effect of dexamethasone implants in eyes with HSO tamponade in patients with PDR. Our preliminary findings suggest that intraoperative use of dexamethasone implants may be a safe and potentially beneficial adjunctive treatment strategy for diabetic TRD patients undergoing phacoemulsification combined with vitrectomy and HSO tamponade. Over the 3-month postoperative observation period, the dexamethasone implant demonstrated potential in reducing inflammatory responses and decreasing the need for postoperative anti-VEGF medications. The findings of this study provide a valuable direction for future research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
XZ: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization. JD: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Software. HL: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Data curation. MS: Software, Writing – review & editing. SX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – original draft, Data curation. YP: Writing – original draft, Data curation. DS: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. BJ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Yau JWY, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, et al. Meta-Analysis for Eye Disease (META-EYE) Study Group.Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. (2012) 35:556–64. doi: 10.2337/dc11-1909
2. Saaddine JB, Honeycutt AA, Narayan KM, Zhang X, Klein R, and Boyle JP. Projection of diabetic retinopathy and other major eye diseases among people with diabetes mellitus: United States, 2005–2050. Arch Ophthalmol. (2008) 126:1740–47. doi: 10.1001/archopht.126.12.1740
3. Ohlhausen M, Payne C, Greenlee T, Chen AX, Conti T, and Singh RP. Impact and characterization of delayed pan-retinal photocoagulation in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. (2021) 223:267–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2020.09.051
4. Antonetti DA, Klein R, and Gardner TW. Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:1227–39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1005073
5. Rübsam A, Parikh S, and Fort PE. Role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:942. doi: 10.3390/ijms19040942
6. Kumagai K, Furukawa M, Ogino N, Larson E, Iwaki M, and Tachi N. Long-term follow-up of vitrectomy for diffuse nontractional diabetic macular edema. Retina. (2009) 29:464–72. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e31819c632f
7. Rosenblatt BJ, Shah GK, Sharma S, and Bakal J. Pars plana vitrectomy with internal limiting membranectomy for refractory diabetic macular edema without a taut posterior hyaloid. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. (2005) 243:20–5. doi: 10.1007/s00417-004-0958-z
8. Semeraro F, Russo A, Morescalchi F, Gambicorti E, Vezzoli S, Parmeggiani F, et al. Comparative assessment of intraocular inflammation following standard or heavy silicone oil tamponade: a prospective study. Acta Ophthalmol. (2019) 97:e97–e102. doi: 10.1111/aos.13830
9. Freeman HM, Elner SG, Tolentino FI, Schepens CL, Elner VM, and Albert DM. Anterior PVR part I: clinical findings and management. In: Freeman HM and Tolentino FI, editors. Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy (PVR). Springer, New York, NY (1988). doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3910-9_3
10. Machemer R, Aaberg TM, Freeman HM, Irvine AR, Lean JS, and Michels RM. An updated classification of retinal detachment with proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. (1991) 112:159–65. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76695-4
11. Huang CH and Yang CM. Recurrent retinal detachment after diabetic vitrectomy. Int Ophthalmol. (2020) 40:1931–9. doi: 10.1007/s10792-020-01366-9
12. Sarao V, Veritti D, Boscia F, and Lanzetta P. Intravitreal steroids for the treatment of retinal diseases. ScientificWorldJournal. (2014) 2014:989501. doi: 10.1155/2014/989501
13. Tamura H, Miyamoto K, Kiryu J, Miyahara S, Katsuta H, Hirose F, et al. Intravitreal injection of corticosteroid attenuates leukostasis and vascular leakage in experimental diabetic retina. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci. (2005) 46:1440–4. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0905
14. Iglicki M, Zur D, Fung A, Gabrielle P-H, Lupidi M, Santos R, et al. TRActional DIabetic reTInal detachment surgery with co-adjuvant intravitreal dexamethasONe implant: the TRADITION STUDY. Acta Diabetol. (2019) 56:1141–7. doi: 10.1007/s00592-019-01357-y
15. Hwang S, Kang SW, Kim KT, Noh H, and Kim SJ. Three-year outcomes of vitrectomy combined with intraoperative dexamethasone implantation for non-tractional refractory diabetic macular edema. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:1292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80350-w
16. Limon U and Sezgin Akçay BI. Efficacy of intravitreal dexamethasone after combined phacoemulsification and pars plana vitrectomy for diabetic tractional retinal detachments. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 38:176–82. doi: 10.1089/jop.2021.0072
17. Castellarin A, Grigorian R, Bhagat N, Del Priore L, and Zarbin MA. Vitrectomy with silicone oil infusion in severe diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. (2003) 87:318–21. doi: 10.1136/bjo.87.3.318
18. Siegfried CJ, Shui Y-B, Tian B, Nork TM, Heatley GA, and Kaufman PL. Effects of vitrectomy and lensectomy on older rhesus macaques: oxygen distribution, antioxidant status, and aqueous humor dynamics. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci. (2017) 58:4003–14. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-21890
19. Romano V, Angi M, Scotti F, del Grosso R, Romano D, Semeraro F, et al. Inflammation and macular oedema after pars plana vitrectomy. Mediators Inflammation. (2013) 2013:971758. doi: 10.1155/2013/971758
20. Kiss C, Richter-Müksch S, Sacu S, Benesch T, and Velikay-Parel M. Anatomy and function of the macula after surgery for retinal detachment complicated by proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. (2007) 144:872–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2007.08.001
21. Liu Y, Luo L, He M, and Liu X. Disorders of the blood-aqueous barrier after phacoemulsification in diabetic patients. Eye (Lond). (2004) 18:900–4. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6701349
22. Tsui I and Schubert HD. Retinotomy and silicone oil for detachments complicated by anterior inferior proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. (2009) 93(9):1228–33. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2008.140988
23. Balakrishnan D, Jain B, Nayaka A, Rani PK, Mukundaprasad V, et al. Role of Tamponade in Vitrectomy for Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy with Vitreous Hemorrhage. Semin Ophthalmol. (2017) 32(4):488–91. doi: 10.3109/08820538.2015.1120757
24. Shen Y-D and Yang C-M. Extended silicone oil tamponade in primary vitrectomy for complex retinal detachment in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: a long-term follow-up study. Eur J Ophthalmol. (2007) 17:954–60. doi: 10.1177/112067210701700614
25. Kocak I and Koc H. Comparison of Densiron 68 and 1–000 cSt silicone oil in the management of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with inferior breaks. Int J Ophthalmol. (2013) 6:81–4. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.01.17
26. Bae SH, Hwang JS, and Yu HG. Comparative analysis of macular microstructure by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography before and after silicone oil removal. Retina (Philadelphia Pa.). (2012) 32:1874–83. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e318246907c
27. Morescalchi F, Costagliola C, Duse S, Gambicorti E, Parolini B, Arcidiacono B, et al. Heavy silicone oil and intraocular inflammation. BioMed Res Int. (2014) 2014:574825. doi: 10.1155/2014/574825
28. Theelen T, Tilanus MAD, and Klevering BJ. Intraocular inflammation following endotamponade with high-density silicone oil. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. (2004) 242:617–20. doi: 10.1007/s00417-004-0898-7
29. Li W, Zheng Q, Wang X, Xu M, and Wu R. Clinical results of Densiron 68 intraocular tamponade for complicated retinal detachment. Ophthalmologica. (2010) 224:354–60. doi: 10.1159/000313817
30. Ozdek S, Yuksel N, Gurelik G, and Hasanreisoglu B. High-density silicone oil as an intraocular tamponade in complex retinal detachments.Canadian journal of ophthalmology. J Canadien D’ophtalmol. (2011) 46:51–5. doi: 10.3129/i10-107
31. Morescalchi F, Duse S, Gambicorti E, Romano MR, Costagliola C, and Semeraro F. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy after eye injuries: an overexpression of growth factors and cytokines leading to a retinal keloid. Mediators Inflammation. (2013) 2013:269787. doi: 10.1155/2013/269787
32. Sherif M and Wolfensberger TJ. Intraocular dexamethasone implant as adjunct to silicone oil tamponade for proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Klinische Monatsblatter fur Augenheilkunde. (2017) 234:501–4. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-122384
33. Pastor JC, Rojas J, Pastor-Idoate S, Di Lauro S, Gonzalez-Buendia L, and Delgado-Tirado S. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy: A new concept of disease pathogenesis and practical consequences. Prog Retin Eye Res. (2016) 51:125–55. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.07.005
34. Lowder C, Belfort R, Lightman S, Foster CS, Robinson MR, Schiffman RM, et al. Dexamethasone intravitreal implant for noninfectious intermediate or posterior uveitis. Arch Ophthalmol (Chicago Ill: 1960). (2011) 129:545–53. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.339
35. Chang-Lin J-E, Burke JA, Peng Q, Lin T, Orilla WC, Ghosn CR, et al. Pharmacokinetics of a sustained-release dexamethasone intravitreal implant in vitrectomized and nonvitrectomized eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci. (2011) 52:4605–9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6387
36. Kim KT, Jang JW, Kang SW, Chae JB, Cho K, and Bae K. Vitrectomy combined with intraoperative dexamethasone implant for the management of refractory diabetic macular edema. Korean J Ophthalmol: KJO. (2019) 33:249–58. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2018.0100
37. Hsu C-R, Hsieh Y-T, Yang C-M, and Lin C-P. Single-dose effect of intravitreal dexamethasone implant for post-vitrectomy macular edema under silicone oil. Ocul Immunol Inflammation. (2023) 31:1587–93. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2021.1970779
38. Altun A, Kanar HS, Aki SF, Arsan A, and Hacisalihoglu A. Effectiveness and safety of coadministration of intravitreal dexamethasone implant and silicone oil endotamponade for proliferative diabetic retinopathy with tractional diabetic macular edema. J Ocular Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 37:131–7. doi: 10.1089/jop.2020.0079
39. Wong D, Kumar I, Quah SA, Ali H, Valldeperas X, and Romano MR. Comparison of postoperative intraocular pressure in patients with Densiron-68 vs conventional silicone oil: a case-control study. Eye (London England). (2009) 23:190–4. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6703055
40. Callanan DG, Gupta S, Boyer DS, Ciulla TA, Singer MA, Kuppermann BD, et al. Dexamethasone intravitreal implant in combination with laser photocoagulation for the treatment of diffuse diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. (2013) 120:1843–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.02.018
41. Haller JA, Bandello F, Belfort R, Blumenkranz MS, Gillies M, Heier J, et al. Dexamethasone intravitreal implant in patients with macular edema related to branch or central retinal vein occlusion twelve-month study results. Ophthalmology. (2011) 118:2453–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.05.014
42. Pichi F, Hay S, and Abboud EB. Inner retinal toxicity due to silicone oil: a case series and review of the literature. Int Ophthalmol. (2020) 40:2413–22. doi: 10.1007/s10792-020-01418-0
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy1, diabetic tractional retinal detachment2, dexamethasone implants 3, pars plana vitrectomy4, heavy silicone oi5
Citation: Zhang X, Dong J, Lu H, Sun M, Xu S, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Sun D and Jiang B (2025) The anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone implants in eyes with heavy silicone oil: a prospective study on vitrectomy for diabetic retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1673884. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1673884
Received: 26 July 2025; Accepted: 06 October 2025;
Published: 17 October 2025.
Edited by:
Khalid Siddiqui, Kuwait University, KuwaitReviewed by:
Ari Andayani, Udayana University, IndonesiaRuksar Fatima, Khaja Bandanawaz University, India
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Dong, Lu, Sun, Xu, Zhang, Peng, Sun and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dawei Sun, c3VuZGF3ZWlAaHJibXUuZWR1LmNu; Bo Jiang, ZXllamlhbmdib0AxMjYuY29t
 Xingguo Zhang
Xingguo Zhang Junliang Dong
Junliang Dong Haomin Lu1
Haomin Lu1 Bo Jiang
Bo Jiang