- 1Endocrinology and Metabolism Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
- 2Alice Lee Centre for Nursing Studies, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
- 3School of Nursing, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang, Henan, China
- 4Ministry of Health Holdings, Singapore, Singapore
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and dual agonists have been shown to induce histological improvements in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). However, current clinical evidence on their effectiveness in improving hepatic fibrosis and cardiovascular outcomes remains limited and inconsistent.
Methods: This study synthesized randomized controlled trials (RCTs) from major databases up to August 30, 2025, focusing on patients with biopsy-confirmed MASH. Pooled mean differences were calculated using either a fixed-effects or random-effects model, depending on the degree of heterogeneity observed among the studies.
Results: Six studies including 1,726 participants were analyzed. Compared with placebo, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists significantly increased the likelihood of histological improvement in MASH without worsening hepatic fibrosis. (OR: 4.51, 95% CI: 3.68 to 5.52). It was associated with a ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis without worsening MASH (OR: 1.78; 95% CI: 1.47to2.16). In addition, it contributed to MASH resolution accompanied by a ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis (OR: 7.42; 95% CI: 2.98to18.48). In subgroup analyses based on post-treatment weight loss, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists demonstrated significant efficacy in promoting hepatic fibrosis resolution without worsening MASH among patients achieving a ≥10% weight loss (OR: 9.59; 95% CI: 4.01to15.18). However, in patients with <10% weight loss, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists did not demonstrate significant differences (OR: 1.30; 95% CI: 0.92to1.83). Moreover, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists achieved a significant pooled reduction in cardiovascular parameters, including total cholesterol (WMD: −4.15 mmol/L; 95% CI: −13.13 to 4.82) and triglycerides (WMD: −17.70 mmol/L; 95% CI: −21.95 to −13.44). Nevertheless, no significant improvement was observed in Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) levels (WMD: −0.67 mmol/L; 95% CI: −6.55 to 5.21).
Conclusion: In patients with MASH who achieve a ≥10% weight loss, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists are associated with significant improvements in hepatic fibrosis, whereas their effect is limited in those with <10% weight loss. However, a significant reduction in LDL-C was observed only among patients achieving substantial (≥10%) weight loss. This finding suggests that for patients requiring comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, additional lipid-lowering strategies may be needed to optimize the effectiveness of the intervention.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42025640318.
Study importance
What is already known?
● GLP-1RAs and dual agonists have been approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity
● These agents significantly reduce body weight, promote MASH resolution, and improve hepatic fibrosis in patients with MASH.
● These agents are associated with improvements in hepatic-related biomarkers, including Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) and Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT).
What does this study add?
● The degree of weight loss plays a crucial role in the improvement of hepatic fibrosis among MASH patients treated with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists.
● Although GLP-1RAs and dual agonists do not directly lower LDL-C in patients with MASH, a significant reduction was observed in those achieving ≥10% weight loss. Conversely, weight loss of <10% was not associated with a reduction in LDL-C.
● This study emphasizes the critical need for monitoring cardiovascular risk in patients with comorbid dyslipidemia.
How might these results change the direction of research or the focus of clinical practice?
● The degree of weight loss may serve as a predictor of hepatic fibrosis improvement in patients with MASH.
● Further research is needed in MASH patients with <10% weight loss to determine whether GLP-1RAs and dual agonists provide meaningful improvements in hepatic fibrosis.
● Monitoring LDL-C levels is essential during treatment with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists, with lipid-lowering interventions implemented as needed.
1 Introduction
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is an increasingly prevalent contributor to the global burden of liver disease, affecting approximately 5% of adults worldwide (1). Its prevalence is substantially higher among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity, reaching 66.4% and 34%, respectively (1, 2). Advanced hepatic fibrosis is also common in these populations, with stage F3 and F4 fibrosis affecting 11.66% and 1.71%, respectively (3). These findings highlight the high prevalence of MASH in overweight and obese populations and its close association with clinically significant and progressive hepatic fibrosis. MASH is characterized by excessive hepatic fat accumulation, which triggers lipotoxicity and subsequently promotes hepatocellular inflammation and injury. This multifactorial condition is closely associated with metabolic dysfunction, with hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance playing central roles in its pathogenesis (3, 4).The development of hepatic fibrosis in MASH results from persistent hepatocellular inflammation and recurrent hepatocyte damage throughout disease progression (5).This pathological process disrupts the balance between synthesis and degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM), leading to excessive ECM deposition and ultimately promoting the development of hepatic fibrosis (6).
In recent years, treatment strategies for MASH have advanced considerably, with both lifestyle interventions and pharmacotherapies showing promising efficacy (7–9). Evidence suggests that a 5–7% reduction in body weight can improve hepatic steatosis, whereas a ≥10% weight loss may help reverse hepatic fibrosis (10–12). Moreover, the introduction of both single and multi-target pharmacological agents has markedly expanded the therapeutic landscape for MASH (13). Treatments using glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), particularly those involving dual agonists, offer distinct therapeutic advantages. Specifically, GLP-1 activation improves insulin sensitivity and promotes weight loss; modulation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptors (GIPR) reduces hepatic lipogenesis and steatosis; and activation of glucagon receptors (GCGR) enhances energy expenditure and lipid mobilization (14–16). It is also important to emphasize that the precise receptor selectivity of GLP-1 RAs and GLP-1/GIP dual agonists underlies their efficacy and safety. GLP-1RAs demonstrate high specificity for GLP-1R, showing no detectable activity on GIPR or GCGR even at concentrations up to 1 μM (17–19). GLP-1/GIP dual agonists efficiently activate both GLP-1R and GIPR, with potency surpassing that of native GLP-1 and GIP, while inducing only weak activation of GCGR at supraphysiological concentrations and remaining completely unable to antagonize glucagon function. Clinical Positron Emission Computed Tomography (PET) imaging further confirmed that these dual agonists show very low GCGR occupancy in humans (11.2 ± 14.4%), with no statistical significance (17–19).Therefore, GLP-1RAs selectively activate GLP-1R without affecting GIPR or GCGR, whereas GLP-1/GIP dual agonists primarily synergistically activate both GLP-1R and GIPR, with no significant pharmacological activity on GCGR. In addition to their core advantage of precise receptor selectivity, GLP-1 RAs and GLP-1/GIP dual agonists can also provide additional physiological protective effects through other mechanisms. For example, regarding vascular endothelial protection, these agents can mitigate oxidative stress by inhibiting the activation of the Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Hydrogen (NADPH) oxidase complex, specifically via downregulation of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase 4(NOX4) expression and blockade of p47^phox translocation. They can also suppress the expression of adhesion molecules, such as Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1(VCAM-1), thereby reducing inflammatory responses and providing multifaceted protection to the vascular endothelium (20, 21). Such multi-target strategies offer a promising approach to address the complex pathophysiology of MASH.
Despite growing interest in GLP-1RAs and dual agonists, current clinical trial evidence remains inconsistent. In particular, their efficacy and safety in improving hepatic fibrosis are unclear, as is their impact on cardiometabolic markers. While reductions in total cholesterol and triglycerides have been observed, effects on Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) remain uncertain. Although recent MASH management guidelines recognize (22) the potential of dual agonists in reducing disease activity and mitigating hepatic fibrosis worsening, conclusive histological evidence for hepatic fibrosis reversal is still lacking (22). Given the critical knowledge gaps outlined above, this meta-analysis aims to: (1) synthesize existing evidence to evaluate the histological efficacy of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists in MASH; (2) assess the dose–response relationship on treatment outcomes; and (3) systematically examine modulating cardiometabolic parameters, thereby clarifying their therapeutic potential in mitigating residual cardiovascular risk, as dysregulated cardiometabolic parameters are recognized contributors to atherosclerotic progression in patients with MASH.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design
The protocol for this meta-analysis was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42025640318). The study was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The PRISMA checklist was adhered to throughout the review to ensure methodological transparency and consistency (23).
This study employs a systematic review approach to synthesize findings from multiple RCTs, aiming to provide a more accurate estimate of the overall treatment effect of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists on hepatic histology and cardiovascular parameters in patients with MASH, and to explore the influence of weight change on their efficacy.
2.2 Literature search strategy
Electronic databases, including the Cochrane Library, Embase, MEDLINE (via PubMed), CENTRAL, and Web of Science, were systematically searched. The initial search was conducted on July 21, 2024, and subsequently updated on August 30, 2025, to identify RCTs evaluating the effects of GLP-1 RAs and dual agonists in the treatment of MASH. Key search terms such as “Non-alcoholic Fatty Hepatic Disease,” “Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis,” “MASH,” “GLP-1 receptor agonist,” “semaglutide,” “dulaglutide,” “dual agonists,” “Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide,” and “Glucose Dependent Insulinotropic Peptide” were used in the search strategy. A detailed description of the search strategy, including the specific search strings, is provided in Supplementary Materials 2. Reference lists from relevant systematic reviews and included studies were also screened for studies to be included. To ensure that all relevant articles were included, searches were conducted in the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), American Diabetes Association (ADA), International Diabetes Federation (IDF), American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), and ClinicalTrials.gov for other potential studies to be included.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria for the studies were as follows: (1) MASH diagnosis confirmed by hepatic biopsy at enrollment; (2) randomized controlled trial (RCT) design; (3) comparison of the efficacy of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists versus placebo in patients with MASH; (4) treatment duration of at least 24 weeks; and (5) primary efficacy endpoints assessed by repeat hepatic biopsy. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) repeated publications; (2) post hoc analysis; (3) articles that did not report main outcome measures defined in this article; and (4) articles that did not provide needed data; (5) all observational studies, reviews, meta-analyses, conference proceedings, editorials, commentaries, and unpublished articles; (6) For studies with overlapping participant pools or data sources, only the most comprehensive papers were selected. Hepatic biopsy has been regarded as the gold standard for diagnosing and staging steatohepatitis and hepatic fibrosis, particularly in patients with unclear clinical symptoms. Therefore, only studies with hepatic biopsy-proven MASH were included (22). MASH is defined as hepatic steatosis (HS) involving ≥5% of hepatic tissue, accompanied by hepatocellular inflammation and injury (e.g., hepatocyte ballooning), with or without hepatic fibrosis. Diagnosis requires hepatic histopathological examination and the exclusion of similar pathological changes attributable to other established etiologies (e.g., viral hepatitis, drug-induced hepatocellular injury) (24, 25).
2.4 Data extraction
All identified records were imported into EndNote (version 21.5) for deduplication. Two independent reviewers performed the study selection and data extraction. Any conflicts in screening or extraction were resolved through discussion or, when necessary, by referral to a third reviewer. A PRISMA flowchart visually depicts the study selection process (Figure 1). Data were extracted into a pre-determined data sheet, which focused on participant demographics (age, gender, body mass index [BMI], body weight, and comorbidity with type 2 diabetes), study characteristics (author, country, type of study, type of funding, and duration of follow-up), and intervention details (including drug names, dosages, and treatment duration). Relevant primary and secondary outcomes were also recorded. The primary outcomes extracted from the included studies were as follows: resolution of MASH without worsening of hepatic fibrosis, an improvement with ≥1-stage hepatic fibrosis without worsening of MASH, and concurrent resolution of MASH with ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis. The secondary outcomes extracted from the included studies were as follows: changes in lipid profiles (e.g., LDL-C, Total Cholesterol [TC], and Triglycerides [TG]), hepatic enzyme levels (e.g., Alanine Aminotransferase [ALT] and Aspartate Aminotransferase [AST]), and body weight. Adverse event outcomes included Gastrointestinal (GI) events such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In the context of existing reviews, the resolution of MASH is defined as the complete absence of hepatic steatosis and ballooning, mild or no inflammatory changes, and no progression in the NAFLD Activity Score (NAS). Consequently, “an improvement of ≥1-stage hepatic fibrosis without worsening of MASH” is defined by three criteria: (1) a ≥1-stage reduction in hepatic fibrosis; (2) no worsening of steatosis, ballooning, or lobular inflammation; and (3) no progression in the NAS (26, 27, 69).
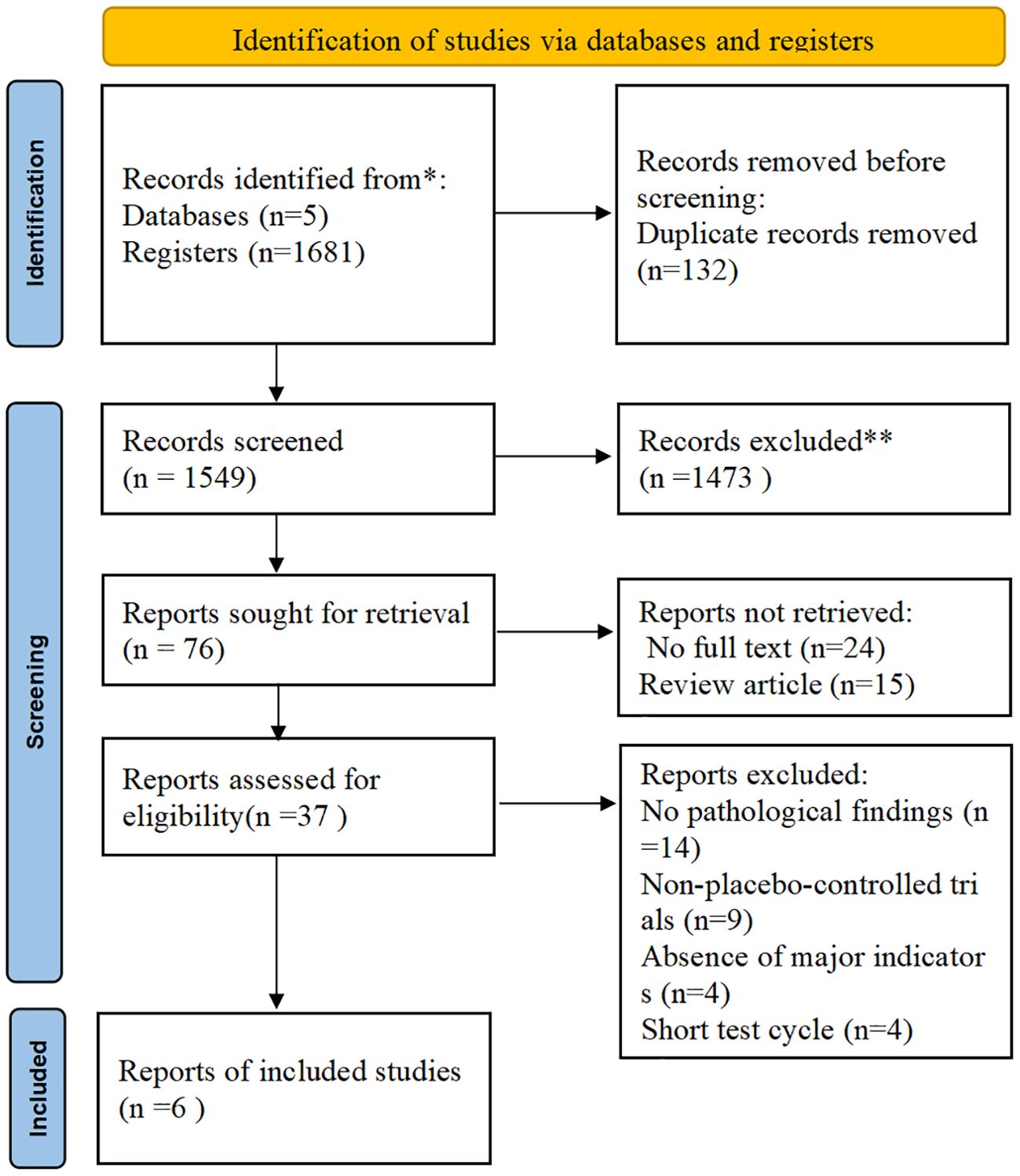
Figure 1. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram. (Source: Page MJ, et al. BMJ 2021;372: n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71. This work is licensed under CC BY 4.0. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
2.5 Risk of bias assessment
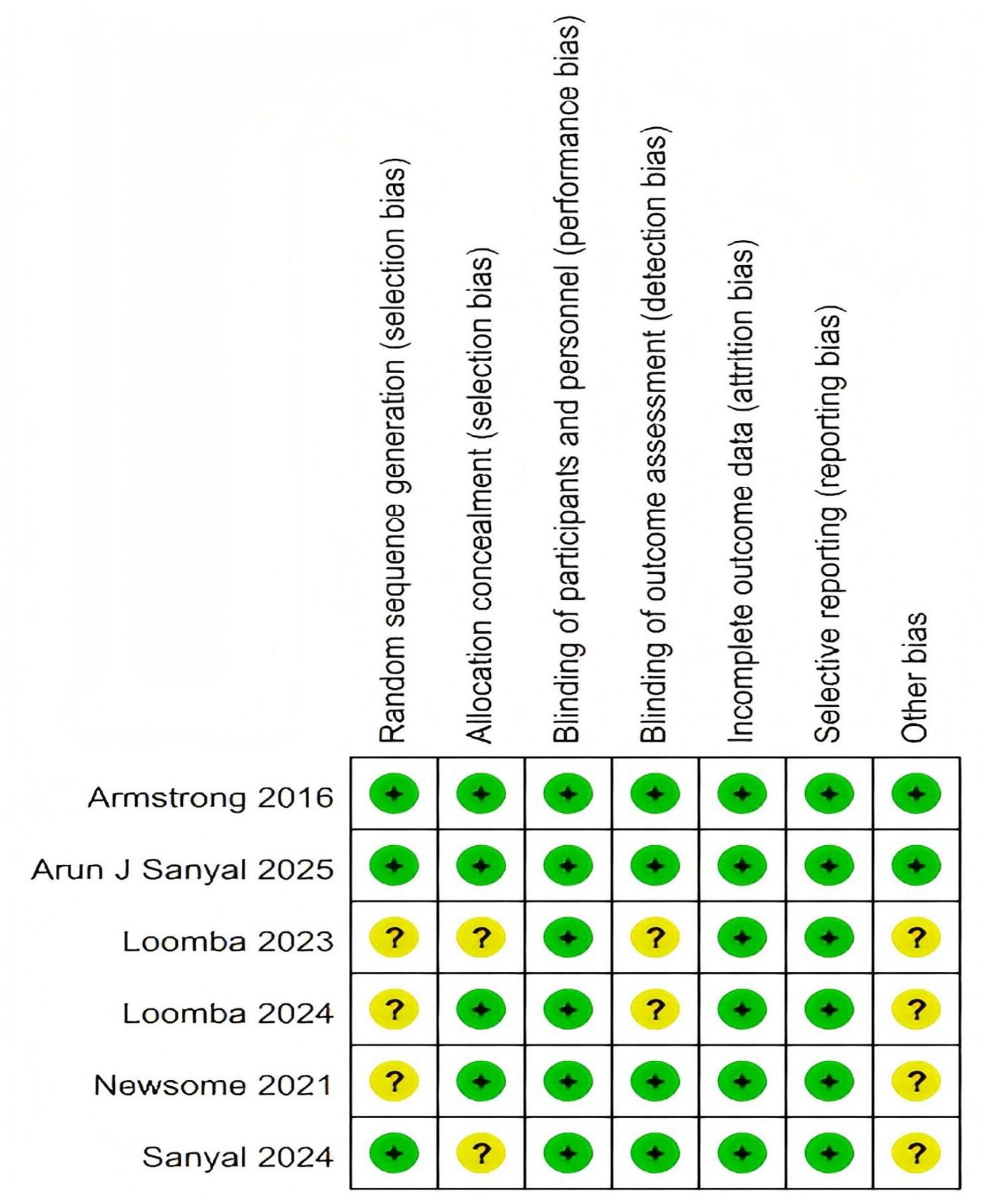
The risk of bias for each included study was independently assessed by two researchers, who were not involved in the studies, using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0 (RoB-2) (28). This tool evaluates bias across six domains: selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, reporting bias, and other potential sources of bias. Judgments were categorized as low risk, some concerns, or high risk of bias. All included studies were rated as high quality, with a low risk of bias (Figure 2, Supplementary Material 3).
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using Stata version 18 and Review Manager (RevMan) version 5.4.1 (29, 30). A meta-analysis was conducted by pooling data from the included RCTs to compare the effectiveness of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists in resolving MASH and improving hepatic fibrosis. Pooled Odds Ratios (OR) were computed across the studies. If the I² value was no more than 50% and P > 0.05, indicating that heterogeneity was negligible, the fixed-effect model was used; otherwise, a random-effects model was used to pool the data (31). Standard Deviation (SD) is required for performing the meta-analysis. However, most of the studies included in this meta-analysis did not provide SDs but only a Standard Error (SE) or a 95% Confidence Intervals (CIs). Therefore, we employed a formula outlined in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions to calculate SDs (32).
Effect sizes and their corresponding 95% CIs were extracted from the primary trial reports and any additional data sources, including Supplementary Appendices. For dichotomous outcomes, ORs were computed (e.g., for the primary outcome and GI adverse events), while Weighted Mean Differences (WMDs) were used for continuous outcomes (e.g., body weight), with both accompanied by 95% CIs. Heterogeneity between included studies was evaluated using the I Squared(I 2) statistic and visual inspection of forest plots (33, 34).
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of included studies
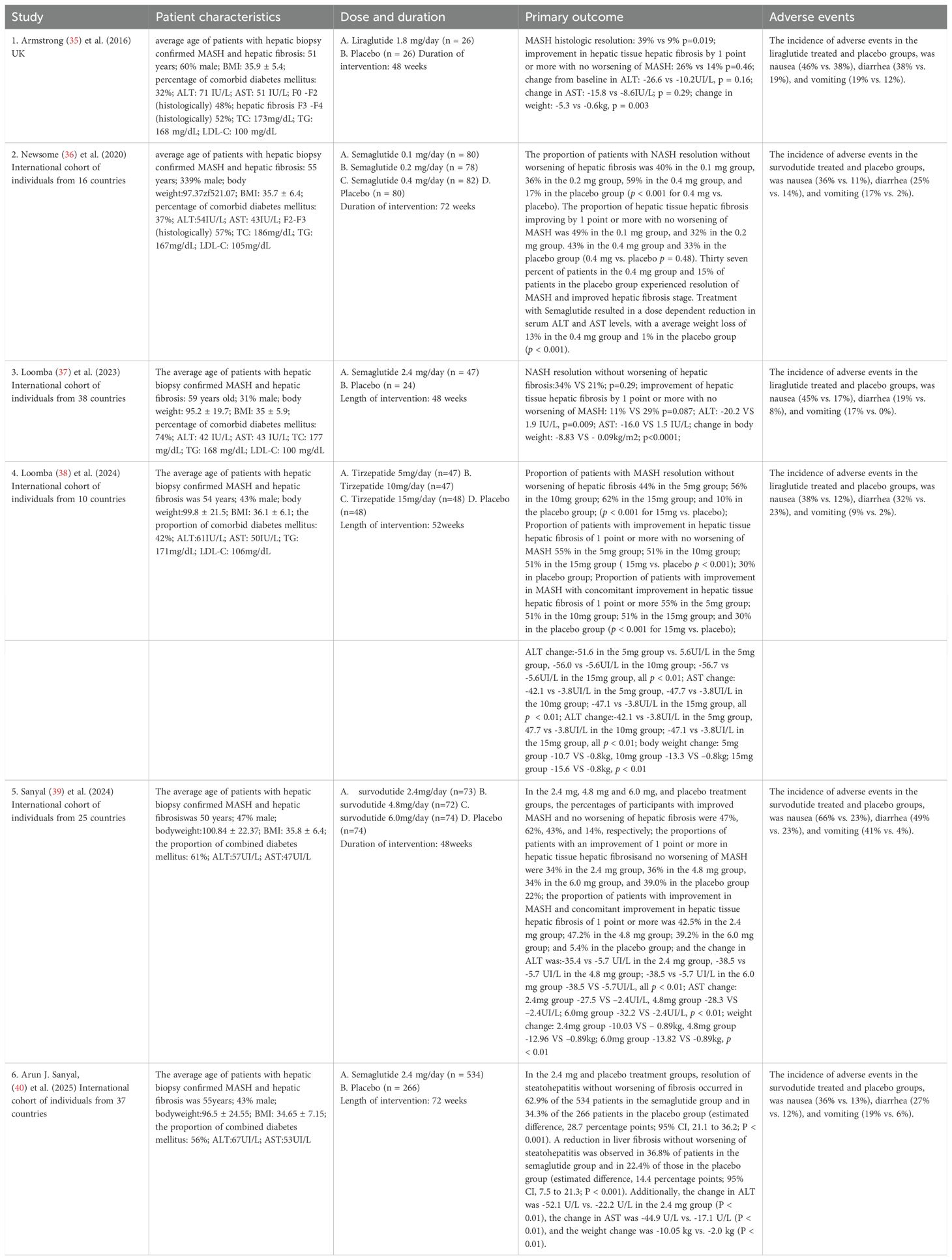
A total of 1,681 publications were identified through the initial search. After title and abstract screening, 76 articles were deemed eligible for full-text review. Of these, 37 underwent full-text assessment, and ultimately, six RCTs involving 1,726 participants were included in the analysis (35–40). Of the included studies, participants received once-daily subcutaneous injections of liraglutide (GLP-1RAs) at a dose of 1.8 mg, with an intervention period of 48 weeks (35). In other studies, participants were administered once-daily subcutaneous semaglutide (GLP-1RAs) at doses of 0.1 mg, 0.2 mg, or 0.4 mg, with an intervention period of 72 weeks (36). Furthermore, both studies employed once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg, with intervention periods of 48 weeks (37) and 72 weeks (40). In addition, participants were administered once weekly subcutaneous tirzepatide (GLP-1/GCG dual agonist) at doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg, with an intervention period of 52 weeks (38), or once weekly subcutaneous survodutide (GLP-1/GIP dual agonist) at doses of 2.4 mg, 4.8 mg, or 6.0 mg, with an intervention period of 48 weeks (39). All studies were phase II trials, except for the study by Arun J. Sanyal (40), which was a phase III trial of semaglutide (35, 39). Specifically, there were six multicenter studies, with North America, Europe, and the Western Pacific being the top regions where the RCTs were conducted. The mean age of participants was 54.39 ± 11.03 years, and the mean BMI was 35.55 ± 6.25 kg/m². The study population comprised 43% males and 57% females. Among MASH patients, 35.63% were classified as F2 and 55.85% as F3 for hepatic fibrosis stage. In addition, 50% of participants had comorbid T2DM, and the average intervention duration was approximately 57 weeks (Table 1).
3.2 Effect of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists on primary outcome
A total of six RCTs including 1,726 participants were incorporated into the analysis (35–40). Compared with placebo, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists were associated with an OR of 4.51 (95% CI: 3.68 to 5.52; I² = 52.2%; p < 0.01) for achieving MASH resolution without worsening of hepatic fibrosis. The ORs for improvement in hepatic fibrosis by ≥ 1-stage without worsening of MASH was 1.78 (95% CI: 1.47 to 2.16; I² = 22.7%; p < 0.01). For achieving both MASH resolution and a ≥ 1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis, the OR was 7.42 (95% CI: 2.98 to 18.48; I² = 81.9%; p < 0.01) (Figure 3).
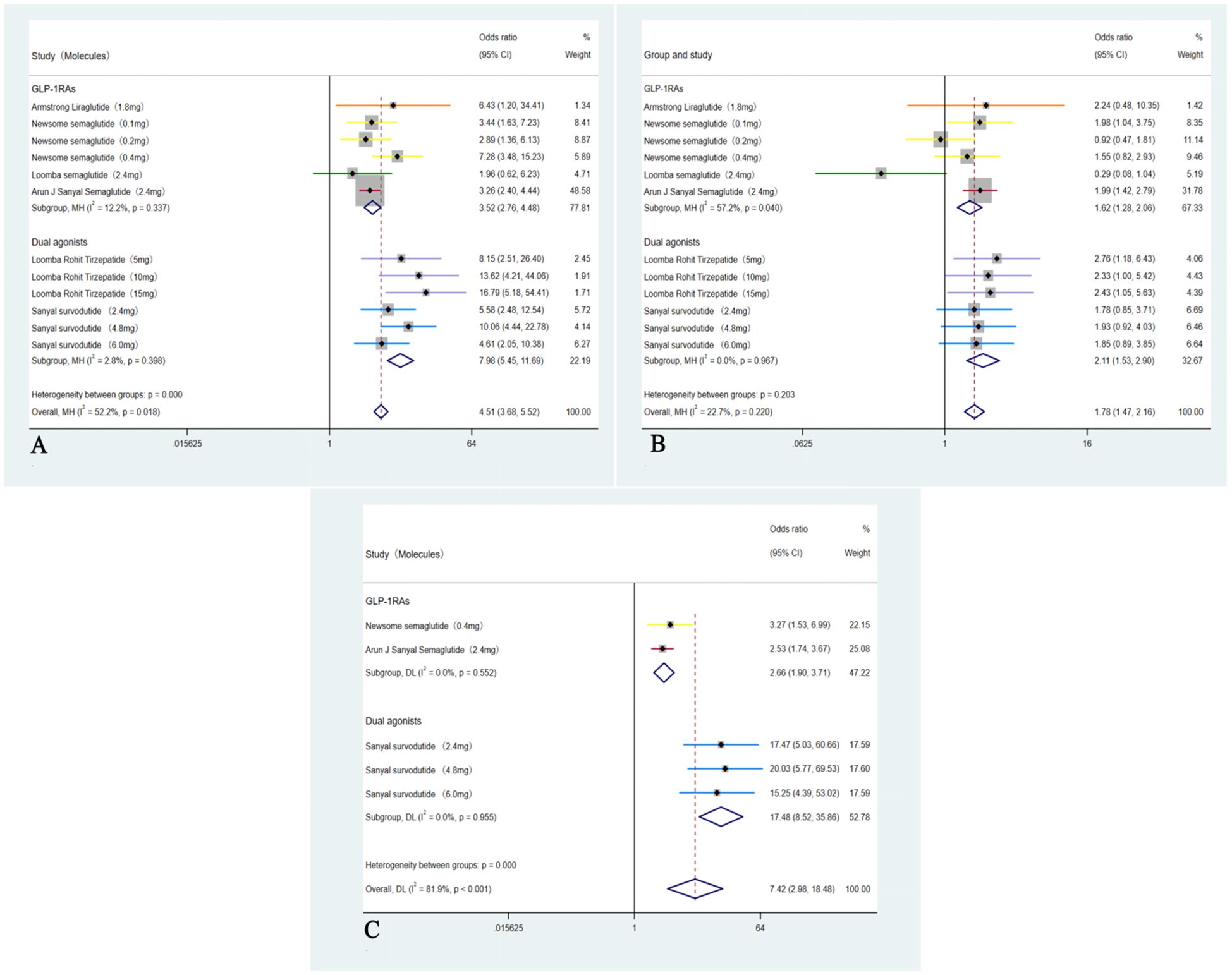
Figure 3. Analysis of primary outcomes: (A) Forest plot of ORs for resolution of MASH without worsening of hepatic fibrosis; (B) Forest plot of ORs for improvement in hepatic fibrosis by ≥1-stage without worsening of MASH; (C) Forest plot of ORs for concurrent resolution of MASH and ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis.
3.2.1 Subgroup analyses
These five studies (35–39) were analyzed to further examine the impact of weight loss on the primary outcomes; subgroup analyses were conducted based on weight loss categories: <10% (GLP-1RAs) and ≥10% (Dual agonists). For the outcome of MASH resolution without worsening of hepatic fibrosis, the <10% weight loss group (GLP-1RAs) showed an OR of 3.94 (95% CI: 2.67 to 5.81; I² = 22.5%; p < 0.01), whereas the ≥10% weight loss group (Dual agonists) demonstrated a higher OR of 23.51 (95% CI: 17.30 to 29.72; I² =0.0%; p < 0.01). Regarding the outcome of ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis without worsening of MASH, the <10% weight loss group (GLP-1RAs) showed an OR of 1.30 (95% CI: 0.92 to 1.82; I² = 54.1%; p = 0.14), indicating no statistically significant difference. In contrast, the ≥10% weight loss group (Dual agonists) demonstrated a significant improvement, with an OR of 9.59 (95% CI: 4.01to 15.18; I² = 0.0%; p < 0.01).Except for the non-significant result observed in the <10% weight loss group (GLP-1RAs) for ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis without worsening of MASH, all other endpoints across the respective groups showed statistically significant differences (p < 0.01). Subgroup analyses for the outcome of achieving both MASH resolution and a ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis could not be performed due to insufficient data. Furthermore, although the study by Arun J. Sanyal et al. (2025) (40) used semaglutide 2.4 mg (a GLP-1RA) and reported weight loss of ≥10%, the relevant outcome data could not be analyzed separately. Consequently, this study was included only in the overall pooled analysis and not in any subgroup analyses (Figure 4).
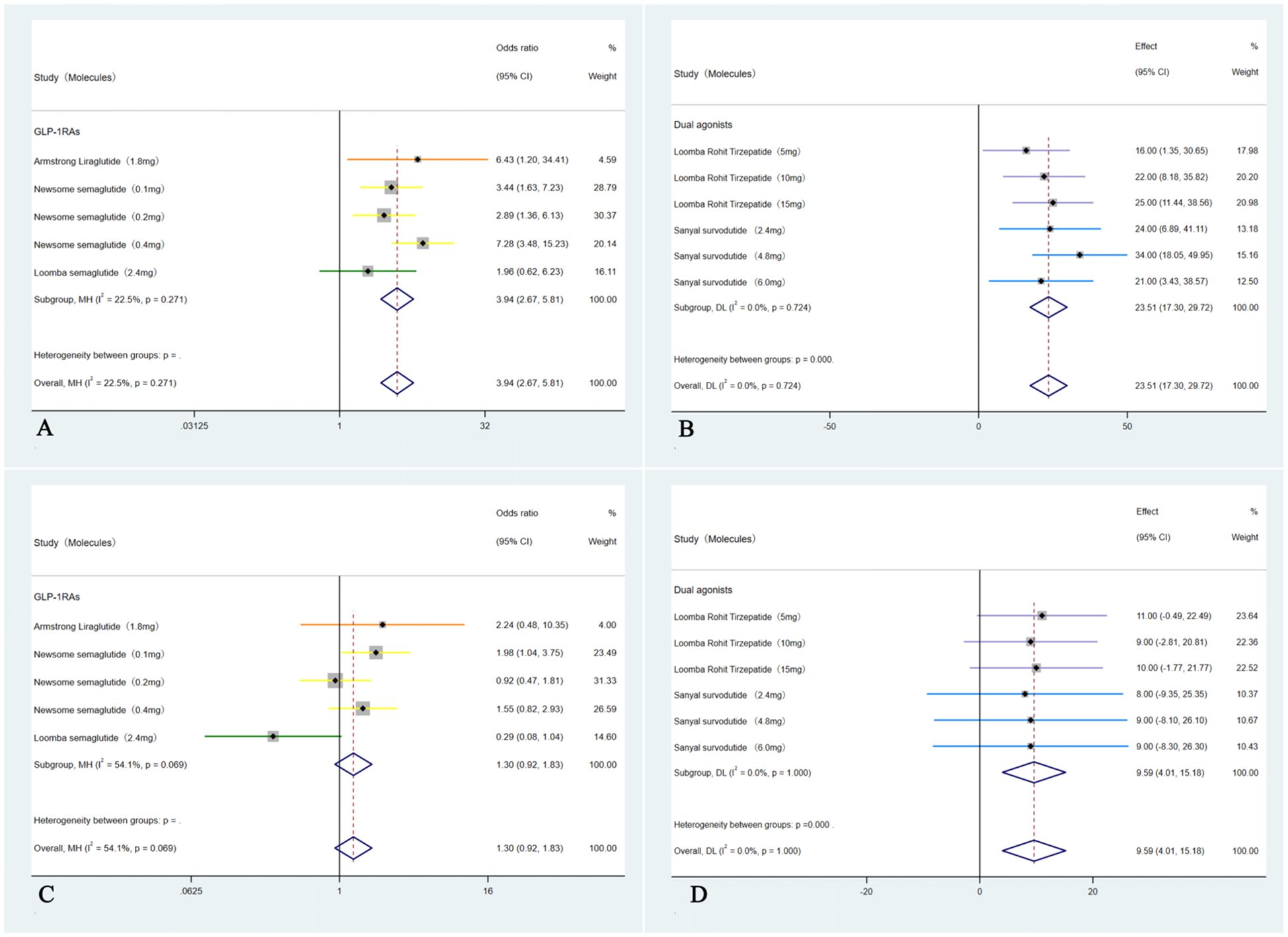
Figure 4. Subgroup analyses of primary outcomes were conducted by categorizing patients according to weight loss: <10% weight loss (GLP-1RAs) and ≥10% weight loss (Dual agonists). The analyses included: (A) Forest plot of ORs for MASH improvement without worsening of hepatic fibrosis in the <10% weight loss (GLP-1RAs) group; (B) Forest plot of ORs for MASH improvement without worsening of hepatic fibrosis in the ≥10% weight loss (Dual agonists) group; (C) Forest plot of ORs for hepatic fibrosis improvement by ≥1 stage without worsening of MASH in the <10% weight loss (GLP-1RAs) group; and (D) Forest plot of ORs for hepatic fibrosis improvement by ≥1 stage without worsening of MASH in the ≥10% weight loss (Dual agonists) group.
3.3 Effect of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists on secondary outcomes
In these six studies (35–40), treatment with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists resulted in a significant pooled reduction in body weight compared to the placebo group, with a WMD of -8.87 kg (95% CI: -10.90 to -6.85 kg; I² = 71.5%, p < 0.01). In addition, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists demonstrated significant improvements in cardiovascular parameters, including TC (WMD = -4.15 mmol/L, 95% CI: -13.13 to 4.82, I² = 84.5%; p = 0.48) and TG (WMD = -17.70 mmol/L, 95% CI: -21.95 to -13.44, I² = 26.5%; p < 0.01). However, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists did not show a significant improvement in LDL-C levels (WMD = -0.67 mmol/L, 95% CI: -6.55 to 5.21, I² = 63.7%; p = 0.13) (Figure 5). GLP-1RAs and dual agonists also demonstrated significant improvements in hepatic enzyme levels, including ALT (WMD = -31.51 U/L, 95% CI: -38.16 to -24.86, I² = 50.4%; p < 0.01) and AST (WMD = -26.29 U/L, 95% CI: -32.82 to -19.77, I² = 63.7%; p < 0.01) (Figure 6).
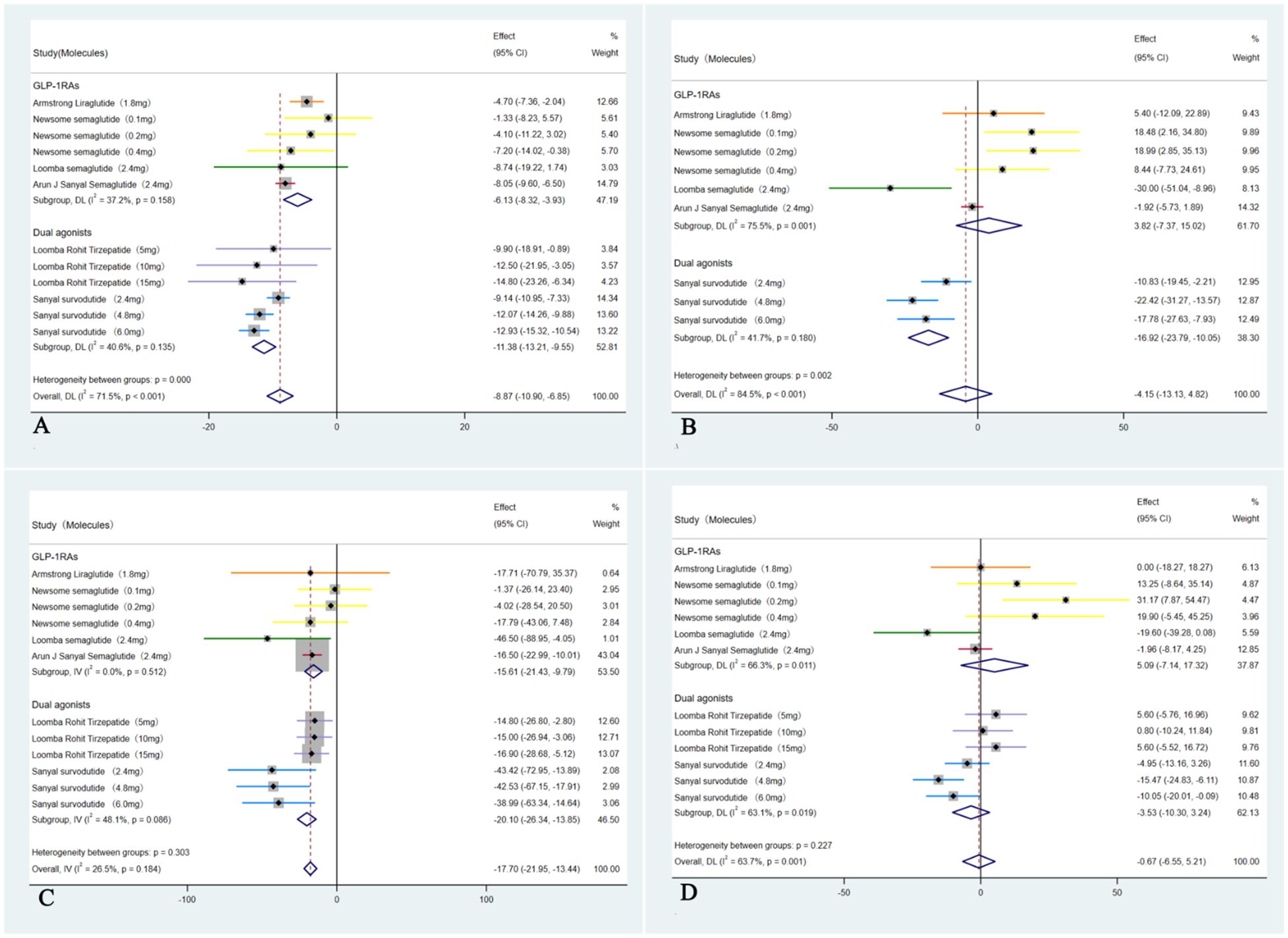
Figure 5. Forest plot of blood lipids levels in MASH patients treated with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists (A: body weight, B: TC, C: TG, D: LDL-C).
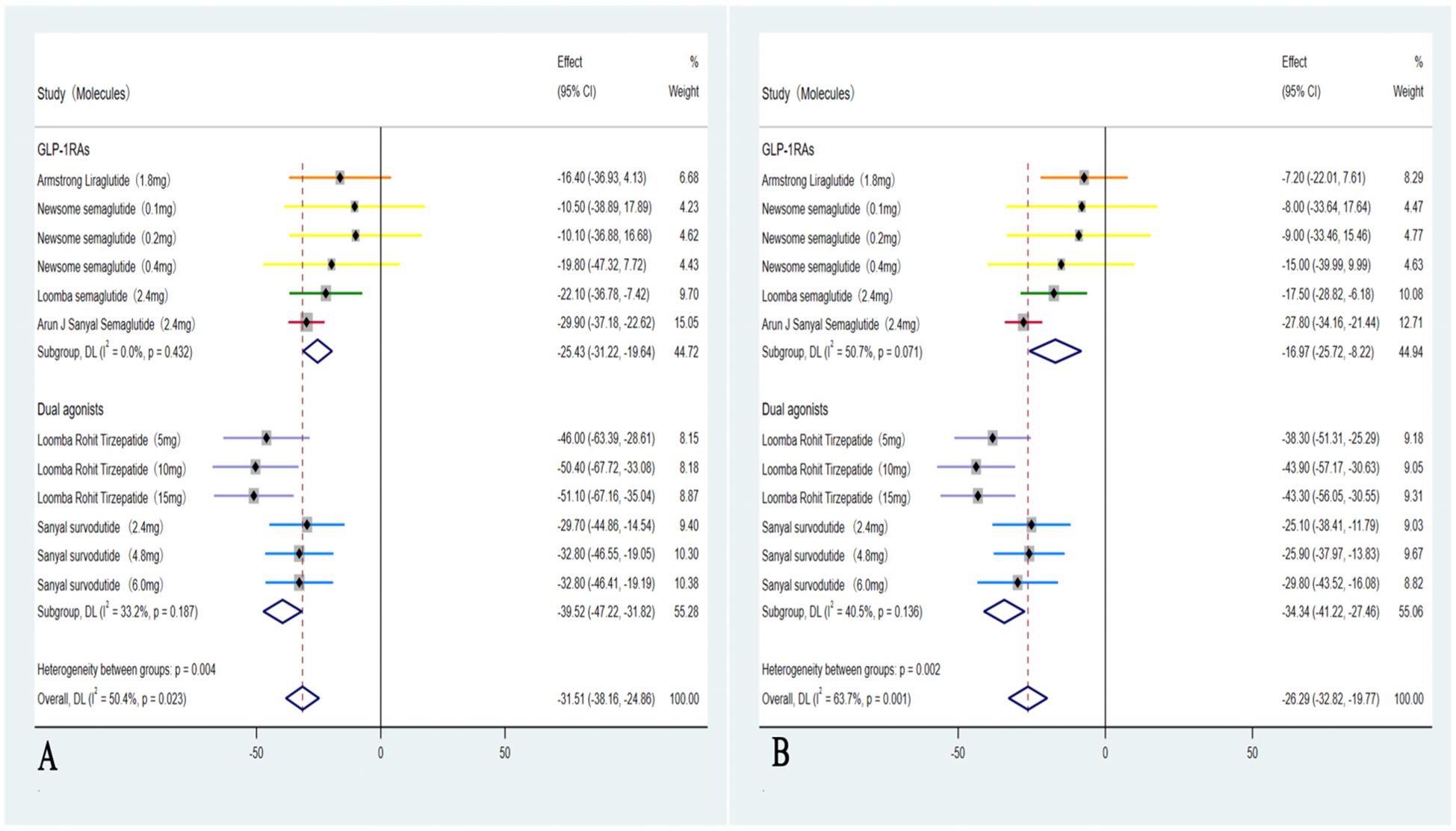
Figure 6. Forest plot of hepatic enzyme levels in MASH patients treated with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists (A: ALT, B: AST).
3.3.1 Subgroup analyses
These five studies (35–39) were evaluated to further investigate the impact on LDL-C, in which a subgroup analysis revealed a significant reduction only among those with ≥10% weight loss group (Dual agonists), with an OR of –3.53 (95% CI: –10.30 to 3.24; I² = 63.1%; p = 0.04). In contrast, weight loss of <10% (GLP-1RAs) was not associated with a statistically significant improvement in LDL-C levels, with an OR of 7.99 (95% CI: –9.31 to 25.30; I² = 69.2%; p = 0.22) (Figure 7).
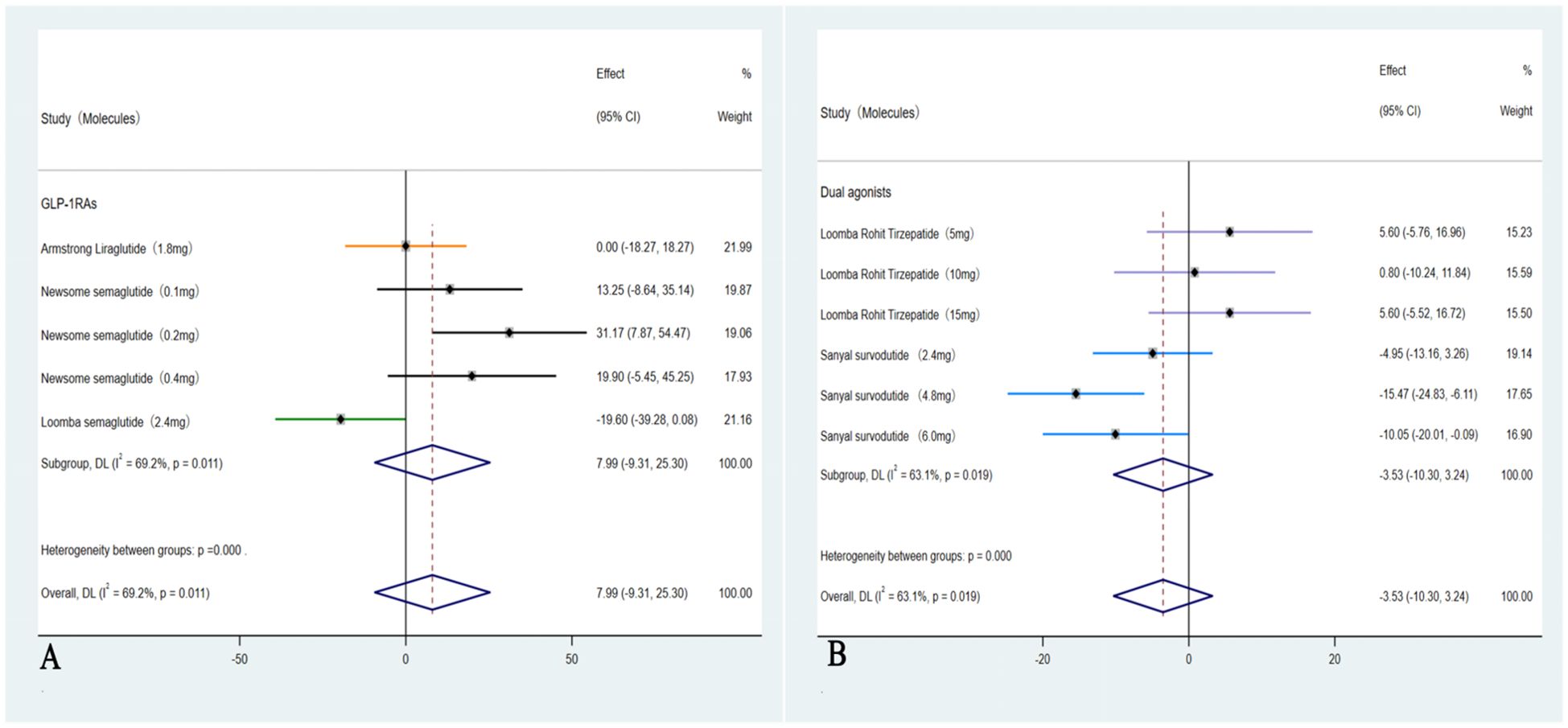
Figure 7. Forest plot of LDL-C changes in subgroups with <10% and ≥ 10% weight loss (A: <10%, B: ≥ 10%).
3.4 GI adverse events associated with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists
In these six studies (35–40), patients treated with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists had significantly higher incidence rate of experiencing GI side effects compared to those receiving a placebo (28.31% (355/1254) VS 23.28% (193/829), OR = 3.43, 95% CI, 2.61 to 4.51, I² = 39.3%; p < 0.01). Among these adverse events, patients had a significantly higher incidence rate of experiencing nausea (41.28% (608/1473) VS 15.53% (162/1043), OR = 4.30, 95% CI, 3.50 to 5.28, I² = 0%; p < 0.01), followed by diarrhea (30.35% (447/1473) VS 16.49% (172/1043), OR = 2.47, 95% CI, 2.02 to 3.03, I² = 0%; p < 0.01) and vomiting (20.84% (307/1473) VS 3.06% (43/1403), OR = 6.20, 95% CI, 4.46 to 8.62, I² = 25.7%; p < 0.01) (Figure 8).
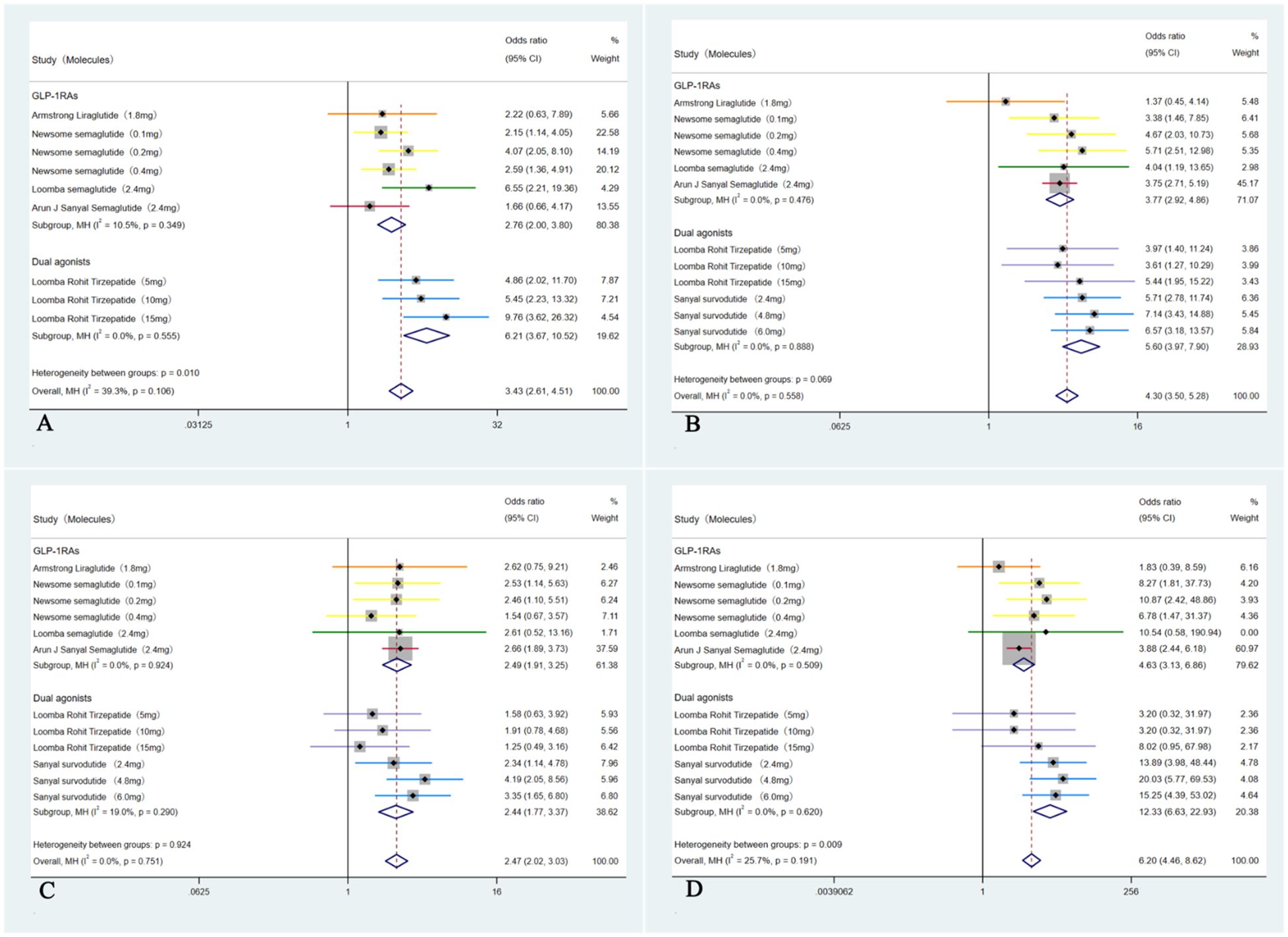
Figure 8. Forest plot of the GI adverse events in MASH patients treated with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists, with subgroups by GI events. (A: overall GI adverse events, B: nausea, C: diarrhea, D: vomiting).
3.5 Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis using the leave-one-out method revealed substantial heterogeneity in the ORs for both MASH resolution and a ≥1-stage improvement in hepatic fibrosis (I² = 81.9%). The study by Sanyal et al. (39) was found to be the primary source of this heterogeneity. After excluding this study, heterogeneity decreased markedly (I² = 0%), while statistically significant outcomes in favor of GLP-1RAs and dual agonist therapy were maintained (OR = 2.65, 95% CI: 1.90 to 3.71, p < 0.01). Notably, despite variations in effect sizes and heterogeneity indices following the exclusion of individual studies, the pooled estimates remained statistically significant in all analyses. This consistency suggests that the results of the meta-analysis are robust.
4 Discussion
A total of 1,726 patients were included, and both GLP-1RAs and dual agonists demonstrated superior efficacy in hepatic fibrosis and resolution of MASH compared to placebo. They also had positive effects on weight loss, hepatic enzyme levels, and TC and TG levels. Notably, our analysis also showed that the degree of weight loss was a significant determinant of hepatic fibrosis improvement in MASH patients. Our analysis further demonstrated that treatment with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists had no substantial effect on LDL-C levels. Although GLP-1RAs and dual agonists do not directly lower LDL-C in patients with MASH, a significant reduction was observed in those who achieved substantial weight loss (≥10%). Conversely, weight loss of <10% was not associated with a significant decrease in LDL-C. Compared with placebo, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists significantly improved histological resolution of MASH without exacerbating hepatic fibrosis, and this finding was highly consistent across included studies. Even a modest weight loss (<10%) can positively impact MASH resolution, whereas greater weight loss (≥ 10%) is associated with a higher rate of MASH resolution and hepatic fibrosis improvement.
Hepatic fibrosis is a pathological response to chronic hepatocellular injury, characterized by excessive accumulation of ECM components (41). Without timely intervention, it can progress to cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation, or hepatocellular carcinoma, significantly increasing the risk of hepatic-related morbidity and mortality (41). Evidence indicates that patients with hepatic fibrosis have a 20% to 40% chance of developing hepatic-related complications, such as ascites and GI bleeding, within five years (42). Moreover, hepatic fibrosis is not only associated with hepatic-related complications but also independently increases the risk of cardiovascular mortality. This is due to the promotion of chronic systemic inflammation and metabolic dysregulation (43). Study shows that patients with moderate to severe hepatic fibrosis have a cardiovascular mortality rate 2 to 3 times higher than the general population. Among these patients, individuals with a Fibrosis 4 score (FIB-4) index greater than 3.25 face a 10-year cardiovascular mortality risk as high as 28.5% (44). In the early stages of hepatic fibrosis, the hepatic’s lobular structure remains intact, allowing activated hepatic stellate cells to revert to a quiescent state with appropriate intervention. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) play a crucial role in degrading excess ECM, highlighting the reversible nature of early-stage fibrosis (45). Therefore, timely antifibrotic therapy not only improves hepatic-related outcomes but also mitigates cardiovascular risks by reducing systemic inflammation and metabolic disturbances. Reported reductions in cardiovascular event risks have been as high as 43% (46).
Excess body weight, particularly visceral adiposity, plays an important role in the pathogenesis of MASH by exacerbating hepatic lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation, thereby accelerating the progression of hepatic fibrosis (47). Weight loss interventions, by reducing body weight, effectively decrease hepatic fat deposition, alleviating steatosis, the initial stage of MASH (10) (11). This weight loss-mediated effect not only mitigates lipotoxicity but also helps normalize hepatic function and reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are key mediators of hepatic fibrosis (48). Furthermore, the anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of weight loss work synergistically with the direct hepatic actions of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists in activating hepatic tissue (49). Thus, modulating body weight through receptor activation represents a promising therapeutic approach, not only for promoting weight loss but also for reversing MASH and halting the progression of hepatic fibrosis.
Although GLP-1RAs and dual agonists have shown potential in improving MASH and hepatic fibrosis, the degree of weight loss plays a significant role in determining the effectiveness of these treatments. The analysis in this study revealed that treatment with GLP-1RAs and dual agonists led to significant improvements in hepatic fibrosis when weight loss was ≥ 10%. However, when weight loss was <10%, the improvement in hepatic fibrosis was not statistically significant. This suggests that the amelioration of hepatic fibrosis induced by GLP-1RAs and dual agonists may be an indirect outcome, dependent on the e degree of weight loss. Consequently, the degree of weight loss during GLP-1RA and dual agonist therapy could serve as a clinical marker to predict potential benefits for hepatic fibrosis. This finding underscores the limitation of relying solely on weight loss-mediated effects for fibrotic resolution. Therefore, there remains a significant need for direct anti-fibrotic therapies in MASH patients. This meta-analysis emphasized the distinct effects of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists on lipid metabolism in patients with MASH. The results demonstrate that GLP-1RAs and dual agonists significantly reduce TG and TC levels, but have a limited effect on LDL-C. The reduction in TG is primarily due to two mechanisms: inhibition of hepatic very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) synthesis (50) and enhanced lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity in adipose tissue (51). The decrease in TC is likely driven by reduced VLDL secretion, suppression of the Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-2 (SREBP-2) pathway (51), and synergistic metabolic effects, including improved insulin sensitivity and weight loss (52). The limited effect on LDL-C may be attributed to three factors: the absence of direct upregulation of (Low-Density Lipoprotein) LDL receptors, reduced VLDL to LDL conversion despite decreased VLDL production, and MASH related hepatic disturbances, such as downregulation of LDL receptors and impaired bile acid metabolism. These findings have important clinical implications. While GLP-1RAs and dual agonists effectively improve TG and TC metabolism in MASH patients, additional lipid-lowering strategies, such as statins, should be considered for those requiring comprehensive lipid management, particularly patients with elevated cardiovascular risk.
In addition, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists have demonstrated important hepatoprotective effects, including notable reductions in serum AST and ALT levels (53). As typical markers of hepatocellular injury and inflammation, elevated ALT and AST levels directly reflect liver cell damage (54). The studies suggest a dual mechanism of action: firstly, these agents exert direct hepatoprotective effects by reducing hepatic lipid accumulation and suppressing inflammatory responses (55); secondly, they confer beneficial effects on hepatic fibrosis (56, 57).This multi-targeted mechanism provides a strong theoretical rationale for applying GLP-1RAs and dual agonists in the treatment of MASH.
This study found that the use of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists is associated with adverse effects, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, with nausea being the most frequently reported. Among the six included studies, the overall incidence of serious adverse events (SAEs) was 12%. Among GLP-1RAs, in the liraglutide treatment group (35), the incidence of SAEs was 8%. GI adverse events, including nausea (46%), diarrhea (38%), and vomiting (19%), primarily occurred during the initial 1–4 weeks of treatment, with nausea peaking in weeks 1–2 (>38%). The treatment discontinuation rate due to adverse events was 8%, including two cases discontinued because of nausea. In the semaglutide treatment group (36), the incidence of serious SAEs was 16%. GI adverse events, including nausea (36%), diarrhea (25%), and vomiting (17%), primarily occurred during the dose-escalation period (weeks 1–16). Treatment discontinuation due to adverse events was 7%, with 4% attributable to GI events. In another semaglutide study (37), the incidence of serious SAEs was 13%. GI events, including nausea (45%), diarrhea (19%), and vomiting (17%), primarily occurred during the dose-escalation period (weeks 1–16). The treatment discontinuation rate due to adverse events was 6%, with two cases due to nausea and one due to vitreous detachment. In the semaglutide treatment group (40), the incidence of serious SAEs was 13.4%. GI adverse events, including nausea (36%), vomiting (19%), and diarrhea (27%), were primarily reported during the dose-escalation phase (weeks 1–24). The treatment discontinuation rate due to adverse events was 2.6%. Among dual receptor agonists, in the tirzepatide treatment group (38), the incidence of serious SAEs was 6%, comparable to the placebo group, with no significant difference observed. GI adverse events, including nausea (38%), diarrhea (32%), and vomiting (9%), were most frequently reported during the dose-escalation phase (weeks 1–12). The treatment discontinuation rate due to adverse events was 4%. In the survodutide treatment group (39), the incidence of serious SAEs was 8%. GI adverse events were more frequent, including nausea (66%), diarrhea (49%), and vomiting (41%), primarily occurring during the rapid dose-escalation phase (weeks 1–24). These events led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients, of which 16% were attributable to GI events. Overall, GI reactions are the most common adverse events associated with these drugs, with average incidences of nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting of 41.28%, 30.35%, and 20.84%, respectively. Other common adverse events include hypoglycemia, occurring more frequently in patients with diabetes (3.4%–34%) than in non-diabetic individuals (0.3%–0.6%), and decreased appetite (13%–31%). SAEs, such as malignancies or cardiovascular events, have been reported occasionally, but are generally not directly attributable to the drugs.
The high incidence of these GI adverse events represents a major limitation to the widespread use of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists (58–60).Consequently, discontinuation rates across GLP-1RA- and dual agonist-based MASH therapies show substantial heterogeneity, primarily driven by their mechanisms of action, including delayed gastric emptying and altered GI motility (61, 62).
In addition, several studies have shown that nausea and vomiting are more common during the first 4–5 weeks of treatment, typically resolving within 8 days after symptom onset (63, 64). Diarrhea typically occurs during the initial 2–4 weeks of treatment. To minimize these GI side effects, clinical guidelines recommend initiating treatment at a low dose and gradually titrating to the therapeutic dose (63). Beyond GI side effects, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists have also been associated with adverse events affecting the pancreas, biliary, and nervous system (65), as well as a 27% incidence of cholelithiasis and a 36% incidence of cholecystitis (66). Neurological adverse effects primarily involve central nervous system symptoms, such as headache, with an incidence of 5–15% (67). Although these adverse events are generally rare (<5%), individual responses may vary significantly, influenced by factors such as comorbidities, baseline disease status, and treatment regimens (67). Therefore, a thorough pre-treatment risk assessment, considering factors such as obesity, weight loss history, pancreatic diseases, neurological disorders, and biliary diseases, is essential. Furthermore, regular monitoring every 12 weeks, including measurements of serum amylase and lipase, is recommended to facilitate early detection of adverse events (68).
5 Limitations
This study systematically analyzed six qualified RCTs published in The New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet, which evaluated the therapeutic effects of GLP-1 RAs and their dual agonists in patients with MASH. Given the relatively recent clinical introduction of these agents and the strict inclusion criteria requiring hepatic biopsy for MASH diagnosis, the limited number of eligible studies may constrain the generalizability and clinical applicability of the findings. Furthermore, substantial variations in baseline characteristics, such as age, gender distribution, duration of intervention, and comorbidities, were observed across the studies. Although statistical methods were employed to control for these confounding factors, the potential impact of these differences on the final results remains considerable. In addition, discrepancies in the types of GLP-1RAs and dual agonists used and the duration of treatment further complicate comparisons of drug efficacy and limit the accurate assessment of long-term effectiveness and safety.
6 Conclusion
This meta-analysis demonstrates that GLP-1RAs and dual agonists can effectively improve hepatocellular inflammation and hepatic fibrosis in patients with MASH. Specifically, when patients achieve a weight loss of ≥10%, these drugs are associated with significant improvements in hepatic fibrosis, whereas the effect is limited in those with less than 10% weight loss. In terms of lipid management, they effectively reduce TC and TG levels. However, GLP-1RAs and dual agonists do not directly lower LDL-C in patients with MASH; a significant reduction was observed only in those who achieved substantial weight loss (≥10%), whereas weight loss of <10% was not associated with a significant decrease in LDL-C. This finding suggests that for patients requiring comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, additional lipid-lowering strategies may be needed to enhance the intervention. From the perspective of hepatoprotective mechanisms, these drugs may play a dual role by reducing hepatic steatosis and suppressing inflammatory cascade responses through lowering serum AST and ALT levels. Based on these findings, when using GLP-1RAs and dual agonists clinically to treat hepatic fibrosis, the impact of weight loss should be carefully considered, and close monitoring of LDL-C levels is recommended to reduce cardiovascular risk. In addition, the common GI side effects (e.g., nausea) associated with these therapies highlight the need for gradual dose titration and routine monitoring. Further studies are warranted to explore the long-term hepatic and cardiovascular outcomes of these therapies in patients with MASH.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ML: Conceptualization, Validation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Software, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Investigation. JH: Data curation, Software, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YH: Validation, Writing – review & editing. HC: Writing – review & editing. WW: Writing – review & editing, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project was funded by the Shaanxi Province Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2024JC-YBMS-765).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1681965/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Le P, Tatar M, Dasarathy S, Alkhouri N, Herman WH, Taksler GB, et al. Estimated burden of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in US adults, 2020 to 2050. JAMA Netw Open. (2025) 8:e2454707. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.54707
2. Younossi ZM, Kalligeros M, and Henry L. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2025) 31:S32–50. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0431
3. Quek J, Chan KE, Wong ZY, Tan C, Tan B, Lim WH, et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty hepatic disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:20–30. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00317-X
4. Powell EE, Wong VW, and Rinella M. Non-alcoholic fatty hepatic disease. Lancet. (2021) 397:2212–24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32511-3
5. Taru V, Szabo G, Mehal W, and Reiberger T. Inflammasomes in chronic hepatic disease: hepatocellular injury, fibrosis worsening and systemic inflammation. J Hepatol. (2024) 81:895–910. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.06.016
6. Zhao YQ, Deng XW, Xu GQ, Lin J, Lu HZ, and Chen J. Mechanical homeostasis imbalance in hepatic stellate cells activation and hepatic fibrosis. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10:1183808. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1183808
7. Eslam M, Sarin SK, Wong VW, Fan JG, Kawaguchi T, Ahn SH, et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Hepatic clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty hepatic disease. Hepatol Int. (2020) 14:889–919. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10094-2
8. Wang D, Miao J, Zhang L, and Zhang L. Research advances in the diagnosis and treatment of MASLD/MASH. Ann Med. (2024) 57:2445780. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2445780
9. Devasia AG, Ramasamy A, and Leo CH. Current therapeutic landscape for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:1778. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041778
10. Vilar-Gomez E, Martinez-Perez Y, Calzadilla-Bertot L, Torres-Gonzalez A, Gra-Oramas B, Gonzalez-Fabian L, et al. Weight loss through lifestyle modification significantly reduces features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. (2015) 149:367–e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005
11. Niu J, Al-Yaman W, Pinyopornpanish K, Park J, Salazar M, Xiao H, et al. The Long-Term Effect of Weight Loss on the Prevention of worsening to Cirrhosis among Patients with Obesity and MASH-Related F3 hepatic fibrosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2024) 21:708. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21060708
12. Brunner K, Henneberg C, Wilechansky R, and Long M. nonalcoholic fatty hepatic disease and Obesity Treatment. Curr Obes Rep. (2019) 8:220–8. doi: 10.1007/s13679-019-00345-1
13. Thomsen RW, Mailhac A, Løhde JB, and PotAtegård A. Real-world evidence on the utilization, clinical and comparative effectiveness, and adverse effects of newer GLP-1RA-based weight-loss therapies. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2025) 27 Suppl 2:66–88. doi: 10.1111/dom.16364
14. Müller T, Adriaenssens A, Ahrén B, Blüher M, Birkenfeld A, Campbell J, et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Mol Metab. (2025) 95:102118. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102118
15. Li Y, Zhou Q, Dai A, Zhao F, Chang R, and Ying T. Structural analysis of the dual agonism at GLP-1R and GCGR. Proc Natl Accad Sci U S A. (2023) 120:e2303696120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2303696120
16. Hartman M, Sanyal A, Loomba R, Wilson J, Nikooienejad A, Bray R, et al. Effects of novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide on biomarkers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1352–5. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1892
17. Al-Zamel N, Al-Sabah S, Luqmani Y, Adi L, Chacko S, Schneider TD, et al. A Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonist Does Not Antagonize Glucagon at Its Receptor but May Act as a Biased Agonist at the GLP-1 Receptor. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:3532. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143532
18. Eriksson O, Haack T, Hijazi Y, Teichert L, Tavernier V, Laitinen I, et al. Receptor occupancy of dual glucagon-like peptide 1/glucagon receptor agonist SAR425899 in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:16758. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73815-5
19. Coskun T, Urva S, Roell WC, Qu H, Loghin C, Moyers JS, et al. LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:1234–1247.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.07.013
20. Nasiri-Ansari N, Androutsakos T, Flessa CM, Kyrou I, Siasos G, Randeva HS, et al. Endothelial cell dysfunction and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A concise review. Cells. (2022) 11:2511. doi: 10.3390/cells11162511
21. Li Q, Lin Y, Wang S, Zhang L, and Guo L. GLP-1 inhibits high-glucose-induced oxidative injury of vascular endothelial cells. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:8008. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06712-z
22. Fan J, Xu XY, Yang RX, Nan YM, Wei L, Jia JD, et al. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty hepatic disease (Version 2024). J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2024) 12:955–74. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00311
23. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
24. Eskridge W, Cryer DR, Schattenberg JM, Gastaldelli A, Malhi H, Allen AM, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic hepatic disease and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: the patient and physician perspective. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:6216. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196216
25. Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty hepatic disease: An international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:202–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039
26. Younossi ZM, Zelber-Sagi S, Lazarus JV, Wong VW, Yilmaz Y, Duseja A, et al. Global consensus recommendations for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. (2025) 11:S0016-5085(25)00632-8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.02.044
27. Harrison SA and Dubourg J. Liver biopsy evaluation in MASH drug development: Think thrice, act wise. J Hepatol. (2024) 81:886–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.06.008
28. Sterne JAC, Savovic J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
30. The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre (2020). [Computer program]. Version 5.4.1.
31. Barili F, Parolari A, Kappetein PA, and Freemantle N. Statistical Primer: heterogeneity, random- or fixed-effects model analyses? Interact Cardiovasc Thoracal Surg. (2018) 27:317–21. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivy163
32. Higgins JPT, Li T, Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, et al eds. Chapter 6: Choosing effect measures and computing estimates of effect. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 6.1. Cochrane: London, United Kingdom. Available online at: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-06section-6-2.
33. Higgins JP and Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
34. Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 6.5. Cochrane, London, United Kingdom (2024). Available online at: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook (Accessed July 22).
35. Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, Barton D, Hull D, Parker R, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. (2016) 387:679–90. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X
36. Newsome PN, Buchholtz K, Cusi K, Linder M, Okanoue T, Ratzui V, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of subcutaneous semaglutide in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:1113–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028395
37. Loomba R, Abdelmalek MF, Armstrong MJ, Jara M, Kjær MS, Krarup N, et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once weekly in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:511–22. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00068-7
38. Loomba R, Hartman ML, Lawitz RJ, Vuppalanchi R, Boursier J, Bugianesi E, et al. Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis with hepatic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. (2024) 391:299–310. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2401943
39. Sanyal AJ, Bedossa P, Fraessdorf M, et al. A phase 2 randomized trial of survodutide in MASH and fibrosis. N Engl J Med. (2024) 391:311–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2401755
40. Sanyal AJ, Newsome PN, Kliers I, et al. Phase 3 trial of semaglutide in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. (2025) 392:2089–99. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2413258
41. Kisseleva T and Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:151–66. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00372-7
42. Poynard T, Mathurin P, Lai CL, Guyader D, Poupon R, Tainturier MH, et al. A comparison of fibrosis progression in chronic hepatic diseases. J Hepatol. (2003) 38:257–65. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00413-0
43. Huang Y, Wan T, Hong Y, Wang X, Jiang X, Yang Y, et al. Impact of NAFLD and fibrosis on adverse cardiovascular events in patients with hypertension. Hypertension. (2025) 82:1012–23. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.24252
44. Xiao J, Wang F, Wong NK, He J, Zhang R, Sun R, et al. Global hepatic disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective. J Hepatol. (2019) 71:212–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.004
45. MB LI, JY LI, and FENG DP. Research advances in the reversal of hepatic fibrosis[J. J Clin Hepatol. (2023) 39:193–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.01.030
46. Simon TG, Roelstraete B, Khalili H, Hagström H, and Ludvigsson JF. Mortality in biopsy-confirmed nonalcoholic fatty hepatic disease: results from a nationwide cohort. Gut. (2021) 70:1375–82. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322786
47. NASH Pathophysiology. Pan NASH: Amsterdam, The Netherlands (2023). Available online at: https://pannash.org/pathophysiology.
48. Pang MD, Bastings JJAJ, Op den Kamp-Bruls YMH, Harrold JA, Kjølbaek L, Halford JCG, et al. The effect of weight loss on whole-body and tissue-specific insulin sensitivity and hepatic lipid content and composition: SWEET substudy. Obes (Silver Spring). (2023) 31:1745–54. doi: 10.1002/oby.23773
49. Sanyal AJ, Kaplan LM, Frias JP, Brouwers B, Wu Q, Thomas MK, et al. Triple hormone receptor agonist retatrutide for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic hepatic disease: a randomized phase 2a trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2037–48. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03018-2
50. He PP, Jiang T, OuYang XP, Liang YQ, Zou JQ, Wang Y, et al. Lipoprotein lipase: Biosynthesis, regulatory factors, and its role in atherosclerosis and other diseases. Clin Chim Acta. (2018) 480:126–37. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.02.006
51. Hendrix S, Kingma J, Ottenhoff R, Valiloo M, Svecla M, Zijlstra LF, et al. Hepatic SREBP signaling requires SPRING to govern systemic lipid metabolism in mice and humans. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5181. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40943-1
52. He H, Liu K, Liu M, Yang AJ, Cheng KW, Lu LW, et al. The impact of medium-chain triglycerides on weight loss and metabolic health in individuals with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:1755–68. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.06.016
53. Xuan Y, Wu D, Zhang Q, Yu Z, Yu J, and Zhou D. Elevated ALT/AST ratio as a marker for NAFLD risk and severity: insights from a cross-sectional analysis in the United States. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1457598. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1457598
54. Zou Y, Zhong L, Hu C, and Sheng G. Association between the alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase ratio and new-onset non-alcoholic fatty hepatic disease in a nonobese Chinese population: a population-based longitudinal study. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19:245. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01419-z
55. Chen LW, Huang MS, Shyu YC, and Chien RN. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase elevation is associated with metabolic syndrome, hepatic steatosis, and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty hepatic disease: A community-based cross-sectional study. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2021) 37:819–27. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12395
56. Thong VD and Quynh BTH. Correlation of Serum Transaminase Levels with hepatic fibrosis Assessed by Transient Elastography in Vietnamese Patients with nonalcoholic fatty hepatic disease. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:1349–55. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S309311
57. Nallagangula KS, Nagaraj SK, Venkataswamy L, and Chandrappa M. hepatic fibrosis: a compilation on the biomarker’s status and their significance during disease worsening. Future Sci OA. (2017) 4:FSO250. doi: 10.4155/fsoa-2017-0083
58. Jalleh RJ, Rayner CK, Hausken T, Jones KL, Camilleri M, and Horowitz M. Gastrointestinal effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 9:957–64. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00188-2
59. Liu L, Chen J, Wang L, Chen C, and Chen L. Association between different GLP-1 receptor agonists and gastrointestinal adverse reactions: A real-world disproportionality study based on FDA adverse event reporting system database. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1043789. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1043789
60. Osei SP, Akomaning E, Florut TF, Sodhi M, Lacy BE, Aldhaleei WA, et al. Gastrointestinal safety assessment of GLP-1 receptor agonists in the US: A real-world adverse events analysis from the FAERS database. Diagnostics. (2024) 14:2829. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14242829
61. He L, Li Q, Yang Y, Li J, Luo W, Huang Y, et al. Pharmacovigilance study of GLP-1 receptor agonists for metabolic and nutritional adverse events. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1416985. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1416985
62. Shetty R, Basheer FT, Poojari PG, Thonga G, Chandran VP, and Acharya LD. Adverse drug reactions of GLP-1 agonists: A systematic review of case reports. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2022) 16:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102427
63. Gorgojo-Martínez JJ, Mezquita-Raya P, Carretero-Gómez J, Castro A, Cebrián-Cuenca A, de Torres-Sánchez A, et al. Clinical recommendations to manage gastrointestinal adverse events in patients treated with Glp-1 receptor agonists: A multidisciplinary expert consensus. J Clin Med. (2022) 12:145. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010145
64. Bettge K, Kahle M, Abd El Aziz MS, Meier JJ, and Nauck MA. Occurrence of nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea reported as adverse events in clinical trials studying glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A systematic analysis of published clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2017) 19:336–47. doi: 10.1111/dom.12824
65. Ayoub M, Chela H, Amin N, Hunter R, Anwar J, Tahan V, et al. Pancreatitis risk associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, considered as a single class, in a comorbidity-free subgroup of type 2 diabetes patients in the United States: A propensity score-matched analysis. J Clin Med. (2025) 14:944. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030944
66. He L, Wang J, Ping F, Yang N, Huang J, Li Y, et al. Association of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use with risk of gallbladder and biliary diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Intern Med. (2022) 182:513–9. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0338
67. Filippatos TD, Panagiotopoulou TV, and Elisaf MS. Adverse effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Rev Diabetes Stud. (2014) 11:202–30. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2014.11.202
68. Ribeiro MA Jr, Tebar GK, Niero HB, and Pacheco LS. Biliary complications associated with weight loss, cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. (2024) 15:95647. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v15.i4.95647
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonists, dual agonists, metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis, hepatic fibrosis, weight loss, cardiovascular disease
Citation: Li M, Hu J, Chin YH, Chew HSJ and Wang W (2025) Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists and dual agonists in the treatment of patients with metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1681965. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1681965
Received: 08 August 2025; Accepted: 22 September 2025;
Published: 08 October 2025.
Edited by:
Yanan Wang, Xi’an Jiaotong University Health Science Center, ChinaReviewed by:
Theodoros Androutsakos, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceZilin Sun, Southeast University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Hu, Han Chin, Chew and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meng Li, bGltZW5nMjAwMEAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Meng Li
Meng Li Jianli Hu
Jianli Hu Yip Han Chin
Yip Han Chin Han Shi Jocelyn Chew
Han Shi Jocelyn Chew Wenru Wang
Wenru Wang