- 1Tuina Department, First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
- 2National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Level Three Laboratory for Tuina Technique Biological Effects, Tianjin, China
- 3Department of Human Development, Teachers College, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Jinlida (JLD) in improving glycemic control and insulin resistance in patients with prediabetes (PD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) through a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Methods: Databases including PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Embase, Scopus, CBM, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP were searched up to July 2025. Randomized controlled trials comparing JLD with controls were included. Pooled analyses were conducted using a random-effects model. Pre-specified subgroup analyses included health status and treatment duration. Additional analyses by baseline FBG level and age were performed to explore residual heterogeneity. Multivariable meta-regression with Knapp-Hartung adjustment further examined potential moderators (e.g., background therapy, baseline FBG level). Publication bias was assessed by funnel plots, Egger’s test, and the trim-and-fill method. Risk of bias and evidence certainty were evaluated using RoB 2.0 and GRADE.
Results: A total of 20 RCTs involving 2,993 participants were included. Compared with controls, JLD significantly reduced: FBG (MD = -0.97, 95% CI: -1.40 to -0.53; p < 0.001), 2h-PG (MD = -1.52, 95% CI: -1.89 to -1.16; p < 0.001), HbA1c (MD = -0.76, 95% CI: -1.00 to -0.52; p < 0.001), HOMA-IR (MD = -0.78, 95% CI: -1.12 to -0.44, p < 0.001). In lipid outcomes, JLD improved: HDL-C (MD = 0.22, 95% CI: 0.12 to 0.32, p < 0.001), LDL-C (MD = -0.69, 95% CI: -1.05 to -0.33; p < 0.001), TC (MD = -0.57, 95% CI: -0.87 to -0.27; p < 0.001), TG (MD = -0.52, 95% CI: -0.72 to -0.31, p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses revealed that JLD produced greater glycemic improvements in shorter-duration trials and in patients with higher baseline fasting glucose (≥10 mmol/L). T2DM patients showed more pronounced reductions in HbA1c, HOMA-IR, and lipid parameters compared with PD. Additionally, JLD significantly improved HDL-C, LDL-C, TC, and TG, with lipid benefits being stronger in T2DM.
Conclusion: JLD may help improve glycemic control, insulin resistance, and lipid profiles in patients with T2DM and prediabetes. Given the varying levels of certainty in the evidence across outcomes, these findings should be interpreted cautiously. Further large-scale, high-quality RCTs are needed to confirm these findings.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD420251124510.
1 Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic and progressive metabolic disorder characterized by sustained hyperglycemia that disrupts the normal metabolism of glucose, lipids, and proteins. Such metabolic disturbances accelerate cellular damage and ultimately impair the function of multiple organ systems, particularly the cardiovascular system, peripheral nerves, and vascular network (1). Recent reports indicate that the number of adult diabetes patients worldwide is as high as 589 million. It is projected that by 2050, the total number of adult diabetes patients globally will increase to 853 million (2). Prediabetes (PD) represents a transitional metabolic stage before the onset of diabetes. Individuals in this transitional phase exhibit glucose levels above the normal range yet still below the threshold for diabetes diagnosis, and these abnormalities are already linked to metabolic disturbances as well as elevated risks of cardiovascular disease, microvascular injury, cancer, and other complications (3, 4). Evidence indicates that nearly one-quarter of PD patients progress to T2DM within 3–5 years, and up to 70% eventually develop diabetes during their lifetime (5, 6). The prevalence of PD and diabetes continues to rise, not only increasing the incidence of complications but also imposing a heavy socioeconomic burden, thereby making their prevention and management an urgent global public health priority (7). Beyond hyperglycemia itself, diabetes is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease, with many patients eventually requiring dialysis, which markedly reduces the quality of life and increases healthcare expenditures (8). Diabetic retinopathy remains a major cause of blindness worldwide (9), while diabetic neuropathy severely impairs daily functioning and substantially contributes to disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) (10). The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 reported that the age-standardized DALY rate for T2DM was 801.5 per 100,000 population, representing a 27.6% increase compared with 1990 (11). From an economic perspective, the American Diabetes Association estimated that the annual cost of diabetes in the United States alone reached USD 412.9 billion in 2022, including direct medical expenditures and productivity losses (12). Collectively, these findings underscore that PD and diabetes are systemic diseases with a profound societal impact.
Currently, the cornerstone of T2DM and PD management includes lifestyle modifications and oral hypoglycemic agents (13). However, these approaches have notable limitations in real-world settings. Lifestyle interventions are often difficult to sustain, particularly among high-risk populations (14). Despite the availability of several pharmacological options, including metformin, sulfonylureas, and SGLT-2 inhibitors, each is accompanied by certain limitations. For instance, prolonged use of metformin may lead to gastrointestinal side effects, impaired vitamin B12 absorption, and, in rare cases, lactic acidosis (15). Sulfonylureas may cause hypoglycemia and weight gain (16), while SGLT-2 inhibitors carry an increased risk of genitourinary tract infections (17). Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore a safe adjunctive therapeutic approach. Moreover, given the progressive nature of T2DM, monotherapy with lifestyle changes or a single antidiabetic agent is often insufficient for long-term metabolic control. Many patients eventually require insulin therapy, which increases psychological and financial burdens.
Over the past decade, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has attracted growing attention as an adjunctive approach in diabetes management. Jinlida (JLD) is a standardized Chinese patent medicine composed of 17 herbs, such as Panax ginseng, Polygonatum sibiricum, Atractylodes lancea, Sophora flavescens, Salvia miltiorrhiza, Pueraria lobata, and Lycium barbarum. It was approved in 2005 for use alongside conventional therapy. T2DM was subsequently listed in the China National Essential Medicines List and National Reimbursement Drug List. Experimental studies indicate that JLD acts on multiple biological targets, enhancing pancreatic β-cell function, stimulating insulin secretion, preventing β-cell apoptosis, and improving insulin resistance.
Previous meta-analyses have examined the efficacy of JLD in patients with T2DM, yet their findings remain inconsistent (18, 19). These reviews were confined to individuals with established T2DM and focused mainly on a limited set of glycemic outcomes, without systematic evaluation of other metabolic indicators or safety profiles. In addition, the potential influences of participant characteristics and intervention parameters, such as age, disease stage, treatment duration, and background therapy, have not been quantitatively explored. However, such factors may substantially affect the metabolic response to JLD and determine its applicability across diverse patient groups. Considering these limitations and the publication of several new randomized controlled trials since early 2022, an updated and comprehensive synthesis is warranted. The present meta-analysis therefore evaluated both T2DM and prediabetes populations and incorporated broader clinical outcomes, including insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), lipid profiles, and adverse events. Furthermore, subgroup and meta-regression analyses were conducted to investigate how participant and intervention characteristics may influence treatment effects. This approach provides a unified analytic framework to clarify the therapeutic potential of JLD and to guide its optimized, evidence-based application in metabolic disease management.
2 Materials and methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis followed the PRISMA 2020 guidelines. The study protocol was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251124510).
2.1 Search strategy
Two reviewers independently searched the literature published between the establishment of the databases and July 2025 in nine databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Embase, Scopus, China Biology Medicine Database (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, and Chinese Scientific Journal Database. At the same time, the references of relevant studies were manually retrieved. The detailed search strategy for each database was provided in Appendix 1.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
1. Study design: Randomized controlled trials.
2. Population: Adults who met the diagnostic criteria for PD or T2DM (20, 21).
3. Intervention measures: JLD Granules alone, or in combination with non-traditional Chinese medicine therapies, such as oral hypoglycemic agents or lifestyle interventions. Trials involving injections, decoctions, patented TCM pills, or herbal extracts were not considered TCM therapies and thus were excluded.
4. Control group: Control arms included placebo or non-TCM therapies, explicitly comprising (i) standard-of-care oral hypoglycemic agents, (ii) lifestyle intensification alone, or (iii) both.
(5) Outcomes: FBG, 2h-PG, Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), HbA1c, Total Cholesterol (TC), Triglycerides (TG), Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C), High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C).
2.3 Exclusion criteria
1. Non-original or incomplete studies: Abstracts, conference proceedings, reviews, case reports, letters, and secondary analyses.
2. Research on serious deficiencies in method and detail reporting.
3. Republished literature.
2.4 Literature selection and data extraction
The screening and data extraction processes were independently performed by two investigators (HYX and XCH). Literature duplicates were eliminated with EndNote 20.1, followed by title and abstract screening to remove non-eligible records. Full texts of potentially relevant studies were further evaluated using the prespecified eligibility criteria to determine final inclusion. Data collection covered general study information (first author, year, location), participant features (such as age, sex, disease duration, and overall health status), intervention details for the experimental group (type, frequency, length of treatment, and dosage), information on the control group, major outcomes, and adverse event reporting.
2.5 Quality assessment
Two researchers (LLM and TQY) independently used the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool ROB 2.0 to evaluate the quality of these studies (22). The Cochrane methodological quality assessment tool consists of seven items, namely: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of subjects and researchers, blinding of outcome evaluators, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other biases. In case of disagreement between the two researchers, a third evaluator reviewed the study to reach a consensus.
2.6 Statistical analysis
To ensure consistency across studies, continuous outcomes originally reported in different units were converted into a common unit before analysis. For continuous outcomes, pooled effect sizes were expressed as mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and for dichotomous outcomes, as risk ratios (RRs) with 95% CIs. In line with the Cochrane Handbook recommendations, when multi-arm trials were encountered, all relevant intervention groups were combined into a single intervention group and all relevant control groups into a single comparator group. All effect sizes were synthesized using a random-effects model with restricted maximum likelihood (REML) estimation. Between-study heterogeneity was evaluated using Cochran’s Q test, Higgins’ I² statistic, and 95% prediction intervals.
Sensitivity analyses were conducted using multiple approaches, including: (1) leave-one-out analysis; (2) exclusion of trials with moderate-to-high risk of bias; (3) exclusion of studies without standardized Western medicine background interventions; (4) alternative continuity corrections for sparse binary outcomes; and (5) residual diagnostics (studentized residuals, Cook’s distance, DFBETAS, hat values, and covariance ratios) to identify potential outliers and influential studies (23, 24).
The pre-specified subgroup analyses included health status (T2DM vs. PD) and treatment duration (<12 vs. ≥12 weeks). Because substantial heterogeneity remained, we conducted additional subgroup analyses by baseline FBG (<7.0, 7.0–9.9, ≥10.0 mmol/L) and age (<45, 45–59, 60–74 years). To further investigate heterogeneity, we performed multivariable random-effects meta-regression with Knapp–Hartung adjustment, incorporating background treatment, age, trial duration, baseline FBG, and health status as covariates. This approach enabled us to assess the moderating effects of multiple clinical and methodological factors and to quantify the proportion of variance explained (R²). Publication bias was examined by funnel plot symmetry and Egger’s regression test when ten or more randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were available for an outcome. If publication bias is detected, the trim-and-fill method will be used to adjust for it. All statistical analyses were performed using R software (Version 4.4.3).
2.7 Evidence quality evaluation
This study applied the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach to evaluate the quality of evidence for primary outcomes (25), considering five domains: risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias. Evidence was rated as high, moderate, low, or very low. Two reviewers (LLM and FS) independently conducted the assessment, with discrepancies resolved through discussion or by consulting a third reviewer. This rigorous process ensured the objectivity and reliability of the evaluation.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection
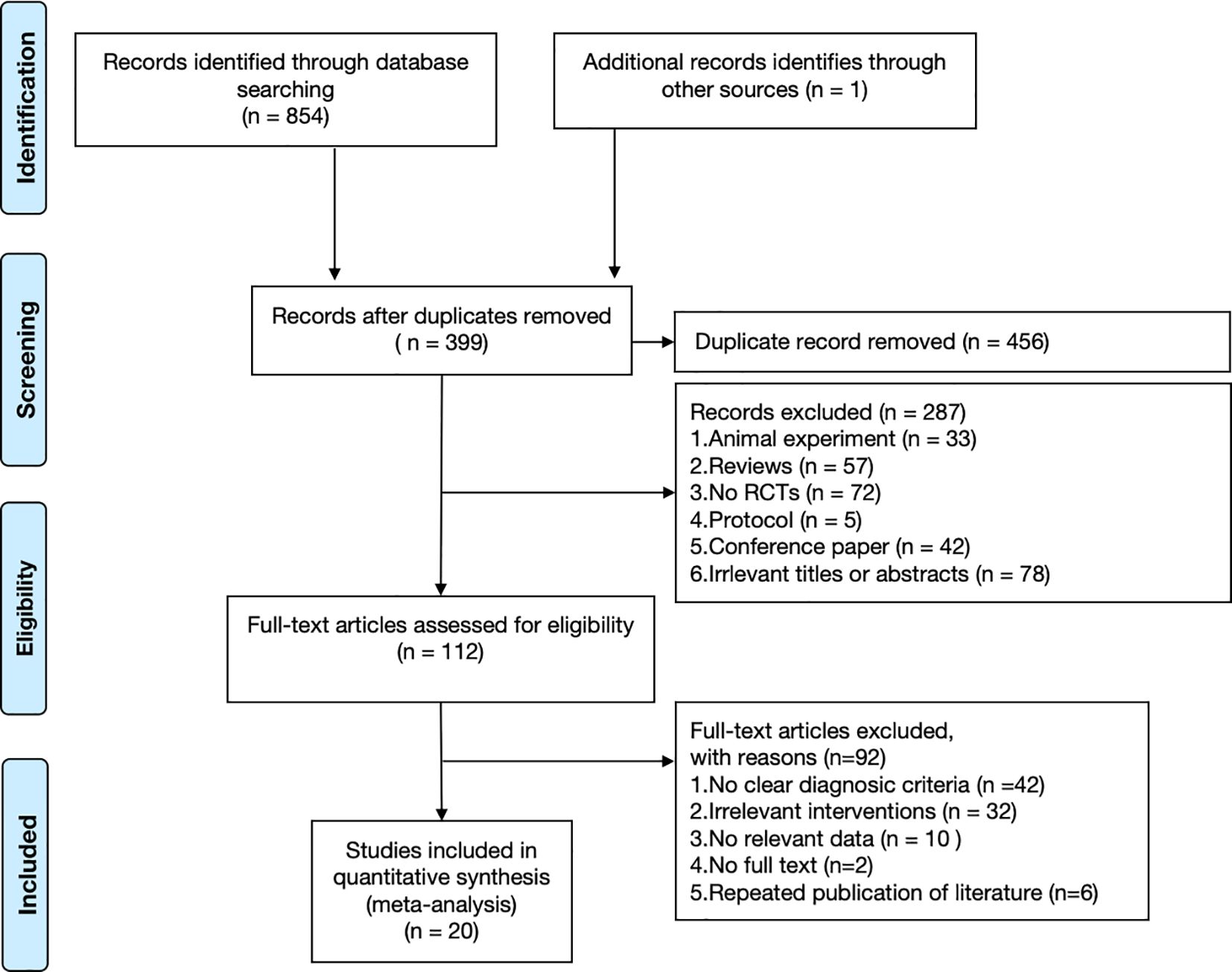
A total of 855 relevant studies were initially retrieved. After removing duplicates, 399 records remained for title and abstract screening. After screening titles and abstracts, 287 records were excluded. Subsequently, 112 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility, and 92 were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria. Ultimately, 20 RCTs were included in the present meta-analysis (26–45). The literature screening process and results are presented in Figure 1.
3.2 Study characteristics
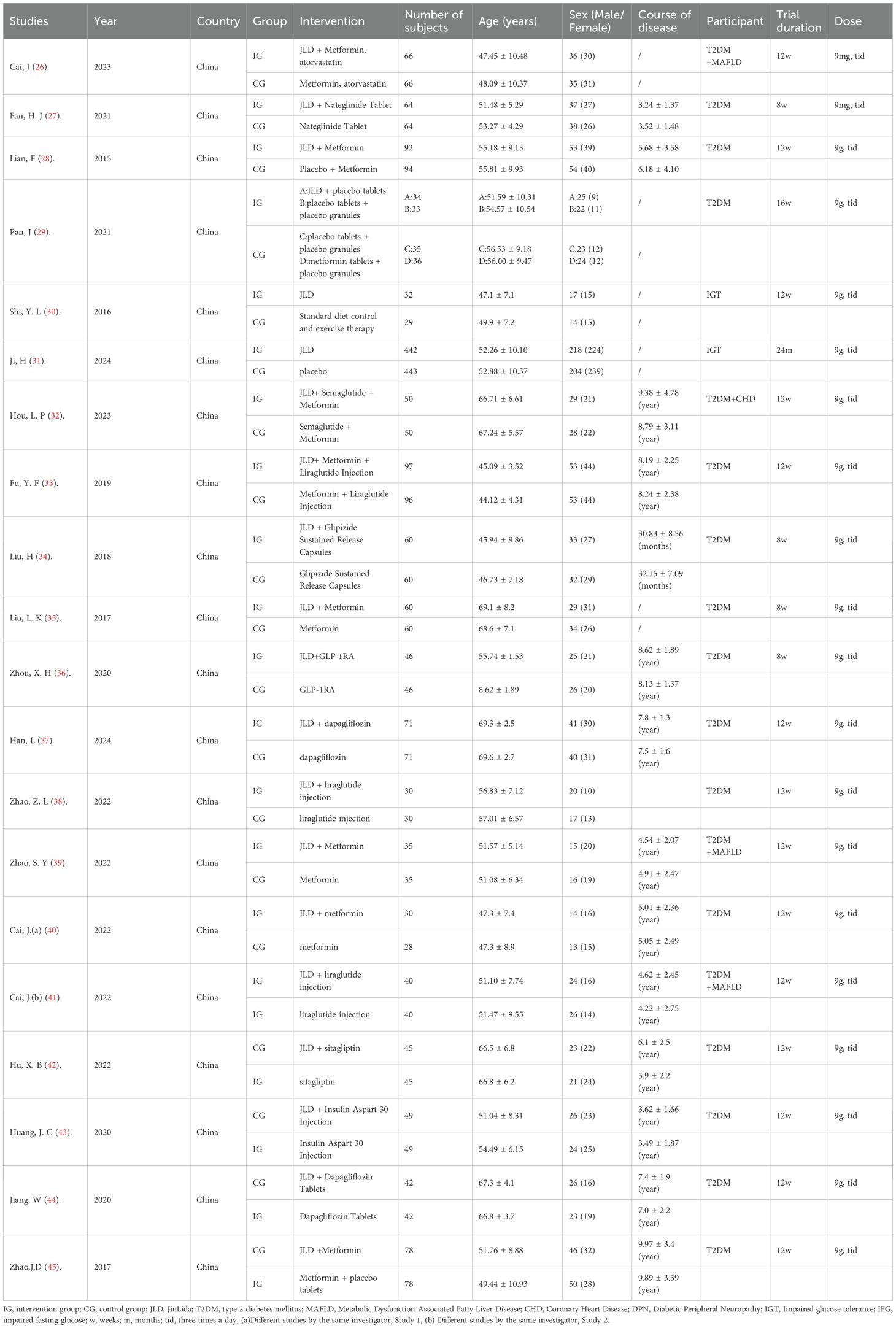
A total of 20 trials involving 2,993 subjects were included in this meta-analysis. These RCTs were published between 2015 and 2024. All studies were conducted in China. Of these, six were published in English and fourteen in Chinese. In two studies, the participants had PD, while in the remaining studies, participants had T2DM. Sample sizes ranged from 58 to 885. The duration of the intervention ranged from 4 weeks to 16 weeks. The average age of participants ranged from (44.12 ± 4.31) to (69.6 ± 2.7) years. The characteristics of the included trials are summarized in Table 1.
3.3 Risk of bias
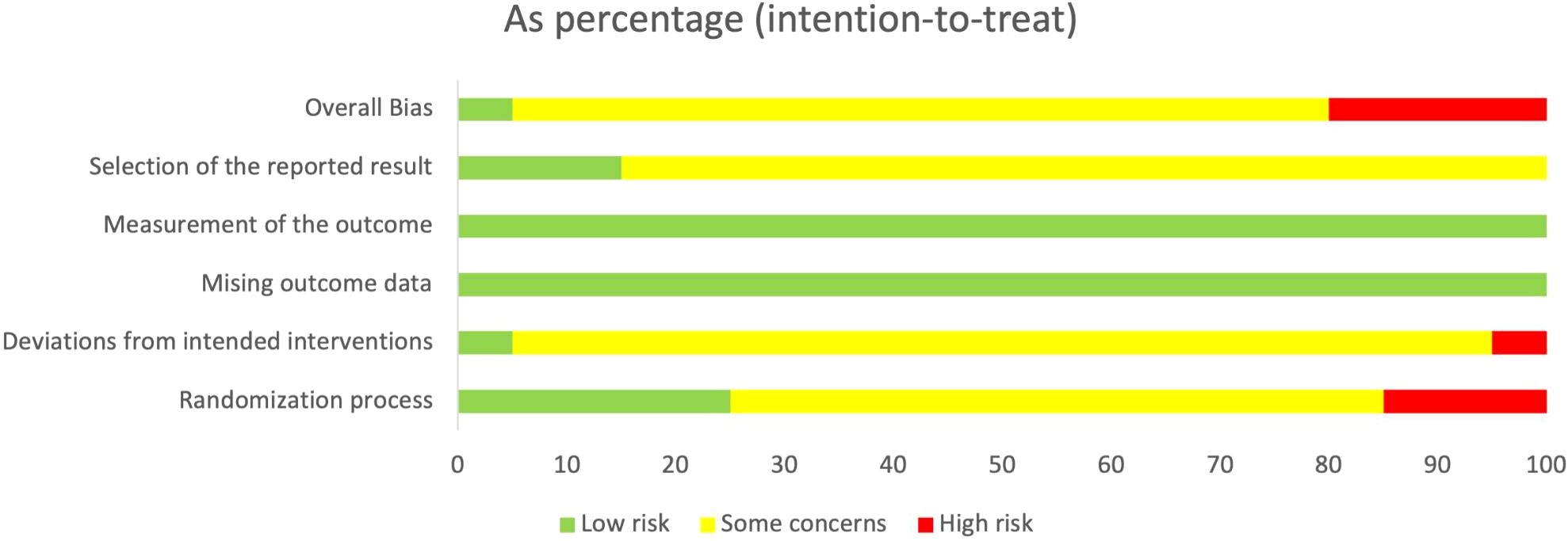
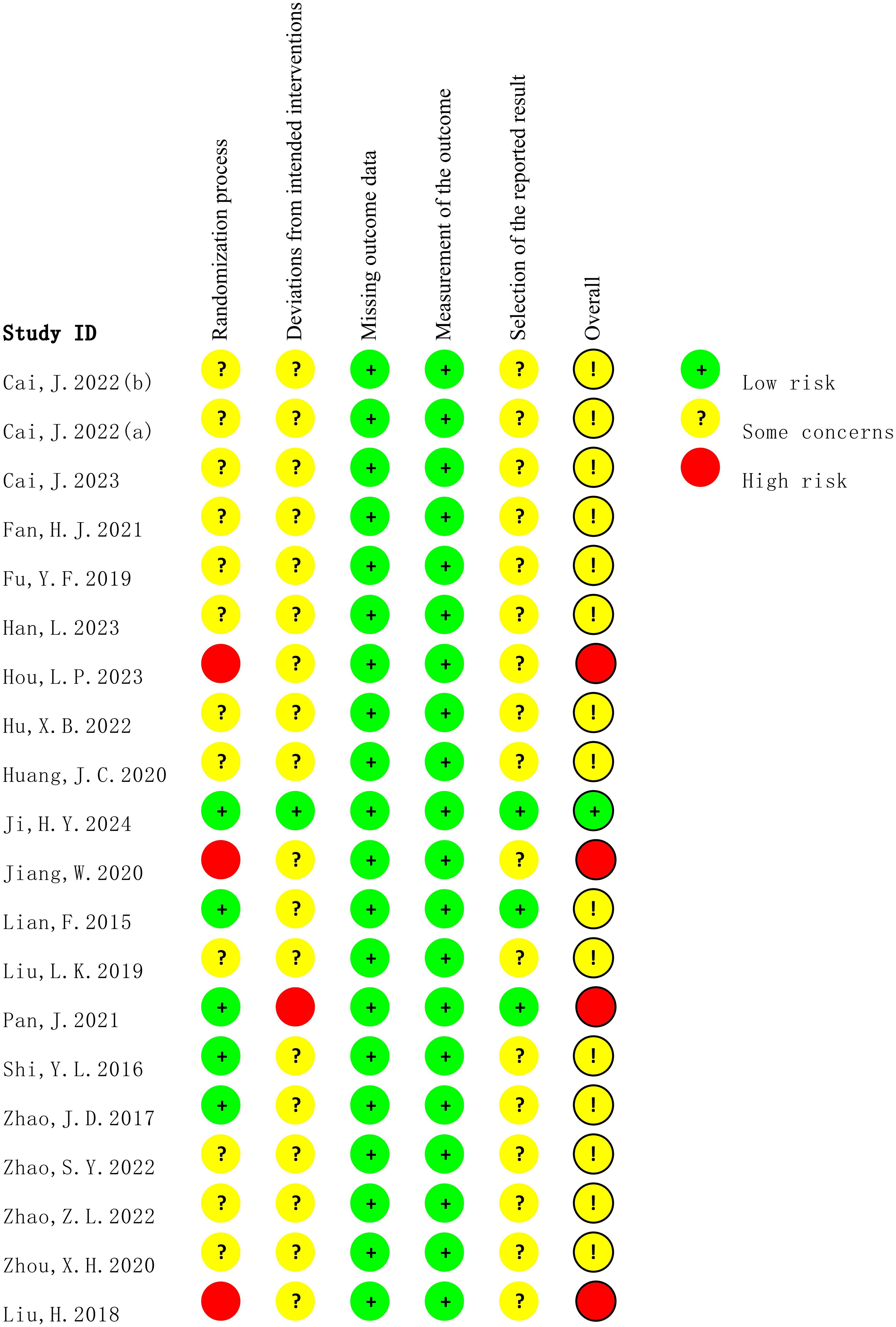
The methodological quality of all included studies was assessed using the ROB 2.0. As shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, most studies reported randomization procedures but were rated as having “some concerns” in the domain of Randomization process due to insufficient description of allocation concealment. Three studies (32, 34, 35) were judged to be at “high risk” in this domain. In the domain of deviations from intended interventions, although most studies did not explicitly apply intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, the proportion of participants who did not adhere to their assigned interventions was less than 5%, which was unlikely to substantially affect the results; therefore, these studies were rated as “low risk” or “some concerns.” However, the study by Pan, J (29). relied on per-protocol (PP) analysis rather than ITT, with a dropout rate of 12.7%, which may have introduced bias, and was thus rated as “high risk.” For outcome measurement, all studies were rated as “low risk,” since the primary outcomes were objectively measured using standardized blood glucose tests. In the domain of selection of the reported result, most studies were judged as having “some concerns,” primarily because they did not clarify whether a pre-specified analysis plan was finalized before unblinding. Overall, most studies were judged to have “some concerns,” and four studies were rated as “high risk” in at least one domain.
3.4 Meta-analysis
3.4.1 Effect of JLD on FBG
A total of 20 studies with 2,993 participants (1,497 in the control group and 1,496 in the treatment group) evaluated the effect of JLD on FBG. Heterogeneity analysis indicated substantial variability among studies (P < 0.001, I² = 94.3%, 95% PI [-2.99, 1.06]). The pooled results showed that JLD significantly reduced FBG compared with the control group (MD = –0.97, 95% CI: –1.40 to –0.53; p < 0.001; Figure 4).
![Forest plot summarizing 20 randomized studies for the labeled glycemic outcome (mean difference, MD). Each study is shown with a red square whose size reflects its weight and a horizontal line for the 95% confidence interval (CI); the zero line is at 0. Most estimates lie to the left of zero, favoring Jinlida over control. The pooled random-effects result (diamond) indicates a reduction: MD = −0.97 (95% CI −1.40 to −0.53). A prediction interval is provided: [−2.99, 1.06]. Heterogeneity is substantial: Tau2 = 0.8869; Chi2 = 332.77 (df = 19, p < 0.0001); I2 = 94.3%. Study names, SEs, weights, and CIs are displayed in the table columns.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1689640/fendo-16-1689640-HTML-r1/image_m/fendo-16-1689640-g004.jpg)
Figure 4. Forest plot of the effect of JLD on FBG. Study-specific mean differences (MDs) are shown as squares, with areas proportional to study weights. Horizontal bars depict 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and the pooled estimate is displayed as a diamond derived from a random-effects model. The vertical reference line at 0 indicates no overall effect.
Subgroup analyses revealed greater reductions in FBG in trials lasting <12 weeks (MD = -2.23, 95% CI: -3.71 to -0.74) compared with those lasting ≥12 weeks (MD = -0.58, 95% CI: -0.78 to -0.39), with the difference significant after Holm correction (p for interaction = 0.0012, P_Holm = 0.0037, R² = 45.63%). Baseline FBG also modified the treatment effect: participants with baseline FBG ≥10.0 mmol/L showed the largest reduction (MD = -2.62, 95% CI: -4.48 to -0.76), those with 7.0–9.9 mmol/L had a moderate reduction (MD = -0.79, 95% CI: -1.02 to -0.55), while those with baseline <7.0 mmol/L showed only a small but statistically significant decrease (MD = -0.18, 95% CI: -0.33 to -0.02; p for interaction = 0.0005, P_Holm = 0.0020, R² = 62.61%). No significant subgroup effects were found for disease status (T2DM vs. PD; p = 0.201, P_Holm = 0.401, R² = 4.10%) or age (p = 0.366, P_Holm = 0.401, R² = 0.51%) (Supplementary Table 1).
3.4.2 Effect of JLD on 2h-PG
A total of 18 studies evaluated 2h-PG, with a combined sample size of 2,781 participants, including 1,391 in the control group and 1,390 in the treatment group. Heterogeneity testing revealed moderate heterogeneity among the studies (p < 0.001, I2 = 77.4%, 95% PI [-2.95, -0.10]). The meta-analysis showed that JLD significantly reduced 2h-PG levels (MD = -1.52, 95% CI: -1.89 to -1.16; p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 5.
![Forest plot showing meta-analysis results of 18 studies comparing mean differences with 95% confidence intervals. Each study is represented by a red square and a horizontal line, indicating the effect estimate and confidence interval. The overall effect is depicted by a diamond at -1.52, with the confidence interval of [-1.89; -1.16]. The prediction interval ranges from [-2.95; -0.10]. Heterogeneity statistics include Tau-squared of 0.4209, Chi-squared of 75.18, degrees of freedom of 17, p-value less than 0.0001, and I-squared of 77.4 percent.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1689640/fendo-16-1689640-HTML-r1/image_m/fendo-16-1689640-g005.jpg)
Figure 5. Forest plot of the effect of JLD on 2h-PG. Each square reflects the MD for an individual trial, scaled to its weight in the meta-analysis. The line across each square represents the 95% CI. The diamond at the bottom summarizes the pooled MD under a random-effects model, with the line at 0 marking the null effect.
For 2h-PG, treatment duration was again a significant moderator. Trials with <12 weeks of follow-up showed larger reductions (MD = -2.22, 95% CI: -2.52 to -1.92) compared with ≥12 weeks (MD = -1.30, 95% CI: -1.69 to -0.90), although this effect lost significance after Holm correction (p for interaction = 0.025, P_Holm = 0.101, R² = 44.53%). Baseline glucose also influenced results: participants with ≥10.0 mmol/L showed the largest benefit (MD = -2.24, 95% CI: -2.69 to -1.79), followed by those with 7.0-9.9 mmol/L (MD = -1.46, 95% CI: -1.87 to -1.04), while <7.0 mmol/L showed smaller and non-significant effects (MD = -1.00, 95% CI: -2.15 to 0.15; p for interaction = 0.173, P_Holm = 0.519, R² = 19.34%). Subgroup effects by disease status (PD vs. T2DM) and age were not statistically significant (all P_Holm > 0.05). Notably, the similarity between the PD subgroup and the <7.0 mmol/L subgroup likely reflects the substantial overlap of patient characteristics. Detailed results are presented in Supplementary Table 2.
3.4.3 Effect of JLD on HbA1c
A total of 17 studies evaluated HbA1c, involving 2,683 participants—1,343 in the control group and 1,340 in the treatment group. Heterogeneity analysis revealed substantial heterogeneity among the included studies (p < 0.001, I2 = 90.9%, 95% PI [-1.77, 0.25]). The results of the meta-analysis showed that compared with the control group, JLD could significantly reduce 2h-PG levels (MD = -0.76, 95% CI: -1.00 to -0.52; p < 0.001), as illustrated in Figure 6.
![Forest plot showing mean differences from multiple studies, with confidence intervals depicted as horizontal lines. Red squares represent effect sizes, and a diamond symbolizes the overall effect size. The plot indicates a pooled mean difference of -0.76 with a 95% confidence interval of [-1.00, -0.52], and high heterogeneity is observed (I² = 90.9%).](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1689640/fendo-16-1689640-HTML-r1/image_m/fendo-16-1689640-g006.jpg)
Figure 6. Forest plot of the effect of JLD on HbA1c. Squares denote individual study estimates (MDs) weighted by sample size contribution, with accompanying 95% CIs as horizontal whiskers. The overall random-effects estimate is presented as a diamond, and the solid vertical line at 0 represents no difference between groups.
Subgroup analyses indicated that shorter trials (<12 weeks) achieved greater reductions in HbA1c (MD = -1.21, 95% CI: -1.68 to -0.75). However, this difference did not remain statistically significant after Holm–Bonferroni correction (p for interaction = 0.029, P_Holm = 0.116, R² = 27%). Regarding baseline glucose, patients with ≥10.0 mmol/L showed a significant reduction (MD = -0.80, 95% CI: -1.11 to -0.49), but subgroup differences were not statistically significant (p for interaction = 0.433, P_Holm = 0.866, R² = 0%). No significant subgroup effects were observed for disease status (p = 0.187, P_Holm = 0.562, R² = 6.2%) or age (p = 0.796, P_Holm = 0.866, R² = 0%), as shown in Supplementary Table 3.
3.4.4 Effect of JLD on HOMA-IR
Twelve studies evaluated HOMA-IR, including 989 participants in the control group and 983 in the treatment group. Heterogeneity analysis revealed substantial heterogeneity (p < 0.001, I² = 92.9%, 95% PI [-2.09, 0.54]). The meta-analysis demonstrated that JLD significantly reduced HOMA-IR compared with control (MD = -0.78, 95% CI: -1.12 to -0.44; p < 0.001), as illustrated in Figure 7.
![Forest plot of randomized studies for the labeled metabolic outcome (mean difference, MD). Each study appears with a red square (size ∝ weight) and a horizontal line showing the 95% confidence interval (CI); the vertical line at 0 indicates no effect. Most estimates lie left of 0, favoring Jinlida over control. The pooled random-effects result (black diamond) shows a reduction: MD = −0.78 (95% CI −1.12 to −0.44). A prediction interval is provided: [−2.09, 0.54]. Between-study heterogeneity is high: Tau2 = 0.3267; Chi2 = 155.27 (df = 11, p < 0.0001); I2 = 92.9%. Study labels, SEs, weights, and CIs are listed in the table columns.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1689640/fendo-16-1689640-HTML-r1/image_m/fendo-16-1689640-g007.jpg)
Figure 7. Forest plot of the effect of JLD on HOMA-IR. Each study’s MD is indicated by a square, with size corresponding to analytic weight. Horizontal lines display 95% CIs, and the pooled random-effects estimate is shown as a diamond. The vertical axis at 0 indicates the line of no effect.
Subgroup analyses showed no significant differences in treatment effect across trial duration (p for interaction = 0.934, P_Holm = 1.000, R² = 0%), disease status (p = 0.522, P_Holm = 1.000, R² = 0%), baseline glucose level (p = 0.763, P_Holm = 1.000, R² = 0%), or age (p = 0.215, P_Holm = 1.000, R² = 5.28%). Detailed results are presented in Supplementary Table 4.
3.4.5 Effect of JLD on HDL-C
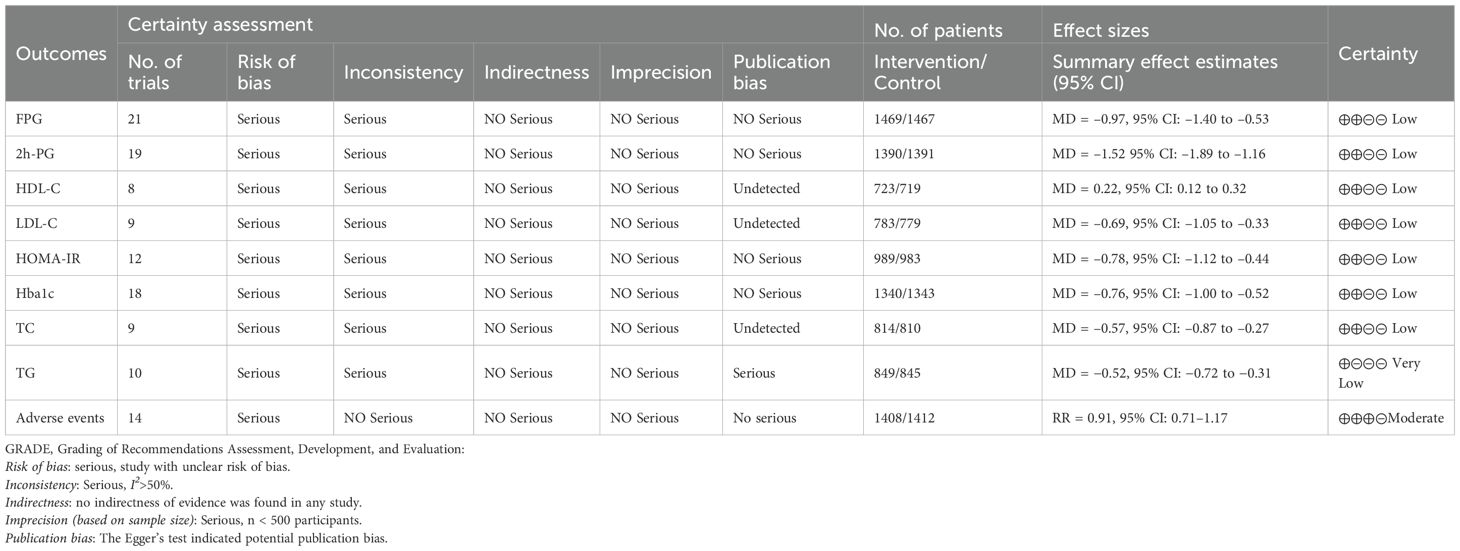
Eight studies evaluated HDL-C, including 1,442 participants (723 in the control group and 719 in the treatment group). Heterogeneity analysis revealed substantial between-study heterogeneity (p < 0.001, I² = 92.6%, 95% PI [-0.11, 0.55]). The meta-analysis demonstrated that JLD significantly increased HDL-C levels compared with the control group (MD = 0.22, 95% CI: 0.12 to 0.32; p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 8.
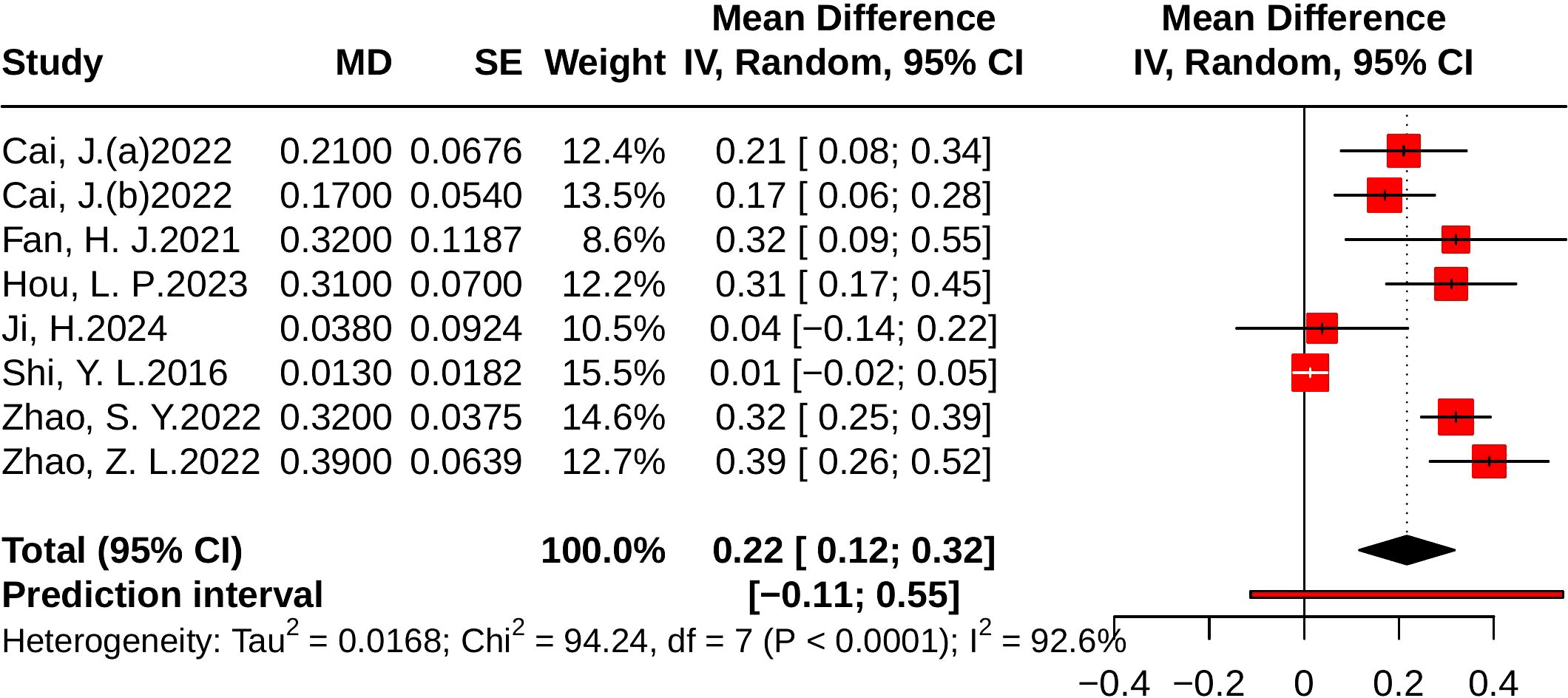
Figure 8. Forest plots of the effect of JLD on HDL-C. Squares reflect study-specific MDs, scaled by weight. The horizontal span of each square shows the 95% CI, while the overall pooled MD from a random-effects model is represented by a diamond. The reference line at 0 denotes no observed effect.
Subgroup analyses indicated greater improvements in T2DM patients (MD = 0.28, 95% CI: 0.21 to 0.35; p for interaction = 0.003, P_Holm = 0.012, R² = 84.2%) and in participants with baseline glucose ≥10.0 mmol/L (MD = 0.39, 95% CI: 0.26 to 0.52; p for interaction = 0.005, P_Holm = 0.015, R² = 89.1%). No significant subgroup effects were observed for trial duration (p = 0.564, P_Holm = 1.000, R² = 0%) or age (p = 0.528, P_Holm = 1.000, R² = 0%). Detailed results are presented in Supplementary Table 5.
3.4.6 Effect of JLD on LDL-C
Nine studies evaluated LDL-C, including 1,562 participants (779 in the control group and 783 in the treatment group). Heterogeneity analysis indicated substantial between-study variability (p < 0.001, I² = 96.1%, 95% PI [-1.97, 0.58]). The meta-analysis demonstrated that JLD significantly reduced LDL-C levels compared with the control group (MD = -0.69, 95% CI: -1.05 to -0.33; p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 9.
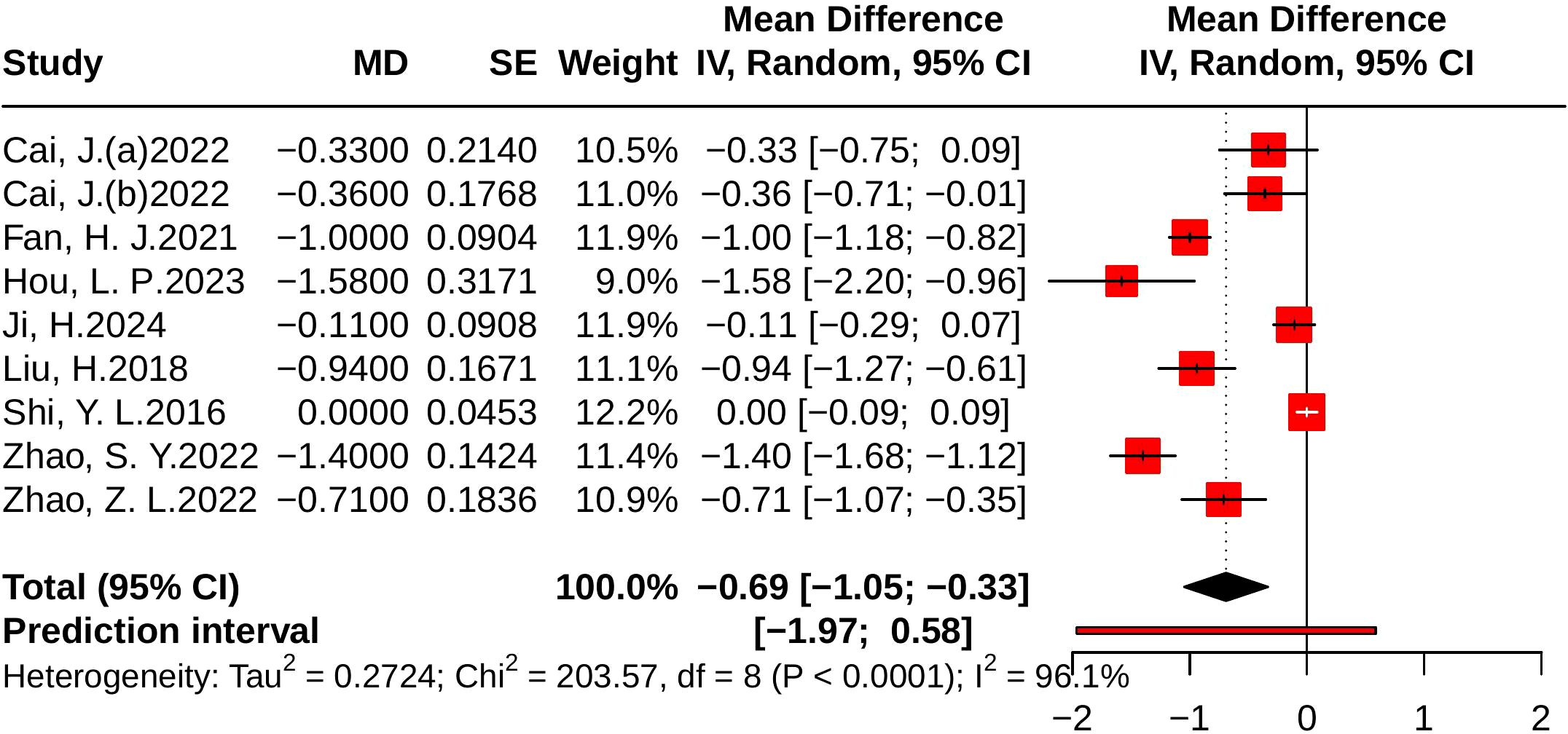
Figure 9. Forest plots of the effect of JLD on LDL-C. Each square corresponds to a trial estimate (MD), with size indicating relative weight. Horizontal lines indicate 95% CIs. The pooled estimate is summarized by a diamond under a random-effects model, with 0 as the null line.
Subgroup analyses suggested greater LDL-C reductions in T2DM patients (MD = -0.89, 95% CI: -1.22 to -0.56; p for interaction = 0.033, P_Holm = 0.133, R² = 52.4%). By baseline glucose level, larger benefits were observed in participants with ≥10.0 mmol/L or 7.0–9.9 mmol/L, although the subgroup difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.128, P_Holm = 0.385, R² = 41.4%). No significant subgroup effects were found for trial duration (p = 0.442, P_Holm = 0.442, R² = 0%) or age (p = 0.143, P_Holm = 0.385, R² = 16.1%). Detailed results are provided in Supplementary Table 6.
3.4.7 Effect of JLD on TC
Nine studies evaluated TC, including 810 in the control group and 814 in the treatment group. Heterogeneity analysis indicated substantial variability (p < 0.001, I² = 89.6%, 95% PI [-1.55, 0.42]). The results of the meta-analysis showed that compared with the control group, JLD significantly reduced TC (MD = -0.57, 95% CI: -0.87 to -0.27; p < 0.001). The corresponding forest plot is presented in Figure 10.
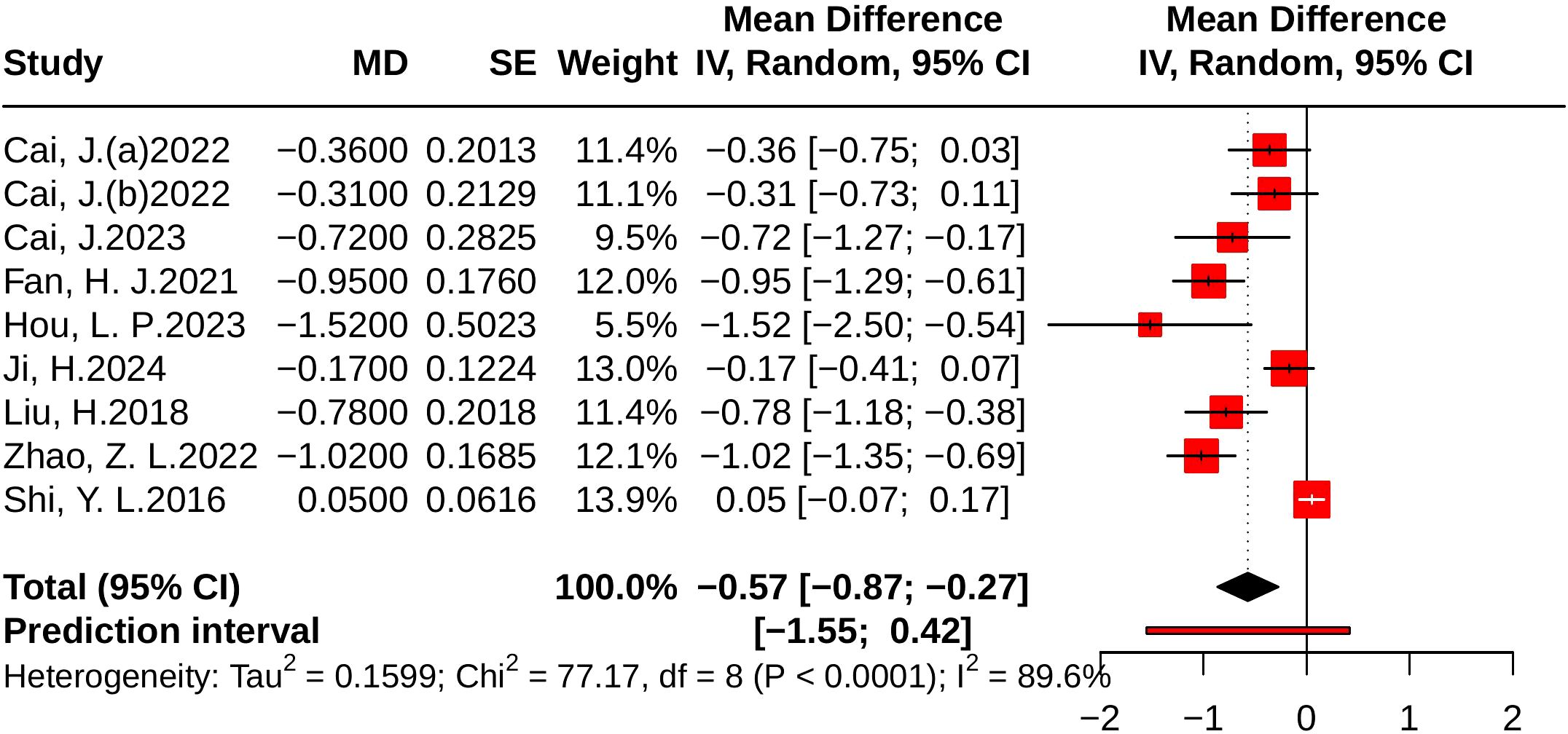
Figure 10. Forest plots of the effect of JLD on TC. Squares show the MDs from individual studies proportional to weight, with horizontal lines indicating 95% CIs. The pooled result is depicted as a diamond derived from the random-effects model, with the vertical line at 0 signifying no effect.
Subgroup analyses suggested greater TC reductions in T2DM patients (MD = -0.75, 95% CI: -1.00 to -0.50; p for interaction = 0.014, P_Holm = 0.057, R² = 71.6%). Patients with baseline glucose ≥10.0 mmol/L experienced larger benefits (MD = -0.92, 95% CI: -1.17 to -0.67); however, the subgroup difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.037, P_Holm = 0.112, R² = 75.8%). No significant subgroup effects were found for trial duration (p = 0.301, P_Holm = 0.301, R² = 11.8%) or age (p = 0.148, P_Holm = 0.296, R² = 11.4%). Detailed results are provided in Supplementary Table 7.
3.4.8 Effect of JLD on TG
Ten studies evaluated TG, including 849 participants in the control group and 845 in the treatment group. Heterogeneity analysis revealed substantial heterogeneity (p < 0.001, I² = 94.5%, 95% PI [-1.20, 0.17]). The meta-analysis showed that, compared with the control group, JLD significantly reduced TG levels (MD = -0.52, 95% CI: -0.72 to -0.31; p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 11.
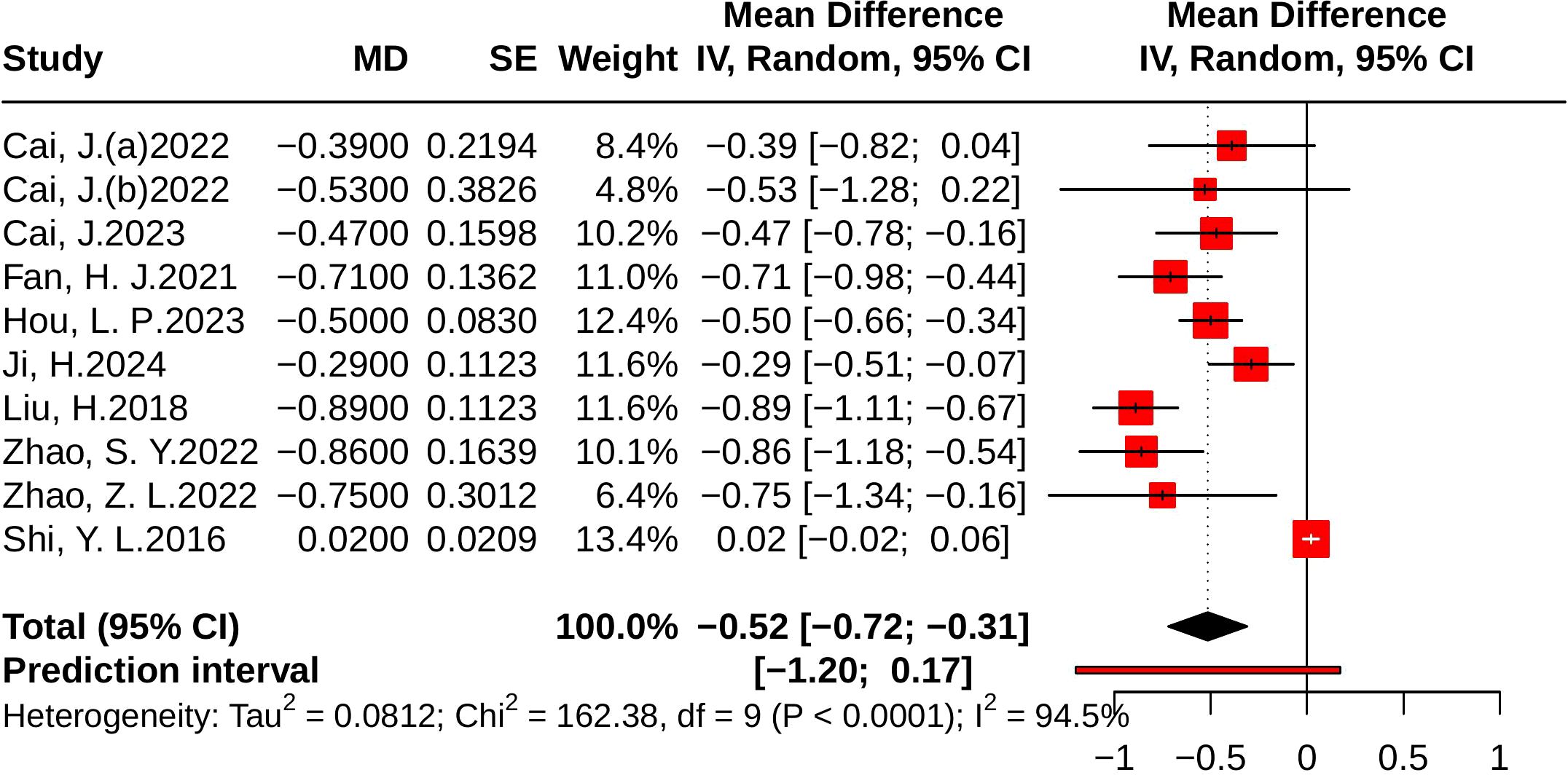
Figure 11. Forest plots of the effect of JLD on TG. Each study’s estimate is plotted as a square scaled to weight, with 95% CIs shown as horizontal lines. The pooled MD from the random-effects model is displayed as a diamond, and the line at 0 indicates no difference.
Subgroup analyses indicated greater TG reductions in T2DM patients (MD = -0.65, 95% CI: -0.80 to -0.50; p for interaction = 0.003, P_Holm = 0.013, R² = 69.7%). Patients with baseline glucose ≥10.0 mmol/L experienced larger benefits (MD = -0.87, 95% CI: -1.08 to -0.67), and subgroup differences remained statistically significant (p = 0.004, P_Holm = 0.013, R² = 78.5%). No significant subgroup effects were found for trial duration (p = 0.099, P_Holm = 0.198, R² = 24.5%) or age (p = 0.948, P_Holm = 0.948, R² = 0%), as illustrated in Supplementary Table 8.
3.4.9 Adverse events
In the safety analysis, a total of 14 randomized controlled trials were included. The pooled results from the random-effects model showed no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the intervention and control groups (RR = 0.91, 95% CI: 0.71–1.17; p = 0.467). The heterogeneity test indicated p = 0.37 and I² = 7.4%, suggesting low between-study heterogeneity, as illustrated in Figure 12.
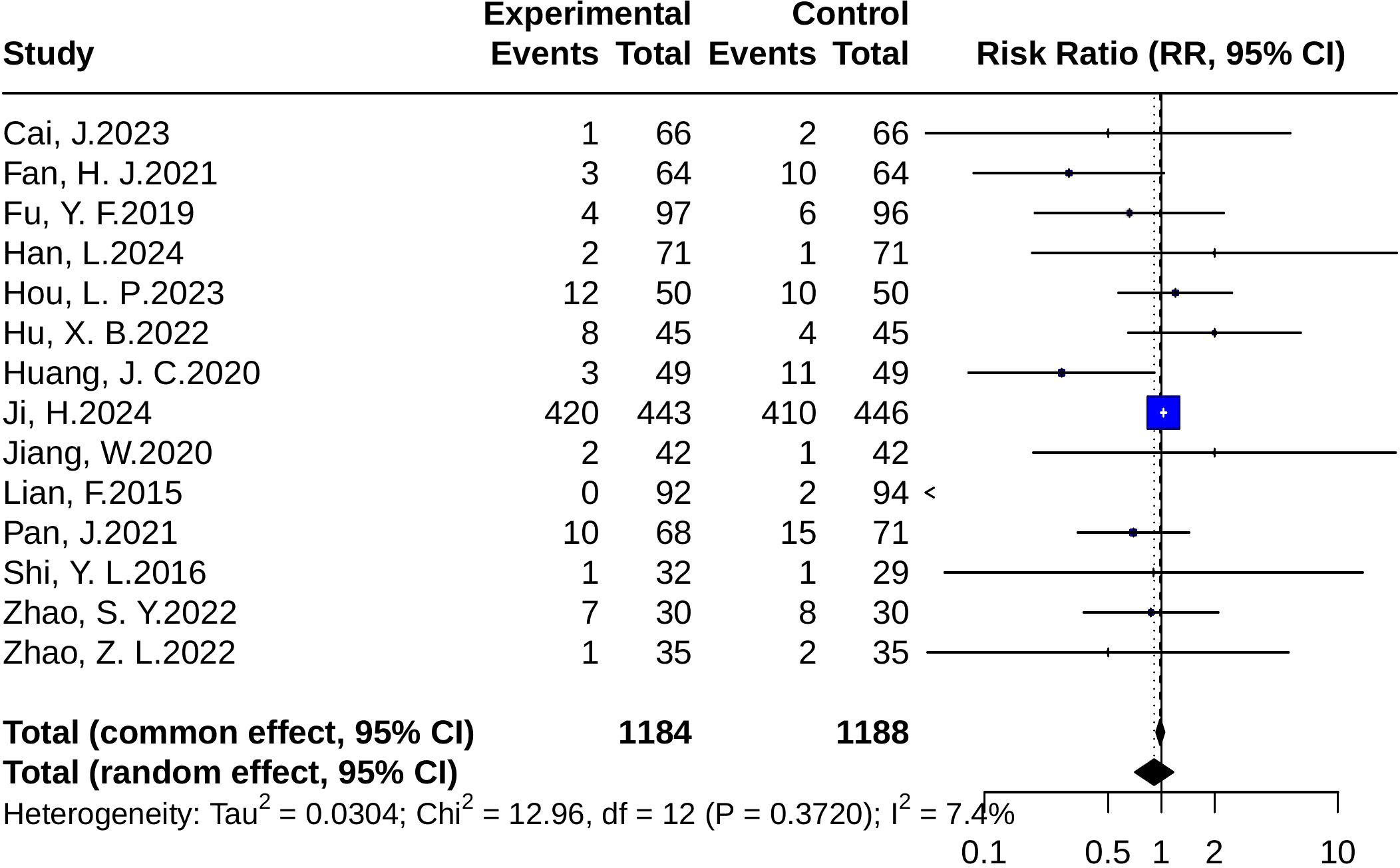
Figure 12. Forest plots of adverse event risk (RR). Squares represent risk ratios (RRs) from individual studies, weighted by study precision. Horizontal bars show 95% CIs. The pooled estimate, obtained with a random-effects model, is represented by a diamond. The vertical line at 1 denotes the null value for risk comparison.
3.4.10 Meta-regression
The results of this meta-analysis indicated that most outcomes exhibited substantial heterogeneity. For outcomes with more than 10 included studies, meta-regression was conducted. The covariates (trial duration, age, baseline FBG, background treatment, and status) explained a large proportion of the heterogeneity in FBG (R² = 81.02%) and HbA1c (R² = 62.98%), with trial duration (<12 weeks) emerging as a significant moderator for both outcomes. For 2hPG, the model explained nearly half of the heterogeneity (R² = 49.93%), although the overall test of moderators was not statistically significant (p = 0.079). For TG, the included moderators accounted for most of the variability (R² = 69.18%), but no individual covariate reached statistical significance. By contrast, the meta-regression model for HOMA-IR yielded a negative R² (-35.73%), suggesting that the selected covariates did not explain the between-study variability and may even have worsened the model fit. Detailed results are presented in Supplementary Tables 9–13.
3.4.11 Sensitivity analyses
To assess the robustness of our findings, several sensitivity analyses were performed. Leave-one-out analysis showed that no single study had a decisive influence on the pooled effect, with results remaining stable (Supplementary Figures 1–8). Excluding high-risk-of-bias studies yielded results consistent with the main analysis (Supplementary Table 14). Similarly, removing trials without standardized Western medicine background interventions did not materially alter the pooled estimates (Supplementary Table 15). Influence diagnostics identified a few studies with some impact on model fit, but exclusion of these studies did not substantially change the results (Supplementary Figures 9–16). For sparse binary outcomes, alternative continuity correction methods were applied to account for zero-event studies, and the results remained consistent (Supplementary Figure 17). Overall, these analyses indicate that our conclusions are robust and not driven by any single study, specific subgroup of studies, or methodological choice.
3.5 Publication bias
Publication bias was assessed using funnel plots and Egger’s test. The funnel plots for FBG, 2hPG, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c appeared largely symmetrical, with Egger’s test yielding non-significant results (p = 0.27, p = 0.64, p = 0.45, and p = 0.23, respectively), suggesting no evidence of substantial publication bias. For the TG outcome, the funnel plot showed some asymmetry, and Egger’s test (p < 0.05) suggested potential publication bias. Before trim-and-fill correction, the pooled effect was significant (MD = -0.52, 95% CI -0.72 to -0.31, p < 0.001). After applying the trim-and-fill method, the adjusted pooled effect size was attenuated and became non-significant (MD = -0.07, 95% CI -0.40 to 0.25, p = 0.661), suggesting that the initial significance may have been influenced by publication bias (Figure 13).
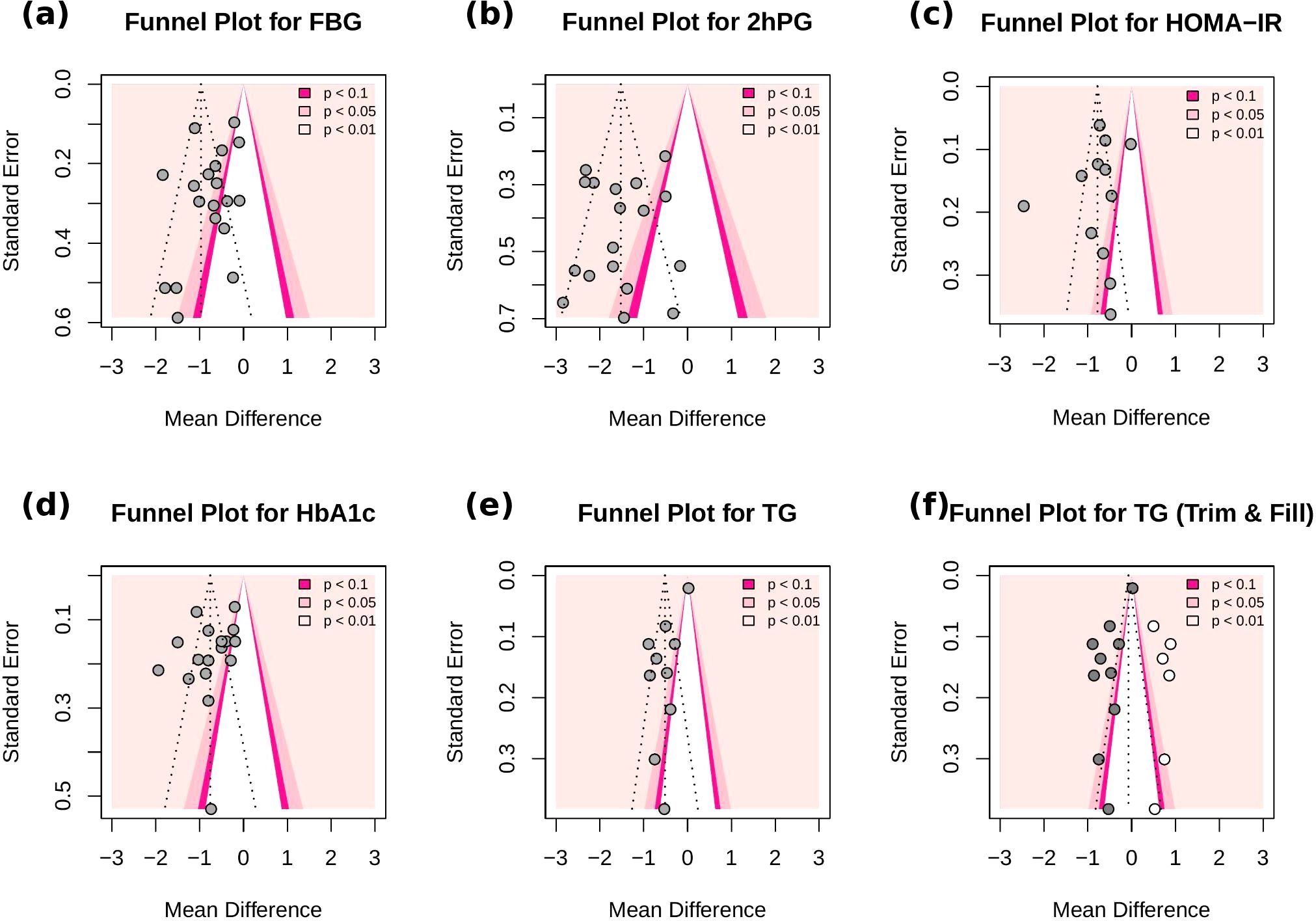
Figure 13. Funnel plots for (a) FBG, (b) 2h-PG, (c) HOMA-IR, (d) HbA1c, (e) TG (f) TG (Trim-and-fill). Each dot represents a study included in the meta-analysis. The vertical line denotes the pooled effect size, and the diagonal dashed lines represent the expected 95% confidence intervals around the effect. Grey dots correspond to the original studies, while white dots indicate imputed studies added by the trim-and-fill method.
3.6 Quality of evidence
The GRADE assessment indicated that, due to risk of bias and inconsistency across the included studies, the overall certainty of evidence was rated as low for most outcomes, including FPG, 2h-PG, HDL-C, LDL-C, HOMA-IR, HbA1c, and TC. In addition, the certainty of evidence for TG was downgraded further to very low because of the combined influence of risk of bias, inconsistency, and potential publication bias. Detailed explanations of the ratings and reasons for downgrading are summarized in Table 2.
4 Discussion
4.1 Main finding
This study investigated the effects of JLD on metabolic outcomes in patients with PD and T2DM. The results indicated that JLD, in addition to standard therapy, significantly lowered FBG, 2h-PG, and HbA1c relative to the control group, highlighting meaningful improvements in glycemic regulation. JLD was also effective in reducing insulin resistance, as reflected by favorable changes in HOMA-IR, and exerted positive effects on lipid profiles by decreasing TC, TG, and LDL-C, while simultaneously increasing HDL-C.
The subgroup analyses provide important insights into the populations most likely to benefit from JLD. Greater improvements were generally observed in shorter trials, suggesting an early therapeutic effect that may diminish or plateau with longer treatment, underscoring the need to evaluate strategies for sustaining long-term efficacy. Baseline glycemic status emerged as a key effect modifier. Patients with fasting glucose ≥10 mmol/L achieved the largest reductions in both fasting and postprandial glucose, as well as more favorable lipid changes, indicating that JLD may be particularly effective in metabolically uncontrolled populations. Compared with PD, patients with T2DM showed more pronounced improvements in HbA1c, HOMA-IR, and lipid profiles. This is likely attributable to their higher baseline glucose levels and more severe β-cell dysfunction, which make them more responsive to pharmacologic or nutritional interventions targeting glucose homeostasis and insulin resistance (46, 47). Nevertheless, even modest reductions in fasting or postprandial glucose among PD participants are clinically meaningful, as they may delay progression to overt diabetes and reduce the risk of long-term complications (48). Overall, these findings suggest that JLD provides clear therapeutic value for T2DM patients with poor metabolic control, while its role as an early intervention in PD remains promising but requires confirmation in larger, long-term studies.
Meta-regression analyses identified trial duration and baseline FBG as significant contributors to between-study heterogeneity. Shorter intervention durations and higher baseline FBG levels were associated with greater reductions in FBG and HbA1c, suggesting a stronger early-phase effect of JLD, which may plateau over time. Background therapy, defined as the use of concomitant glucose-lowering medications, was also included as a moderator. Although it did not reach statistical significance, the direction of effect was consistent: studies without background medications tended to report larger glycemic improvements (e.g., FBG: β = 0.96, 95% CI −0.10 to 2.01, p = 0.076). This trend may be partially explained by a ceiling effect, whereby patients already receiving hypoglycemic drugs have a limited capacity for further glucose reduction. In contrast, in trials in which JLD was administered as monotherapy, a broader therapeutic window may allow its effects to be more fully observed. Background therapy was not a statistically significant independent predictor. However, its inclusion in the FBG model (R² = 81%) suggests a potential interaction with other moderators. This model explained the largest proportion of heterogeneity, indicating its relevance to treatment response. These findings underscore the need to standardize and report background treatments clearly in clinical trials, as variability in co-interventions may otherwise obscure or exaggerate the observed efficacy of the intervention.
4.2 Comparison of similar studies
Two prior meta-analyses have summarized the clinical efficacy of JLD in patients with T2DM, yet their conclusions were not fully consistent. Lian et al. synthesized 15 RCTs involving 1,810 participants and reported significant reductions in HbA1c, FPG, and 2h-PG (19). In contrast, Zhao et al. screened 22 RCTs but, due to methodological restrictions, included only three low–risk–of–bias studies (441 participants) in quantitative synthesis (18). Their analysis showed only a marginal decrease in HbA1c (MD −0.283%, 95% CI −0.561 to −0.004; p = 0.046) and no significant changes in FPG or 2h-PG. Thus, while Lian et al. suggested clear glycemic benefits, Zhao et al. reported more conservative estimates based on stricter inclusion criteria. Building upon this foundation, the present study expands the evidence base both quantitatively and conceptually. We extended the search to July 2025 and identified 20 randomized controlled trials including 2,993 participants. The updated evidence base also incorporated several recently published high-quality studies. In addition to patients with established T2DM, we included those with prediabetes, allowing for a broader assessment across the spectrum of dysglycemia. Beyond the three glycemic endpoints emphasized previously, our analysis systematically synthesized outcomes related to HOMA-IR, lipid metabolism (TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C), and safety, thereby constructing a more comprehensive profile of JLD’s metabolic effects. Methodologically, this study performed comprehensive sensitivity analyses to assess the robustness of pooled estimates across different statistical models and study quality levels. Furthermore, this study also introduces subgroup analyses and multivariable random-effects meta-regression to explore how participant characteristics and intervention parameters influence therapeutic outcomes—an approach not undertaken in earlier reviews. These analyses revealed that individuals with higher baseline glycemia or established T2DM tended to achieve greater short-term glycemic improvements, while those with prediabetes showed potential preventive benefits. Moreover, trials with shorter treatment duration or lighter background therapy demonstrated larger effect sizes.
Collectively, our findings refine and extend the conclusions of earlier reviews. Compared with Zhao et al., who reported only modest glycemic benefits and limited interpretability due to the small number of studies, our results confirm consistent improvements in HbA1c, FPG, and 2h-PG and further demonstrate significant enhancements in insulin sensitivity and lipid regulation. This multidimensional evidence framework provides an updated and clinically relevant understanding of JLD’s efficacy and safety across different stages of metabolic dysregulation. By quantitatively analyzing how participant characteristics and treatment parameters shape these outcomes, our study offers practical guidance for optimizing therapeutic strategies and supports more targeted, effective, and individualized TCM interventions that benefit diverse patient populations.
4.3 Mechanisms of JLD
JLD is derived from a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulation that adheres to the therapeutic principles of “tonifying Qi, nourishing Yin, strengthening the spleen, and promoting fluid metabolism.” It comprises multiple herbal components with demonstrated hypoglycemic properties. Evidence from animal experiments and preclinical studies indicates that JLD regulates glucose and lipid metabolism through multiple mechanisms. Specifically, JLD has been shown to stimulate brown adipose tissue (BAT) thermogenesis by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and promoting fatty acid oxidation (49). It also improves insulin signaling and reduces JNK and p38 MAPK phosphorylation, thereby counteracting high-fat-diet–induced hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance, while also exerting antioxidant activity (50). Furthermore, JLD activates AMPK to protect β-cells and stimulates the PPARα/ABCA1 pathway, thereby improving glucose–lipid metabolism, reducing hepatic lipid deposition, and alleviating insulin resistance (51). In addition, JLD may slow β-cell aging and suppress the release of SASP-related cytokines, thereby improving insulin secretion and correcting metabolic dysfunction in PD (52). In vitro experiments have further demonstrated that JLD enhances insulin secretion, promotes β-cell proliferation, and inhibits apoptosis under high-glucose conditions. Mechanistically, JLD increases the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, decreases pro-apoptotic proteins such as Caspase-3 and Bax, and prevents excessive phosphorylation of Smad2/3 within the insulin signaling pathway (53). Collectively, these findings suggest that JLD exerts antidiabetic effects through dual mechanisms: improving insulin resistance and preserving islet function. Additionally, network pharmacology analyses have identified several active compounds in JLD, including quercetin and luteolin, which target key signaling pathways such as PI3K-AKT, PTGS2, and AGE–RAGE. These pathways are critically involved in regulating signal transduction, apoptosis, gene expression, and inflammatory responses (54).
4.4 Limitations and future research
This review has several limitations that should temper interpretation. First, between-study heterogeneity was substantial. Meta-regression suggested that intervention duration and baseline FBG explained a meaningful proportion of the variability in glycemic outcomes; background therapy was also modeled as a moderator. Although this term did not consistently reach statistical significance, its direction was concordant with the overall pattern of findings, indicating that differences in background care likely contributed to the observed dispersion. Second, methodological quality varied across studies. This variation was especially evident in trials conducted in China before 2018. Such differences may have influenced the pooled estimates. The adoption of CONSORT-aligned practices has historically been incomplete. Prospective registration and public availability of protocols or statistical analysis plans (SAPs) were often limited. Many studies used small, single-center designs with constrained monitoring. In addition, practical barriers to robust allocation concealment and multi-level blinding likely introduced domain-specific biases. Inadequate sequence generation or concealment can lead to selection bias, which often inflates effect estimates. Limited blinding of participants, personnel, or outcome assessors may introduce performance or detection bias. The direction of such bias is uncertain and may depend on co-interventions and how outcomes are measured. Additional concerns include the inconsistent handling of missing data and occasional reliance on per-protocol rather than intention-to-treat analyses, both of which can shift estimates toward statistical significance. To empirically address these risks within this methodological context, we prespecified and conducted a sensitivity analysis excluding trials rated as high risk of bias according to RoB 2.0. After exclusion, the pooled effects for primary outcomes remained directionally consistent and statistically significant, with only modest attenuation, suggesting that our conclusions are not materially driven by high-risk designs. Nonetheless, this check has inherent constraints—exclusions reduce power, incomplete reporting of concomitant therapy leaves room for residual confounding, and earlier small studies may differ systematically from later trials—so the magnitude of the effect should be interpreted with caution. Third, evidence in PD remains limited. Although two relatively large RCTs were included, the overall number of PD trials was small, limiting the precision and generalizability of subgroup estimates. Fourth, all included studies used the same labeled dose of JLD. This uniformity prevents any assessment of dose–response relationships. It also makes comparisons across different dosing regimens impossible. As a result, the optimal dose and the exposure–response relationship cannot be determined based on the current evidence. Finally, all included studies were conducted in China, which may restrict external validity across other health systems, ethnicities, and care pathways.
Future research should address the following priorities to strengthen the evidence base. Research should prioritize multicenter, adequately powered RCTs with prospective registration and publicly available protocols/SAPs; rigorous randomization with allocation concealment (e.g., centralized systems or opaque sequential allocation) and blinding (or blinded outcome adjudication when double blinding is infeasible); intention-to-treat analyses with transparent handling of missing data; and harmonized outcome measurements, including core outcome sets, standardized assay methods and units, and prespecified time points. Greater population diversity and longer follow-up periods are needed to evaluate clinical endpoints (e.g., cardiovascular outcomes) and to determine the optimal treatment duration and combination strategies with standard care. In addition, dose-finding and dose-ranging trials (including multi-arm designs) and modeling-based exposure–response analyses are warranted to identify the minimal effective and optimal dosing of JLD and to test whether benefits differ across dosing strategies. Finally, mechanistic and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies are warranted to clarify the underlying biological pathways and to strengthen causal inference regarding JLD’s glycemic and lipid effects.
5 Conclusion
This study indicates that JLD has potential efficacy in improving glycemic control and insulin resistance in individuals with PD and T2DM. Additionally, JLD exerts favorable effects on lipid metabolism by lowering TC, TG, and LDL-C, while simultaneously increasing HDL-C levels, with lipid-modulating effects being more pronounced in T2DM patients. Subgroup analyses further revealed that greater benefits were observed in shorter-duration trials and in patients with higher baseline fasting glucose, suggesting that JLD may be particularly effective in metabolically uncontrolled populations. Overall, the findings suggest that JLD may serve as an effective adjuvant therapy for the management of T2DM and PD. Nevertheless, several limitations should be acknowledged, including considerable heterogeneity across included studies and relatively small sample sizes in some subgroups, which may reduce the statistical robustness of the findings. Future research should prioritize rigorously designed, large-scale, multicenter RCTs to further substantiate the efficacy and safety of JLD across diverse populations and clarify its clinical applicability.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
LL: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QT: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YH: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CX: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SF: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. TT: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was jointly supported by the National Science and Technology Innovation 2030, Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases–National Science and Technology Major Project (Grant Nos. 2024ZD0524300 and 2024ZD0524306) and the Tianjin Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio Construction Project (No. tjmzy2405).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1689640/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Dilworth L, Facey A, and Omoruyi F. Diabetes mellitus and its metabolic complications: the role of adipose tissues. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:7644. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147644
2. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas (2025). Brussels: International Diabetes Federation. Available online at: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/idf-diabetes-atlas-2025/ (Accessed August 4, 2025).
3. Brannick B and Dagogo-Jack S. Prediabetes and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology and interventions for prevention and risk reduction. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2018) 47:33–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2017.10.001
4. Hsu JC, Yang YY, Chuang SL, Lee JK, and Lin LY. Prediabetes increases the risk of major limb and cardiovascular events. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:348. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02085-y
5. Tabák AG, Herder C, Rathmann W, Brunner EJ, and Kivimäki M. Prediabetes: a high-risk state for diabetes development. Lancet. (2012) 379:2279–90. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60283-9
6. de Souza CF, Gross JL, Gerchman F, and Leitão CB. Prediabetes: diagnosis, evaluation of chronic complications, and treatment. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. (2012) 56:275–84. doi: 10.1590/s0004-27302012000500001
7. Chung JYF, Lan HY, and Tang PMK. New insights into traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Integr Med Nephrol Androl. (2023) 10:e00026. doi: 10.1097/IMNA-D-22-00026
8. Probst JC, Yell N, Benavidez GA, Hardin JW, Glover SH, Crouch EL, et al. Dialysis more available than patient education in counties with high diabetes prevalence. Prev Chronic Dis. (2024) 21:E60. doi: 10.5888/pcd21.240052
9. Cheung N, Mitchell P, and Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. (2010) 376:124–36. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62124-3
10. Zhang Y, Lazzarini PA, McPhail SM, van Netten JJ, Armstrong DG, and Pacella RE. Global disability burdens of diabetes-related lower-extremity complications in 1990 and 2016. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:964–74. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1614
11. Safiri S, Karamzad N, Kaufman JS, Nejadghaderi SA, Bragazzi NL, Sullman MJM, et al. Prevalence, deaths and disability-adjusted life-years due to type 2 diabetes and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:838027. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.838027
12. Parker ED, Lin J, Mahoney T, Ume N, Yang G, Gabbay RA, et al. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. @ in 2022. Diabetes Care. (2024) 47:26–43. doi: 10.2337/dci23-0085
13. Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. (2002) 346:393–403. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012512
14. Galaviz KI, Narayan KMV, Lobelo F, and Weber MB. Lifestyle and the prevention of type 2 diabetes: A status report. Am J Lifestyle Med. (2018) 12:4–20. doi: 10.1177/1559827615619159
15. Guo L-X, Liu G-E, Chen L, Wang H-F, Guo J, Zheng X-L, et al. Comparison of clinical efficacy and safety of metformin sustained-release tablet (II) (Dulening) and metformin tablet (Glucophage) in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:712200. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.712200
16. Ghusn W, Hurtado MD, and Acosta A. Weight-centric treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obes Pillars. (2022) 4:100045. doi: 10.1016/j.obpill.2022.100045
17. Yang H, Choi E, Park E, Na E, Chung SY, Kim B, et al. Risk of genital and urinary tract infections associated with SGLT-2 inhibitors as an add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study in Korea. Pharmacol Res Perspect. (2022) 10:e00910. doi: 10.1002/prp2.910
18. Zhao X, Liu L, and Liu J. Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus using the traditional Chinese medicine Jinlida as an add-on medication: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1018450. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1018450
19. Lian F, Jin D, Bao Q, Zhao Y, and Tong X. Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine Jinlida granules as an add-on therapy for type 2 diabetes: A system review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Diabetes. (2019) 11:540–51. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12877
20. Aschner P. New IDF clinical practice recommendations for managing type 2 diabetes in primary care. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2017) 132:169–70. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.09.002
21. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:S19–40. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S002
22. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
23. Viechtbauer W and Cheung MW. Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. (2010) 1:112–25. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.11
24. Shi C, Ren Z, Zhao C, Zhang T, and Chan SH. Shame, guilt, and posttraumatic stress symptoms: A three-level meta-analysis. J Anxiety Disord. (2021) 82:102443. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2021.102443
25. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. (2008) 336:924–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
26. Cai J, Xia X, Qiao J, Gao Y, Li H, and Liu Y. Effect of Jinlida granule on glycolipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammatory factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Trop J Pharm Res. (2023) 22:597–603. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v22i3.17
27. Fan HJ, Sun XF, Yin L, Yang X, and Dong QJ. Clinical study on Jinlida Granules combined with nateglinide in treatment of type 2 diabetes. Drugs Clinic. (2021) 36:269–73. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2021.02.012
28. Lian F, Tian J, Chen X, Li Z, Piao C, Guo J, et al. The efficacy and safety of chinese herbal medicine jinlida as add-on medication in type 2 diabetes patients ineffectively managed by metformin monotherapy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0130550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130550
29. Pan J, Xu Y, Chen S, Tu Y, Mo Y, Gao F, et al. The effectiveness of traditional chinese medicine jinlida granules on glycemic variability in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A double-blinded, randomized trial. J Diabetes Res. (2021) 2021:6303063. doi: 10.1155/2021/6303063
30. Shi YL, Liu WJ, Zhang XF, Su WJ, Chen NN, Lu SH, et al. Effect of chinese herbal medicine jinlida granule in treatment of patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Chin Med J (Engl). (2016) 129:2281–6. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.190676
31. Ji H, Zhao X, Chen X, Fang H, Gao H, Wei G, et al. Jinlida for diabetes prevention in impaired glucose tolerance and multiple metabolic abnormalities: the FOCUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. (2024) 184(7):727–35. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.1190
32. Hou LP, Geng JL, Gu W, and Zhang XK. Effect of Jinlida granules combined with semaglutide on glucose and lipid metabolism, cardiac function and vascular endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with coronary heart disease. J Chin Med. (2023) 42(7):39–43. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2024.07.009
33. Fu YF, Zhang SL, and Tan LM. Clinical observation of Jinlida granules combined with liraglutide and metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin Pharm. (2019) 28:53–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2019.08.019
34. Liu H. Clinical study of Jinlida granules combined with glipizide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mod Drugs Clin. (2018) 33:1490–3. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2018.06.044
35. Liu LK, Feng XP, Wang Y, Yang TS, Ou X, and Jia LH. Effects of Jinlida granules combined with metformin on blood glucose and serum inflammatory factors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes; Efficacy observation of Jinlida granules combined with insulin pump in short-term intensive therapy of gestational diabetes mellitus. Chin J Clin Healthc. (2017) 20:71–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6790.2017.01.022
36. Zhou XH, Liu SY, and Lin YJ. Clinical study of Jinlida granules combined with dulaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mod Drugs Clin. (2020) 35:1584–7. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.08.017
37. Han L, Wen XJ, and Chen YJ. Therapeutic effect of Jinlida granules combined with dapagliflozin in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin J Multi-Organ Dis Elderly. (2023) 22:367–71. doi: 10.11915/j.issn.1671-5403.2023.05.75
38. Zhao ZL, Fang GQ, and Geng JL. Clinical efficacy of Jinlida granules combined with liraglutide in type 2 diabetes patients with poor efficacy of insulin pump intensive therapy and its effect on blood lipids and ET-1. J Chin Med. (2022) 40:242–6. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2022.06.056
39. Zhao SY, Zhao YZ, Su YJ, Zhao L, and Wang HL. Effect of Jinlida granules on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med. (2022) 49:95–9. doi: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2022.06.026
40. Cai J, Zheng ZK, Zhang MY, Dong LN, Jin K, Qiao JM, et al. Observation on the efficacy of Jinlida granules in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the theory of “treating from the spleen. J Mod Integr Tradit Chin West Med. (2022) 31:770–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2022.06.008
41. Cai J, Zhao ZG, Zheng ZK, Zhang MY, Xia X, and Wei M. Clinical efficacy of Jinlida granules combined with liraglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. J Difficult Complic cases. (2022) 21:399–403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2022.04.013
42. Hu XB. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin combined with Jinlida granules in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin J Geriatr Healthc Med. (2022) 20:55–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2671.2022.01.01
43. Huang JC, Ding SQ, and Wang MY. Explore the clinical efficacy and safety of Jinlida granules combined with insulin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes based on adaptive immunity. World J Integr Tradit West Med. (2020) 15(11):2062–6. doi: 10.13935/j.cnki.sjzx.201120
44. Jiang W, Bai MM, Wang HF, and Zhao J. Clinical study of Jinlida granules combined with dapagliflozin in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mod Drugs Clin. (2020) 35:553–7. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.03.034
45. Zhao JD, Li Y, Liu SF, Cao HB, Pei GY, Ha TJ, et al. Clinical observation of Jinlida granules combined with metformin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Tianjin Univ Tradit Chin Med. (2017) 36:348–51. doi: 10.11656/j.issn.1673-9043.2017.05.08
46. Abdul-Ghani MA, Tripathy D, and DeFronzo RA. Contributions of beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance to the pathogenesis of impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. Diabetes Care. (2006) 29:1130–9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.2951130
47. Defronzo RA. Banting Lecture. From the triumvirate to the ominous octet: a new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. (2009) 58:773–95. doi: 10.2337/db09-9028
48. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, et al. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. (2000) 321:405–12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7258.405
49. Zhang H, Hao Y, Wei C, Yao B, Liu S, Zhou H, et al. Chinese medicine Jinlida granules improve high-fat-diet induced metabolic disorders via activation of brown adipose tissue in mice. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 114:108781. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108781
50. Liu Y, Song A, Zang S, Wang C, Song G, Li X, et al. Jinlida reduces insulin resistance and ameliorates liver oxidative stress in high-fat fed rats. J Ethnopharmacol. (2015) 162:244–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.12.040
51. Li CR, Hao YY, Liu Y, Gu JJ, Zhang SL, and Gao HL. Effects of Jinlida on glycolipid metabolism disorders and the PPARα/ABCA1 pathway in insulin-resistant rats. World Sci Technol Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med. (2023) 25:1382–9. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.5699.R.20230719.1352.024 (Accessed August 6, 2025).
52. Wang ZX and Jia ZH. Study on the effects of Jinlida on senescent pancreatic β-cells in prediabetes. Shenyang Pharm Univ, Shenyang, China (2024). doi: 10.27111/d.cnki.ghyku.2024.000586
53. Chen W, Wang ZY, Fu YJ, Liu ZW, and Le L. Effects of Jinlida granules on proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells in mice under high glucose conditions. Herald Med. (2022) 41:1312–7. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/42.1293.R.20220120.1231.008 (Accessed August 6, 2025).
Keywords: Jinlida, type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, systematic review, meta-analysis, glycemic control
Citation: Li L, Tan Q, Zhang S, Huang Y, Xu C, Fan S, Li H and Tan T (2025) The impact of Jinlida on blood glucose control and insulin resistance in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1689640. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1689640
Received: 21 August 2025; Accepted: 27 October 2025;
Published: 17 November 2025.
Edited by:
Arrigo Francesco Giuseppe Cicero, University of Bologna, ItalyReviewed by:
Li Jiang, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, ChinaAmir Hosein Jafarpour, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Li, Tan, Zhang, Huang, Xu, Fan, Li and Tan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Tan, MTMwNzIyNDA5NzdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Huanan Li, bGlodWFuYW4xOTg0QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Limeng Li
Limeng Li Qingyin Tan3†
Qingyin Tan3† Shun Fan
Shun Fan Huanan Li
Huanan Li