- 1College of Life Sciences, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 2Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Biomanufacturing Techenology, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
The interaction between bone and muscle was traditionally considered to be mechanical. However, recent insights into the endocrine functions of these two tissues have led to an emerging concept that bone-muscle biochemical crosstalk occurs through soluble factors. In light of the identification of novel bone-derived factors in recent years, more focus has been shifted to the role of bone in this partnership. Primary factors identified include osteocalcin (Ocn), fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), sclerostin (Sost), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), fibroblast growth factor 9 (FGF9), Wnt3a, and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β). This review aims to summarize the current knowledge regarding the influence of bone-derived factors on muscle function. A comprehensive understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying bone-muscle communication may facilitate the identification of potential therapeutic strategies for the twin diseases of osteoporosis and sarcopenia.
1 Introduction
Osteoporosis and sarcopenia, which are characterized by the deterioration of bone strength and muscle function, respectively, are frequently regarded as inevitable consequences of the aging process. These conditions have emerged as significant public health concerns, affecting over 1.7 billion people worldwide (1). Bone loss is often concomitant with a decline in muscle mass and function, suggesting that osteoporosis and sarcopenia develop in tandem, thereby increasing the risk of bone fractures. Bone and skeletal muscle, two major components of the musculoskeletal system, are intimately and mechanically connected. Bone serves as an attachment site for skeletal muscle, while muscle exerts force on the bone to facilitate movement (2). This mechanical linkage is essential not only for normal development and locomotion but also plays a pivotal role in the alterations of both tissues resulting from disease and aging (3). Furthermore, a growing body of evidence supports the notion that bone and muscle function as endocrine organs, affecting various other tissues and organs, including the liver, adipose tissue, kidneys, and pancreas [reviewed by Karsenty and Olson (4)]. Given the intricate relationship between bone and muscle, it is posited that the development and maintenance of these two tissues are governed by a variety of biochemical factors beyond mechanical. Currently, the growing identification of novel “myokines” has redirected attention toward the role of muscle in this interrelationship (5–7); however, the contributions of bone-derived factors and their effects on skeletal muscle should not be ignored. In this context, we aim to summarize recent findings concerning the role of bone-derived factors in the regulation of skeletal muscle function. Research on the crosstalk between bone and muscle presents a significant opportunity for identifying potential therapeutic targets for the dual conditions of osteoporosis and sarcopenia.
2 Bone and muscle interaction: basic and clinic evidence
Bone and muscle are originated from the same paraxial mesoderm in early fetal stage (8). An intimate association from embryogenesis, through development and growth, and into aging each other has been well-described in several excellent reviews (9–12). During embryogenesis, bone-tendon-muscle (BTM) units develop in a coordinated manner, with muscle contraction essential for bone and joint formation (13, 14). Muscle-tendon attachment sites transmit force from muscle to tendon, highlighting the interdependence of muscle and tendon development. Mesenchymal precursors condense at future bone sites, differentiating into chondrocytes or osteoblasts, guided primarily by mechanical cues (15). Once formed, bone undergoes continuous modeling during postnatal growth, followed by remodeling throughout the life cycle. This process is orchestrated by the coordinated actions of osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and osteocytes, which function to repair micro-damage and adapt to changes in mechanical stimuli. Osteoclasts are responsible for bone resorption, while osteoblasts facilitate the subsequent deposition of the mineralized matrix. Osteocytes, embedded within the mineralized bone matrix, are highly sensitive to external mechanical stimuli and adapt to changes through bone formation and resorption. Notably, osteocytes are considered the primary mechanical sensors and play a crucial signaling role. They secrete paracrine factors that regulate osteoblast and osteoclast activity, as well as endocrine signals (15, 16).
During embryogenesis, myogenesis occurs concurrently with bone development, involving the differentiation of mesodermal precursors into myoblasts, which subsequently fuse to form myotubes. Specifically, the commitment of mesodermal precursor cells to the myogenic lineage takes place within the somites of limb muscles, primarily regulated by Pax3 and Pax7. These precursors further differentiate into multinucleated syncytia, eventually maturing into muscle fibers with the involvement of external signals such as Myf5 and MyoD (17). Muscle satellite cells (SCs), a specialized subset of myogenic precursors, are located between the basal lamina and sarcolemma in resting muscles. Upon activation due to injury or growth stimuli, SCs initiate a myogenic differentiation program and integrate into existing myofibers (18, 19). In general, the increase in muscle mass and force in adults is primarily regulated by the hypertrophy of myofibers and the enhanced contractile capacity of individual myofibers, respectively. The close proximity and developmental similarities between bone and muscle suggest that overlapping signaling pathways may co-regulate the accrual of both tissues. Supporting this notion, studies have shown that MyoD-deficient mice exhibit significant abnormalities in bone development and mineralization during muscle formation (20). Conversely, bone-derived Indian hedgehog (Ihh) has been found to promote myoblast survival and myogenesis during developmental stages (21). However, it remains unclear how bone biochemically communicates with muscle during childhood and adulthood, and whether similar interactions occur in the aging process.
Osteoporosis and sarcopenia are two prevalent clinical disorders that frequently co-occur and significantly diminish the quality of life in the elderly population. Age-related sarcopenia is characterized by a systemic and progressive decline in muscle mass, strength, and function. From a biomechanical perspective, substantial evidence indicates a positive correlation between increased muscle mass and elevated bone mineral density (BMD), as well as a reduced risk of fractures (22). Furthermore, muscle strength and function have been shown to be associated with BMD and fracture risk (23). Kaji and colleagues found that higher lean body mass (LBM) is linked to increased BMD and a lower risk of fractures, particularly in postmenopausal women (24). Both muscle and bone mass can be augmented through anabolic exercise and tend to decline during periods of catabolic disuse or immobilization. Beyond mechanical interactions, bone fractures represent pathological conditions where biochemical factors significantly influence the healing process. For instance, fractures covered with muscle flaps exhibit more rapid healing compared to those covered solely with skin (25, 26). In summary, the mechanical interactions between bone and muscle, as well as the mechanisms underlying muscle-to-bone communication, have been extensively documented (10, 11, 27). However, a more comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in bone-to-muscle signaling remains an area of ongoing research.
3 Endocrine function of skeleton
Bone has long been recognized as a structural organ essential for maintaining exercise capacity, calcium homeostasis, and the hematopoietic niche. Traditionally, bone, as a target tissue, responds to hormones such as parathyroid hormone (PTH), sex steroids, and calcitonin. Emerging evidence indicates that the skeleton itself secretes at least two hormones, fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and osteocalcin, which can influence the function of distant tissues. Several comprehensive reviews have explored the endocrine role of bone in the regulation of glucose tolerance, energy expenditure, and phosphate metabolism (16, 28, 29). This underscores the notion that bone serves not only as a structural scaffold in the human body but also as a modulator of various metabolic processes. It is well-established that bone acts as a significant reservoir of circulating factors and osteogenic growth factors, which are deposited in the matrix by osteoblasts and released by osteoclasts during bone resorption. Given that osteocytes constitute approximately 90-95% of bone cells and possess extensive dendritic processes, these cells are likely the primary source of multiple circulating factors in adult bone. An initial investigation conducted by Beno and colleagues (30) revealed that molecules with a molecular weight of up to 70 kDa can readily permeate the osteocyte-lacunar-canalicular network following the injection of small dyes into the mouse tail vein. This finding suggests that canalicular fluid has unobstructed access to the circulatory system, allowing osteocyte-derived factors to potentially enter the bloodstream and exert effects on distant target cells, such as muscle cells.
4 Bone-derived factors and their effects on muscle
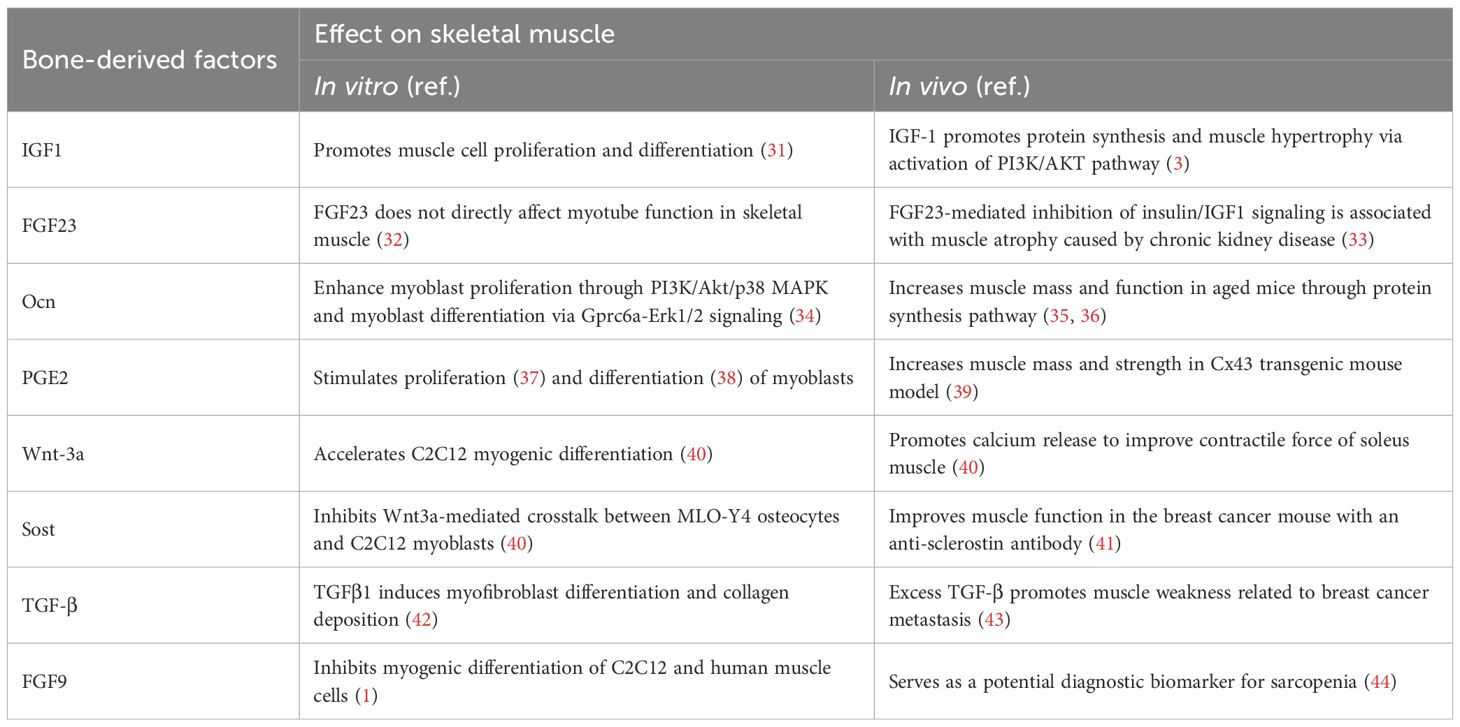
Bone serves as a key reservoir for mineral and matrix proteins and regulates skeletal muscle through the release of bone-derived factors into the bloodstream. Several of these factors include osteocalcin, FGF23, IGF1, sclerostin, PGE2, FGF9, Wnt3a, and TGF-β. We will discuss their effects on skeletal muscle, as detailed below (Table 1).
4.1 Osteocalcin
Osteocalcin (Ocn) is an osteoblast-specific secreted protein, and therefore its serum concentration serves as a biochemical marker for bone formation (45, 46). This small peptide is post-translationally modified on three specific glutamate residues by the vitamin K-dependent γ-glutamyl carboxylase (GGCX). GGCX catalyzes the conversion of glutamate acid into γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla-Ocn), which has a high affinity for bone matrix. The acidic environment generated during bone resorption promotes decarboxylation of Gla-Ocn deposited in the bone matrix to uncarboxylated osteocalcin (Glu-Ocn) and thereby increases its bioavailability. There are three factors that affect Glu-Ocn bioavailability, including leptin, glucocorticoids and delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) (45). Thus, two forms of osteocalcin exist in the circulation, Gla-Ocn and Glu-Ocn. Only the latter form acts as a hormone (47). Glu-Ocn can signal to muscle cells via its unique known receptor: Gprotein-coupled receptor 6a (Gprc6a). A primary effect of Glu-Ocn on muscle is to increase insulin sensibility (48) and energy expenditure (49). For example, Ocn−/− mice has more visceral fat without be obese than the control littermates. During exercise, Glu-Ocn signaling is conducive to the increase in muscle function. In this regard, Mera and colleagues (35) have shown, through its injections in wild-type mice and the analysis of female mice lacking Gprc6a specifically in myofibers, that bone-derived hormone Glu-Ocn enhances exercise capacity because it favors the catabolism of glucose and fatty acids in myofibers to generate ATP. Interestingly, Glu-Ocn signaling also promotes the expression and release of interleukin-6 (IL-6), a myokine whose circulating level increases during exercise. In turn, IL-6 acts in a feed-forward loop to stimulate bone resorption as well as bioactive Glu-Ocn production and secretion (50). It is worth noting that as muscle function increases, Glu-Ocn signaling also facilitates a gain in muscle mass (36). In contrast, the mice lacking tyrosine phosphatase (Esp-/-), an enzyme that inhibits osteocalcin function, showed an increase in muscle mass. Interestingly, muscle mass, maxmum contraction force, grip strength, fiber numbers and myosin heavy chain isoforms are altered in mice with targeted deletion of connexin 43 in osteoblast/osteocytes (51). Importantly, the Ocn circulation levels are reduced in these connexin 43 mutant mice but there is unchanged for the insulin level or glucose homeostasis. Injections of glu-OC into the conditional knockout mice rescue some of the abnormal muscle phenotypes, including body weight, cross-sectional area (CSA) and grip strength. It at least in part implied that osteocalcin is necessary to maintain muscle mass and function. An in vitro study revealed that glu-OC is a potent promoter of cell proliferation via PI3K/Akt/p38 MAPK pathways and myogenic differentiation via GPRC6A-ERK1/2 signaling (34). Taken together, these novel exciting data suggest that osteocalcin, especially for its active form (glu-OC), play an important role in the bone and muscle communication.
4.2 FGF-23
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23), an endocrine factor produced by osteocytes, is crucial for regulating phosphate homeostasis in the kidney (52). Its expression in osteocytes is regulated by Phosphate Regulating Neutral Endopeptidase on Chromosome X (PHEX) and Dentin Matrix Protein 1(DMP1), which are promotor of bone mineralization. In the absence of either PHEX or DMP1, high levels of FGF23 promote phosphate excretion by the kidney, leading to osteomalacia and rickets. Interestingly, several lines of evidence showed that maintaining normal phosphate level may attenuate age-related muscle disorders, although the direct effects of phosphate and FGF23 on muscle have not yet dissociated (53, 54). In DMP1-/- mice, a model of autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets, EDL and soleus muscles function was reduced but cardiac force production was not affected (3, 55). The deficiency of FGF23 or α-Klotho is correlated with muscle wasting, as demonstrated convincingly in animal models (56). These findings suggest that FGF23 appears to work indirectly or in synergy with the cofactors. Therefore, the use of the anti-α-Klotho neutralizing antibody to block FGF23 signaling may be an alternative strategy to maintain muscle mass without affecting renal function. Central to the role of FGF23 in bone and muscle communication, a recent report indicated that the muscle metabolite β-aminoisobutyric acid (L-BAIBA) promotes FGF23 production in osteocytes. However, this effect is lost in aged mice due to the downregulation of its receptor MRGPRD in bone (53). Interestingly, intermittent treadmill exercise favors renal phosphate excretion, which is consistent with previous findings of high levels of FGF23 with exercise are correlated with reduced phosphate (57). Overall, these data suggest that FGF23 appears to protect muscle function from increased phosphate under pathological conditions, which may be impaired during aging due to the low expression of MRGPRD and lack of BAIBA responsiveness in osteocytes.
4.3 IGF-1
Insulin-like growth factor1 (IGF1), produced by osteoblasts and osteocytes, is an important regulator of skeletal muscle mass by promoting both proliferation and differentiation of myoblast during muscle development. For example, adult muscle has evident and dramatic hypertrophic effect via activation of IGF-1/Akt signaling pathway (58). The hypertrophic muscle had increased absolute force but no change for specific force compared to control mice (59). In a mouse model of conditional knockout of IGF1 in osteocytes, the IGF-1 mRNA expression level was decreased in bone and muscle although no difference in muscle fiber number, size and morphology was observed (60). Similarly, bone morphogenetic protein2 (BMP2) signaling was also shown to promote adult muscle mass. However, BMP2 signaling-induced muscle hypertrophy showed an increase in absolute muscle force and unchanged or even slightly reduced specific muscle force compared to control mice (61).
4.4 TGF-β superfamily
Bone is a large reservoir for transforming growth factor (TGF-β), which are deposited into the mineralized bone matrix by osteoblast. The TGF-β superfamily is composed of a plethora of ligands with different selectivity for specific receptor subtypes. The TGF-β signaling is an orchestrator of diverse biological process related to proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis, tissue homeostasis and regeneration (8). Then, subsets of TGF-β ligands family transduce the signal through downstream effectors Smad transcription factors. Activin, certain growth and difference factors (GDF) such as myostatin, GDF8, GDF11 and TGF-β can stimulate activity of smad2 and smad3. Notably, TGF-β and its family member (myostatin and activin) can lead to muscle atrophy or reduced function. Both TGF-β and activin are released into circulation from bone matrix by osteoclasts-mediated bone resorption, but their effect on muscle is different. Activin causes strongly muscle weakness with reduced muscle mass and force production using an adenovirus vector in mice. On the contrary, mice treated with TGF-β showed reduced raw and specific force production but unchanged in muscle mass (62). Waning and colleagues showed that bone-derived TGF-β is the cause of skeletal muscle weakness in the setting of osteolytic cancer through increased muscle oxidative stress and calcium mishandling (43). In contrast to the negative effects of myostatin, activin and TGF-β signaling in muscles, BMP-2 signaling leads to muscle hypertrophy as like IGF-1 (31). However, the contribution of TGF-β and BMP-2 signaling in muscle to protein balance remains to be determined.
4.5 Regulators of Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a critical pathway that affects both bone and muscle health. The osteocyte appears to transmit mechanical signals to cells on the bone surface through the wnt/β-catenin pathway. Wnt proteins are involved in embryonic muscle development and muscle growth in response to overload (57). Wnt3a was found to enhance the mRNA expression of muscle regulatory factors (MRFs)-MyoD and Myogenin, thus promote differentiation of C2C12 myoblast. Sclerostin (Sost) secreted by mature osteocytes is one of inhibitors of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. An in vitro study by Huang et al. (40) showed that sost inhibits the effect of Wnt 3a on the C2C12 differentiation, suggesting a potential negative role of sost in myogenic differentiation. Yet, osteocytes are mechanosensory cells that coordinate adaptive responses of the skeleton to mechanical loading although the mechanism of bone mechanosensation is not fully clear (16). Several lines of evidence showed that the expression of sost increases in the absence of load (63, 64). Thus, sost is considered to be responsible for disuse-induced osteoporosis. Irisin, an exercise hormone, is secreted by the skeletal muscle during exercise. Colaianni et al. (65) found that recombinant irisin can maintain sost expression in long bone of unloaded mice at control level. In addition, the expected increase in Rankl/OPG ratio was blunted by irisin that attenuated the disuse-induced OPG reduction. The modulation of OPG and sost by irisin could be linked, because Rankl/OPG balance is also controlled by sost (66). These findings imply that the myokine irisin modulates the sost expression, and thereby promotes osteoclast formation and activity.
Although the role of sost in bone-muscle crosstalk has been hypothesized, but its pharmacological regulation of muscle tissue is not fully clear. Romosozumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody against sost that was FDA-approved for the treatment of osteoporosis. A cross-sectional clinical study of community-dwelling elderly Korean population found that participants with sarcopenia, low muscle mass and strength have significantly lower serum sost levels (67). In addition, clinical data showed that romosozumab effectively increases BMD of lumbar spine and total hip by 13.7% and 6.2 from the baseline, respectively (68). Unfortunately, the major positive impacts of romosozumab on muscle tissue or its effectiveness in the treatment of sarcopenia are not expected.
4.6 PGE2
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), signaling molecule derived from arachidonic acid by cyclooxygenase (69), is related with multiple physiological process including inflammation, muscle regeneration and cancer development (38). Brotto’s lab previously demonstrated that osteocyte-derived PGE2 enhanced C2C12 myoblast proliferation (37) and differentiation (38), suggesting PGE2 is essential for skeletal muscle myogenesis. Recently, a study by Palla et al. (70) uncovered PGE2 signaling rejuvenates age-related decline in muscle mass and strength. Elevated 15-PGDH level in aged muscle, a PGE2-degrading enzyme, leads to muscle atrophy and decreased muscle strength. A physiological restoration of PGE2 level after 15-PGDH inhibition effectively augments mitochondrial function, thereby increasing muscle mass and strength. In addition, our group has generated two transgenic mouse models to study the distinct roles of Cx43-based hemichannels and gap junctions in bone-muscle crosstalk. Blockage of these two channels in osteocytes reduces fast-twitch muscle mass and PGE2 release in circulation. Interestingly, the injection of PGE2 to the transgenic mice partially rescues the muscle phenotypes (39). In aged transgenic mouse model, impairment of Cx43 hemichannels results in reduced PGE2 level in osteocytes, thereby activating TGFβ/smad2/3 pathway to promote collagen deposition in aged muscle (71). In addition to osteocytes, osteoblasts can also produce PGE2 and promote bone resorption, which is partially driven by activation of muscle-derived IL-6. Mechanistically, IL-6 appears to stimulate bone resorption through osteoblast-derived PGE2-dependent osteoclast activation (72). Therefore, PGE2 plays an important role in bone turnover and myogenic differentiation of myoblasts with unknown mechanisms, making it potentially essential for muscle myogenesis. These findings imply bone-derived PGE2 is a powerful factor in the regulation of muscle mass and strength.
4.7 FGF9
Fibroblast growth factor 9 (FGF9), a member of the FGF family, are mainly expressed in different cell types of skeleton. A previous study by McCormick et al. (73) showed that FGF9 was moderately expressed in primary osteocytes isolated from young mouse femurs and osteoid osteocytes. Moreover, in vitro experiments using the newly established osteoblast-like cell lines (OmGFP66 and OmGPF10) found that FGF23 level was significantly increased when the differentiation of osteoblasts into osteocytes. Treatment of OmGFP66 with FGF9 upregulates FGF23 mRNA expression and increases FGF23 protein secretion (74). Using C2C12 myoblast cell lines and human cells, Huang et al. (1) observed the inhibitory effects of FGF9 on myogenic differentiation, reducing the expression of myogenic factors MyoG and Mhc. Thus, FGF9 might function as a regulatory factor from bone cells to affect muscle growth, however, additional in vivo evidence will be required to support the concept.
5 Conclusions and future prospects
Evidence from numerous findings has revealed that bone and muscle are tightly coupled in both development and function. The endocrine role of bone and its interactions in bone-muscle crosstalk has recently gained great attention (75–77). Consequently, investigating the pathophysiological roles of bone-derived factors has emerged as a compelling area of research. In this concise review, we provide an overview of the current understanding of bone-muscle crosstalk and the role of bone-derived factors in regulating skeletal muscle function (Figure 1). However, due to the multitude of factors that similarly both affect bone and muscle, distinguishing bone-specific effects from local paracrine actions or influences originating from other organs presents a challenge. The identification of additional bone-derived factors is anticipated to offer promising targets for diagnostic biomarkers and the development of therapeutic interventions.
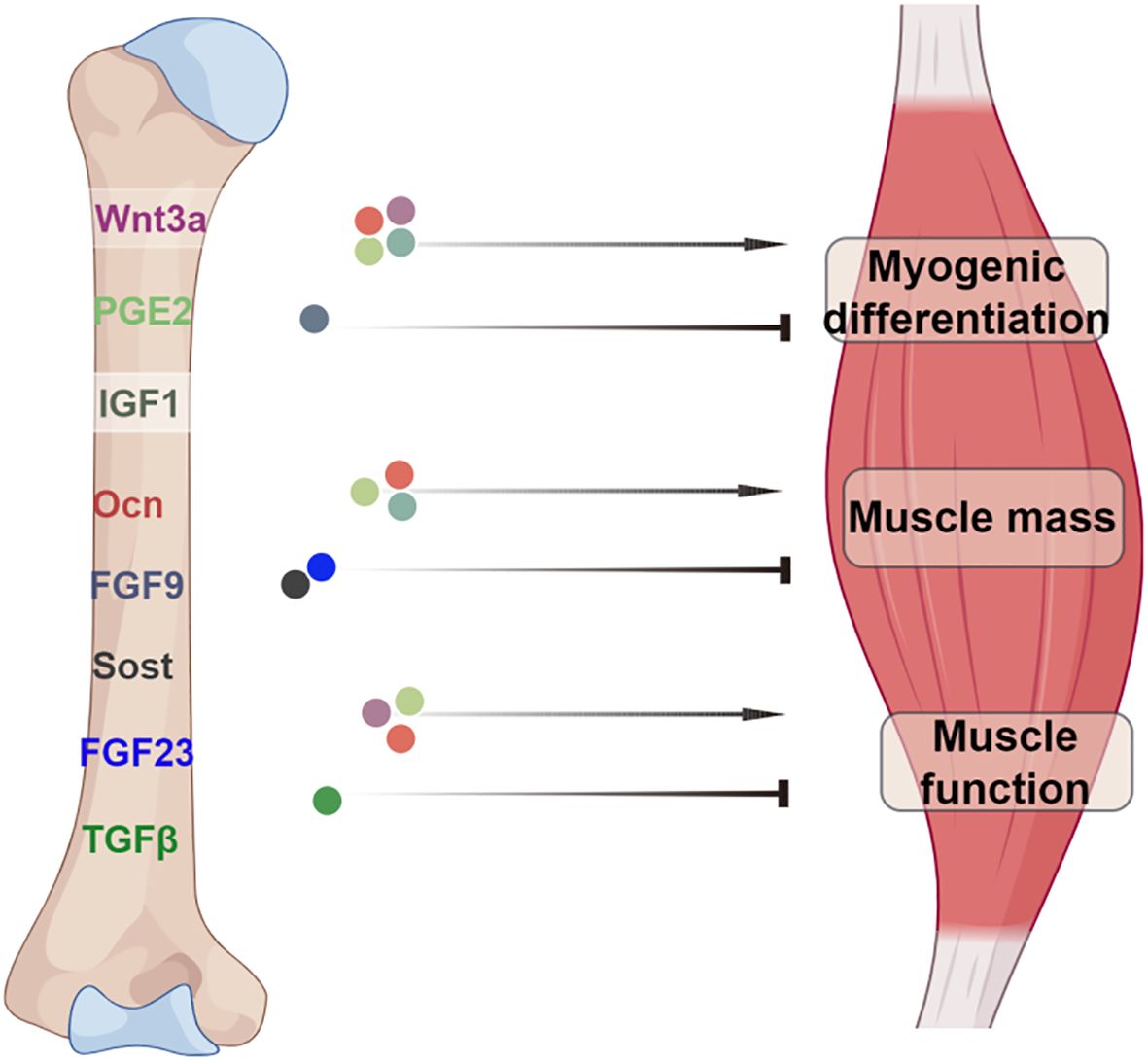
Figure 1. A model illustrating the role of bone-derived factors in bone-muscle axis. The bone factors Ocn, PGE2, and IGF1 not only have positive effects on myogenic differentiation but also on muscle mass. Wnt3a, PGE2 and Ocn have positive role in the regulation of muscle function. In contrast, the factors sost, FGF23, FGF9 and TGFβ exert negative effects on muscle physiology. Image created with Figdraw.com, with permission.
Age-related sarcopenia leads to impaired balance, diminished endurance, and decreased mobility, which increase the susceptibility of elderly individuals to fractures due to concurrent osteoporosis. The traditional approaches to improve bone mass and quality primarily focused on high-impact loading through gravitational forces to induce bone deformation, which is essential for bone formation. Therefore, understanding the molecular basis of bone-muscle crosstalk is crucial for developing effective therapies for the twin diseases of osteoporosis and sarcopenia, especially for the elderly who cannot bear vigorous training intervention. It is worth noting that these two diseases often exhibit sex-specific prevalence and progression in clinical practice. Thus, the effect of sex hormones on the expression of aforementioned endocrine factors should not be ignored. For example, irisin deficiency can protect osteocytes against low-calcium diet-induced bone resorption in female mice, but not male (78). Recently, Kaji’s group reported that androgen deficiency, rather than estrogen, reduces irisin expression in the muscle of mice (79). These findings suggest the sex-specific differences of irisin in bone resorption and bone-muscle communication. Pharmacological or nutritional interventions are also necessary to modify biochemical factors and signaling pathways, optimizing training strategies to reduce mechanical impacts from frailty. A key question is whether we can integrate treatments for muscle and bone diseases rather than addressing them separately. Ongoing research should aim to discover new bone-specific factors and encourage collaboration between basic, clinical, and translational studies.
Author contributions
GL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft. MQ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. SL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China (Grant No. 2023QN03027), Inner Mongolia Agricultural University High-level/Outstanding Doctoral Introduction Talents Research Start-up Project (Grant No. NDYB 2021-23), Innovation Team of Higher Education Institutions in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Grant No.NMGIRT2219) and Innovation Training Program (Grant No.202410129050).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
Ocn: Osteocalcin
FGF23: fibroblast growth factor 23
IGF1: Insulin-like Growth Factor1
SOST: sclerostin
PGE2: prostaglandin E2
FGF9: fibroblast growth factor 9
TGFβ: transforming growth factor β
Pax3: paired box 3
DMP1: dentin Matrix Protein 1
Myf5: Myogenic Factor 5
Myod: Myogenic regulatory factor
SCs: satellite cells
Ihh: Indian hedgehog
BMD: bone mineral density
LBM: lean body mass
PTH: parathyroid hormone (PTH)
MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase
GPRC6a: G-Protein Coupled Receptor 6a
glu-Ocn: uncarboxylated osteocalcin
gla-Ocn: γ-carboxylated osteocalcin
CSA: cross-sectional area
PHEX: Phosphate-regulating neutral Endopeptidase X-linked
BMP2: bone morphogenetic protein 2
EDL: Extensor digitorum longus
GDF8: Growth and differentiation factor 8
GDF11: Growth and differentiation factor 11
15-PGDH: 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase
L-BAIBA: β-aminoisobutyric acid
MRGPRD: Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor type D
GGCX: γ-glutamyl carboxylase
Sost: Sclerostin
Rankl: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa b ligand
OPG: Osteoprotegerin
IL-6: interleukin6
References
1. Huang J, Wang K, Shiflett LA, Brotto L, Bonewald LF, Wacker MJ, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 9 (FGF9) inhibits myogenic differentiation of C2C12 and human muscle cells. Cell Cycle. (2019), 18:3562–80. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1691796
2. Bonewald L. Use it or lose it to age: A review of bone and muscle communication. Bone. (2019) 120:212–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.11.002
3. Regan JN, Trivedi T, Guise TA, and Waning DL. The role of TGFβ in bone-muscle crosstalk. Curr Osteoporos Rep. (2017) 15:18–23. doi: 10.1007/s11914-017-0344-5
4. Karsenty G and Olson EN. Bone and muscle endocrine functions: unexpected paradigms of inter-organ communication. Cell. (2016) 164:1248–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.043
5. Zhao QH, Chen YN, and Mao GZ. Muscle-bone crosstalk: involvement of myokines in the regulation of osteoporosis. Eur Cells Mater. (2024) 48:115–36. doi: 10.22203/eCM.v048a07
6. Ma S, Xing X, Huang H, Gao X, Xu X, Yang J, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived extracellular vesicles transport glycolytic enzymes to mediate muscle-to-bone crosstalk. Cell Metab. (2023) 35:2028–43. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.10.013
7. Magarò MS, Bertacchini J, Florio F, Zavatti M, Potì F, Cavani F, et al. Identification of sclerostin as a putative new myokine involved in the muscle-to-bone crosstalk. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:71. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9010071
8. Sartori R and Sandri M. BMPs and the muscle-bone connection. Bone. (2015) 80:37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.05.023
9. Brotto M and Bonewald L. Bone and muscle: Interactions beyond mechanical. Bone. (2015) 80:109–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.02.010
10. DiGirolamo DJ, Kiel DP, and Esser KA. Bone and skeletal muscle: neighbors with close ties. J Bone Miner Res. (2013) 28:1509–18. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1969
11. Laurent MR, Dubois V, Claessens F, Verschueren SM, Vanderschueren D, Gielen E, et al. Muscle-bone interactions: From experimental models to the clinic? A critical update. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2016) 432:14–36. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.10.017
12. Ferrucci L, Baroni M, Ranchelli A, Lauretani F, Maggio M, Mecocci P, et al. Interaction between bone and muscle in older persons with mobility limitations. Curr Pharm Des. (2014) 20:3178–97. doi: 10.2174/13816128113196660690
13. Rolfe R, Roddy K, and Murphy P. Mechanical regulation of skeletal development. Curr Osteoporos Rep. (2013) 11:107–16. doi: 10.1007/s11914-013-0137-4
14. Murray PDF and Drachm DB. The role of movement in the development of joints and related structures: the head and neck in the chick embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. (1959) 22:349–71.
15. Regan JN, Waning DL, and Guise TA. Skeletal muscle Ca(2+) mishandling: Another effect of bone-to-muscle signaling. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2016) 49:24–9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.11.007
16. Dallas SL, Prideaux M, and Bonewald LF. The osteocyte: an endocrine cell … and more. Endocr Rev. (2013) 34:658–90. doi: 10.1210/er.2012-1026
17. Buckingham M and Vincent SD. Distinct and dynamic myogenic populations in the vertebrate embryo. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2009) 19:444–53. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.08.001
18. Hawke TJ and Garry DJ. Myogenic satellite cells: physiology to molecular biology. J Appl Physiol. (2001) 91:534–51. doi: 10.1152/jappl.2001.91.2.534
19. Zammit P. Kinetics of Myoblast Proliferation Show That resident satellite cells are competent to fully regenerate skeletal muscle fibers. Exp Cell Res. (2002) 281:39–49. doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5653
20. Nowlan NC, Bourdon C, Dumas G, Tajbakhsh S, Prendergast PJ, and Murphy P. Developing bones are differentially affected by compromised skeletal muscle formation. Bone. (2010) 46:1275–85. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.11.026
21. Bren-Mattison Y, Hausburg M, and Olwin BB. Growth of limb muscle is dependent on skeletal-derived Indian hedgehog. Dev Biol. (2011) 356:486–95. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.06.002
22. Kaji H. Interaction between muscle and bone. J Bone Met. (2014) 21:29–40. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2014.21.1.29
24. Kaji H. Linkage between muscle and bone: common catabolic signals resulting in osteoporosis and sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr. (2013) 16:272–7. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32835fe6a5
25. Hamrick MW, McNeil PL, and Patterson SL. Role of muscle-derived growth factors in bone formation. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. (2010) 10:64–70.
26. Richards RR, McKee M, Paitich C, Anderson G, and Bertoia J. A comparison of the effects of skin coverage and muscle flap coverage on the early strength of union at the site of osteotomy after devascularization of a segment of canine tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. (1991) 73:1323–30. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199173090-00006
27. Avin KG, Bloomfield SA, Gross TS, and Warden SJ. Biomechanical aspects of the muscle-bone interaction. Curr Osteoporos Rep. (2015) 13:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11914-014-0244-x
28. Fukumoto S and Martin TJ. Bone as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrin Met. (2009) 20:230–6. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.02.001
29. Guntur AR and Rosen CJ. Bone as an endocrine organ. Endocr Pract. (2012) 18:758–62. doi: 10.4158/EP12141.RA
30. Beno T, Yoon YJ, Cowin SC, and Fritton SP. Estimation of bone permeability using accurate microstructural measurements. J Biomech. (2006) 39:2378–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.08.005
31. Schiaffino S and Mammucari C. Regulation of skeletal muscle growth by the IGF1-Akt/PKB pathway: insights from genetic models. Skeletal muscle. (2011) 1:1–14. doi: 10.1186/2044-5040-1-4
32. Avin KG, Vallejo JA, Chen NX, Wang K, Touchberry CD, Brotto M, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 does not directly influence skeletal muscle cell proliferation and differentiation or ex vivo muscle contractility. Am J Physiol-Endoc M. (2018) 315:E594–604. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00343.2017
33. Kido S, Hashimoto Y, Segawa H, Tatsumi S, and Miyamoto KI. Muscle atrophy in patients wirh ckd results from FGF23/klotho-mediated supression of insulin/IGF-1 signaling. Kidney Res Clin Prac. (2012) 31:A44. doi: 10.1016/j.krcp.2012.04.435
34. Liu S, Gao F, Wen L, Ouyang M, Wang Y, Wang Q, et al. Osteocalcin induces proliferation via positive activation of the PI3K/akt, P38 MAPK pathways and promotes differentiation through activation of the GPRC6A-ERK1/2 pathway in C2C12 myoblast cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2017) 43:1100–12. doi: 10.1159/000481752
35. Mera P, Laue K, Ferron M, Confavreux C, Wei J, Galan-Diez M, et al. Osteocalcin signaling in myofibers is necessary and sufficient for optimum adaptation to exercise. Cell Metab. (2016) 23:1078–92. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.004
36. Mera P, Laue K, Wei J, Berger JM, and Karsenty G. Osteocalcin is necessary and sufficient to maintain muscle mass in older mice. Mol Metab. (2016) 5:1042–7. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.07.002
37. Mo C, Zhao R, Vallejo J, Igwe O, Bonewald L, Wetmore L, et al. Prostaglandin E2 promotes proliferation of skeletal muscle myoblasts via EP4 receptor activation. Cell Cycle. (2015) 14:1507–16. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1026520
38. Mo C, Romero-Suarez S, Bonewald L, Johnson M, and Brotto M. Prostaglandin E2 from clinical applications to its potential role in bone-muscle crosstalk and myogenic differentiation. Recent Pat Biotechnol. (2012) 6:223–9. doi: 10.2174/1872208311206030223
39. Li G, Zhang L, Ning K, Yang B, Acosta FM, Shang P, et al. Osteocytic connexin43 channels regulate bone-muscle crosstalk. Cells. (2021) 10:237. doi: 10.3390/cells10020237
40. Huang J, Romero-Suarez S, Lara N, Mo C, Kaja S, Brotto L, et al. Crosstalk between MLO-Y4 osteocytes and C2C12 muscle cells is mediated by the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. JBMR Plus. (2017) 1:86–100. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10015
41. Hesse E, Schröder S, Brandt D, Pamperin J, Saito H, and Taipaleenmäki H. Sclerostin inhibition alleviates breast cancer–induced bone metastases and muscle weakness. JCI Insight. (2019) 4:e125543. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.125543
42. Wettlaufer SH, Penke LR, Okunishi K, and Peters-Golden M. Distinct PKA regulatory subunits mediate PGE2 inhibition of TGFbeta-1-stimulated collagen I translation and myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2017) 313:L722–31. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00131.2017
43. Waning DL, Mohammad KS, Reiken S, Xie W, Andersson DC, John S, et al. Excess TGF-beta mediates muscle weakness associated with bone metastases in mice. Nat Med. (2015) 21:1262–71. doi: 10.1038/nm.3961
44. Zhang P, Du Y, Zhong X, Wang Y, and Pan T. Identification of potential shared core biomarkers in type 2 diabetes and sarcopenia. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:25439. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10200-0
45. Mizokami A, Kawakubo-Yasukochi T, and Hirata M. Osteocalcin and its endocrine functions. Biochem Pharmacol. (2017) 132:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.02.001
46. Kanazawa I. Osteocalcin as a hormone regulating glucose metabolism. World J Diabetes. (2015) 6:1345–54. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i18.1345
47. Zoch ML, Clemens TL, and Riddle RC. New insights into the biology of osteocalcin. Bone. (2016) 82:42–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.05.046
48. Lee NK, Sowa H, Hinoi E, Ferron M, Ahn JD, Confavreux C, et al. Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell. (2007) 130:456–69. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.047
49. Ferron M, McKee MD, Levine RL, Ducy P, and Karsenty G. Intermittent injections of osteocalcin improve glucose metabolism and prevent type 2 diabetes in mice. Bone. (2012) 50:568–75. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.04.017
50. Chowdhury S, Schulz L, Palmisano B, Singh P, Berger JM, Yadav VK, et al. Muscle-derived interleukin 6 increases exercise capacity by signaling in osteoblasts. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:2888–902. doi: 10.1172/JCI133572
51. Shen H, Grimston S, Civitelli R, and Thomopoulos S. Deletion of connexin43 in osteoblasts/osteocytes leads to impaired muscle formation in mice. J Bone Miner Res. (2015) 30:596–605. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2389
52. Quarles LD. Role of FGF23 in vitamin D and phosphate metabolism: implications in chronic kidney disease. Exp Cell Res. (2012) 318:1040–8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.02.027
53. Sakamoto E, Kitase Y, Fitt AJ, Zhu Z, Awad K, Brotto M, et al. Both enantiomers of β-aminoisobutyric acid BAIBA regulate Fgf23 via MRGPRD receptor by activating distinct signaling pathways in osteocytes. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114397. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114397
54. Alcalde-Estévez E, Sosa P, Asenjo-Bueno A, Plaza P, Valenzuela PL, Naves-Díaz M, et al. Dietary phosphate restriction prevents the appearance of sarcopenia signs in old mice. J Cachexia Sarcopeni. (2023) 14:1060–74. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13194
55. Wacker MJ, Touchberry CD, Silswal N, Brotto L, Elmore CJ, Bonewald LF, et al. Skeletal muscle, but not cardiovascular function, is altered in a mouse model of autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets. Front Physiol. (2016) 7:173. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00173
56. Afsar RE, Afsar B, and Ikizler TA. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and muscle wasting: a metabolic point of view. Kidney Int Rep. (2023) 8:1301–14. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.04.027
57. Welc SS, Brotto M, White KE, and Bonewald LF. Aging: A struggle for beneficial to overcome negative factors made by muscle and bone. Mech Ageing Dev. (2025) 224:112039. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2025.112039
58. Egerman MA and Glass DJ. Signaling pathways controlling skeletal muscle mass. Crit Rev Biochem Mol. (2014) 49:59–68. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.857291
59. Blaauw B, Canato M, Agatea L, Toniolo L, Mammucari C, Masiero E, et al. Inducible activation of Akt increases skeletal muscle mass and force without satellite cell activation. FASEB J. (2009) 23:3896–905. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-131870
60. Sheng MH, Zhou XD, Bonewald LF, Baylink DJ, and Lau KH. Disruption of the insulin-like growth factor-1 gene in osteocytes impairs developmental bone growth in mice. Bone. (2013) 52:133–44. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2012.09.027
61. Sartori R, Gregorevic P, and Sandri M. TGFβ and BMP signaling in skeletal muscle: potential significance for muscle-related disease. Trends Endocrin Met. (2014) 25:464–71. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.06.002
62. Mendias CL, Gumucio JP, Davis ME, Bromley CW, Davis CS, and Brooks SV. Transforming growth factor-beta induces skeletal muscle atrophy and fibrosis through the induction of atrogin-1 and scleraxis. Muscle Nerve. (2012) 45:55–9. doi: 10.1002/mus.22232
63. Spatz JM, Fields EE, Yu EW, Pajevic PD, Bouxsein ML, Sibonga JD, et al. Serum sclerostin increases in healthy adult men during bed rest. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:E1736–1740. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1579
64. Robling AG, Niziolek PJ, Baldridge LA, Condon KW, Allen MR, Alam I, et al. Mechanical stimulation of bone in vivo reduces osteocyte expression of Sost/sclerostin. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:5866–75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705092200
65. Colaianni G, Mongelli T, Cuscito C, Pignataro P, Lippo L, Spiro G, et al. Irisin prevents and restores bone loss and muscle atrophy in hind-limb suspended mice. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:2811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02557-8
66. Colaianni G, Brunetti G, Colucci SC, and Grano M. Myokine—Irisin—and its effects linking bone and muscle function. Clin Rev Bone Mineral Metab. (2018) 16:16–21. doi: 10.1007/s12018-017-9240-x
67. Ahn S, Jung H, and Lee E. Decreased serum level of sclerostin in older adults with sarcopenia. Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 37:487–96. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1428
68. Kirk B, Zanker J, and Duque G. Osteosarcopenia: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment—facts and numbers. J Cachexia Sarcopeni (2020) 11:609–18. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12567
69. Tagliaferri C, Wittrant Y, Davicco MJ, Walrand S, and Coxam V. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev. (2015) 21:55–70. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2015.03.002
70. Palla AR, Ravichandran M, Wang YX, Alexandrova L, Yang AV, Kraft P, et al. Inhibition of prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-PGDH rejuvenates aged muscle mass and strength. Science. (2021) 371:eabc8059. doi: 10.1126/science.abc8059
71. Li G, Zhang L, Lu Z, Yang B, Yang H, Shang P, et al. Connexin 43 channels in osteocytes are necessary for bone mass and skeletal muscle function in aged male mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:13506. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113506
72. Dong Y, Yuan H, Ma G, and Cao H. Bone-muscle crosstalk under physiological and pathological conditions. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2024) 81:310. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05331-y
73. McCormick L, Wang K, and Tiede-Lewis L. Role of FGF9 in promotion of early osteocyte differentiation and as a potent inducer of fgf23 expression in osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res. (2016) 31:S39.
74. Wang K, Le L, Chun BM, Tiede-Lewis LM, Shiflett LA, Prideaux M, et al. A novel osteogenic cell line that differentiates into GFP-tagged osteocytes and forms mineral with a bone-like lacunocanalicular structure. J Bone Miner Res. (2019) 34:979–95. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3720
75. He T, Qin L, Chen S, Huo S, Li J, Zhang F, et al. Bone-derived factors mediate crosstalk between skeletal and extra-skeletal organs. Bone Res. (2025) 13:49. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00424-1
76. Kirk B, Lombardi G, and Duque G. Bone and muscle crosstalk in ageing and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2025) 21:375–90. doi: 10.1038/s41574-025-01088-x
77. He C, He W, Hou J, Chen K, Huang M, Yang M, et al. Bone and muscle crosstalk in aging. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:585644. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.585644
78. Shimonty A, Pin F, Prideaux M, Peng G, Huot J, Kim H, et al. Deletion of FNDC5/irisin modifies murine osteocyte function in a sex-specific manner. Elife. (2024) 12:RP92263. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92263
Keywords: bone, muscle, endocrine organ, bone-derived factors, osteoporosis, sarcopenia
Citation: Li G, Qi M and Liang S (2025) The role of bone-derived factors in bone and muscle communication. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1702104. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1702104
Received: 09 September 2025; Accepted: 29 September 2025;
Published: 14 October 2025.
Edited by:
Giacomina Brunetti, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyReviewed by:
Tullia Maraldi, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Li, Qi and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guobin Li, Z3VvYmlubEAxMjYuY29t
 Guobin Li
Guobin Li Mingyan Qi1
Mingyan Qi1