- 1Department of Dermatology & Rare Disease Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of Outpatient, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Background: Ofatumumab, a fully human anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody administered subcutaneously and indicated for multiple sclerosis, might theoretically be effective for patients with pemphigus vulgaris (PV).
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of ofatumumab in patients with PV.
Methods: This cohort study was based on a registry database of autoimmune bullous diseases at West China Hospital (AIBD-WCH), including two groups. One was ofatumumab (OFA) group, involving patients receiving ofatumumab subcutaneous injections (2×20mg, 2 weeks apart) and systemic glucocorticoids with/without immunosuppressant. The glucocorticoids control (GC) group was matched using propensity score matching in a 1:2 ratio based on sex, age and body mass index. Both groups completed regular follow-up for 52 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving complete remission during therapy (CRDT) at week 52. Secondary endpoints included maintaining treatment (MT) with daily prednisone doses <0.2 mg/kg/d, relapse rate, the change of pemphigus disease area index and cumulative glucocorticoid doses. Safety results were also collected.
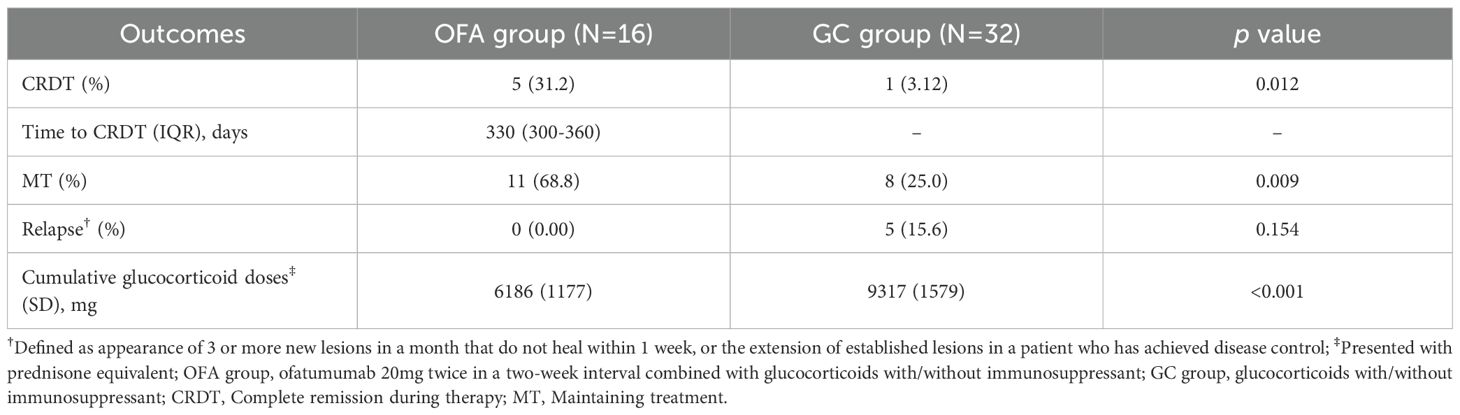
Results: Sixteen and thirty-two patients were included in OFA and GC groups, respectively. At week 52, more patients in OFA group achieved CRDT (31.2% versus 3.12%, p=0.012) and MT (68.8% versus 25.0%, p=0.009). Furthermore, patients in OFA group took lower cumulative glucocorticoid doses by week 52 (6186 [SD: 1177]mg versus 9317 [SD: 1579]mg, p<0.001). A patient in OFA group experienced gastric hemorrhage, which was judged to be unrelated to ofatumumab, while two in GC group developed lung infections.
Conclusions: Ofatumumab combined with glucocorticoids demonstrated favorable effectiveness compared with GC group, without increasing severe adverse events.
1 Introduction
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is a chronic, life-threatening autoimmune bullous disease (AIBD) characterized by erythema, blisters, and erosions on the mucosa and/or skin (1). Autoreactive B cells play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of PV, which can differentiate into plasma cells that secrete autoantibodies targeting desmoglein (Dsg) 1 and 3, leading to acantholysis and blister formation. Rituximab, a chimeric murine/human monoclonal antibody against CD20 on the surface of B cells, has demonstrated efficacy in patients with PV and is now listed as a first-line treatment for moderate to severe cases (2). Although rituximab has guideline-recommended protocols (2) (2×1000 mg, 2 weeks apart or 4×375 mg/m2, 1 week apart), there are ongoing discussions about alternative dosing and frequency options (3–6). Moreover, studies focusing on the long-term prognosis of patients receiving rituximab reported relapse rates of 63%-100% after a single cycle of infusion (7, 8). Other limitations of rituximab include the administration of intravenous infusion, severe adverse events (AEs) and the costs of hospitalization.
Ofatumumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting CD20 administered subcutaneously and indicated for multiple sclerosis (MS) (9). Over the years, it has been reported to be used in various autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and ANCA-associated vasculitis (10–12). Applications of ofatumumab in pemphigus have been reported in several cases including from our center (13, 14). Recently, a cohort study reported that ofatumumab facilitated rapid disease control in patients with pemphigus compared with the conventional group in 36-week observation (15). However, longer-term data on its effectiveness and safety, and the exploration on alternative injection regimen are still needed. Herein, we present a cohort study that lasted for 52 weeks to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of ofatumumab combined with oral glucocorticoids in PV patients. We hope this study can provide foundational knowledge and regimen references for treating PV with ofatumumab.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data source
The data used in this study derived from a registry database: autoimmune bullous diseases at West China Hospital (AIBD-WCH). The database has been including patients diagnosed with AIBD at the Department of Dermatology, West China Hospital since 1 June 2017, with continuous updates in their medical data. In detail, we systematically collected the patients’ demographical and clinical disease characteristics at their first visit and renewed their data at each visit longitudinally. The database was approved by the biomedical research ethics committee of West China Hospital of Sichuan University (Approval number: 2017–241) and conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. All participants have signed informed consent.
2.2 Study design and participants
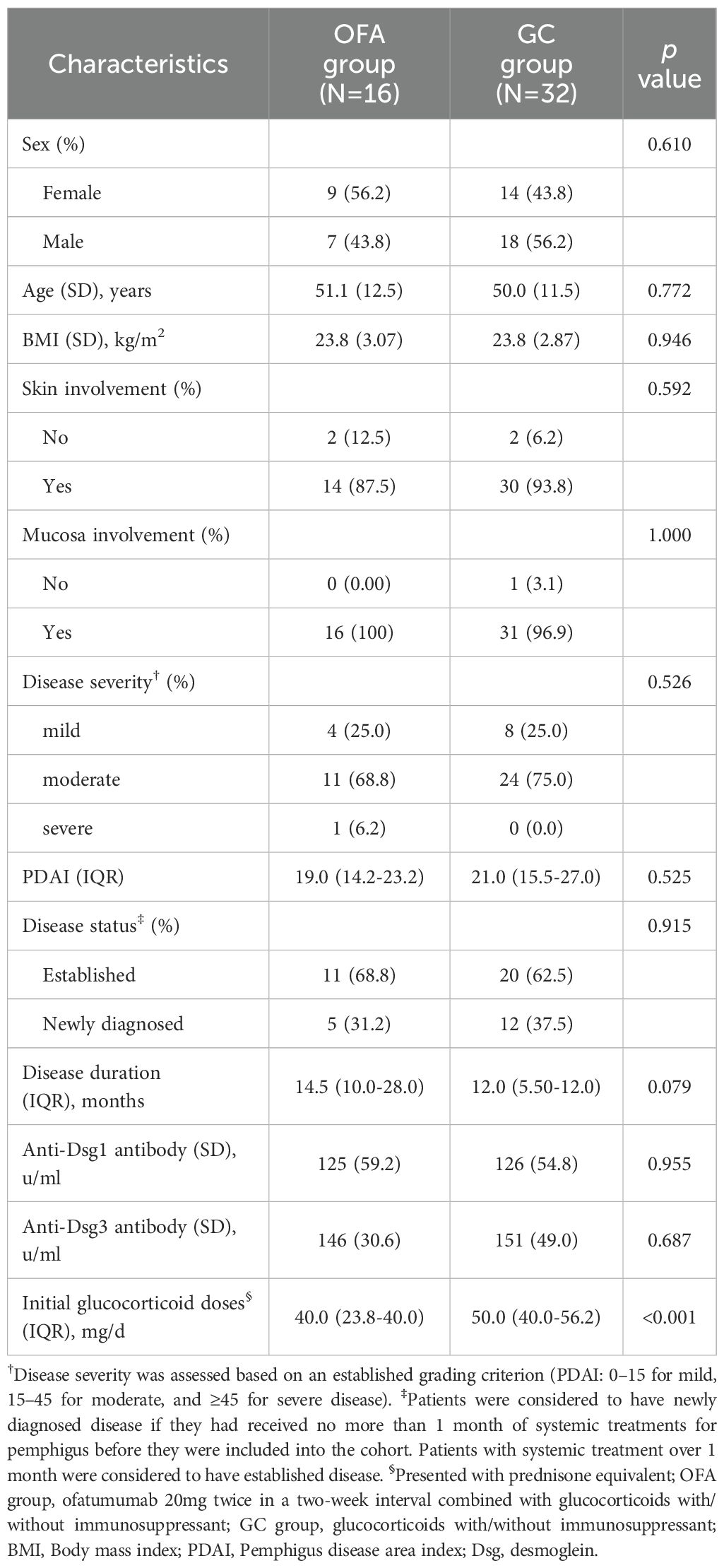
This is a cohort study including two groups, the study design is shown in Figure 1. Ofatumumab (OFA) group included patients receiving ofatumumab injections and systemic glucocorticoids, with or without conventional immunosuppressants. Inclusion criteria for this group were patients: (i)aged between 18 and 80 years, (ii)with a confirmed diagnosis of PV (based on the clinical presentation, histopathological biopsy, enhancing levels of anti-Dsg1 and/or Dsg3 antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and direct immunofluorescence assay showing immunoglobulin G intercellular deposition of epithelium) (2). Exclusion criteria of OFA group included: (i)known active infections or recent infections which required oral antibiotic treatment within 2 weeks prior to the study, (ii)severe organ dysfunctions, (iii)current malignancies or malignancies within the past 10 years, (iv)pregnancy and breastfeeding or planning to get pregnant, (v)vaccination within 6 weeks prior to the study, (vi)rituximab or other B-cell-targeted therapy within 12 months prior to the study, (vii)plasmapheresis or plasma exchange, immunoadsorption or intravenous immunoglobulins within 8 weeks prior to the study, (viii)refusing written informed consent.

Figure 1. Study design, treatment and follow-up course. OFA group involved patients receiving ofatumumab injections (2×20mg, 2 weeks apart) and systemic glucocorticoids, with or without conventional immunosuppressants. The patients in GC group were 1:2 matched from the AIBD-WCH based on sex, age and BMI. Both groups were regularly followed up for 52 weeks. AIBD-WCH, autoimmune bullous diseases at West China Hospital; OFA group, ofatumumab group; GC group, glucocorticoids group.
The glucocorticoid control (GC) group included patients with at least one year of regular follow-up in the AIBD-WCH database. In these patients, propensity score matching (PSM) was performed at a 1:2 ratio using nearest-neighbor matching and a caliper of 0.2 without replacement, based on sex, age and body mass index (BMI).
Disease severity was assessed based on an established grading criterion (PDAI: 0–15 for mild, 15–45 for moderate, and ≥45 for severe disease) (16). Patients were considered to have newly diagnosed disease if they had received no more than 1 month of systemic treatments for pemphigus before they were included into the cohort. Patients with systemic treatment over 1 month were considered to have established disease.
2.3 Treatment and follow-up
Patients in OFA group received 20mg ofatumumab subcutaneous injection on day 1 and day 15, respectively. Systemic prednisone was initiated at 0.2-1.0 mg/kg/d, with or without conventional immunosuppressants depending on the disease status and severity. Patients in GC group received initial oral prednisone equivalent at a dosage of 0.5-1.0 mg/kg/d, with or without conventional immunosuppressants. The patients were followed up regularly for 52 weeks. The regimens were adjusted according to the disease conditions and laboratory indicators at each visit, and the maintenance dose of ofatumumab was available if necessary.
2.4 Outcome measures
The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved complete remission during therapy (CRDT) at week 52: the absence of new or established lesions while the patient is receiving prednisone equivalent at a dose of 10mg/d or less and/or minimal adjuvant therapy for at least 2 months (2). Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients who achieved maintaining treatment (MT) at week 52, defined as the absence of new or established lesions with prednisone equivalent tapered to 0.2 mg/kg/d or lower (17), the number of patients experiencing disease relapse, the change of pemphigus disease area index (PDAI) activity score from baseline and cumulative oral glucocorticoids dose over the 52-week observation. Relevant laboratory indicators including serum anti-Dsg1 and anti-Dsg3 antibody levels and absolute CD19+ B cell count of OFA group were assessed regularly. AEs were recorded accurately and evaluated in Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were presented with measures of central tendency (mean, median) and dispersion (SD, IQR). For normally distributed data, means were compared using the student’s t-test. The Mann-Whitney test was used for non-normally distribution. Categorical variables were described by frequencies and proportions and compared using the Chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test. Logistic regression was performed to adjust for potential confounders and assess the independent effect of ofatumumab on treatment effectiveness. Linear mixed-effects models were used to analyze repeated measures data, including PDAI scores and anti-Dsg1/3 antibody levels. The significance level was set at 0.05 and all statistical tests were two-sided. R version 4.3.1 and GraphPad Prism 10.0 were used for statistical analyses and illustration.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
In total, 16 patients with PV were included in the OFA group, and 32 patients were included in the GC group, matched by sex, age, and BMI. At baseline, no significant difference was observed in sex, age, BMI, skin/mucosa involvement, severity, PDAI, disease status, duration, and anti-Dsg1/3 antibody levels between the two groups (Table 1). The patients in OFA group received lower initial prednisone doses than those in GC group (40.0 [23.8-40.0] mg/d versus 50.0 [40.0-56.2] mg/d, p<0.001).
3.2 Comparison of outcome indicators between two groups
One patient in OFA group received a third injection at week 32. At week 52, 5 out of 16 patients (31.2%) in OFA group achieved CRDT, compared with 1 out of 32 patients (3.12%) in GC group (p=0.012) (Table 2). The proportion of patients who achieved MT at week 52 was significantly higher in OFA group than in GC group [11 out of 16 (68.8%) versus 8 of 32 (25.0%), p=0.009]. To adjust for potential confounding by baseline prednisone doses, bivariate logistic regressions were performed, focusing on the achievement of CRDT and MT (Supplementary Tables 1, 2). The adjusted OR of ofatumumab treatment was 14.94 (95% CI: 1.24-179.96) for CRDT and 9.65 for MT (95% CI: 1.68-55.46).
There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who experienced relapse between the two groups. By week 52, the mean cumulative prednisone exposure of OFA group was lower compared with that of GC group (6186 [SD: 1177]mg versus 9317 [SD: 1579]mg, p<0.001). There was no significant difference in the application or type of conventional immunosuppressants between the two groups.
Over the 52-week observation, both groups showed a steadily decreasing trend in PDAI, with no significant differences in PDAI changes between the two groups at each visit (Figure 2A, Supplementary Table 3). The OFA group received significantly less daily prednisone doses than the GC group from week 0 to week 52 (Figure 2B, Supplementary Table 4). Supplementary Image 1 displays the treating course of a refractory patient in OFA group.

Figure 2. The change of outcome indicators during the study. (A) The change of PDAI (B) Daily prednisone doses (C) Serum anti-Dsg1 antibody level (D) Serum anti-Dsg3 antibody level (E) Absolute CD19+B cell count. The blue lines represent OFA group. The red lines represent GC group. PDAI, pemphigus disease area index; Dsg, desmoglein.
Moreover, we performed exploratory subgroup analysis according to treatment history (Supplementary Table 5). In both subgroups, the proportions of patients achieving CRDT and MT in the OFA group show higher trend compared with those of the GC group. Additionally, among the five patients who were newly diagnosed and received ofatumumab as first-line therapy, 2 (40.0%) achieved CRDT, compared with 3 out of 11 (27.3%) among patients with established disease.
3.3 Laboratory findings
At each visit, no significant difference in anti-Dsg1/3 antibody levels was found between the two groups (Figures 2C, D, Supplementary Table 3). Anti-Dsg1 antibody levels decreased from baseline to week 52 in both groups. Anti-Dsg3 antibody of patients in OFA group decreased until week 36 and then started to increase. After the injection of ofatumumab, the absolute CD19+ B cell counts of patients in OFA group decreased rapidly and remained depleted (defined as 8 cells/μL) by week 24. Afterwards, the median CD19+B cell count increased steadily by week 52 (Figure 2E).
3.4 Adverse events between two groups
Injection-related reactions (IRRs) were observed in 4 patients (25%) within 24 hours after ofatumumab injection. In the OFA group, one patient experienced a grade 3 AE (gastric hemorrhage) 25 days after ofatumumab administration and 30 days after initiation of glucocorticoids, causing hospitalization for 6 days. Given the patient’s history of chronic alcoholic gastritis and the concurrent use of high-dose prednisone (50 mg/d), this AE was assessed unrelated to ofatumumab. Two patients in GC group developed grade 3 AEs (lung infections). The details of all AEs over 52 weeks are provided in Supplementary Table 6.
4 Discussion
This cohort study, lasting for 52 weeks, shows that the application of ofatumumab (2×20mg, 2 weeks apart) in patients with PV demonstrated better effectiveness compared with the GC group. At week 52, higher proportion of patients in the OFA group achieved CRDT and MT compared with the GC group. Throughout the entire study, the OFA group received lower daily and cumulative glucocorticoid doses than the GC group. No severe AE related to ofatumumab was reported in the OFA group. The subcutaneous administration of ofatumumab is more convenient, accessible, and acceptable for patients with pemphigus compared to the intravenous infusion of rituximab, which typically requires inpatient clinic visits. Furthermore, due to its fully human structure, ofatumumab is theoretically less immunogenic, potentially reducing the risk of adverse effects associated with anti-drug antibody formation.
The proportion of patients achieving CRDT in our study was 31.2%, appearing lower compared with the data reported in previous studies on rituximab, which ranged from 40% to 100% (3, 5, 6, 8, 18, 19). These differences can be attributed to variations in study designs, patient conditions, treatment protocols and glucocorticoid-tapering regimens. In our cohort study conducted in a real-world setting, we adopted a conservative and individualized tapering protocol to minimize the risk of relapse, resulting in a delayed reduction to a prednisone dose of 10mg/kg/d. Therefore, it’s difficult to directly compare the efficacy of ofatumumab and rituximab based on the endpoint of CR. A well-designed head-to-head study would be suitable for this purpose. At week 52, a significantly higher proportion of patients in the OFA group achieved MT compared with the GC group, suggesting a favorable steroid-sparing effect from the perspective of personalized therapy.
In the newly diagnosed subgroup, we observed a trend toward a higher proportion of patients achieving CRDT compared with those with established disease. This finding aligns with the results from rituximab studies, suggesting that early application of ofatumumab might benefit patients with PV (20, 21).
No patient in our study experienced relapse by week 52, which somehow differed from the relapse data from previous studies (for instance, around 25% in the first year with rituximab (3)). Several factors may explain this difference. Firstly, as descripted above, our tapering protocols differed from those in prior studies. We adjusted prednisone doses based on each patient’s disease condition and immune biomarkers at each visit, generally in a lower tapering speed rather than rescue treatment, aiming to reduce the relapse risk. Another reason was the varying distributions of disease severity, a known risk factor for disease relapse (22). In our study, the OFA group consisted primarily of mild to moderate patients (PDAI: 19.0 (14.2-23.2)), while previous studies typically focused on moderate to severe patients. Additionally, we did observe that a refractory patient in the OFA group whose B cell count increased to 61 cells/μL with a high anti-Dsg1 antibody level by week 32. As a result, a third injection of ofatumumab was administered. Following this adjuvant dose, the anti-Dsg1 antibody level decreased rapidly along with the B cell count, and no relapse occurred by week 52.
Reducing oral glucocorticoid doses is a key objective in the development of new therapies for PV. Since baseline, the daily prednisone doses of the OFA group were significantly lower than those in the GC group over the follow-up. Nevertheless, higher proportion of patients in the OFA group achieved CRDT and MT, and the PDAI showed no significant differences at each visit. As a result, patients in the OFA group took lower cumulative prednisone dose compared with the GC group by week 52. These findings align with the results from the Ritux3 trial (3), supporting the robust steroid-sparing effect of ofatumumab.
Plenty of research proposed the association between B cell repopulation and relapse (7, 23, 24). Our data presented increasing trend in B cell count and anti-Dsg3 antibody level since week 24, similar to the data from rituximab (3). It remained below 40 cells/μL by week 52, which is not entirely consistent with the simulated data from the pharmacokinetics study (25). This discrepancy might because of the application of glucocorticoid, inhibiting lymphocytes proliferation. The anti-Dsg3 level also started to elevate at week 36 but remained below the predictive relapse cutoff of 130 U/mL by week 52, consistent with the absence of relapse (23, 26). This could be explained by the recovery of memory B cells secreting different types of IgG subclass, including non-pathogenic antibodies (27). Overall, further data on B cells and auto-antibodies in patients with pemphigus following anti-CD20 therapy are needed to predict prognosis more accurately.
The OFA group demonstrated good tolerability. IRRs occurred in 25% of patients, consistent with the 24.1% reported in the ASCLEPIOS II trial in MS (9), and similar with the 22% of infusion related reactions observed in the RCT of rituximab in pemphigus (19). One severe AE (gastric hemorrhage) was observed in the OFA group (6.3%), versus 22% observed in the safety data for 52 weeks from rituximab (19). The most common AEs in the OFA group included elevation of liver enzymes and gastrointestinal disorders, likely related to the use of conventional immunosuppressants and glucocorticoids. Whereas, the most frequent AEs reported in the phase III RCT in MS include IRRs, nasopharyngitis, headache, upper respiratory tract infection and urinary tract infection (9). The difference in AEs between the OFA group in our study and phase III RCT in MS may lie on GC application. In addition, the highest AE in GC group was osteoporosis, which was not reported in the OFA group, suggesting an encouraging protective effect of ofatumumab against glucocorticoid-induced side effects.
The main limitation of this study is the small sample size, especially the limited number of severe pemphigus, confining further stratified analysis. The 52-week follow-up also constrains the assessment of long-term outcomes.
In conclusion, this study suggests ofatumumab is well-tolerant, effective and convenient for patients with PV, showing favorable steroid-sparing effects in the entire treatment course. The feature of subcutaneous administration enables ofatumumab a potentially convenient option for patients with PV. Further studies are needed to explore the optimal timing of adjuvant ofatumumab injection. Furthermore, prospective head-to-head trials can be conducted to compare the efficacy of ofatumumab and rituximab in patients with PV.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by biomedical research ethics committee of West China Hospital of Sichuan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
XwZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. PT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MWe: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. XlZ: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YX: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. XF: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. JL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. MWa: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. MZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. GK: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LJ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. JW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. WL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province [2024NSFSC1626] and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [2024M752267].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1537334/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Clinical pictures of a refractory patient in OFA group. PDAI at week 0: 23, PDAI at week 4: 26 (experienced COVID-19 infection), PDAI at week 12: 7, PDAI at week 24: 5, PDAI at week 52: 3.
Abbreviations
AIBD, autoimmune bullous disease; AIBD-WCH, autoimmune bullous diseases at West China Hospital; BMI, body mass index; CRDT, complete remission during therapy; Dsg, desmoglein; GC, glucocorticoid; MS, multiple sclerosis; MT, maintaining treatment; OFA, ofatumumab; PDAI, pemphigus disease area index; PSM, propensity score matching; PV, pemphigus vulgaris.
References
1. Kasperkiewicz M, Ellebrecht CT, Takahashi H, Yamagami J, Zillikens D, Payne AS, et al. Pemphigus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2017) 3:17026. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.26
2. Murrell DF, Peña S, Joly P, Marinovic B, Hashimoto T, Diaz LA, et al. Diagnosis and management of pemphigus: Recommendations of an international panel of experts. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2020) 82:575–85.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.021
3. Joly P, Maho-Vaillant M, Prost-Squarcioni C, Hebert V, Houivet E, Calbo S, et al. First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux 3): a prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet. (2017) 389:2031–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30070-3
4. Zhou X, Zhan T, Xu X, Lan T, Hu H, Xia D, et al. The efficacy and safety of low-dose rituximab in the treatment of pemphigus vulgaris: a cohort study. J Dermatolog Treat. (2024) 35:1:2302071. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2024.2302071
5. Kanwar AJ, Vinay K, Sawatkar GU, Dogra S, Minz RW, Shear NH, et al. Clinical and immunological outcomes of high- and low-dose rituximab treatments in patients with pemphigus: a randomized, comparative, observer-blinded study. Br J Dermatol. (2014) 170:1341–9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12972
6. Zhang J, Huang X, Zhang Z, Zhao P, Chen W, Liang Y, et al. Clinical observation of different doses of rituximab for the treatment of severe pemphigus: A single-center prospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2023) 88:500–2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1187
7. Saleh MA. A prospective study comparing patients with early and late relapsing pemphigus treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2018) 79:97–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.029
8. Shimanovich I, Baumann T, Schmidt E, Zillikens D, and Hammers CM. Long-term outcomes of rituximab therapy in pemphigus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2020) 34:2884–9. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16561
9. Hauser SL, Bar-Or A, Cohen JA, Comi G, Correale J, Coyle PK, et al. Ofatumumab versus teriflunomide in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:546–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1917246
10. Kurrasch R, Brown JC, Chu M, Craigen J, Overend P, Patel B, et al. Subcutaneously administered ofatumumab in rheumatoid arthritis: A phase I/II study of safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. J Rheumatol. (2013) 40:1089–96. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.121118
11. Masoud S, McAdoo SP, Bedi R, Cairns TD, and Lightstone L. Ofatumumab for B cell depletion in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus who are allergic to rituximab. Rheumatology. (2018) 57:1156–61. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key042
12. McAdoo SP, Bedi R, Tarzi R, Griffith M, Pusey CD, and Cairns TD. Ofatumumab for B cell depletion therapy in ANCA-associated vasculitis: a single-centre case series. Rheumatology. (2016) 55:1437–42. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew199
13. Zhang X, Xiao Y, Li X, Wang J, Zhou X, Wang Y, et al. Ofatumumab subcutaneous injection successfully treated patients with pemphigus vulgaris relapse post rituximab. J Dermatol. (2024) 51:1026–30. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.17108
14. Klufas DM, Amerson E, Twu O, Clark L, and Shinkai K. Refractory pemphigus vulgaris successfully treated with ofatumumab. JAAD Case Rep. (2020) 6:734–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.05.034
15. Mao J, Bao S, Chen Y, Zhuang Z, Chen W, Li G, et al. Evaluation of combination therapy with ofatumumab and systemic corticosteroids for pemphigus: A multi-centre cohort study. Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2024) 39(3):e244-7. doi: 10.1111/jdv.20245
16. Boulard C, Duvert Lehembre S, Picard-Dahan C, Kern JS, Zambruno G, Feliciani C, et al. Calculation of cut-off values based on the Autoimmune Bullous Skin Disorder Intensity Score (ABSIS) and Pemphigus Disease Area Index (PDAI) pemphigus scoring systems for defining moderate, significant and extensive types of pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. (2016) 175:142–9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.14405
17. Committee for Guidelines for the Management of Pemphigus Disease, Amagai M, Tanikawa A, Shimizu T, Hashimoto T, Ikeda S, et al. Japanese guidelines for the management of pemphigus. J Dermatol. (2014) 41:471–86. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12486
18. Kushner CJ, Wang S, Tovanabutra N, Tsai DE, Werth VP, and Payne AS. Factors associated with complete remission after rituximab therapy for pemphigus. JAMA Dermatol. (2019) 155:1404–9. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3236
19. Werth VP, Joly P, Mimouni D, Maverakis E, Caux F, Lehane P, et al. Rituximab versus mycophenolate mofetil in patients with pemphigus vulgaris. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:2295–305. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028564
20. Tedbirt B, Maho-Vaillant M, Houivet E, Mignard C, Golinski ML, Calbo S, et al. Sustained remission without corticosteroids among patients with pemphigus who had rituximab as first-line therapy: follow-up of the ritux 3 trial. JAMA Dermatol. (2024) 160:290–6. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.5679
21. Nosrati A, Mimouni T, Hodak E, Gdalevich M, Oren-Shabtai M, Levi A, et al. Early rituximab treatment is associated with increased and sustained remission in pemphigus patients: A retrospective cohort of 99 patients. Dermatol Ther. (2022) 35:e15397. doi: 10.1111/dth.15397
22. Mignard C, Maho-Vaillant M, Golinski ML, Balayé P, Prost-Squarcioni C, Houivet E, et al. Factors associated with short-term relapse in patients with pemphigus who receive rituximab as first-line therapy: A post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. (2020) 156:545–52. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0290
23. Albers LN, Liu Y, Bo N, Swerlick RA, and Feldman RJ. Developing biomarkers for predicting clinical relapse in pemphigus patients treated with rituximab. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2017) 77:1074–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.07.012
24. Feldman RJ, Christen WG, and Ahmed AR. Comparison of immunological parameters in patients with pemphigus vulgaris following rituximab and IVIG therapy: Immunological parameters in patients with PV treated with rituximab and IVIG. Br J Dermatol. (2012) 166:511–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10658.x
25. Yu H, Graham G, David OJ, Kahn JM, Savelieva M, Pigeolet E, et al. Population pharmacokinetic–B cell modeling for ofatumumab in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. CNS Drugs. (2022) 36:283–300. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00895-w
26. Abasq C, Mouquet H, Gilbert D, Tron F, Grassi V, Musette P, et al. ELISA testing of anti–desmoglein 1 and 3 antibodies in the management of pemphigus. Arch Dermatol. (2009) 145:529–35. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2009.9
Keywords: pemphigus, therapy, ofatumumab, CD20 monoclonal antibody, B cell depletion, biologics
Citation: Zhang X, Wang Y, Tan P, Zhou X, Xiao Y, Feng X, Li J, Wei M, Zou M, Kim G, Jiang L, Li X, Wang J, Wang M and Li W (2025) The effectiveness and safety of ofatumumab for the treatment of pemphigus vulgaris: a cohort study based on a registry database. Front. Immunol. 16:1537334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1537334
Received: 30 November 2024; Accepted: 09 July 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Soheil Tavakolpour, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, United StatesReviewed by:
Xuming Mao, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesVivien Hebert, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) de Rouen, France
Kamran Balighi, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Tan, Zhou, Xiao, Feng, Li, Wei, Zou, Kim, Jiang, Li, Wang, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Li, bGl3ZWloeF9oeHl5QHNjdS5lZHUuY24=; Mi Wang, Mzc2OTQ2NTgyQHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiwen Zhang
Xiwen Zhang Yiyi Wang1†
Yiyi Wang1† Yue Xiao
Yue Xiao Xun Feng
Xun Feng Jishu Li
Jishu Li Wei Li
Wei Li