- 1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Hangzhou, China
- 2First School of Clinical Medicine, Zhejiang Chinese Medicine University, Hangzhou, China
- 3Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Hangzhou, China
- 4Research and Development Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Hangzhou, China
Background: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are particularly vulnerable to infections, with herpes zoster (HZ) being the most common opportunistic infection. This meta-analysis aimed to systematically review the available literature on the prevalence, incidence, and risk factors of HZ in SLE patients.
Methods: A comprehensive search through Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library was conducted for studies published up to November 1, 2024. Both observational studies (including cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional) and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included, with study types selected according to the specific objectives. Funnel plots and Egger’s test were employed to assess publication bias. Hazard ratios (HRs) and odds ratios (ORs) were converted to relative risks (RRs), and pooled estimates were calculated using a fixed-effect or random-effects model.
Results: A total of 51 studies with 246, 822 SLE patients were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled prevalence and incidence of SLE-HZ were 12.3% (95%CI 10.5-14.1) and 22.0 cases per 1000 person-years (95%CI 17.4-27.9). Glucocorticoids use (RRs=2.83, 95%CI 2.10-3.81), cyclophosphamide use (RRs=2.52, 95%CI 1.60-3.98), mycophenolate mofetil use (RRs=3.00, 95%CI 1.07-8.40), azathioprine use (RRs=1.40, 95%CI 1.18-1.67), anifrolumab use (RRs=2.59, 95%CI 1.52-4.41), having lymphopenia (RRs=2.31, 95%CI 1.54-3.46), and the presence of comorbid conditions such as renal involvement (RRs= 1.80, 95%CI 1.34-2.42) were identified to increase the risk of HZ in SLE patients.
Conclusion: The existing evidence highlights the both high prevalence and incidence of HZ in SLE patients. By identifying risk factors associated with the development of HZ in SLE patients, optimization of management strategies and treatment choices can be achieved. Concurrently, physicians could be better equipped to choose patients who would most likely gain from the HZ vaccine.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024331310, identifier CRD42024331310.
Introduction
Herpes zoster (HZ) arises from the reactivation of the latent varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is particularly prevalent and prone to dissemination in geriatric and immunocompromised individuals, potentially posing a life-threatening risk (1). Among these populations, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients are particularly susceptible to VZV reactivation (2, 3). The incidence of herpes zoster infection (HZI) among SLE patients ranges from 2.54 to 91.4 cases per 1000 patient-years (PYs) (2, 4–6), with a risk that is 2-8 times greater than other rheumatic diseases and 5-16 times higher than in the general population (7–9). SLE patients also face an elevated risk for postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), which is 2.3 times higher than the general population (10).
Although fatalities related to HZI in SLE patients are rarely reported, hospitalizations related to HZ have notably increased in recent years (11, 12). The burden of HZ and PHN on healthcare systems is substantial, significantly impacting both patient well-being and quality of life. Recent reviews suggested a focus on preventing specific infections in SLE, particularly VZV, due to the potential increased risks associated with new therapies (13). Hence, identifying risk factors for HZ in the SLE population is imperative for early detection and intervention.
Although successive studies have reported that the prevalence and incidence of HZ, as well as factors such as high-dose glucocorticoids (GCs) therapy, immunosuppressants, comorbidities (e.g., renal insufficiency), and autoantibodies, may contribute to the risk of HZI (14–17), the results are inconsistent (18–21). This inconsistency may be attributed to differences in sample size, conducted region, and patient characteristics. Thus, our systematic review aims to assess the prevalence, incidence, and associated factors of HZ in studies involving SLE patients. Furthermore, we will attempt to aggregate data related to HZ events as much as possible.
Methods
This systematic review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (22), which help ensure transparency and reproducibility in systematic reviews. The protocol was pre-registered in PROSPERO (CRD 42024331310).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
We included studies published in English with full-text availability that reported outcomes related to the prevalence, incidence, or risk factors of HZ among SLE patients. Different study designs were included according to the specific objective of each analysis. Cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies were used to estimate prevalence. Only cohort studies were included to assess incidence. For evaluating risk factors, we included cohort and case-control studies. In addition, when assessing the efficacy and safety of biological agents in patients with SLE, some randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have reported the incidence of HZ as an adverse outcome. Accordingly, these RCTs were included in our analysis to estimate the relative risk of HZ associated with biologic therapy.
SLE patients were required to meet the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria (23, 24) or the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9-CM code 710.0; ICD-10-CM code M32.0-M32.1, M32.9). HZ cases were identified based on physician-reported ICD codes (ICD-9-CM code 053; ICD-10-CM code B02). Those diagnosed by typical vesicular eruption developing in a dermatomal distribution were also included, as recommended by the 2016 European consensus guidelines (25). Only patients with a history of HZ following the diagnosis of SLE were considered. Studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded, along with letters, reviews, commentaries, conference abstracts, and case reports.
Literature search
We searched Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library from their inception to November 1, 2024. The search strategy incorporated medical subject headings (MeSH) and free-text keywords, including ‘herpes zoster’, ‘ systemic lupus erythematosus’, ‘prevalence’, ‘incidence’, ‘risk factor’, and their associated variations. The full search strategy is documented in Supplementary Table S1. A thorough search was conducted by screening the bibliographies of every relevant study manually. According to the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, two independent reviewers screened the literature based on titles and abstracts, followed by a full-text review. Discrepancies were resolved by consulting a third reviewer.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two researchers independently extracted data from the included studies, with subsequent cross-checking to ensure accuracy. Data encompassed study characteristics: the first author, publication year, study design, country, study period; population characteristics: total number of subjects, age, gender; outcome definitions: diagnostic methods for SLE and HZ, number of HZ patients, reported prevalence and incidence rates (IRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and risk factors associated with the outcomes. When reported, data on recurrence, hospitalization, dermatologic involvement sites, and complications were extracted. For risk factors, priority was given to extracting adjusted confounders. No additional information was sought from the original authors.
The quality of each cohort or case-control study was assessed by the same reviewers using the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS) (26), while cross-sectional study quality was evaluated using the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) guidelines (27). RCTs were assessed by the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Any disagreements were resolved by QS-L.
Statistical analysis
For prevalence estimates, the numerator was the number of HZ after SLE onset, while the denominator was the total number of SLE patients. Incidence rate was calculated by dividing the number of new cases by the total person time, with results presented per 1000 patient-years. Recurrence was defined as the subsequent episodes after the initial occurrence in HZ patients. Risk factors reported in at least two studies were analyzed using pooled RRs for dichotomous variables and weighted mean differences (WMDs) for continuous variables such as SLE disease duration. Given the low incidence of HZ (approximately 10%), OR was treated as the reasonable approximation of RR when pooling the risk factors (28). HR was directly considered as RR, consistent with the approach used in the previous study (29, 30). Additionally, relative risk was calculated to evaluate the risk of receiving biologic drugs (31). When data could not be combined due to substantial clinical or methodological heterogeneity or insufficient studies, the results were reported qualitatively. Heterogeneity was deemed significant when I2 exceeded 50% or when P value in the Q test was below 0.1 (32), prompting the application of a random effects model (33). Subgroup analyses were performed to explore potential sources of heterogeneity based on geographical region (Asia vs. North America vs. South America vs. Europe vs. Africa), publication year (before 2014 vs. 2014-2024), sample size (<100 vs. 100-1000 vs. >1000), and diagnostic modality of SLE and HZ [classic clinical manifestations vs. unclear (identify patient from ICD codes)]. Furthermore, we conducted additional meta-regressions to investigate potential sources of heterogeneity. The independent variables included were consistent with those applied in the subgroup analysis. Sensitivity analysis was performed by sequentially omitting individual studies. Egger’s regression and funnel plots were used to evaluate publication bias in meta-analyses with 10 or more papers (34). Subsequent sensitivity analysis using the trim-and-fill procedure was carried out to identify potential “missing studies” and investigate their impact on the pooled effect estimate, in cases where significant publication bias was detected (35, 36). The interaction test for subgroups were undertaken by Review Manager V.5.4, while the other data analyses were conducted using Stata version 18.0 (StataCorp, LLC, College Station, TX, authorized by The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University).
Results
Study selection
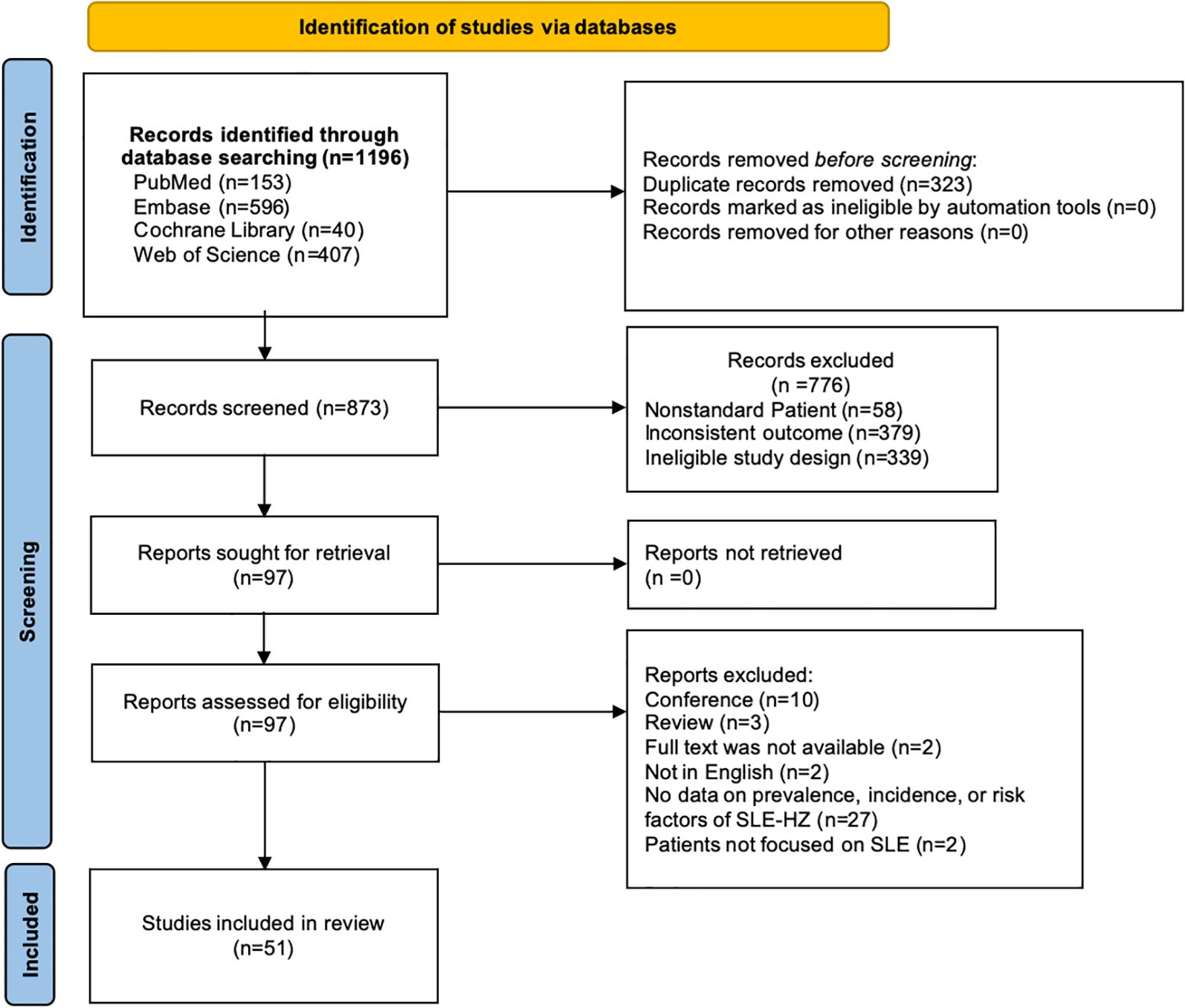
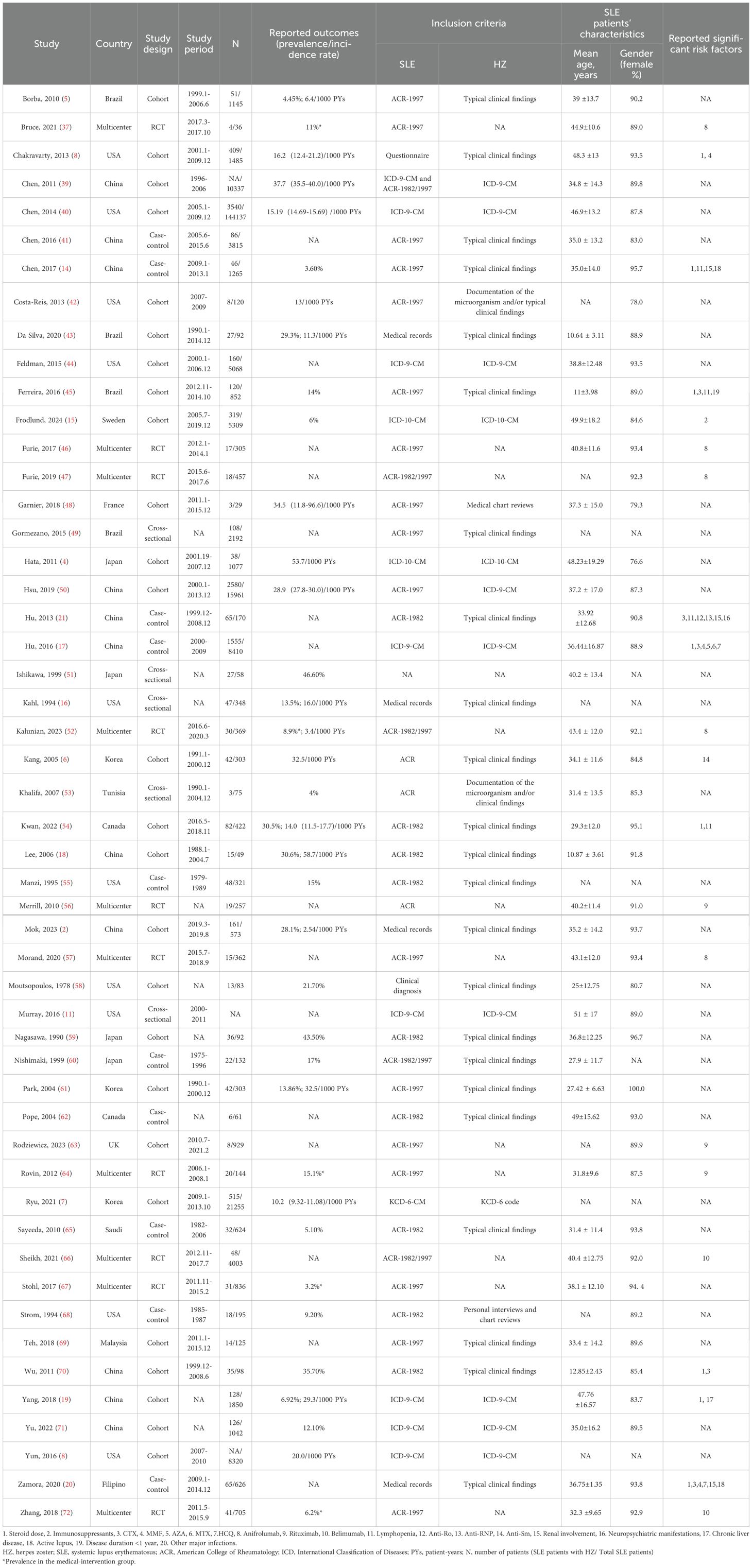
Our literature found a total of 1,196 records. After eliminating duplicates (n=323) and studies that did not meet the eligibility criteria (n=776), 51 eligible studies were ultimately included. Of these, 14 studies addressed both prevalence/incidence and risk factors, 28 studies focused solely on prevalence or incidence, and 9 studies were dedicated exclusively to risk factors (Figure 1). All studies included were published between 1978 to 2024 and consisted of 26 cohort studies, 10 case-control studies, 5 cross-sectional studies, and 10 RCTs. Sample sizes varied from 29 to 21,255 SLE patients, of which seventeen studies enrolled >1000 patients. Females constituted the majority of the enrolled population. The detailed characteristics are displayed in Table 1. All studies were classified as moderate to high quality. (Supplementary Table S2)
Prevalence of HZ in SLE
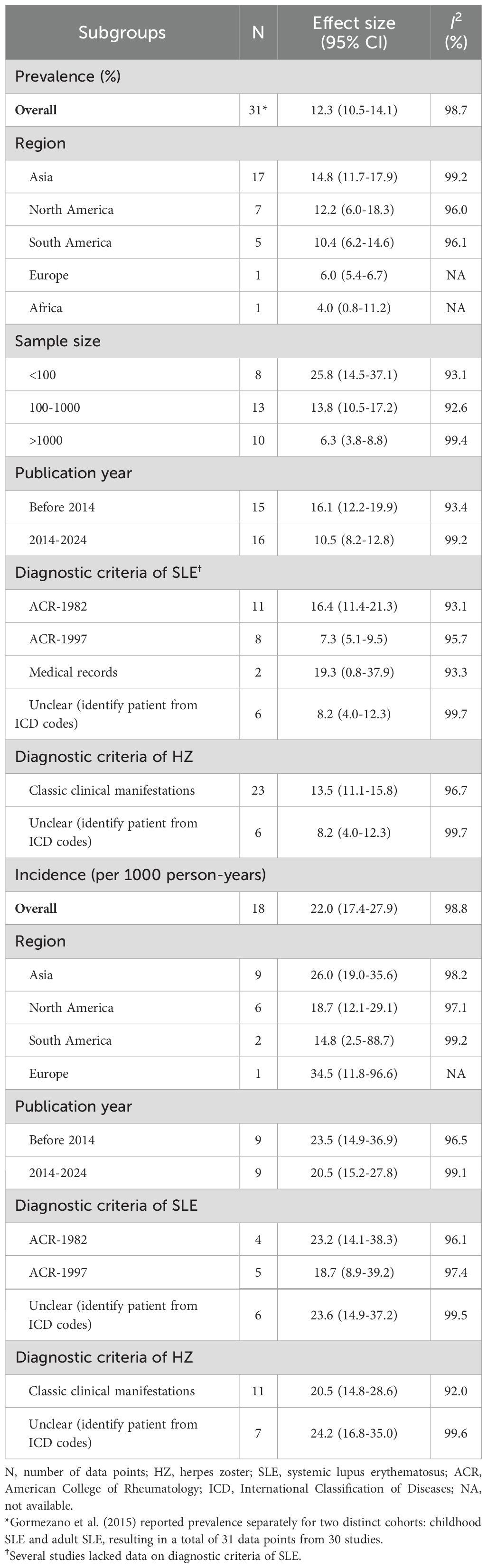
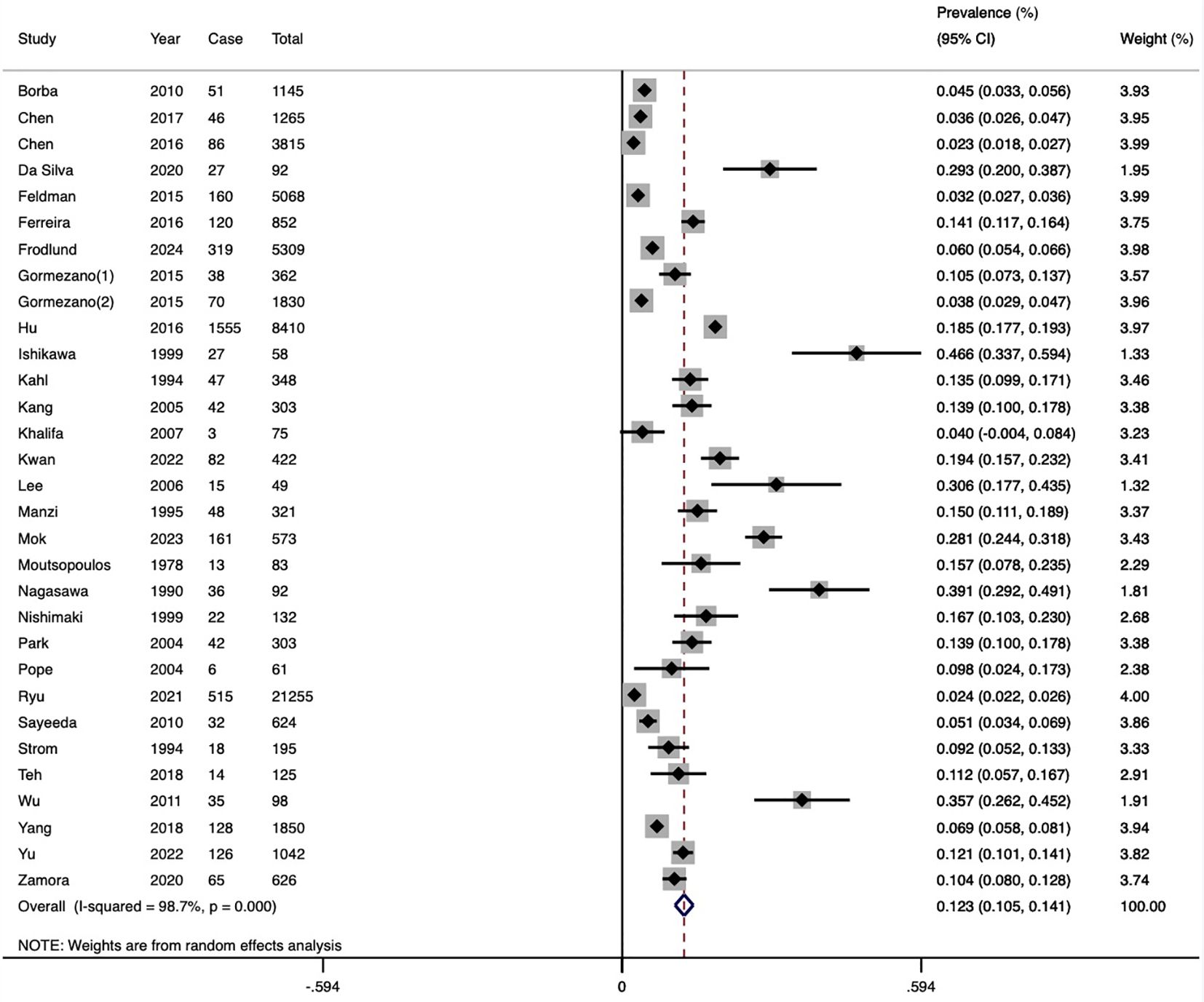
Thirty studies (including cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional designs) reported the prevalence of HZ, with a total of 3,949 patients with HZ among 56,783 SLE patients. The pooled prevalence was 12.3% (95%CI 10.5-14.1, I2 = 98.7%), indicating substantial heterogeneity (Figure 2). Subgroup analysis results revealed the highest prevalence was observed in Asia (14.8%, 95%CI 11.7-17.9), followed by North America (12.2%, 95%CI 6.0-18.3), and South America (10.4%, 95%CI 6.2-14.6). Only one study each was from Europe and Africa. Studies with less than 100 participants had a higher prevalence (25.8%) than those with 100–1000 participants (13.8%) and more than 1000 participants (6.3%). The prevalence in the past decade was 10.5% (95%CI 8.2-12.8), which was lower than the prevalence rate in the previous decade (16.1%, 95%CI 12.2-19.9). Furthermore, prevalence based on the ACR-1982 (16.4%) was higher than ACR-1997 (7.3%) and ICD codes (8.2%). Diagnoses based on typical clinical findings showed a higher prevalence of HZ than ICD codes (13.5 vs 8.2%) (Table 2). The results of the meta-regression analyses revealed that sample size influenced the pooled HZ prevalence among patients with SLE significantly (Supplementary Table S3).
Publication bias was evident in the asymmetrical funnel plot, with a significant Egger’s test result (P<0.001) (Supplementary Figure S1). To address this, we employed the trim-and-fill method to explore the impact of “missing studies” on the pooled prevalence. After including the two “missing” studies, the new pooled estimate was less variable at 11.3 (95% CI 9.5-13.1), indicating the robustness of the previous results despite potential publication bias. Sensitivity analysis indicated no significant changes in the overall estimates after omitting any study (Supplementary Figure S2).
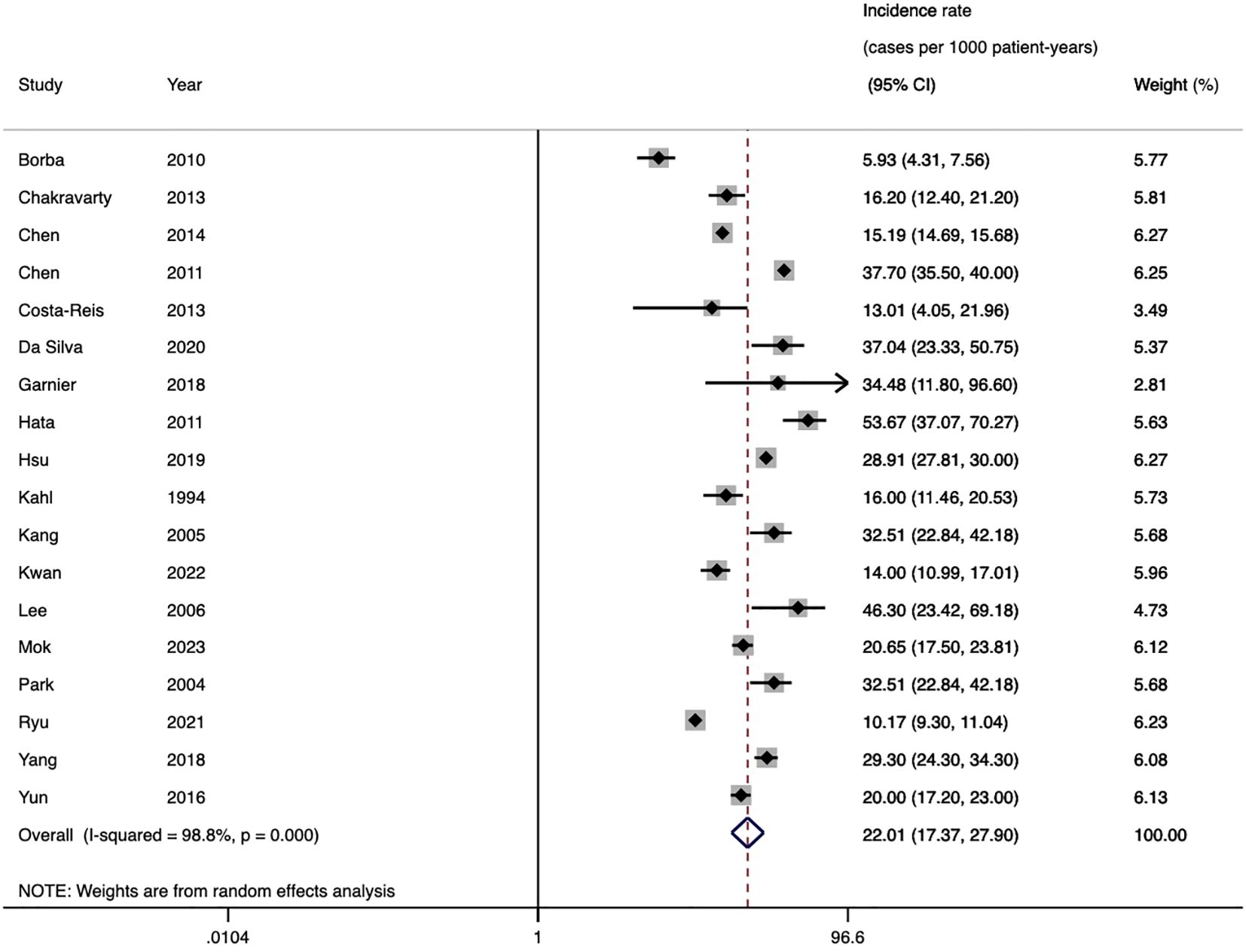
Incidence rate of HZ in SLE
The pooled incidence of HZ across 18 cohort studies was 22.0 cases per 1,000 patient-years (95%CI 17.4-27.9, I2 = 98.8%) (Figure 3). Stratified by region, the highest incidence was observed in Asia (26.0/1000 PYs), followed by North America (18.7/1000 PYs) and South America (14.8/1000 PYs). The studies published ten years ago reported higher incidence (23.5/1000 PYs) than the recent ten years (20.5/1000 PYs). Diagnoses based on typical clinical findings showed a lower incidence of HZ than ICD codes (20.5/1000 PYs vs 24.2/1000 PYs). Subgroup analysis based on diagnostic criteria of SLE revealed consistent results between ICD codes and ACR-1982 groups (23.2/1000 PYs vs 23.6/1000 PYs). Diagnoses based on ACR-1997 showed a lower incidence (18.7/1000 PYs) (Table 2). None of the above factors were considered to be significant contributors to heterogeneity in incidence subgroup analyses and meta-regression analyses (Supplementary Table S3).
Sensitivity analysis revealed no significant changes in the incidence estimates after omitting any individual study (Supplementary Figure S3). Funnel plots and Egger’s meta-regression tests (t=0.17, P=0.869) indicated no significant publication bias (Supplementary Figure S4).
Risk factors associated with HZ in SLE
Risk factors were categorized into three groups: demographics, which include gender and age at SLE diagnosis; clinical features including duration between the onset of SLE and HZ, lupus disease activity, complications of HZ (e.g., renal involvement, neuropsychiatric manifestations); laboratory data, such as autoantibody, leucopenia, lymphopenia; therapeutic variables include GCs, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), cyclophosphamide (CTX), azathioprine (AZA), cyclosporine A (CsA), methotrexate (MTX), antimalarial [chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)], and biological drugs (belimumab, anifrolumab, and rituximab).
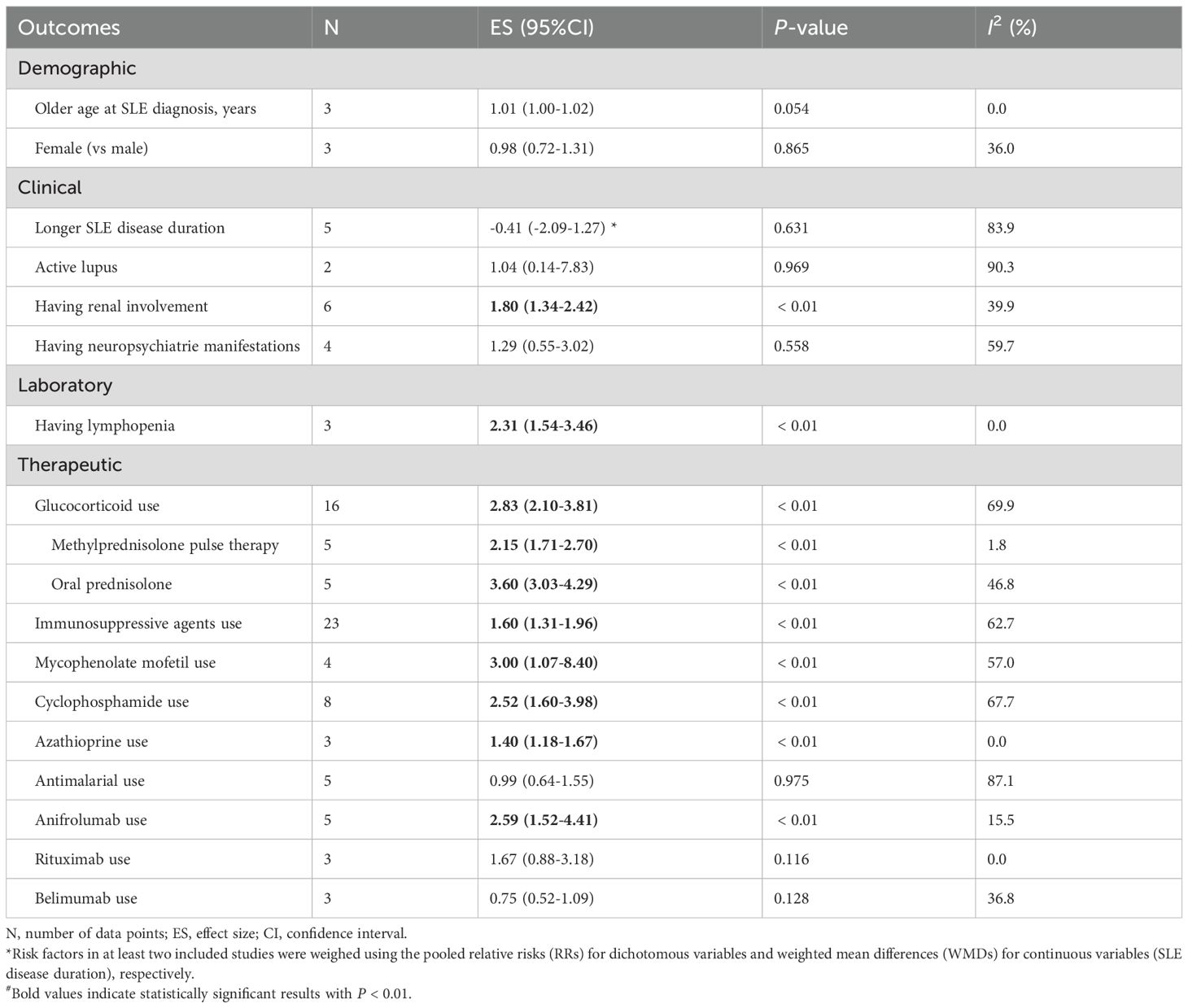
Among the demographic factors, our pooled effects did not find any significant association between older age at SLE diagnosis (RRs=1.01, 95%CI 1.00-1.02) (15, 38, 54) and female (RRs=0.98, 95%CI 0.72-1.31) (15, 38, 54) with the development of HZ. Patients with renal involvement were more likely to be HZ (RRs= 1.80, 95%CI 1.34-2.42) (14, 18–21, 70), while no significant association was found with neuropsychiatric manifestations (RRs=1.29, 95%CI 0.55-3.02) (18, 19, 21, 70). Longer SLE disease duration also showed no correlation with HZ occurrence (WMD=-0.41, 95%CI -2.09 - 1.27) (18, 20, 21, 45, 54). The included studies assessed lupus disease activity using the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) or the Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment-SLEDAI score. Patients were defined as active SLE if the SLEDAI score was ≥6 or SELENA-SLEDAI > 3 (73, 74). In our meta-analysis, the combined results of two studies showed no statistically significant association between active lupus and SLE-HZ (RRs=1.04, 95%CI 0.14-7.83) (14, 20). Regarding clinical factors, three studies found lymphopenia (lymphocyte count < 1,500/mm3) was inclined to be HZ (RRs=2.31, 95%CI 1.54-3.46) (14, 21, 45). Based on the medication used, we found using GCs was associated with a higher risk of HZI (RRs= 2.83, 95%CI 2.10-3.81) (14, 15, 17–21, 38, 45, 54, 70). Specifically, long-term oral prednisone (RRs=3.60, 95%CI 3.03-4.29) (17, 21, 45, 70) posed a greater risk than intravenous methylprednisolone therapy (RRs=2.15, 95%CI 1.71-2.70) (17, 18, 45, 70). Additionally, the use of immunosuppressants is linked to an increased occurrence of HZ (RRs=1.60, 95%CI 1.31-1.96) (15, 17–21, 38, 45, 54, 70). Pooled effects indicated that receiving CTX (RRs=2.52, 95%CI 1.60-3.98) (17, 18, 20, 21, 45, 65, 70), MMF (RRs=3.00, 95%CI 1.07-8.40) (17, 18, 20, 38), AZA (RRs=1.40, 95%CI 1.18-1.67) (17, 18, 20) therapies were all associated with a higher risk of HZI. No association was found with antimalarial drugs (RRs=0.99, 95%CI 0.64-1.55) (15, 17, 20, 38, 54). Patients receiving anifrolumab tends to develop HZ (RRs=2.59, 95%CI 1.52-4.41) (37, 46, 47, 52, 57), while we don’t find the significant result from rituximab and belimumab (RRs=1.67, 95%CI 0.88-3.18; RRs=0.75, 95%CI 0.52-1.09) (Table 3).
Funnel plot (Supplementary Figure S5) and Egger’s tests indicated no significant publication bias in GCs usage (P=0.591). Visual inspection of the funnel plot (Supplementary Figure S6) suggested some asymmetry in immunosuppressants usage, with two studies falling outside the funnel boundaries. This variability may be due to that this analysis included all types immunosuppressants, leading to heterogeneity among studies. However, Egger’s test indicated no significant publication bias (P=0.135).
Other clinical manifestations of HZ in SLE
Seventeen studies reported the recurrence rate of HZ, with 131 out of 878 patients experiencing multiple episodes. The pooled analysis of recurrence rate was 13.2% (95%CI 9.1%-17.2%, Supplementary Figure S7). Five studies reported the hospitalization of HZ in SLE patients, and the pooled effects was 23.5% (95%CI 7.2-39.8, Supplementary Figure S8). Pooled data from six studies showed that approximately 8.3% of patients developed disseminated HZ (Supplementary Figure S9). A summary of eleven studies indicated that 13.1% of patients with HZI developed post-herpetic neuralgia (Supplementary Figure S10). In the classification of dermatomal distribution reported in 6 studies, the thoracic nerve (54.8%) was the most common nerve involved by herpes zoster, followed by lumbar (14.5%), cranial (10.1%), cervical (9.6%), and sacral nerves (9.3%).
Discussion
Our review systematically explored the existing evidence regarding the prevalence, incidence, and risk factors for HZ in patients with SLE. Due to immune system deficiencies, SLE patients experience a considerable reduction in VZV-specific CD4 T cells, which elevates their risk of developing HZ (61). The high overall prevalence and incidence of HZ observed in our study (12.3% and 22.0 cases per 1000 person-years, respectively) further indicate that HZ is a prevalent infection among SLE patients. The occurrence of HZ varies across geographical groups. An elevated rate has been noted in Asian populations, particularly in Japan, which is consistent with prior study outcomes (75). The underlying reasons remain unclear, although it has been suggested that genetic predisposition, environmental factors, socioeconomic factors, and medical conditions that differ across regions may contribute (76). Notably, the data from Asia were relatively derived from studies with smaller sample sizes, which may result in less robust estimates of the incidence and prevalence of SLE-HZ. Further research is warranted to discover why SLE patients in Asia, particularly in East Asia, are at a greater risk for HZ. Our results indicate that the burden of HZ among SLE patients have decreased in the past decade, likely reflecting advancements in SLE management strategies, improved therapies, and increased vaccine accessibility (77–80). Both subgroup analyses and meta-regression analyses evaluating the prevalence indicated that sample size may influence the pooled results. As studies employed a small sample size commonly reported a higher prevalence, the longitudinal studies involving larger cohorts of SLE are necessary. In contrast, the incidence data showed no significant between-subgroup heterogeneity across the same variables. This may be explained by the smaller number of included studies and the greater consistency in study design, thereby reducing methodological variation. Moreover, incidence reflects new-onset HZ events, which are less likely to be influenced by historical or cumulative factors than prevalence.
Furthermore, the HZ recurrence rate (13.2%) and PHN (13.1%) reported in our study were both greater than the general population (81). As one of the most significant complications of HZ, PHN often persists for years and is difficult to treat (82). These complications contribute to increased hospitalization rates and impose a substantial economic burden on patients. Thus, it is of great importance to identify and evaluate the factors that may predispose SLE patients to the development of HZ.
A total of 14 factors were summarized and explored, among which lymphopenia, renal involvement, GCs use, immunosuppressive agents use (CTX, MMF, AZA), and anifrolumab use were predisposing factors. Female sex is generally recognized as a risk factor for HZ (3), but our study did not identify a significant association. This discrepancy may be attributed to the predominance of females in the SLE cohort, which may mitigate the impact of gender on HZ risk. As we know, HZ is predominantly observed in elderly individuals and less frequent in those under 18 in both the general population and patients with other immunodeficiency conditions (8). Interestingly, current research indicated that the occurrence of HZ may be more common in the younger SLE group (18-30 years) (8, 39). Compared to healthy children, the occurrence of HZ in pediatric SLE patients could be up to 40-fold higher (18). This may result from fulminant renal injury and greater disease severity at a younger age, requiring higher doses and longer durations of GCs and immunosuppressive drugs, which in turn leads to latent virus reactivation (71, 83). Previous studies have often suggested an association between HZ and active lupus, with a greater tendency to develop dissemination (65). The inflammatory environment during disease flares may alter immune cell function, impacting VZV-specific B cell activation and subsequent antibody production (84). However, several studies have found that HZ occurs during periods of SLE remission more often (16, 20, 45). Additionally, no direct correlation between SLE disease activity and HZI was identified in our analysis. The observed heterogeneity may be attributed to confounding clinical factors such as differences in treatment regimens. As noted in one study (54), SLEDAI scores were not associated with HZ events in multivariable analysis when GCs dosing was excluded. This supports the hypothesis that the observed association between SLEDAI and HZ may be driven by the inclusion of glucocorticoid dosing (a factor independently associated with HZ risk). Laboratory markers associated with disease activity, including elevated anti-dsDNA antibodies, increased ESR, elevated CRP, and decreased complement levels (C3, C4), were also not found to be correlated with an increased risk of HZ.
Beyond the inherent immune dysfunction, medications play a critical role in increasing risk of HZ among SLE patients. Patients with SLE often require GCs and other immunosuppressive drugs to control disease activity. While these medications effectively manage disease progression by suppressing the hyperactive humoral immunity, they simultaneously impair cellular immunity, increasing susceptibility to infections (17). Our findings further corroborate this risk. Notably, the use of high-dose GCs (≥30 mg prednisone or ≥1 mg/kg/d, or equivalent dose) was significantly attached to an increased risk of infection. Moreover, we found that intravenous methylprednisolone had a lower risk than oral prednisone, further underscoring the critical role of GC usage patterns in infection risk. Long-term exposure to oral prednisone during maintenance therapy results in cumulative immunosuppressive effects, whereas methylprednisolone pulse therapy is typically used for short-term pulse therapy, reducing the cumulative side effects. This finding supports that the use of repeated methylprednisolone pulses combined with tapered oral prednisone can improve the complete remission rate in lupus nephritis (LN) and reduce corticosteroid adverse effects (85, 86). Our results also showed that SLE patients receiving other immunosuppressive therapies, including CTX, MMF, AZA, were much more likely to develop HZ. Using two or more immunosuppressive medications may result in cumulative inhibitory effects particularly, thereby incrementally elevating the risk of HZ (17). In addition, the dose of therapeutic drug use often correlates to lupus activity. Increased dosages and more intensive use of immunosuppressive agents are often necessary to manage active LN and prevent further renal damage, which explains why complications such as renal involvement, neuropsychiatrie manifestations, and other organ dysfunctions may indirectly be risk factors. As the standard of care for SLE, prior research has found that HCQ offers a pleiotropic protective effect against infection (20). However, our pooled analysis also did not identify a significant impact of antimalarial drugs on HZ occurrence. Furthermore, influenced by disease activity and medication treatment, specific immune alterations such as lymphopenia are linked to an increased risk of HZ (87). Anti-Ro and anti-RNP antibodies have been identified as risk factors for HZ, possibly because these autoantibodies may induce lymphocyte apoptosis or impair lymphocyte function (21). Consequently, the presence of these autoantibodies may disrupt cellular immunity, thereby accounting for the greater risk of HZ in these patients.
Emerging target-specific biological drugs, such as anifrolumab, belimumab, rituximab, sifalimumab, are effective treatment options for SLE (88). Nevertheless, some of these therapies are associated with an increased risk of infections. Our findings indicate that using anifrolumab further increases the incidence of clinically relevant HZ episodes. Given the close connection between type I interferon (IFN) signaling and antiviral immunity, it is not surprising that anifrolumab, therapeutic targeting of the type I IFN system, is linked to an increased risk of HZ (89). In addition, among patients receiving anifrolumab, a high risk of HZ may also be associated with the presence of active LN, likely due to the secondary immunodeficiency and underlying kidney disease (78). While anifrolumab may improve long-term outcomes in SLE patients with or without LN, it has raised concerns about a heightened risk of severe viral infections, including but not limited to HZ but potentially including COVID-19. Besides, HZ may also reactivate as a result of rituximab’s suppression of B cells (63). In contrast, belimumab has demonstrated efficacy in SLE treatment, reducing the need for steroids while not significantly raising infections risk (90). Likewise, ustekinumab has also not been found to promote opportunistic infections during its use (91). Additionally, recent studies have proposed that non-immunosuppressive therapies, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), may also provide potential therapeutic value for patients with LN and other SLE comorbidities without significantly increasing the risk of HZI (92, 93). Thus, for patients with moderate to severe SLE, particularly those with active manifestations such as LN, it is advisable to optimize disease management by utilizing biologic agents (e.g., belimumab) or other therapies to lessen reliance on GCs and lower the long-term infection risk (63). Regardless, treatment strategies should take into account the biologic agents type and the patient’s comorbid conditions. Further research is warranted to better understand how to balance the therapeutic efficacy of biologics with their potential adverse effects.
The emergence of novel therapeutics for SLE, such as interferon inhibitors, has heightened the focus on preventing HZ. Although guidelines advocate the use of the live-attenuated vaccine for the prevention of herpes zoster in healthy adults (>60 years), data on the application of vaccines in immunocompromised hosts are scarce, as their administration is generally contraindicated in these patients. Large retrospective studies have demonstrated that, regardless of medication status, the HZ vaccine effectively reduces the incidence of HZ over a 2-year follow-up period, providing approximately 5 years of protection for autoimmune disease patients (80). Recent studies indicate that SLE patients exhibit good tolerance to the newer recombinant subunit vaccine (Shingrix), with no reports of severe adverse events or disease flares (94). Therefore, the HZ vaccine can be considered in patients with SLE before intensive immunosuppressive therapy. However, it is best given when SLE is in a stable phase and minimal immunosuppression is required vaccination (95, 96). This aligns with the 2019 EULAR guidelines on vaccination in patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases, including SLE (80). Besides, studies have suggested that adults with underlying comorbidities associated with an elevated risk of HZ may be candidates for earlier vaccination, based on a cost-effectiveness evaluation (3). Vaccination against VZV may also help mitigate the specific risk associated with targeted biologic therapies, such as anifrolumab, in this vulnerable population. Future studies should incorporate vaccination status to better evaluate its protective effects and identify optimal immunization strategies in this vulnerable population.
Strengths and limitations
Our study possesses several advantages. Firstly, this systematic review and meta-analysis provides a comprehensive analysis of the prevalence, incidence, recurrence, and potential risk factors for HZ in SLE patients. The higher incidence rate relative to prevalence implies that HZ might have a shorter disease course and a higher cure rate. Secondly, the majority of the data included were multivariable-adjusted effect estimates, effectively controlling the influence of confounding factors (such as age, sex, etc.).
However, some shortcomings should be noted. Although our results did not indicate significant publication bias, some eligible studies may not have been fully accessible, and negative findings might have remained unpublished. As a result, certain data related to prevalence, incidence, and risk factors may have been missed. Among the studies we included, only one was conducted in Africa and one in Europe, indicating an underrepresentation that may limit the generalizability of the findings. To address this concern, we conducted an additional analysis excluding these two studies. The pooled estimate remained consistent at 13% (95% CI 0.11-0.15, Supplementary Figure S11), indicating that the limited geographic diversity had minimal impact on the overall results. Nevertheless, caution is still needed when extrapolating our findings to populations in underrepresented regions. Further research from these areas such as Africa and Europe is warranted to improve the global applicability of the evidence. Despite controlling for potential confounding factors and excluding outlier studies, significant heterogeneity remains in the data. This may be due to inherent limitations of meta-analysis, such as variability in study design and populations (97, 98). Besides, some risk factors, such as disease activity, were reported in only a few studies, which may lead to biased effect estimates. Additionally, abnormal laboratory markers [e.g., anti-IFN-α autoantibodies (99), anti-Ro and anti-RNP antibodies (21)] may contribute to the prediction of HZ. However, due to sufficient clinical data, further exploration of these factors is not feasible. Consequently, more well-designed, large-scale, prospective studies employing standardized data collection and reporting procedures are needed to better elucidate the role of these factors in the development of HZ in SLE patients.
Conclusion
The existing evidence demonstrates that the prevalence and incidence of HZ are significantly higher among SLE patients compared to the general population, especially in those with active LN. Medication regimens and relevant laboratory markers offer important predictive information for assessing the risk of HZ. Therefore, future efforts are required to raise awareness of infections among SLE patients and develop preventive strategies, including vaccination and appropriate drug management.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
H-FW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. YG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. ZL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. SL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. YC: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. Q-SL: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the 2024 Undergraduate Education Teaching Reform Project of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Grant No.YB24003) and the 2024 Scientific Research Projects of the Affiliated Hospitals of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Grant No.2024FSYYZZ01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1544218/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Habel LA, Ray GT, Silverberg MJ, Horberg MA, Yawn BP, Castillo AL, et al. The epidemiology of herpes zoster in patients with newly diagnosed cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2013) 22:82–90. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-12-0815
2. Mok CC, Ho LY, Tse SM, Chan KL, and To CH. Prevalence and risk factors of herpes zoster infection in patients with rheumatic diseases not receiving biologic or targeted therapies. Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 42:1019–26. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06450-2
3. Kawai K and Yawn BP. Risk factors for herpes zoster: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. (2017) 92:1806–21. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2017.10.009
4. Hata A, Kuniyoshi M, and Ohkusa Y. Risk of herpes zoster in patients with underlying diseases: A retrospective hospital-based cohort study. Infection. (2011) 39:537–44. doi: 10.1007/s15010-011-0162-0
5. Borba EF, Ribeiro ACM, Martin P, Costa LP, Guedes LKN, and Bonfá E. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of herpes zoster in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Rheumatol. (2010) 16:119–22. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e3181d52ed7
6. Kang TY, Lee HS, Kim TH, Jun JB, and Yoo DH. Clinical and genetic risk factors of herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. (2005) 25:97–102. doi: 10.1007/s00296-003-0403-3
7. Ryu HJ, Han J-O, Lee SA, Seo MR, Choi HJ, Ko K-P, et al. Risk factors for herpes zoster in patients with rheumatic diseases: A nationwide cohort study in Korea. Rheumatology. (2021) 60:2427–33. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa636
8. Yun H, Yang S, Chen L, Xie F, Winthrop K, Baddley JW, et al. Risk of herpes zoster in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: implications for vaccination. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:2328–37. doi: 10.1002/art.39670
9. Furer V, Rondaan C, Heijstek M, van Assen S, Bijl M, Agmon-Levin N, et al. Incidence and prevalence of vaccine preventable infections in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (Aiird): A systemic literature review informing the 2019 update of the eular recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with aiird. RMD Open. (2019) 5:e001041. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2019-001041
10. Jih JS, Chen YJ, Lin MW, Chen YC, Chen TJ, Huang YL, et al. Epidemiological features and costs of herpes zoster in Taiwan: A national study 2000 to 2006. Acta Derm Venereol. (2009) 89:612–6. doi: 10.2340/00015555-0729
11. Murray SG, Schmajuk G, Trupin L, Gensler L, Katz PP, Yelin EH, et al. National lupus hospitalization trends reveal rising rates of herpes zoster and declines in pneumocystis pneumonia. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0144918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144918
12. Nossent J, Keen H, Preen DB, and Inderjeeth CA. Temporal trends in hospitalisation for opportunistic infections in lupus patients in western Australia. Lupus. (2022) 31:1434–40. doi: 10.1177/09612033221115965
13. Kostopoulou M, Mukhtyar CB, Bertsias G, Boumpas DT, and Fanouriakis A. Management of systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic literature review informing the 2023 update of the eular recommendations. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) 83:1489–501. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-225319
14. Chen D, Li H, Xie J, Zhan Z, Liang L, and Yang X. Herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical features, complications and risk factors. Exp Ther Med. (2017) 14:6222–8. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5297
15. Frodlund M, Jönsen A, Remkus L, Telg G, Söderdahl F, and Leonard D. Glucocorticoid treatment in sle is associated with infections, comorbidities and mortality—a national cohort study. Rheumatol (United Kingdom). (2024) 63:1104–12. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead348
16. Kahl LE. Herpes zoster infections in systemic lupus erythematosus: risk factors and outcome. J Rheumatol. (1994) 21:84–6.
17. Hu SCS, Yen FL, Wang TN, Lin YC, Lin CL, and Chen GS. Immunosuppressive medication use and risk of herpes zoster (Hz) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (Sle): A nationwide case-control study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2016) 75:49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.059
18. Lee PPW, Lee T-L, Ho M-K, Wong WHS, and Lau Y-L. Herpes zoster in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus - incidence, clinical characteristics and risk factors. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (2006) 25:728–32. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000226841.03751.1f
19. Yang SC, Lai YY, Huang MC, Tsai CS, and Wang JL. Corticosteroid dose and the risk of opportunistic infection in a national systemic lupus erythematosus cohort. Lupus. (2018) 27:1819–27. doi: 10.1177/0961203318792352
20. Zamora LD, Collante MTM, and Navarra SV. Risk factors for herpes zoster infection among filipinos with systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis. (2020) 23:197–202. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.13725
21. Hu SC-S, Lin C-L, Lu Y-W, Chen G-S, Yu H-S, Wu C-S, et al. Lymphopaenia, anti-ro/anti-rnp autoantibodies, renal involvement and cyclophosphamide use correlate with increased risk of herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. (2013) 93:314–8. doi: 10.2340/00015555-1454
22. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The prisma 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
23. Hochberg MC. Updating the american college of rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (1997) 40:1725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400928
24. Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (1982) 25:1271–7. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101
25. Werner RN, Nikkels AF, Marinović B, Schäfer M, Czarnecka-Operacz M, Agius AM, et al. European consensus-based (S2k) guideline on the management of herpes zoster - guided by the european dermatology forum (Edf) in cooperation with the european academy of dermatology and venereology (Eadv), part 1: diagnosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2017) 31:9–19. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13995
26. Wells G, Shea B, and O’Connell J. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (Nos) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Ottawa Health Research Institute Web site (2014). p. 7. Available at: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (Accessed October 10, 2024)
27. Zeng X, Zhang Y, Kwong JS, Zhang C, Li S, Sun F, et al. The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: A systematic review. J Evid Based Med. (2015) 8:2–10. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12141
28. Richardson DB, Kinlaw AC, MacLehose RF, and Cole SR. Standardized binomial models for risk or prevalence ratios and differences. Int J Epidemiol. (2015) 44:1660–72. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyv137
29. Ou YN, Tan CC, Shen XN, Xu W, Hou XH, Dong Q, et al. Blood pressure and risks of cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 209 prospective studies. Hypertension. (2020) 76:217–25. doi: 10.1161/hypertensionaha.120.14993
30. Ma X, Chu H, Han K, Shao Q, Yu Y, Jia S, et al. Postoperative delirium after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2023) 71:646–60. doi: 10.1111/jgs.18104
31. Tenny S and Hoffman MR. Relative risk. StatPearls. (2017). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430824.
32. Higgins JP and Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
33. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, and Rothstein HR. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. (2010) 1:97–111. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.12
34. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, and Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Bmj. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
35. Duval S and Tweedie R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. (2000) 56:455–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x
36. Shi L and Lin L. The trim-and-fill method for publication bias: practical guidelines and recommendations based on a large database of meta-analyses. Med (Baltimore). (2019) 98:e15987. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000015987
37. Bruce IN, Nami A, Schwetje E, Pierson ME, Rouse T, Chia YL, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of subcutaneous anifrolumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, active skin disease, and high type I interferon gene signature: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2021) 3:e101–e10. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(20)30342-8
38. Chakravarty EF, Michaud K, Katz R, and Wolfe F. Increased incidence of herpes zoster among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2013) 22:238–44. doi: 10.1177/0961203312470186
39. Chen H-H, Chen Y-M, Chen T-J, Lan J-L, Lin C-H, and Chen D-Y. Risk of herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A three-year follow-up study using a nationwide population-based cohort. Clinics. (2011) 66:1177–82. doi: 10.1590/s1807-59322011000700009
40. Chen SY, Suaya JA, Li Q, Galindo CM, Misurski D, Burstin S, et al. Incidence of herpes zoster in patients with altered immune function. Infection (2014) 42(2):325–34. doi: 10.1007/s15010-013-0550-8
41. Chen D, Xie J, Chen H, Yang Y, Zhan Z, Liang L, et al. Infection in Southern Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: spectrum, drug resistance, outcomes, and risk factors. J Rheumatol. (2016) 43(9):1650–6. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.151523
42. Costa-Reis P, Nativ S, Isgro J, Rodrigues T, Yildirim-Toruner C, Starr A, et al. Major infections in a cohort of 120 patients with juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. (2013) 149(3):442–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2013.08.009
43. Da Silva AMPDS, De Moraes-Pinto MI, Succi RCM, Terreri MT, and Machado DM. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of herpes zoster in patients with Hiv/Aids and those with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediat Inf Disease J. (2020) 39(7):624–7. doi: 10.1097/inf.0000000000002617
44. Feldman CH, Hiraki LT, Winkelmayer WC, Marty FM, Franklin JM, Kim SC, et al. Serious infections among adult medicaid beneficiaries with systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2015) 67(6):1577–85. doi: 10.1002/art.39070
45. Ferreira JCOA, Marques HH, Ferriani MPL, Gormezano NWS, Terreri MT, Pereira RM, et al. Herpes zoster infection in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus patients: A large multicenter study. Lupus. (2016) 25:754–9. doi: 10.1177/0961203315627203
46. Furie R, Khamashta M, Merrill JT, Werth VP, Kalunian K, Brohawn P, et al. Anifrolumab, an anti-interferon-Α Receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2017) 69:376–86. doi: 10.1002/art.39962
47. Furie RA, Morand EF, Bruce IN, Manzi S, Kalunian KC, Vital EM, et al. Type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus (Tulip-1): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. (2019) 1:e208–e19. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(19)30076-1
48. Garnier C, Ribes D, Chauveau D, Huart A, Pugnet G, Adoue D, et al. Zoster after cyclophosphamide for systemic lupus erythematosus or vasculitis: incidence, risk factors, and effect of antiviral prophylaxis. J Rheumatol. (2018) 45(11):1541–8. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.180310
49. Gormezano NWS, Silva CA, Otsuzi CI, Barros DL, Da Silva MA, Sallum AME, et al. Higher prevalence and distinct features of herpes zoster infection in children than adults with systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediat Inf Dis J. (2015) 34(8):905–7. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000756
50. Hsu C-Y, Ko C-H, Wang J-L, Hsu T-C, and Lin C-Y. Comparing the burdens of opportunistic infections among patients with systemic rheumatic diseases: a nationally representative cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2019) 21(1). doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1997-5
51. Ishikawa O, Abe M, and Miyachi Y. Herpes zoster in japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. (1999) 24(4):327–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2230.1999.00490.x
52. Kalunian KC, Furie R, Morand EF, Bruce IN, Manzi S, Tanaka Y, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled phase iii extension trial of the long-term safety and tolerability of anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2023) 75:253–65. doi: 10.1002/art.42392
53. Khalifa M, Kaabia N, Bahria F, Ben Jazia E, Bouajina E, Letaief AO, et al. Infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Medecine Et Maladies Infectieuses (2007) 37(12):792–5. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2007.07.003
54. Kwan A, Al Rayes H, Lazova T, Anderson N, Bonilla D, Su J, et al. Herpes zoster in sle: prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Lupus Sci Med. (2022) 9. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2021-000574
55. Manzi S, Kuller LH, Kutzer J, Pazin GJ, Sinacore J, Medsger Jr TA, et al. Herpes zoster in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. (1995) 22(7):1254–8
56. Merrill JT, Neuwelt CM, Wallace DJ, Shanahan JC, Latinis KM, Oates JC, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: the randomized, double-blind, phase ii/iii systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62(1):222–33. doi: 10.1002/art.27233
57. Morand EF, Furie R, Tanaka Y, Bruce IN, Askanase AD, Richez C, et al. Trial of anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:211–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1912196
58. Moutsopoulos HM, Gallagher JD, Decker JL, and Steinberg AD. Herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (1978) 21(7):798–802. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210710
59. Nagasawa K, Yamauchi Y, Tada Y, Kusaba T, Niho Y, Yoshikawa H, et al. High-incidence of herpes-zoster in patients with systemic lupus-erythematosus - an immunological analysis. Ann Rheumat Dis. (1990) 49(8):630–3. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.8.630
60. Nishimaki T, Watanabe K, Satho Y, Okubo M, Kaise S, Miyata M, et al. Viral, fungal and mycobacterial infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Japanese J Rheumatol. (1999) 9(1):45–54. doi: 10.3109/bf03041258
61. Park HB, Kim KC, Park JH, Kang TK, Lee HS, Kim TH, et al. Association of reduced cd4 T cell responses specific to varicella zoster virus with high incidence of herpes zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. (2004) 31:2151–5.
62. Pope JE, Krizova A, Ouimet JM, Goodwin JL, and Laskin MD. Close association of herpes zoster reactivation and systemic lupus erythematosus (sle) diagnosis: case-control study of patients with Sle or noninflammatory musculoskeletal disorders. J Rheumatol. (2004) 31(2):274–9.
63. Rodziewicz M, Dyball S, Lunt M, McDonald S, Sutton E, Parker B, et al. Early infection risk in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with rituximab or belimumab from the british isles lupus assessment group biologics register (Bilag-br): A prospective longitudinal study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5:e284–e92. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00091-7
64. Rovin BH, Furie R, Latinis K, Looney RJ, Fervenza FC, Sanchez-Guerrero J, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active proliferative lupus nephritis: the lupus nephritis assessment with rituximab study. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64(4):1215–26. doi: 10.1002/art.34359
65. Sayeeda A, Al Arfaj H, Khalil N, and Al Arfaj AS. Herpes zoster infections in sle in a university hospital in Saudi Arabia: risk factors and outcomes. Autoimmune Dis. (2010) 1. doi: 10.4061/2010/174891
66. Sheikh SZ, Scheinberg MA, Wei JC, Tegzova D, Stohl W, de Toledo RA, et al. Mortality and adverse events of special interest with intravenous belimumab for adults with active, autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus (base): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 4 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. (2021) 3(2):e122–30. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(20)30355-6
67. Stohl W, Schwarting A, Okada M, Scheinberg M, Doria A, Hammer AE, et al. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus: a fifty-two-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2017) 69(5):1016–27. doi: 10.1002/art.40049
68. Strom BL, Reidenberg MM, West S, Snyder ES, Freundlich B, Stolley PD, et al. Shingles, allergies, family medical history, oral contraceptives, and other potential risk factors for systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Epidemiol. (1994) 140(7):632–42. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117302
69. Teh CL, Wan SA, and Ling GR. Severe infections in systemic lupus erythematosus: disease pattern and predictors of infection-related mortality. Clin Rheumatol. (2018) 37(8):2081–6. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4102-6
70. Wu S-A, Yeh K-W, Yao T-C, and Huang J-L. Association of herpes zoster infection with clinical characteristics and <I>Mbl2</I> gene polymorphisms in chinese children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (2011) 30:656–60. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182127b67
71. Yu C-Y, Kuo C-F, Chou IJ, Chen J-S, Lu H-Y, Wu C-Y, et al. Comorbidities of systemic lupus erythematosus prior to and following diagnosis in different age-at-onset groups. Lupus. (2022) 31:963–73. doi: 10.1177/09612033221100908
72. Zhang F, Bae SC, Bass D, Chu M, Egginton S, Gordon D, et al. A pivotal phase III, randomised, placebo-controlled study of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus located in China, Japan and South Korea. Ann Rheum Dis (2018) 77(3):355–63. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211631
73. Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, and Chang CH. Derivation of the sledai. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The committee on prognosis studies in sle. Arthritis Rheum. (1992) 35:630–40. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606
74. Petri M, Kim MY, Kalunian KC, Grossman J, Hahn BH, Sammaritano LR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. (2005) 353:2550–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa051135
75. Winthrop KL, Nash P, Yamaoka K, Mysler E, Khan N, Camp HS, et al. Incidence and risk factors for herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving upadacitinib: A pooled analysis of six phase iii clinical trials. Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) 81:206–13. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220822
76. Barber MRW, Drenkard C, Falasinnu T, Hoi A, Mak A, Kow NY, et al. Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2021) 17:515–32. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00668-1
77. Feldman CH, Xu C, and Costenbader KH. Avoidable acute care use for vaccine-preventable illnesses among medicaid beneficiaries with lupus. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2021) 73:1236–42. doi: 10.1002/acr.24628
78. Steiger S, Ehreiser L, Anders J, and Anders HJ. Biological drugs for systemic lupus erythematosus or active lupus nephritis and rates of infectious complications. Evidence from large clinical trials. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:999704. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.999704
79. Jansen MHA, Rondaan C, Legger GE, Minden K, Uziel Y, Toplak N, et al. Eular/pres recommendations for vaccination of paediatric patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases: update 2021. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:35–47. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2022-222574
80. Furer V, Rondaan C, Heijstek MW, Agmon-Levin N, Van Assen S, Bijl M, et al. 2019 Update of eular recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheumatic Dis. (2020) 79:39–52. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215882
81. Sun X, Wei Z, Lin H, Jit M, Li Z, and Fu C. Incidence and disease burden of herpes zoster in the population aged ≥50 years in China: data from an integrated health care network. J Infect. (2021) 82:253–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.12.013
82. Forbes HJ, Bhaskaran K, Thomas SL, Smeeth L, Clayton T, Mansfield K, et al. Quantification of risk factors for postherpetic neuralgia in herpes zoster patients: A cohort study. Neurology. (2016) 87:94–102. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000002808
83. Mina R and Brunner HI. Pediatric lupus–are there differences in presentation, genetics, response to therapy, and damage accrual compared with adult lupus? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. (2010) 36:53–80. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2009.12.012
84. Sun X, Zang Y-S, Xu Y, and Wang W. Assessment of the humoral immune status of varicella-zoster virus in patients with diffuse connective tissue diseases. Front Med. (2024) 11:1470068. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1470068
85. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Ugarte A, Saint-Pastou Terrier C, Lazaro E, Iza A, Couzi L, et al. Repeated pulses of methyl-prednisolone with reduced doses of prednisone improve the outcome of class iii, iv and V lupus nephritis: an observational comparative study of the lupus-cruces and lupus-bordeaux cohorts. Autoimmun Rev. (2017) 16:826–32. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.05.017
86. Ruiz-Arruza I, Lozano J, Cabezas-Rodriguez I, Medina JA, Ugarte A, Erdozain JG, et al. Restrictive use of oral glucocorticoids in systemic lupus erythematosus and prevention of damage without worsening long-term disease control: an observational study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2018) 70:582–91. doi: 10.1002/acr.23322
87. Kandane-Rathnayake R, Louthrenoo W, Golder V, Luo SF, Wu YJ, Lateef A, et al. Independent associations of lymphopenia and neutropenia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A longitudinal, multinational study. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2021) 60:5185–93. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab217
88. Steiger S and Anders HJ. Interferon blockade in lupus: effects on antiviral immunity. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2022) 18:415–6. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00581-0
89. Ishihara R, Watanabe R, Shiomi M, Katsushima M, Fukumoto K, Yamada S, et al. Exploring the link between varicella-zoster virus, autoimmune diseases, and the role of recombinant zoster vaccine. Biomolecules. (2024) 14(7):739. doi: 10.3390/biom14070739
90. Chan J, Walters GD, Puri P, and Jiang SH. Safety and efficacy of biological agents in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (Sle). BMC Rheumatol. (2023) 7:37. doi: 10.1186/s41927-023-00358-3
91. van Vollenhoven RF, Hahn BH, Tsokos GC, Wagner CL, Lipsky P, Touma Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, an il-12 and il-23 inhibitor, in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a multicentre, double-blind, phase 2, randomised, controlled study. Lancet. (2018) 392:1330–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32167-6
92. Ma KS, Lo JE, Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC, and Costenbader KH. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the primary prevention of cardiovascular, renal events, and safety outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and comorbid type 2 diabetes: A population-based target trial emulation. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2024) 77(4):414–22. doi: 10.1002/art.43037
93. Yen FS, Wang SI, Hsu CC, Hwu CM, and Wei JC. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and nephritis among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2416578. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16578
94. Park JK, Kim M, Jung JI, Kim JY, Jeong H, Park JW, et al. Immunogenicity, reactogenicity, and safety of two-dose adjuvanted herpes zoster subunit vaccine in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in South Korea: A single- centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Rheumatol. (2024) 6:e352–e60. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00084-5
95. Mok CC. Herpes zoster vaccination in systemic lupus erythematosus: the current status. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2019) 15:45–8. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1514228
96. Hasni S. Should we vaccinate all sle patients against papillomavirus and herpes zoster? Lupus Sci Med. (2021) 8:A1. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2021-la.1
97. Kamiya H and Panlaqui OM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease related to anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (Ccp) antibody. BMJ Open. (2021) 11:e040465. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040465
98. Xie S, Li S, Chen B, Zhu Q, Xu L, and Li F. Serum anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and rheumatoid factor increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: A meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 40:4533–43. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05808-2
99. Mathian A, Breillat P, Dorgham K, Bastard P, Charre C, Lhote R, et al. Lower disease activity but higher risk of severe Covid-19 and herpes Zoster in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with pre-existing autoantibodies neutralising ifn-Α. Ann Rheumatic Dis. (2022) 81:1695–703. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-222549
Keywords: systemic lupus erythematosus, herpes zoster, incidence, prevalence, risk factor
Citation: Wang H-F, Gao Y, Lin Z, Liu S, Cao Y and Li Q-S (2025) Prevalence, incidence, and risk factors for herpes zoster in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1544218. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1544218
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 10 July 2025;
Published: 01 August 2025.
Edited by:
Elias Adel Rahal, American University of Beirut, LebanonReviewed by:
Subba Chintalacharuvu, Genentech Inc., United StatesXun Li, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Yiquan Xiong, Sichuan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Gao, Lin, Liu, Cao and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Cao, Y2FveWkxOTY1QDE2My5jb20=; Qiu-Shuang Li, MjAxNjMwNTdAemNtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
 Hong-Fei Wang
Hong-Fei Wang Yan Gao3
Yan Gao3 Zheng Lin
Zheng Lin Yi Cao
Yi Cao Qiu-Shuang Li
Qiu-Shuang Li