Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the malignancies with the highest mortality rates, and outcomes are particularly poor in cases of liver metastasis. Early or recurrent metastatic PDAC significantly worsens patient outcomes and presents substantial clinical challenges. Checkpoint-based immunotherapy has largely been ineffective for most pancreatic cancer patients. This ineffectiveness is not well understood, as clinical trials often involve patients with advanced diseases, such as liver and peritoneal metastases, while most preclinical studies focus on primary tumors. Recent findings indicate that the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) is a major obstacle to effective immunotherapy in PDAC, with the metastatic immune microenvironment differing significantly from that of primary tumors. This review explores the distinct immunosuppressive mechanisms at various stages of PDAC progression, including primary tumors, pre-metastatic niches, and metastatic sites. Myeloid cells, such as tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), play pivotal roles in shaping the TME and suppressing anti-tumor immunity. Particular focus is placed on current clinical immunotherapy strategies targeting myeloid cells, and combinations with conventional chemoradiotherapy, considering contemporary knowledge and future trends. Advancements in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and spatial transcriptomics have provided deeper insights into the molecular intricacies and diversity of PDAC, revealing potential therapeutic targets. Innovative strategies targeting myeloid cells, including CD40 agonists and CSF-1R inhibitors, are being explored to reprogram the TME and enhance the efficacy of immunotherapies.
Introduction
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) presents significant treatment challenges due to its prolonged asymptomatic phase, early liver metastasis, and high resistance to therapies (1). Post-surgical survival rates are low, with only 34% of patients surviving one year after a liver metastasis diagnosis (2). Chemotherapy and surgery continue to be the primary treatment options; however, only 15%–20% of patients qualify for surgical intervention at the time of diagnosis (3). Although immunotherapy has shown efficacy in treating other malignancies such as metastatic melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and non-small cell lung cancer (4, 5), its application in PDAC has yielded disappointing results (6–9). A 2020 study found that only 1.01% (636 out of 63,154) of post-surgical PDAC patients received immunotherapy (9). Combined with chemoradiation, it improved median overall survival (29.31 vs. 23.66 months, p < 0.0001) and survival rates at 1 year (88% vs. 81%) and 2 years (60% vs. 49%) (9). However, trials like a 2019 durvalumab study and a 2010 ipilimumab trial showed no survival benefit in metastatic pancreatic cancer (7, 8). This ineffectiveness may be attributed to the advanced disease stages of patients in clinical trials, which often include liver and peritoneal metastases, while most preclinical studies focus on primary tumors. Moreover, preclinical studies suggest that combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with myeloid cell targeting could offer more promising treatment outcomes (10, 11).
The establishment of liver metastatic tumors requires cancer cells to navigate complex steps within a foreign microenvironment, evade immune detection, and successfully colonize distant tissues. The process of liver metastasis is influenced by both tumor-intrinsic and extrinsic factors, beyond mere genomic alterations. The tumor microenvironment (TME) is critical for cancer initiation and progression (12–14). PDAC exhibits low immunogenicity, which hinders the production and release of new antigens, leading to reduced levels of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) (15, 16). Cytotoxic T lymphocytes are essential anticancer effector cells, and their activation by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) is crucial for effective T cell responses (17). The coexistence of inflammatory and immunomodulatory signals in the pancreatic TME leads to dysregulated repair and cytotoxic responses (18). Within the TME, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are the most abundant antigen-presenting cells (APCs), yet they often have poor antigen-presenting capacity, acting as the main immune infiltrate and being associated to poor patient outcomes (19, 20). Embryo-derived tissue-resident macrophages (21–23), and bone-marrow-derived precursors, such as circulating Ly6C+ monocytes, may sustain TAM levels (24–26). Studies suggest that macrophages of distinct ontogenic origins exhibit divergent functional roles, depending on the tumor type. Macrophages in tumors and at (pre)metastatic sites possess dual origins and distinct functions. Effective therapeutic intervention therefore requires a thorough understanding of the sources that sustain macrophages in malignant tissues, and elucidating the heterogeneity of TAM origin and function at each metastatic step could provide valuable insights for PDAC treatment.
This review delves into the characteristic features of immunosuppression at various stages of PDAC progression, including primary tumors, pre-metastatic niches, and metastatic sites. Myeloid cells, such as tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), play pivotal roles in shaping the TME and restraining anti-tumor immunity. Recent advancements in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and spatial resolved transcriptomic analysis have provided deeper insights into the molecular intricacies and diversity of PDAC, revealing potential therapeutic targets. Innovative strategies targeting myeloid cells, including CD40 agonists and CSF-1R inhibitors, are being explored to reprogram the TME and enhance the efficacy of immunotherapies.
Stage-specific immunosuppressive landscapes in PDAC progression
To provide a comprehensive visual summary of the immunosuppressive landscape in PDAC progression, we propose schematic representations of the TME at three critical stages: primary tumor, pre-metastatic niche, and metastatic site (Figure 1).
Figure 1
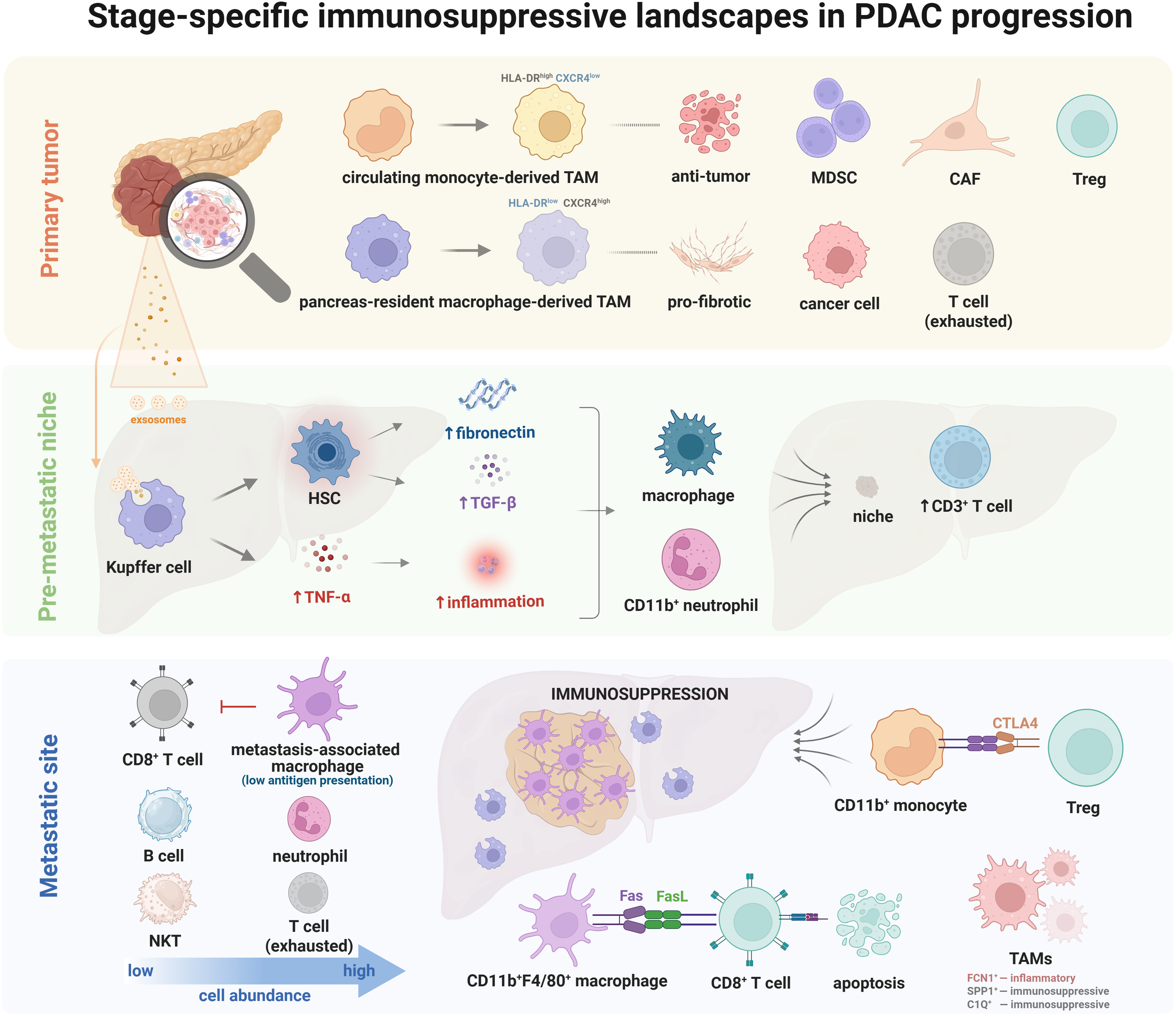
Schematic representations of the TME at three critical stages: primary tumor, pre-metastatic niche, and metastatic site.
Primary tumor microenvironment
The PDAC primary tumor exhibits a unique tripartite immunosuppressive architecture dominated by myeloid cells, such as TAMs, MDSCs, and neutrophils, dominate the immune landscape in pancreatic tumors (27, 28). This has led to extensive research into their roles in PDAC biology, particularly their impact on immune suppression. In PDAC cells, oncogenic KRAS signaling induces the secretion of GM-CSF, which attracts immunosuppressive MDSCs (28, 29). TAMs, originating from both tissue-resident macrophages and circulating monocytes, play essential yet potentially distinct roles in shaping the TME and inhibiting the adaptive immune response (27). In an orthotopic mouse model of PDAC, monocyte-derived TAMs (HLA-DRhighCXCR4low) exhibited an antitumor phenotype, characterized by strong antigen-presenting capabilities (27). In contrast, pancreas-resident macrophages (HLA-DRlowCXCR4high) developed a pro-fibrotic transcriptional profile, thereby promoting a desmoplastic reaction (27). However, these findings need validation in human PDAC tumors.
The limited success of immune checkpoint blockade in PDAC is complex, involving deficiencies in natural T cell responses, partly due to ineffective T cell priming and/or T cell exclusion (30, 31). New strategies targeting MDSCs and TAMs to induce anti-tumor immunity and enhance checkpoint inhibition in pancreatic cancer are being explored (11, 28, 29, 32–34). For instance, arginase 1 in TAMs suppresses immune responses by inhibiting T cell activation, and systemic treatment with the arginase inhibitor CB-1158 sensitizes PDAC to anti-PD1 immune checkpoint blockade (35). Additionally, novel agonists targeting the CD11b/CD18 receptor on tumor-infiltrating myeloid subsets have demonstrated promising preclinical results and are currently undergoing clinical trials (10, 36). Another strategy involves using CD40 agonists to reprogram macrophages into a less immunosuppressive state, which facilitates CD8+ T cell infiltration and transforms a ‘cold’ tumor into a ‘hot’ tumor (37). Thus, effective cancer immune surveillance in pancreatic tumor resistant to checkpoint inhibition can be achieved by coactivating complementary myeloid signaling pathways.
Advancements in spatial resolved transcriptomics and scRNA-seq have revealed the molecular complexity (Table 1), tumor heterogeneity, and functional specificity of resected PDAC, showing dynamic changes in the TME as the disease progresses (38–42). Typically, ductal cells are not predominant; instead, there is an accumulation of tumor-infiltrating immune cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), and dense extracellular matrices from early to late PDAC stages. Anti-tumor immune responses arise but are suppressed by regulatory T cells (Tregs), exhausted T cells, and TAMs as the tumor progresses (38, 43, 44). Moffitt et al. combined 92 scRNA-seq samples from seven studies to develop a reproducible PDAC atlas, emphasizing tumor-TME interdependence (45). This atlas offers a detailed overview of the signaling interactions that regulate PDAC. It was observed that patients with activated stroma exhibit increased M2-like macrophages and Tregs. In contrast, patients with ‘normal’ stroma show M1-like macrophage recruitment and elevated levels of effector and exhausted T cells (39). By integrating clinical histopathology with multi-tiered OMICs analyses, Barbara et al. identified ‘subTMEs,’ with regional relationships to tumor immunity, subtypes, differentiation, and treatment response. The study demonstrated that multiple ecotypes within individual patients provide a more intricate perspective than the mutually exclusive subtypes identified by scRNA-seq studies, thereby highlighting the molecular intricacies and heterogeneity of the TME (46). This complexity can only be fully understood through spatial analysis (47). Collectively, these studies underscore the necessity of spatial sequencing to characterize the polyclonal and heterogeneous nature of PDAC tumors.
Table 1
| Parameter | scRNA-seq | Spatial transcriptomics |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial Context | Lost during dissociation. | Retained in situ. |
| Resolution | Single-cell. | Varies (subcellular to multi-cell). |
| Applications | Cell identity, heterogeneity, dynamic changes. | Tissue organization, spatial niches. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, can profile hundreds of thousands of cells efficiently. | Limited by method: array-based SRT like Visium can cover large tissue areas, but imaging-based methods may be slower and less scalable. |
| Complexity | Established protocols. | Higher technical challenges. |
| Platform | E.g., 10x Genomics Chromium Controller, established and widely used. | E.g., Visium (10x Genomics, 55 μm), High-resolution Visium (10x Genomics, 2 μm), GeoMx (Nanostring), CosMx, MERSCOPE, still evolving. |
| Challenges | Requires tissue dissociation, may induce stress/cell death, not suitable for neurons without specialized protocols; high dropout rates. | Trade-offs between resolution and gene coverage; imaging-based methods require long microscopy times (hours to days); array-based methods may mix mRNA from multiple cells, risking mRNA diffusion. |
Advantages and disadvantages of scRNA-seq and spatial transcriptomics (46).
Pre-metastatic niche
Only 25% of PDAC patients are diagnosed at a stage amenable to complete surgical resection, with the majority of research focusing on early-stage disease, which represents a small portion of the patient population (45, 48–50). Understanding how PDAC cells evade immune attacks during circulation is a critical future challenge. After escaping the primary tumor, cancer cells must avoid immune detection and elimination to reach and colonize distant organs (51–53). Recent studies suggest that metastatic sites, especially the liver, undergo microenvironmental changes that support metastatic growth even before metastasis is clinically evident. These changes, known as “pre-metastatic niches,” are driven by signals from the primary pancreatic tumor, which have tumor-supportive and immune-suppressive characteristics (54–58). These signals reprogram resident cell phenotypes, alter the extracellular matrix, and affect immune cell infiltration, thereby supporting the expansion of disseminated tumor cells (51, 59, 60).
Immunosurveillance can impede each phase of tumor progression, including metastasis. Consequently, tumors and their metastatic counterparts must devise mechanisms to evade immune destruction, such as creating an immunosuppressive pre-metastatic niche. Regulatory or immunosuppressive cells, such as MDSCs, macrophages, and Treg cells within this niche, can inhibit anti-tumor immune responses (61, 62). In particular, macrophage recruitment to the liver is a key feature of the early liver pre-metastatic niche, evident even during the PanIN stages (54), as demonstrated by Bruno et al. for the first time that the uptake of PDAC-derived exosomes by Kupffer cells leads to the secretion of transforming growth factor and increased fibronectin production by hepatic stellate cells. This process attracts bone marrow-derived macrophages (and potentially neutrophils) to the liver, creating a favorable environment for liver metastasis. This mechanism was further corroborated by a recent study demonstrating that fatty acid cargo in tumor-derived extracellular vesicles and particles, particularly palmitic acid, induces TNFα secretion by Kupffer cells, generating a pro-inflammatory microenvironment (63). More recently, it was revealed that pre-metastatic livers in PDAC patients show a significant inflammatory response, marked by increased infiltration of CD11b+ neutrophils and macrophages, as well as CD3+ lymphocyte subsets at the time of resection, compared to non-cancerous livers (64). This was observed regardless of whether the future metastatic sites were the lungs or liver (64). This study highlights that myeloid cell infiltration in the liver is an early indicator of PDAC metastasis and a defining feature of the liver pre-metastatic niche. This event precedes T cell infiltration, which occurs later in the progression of pancreatic cancer and may signal anti-tumor activity. Nevertheless, the early stages of metastasis are marked by increased neutrophil infiltration and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formation, although the specific role of NETs in liver metastasis remains to be clarified (64).
Metastatic liver microenvironment
Since radical surgery is not typically used for advanced or metastatic stages, it is rather difficult to obtain matched primary and metastatic samples for spatial transcriptomics. Bulk RNA sequencing studies have revealed that metastatic TMEs exhibit pronounced immunosuppression, rich in metastasis-associated macrophages (MAMs) and neutrophils, and have low levels of T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells (65, 66). However, bulk transcriptomics average gene expression, missing distinct microenvironmental ecosystems. To thoroughly comprehend the exact spatial and cellular contexts of these molecular alterations, it is vital to address localized heterogeneous signals (67). ScRNA-seq has revealed the diversity within PDAC (39, 68–72). Although some investigations have concentrated on primary pancreatic tumors, the spatial distribution of different cell clusters and the biology of metastasis have only recently been disclosed (46). In metastatic PDAC livers, macrophage populations with opposing roles can coexist in the same tumor (46, 66, 73). Specifically, Kupffer cells, found at the periphery of metastatic lesions, display inflammatory and pro-fibrotic signatures while monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMs), located in the core areas, show diverse immunostimulatory and immunosuppressive signatures (66, 73). Early in PDAC metastasis, a subpopulation of MoMs with low antigen presentation gene expression and an efferocytosis gene signature compromised CD8+ T cell activation thus leading to immune suppression (66). Khaliq et al. employed spatially resolved transcriptomics and ecotype assessments to assess the metastatic TME, identifying a unique ecotype at the invasive tumor margin with a variety of immune-related genes (46). This ecotype comprises both tumor-promoting factors, such as M2-like TAM and Treg cells, and tumor-suppressing components, including cytotoxic T cells and M1-like TAM, which cannot be entirely represented by single-cell RNA sequencing alone, underscore this ecotype as a promising target for immunotherapy. In addition, TAM subtypes with differing functions, such as inflammatory FCN1+ and immunosuppressive SPP1+ and C1Q+ phenotypes, co-occur within tumors. This further supports findings that TAMs with both roles exist simultaneously in the same TME. Taken together, spatially resolved transcriptomics of matched primary and metastatic PDAC samples offer critical insights into metastatic PDAC biology and are crucial for future therapeutic research. However, the current 55 μm spatial resolution might not sufficiently represent the intricacies of cellular interactions, underscoring the necessity for higher-resolution spatial transcriptomics. Future research should also explore the roles of Kupffer cell subpopulations in PDAC liver metastasis and develop therapies targeting immunosuppressive macrophages or their signaling pathways that enable these immunosuppressive traits. Comprehending the spatial organization of tumor ecosystems and the dynamics of cellular interactions is essential for deepening our knowledge of metastatic PDAC biology and the development of effective therapies.
Targeting the immunosuppressive environment has shown promise as a therapeutic approach for various cancers (74, 75). However, in primary PDAC, the effectiveness of immunotherapies is limited due to the desmoplastic and nonimmunogenic tumor microenvironment, which lacks CTL infiltration (76–79). Although it has been proposed that liver metastasis correlates with a poor response to immunotherapy in cancer patients (80), recent studies have found that the metastatic TME contains a relatively higher infiltration of immune cells, including exhausted tumoricidal CTLs, compared to primary PDAC (81), suggesting that targeting the immunosuppressive microenvironment could be a more feasible and viable strategy for treating liver metastasis of PDAC (52, 82). Paradoxically, while liver metastases exhibit localized immune infiltration, they concurrently induce systemic immunosuppression, leading to a widespread reduction in T cells and decreased effectiveness of immunotherapy in preclinical models (80, 83). Lee et al. were the first to report that immune suppression was antigen-specific and involved the coordinated activation of Tregs along with the modulation of intratumoral CD11b+ monocytes (83). Yu et al. further identified hepatic monocyte-derived CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages as key mediators that trigger antigen-specific CD8+ T cell apoptosis through the Fas–FasL pathway within the liver metastatic microenvironment. However, these findings require further investigation and validation in human metastatic PDAC contexts (80).
In PDAC liver metastasis, monocytes and macrophages accumulate and often exhibit an immunosuppressive phenotype, promoting tumor growth and reducing immunotherapy effectiveness (84–87). However, when activated appropriately, macrophages can mediate the phagocytosis of cancer cells, engage in cytotoxic tumor killing, and interact effectively with components of both the innate and adaptive immune systems (87). Genetic engineering to induce cytokine expression in liver macrophages, such as Kupffer cells and TAMs, could transform the liver tumor TME into an immune-reactive state, enhancing protective immune responses to tumor (88). Astuti et al. recently demonstrated that efferocytosis reprograms macrophages towards an immunosuppressive phenotype. Inhibiting efferocytic macrophages, either genetically or pharmacologically, has been shown to restore tumor immunity in early PDAC liver metastasis and hinder metastatic growth (66). A recent study pinpointed macrophage-derived granulin as a key factor in T-cell exclusion in metastatic PDAC. It also highlighted the potential of targeting granulin alongside the immune checkpoint inhibitor αPD-1 to treat metastatic PDAC (81). A novel approach involving liver macrophage-targeted IFNa gene transfer was devised to modify KCs adjacent to liver metastases as well as TAMs in preclinical metastasis mouse models. Although some mice showed resistance due to impaired MHC-II-restricted antigen presentation in APCs, combining CTLA-4 blockade with IFNα lentivirus overcame this resistance, activating both innate and adaptive immune responses (89). These findings support developing tailored approaches that focus on suppressive macrophage clusters or the factors that convert macrophages into immune-suppressing cells in metastatic PDAC settings.
Clinical strategies and their mechanistic insights
The following table summarizes the latest clinical strategies targeting myeloid cells in PDAC, detailing their targets, mechanisms, and current trial status (Table 2). It includes CD40 agonists, CSF-1R inhibitors, CD11b agonists, CCR2 inhibitors, BTK inhibitors, and emerging chemokine receptor inhibitors, such as CXCR2 and CXCR4 antagonists, highlighting the diverse immune modulating approaches to reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
Table 2
| Strategy | Target | Mechanism | Status | NCT number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD40 agonists (e.g., mitazalimab) |
CD40 on macrophages and other immune cells | Activates macrophages to M1 phenotype, enhances T cell priming (90, 91) | In phase Ib/II trials | NCT04888312 |
| CSF-1R inhibitors (e.g., IMC-CS4) | CSF-1R on macrophages | Depletes TAMs, reprograms remaining macrophages to be anti-tumor (32) | Phase I trial (complete) | NCT01346358 |
| CD11b agonists (e.g., GB1275) |
CD11b on myeloid cells | Repolarizes TAMs, enhances T cell immunity (10) | Phase I trial (complete) | NCT04060342 |
| CCR2 inhibitors (e.g., PF-04136309, BMS-813160) |
CCR2 on monocytes | Blocks monocyte recruitment to the tumor (92) | phase Ib/II (complete), with some toxicity concerns | NCT02732938 NCT03496662 |
| BTK inhibitors (e.g., ibrutinib) |
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in immune cells | Modulates myeloid and T cells to enhance anti-tumor immune responses (93) | In phase III trials | NCT02436668 |
| CXCR2 inhibitors (e.g., AZD5069) |
CXCR2 on neutrophils and MDSCs | Inhibits neutrophil and MDSC recruitment to the TME (94), enhances T cell infiltration and chemotherapy/immunotherapy efficacy (95) | phase Ib/II (complete) | NCT02583477 |
| CXCR4 inhibitors (e.g., motixafortide) |
CXCR4 on immune and tumor cells | Disrupts CXCR4–CXCL12 axis, inhibits tumor cell homing, metastasis, and immunosuppression, enhances anti-PD-1/PD-L1 responses (96) | phase IIa (complete) | NCT02826486 |
Clinical strategies targeting myeloid cells in PDAC.
CD40 agonists
Emerging strategies to reprogram TAMs through phagocytic activation have opened new frontiers in PDAC immunotherapy (97). Pioneering studies in pancreatic cancer patients revealed that anti-CD40 agonistic antibodies not only stimulate macrophage-mediated tumor cell engulfment but also enhance dendritic cell (DC) cross-presentation and T-cell priming (90). While it was first assumed these antibodies exclusively targeted macrophages, subsequent investigations demonstrated they also enhance dendritic cell (DC) function and improve T-cell priming (98, 99). CD40 agonists, such as mitazalimab, target the CD40 receptor on macrophages and other immune cells, transforming TAMs from an M2 (immunosuppressive) to an M1 (immune-supportive) phenotype. This shift facilitates the degradation of fibrotic stroma, enhances tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy, and improves T cell infiltration (90, 91). Driven by preclinical observations (98–100), the first-in-human dose-finding study of APX005M (agonistic CD40 monoclonal antibody) has shown on-target effects and a manageable safety profile (101). The combination of CD40 agonists with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy has shown promise in patients with metastatic PDAC (102, 103). However, the structural variations among CD40 agonists impact their safety profiles, with systemic administration potentially leading to dose-limiting immune-related adverse effects (37). Mitazalimab, a second-generation CD40 antibody, has demonstrated clinical activity and a favorable safety profile in advanced-stage solid tumors (101, 104). Supported by preclinical data (105), a phase II trial combining mitazalimab with modified FOLFIRINOX in metastatic PDAC patients showed manageable safety and anti-tumor activity, supporting further development in a phase III trial (106).
CSF-1R inhibitors
CSF-1R inhibitors, such as IMC-CS4, target the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor on macrophages, depleting protumor TAM subsets and reprogramming remaining macrophages to bolster tumor-suppressing immunity. This enhances interferon responses and increases cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) infiltration, preventing tumor growth (32). A recent trial combining IMC-CS4 with GVAX, cyclophosphamide, and pembrolizumab in PDAC patients showed increased CTL levels, suggesting macrophage reprogramming rather than depletion. This suggests that IMC-CS4 reprogrammed macrophages rather than depleting them (107). However, its effectiveness in metastatic PDAC remains uncertain, indicating a need for further validation.
CD11b agonists
CD11b agonists, such as GB1275 and ADH-503, target the CD11b receptor on myeloid cells, repolarizing TAMs to enhance antitumor T cell immunity. This strategy makes checkpoint inhibitors effective in previously unresponsive PDAC models by reprogramming immunosuppressive myeloid cells (10). GB1275 is in early clinical development, with preclinical data supporting its potential in immunotherapeutic combinations (36). This approach is an unexpected detail, as it highlights a novel target for enhancing PDAC immunotherapy, though its clinical impact is still being explored.
CCR2 inhibitors
Despite limited clinical benefit and some off-target toxicities in early trials, CCR2 inhibitor therapy remains a promising approach for PDAC due to its ability to disrupt the CCL2–CCR2 chemokine axis, which recruits immunosuppressive TAMs to the TME. In a phase Ib trial (NCT01413022), the CCR2 inhibitor PF-04136309 combined with FOLFIRINOX in patients with borderline resectable or locally advanced PDAC achieved a 49% objective response rate and a 97% disease control rate, with manageable toxicities, demonstrating reduced TAM infiltration and increased effector T cell presence (108). A phase Ib trial (NCT02732938) evaluating PF-04136309 with nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine in metastatic PDAC reported improved overall survival (29% vs. 19% at 12 months) compared to historical chemotherapy controls, though pulmonary toxicity was noted (109). Preclinical studies further support CCR2 inhibition’s potential to enhance anti-PD-1 immunotherapy and chemotherapy by increasing CD8+ T cell recruitment and reducing regulatory T cells or TAMs (110, 111). These findings, coupled with a recently completed trial like NCT03496662 (BMS-813160 with nivolumab and chemotherapy), suggest that optimizing CCR2 inhibitor dosing and combination strategies could overcome current limitations, making this approach a promising avenue for further investigation.
BTK inhibitors
BTK inhibitors, such as ibrutinib, target Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in immune cells, including myeloid cells, modulating their interaction with T cells to enhance anti-tumor responses. A study demonstrated ibrutinib’s modulation of myeloid and T cells in metastatic PDAC, supporting its role in immune cell crosstalk (93). However, the phase III RESOLVE trial combining ibrutinib with frontline chemotherapy failed to improve survival outcomes in patients with metastatic PDAC (112). While BTK inhibition shows mechanistic promise, its clinical translation necessitates patient stratification.
Chemokine receptor inhibitors: CXCR2 and CXCR4
In addition to the agents discussed, CXCR2 and CXCR4 inhibitors are gaining attention for their potential to modulate the PDAC TME. CXCR2 inhibitors, such as AZD5069, target neutrophil and MDSC recruitment driven by ligands like CXCL1 and CXCL5, which are upregulated in PDAC and correlate with poor outcomes (94). A phase II clinical trial (NCT02583477) is evaluating AZD5069 in combination with standard therapies in PDAC, building on preclinical evidence that CXCR2 blockade enhances T cell infiltration and chemotherapy efficacy (95). CXCR4 inhibitors (e.g., plerixafor, motixafortide) disrupt the CXCR4–CXCL12 axis, inhibiting tumor cell homing, metastasis, and immunosuppression, with clinical trials (NCT02826486, NCT03168139) showing improved T cell responses and synergy with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies in metastatic PDAC (96, 113, 114). Future research on CXCR2 and CXCR4 inhibitors in PDAC should prioritize combination therapies with checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy, leveraging high-resolution spatial transcriptomics to map neutrophil and macrophage interactions for precise targeting. Focusing on metastatic PDAC, particularly liver metastases, will address critical needs by disrupting tumor homing and immunosuppression.
While myeloid-targeted therapeutic strategies hold considerable potential in PDAC, several scientific and clinical challenges warrant careful consideration. First, the therapeutic window of these approaches may be constrained by on-target toxicities, as exemplified by pulmonary complications observed with CCR2 inhibitor administration. Second, the heterogeneous distribution of myeloid cell subsets across patients introduces variability in treatment responsiveness, necessitating deeper biological insights. Furthermore, our current understanding of dynamic immune-stromal crosstalk remains incomplete due to technical limitations in resolving spatial cellular interactions. To address these barriers, the field is progressively exploring multimodal solutions: combining myeloid modulators with conventional chemo-radiotherapy regimens could amplify therapeutic synergy; advancing nanoparticle-based delivery systems might enhance target specificity while reducing off-tissue effects; and implementing single-cell spatial transcriptomic platforms could decode microenvironmental architecture with unprecedented resolution. Looking forward, the evolution of PDAC immunotherapy may depend on intelligently designed combination strategies that simultaneously engage multiple immunosuppressive pathways, thereby reshaping the tumor ecosystem through coordinated mechanistic interventions.
Conclusions
To provide a comprehensive visual summary of the immunosuppressive landscape in PDAC progression, we propose schematic representations of the TME at three critical stages: primary tumor, pre-metastatic niche, and metastatic site (Figure 1). These schematics illustrate key cellular components (e.g., TAMs, MDSCs, neutrophils, Tregs) and molecular interactions (e.g., GM-CSF, TGF-β, CXCR2 signaling) that dominate each stage. For instance, the primary tumor schematic highlights the desmoplastic stroma and myeloid cell-driven immunosuppression, while the pre-metastatic niche emphasizes liver-specific adaptations such as Kupffer cell reprogramming via tumor-derived exosomes. The metastatic TME schematic depicts the coexistence of immunosuppressive (SPP1+ TAMs) and inflammatory (FCN1+ TAMs) macrophage subsets within spatially distinct tumor regions. These figures integrate findings from recent scRNA-seq and spatial transcriptomic studies (38, 46, 66), offering a roadmap for targeting stage-specific myeloid vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, the immunosuppressive environment of PDAC presents significant challenges for effective cancer treatment. This review highlights several key findings and future directions in the field of PDAC research and therapy. PDAC is characterized by a highly immunosuppressive TME, which includes diverse myeloid cells such as TAMs and MDSCs. These cells suppress anti-tumor immunity and promote tumor progression. Advancements in scRNA-seq and spatial transcriptomics have revealed the molecular complexity and heterogeneity of PDAC, showing dynamic changes in the TME. Studies have identified distinct immune cell populations and their interactions, providing insights into immune suppression mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Metastatic sites, particularly the liver, undergo microenvironmental changes that support metastatic growth even before metastasis is clinically evident. These pre-metastatic niches are characterized by the recruitment of immunosuppressive cells, such as MDSCs, macrophages, and Tregs. Targeting myeloid cells in PDAC has shown promise in enhancing anti-tumor immunity. CD40 agonists, CSF-1R inhibitors, and other novel therapeutic approaches have demonstrated potential in reprogramming macrophages and improving immunotherapy efficacy. These strategies aim to shift TAMs from an M2 to an M1 phenotype, enhance CTL infiltration, and prevent tumor growth. Future research should focus on higher-resolution spatial transcriptomics to capture the complexities of cellular interactions within the TME. Exploring combination treatments that target multiple immunosuppressive pathways simultaneously could enhance immunotherapy efficacy. Developing tailored therapies that focus on specific immunosuppressive pathways, such as the Fas–FasL pathway or the efferocytosis gene signature, could help overcome immune resistance in PDAC. By addressing these future directions, researchers can expand our insight into PDAC biology and develop more successful therapeutic strategies to overcome the immunosuppressive barriers of the TME, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Statements
Author contributions
RG: Investigation, Writing – original draft. YC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. CL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. QY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82303933) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2022QH241).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Halbrook CJ Lyssiotis CA Pasca di Magliano M Maitra A . Pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges. Cell. (2023) 186:1729–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.02.014
2
Zambirinis CP Midya A Chakraborty J Chou JF Zheng J McIntyre CA et al . Recurrence after resection of pancreatic cancer: can radiomics predict patients at greatest risk of liver metastasis? Ann Surg Oncol. (2022) 29:4962–74. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11579-0
3
Kleeff J Korc M Apte M La Vecchia C Johnson CD Biankin AV et al . Pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2016) 2:16022. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.22
4
Topalian SL Sznol M McDermott DF Kluger HM Carvajal RD Sharfman WH et al . Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:943–54. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02272
5
Brahmer JR Drake CG Wollner I Powderly JD Picus J Sharfman WH et al . Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:715–23. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02270
6
Brahmer JR Tykodi SS Chow LQ Hwu WJ Topalian SL Hwu P et al . Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:2455–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200694
7
O'Reilly EM Oh DY Dhani N Renouf DJ Lee MA Sun W et al . Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab for patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2019) 5:1431–8. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.1588
8
Royal RE Levy C Turner K Mathur A Hughes M Kammula US et al . Phase 2 trial of single agent Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Immunother. (2010) 33:828–33. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181eec14c
9
Amin S Baine M Meza J Alam M Lin C . The impact of immunotherapy on the survival of pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients who received definitive surgery of the pancreatic tumor: a retrospective analysis of the National Cancer Database. Radiat Oncol. (2020) 15:139. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01569-5
10
Panni RZ Herndon JM Zuo C Hegde S Hogg GD Knolhoff BL et al . Agonism of CD11b reprograms innate immunity to sensitize pancreatic cancer to immunotherapies. Sci Transl Med. (2019) 11. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau9240
11
Gulhati P Schalck A Jiang S Shang X Wu C-J Hou P et al . Targeting T cell checkpoints 41BB and LAG3 and myeloid cell CXCR1/CXCR2 results in antitumor immunity and durable response in pancreatic cancer. Nat Cancer. (2023) 4:62–80. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00500-z
12
DeNardo DG Ruffell B . Macrophages as regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. (2019) 19:369–82. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0127-6
13
Engblom C Pfirschke C Pittet MJ . The role of myeloid cells in cancer therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. (2016) 16:447–62. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.54
14
Mantovani A Marchesi F Malesci A Laghi L Allavena P . Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2017) 14:399–416. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.217
15
Łuksza M Sethna ZM Rojas LA Lihm J Bravi B Elhanati Y et al . Neoantigen quality predicts immunoediting in survivors of pancreatic cancer. Nature. (2022) 606:389–95. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04735-9
16
Sasaki K Takano S Tomizawa S Miyahara Y Furukawa K Takayashiki T et al . C4b-binding protein α-chain enhances antitumor immunity by facilitating the accumulation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40:212. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02019-0
17
Palucka AK Coussens LM . The basis of oncoimmunology. Cell. (2016) 164:1233–47. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.049
18
Caronni N La Terza F Vittoria FM Barbiera G Mezzanzanica L Cuzzola V et al . IL-1β+ macrophages fuel pathogenic inflammation in pancreatic cancer. Nature. (2023) 623:415–22. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06685-2
19
Lewis CE Pollard JW . Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:605–12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4005
20
Qian BZ Pollard JW . Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell. (2010) 141:39–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.014
21
Gomez Perdiguero E Klapproth K Schulz C Busch K Azzoni E Crozet L et al . Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature. (2015) 518:547–51. doi: 10.1038/nature13989
22
Jenkins SJ Ruckerl D Cook PC Jones LH Finkelman FD van Rooijen N et al . Local macrophage proliferation, rather than recruitment from the blood, is a signature of TH2 inflammation. Science. (2011) 332:1284–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1204351
23
Perdiguero EG Geissmann F . The development and maintenance of resident macrophages. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:2–8. doi: 10.1038/ni.3341
24
Movahedi K Laoui D Gysemans C Baeten M Stangé G Van den Bossche J et al . Different tumor microenvironments contain functionally distinct subsets of macrophages derived from Ly6C(high) monocytes. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:5728–39. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4672
25
Franklin RA Liao W Sarkar A Kim MV Bivona MR Liu K et al . The cellular and molecular origin of tumor-associated macrophages. Science. (2014) 344:921–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1252510
26
Qian BZ Li J Zhang H Kitamura T Zhang J Campion LR et al . CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis. Nature. (2011) 475:222–5. doi: 10.1038/nature10138
27
Zhu Y Herndon JM Sojka DK Kim KW Knolhoff BL Zuo C et al . Tissue-resident macrophages in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma originate from embryonic hematopoiesis and promote tumor progression. Immunity. (2017) 47:323–38.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.07.014
28
Bayne LJ Beatty GL Jhala N Clark CE Rhim AD Stanger BZ et al . Tumor-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor regulates myeloid inflammation and T cell immunity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell. (2012) 21:822–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.04.025
29
Pylayeva-Gupta Y Lee KE Hajdu CH Miller G Bar-Sagi D . Oncogenic Kras-induced GM-CSF production promotes the development of pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Cell. (2012) 21:836–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.04.024
30
Bear AS Vonderheide RH O'Hara MH . Challenges and opportunities for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. (2020) 38:788–802. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.08.004
31
Stromnes IM Hulbert A Pierce RH Greenberg PD Hingorani SR . T-cell localization, activation, and clonal expansion in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res. (2017) 5:978–91. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0322
32
Zhu Y Knolhoff BL Meyer MA Nywening TM West BL Luo J et al . CSF1/CSF1R blockade reprograms tumor-infiltrating macrophages and improves response to T-cell checkpoint immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer models. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:5057–69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3723
33
Candido JB Morton JP Bailey P Campbell AD Karim SA Jamieson T et al . CSF1R(+) macrophages sustain pancreatic tumor growth through T cell suppression and maintenance of key gene programs that define the squamous subtype. Cell Rep. (2018) 23:1448–60. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.131
34
Liu X Hogg GD DeNardo DG . Rethinking immune checkpoint blockade: ‘Beyond the T cell’. J ImmunoTherapy Cancer. (2021) 9:e001460. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001460
35
Menjivar RE Nwosu ZC Du W Donahue KL Hong HS Espinoza C et al . Arginase 1 is a key driver of immune suppression in pancreatic cancer. Elife. (2023) 12. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80721
36
DeNardo DG Galkin A Dupont J Zhou L Bendell J . GB1275, a first-in-class CD11b modulator: rationale for immunotherapeutic combinations in solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003005
37
Vonderheide RH . CD40 agonist antibodies in cancer immunotherapy. Annu Rev Med. (2020) 71:47–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-062518-045435
38
Chen K Wang Q Li M Guo H Liu W Wang F et al . Single-cell RNA-seq reveals dynamic change in tumor microenvironment during pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Malignant progression. EBioMedicine. (2021) 66:103315. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103315
39
Oh K Yoo YJ Torre-Healy LA Rao M Fassler D Wang P et al . Coordinated single-cell tumor microenvironment dynamics reinforce pancreatic cancer subtype. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5226. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40895-6
40
Cui Zhou D Jayasinghe RG Chen S Herndon JM Iglesia MD Navale P et al . Spatially restricted drivers and transitional cell populations cooperate with the microenvironment in untreated and chemo-resistant pancreatic cancer. Nat Genet. (2022) 54:1390–405. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01157-1
41
Li Y Du Y Li R Zhong W Zou X Li L et al . Spatial transcriptomics in pancreatic cancer: Advances, prospects and challenges. Crit Rev Oncology/Hematology. (2024) 203:104430. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104430
42
Kim S Leem G Choi J Koh Y Lee S Nam S-H et al . Integrative analysis of spatial and single-cell transcriptome data from human pancreatic cancer reveals an intermediate cancer cell population associated with poor prognosis. Genome Medicine. (2024) 16:20. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01287-7
43
Arina A Corrales L Bronte V . Enhancing T cell therapy by overcoming the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Semin Immunol. (2016) 28:54–63. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.01.002
44
Munn DH Bronte V . Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Immunol. (2016) 39:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.10.009
45
Moffitt RA Marayati R Flate EL Volmar KE Loeza SG Hoadley KA et al . Virtual microdissection identifies distinct tumor- and stroma-specific subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Genet. (2015) 47:1168–78. doi: 10.1038/ng.3398
46
Khaliq AM Rajamohan M Saeed O Mansouri K Adil A Zhang C et al . Spatial transcriptomic analysis of primary and metastatic pancreatic cancers highlights tumor microenvironmental heterogeneity. Nat Genet. (2024) 56:2455–65. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01914-4
47
Grünwald BT Devisme A Andrieux G Vyas F Aliar K McCloskey CW et al . Spatially confined sub-tumor microenvironments in pancreatic cancer. Cell. (2021) 184:5577–92.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.022
48
Bailey P Chang DK Nones K Johns AL Patch AM Gingras MC et al . Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature. (2016) 531:47–52. doi: 10.1038/nature16965
49
Chan-Seng-Yue M Kim JC Wilson GW Ng K Figueroa EF O'Kane GM et al . Transcription phenotypes of pancreatic cancer are driven by genomic events during tumor evolution. Nat Genet. (2020) 52:231–40. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0566-9
50
Raghavan S Winter PS Navia AW Williams HL DenAdel A Lowder KE et al . Microenvironment drives cell state, plasticity, and drug response in pancreatic cancer. Cell. (2021) 184:6119–37.e26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.11.017
51
Liu Y Cao X . Characteristics and significance of the pre-metastatic niche. Cancer Cell. (2016) 30:668–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.09.011
52
Wang X Hu LP Qin WT Yang Q Chen DY Li Q et al . Identification of a subset of immunosuppressive P2RX1-negative neutrophils in pancreatic cancer liver metastasis. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:174. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20447-y
53
Garner H de Visser KE . Immune crosstalk in cancer progression and metastatic spread: a complex conversation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:483–97. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0271-z
54
Costa-Silva B Aiello NM Ocean AJ Singh S Zhang H Thakur BK et al . Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat Cell Biol. (2015) 17:816–26. doi: 10.1038/ncb3169
55
Grünwald B Harant V Schaten S Frühschütz M Spallek R Höchst B et al . Pancreatic premalignant lesions secrete tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1, which activates hepatic stellate cells via CD63 signaling to create a premetastatic niche in the liver. Gastroenterology. (2016) 151:1011–24.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.043
56
Seubert B Grünwald B Kobuch J Cui H Schelter F Schaten S et al . Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-1 creates a premetastatic niche in the liver through SDF-1/CXCR4-dependent neutrophil recruitment in mice. Hepatology. (2015) 61:238–48. doi: 10.1002/hep.27378
57
Aiello NM Bajor DL Norgard RJ Sahmoud A Bhagwat N Pham MN et al . Metastatic progression is associated with dynamic changes in the local microenvironment. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:12819. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12819
58
Connolly MK Mallen-St Clair J Bedrosian AS Malhotra A Vera V Ibrahim J et al . Distinct populations of metastases-enabling myeloid cells expand in the liver of mice harboring invasive and preinvasive intra-abdominal tumor. J Leukoc Biol. (2010) 87:713–25. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0909607
59
Gumberger P Bjornsson B Sandström P Bojmar L Zambirinis CP . The liver pre-metastatic niche in pancreatic cancer: A potential opportunity for intervention. Cancers. (2022) 14:3028. doi: 10.3390/cancers14123028
60
Peinado H Zhang H Matei IR Costa-Silva B Hoshino A Rodrigues G et al . Pre-metastatic niches: organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. (2017) 17:302–17. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.6
61
Liu Y Cao X . Immunosuppressive cells in tumor immune escape and metastasis. J Mol Medicine. (2016) 94:509–22. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1376-x
62
McAllister SS Weinberg RA . The tumour-induced systemic environment as a critical regulator of cancer progression and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. (2014) 16:717–27. doi: 10.1038/ncb3015
63
Wang G Li J Bojmar L Chen H Li Z Tobias GC et al . Tumour extracellular vesicles and particles induce liver metabolic dysfunction. Nature. (2023) 618:374–82. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06114-4
64
Bojmar L Zambirinis CP Hernandez JM Chakraborty J Shaashua L Kim J et al . Multi-parametric atlas of the pre-metastatic liver for prediction of metastatic outcome in early-stage pancreatic cancer. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2170–80. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03075-7
65
Yang J Lin P Yang M Liu W Fu X Liu D et al . Integrated genomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals unique characteristics of hepatic metastases and pro-metastatic role of complement C1q in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genome Biol. (2021) 22:4. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02222-w
66
Astuti Y Raymant M Quaranta V Clarke K Abudula M Smith O et al . Efferocytosis reprograms the tumor microenvironment to promote pancreatic cancer liver metastasis. Nat Cancer. (2024) 5:774–90. doi: 10.1038/s43018-024-00731-2
67
Li X Wang CY . From bulk, single-cell to spatial RNA sequencing. Int J Sci. (2021) 13:36. doi: 10.1038/s41368-021-00146-0
68
Peng J Sun BF Chen CY Zhou JY Chen YS Chen H et al . Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intra-tumoral heterogeneity and Malignant progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Res. (2019) 29:725–38. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0195-y
69
Hwang WL Jagadeesh KA Guo JA Hoffman HI Yadollahpour P Reeves JW et al . Single-nucleus and spatial transcriptome profiling of pancreatic cancer identifies multicellular dynamics associated with neoadjuvant treatment. Nat Genet. (2022) 54:1178–91. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01134-8
70
Zhang S Fang W Zhou S Zhu D Chen R Gao X et al . Single cell transcriptomic analyses implicate an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer liver metastasis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5123. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40727-7
71
Storrs EP Chati P Usmani A Sloan I Krasnick BA Babbra R et al . High-dimensional deconstruction of pancreatic cancer identifies tumor microenvironmental and developmental stemness features that predict survival. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2023) 7:105. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00455-z
72
Wang Y Liang Y Xu H Zhang X Mao T Cui J et al . Single-cell analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma identifies a novel fibroblast subtype associated with poor prognosis but better immunotherapy response. Cell Discov. (2021) 7:36. doi: 10.1038/s41421-021-00271-4
73
Li S Yu J Huber A Kryczek I Wang Z Jiang L et al . Metabolism drives macrophage heterogeneity in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Rep. (2022) 39:110609. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110609
74
Nong C Guan P Li L Zhang H Hu H . Tumor immunotherapy: Mechanisms and clinical applications. MedComm – Oncology. (2022) 1:e8. doi: 10.1002/mog.v1.1
75
Gao M Shi J Xiao X Yao Y Chen X Wang B et al . PD-1 regulation in immune homeostasis and immunotherapy. Cancer Letters. (2024) 588:216726. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216726
76
Nevala-Plagemann C Hidalgo M Garrido-Laguna I . From state-of-the-art treatments to novel therapies for advanced-stage pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2020) 17:108–23. doi: 10.1038/s41571-019-0281-6
77
Goehrig D Nigri J Samain R Wu Z Cappello P Gabiane G et al . Stromal protein βig-h3 reprogrammes tumour microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. Gut. (2019) 68:693–707. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317570
78
Yu B Shao S Ma W . Frontiers in pancreatic cancer on biomarkers, microenvironment, and immunotherapy. Cancer Letters. (2025) 610:217350. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217350
79
Zhang R Peng J Zhang Y Zheng K Chen Y Liu L et al . Pancreatic cancer cell-derived migrasomes promote cancer progression by fostering an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Cancer Letters. (2024) 605:217289. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217289
80
Yu J Green MD Li S Sun Y Journey SN Choi JE et al . Liver metastasis restrains immunotherapy efficacy via macrophage-mediated T cell elimination. Nat Medicine. (2021) 27:152–64. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1131-x
81
Quaranta V Rainer C Nielsen SR Raymant ML Ahmed MS Engle DD et al . Macrophage-derived granulin drives resistance to immune checkpoint inhibition in metastatic pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. (2018) 78:4253–69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3876
82
Kenkel JA Tseng WW Davidson MG Tolentino LL Choi O Bhattacharya N et al . An immunosuppressive dendritic cell subset accumulates at secondary sites and promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:4158–70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2212
83
Lee JC Mehdizadeh S Smith J Young A Mufazalov IA Mowery CT et al . Regulatory T cell control of systemic immunity and immunotherapy response in liver metastasis. Sci Immunol. (2020) 5. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aba0759
84
Nielsen SR Quaranta V Linford A Emeagi P Rainer C Santos A et al . Macrophage-secreted granulin supports pancreatic cancer metastasis by inducing liver fibrosis. Nat Cell Biol. (2016) 18:549–60. doi: 10.1038/ncb3340
85
Tsilimigras DI Brodt P Clavien PA Muschel RJ D'Angelica MI Endo I et al . Liver metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:27. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00261-6
86
Doak GR Schwertfeger KL Wood DK . Distant relations: macrophage functions in the metastatic niche. Trends Cancer. (2018) 4:445–59. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.03.011
87
Mantovani A Allavena P Marchesi F Garlanda C . Macrophages as tools and targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2022) 21:799–820. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00520-5
88
Correia AL . Locally sourced: site-specific immune barriers to metastasis. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:522–38. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00836-2
89
Kerzel T Giacca G Beretta S Bresesti C Notaro M Scotti GM et al . In vivo macrophage engineering reshapes the tumor microenvironment leading to eradication of liver metastases. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41:1892–910.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.09.014
90
Beatty GL Chiorean EG Fishman MP Saboury B Teitelbaum UR Sun W et al . CD40 agonists alter tumor stroma and show efficacy against pancreatic carcinoma in mice and humans. Science. (2011) 331:1612–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1198443
91
Long KB Gladney WL Tooker GM Graham K Fraietta JA Beatty GL . IFNγ and CCL2 cooperate to redirect tumor-infiltrating monocytes to degrade fibrosis and enhance chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Discov. (2016) 6:400–13. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-1032
92
Mitchem JB Brennan DJ Knolhoff BL Belt BA Zhu Y Sanford DE et al . Targeting tumor-infiltrating macrophages decreases tumor-initiating cells, relieves immunosuppression, and improves chemotherapeutic responses. Cancer Res. (2013) 73:1128–41. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2731
93
Sinha M Betts C Zhang L Griffith MJ Solman I Chen B et al . Modulation of myeloid and T cells in vivo by Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005425
94
Steele CW Karim SA Leach JDG Bailey P Upstill-Goddard R Rishi L et al . CXCR2 inhibition profoundly suppresses metastases and augments immunotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. (2016) 29:832–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.04.014
95
Highfill SL Cui Y Giles AJ Smith JP Zhang H Morse E et al . Disruption of CXCR2-mediated MDSC tumor trafficking enhances anti-PD1 efficacy. Sci Transl Med. (2014) 6:237ra67. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007974
96
Biasci D Smoragiewicz M Connell CM Wang Z Gao Y Thaventhiran JED et al . CXCR4 inhibition in human pancreatic and colorectal cancers induces an integrated immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2020) 117:28960–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2013644117
97
Zhang L Wang Z Liu K Liu Y Wang S Jiang W et al . Targets of tumor microenvironment for potential drug development. MedComm – Oncology. (2024) 3:e68. doi: 10.1002/mog2.v3.1
98
Morrison AH Diamond MS Hay CA Byrne KT Vonderheide RH . Sufficiency of CD40 activation and immune checkpoint blockade for T cell priming and tumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2020) 117:8022–31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918971117
99
Byrne KT Vonderheide RH . CD40 stimulation obviates innate sensors and drives T cell immunity in cancer. Cell Rep. (2016) 15:2719–32. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.058
100
Winograd R Byrne KT Evans RA Odorizzi PM Meyer AR Bajor DL et al . Induction of T-cell immunity overcomes complete resistance to PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade and improves survival in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res. (2015) 3:399–411. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0215
101
Irenaeus SMM Nielsen D Ellmark P Yachnin J Deronic A Nilsson A et al . First-in-human study with intratumoral administration of a CD40 agonistic antibody, ADC-1013, in advanced solid Malignancies. Int J Cancer. (2019) 145:1189–99. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v145.5
102
O'Hara MH O'Reilly EM Varadhachary G Wolff RA Wainberg ZA Ko AH et al . CD40 agonistic monoclonal antibody APX005M (sotigalimab) and chemotherapy, with or without nivolumab, for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:118–31. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30532-5
103
Padrón LJ Maurer DM O'Hara MH O'Reilly EM Wolff RA Wainberg ZA et al . Sotigalimab and/or nivolumab with chemotherapy in first-line metastatic pancreatic cancer: clinical and immunologic analyses from the randomized phase 2 PRINCE trial. Nat Med. (2022) 28:1167–77. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01829-9
104
Moreno V Perets R Peretz-Yablonski T Fourneau N Girgis S Guo Y et al . A phase 1 study of intravenous mitazalimab, a CD40 agonistic monoclonal antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. (2023) 41:93–104. doi: 10.1007/s10637-022-01319-2
105
Smith KE Jimenez DG Thagesson M Nilsson A Coaña YPd Ambarkhane S et al . Mitazalimab, a potent CD40 agonist in combination with FOLFIRINOX demonstrates changes consistent with increased immune activation in TME and peripheral blood in a preclinical pancreatic cancer tumor model. Cancer Res. (2024) 84(6_Supplement):2376. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2024-2376
106
Van Laethem JL Borbath I Prenen H Geboes KP Lambert A Mitry E et al . Combining CD40 agonist mitazalimab with mFOLFIRINOX in previously untreated metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (OPTIMIZE-1): a single-arm, multicentre phase 1b/2 study. Lancet Oncol. (2024) 25:853–64. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(24)00263-8
107
Arielle Urman YD Wang H Burkhart RA He J Jaffee EM Narang AK et al . Safety and immunologic impact of neoadjuvant/adjuvant GM-CSF-secreting allogenic pancreatic tumor cell vaccine (GVAX) combined with cyclophosphamide, pembrolizumab, and macrophage-targeting CSF1R inhibitor IMC-CS4 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. (2024) 84 (7_Supplement):CT134. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2024-CT134
108
Nywening TM Wang-Gillam A Sanford DE Belt BA Panni RZ Cusworth BM et al . Targeting tumour-associated macrophages with CCR2 inhibition in combination with FOLFIRINOX in patients with borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer: a single-centre, open-label, dose-finding, non-randomised, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17:651–62. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00078-4
109
Noel M O'Reilly EM Wolpin BM Ryan DP Bullock AJ Britten CD et al . Phase 1b study of a small molecule antagonist of human chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 (PF-04136309) in combination with nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine in first-line treatment of metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Invest New Drugs. (2020) 38:800–11. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00830-3
110
Tu MM Abdel-Hafiz HA Jones RT Jean A Hoff KJ Duex JE et al . Inhibition of the CCL2 receptor, CCR2, enhances tumor response to immune checkpoint therapy. Commun Biol. (2020) 3:720. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01441-y
111
Nywening TM Belt BA Cullinan DR Panni RZ Han BJ Sanford DE et al . Targeting both tumour-associated CXCR2(+) neutrophils and CCR2(+) macrophages disrupts myeloid recruitment and improves chemotherapeutic responses in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gut. (2018) 67:1112–23. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-313738
112
Tempero M Oh DY Tabernero J Reni M Van Cutsem E Hendifar A et al . Ibrutinib in combination with nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: phase III RESOLVE study. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:600–8. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.070
113
Feig C Jones JO Kraman M Wells RJ Deonarine A Chan DS et al . Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2013) 110:20212–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320318110
114
Bockorny B Semenisty V Macarulla T Borazanci E Wolpin BM Stemmer SM et al . BL-8040, a CXCR4 antagonist, in combination with pembrolizumab and chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer: the COMBAT trial. Nat Med. (2020) 26:878–85. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0880-x
Summary
Keywords
pancreatic cancer, immunotherapy, macrophage, monocyte, liver metastases
Citation
Gong R, Chen Y, Li C, Zhang H, Liu Z and Yu Q (2025) Targeting myeloid cells in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: from primary tumors to liver metastasis. Front. Immunol. 16:1555036. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1555036
Received
03 January 2025
Accepted
28 April 2025
Published
16 May 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Susanna Mandruzzato, University of Padua, Italy
Reviewed by
Zhifang Zhang, City of Hope National Medical Center, United States
Michael Dwinell, Medical College of Wisconsin, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Gong, Chen, Li, Zhang, Liu and Yu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zimin Liu, liuzimin@qdu.edu.cn; Qian Yu, u3004582@connect.hku.hk
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.