- 1School of Basic Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 3Department of Maxillofacial and Otorhinolaryngological Oncology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin’s Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Basic and Translational Medicine on Head & Neck Cancer, Tianjin, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin, China
- 4National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Diseases, Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
- 5Key Laboratory of Adult Stem Cell Translational Research, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Guiyang, China
- 6Department of Microbiology, Immunology & Molecular Genetics, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Introduction: CDK2 (Cyclin-dependent kinase 2) is an oncogenic cyclin-dependent kinase with potent mitogenic and immunosuppressive functions. Despite extensive research on CDK2 inhibitors, the lack of selectivity has made it unclear whether CDK2 inhibition specifically facilitate immunogenic cell death.
Methods: We used CRISPR-Cas9 system to generate Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells. Tumor cells were inoculated subcutaneously into mice while administering MTX (mitoxantrone) or anti-PD-1 antibodies treatment to observe tumor growth curves. Next, immune cell infiltration in tumor microenvironment was detected by immunofluorescence. Furthermore, apoptosis pathway was evaluated by flow cytometry and western blot. The hallmarks of immunogenic cell death were detected by flow cytometry, ELISA or qRT-PCR.
Results: We found that mice bearing Cdk2-/- cancer cells exhibit slower tumor growth than WT cells after anthracycline analogue MTX treatment, and this phenomenon is dependent on the immune system. Furthermore, our data exhibits that Cdk2-/- cancer cells treated with MTX trigger a more robust immunostimulatory responses than WT cells, including apoptosis stress response, surface calreticulin expression, endoplasmic reticulum stress response, HMGB1 (High Mobility Group Box 1) release, and type-1 interferon response.
Discussion: This study not only suggests that CDK2 inhibition improves the outcome of chemotherapy by enhancing the type-1 interferon response but also investigates the synergistic effects of CDK2 inhibition with MTX or anti-PD-1 antibodies in immunocompetent mice.
Introduction
The antitumor immune response is shaped by a complex interplay within the tumor microenvironment, encompassing TILs (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes), PD-L1 (Programmed Death-Ligand 1) expression, mutational burden, neoantigen presentation, and an IFN-γ(interferon-γ) gene signature (1–4). Despite the therapeutic potential of anti-PD-1 therapy, tumors that lack effective antigen presentation or adequate T cell infiltration remain largely unresponsive, underscoring the necessity for complementary strategies to modulate the immunosuppressive tumor environment (5). Inducing ICD (immunogenic cell death) within tumors represents a strategic approach, characterized by the release of DAMPs (damage-associated molecular patterns) that stimulate immune activity (6–9). For example, ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) engages purinergic receptors attracting myeloid cells into the tumor bed (7, 10). The ‘eat-me’ signal calreticulin translocates to the plasma membrane, facilitating tumor antigen transfer to dendritic cells (11, 12). HMGB1 activates toll-like receptor 4 on dendritic cells, promoting their maturation (13). The type-1 interferon response leads to autocrine activation of IFNAR (interferon α/β receptors), resulting in CXCL9 (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9) and CXCL10 (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10) production, which subsequently stimulates T lymphocyte infiltration into the tumor (14). Cytotoxic agents such as anthracycline analogue MTX, oxaliplatin, radiation therapy, and oncolytic viruses have been shown to induce ICD, thereby enhancing tumor immunogenicity and promoting the recruitment and activation of APCs (antigen-presenting cells) and T cells (8, 14–17).
CDK2 has a pivotal role in facilitating tumorigenesis. As a key regulator of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways, its activity is important in the unregulated cell cycle and proliferation (18–22). CDK2 is implicated not merely in the cellular cycle process, but the inhibition of CDK2 within tumor cells is also instrumental in eliciting anti-neoplastic immune reactions (3, 23). Other CDKs also play an important role in anti-tumor immunity (24–27).
CDKs inhibitors combined with chemotherapy drugs can enhance anti-tumor efficacy (28–30). Although chemotherapeutic agents are known to induce ICD, the efficacy exhibits variability. Combining anthracyclines with CDK2 inhibition presents a therapeutic strategy, leveraging the immunostimulatory properties of both. The concomitant administration of chemotherapy with CDK2 inhibitor elicited a more potent therapeutic pathway compared to chemotherapy as a sole treatment modality (31). Our findings indicate that Cdk2-/- tumor cells combined anthracyclines trigger a more robust series of immunostimulatory stress pathways than WT cells, including apoptosis stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, HMGB1 release, and type-1 interferon response, stimulate DCs and T cells infiltration. These responses collectively foster a protective anticancer immune reaction.
1Many studies indicated that ICD-based immunotherapy, that was chemotherapy drugs combined with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, significantly enhances anti-tumor efficacy (32–35). Also, CDKs inhibitor can enhance PD-L1 protein expression and programmed cell death protein 1 immune checkpoint blockade efficacy (24, 29, 36). Advances in understanding ICD have revealed that inhibitor of CDKs, Dinaciclib, can modulate cancer cell immunogenicity and augment the overall efficacy of anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade (3, 37). Nevertheless, Dinaciclib, which is a selective CDK inhibitor targeting CDK1, CDK2, CDK5, and CDK9, appears to be insufficient in conclusively demonstrating the role of CDK2 in tumor immunogenicity (3, 38) and a role for the specific inhibition of CDKs in inducing ICD has not been described. Here, we demonstrate that Cdk2-/- tumor cells not only sensitize MTX-induced ICD to drive the expression of ICD hallmarks, stimulate immune cell infiltration, and inhibit tumor growth but also enhance the effects of anti-PD-1 therapy to provoke a robust anticancer immune response, result in enhanced anti-tumor immunity, culminating in tumor regression, suggesting a synergistic therapeutic relationship.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Cells were cultured in DMEM (Solarbio, Cat 11995), supplemented with 10% FBS (Cat 10099141) and 100 U/mL penicillin and streptomycin (Cat 15140122) from Thermo Fisher Scientific. Cells were incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2.
Cdk2-/- cancer cell line generation and transfection
Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were generated by synthesizing sgRNA sequences targeting Cdk2 and cloning them into the LentiCRISPR V2 vector (Feng Zhang’s gift, Addgene plasmid #52961). Lentivirus was produced in 293T cells through co-transfection with pMD2.G (Addgene plasmid #12259), psPAX2 (Addgene plasmid #12260), and either the Cdk2 or control vector plasmid. Virus supernatant was collected 48 hours post-transfection, filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and stored at -80°C or used immediately. After 48 hours of infection, cells were cultured in puromycin selection medium (4 μg/ml) for at least 7 days. Monoclonal cells in 96-well plates were obtained using the FACSAria™ III cell sorter (Becton Dickinson, San José, CA, USA). sgRNA sequences: F:5’-CACCGTTGTGGCGCTTAAGAAGATC-3’; R:5’- AAACGATCTTCTTAAGCGCCACAAC-3’.
Overexpression vectors and transfection
For CD39 overexpression, the dCAS9-CD39_GFP plasmid was constructed with GENEWIZ’s assistance. The dCAS9-VP64_GFP plasmid (Addgene Cat #61422) was digested with BamHI and NheI, replacing the VP64 sequence with CD39 cDNA obtained via gene synthesis. 293T cells were transfected with the dCAS9-VP64_GFP plasmid, packaging plasmid psPAX2 (Addgene Cat #12260), and envelope pMD2.G (Addgene Cat #12259) using Lipofectamine 3000 following the manufacturer’s instructions. Lentivirus was harvested from the cell culture medium (DMEM+10% FBS) after 48 hours, collected by centrifugation, filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and stored at -80°C or used immediately. Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were infected with CD39 lentivirus for 48 hours, and infected positive cells were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. For CDK2 overexpression, a dCAS9-CDK2_GFP plasmid was constructed with GENEWIZ’s help (Cdk2 cDNA obtained via gene synthesis). The CDK2 sgRNA base sequence in the dCAS9-CDK2_GFP plasmid was altered without changing the encoded amino acid to avoid CRISPR CAS9 enzyme cleavage (5’TGTGGCGCTTAAGAAGATCCGGCTCGACACT3’ to 5’TAGTCGCCCTAAAAAAAATAAGATTGGATACGG3’). For mutant CDK2 (T160A) overexpression, a dCAS9-CDK2T160A_GFP plasmid was constructed with GENEWIZ’s assistance, altering the CDK2 sgRNA base sequence without changing the encoded amino acid.
Tumor models
Animal experimental protocols received approval from the Guizhou Medical University Animal Ethics Committee. Naïve female C57BL/6N and athymic nude BALB/c mice (Nu/Nu) were obtained from Beijing Vital River Company. Tlr4-/- C57BL/6 mice, aged 6–8 weeks, were sourced from the Model Animal Research Center of Nanjing University. Mice were randomly assigned to designated groups (5–10 mice per group) prior to inoculation. Tumor cells (2×10^6 cells in 100 μl PBS per mouse) were subcutaneously implanted in C57BL/6N mice or 1×10^6 cells μl PBS per mouse for Nu/Nu mice. Chemotherapy via intraperitoneal injection of MTX (1 mM, 200 μl) administered in three doses (days 5, 7, 10 or days 7, 9, 11, it depends on the tumor sizes at days 5). When necessary, mice received intraperitoneal injections of blocking antibodies (200 μg per injection) against IFNAR (InVivoMAb, Clone: MAR1-5A3, BioXcell) on days 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 14, 18, or intravenous injections of blocking antibodies against PD-1 (InVivoMAb, Clone: RMP1-14, BioXcell) on days 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17. All mice were euthanized by CO2 asphyxiation. Tumor growth was monitored through periodic caliper measurements, calculated as the product of tumor length and width. Animals were euthanized when tumor volume reached 300 mm². Tumor progression was tracked 2–3 times per week and presented as error bars of mean ± SEM at each time point.
Western blot
MCA205 WT cells were treated with 1 μM MTX or 20 ng/ml TNFα for 24h. Cells were treated or not as described and lysed in lysis buffer (Cat P0013, Beyotime) and protein concentration was determined using BCA Protein Assay Kit (Cat P0011, Beyotime). Equal amounts of total protein were separated by SDS-PAGE gels (10% or 12.5%) and transferred to 0.45 μm PVDF membranes. Membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat milk in TBST. Then the membranes were incubated with specific primary antibodies: PARP (catalog 9542S), FLIP (catalog 56343S), CASPASE-3 (catalog 9665S), Cleaved-CASPASE-3 (catalog 9664S), CASPASE-8 (catalog 4790S), Cleaved-CASPASE-8 (catalog 8592S), β- TUBULIN (catalog 2146T); Subsequently, incubated with second antibodies: Anti-mouse IgG, HRP-linked Antibody (catalog 7076) or Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody (catalog 7074) (Cell Signaling Technology). The membranes were scanned with the ChemiDoc XRS+ system (Bio-Rad, USA).
qRT-PCR
WT and Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were treated with 1μM MTX for 24h. After total cellular RNA was extracted, RNA concentration was determined using the Nanodrop machine and software (Thermo Fisher Scientific). A total of 4 μg RNA was used to generate cDNA with PrimeScript™ II 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit for qRT-PCR (Cat 6110A, TaKaRa). Cxcl10, Gbp4, Ccl7, Rasd2, Parp14, Oasl2 and Gapdh relative copy number were determined by calculating the fold change difference in the gene of interest relative to Gapdh. qRT-PCR was performed on the Applied Biosystems 7500 machine. All the sequences used in the present study were listed in Supplementary Table S1.
Dataset analysis
The method of correlation analysis is the Spearman rank correlation coefficient. Statistical analyses and data visualization were conducted utilizing R software, specifically version 3.6.3. The R package employed in this research is GSVA, version 1.34.0, as described by Hänzelmann et al. (2013). The algorithm for immune infiltration within the study is ssGSEA, which is integrated within the GSVA package. The focal disease under investigation is Sarcoma. The dataset utilized in this analysis is derived from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), accessible at https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/, specifically the SARC project level 3 HTSeq-FPKM formatted RNA sequencing data. In terms of data transformation, the RNA sequencing data, initially in FPKM format, was converted to TPM (Transcripts Per Million) format and subsequently log2 transformed to normalize the data distribution. Data filtering in this study involved the exclusion of control and normal samples, for that not all projects encompass control/normal samples. To further augment the dataset, markers indicative of 24 distinct immune cell types were sourced from a publication in Immunity by Bindea, Gabriela, et al. (2013), which provides a comprehensive delineation of cell classifications and descriptions. Assessment of normality was undertaken using the Shapiro-Wilk test, while variance homogeneity was evaluated via Levene’s test. The P-values were determined employing an independent samples CDK2 expression data in patients treated with nivolumab were obtained from the GEO dataset GSE91061. A publication in Cell by Nadeem Riaz et al. (2017), which provides a comprehensive description of patient samples.
ATP release quantification
WT and Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were seeded at 3×10^4 cells per well in a 24-well plate. The following day, the medium in all wells was replaced with pre-warmed fresh medium (300 μl per well), with or without 2 μM MTX. After 24 hours, supernatants were collected, centrifuged at 500×g to remove cell debris, and used immediately to measure ATP release using the ENLITEN® ATP Assay System (Promega, FF2000, Madison, WI, USA). Chemiluminescence signals were measured using a VICTOR™ X multilabel reader (PerkinElmer).
Cell death, calreticulin exposure and HMGB1 release
WT and Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were seeded at 3×10^4 cells per well in a 24-well plate. The following day, the medium in all wells was replaced with pre-warmed fresh medium (300 μl per well), with or without 1 μM MTX. Collected cells and supernatants every 8 hours. Early or late apoptosis was analyzed using DAPI and Annexin V staining (BD Pharmingen™, Le Pont-De-Claix, France) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Calreticulin exposure was evaluated by surface staining using a rabbit monoclonal antibody (dilution 1:500, clone EPR3924, Ref: AJ1124a, ABGENT), followed by Alexa 488-conjugated goat anti-rat IgG (H+L) secondary antibody (dilution 1:500, Life Technologies). For the HMGB1 release assay, cell lines were seeded and treated with 1 μM MTX under conditions identical to the ENLITEN® ATP Assay. Supernatants were collected after 24 hours, centrifuged to remove cell debris, and used immediately for ELISA-based quantifications (IBL International GMBH, Ref ST51011). Plates were read using a VICTOR™ X multilabel reader (PerkinElmer).
Statistical analyses
All results are presented as means ± SEM from n = 3 to 6 parallel assessments, with similar results observed in at least two independent experiments. Statistical differences were evaluated using unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test. Statistical analyses and histograms were generated using GraphPad Prism 5 software (San Diego, CA, USA).
Results
Cdk2-/- tumor cells are sensitive to chemotherapy and dependent on the immune system
We used CRISPR-Cas9 technology to generate Cdk2-/- MCA205 fibrosarcomas cells that lacked Cdk2 expression. We have demonstrated through the western blot method that CDK2 protein is not expressed in Cdk2-/- cells (Figure 1A). In response to the anthracycline analogue MTX, Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells exhibited a stronger chemotherapeutic response to MTX in vivo than WT cells (Figure 1B). However, the enhanced chemotherapeutic response of Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells was not observed in T cell-deficient nu/nu mice (Figures 1C, D). Despite the fact that Cdk2-/- MCA205 tumors grew slower than WT, Cdk2-/- tumors after MTX treatment were statistically different from tumors without chemotherapy. There was no difference between the WT tumor curves with or without chemotherapy (Figure 1B) using unpaired Mann-Whitney U test, while there was difference between the WT endpoint tumor sizes with or without chemotherapy using unpaired Student’s t-test (Figure 1D). These results suggest that depletion of Cdk2 enhances the efficacy of anthracyclines in an immune dependent fashion.
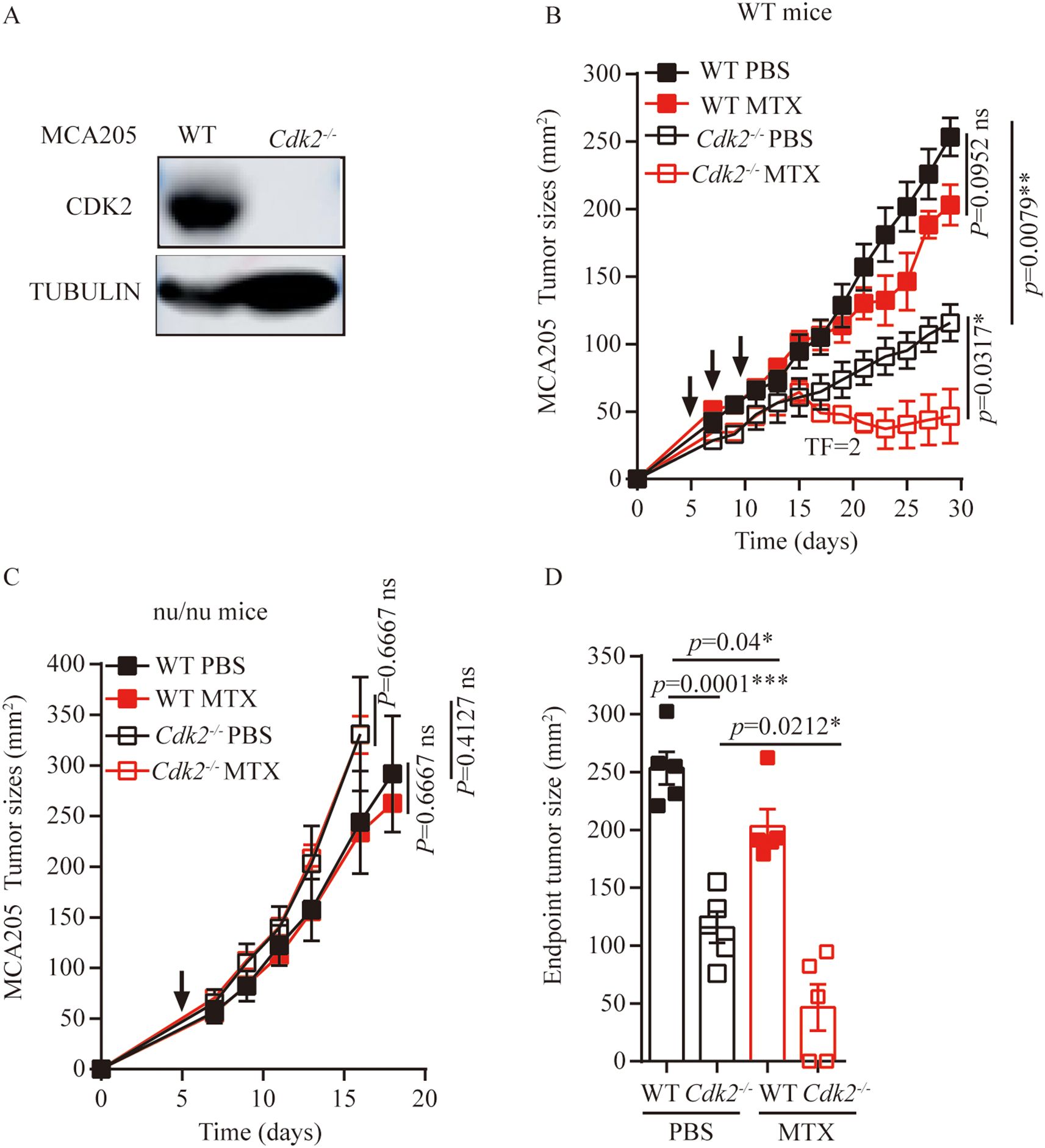
Figure 1. Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells enhance the therapeutic efficacy of MTX through an immune-dependent mechanism. (A), Western blot showing expression of indicated proteins in WT, Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells. (B), Immunocompetent mice bearing WT or Cdk2-/- MCA205 fibrosarcomas received intraperitoneal injections of PBS or MTX (1mM/200 μL/mouse). (C), Athymic nude mice (nu/nu) with WT or Cdk2-/- MCA205 fibrosarcomas were treated as descried. (D), Tumor sizes at 29 days were compared among MTX treated cancers with the indicated genotype. Tumor sizes, monitored 2–3 times weekly, were presented as mean ± SEM at each time point. Each group comprised 5–6 mice, with experiments repeated at least twice. Tumor growth curve differences were analyzed using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test, while endpoint tumor sizes differences were analyzed using the unpaired Student’s t-test; asterisks denote statistical significance (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns, nonsignificant). Arrows indicate dosing dates (days 5, 7, 10). TF, tumor free.
Enhanced local immune response of Cdk2-/- tumors responding to anthracyclines
As mentioned above, Cdk2-/- tumors growing smaller on immunocompetent mice than WT tumors in response to MTX treatment. Therefore, we analyzed the difference in immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment between WT tumors and Cdk2-/- tumors after MTX treatment. And we found that Cdk2-/- tumors exhibited a major alteration on their immune cell infiltration. Specifically, within 48 hours post-chemotherapy, Cdk2-/- tumors manifested a denser infiltration by CD8+ cells (Figures 2A, B) than did control tumors. Similarly, the frequency of CD11c+ cells (Figures 2A, B) increased by immunofluorescence, followed by microscopic quantitation. Moreover, through analysis of TCGA, we found that sarcoma patients with low expression of CDK2 had higher enrichment scores of T cells, DC, NK cells, macrophages and neutrophils (Figures 2C–H). Altogether, these results suggest that the combination of MTX plus Cdk2 depletion can stimulate a particularly immune-mediated chemotherapeutic response.
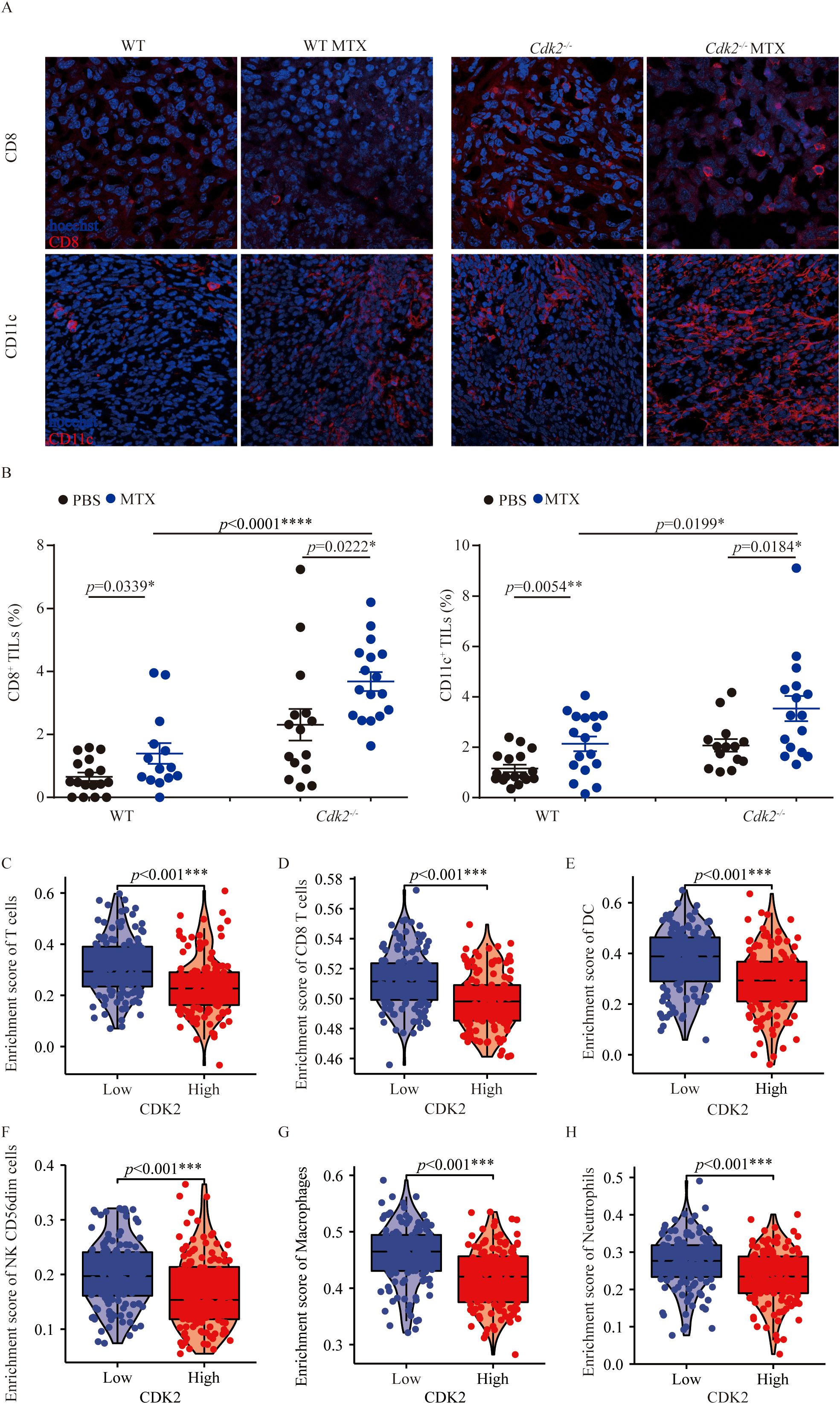
Figure 2. Cdk2 deletion in fibrosarcoma promotes immune cell infiltration after MTX treatment. Mice with WT or Cdk2-/- tumors were injected (i.p.) with PBS or MTX. Tumor samples, collected 48 hours post-treatment, underwent immunofluorescence staining. Representative images from MTX-treated tumors were shown in (A). Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ cells (left) and CD11c+ cells (right) were quantified as a percentage of all nucleated (Hoechst+) cells in the same field. Enrichment of T cells (C), CD8+ T cells (D), DC (E), NK cells (F), Macrophages (G), and Neutrophils (H) was assessed in low versus high CDK2 expression in sarcomas patients. The GSVA package in R [version 1.34.0] calculated immune infiltration in sarcomas (control/normal removed) from TCGA, with RNAseq data in HTSeq-FPKM format converted to TPM format and log2 transformed. Normality (Shapiro-Wilk test) and variance homogeneity (Levene’s test) were evaluated, and P-values were determined by independent samples T-test. Each group contained 5 tumor samples, each point representing a different field. Non-consecutive sections from the same tissue were randomly selected, images captured from both tumor centers and peripheries. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 (unpaired Student t test).
Cdk2-/- cancer cells are more susceptible to apoptosis responding to MTX
MTX has its ability to induce cytotoxicity and immunogenic cell death (8, 39).
As mentioned above, Cdk2-/- tumors are more sensitive to MTX and can promote the infiltration of immune cells into the tumor microenvironment. We found that Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were more prone to apoptosis than WT after treatment with MTX. We noticed that the proportion of early apoptosis (AnnexinV+ DAPI-) and late apoptosis (AnnexinV+ DAPI+) in Cdk2-/- cells increased after MTX treatment (Figures 3A, B), and the representative flow scatter plot is shown in Figure 3A. Similarly, we found that cleaved-caspase and cleaved-PARP proteins, which promote apoptosis, exhibited high expression and FLIP, which inhibits apoptosis, exhibited low expression in Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells after treatment with MTX or TNFα by western blot (Figures 3C, D).
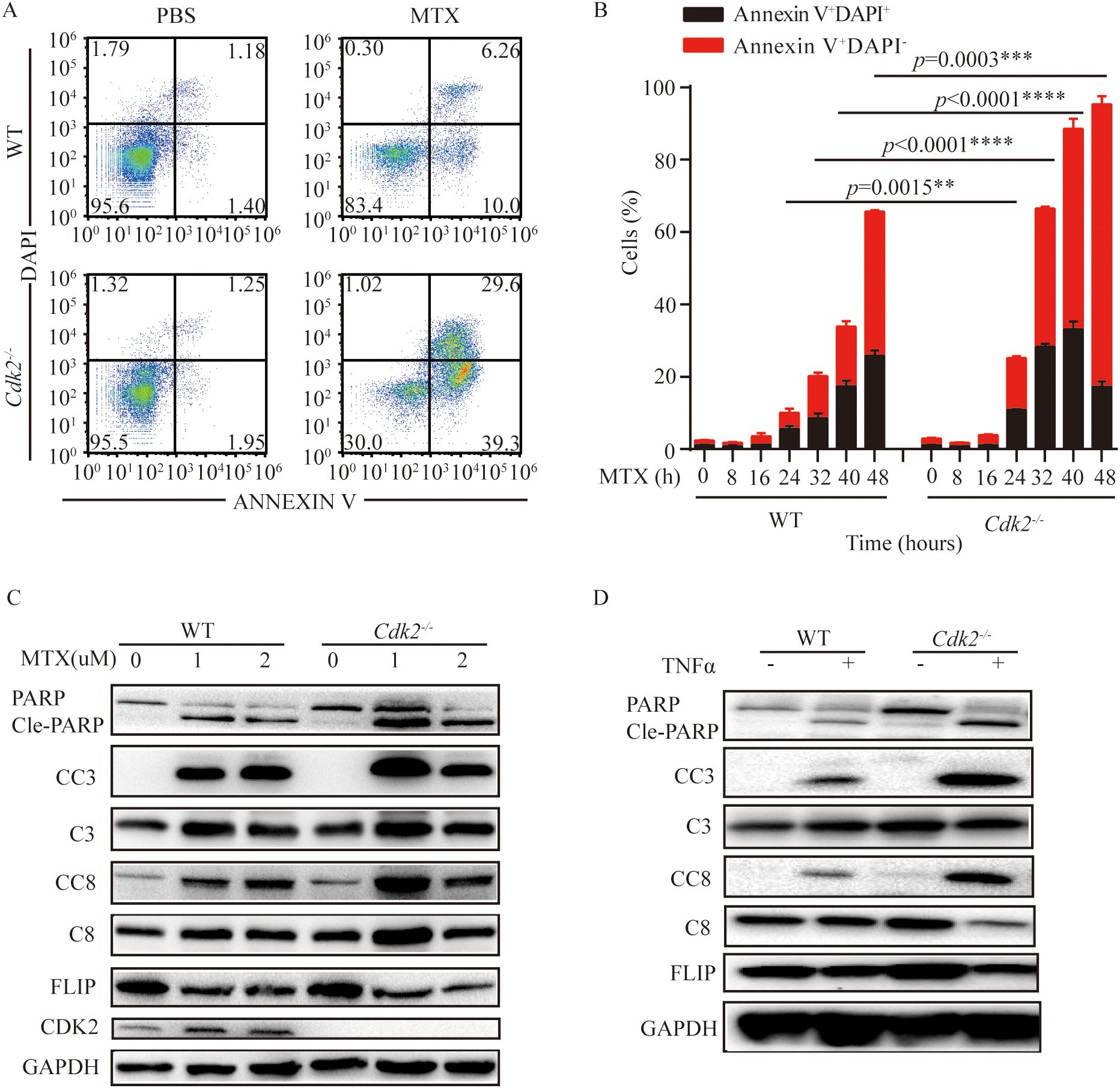
Figure 3. Cdk2-/- cells were more prone to apoptosis than WT cells after MTX treatment. (A, B) WT and Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were treated with MTX in vitro using 6 well plates. Cells were collected at specified times to assess apoptosis via Annexin V-FITC and DAPI staining. Typical dot plots are presented at 24 h (A), the mean ± SEM (n=3 independent experiments) of percentages of cells in early and late apoptosis (Annexin V+ DAPI+) were plotted (B). (C, D) WT and Cdk2-/- cells were treated with or without MTX (C) or TNFα (D) for 24 hours, then western blot analysis of apoptosis-related proteins in WT and Cdk2-/- cells was conducted. Experiments were repeated at least twice. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 (unpaired Student’s t test). PARP, Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; Cle-PARP, Cleaved PARP; CC3, Cleaved Caspase-3; C3, Caspase-3; CC8, Cleaved Caspase-8; C8, Caspase-8; FLIP, FLICE/caspase8-inhibitoryproteins; CDK2, Cyclin-dependent kinase 2; GAPDH, Cyclin-dependent kinase 2.
Essential role for the type I IFN pathway in the improved chemotherapeutic response of Cdk2-/- tumors
MTX can stimulate a series of stress and death pathways, including apoptosis, exposure of calreticulin upon endoplasmic reticulum stress, nuclear exodus of HMGB1 resulting from secondary necrosis, autophagy-linked ATP release, and the production of chemokines (such as CXCL10) subsequent to type-1 interferon response to induce immunogenic cell death. Since MTX is an inducer of immunogenic cell death, we analyzed the changes in immunogenic cell death markers after MTX treatment at the cellular level. Accordingly, calreticulin exposure could be induced by MTX in Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells, moreover Cdk2-/- cells exhibited an increased calreticulin exposure after 4 hours (Figures 4A, B). Similarly, Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells cultured with MTX released more HMGB1 than WT cells (Figure 4C). Since HMGB1 can be recognized by TLR4 on immune cells and activate anti-tumor immunity, we used Tlr4-/- mice to block extracellular HMGB1 triggered antitumor immunity. We subcutaneously implanted WT and Cdk2-/- cancer cells into C57 mice and Tlr4-/- mice respectively. We found that tumors grew slower with Cdk2-/- cells than those with WT cells in both C57 and Tlr4-/- mice, which suggested that HMGB1-TLR4 signaling is dispensable for Cdk2-/- cells increased immunogenicity (Figure 4D).
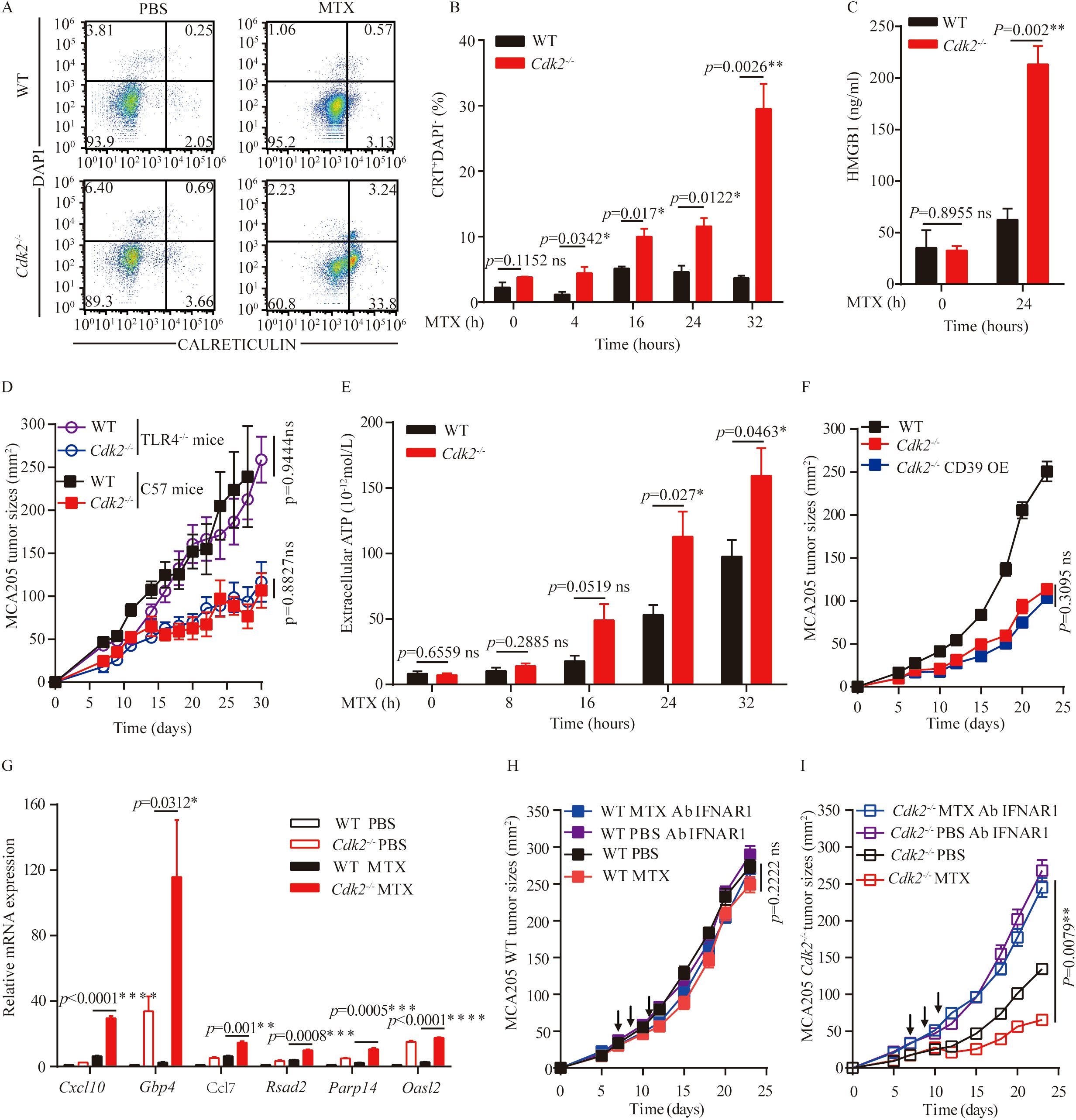
Figure 4. Impact of Cdk2 deficiency on the hallmarks of immunogenic cell death. (A, B) WT and Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells were treated with MTX in vitro in 6-well plates, and at the indicated time points, cells were collected to assess surface calreticulin exposure using rat monoclonal anti-Calreticulin antibody. Typical dot plots (A) and quantitative data (B) are presented. (C) HMGB1 protein levels in supernatants from WT or Cdk2-/- cells pre-treated with MTX for 24 hours were measured by ELISA. (D) Growth curves of immunocompetent mice bearing WT, Cdk2-/-, or CD39 overexpressing Cdk2-/- MCA205 tumors are shown. (E) Supernatants from WT or Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells treated with MTX at different times were collected to quantify ATP release using the luciferase bioluminescence assay. (F) Tumor growth in mice bearing MCA205 cells with WT, Cdk2-/-, or Cdk2-/- CD39-overexpression genotypes. (G) Type I IFN-related gene expression, with or without MTX treatment for 16 hours, was measured in WT and Cdk2-/- tumor cells. Relative expression levels compared to untreated WT MCA205 cells were calculated using the 2^-ddCT method and expressed as fold-change. (H, I) WT (H) or Cdk2-/- (I) MCA205 tumor cells were inoculated into immunocompetent mice, mice received injections of PBS, MTX, or neutralizing IFNAR1 antibodies (i.p.). Arrows indicate the timing of MTX injections. All groups contained 5 mice, with experiments repeated twice. For gene expression data, unpaired Student’s t-test was applied. Tumor growth differences were assessed using the unpaired Mann-Whitney U test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant. Arrows indicate dosing dates (MTX treatment at days 7, 9, 11).
ATP is a key damage-associated molecular pattern in ICD in addition to HMGB1 and CRT. We found that Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells released more ATP than WT cells in response to MTX (after 24 hours), as indicated by the measurement of extracellular ATP (Figure 4E). The increase of ATP release in Cdk2-/- cells and enhanced dendritic cells infiltration in Cdk2-/- tumors suggested that ATP might play a critical role in antitumor immunity in Cdk2-/- tumors. To abolish extracellular ATP in tumor microenvironment, we overexpressed the ATP hydrolase CD39 protein in Cdk2-/- cells, and inoculated the obtained stable cell lines into C57 mice subcutaneously. The tumor growths of Cdk2-/- and Cdk2-/–CD39 overexpression cells were similar and slower than those of WT MCS205 cells, which suggest that their differences in ATP release might not be responsible for their differential tumor growth rates (Figure 4F). More importantly, we demonstrated that Cdk2 deficiency increased the expression of ISGs than WT in response to MTX treatment (Figure 4G), as determined by qRT-PCR analyses. These upregulated ISGs (Interferon-Stimulated Genes) included the antiviral genes Parp14, a number of other type-1 interferon-induced genes (such as Gbp4, Oasl2 and Rsad2), as well as to the chemokine-encoding gene Cxcl9 and Ccl7, which code for CXCR3 ligands and CCR ligands respectively (Figure 4G). To further determine if the interferon signaling pathway is involved in MTX-mediated anti-tumor effects in Cdk2-/- tumors, we treated C57 mice carrying Cdk2-/- MCA205 tumors with antibodies that neutralize IFNAR1. We found that antibodies reduced the efficacy of chemotherapy against Cdk2-/- tumors and also eliminated the difference in the therapeutic response between WT and Cdk2-/- tumors (Figures 4H, I). Together, our above studies indicate that the increase of MTX-induced immunogenicity in tumors carrying Cdk2-/- cancer cells were dependent upon the elevated type-1 interferon response.
CDK2 kinase activity is involved in the enhanced chemotherapeutic response of Cdk2-/- tumors
If CDK2 inhibited the local immune response by virtue of its function as a kinase protein, reconstitution of Cdk2-/- cancer cells with WT but not the kinase inactive T160A mutant Cdk2 should reverse the phenotype. Accordingly, we found that the enhanced MTX anti-tumor responses of Cdk2-/- cancer cells over WT cells were abolish with WT Cdk2 but not Cdk2T160A reconstitution (Figures 5A–D). Validation of CDK2 expression was confirmed through Western blot analysis following re-introduction of WT or mutant Cdk2 into Cdk2-/- cells (Figure 5E). These results indicate that CDK2 kinase activity have essential role in the anti-tumor effects of MTX.
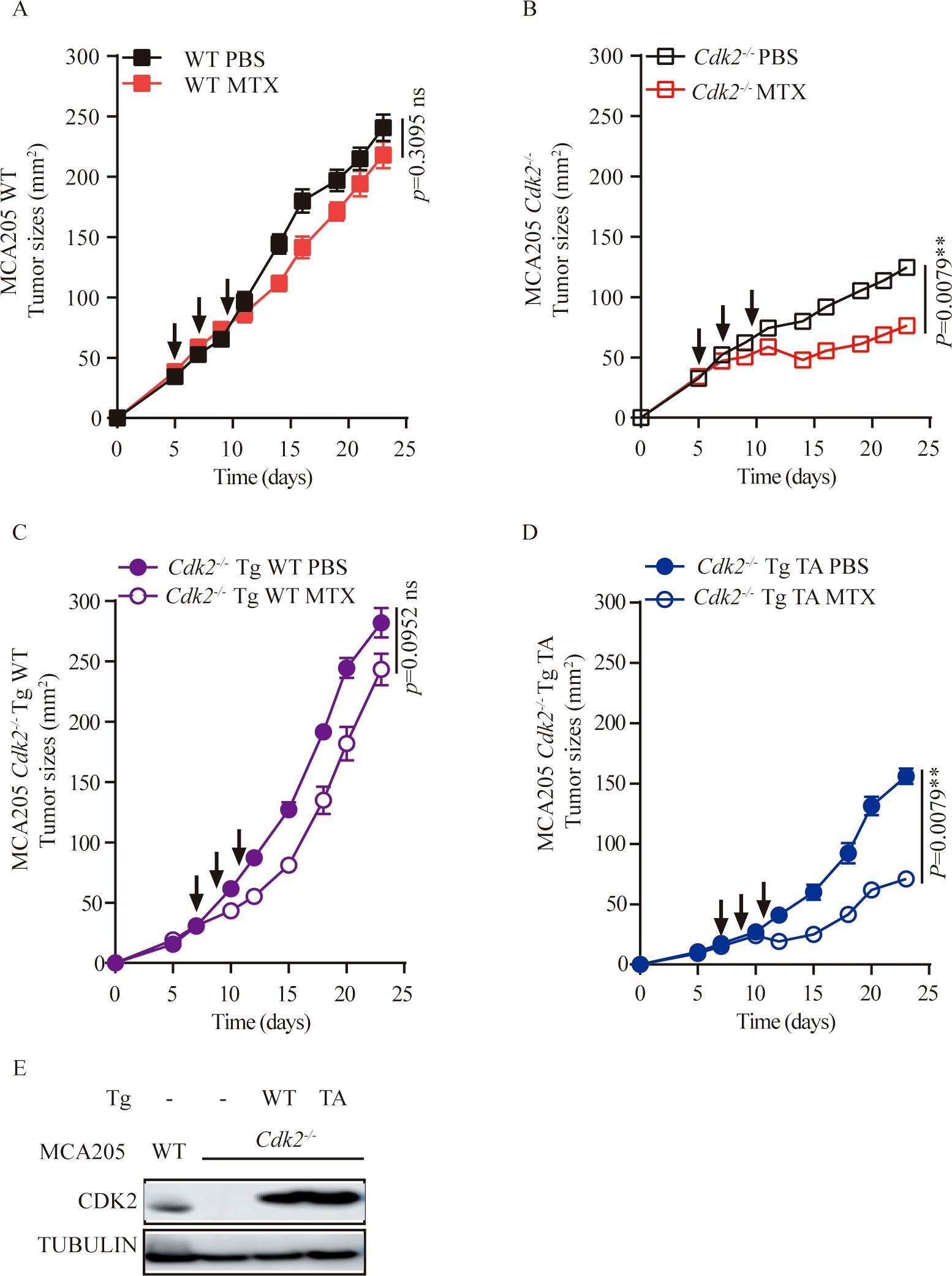
Figure 5. Re-introduction of WT, but not mutant Cdk2 abolishes the therapeutic advantage of Cdk2-/- tumors. (A-D) WT or mutated (T160A) forms of Cdk2 were stably transfected into Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells. The responsiveness of Cdk2-/- Tg WT (C) or Cdk2-/- Tg T160A (D) to chemotherapy was compared to that of WT (A) and Cdk2-/- (B) tumors, in immunocompetent mice. Arrows indicate the time when MTX was administrated. (E) Validation of CDK2 expression upon re-introduction of WT or mutant Cdk2 into Cdk2-/- cells. All groups included at least 5 mice and one representative experiment out of two is shown. **p<0.01, ns, not significant (unpaired Student t test).
Cdk2 deletion is sensitive to anti-PD-1 therapy
Anti-PD-1 antibodies are commonly used clinically as immune checkpoint inhibitors. Many studies indicated that ICD-based immunotherapy, that was chemotherapy drugs combined with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, significantly enhances anti-tumor efficacy (32–35). Also, CDKs inhibitor can enhance PD-L1 protein expression and programmed cell death protein 1 immune checkpoint blockade efficacy (24, 29, 36). First, we compared the expression of CDK2 in patients with advanced melanoma who responded to anti-PD-1 therapy and those who did not responded using publicly available dataset (GSE91061). We found that CDK2 expression was reduced in responding patients compared with non-responding patients (Figure 6A). At the same time, we analyzed that there was no statistical difference in the expression of CDK2 before and after anti-PD-1 treatment in the non-responsive patient group. However, there was a statistical difference in the expression of CDK2 before and after anti-PD-1 treatment in the responding patient group (Figure 6B). Therefore, we explored the effect of inhibiting CDK2 expression in combination with anti-PD-1 antibodies in vivo experiments in mouse models. We found that after tail vein injection of anti-PD-1 antibodies into mice bearing WT or Cdk2-/- cancer cells, the Cdk2-/- tumors plus anti-PD-1 Ab grow slower than Cdk2-/- PBS group (Figures 6C, D), but there was no statistical difference in WT tumors with or without anti-PD-1 Ab treatment (Figures 6C, D). These data demonstrate that suppressing CDK2 enhances the antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 antibody.
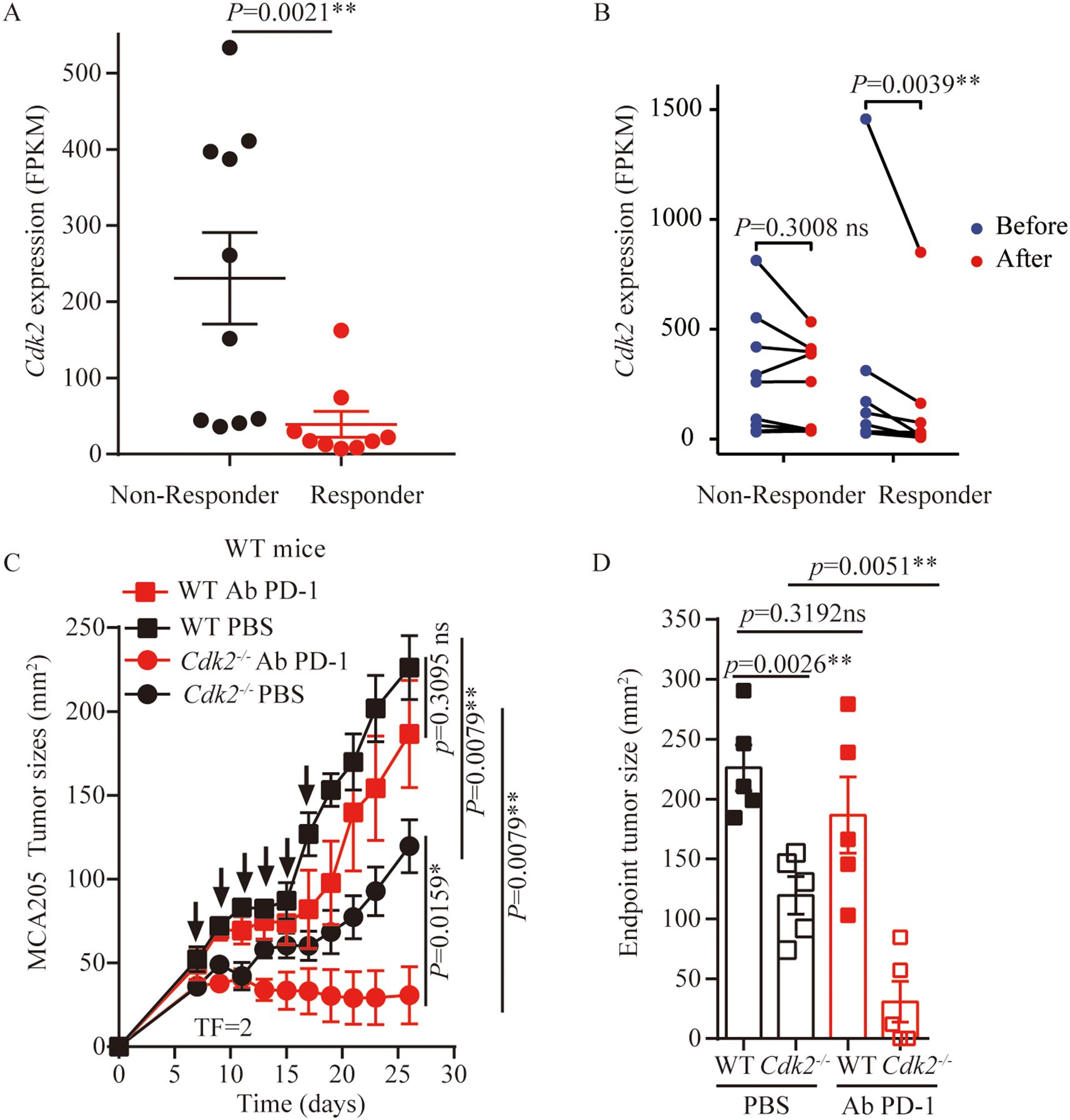
Figure 6. Cdk2-/- tumors combined with anti-PD-1 treatment exhibited better outcome than WT tumors. (A) Expression of CDK2 in patients with melanoma who benefited from nivolumab treatment and those who did not benefit, data from GSE91061. (B) CDK2 expression is reduced in people who respond to anti-PD-1 therapy, data from GSE91061. (C) WT tumors’ responsiveness to anti-PD-1 antibodies (i.v) was compared with Cdk2-/- tumors in immunocompetent mice, arrows marking anti-PD-1 antibody administration. (D) Tumor sizes at 26 days were compared among anti-PD-1 antibodies treated cancers with the indicated genotype. Each group included at least 5 mice. For Cdk2 gene expression, the Mann-Whitney test and Wilcoxon rank test were used. Tumor growth comparisons employed the unpaired Mann-Whitney U test. Endpoint tumor sizes differences were analyzed using the unpaired Student’s t-test. Response categories included CR/PR/SD, with non-response as PD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns, not significant.
Conclusion
Previous studies provided compelling evidence that the CDK inhibitors can synergize with anthracyclines to mediate antitumor effects in preclinical models (28–30), thereby highlighting a potential mechanism for combinatorial therapy. According to the result that the enhanced chemotherapeutic response of Cdk2-/- MCA205 cells was not observed in T cell-deficient nu/nu mice, which indicates that, in the context of MTX, inhibition of CDK2 enhances anti-tumor immune responses, which may dependent on host T lymphocytes. Additionally, there is increased infiltration of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. In vitro experiments reveal that CDK2 inhibition promotes immunogenic cell death. Type I interferon response plays a crucial role in the effect of CDK2 inhibition combined with MTX treatment, and the anti-tumor effect of MTX plus Cdk2 deletion is related to its kinase activity. Furthermore, CDK2 inhibition improves the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy.
Although literature reported that CDK inhibitors can promote immunogenic cell death, whether Cdk2 deficiency amplified the induction of ICD by anthracyclines remain to be elucidated. However, our findings suggest that Cdk2-/- tumor cells can enhance ICD triggered by anthracyclines. Our observations indicate that anthracycline-based chemotherapy is more efficacious against tumors when combined with Cdk2 deletion, suggesting a synergistic interaction between CDK2 inhibition and anthracyclines. This synergistic effect was observed in immunocompetent mice but not in nu/nu mice. These results emphasize the role of the immune system in mediating the therapeutic interaction between CDK2 inhibition and anthracycline chemotherapy. We also observed that there was more immune cell infiltration in tumors treated with MTX than without MTX, especially in Cdk2-/- tumors. The enhanced infiltration of dendritic cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes in Cdk2-/- tumors post-chemotherapy indicates a robust immune response, which may be attributed to the decreased growth observed in these tumors. This decreased tumor growth may reflect the heightened activity of immune effectors in the tumor microenvironment, potentially priming the tumors for a more effective immune attack. Our data suggests that Cdk2 deficiency does not directly augment the cytotoxic action of anthracyclines, but enhances the secretion and expression of molecules related with immunogenic cell death, including ATP, HMGB1, CRT, and the production of immunostimulatory CXCR3 ligands like Cxcl10, implying that the observed synergy is immune-mediated rather than a consequence of increased direct cytotoxicity. This finding is consistent with literatures suggesting that the immune system plays a critical role in the efficacy of chemotherapy (40–43).
Although an increased expression of ICD-related molecules is observed in vitro, we observe that the tumor growth of Cdk2-/- cells with increased HMGB1 release in Tlr4-/- mice remained similar to that in C57 mice. The tumor growth of Cdk2-/- tumor cells overexpressing CD39 is comparable to that of Cdk2-/- tumor cells. However, the application of interferon receptor-blocking antibodies revers this effect, the loss of the favorable interaction between CDK2 inhibition and anthracycline-based chemotherapy upon neutralization of the common type-1 interferon receptor, establishes a cause-effect relationship between the exacerbated type-1 interferon-related response and the efficacy of the combined treatment. These results suggest that the type-I interferon response play a crucial anti-tumor role when CDK2 inhibition is combined with chemotherapy. By subcutaneously implanting restoration of Cdk2-/- cancer cells with WT Cdk2 or Cdk2T160A into C57 mice, we observed that the combination of Cdk2T160A cells with MTX remained more effective than the replenished Cdk2-/- cancer cells. These results suggest that CDK2 kinase activity is involved in the improved chemotherapeutic response of Cdk2-/- tumors. Additionally, we observed that mice implanted with Cdk2-/- cells exhibited a better response to anti-PD-1 combination therapy than those implanted with WT cells. Analysis of the dataset also revealed that patients with a good response to anti-PD-1 therapy showed reduced CDK2 expression. These phenomena may be attributed to heightened sensitivity to immunogenic cell death, increased ISG expression and PD-L1 expression in tumor cells after CDK2 inhibition.
In conclusion, our study reveals that CDK2 inhibition enhances the antitumor effects and induces ICD with anthracycline-based chemotherapy. The findings suggest that CDK2 inhibition, in combination with anthracyclines or anti-PD-1 therapy, may offer a therapeutic strategy in cancer treatment. In recent years, with the advancement of molecular technology, PROTAC-targeted protein degradation technology has gained widespread attention due to its high specificity (44, 45). There have also been numerous reports on PROTAC degraders targeting CDK2 (46–48). Further research is warranted to explore the detailed molecular mechanisms and to evaluate the clinical applicability of this combinatorial approach, particularly in tumors that are ‘addicted’ to CDK2, where the cell-autonomous and immunological effects of CDK2 inhibition may complement each other advantageously.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Guizhou Laboratory Animal Engineering Technology Center & Laboratory Animal Center of Guizhou Medical University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YC: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. WL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. QC: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. CP: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. YT: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Resources, Writing – review & editing. GC: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82303191 to YC, 32160168 to L. Shu), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2024MD763955 to YC), Young Talents Plan of Guizhou Medical University (22QNRC20 and XBHJ(2023)016 to YC), Doctor Start-up Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (gyfybsky-2023-16 to YC)), and in part by the Guizhou Province’s Science and Technology Major Project (QianCXTD(2021)002 and GCC(2023)034 to L. Shu), the Guizhou Medical University Key Laboratory Project ((2024)004 to L. Shu), Grant from Key Lab for Chronic Disease Biomarkers of Guizhou Medical University (No.2024fy004 to YC) and Key Laboratory for Cancer Prevention and treatment of Guizhou Province (QKHPT(2025)031 to YC).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the help of animal facility and Research Platform at Center for Tissue Engineering and Stem Cell Research. We also appreciate the help of animal facility at Guizhou Laboratory Animal Engineering Technology Center & Laboratory Animal Center of Guizhou Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1570040/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Ayers M, Lunceford J, Nebozhyn M, Murphy E, Loboda A, Kaufman DR, et al. IFN-γ-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:2930–40. doi: 10.1172/JCI91190
2. Schumacher TN and Schreiber RD. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science. (2015) 348:69–74. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4971
3. Hossain DMS, Javaid S, Cai M, Zhang C, Sawant A, Hinton M, et al. Dinaciclib induces immunogenic cell death and enhances anti-PD1-mediated tumor suppression. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:644–54. doi: 10.1172/JCI94586
4. Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku IP, Taylor EJ, Robert L, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature. (2014) 515:568–71. doi: 10.1038/nature13954
5. Hu J, He J, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Fang K, Dong Y, et al. Ultrasound combined with nanobubbles promotes systemic anticancer immunity and augments anti-PD1 efficacy. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e003408. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003408
6. Fucikova J, Kralikova P, Fialova A, Brtnicky T, Rob L, Bartunkova J, et al. Human tumor cells killed by anthracyclines induce a tumor-specific immune response. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:4821–33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0950
7. Yang H, Yamazaki T, Pietrocola F, Zhou H, Zitvogel L, Ma Y, et al. STAT3 inhibition enhances the therapeutic efficacy of immunogenic chemotherapy by stimulating type 1 interferon production by cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:3812–22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1122
8. Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, and Zitvogel L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol. (2013) 31:51–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-100008
9. Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, and Vandenabeele P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2012) 12:860–75. doi: 10.1038/nrc3380
10. Martins I, Wang Y, Michaud M, Ma Y, Sukkurwala AQ, Shen S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ATP secretion during immunogenic cell death. Cell Death Differ. (2014) 21:79–91. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.75
11. Panaretakis T, Joza N, Modjtahedi N, Tesniere A, Vitale I, Durchschlag M, et al. The co-translocation of ERp57 and calreticulin determines the immunogenicity of cell death. Cell Death Differ. (2008) 15:1499–509. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.67
12. Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, et al. Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med. (2007) 13:54–61. doi: 10.1038/nm1523
13. Yamazaki T, Hannani D, Poirier-Colame V, Ladoire S, Locher C, Sistigu A, et al. Defective immunogenic cell death of HMGB1-deficient tumors: compensatory therapy with TLR4 agonists. Cell Death Differ. (2014) 21:69–78. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.72
14. Sistigu A, Yamazaki T, Vacchelli E, Chaba K, Enot DP, Adam J, et al. Cancer cell-autonomous contribution of type I interferon signaling to the efficacy of chemotherapy. Nat Med. (2014) 20:1301–9. doi: 10.1038/nm.3708
15. Donnelly OG, Errington-Mais F, Steele L, Hadac E, Jennings V, Scott K, et al. Measles virus causes immunogenic cell death in human melanoma. Gene Ther. (2013) 20:7–15. doi: 10.1038/gt.2011.205
16. Tesniere A, Schlemmer F, Boige V, Kepp O, Martins I, Ghiringhelli F, et al. Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin. Oncogene. (2010) 29:482–91. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.356
17. Casares N, Pequignot MO, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Roux S, Chaput N, et al. Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J Exp Med. (2005) 202:1691–701. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050915
18. Malumbres M and Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. (2009) 9:153–66. doi: 10.1038/nrc2602
19. Łukasik P, Załuski M, and Gutowska I. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) and their role in diseases development-review. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:2935. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062935
20. Zabihi M, Lotfi R, Yousefi AM, and Bashash D. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: from biology to tumorigenesis and therapeutic opportunities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:1585–606. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04135-6
21. Tadesse S, Caldon EC, Tilley W, and Wang S. Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitors in cancer therapy: an update. J Medicinal Chem. (2018) 62:4233–51. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01469
22. MacLachlan TK, Sang N, and Giordano A. Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and cdk inhibitors: implications in cell cycle control and cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. (1995) 5:127–56. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukarGeneExpr.v5.i2.20
23. Chen Y, Cai Q, Pan C, Liu W, Li L, Liu J, et al. CDK2 inhibition enhances antitumor immunity by increasing IFN response to endogenous retroviruses. Cancer Immunol Res. (2022) 10:525–39. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-21-0806
24. Goel S, DeCristo MJ, Watt AC, BrinJones H, Sceneay J, Li BB, et al. CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity. Nature. (2017) 548:471–5. doi: 10.1038/nature23465
25. Zhang H, Christensen CL, Dries R, Oser MG, Deng J, Diskin B, et al. CDK7 inhibition potentiates genome instability triggering anti-tumor immunity in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. (2020) 37:37–54.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.11.003
26. Zhang J, Bu X, Wang H, Zhu Y, Geng Y, Nihira NT, et al. Cyclin D-CDK4 kinase destabilizes PD-L1 via cullin 3-SPOP to control cancer immune surveillance. Nature. (2018) 553:91–5. doi: 10.1038/nature25015
27. Fan H, Liu W, Zeng Y, Zhou Y, Gao M, Yang L, et al. DNA damage induced by CDK4 and CDK6 blockade triggers anti-tumor immune responses through cGAS-STING pathway. Commun Biol. (2023) 6:1041. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05412-x
28. Luke JJ, D'Adamo DR, Dickson MA, Keohan ML, Carvajal RD, Maki RG, et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol potentiates doxorubicin efficacy in advanced sarcomas: preclinical investigations and results of a phase I dose-escalation clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 18:2638–47. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3203
29. Wu J, Wang W, Gao L, Shao X, and Wang X. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors enhance programmed cell death protein 1 immune checkpoint blockade efficacy in triple-negative breast cancer by affecting the immune microenvironment. Cancer. (2024) 130:1449–63. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v130.S8
30. Kumarasamy V, Ruiz A, Nambiar R, Witkiewicz AK, and Knudsen ES. Chemotherapy impacts on the cellular response to CDK4/6 inhibition: distinct mechanisms of interaction and efficacy in models of pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. (2020) 39:1831–45. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1102-1
31. Jian Y, Huang X, Fang L, Wang M, Liu Q, Xu H, et al. Actin-like protein 6A/MYC/CDK2 axis confers high proliferative activity in triple-negative breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40:56. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01856-3
32. Chen Q, Zhou S, Ding Y, Chen D, Dahiru NS, Tang H, et al. A bio-responsive, cargo-catchable gel for postsurgical tumor treatment via ICD-based immunotherapy. J Control Release. (2022) 346:212–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.015
33. Moon Y, Shim MK, Choi J, Yang S, Kim J, Yun WS, et al. Anti-PD-L1 peptide-conjugated prodrug nanoparticles for targeted cancer immunotherapy combining PD-L1 blockade with immunogenic cell death. Theranostics. (2022) 12:1999–2014. doi: 10.7150/thno.69119
34. Shi H. Oxaliplatin and checkpoint inhibitor induces immunogenic cells death and promotes therapeutic efficacy in the model of murine triple positive breast cancer. Stud Health Technol Inform. (2023) 308:329–40. doi: 10.3233/SHTI230857
35. Zhou M, Luo C, Zhou Z, Li L, and Huang Y. Improving anti-PD-L1 therapy in triple negative breast cancer by polymer-enhanced immunogenic cell death and CXCR4 blockade. J Control Release. (2021) 334:248–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.04.029
36. Cheung A, Chenoweth AM, Quist J, Sow HS, Malaktou C, Ferro R, et al. CDK inhibition primes for anti-PD-L1 treatment in triple-negative breast cancer models. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:3361. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143361
37. Huang J, Chen P, Liu K, Liu J, Zhou B, Wu R, et al. CDK1/2/5 inhibition overcomes IFNG-mediated adaptive immune resistance in pancreatic cancer. Gut. (2021) 70:890–9. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320441
38. Saqub H, Proetsch-Gugerbauer H, Bezrookove V, Nosrati M, Vaquero EM, de Semir D, et al. Dinaciclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, suppresses cholangiocarcinoma growth by targeting CDK2/5/9. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:18489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75578-5
39. Bausart M, Rodella G, Dumont M, Ucakar B, Vanvarenberg K, Malfanti A, et al. Combination of local immunogenic cell death-inducing chemotherapy and DNA vaccine increases the survival of glioblastoma-bearing mice. Nanomedicine. (2023) 50:102681. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2023.102681
40. Park YH, Lal S, Lee JE, Choi YL, Wen J, Ram S, et al. Chemotherapy induces dynamic immune responses in breast cancers that impact treatment outcome. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:6175. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19933-0
41. Sharma A, Jasrotia S, and Kumar A. Effects of chemotherapy on the immune system: implications for cancer treatment and patient outcomes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2024) 397:2551–66. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02781-2
42. Braun DP and Harris JE. Modulation of the immune response by chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. (1981) 14:89–122. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90012-7
43. Merlano MC, Denaro N, Galizia D, Ruatta F, Occelli M, Minei S, et al. How chemotherapy affects the tumor immune microenvironment: A narrative review. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:1822. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081822
44. Sakamoto KM, Kim KB, Kumagai A, Mercurio F, Crews CM, and Deshaies RJ. Protacs: chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2001) 98:8554–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.141230798
45. Guedeney N, Cornu M, Schwalen F, Kieffer C, and Voisin-Chiret AS. PROTAC technology: A new drug design for chemical biology with many challenges in drug discovery. Drug Discovery Today. (2023) 28:103395. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.103395
46. Wang L, Shao X, Zhong T, Wu Y, Xu A, Sun X, et al. Discovery of a first-in-class CDK2 selective degrader for AML differentiation therapy. Nat Chem Biol. (2021) 17:567–75. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00742-5
47. Hati S, Zallocchi M, Hazlitt R, Li Y, Vijayakumar S, Min J, et al. AZD5438-PROTAC: A selective CDK2 degrader that protects against cisplatin- and noise-induced hearing loss. Eur J Med Chem. (2021) 226:113849. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113849
Keywords: immunogenic cell death, CDK2, anti-PD-1 therapy, type-1 interferon response, MTX
Citation: Chen Y, Liu W, Cai Q, Pan C, Yin Z, Tang Y, He Z, Cheng G and Shu L (2025) CDK2 inhibition sensitizes anthracycline-induced immunogenic cell death and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy. Front. Immunol. 16:1570040. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1570040
Received: 02 February 2025; Accepted: 05 May 2025;
Published: 10 June 2025.
Edited by:
Huanling Lai, Guangzhou National Laboratory, ChinaReviewed by:
Zebo Jiang, Zhuhai Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese & Western Medicine, ChinaFabio Scirocchi, Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital (IRCCS), Italy
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Liu, Cai, Pan, Yin, Tang, He, Cheng and Shu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liping Shu, Z3lzbHA0NTZAZ21jLmVkdS5jbg==; Genhong Cheng, Z2NoZW5nQG1lZG5ldC51Y2xhLmVkdQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡These authors share senior authorship
 Yu Chen
Yu Chen Wancheng Liu
Wancheng Liu Qiaomei Cai3†
Qiaomei Cai3† Chaohu Pan
Chaohu Pan Genhong Cheng
Genhong Cheng