- 1Department of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Chengdu First People’s Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of General Surgery, The Third Hospital of Mianyang Sichuan Mental Health Center, Mianyang, Sichuan, China
- 4West China Center of Excellence for Pancreatitis, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Background: Immune and inflammatory disorders are part of the complex pathophysiological processes that exacerbate severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) and subsequent infection. Thymosin alpha 1 (Tα1) is an important immunomodulatory agent in clinical practice, but there is a lack evidence to prove its effectiveness in improving the condition of SAP patients. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy in meta-analysis.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) up to February 1, 2025. Randomized controlled studies comparing the efficacy of Tα1 as intervention measure with non-Tα1 in improving immune regulation for patients with SAP were included. Review Manager 5.3 was used to assess endpoints in the meta-analysis.
Results: Five randomized controlled trials comprising 706 patients with SAP were included. The results indicated that Tα1 could increase the percentages of CD4+ cells (MD=4.53, 95%CI [3.02, 6.04], P<0.00001) and improve the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (MD=0.42, 95%CI [0.26, 0.58], P<0.00001) in SAP patients. There was no statistically significant decrease in CD8+ cells. For inflammation, lower-dose Tα1 could significantly reduce C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (mg/L) (MD=-30.12, 95%CI [-35.75, -24.49], P<0.00001), while higher-dose Tα1 showed no statistically significant difference (MD=-3.83, 95%CI [-12.14, 4.49], P=0.37). In terms of infection, the immunomodulatory therapy of Tα1 obviously reduced the overall incidence of extrapancreatic infections in SAP patients (RR=0.56, 95%CI [0.40, 0.78], P=0.0005), especially for blood (RR=0.60, 95%CI [0.38, 0.94], P=0.03) and abdominal (RR=0.38, 95%CI [0.19, 0.78], P<0.0001), while the reduction in lung infections was not statistically significant. Regarding hospital stay (days), Tα1 did not significantly reduce the time spent (MD=-4.22, 95%CI [-11.53, 3.10], P=0.26). However, Tα1 reduced the APACHE II score (MD=-1.52, 95%CI [-2.22, -0.83], P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Tα1 can regulate the balance of immune cells and alleviate immune suppression in SAP patients, including increasing CD4+ T cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratios. Tα1 may exert anti-inflammatory and extrapancreatic infection-preventive effects on SAP patients and improve their condition or prognosis. More researches are needed to validate the results.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero, identifier CRD42024570517.
Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is mainly caused by premature activation of pancreatic enzymes and self-digestion due to factors such as gallstones, hypertriglyceridemia, and alcohol (1–5). The process triggers local pancreatic tissue or systemic inflammatory responses, often manifested as symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and even shock (6). The incidence rate of AP was reported to increase all over the world, with an increase of about 3.07% from 1956 to 2016 (7). About 20% to 30% of the patients are severe acute pancreatitis (SAP), with a mortality rate of over 30% (8, 9). Although the proportion of SAP is lower than that of mild or moderate cases, it has the characteristics of complex disease course, poor prognosis, and high mortality rate.
SAP is often accompanied by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), persistent organ failure (POF), and severe complications. SIRS is a significant predictor of poor prognosis in SAP, with the majority of deaths due to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). Multi-center international studies have shown that 58% of patients with AP exhibit SIRS, 11% progress to POF, and 2.5% of patients ultimately die from the disease (10, 11). Both early onset or persistent SIRS, and a highest SIRS score of 3 or higher, are independently associated with an increased risk of POF. A retrospective analysis (12) in the United States revealed that the overall prevalence of organ failure in SAP patients was as high as 52%, with those suffering from multiple organ failure experiencing longer hospital stays and a higher mortality risk compared to those without organ failure. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis is characterized by significant necrosis of pancreatic parenchyma and peripancreatic tissue. It may initially manifest as a SIRS similar to SAP, but more often leads to infection. It was reported that approximately 30%-40% of patients with necrotizing pancreatitis were at risk of developing infected pancreatic necrosis, with infected patients facing more than double the mortality risk of those without infection (13, 14). Consequently, curtailing the incidence of SIRS and infectious complications is a crucial strategy for enhancing the prognosis of SAP patients.
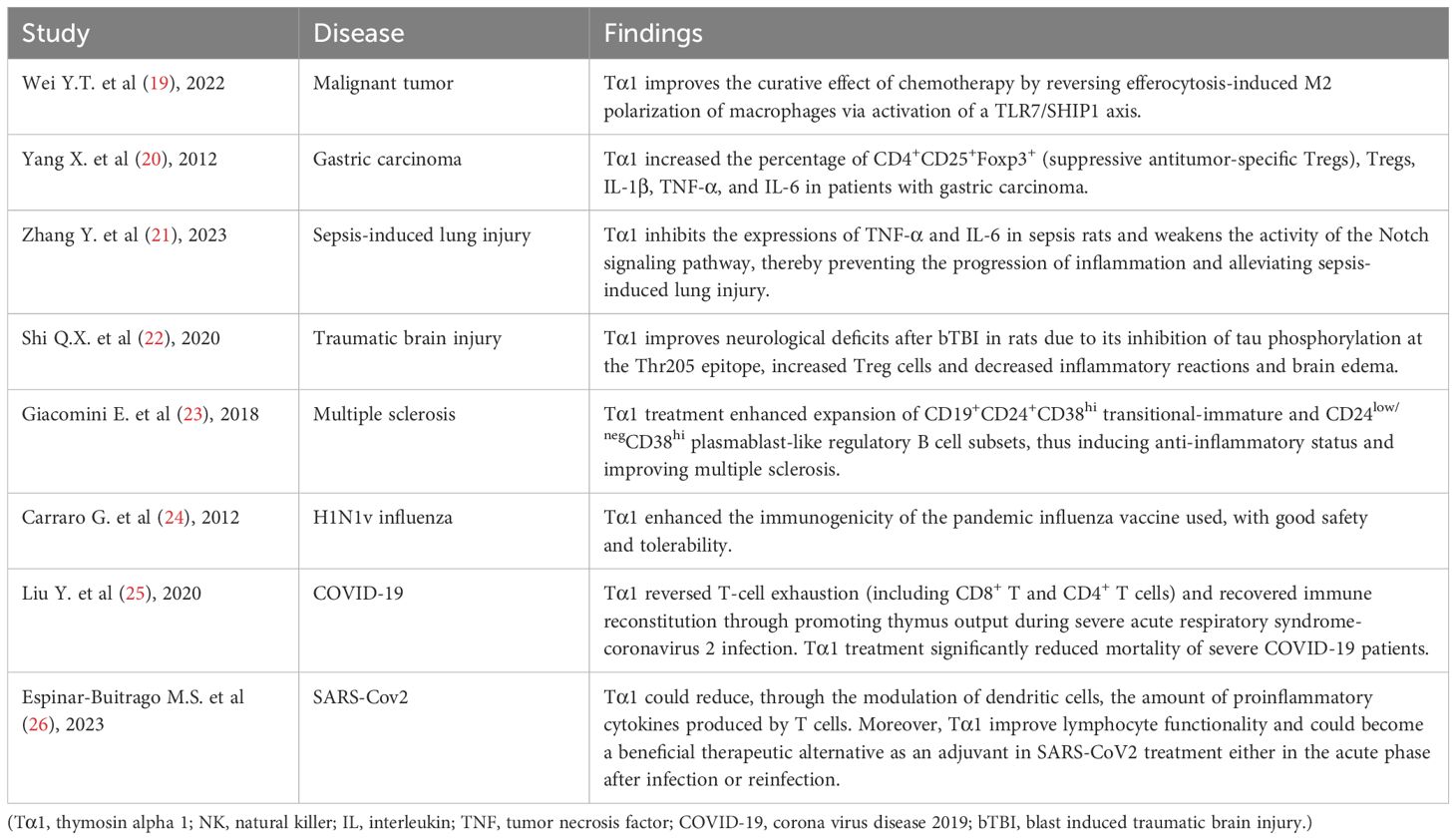
Imbalance in the regulation of immune inflammatory response in the body, whether it is pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory response dominant, may lead to the deterioration or even death of SAP disease (15). Immunomodulatory therapy is considered an important means in improving the prognosis of SAP patients, such as targeting immune cells and using mesenchymal stem cells for regulation (16). It has been found that decrease in CD4+ T lymphocyte levels and CD4+/CD8+ T lymphocyte ratio indicates a poor prognosis (17). Biological research has demonstrated that thymosin alpha 1 (Tα1) can stimulate the proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of T cells in the thymus (18). This process may elevate CD4+ T lymphocyte levels and bolster the CD4+/CD8+ ratio, thereby enhancing immune function. Previous clinical studies (19–26) have found that Tα1 has a beneficial immunomodulatory effect in patients with a variety of diseases, including malignant tumors, sepsis-induced lung injury, and COVID-19 (Table 1). However, there is insufficient evidence to suggest that it has beneficial therapeutic effect in patients with SAP. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis of Tα1 for immunomodulatory therapy in SAP patients.
Materials and methods
Retrieval strategy
To ensure the comprehensiveness and timeliness of our research, our literature search work covered PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), from the starting point of each database until February 1, 2025. The following were the English search terms for this study: (‘severe acute pancreatitis’ OR ‘acute pancreatitis’ OR ‘severe pancreatitis’ OR ‘SAP’ OR ‘pancreatic necrosis’ OR ‘pancreatic infection’) AND (‘thymosin alpha 1’ OR ‘thymosin α1’ OR ‘Talpha1’ OR ‘Tα1’ OR ‘TA1’ OR ‘thymus hormones’). The specific retrieval strategy for each database can be found in Supplementary Appendix 1. No language or country restrictions were imposed during the search process. Related publications comparing Tα1 with non-Tα1 treatment (including placebo or standard treatment) to improve inflammation or infection in patients with SAP were considered. Some publications with reliable data from other sources such as grey literature, unpublished studies, or ongoing clinical trials would also be comprehensively considered. In this study, Tα1 and non-Tα1 treatment were used as intervention and control measures, respectively. Changes in percentages of lymphocyte (including CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+), C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and number of infections (including blood, lungs, and abdominal cavity) after treatment were primary outcomes. The length of hospital stay and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score were secondary outcomes. We performed the meta-analysis based on Preferred Reporting Item for Systematic Reviews and Meta Analyses (PRISMA) statement to ensure the high quality of our work (27, 28). This study has been registered in the International Prospective Systematic Reviews Registry (PROSPERO) with registration number CRD42024570517.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Two researchers reviewed potential and relevant manuscripts that had been published. Studies that met the following selection criteria would be included in the meta-analysis: (1) RCTs evaluating the immunomodulatory therapy of Tα1. (2) The research subjects were SAP patients without gender, age, race, or regional restrictions. (3) The research content included evaluating the efficacy comparison of Tα1 and non-Tα1 in improving inflammation or infection prevention in SAP patients. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria, such as without Tα1 intervention or patients with pancreatitis, would be excluded. (2) Patients with mild acute pancreatitis (MAP) or moderately severe acute pancreatitis (MSAP) would be excluded based on the severity of their condition. In addition, pancreatic cancer patients would also be excluded. (3) Duplicate publications, review articles, editorials, case reports, and animal experiments were excluded. The process of including or excluding published studies was independently completed by two researchers. Any disagreements would be resolved through mutual discussion or consultation with a third author to reach a consensus.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Thorough examination of the selected studies, two reviewers meticulously extracted the necessary data using a standardized table format. The essential data points included were as follows: the lead author’s name, publication year, sample size, treatment duration, intervention types and dosages, lymphocyte percentages around one week and final percentages (including specifics for CD4+, CD8+, and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio), CRP levels around one week and final levels, the count of patients with infections (encompassing blood, lung, and abdominal infections), length of hospital stay, and the APACHE II score. Herein, lymphocyte percentages, CRP levels, and number of infections were examined as the main outcomes. The length of hospital stay and APACHE II score were the additional outcomes. Any ambiguous data that needs to be supplemented or clarified was provided with more details by contacting the corresponding author. For quality assessment of the studies, Jadad scale including the generation of random sequences, randomization concealment, blinding, withdrawal and dropout was used to score the quality of each study. 1–3 points were considered low quality, and 4–7 points were considered high quality.
Data analysis and publication bias
We conducted statistical analysis on the data using Review Manager version 5.3. We utilized Risk Ratio (RR) for the analysis of dichotomous data and Weighted Mean Difference (WMD) or Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) for continuous data, with a 95% confidence interval (CI) for both. Cochrane’s Q-test and the Inconsistency index (I²) were employed to assess statistical heterogeneity among the included studies. Heterogeneity was considered low if the I² value was less than 50% (I²<50%) and the p-value was greater than 0.1, in which case a fixed-effects model was applied for the pooled analysis. If moderate heterogeneity (75%≥I²≥50%) was detected, a random-effects model was selected. Furthermore, if high heterogeneity (I²>75%) was indicated, we would conduct subgroup analysis or sensitivity analysis to reveal the potential sources of this variability. If clinical and methodological homogeneity was maintained despite statistical heterogeneity, a random-effects model was utilized to offer a more cautious interpretation of intervention effects. All P-values were two-tailed, and a P-value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. Moreover, we selected CD4+ percentages and CRP levels to examine publication bias using Egger’s test of Stata 14.0. And we used Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) 2.0 for qualitative bias assessment (29).
Results
Literature search and screening
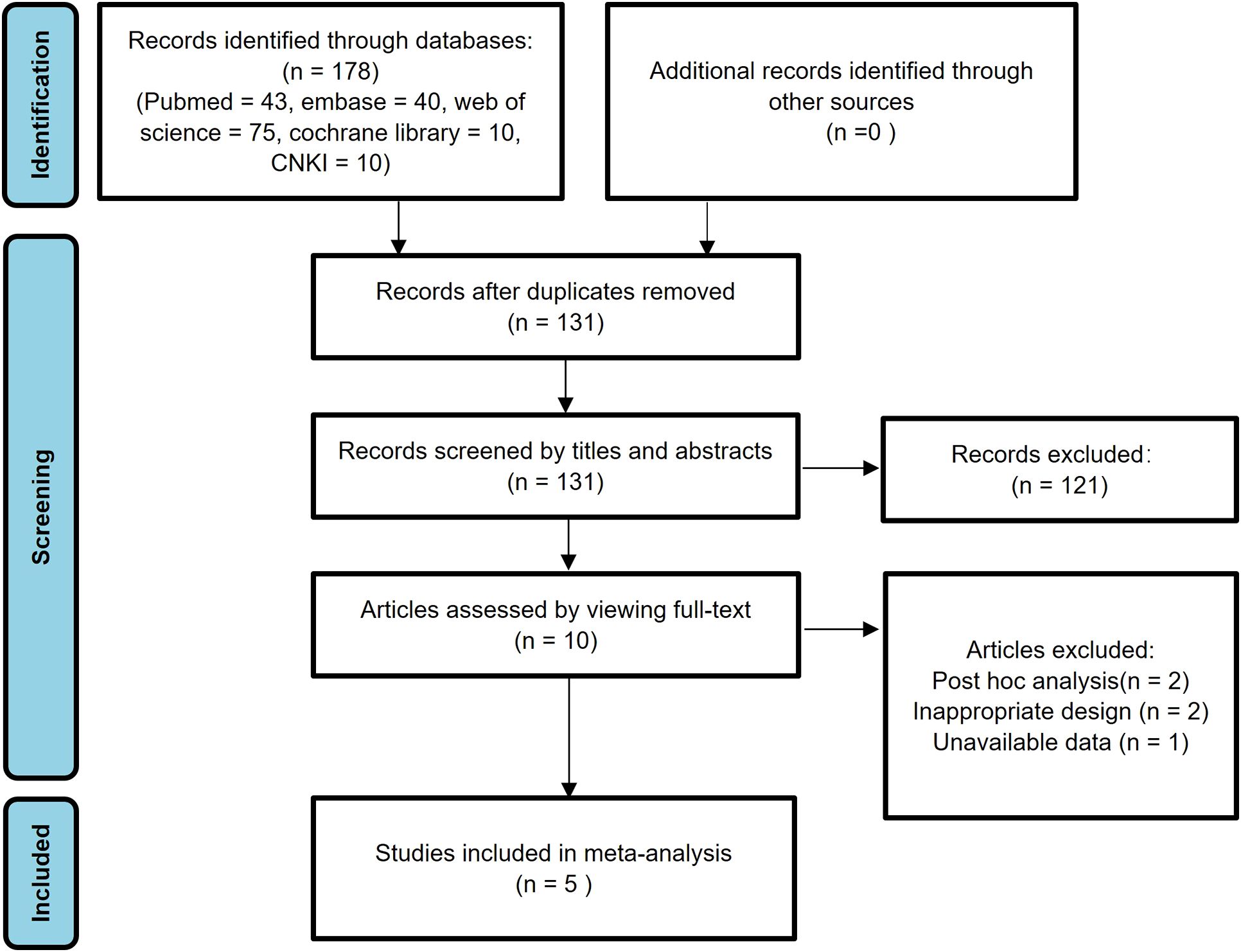
In the initial search, a total of 178 studies were identified. Subsequently, 47 studies were excluded due to duplicate publications. After reviewing the titles and abstracts, an additional 121 studies were excluded due to irrelevant research content, animal experiments, reviews, comments, and case reports. After carefully examining the full texts of the remaining 10 studies, 2 post hoc analysis studies and 2 poorly designed studies were further excluded. Furthermore, one study was excluded due to the unavailability of data. Ultimately, the meta-analysis encompassed 5 eligible published studies (30–34). Figure 1 provides a visual representation of the research selection process, detailing each stage of study identification, screening, and exclusion.
Literature characteristics and quality assessment
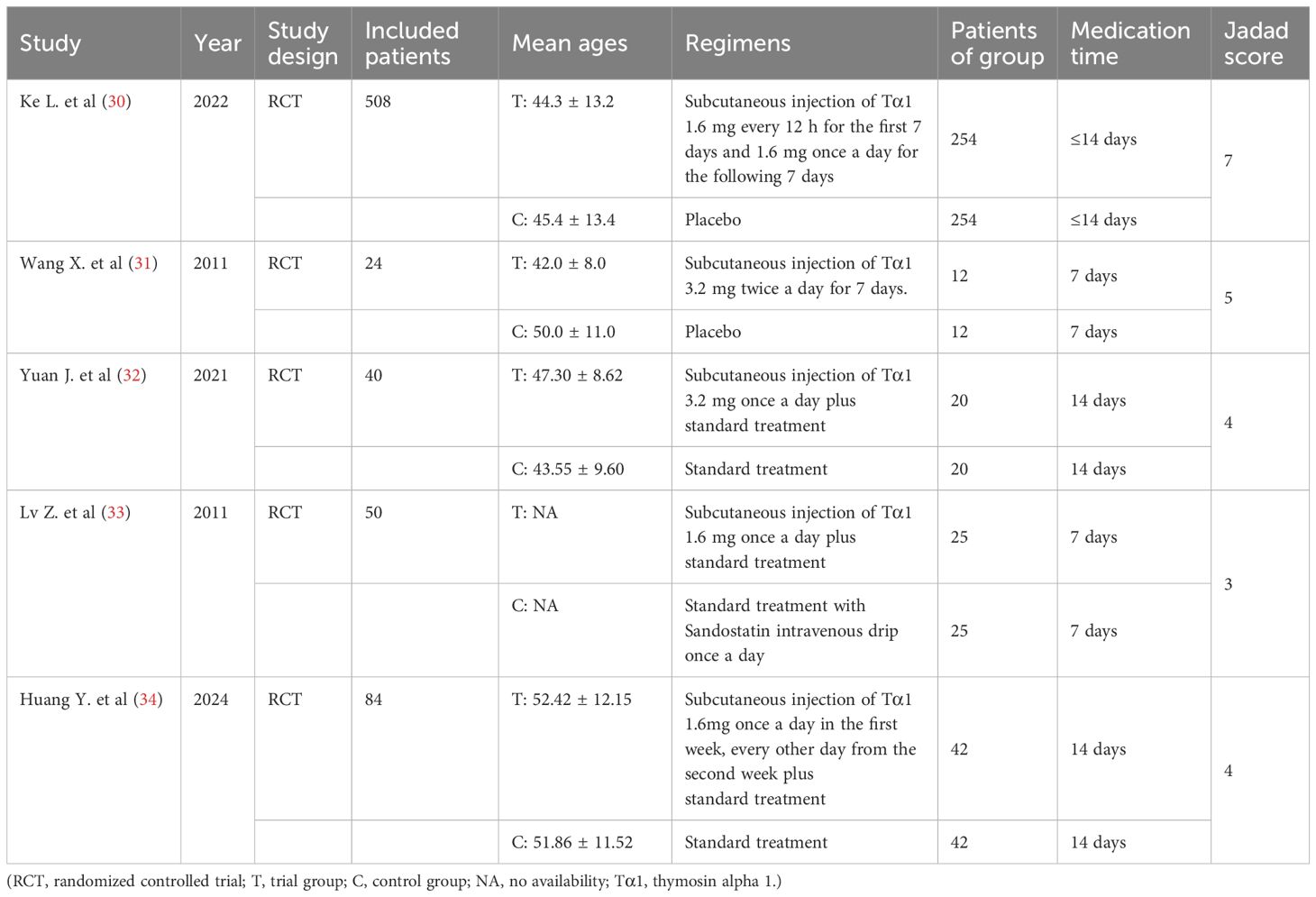
The analysis comprised 5 studies (30–34), encompassing a total of 706 patients with SAP. All of the five studies were RCTs, with four of them being high-quality articles (30–32, 34) and one assessed as low-quality (33). In addition, two of them were from English databases (30, 31), and three were published in Chinese (32–34). Their Chinese names could be found in Supplementary Table S1. These manuscripts were primarily published as full-text articles from 2011 to 2024. In the intervention group, Tα1 was administered via a separate subcutaneous injection as the main measure, whereas the control group received either a placebo or standard treatment alone. All participants in the studies were classified as severe patients. There were no significant differences in the baseline data between the intervention and control groups (including age, gender, partial etiology and lab values), ensuring a fair comparison for the meta-analysis. We extracted the foundational data from the included articles and conducted a thorough quality assessment using Jadad score, as detailed in Table 2.
Lymphocyte percentages
Four studies (31–34) reported the percentages of CD4+ and three studies (31–33) reported the percentages of CD8+ around one week. The average percentages of CD4+ in the intervention group and the control group were approximately 46.9% and 36.7%, while the percentages for CD8+ were 23.5% and 25.0%, respectively. High heterogeneity was determined using Cochrane’s Q-test for two groups of CD4+ cells (degrees of freedom [df]=3, I2 = 98%, P<0.00001), while CD8+ cells showed low heterogeneity (df=2, I2 = 0%, P=0.54). However, when sensitivity analysis was conducted on studies reporting CD4+ cells, heterogeneity was significantly reduced after excluding one study (33) (df=2, I2 = 0%, P=0.41). Subsequently, we chose fixed-effects analysis for both CD4+ and CD8+ cells. The results showed that compared with the control group, the percentages of CD4+ in the treatment group increased significantly and had statistical differences (MD=4.53, 95%CI [3.02, 6.04], P<0.00001) (Figure 2), while CD8+ cells decreased slightly and did not reach statistical differences (MD=-1.92, 95%CI [-4.36, 0.51], P=0.12) (Figure 2). Even if we excluded the same study as CD4+ cells again, there was still no statistically significant difference in the trend of CD8+ results (MD=-0.15, 95%CI [-4.26, 3.95], P=0.94). Therefore, we chose to keep it in our analysis.
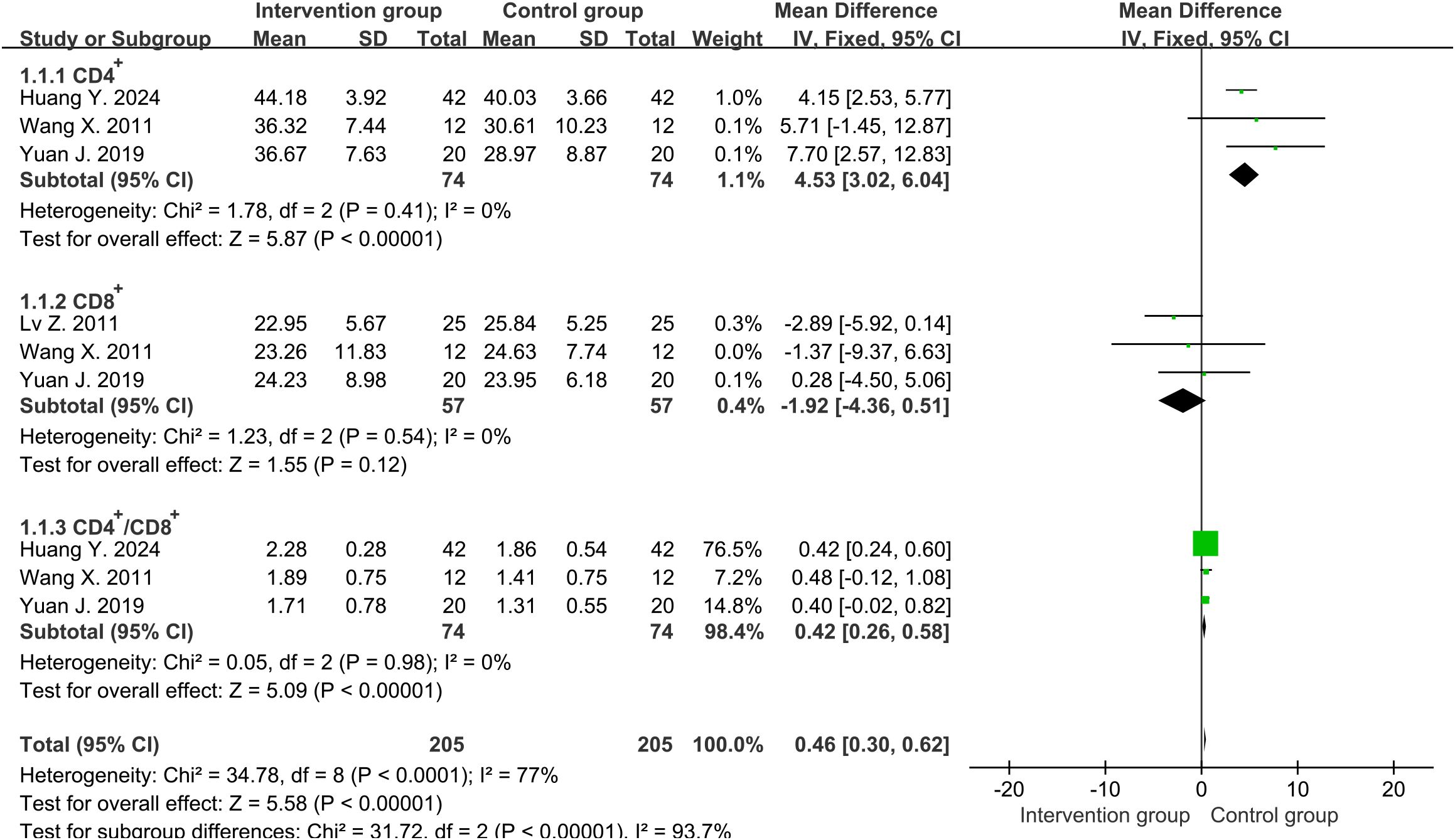
Figure 2. Forest plot of lymphocyte percentages around one week (including CD4+, CD8+ and CD4+/CD8+ ratio).
Four studies (31–34) reported the ratio of CD4+ to CD8+ around one week. High heterogeneity was discovered among them (df=3, I2 = 90%, P<0.00001). However, heterogeneity was significantly reduced after excluding one study (33) (df=2, I2 = 0%, P=0.98). The results in fixed-effects showed that the CD4+/CD8+ ratio in the intervention group was significantly higher than that in the control group (MD=0.42, 95%CI [0.26, 0.58], P<0.00001) (Figure 2).
Similarly, we analyzed the final lymphocyte percentages (including CD4+, CD8+ and CD4+/CD8+ ratio). The analysis conclusions are basically similar to the results around one week (Supplementary Figure S1).
CRP levels
Four studies (30, 32–34) reported the CRP levels (mg/L) around one week, with an average of 91.9mg/L and 100.0mg/L in the intervention and control groups, respectively. There was high heterogeneity between two groups (df=3, I2 = 91%, P<0.00001). Through sensitivity analysis, heterogeneity was not significantly reduced. We divided the study into higher-dose (3.2 mg per day) and lower-dose (1.6 mg per day) subgroups, with significant reduction in heterogeneity. Therefore, it was possible that the heterogeneity source was caused by drug dosage. The results in random-effects showed that the overall levels of CRP in the intervention group were lower than those in the control group (MD=-18.45, 95%CI [-33.26, -3.64], P=0.01) (Figure 3). Subgroup analysis showed that the lower-dose group performed more significantly (MD=-30.12, 95%CI [-35.75, -24.49], P<0.00001), while the higher-dose group showed no statistical difference (MD=-3.83, 95%CI [-12.14, 4.49], P=0.37).
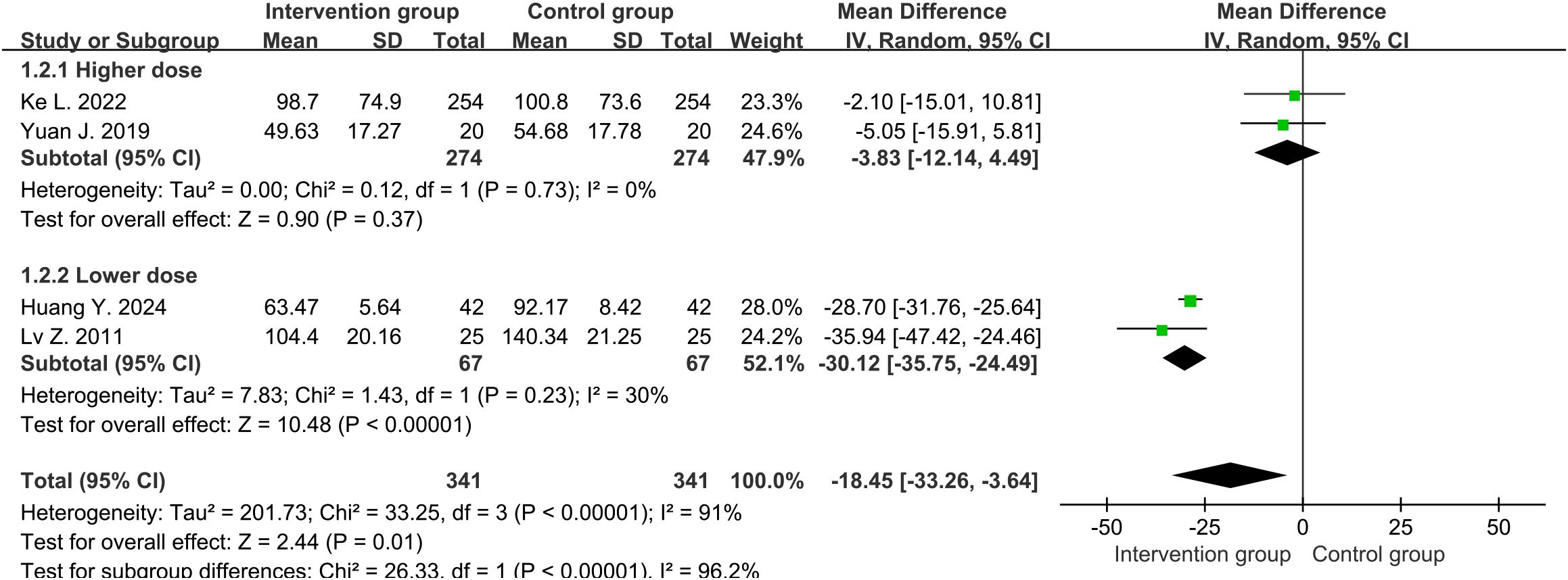
Figure 3. Forest plot of C-reactive protein levels around one week (including subgroup analysis of higher and lower doses).
In addition, we analyzed the final CRP levels (mg/L). The final conclusions of the overall levels of CRP and subgroup analysis are consistent with those results around one week (Supplementary Figure S2).
Patients with infections
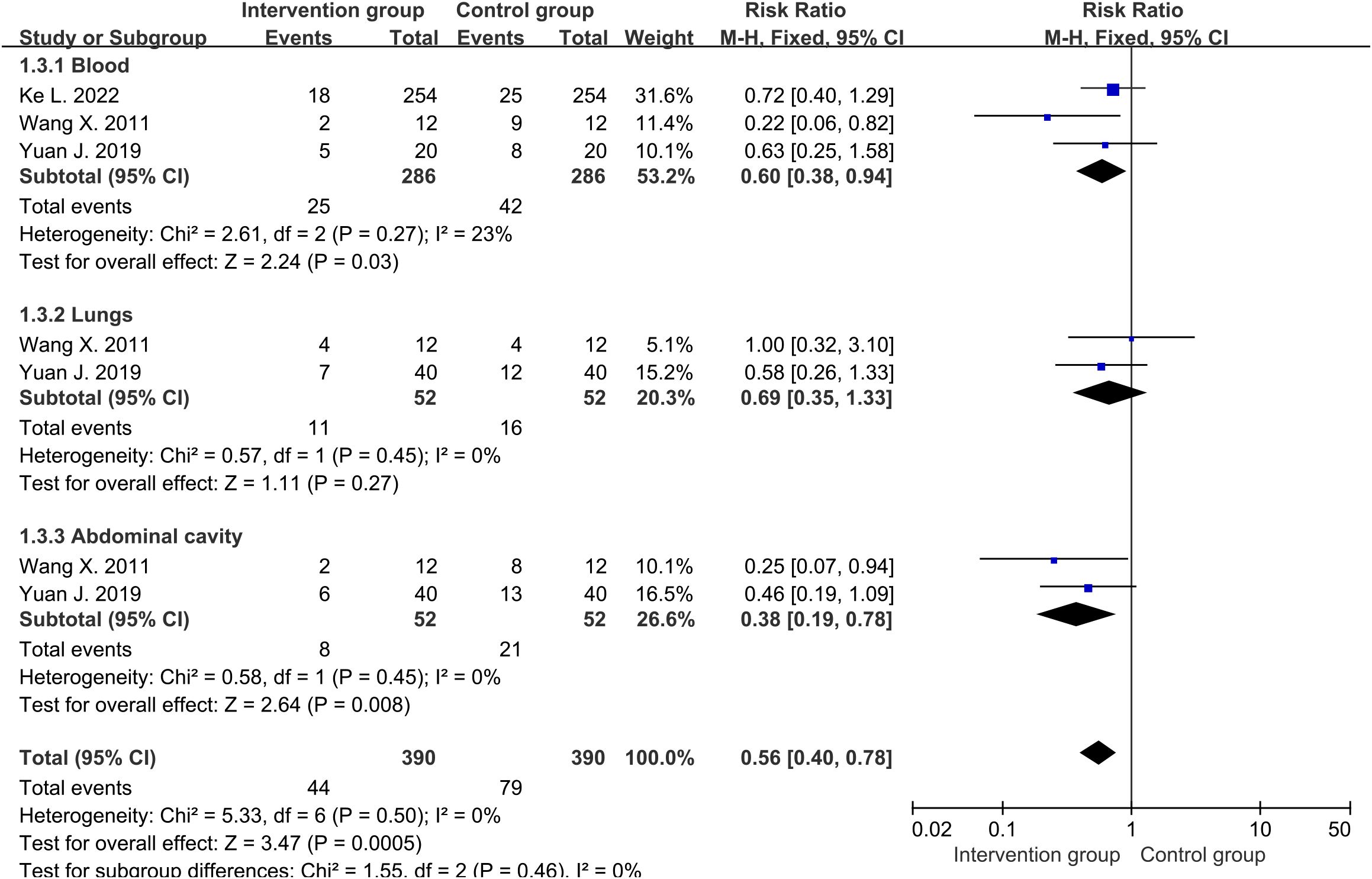
There were three studies (30–32) reporting the final number of blood infections, and two studies (31, 32) reporting the number of lung and abdominal infections. The average infection rate of the intervention group was about 14.3%, while that of the control group was about 25.9%. Cochrane’s Q-test revealed low heterogeneity among studies involving blood, lungs, and abdominal cavity. Therefore, fixed-effects were used to analyze them. The results showed that the overall infection rate of the intervention group was significantly lower than that of the control group (RR=0.56, 95%CI [0.40, 0.78], P=0.0005) (Figure 4), with less infections of blood (RR=0.60, 95%CI [0.38, 0.94], P=0.03) and abdominal (RR=0.38, 95%CI [0.19, 0.78], P=0.008) being the most significant. There was a relatively lower trend of lung infection in intervention group, but it had not reached statistical significance (RR=0.69, 95%CI [0.35, 1.33], P=0.27).
Length of hospital stay
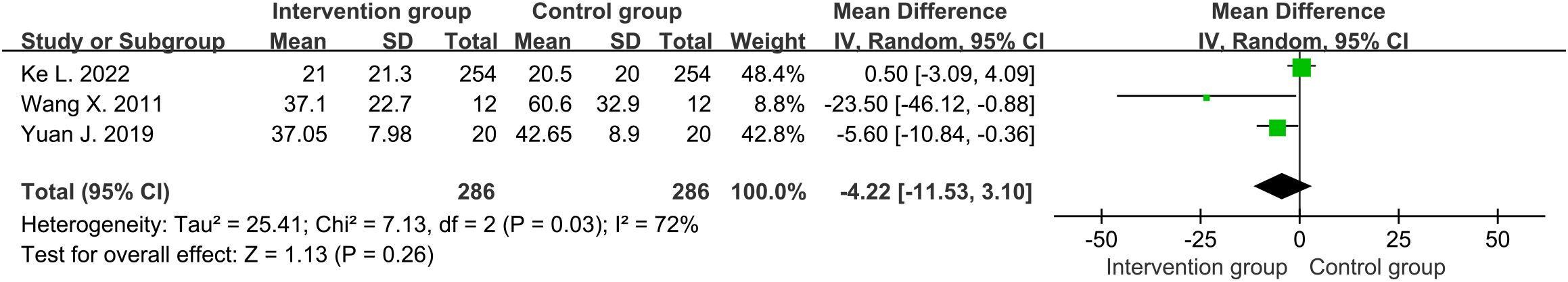
Three studies (30–32) reported the overall length of hospital stay (days) for SAP patients. The average length of hospital stay in the intervention group was about 22.8 days, while the control group was about 23.7 days. Moderate heterogeneity was detected among the included studies (df=2, I2 = 72%, P=0.03). No significant difference was found in the overall length of hospital stay between intervention group and control group through random-effects (MD=-4.22, 95%CI [-11.53, 3.10], P=0.26) (Figure 5)
APACHE II score
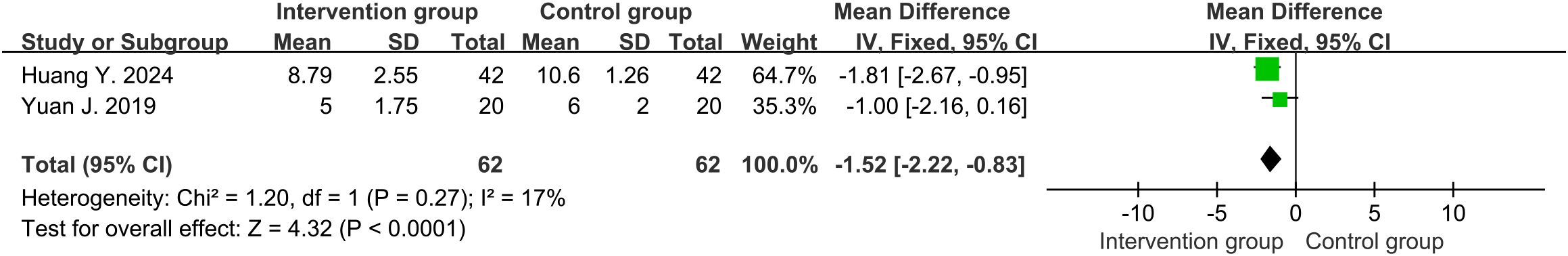
Three studies (32–34) reported the APACHE II score. High heterogeneity was discovered among them (df=2, I2 = 93%, P<0.00001). The results in random-effects showed that the intervention group had lower APACHE II score than the control group (MD=-3.37, 95%CI [-6.24, -0.49], P=0.02) (Supplementary Figure S3). Heterogeneity significantly decreased when a study (33) was excluded (df=1, I2 = 17%, P=0.27). Its overall treatment time (7 days) was shorter than the other two studies (10 and 14 days), which might be a source of heterogeneity. The results using a fixed-effects model still led to the same conclusion (MD=-1.52, 95%CI [-2.22, -0.83], P<0.0001) (Figure 6).
Publication bias test
Due to the limited number of studies included, we chose percentages of CD4+ and CRP levels to evaluate publication bias. The P-values for percentages of CD4+ and CRP levels using Egger test were 0.385 and 0.195 (P>0.05), respectively, indicating that there was no significant publication bias. In addition, partial subgroup analysis (including lymphocyte ratio, inflammation, and infection) based on language was used to test for bias. Meaningful merging results (including two or more) were consistent with the trend of the original results mentioned above (Supplementary Figures S4-S6). According to Cochrane RoB 2.0 assessment, it was found that the publication bias in English articles was low-risk (Supplementary Tables S2, S3 and S7). Some aspects of the Chinese article had ‘some concerns’, but none of them had reached high-risk bias (Supplementary Tables S4-S7).
Discussion
Imbalance of immune regulation in the body is an important reason for the progression of pancreatitis to severe or even death in SAP patients. Excessive activation of local inflammatory cells and mediators can lead to increased capillary permeability, exacerbating the inflammatory response and transforming it into SIRS. Persistent SIRS leads to circulatory, respiratory, or renal failure, resulting in MODS and significantly increased mortality rates (35). Compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS), as a negative feedback regulation, can help the body suppress excessive inflammatory reactions (36). However, excessive CARS effect may lead to a decrease in the expression of human leukocyte antigen-DR (HLA-DR), resulting in immune suppression and significantly increasing the risk of infection in the body (37–39). In addition, as an important component of the immune system, the lymphocyte ratio in SAP patients is significantly reduced (40, 41). T cell subpopulation analysis showed that multiple cell lines were inhibited in AP, including cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and CD4+ T cell counts (42, 43). In severe cases, CD4+ T cell counts have been reported to decrease more significantly than CD8+ cells, and lead to a decrease in CD4+/CD8+ ratio (17, 42, 44). Some subsets and functions of CD4+ T cells differentiation can be viewed in Supplementary Figure S7. The reduction of some differentiation types may further increase the risk of infection and death for SAP patients (45). Therefore, it is necessary to improve the prognosis of SAP patients through immunomodulatory therapy.
At present, the main goal of immunomodulatory therapy is to regulate the maturation, apoptosis, and differentiation of immune cells through immune stimulation, restoring the balance of immune cell quantity and function (46). This method may also be used in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs targeting certain cytokines (including NF-κB, TNF-α, interleukins, and platelet activating factors) for multi strategy treatment (47, 48). Immune stimulation methods such as the use of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interferon (IFN)-γ have been reported to increase the expression level of HLA-DR on monocytes or restore the balance between T helper cell 1 (Th1) and Th2 (49, 50). But clinical studies on these findings are still scarce. Interestingly, Tα1 can restore serum CD4+ T cell levels and CD4+/CD8+ ratio, and has also been increasingly used in clinical studies for immune regulation therapy of SAP in recent years (30–34, 51, 52). However, there is currently insufficient evidence to prove its efficacy, and this meta-analysis is needed to explore the immunomodulatory therapeutic effect of Tα1 on SAP patients.
Our research findings suggest that Tα1 may improve immune regulation in SAP patients. Tα1 is a peptide naturally present in the thymus, and it has long been believed to alter, enhance, and restore immune function. Tα1 can serve as an enhancer for immune function decline caused by a decrease in T cell related components. Tα1 interacts with Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and activates dendritic cells and precursor T cells, increasing the number of T helper cells and transferring to Th1 class, thereby increasing the expression of cytokines such as IL-2, IFN-α, and the activity of NK cells (53). Animal experimental studies (52, 54) have shown that Tα1 can alleviate pancreatitis by balancing CD3+/CD4+/CD8+ T cells and reducing cytokine release, reducing cell damage, thereby relieving the severity of the pancreas and improving the survival rate of SAP mice. The condition of AP is closely related to the level of CD4+ T lymphocytes, and its possible mechanism is that IL-22 can protect mice from AP invasion, while CD4+ T lymphocytes are the main source of IL-22 in pancreatic tissue (55, 56). Our analysis results indicated that the use of Tα1 immunomodulatory therapy significantly increased CD4+ T cells, CD4+/CD8+ ratio around one week, and slightly decreased CD8+ T cells levels in SAP patients. The conclusion remained consistent in the final percentages. This suggested that Tα1 might tend to improve the number of CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood of SAP patients, thereby regulating immune balance and preventing immune suppression.
CRP levels increase during plasma inflammation and are a commonly used biomarker for assessing the degree of inflammation in the body. In patients with SAP, a strong negative correlation has been found between CRP levels and the proportion of T helper cells (57). Tα1 possesses the capacity to prevent pro-inflammatory cytokine storms and potential autoimmune events. This is due to its ability to activate indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase in plasma cell like dendritic cells, leading to the production of IL-10 and an increase in regulatory T cells, and ultimately inhibiting excessive cytokine production (58–60). In addition, it may reduce M1 activation of macrophages and lower the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF - α, IL-1 β and IL-6 (61). In a word, these processes allow for a balanced control of inflammation and tolerance. Our study found that lower doses (1.6 mg per day) of Tα1 significantly reduced CRP levels in SAP patients, while there was no significant difference between the two groups at higher doses (3.2 mg per day). Interestingly, the analysis conclusion of final CRP levels remained consistent with it around one week. It is unknown whether high-dose Tα1 affects the differentiation trend of CD4+ T cell subsets in SAP patients and affects therapeutic efficacy. But it can be speculated that low-dose Tα1 may be more used for immune regulation and maintaining immune homeostasis, reducing autoimmune reactions and inflammation in SAP patients. However, it requires more research to confirm.
Infectious pancreatic necrosis (IPN), as a local infection of the pancreas, is mainly caused by secondary infection of pancreatic necrotic tissue. For the infectious necrosis, in addition to using antibiotics, invasive interventions such as percutaneous puncture drainage, endoscopic drainage, or surgical debridement can be used to remove necrotic tissue and infected lesions (62). In the articles we included, a study predicting IPN had the highest number of patients (30). Although patients using Tα1 showed a trend toward lower incidence of IPN compared to those using a placebo during hospitalization (15.7% vs 18.1%) and within 90 days after randomization (22.4% vs 25.6%), there was a lack of statistical difference. And it did not perform well in some invasive interventions. Ke L. et al. (30) proposed that future trials need to determine the selection of the best patient, most effective dose, and duration of Tα1 treatment. These factors may have some impact on the results.
Extrapancreatic infection (EPI) is a common clinical complication in AP patients during hospitalization, referring to infections of other organs except pancreas, including blood, respiratory tract, abdominal cavity, and urinary tract. A meta-analysis (63) of 19 studies involving 1741 patients showed that the incidence of complications from EPI was 32% (95% CI 23-41%), with the most common being respiratory infections (9.2%) and bacteremia (8.4%). Multiple studies (64–66) have found that prophylactic use of antibiotics is common in SAP, but routine early prophylactic antibiotic use does not have significant clinical benefits for SAP patients. The guidelines of the American gastroenterological association institute and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) in 2018 suggested that prophylactic use of antibiotics was not recommended for patients predicted to have severe or necrotizing pancreatitis (67, 68). However, Tα1, as an immunomodulator, has been widely used and tested in a wide range of clinical applications, including viral, fungal and bacterial infectious diseases (53). Our results found that the overall incidence rate of EPI in SAP patients after Tα1 immunomodulation treatment was about 14.3%, significantly lower than that in the control group (about 25.9%). Specifically, there was a significant difference in preventing blood and abdominal infections, while the effect was slightly lower in preventing pulmonary infections. In addition, based on the results of final lymphocyte percentages (including CD4+ T cells, CD4+/CD8+ratio), patients in the Tα1 group appeared to exhibit less pronounced immunosuppression. Tα1 may reduce the exhaustion of T cells in SAP patients and maintain the number and function of effector T cells, thus playing a sustained role in preventing or eliminating infections. In summary, Tα1 has a certain effect on preventing EPI in SAP patients.
The length of hospital stay in the studies we included was generally between 3 and 4 weeks. The duration is significantly longer than mild to moderate patients (69). Our results indicated that Tα1 had a trend of reducing hospitalization time for SAP patients. However, it is not sufficient to achieve statistical significance. The average length of hospital stay for SAP patients is influenced by multiple factors. A retrospective study found that organ dysfunction at presentation or during admission, concurrent infections, need for enteral tube placement and in-hospital interventions were associated with increased length of hospital stay for acute necrotizing pancreatitis (70). Some studies showed that early enteral nutrition, good control of blood glucose levels and the use of Chinese herbal medicine were associated with decreased length of hospital stay (71–75). However, most of the patients included were severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis, and the study conducted by Ke L. et al. (30) found that there was no statistical difference in the incidence of IPN and some invasive interventions. Perhaps the main impact on hospitalization time may be other factors or intervention measures, and the effect of Tα1 in this regard appears to be relatively weak.
The severity of SAP patients’ condition upon admission needs to be quickly assessed through some scoring criteria. At present, there are still different opinions on the advantages and disadvantages of different scoring systems, including APACHE II score, Bedside Index of Severity in Acute Pancreatitis (BISAP), Ranson’s score and Modified Computed Tomography Severity Index (MCTSI) (76–78). The APACHE II score was mainly mentioned in the studies we included. It scores based on the patient’s physiological parameters, age, and chronic health status. It helps to quickly assess the severity of SAP patients’ conditions and has some value in guiding treatment and prognosis. It is known as the ‘gold standard’ for predicting severely ill patients in individual intensive care units worldwide (79). According to our analysis results, the APACHE II score of the treatment group was relatively lower than that of the control group. We believe that using Tα1 for immune regulation may improve the condition and prognosis of SAP patients.
Regarding the adverse events of Tα1, there is insufficient data to report it in the included study. However, it has been reported that Tα1 has good tolerability in a wide population, including elderly patients, children, and immunocompromised patients, and no any significant adverse events in patients with organ dysfunction (24, 80). Further research is required to substantiate the safety of its use in patients with SAP.
In this study, we chose to analyze some outcomes around one week in addition to the final outcomes. This reduces the impact of inconsistent medication time on the final results, proving the reliability of the conclusion. Although our study has found some beneficial effects of Tα1 on SAP patients as the first meta-analysis, there are still some shortcomings in the study. First, we have included relatively few studies, and more studies are needed to confirm the results. Secondly, due to limited data included in the study, we are unable to comprehensively analyze the efficacy and safety of Tα1. If possible, more outcome measures (such as clinical symptoms, mortality rate, adverse events) could be added in the future. Thirdly, the dosage of Tα1 used in the included studies is not completely consistent, which may lead to high heterogeneity in some results and affect stability. Finally, one study (33) is of low quality and has been assessed as ‘some concerns’ about publication bias according to Jadad scale and Cochrane RoB 2.0. This is also the reason why we excluded it in some result analysis. More high-quality research is needed to validate the immunomodulatory effect of Tα1 on SAP.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that Tα1 can regulate the balance between immune cells in SAP patients, including increasing CD4+ T cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratios. Furthermore, Tα1 may exert anti-inflammatory and EPI-preventive effects on SAP patients, and ultimately improve their condition or prognosis. However, more research is needed to validate these results.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. JY: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft. YM: Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft. PZ: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. WX: Visualization, Writing – original draft. WT: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82174264) and Technology Agency of Sichuan Province Foundation Project (2024NSFSC0055).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1571456/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Manohar M, Verma AK, Venkateshaiah SU, Sanders NL, and Mishra A. Pathogenic mechanisms of pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. (2017) 8:10–25. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v8.i1.10
2. Shah AP, Mourad MM, and Bramhall SR. Acute pancreatitis: current perspectives on diagnosis and management. J Inflammation Res. (2018) 11:77–85. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S135751
3. Xie X and Fei S. Research progress on the etiology of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis. Int J Surg. (2020) 47:342–6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115396-20191216-00234
4. Kusiak AA, Jakubowska MA, Stopa KB, Zhang X, Huang W, Gerasimenko JV, et al. Activation of pancreatic stellate cells attenuates intracellular Ca(2+) signals due to downregulation of TRPA1 and protects against cell death induced by alcohol metabolites. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:744. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05186-w
5. Saluja A, Dudeja V, Dawra R, and Sah RP. Early intra-acinar events in pathogenesis of pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2019) 156:1979–93. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.268
6. Johnson CD, Besselink MG, and Carter R. Acute pancreatitis. BMJ. (2014) 349:g4859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g4859
7. Iannuzzi JP, King JA, Leong JH, Quan J, Windsor JW, Tanyingoh D, et al. Global incidence of acute pancreatitis is increasing over time: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. (2022) 162:122–34. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.043
8. Leppäniemi A, Tolonen M, Tarasconi A, Segovia-Lohse H, Gamberini E, Kirkpatrick AW, et al. 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. World J Emerg Surg. (2019) 14:27. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0247-0
9. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis–2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. (2013) 62:102–11. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779
10. Machicado JD, Gougol A, Tan X, Gao X, Paragomi P, Pothoulakis I, et al. Mortality in acute pancreatitis with persistent organ failure is determined by the number, type, and sequence of organ systems affected. United Eur Gastroenterol J. (2021) 9:139–49. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12057
11. Gougol A, Paragomi P, Pothoulakis I, Talukdar R, Kochar R, Goenka MK, et al. Temporal relationship between SIRS, organ failure, and death in acute pancreatitis: Data from a large, multicenter, international study (APPRENTICE study group). Pancreas. (2018) 47:1389. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001177
12. Vege SS, Gardner TB, Chari ST, Munukuti P, Pearson RK, Clain JE, et al. Low mortality and high morbidity in severe acute pancreatitis without organ failure: a case for revising the Atlanta classification to include “moderately severe acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. (2009) 104:710–5. doi: 10.14309/00000434-200903000-00032
13. Beger HG, Rau B, Mayer J, and Pralle U. Natural course of acute pancreatitis. World J Surg. (1997) 21:130–5. doi: 10.1007/s002689900204
14. Werge M, Novovic S, Schmidt PN, and Gluud LL. Infection increases mortality in necrotizing pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology. (2016) 16:698–707. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2016.07.004
15. Munir F, Jamshed MB, Shahid N, Hussain HM, Muhammad SA, Mamun AA, et al. Advances in immunomodulatory therapy for severe acute pancreatitis. Immunol Lett. (2020) 217:72–6. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.11.002
16. He G, Xiong G, Lu S, Xu S, and Chen K. Progresses of immunomodulatory therapy in sever acute pancreatitis. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. (2017) 29:954–7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.10.020
17. Yang Z, Zhang Y, Dong L, Yang C, Gou S, Yin T, et al. The reduction of peripheral blood CD4+ T cell indicates persistent organ failure in acute pancreatitis. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e125529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125529
18. Xue XC, Yan Z, Li WN, Li M, Qin X, Zhang C, et al. Construction, expression, and characterization of thymosin alpha 1 tandem repeats in Escherichia coli. BioMed Res Int. (2013) 2013:720285. doi: 10.1155/2013/720285
19. Wei YT, Wang XR, Yan C, Huang F, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. Thymosin α-1 reverses M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages during efferocytosis. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:1991–2002. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-4260
20. Yang X, Qian F, He HY, Liu KJ, Lan YZ, Ni B, et al. Effect of thymosin alpha-1 on subpopulations of Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T cells (Tregs) in vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2012) 45:25–32. doi: 10.1590/S0100-879X2011007500159
21. Zhang Y, Xia D, Li L, Gu Y, Shi L, Ma C, et al. Thymosin α1 alleviates lung injury in sepsis rats via Notch signaling pathway. Panminerva Med. (2023) 65:413–4. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.20.03856-2
22. Shi QX, Chen B, Nie C, Zhao ZP, Zhang JH, Si SY, et al. Improvement in cognitive dysfunction following blast induced traumatic brain injury by thymosin α1 in rats: Involvement of inhibition of tau phosphorylation at the Thr205 epitope. Brain Res. (2020) 1747:147038. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147038
23. Giacomini E, Rizzo F, Etna MP, Cruciani M, Mechelli R, Buscarinu MC, et al. Thymosin-α1 expands deficient IL-10-producing regulatory B cell subsets in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler. (2018) 24:127–39. doi: 10.1177/1352458517695892
24. Carraro G, Naso A, Montomoli E, Gasparini R, Camerini R, Panatto D, et al. Thymosin-alpha 1 (Zadaxin) enhances the immunogenicity of an adjuvated pandemic H1N1v influenza vaccine (Focetria) in hemodialyzed patients: a pilot study. Vaccine. (2012) 30:1170–80. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.014
25. Liu Y, Pan Y, Hu Z, Wu M, Wang C, Feng Z, et al. Thymosin alpha 1 reduces the mortality of severe coronavirus disease 2019 by restoration of lymphocytopenia and reversion of exhausted T cells. Clin Infect Dis. (2020) 71:2150–7. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa630
26. Espinar-Buitrago MS, Tarancon-Diez L, Vazquez-Alejo E, Magro-Lopez E, Genebat M, Romero-Candau F, et al. The use of alpha 1 thymosin as an immunomodulator of the response against SARS-Cov2. Immun Ageing. (2023) 20:32. doi: 10.1186/s12979-023-00351-x
27. Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. (2015) 4:1. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
28. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
29. Sterne J, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
30. Ke L, Zhou J, Mao W, Chen T, Zhu Y, Pan X, et al. Immune enhancement in patients with predicted severe acute necrotising pancreatitis: a multicentre double-blind randomised controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. (2022) 48:899–909. doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06745-7
31. Wang X, Li W, Niu C, Pan L, Li N, and Li J. Thymosin alpha 1 is associated with improved cellular immunity and reduced infection rate in severe acute pancreatitis patients in a double-blind randomized control study. Inflammation. (2011) 34:198–202. doi: 10.1007/s10753-010-9224-1
32. Yuan J. Clinical study on the changes of immune function and the role of thymosin α1 in acute pancreatitis. Luzhou, Sichuan, China: Southwest Medical University (2019).
33. Lv Z, Li K, Wang M, and Liu Q. Study on the efficacy of thymosin α1 in treating severe acute pancreatitis. J Bethune Military Med Coll. (2011) 9:252–4. doi: 10.16485/j.issn.2095-7858.2011.04.030
34. Huang Y, Ding J, Fan H, Wang Y, and Wang X. The efficacy of Thymosin Alpha 1 in treating severe acute pancreatitis and its impact on patients’ cellular immune status and inflammatory mediators. Modern Med J China. (2024) 26:47–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9463.2024.01.010
35. Beger HG and Rau BM. Severe acute pancreatitis: Clinical course and management. World J Gastroenterol. (2007) 13:5043–51. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i38.5043
36. Sendler M, van den Brandt C, Glaubitz J, Wilden A, Golchert J, Weiss FU, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome regulates development of systemic inflammatory response and compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndromes in mice with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:253–69. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.040
37. Kylänpää ML, Repo H, and Puolakkainen PA. Inflammation and immunosuppression in severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2010) 16:2867–72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2867
38. Novotny AR, Reim D, Assfalg V, Altmayr F, Friess HM, Emmanuel K, et al. Mixed antagonist response and sepsis severity-dependent dysbalance of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses at the onset of postoperative sepsis. Immunobiology. (2012) 217:616–21. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2011.10.019
39. Lin ZQ, Guo J, Xia Q, Yang XN, Huang W, Huang ZW, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-DR expression on peripheral monocytes may be an early marker for secondary infection in severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. (2013) 60:1896–902. doi: 10.5754/hge13313
40. Qi X, Yang F, Huang H, Du Y, Chen Y, Wang M, et al. A reduced lymphocyte ratio as an early marker for predicting acute pancreatitis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:44087. doi: 10.1038/srep44087
41. Zhao Z, Shen J, Zhang D, and Shen J. The prognostic role of peripheral lymphocyte subsets in patients with acute pancreatitis. Am J Med Sci. (2019) 357:242–6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2018.12.008
42. Uehara S, Gothoh K, Handa H, Tomita H, and Tomita Y. Immune function in patients with acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2003) 18:363–70. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.02979.x
43. Dabrowski A, Osada J, Dabrowska MI, and Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska U. Monocyte subsets and natural killer cells in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. (2008) 8:126–34. doi: 10.1159/000123605
44. Pietruczuk M, Dabrowska MI, Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska U, and Dabrowski A. Alteration of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2006) 12:5344–51. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i33.5344
45. Adrie C, Lugosi M, Sonneville R, Souweine B, Ruckly S, Cartier JC, et al. Persistent lymphopenia is a risk factor for ICU-acquired infections and for death in ICU patients with sustained hypotension at admission. Ann Intensive Care. (2017) 7:30. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0242-0
46. Li J, Yang WJ, Huang LM, and Tang CW. Immunomodulatory therapies for acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:16935–47. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.16935
47. Werner J, Hartwig W, Hackert T, Kaiser H, Schmidt J, Gebhard MM, et al. Multidrug strategies are effective in the treatment of severe experimental pancreatitis. Surgery. (2012) 151:372–81. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.07.041
48. Pereda J, Sabater L, Cassinello N, Gómez-Cambronero L, Closa D, Folch-Puy E, et al. Effect of simultaneous inhibition of TNF-alpha production and xanthine oxidase in experimental acute pancreatitis: the role of mitogen activated protein kinases. Ann Surg. (2004) 240:108–16. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000129343.47774.89
49. Kylanpaa ML, Mentula P, Kemppainen E, Puolakkainen P, Aittomaki S, Silvennoinen O, et al. Monocyte anergy is present in patients with severe acute pancreatitis and is significantly alleviated by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interferon-gamma in vitro. Pancreas. (2005) 31:23–7. doi: 10.1097/01.mpa.0000164449.23524.94
50. Flohé SB, Agrawal H, Flohé S, Rani M, Bangen JM, and SChade FU. Diversity of interferon gamma and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in restoring immune dysfunction of dendritic cells and macrophages during polymicrobial sepsis. Mol Med. (2008) 14:247–56. doi: 10.2119/2007-00120.Flohe
51. Zhou J, Mao W, Ke L, Chen T, He W, Pan X, et al. Thymosin alpha 1 in the prevention of infected pancreatic necrosis following acute necrotising pancreatitis (TRACE trial): protocol of a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. BMJ Open. (2020) 10:e37231. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037231
52. Yao W, Zhu Q, Yuan Y, Qiao M, Zhang Y, and Zhai Z. Thymosin alpha 1 improves severe acute pancreatitis in rats via regulation of peripheral T cell number and cytokine serum level. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2007) 22:1866–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04699.x
53. Camerini R and Garaci E. Historical review of thymosin α 1 in infectious diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2015) 15 Suppl 1:S117–27. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2015.1033393
54. Wang X, Zeng X, Yang B, Zhao S, Chen W, and Guo X. Efficacy of thymosin α1 and interferon α for the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis in a rat model. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 12:6775–81. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4277
55. Demols A, Le Moine O, Desalle F, Quertinmont E, Van Laethem JL, and Devière J. CD4(+)T cells play an important role in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. (2000) 118:582–90. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(00)70265-4
56. Xue J, Nguyen DT, and Habtezion A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates pancreatic IL-22 production and protects mice from acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2012) 143:1670–80. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.08.051
57. Curley PJ, McMahon MJ, Lancaster F, Banks RE, Barclay GR, Shefta J, et al. Reduction in circulating levels of CD4-positive lymphocytes in acute pancreatitis: relationship to endotoxin, interleukin 6 and disease severity. Br J Surg. (1993) 80:1312–5. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800801031
58. Romani L, Bistoni F, Perruccio K, Montagnoli C, Gaziano R, Bozza S, et al. Thymosin alpha1 activates dendritic cell tryptophan catabolism and establishes a regulatory environment for balance of inflammation and tolerance. Blood. (2006) 108:2265–74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-004762
59. Romani L, Bistoni F, Montagnoli C, Gaziano R, Bozza S, Bonifazi P, et al. Thymosin alpha1: an endogenous regulator of inflammation, immunity, and tolerance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2007) 1112:326–38. doi: 10.1196/annals.1415.002
60. Pierluigi B, D’Angelo C, Fallarino F, Moretti S, Zelante T, Bozza S, et al. Thymosin alpha1: the regulator of regulators? Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2010) 1194:1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05465.x
61. Novoselova EG, Glushkova OV, Khrenov MO, Lunin SM, Sharapov MG, Goncharov RG, et al. The thymic hormone thymosin-1α Reduces the pro-inflammatory response of raw 264.7 cells induced by endotoxin. Mol Biol (Mosk). (2023) 57:1006–16. doi: 10.1134/S0026893323060110
62. Baron TH, DiMaio CJ, Wang AY, and Morgan KA. American gastroenterological association clinical practice update: management of pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:67–75. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.064
63. Brown LA, Hore TA, Phillips AR, Windsor JA, and Petrov MS. A systematic review of the extra-pancreatic infectious complications in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. (2014) 14:436–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2014.09.010
64. García-Barrasa A, Borobia FG, Pallares R, Jorba R, Poves I, Busquets J, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ciprofloxacin prophylaxis in patients with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg. (2009) 13:768–74. doi: 10.1007/s11605-008-0773-7
65. Nakaharai K, Morita K, Jo T, Fushimi K, and Yasunaga H. Early prophylactic antibiotics for severe acute pancreatitis: A population-based cohort study using a nationwide database in Japan. J Infect Chemother. (2018) 24:753–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2018.05.009
66. Isenmann R, Rünzi M, Kron M, Kahl S, Kraus D, Jung N, et al. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment in patients with predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gastroenterology. (2004) 126:997–1004. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.12.050
67. Arvanitakis M, Dumonceau JM, Albert J, Badaoui A, Bali MA, Barthet M, et al. Endoscopic management of acute necrotizing pancreatitis: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) evidence-based multidisciplinary guidelines. Endoscopy. (2018) 50:524–46. doi: 10.1055/a-0588-5365
68. Crockett SD, Wani S, Gardner TB, Falck-Ytter Y, and Barkun AN. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on initial management of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2018) 154:1096–101. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.032
69. Ramírez-Maldonado E, López GS, Pueyo EM, Sánchez-García A, Mayol S, González S, et al. Immediate oral refeeding in patients with mild and moderate acute pancreatitis: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial (PADI trial). Ann Surg. (2021) 274:255–63. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004596
70. Obaitan I, Wehbe H, Easler JJ, Stethen JT, Mahendraker N, Tong Y, et al. Factors predictive of hospital length of stay in patients with an index episode of acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Pancreatology. (2024) 24:32–40. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2023.11.008
71. Melanie P, Ahmad N, Thiruvengadam M, and W HK. S13 Early feeding rates in acute pancreatitis is associated with decreased length of hospitalization. Am J Gastroenterol. (2022) 117:e12. doi: 10.14309/01.ajg.0000856692.43734.28
72. Wang D, Lu J, Zhang P, Hu Z, and Shi Y. Relationship between blood glucose levels and length of hospital stay in patients with acute pancreatitis: An analysis of MIMIC-III database. Clin Transl Sci. (2023) 16:246–57. doi: 10.1111/cts.13445
73. Liu M and Gao C. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of total parenteral nutrition and enteral nutrition on the prognosis of patients with acute pancreatitis. Ann Palliat Med. (2021) 10:10779–88. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2469
74. Zheng R, Zhang L, Tian R, Li N, Lei X, Jing L, et al. The effect of Xuebijing injection for severe acute pancreatitis: a Meta analysis. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. (2015) 27:682–6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.08.013
75. Lu X, Xiao W, Kang X, Yu J, and Fan Z. The effect of Chinese herbal medicine on non-biliogenic severe acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2014) 155:21–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.040
76. Venkatesh NR, Vijayakumar C, Balasubramaniyan G, Chinnakkulam KS, Sundaramurthi S, G SS, et al. Comparison of different scoring systems in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis: a prospective observational study. Cureus. (2020) 12:e6943. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6943
77. Chauhan R, Saxena N, Kapur N, and Kardam D. Comparison of modified Glasgow-Imrie, Ranson, and Apache II scoring systems in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Pol Przegl Chir. (2022) 95:6–12. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0015.8384
78. Harshit KA and Singh GM. A comparison of APACHE II, BISAP, Ranson’s score and modified CTSI in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis based on the 2012 revised Atlanta Classification. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). (2018) 6:127–31. doi: 10.1093/gastro/gox029
79. Czajka S, Ziębińska K, Marczenko K, Posmyk B, Szczepańska AJ, and Krzych ŁJ. Validation of APACHE II, APACHE III and SAPS II scores in in-hospital and one year mortality prediction in a mixed intensive care unit in Poland: a cohort study. BMC Anesthesiol. (2020) 20:296. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-01203-7
Keywords: thymosin alpha 1, inflammation, infection, severe acute pancreatitis, immune regulation, meta-analysis
Citation: Tian Y, Yao J, Ma Y, Zhang P, Zhou X, Xie W and Tang W (2025) Thymosin alpha 1 alleviates inflammation and prevents infection in patients with severe acute pancreatitis through immune regulation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1571456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1571456
Received: 05 February 2025; Accepted: 28 May 2025;
Published: 17 June 2025.
Edited by:
Rajeev K. Tyagi, Institute of Microbial Technology (CSIR), IndiaReviewed by:
Srujan Marepally, Center for Stem Cell Research (CSCR), IndiaLu Ke, Nanjing University, China
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Yao, Ma, Zhang, Zhou, Xie and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenfu Tang, dGFuZ3dmQHNjdS5lZHUuY24=
 Yong Tian
Yong Tian Jiaqi Yao
Jiaqi Yao Yihan Ma2
Yihan Ma2 Pengcheng Zhang
Pengcheng Zhang Wenjie Xie
Wenjie Xie Wenfu Tang
Wenfu Tang