- 1School of Basic Medical Sciences, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, China
- 2School of Clinical Medicine, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi, China
- 3School of Medical Imaging, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, China
- 4Department of Gastroenterology, Yang Zhou Hong Quan Hospital, Yang Zhou, China
- 5Department of Anesthesiology, Mudanjiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Mudanjiang, China
- 6School of Stomatology, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, China
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a traumatic disease of the central nervous system that can result in significant tissue damage and neurological dysfunction. The pathophysiological process of SCI encompasses both primary and secondary injuries, involving various pathological mechanisms such as oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy, ferroptosis, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a neuroprotective transcription factor intricately linked to these pathological processes. Upon exposure to external stimuli, Nrf2 undergoes increased nuclear transcription, regulating the expression of various antioxidant genes and directly modulating genes associated with the aforementioned pathological mechanisms to counteract the resultant alterations. Substantial evidence suggests that Nrf2 may be a potential therapeutic target for SCI. Activation of the Nrf2-related signaling pathway effectively inhibits neuronal death following SCI and promotes the recovery of multiple neurological functions. This review provides an overview of recent research on SCI, examines the physiological roles and mechanisms of Nrf2 in SCI, and explores therapeutic strategies targeting this signaling pathway, including non-coding RNAs, natural and synthetic compounds, and other treatments for SCI.
1 Introduction
Spinal cord injury is a debilitating condition of the central nervous system caused by either traumatic or non-traumatic factors. It often results in profound motor, sensory, and autonomic dysfunction (1). SCI and its complications impose considerable long-term physical, mental, and economic burdens on patients and their families (2). It is estimated that the global incidence of SCI ranges from 250,000 to 500,000 cases annually. With the rise in extreme sports and traffic accidents, both morbidity and mortality associated with SCI have been increasing, further straining the healthcare system (3–5).
Pathophysiologically, SCI is categorized into two distinct stages: primary injury and secondary injury (6). The former, resulting from the initial trauma to the spinal cord, leads directly to structural damage and nerve tissue loss (7). In contrast, the latter involves a cascade of biological events—including immune cell infiltration, oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, accumulation of excitotoxic neurotransmitters (such as glutamate), disruption of ion homeostasis, and mitochondrial dysfunction—which collectively exacerbate the extent of neuronal damage and promote further neuronal apoptosis (8). Among these mechanisms, immune cell infiltration, inflammatory responses, and oxidative stress play pivotal roles in the progression of SCI. Following the primary injury, vascular damage induces hemorrhage within the spinal cord, which is subsequently followed by the infiltration of peripheral immune cells—such as monocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages—into the spinal tissue (9). These immune cells facilitate the release of inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) (10). The combined effects of immune cell infiltration and cytokine release promote neuroinflammation (11). Although inflammation initially contributes to debris clearance and tissue repair, excessive or prolonged inflammation can result in neuronal apoptosis and further tissue damage (12). Additionally, the destruction of microvessels and the release of hemoglobin from lysed red blood cells lead to the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), inducing oxidative stress (13). Elevated ROS levels can cause lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction, ultimately triggering iron dysregulation and neuronal apoptosis (14). The interplay between inflammation and oxidative stress further worsens the pathological process, creating a vicious cycle of tissue damage (12). The primary injury occurs immediately upon trauma, resulting in irreversible damage to the affected site. However, the molecular and cellular pathological changes associated with secondary injury are reversible (15). Consequently, the optimal treatment for SCI focuses on inhibiting secondary injury while promoting the recovery of neurological function (16). Current management strategies include surgery, pharmacological interventions, electrical stimulation, cell transplantation, and rehabilitation. However, their effectiveness is limited due to the complex pathophysiology of SCI (17, 18). Therefore, developing effective strategies for treating SCI with secondary injury remains a major challenge.
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a key member of the transcription factor family, ubiquitously expressed across various cell types (19). It reduces cellular damage caused by external stimuli by regulating the transcription of defense genes, playing a crucial role in maintaining intracellular homeostasis (20). Extensive evidence underscores the critical role of Nrf2 in regulating redox homeostasis (21). Under normal conditions, Nrf2 interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex formed by kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 (Keap1) in the cytoplasm, leading to its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation (22). In response to oxidative stress, Nrf2 is released and translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to the enhancer region of antioxidant response elements (ARE), promoting the expression of antioxidant genes and thereby counteracting oxidative damage (23, 24). Aside from its role in the antioxidant response, Nrf2 is involved in various cellular processes, including inflammation, iron metabolism, DNA repair, autophagy, and mitochondrial membrane integrity (18). Dysregulation of the Nrf2-related signaling pathway can contribute to the onset and progression of multiple pathological conditions, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular conditions, and cancer (25–27). For example, in Parkinson’s disease, dysregulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway may exacerbate oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, leading to neuronal damage and cell death (28). Nrf2 activity is intricately regulated through complex transcriptional and post-translational mechanisms, enabling it to coordinate cellular responses and adaptations to diverse pathological stresses and maintain homeostasis (29). In recent years, an increasing number of studies have demonstrated that activation of the Nrf2-related signaling pathway can significantly promote the recovery and improvement of spinal cord nerve function after SCI (30–35).
Nrf2 plays a crucial role in secondary injury after SCI (36), numerous studies have demonstrated that Nrf2 enhances the expression of several protective genes such as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), superoxide dismutases (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), catalase (CAT), and NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). This action helps mitigate injury and promotes nerve repair after SCI (37–39). Additionally, several non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), biological macromolecules, and natural or synthetic compounds have been identified as activators of Nrf2 (40–42). These agents regulate the aforementioned pathological changes by activating the Nrf2-related signaling pathway, providing neuroprotective effects. Consequently, Nrf2 may serve as a promising therapeutic target for SCI. This review offers an in-depth analysis of Nrf2’s structure and regulation, while summarizing its mechanisms in SCI (Figure 1). Additionally, it explores the potential of ncRNAs, natural or synthetic compounds, biological macromolecules, and other therapeutic strategies to target this signaling pathway for effective SCI treatment.
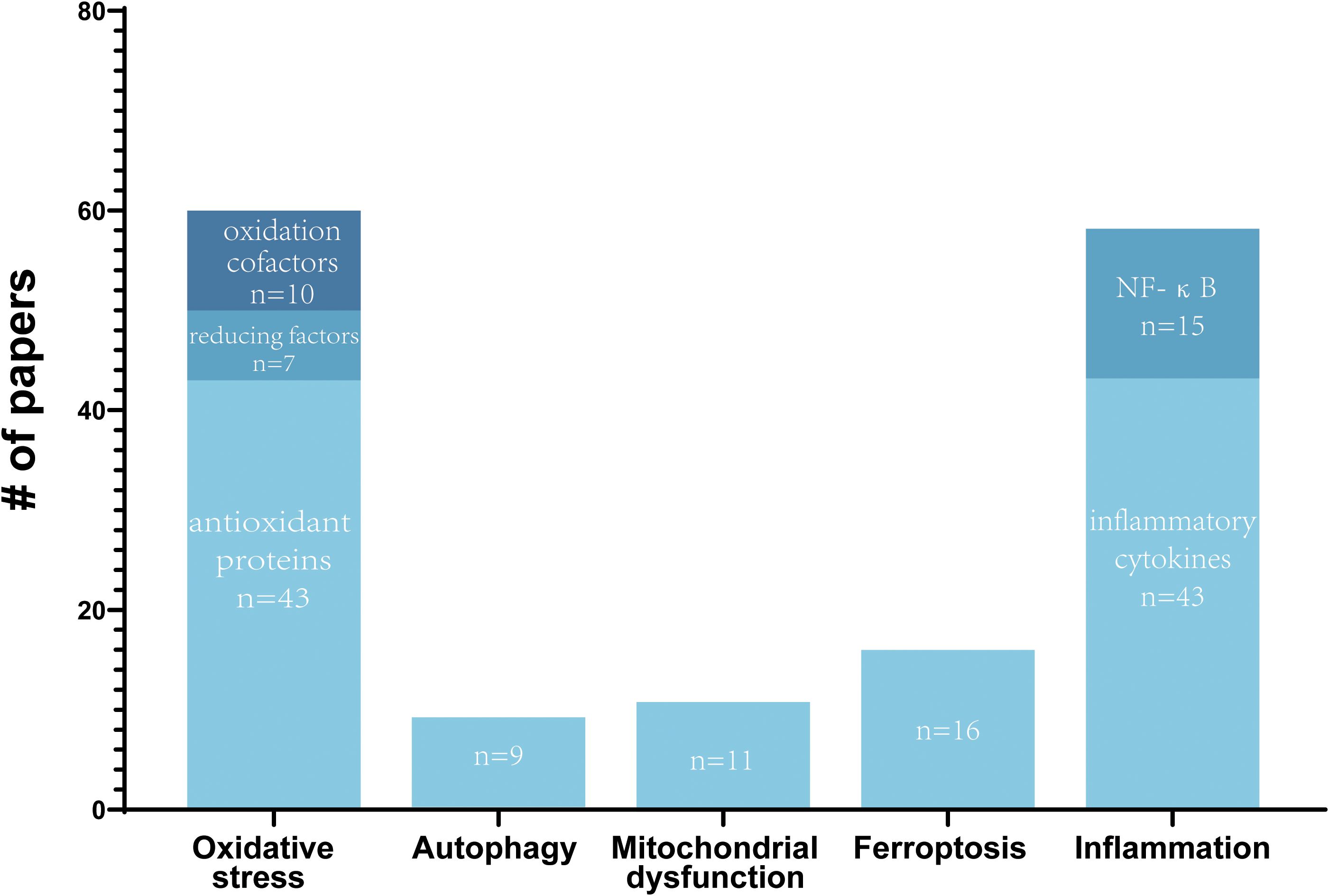
Figure 1. Summary of reported molecular mechanisms of Nrf2 in SCI. The number of papers by reported molecular mechanisms of Nrf2 in SCI are shown. Some papers report multiple molecular mechanisms.
2 The structure of Nrf2 and its upstream regulation in SCI
Nrf2 is a member of the Cap’n’Collar (CNC) family of basic-region leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors and is widely expressed across various mammalian cell types (43). The Nrf2 protein, which consists of 605 amino acids, contains seven highly conserved regions known as Nrf2-ECH homology (Neh) domains, labeled Neh1 through Neh7. These domains are crucial for its function in cellular stress responses, particularly in regulating the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense and detoxification (44). Neh1 includes the CNC-bZIP region, which forms a heterodimer with the leucine zipper motif of the small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma (sMaf) proteins in the nucleus. This heterodimer is responsible for recognizing and binding to the DNA gene sequence on ARE, thereby activating the transcription of target genes and regulating the expression of downstream antioxidant proteins (45). Neh2 interacts with Keap1 via its DLG and ETGE binding units, suppressing Nrf2’s transcriptional activity and promoting its degradation (46). The Neh3 domain, located at the carboxyl terminus of Nrf2, serves as a transactivation domain that interacts with chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 6 (CHD6) to sustain Nrf2 transcriptional activity (47). Neh4 and Neh5 domains are independent activation regions that regulate Nrf2 transcription through interactions with the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) binding protein (CBP) (48). Neh6 contains DSGIS and DSAPGS motifs that can bind with β-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP), playing a role in maintaining Nrf2 stability (49). Furthermore, glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) enhances Nrf2 ubiquitination and degradation by phosphorylating DSGIS, facilitating the binding of Nrf2 to β-TrCP (50). Neh7 inhibits Nrf2 activity by binding to retinoic X receptor α (RXRα) (51) (Figure 2A).
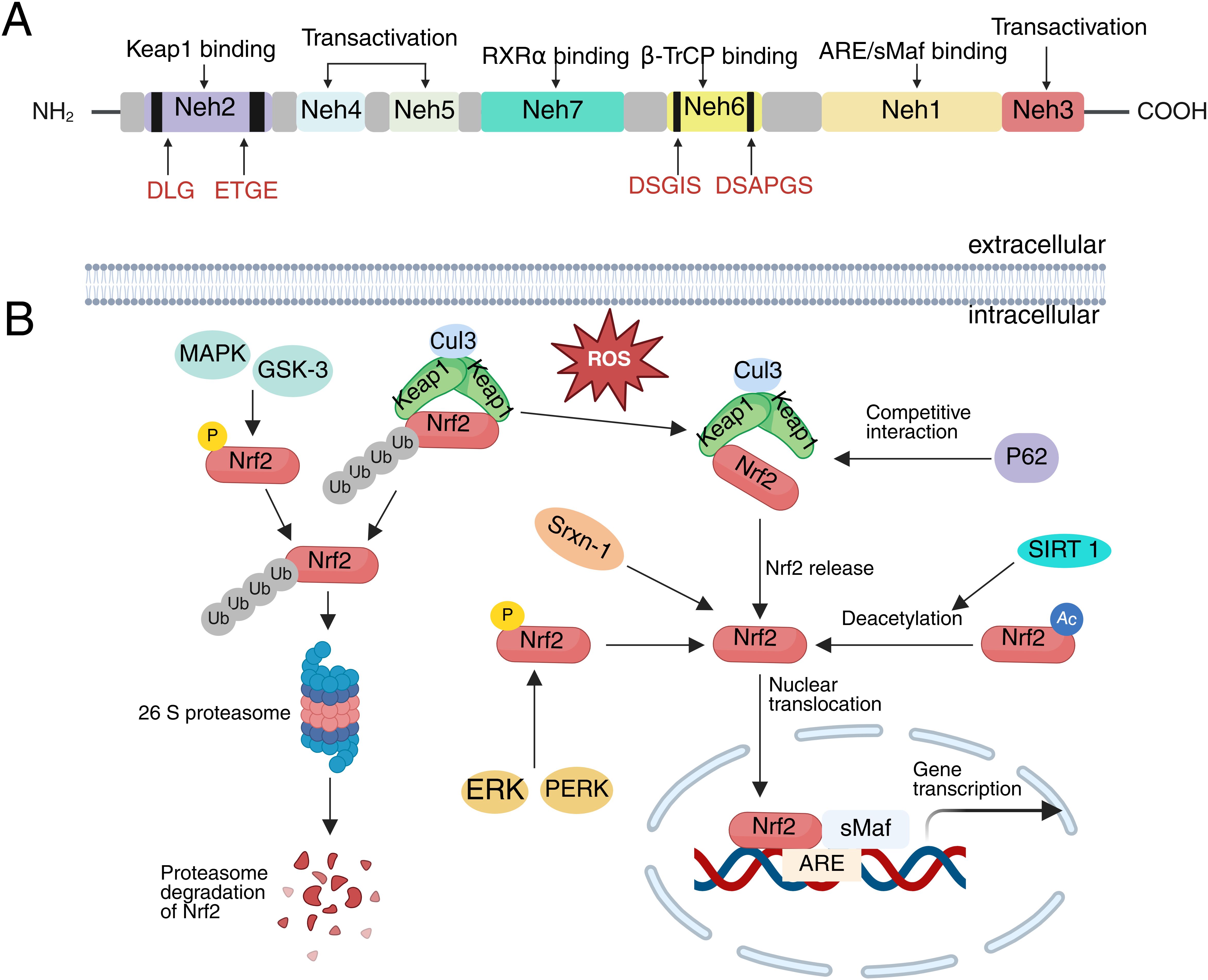
Figure 2. The structure of Nrf2 and its upstream regulation in SCI. (A) The domain structure of Nrf2, (B) Activation and Degradation of Nrf2.
In SCI, the upstream regulatory mechanisms of Nrf2 involve several complexes signaling pathways and molecular interactions. These mechanisms are critical for enabling Nrf2 to exert its cytoprotective effects, as they govern its activation and regulation in response to pathological and physiological changes such as oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy induced by SCI (52). The classical activation pathway of Nrf2 is primarily regulated by Keap1, a negative regulator of Nrf2 (45). Under physiological conditions, Keap1 in the cytoplasm binds to the ETGE and DLG motifs of Nrf2 and subsequently interacts with Cul3 via the Neh6 domain of Nrf2, promoting its ubiquitination and rapid degradation by the 26S proteasome (53, 54). Upon stimulation by oxidative stress or electrophiles, cysteine residues within Keap1 undergo oxidation and conformational changes. These alterations lead to an unstable association between Nrf2 and Keap1, thereby inhibiting the ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2 (55, 56). As a result, Nrf2 is released and translocates into the nucleus, where it heterodimerizes with sMaf. This complex ultimately binds to ARE, inducing transcriptional expression of genes encoding antioxidant enzymes and phase II detoxification enzymes (57). After SCI, Nrf2 is predominantly activated through this classical pathway, exerting a cytoprotective role (58).
Following SCI, in addition to the classical Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway for Nrf2 activation, Keap1-independent pathways exist that do not rely on the oxidation of cysteine residues in Keap1 (59). These pathways involve the phosphorylation and deacetylation of Nrf2 through the direct interaction of other proteins with Keap1, leading to the release and activation of Nrf2. Sequestosome 1 (P62/SQSTM1) is a multifunctional protein that binds to microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) to guide damaged substrates to autophagosomes for ubiquitination and degradation (60). Notably, P62 and Nrf2 share similar amino acid sequences. When autophagy is impaired following SCI, P62 competes with Nrf2 to bind Keap1, thereby preventing Keap1-mediated degradation of Nrf2 and promoting its nuclear translocation (61, 62). In addition to competitively binding Keap1, P62 can directly promote the degradation of Keap1 through selective autophagy, further activating Nrf2 (63). Sulfiredoxin-1 (Srxn1) is an endogenous antioxidant protein that can directly interact with Nrf2 and facilitate its translocation to the nucleus, thereby increasing its nuclear expression levels (64). Following SCI, this activity of Srxn1 helps to enhance Nrf2 function, improving the cellular response to oxidative stress. In addition, several kinases also phosphorylate Nrf2 and regulate its activity. For instance, protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) and extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) phosphorylate Nrf2 following SCI and promote its translocation to the nucleus (56, 65–68). Conversely, phosphorylation of Nrf2 by GSK-3β and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) promotes its degradation (69). Additionally, Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), a highly conserved NAD+-dependent deacetylase, can directly deacetylate Nrf2, promoting its nuclear translocation and enhancing its ability to bind to DNA, thereby increasing Nrf2 transcriptional activity following SCI (70) (Figure 2B). The upstream regulation of Nrf2 in SCI is multifaceted, involving protein-protein interactions, post-translational modifications, and transcriptional control. These regulatory mechanisms contribute to the sustained activation of Nrf2 following SCI. Activated Nrf2 performs multiple protective functions: it upregulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes, thereby mitigating oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage, and suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory factors, consequently attenuating inflammatory responses (70, 71). Additionally, Nrf2 regulates iron metabolism, reducing the risk of ferroptosis (32). It also promotes a microenvironment conducive to neural tissue repair by maintaining mitochondrial integrity and enhancing autophagy (72). Collectively, these mechanisms underscore the potential of Nrf2 as a key therapeutic target in SCI.
3 The role of Nrf2 in spinal cord injury
In the previous section, we discussed the complex structure of Nrf2 and its diverse and tightly regulated mechanisms of action. Many studies have confirmed that the activation of Nrf2-related signaling pathways plays a key role after SCI (73–75). In addition to directly regulating the oxidative stress response, Nrf2 also affects several other pathophysiological processes associated with SCI, such as inflammation, autophagy, iron metabolism, axon regeneration, and mitochondrial function. Given that the genes regulated by Nrf2 are involved in multiple dimensions of SCI pathology, its role in SCI is likely to be complex and multifactorial (75, 76). Therefore, we subsequently summarize the functional contributions of Nrf2 in SCI based on current research findings.
3.1 Nrf2 regulates oxidative stress
Primary injury of SCI leads to microvascular rupture, resulting in the destruction and lysis of numerous red blood cells and hemoglobin. Hypoxia and the accumulation of free iron in the injured area stimulate the production of excessive ROS (77). Under normal conditions, ROS are essential for regulating cellular functions such as neuronal activity and cell signaling pathways. However, excessive ROS can lead to lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, inflammation, and cell death, ultimately resulting in severe neurological dysfunction (78).
Nrf2 regulates the antioxidant system through multiple pathways, effectively lowering ROS levels following SCI. First, Nrf2 facilitates the breakdown of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide by regulating the activities of SOD, GPX, CAT, and NQO1. For instance, several studies have demonstrated that Nrf2 activation in SCI rat neuronal cells increases the expression of SOD, GPX, CAT, and glutathione (GSH), inhibiting malondialdehyde production and functioning as an antioxidant (79–81). Activation of the Nrf2 pathway also stimulates NQO1 expression. NQO1 catalyzes the reduction of quinones to hydroquinones, facilitating their clearance and preventing ROS generation from quinones via a single-step, double-electron reduction (38, 82). Nrf2 can reduce oxidative stress by boosting the expression of reducing factors. Upon activation, Nrf2 enhances the expression of the glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic (GCLC) subunit, which plays a key role in regulating GSH synthesis (83). Additionally, Nrf2 helps inhibit oxidative reactions by promoting the regeneration of oxidative cofactors and proteins (42). Furthermore, Nrf2 can directly stimulate the production of antioxidant proteins. For instance, salidroside activates Nrf2, which in turn promotes the expression of thioredoxin 1 (Trx1). This activation inhibits thioredoxin-interacting proteins, thereby exerting an antioxidant effect (84). Experiments have also confirmed that activation of Nrf2 signaling directly targets the ARE elements in the HO-1 and NQO1 genes, regulating their transcriptional activity and inducing the expression of antioxidant proteins (85–87) (Figure 3). In summary, Nrf2 mitigates oxidative stress injury after spinal cord injury (SCI) by regulating the expression of various antioxidant enzymes, demonstrating significant potential in reducing lipid peroxidation and preserving cell membrane integrity.
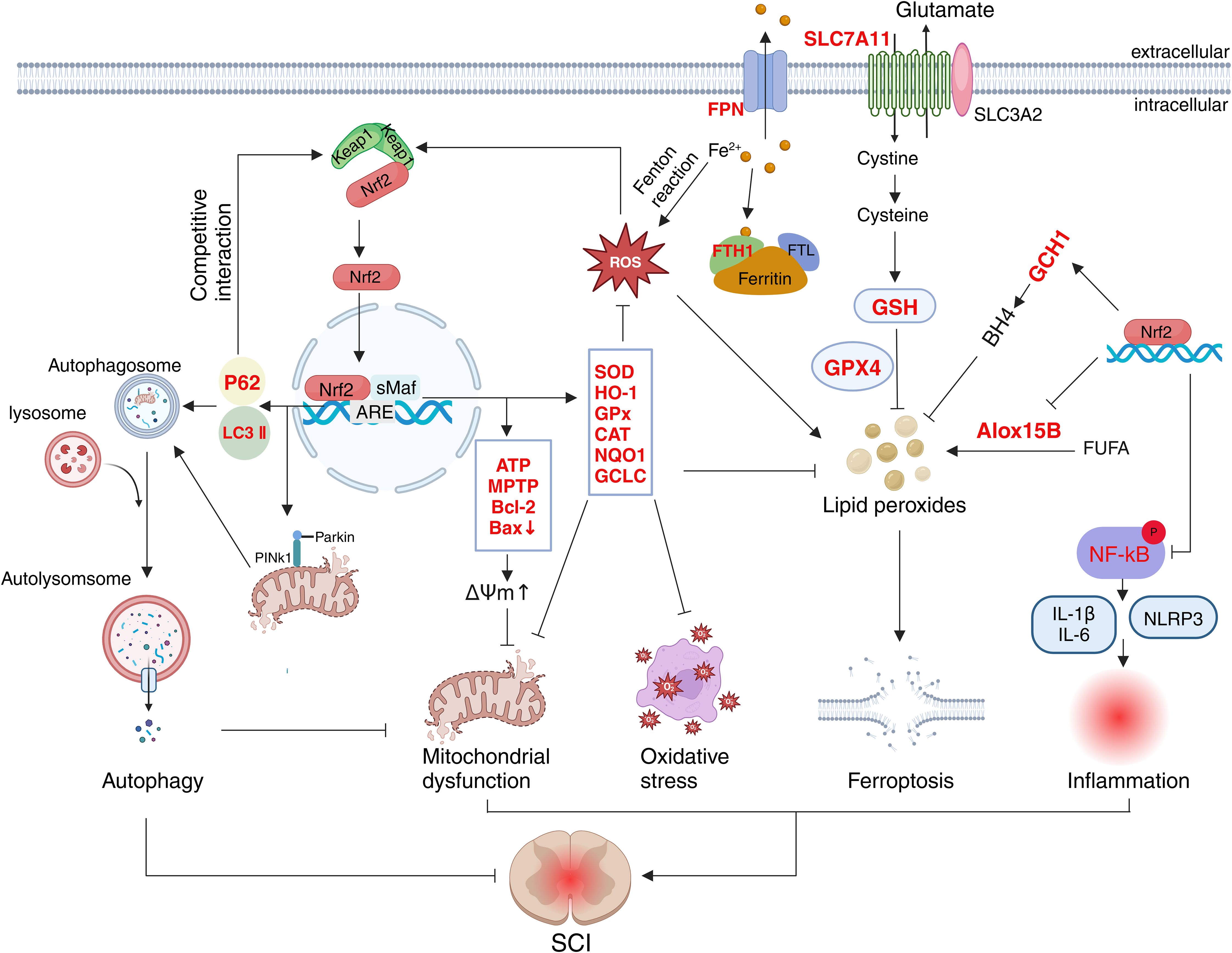
Figure 3. Schematic representation of the multifaceted role of Nrf2 in SCI. The target molecules of Nrf2 (marked in red) are involved in oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, autophagy, inflammation and ferroptosis.
3.2 Nrf2 regulates inflammation and immune cell infiltration
In addition to oxidative stress, inflammatory responses mediated by immune cells and inflammatory factors play a critical role in secondary injury following SCI. Local trauma resulting from SCI disrupts the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) and the local microenvironment, leading to the infiltration of monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes, as well as the release of inflammatory mediators at the injury site (88). These immune cells promote the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Ultimately, the interplay between various immune cells and cytokines results in a severe inflammatory response (15). While inflammation plays a beneficial role in the early stages after SCI, such as debris clearance and tissue repair, excessive immune cell infiltration remains a major contributor to neurological dysfunction (11, 89). After SCI, Nrf2 activation can mitigate the inflammatory response and protect nerve cells by regulating the activity of microglia, monocytes, and macrophages. Studies have demonstrated that activation of Nrf2 can inhibit microglial activation and reduce the expression of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β (70, 81, 90). Additionally, Various stimuli following SCI activate inflammasomes, leading to the release of inflammatory factors and subsequent cellular damage. Nrf2 also exerts an inhibitory effect on inflammasome activity. For example, an experiment demonstrated that activation of the Nrf2-related signaling inhibited the production of NLRP3 inflammasomes and increased neuronal survival (91). Notably, Nrf2 also exerts regulatory effects on immune cells such as lymphocytes and neutrophils in other disease models (69, 92, 93). However, there is currently no direct evidence that Nrf2 plays a similar regulatory role in SCI models; therefore, further research is required to confirm this hypothesis.
In addition, Nrf2 participates in neuro-immune interactions by regulating communication between the nervous system and immune cells, which is essential for coordinating inflammation and oxidative stress after SCI. Following SCI, Nrf2 activation in injured neurons and astrocytes promotes the release of neurotrophic factors and antioxidants (94, 95). These neuromodulators act directly on immune cells to inhibit their excessive activation (96). Furthermore, studies have shown that Nrf2 activation in injured neurons reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, thereby decreasing the permeability of the blood-spinal cord barrier (97, 98). Notably, maintaining the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier limits the abnormal infiltration of peripheral immune cells and suppresses their pro-inflammatory effects (99). Therefore, it is reasonable to speculate that Nrf2-mediated neuro-immune interaction constitutes a positive feedback loop associated with anti-inflammation and is important for the recovery of neurological function. Additionally, Nrf2 activation in microglia promotes macrophage polarization from the M1 to the M2 phenotype, and M2 macrophages secrete the anti-inflammatory factor interleukin-10 (IL-10), thereby exerting an anti-inflammatory effect during spinal cord repair (86, 100, 101). Conversely, in immune cells, Nrf2 activation can inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway, thus reducing the release of inflammatory mediators and alleviating inflammatory damage to neurons (102–104) (Figure 3). While Nrf2 mechanisms in SCI have been extensively studied, neuro-immune interactions remain underexplored despite their dual role as both drivers of secondary injury and therapeutic targets for neural repair. In-depth investigation of the specific mechanisms of Nrf2 in these interactions may facilitate the identification of new therapeutic targets and strategies, thereby improving the prognosis and quality of life of patients with spinal cord injury.
3.3 Nrf2 regulates mitochondrial function
Mitochondrial dysfunction represents another critical pathological process in SCI. Mitochondria, which contain their own unique DNA (mtDNA), are essential for the life activities of nerve cells. They act as the energy powerhouses of the cell and play a key role in regulating fatty acid oxidation, amino acid metabolism, neurogenesis, ROS production, apoptosis, and calcium ion homeostasis (105, 106). Studies have shown that mitochondrial dysfunction is closely associated with the pathological processes after SCI (35, 75, 107). During the acute phase of SCI, substantial changes in mitochondrial morphology and function occur, including mitochondrial swelling, loss of cristae structure, and a more relaxed endoplasmic reticulum. These alterations lead to increased ROS production and reduced ATP synthesis, causing oxidative damage to lipids and DNA, and ultimately triggering neuronal apoptosis (108–111).
Studies have demonstrated that Nrf2 plays a protective role in mitochondrial dysfunction after SCI through various regulatory mechanisms (112, 113). The activation of Nrf2 can induce the expression of multiple antioxidant enzymes and mitigate oxidative stress, thereby safeguarding mitochondria from damage. Experiments have confirmed that Nrf2 activation can promote the production of antioxidant enzymes such as HO-1, SOD2, NQO1, and GSH, thereby protecting mitochondria (100, 114). In nerve cells, Nrf2 can also regulate mitochondrial respiration and NADPH oxidase activity, thereby influencing ROS production (115). In addition to regulating oxidative stress, Nrf2 mitigates mitochondrial damage by regulating apoptosis following SCI. Mitochondrial disruption and membrane potential disorder represent irreversible points in the apoptosis cascade (116). In vitro model of spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury, researchers found that Nrf2 maintained the stability of mitochondrial membrane potential and prevented mitochondrial swelling and rupture by enhancing mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) activity and ATP levels (117). Another study has shown that Nrf2 can also maintain membrane potential and mitochondrial membrane stability by increasing anti-apoptotic protein expression and inhibiting pro-apoptotic protein expression, thereby reducing neuronal apoptosis (118). Additionally, Nrf2 activates PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy, promoting the recovery of mitochondrial function (119) (Figure 3). As the primary source of cellular energy, mitochondria are essential for most physiological activities (120). Further research is required to determine whether there is a synergistic effect between Nrf2-mediated improvement of mitochondrial dysfunction and other pathophysiological processes, such as oxidative stress and inflammation. Elucidating such interactions may reveal novel therapeutic targets to improve outcomes in SCI management.
3.4 Nrf2 regulates ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is also a significant component of the pathogenesis of SCI, further exacerbating neuronal death and dysfunction (121). Ferroptosis is a newly discovered form of iron-dependent programmed cell death, the primary mechanism involves iron metabolism dysregulation and ROS production, leading to PUFA lipid peroxidation, membrane damage, and cell death (122, 123). Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), a lipid repair enzyme, converts toxic lipid hydroperoxides (L-OOH) to non-toxic lipid alcohols (L-OH) on the cell membrane, thereby mitigating the effects of ferroptosis (124, 125). Additionally, System Xc- (a cystine/glutamate antiporter system) increases cellular uptake of cystine, promoting the synthesis of GSH, which is essential for maintaining GPX4 activity (126–128). Solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11/xCT) is a critical subunit of the system Xc- and plays a significant transport role (129). Therefore, GPX4 and its upstream regulators are critical determinants in modulating ferroptosis.
Recent research indicates that ferroptosis is closely related to the pathophysiological process of SCI (121). Following SCI, tissue necrosis and red blood cell destruction at the injury site led to increased local iron ion and ROS levels, resulting in elevated lipid peroxide production and, ultimately, ferroptosis (130). Studies have confirmed that Nrf2 activation promotes the expression of GPX4 and its upstream regulators, thereby reducing lipid peroxide accumulation, inhibiting ferroptosis, promoting neuronal survival, and alleviating SCI symptoms (32, 131). Furthermore, studies revealed that Nrf2 also upregulates GSH and SLC7A11 expression, further inhibiting ferroptosis after SCI (131, 132). In addition, the activation of Nrf2 lowers the levels of free iron ions and boosts the expression of ferroportin (FPN) and ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), which helps to mitigate ferroptosis-related damage following SCI (133). Notably, Nrf2 also inhibited the expression and activity of Alox15B, a lipoxygenase responsible for catalyzing the production of lipid peroxides from polyunsaturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids, thereby leading to ferroptosis (134). In addition to these mechanisms, Nrf2 promotes the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, GSH, HO-1, and GPX, thereby reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting ferroptosis (135, 136). Furthermore, Nrf2 activates the GTP cyclohydroxylase 1 (GCH1)/tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) signaling pathway, reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting ferroptosis. A recent study found that Nrf2 enhances the expression of GCH1, a key enzyme in the synthesis of BH4, which plays a key role in producing superoxide radicals (137–139) (Figure 3). Current evidence indicates that Nrf2 activation mitigates ferroptosis and ameliorates SCI through multiple mechanisms. However, systematic investigations into precise mechanisms and potential interactions or synergistic effects among these pathways remain insufficient.
3.5 Nrf2 regulates autophagy
Autophagy is an intracellular catabolic process that facilitates the degradation and recycling of damaged proteins, organelles, and other cellular components (140). This process can be broadly categorized into three types: macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy, with macroautophagy being the most extensively studied form (141). In response to stimuli such as hypoxia or stress, phagosomes are formed through membrane extensions from the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and other organelles. These phagosomes encapsulate damaged proteins and organelles to create autophagosomes. Subsequently, autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes to form autolysosomes where the degradation and recycling of damaged proteins and organelles occur (142–144). Autophagy serves as a critical defense mechanism within the body and plays a significant role in the pathophysiological processes of SCI. Most studies suggest that moderate autophagy following SCI helps remove damaged organelles and proteins, maintaining cellular homeostasis and promoting cell survival (145–147). However, other studies indicate that excessive activation or dysregulation of autophagy may have adverse effects, leading to autophagic cell death and exacerbating nerve damage (145, 148). This indicates that investigations of autophagy should extend beyond its cytoprotective functions to include its potential adverse effects. Specifically, it is critical to examine the mechanisms underlying the transition of autophagy from a protective to a harmful role, including abnormal activation of signaling pathways and failures in feedback regulation.
Studies have shown that activation of Nrf2 enhanced the expression of autophagy-related proteins, including P62, LC3, and Beclin-1, thereby promoting autophagy and ultimately exerting a neuroprotective effect (33, 72, 119). Notably, as previously mentioned, P62 can compete with Nrf2 for binding to Keap1, leading to the release and nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Thus, this reciprocal regulation between P62 and Nrf2 forms a positive feedback loop that is significant for cytoprotection. Furthermore, other studies have shown that mitophagy, a specialized form of autophagy, plays a key role in SCI (119, 147). Mitophagy removes damaged or excess mitochondria through autophagy, maintaining mitochondrial number stability and energy metabolism (149) (Figure 3). This finding underscores the therapeutic potential of mitophagy in the treatment of spinal cord injuries, as it may protect neurons by modulating mitochondrial quality and energy metabolism. However, the mechanisms underlying the interaction between mitophagy and other cellular processes require further investigation.
3.6 Nrf2-mediated protective effects on neuronal populations
Beyond the previously described neuroprotective molecular mechanisms, Nrf2 may also influence specific neuronal populations within the central nervous system (CNS). Neuronal populations refer to collections of neurons within the CNS categorized by characteristics such as origin, function, projection pathways, or molecular features (150). These populations are broadly classified into afferent (sensory) neurons, efferent (motor) neurons, and intrinsic spinal cord neurons. Key efferent populations originating from the brain and brainstem include corticospinal tract (CST), rubrospinal tract (RST), and vestibulospinal tract (VST) neurons (151). Afferent populations encompass sensory neurons, notably those within the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) cells (152). Collectively, these neuronal groups form essential circuits for sensory perception, information integration, and motor execution, thereby mediating the spinal cord’s role in sensorimotor function and adaptation. SCI induces neuronal damage through direct mechanical trauma and secondary injury mechanisms (99). Mechanical injury causes axonal disruption, neuronal cell body damage, and the breakdown of neural networks. Secondary pathological processes—including immune cell infiltration, inflammatory responses, and oxidative stress—exacerbate neuronal death and dysfunction (153). These cascades impair neuronal survival, disrupt synaptic signaling, and perpetuate long-term neurological deficits (13).
As previously mentioned, the activation of Nrf2 can facilitate the recovery of neuronal activity and function following spinal cord injury by modulating immune cells, inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, ferroptosis, and autophagy (82, 97, 119). Nrf2 contributes to the survival of neuronal populations and enhances axonal regeneration, partly through mechanisms involving the upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Consistent with this, research in SCI rat models indicates that Nrf2 activation elevates BDNF expression, correlating with enhanced neuronal plasticity and improved motor function recovery (154, 155). Furthermore, gene network analyses further identify Nrf2 as a critical regulator of axon regeneration-associated genes integral to axonal regeneration, a process fundamental to neurological restoration after traumatic injury (156). Experimental evidence confirms that Nrf2 activation enhances neurological recovery in rodent SCI models by promoting axonal regrowth (34). Mechanistically, Nrf2 upregulates Microtubule-Associated Protein 1B (MAP1B) transcription, a key driver of axon regeneration. MAP1B overexpression and phosphorylation facilitate axonal elongation, while Nrf2-mediated mitochondrial enhancement provides metabolic support for regeneration (157). Concurrently, Nrf2 bolsters neuronal oxidative stress tolerance, improving survival at injury sites (113). Collectively, these mechanisms contribute to functional restoration post-SCI. Although numerous studies underscore the beneficial impact of Nrf2 activation on neuronal populations post-SCI, the specific subpopulations affected and the precise underlying molecular mechanisms warrant further investigation.
4 Therapeutic potential of targeting Nrf2 signaling in SCI
Nrf2 is a classical signaling pathway involved in response to oxidative stress, playing a critical role in secondary injury following SCI (18). Aside from its antioxidant functions, Nrf2 also modulates various pathological processes such as inflammation, mitochondrial function, iron metabolism, autophagy, glial scar formation, and axon regeneration after SCI. These actions are essential for the recovery of nerve function post-injury. Consequently, Nrf2 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for SCI. In recent years, numerous studies have demonstrated that various non-coding RNAs, biomolecules, and drugs can activate the Nrf2-related signaling pathway, promoting the recovery of neurological function post-SCI (158, 159).
4.1 Non‐coding RNA
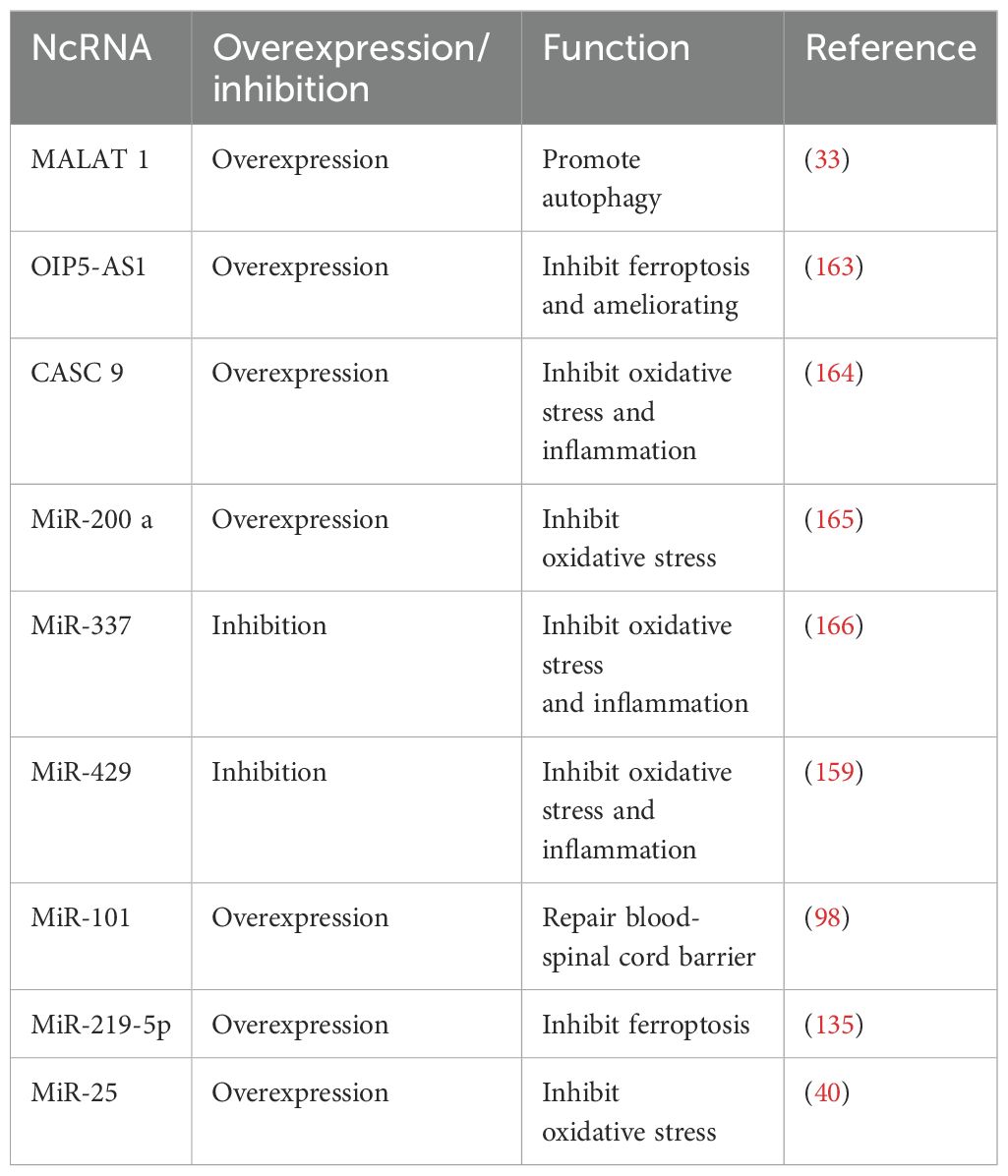
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) refers to a class of RNA molecules that do not encode proteins, including microRNA (miRNA), long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), circular RNA (circRNA), and others (160). These molecules play crucial roles in the regulation of gene expression, chromatin remodeling, RNA processing modifications, and various other biological processes (161). Studies have shown that many miRNAs and lncRNAs regulate the pathophysiological processes of spinal cord injury by activating or inhibiting the Nrf2-related signaling pathway. For instance, previous studies have confirmed that miR-429 is highly expressed in SCI rats, and its inhibition can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation by activating the Nrf2 pathway (159). Additionally, overexpression of lncRNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) has been shown to activate Nrf2, promote autophagy, and inhibit neuronal apoptosis (33). Notably, MALAT1 exhibits a contrasting regulatory role in certain tumors (162). However, whether its activation of Nrf2 in SCI could contribute to uncontrolled cell proliferation requires further investigation. According to reports, the expression of lncRNA OIP5-AS1 is decreased in SCI rats, and its overexpression can inhibit ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby effectively improving SCI (163). Furthermore, other ncRNAs, such as CASC9, MiR-200a, MiR-337, and MiR-101, also contribute to alleviating spinal cord injury by regulating oxidative stress responses, autophagy mechanisms, inflammatory reactions, ferroptosis pathways, and mitochondrial functions (98, 164–166) (Table 1).
4.2 Natural or synthetic compounds
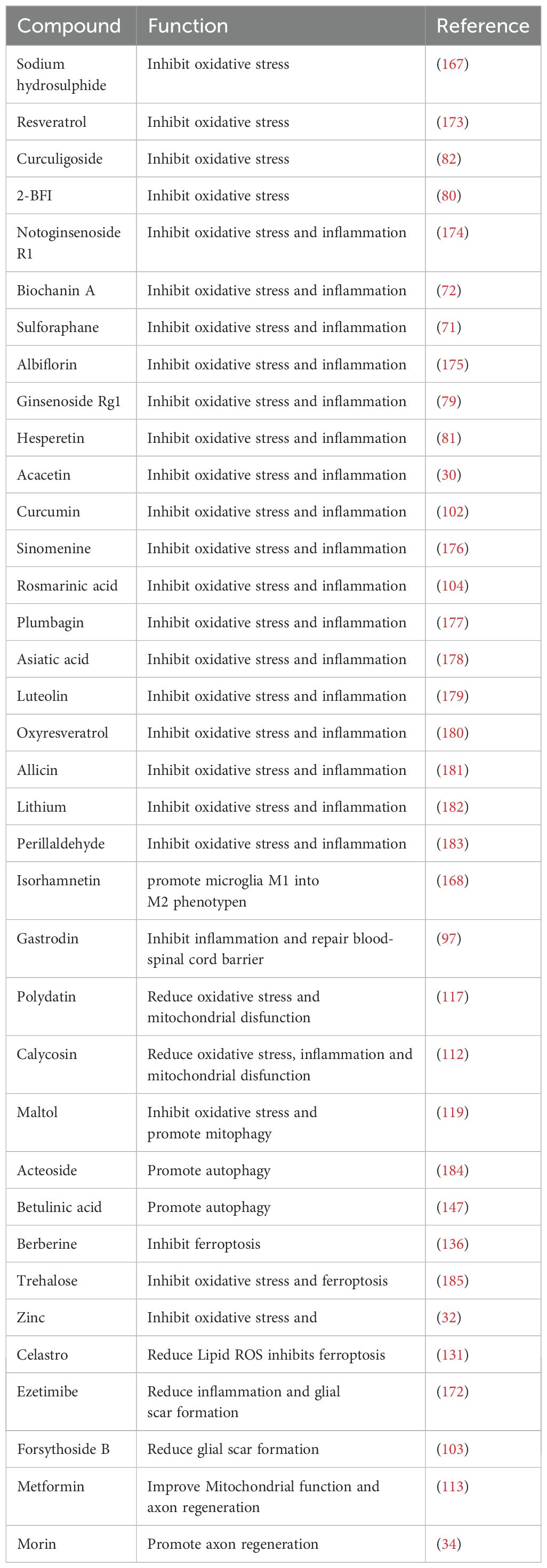
In recent years, numerous studies have demonstrated that various natural and synthetic compounds derived from plants can exert neuroprotective effects following SCI by activating the Nrf2-related signaling pathway (80, 97, 119, 167, 168). These compounds not only inhibit oxidative stress, inflammation, and ferroptosis, but also reduce glial scar formation, improve mitochondrial function, restore the integrity of the blood-brain barrier, and promote autophagy and axonal regeneration. For example, sulforaphane, an organic sulfide extracted from cruciferous vegetables, exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (169). In SCI rat models, treatment with sulforaphane was shown to mitigate oxidative stress and inflammatory responses by activating Nrf2, thereby playing a crucial neuroprotective role (71). Polydatin is a natural compound with antioxidant effects (170). According to reports, it could alleviate neuronal cell damage induced by mitochondrial dysfunction by activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway after SCI (117). Additionally, Zinc is a trace element in the human body that is essential for neurodevelopment, neurotransmission, and sensory processing (171). Several studies have indicated that zinc enhances Nrf2 expression after SCI, thereby reducing oxidative stress and ferroptosis (32). Ezetimibe is a medication commonly used to treat hypercholesterolemia. Recent research has demonstrated that ezetimibe can upregulate Nrf2 expression post-SCI while inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and glial scar formation (172). Ezetimibe, a drug used to treat hypercholesterolemia, has recently been shown to upregulate Nrf2 expression following spinal cord injury (SCI), thereby reducing oxidative stress, attenuating inflammatory responses, and suppressing glial scar formation [137]. While this finding highlights the potential for repurposing traditional drugs, the specific mechanisms underlying ezetimibe’s protective effects on spinal cord white matter integrity require further investigation. Furthermore, various compounds can activate the Nrf2-related signaling pathway to alleviate SCI (97, 103, 112, 113, 119, 167, 168, 173–185) (Table 2).
4.3 Biomolecules
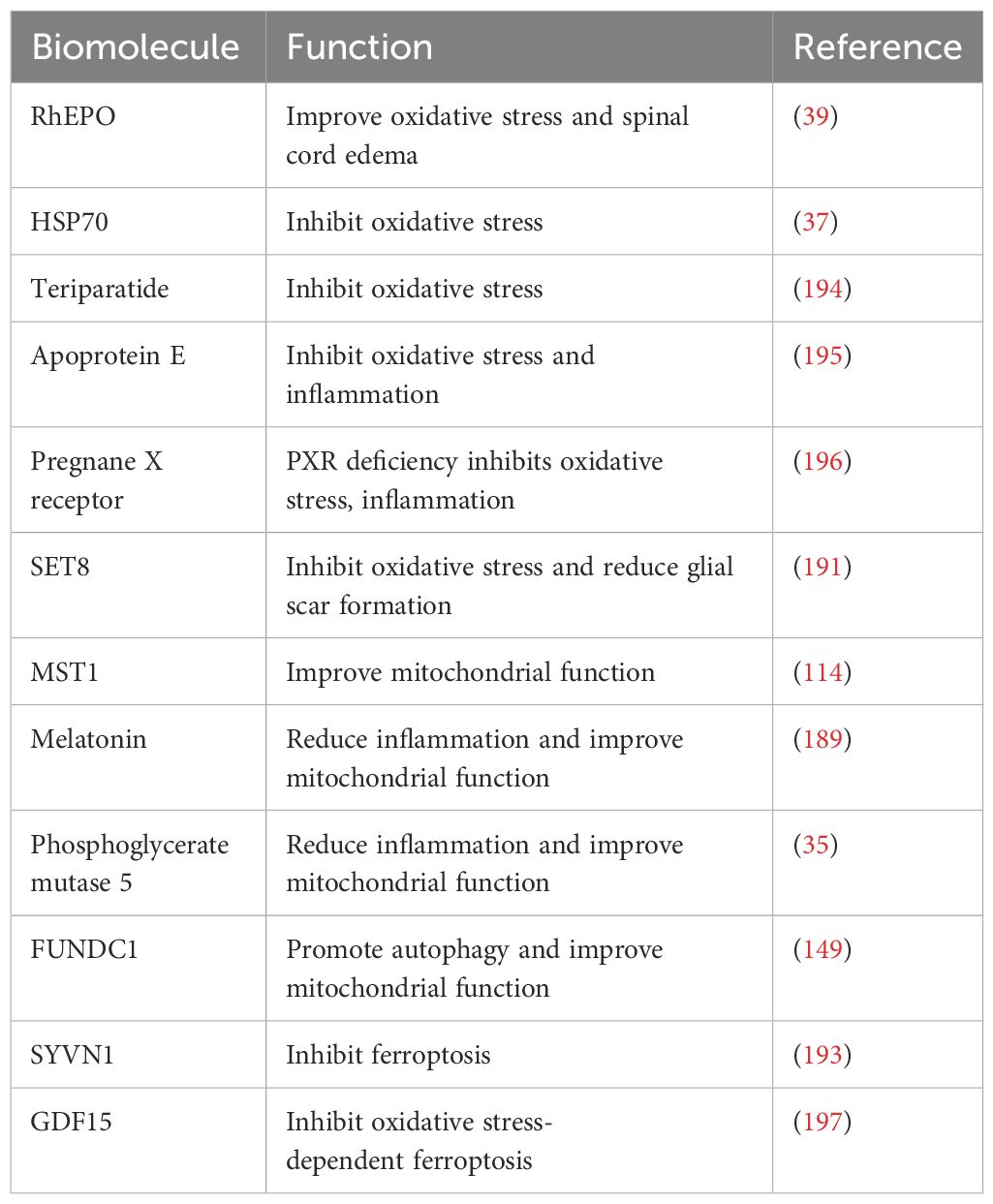
Biomolecules are a class of proteins with a wide range of biological activities and significant potential in treating spinal cord injury (186). For example, recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) is a protein hormone generated through genetic recombination technology. Beyond its role in stimulating the production of pre-red blood cells, erythropoietin (EPO) also possesses neuroprotective properties (187). According to reports, rhEPO can increase the expression of NQO1 and glutathione S-transferases (GST) by activating Nrf2, thereby reducing oxidative stress and spinal cord edema (39). Melatonin, a hormone secreted by the human pineal gland, exerts neuroprotective effects on various nervous system diseases (188). Studies have shown that melatonin inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome by stimulating the Nrf2/ARE pathway, thereby reducing inflammatory responses and mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction (189). SET8 is currently the only lysine methyltransferase identified that can specifically monomethylate the lysine 20 position of histone H4. This modification plays crucial roles in transcription regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA damage repair (190). Overexpression of SET8 can alleviate oxidative stress and reduce glial scar formation by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway (191). Synoviolin 1 (SYVN1) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in various cellular biological processes (192). Experiments have confirmed that SYVN1 overexpression could enhance the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and inhibit ferroptosis in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury (193). Although this study provides preliminary evidence supporting the potential therapeutic application of SYVN1 in SCI treatment, it does not fully elucidate the regulatory mechanisms through which SYVN1 overexpression modulates ferroptosis-related proteins such as GPX4 and ferroportin. Furthermore, as SYVN1 functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase, its role in regulating protein homeostasis may be intricately linked to the pathophysiology of SCI. Additional investigations are required to validate these hypotheses and elucidate the underlying mechanisms. Furthermore, we summarized other biomacromolecules that attenuate SCI by activating Nrf2-related signaling pathway (194–197) (Table 3).
4.4 Stem cells, exosomes, and a ketogenic diet
In addition to ncRNAs, compounds, and biological macromolecules, several studies have found that stem cell transplantation, exosomes, and a ketogenic diet can also target Nrf2 and alleviate SCI. For instance, bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) are multilineage cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into various cell types, and they are widely found in bone marrow and other tissues (198). Studies have confirmed that the combined treatment of BMSCs and plumbagin could alleviate SCI through the activation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and Nrf2-related signaling pathway (199). In addition, exosomes are vesicles secreted by cells into the extracellular space and are considered potential drug candidates for treating various diseases (200). Studies have found that microglia-derived exosomes (MG-Exos) can induce the expression of downstream antioxidant-related genes such as NQO1, GCLC, and CAT by activating the Nrf2-related signaling pathway, thereby promoting angiogenesis and neurological function recovery after SCI (201). Furthermore, the ketogenic diet is a dietary pattern characterized by high fat, low carbohydrate, and moderate protein intake, which simulates a state of human starvation and uses ketone bodies produced by fat metabolism as an energy source (202). Studies have shown that the ketogenic diet induced Nrf2 activation and reduced oxidative stress and inflammation (203).
5 Conclusion
The primary injury in SCI is usually irreversible, whereas the pathological process of the secondary injury can be reversed. Therefore, the treatment strategy for SCI should focus on blocking the progression of the latter and promoting nerve regeneration and functional recovery. Nrf2 can play a neuroprotective role by regulating various pathways. In this review, we provide an in-depth analysis of Nrf2’s structure and regulation, summarize its mechanisms in SCI, and explore the therapeutic potential of targeting this signaling pathway. Activation of the Nrf2-related signaling pathway is beneficial for reducing tissue damage and promoting neurological function recovery after SCI. This involves mechanisms such as antioxidative stress, anti-inflammation, regulation of mitochondrial function, activation of autophagy, and inhibition of ferroptosis. Therefore, we propose that Nrf2 is a valuable therapeutic target. Despite the fundamental understanding of the relationship between the complex pathophysiological mechanisms of SCI and Nrf2-related signaling pathway, some deficiencies and challenges remain that need to be addressed by future studies. First, the pathophysiological changes in SCI are a dynamic process, and different therapeutic strategies may be required to target different stages after injury. Further studies are essential to elucidate the role and regulatory mechanisms of the Nrf2-related signaling pathway at various stages of SCI. Additionally, while numerous natural and synthetic compounds have been identified that target the activation of the Nrf2-related signaling pathway and mitigate SCI in animal or cellular models, current research seldom addresses the long-term effects and potential side effects associated with Nrf2 activation. These factors must be considered for future clinical applications. Furthermore, Collaboration among neuroscientists, molecular biologists, pharmacologists, and clinicians will facilitate the translation of Nrf2-related therapeutics from laboratory settings to clinical practice. Finally, ncRNAs and stem cell therapies have demonstrated promise in treating SCI, however, more comprehensive investigations are required to unravel their complex mechanisms of action and to expand targeted therapeutic options for SCI.
Author contributions
TX: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. XL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. TW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. FG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HY: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by the Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation Project (No. LH2022H097); Heilongjiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project (No. ZHY2024-212).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. He W, Li ZQ, Gu HY, Pan QL, and Lin FX. Targeted therapy of spinal cord injury: inhibition of apoptosis is a promising therapeutic strategy. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 61:4222–39. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03814-w
2. Chay W and Kirshblum S. Predicting outcomes after spinal cord injury. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. (2020) 31:331–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pmr.2020.03.003
3. Anjum A, Yazid MD, Fauzi Daud M, Idris J, Ng AMH, Selvi Naicker A, et al. Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(20):7533. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207533
4. Karsy M and Hawryluk G. Modern medical management of spinal cord injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2019) 19:65. doi: 10.1007/s11910-019-0984-1
5. Liu Y, Yang X, He Z, Li J, Li Y, Wu Y, et al. Spinal cord injury: global burden from 1990 to 2019 and projections up to 2030 using bayesian age-period-cohort analysis. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1304153. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1304153
6. Zhang Y, Al Mamun A, Yuan Y, Lu Q, Xiong J, Yang S, et al. Acute spinal cord injury: pathophysiology and pharmacological intervention (Review). Mol Med Rep. (2021) 23(6):417. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12056
7. Yin J, Gong G, Wan W, and Liu X. Pyroptosis in spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci. (2022) 16:949939. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.949939
8. Alcántar-Garibay OV, Incontri-Abraham D, and Ibarra A. Spinal cord injury-induced cognitive impairment: A narrative review. Neural Regener Res. (2022) 17:2649–54. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.339475
9. Zhang Y, Tang X, Dai J, Li Y, and Ma J. Unveiling vital biomarkers and immune infiltration profiles in endoplasmic reticulum stress following spinal cord injury. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:29981. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81844-7
10. Hellenbrand DJ, Quinn CM, Piper ZJ, Elder RT, Mishra RR, Marti TL, et al. The secondary injury cascade after spinal cord injury: an analysis of local cytokine/chemokine regulation. Neural Regener Res. (2024) 19:1308–17. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.385849
11. Hellenbrand DJ, Quinn CM, Piper ZJ, Morehouse CN, Fixel JA, and Hanna AS. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: A review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflamm. (2021) 18:284. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02337-2
12. Li X, Jiao K, Liu C, Li X, Wang S, Tao Y, et al. Bibliometric analysis of the inflammation expression after spinal cord injury: current research status and emerging frontiers. Spinal Cord. (2024) 62:609–18. doi: 10.1038/s41393-024-01038-w
13. Hu X, Xu W, Ren Y, Wang Z, He X, Huang R, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:245. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01477-6
14. Yin Z, Wan B, Gong G, and Yin J. Ros: executioner of regulating cell death in spinal cord injury. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1330678. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1330678
15. Liu X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, and Qian T. Inflammatory response to spinal cord injury and its treatment. World Neurosurg. (2021) 155:19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.07.148
16. Zeller SL, Stein A, Frid I, Carpenter AB, Soldozy S, Rawanduzy C, et al. Critical care of spinal cord injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2024) 24:355–63. doi: 10.1007/s11910-024-01357-8
17. Shah M, Peterson C, Yilmaz E, Halalmeh DR, and Moisi M. Current advancements in the management of spinal cord injury: A comprehensive review of literature. Surg Neurol Int. (2020) 11:2. doi: 10.25259/sni_568_2019
18. Xiao CL, Lai HT, Zhou JJ, Liu WY, Zhao M, and Zhao K. Nrf2 signaling pathway: focus on oxidative stress in spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 61(2):2230–49. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04394-z
19. Buendia I, Michalska P, Navarro E, Gameiro I, Egea J, and León R. Nrf2-are pathway: an emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther. (2016) 157:84–104. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.11.003
20. Che J, Yang X, Jin Z, and Xu C. Nrf2: A promising therapeutic target in bone-related diseases. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115748. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115748
21. Li Y, Tuerxun H, Liu X, Zhao Y, Wen S, Li Y, et al. Nrf2–a hidden bridge linking cancer stem cells to ferroptosis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2023) 190:104105. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104105
22. Sykiotis GP and Bohmann D. Stress-activated cap'n'collar transcription factors in aging and human disease. Sci Signal. (2010) 3:re3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3112re3
23. Sivinski J, Zhang DD, and Chapman E. Targeting nrf2 to treat cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2021) 76:61–73. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.06.003
24. Kumar A and Mittal R. Nrf2: A potential therapeutic target for diabetic neuropathy. Inflammopharmacology. (2017) 25:393–402. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0339-y
25. Uruno A and Yamamoto M. The keap1-nrf2 system and neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2023) 38:974–88. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0234
26. Ungvari Z, Tarantini S, Nyúl-Tóth Á, Kiss T, Yabluchanskiy A, Csipo T, et al. Nrf2 dysfunction and impaired cellular resilience to oxidative stressors in the aged vasculature: from increased cellular senescence to the pathogenesis of age-related vascular diseases. Geroscience. (2019) 41:727–38. doi: 10.1007/s11357-019-00107-w
27. Iqbal MJ, Kabeer A, Abbas Z, Siddiqui HA, Calina D, Sharifi-Rad J, et al. Interplay of oxidative stress, cellular communication and signaling pathways in cancer. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:7. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01398-5
28. Mayer C, Riera-Ponsati L, Kauppinen S, Klitgaard H, Erler JT, and Hansen SN. Targeting the nrf2 pathway for disease modification in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1437939. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1437939
29. Aranda-Rivera AK, Cruz-Gregorio A, Pedraza-Chaverri J, and Scholze A. Nrf2 activation in chronic kidney disease: promises and pitfalls. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11(6):1112. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061112
30. Zhang X, Xu L, Chen X, Zhou X, and Cao L. Acacetin alleviates neuroinflammation and oxidative stress injury via the nrf2/ho-1 pathway in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Transl Neurosci. (2022) 13:483–94. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0266
31. Abdanipour A, Nikfar A, Nikbakht Rad M, Jafari Anarkooli I, and Mansouri M. Neuroprotective effect of L-deprenyl on the expression level of the mst1 gene and inhibition of apoptosis in rat-model spinal cord injury. Iran J Basic Med Sci. (2022) 25:53–9. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2022.58031.12894
32. Ge MH, Tian H, Mao L, Li DY, Lin JQ, Hu HS, et al. Zinc attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury by activating nrf2/gpx4 defense pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2021) 27:1023–40. doi: 10.1111/cns.13657
33. Hu J, Huang K, Bao F, Zhong S, Fan Q, and Li W. Low-dose lipopolysaccharide inhibits spinal cord injury-induced neuronal apoptosis by regulating autophagy through the lncrna malat1/nrf2 axis. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e15919. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15919
34. Jin H, Qi F, Chu F, Liu C, Qian T, Zeng W, et al. Morin improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats by enhancing axon regeneration via the nrf2/ho-1 pathway. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:5754–66. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7234
35. Dai C, Qu B, Peng B, Liu B, Li Y, Niu C, et al. Phosphoglycerate mutase 5 facilitates mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in spinal tissues after spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 116:109773. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109773
36. Zheng Q, Wang D, Lin R, and Xu W. Pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and autophagy in spinal cord injury: regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Neural Regener Res. (2024) 19(10):2787–806. doi: 10.4103/nrr.Nrr-d-24-00112
37. Deng B, He X, Wang Z, Kang J, Zhang G, Li L, et al. Hsp70 protects pc12 cells against tbhp-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress by activating the nrf2/ho-1 signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. (2024) 60:868–78. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00924-0
38. Dinkova-Kostova AT and Talalay P. Nad(P)H:Quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (Nqo1), a multifunctional antioxidant enzyme and exceptionally versatile cytoprotector. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2010) 501:116–23. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.03.019
39. Jin W, Ming X, Hou X, Zhu T, Yuan B, Wang J, et al. Protective effects of erythropoietin in traumatic spinal cord injury by inducing the nrf2 signaling pathway activation. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. (2014) 76:1228–34. doi: 10.1097/ta.0000000000000211
40. Guo Y and Niu S. Mir-25 protects pc-12 cells from H(2)O(2) mediated oxidative damage via wnt/B-catenin pathway. J Spinal Cord Med. (2018) 41:416–25. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2017.1336319
41. Li D, Tian H, Li X, Mao L, Zhao X, Lin J, et al. Zinc promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury by activating nrf2/ho-1 defense pathway and inhibiting inflammation of nlrp3 in nerve cells. Life Sci. (2020) 245:117351. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117351
42. Kryl'skii ED, Popova TN, Safonova OA, Stolyarova AO, Razuvaev GA, and de Carvalho MAP. Transcriptional regulation of antioxidant enzymes activity and modulation of oxidative stress by melatonin in rats under cerebral ischemia / reperfusion conditions. Neuroscience. (2019) 406:653–66. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.01.046
43. Liu T, Lv YF, Zhao JL, You QD, and Jiang ZY. Regulation of nrf2 by phosphorylation: consequences for biological function and therapeutic implications. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 168:129–41. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.034
44. Hao W, Li M, Cai Q, Wu S, Li X, He Q, et al. Roles of nrf2 in fibrotic diseases: from mechanisms to therapeutic approaches. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:889792. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.889792
45. Ulasov AV, Rosenkranz AA, Georgiev GP, and Sobolev AS. Nrf2/keap1/are signaling: towards specific regulation. Life Sci. (2022) 291:120111. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120111
46. Chen N, Hu M, Jiang T, Xiao P, and Duan JA. Insights into the molecular mechanisms, structure-activity relationships and application prospects of polysaccharides by regulating nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Carbohydr Polym. (2024) 333:122003. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122003
47. Wang T, Liang X, Abeysekera IR, Iqbal U, Duan Q, Naha G, et al. Activation of the nrf2-keap 1 pathway in short-term iodide excess in thyroid in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:4383652. doi: 10.1155/2017/4383652
48. Sivandzade F, Prasad S, Bhalerao A, and Cucullo L. Nrf2 and nf-κb interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. (2019) 21:101059. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.11.017
49. Zamponi E, Zamponi N, Coskun P, Quassollo G, Lorenzo A, Cannas SA, et al. Nrf2 stabilization prevents critical oxidative damage in down syndrome cells. Aging Cell. (2018) 17:e12812. doi: 10.1111/acel.12812
50. Srivastava R, Fernández-Ginés R, Encinar JA, Cuadrado A, and Wells G. The current status and future prospects for therapeutic targeting of keap1-nrf2 and B-trcp-nrf2 interactions in cancer chemoresistance. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 192:246–60. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.09.023
51. Wang H, Liu K, Geng M, Gao P, Wu X, Hai Y, et al. Rxrα Inhibits the nrf2-are signaling pathway through a direct interaction with the neh7 domain of nrf2. Cancer Res. (2013) 73:3097–108. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-3386
52. Li K, Lu L, Yao X, Wu Z, Sun P, Wen X, et al. The nfatc2/nrf2 cascade regulates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by controlling inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress. Regener Ther. (2025) 28:126–33. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.11.014
53. Silva-Islas CA and Maldonado PD. Canonical and non-canonical mechanisms of nrf2 activation. Pharmacol Res. (2018) 134:92–9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.06.013
54. Zhang DD. Mechanistic studies of the nrf2-keap1 signaling pathway. Drug Metab Rev. (2006) 38:769–89. doi: 10.1080/03602530600971974
55. Liu S, Pi J, and Zhang Q. Signal amplification in the keap1-nrf2-are antioxidant response pathway. Redox Biol. (2022) 54:102389. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102389
56. Bryan HK, Olayanju A, Goldring CE, and Park BK. The nrf2 cell defence pathway: keap1-dependent and -independent mechanisms of regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. (2013) 85:705–17. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.11.016
57. Motohashi H and Yamamoto M. Nrf2-keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med. (2004) 10:549–57. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.09.003
58. Kanninen KM, Pomeshchik Y, Leinonen H, Malm T, Koistinaho J, and Levonen AL. Applications of the keap1-nrf2 system for gene and cell therapy. Free Radic Biol Med. (2015) 88(Pt B):350–61. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.037
59. Krajka-Kuźniak V, Paluszczak J, and Baer-Dubowska W. The nrf2-are signaling pathway: an update on its regulation and possible role in cancer prevention and treatment. Pharmacol Rep. (2017) 69:393–402. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2016.12.011
60. Qin JJ, Cheng XD, Zhang J, and Zhang WD. Dual roles and therapeutic potential of keap1-nrf2 pathway in pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. Cell Commun Signal. (2019) 17:121. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0435-2
61. Lau A, Wang XJ, Zhao F, Villeneuve NF, Wu T, Jiang T, et al. A noncanonical mechanism of nrf2 activation by autophagy deficiency: direct interaction between keap1 and P62. Mol Cell Biol. (2010) 30:3275–85. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00248-10
62. Jiang T and He Y. Recent advances in the role of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 in spinal cord injury: regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic options. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:851257. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.851257
63. Baird L and Yamamoto M. The molecular mechanisms regulating the keap1-nrf2 pathway. Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 40(13):e00099–20. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00099-20
64. Wu Z, Lu Z, Ou J, Su X, and Liu J. Inflammatory response and oxidative stress attenuated by sulfiredoxin−1 in neuron−Like cells depends on nuclear factor erythroid−2−Related factor 2. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:4734–42. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11545
65. Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Anton MI, Floria M, Seritean Isac PN, Hurjui LL, et al. Oxidative stress and nrf2/keap1/are pathway in diabetic kidney disease (Dkd): new perspectives. Biomolecules. (2022) 12(9):1227. doi: 10.3390/biom12091227
66. Pi J, Bai Y, Reece JM, Williams J, Liu D, Freeman ML, et al. Molecular mechanism of human nrf2 activation and degradation: role of sequential phosphorylation by protein kinase ck2. Free Radic Biol Med. (2007) 42:1797–806. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.001
67. Almeida LM, Pinho BR, Duchen MR, and Oliveira JMA. The perks of mitochondria protection during stress: insights for perk modulation in neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. (2022) 97:1737–48. doi: 10.1111/brv.12860
68. Yuan X, Xu C, Pan Z, Keum YS, Kim JH, Shen G, et al. Butylated hydroxyanisole regulates are-mediated gene expression via nrf2 coupled with erk and jnk signaling pathway in hepg2 cells. Mol Carcinog. (2006) 45:841–50. doi: 10.1002/mc.20234
69. He F, Ru X, and Wen T. Nrf2, a transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(13):4777. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134777
70. Chen S, Ye J, Wu G, Shi J, Li X, Chen X, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 inhibition ameliorates microglia-mediated neuro-inflammation via the sirt1/nrf2 pathway after traumatic spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. (2023) 37:503–18. doi: 10.1177/15459683231183716
71. Benedict AL, Mountney A, Hurtado A, Bryan KE, Schnaar RL, Dinkova-Kostova AT, et al. Neuroprotective effects of sulforaphane after contusive spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. (2012) 29:2576–86. doi: 10.1089/neu.2012.2474
72. Li X, Fu J, Guan M, Shi H, Pan W, and Lou X. Biochanin a attenuates spinal cord injury in rats during early stages by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammasome activation. Neural Regener Res. (2024) 19:2050–6. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390953
73. Samarghandian S, Pourbagher-Shahri AM, Ashrafizadeh M, Khan H, Forouzanfar F, Aramjoo H, et al. A pivotal role of the nrf2 signaling pathway in spinal cord injury: A prospective therapeutics study. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. (2020) 19:207–19. doi: 10.2174/1871527319666200604175118
74. Zhou Z, Liu C, Chen S, Zhao H, Zhou K, Wang W, et al. Activation of the nrf2/are signaling pathway by probucol contributes to inhibiting inflammation and neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:52078–93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19107
75. Guo X, Kang J, Wang Z, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhu D, et al. Nrf2 signaling in the oxidative stress response after spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. (2022) 498:311–24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.007
76. Hiebert P. The nrf2 transcription factor: A multifaceted regulator of the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol Plus. (2021) 10:100057. doi: 10.1016/j.mbplus.2021.100057
77. Li H, Kong R, Wan B, Yang L, Zhang S, Cao X, et al. Initiation of pi3k/akt pathway by igf-1 decreases spinal cord injury-induced endothelial apoptosis and microvascular damage. Life Sci. (2020) 263:118572. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118572
78. Ma Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2013) 53:401–26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140320
79. Zhang Z, Yang K, Mao R, Zhong D, Xu Z, Xu J, et al. Ginsenoside rg1 inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation in rats with spinal cord injury via nrf2/ho-1 signaling pathway. Neuroreport. (2022) 33:81–9. doi: 10.1097/wnr.0000000000001757
80. Lin X, Zhu J, Ni H, Rui Q, Sha W, Yang H, et al. Treatment with 2-bfi attenuated spinal cord injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via the nrf2 signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci. (2019) 13:567. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00567
81. Liu Z, Tu K, Zou P, Liao C, Ding R, Huang Z, et al. Hesperetin ameliorates spinal cord injury by inhibiting nlrp3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis through enhancing nrf2 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 118:110103. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110103
82. Hou Y, Liang C, Sui L, Li Y, Wang K, Li X, et al. Curculigoside regulates apoptosis and oxidative stress against spinal cord injury by modulating the nrf-2/nqo-1 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 62(3):3082–97. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04409-9
83. Li W, Jiang D, Li Q, Yao S, Sun X, Yang Y, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced preconditioning protects against traumatic spinal cord injury by upregulating nrf2 expression in rats. Life Sci. (2016) 162:14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.08.008
84. Li F, Mao Q, Wang J, Zhang X, Lv X, Wu B, et al. Salidroside inhibited cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via nrf2/trx1 signaling pathway. Metab Brain Dis. (2022) 37:2965–78. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01061-x
85. Li Z, Wu F, Xu D, Zhi Z, and Xu G. Inhibition of trem1 reduces inflammation and oxidative stress after spinal cord injury (Sci) associated with ho-1 expressions. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 109:2014–21. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.159
86. Wang Y, Xiong Z, Qiao Y, Zhang Q, Zhou G, Zhou C, et al. Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid modulates macrophage polarization and schwann cell migration to accelerate spinal cord injury repair in rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2024) 30:e14642. doi: 10.1111/cns.14642
87. Luo Y, He YZ, Wang YF, Xu YX, and Yang L. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes ameliorate spinal cord injury in rats by activating the nrf2/ho-1 pathway and regulating microglial polarization. Folia Neuropathol. (2023) 61:326–35. doi: 10.5114/fn.2023.130455
88. Li C, Xiong W, Wan B, Kong G, Wang S, Wang Y, et al. Role of peripheral immune cells in spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2022) 80:2. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04644-0
89. Jin Y, Song Y, Lin J, Liu T, Li G, Lai B, et al. Role of inflammation in neurological damage and regeneration following spinal cord injury and its therapeutic implications. Burns Trauma. (2023) 11:tkac054. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkac054
90. Kim Y, Kim J, Ahn M, and Shin T. Lithium ameliorates rat spinal cord injury by suppressing glycogen synthase kinase-3β and activating heme oxygenase-1. Anat Cell Biol. (2017) 50:207–13. doi: 10.5115/acb.2017.50.3.207
91. Yang H, Hu B, Wang X, Chen W, and Zhou H. The effects of hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1 (Hapln1) in ameliorating spinal cord injury mediated by nrf2. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (2024) 71:929–39. doi: 10.1002/bab.2587
92. Pant T, Uche N, Juric M, Zielonka J, and Bai X. Regulation of immunomodulatory networks by nrf2-activation in immune cells: redox control and therapeutic potential in inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. (2024) 70:103077. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103077
93. He F, Antonucci L, and Karin M. Nrf2 as a regulator of cell metabolism and inflammation in cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2020) 41:405–16. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaa039
94. Zhao W, Gasterich N, Clarner T, Voelz C, Behrens V, Beyer C, et al. Astrocytic nrf2 expression protects spinal cord from oxidative stress following spinal cord injury in a male mouse model. J Neuroinflamm. (2022) 19:134. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02491-1
95. Kan S, Feng S, Zhao X, Chen Z, Zhou M, Liu L, et al. Uamc-3203 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:20180. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70926-1
96. Vomund S, Schäfer A, Parnham MJ, Brüne B, and von Knethen A. Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18(12):2772. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122772
97. Du F, Wang X, Shang B, Fang J, Xi Y, Li A, et al. Gastrodin ameliorates spinal cord injury via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Acta Biochim Pol. (2016) 63:589–93. doi: 10.18388/abp.2016_1272
98. Yu DS, Wang YS, Bi YL, Guo ZP, Yuan YJ, Tong SM, et al. Salvianolic acid a ameliorates the integrity of blood-spinal cord barrier via mir-101/cul3/nrf2/ho-1 signaling pathway. Brain Res. (2017) 1657:279–87. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.12.007
99. Lin J, Sun Y, Xia B, Wang Y, Xie C, Wang J, et al. Mertk Reduces Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Permeability through the Rhoa/Rock1/P-Mlc Pathway after Spinal Cord Injury. Neurosci Bull. (2024) 40:1230–44. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01199-x
100. Liu W, Tang P, Wang J, Ye W, Ge X, Rong Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from melatonin-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells containing usp29 repair traumatic spinal cord injury by stabilizing nrf2. J Pineal Res. (2021) 71:e12769. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12769
101. Peng B, Hu J, Sun Y, Huang Y, Peng Q, Zhao W, et al. Tangeretin alleviates inflammation and oxidative response induced by spinal cord injury by activating the sesn2/keap1/nrf2 pathway. Phytother Res. (2024) 38:4555–69. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8294
102. Wu F, Lin Y, Xiao L, Chen Q, Lin F, and Li R. Administration with curcumin alleviates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating anti-oxidative stress and microglia activation-mediated neuroinflammation via nrf2/nf-Kb axis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. (2024) 60:172–82. doi: 10.1007/s11626-023-00846-3
103. Xia M, Zhang Y, Wu H, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Li G, et al. Forsythoside B attenuates neuro-inflammation and neuronal apoptosis by inhibition of nf-Kb and P38-mapk signaling pathways through activating nrf2 post spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 111:109120. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109120
104. Ma Z, Lu Y, Yang F, Li S, He X, Gao Y, et al. Rosmarinic acid exerts a neuroprotective effect on spinal cord injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via modulating the nrf2/ho-1 and tlr4/nf-Kb pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2020) 397:115014. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115014
105. Garone C, De Giorgio F, and Carli S. Mitochondrial metabolism in neural stem cells and implications for neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:238. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05041-w
106. Cantó-Santos J, Grau-Junyent JM, and Garrabou G. The impact of mitochondrial deficiencies in neuromuscular diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). (2020) 9(10):964. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100964
107. Slater PG, Domínguez-Romero ME, Villarreal M, Eisner V, and Larraín J. Mitochondrial function in spinal cord injury and regeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2022) 79:239. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04261-x
108. Yu WR, Liu T, Fehlings TK, and Fehlings MG. Involvement of mitochondrial signaling pathways in the mechanism of fas-mediated apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Eur J Neurosci. (2009) 29:114–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06555.x
109. Schmidt J and Quintá HR. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a target in spinal cord injury: intimate correlation between pathological processes and therapeutic approaches. Neural Regener Res. (2023) 18:2161–6. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.369094
110. Yeo JE, Kim JH, and Kang SK. Selenium attenuates ros-mediated apoptotic cell death of injured spinal cord through prevention of mitochondria dysfunction; in vitro and in vivo study. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2008) 21:225–38. doi: 10.1159/000113764
111. Ding LZ, Xu J, Yuan C, Teng X, and Wu QM. Mir-7a ameliorates spinal cord injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:11–7. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202001_19890
112. Ruan Y, Cai Z, Kang Z, Liang J, Tian H, Yu Q, et al. Calycosin activates nrf2/keap1 signaling to ameliorate hydrogen peroxide-induced spinal cord neuron death and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2024) 38:e23808. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23808
113. Wang H, Zheng Z, Han W, Yuan Y, Li Y, Zhou K, et al. Metformin Promotes Axon Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Stabilizing Microtubule. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:9741369. doi: 10.1155/2020/9741369
114. Huang W, Wu D, Cai C, Yao H, Tian Z, Yang Y, et al. Inhibition of mst1 ameliorates neuronal apoptosis via gsk3β/B-trcp/nrf2 pathway in spinal cord injury accompanied by diabetes. Redox Biol. (2024) 71:103104. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103104
115. Kovac S, Angelova PR, Holmström KM, Zhang Y, Dinkova-Kostova AT, and Abramov AY. Nrf2 regulates ros production by mitochondria and nadph oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2015) 1850:794–801. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.11.021
116. Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB, and Sil PC. Oxidative stress: the mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol. (2013) 87:1157–80. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1034-4
117. Zhan J, Li X, Luo D, Yan W, Hou Y, Hou Y, et al. Polydatin attenuates ogd/R-induced neuronal injury and spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury by protecting mitochondrial function via nrf2/are signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:6687212. doi: 10.1155/2021/6687212
118. Lv R, Du L, Zhang L, and Zhang Z. Polydatin attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and microglia apoptosis via nrf2/ho-1 pathway. Life Sci. (2019) 217:119–27. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.11.053
119. Mao Y, Du J, Chen X, Al Mamun A, Cao L, Yang Y, et al. Maltol promotes mitophagy and inhibits oxidative stress via the nrf2/pink1/parkin pathway after spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:1337630. doi: 10.1155/2022/1337630
120. Casanova A, Wevers A, Navarro-Ledesma S, and Pruimboom L. Mitochondria: it is all about energy. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1114231. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1114231
121. Li F, Wang H, Chen H, Guo J, Dang X, Ru Y, et al. Mechanism of ferroptosis and its role in spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:926780. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.926780
122. Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao N, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:88. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
123. Pope LE and Dixon SJ. Regulation of ferroptosis by lipid metabolism. Trends Cell Biol. (2023) 33:1077–87. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.05.003
124. Ursini F and Maiorino M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of gsh and gpx4. Free Radic Biol Med. (2020) 152:175–85. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
125. Liu Y, Wan Y, Jiang Y, Zhang L, and Cheng W. Gpx4: the hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2023) 1878:188890. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188890
126. Sato H, Kuriyama-Matsumura K, Siow RC, Ishii T, Bannai S, and Mann GE. Induction of cystine transport via system X-C and maintenance of intracellular glutathione levels in pancreatic acinar and islet cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1998) 1414:85–94. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(98)00159-x
127. Giraudi PJ, Bellarosa C, Coda-Zabetta CD, Peruzzo P, and Tiribelli C. Functional induction of the cystine-glutamate exchanger system xc(-) activity in sh-sy5y cells by unconjugated bilirubin. PloS One. (2011) 6:e29078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029078
128. Li FJ, Long HZ, Zhou ZW, Luo HY, Xu SG, and Gao LC. System X(C) (-)/gsh/gpx4 axis: an important antioxidant system for the ferroptosis in drug-resistant solid tumor therapy. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:910292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.910292
129. Ishimoto T, Nagano O, Yae T, Tamada M, Motohara T, Oshima H, et al. Cd44 variant regulates redox status in cancer cells by stabilizing the xct subunit of system xc(-) and thereby promotes tumor growth. Cancer Cell. (2011) 19:387–400. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.038
130. Chen Y, Liu S, Li J, Li Z, Quan J, Liu X, et al. The latest view on the mechanism of ferroptosis and its research progress in spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:6375938. doi: 10.1155/2020/6375938
131. Shen W, Li C, Liu Q, Cai J, Wang Z, Pang Y, et al. Celastrol inhibits oligodendrocyte and neuron ferroptosis to promote spinal cord injury recovery. Phytomedicine. (2024) 128:155380. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155380
132. Wu S, Chen Z, Wu Y, Shi Q, Yang E, Zhang B, et al. Adsc-Exos Enhance Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis and Promoting the Survival and Function of Endothelial Cells through the Nrf2/Slc7a11/Gpx4 Pathway. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 172:116225. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116225
133. Ni C, Ye Q, Mi X, Jiao D, Zhang S, Cheng R, et al. Resveratrol inhibits ferroptosis via activating nrf2/gpx4 pathway in mice with spinal cord injury. Microsc Res Tech. (2023) 86:1378–90. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24335
134. Zhou H, Yin C, Zhang Z, Tang H, Shen W, Zha X, et al. Proanthocyanidin promotes functional recovery of spinal cord injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. J Chem Neuroanat. (2020) 107:101807. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101807
135. Dong J, Gong Z, Bi H, Yang J, Wang B, Du K, et al. Bmsc-derived exosomal mir-219-5p alleviates ferroptosis in neuronal cells caused by spinal cord injury via the ube2z/nrf2 pathway. Neuroscience. (2024) 556:73–85. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.06.011
136. Ma H, Xing C, Wei H, Li Y, Wang L, Liu S, et al. Berberine attenuates neuronal ferroptosis via the ampk-nrf2-ho-1-signaling pathway in spinal cord-injured rats. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 142:113227. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113227
137. Fanet H, Capuron L, Castanon N, Calon F, and Vancassel S. Tetrahydrobioterin (Bh4) pathway: from metabolism to neuropsychiatry. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2021) 19:591–609. doi: 10.2174/1570159x18666200729103529
138. Liu Y, Lu S, Wu LL, Yang L, Yang L, and Wang J. The diversified role of mitochondria in ferroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:519. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06045-y
139. Chen Y, Li B, Quan J, Li Z, Li Y, and Tang Y. Inhibition of ferroptosis by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in acute spinal cord injury: role of nrf2/gch1/bh4 axis. Neurospine. (2024) 21:642–55. doi: 10.14245/ns.2448038.019
140. Visintin R and Ray SK. Specific micrornas for modulation of autophagy in spinal cord injury. Brain Sci. (2022) 12(2):247. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020247
141. Rein T. Is autophagy involved in the diverse effects of antidepressants? Cells. (2019) 8(1):44. doi: 10.3390/cells8010044
142. Lipinski MM, Wu J, Faden AI, and Sarkar C. Function and mechanisms of autophagy in brain and spinal cord trauma. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2015) 23:565–77. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6306
143. Glick D, Barth S, and Macleod KF. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. (2010) 221:3–12. doi: 10.1002/path.2697
144. Liu S, Yao S, Yang H, Liu S, and Wang Y. Autophagy: regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:648. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06154-8
145. Li Y, Lei Z, Ritzel RM, He J, Li H, Choi HMC, et al. Impairment of autophagy after spinal cord injury potentiates neuroinflammation and motor function deficit in mice. Theranostics. (2022) 12:5364–88. doi: 10.7150/thno.72713
146. Chen HC, Fong TH, Lee AW, and Chiu WT. Autophagy is activated in injured neurons and inhibited by methylprednisolone after experimental spinal cord injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2012) 37:470–5. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318221e859
147. Wu C, Chen H, Zhuang R, Zhang H, Wang Y, Hu X, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits pyroptosis in spinal cord injury by augmenting autophagy via the ampk-mtor-tfeb signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:1138–52. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.57825
148. Jung S, Jeong H, and Yu SW. Autophagy as a decisive process for cell death. Exp Mol Med. (2020) 52:921–30. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0455-4
149. Chen D, Zhou L, Chen G, Lin T, Lin J, Zhao X, et al. Fundc1-induced mitophagy protects spinal cord neurons against ischemic injury. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:4. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01780-9
150. Zeng H and Sanes JR. Neuronal cell-type classification: challenges, opportunities and the path forward. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2017) 18:530–46. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.85
151. Siebert JR, Kennedy K, and Osterhout DJ. Neurons are not all the same: diversity in neuronal populations and their intrinsic responses to spinal cord injury. ASN Neuro. (2025) 17:2440299. doi: 10.1080/17590914.2024.2440299
152. Lin YT and Chen JC. Dorsal root ganglia isolation and primary culture to study neurotransmitter release. J Vis Exp. (2018) 140(140):57569. doi: 10.3791/57569
153. Lin M, Alimerzaloo F, Wang X, Alhalabi O, Krieg SM, Skutella T, et al. Harnessing stem cell-derived exosomes: A promising cell-free approach for spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2025) 16:182. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04296-4
154. Han D, Chen S, Fang S, Liu S, Jin M, Guo Z, et al. The neuroprotective effects of muscle-derived stem cells via brain-derived neurotrophic factor in spinal cord injury model. BioMed Res Int. (2017) 2017:1972608. doi: 10.1155/2017/1972608
155. Li R, Han J, Chen B, and Shang J. Homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2-modified rat spinal astrocytes affect neurofunctional recovery after spinal cord injury. Curr Neurovasc Res. (2022) 19:171–80. doi: 10.2174/1567202619666220601111715
156. Kim HJ, Saikia JM, Monte KMA, Ha E, Romaus-Sanjurjo D, Sanchez JJ, et al. Deep scrna sequencing reveals a broadly applicable regeneration classifier and implicates antioxidant response in corticospinal axon regeneration. Neuron. (2023) 111:3953–69.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.09.019
157. Wang Q, Gao P, Liu H, Chen J, Tang P, Zhao S, et al. Git1 promotes axonal growth in an inflammatory environment by promoting the phosphorylation of map1b. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:7474177. doi: 10.1155/2022/7474177
158. Kahroba H, Ramezani B, Maadi H, Sadeghi MR, Jaberie H, and Ramezani F. The role of nrf2 in neural stem/progenitors cells: from maintaining stemness and self-renewal to promoting differentiation capability and facilitating therapeutic application in neurodegenerative disease. Ageing Res Rev. (2021) 65:101211. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101211
159. Li W, Tang T, Yao S, Zhong S, Fan Q, and Zou T. Low-dose lipopolysaccharide alleviates spinal cord injury-induced neuronal inflammation by inhibiting microrna-429-mediated suppression of pi3k/akt/nrf2 signaling. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 61:294–307. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03483-9
160. Ma B, Wang S, Wu W, Shan P, Chen Y, Meng J, et al. Mechanisms of circrna/lncrna-mirna interactions and applications in disease and drug research. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 162:114672. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114672
161. Antonazzo G, Gaudet P, Lovering RC, and Attrill H. Representation of non-coding rna-mediated regulation of gene expression using the gene ontology. RNA Biol. (2024) 21:36–48. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2408523
162. Wu Y, Sarkissyan M, Ogah O, Kim J, and Vadgama JV. Expression of malat1 promotes trastuzumab resistance in her2 overexpressing breast cancers. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 1212(7):1918. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071918
163. Jiang Z, Zhang W, and Zhang J. Lncrna oip5-as1 regulates ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated apoptosis in spinal cord injury by targeting the mir-128-3p/nrf2 axis. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e37704. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37704
164. Guan C and Wang Y. Lncrna casc9 attenuates lactate dehydrogenase-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation in spinal cord injury via sponging mir-383-5p. Inflammation. (2021) 44:923–33. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01387-7
165. Wang X, Ye L, Zhang K, Gao L, Xiao J, and Zhang Y. Upregulation of microrna-200a in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances the repair of spinal cord injury in rats by reducing oxidative stress and regulating keap1/nrf2 pathway. Artif Organs. (2020) 44:744–52. doi: 10.1111/aor.13656
166. Xia P, Gao X, Duan L, Zhang W, and Sun YF. Mulberrin (Mul) reduces spinal cord injury (Sci)-induced apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in rats via mirorna-337 by targeting nrf-2. BioMed Pharmacother. (2018) 107:1480–7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.082
167. Kesherwani V, Nelson KS, and Agrawal SK. Effect of sodium hydrosulphide after acute compression injury of spinal cord. Brain Res. (2013) 1527:222–9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.06.023
168. Chen F, Hu M, Shen Y, Zhu W, Cao A, Ni B, et al. Isorhamnetin promotes functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury by abating oxidative stress and modulating M2 macrophages/microglia polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. (2021) 895:173878. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173878
169. Men X, Han X, Oh G, Im JH, Lim JS, Cho GH, et al. Plant sources, extraction techniques, analytical methods, bioactivity, and bioavailability of sulforaphane: A review. Food Sci Biotechnol. (2024) 33:539–56. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01434-7
170. Liu K, Liu J, Xu A, and Ding J. The role of polydatin in inhibiting oxidative stress through sirt1 activation: A comprehensive review of molecular targets. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 331:118322. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118322
171. Krall RF, Tzounopoulos T, and Aizenman E. The function and regulation of zinc in the brain. Neuroscience. (2021) 457:235–58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.01.010
172. Rong W, Li H, Yang H, Yuan B, Zhu J, Deng J, et al. Ezetimibe attenuates functional impairment via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation in traumatic spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). (2023) 69:175–80. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2023.69.6.26
173. Tang S, Botchway BOA, Zhang Y, Wang X, Huang M, and Liu X. Resveratrol can improve spinal cord injury by activating nrf2/ho-1 signaling pathway. Ann Anat. (2024) 251:152180. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2023.152180
174. Luo H, Bao Z, Zhou M, Chen Y, and Huang Z. Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis, and inflammation via activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway. Neuroreport. (2022) 33:451–62. doi: 10.1097/wnr.0000000000001803
175. Fang P, Wang Y, Sun F, Lin H, and Zhang X. Effects of albiflorin on oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in rats with acute spinal cord injury. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2023) 11:e1015. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1015
176. Zhang L, Zhang W, Zheng B, and Tian N. Sinomenine attenuates traumatic spinal cord injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via nrf2 pathway. Neurochem Res. (2019) 44:763–75. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-02706-z
177. Zhang W, Cheng L, Hou Y, Si M, Zhao YP, and Nie L. Plumbagin Protects against Spinal Cord Injury-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Wistar Rats through Nrf-2 Upregulation. Drug Res (Stuttg). (2015) 65:495–9. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1389950
178. Jiang W, Li M, He F, Bian Z, He Q, Wang X, et al. Neuroprotective effect of asiatic acid against spinal cord injury in rats. Life Sci. (2016) 157:45–51. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.004
179. Fu J, Sun H, Zhang Y, Xu W, Wang C, Fang Y, et al. Neuroprotective effects of luteolin against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. J Med Food. (2018) 21:13–20. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2017.4021
180. Du H, Ma L, Chen G, and Li S. The effects of oxyresveratrol abrogates inflammation and oxidative stress in rat model of spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17:4067–73. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8294
181. Lv R, Mao N, Wu J, Lu C, Ding M, Gu X, et al. Neuroprotective effect of allicin in a rat model of acute spinal cord injury. Life Sci. (2015) 143:114–23. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.11.001
182. Zhao YJ, Qiao H, Liu DF, Li J, Li JX, Chang SE, et al. Lithium promotes recovery after spinal cord injury. Neural Regener Res. (2022) 17:1324–33. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.327348
183. Zheng W, Liu B, and Shi E. Perillaldehyde alleviates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating the nrf2 pathway. J Surg Res. (2021) 268:308–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2021.06.055
184. Ning S, Chen Y, Shao J, Zhu H, Zhang Z, and Miao J. The effects of acteoside on locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury - the role of autophagy and apoptosis signaling pathway. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 175:116607. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116607
185. Gong F, Ge T, Liu J, Xiao J, Wu X, Wang H, et al. Trehalose inhibits ferroptosis via nrf2/ho-1 pathway and promotes functional recovery in mice with spinal cord injury. Aging (Albany NY). (2022) 14:3216–32. doi: 10.18632/aging.204009
186. Führmann T, Anandakumaran PN, and Shoichet MS. Combinatorial therapies after spinal cord injury: how can biomaterials help? Adv Healthc Mater. (2017) 6(10):10.1002/adhm.201601130. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601130
187. Celorrio M, Rhodes J, Shumilov K, Moritz J, Xiao S, Anabayan I, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin induces neuroprotection, activates mapk/creb pathway, and rescues fear memory after traumatic brain injury with delayed hypoxemia in mice. Brain Res. (2022) 1795:148074. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2022.148074
188. Melhuish Beaupre LM, Brown GM, Gonçalves VF, and Kennedy JL. Melatonin's neuroprotective role in mitochondria and its potential as a biomarker in aging, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry. (2021) 11:339. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01464-x
189. Wang H, Wang H, Huang H, Qu Z, Ma D, Dang X, et al. Melatonin attenuates spinal cord injury in mice by activating the nrf2/are signaling pathway to inhibit the nlrp3 inflammasome. Cells. (2022) 11(18):2809. doi: 10.3390/cells11182809
190. Fang J, Feng Q, Ketel CS, Wang H, Cao R, Xia L, et al. Purification and functional characterization of set8, a nucleosomal histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase. Curr Biol. (2002) 12:1086–99. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00924-7
191. Li X, Qian Y, Shen W, Zhang S, Han H, Zhang Y, et al. Mechanism of set8 activates the nrf2-keap1-are signaling pathway to promote the recovery of motor function after spinal cord injury. Mediators Inflammation. (2023) 2023:4420592. doi: 10.1155/2023/4420592
192. Shi Y, Yang Y, Xu W, Shi D, Xu W, Fu X, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase syvn1 is a key positive regulator for gsdmd-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:106. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04553-x
193. Guo L, Zhang D, Ren X, and Liu D. Syvn1 attenuates ferroptosis and alleviates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by regulating the hmgb1/nrf2/ho-1 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 123:110802. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110802
194. Ai G, Xiong M, Deng L, Zeng J, and Xiao Q. Research progress on the inhibition of oxidative stress by teriparatide in spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1358414. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1358414
195. Yang X, Chen S, Shao Z, Li Y, Wu H, Li X, et al. Apolipoprotein E deficiency exacerbates spinal cord injury in mice: inflammatory response and oxidative stress mediated by nf-Kb signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci. (2018) 12:142. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00142
196. Xuan LN, Hu ZX, Jiang ZF, Zhang C, Sun XW, Ming WH, et al. Pregnane X receptor (Pxr) deficiency protects against spinal cord injury by activating nrf2/ho-1 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:3460–78. doi: 10.1111/cns.14279
197. Xia M, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Li R, Zhao T, Chen L, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 regulates oxidative stress-dependent ferroptosis post spinal cord injury by stabilizing the P62-keap1-nrf2 signaling pathway. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:905115. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.905115
198. Fu X, Liu G, Halim A, Ju Y, Luo Q, and Song AG. Mesenchymal stem cell migration and tissue repair. Cells. (2019) 8(8):784. doi: 10.3390/cells8080784
199. Yang W, Yang Y, Yang JY, Liang M, and Song J. Treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with plumbagin alleviates spinal cord injury by affecting oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptotis and the activation of the nrf2 pathway. Int J Mol Med. (2016) 37:1075–82. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2498
200. Dai J, Su Y, Zhong S, Cong L, Liu B, Yang J, et al. Exosomes: key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2020) 5:145. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00261-0
201. Peng W, Wan L, Luo Z, Xie Y, Liu Y, Huang T, et al. Microglia-derived exosomes improve spinal cord functional recovery after injury via inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting the survival and function of endothelia cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:1695087. doi: 10.1155/2021/1695087
202. Batch JT, Lamsal SP, Adkins M, Sultan S, and Ramirez MN. Advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet: A review article. Cureus. (2020) 12:e9639. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9639
Keywords: spinal cord injury, Nrf2, oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis
Citation: Xie T, Xu J, Liu X, Yu Y, Lu Y, Wang T, Gao F and Yuan H (2025) Mechanistic insights into Nrf2-driven pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting in spinal cord injury. Front. Immunol. 16:1574834. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1574834
Received: 11 February 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 10 July 2025.
Edited by:
Ashwin Kotnis, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Xie, Xu, Liu, Yu, Lu, Wang, Gao and Yuan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Yuan, aHVpeXVhbjE5ODJAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Hui Yuan, orcid.org/0000-0001-5646-9447
 Tao Xie
Tao Xie Jiyu Xu
Jiyu Xu Xinyu Liu1
Xinyu Liu1 Hui Yuan
Hui Yuan