- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, Mianyang Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Mianyang, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the Second People’s Hospital of Deyang City, Deyang, Sichuan, China
Objective: The prognostic role of the hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been widely reported, but the results remain controversial. Therefore, we aim to evaluate the prognostic and clinicopathological value of the HALP score in NSCLC through a pooled analysis.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and the ClinicalTrials.gov databases in December 2024 to identify studies evaluating the relationship between the pretreatment HALP score and outcomes in NSCLC patients. Eligible studies included patients treated with surgical resection, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. The HALP score was calculated using peripheral blood levels of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocytes, and platelets measured before treatment. Data were extracted and analyzed to determine the association of the HALP score with overall survival (OS), disease/progression/recurrence-free survival (DFS/PFS/RFS), and clinicopathological characteristics. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses were performed to ensure the robustness and reliability of the results.
Results: A total of 10 studies involving 7024 patients were included. The results demonstrated that patients with lower pretreatment HALP score had worse OS (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.73, 95% confidence interval [95% CI]: 1.27-2.34, p < 0.001) and DFS/PFS/RFS (HR = 1.86, 95% CI: 1.30-2.64, p < 0.001). The results remained consistent across subgroup analyses based on study characteristics and sensitivity analyses. Additionally, a lower HALP score was significantly associated with age (odds ratio [OR] = 1.43, 95% CI: 1.15-1.78, p = 0.001) and tumor size (OR = 0.54, 95% CI: 0.38-0.76, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The HALP score is a valuable prognostic biomarker for predicting survival outcomes in NSCLC patients. Its ability to integrate multiple aspects of systemic inflammation and nutritional status makes it a promising tool for improving risk stratification and guiding treatment decisions. Future studies should continue to validate this finding in prospective, multicentre trials.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer is the most common type of cancer worldwide, with an estimated 2.5 million new cases and over 800,000 deaths reported globally in 2022 (1). Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the most common type of lung cancer, accounts for 85% of all cancer cases (2). Despite the emergence of new therapeutic strategies in recent years, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies for driver mutations, which have led to improved patient survival, the prognosis of the NSCLC remains worrisome (3). Studies have shown that the survival of NSCLC patients is influenced by various factors, including tumor stage, grade, treatment strategy, and the patient’s overall condition (4). Additionally, the heterogeneity in cancer patient prognosis has led to confusion among clinicians. Therefore, identifying effective biomarkers or scoring systems to predict prognosis is crucial for improving patient prognosis assessment and developing personalized treatment plans.
Research has demonstrated that inflammation plays an indispensable role in cancer development, tumor angiogenesis, and metastasis (5). In recent years, several inflammatory biomarkers, such as the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (MLR), have been demonstrated to be associated with cancer prognosis (5, 6). However, they each reflect only a single inflammatory or immune parameter and are susceptible to non-tumor factors, suggesting that the predictive power of prognosis remains limited (7). The hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score, as a novel prognostic evaluation tool, has gradually attracted the attention of researchers. Currently, the HALP score has indicated significant potential in prognostic evaluation across various cancers. Chen et al. (8) found that the HALP score could independently predict survival in gastric cancer patients and was closely related to overall prognosis. Preoperative HALP score was also considered an independent prognostic factor for cancer-specific survival in renal cell carcinoma and esophageal cancer (9, 10). These studies have illustrated that the HALP score reflects the patient’s systemic nutritional status, inflammatory response, and immune function and overcomes the limitations of single markers that focus primarily on inflammation, thus providing valuable information for the prognostic assessment of cancer patients.
Despite the prognostic efficacy of the HALP score in NSCLC has been reported, current findings are somewhat controversial, and most studies have small sample sizes, limiting the generalizability of their conclusions (11–13). Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the prognostic role of the HALP score in patients with NSCLC and to explore its correlation with patients’ clinicopathological characteristics through a meta-analysis. This will help provide new reference points for clinical practice and further advance the application research of the HALP score in cancer prognosis assessment.
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy
The meta-analysis and systematic review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and the Assessing the methodological quality of systematic reviews 2 (AMSTAR 2) Guidelines (14, 15). The analysis protocol was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024565673). Comprehensive searches were performed across multiple databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and the ClinicalTrials.gov to identify relevant studies published up to December 2024. Search strategies combined both controlled vocabulary and free-text terms, with key terms including “hemoglobin,” “albumin”, “lymphocyte”, “platelet”, “HALP”, “lung neoplasms”, “lung cancer”, “lung carcinoma”, “lung adenocarcinoma”, “non-small cell lung cancer”, and “NSCLC”. We also manually searched the reference lists of relevant reviews and meta-analyses to identify potential literature. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion, with final arbitration by a third author if necessary.
2.2 Selection criteria
The two authors conducted literature screening based on the following inclusion criteria: (1) study types included prospective or retrospective cohort studies, (2) study subjects were patients diagnosed with NSCLC, (3) the intervention involved assessing the pretreatment HALP score of patients and dividing them into high and low groups, (4) outcome measures included overall survival (OS), progression/disease/recurrence-free survival (PFS/DFS/RFS), and/or clinicopathological characteristics. Exclusion criteria comprised reviews, case reports, conference abstracts, and commentary articles, as well as duplicate publications, studies not involving NSCLC patients, and studies lacking sufficient data for extraction and analysis.
2.3 Data extraction and quality assessment
We extracted data according to predefined criteria, including the following details: study basic information (authors, publication year, country), patient characteristics (gender, sample size, age, smoking history, median follow-up time), intervention measures (therapeutic measures, HALP cut-off, and the method of determining HALP cut-off), survival outcomes (OS, PFS, DFS, and/or RFS), and statistical analysis (hazard Ratio [HR] with its 95% confidence interval [CI]). In this study, we utilized the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) to assess the quality of included studies (16), which includes selection of study groups, comparability between groups, and assessment of outcomes. The NOS score ranges from 0 to 9, with studies scoring 7 or higher considered high quality. Two independent researchers conduct this process, and any discrepancies are resolved through discussion or adjudicated by a third researcher.
2.4 Statistical analyses
The data analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.4 and Stata 16.0 software. We assessed heterogeneity among studies using the I² statistic and Q test. Heterogeneity was considered significant if I² > 50% or P < 0.1, and a random-effects model was used for meta-analysis; otherwise, a fixed-effects model was employed. HR and their 95% CI served as the effect size metric in this study. To explore potential sources of heterogeneity, we conducted subgroup analyses based on patient characteristics, treatment modalities, and HALP cut-off values. In addition, meta-regression analyses were performed to assess whether covariates contributed to heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis was carried out by sequentially omitting individual studies to evaluate the robustness and stability of the overall results. Publication bias was assessed using both Egger’s test and Begg’s test, with funnel plots used for visual inspection. In cases where significant publication bias was detected, the trim-and-fill method was applied to estimate the adjusted effect size. All statistical tests were two-sided, and a P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection and characteristics
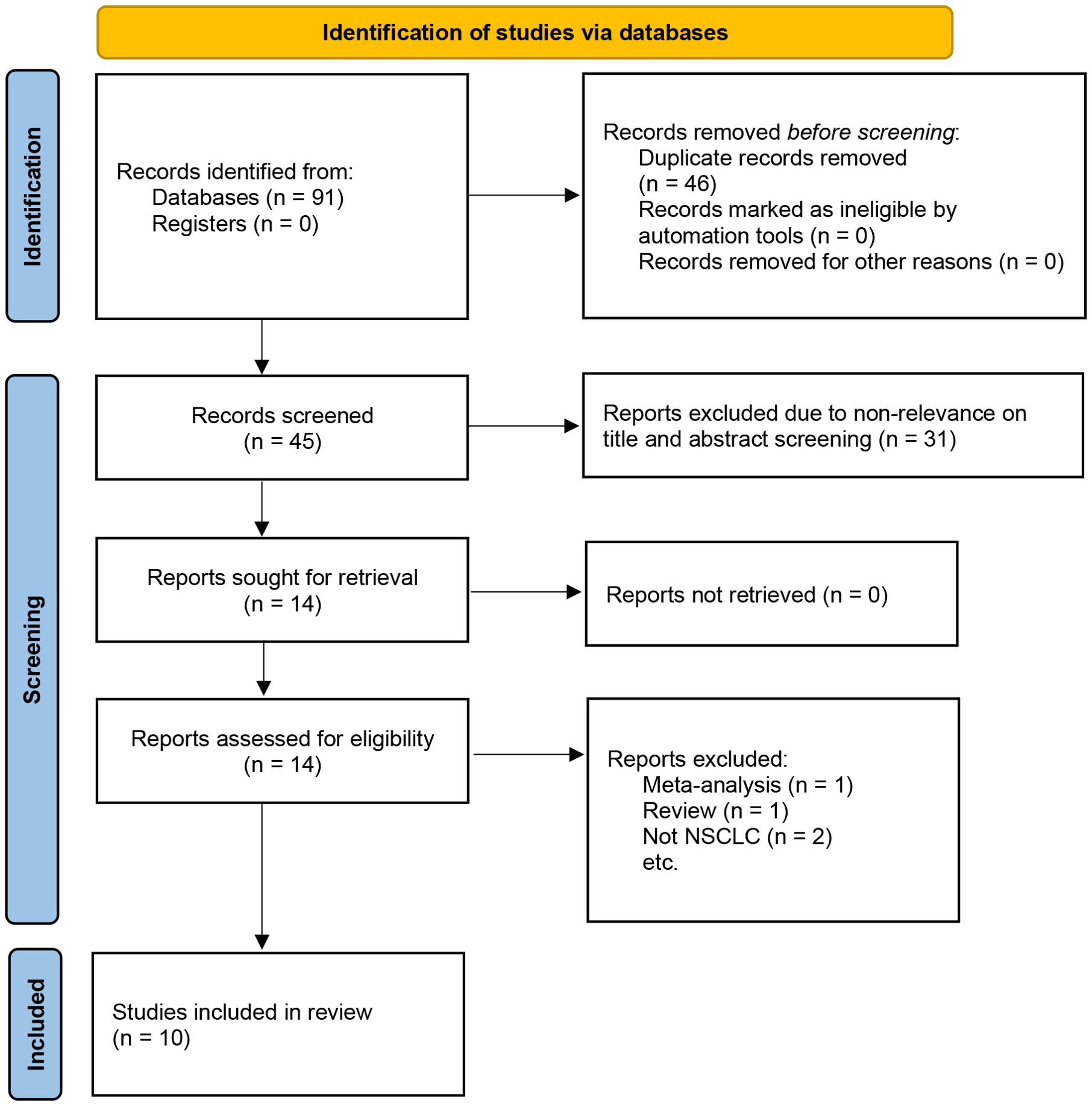
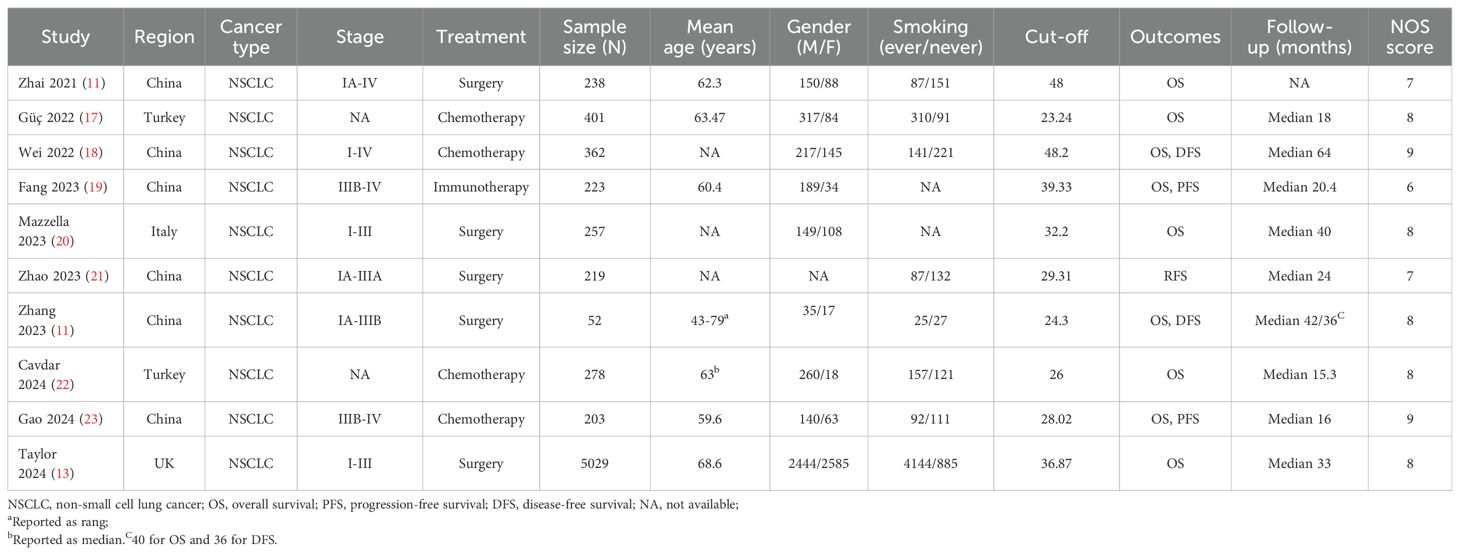
The initial search identified 421 articles, and after removing duplicates, 345 articles remained. By reading the titles and abstracts, 319 articles were excluded. After reading the full texts of 26 articles, 15 were excluded. Finally, 10 articles with 7024 patients were included in the meta-analysis (Figure 1) (11–13, 17–23). Among these studies, 5 involved therapeutic resection (11–13, 20, 21), 4 involved adjuvant chemotherapy (17, 18, 22, 23), and one used immunotherapy (19). The included studies were published between 2021 and 2024. Six studies were from China (11, 12, 18, 19, 21, 23), two from Turkey (17, 22), and the remaining two were from Italy and the United Kingdom (13, 20). The sample sizes of the included studies ranged from 52 to 5,029 cases, with HALP cut-off values ranging from 24.3 to 48.2. The median follow-up period of the included studies ranged from 25.3 to 64 months, but one study did not report the follow-up times (11). Additionally, nine studies reported the association between HALP and OS (11–13, 17–20, 22, 23), two studies examined the relationship between HALP and DFS (12, 18), two studies reported the association between HALP and PFS (19, 23), and one study investigated the relationship between HALP and RFS (21). The NOS scores of nine studies were ≥7, indicating that the overall quality of the included studies was high (Supplementary Table S1). The main characteristics and quality assessment results of the included studies are summarized in Table 1.
3.2 HALP and clinicopathological characteristics
In this study, we explored the correlation between HALP score and various clinicopathological characteristics, including age, gender, smoking history, tumor size, lymph node metastasis, and overall staging (Figure 2). The results indicated that HALP score was significantly associated with age (old vs young: OR = 1.43, 95% CI 1.15-1.78, p = 0.001) and tumor size (large vs small: OR = 0.54, 95% CI 0.38-0.76, p < 0.001), while no significant associations were found with gender (male vs female: OR = 0.80, 95% CI 0.50-1.29, p = 0.36), smoking history (ever vs never: OR = 0.72, 95% CI 0.47-1.11, p = 0.14), lymph node metastasis (yes vs no: OR = 0.92, 95% CI 0.66-1.27, p = 0.60), or overall stage (III-IV vs I-II: OR = 0.47, 95% CI 0.17-1.34, p = 0.16).
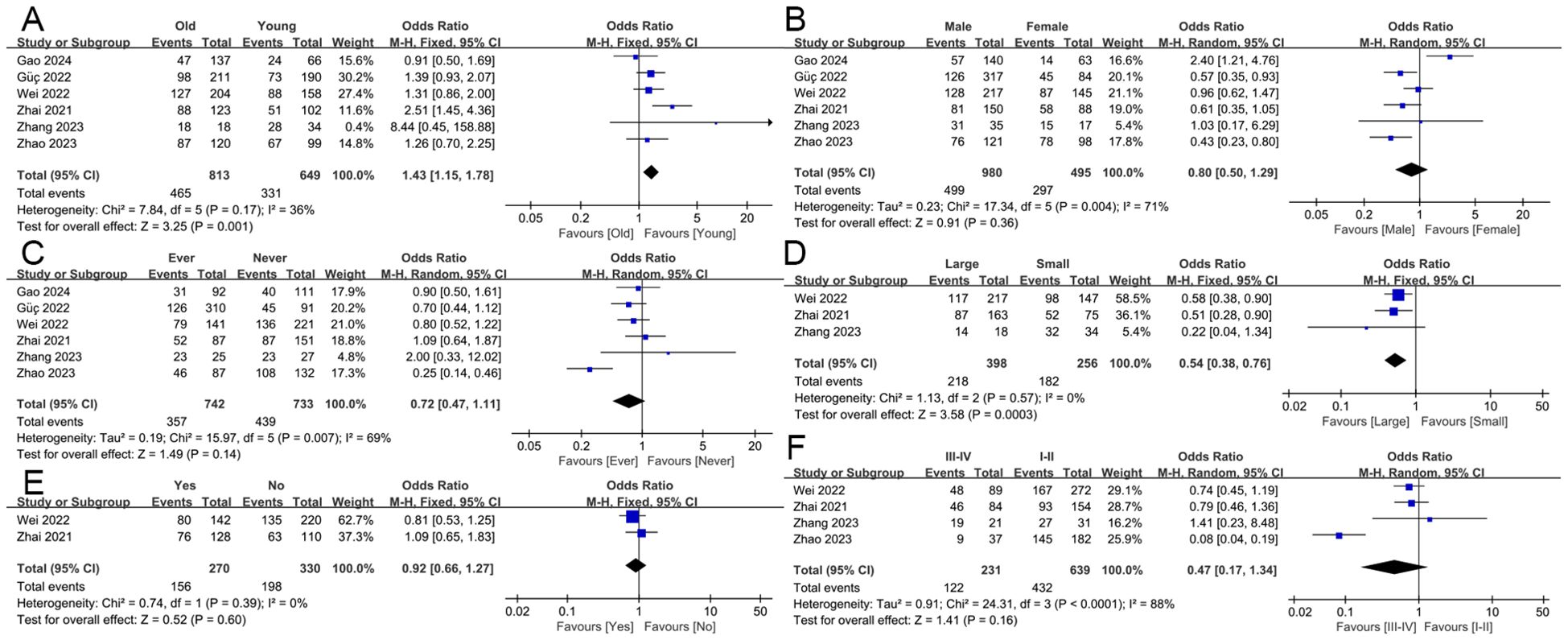
Figure 2. The association of the HALP score with clinicopathological characteristics. including age (A), gender (B), smoking history (C), tumor size (D), lymph node metastasis (E), and overall staging (F).
3.3 HALP and OS
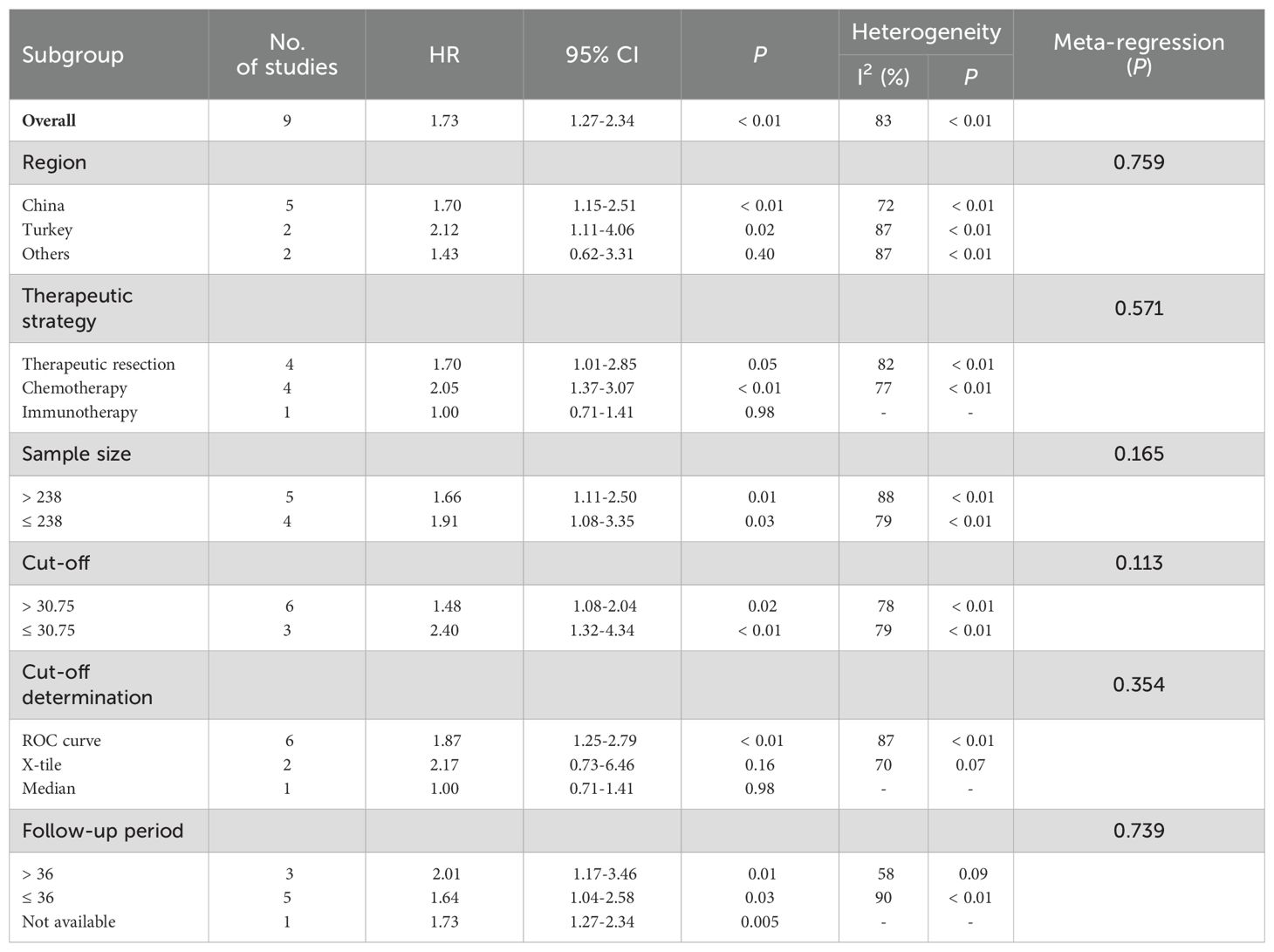
A total of eight studies explored the correlation between HALP score and OS in patients with NSCLC (11–13, 17–20, 22, 23). The pooled analysis revealed that a lower pre-treatment HALP score was significantly associated with poorer OS (HR = 1.73, 95% CI 1.27-2.34, p < 0.001, Figure 3A), with substantial heterogeneity observed among the included studies (I2 = 83%, p < 0.001). To further investigate potential sources of heterogeneity, subgroup analyses were conducted based on study region, therapeutic strategy, sample size, HALP cut-off value, and follow-up duration (Table 2). These subgroup analyses largely supported the overall findings. However, no significant association between the HALP score and OS was observed in the subgroup of studies conducted in other regions (p = 0.40). With respect to cut-off value determination methods, only studies using ROC curve-derived thresholds showed a significant association between low HALP score and poor OS (p < 0.01), while those using X-tile (p = 0.16) or the median value (p = 0.98) did not yield statistically significant results. Regarding therapeutic strategy, in the subgroup of patients receiving chemotherapy, the HALP score was significantly associated with OS (p < 0.01), while in the subgroup of patients undergoing therapeutic resection, the correlation between HALP score and OS was not statistically significant (p = 0.05).
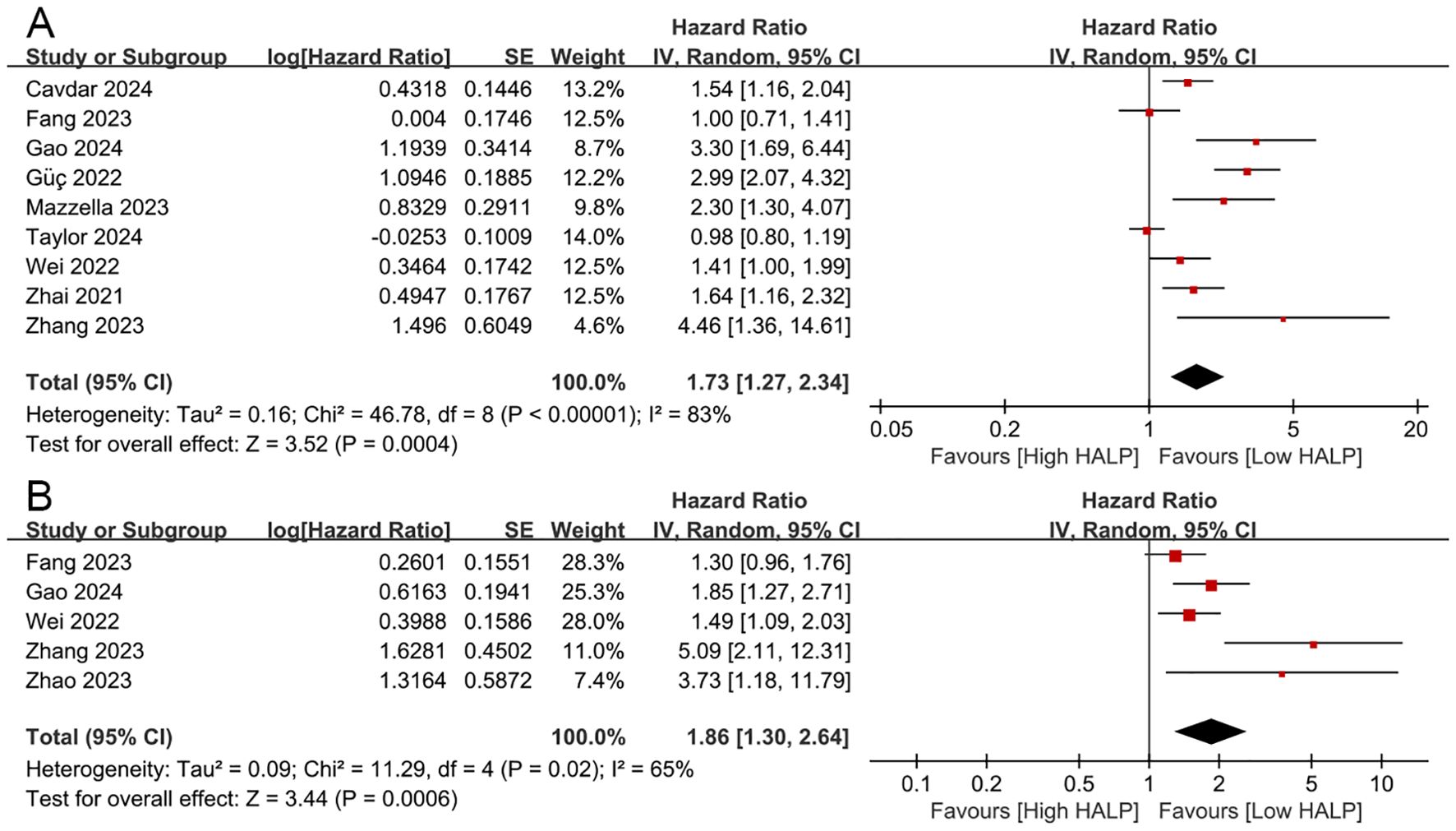
Figure 3. The prognostic impact of the HALP score on overall survival (A) and disease/progression/recurrence-free survival (B).
To further evaluate whether these study-level characteristics contributed to heterogeneity, meta-regression analysis was performed. The results indicated that none of the examined variables, including the method used for HALP cut-off determination, significantly explained the heterogeneity (all p > 0.05). This suggests that while subgroup trends exist, the differences observed across subgroups may not be sufficient to account for the overall heterogeneity in a statistically meaningful way.
3.4 HALP and DFS/PFS/RFS
Four studies investigated the correlation between HALP score and DFS/PFS/RFS in patients with NSCLC (12, 18, 19, 21, 23). The results revealed that decreased HALP score was significantly associated with worse DFS/PFS/RFS (HR = 1.86, 95% CI 1.30-2.64, p < 0.001, Figure 3B), with higher heterogeneity among the studies (I² = 65%, p = 0.02).
3.5 Sensitivity analyses
We performed a sensitivity analysis to assess the reliability of the combined results for OS and DFS/PFS/RFS. The overall HR estimates for both outcomes did not significantly change after removing each study sequentially from the analysis (Figure 4), supporting the conclusion that the meta-analysis results are relatively stable and reliable.
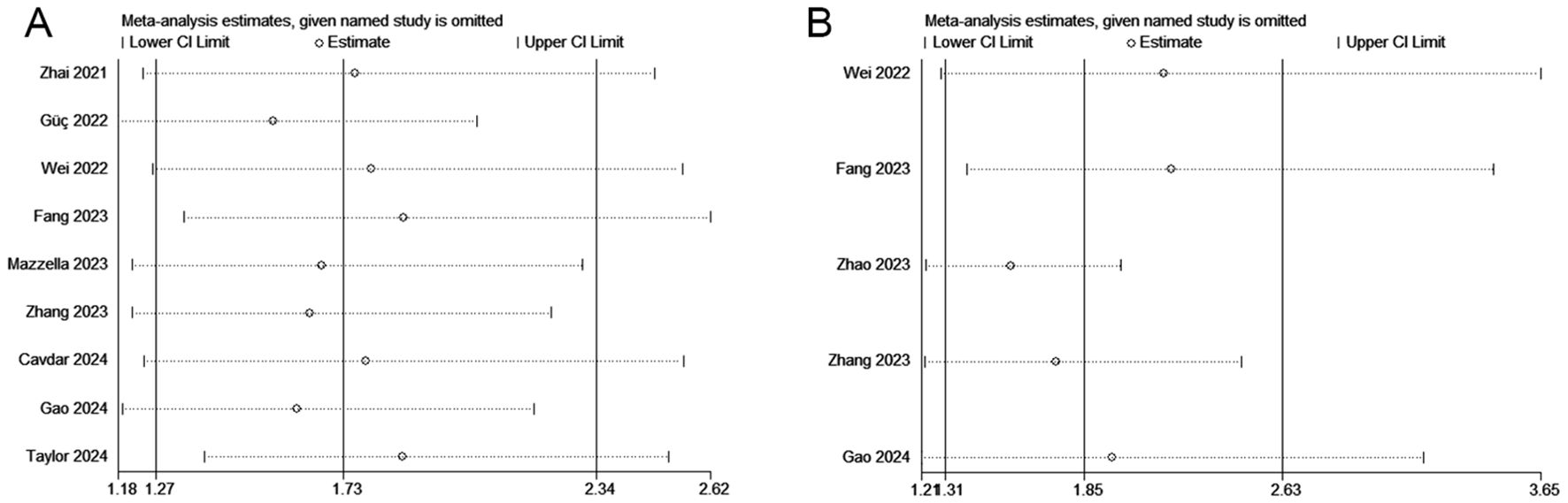
Figure 4. Sensitivity analyses regarding overall survival (A) and disease/progression/recurrence-free survival (B).
3.6 Publication bias
We used Begg’s funnel plot and Egger’s test to evaluate publication bias among the included studies. The results indicated asymmetry in the funnel plot, and Egger’s test also showed statistical significance (OS: p = 0.023, DFS/PFS/RFS: p = 0.037, Figure 5), suggesting the potential presence of publication bias in our findings. Consequently, we performed the trim-and-fill analysis to adjust for potential publication bias. The results further demonstrated that our results remained robust (OS: HR = 1.651, 95% CI 1.224-2.227, p = 0.001; DFS/PFS/RFS: HR = 1.514, 95% CI 1.017-2.254, p = 0.041).
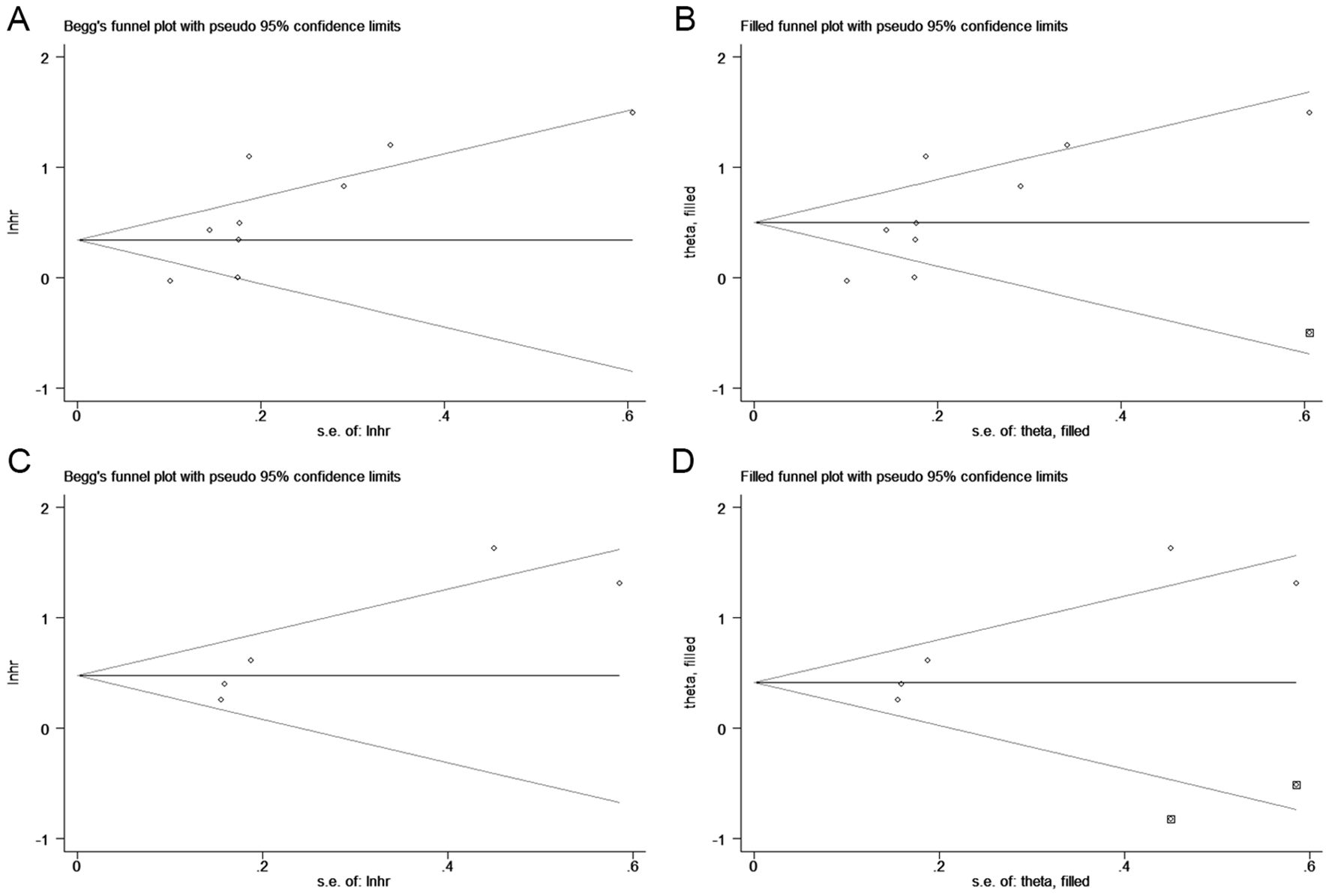
Figure 5. Funnel plots for detecting publication bias in terms of overall survival (A, B) and disease/progression/recurrence-free survival (C, D).
4 Discussion
Despite continuous advancements in diagnostic technologies and therapeutic methods, the incidence and mortality rates of lung cancer remain elevated compared to most other cancers (1, 24). Therefore, there is an urgent need for new biomarkers to predict the prognosis and guide the treatment strategies for lung cancer. As the most common type of lung cancer, the prognosis of NSCLC has been a primary focus for researchers. The HALP score is a novel, simple, and practical biomarker system that evaluates the systemic inflammatory status and nutritional condition of patients by combining hemoglobin levels, albumin levels, lymphocyte counts, and platelet counts (8). Several studies have reported on the prognostic value of the HALP score in NSCLC, but the results are still inconsistent (18–20). Here, we conduct a comprehensive literature review and present the first meta-analysis to evaluate the relationship between the HALP score and the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of NSCLC patients, aiming to better inform clinical practice.
Through a comprehensive analysis of multiple studies, we found that a lower pretreatment HALP score was significantly associated with inferior OS and DFS/PFS/RFS. The results remained robust and reliable after subgroup and sensitivity analyses. Residence’s attention was drawn to the fact that in the heterogeneity test, we found a high degree of heterogeneity between studies. To explore potential sources of heterogeneity, we conducted subgroup analyses based on population information and study characteristics. The results did not reveal significant sources of heterogeneity, suggesting that region, sample size, cut-off value, and duration of follow-up may not be the main factors influencing the heterogeneity of the overall effect. In addition, sensitivity analyses showed that the combined effect sizes did not change significantly, either through the exclusion of study with large sample sizes (Taylor et al. (13)), or the exclusion of individual studies one by one, implying that the results of the present analysis have excellent robustness and reliability. Furthermore, this study also indicated that patients with lower HALP score tend to be older and had larger tumor size. These findings suggest that the HALP score could be an extremely valuable biomarker for predicting the survival outcomes in patients with NSCLC and has the potential to improve risk stratification.
The findings of this present study are generally consistent with results from various malignant tumors. Preoperative lower HALP score was significantly associated with poorer OS and PFS in patients with breast cancer (25). Xiong et al. (26) demonstrated that the HALP score has good predictive performance for lymph node metastasis and recurrence in endometrial cancer. Recent studies have also confirmed that the HALP score was an independent prognostic factor for unresectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (27). Furthermore, a previous meta-analysis investigated the relationship between HALP and solid tumors (28); however, the limited number of studies included on NSCLC may have reduced the reliability of the results. Therefore, more researches were included in this study and relevant clinicopathological characteristics were analyzed, providing a more comprehensive and reliable evidence base for our conclusions.
Inflammation is the body’s response to tissue damage caused by physical injury, infection, exposure to toxins or other types of trauma (29–31). The body’s inflammatory response causes cellular changes and an immune response that leads to repair of damaged tissue and cell proliferation at the site of the damaged tissue (32). However, a sustained inflammatory response disrupts DNA repair mechanisms and cell cycle checkpoints, leading to chromosomal aberrations and thus promoting cancer development (33). In addition, inflammatory mediators in the inflammatory microenvironment assist tumor cells to proliferate, expand and evade immune surveillance (34). Therefore, immune-inflammation is regarded as a key factor in tumorigenesis and progression (35). The HALP score is considered as a potential predictor of cancer prognosis because it combines four indicators, namely haemoglobin, albumin, lymphocytes and platelets, which can comprehensively reflect the systemic inflammatory response and nutritional status of cancer patients. However, the specific mechanism by which HALP score affects cancer prognosis remains unclear.
Hemoglobin is the main component of red blood cells and is responsible for oxygen transport (36). Low hemoglobin levels are commonly associated with anemia, which leads to tissue hypoxia and can drive tumor cells to adapt to the low-oxygen environment through angiogenesis (37). Anemia may also inhibit anti-tumor immune responses possibly by affecting the immune system, which in turn promotes the escape and growth of tumor cells. Additionally, anemia may affect the overall health status and treatment tolerance of cancer patients to some extent (38). A large body of evidence suggests that low hemoglobin levels are associated with a poorer prognosis in patients with NSCLC (39–41). Serum albumin is an important indicator for assessing host inflammation and nutritional status. Low levels of albumin are common in patients with advanced cancer, suggesting that the body is in a state of chronic malnutrition. Malnutrition weakens the body’s immune response and reduces the effectiveness of anti-tumor therapy, which in turn affects the prognosis of patients (42, 43). Additionally, lymphocytes are regarded as an important component of the immune system, and a reduction in their level often indicates a decline in immune function (44). Tumor cells frequently employ immune evasion mechanisms to inhibit lymphocyte function, thereby promoting tumor progression and metastasis (45). Infiltrating lymphocytes have been reported to significantly affect tumor prognosis and response to chemotherapy (46). Notably, platelets have been shown to play a key role in the metastatic ability of cancer. Platelets can accelerate tumor growth and metastasis by releasing growth factors that promote tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis (47, 48). Platelets also play an important role in inflammatory processes, and tumor-associated chronic inflammatory responses can exacerbate tumor progression by promoting platelet aggregation and activation, which in turn exacerbates tumor progression (49, 50). Elevated platelet levels have also been shown to be associated with poor prognosis in tumors (51, 52). Therefore, a lower HALP score, which reflects lower levels of hemoglobin, albumin, and lymphocytes, and/or higher platelet levels, is significantly associated with poorer survival in patients.
In recent years, significant progress has been made in prognostic modelling of NSCLC, including key factors such as pathological features, molecular analyses and imaging features (53–56). However, these models have certain limitations. For example, gene expression profiling may be affected by systemic disease (57), and imaging models may be subjective due to physician experience and bias (58). In addition, the high cost and radiation risk of advanced imaging techniques such as PET-CT and MRI limit intensive follow-up and may cause psychological distress (59, 60). Therefore, although these models are effective in predicting prognosis, their invasiveness and high cost make them difficult to disseminate. A routine blood test is a simple, quick and common test that is performed when almost all cancer patients are admitted to hospital. It provides important information about metabolism, inflammation and the internal environment (61, 62), and can be used to guide medication in addition to aiding diagnosis (63). Thus, haematological markers provide a valuable reference for physicians and have great clinical value and potential for practical application (58).
Previous studies have reported that a variety of inflammatory markers, such as NLR and PLR, can be used to predict the prognosis of different malignancies (5, 6). However, these markers reflect only one aspect of a patient’s overall health status, whereas treatment outcomes are influenced by a combination of factors, including the patient’s inflammatory response, nutritional status, and immune function (25). This highlights the importance of a comprehensive and multidimensional approach when assessing a patient’s overall health and prognosis. Since its inception, the HALP score has received much attention as a novel biomarker reflecting systemic inflammation and nutritional status, and has been used to predict a wide range of clinical outcomes in a variety of cancers (64). For instance, recent evidence has demonstrated that the HALP score exhibits superior predictive accuracy for OS in breast cancer patients compared to other commonly used inflammatory and nutritional markers (25). Importantly, in the context of NSCLC, Mazzella et al. (20) reported that the HALP score outperformed established inflammatory markers, such as derived NLR (dNLR) and PLR, in survival prediction. Their ROC curve analysis revealed a higher area under the curve (AUC) for HALP, indicating its stronger prognostic value. Together, these findings support the HALP score as a simple yet valuable prognostic tool that can aid clinical decision-making. Specifically, for newly diagnosed NSCLC patients, the HALP score may provide critical prognostic information to help physicians better evaluate patients’ overall health and survival expectations, thereby facilitating more individualized and optimized treatment strategies. Nevertheless, the independent prognostic value and superiority of the HALP score in NSCLC warrant further validation.
In this analysis, most of the included studies were from the same country (China), which may limit the widespread clinical use of the HALP score. In addition, we also observed that in the subgroup with chemotherapy, patients with lower pre-treatment HALP score had poorer OS, whereas no statistically significant association was found in the subgroup undergoing curative resection or in the single immunotherapy-based study. Indeed, patients selected for surgery tend to have earlier-stage disease and may be less influenced by baseline nutritional/inflammatory status, whereas those requiring chemotherapy (often for more advanced or unresectable tumors) may be more vulnerable to systemic factors captured by HALP. This discrepancy suggests that the prognostic utility of HALP could be context-dependent, providing stronger risk discrimination in the chemotherapy setting. Differences in healthcare systems, patient selection, and treatment protocols can have an impact on the applicability of HALP, especially in the context of studies that are predominantly from the same country. Such regional and practice-pattern variations may limit the generalizability of our findings. Consequently, future research should undertake cross-regional and multicentre collaborations to establish universally applicable HALP thresholds, while accounting for local clinical characteristics and predominant treatment modalities.
This meta-analysis has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, significant heterogeneity was observed across studies, potentially undermining the robustness and generalizability of the pooled estimates. While subgroup and sensitivity analyses were performed, unmeasured confounding due to differences in patient characteristics, tumor stages, and treatment modalities cannot be entirely excluded. Second, detailed treatment protocols, including surgical approaches and postoperative management, were not uniformly reported across studies, which may limit the interpretability of subgroup analyses. Third, inflammatory biomarkers in peripheral blood may be affected by infection, steroid therapy, or other medications that could not be evaluated in this study. Fourth, methodological differences in HALP calculation and the lack of a standardized cut-off threshold may impair comparability and data synthesis. Fifth, information regarding the management of anemia, such as pre-treatment blood transfusions or nutritional interventions, was not consistently reported in the included studies, which may have influenced HALP scores and should be considered in future prospective research. Lastly, some studies had relatively short follow-up durations, which may be insufficient to capture long-term survival outcomes associated with HALP. Future prospective, multicenter studies with standardized protocols, comprehensive data collection, and longer follow-up are warranted to validate and refine the prognostic utility of HALP in NSCLC. In addition, potential interventions aimed at improving HALP components—such as nutritional support, correction of anemia, and anti-inflammatory strategies—should be further investigated to determine whether optimizing the HALP score may translate into improved survival outcomes.
5 Conclusions
In summary, our pooled analysis indicates that lower pre-treatment HALP score are associated with poorer survival outcomes in NSCLC patients. These findings highlight the potential of the HALP score as an effective prognostic biomarker, providing crucial prognostic information for NSCLC patients. Future studies should continue to validate these findings in diverse patient populations and in prospective, multicentre trials, and explore the integration of HALP score with other prognostic markers to further refine risk stratification and treatment approaches.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
QL: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. MC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. HZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. General Program of Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2022NSFSC0814).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1576326/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS. Lung cancer 2020: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med. (2020) 41:1–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2019.10.001
3. Li Y, Wang N, Huang Y, He S, Bao M, Wen C, et al. CircMYBL1 suppressed acquired resistance to osimertinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Genet. (2024), 284–285:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2024.04.001
4. Rami-Porta R, Bolejack V, and Goldstraw P. The new tumor, node, and metastasis staging system. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. (2011) 32:44–51. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1272868
5. Portale G, Bartolotta P, Azzolina D, Gregori D, and Fiscon V. Prognostic role of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte, and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio in operated rectal cancer patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg. (2023) 408:85. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-02786-8
6. Nøst TH, Alcala K, Urbarova I, Byrne KS, Guida F, Sandanger TM, et al. Systemic inflammation markers and cancer incidence in the UK Biobank. Eur J Epidemiol. (2021) 36:841–8. doi: 10.1007/s10654-021-00752-6
7. Panakkal N, Lekshmi A, Saraswathy VV, and Sujathan K. Effective lung cancer control: An unaccomplished challenge in cancer research. CytoJournal. (2023) 20:16. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_36_2022
8. Chen XL, Xue L, Wang W, Chen HN, Zhang WH, Liu K, et al. Chen ZX et al: Prognostic significance of the combination of preoperative hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet in patients with gastric carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:41370–82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i38
9. Peng D, Zhang CJ, Tang Q, Zhang L, Yang KW, Yu XT, et al. Prognostic significance of the combination of preoperative hemoglobin and albumin levels and lymphocyte and platelet counts (HALP) in patients with renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. BMC Urol. (2018) 18:20. doi: 10.1186/s12894-018-0333-8
10. Feng JF, Wang L, and Yang X. The preoperative hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet (HALP) score is a useful predictor in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. (2021) 21:773–81. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.5666
11. Zhai B, Chen J, Wu J, Yang L, Guo X, Shao J, et al. Predictive value of the hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after radical lung cancer surgery. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:976. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2120
12. Zhang T, Liu W, and Xu C. Correlation analysis of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, platelet score and platelet to albumin ratio and prognosis in patients with lung adenosquamous carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1166802. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1166802
13. Taylor M, Evison M, Michael S, Obale E, Fritsch NC, Abah U, et al. Granato F et al: Pre-Operative Measures of Systemic Inflammation Predict Survival After Surgery for Primary Lung Cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. (2024) 25:460–467.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2024.04.018
14. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
15. Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. Bmj. (2017) 358:j4008. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j4008
16. Zeng X, Zhang Y, Kwong JS, Zhang C, Li S, Sun F, et al. The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: a systematic review. J Evidence-Based Med. (2015) 8:2–10. doi: 10.1111/jebm.2015.8.issue-1
17. Güç ZG, Alacacıoğlu A, Kalender ME, Oflazoğlu U, Ünal S, Yıldız Y, et al. HALP score and GNRI: Simple and easily accessible indexes for predicting prognosis in advanced stage NSCLC patients. The İzmir oncology group (IZOG) study. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:905292. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.905292
18. Wei S, Shao J, Wang J, and Wang G. The preoperative hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet score is a prognostic factor for non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy: a retrospective study. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:457. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1097
19. Fang Q, Yu J, Li W, Luo J, Deng Q, Chen B, et al. Prognostic value of inflammatory and nutritional indexes among advanced NSCLC patients receiving PD-1 inhibitor therapy. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2023) 50:178–90. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13740
20. Mazzella A, Maiolino E, Maisonneuve P, Loi M, and Alifano M. Systemic inflammation and lung cancer: is it a real paradigm? Prognostic value of inflammatory indexes in patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancers. (2023) 15:1854. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061854
21. Zhao B, Guo H, Wu W, and Duan G. Hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet (HALP) score can predict the prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Asian J Surg. (2023) 46:4891–2. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2023.05.152
22. Cavdar E, Karaboyun K, and Kara K. Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic role of laboratory indices in advanced lung cancer patients. Asia-Pacific J Clin Oncol. (2024). doi: 10.1111/ajco.14092
23. Gao S, Huang Q, Wei S, Lv Y, Xie Y, and Hao Y. Prognostic nomogram based on pre-treatment HALP score for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo Brazil). (2024) 79:100371. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100371
24. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
25. Jiang T, Sun H, Xue S, Xu T, Xia W, Wang Y, et al. Prognostic significance of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score in breast cancer: a propensity score-matching study. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24:230. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03419-w
26. Xiong Y, Yong Y, and Wang Y. Clinical value of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet indexes in predicting lymph node metastasis and recurrence of endometrial cancer: a retrospective study. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e16043. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16043
27. Shi Y, Shen G, Zeng Y, Ju M, Chen X, He C, et al. Predictive values of the hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet score (HALP) and the modified -Gustave Roussy immune score for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 123:110773. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110773
28. Xu H, Zheng X, Ai J, and Yang L. Hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score and cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 13,110 patients. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 114:109496. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109496
29. Nathan C and Ding A. Nonresolving inflammation. Cell. (2010) 140:871–82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.029
30. Singh N, Baby D, Rajguru JP, Patil PB, Thakkannavar SS, and Pujari VB. Inflammation and cancer. Ann Afr Med. (2019) 18:121–6. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_56_18
31. Serhan CN and Savill J. Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:1191–7. doi: 10.1038/ni1276
32. Medzhitov R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature. (2008) 454:428–35. doi: 10.1038/nature07201
33. Li Z, Zheng Z, Ruan J, Li Z, and Tzeng CM. Chronic inflammation links cancer and parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. (2016) 8:126. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00126
34. Ritter B and Greten FR. Modulating inflammation for cancer therapy. J Exp Med. (2019) 216:1234–43. doi: 10.1084/jem.20181739
35. Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S, Sandur SK, Pandey MK, and Sethi G. Inflammation and cancer: how hot is the link? Biochem Pharmacol. (2006) 72:1605–21. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.06.029
36. Salhany JM, Mathers DH, and Eliot RS. Molecular basis for oxygen transport. Hemoglobin Funct controlling factors. Adv Cardiol. (1973) 9:53–67. doi: 10.1159/000393425
37. Dicato M, Plawny L, and Diederich M. Anemia in cancer. Ann oncology: Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2010) 21 Suppl 7:vii167–172. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq284
38. Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen H, et al. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:157. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1089-9
39. Tomita M, Shimizu T, Hara M, Ayabe T, and Onitsuka T. Impact of preoperative hemoglobin level on survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Anticancer Res. (2008) 28:1947–50.
40. Zhang YH, Lu Y, Lu H, Zhang MW, Zhou YM, Li XL, et al. Pre-treatment hemoglobin levels are an independent prognostic factor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. (2018) 9:44–9. doi: 10.3892/mco.2018.1628
41. Chen C, Song Z, Wang W, and Zhou J. Baseline anemia and anemia grade are independent prognostic factors for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. (2021) 14:59. doi: 10.3892/mco.2021.2221
42. Gupta D and Lis CG. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: a systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr J. (2010) 9:69. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-9-69
43. Deme D and Telekes A. Prognostic importance of albumin in oncology. Orvosi hetilap. (2018) 159:96–106. doi: 10.1556/650.2018.30885
44. Quigley DA and Kristensen V. Predicting prognosis and therapeutic response from interactions between lymphocytes and tumor cells. Mol Oncol. (2015) 9:2054–62. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.10.003
45. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, and Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. (2008) 454:436–44. doi: 10.1038/nature07205
46. Wang S, Sun J, Chen K, Ma P, Lei Q, Xing S, et al. Liu Y et al: Perspectives of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte treatment in solid tumors. BMC Med. (2021) 19:140. doi: 10.1186/s12916-021-02006-4
47. Haemmerle M, Stone RL, Menter DG, Afshar-Kharghan V, and Sood AK. The platelet lifeline to cancer: challenges and opportunities. Cancer Cell. (2018) 33:965–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.03.002
48. Li S, Lu Z, Wu S, Chu T, Li B, Qi F, et al. The dynamic role of platelets in cancer progression and their therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Cancer. (2024) 24:72–87. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00639-6
49. Thomas MR and Storey RF. The role of platelets in inflammation. Thromb haemostasis. (2015) 114:449–58. doi: 10.1160/TH14-12-1067
50. Franco AT, Corken A, and Ware J. Platelets at the interface of thrombosis, inflammation, and cancer. Blood. (2015) 126:582–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-08-531582
51. Hou C, Jiang F, Ma H, Zhu Q, Wang Z, Zhao B, et al. Qian Y et al: Prognostic role of preoperative platelet, fibrinogen, and D-dimer levels in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter prospective study. Thorac Cancer. (2019) 10:304–11. doi: 10.1111/tca.2019.10.issue-2
52. Menczer J. Preoperative elevated platelet count and thrombocytosis in gynecologic Malignancies. Arch gynecology obstetrics. (2017) 295:9–15. doi: 10.1007/s00404-016-4212-9
53. Sriram KB, Larsen JE, Yang IA, Bowman RV, and Fong KM. Genomic medicine in non-small cell lung cancer: paving the path to personalized care. Respirology (Carlton Vic). (2011) 16:257–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2010.01892.x
54. Warth A. Diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction of non-small cell lung cancer. Importance of morphology, immunohistochemistry and molecular pathology. Der Pathologe. (2015) 36 Suppl 2:194–200. doi: 10.1007/s00292-015-0085-0
55. Lei B, Zhang H, Sun J, Wang L, Ruan M, Yan H, et al. The potential of basal F-18-FDG PET/CT in evaluating prognosis and benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy after tumor resection of stage IB(T2, ≤ 3 cm with VPI, N0, M0)NSCLC. Clin Lung Cancer. (2025) 26:18–28.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2024.11.001
56. Yolchuyeva S, Ebrahimpour L, Tonneau M, Lamaze F, Orain M, Coulombe F, et al. Joubert P et al: Multi-institutional prognostic modeling of survival outcomes in NSCLC patients treated with first-line immunotherapy using radiomics. J Trans Med. (2024) 22:42. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04854-z
57. Čelešnik H and Potočnik U. Blood-based mRNA tests as emerging diagnostic tools for personalised medicine in breast cancer. Cancers. (2023) 15:1087. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041087
58. Wei C, Liang Y, Mo D, Lin Q, Liu Z, Li M, et al. Cost-effective prognostic evaluation of breast cancer: using a STAR nomogram model based on routine blood tests. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1324617. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1324617
59. Buck AK, Herrmann K, and Schreyögg J. PET/CT for staging lung cancer: costly or cost-saving? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2011) 38:799–801. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1803-3
60. Riely GJ, Wood DE, Ettinger DS, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, et al. Non-Small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Network: JNCCN. (2024) 22:249–74. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2204.0023
61. Mao JR, Lan KQ, Liu SL, Liu C, Xie SY, Li SC, et al. Can the prognosis of individual patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma be predicted using a routine blood test at admission? Radiother Oncol. (2023) 179:109445. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2022.109445
62. Siau K. Routine blood tests are a basic screening tool for serious pathology. Bmj. (2017) 357:j2675. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j2675
63. Hopkins AM, Rowland A, Kichenadasse G, Wiese MD, Gurney H, McKinnon RA, et al. Predicting response and toxicity to immune checkpoint inhibitors using routinely available blood and clinical markers. Br J Cancer. (2017) 117:913–20. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.274
Keywords: HALP score, NSCLC, prognostic, survival, biomarker
Citation: Li Q, Chen M, Zhao H and Zeng J (2025) The prognostic and clinicopathological value of HALP score in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 16:1576326. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1576326
Received: 13 February 2025; Accepted: 11 June 2025;
Published: 26 June 2025.
Edited by:
Jehad Charo, Roche (Switzerland), SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Akif Turna, Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa, TürkiyeHaiyang Li, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Li, Chen, Zhao and Zeng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qin Li, bGlxaW42ODQ5QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Qin Li
Qin Li Mengqi Chen2†
Mengqi Chen2†