- 1School of Basic Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 2Department of Blood Transfusion, Xi’an International Medical Center Hospital, Xi’an, China
- 3Scientific Technology Center of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 4Ningxia Key Laboratory of Prevention and Control of Common Infectious Diseases, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 5Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 6Clinical Laboratory, Shiyan Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital, Shiyan, China
- 7Department of Respiratory Medicine, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 8Center for Neurological Diseases, The First Hospital of Shizuishan, Affiliated of Ningxia Medical University, Shizuishan, China
Introduction: Parasites and parasite-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) can protect against inflammatory diseases, such as asthma. M2a macrophages facilitate the development of allergic asthma. miR-10a-5p is closely associated with asthma, and emu-miR-10a-5p (encapsulated in Echinococcus multilocularis EVs), shares seed-site sequences with mature human and mouse miRNAs.
Methods: We purified EVs by centrifugation, and characterized the EVs via nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). We used MH-S cells to construct the M2a polarization model. The gene expression changes in MH-S cells after transfect with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics was analyzed through transcriptome sequencing. We established a mouse model of ovalbumin (OVA)-induced allergic asthma. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Masson’s trichrome, and periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining were used to detect airway inflammation in the lung tissues. RT-qPCR, flow cytometry and Western Blot assays were performed to validate the expression of related genes and proteins.
Results: Here, we observed that E. multilocularis-derived EVs and their encapsulated emu-miR-10a-5p transcripts inhibited macrophage M2a polarization. We also found that emu-miR-10a-5p targeted leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) mRNA and inhibited the downstream Janus kinase 1 (JAK1)–signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)-signaling pathway. We established a mouse model of ovalbumin (OVA)-induced allergic asthma and found that emu-miR-10a-5p alleviated pulmonary inflammation in mice with allergic asthma while inhibiting the accumulation of pulmonary M2a macrophages. emu-miR-10a-5p intervention inhibited LIF and JAK1–STAT3 signaling in the lungs of mice with allergic asthma.
Discussion: These findings suggest that emu-miR-10a-5p encapsulated in E. multilocularis EVs might regulate M2a macrophage polarization via the JAK1–STAT3 pathway by targeting and binding LIF in a cross-species manner, thereby alleviating airway inflammation in mice with allergic asthma. These findings enhance the current understanding of the mechanisms underlying immune regulation during infection and the maintenance of immune stability.
Introduction
Asthma is the most common chronic respiratory disease, affecting approximately 334 million people worldwide, with a high incidence in developed countries (1). Allergic asthma is the most common form of asthma (2). Although glucocorticoids can reduce asthma-related morbidity and mortality, the global impact of asthma remains high, and the prevalence of the disease is apparently increasing in developing countries (3, 4).
Macrophages are the most abundant immune cells in the lungs and play a key role in maintaining the immune response to respiratory inflammation (5, 6). Macrophages can be polarized into classically activated (M1) and alternatively activated (M2) phenotypes, corresponding to Th1 and Th2 differentiation of helper T cells, respectively (7). Increased M2 macrophage activation is thought to play a key role in allergic asthma by activating the Th2 cell response (7–9). M2 macrophages are further subdivided into M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d subtypes, with M2a macrophages being the most closely associated with asthma (10, 11).
Parasites can regulate the host immune system to evade immune rejection, a strategy that promotes the long-term survival of parasites and leads to chronic infections (12). Such regulation can also protect the body from inflammatory diseases caused by dysregulated immune responses (13). Research has shown that some worm infections confer protection against allergic diseases, such as asthma (14). For example, Schistosoma infection inhibits the development of airway inflammation in mice with allergic asthma, and Echinococcus granulosus infection significantly reduces ovalbumin (OVA)-induced eosinophilic infiltration and mucus production in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of mice with allergic asthma and improves airway hyperresponsiveness (15–17). Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are key factors in host–parasite interactions. EVs, approximately 30–150 nm in diameter (18), are secreted by all living cells. EVs typically transport proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids and can potentially serve as immunomodulatory targeting host cells (19). EVs can become internalized by multiple host cells and can regulate host immune responses through the bioactive substances they carry, such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. EVs are rich in non-coding RNAs, especially microRNAs (miRNAs), which specifically bind to target mRNAs, leading to mRNA degradation or inhibiting protein translation, ultimately downregulating targeted proteins. Parasitic miRNAs exist in animal and human bodily fluids and regulate host genes in a cross-species manner (20). E. granulosus-derived EVs and encapsulated egr-miR-277a-3p promoted dendritic cell (DC) maturation and differentiation in a cross-species manner, thereby regulating the host immune response (21). Emu-miR-4989-3p encapsulated in the EVs of E. multilocularis played a role in nitric oxide production in macrophages, tumor necrosis-alpha production, and the production of several key components involved in the lipopolysaccharide–Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway, thereby participating in immunomodulation (22). However, the roles of miRNAs derived from E. multilocularis EVs in allergic asthma have not been elucidated.
Sera from mice infected with E. multilocularis contained emu-miR-10a-5p (23), suggesting that emu-miR-10a-5p can be delivered to the host. Emu-miR-10a-5p shares seed-site sequences with mature miRNAs from both human and mouse sources and may alter the expression of the corresponding host mRNA, signaling a potential advantage for parasite invasion. Therefore, we speculate that emu-miR-10a-5p may participate in parasite infection and immune responses and play important roles in host–parasite interactions. In addition, previous data suggest that miR-10a-5p is closely associated with asthma and may be a candidate for treating asthma (24, 25).
In this study, we found that EVs and emu-miR-10a-5p secreted by E. multilocularis act on the JAK1–STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting and binding to leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), inhibiting M2a macrophage polarization and thereby alleviating OVA-induced allergic asthma.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
Our research on experimental animals was authorized by the Ethics Committee of Ningxia Medical University (license number: SYXK2020–0001). The data obtained met the relevant ethical requirements.
Animals and treatments
BALB/c female mice, aged 6–8 weeks and weighing 18–25 g, were purchased from Beijing HFK Bioscience (license number: SCXK (Beijing) 2024–0003). All mice were housed in a specific pathogen-free environment. Mouse experiments and euthanasia procedures were conducted in accordance with the animal welfare guidelines of Ningxia Medical University.
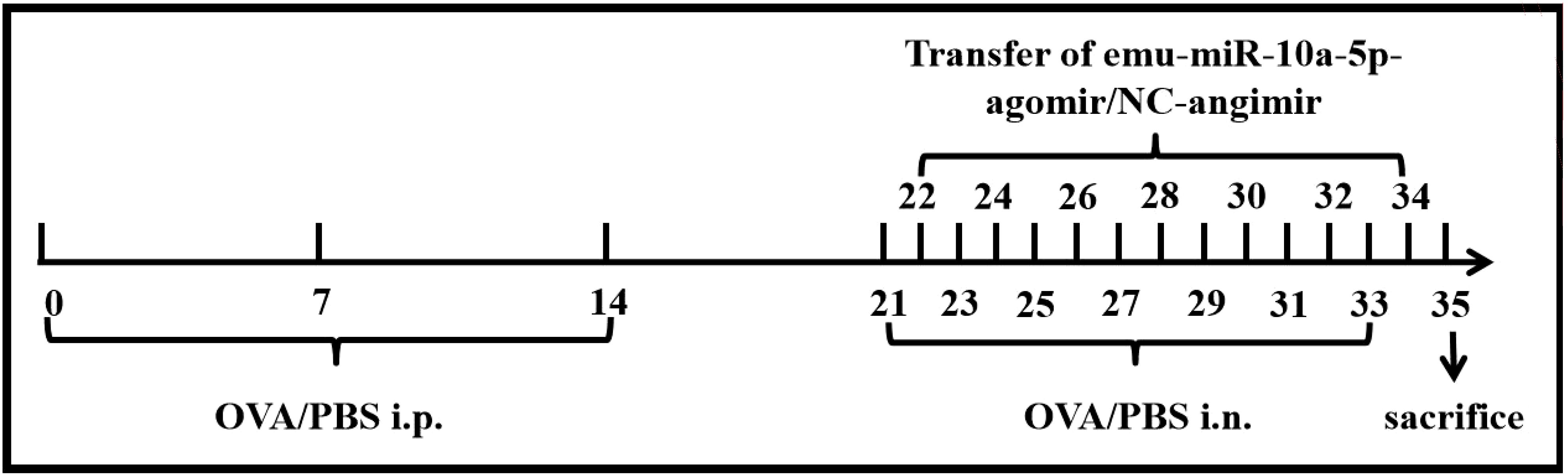
The mice were randomly divided into four groups: the control, OVA, OVA +NC-agomir, and OVA+emu-miR-10a-5p-agomir groups. Asthma was induced and treated as shown in Figure 1. Briefly, all mice were sensitized with 200 μL sensitizing solution: 20 μg OVA (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and 50 μL Al(OH)3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Xian, China) via intraperitoneal injection on days 0, 7, and 14. On days 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, and 33, nasal drops were administered with 20 μL OVA (100 μg) solution. On days 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, and 34, agomirs were injected via the tail vein at a concentration of 3 OD (dissolve in 200 μL DEPC water). The emu-miR-10a-5p and control agomirs were designed and synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China).
Isolation and characterization of EVs
PSCs (n = 2,000) were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagles’ medium (DMEM; Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 30% exosome-depleted fetal bovine serum (VivaCell, Shanghai, China) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin in 100 cm2 cell culture dishes at 37°C and 5% CO2. The PSC culture medium was harvested every 72 h. The medium was collected and centrifuged sequentially at 1500, 2000, 10,000, and 120,000 × g for 30, 30, 60, and 90 min, respectively. All centrifugations were carried out at 4°C. The purified EVs were resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and stored at -80°C for subsequent experiments. We measured EV particle sizes and concentrations via nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and characterized the EVs via transmission electron microscopy (TEM) as described previously (26).
Cell culture
MH-S cells (mouse alveolar macrophages) were procured from ProCell (CL-0597, Wuhan, China). Cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 10% serum (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific), 0.05 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (Solarbio Science & Technology, Beijing, China) at 37°C with 5% CO2. M2a polarization in MH-S cells was induced by interleukin (IL)-4 (20 ng/mL; BioLegend, USA) and IL-13 (20 ng/mL; BioLegend, USA). The emu-miR-10a-5p mimic, LIF small-interfering RNA (siRNA), and negative controls (NCs) were designed and synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China). Cells were transfected using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
HEK293T cells were cultured in DMEM (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 10% serum and 1% penicillin–streptomycin at 37°C with 5% CO2.
Isolating naïve cluster of differentiation 4+ T cells
Mice were anesthetized, sacrificed, and immersed in 75% alcohol, after which their spleens were aseptically obtained. Lymphocytes were isolated using a Mouse Spleen Lymphocyte Isolation Medium Kit (Tianjin Haoyang Biopharmaceutical, China). Naïve CD4+ T cells were purified using a Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Germany).
Culturing naïve CD4+ T cells with MH-S cells
Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 10% serum (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (Solarbio Science & Technology) at 37°C with 5% CO2. Each 24-well plate (coated with anti-CD3, 1 mg/mL; Thermo Fisher Scientific) contained 5 × 105 naïve CD4+ T cells, 1 × 105 MH-S cells treated under different conditions, and soluble anti-CD28 (0.2 mg/mL, Thermo Fisher Scientific). The phenotype of the naïve CD4+ T cells was observed via flow cytometry after 3 days.
Tissue staining and flow cytometry
Lung and spleen tissues were processed into single-cell suspensions. Next, the concentration was adjusted to 1 × 107 cells/mL, and 100 μL of cells was taken from each tube for staining. Lung macrophages were incubated with antibodies against EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 1 (F4/80), CD11c, and CD86 at 4°C for 30 min; fixed at 25°C for 30 min and finally incubated with a membrane-breaking solution and an anti-CD206 antibody at 4°C for 30 min. MH-S cells were collected after 48 h of culture, incubated with anti-F4/80 at 4°C for 30 min, fixed at 25°C for 30 min, and finally incubated with membrane-breaking solution and anti-CD206 at 4°C for 30 min. To stain lung eosinophils, we incubated them with antibodies against CD45, CD11C, and sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin F (siglec-F) for 30 min at 4°C. Th1/2 cells were stained by first preparing them as single-cell suspensions and incubating them with cell activation cocktail (BioLegend, USA) for 5 h at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. Then, the cells were incubated on ice for 30 min with antibodies against CD3 and CD4, fixed at 25°C for 30 min, and finally incubated on ice for 30 min with membrane-breaking solution, anti-interferon-γ and anti-IL-4. Staining was followed by detection with a FACSCelesta instrument (Becton Dickinson, Beijing, China) and analysis with FlowJo software.
The following reagents for flow cytometry were obtained from BioLegend (USA): PE-anti-F4/80, APC-anti-CD206, FITC-anti-CD11c, APC-anti-siglec-F, APC-anti-CD3, FITC-anti-CD4, PE-anti-IL-4, PerCp-cy5.5-anti-IFN-γ, Cell Activation Cocktail with Brefeldin A, and Intracellular Staining Permeabilization Wash Buffer. We also obtained BV421-anti-CD86 and APC-cy7-anti-CD45 from BD Pharmingen (USA).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis
After the mice were anesthetized and sacrificed, their eyeballs were removed to obtain blood, and the serum was separated via centrifugation. OVA-specific IgE was detected using a mouse OVA-specific IgE (OVA-sIgE) ELISA Kit (Nanjing Boyan Biotechnology, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis
Total RNA was extracted from cells using TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Total RNA was extracted from mouse lung tissue using an RNAprep Pure Tissue Kit (TianGen, Beijing, China). Reverse transcription of mRNA was performed using PrimeScript™ RT Master Mix (Takara Biomedical Technology, Beijing, China). mRNA-expression levels were detected using Bestar® SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix (DBI® Bioscience). miRNAs were reverse transcribed and detected using the All-in-One miRNA RT-qPCR Detection Kit (GeneCopoeia, Rockville, MD). U6 small nuclear RNA and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase RNA were detected as endogenous references and gene expression was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCT method. The primer sequences are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Western blot analysis
The total protein in MH-S cells was extracted using a Total Protein Extraction Kit (KeyGEN, Nanjing, China), and the concentrations were measured using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (KeyGEN). Antibodies against LIF (ab113262, 1:1000), JAK1 (ab133666, 1:2000), and STAT3 (ab68153, 1:2000) were obtained from Abcam (Shanghai, China), Antibodies against CD9 (13174, 1:1000), CD63 (52090, 1:1000), p-JAK1 (74129, 1:1000), and p-STAT3 (9145, 1:1000) were obtained from (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, Massachusetts, USA). An antibody against β-actin (BS6007MH, 1:10000) and the secondary antibody (BS20241-Y, 1:20000) was obtained from Bioworld Technology (Minneapolis, MN, USA). Protein-expression assays were performed using the ECL Detection Kit (KeyGen Biotech) and the ChemiDoc Touch Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Shanghai, China).
Dual-luciferase reporter assay
Direct association of LIF transcripts with emu-miR-10a-5p was verified using the Luciferase-3′-UTR Reporter System. The complete fragment of the LIF 3′-untranslated region (UTR) located downstream of the Renilla luciferase coding sequence (XhoI/NotI site) was cloned into the psiCHECK-2 plasmid (Promega, Shanghai, China). The resulting plasmid was then co-transfected with the emu-miR-10a-5p mimic or NC (50 ng) into HEK293T cells. The cells were incubated at 37°C for 48 h and collected. Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured using the Dual Glo Dual Luciferase Assay System (Promega, Shanghai, China). For each sample, the firefly luciferase activity was normalized to that of Renilla luciferase.
Histopathologic analysis
Left lung tissues were fixed in 10% formalin and embedded in paraffin. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Masson’s trichrome, and periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining were used to detect airway inflammation, collagen deposition, and mucus production in the lung tissues.
Immunofluorescence analysis
For IF analysis, paraffin-embedded blocks were processed as previously described (27). Primary antibodies against F4/80 (ab300421, 1:500, Abcam), arginase 1 (Arg1; TD6657, 1:500, Abmart, Shanghai, China), and LIF (ab113262, 1:500, Abcam) were added to the blocks dropwise, and then they were incubated at 4°C overnight. On the following day, the blocks were rinsed five times with PBS, Cy3-conjugated goat anti-rabbit (1:200; Proteintech, China) was added dropwise, and the blocks were incubated at 37°C for 1.5 h, avoiding light. Finally, the nuclei were stained with 4', 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (Beyotime, China) and imaged using a panoramic slice scanner (PANNORAMIC MIDI, 3DHISTECH, Hungary).
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism Software 8.0 (GraphPad Software) and processed as mean ± the standard deviation. Student’s t-test was used to analyze differences in the data from the two groups, and differences were considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
Results
Identification and characterization of EVs
E. multilocularis Qinghai isolate (Chinese mainland strain, Qinghai population) was maintained in BALB/c mice in our laboratory. Protoscoleces (PSCs) were obtained from these mice (Figures 2A, B). To confirm that EVs were successfully isolated, their sizes and morphologies were characterized via TEM and NTA. Vesicles with round or oval membranes less than 200 nm in diameter were observed via TEM (Figure 2C), and the main peaks of the vesicles were between 100 and 130 nm (Figure 2D). Our western blot results confirmed the presence of the EV-marker proteins, CD63 and CD9 (Figure 2E).
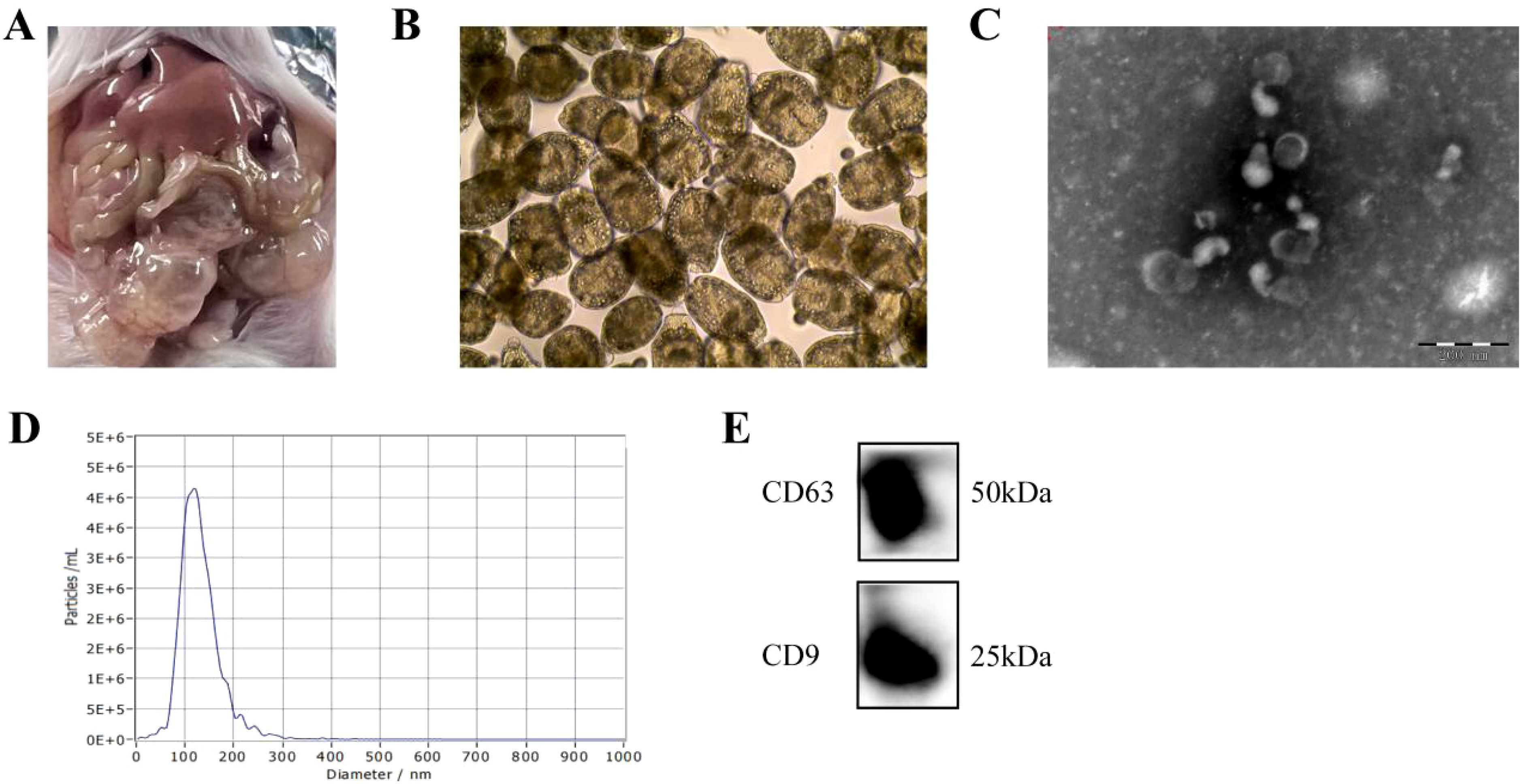
Figure 2. Identification and characterization of EVs secreted by E. multilocularis. (A) Anatomical view of protoscolex intraperitoneally infected mice. (B) Observation of the PSC under the light microscope. (C) TEM images of EVs. Scale bars = 200 nm. (D) The size distribution of EVs was analyzed via NTA. (E) The encapsulation of CD9 and CD63 in EVs was determined using western blotting.
E. multilocularis EVs and encapsulated emu-miR-10a-5p regulated M2a macrophage polarization
We used IL-4 and IL-13 to induce M2a polarization in MH-S cells and co-cultured them with EVs. Our RT-qPCR results revealed lower expression levels of M2a genes (found in inflammatory zone 1 [Fizz1], Arg1, macrophage mannose receptor 1 [Mrc1], and Ym1 [chitinase-like protein 3]) in the transfection group than in the induction group (Figure 3A). F4/80 and CD206 were detected as M2a macrophage markers. Our flow cytometry results showed that the proportion of M2a macrophages decreased compared with that in the induction group (Figure 3B). Previous data demonstrated that emu-miR-10a-5p was encapsulated in E. multilocularis EVs (22), which was confirmed in this study (Supplementary Figures S1A, B). In addition, E. multilocularis EVs can increase the expression of emu-miR-10a-5p in macrophages (Supplementary Figure S1C), indicating that E. multilocularis EVs can deliver emu-miR-10a-5p to macrophages.
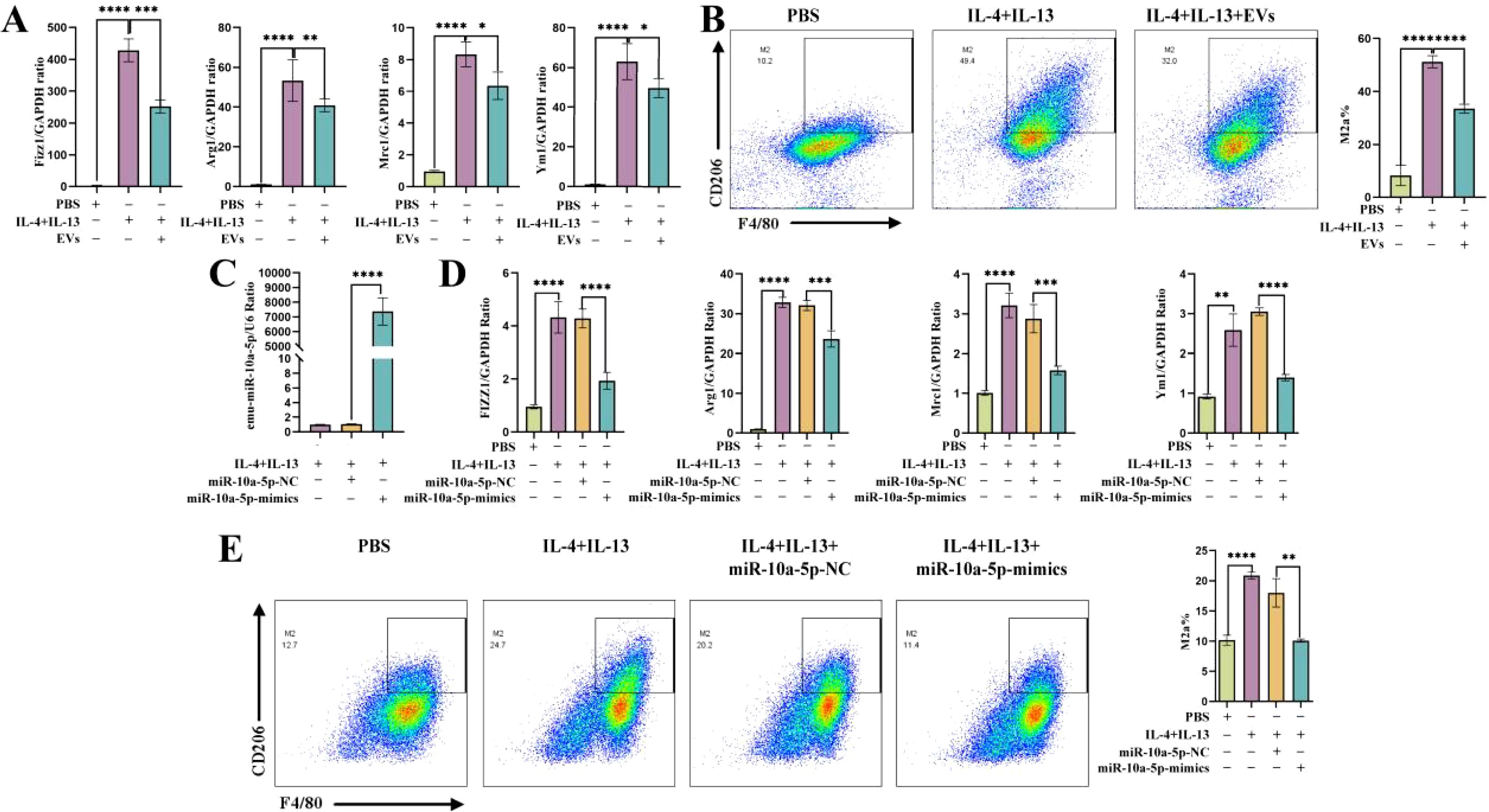
Figure 3. E. multilocularis EVs and encapsulated emu-miR-10a-5p regulated M2a macrophage polarization. (A) mRNA-expression levels of Fizz1, Arg1, Mrc1, and Ym1 in macrophages after co-culturing them with EVs, as determined using RT-qPCR. (B) Flow cytometry was used to detect M2a-type macrophages after co-culture with EVs. (C) emu-miR-10a-5p expression detected using RT-qPCR. (D) mRNA-expression levels of Fizz1, Arg1, Mrc1, and Ym1 in macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics, as determined via RT-qPCR. (E) Flow cytometry was performed to detect M2a-type macrophages after transfection with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics. Except (B) n=3, the remaining experiments n=9. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
MH-S cells were transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics or NC mimics and cultured in the presence of IL-4 and IL-13 to promote M2a polarization. Our RT-qPCR results showed that miR-10a-5p expression was higher in the induction group than in the control group and that the expression of M2a genes was higher in the induction group (Figures 3C, D). Our flow cytometry results showed that the proportion of M2a macrophages was higher in the induction group (Figure 3E).
Overall, these results confirmed that E. multilocularis EVs and encapsulated emu-miR-10a-5p inhibited macrophage polarization towards the M2a phenotype.
emu-miR-10a-5p might regulate M2a polarization in macrophages by targeting LIF and its pathways
To further investigate how emu-miR-10a-5p regulates macrophage M2a polarization, we screened emu-miR-10a-5p target genes via transcriptome sequencing. The results of repeat correlation assessment (Figure 4A) and principal component analysis (Figure 4B) indicated that the sequenced samples showed tight clustering, with high intragroup similarity and good repeatability. Comparison with the blank group revealed 248 upregulated genes in the M2a-polarized group. Comparison with the M2a-polarized group showed 224 downregulated genes after transfection with emu-miR-10a-5p (Supplementary Figure S2A, B). Comparison with the blank group indicated that Mrc1 was upregulated in the M2a group and downregulated after transfection with emu-miR-10a-5p, consistent with our RT-qPCR results. Next, we conducted Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes and Gene Ontology analyses with the identified differentially expressed genes (Supplementary Figures S2C–F). We focused on highly enriched pathways, such as “immune response” and “cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction.” The Lif gene showed the most significant differences and was selected as a candidate target gene for emu-miR-10a-5p.
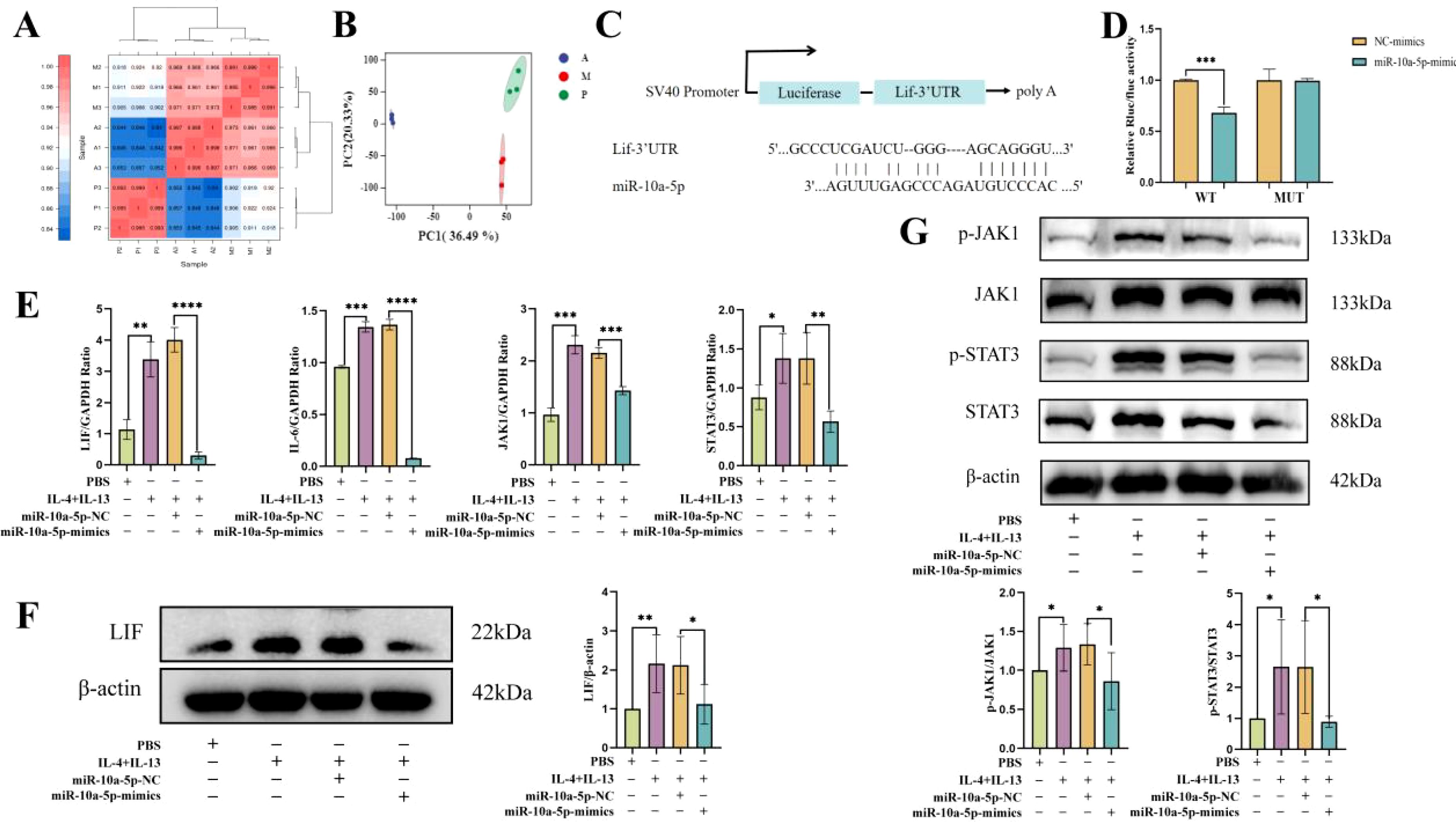
Figure 4. emu-miR-10a-5p regulated the JAK1–STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting LIF. Transcriptome sequencing was used to analyze gene expression. P represents the blank group, M represents the M2a-polarized group, and A represents the M2a-polarized group transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p. (A) Repeat correlation assessment. (B) Principal component analysis. (C) Binding site of emu-miR-10a-5p on LIF. (D) Luciferase activity was observed after emu-miR-10a-5p–LIF binding, as measured in dual-luciferase reporter assays. (E) mRNA-expression levels of Lif, IL-6, Jak1, and Stat3 in macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics, as determined using RT-qPCR. (F) LIF expression in macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics was determined using western blotting. (G) JAK1 and STAT3 expression in macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics, as determined using western blotting. (E) n=9, (F) and (G) n=5-6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
Our dual-luciferase assay results showed that co-transfecting emu-miR-10a-5p mimics significantly inhibited the luciferase activity of the LIF wild-type 3'-UTR constructs in 293T cells (Figures 4C, D). LIF can activate the JAK–STAT3 pathway by inducing the heterodimerization between the LIF receptor and the signal-transduction protein, gp130 (28); JAK1 is the kinase initially targeted by LIF (29). In addition, mounting evidence suggests that the JAK1–STAT3 signaling pathway participates in M2 macrophage polarization (30, 31). We examined the effect of emu-miR-10a-5p on the LIF and JAK1–STAT3 signaling pathways in MH-S cells. RT-qPCR and western blotting data showed that emu-miR-10a-5p significantly inhibited LIF expression and JAK1–STAT3 signaling in M2a macrophages (Figures 4E–G).
These findings indicate that emu-miR-10a-5p inhibited the JAK1–STAT3 signaling pathway by the targeted inhibition of LIF.
LIF modulated M2a macrophage polarization via the JAK1–STAT3 signaling pathway
To further clarify whether emu-miR-10a-5p regulates macrophage M2a polarization via LIF–JAK1–STAT3 signaling, we first infected cells with lentiviruses overexpressing LIF (OE-LIF) or transfected them with LIF siRNA. We successfully silenced or overexpressed LIF, and the LIF siRNA-346 fragment was more effective than other siRNAs tested (Supplementary Figure S3). Therefore LIF siRNA-346 was used in subsequent experiments, referred to simply as siRNA LIF. Comparison with the siRNA-NC group showed that the siRNA-LIF group had decreased JAK1 and STAT3 expression at 48 h post-transfection. Opposite results were observed in the transfected OE-LIF group (Figures 5A, B). The expression of M2a genes and the proportion of M2a macrophages were lower after siRNA-LIF transfection than after siRNA-NC transfection, whereas the opposite results were observed with the transfected OE-LIF group (Figures 5C, D). In conclusion, LIF promoted JAK1–STAT3 signaling and modulated M2a polarization in macrophages.

Figure 5. LIF modulated M2a macrophage polarization via the JAK1–STAT3 signaling pathway (A) Jak1 and Stat3 mRNA-expression levels in macrophages were determined via RT-qPCR after OE-LIF infection or siRNA-LIF transfection. (B) The protein levels of p-JAK1, JAK1, p-STAT3, and STAT3 in macrophages after OE-LIF infection or siRNA-LIF transfection were assessed via western blotting. (C) Fizz1, Arg1, Mrc1, and Ym1 mRNA-expression levels in macrophages after OE-LIF infection or siRNA-LIF transfection were determined via RT-qPCR analysis. (D) Flow cytometry was used to detect the indicated proteins in macrophages after OE-LIF infection or siRNA-LIF transfection. Except (B) n=5-6, the remaining experiments n=9. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
Combined effects of emu-miR-10a-5p and LIF on M2a macrophage polarization and JAK1–STAT3 signaling
To further verify the effects of emu-miR-10a-5p and LIF on macrophage M2a polarization, we co-transfected macrophages with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics and OE-LIF (with NC mimics + OE-NC as controls) and assessed M2a levels. RT-qPCR and flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that the emu-miR-10a-5p mimics+OE-LIF group reversed their individual effects, reaching levels similar to the NC-mimics+OE-NC group (Figures 6A, B). In agreement, RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that the combined treatment alleviated alterations in the JAK1–STAT3 pathway (Figure 6C). These results suggest that emu-miR-10a-5p, in combination with LIF, affect M2a macrophage polarization through the LIF–JAK1–STAT3 axis.
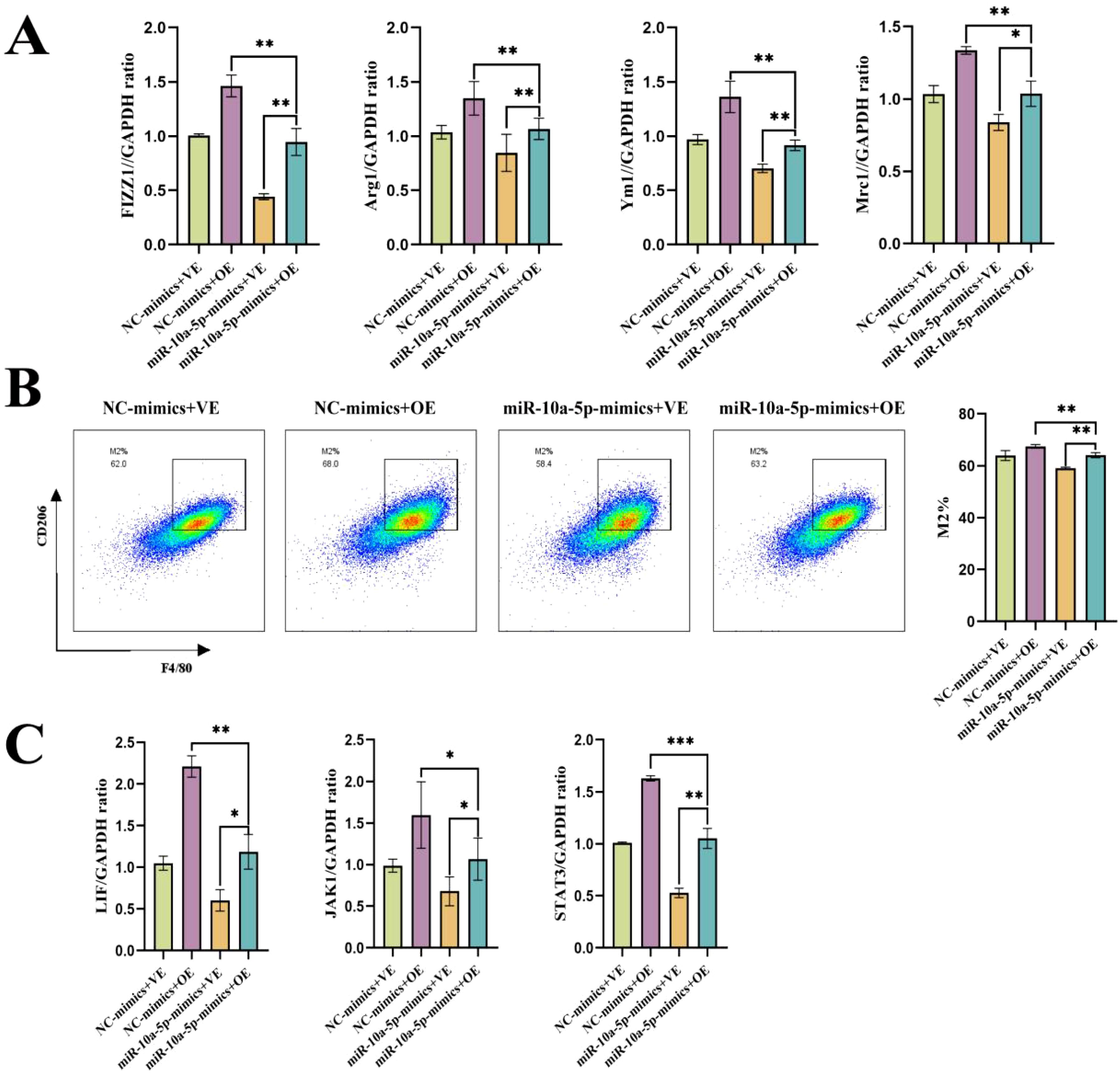
Figure 6. emu-miR-10a-5p and LIF together can rescue their individual effects on M2a macrophage polarization. (A) mRNA-expression levels of Fizz1, Arg1, Mrc1, and Ym1 in macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics and infected with an OE-LIF lentivirus were determined via RT-qPCR. (B) Flow cytometry was used to measure the expression of the indicated proteins in macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics and infected with an OE-LIF lentivirus. (C) mRNA-expression levels of Lif, Jak1, and Stat3 in macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p mimics and infected with an OE-LIF lentivirus were measured via RT-qPCR. All experiments n=9. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
emu-miR-10a-5p relieved airway inflammation in mice with allergic asthma
Next, we established a mouse model of allergic asthma to investigate the role of emu-miR-10a-5p. H&E staining showed that mice in the OVA and OVA+NC agomir groups had thicker airway epithelia and more inflammatory cell infiltration around the bronchus than the control group. Masson’s staining showed significantly more hyperplasia of peribronchial collagen fibers in OVA and OVA+NC agomir mice than in the control group. PAS staining showed substantially more mucus secretion in the OVA and OVA+NC agomir groups than in the control group. These pathological changes were alleviated to a certain extent after emu-miR-10a-5p intervention (Figure 7A). Serum-specific IgE and pulmonary eosinophil levels increased in mice with allergic asthma and decreased after emu-miR-10a-5p intervention (Figures 7B, D). We also detected emu-miR-10a-5p in mouse lung tissues, finding that its expression only increased in the OVA+emu-miR-10a-5p-agomir group, indicating the successful tail vein intervention (Figure 7C). These results suggested that emu-miR-10a-5p relieved airway inflammation in mice with allergic asthma.
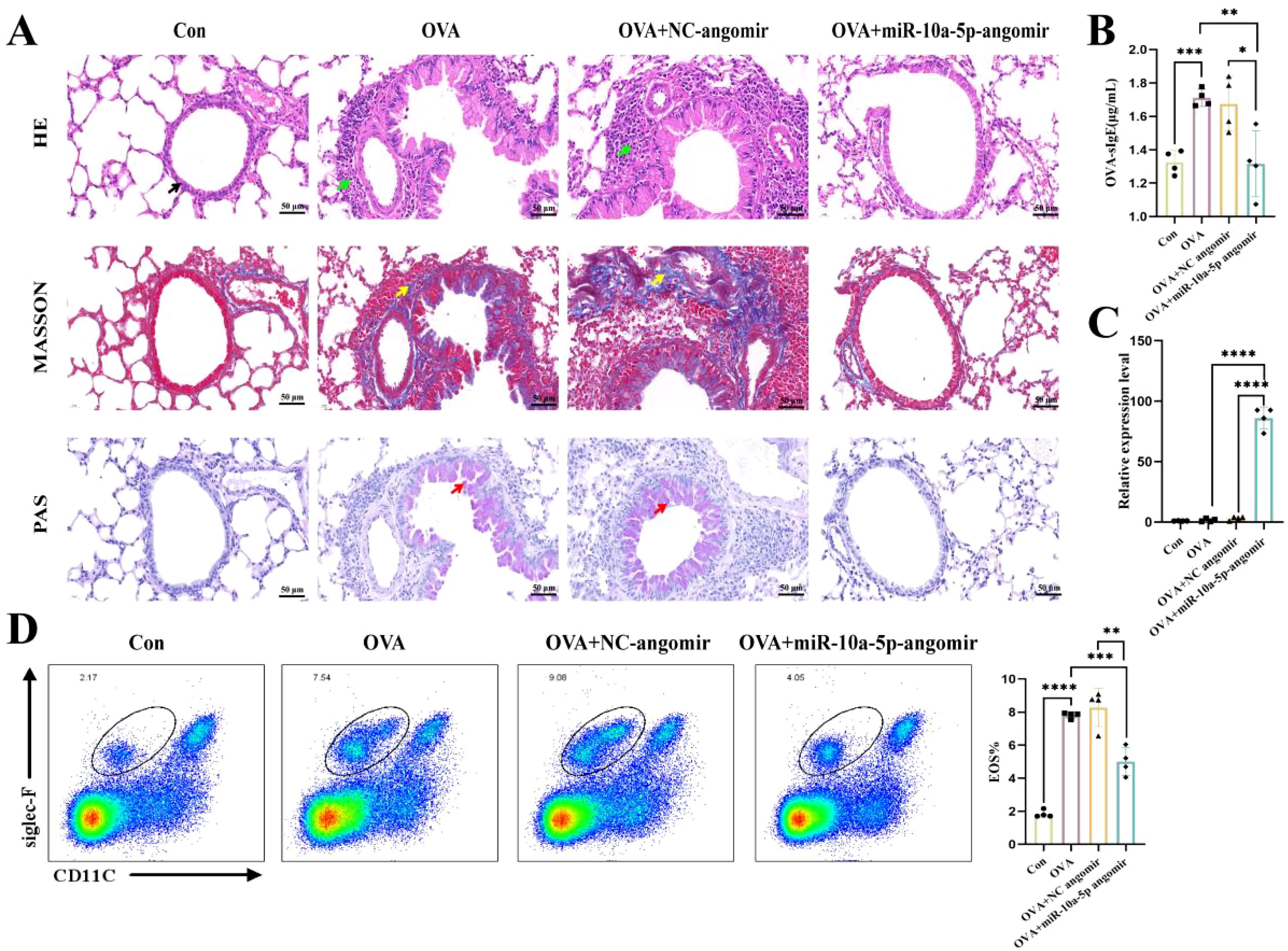
Figure 7. emu-miR-10a-5p relieved airway inflammation in mice with allergic asthma. (A) Morphological observations of H&E, Masson’s, and PAS staining in mouse lung tissues. Magnification: 40×, scale bar: 50 μm. The black arrows point to airway epithelial cells, the green arrows point to inflammatory cells, the yellow arrows point to blue-stained collagen fibers, and the red arrows point to proliferating goblet cells. (B) OVA-specific IgE expression in mouse serum was determined via ELISA analysis. (C) emu-miR-10a-5p expression in mouse lungs was determined via RT-qPCR analysis. (D) Flow cytometry was used to detect eosinophils in mouse lung tissues. All experiments n=4-6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
emu-miR-10a-5p inhibited LIF–JAK1–STAT3 signaling and M2a macrophage polarization in lung macrophages from mice with allergic asthma
To elucidate whether emu-miR-10a-5p might alleviate allergic asthma by inhibiting macrophage M2a polarization, we examined changes in the macrophage phenotypes in the lungs of various groups of mice. We observed no significant difference in the proportion of M1-type macrophages in the lung tissues among all treatment groups; however, M2a macrophages and associated genes were upregulated in allergic asthmatic mice but downregulated after emu-miR-10a-5p intervention (Figures 8A, B, D). Our RT-qPCR results showed that Lif, Jak1, and Stat3 transcription increased in lung tissues from mice with allergic asthma and decreased after emu-miR-10a-5p intervention (Figure 8C). Immunofluorescence analysis showed that LIF expression in lung macrophages from allergic asthmatic mice increased and decreased after emu-miR-10a-5p intervention (Figure 8E). These results are consistent with those of our in vitro experiments, suggesting that emu-miR-10a-5p inhibited M2a macrophage polarization in lungs via the LIF–JAK1–STAT3 axis in vivo.
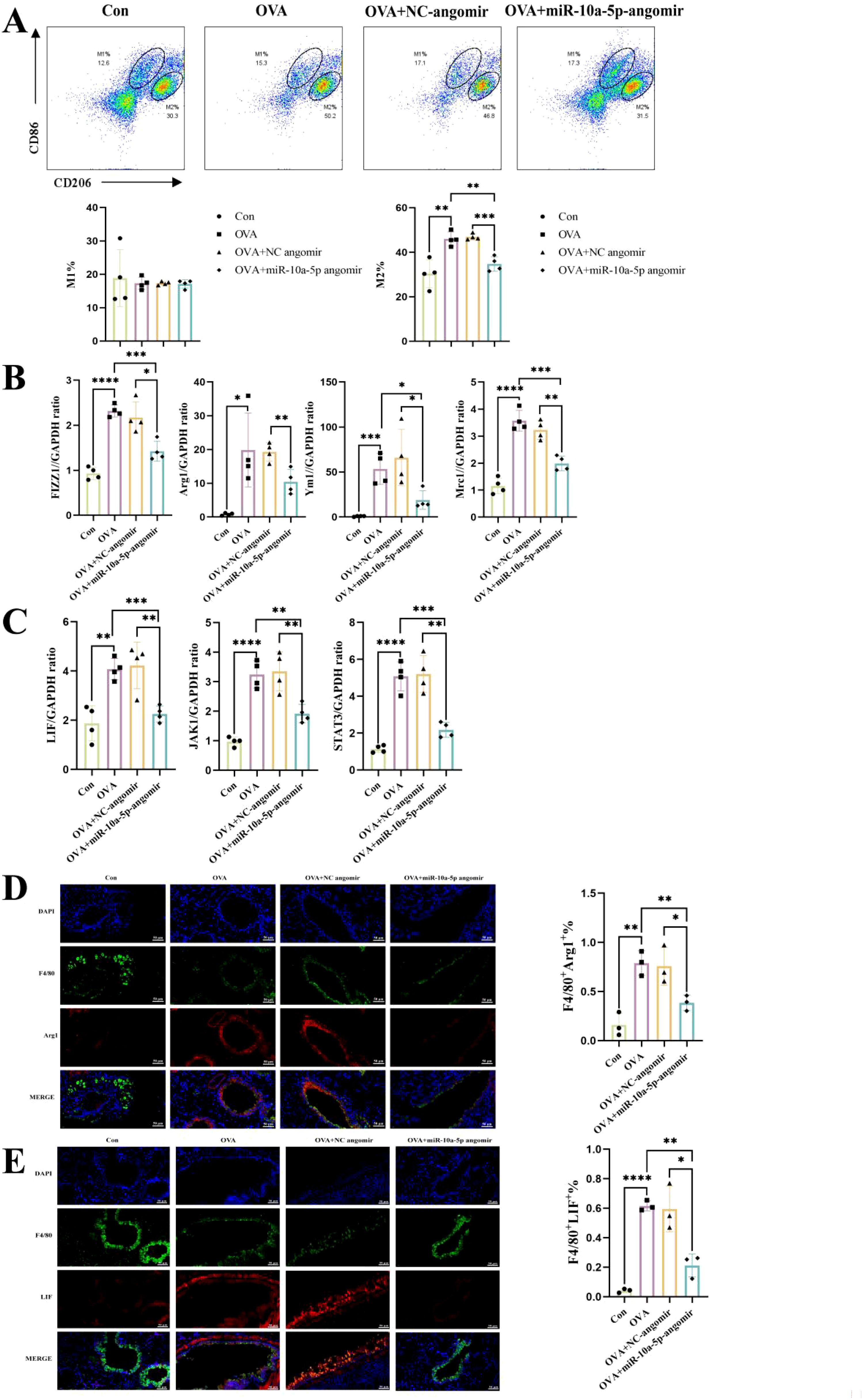
Figure 8. emu-miR-10a-5p inhibited LIF–JAK1–STAT3 signaling in lung macrophages from mice with allergic asthma and inhibited M2a polarization. (A) Flow cytometry was used to detect M1 and M2 macrophages in mouse lung tissues. (B) The mRNA-expression levels of Fizz1, Arg1, Mrc1, and Ym1 in mouse lungs were determined via RT-qPCR. (C) The mRNA-expression levels of Lif, Jak1, and Stat3 in mouse lungs were determined via RT-qPCR. (D) M2a macrophages in mouse lungs were detected via IF analysis (magnification: 40×, scale bar: 50 μm). (E) LIF expression in mouse lung macrophages was detected via IF analysis (magnification: 40×, scale bar: 50 μm). All experiments n=4-6.
In addition, we sought to explore whether the intervention of emu-miR-10a-5p can correct the Th1/2 imbalance in the lung and spleen of mice with allergic asthma. (Supplementary Figures S4A–D). To further explore how emu-miR-10a-5p affects CD4+ T cell differentiation, we transfected macrophages with emu-miR-10a-5p-mimics and co-cultured them with mouse spleen CD4+ T cells. Flow cytometry showed that co-culturing naïve CD4+ T cells with M2a macrophages tended to promote Th2 cell differentiation and inhibit Th1 cell differentiation, whereas co-culturing naïve CD4+ T cells with macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p showed the opposite effects (Supplementary Figures S4E, F).
Discussion
Building on the hygiene hypothesis, interest in studying parasite regulation of the immune system has been increasing. Some parasites and their products can protect the host from immune diseases, such as allergies, immune deficiency, and metabolic syndrome, either directly or by suppressing the inflammatory response (32). Several derivatives of parasite can relieve allergic OVA-induced asthma (32–35). Parasite miRNAs and antigens carried by parasite-derived exosomes play crucial roles in exchanging information and host–parasite interactions. E. granulosus PSC-derived exosome-like vesicles can be internalized by bone marrow-derived DCs to deliver egr-miR-277a-3p, which modulates the host immune response (21). However, few studies have been conducted on parasite-derived exosomes and the parasitic miRNAs they carry in allergic asthma.
emu-miR-10a-5p was highly expressed in EVs secreted by E. multilocularis (22), and interestingly, its sequence was identical to that of E. granulosus egr-miR-10a-5p. E. granulosus EVs showed high expression of egr-miR-10a-5p (36). In addition, sera from E. granulosus-infected mice contained emu-miR-10a-5p (23), suggesting that emu-miR-10a-5p likely helps regulate host cell immune responses. In this study, we demonstrated that E. multilocularis EVs and encapsulated emu-miR-10a-5p inhibited M2a macrophage polarization. In addition, emu-miR-10a-5p alleviated OVA-induced airway inflammation (including reducing eosinophilic infiltration into the airway and decreasing serum IgE levels) by inhibiting macrophage polarization toward the M2a phenotype. We searched for downstream target mRNA molecules via transcriptome sequencing to further investigate how emu-miR-10a-5p can inhibit M2a macrophage polarization in allergic asthma. We screened the candidate molecule LIF and verified its binding with emu-miR-10a-5p.
LIF is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family that plays important roles in homeostasis and disease, primarily through the JAK–STAT, mitogen-activated protein kinase–extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways. Mounting evidence suggests that LIF is associated with the development of asthma (37–39), LIF might function as a proinflammatory cytokine in the airways by augmenting eosinophil recruitment and activation (40). Evidence exists that LIF promotes M2 macrophage polarization through STAT3 (41, 42). In this study, we demonstrated for the first time that LIF regulated M2a polarization of mouse alveolar macrophages (MH-S cells) via JAK1–STAT3 signaling. Moreover, we showed that emu-miR-10a-5p targeted LIF to inhibit macrophage M2a polarization through the same pathway, ultimately alleviating airway inflammation in allergic asthmatic mice. These results help us understand the roles of LIF in macrophage polarization and asthma pathogenesis.
Abnormal regulation of hsa-miR-10a-5p in bronchial epithelial cells may be an important mechanism underlying asthma (24). hsa-miR-10 can prevent airway smooth muscle cell proliferation by inhibiting PI3K signaling, making PI3K a potential target for treating lung diseases such as asthma (43). mmu-miR-10a-5p was upregulated in the exosomes of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from asthmatic mice, promoted lung epithelial cell proliferation in mice, and downregulated Nfat5 and Map2k6 (25). Elevating mmu-miR-10a-5p levels inhibited proinflammatory gene expression in RAW264.7 macrophages and promoted the differentiation of C3H10T1/2 cells into brown adipocytes (44). And mmu-miR-10a-5p has strong potential for clinical application of cancer treatment (45). The seed sequences of emu-miR-10a-5p, hsa-miR-10a-5p, and mmu-miR-10a-5p were identical (5'-ACCCUGUA-3'), suggesting that emu-miR-10a-5p can potentially alter host mRNA expression. mmu-miR-10a-5p can act on IL-6R and thus reduce IL-6-induced cartilage cell ferroptosis (46). We also observed in our study that emu-miR-10a-5p can reduce IL-6 expression.
In this study, macrophages transfected with emu-miR-10a-5p tended to induce naïve CD4+ T cell differentiation to Th1 cells, and emu-miR-10a-5p tended to reverse the Th1/Th2 balance in mice with allergic asthma, consistent with our in vitro results. However, these differences were not statistically significant. These observations suggest that the alleviating effect of emu-miR-10a-5p on allergic asthma may occur primarily through the modulation of macrophage polarization or that other immune cells (such as DCs) may play a role in the Th1/Th2 balance; however, the specific mechanisms should be studied further.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our findings demonstrated that E. multilocularis-derived EVs could alleviate macrophage M2a polarization and that encapsulated emu-miR-10a-5p can target LIF and inhibit macrophage M2a polarization via JAK1–STAT3 signaling, subsequently alleviating airway inflammation in OVA-induced allergic asthma mice (Figure 9).
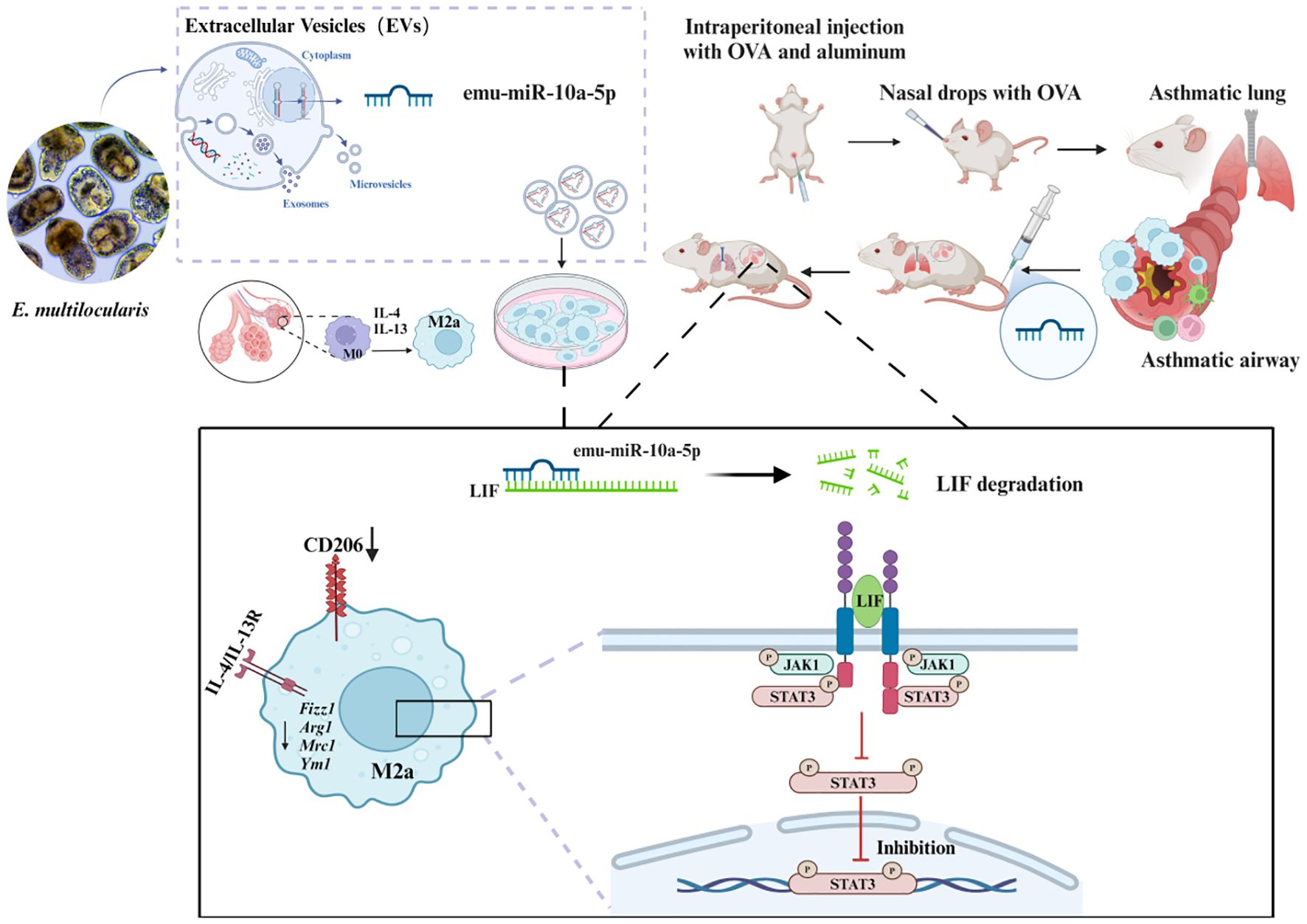
Figure 9. Schematic representation of the mechanism by which E. multilocularis-derived EVs could alleviate macrophage M2a polarization and that encapsulated emu-miR-10a-5p can target LIF and inhibit macrophage M2a polarization via JAK1-STAT3 signaling, subsequently alleviating airway inflammation in OVA-induced allergic asthma mice.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Ethics Committee of Ningxia Medical University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YX: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RW: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. DS: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JX: Validation, Writing – review & editing. XG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. MY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YB: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JW: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32160181), the Ningxia Natural Science Found Project (2021AAC03406) (2022AAC02076).
Acknowledgments
We thank Ningxia Medical University Science and Technology Center for the experimental environment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1577349/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, and Reddel HK. Asthma. Lancet. (2018) 391:783–800. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)33311-1
2. Schatz M and Rosenwasser L. The allergic asthma phenotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2014) 2:645–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2014.09.004
3. Wenzel SE. Asthma phenotypes: the evolution from clinical to molecular approaches. Nat Med. (2012) 18:716–25. doi: 10.1038/nm.2678
4. Hong J, Bao Y, Chen A, Li C, Xiang L, Liu C, et al. Chinese guidelines for childhood asthma 2016: major updates, recommendations and key regional data. J Asthma. (2018) 55:1138–46. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2017.1396474
5. Sica A and Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:787–95. doi: 10.1172/jci59643
6. Balhara J and Gounni AS. The alveolar macrophages in asthma: A double-edged sword. Mucosal Immunol. (2012) 5:605–9. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.74
7. Xia L, Wang X, Liu L, Fu J, Xiao W, Liang Q, et al. Lnc-baz2b promotes M2 macrophage activation and inflammation in children with asthma through stabilizing baz2b pre-mrna. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2021) 147:921–32.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.06.034
8. Han X, Huang S, Xue P, Fu J, Liu L, Zhang C, et al. Lncrna ptpre-as1 modulates M2 macrophage activation and inflammatory diseases by epigenetic promotion of ptpre. Sci Adv. (2019) 5:eaax9230. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax9230
9. Abdelaziz MH, Abdelwahab SF, Wan J, Cai W, Huixuan W, Jianjun C, et al. Alternatively activated macrophages; a double-edged sword in allergic asthma. J Transl Med. (2020) 18:58. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02251-w
10. Liang Q, Fu J, Wang X, Liu L, Xiao W, Gao Y, et al. Circs100a11 enhances M2a macrophage activation and lung inflammation in children with asthma. Allergy. (2023) 78:1459–72. doi: 10.1111/all.15515
11. Xiao Y, Zhang H, Liu Y, Mo L, Liao Y, Huang Q, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress drives macrophages to produce il-33 to favor th2 polarization in the airways. J Leukoc Biol. (2024) 115:893–901. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiad109
12. van Riet E, Hartgers FC, and Yazdanbakhsh M. Chronic helminth infections induce immunomodulation: consequences and mechanisms. Immunobiology. (2007) 212:475–90. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.03.009
13. McSorley HJ, Hewitson JP, and Maizels RM. Immunomodulation by helminth parasites: defining mechanisms and mediators. Int J Parasitol. (2013) 43:301–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2012.11.011
14. Wammes LJ, Mpairwe H, Elliott AM, and Yazdanbakhsh M. Helminth therapy or elimination: epidemiological, immunological, and clinical considerations. Lancet Infect Dis. (2014) 14:1150–62. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(14)70771-6
15. Pacífico LG, Marinho FA, Fonseca CT, Barsante MM, Pinho V, Sales-Junior PA, et al. Schistosoma mansoni antigens modulate experimental allergic asthma in a murine model: A major role for cd4+ Cd25+ Foxp3+ T cells independent of interleukin-10. Infect Immun. (2009) 77:98–107. doi: 10.1128/iai.00783-07
16. Mo HM, Lei JH, Jiang ZW, Wang CZ, Cheng YL, Li YL, et al. Schistosoma japonicum infection modulates the development of allergen-induced airway inflammation in mice. Parasitol Res. (2008) 103:1183–9. doi: 10.1007/s00436-008-1114-1
17. Wang H, Li J, Pu H, Hasan B, Ma J, Jones MK, et al. Echinococcus granulosus infection reduces airway inflammation of mice likely through enhancing il-10 and down-regulation of il-5 and il-17a. Parasit Vectors. (2014) 7:522. doi: 10.1186/s13071-014-0522-6
18. Hessvik NP and Llorente A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2018) 75:193–208. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2595-9
19. Weber JI, Rodrigues AV, Valério-Bolas A, Nunes T, Carvalheiro M, Antunes W, et al. Insights on host-parasite immunomodulation mediated by extracellular vesicles of cutaneous leishmania shawi and leishmania guyanensis. Cells. (2023) 12(8):1101. doi: 10.3390/cells12081101
20. Sarkies P and Miska EA. Molecular biology. Is there social RNA? Science. (2013) 341:467–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1243175
21. Zhang X, Gong W, Duan C, Cai H, Shen Y, and Cao J. Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces-derived exosome-like vesicles and egr-mir-277a-3p promote dendritic cell maturation and differentiation. Cells. (2022) 11(20):3220. doi: 10.3390/cells11203220
22. Ding J, He G, Wu J, Yang J, Guo X, Yang X, et al. Mirna-seq of echinococcus multilocularis extracellular vesicles and immunomodulatory effects of mir-4989. Front Microbiol. (2019) 10:2707. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02707
23. Guo X and Zheng Y. Expression profiling of circulating mirnas in mouse serum in response to echinococcus multilocularis infection. Parasitology. (2017) 144:1079–87. doi: 10.1017/s0031182017000300
24. Tsai MJ, Tsai YC, Chang WA, Lin YS, Tsai PH, Sheu CC, et al. Deducting microrna-mediated changes common in bronchial epithelial cells of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-a next-generation sequencing-guided bioinformatic approach. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(3):553. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030553
25. Tang B, Wu Y, Fang H, Wu Y, and Shi K. Small rna sequencing reveals exosomal mirnas involved in the treatment of asthma by scorpio and centipede. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:1061407. doi: 10.1155/2020/1061407
26. Shi C, Zhou X, Yang W, Wu J, Bai M, Zhang Y, et al. Proteomic analysis of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles from mice with echinococcus granulosus at different infection stages and their immunomodulatory functions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:805010. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.805010
27. Bai M, Zhou Z, Yin M, Wang M, Gao X, and Zhao J. The use of metagenomic and untargeted metabolomics in the analysis of the effects of the lycium barbarum glycopeptide on allergic airway inflammation induced by artemesia annua pollen. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 337:118816. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118816
28. Wang L, Jiang Z, Huang D, Duan J, Huang C, Sullivan S, et al. Jak/stat3 regulated global gene expression dynamics during late-stage reprogramming process. BMC Genomics. (2018) 19:183. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4507-2
29. Ernst M, Oates A, and Dunn AR. Gp130-mediated signal transduction in embryonic stem cells involves activation of jak and ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Biol Chem. (1996) 271:30136–43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.47.30136
30. Lu R, Zhang L, Wang H, Li M, Feng W, and Zheng X. EChinacoside exerts antidepressant-like effects through enhancing bdnf-creb pathway and inhibiting neuroinflammation via regulating microglia M1/M2 polarization and jak1/stat3 pathway. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:993483. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.993483
31. Huang X, Wang J, Guan J, Zheng Z, Hao J, Sheng Z, et al. Exosomal circsafb2 reshaping tumor environment to promote renal cell carcinoma progression by mediating M2 macrophage polarization. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:808888. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.808888
32. Kim HJ, Kang SA, Yong TS, Shin MH, Lee KJ, Park GM, et al. Therapeutic effects of echinococcus granulosus cystic fluid on allergic airway inflammation. Exp Parasitol. (2019) 198:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2019.02.003
33. Zhang W, Li L, Zheng Y, Xue F, Yu M, Ma Y, et al. Schistosoma japonicum peptide sjmhe1 suppresses airway inflammation of allergic asthma in mice. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:7819–29. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14661
34. Schnoeller C, Rausch S, Pillai S, Avagyan A, Wittig BM, Loddenkemper C, et al. A helminth immunomodulator reduces allergic and inflammatory responses by induction of il-10-producing macrophages. J Immunol. (2008) 180:4265–72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.6.4265
35. Ebner F, Hepworth MR, Rausch S, Janek K, Niewienda A, Kühl A, et al. Therapeutic potential of larval excretory/secretory proteins of the pig whipworm trichuris suis in allergic disease. Allergy. (2014) 69:1489–97. doi: 10.1111/all.12496
36. Zhang X, Gong W, Cao S, Yin J, Zhang J, Cao J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of non-coding rna profiles of exosome-like vesicles from the protoscoleces and hydatid cyst fluid of echinococcus granulosus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2020) 10:316. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00316
37. Hu CP, Feng JT, Tang YL, Zhu JQ, Lin MJ, and Yu ME. Lif upregulates expression of nk-1r in nhbe cells. Mediators Inflammation. (2006) 2006:84829. doi: 10.1155/mi/2006/84829
38. Lin MJ, Lao XJ, Liu SM, Xu ZH, and Zou WF. Leukemia inhibitory factor in the neuroimmune communication pathways in allergic asthma. Neurosci Lett. (2014) 563:22–7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.01.023
39. Dill-McFarland KA, Altman MC, Esnault S, Jarjour NN, Busse WW, and Rosenkranz MA. Molecular pathways underlying lung-brain axis signaling in asthma: relevance for psychopathology and neuroinflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2024) 153:111–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.07.025
40. Zheng X, Knight DA, Zhou D, Weir T, Peacock C, Schellenberg RR, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor is synthesized and released by human eosinophils and modulates activation state and chemotaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (1999) 104:136–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70125-9
41. Yu S, Li Q, Wang Y, Cui Y, Yu Y, Li W, et al. Tumor-derived lif promotes chemoresistance via activating tumor-associated macrophages in gastric cancers. Exp Cell Res. (2021) 406:112734. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112734
42. Chaparro V, Leroux LP, Lebourg A, Chagneau S, Graber TE, Alain T, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor drives transcriptional programs that promote lipid accumulation and M2 polarization in macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. (2024) 117(1):qiae178. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae178
43. Hu R, Pan W, Fedulov AV, Jester W, Jones MR, Weiss ST, et al. Microrna-10a controls airway smooth muscle cell proliferation via direct targeting of the pi3 kinase pathway. FASEB J. (2014) 28:2347–57. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-247247
44. Cho YK, Son Y, Kim SN, Song HD, Kim M, Park JH, et al. Microrna-10a-5p regulates macrophage polarization and promotes therapeutic adipose tissue remodeling. Mol Metab. (2019) 29:86–98. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.08.015
45. Singh R, Ha SE, Yu TY, and Ro S. Dual roles of mir-10a-5p and mir-10b-5p as tumor suppressors and oncogenes in diverse cancers. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26(1):415. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010415
Keywords: asthma, extracellular vesicle, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), M2a macrophage, emu-miRNA-10a-5p
Citation: Xin Y, Wen R, Song D, Xiao J, Gao X, Yin M, Bai Y, Wang J, Zhou X and Zhao J (2025) Emu-miR-10a-5p in Echinococcus multilocularis-derived-extracellular vesicles alleviates airway inflammation in mice with allergic asthma by inhibiting macrophage M2a polarization through LIF-mediated JAK1–STAT3 signaling. Front. Immunol. 16:1577349. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1577349
Received: 15 February 2025; Accepted: 06 May 2025;
Published: 27 May 2025.
Edited by:
Bruno D’Agostino, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, ItalyReviewed by:
Carl De Trez, Vrije University Brussels, BelgiumLiyang Dong, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, China
Copyright © 2025 Xin, Wen, Song, Xiao, Gao, Yin, Bai, Wang, Zhou and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Wang, bnh3YW5namllQDEyNi5jb20=; Xiangyu Zhou, WlhZODM5Njk4QDE2My5jb20=; Jiaqing Zhao, emhhb2pxQG54bXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors share first authorship
 Yunzhuo Xin1,2†
Yunzhuo Xin1,2† Jiaqing Zhao
Jiaqing Zhao