- 1Department of Respiratory Medicine, Shandong Provincial Third Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Neurology, Shandong Provincial Third Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 3Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Jiaozhou Central Hospital, Qingdao, Shandong, China
- 4Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China
- 5Shandong Provincial Third Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 6Department of Neurosurgery, Shandong Provincial Third Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, China
Background: While clinical trials confirm the therapeutic value of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors in diffuse pleural mesothelioma, their real-world safety and efficacy profiles remain incompletely defined. This meta-analysis synthesizes clinical evidence to comprehensively evaluate these outcomes, addressing an urgent need for robust real-world evidence.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library were systematically searched for relevant studies. Outcomes including median progression-free survival (mPFS), median overall survival (mOS), 1-year overall survival (1-y OS), 1 year progression-free survival (1-year PFS),objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), complete response(CR),partial response (PR), stable disease(SD), progressive disease(PD), treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and ≥grade 3 TRAEs were extracted for further analysis. The risk of bias was assessed by subgroup analysis.
Results: 14 articles with 1345 patients were identified and subjected to meta-analysis. With regard to survival analysis, the pooled mOS and mPFS were 6.66 months (95%CI 4.85-9.16) and 2.92 months (95%CI 2.23-3.83), respectively. In terms of tumor response, the pooled ORR and DCR were 21% (95%CI 6%-41%) and 49% (95%CI 27%-71%), respectively. The pooled AEs rate and ≥ grade 3 AEs rate were 94% (95%CI 86%-99%) and 44% (95%CI 30%-58%).
Conclusion: PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors have shown effective clinical responses in the treatment of Diffuse Pleural Mesothelioma (DPM). Although the incidence of adverse reactions is high, they are generally tolerable.
Systematic Review Registration: www.inplasy.com, identifier INPLASY202520045.
1 Introduction
Diffuse pleural mesothelioma (DPM), a rare but highly aggressive neoplasm arising from the mesothelial lining of the pleural cavity, is characterized by insidious onset and dismal prognosis, with a documented 5-year survival rate below 10% across major epidemiological studies (1–3). The predominant clinical manifestations in early disease stages include progressive pleuritic chest pain exacerbated by respiratory movements or positional changes, accompanied by dyspnea secondary to pulmonary parenchymal compression and pleural effusion accumulation (4, 5). Asbestos exposure remains the principal etiological determinant, with a characteristic latency period spanning 20–50 years between initial exposure and clinical diagnosis (6, 7). Despite global asbestos restriction policies (8), persistent mining activities in developing economies and prolonged disease latency contribute to geographically heterogeneous incidence patterns, with rising trends observed in multiple regions (9).
Histologically, DPM demonstrates three distinct subtypes: epithelioid (60-70% of cases, associated with relatively favorable prognosis), biphasic (20-35%), and sarcomatoid (10-15%, correlating with aggressive clinical course) (10–12). Significant gender disparities exist, with male predominance in incidence (male:female ratio ≈3:1) contrasting with superior survival outcomes in female patients (13). Current management employs multimodal strategies integrating cytoreductive surgery, platinum-based chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and emerging immunotherapies (14, 15). Recent data from the MARS2 trial challenge the role of cytoreductive surgery, demonstrating no survival benefit for pleurectomy/decortication compared to systemic therapy alone. Consequently, multimodal strategies now prioritize systemic therapies including immunotherapy. Nevertheless, therapeutic efficacy remains suboptimal, as evidenced by population-based registry data demonstrating median overall survival (OS) of 9.9-10.3 months across international cohorts (16, 17). The clinical challenge is compounded by frequent late-stage diagnosis precluding surgical intervention and high recurrence rates post-resection, even in early-stage operable cases (18). In 2004, the cisplatin-pemetrexed regimen became a first-line standard for unresectable disease based on EMPHACIS trial evidence (14). Subsequent phase III trials (MAPS study) demonstrated a modest 2.7-month OS improvement with bevacizumab augmentation of this backbone regimen (19). The persistent therapeutic limitations underscore the imperative for novel treatment modalities. The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors has revolutionized DPM management, particularly targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways. Mechanistically, PD-1/PD-L1 interaction facilitates tumor immune evasion through T-cell anergy induction, while CTLA-4 modulates early T-cell activation via competitive CD80/86 binding (20, 21). The non-redundant nature of these pathways provides a rationale for combinatorial blockade to achieve synergistic anti-tumor immunity (22), an approach validated in multiple malignancies (23–25). The landmark CheckMate 743 phase III trial demonstrated superior OS with nivolumab/ipilimumab dual checkpoint inhibition versus chemotherapy (median OS 18.1 vs. 14.1 months; HR 0.74, 95%CI 0.60-0.91; p=0.002), leading to FDA/EMA approval for first-line unresectable DPM (26–29). This paradigm shift established immunotherapy as a new standard of care.
Recent observational studies challenge the real-world generalizability of clinical trial outcomes. Schmid et al. reported suboptimal efficacy and unmitigated toxicity profiles with dual checkpoint inhibition compared to conventional regimens (30). This efficacy discordance between controlled trials and real-world practice may stem from differences in patient selection criteria, comorbidity burden, and treatment protocols. To resolve these controversies and comprehensively evaluate therapeutic efficacy, we conducted a systematic meta-analysis synthesizing all available clinical evidence on dual immune checkpoint inhibition in DPM. This investigation aims to clarify the risk-benefit profile of this therapeutic strategy across diverse clinical contexts.
2 Methods
2.1 Article searching
This meta-analysis strictly followed the guidelines specified in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta Analyses (PRISMA) checklist (31).The PRISMA checklist ensures a comprehensive and transparent reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, emphasizing methodological clarity and quality. The study protocol has been registered with the International Platform of Registered Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (INPLASY) (Registration ID: INPLASY202520045). Online databases (Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed) were searched for relevant clinical trials published from the establishment of these databases through November 30, 2024. Search terms included: “anti-PD-1”, “anti-PD-L1”, “anti-CTLA-4”, “immune checkpoint inhibitors”,”nivolumab”, “ipilimumab”, “tremelimumab”,”durvalumab”, AND “pleural mesothelioma”, “malignant pleural mesothelioma”, “ diffuse pleural mesothelioma”, “malignant pleural mesothelioma”,”MPM” and”DPM”. In addition to utilizing free search terms and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) for searching within titles or abstracts, we screened the references of selected articles to ensure comprehensive retrieval. In cases of duplicate publications, more comprehensive studies were chosen for subsequent meta-analysis. All information was extracted by 2 authors independently, and any consensus was resolved through negotiation.
2.2 Study selection
Obtained records were exported to EndNote software (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA).After removing the duplicate publications, two review authors independently reviewed the title/abstract of the articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Afterward, the same two authors screened the full-texts of the selected records, independently. Discrepancies were resolved by consulting a third author.
2.3 Eligibility criteria
Trials were included if the following criteria were met (1): adults (≥18 years)had a histologically proven diagnosis of diffuse pleural mesothelioma with locally advanced or metastatic disease; (2):a PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors with or without other standard treatments was given to one of the study arms; and (3):outcomes of interest in terms of efficacy (i.e. median overall survival (mOS), median progression-free survival (mPFS), 1-year overall survival (1-y OS), 1 year progression-free survival (1-year PFS),objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), complete response(CR),partial response (PR), stable disease(SD), progressive disease(PD), and safety (i.e. Treatment - Related Adverse Event(TRAEs) and ≥ grade 3 TRAEs)were reported.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Patients who do not have diffuse pleural mesothelioma;(2)animal experiments, cell research, reviews, meta-analyses, duplicates, case reports, or letters were not taken into consideration; and (3) studies with patient number less than 10 were excluded. Two investigators independently identified potential eligible articles through inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any disagreement regarding study inclusion was resolved between these two or with a third investigator.
2.4 Data extraction and quality assessment
Two researchers conducted independent literature searches, following predetermined criteria and specified strategies. This approach ensures a thorough and unbiased exploration of available literature, utilizing a systematic and structured methodology. Meticulous data extraction was performed, encompassing essential details such as authors, publication year, country, age, sample size, gender, age, stage, median follow-up, drugs, dose, number of treatment lines, research scale, and research methods, including mOS, PFS,1-y OS, 1-y PFS, DCR, ORR, CR,PR,SD,PD,TRAEs、≥ grade 3TRAEs. All included studies were treated as non-randomized trials. The quality of each study was meticulously evaluated using the methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS) (32). Studies scoring above 12 points were considered high-quality indicators. This stringent evaluation ensures that only studies meeting robust methodological standards contribute to the overall analysis.
2.5 Data synthesis
The primary efficacy endpoint was to estimate the mOS and mPFS after receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors treatment regimens and the secondary efficacy endpoint was to estimate the pooled rate of 1-y OS, 1-y PFS, DCR, ORR, CR,PR,SD,PD. The safety outcomes were the pooled rates of TRAEs and ≥ grade 3 TRAEs, We used Cochrane’s Q statistic to assess between-study heterogeneity and calculated the Isquare statistic. A random-effect model was applied if obvious heterogeneity was present (I2 >50%), otherwise, a fixed-effect model was chosen (33). The subgroup analysis was conducted according to region(Europe, Other), sample (≥60, <60), Research scale(Single-center, multicenter), Research methods (prospective, retrospective) and Number of treatment lines (1Line, 2Line/latter Line, Any). Differences between groups were tested by the chi-square test. We used STATA version 18.0 (34) to calculate the pooled rates with metaprop command, which requires a nominator and a denominator (which is the total sample size) and some other options like random or fixed effects model. This command was built on the existing Stata command metan, which is routinely used to pool ratios and differences of means (35). A p-value less than 0.05 were treated as statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection and characteristics of the included studies
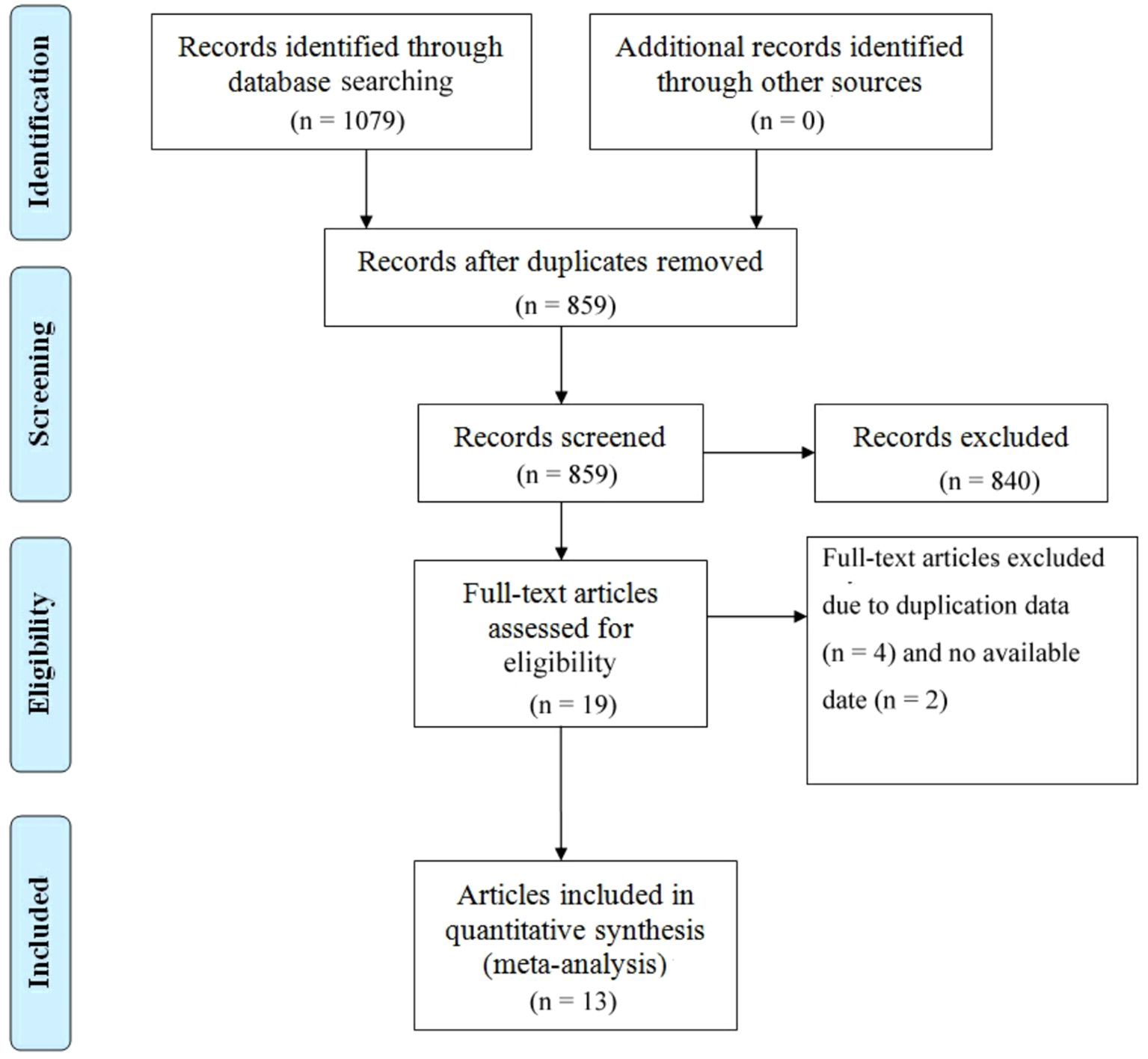
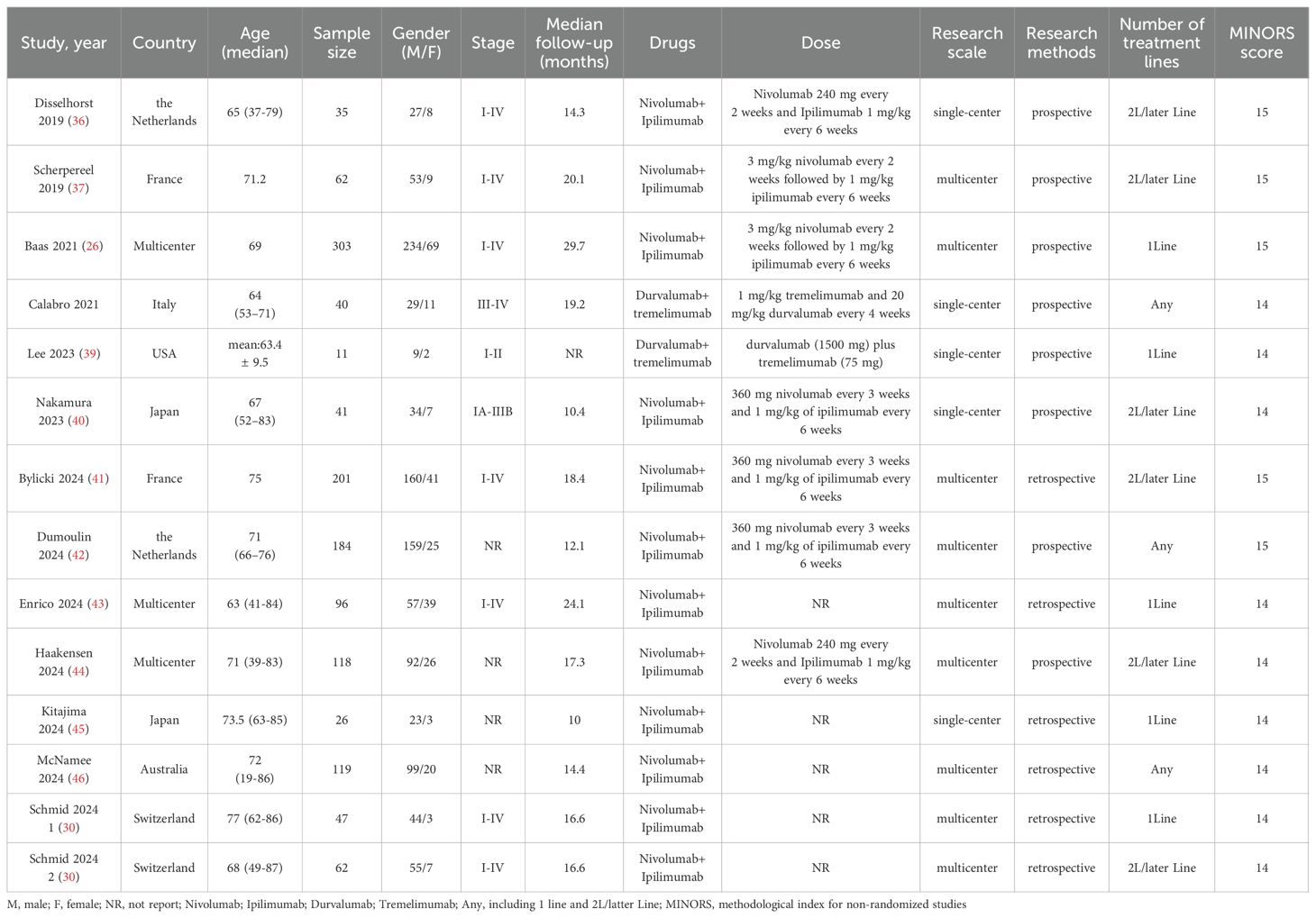
There were 1079 documents searched from the databases. Of these, 220 replicated studies were deleted. After reading the title and abstract of each article, 19 articles were screened out. Of those, 4 articles were excluded because of duplicate data, and 2 articles lacking available data were also excluded. Finally, a total of 13 articles meeting the criteria were selected with a total of 1,345 patients (26, 30, 36–46). An article by Schmid includes two cohorts of PD-1 inhibitors plus CTLA-4 inhibitors, one for first-line therapy and the other for second-line therapy (30). We considered the number of treatment lines to be an important source of heterogeneity and therefore discussed them separately. Figure 1 summarizes the detailed information about article selection. The 6 and 8 included research cohorts were eligible for mOS and mPFS, respectively. The 4、9 and 13 included cohorts were eligible for 1-y OS 、1-y PFS and ORR, respectively. The 12 included cohorts were eligible for CR、PR、DCR、TRAEs and ≥ grade 3 TRAEs data analysis, and 11 were eligible for PD、SD data analysis. Table 1 lists the characteristics of the 14 cohorts. The extracted characteristics were summarized as follows: authors, publication year, country, age, sample size, gender, age, stage, median follow-up, drugs, dose, number of treatment lines, research scale, and research methods.
3.2 Quality assessment
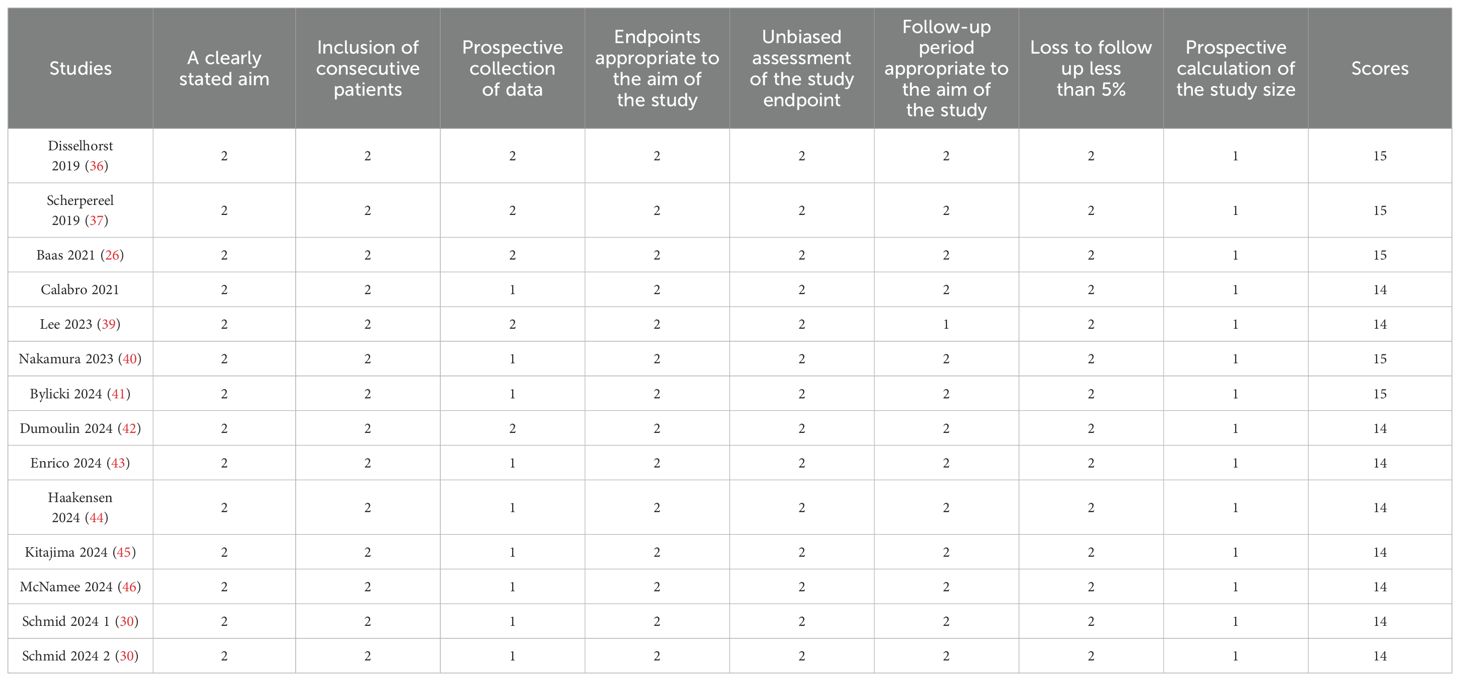
13 non-randomized studies were assessed using the methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS), which categorized studies into three dimensions based on eight items, including stated aim, population election, endpoints, and prospective calculation. The quality assessment details are shown in Table 2.
3.3 Efficacy
3.3.1 Survival
Six trials with a total of 732 patients were included to determine the mOS of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor and CTLA-4 inhibitor. As shown in Figure 2A, the random-effect model meta-analysis illuminated that the pooled mOS was 15.17months (95%CI 11.25-19.09,I2 = 89.4%, P<0.0001), suggesting that PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors achieved good mOS in the treatment of DPM. We also analyzed the mPFS of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor and CTLA-4 inhibitor in DPM. As shown in Figure 2B, the pooled mPFS of 944 patients in 8 studies was 5.84months (95%CI: 4.20-7.48, I2 = 98.3%, P<0.0001). The result suggests that PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and CTLA-4 inhibitors performed well in terms of mPFS in the treatment of DPM. According to Figure 3A, the meta - analysis based on the random - effect model demonstrated that the combined 1-y OS rate of nine trials (with 909 patients in total) was 60% (95% CI:53%-67%, I2 = 75.66%, P<0.0001). As shown in Figure 3B, by using data from four trials involving 446 patients with DPM, the meta - analysis with the fixed - effect model showed that the combined 1 - year PFS rate was 29% (95%CI 24% - 34%,I2 = 11.04%,P=0.34).The findings indicate that PD - 1/PD - L1 inhibitors and CTLA - 4 inhibitors had a good performance regarding 1 – y OS and 1 – y PFS when treating DPM.
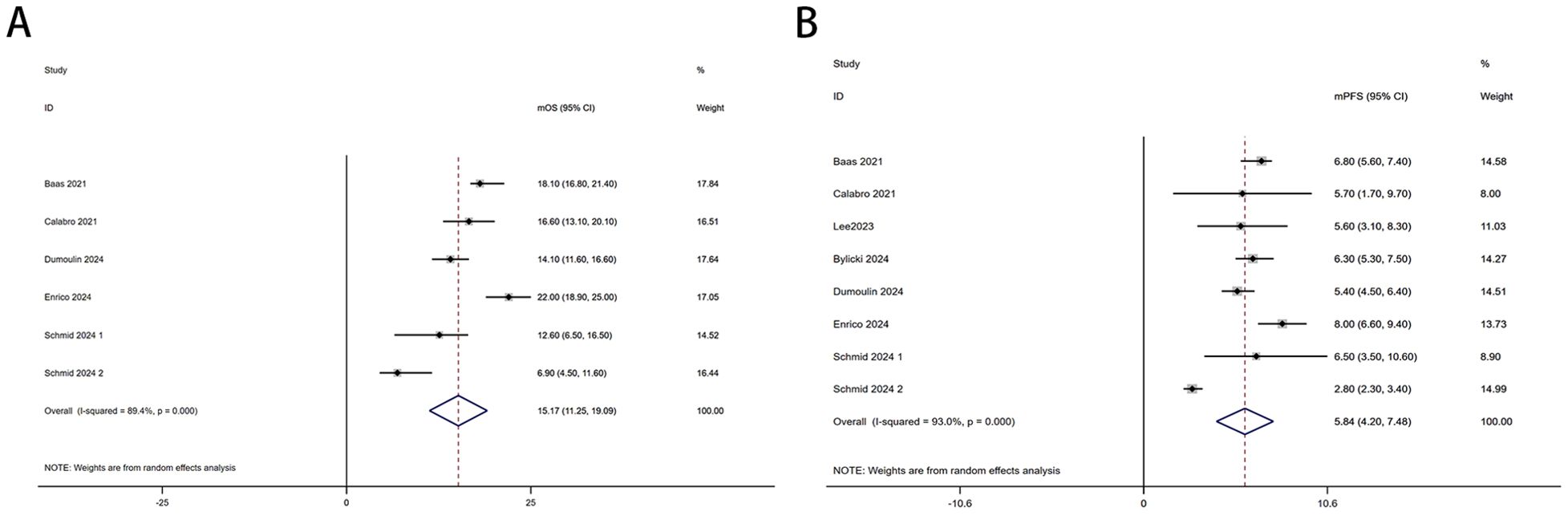
Figure 2. Forest plot for the (A)median overall survival (mOS) and (B) median progression-free survival (mPFS) in DPM patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
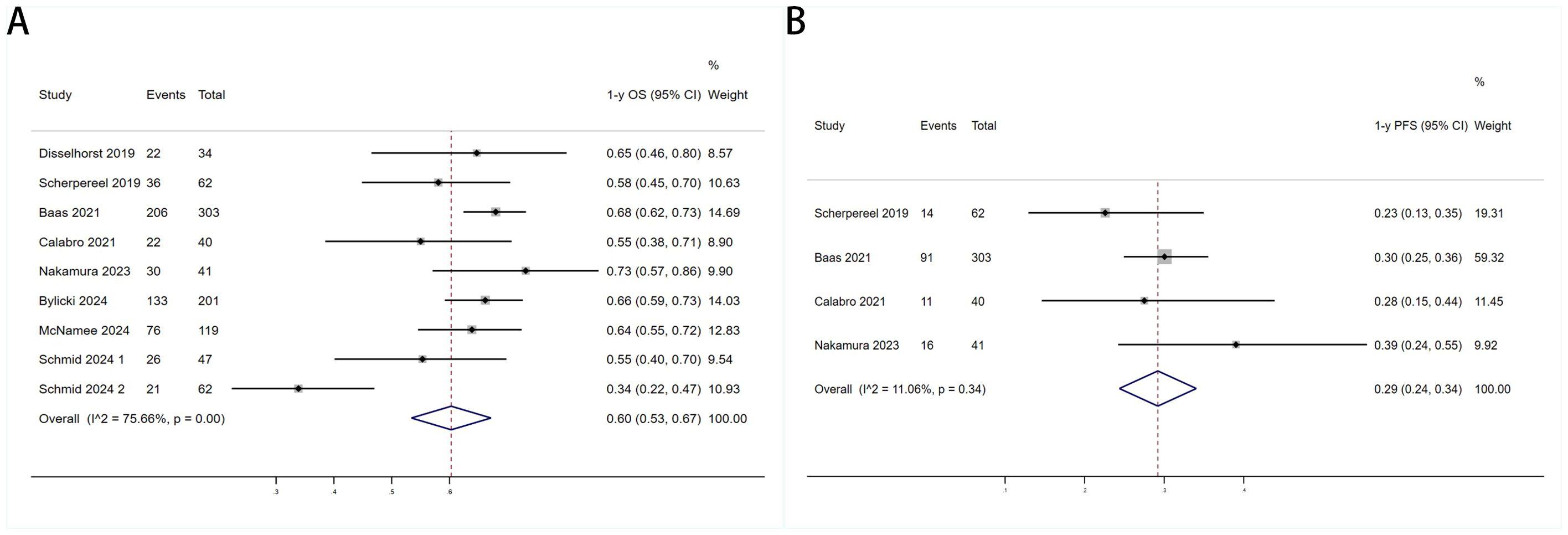
Figure 3. Forest plot for the (A)1 year overall survival (1-y OS) and (B) 1 year progression-free survival (1-y PFS) in DPM patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
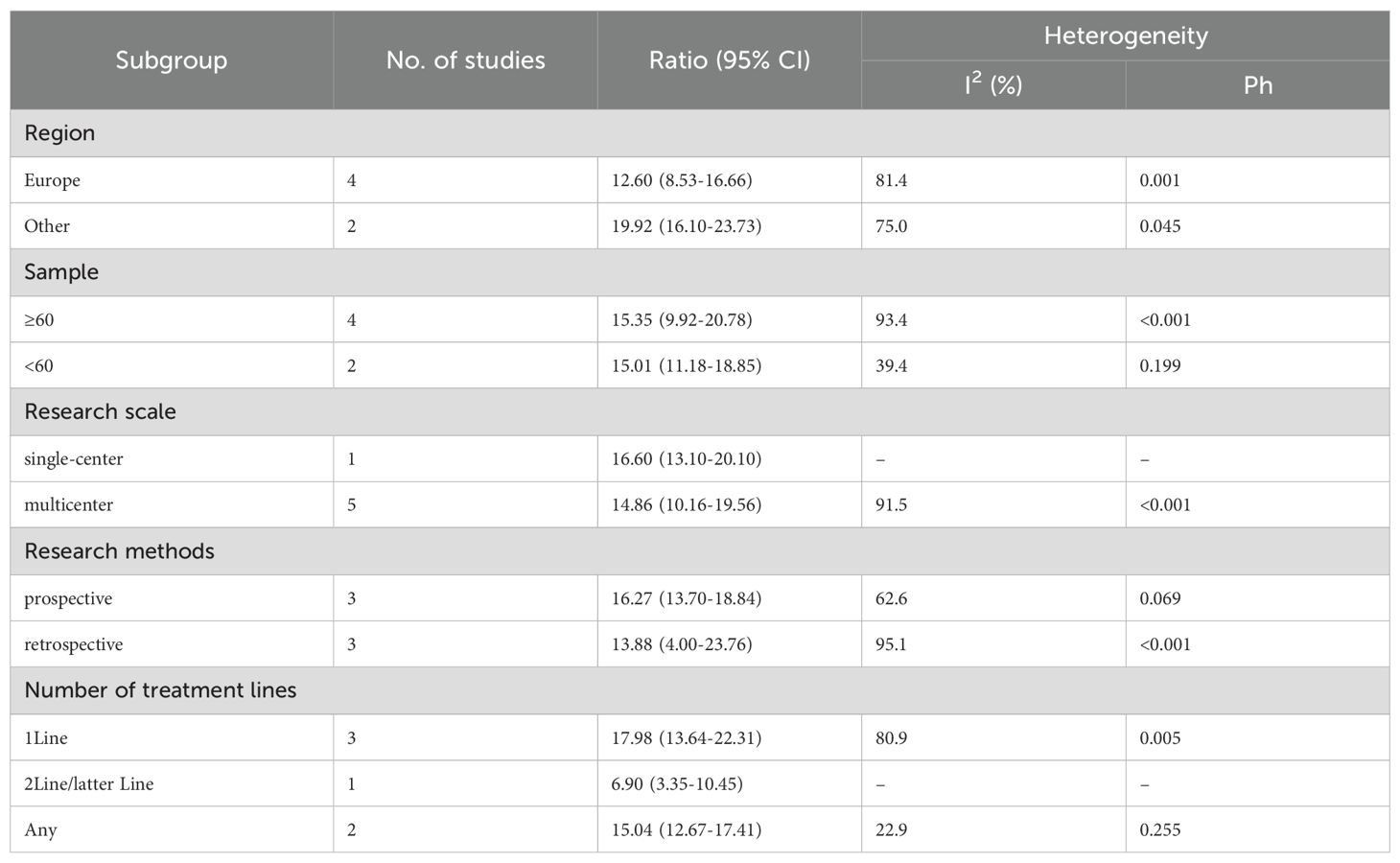
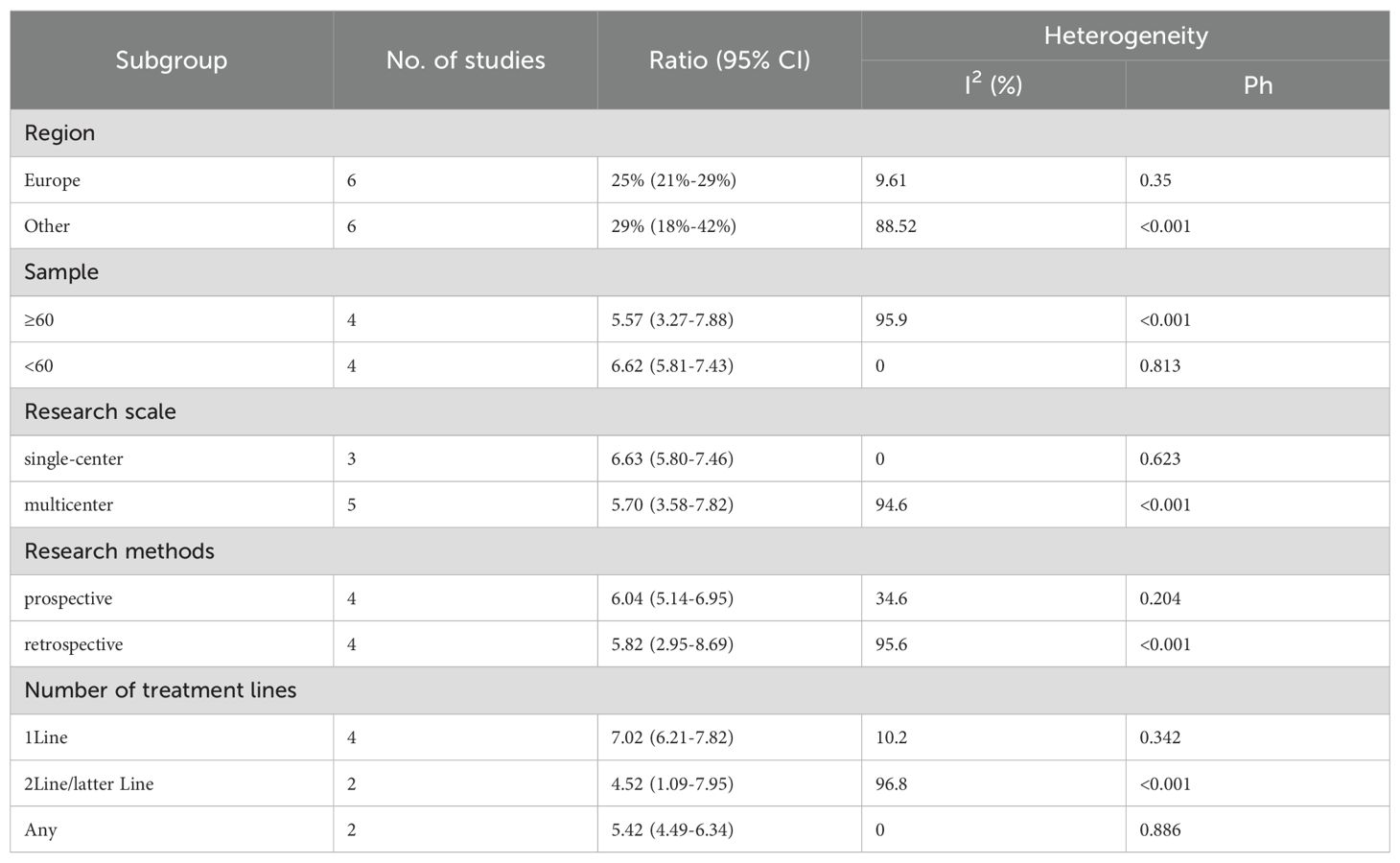
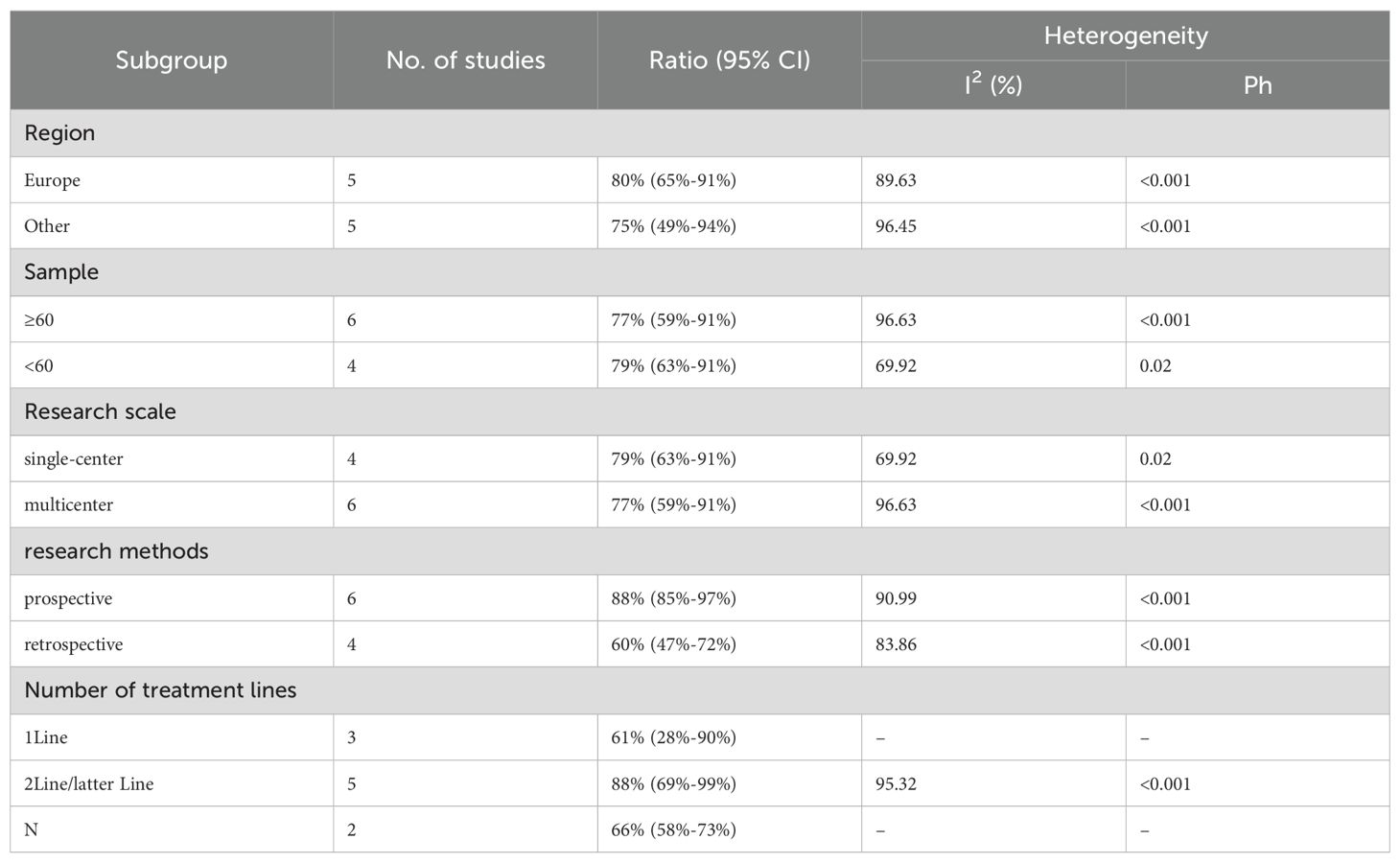
We performed subgroup analyses based on regions (Europe, other regions), sample sizes (≥60, <60), research scales (single - center, multi - center), research methods (prospective, retrospective), and the number of treatment lines (1Line, 2Line/Later Line, Any) to further analyze PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors’ efficacy. From Table 3, in the subgroup analysis, the DPM patient groups treated with PD - 1/PD - L1 inhibitors and CTLA - 4 inhibitors, including those from Europe, in single - center studies, with a sample size of 60 or more, those in prospective studies, and receiving 1 Line treatment, may benefit more in terms of mOS. As shown in Table 4, subgroup analysis revealed that the mPFS of DPM patients receiving PD - 1/PD - L1 inhibitors and CTLA - 4 inhibitors was significantly better in the following scenarios: in other regions, when the sample size was less than 60, in single - center studies, in prospective studies and in 1 Line treatment. Judging from Table 5, in the subgroup analysis of the patient groups treated with PD - 1/PD - L1 inhibitors and CTLA - 4 inhibitors, it is indicated that the 1 – y OS of DPM patient groups in the subgroups of other regions, sample size less than 60, single - center studies, prospective studies, and 1Line treatment is higher than that of other subgroups. Because 1-y PFS included few articles, no subgroup analysis was performed.
3.3.2 Response rates
Twelve trials with a total of 1300 patients were included to determine the ORR of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor and CTLA-4 inhibitor. As shown in Figure 4A, the random-effect model meta-analysis illuminated that the pooled ORR was 27% (95%CI:22%-32%, I2 = 74.55%, P<0.001), suggesting that PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors achieved good ORR in the treatment of DPM. In terms of DCR, we included 12 studies with 1182 patients. The pooled estimate of DRR was 64%, (95% CI: 56%-71%, I2 = 85.81%, P<0.001, Figure 4B).It can be indicated from these findings that PD - 1/PD - L1 inhibitors and CTLA - 4 inhibitors performed well in improving the DCR when treating patients with DPM. According to Figure 5A, the meta - analysis based on the random - effect model demonstrated that the combined CR of twelve trials (with 1246 patients in total) was 1% (95% CI: 0-1%, I2 = 14.65%, P=0.30, Figure 5A). Similarly, by using data from twelve trials involving 1246 patients with DPM, the meta-analysis with the random - effect model showed that the combined PR was 26% (95CI: 21% - 31%,I2 = 72.39%, P<0.001, Figure 5B).As presented in Figure 6A, the meta-analysis conducted under the random - effect model revealed that the pooled SD rate across eleven trials, which included a total of 1128 patients, was 37% (95% confidence interval: 31% - 43%, I² = 76.96%, P < 0.001, Figure 6A). In a similar vein, by analyzing data from twelve trials involving 1246 patients with DPM, the meta - analysis using the random - effect model indicated that the combined PD rate was 31% (95%CI: 24% - 38%, I² = 83.27%, P < 0.001, Figure 6B), as depicted in Figure 6B.
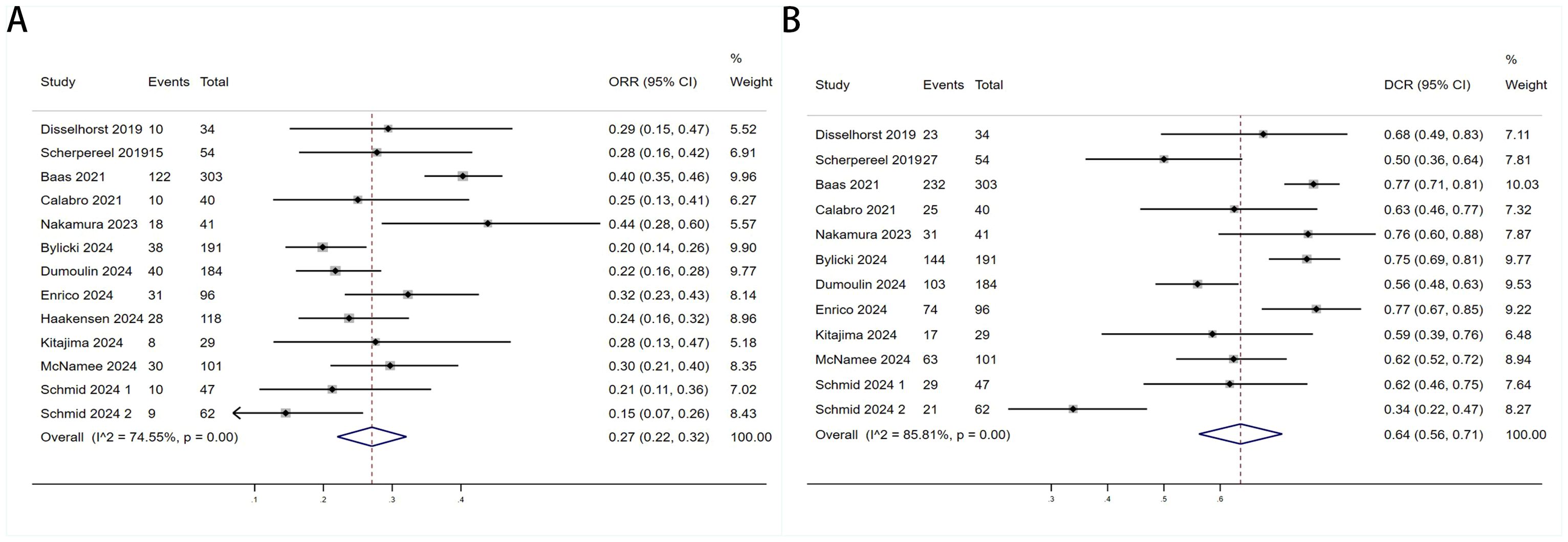
Figure 4. Forest plot for the (A) Objective response rate (ORR) and (B) Disease control rate (DCR) in DPM patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
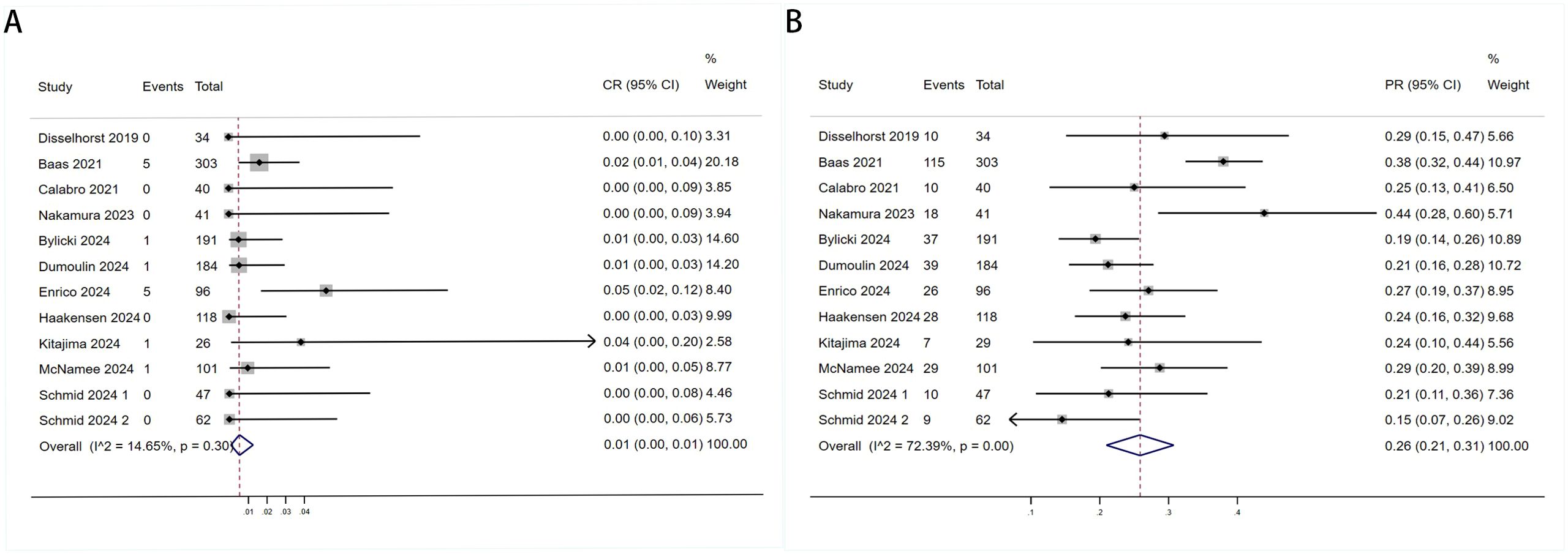
Figure 5. Forest plot for the (A) Complete Response (CR) and (B) Partial Response (PR) in DPM patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
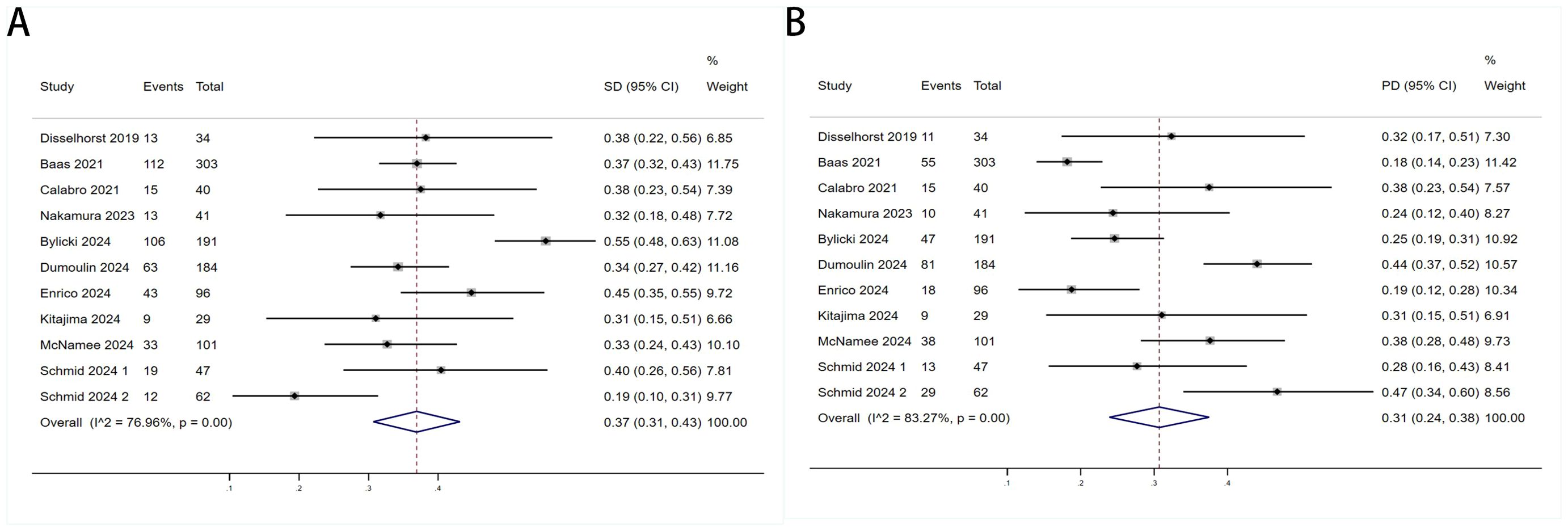
Figure 6. Forest plot for the (A) Sta and (B) Progressive Disease (PD) in DPM patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
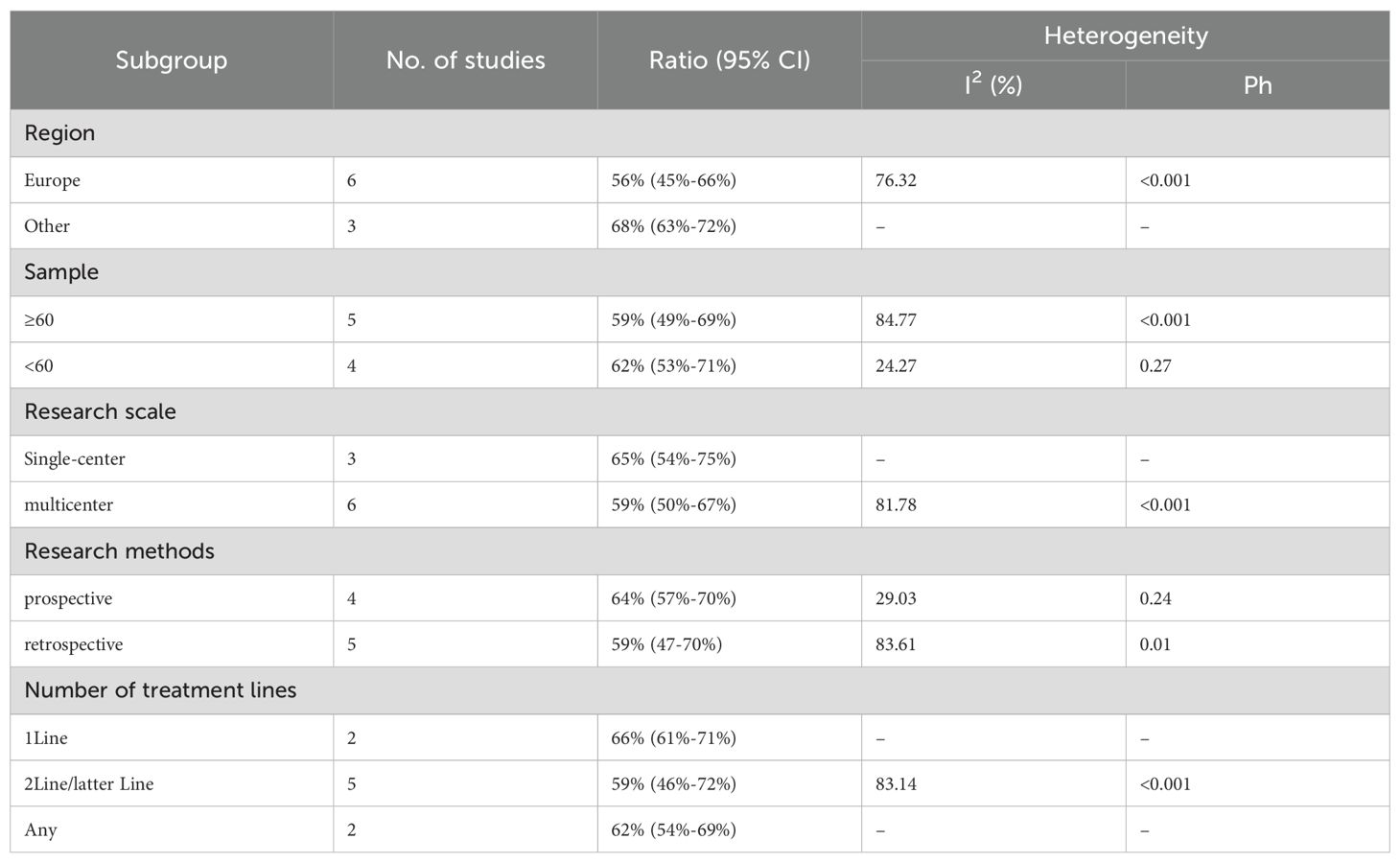
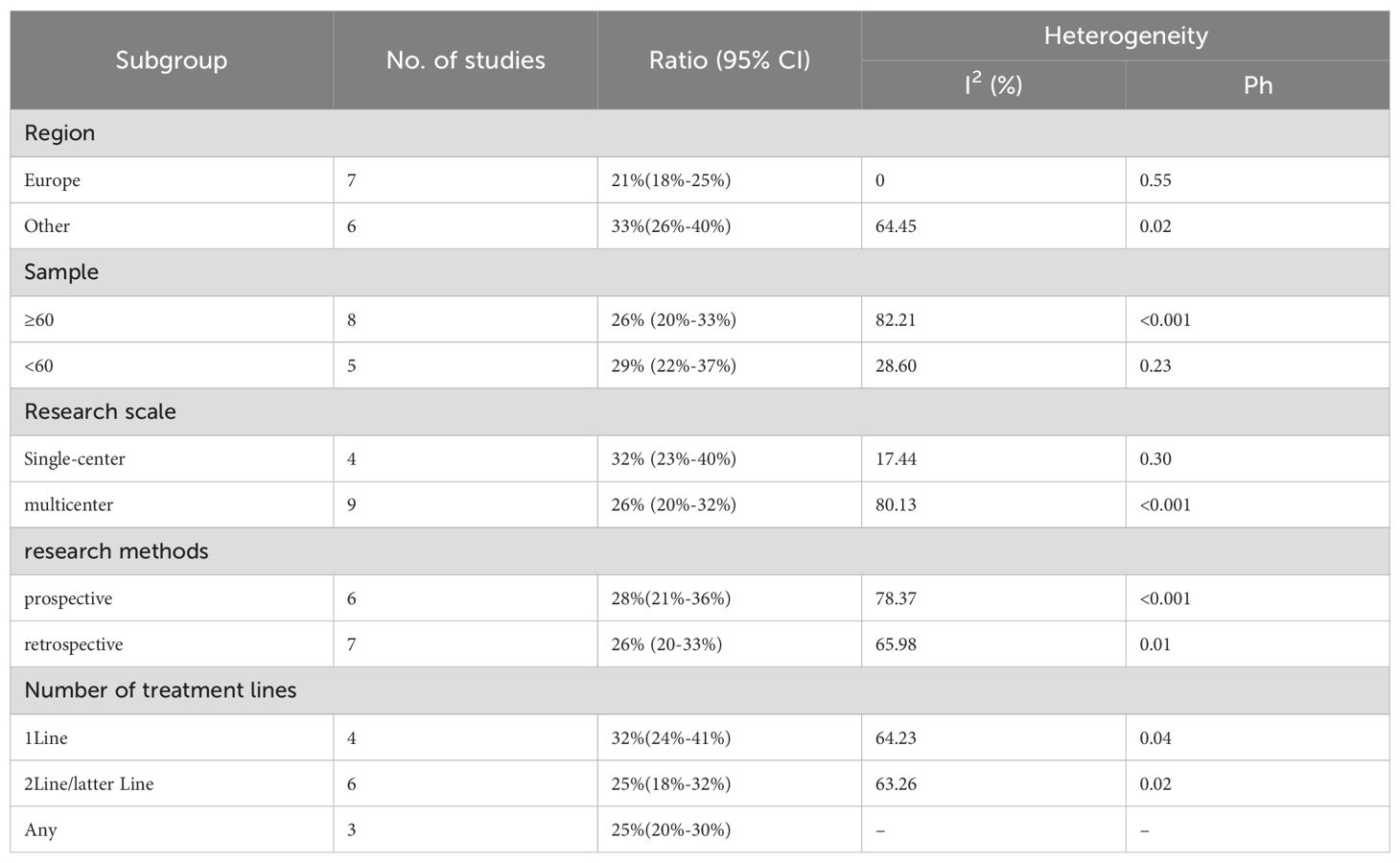
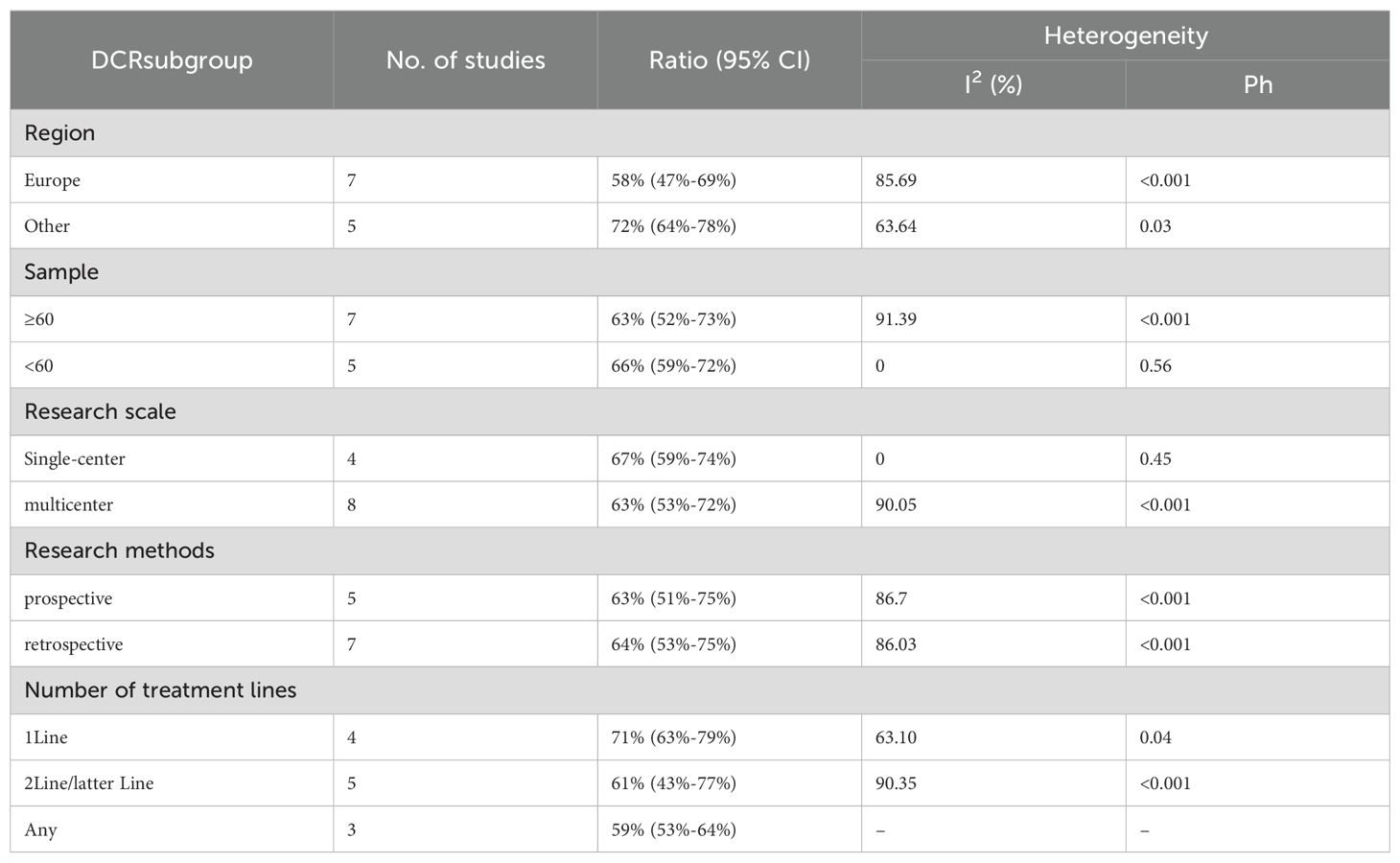
We conducted subgroup analyses based on regions (Europe, other regions), sample sizes (≥60, <60), research scales (single - center, multi - center), research methods (prospective, retrospective), and the number of treatment lines (1Line, 2Line/Later Line, Any) to further analyze the relationship between PD - 1/PD - L1 and CTLA - 4 immune checkpoint inhibitors and the tumor response rate of patients. As shown in Table 6 subgroup analysis revealed that the ORR of DPM patients receiving PD - 1/PD - L1 inhibitors and CTLA - 4 inhibitors was significantly better in the following situations: in other regions, when the sample size was less than 60, in single - center studies, in prospective studies, and 1Line treatment. From Table 7, we can tell that the DCR of DPM patients in subgroups such as other, sample size less than 60, single - center studies, retrospective studies, and 1Line treatment are greater than that of other subgroups.
3.4 Safety
The TRAEs (any grades and ≥grade 3) associated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1+anti-CTLA-4 in treating DPM were analyzed. Most patients went through grades 1–2 TRAEs and were well tolerated. There were 10 studies with data about any grade TRAEs rate and 12 studies with data about ≥ grade 3 TRAEs. Figure 7 showed the pooled TRAEs rate was 75% (95%CI:64%-87%, I2 = 96.9%, P<0.001, Figure 7A) and ≥ grade 3 TRAEs rate was 28% (95%CI:22%-34%, I2 = 81.9%, P<0.001, Figure 7B).
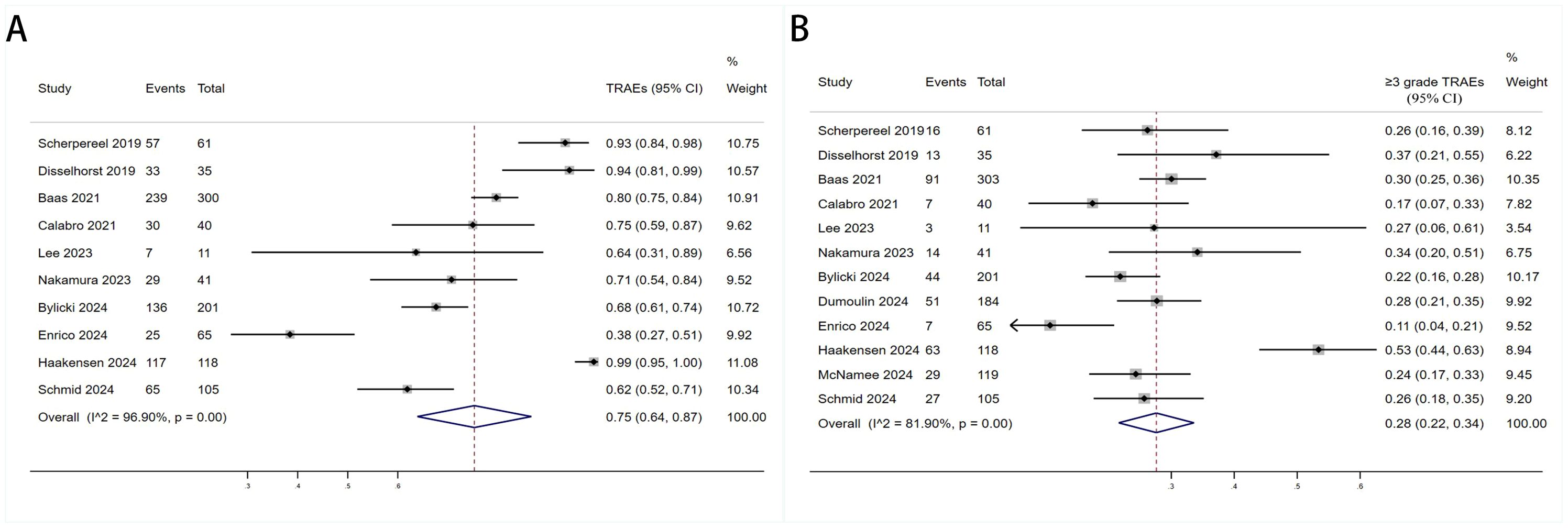
Figure 7. Forest plot for the (A) Treatment - Related Adverse Event (TRAE) and (B) Progressive Disease (PD) ≥3grade TRAE in DPM patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
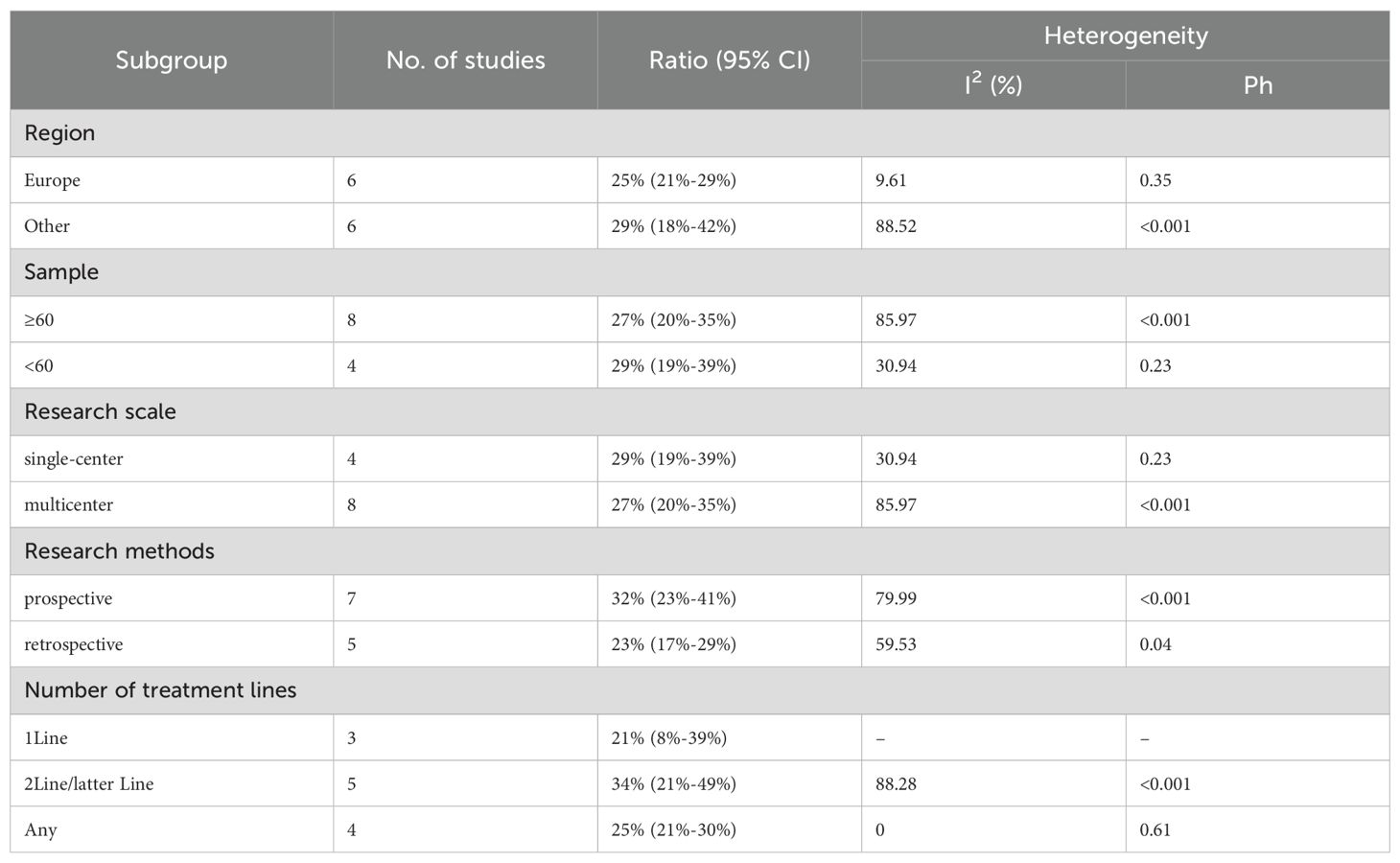
We conducted a subgroup analysis of the results of TRAEs and ≥ grade 3 TRAEs. According to the subgroup analysis in Table 8 and Table 9, we explored factors such as region, sample size, research scale, research methods and number of treatment lines, which could be an important source of heterogeneity. Europe had a higher incidence of TRAEs (80% vs. 75%) but a less incidence of ≥ grade 3 TRAEs (25% vs. 29%) than other. When sample size <60, TRAEs (79% vs. 77%) and ≥ grade 3 TRAEs (29% vs. 27%) have become more common than sample size≥60. The subgroup analysis also indicated that it was likely that multicenter had a higher incidence of TRAEs (79% vs. 77%) but a less incidence of ≥ grade 3 TRAEs (27% vs. 29%) than single-center. The prospective subgroup showed a clearly higher incidence of TRAEs (88% vs. 60%) and ≥grade 3 TRAEs (32% vs. 23%). According to number of treatment lines,1Line group had lower ratio of AEs (61% vs. 66% vs. 88%) than Any and 2Line/latter Line.
4 Discussion
The advent of T-cell-centered immunotherapies, such as PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors, has significantly reshaped treatment paradigms across various cancers. However, only a select few tumor types exhibit sensitivity to single-agent immune checkpoint inhibition, and the underlying biological mechanisms driving these responses remain poorly understood (47). A review of clinical trials using Tremelimumab monotherapy in diffuse pleural mesothelioma demonstrated an objective response rate (ORR) in the modest range of 3%-13%, with a median progression-free survival (mPFS) of 6.2 months and median overall survival (mOS) of 11 months (48). Similarly, a single-arm study by Josine et al., which treated 34 patients with recurrent malignant pleural tumors using nivolumab, reported a median PFS of 2.6 months (95% CI: 2.23–5.49) and median OS of 11.8 months (95% CI: 9.7–15.7). Other studies on single-agent immunosuppressants in DPM have shown comparable efficacy, though generally lower than the pooled data (49, 50). The low tumor mutational burden (TMB) in DPM (51) and the sparsity of anti-tumor immune cells in its tumor microenvironment (TME) (52) likely contribute to the relatively limited clinical benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy in this patient population.
In our meta-analysis, the combination of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors yielded a pooled median OS (mOS) of 15.17 months (95% CI: 11.25–19.09) and mPFS of 5.84 months (95% CI: 4.20–7.48). The pooled ORR and disease control rate (DCR) were 27% (95% CI: 22%-32%) and 64% (95% CI: 56%-71%), respectively. Prior to the introduction of dual immune checkpoint inhibitors, the first-line treatment for unresectable DPM involved platinum-pemetrexed chemotherapy. In the landmark CheckMate 743 trial, the chemotherapy group exhibited a mOS of 14.1 months (95% CI: 12.4–16.2) and mPFS of 7.2 months (95% CI: 6.9–8.0), with an ORR of 43% and a DCR of 85%. Similarly, Vogelzang’s phase 3 study reported an mOS of 12.1 months and mPFS of 5.7 months with platinum-pemetrexed, with an ORR of 41.3%. An Italian study evaluating ramucirumab-gemcitabine in 164 mesothelioma patients found a median OS of 13.8 months (53), also lower than the mOS of 15.17 months observed with dual checkpoint blockade. These findings suggest that dual checkpoint inhibition with PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors offers superior overall survival compared to platinum-pemetrexed chemotherapy, though it remains inferior in mPFS, ORR, and DCR. Imaging of DPM is complicated by the diffuse nature of the disease and indistinct tumor margins (54), making overall survival a more reliable and objective endpoint for evaluating efficacy in this context (26). The combination of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors, however, provides significant long-term survival benefits. Notably, the 1-year OS rate of 60% (95% CI: 53%-67%) and 1-year PFS rate of 29% (95% CI: 24%-34%) support the durability of clinical benefit in certain patients. While these figures are numerically lower than those seen in hypermutated malignancies like melanoma (55), they represent a notable improvement over traditional cytotoxic regimens in DPM, a tumor class historically resistant to systemic therapies. The observed survival benefit is likely driven by the synergistic activation of T-cells via dual blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways, potentially enhancing T-cell priming, infiltration, and tumor microenvironment modulation (56).
As anticipated, the incidence of any-grade treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) (75%) and grade ≥3 TRAEs (28%) exceeded those reported for monotherapy and chemotherapy (26, 48). These events, primarily immune-related adverse effects, can involve multiple organ systems, including the gastrointestinal, hepatic, pulmonary, and musculoskeletal systems. However, our understanding of their pathogenesis remains incomplete (57). Despite the high incidence of TRAEs, only a small percentage of patients discontinued therapy due to clinically relevant toxicity, with most adverse events being reversible with systemic glucocorticoids and managed safely. Furthermore, when adjusted for exposure, the incidence of TRAEs associated with nivolumab and ipilimumab was lower than with chemotherapy. Interestingly, both the CheckMate-743 trial and a real-world study by Enrico et al. found that patients who discontinued treatment due to TRAEs had a better median OS (26, 43). We hypothesize that the occurrence of TRAEs may correlate with drug dosage, treatment cycle number, and patient health status. These observations emphasize the importance of careful patient selection, proactive monitoring, and multidisciplinary management to mitigate the risk of severe toxicity.
The sequencing of dual immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1 and anti-CTLA-4) with chemotherapy remains an area of active research (58). The enhanced benefit in non-epithelioid DPM may reflect chemotherapy’s limited efficacy in this subtype (10), establishing nivolumab/ipilimumab as preferred first-line for unresectable non-epithelioid disease. For epithelioid DPM, first-line optimal therapy remains undefined. Our subgroup analysis suggests first-line dual immunotherapy outperforms later-line regimens in survival, response, and safety across histologies. However, these findings warrant cautious interpretation given small sample sizes and retrospective design in some studies. Additionally, prospective trials reported better outcomes than real-world studies (43), likely reflecting the latter’s inclusion of more ECOG 2 and non-epithelioid patients. Due to limited histology-stratified reporting, meta-regression was unfeasible; future studies should prioritize histology-specific analyses to guide personalized therapy.
5 Limitations
Several limitations must be acknowledged. First, the sample sizes of most included studies were small, limiting statistical power for subgroup analyses. Second, our analysis relied on aggregated data from published articles rather than individual patient-level data, potentially introducing biases in data interpretation. Third, efficacy comparisons across heterogeneous clinical settings (e.g., first-line vs. later-line therapy) introduce complexity; while subgroup analyses suggested superior outcomes with first-line treatment (Tables 3–7), variability in prior therapies, dosing schedules, and patient comorbidities may confound these results. Fourth, the lack of biomarker-driven patient stratification (e.g., PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden) precludes identification of predictive response factors. Therefore, future large-scale prospective trials with standardized treatment protocols and biomarker assessment are needed to validate the efficacy and safety of PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibitor combinations in diffuse pleural mesothelioma.
6 Conclusion
In summary, our meta-analysis demonstrates that dual PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 blockade provides clinically meaningful survival benefits with acceptable safety in DPM, supporting its application in clinical practice. Critically, future research must prioritize biomarker discovery (e.g., PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden, inflammatory gene signatures) to identify patients most likely to benefit, enabling personalized therapeutic strategies.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author contributions
PS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LL: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NM: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. JG: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Janes SM, Alrifai D, and Fennell DA. Perspectives on the treatment of Malignant pleural mesothelioma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:1207–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1912719
2. Beasley MB, Galateau-Salle F, and Dacic S. Pleural mesothelioma classification update. Virchows Arch. (2021) 478:59–72. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03031-7
3. Van Gerwen M, Alpert N, Wolf A, Ohri N, Lewis E, Rosenzweig KE, et al. Prognostic factors of survival in patients with Malignant pleural mesothelioma: an analysis of the national cancer database. Carcinogenesis. (2019) 40:529–36. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz004
4. Walker SL, Vaughan Dickson V, and Cacchione PZ. A pilot mixed-methods study of Malignant pleural mesothelioma symptoms. Oncol Nurs Forum. (2022) 49:615–23. doi: 10.1188/22.ONF.615-623
5. Mendoza TR, Williams LA, Keating KN, Siegel J, Elbi C, Nowak AK, et al. Evaluation of the psychometric properties and minimally important difference of the md anderson symptom inventory for Malignant pleural mesothelioma (Mdasi-mpm). J Patient Rep Outcomes. (2019) 3:34. doi: 10.1186/s41687-019-0122-5
6. Carbone M, Adusumilli PS, Alexander HR Jr., Baas P, Bardelli F, Bononi A, et al. Mesothelioma: scientific clues for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. (2019) 69:402–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21572
7. Kato K, Gemba K, Ashizawa K, Arakawa H, Honda S, Noguchi N, et al. Low-dose chest computed tomography screening of subjects exposed to asbestos. Eur J Radiol. (2018) 101:124–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.02.017
8. International Ban Asbestos Secretariat. Available online at: http://Www.Ibasecretariat.Org/Alpha_Ban_List.Php2023 (Accessed October 20, 2023).
9. Mukhopadhyay D, Cocco P, Orru S, Cherchi R, and De Matteis S. The role of micrornas as early biomarkers of asbestos-related lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pulmonology. (2025) 31:2416792. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2024.02.002
10. Zhang Y, Li R, Gu Y, LiZhu Y, Liu X, and Zhang S. Clinical, laboratory, histological, radiological, and metabolic features and prognosis of Malignant pleural mesothelioma. Medicina (Kaunas). (2022) 58:1874. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121874
11. Mansur A, Potter AL, Zurovec AJ, Nathamuni KV, Meyerhoff RR, Berry MF, et al. An investigation of cancer-directed surgery for different histologic subtypes of Malignant pleural mesothelioma. Chest. (2023) 163:1292–303. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.12.019
12. Bille A, Krug LM, Woo KM, Rusch VW, and Zauderer MG. Contemporary analysis of prognostic factors in patients with unresectable Malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol. (2016) 11:249–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.10.003
13. Sirri E, Kieschke J, Vohmann C, Katalinic A, Nennecke A, Ressing M, et al. Survival of Malignant mesothelioma and other rare thoracic cancers in Germany and the United States: A population-based study. Int J Cancer. (2020) 147:1548–58. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32931
14. Kindler HL, Ismaila N, and Hassan R. Treatment of Malignant pleural mesothelioma: american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline summary. J Oncol Pract. (2018) 14:256–64. doi: 10.1200/JOP.17.00012
15. Stevenson J, Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, et al. Nccn guidelines(R) insights: mesothelioma: pleural, version 1.2024. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2024) 22:72–81. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2024.0014
16. Bou-Samra P, Chang A, Azari F, Kennedy G, Segil A, Guo E, et al. Epidemiological, therapeutic, and survival trends in Malignant pleural mesothelioma: A review of the national cancer database. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:12208–20. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5915
17. Brims F, Kumarasamy C, Menon L, Olsen N, de Klerk N, and Franklin P. The western Australian mesothelioma registry: analysis of 60 years of cases. Respirology. (2024) 29:288–94. doi: 10.1111/resp.14648
18. Baldini EH, Richards WG, Gill RR, Goodman BM, Winfrey OK, Eisen HM, et al. Updated patterns of failure after multimodality therapy for Malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2015) 149:1374–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.10.128
19. Wang K, Coutifaris P, Brocks D, Wang G, Azar T, Solis S, et al. Combination anti-pd-1 and anti-ctla-4 therapy generates waves of clonal responses that include progenitor-exhausted cd8(+) T cells. Cancer Cell. (2024) 42:1582–97.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.08.007
20. Sharpe AH and Pauken KE. The diverse functions of the pd1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol. (2018) 18:153–67. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.108
21. Sobhani N, Tardiel-Cyril DR, Davtyan A, Generali D, Roudi R, and Li Y. Ctla-4 in regulatory T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13(6):1440. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061440
22. Guha P, Heatherton KR, O’Connell KP, Alexander IS, and Katz SC. Assessing the future of solid tumor immunotherapy. Biomedicines. (2022) 27(2):256–63. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030655
23. Rozeman EA, Hoefsmit EP, Reijers ILM, Saw RPM, Versluis JM, Krijgsman O, et al. Survival and biomarker analyses from the opacin-neo and opacin neoadjuvant immunotherapy trials in stage iii melanoma. Nat Med. (2021) 27:256–63. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-01211-7
24. van Dijk N, Gil-Jimenez A, Silina K, Hendricksen K, Smit LA, de Feijter JM, et al. Preoperative ipilimumab plus nivolumab in locoregionally advanced urothelial cancer: the nabucco trial. Nat Med. (2020) 26:1839–44. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1085-z
25. Hellmann MD, Callahan MK, Awad MM, Calvo E, Ascierto PA, Atmaca A, et al. Tumor mutational burden and efficacy of nivolumab monotherapy and in combination with ipilimumab in small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. (2018) 33:853–61.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.04.001
26. Baas P, Scherpereel A, Nowak AK, Fujimoto N, Peters S, Tsao AS, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable Malignant pleural mesothelioma (Checkmate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2021) 397:375–86. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32714-8
27. Peters S, Scherpereel A, Cornelissen R, Oulkhouir Y, Greillier L, Kaplan MA, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy in patients with unresectable Malignant pleural mesothelioma: 3-year outcomes from checkmate 743. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:488–99. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.01.074
28. Food and Drug Administration. Fda Approves Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online at: https://Www.Fda.Gov/Drugs/Resources-Informationapproved-Drugs/Fda-Approves-Nivolumab-and-Ipilimumabunresectable-Malignant-Pleural-Mesothelioma (Accessed January 4, 2024).
29. Ema Recommends Extension of Therapeutic Indications for Nivolumab and Ipilimumabn. Available online at: https://Www.Esmo.Org/Oncology-News/Ema-Recommendsextension-of-Therapeutic-Indications-for-Nivolumab-and-Ipilimumab (Accessed July 18, 2022).
30. Schmid S, Holer L, Gysel K, Koster KL, Rothschild SI, Boos LA, et al. Real-World outcomes of patients with Malignant pleural mesothelioma receiving a combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab as first- or later-line treatment. JTO Clin Res Rep. (2024) 5:100735. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2024.100735
31. Moher D LA, Tetzlaff J, and Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the prisma statement. Open Med. (2009) 3:123–30. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
32. Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, and Chipponi J. Methodological index for non-Randomized studies (Minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg. (2003) 73:712–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
33. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:ED000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
35. Nyaga VN, Arbyn M, and Aerts M. Metaprop: A stata commandtoperform meta-analysis of binomial data. Arch Of Public Health. (2014) 72(1):39. doi: 10.1186/2049-3258-72-39
36. Disselhorst MJ, Quispel-Janssen J, Lalezari F, Monkhorst K, de Vries JF, van der Noort V, et al. Ipilimumab and nivolumab in the treatment of recurrent Malignant pleural mesothelioma (Initiate): results of a prospective, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med. (2019) 7:260–70. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30420-X
37. Scherpereel A, Mazieres J, Greillier L, Lantuejoul S, Do P, Bylicki O, et al. Nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with relapsed Malignant pleural mesothelioma (Ifct-1501 maps2): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, non-comparative, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2019) 20:239–53. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30765-4
38. Calabro L, Morra A, Giannarelli D, Amato G, D’Incecco A, Covre A, et al. Tremelimumab combined with durvalumab in patients with mesothelioma (Nibit-meso-1): an open-label, non-randomised, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir Med. (2018) 6:451–60. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30151-6
39. Lee HS, Jang HJ, Ramineni M, Wang DY, Ramos D, Choi JM, et al. A phase ii window of opportunity study of neoadjuvant pd-L1 versus pd-L1 plus ctla-4 blockade for patients with Malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:548–59. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2566
40. Nakamura A, Hashimoto M, Kondo N, Matsumoto S, Kuroda A, Minami T, et al. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab with ipilimumab for recurrent Malignant pleural mesothelioma after primary surgical intervention. Int J Clin Oncol. (2023) 28:409–15. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02292-3
41. Bylicki O, Guisier F, Scherpereel A, Daniel C, Swalduz A, Grolleau E, et al. Real-world efficacy and safety of combination nivolumab plus ipilimumab for untreated, unresectable, pleural mesothelioma: the meso-immune (Gfpc 04-2021) trial. Lung Cancer. (2024) 194:107866. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2024.107866
42. Dumoulin DW, Douma LH, Hofman MM, van der Noort V, Cornelissen R, de Gooijer CJ, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab in the real-world setting in patients with mesothelioma. Lung Cancer. (2024) 187:107440. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107440
43. Enrico D, Gomez JE, Aguirre D, Tissera NS, Tsou F, Pupareli C, et al. Efficacy of first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable pleural mesothelioma: A multicenter real-world study (Immunomeso latam). Clin Lung Cancer. (2024) 25:723–31.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2024.09.005
44. Haakensen VD, Ojlert AK, Thunold S, Farooqi S, Nowak AK, Chin WL, et al. Uv1 telomerase vaccine with ipilimumab and nivolumab as second line treatment for pleural mesothelioma - a phase ii randomised trial. Eur J Cancer. (2024) 202:113973. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2024.113973
45. Kitajima K, Kuribayashi K, Minami T, Yokoyama H, Nakamura A, Hashimoto M, et al. Comparison of fdg-pet/ct and ct for evaluation of tumor response to nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination therapy and prognosis prediction in patients with unresectable Malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncotarget. (2024) 15:408–17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28594
46. McNamee N, Harvey C, Gray L, Khoo T, Lingam L, Zhang B, et al. Brief report: real-world toxicity and survival of combination immunotherapy in pleural mesothelioma-riomeso. J Thorac Oncol. (2024) 19:636–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.11.014
47. Popat S, Curioni-Fontecedro A, Dafni U, Shah R, O'Brien M, Pope A, et al. A multicentre randomised phase iii trial comparing pembrolizumab versus single-agent chemotherapy for advanced pre-treated Malignant pleural mesothelioma: the european thoracic oncology platform (Etop 9-15) promise-meso trial. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1734–45. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.009
48. Calabrò L, Morra A, Fonsatti E, Cutaia O, Fazio C, Annesi D, et al. Efficacy and safety of an intensified schedule of tremelimumab for chemotherapy-resistant Malignant mesothelioma: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir Med. (2015) 3:301–9. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00092-2
49. Maio M, Scherpereel A, Calabrò L, Aerts J, Perez SC, Bearz A, et al. Tremelimumab as second-line or third-line treatment in relapsed Malignant mesothelioma (Determine): A multicentre, international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:1261–73. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30446-1
50. Tagliamento M, Bironzo P, Curcio H, De Luca E, Pignataro D, Rapetti SG, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of trials assessing pd-1/pd-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors activity in pre-treated advanced stage Malignant mesothelioma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2022) 172:103639. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103639
51. Bueno R, Stawiski EW, Goldstein LD, Durinck S, De Rienzo A, Modrusan Z, et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of Malignant pleural mesothelioma identifies recurrent mutations, gene fusions and splicing alterations. Nat Genet. (2016) 48:407–16. doi: 10.1038/ng.3520
52. Harber J, Kamata T, Pritchard C, and Fennell D. Matter of time: the tumor-immune microenvironment of mesothelioma and implications for checkpoint blockade efficacy. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9(9):e003032. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003032
53. Pinto C, Zucali PA, Pagano M, Grosso F, Pasello G, Garassino MC, et al. Gemcitabine with or without ramucirumab as second-line treatment for Malignant pleural mesothelioma (Rames): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:1438–47. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00404-6
54. Jarow JP, Lerner SP, Kluetz PG, Liu K, Sridhara R, Bajorin D, et al. Clinical trial design for the development of new therapies for nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer: report of a food and drug administration and american urological association public workshop. Urology. (2014) 83:262–4. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.10.030
55. Zhang B, Zhou YL, Chen X, Wang Z, Wang Q, Ju F, et al. Efficacy and safety of ctla-4 inhibitors combined with pd-1 inhibitors or chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 68:131–6. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.034
56. Wei SC, Duffy CR, and Allison JP. Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Discov. (2018) 8:1069–86. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0367
57. Park R, Lopes L, Cristancho CR, Riano IM, and Saeed A. Treatment-related adverse events of combination immune checkpoint inhibitors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:258. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00258
58. Matsumoto K, Shiroyama T, Kuge T, Miyake K, Yamamoto Y, Yoneda M, et al. Impact of treatment timing and sequence of immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-angiogenic agents for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. (2021) 162:175–84. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.11.008
Keywords: PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4, immune checkpoint inhibitors, malignant pleural mesothelioma
Citation: Sun P, Song D, Ma N, Hou S, Liu L, Gao J and Tian Y (2025) Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of diffuse pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1578746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1578746
Received: 18 February 2025; Accepted: 12 August 2025;
Published: 02 September 2025.
Edited by:
Elia Ranzato, Università del Piemonte Orientale, ItalyReviewed by:
Anand Singh, National Cancer Institute (NIH), United StatesMarjorie Zauderer, New York Medical College, United States
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Song, Ma, Hou, Liu, Gao and Tian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanyan Tian, dHl5ODk5OUAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Peiyuan Sun1†
Peiyuan Sun1† Dandan Song
Dandan Song Ning Ma
Ning Ma Shufu Hou
Shufu Hou