- 1Department of Biological Engineering, Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, Zigong, China
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Fushun People’s Hospital, Zigong, China
- 3Department of Genetics, Faculty of Agriculture, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
- 4State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 5Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, United States
- 6Division of Internal Medicine-Clinical Hematology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Introduction: Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) has emerged as a promising antibody therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) independent of antibiotics. However, the roles and differences of IgY antibodies targeting various genes against H. pylori remain unclear.
Methods: The recombinant antigens of five colonization-related genes — FlaA, BabA2, NapA, HpaA, and UreB — are prepared using a prokaryotic expression system and then subject to immunize laying hens for IgY production. Subsequently, their biological activities are evaluated, including blocking bacterial growth, attenuating infection in GES-1 cells, and eradicating H. pylori in gastritis mouse models.
Results: These IgY antibodies can recognize the full-length antigens of H. pylori and exhibit a direct inhibitory effect on the growth and infection of H. pylori with dose-dependent characteristics. Among these, anti-FlaA IgY shows greater antibacterial activity in inhibiting H. pylori growth and preventing adhesion to GES-1 cells. Oral administration of these IgY antibodies for two weeks (20.0 mg·kg−1·day−1) achieves a 25% to 37.5% eradication rate of H. pylori infection in mice. Interestingly, combination treatment with these IgY antibodies, based on their different roles, enhances antibacterial benefits and significantly promotes the recovery of gastrointestinal function.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that IgY antibodies against colonization-related genes can directly block the growth and infection of H. pylori, and combination treatment with these antibodies offers more advantages in combating H. pylori.
1 Introduction
H. pylori is the leading cause of chronic and atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcers, gastric lymphoma, and gastric carcinoma. Successful colonization is crucial for H. pylori infection, which involves various genes, including urease (1, 2), flagella (3), blood-group antigen-binding adhesin (BabA) (4), H. pylori adhesin A (HpaA) (5), and neutrophil-activating protein (NapA) (6). Each of these genes plays distinct roles during infection, such as facilitating bacterial movement, neutralizing gastric acid, and enhancing adhesion and infection in the stomach’s highly acidic environment. These genes are considered potential targets for developing various vaccines and treatments for H. pylori eradication. Among these, immunoglobulin Y (IgY) has emerged as a promising antibody therapy for H. pylori eradication.
IgY is an antibody produced by B lymphocytes after immunizing laying hens with specific antigens. It is enriched in egg yolk, yielding over 100 mg of IgY per egg. IgY is structurally and functionally similar to human IgG, and it has been widely used in the diagnosis and treatment of both animal and human diseases due to its high stability, specificity, safety, and efficacy (7–10). The application of IgY to the eradication therapy of H. pylori has been of great interest to researchers. Several laboratories developed IgY antibodies against H. pylori in the early stages based on whole bacteria or urease subunit B (UreB) antigens (11–13). Although it can significantly improve patients’ clinical symptoms, IgY does not exhibit the same efficacy as antibiotics in eradicating H. pylori infection, which limits its clinical development. In recent years, researchers have explored new targets for developing IgY antibodies and have verified their anti-H. pylori effect (1, 12, 14), thanks to a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of H. pylori infection.
As research on the mechanisms of H. pylori infection deepens, more genes will be identified as potential targets for IgY antibodies. However, their anti-bacterial roles and differences against H. pylori remain unclear, as does the question of whether it is more effective to eradicate H. pylori when these antibodies are combined at the same dose or lower doses. To address these questions, IgY antibodies targeting five different colonization-related genes—FlaA, BabA2, NapA, HpaA, and UreB—are prepared, and their antibacterial activities are systematically evaluated under the same experimental conditions, both in vivo and in vitro. Our research will provide new insights for developing combined treatment regimens using IgY antibodies to enhance efficacy in combating H. pylori infection.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Protein Marker, DNA Marker, 2× PCR Mix Reagent, and Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) membranes were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Selective medium for H. pylori culture (No. HB8647), trimethoprim (TMP) (No HB8646a), diaminobenzidine (DAB) substrate solution, and 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substrate solution, were obtained from Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) and Ni-NTA agarose purification resins were acquired from Shanghai BioEngine Sci-Tech Co., Ltd. Kanamycin and ampicillin were purchased from Biosharp. The HRP-conjugated goat anti-chicken IgY and HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse IgG were both sourced from Sigma-Aldrich, while the FITC-conjugated goat anti-chicken IgY was obtained from AbBox solution Co., Ltd.
The recombinant DNA and its plasm ids, including pET-32a(+)-BabA2, pET-32a(+)-UreB, pET-32a(+)-HpaA, pET-28a(+)-FlaA, and pET-28a(+)-NapA, were synthesized and constructed by the General Bio (Anhui) Co., Ltd. The recombinant DNA sequences of BabA2, UreB, HpaA, FlaA, and NapA are provided in the supplementary files. The H. pylori strain (ATCC 700392) and the clinical isolate (generously gifted by Dr. Juan Liao at Sichuan University) are stored in our lab.
2.2 Animal
Female BALB/c mice (n=120) at 6 weeks of age were acquired from Chengdu Dashuo Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd (Sichuan Province, China). The animals were housed in controlled environmental conditions with room temperature (RT) regulated at 22 ± 3°C and humidity levels maintained at approximately 56% (± 10%). A standardized 12 h light/dark cycle (08:00-20:00 light phase) was implemented throughout the study period. Ad libitum access to water and standard laboratory feed was provided. Body mass measurements were systematically recorded at three-day intervals using calibrated analytical balances. Following a 7-day acclimatization period to ensure physiological stabilization, experimental protocols were initiated. All procedures involving animal subjects were conducted in accordance with the ethical guidelines approved by Sichuan University’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, IACUC (Ethical Approval ID: 20230307036). For animal euthanasia, BALB/c mice were injected intraperitoneally with pentobarbital sodium, following the European Directive 2010/63/EU.
2.3 Preparation of recombinant antigens
Five recombinant plasmids, including pET-32a(+)-BabA2, pET-32a(+)-UreB, pET-32a(+)-HpaA, pET-28a(+)-FlaA, and pET-28a(+)-NapA, were individually transformed into BL21 (DE3) competent cells, respectively, and the positive transformants were verified by colony PCR. After identification, the expression and purification of recombinant antigens were conducted as previously described (15). The recombinant antigens were induced under 1.0 mM IPTG for 6 h. Then, the BabA2, UreB, FlaA, and NapA antigens were purified and renatured by washing and gradient dialysis with urea, while the HpaA antigen was purified using Ni2+-affinity chromatography. All prepared recombinant antigens were further analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
2.4 Immunization and IgY antibodies preparation
For immunization studies, 42-day-old Leghorn chickens (n = 36) were acclimatized in controlled isolators with 12 h photoperiod regulation, maintaining 23°C (± 2°C) RT and 75% (± 5%) humidity. Nutritional requirements were met with a standardized poultry diet and automated watering systems. For primary immunization, the five recombinant antigens (adjusted to 1.0 mg/mL) were emulsified with an equal volume of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA), with 200 μL administered per antigen. Subsequent booster immunizations utilized Incomplete Freund’s Adjuvant (IFA) following the same emulsification protocol. The thirty chickens were then randomly divided into five groups (six chickens per group) and immunized with FlaA, UreB, BabA2, NapA, and HpaA, respectively. The remaining 6 chickens are used for PBS immunization. Immunizations were performed intramuscularly at two sites on the breast at 21 weeks of age, followed by two booster immunizations at two-week intervals. Eggs were collected daily for two weeks after the final immunization. IgY antibodies were prepared from egg yolks using the water-dilution method, as previously described (16). Next, recombinant antigens BabA2, UreB, FlaA, NapA, and HpaA were individually coated (1.0 μg per well) and used to determine their corresponding antibody titers via ELISA, as previously described (17).
2.5 Effects of IgY antibodies on the growth of H. pylori
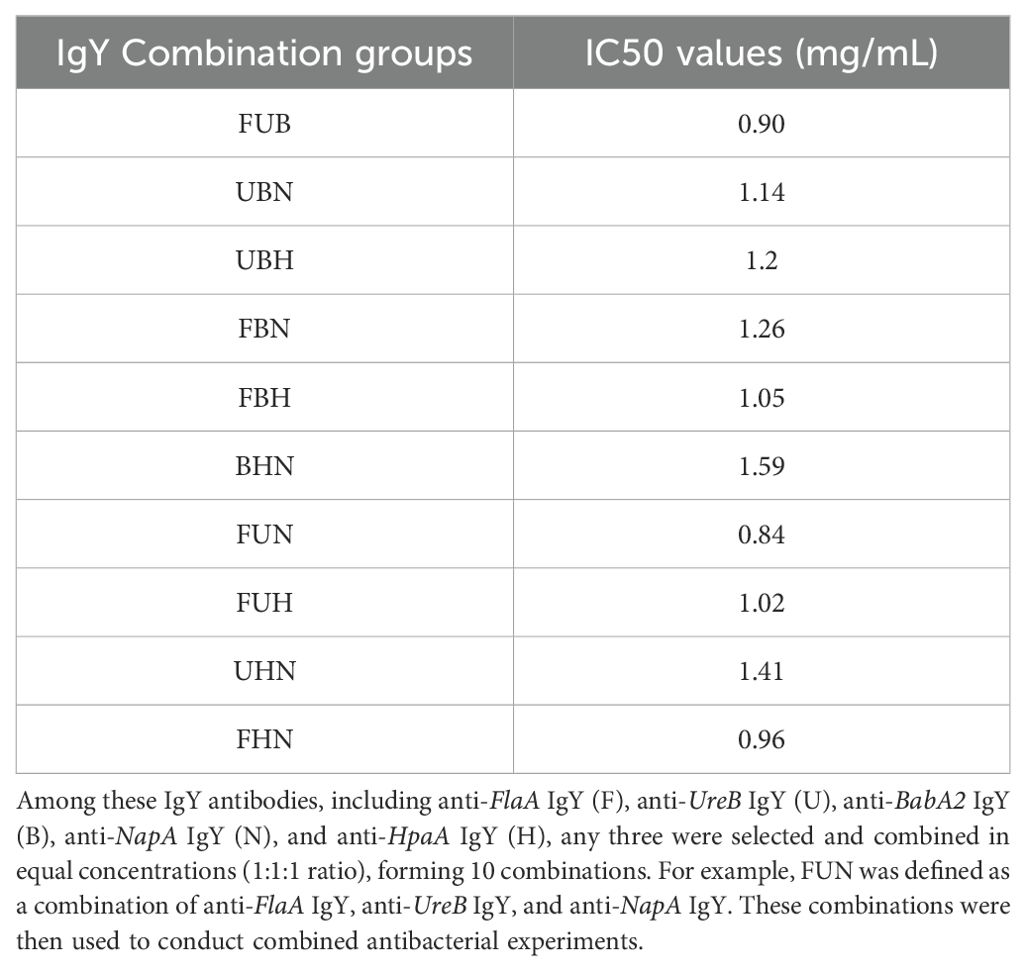
The preparation of H. pylori was done using an H. pylori selective medium. To investigate the effect of each IgY antibody on the growth of H. pylori, 50 μL of H. pylori solution (5 × 107 CFU/mL) was added to each well of a 96-well plate. The concentrations of each IgY antibody were adjusted to 6 mg/mL, 4 mg/mL, and 2 mg/mL using the H. pylori selective medium. Then, 50 μL of each IgY antibody solution was added to the corresponding wells, mixed thoroughly, and co-incubated under anaerobic conditions at 37°C. After 24 h, the culture from each well was plated onto H. pylori selective solid medium and further incubated anaerobically at 37°C for 3–5 days. Colony counts were performed using the dilution plate count method, and the inhibitory rate was calculated. Furthermore, among these five antibodies (anti-FlaA IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, anti-UreB IgY, anti-NapA IgY, and anti-HpaA IgY), any three were selected and combined in equal concentrations (1:1:1 ratio) without changing the total antibody concentration, forming 10 combinations (Table 1). These combinations were then used to conduct combined antibacterial experiments.
2.6 Immunofluorescence staining
GES-1 cells were seeded at a density of 3×104 cells/well in 96-well plates and cultured overnight at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. Each IgY antibody concentration was adjusted with DMEM medium and added to the 96-well plate for co-incubation with cells at a working concentration of 2 mg/mL. H. pylori were subsequently added to the wells at 1.0 × 106 CFU/well and co-cultured with GES-1 cells for a 12 h infection period. Subsequently, immunofluorescence staining was conducted to observe the infection of GES-1 cells by H. pylori. Briefly, 200 μL of primary IgY antibody solution (a mixture of anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, anti-HpaA IgY, and anti-NapA IgY in a ratio of 1:1:1:1:1, with a total concentration of 50 μg/mL) containing 3% FBS was added into wells and incubated at RT for 2 h. After three additional PBS washes, a secondary antibody of FITC-labeled goat anti-chicken IgY (diluted 1:250) was added and incubated at 4°C for 45 minutes in the dark. Finally, the wells were washed five times with PBS, 200 μL of DAPI (1.0 μg/mL) was added for 5 minutes at RT, the staining solution was discarded, and the samples were washed with PBS again. Finally, GES-1 cells were observed and photographed under a fluorescence microscope, and the ImageJ software was used for calculating and analyzing images.
2.7 Establishment of H. pylori-infected mice model
The H. pylori strain (ATCC 700392) was used to establish a mouse gastritis model. Mice (n = 110) underwent a 7-day gastric preconditioning protocol involving daily oral gavage with 0.1 mL of 3% sodium bicarbonate solution, followed 10 minutes later by administration of 0.1 mL of 50% ethanol solution. On day 8, mice were fasted for 12 h or overnight, then gavaged with 0.1 mL of 3% sodium bicarbonate solution, followed 10 minutes later by 0.2 mL of a bacterial solution containing 5 × 109 CFU/mL of H. pylori. Food and water were resumed 2 h post-infection. H. pylori infection was performed by gavage every 3 days for 3 weeks. One week after the final infection (day 35), fecal samples were analyzed using rapid urease testing to confirm H. pylori infection. Five test-positive mice were randomly selected for euthanasia with intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium and dissection, and gastric mucosal fluid was inoculated onto solid culture media and incubated for 5 days. The infection status of these mice was further evaluated based on the H. pylori culture results.
2.8 Dietary IgY antibodies and eradication rate evaluation
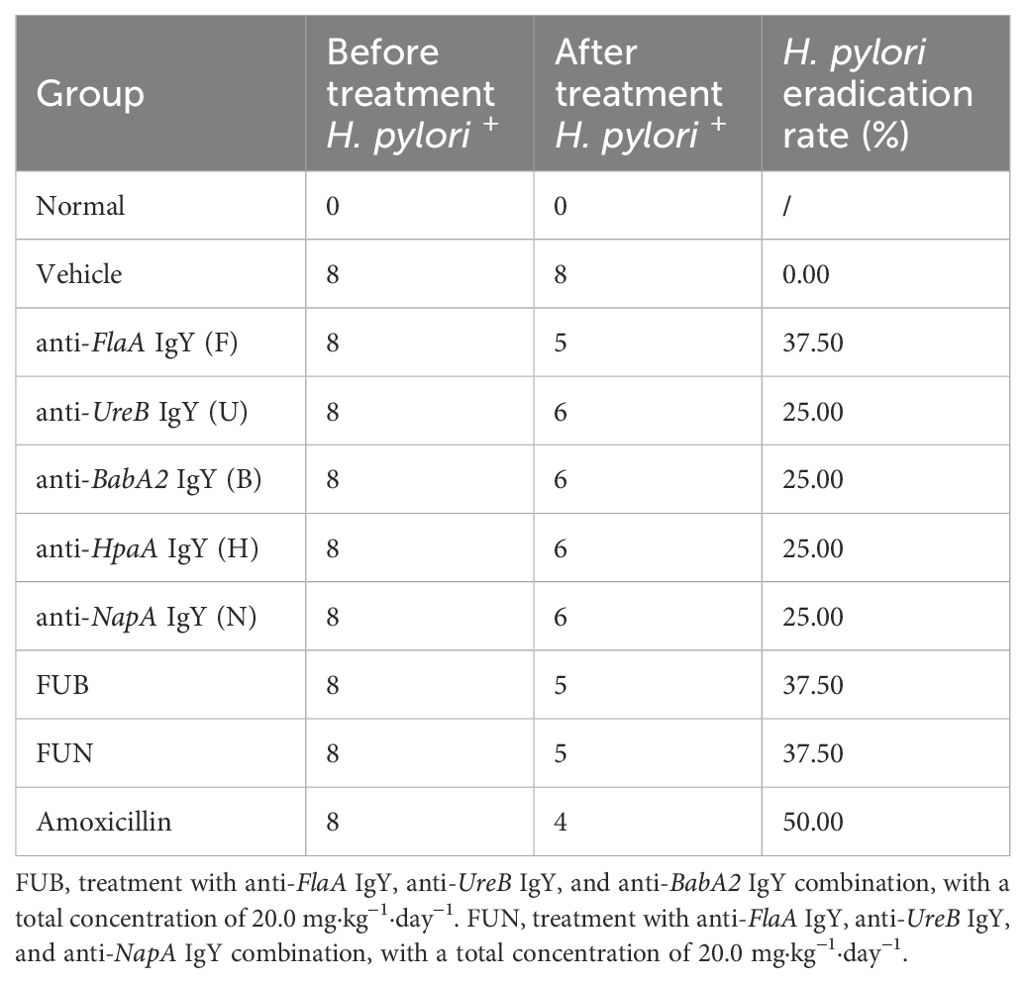
H. pylori-infected mice (n = 72) were randomly divided into nine treatment groups of 8 mice each: PBS vehicle treatment group, amoxicillin treatment group, anti-BabA2 IgY treatment group, anti-FlaA IgY treatment group, anti-NapA IgY treatment group, anti-UreB IgY treatment group, anti-HpaA IgY treatment group, a combination treatment group with FUN (including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY, and anti-NapA IgY), and a combination treatment group with FUB (including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY, and anti-BabA2 IgY). On day 36, IgY antibodies treatments were administered by gavage at a dose of 20.0 mg/kg of IgY antibody or its combinations, given once daily for 2 weeks. On day 51, treatments were terminated, and fresh feces were collected from the mice. A rapid urease test (RUT) was conducted to evaluate the eradication rate of H. pylori. Additionally, a non-infected mouse group (n = 8) served as the normal control.
2.9 Evaluation of gastric emptying rate and intestinal propulsion rate
After collecting the feces, the mice were fasted for 12 h, after which a carbon ink solution was administered by gavage at a dose of 0.1 mL per mouse. Euthanasia was performed 30 minutes later, and the stomach, small intestine, cecum, and colon were collected. The total weight and net weight of the stomach were recorded first. The gastric emptying rate was evaluated based on the residual rate of gastric contents using the formula: gastric content residual rate (%) = [(gastric weight - gastric net weight)/carbon ink dosage] × 100%. Next, the distance from the pylorus to the carbon ink and the total length of the intestine were measured for each group of mice. The propulsion rate (%) was calculated as (distance of carbon ink propulsion in the small intestine (cm)/total length of the small intestine (cm)) × 100%.
2.10 Histopathological examination
The stomach was fixed in a 4% paraformaldehyde solution. Paraffin-embedded tissue slides were prepared with 3 µm and stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE), and then tissue damage and inflammation were examined and photographed under a light microscope. To objectively evaluate inflammation, four non-overlapping microscopic fields from three independent tissue sections per mouse were randomly selected. These submucosal inflammatory cell infiltrations were determined independently by two pathologists. Data were normalized to the submucosal area (mm²) measured via ImageJ’s polygon tool, and results were expressed as mean ± SEM cells/mm².
2.11 Serum anti-H. pylori antibody detection by ELISA
After euthanasia, whole blood was collected and allowed to clot at RT for 3 h. The clotted sample was then centrifuged at 500 ×g for 5 minutes to pellet cellular debris, after which the supernatant serum was carefully aspirated using a pipette. The antisera against H. pylori were quantified using indirect ELISA. Briefly, the coating antigens comprised five purified recombinant antigens: FlaA, UreB, BabA2, HpaA, and NapA, totaling 1 μg per well. After blocking the plates with 5% skim milk in PBST for 2 h at RT, they were incubated with mouse serum diluted at 1:50 for 2 h at RT. Next, washed with PBST and then incubated with HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse IgG for 1 h at 37°C. After an additional wash with PBST, TMB solution was added to each well. The plates were then incubated in the dark for 10 minutes, after which the reaction was terminated by adding H2SO4 to each well. The value was measured at 450 nm using a microtiter plate reader.
2.12 Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM derived from triplicate independent trials. Statistical comparisons were conducted through one-way ANOVA (SPSS 22.0) among treatment groups, with significance thresholds set at *p < 0.05 (significant) and **p < 0.01 (very significant).
3 Results
3.1 Preparation of recombinant antigens
After transformation with five individual plasmids containing recombinant DNA of BabA2, FlaA, UreB, NapA, and HpaA, the corresponding positive transformants were identified by colony PCR using specific primers (Supplementary Figure 1A). After 6 h of IPTG induction with 1.0 mM, the results of SDS-PAGE showed that five recombinant antigens were successfully expressed, and their molecular weights were consistent with the expected sizes (Supplementary Figure 1B). After purification, specific protein bands corresponding to BabA2, FlaA, UreB, NapA, and HpaA were observed at approximate sizes of 65 kDa, 55 kDa, 80 kDa, 20 kDa, and 45 kDa, respectively, as shown in Figure 1a.
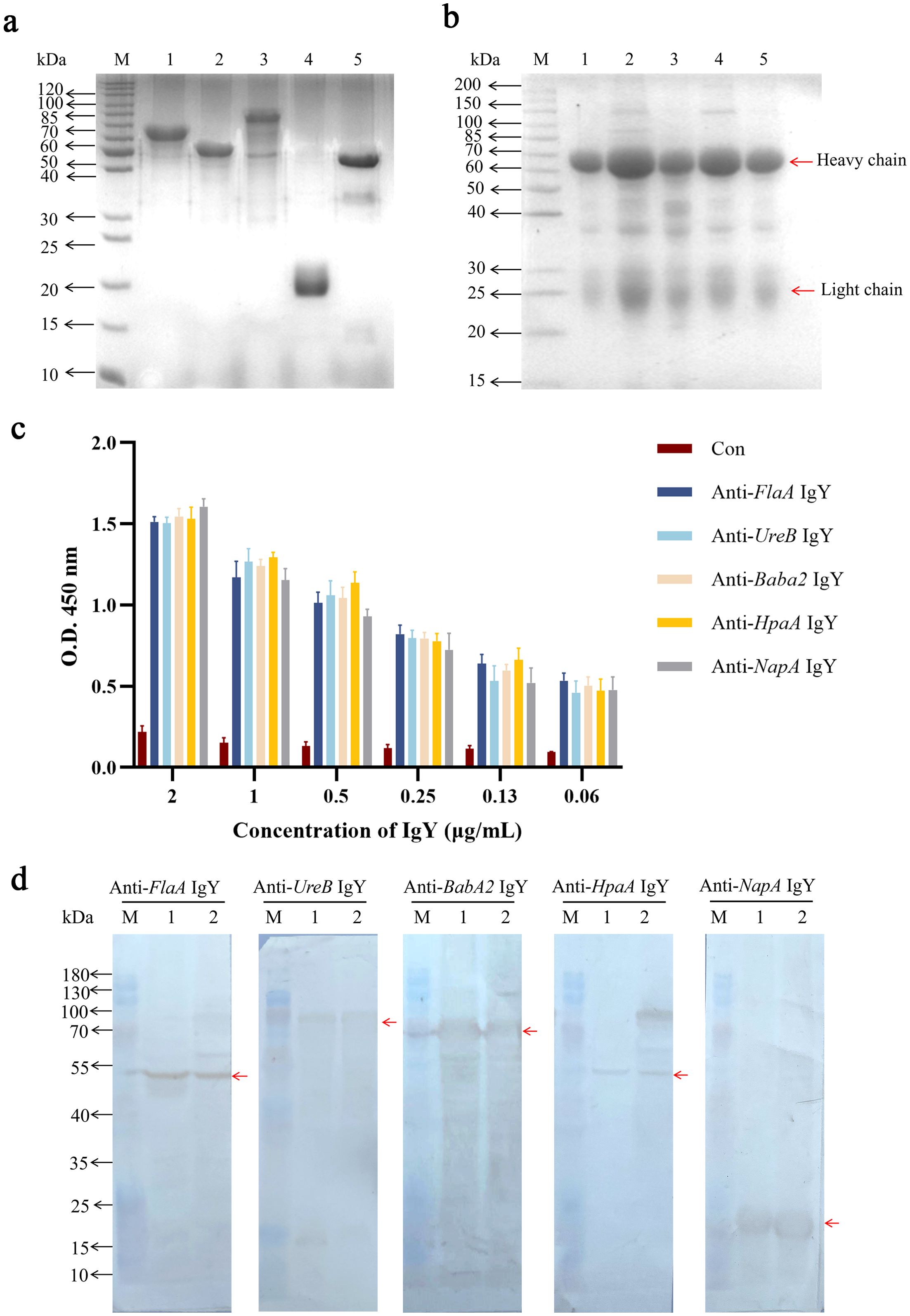
Figure 1. Preparation and identification of IgY antibodies. (a) SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified recombinant antigens. Lane M: the standard protein marker; Lanes 1 to 5: the purified recombinant antigens of BabA2, FlaA, UreB, NapA, and HpaA after purification, respectively. (b) SDS-PAGE analysis of the isolated IgY antibodies from egg yolk. Lane M: the standard protein marker; Lanes 1 to 5: the isolated IgY antibodies of anti-BabA2 IgY, anti-UreB IgY, anti-FlaA IgY, anti-NapA IgY, and anti-HpaA IgY, respectively. (c) ELISA analysis of isolated IgY antibodies using purified recombinant antigens as coating antigens. The data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 4). Con, PBS-IgY Control. (d) The binding abilities of IgY antibodies, including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, anti-HpaA IgY, and anti-NapA IgY, to the whole bacterial antigens of two H. pylori strains, including FlaA, UreB, BabA2, HpaA, and NapA, were evaluated by using Western Blotting, respectively. Lane M: the standard protein marker; Lane 1: the standard H. pylori strain (ATCC 700392); Lane 2: clinical isolate of H. pylori.
3.2 Purification and identification of IgY antibodies
IgY antibodies were extracted using the water dilution method, and the results of SDS-PAGE showed that these IgY antibodies containing the respective anti-antigen (BabA2, UreB, FlaA, NapA, and HpaA) were successfully extracted. These IgY antibodies showed two major bands at approximately 35 KDa and 70 KDa, which corresponded to the light- and heavy-chain of IgY antibody, respectively (Figure 1b). Further ELISA analysis showed that the titers of these IgY antibodies reached up to 0.06 μg/mL (P/N ratio greater than 2.1) (Figure 1c). These antibodies can also recognize the corresponding recombinant antigens as well as the H. pylori whole bacterial antigens at the expected molecular weights determined by Western Blot (Figure 1d, Supplementary Figure 2).
3.3 Inhibitory effect of IgY antibodies on the growth of H. pylori
The antibodies, including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, anti-UreB IgY, anti-NapA IgY, and anti-HpaA IgY, were co-cultured with H. pylori, respectively. As shown in Figure 2, the growth of H. pylori could be significantly inhibited by IgY antibodies at different concentrations, exhibiting dose-dependent characteristics. Compared to other IgY antibodies, anti-FlaA IgY demonstrated the greatest inhibitory effect on H. pylori, while anti-UreB IgY exhibited the weakest antibacterial effect on H. pylori.
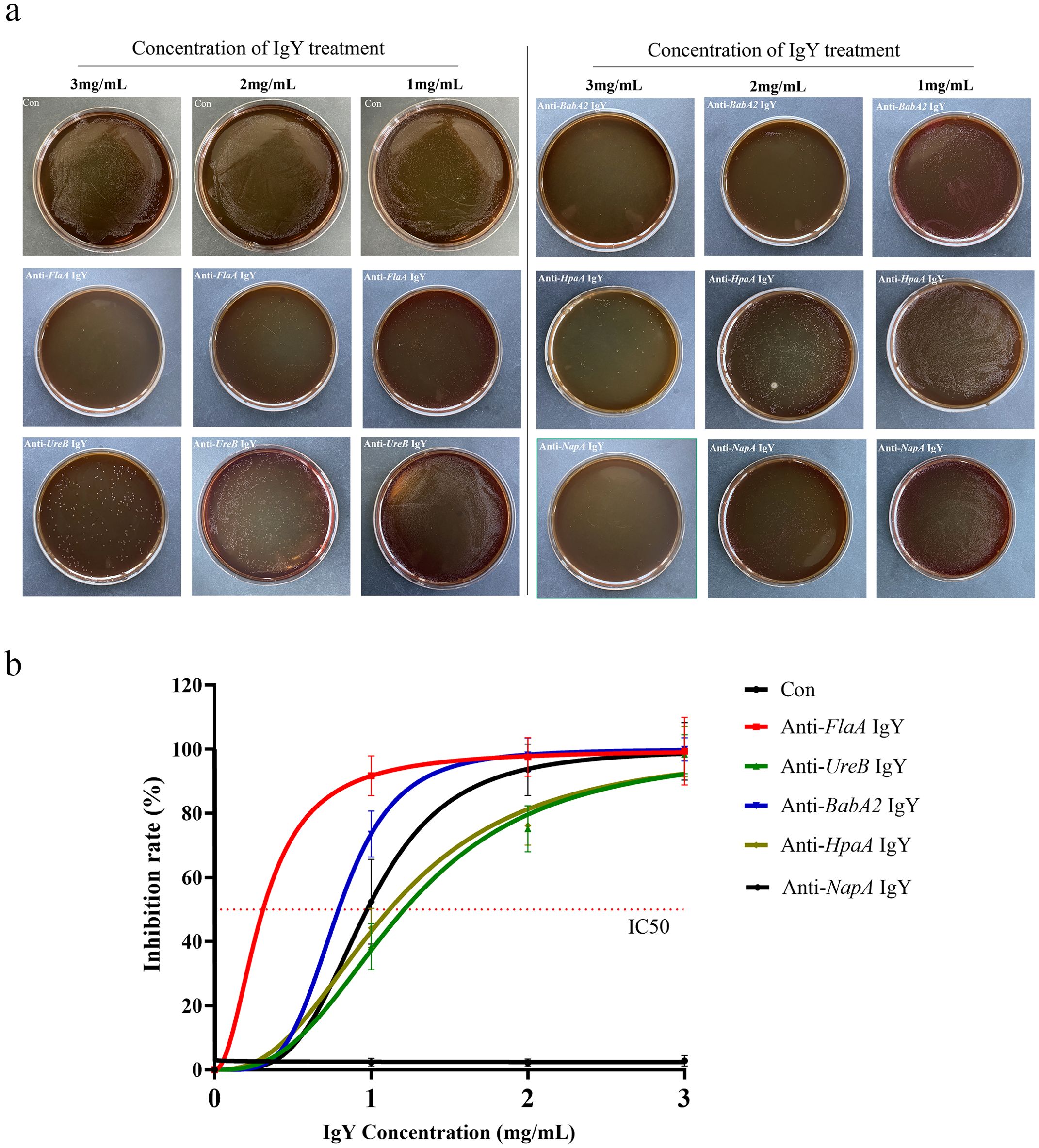
Figure 2. Inhibition rate of IgY antibodies on the growth of H. pylori. (a) Different concentrations of IgY antibodies (anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, anti-HpaA IgY, and anti-NapA IgY) were co-cultured with H. pylori as described in the Materials and Methods section. (b)The dilution plate count method was used for colony counting, and the inhibitory rate was calculated. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=4). Con, PBS-IgY Control.
Furthermore, among these five IgY antibodies, any three were selected and combined in equal concentrations (l:1:1 ratio)to conduct a combined antibacterial experiment. As shown in Table 1, the FUN combination (including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY, and anti-NapA IgY) and the FUB combination (including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY, and anti-BabA2 IgY) exhibited the strong antimicrobial advantage in vitro, with IC50 values of 0.84 mg/mL and 0.90 mg/mL, respectively, when compared to other combination groups. Unexpectedly, the FBN combination group (including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, and anti-NapA IgY) demonstrated relatively poor antibacterial effects. Therefore, these two combinations, including FUN and FUB, were then applied to subsequent antimicrobial experiments.
3.4 Inhibitory effect of IgY antibodies on H. pylori infection in GES-1 cells
To investigate the preventive effect of IgY antibodies on H. pylori infection, the IgY antibodies were added to the well for co-incubation with GES-1 cells. As shown in Figure 3, H. pylori significantly adhered to and infected GES-1 cells. Each IgY antibody treatment could significantly inhibit the adhesion of H. pylori to the cells at various levels (p < 0.05). Among the single treatment groups, anti-FlaA IgY exhibited a better inhibitory effect on H. pylori infection, while anti-UreB IgY showed a moderate preventive effect. Additionally, the combination treatment groups, FUN and FUB, also exhibited similar inhibitory effects as anti-FlaA IgY on H. pylori infection at the same concentration (total 2.0 mg/mL).
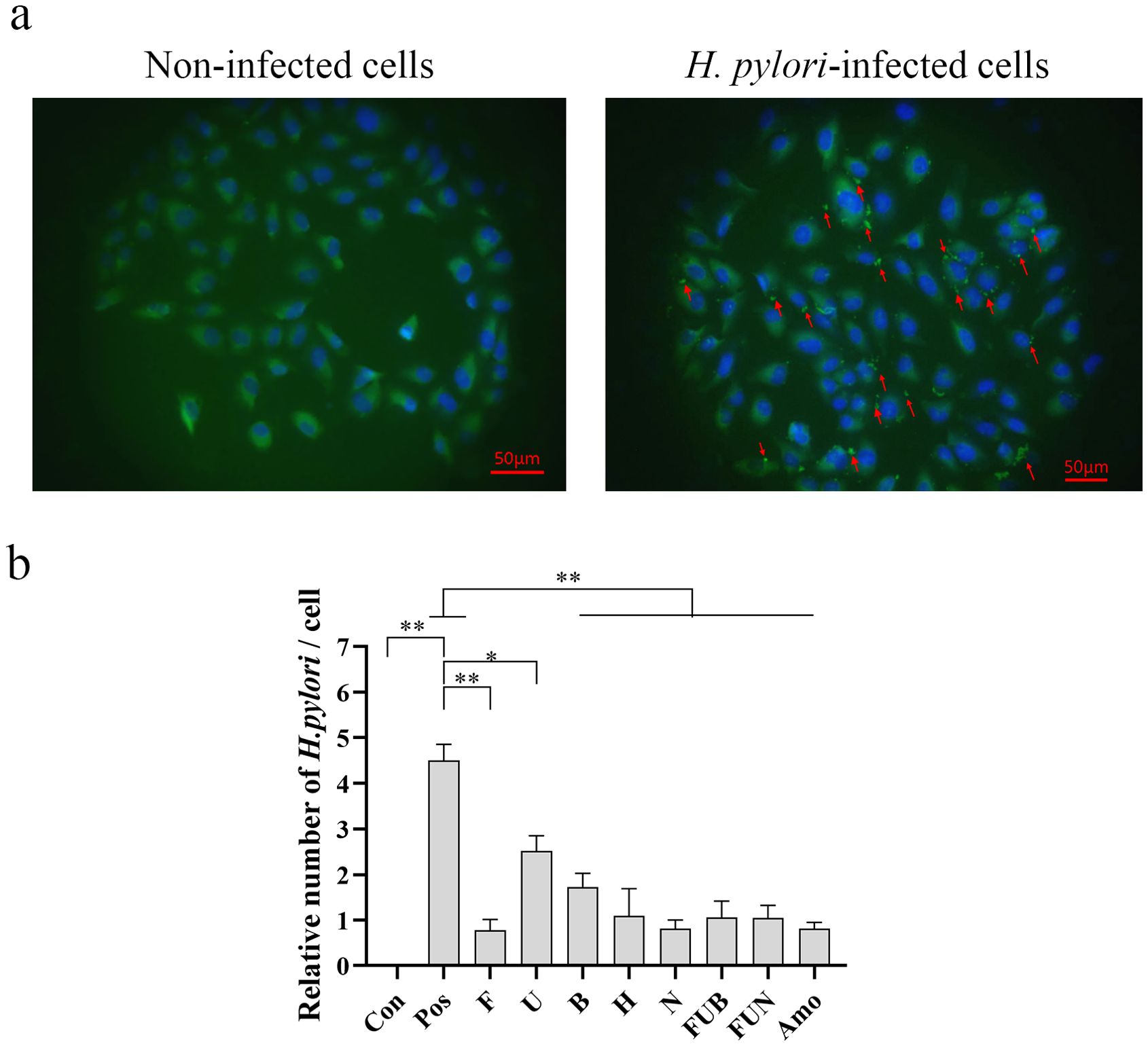
Figure 3. Inhibitory effects of IgY antibodies on H. pylori infection in GES-1 cells determined by immunofluorescence staining. After treatment with IgY antibodies, the H. pylori infection in GES-1 cells was evaluated using immunofluorescence staining. (a), Representative images of the immunofluorescence staining under a fluorescence microscope (Scale bars, 50 μm). In the absence of H. pylori adhesion to GES-1 cells, no significant fluorescence signal is observed on the cell surface (left). In contrast, when bacteria adhere to the cells, a distinct fluorescent signal localizes to the cell surface (red arrow, right). (b) Quantitative analysis of H. pylori infection in GES-1 cells. The arrow indicates the adhesion of H. pylori to GES-1 cells. Con, non-infected cells; pos, H. pylori-infected cells; F, anti-FlaA IgY treatment; U, anti-UreB IgY treatment; B, anti-BabA2 IgY treatment; H, anti-HpaA IgY treatment; N, anti-NapA IgY treatment; FUB, treatment with anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY and anti-BabA2 IgY combination; FUN, treatment with anti-FlaA IgY, anti-UreB IgY and anti-NapA IgY combination; Amo, amoxicillin treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=4). *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01.
3.5 Eradication rate of IgY treatment
The strategy for H. pylori infection and IgY antibodies treatment in this study is shown in Figure 4a. After 3 weeks of H. pylori infection, the feces of the mice were tested using the rapid urease test (RUT), and the results indicated that 73.6% of the mice tested positive. Furthermore, 5 mice with a positive RUT test were randomly selected for H. pylori culture. The colonies on the plates were transparent, moist, and exhibited a flat morphology, staining red with Gram stain. These suspected colonies were confirmed as H. pylori through colony PCR (Supplementary Figure 3), indicating successful colonization of the gastric mucosa in the mice. In addition, compared with the normal control group, the H. pylori-infected group exhibited some characteristics of malaise, reduced appetite, constipation, and weight loss (p< 0.05) (Supplementary Table 1).
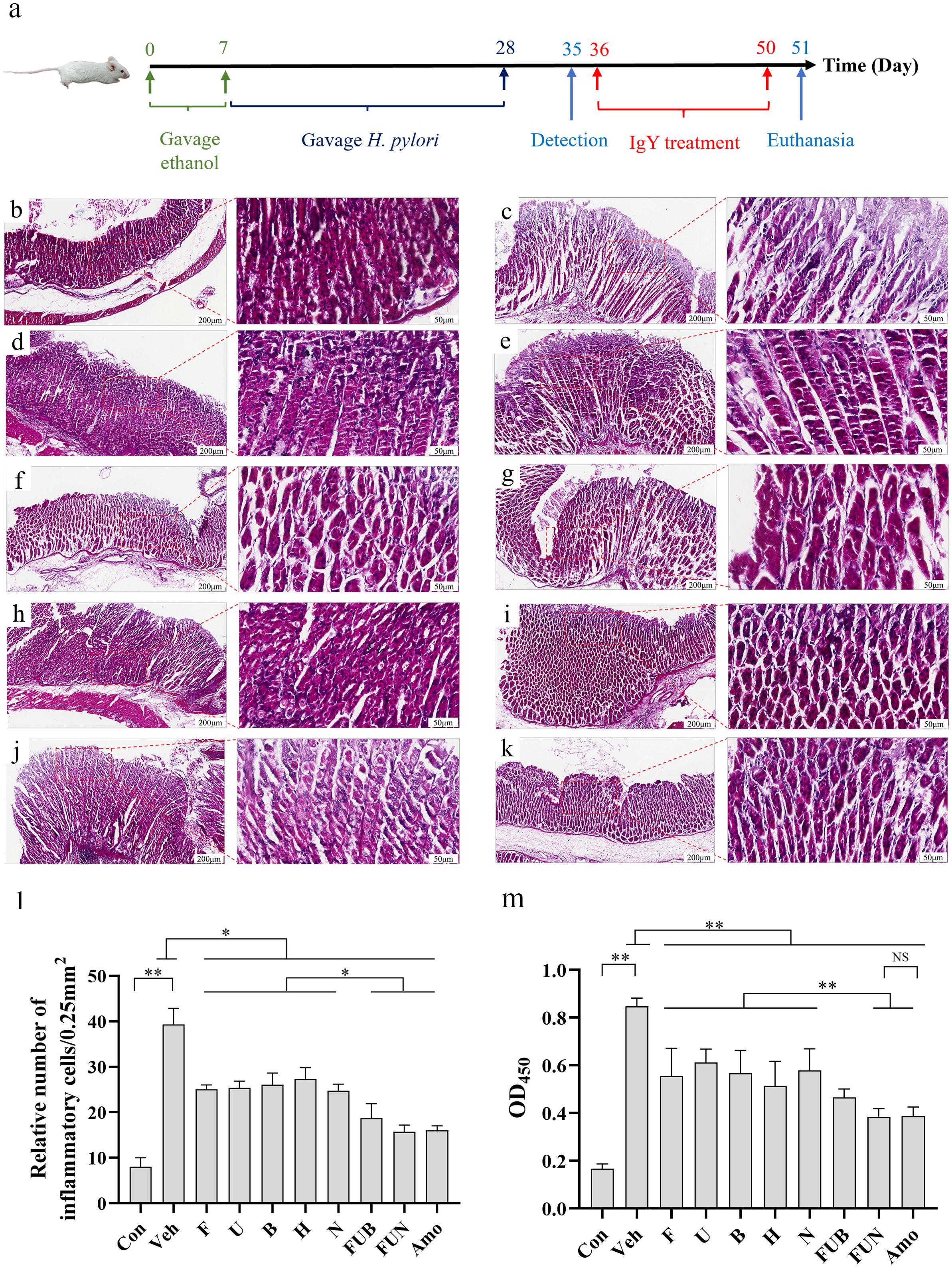
Figure 4. H. pylori-infected mice model establishment and IgY antibodies treatment. (a) Schematic diagram illustrating the establishment of the H. pylori-infected mice model and the treatment with IgY antibodies. Histopathological analysis of the gastric mucosa of mice infected with H. pylori (ATCC 700392), followed by treatment with IgY antibodies (20 mg·kg−1·day−1). Representative images of the gastric mucosa with H&E staining are displayed (Scale bars, 200 μm or 50 μm, as indicated in figures). Groups include: Normal mice group (Con) (b), H. pylori + PBS vehicle group (Veh) (c), H. pylori + anti-FlaA IgY group (F) (d), H. pylori + anti-UreB IgY group (U) (e), H. pylori + anti-BabA2 IgY group (B) (f), H. pylori + anti-HpaA IgY group (H) (g), H. pylori + anti-NapA IgY group (N) (h), H. pylori + FUB group (FUB) (i), H. pylori + FUN group (FUN) (j), and H. pylori + Amoxicillin group (k). In comparison to the IgY-treated groups, the H. pylori + vehicle group exhibited altered gastric mucosal morphology, including degeneration of villi and infiltration of inflammatory cells. (l) Quantitative analysis for submucosal inflammatory cell infiltration. (n = 8). (m) Serum anti-H. pylori antibody detection by ELISA. (n = 8). *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01.
IgY treatment in each group achieved initial H. pylori eradication. Notably, anti-FlaA IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, and anti-HpaA IgY were the first confirmed to eradicate H. pylori infection, with eradication rates of 37.5%, 25%, and 25%, respectively. In addition, the eradication rate of H. pylori in both the FUB combination and the FUN combination was 37.5% (Table 2), while the eradication rate in the amoxicillin treatment group was 50%. Interestingly, after two weeks of IgY antibodies treatment, the diet and body weight of the mice significantly recovered compared to the vehicle (p < 0.05) (Supplementary Table 1).
3.6 Histological findings
The gastric mucosal cells in non-infected mice were usually tightly packed, with intact tissue structure and clear lamina propria. The ratio of chief cells to parietal cells was within the normal range, and the morphology of these cells appeared intact, with inflammatory cell infiltrates being absent or rare. However, H. pylori infection caused significant damage to the gastric mucosa, degeneration of cell morphology, and pronounced inflammatory cell infiltration was observed. In single IgY treatment groups, the morphology of cells was comparatively intact, and the inflammatory cell infiltration and tissue damage were significantly reduced compared to the H. pylori-infected group. Interestingly, the FUN combination treatment significantly improved tissue repair and decreased immune cell infiltration, demonstrating effects similar to those of amoxicillin treatment (Figures 4b-l). In addition, IgY treatments—especially the FUN combination—exhibited a similar trend in significantly decreasing the antibody titer of anti-H. pylori serum compared to amoxicillin, suggesting that the H. pylori infection was significantly reduced after IgY treatments (Figure 4m).
3.7 Effects on gastric emptying rate and intestinal propulsion rate
H. pylori infection significantly impaired gastrointestinal function in mice by inhibiting gastric emptying and intestinal propulsion (Figures 5a–c). However, treatment with IgY antibodies notably restored gastrointestinal function in H. pylori-infected mice at various levels, improving the intestinal propulsion rate and reducing the gastric residual rate (p < 0.05). Notably, the combinations of IgY antibodies, specifically FUN and FUB, enhanced gastric emptying capacity and restored intestinal propulsion to levels comparable to normal mice (Figures 5a–c).
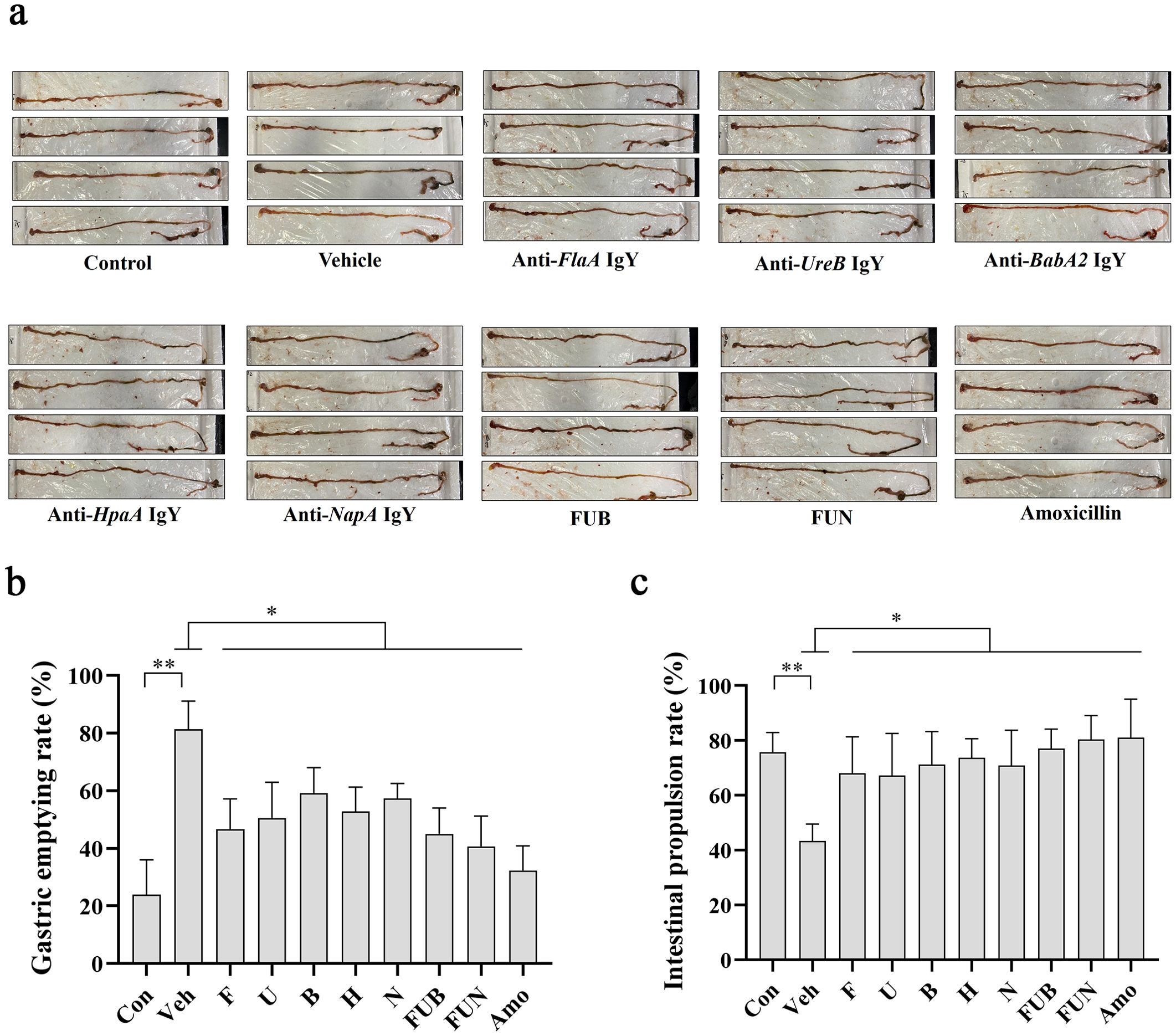
Figure 5. Gastric residual rate and intestinal propulsion rate. (a) Schematic diagram of the mouse intestinal tract after IgY treatments as indicated. The gastric residual rate (b) and intestinal propulsion rate (c) were calculated as described in the Materials and Methods section for each mouse in 10 groups, including normal mice group (Con), H. pylori + PBS vehicle group (veh), H. pylori + anti-FlaA IgY group (F), H. pylori + anti-UreB IgY group (U), H. pylori + anti-BabA2 IgY group (B), H. pylori + anti-HpaA IgY group (H), H. pylori + anti-NapA IgY group (N), H. pylori+ FUB group (FUB), H. pylori + FUN group (FUN), and H. pylori + Amoxicillin group (Amo). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8). * P < 0.05. ** P < 0.01.
4 Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the antimicrobial roles of five IgY antibodies in vivo and in vitro within the same experimental system, confirming FlaA as a promising target against H. pylori. Although five IgY antibodies, including anti-FlaA IgY, anti-BabA2 IgY, anti-NapA IgY, anti-HpaA IgY, and anti-UreB IgY, exhibited a directly inhibitory role on H. pylori growth and adhesion, their antimicrobial effects varied in vitro. The direct effects of these IgY antibodies on H. pylori growth were ranked as follows: anti-FlaA IgY > anti-BabA2 IgY > anti-NapA IgY > anti-HpaA IgY ≈ anti-UreB IgY, while the effects on H. pylori infection to GES-1 cells were ranked as anti-FlaA IgY ≈ anti-NapA IgY > anti-HpaA IgY > anti-BabA2 IgY > anti-UreB IgY. Among these IgY antibodies, the anti-FlaA IgY exhibited an obvious advantage over other individual antibodies against H. pylori infection.
Additionally, we identified two effective combinations of IgY antibodies: FUN and FUB. These combinations showed significant advantages in inhibiting the growth and infection of H. pylori while promoting the recovery of gastrointestinal function at the same dosage. Although IgY antibodies have exhibited significant efficacy in recent clinical studies targeting H. pylori infection (17–19), their therapeutic effectiveness remains inferior to that of traditional antibiotic treatments. Therefore, based on the different functions and roles of genes during H. pylori infection, employing a combination strategy with IgY antibodies to enhance their anti-H. pylori efficacy is a crucial focus in developing IgY antibody-based drugs. BabA2, HpaA, and NapA are important adhesins of H. pylori that promote the infection of cells by H. pylori. HpaA is expressed in almost all H. pylori (20), and the anti-HpaA IgY exhibits antibacterial adhesion effects similar to those of anti-BabA2 IgY in our test. BabA2 is a crucial adhesin that shows a high rate of positive serum antibody detection in patients with H. pylori infection (21). Antibodies or vaccines targeting BabA2 can effectively block H. pylori infection and significantly reduce the incidence of ulcers and gastric cancer (22). Therefore, BabA2 was included in the antibody combination for our animal experiments. UreB is widely expressed in H. pylori and is considered one of the first targets for developing IgY antibodies. Its effectiveness has been validated in both animal and human clinical trials (13, 23). In this study, anti-UreB IgY exhibited relatively low activity against H. pylori growth and adhesion in vitro compared to other antibodies. However, it demonstrated similar H. pylori eradication effects to the other IgY antibodies in in vivo assays, which may be attributed to its gastric acid-neutralizing effect (24). Therefore, UreB was included in the antibody combination for in vivo experiments. Based on these considerations, we designed and identified two combinations with enhanced anti-H. pylori efficacy, namely FUN and FUB, which targeted different processes related to bacterial colonization, including blocking movement, creating a suitable environment, and inhibiting adhesion.
Notably, factors such as target selection, IgY antibody dosage, and treatment duration may be key factors affecting the antimicrobial activity of IgY in initial Helicobacter pylori eradication. Firstly, different genes play distinct roles in the infection and colonization processes of H. pylori. Therefore, it is hypothesized that IgY antibodies targeting different genes should exhibit varying antibacterial efficacies. Findings from this study revealed differences in the inhibitory effects of IgY antibodies targeting five different colonization-related genes, with anti-FlaA IgY demonstrating the strongest antibacterial activity. Urease was the earliest target developed for H. pylori-specific IgY. Both animal studies and human tests have shown that urease-targeted IgY significantly reduces H. pylori infection load, promotes gastric mucosal repair, and alleviates clinical symptoms (13, 14, 25). However, oral administration of urease-targeted egg yolk antibodies (IgY) alone fails to achieve clinical eradication of H. pylori (eradication rate: 0%) (25). Therefore, developing multivalent IgY that simultaneously targets multiple genes is necessary to achieve complementary or synergistic effects, thereby enhancing IgY’s efficacy in eradicating H. pylori infections. In this study, we identified two combinations, FUB and FUN, which not only demonstrated antimicrobial advantages but also promoted gastrointestinal recovery in mice, confirming the feasibility of combination therapy against H. pylori infection.
In addition to gene targets, the dosage of IgY significantly impacts its antibacterial efficacy (26). In this study, the antimicrobial activity of single IgY treatment exhibited a significant dose-dependent characteristic (Figure 2). In the previous study, a 30.8% first eradication rate was achieved with the oral administration of 100 mg of IgY once daily (16), while Hao et al. reported an eradication rate of 50.74% with a dosage of 250 mg of IgY taken orally twice daily (18). Although there are some differences in the targets, high doses are beneficial for the eradication of H. pylori in vivo. Notably, the total dosage of the antibody combination was designed to be consistent with that of single antibody treatments in our tests. However, the antibacterial effects and promotion of gastrointestinal function recovery were superior to those of single antibody treatments, potentially indicating a synergistic effect between IgY antibodies. Therefore, future studies should fully consider the characteristics of the targets and the dosage of IgY antibodies to achieve the best eradication effect against H. pylori.
Finally, the duration of oral IgY administration represents another critical yet underexplored variable. Unfortunately, no clinical evidence currently exists regarding the impact of prolonged IgY treatment on H. pylori eradication efficacy. Our group has initiated systematic investigations to address this question. In addition, there are some limitations in this study, including the prepared IgY not representing the effective concentration of respective antigen-specific antibodies due to the lack of affinity purification. To address this limitation and ensure the accuracy of our results, we implemented the following measures: first, we standardized the antibody preparation protocol, including consistent antigen immunization dosage, administration method, and extraction procedures; second, we included a PBS-immunized control group, in which PBS-IgY antibody was prepared identically and used as a negative control in antibody titer assays (Figure 1c) and in vitro antibacterial evaluations (Figures 2a, b).
5 Conclusion
These IgY antibodies against colonization-related genes show a direct role in blocking the growth and infection of H. pylori, and their combination treatment could offer greater benefits against H. pylori infection and promote the recovery of gastrointestinal function.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), Sichuan University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YD: Data curation, Writing – original draft. RG: Writing – review & editing. WH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. RG: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AE-S: Writing – review & editing. XJ: Writing – review & editing. YX: Writing – review & editing. MB: Writing – review & editing. ZL: Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program (Grant No. 2023NSFSC0586, 24GJHZ0088).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Correction note
This article has been corrected with minor changes. These changes do not impact the scientific content of the article.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1582250/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Motamedi H, Abiri R, Salari F, Jalili C, and Alvandi A. Reduction of UreB and CagA expression level by siRNA construct in Helicobacter pylori strain SS1. BMC Microbiol. (2023) 23:401. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-03143-x
2. Ghasemi A, Wang S, Sahay B, Abbott JR, and Curtiss R. Protective immunity enhanced Salmonella vaccine vectors delivering Helicobacter pylori antigens reduce H. pylori stomach colonization in mice. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1034683. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1034683
3. Asakura H, Churin Y, Bauer B, Boettcher JP, Bartfeld S, Hashii N, et al. Helicobacter pylori HP0518 affects flagellin glycosylation to alter bacterial motility. Mol Microbiol. (2010) 78:1130–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07393.x
4. Chen M-Y, He C-Y, Meng X, and Yuan Y. Association of Helicobacter pylori babA2 with peptic ulcer disease and gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. (2013) 19:4242–51. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4242
5. Banga Ndzouboukou J-L, Lei Q, Ullah N, Zhang Y, Hao L, and Fan X. Helicobacter pylori adhesins: HpaA a potential antigen in experimental vaccines for H. pylori. Helicobacter. (2021) 26:e12758. doi: 10.1111/hel.12758
6. Fu H-W and Lai Y-C. The Role of Helicobacter pylori Neutrophil-Activating Protein in the Pathogenesis of H. pylori and Beyond: From a Virulence Factor to Therapeutic Targets and Therapeutic Agents. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 24:91. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010091
7. Wang X, Li J, Su Y, Chang C, and Yang Y. Freeze-thaw treatment assists isolation of IgY from chicken egg yolk. Food Chem. (2021) 364:130225. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130225
8. Leiva CL, Gallardo MJ, Casanova N, Terzolo H, and Chacana P. IgY-technology (egg yolk antibodies) in human medicine: A review of patents and clinical trials. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 81:106269. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106269
9. Thirumalai D, Visaga Ambi S, Vieira-Pires RS, Xiaoying Z, Sekaran S, and Krishnan U. Chicken egg yolk antibody (IgY) as diagnostics and therapeutics in parasitic infections - A review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2019) 136:755–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.118
10. Zhang XY, Isah MB, Dang M, Morgan PM, Sienczyk M, Bradley D, et al. Editorial: IgY technology: theory, technical aspects, applications, and innovations. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1267926. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1267926
11. Zhai K, Gong Y, Sun L, He L, Xue Z, Yang Y, et al. DNA starvation/stationary phase protection protein of Helicobacter pylori as a potential immunodominant antigen for infection detection. Helicobacter. (2023) 28:e12955. doi: 10.1111/hel.12955
12. Hong KS, Ki M-R, Ullah HMA, Lee E-J, Kim YD, Chung M-J, et al. Preventive effect of anti-VacA egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) on Helicobacter pylori -infected mice. Vaccine. (2018) 36:371–80. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.11.082
13. Horie K, Horie N, Abdou AM, Yang J-O, Yun S-S, Chun H-N, et al. Suppressive effect of functional drinking yogurt containing specific egg yolk immunoglobulin on helicobacter pylori in humans. J Dairy Sci. (2004) 87:4073–9. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73549-3
14. Yang Y-H, Park D, Yang G, Lee SH, Bae DK, Kyung J, et al. Anti-Helicobacter pylori effects of IgY from egg york of immunized hens. Lab Anim Res. (2012) 28:55–60. doi: 10.5625/lar.2012.28.1.55
15. Du Y, Li G, Li X, Jian X, Wang X, Xie Y, et al. Dietary immunoglobulin Y by targeting both gbpB and gtfB enhances the anticaries effect in rats. Int Dental J. (2024) 74(6):1298–305. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.05.006
16. Li ZX, Hu WD, Li BC, Li TY, Zhou XY, and Zhang Z. Egg yolk IgY against RHDV capsid protein VP60 promotes rabbit defense against RHDV infection. Veterinary Immunol Immunopathology. (2014) 157:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2013.10.002
17. Guo R, Wu S, Guan L, Xie Y, Yang X, Li Z, et al. Dietary multivalent anti- Helicobacter pylori immunoglobulin Y significantly increase the H. pylori eradication and improve the clinical symptoms in patients. Helicobacter. (2021) 26:e12843. doi: 10.1111/hel.12843
18. Cheng S, Li H, Luo J, Chi J, Zhao W, Lin J, et al. Egg yolk antibody combined with bismuth-based quadruple therapy in Helicobacter pylori infection rescue treatment: a single-center, randomized, controlled study. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1150129. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1150129
19. Hao N, Liu B, Zhao M, Lu M, Chen F, Kang J, et al. Real-world evidence of a novel tetravalent immunoglobulin Y effectiveness and safety in patients with the refractory Helicobacter pylori infection. BMC Infect Dis. (2024) 24:647. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09498-4
20. Carlsohn E, Nyström J, Bölin I, Nilsson CL, and Svennerholm A-M. HpaA is essential for Helicobacter pylori colonization in mice. Infect Immun. (2006) 74:920–6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.920-926.2006
21. Bustos-, Salinas-Pinta M, Vicuña-Almeida Y, de Oliveira RB, and Baldeón-Rojas L. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori genotypes: cagA, vacA (m1), vacA (s1), babA2, dupA, iceA1, oipA and their association with gastrointestinal diseases. A cross-sectional study in Quito-Ecuador. BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:197. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02838-9
22. Bugaytsova JA, Piddubnyi A, Tkachenko I, Rakhimova L, Edlund JO, Thorell K, et al. Vaccination with Helicobacter pylori attachment proteins protects against gastric cancer. bioRxiv : preprint server Biol. (2023). doi: 10.1101/2023.05.25.542131
23. Mony TJ, Kwon H-S, Won M-K, Kang Y-M, Lee S-H, Kim S-Y, et al. Anti-urease immunoglobulin (IgY) from egg yolk prevents Helicobacter pylori infection in a mouse model. Food Agric Immunol. (2019) 30:662–76. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2019.1617251
24. Malfertheiner P, Camargo MC, El-Omar E, Liou J-M, Peek R, Schulz C, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9:19. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00431-8
25. Suzuki H, Nomura S, Masaoka T, Goshima H, Kamata N, Kodama Y, et al. Effect of dietary anti-Helicobacter pylori-urease immunoglobulin Y on Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2004) 20 Suppl 1:185–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02027.x
Keywords: immunoglobulin Y, Helicobacter pylori, growth, infection, eradication rate
Citation: Deng S, Luo X, Du Y, Elbaiomy RG, He W, Guo R, El-Sappah AH, Jian X, Xie Y, Bakeer M, Li Z and Zhang Z (2025) Immunoglobulin Y antibodies against colonization-related genes block the growth and infection of Helicobacter pylori. Front. Immunol. 16:1582250. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1582250
Received: 24 February 2025; Accepted: 03 June 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025; Corrected: 03 July 2025.
Edited by:
Xy Zhang, University of Minho, PortugalReviewed by:
Shahram Nazarian, Imam Hossein University, IranAbdulmalik Abdullahi Salman, Ahmadu Bello University, Nigeria
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Luo, Du, Elbaiomy, He, Guo, El-Sappah, Jian, Xie, Bakeer, Li and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhi Zhang, emhhbmd6aGlAc3VzZS5lZHUuY24=; Zaixin Li, MTIxNjk5MzU0NEBxcS5jb20=; Mohammed Bakeer, QmFrZWVyaGVtYXRvbG9neUBBemhhci5lZHUuZWdhbmQ=; YmFrZWVyaGFlbWF0b2xvZ3lAZ21haWwuY29t
 Shiyuan Deng
Shiyuan Deng Xiaoling Luo2
Xiaoling Luo2 Rania G. Elbaiomy
Rania G. Elbaiomy Ahmed H. El-Sappah
Ahmed H. El-Sappah