- 1Department of Oncology, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Background: Acupuncture and moxibustion have been shown to be safe and effective methods for bidirectional immunomodulatory function. Clinical practice and many studies have shown that acupuncture and moxibustion have a certain clinical effect on immune promotion in patients with malignant tumors.
Methods: Eight electronic databases were searched systematically for articles published through December 31, 2024. Study Selection Randomized controlled trial studies (RCTs) that reported The number of T lymphocytes cells in patients with malignant tumors who received acupuncture and/or moxibustionon treatment were included. For continuous variables, effect estimates were calculated as mean difference (MD); and for dichotomous variables, the risk ratio (RR) was calculated. A funnel plot was used to analyze potential publication bias.
Results: 33 studies involving 2610 participants were included. Patients who received acupuncture and/or moxibustion treatment had higher CD3+, CD4+, CD4+/CD8+ and natural killer (NK) cell levels, but lower CD8+ levels. At the same time, the anti-tumor treatment effect was better than that of the control group.
Conclusions: Evidence from this meta-analysis, acupuncture and moxibustion can enhance the immune function and improve the prognosis of malignant tumor patients. Further studies are recommended to support and confirm these findings.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42023465759.
Introduction
According to Global Cancer Statistics 2020, there are 19.3 million new cancer cases and nearly 10 million cancer deaths estimatedly in worldwide, while the incidence and mortality of cancer are increasing year by year. It is estimated that by 2040, the global cancer burden will reach 28.4 million cases, an increase of 47% over 2020. The global situation of cancer prevention and control is grim (1). A weakened immune system leads to the development of tumors, and studies have shown that immune function is closely related to the prognosis of cancer (2). Recently, immunotherapy based on activating and enhancing the patient’s immune system has shown anti-tumor effects (3). Immunotherapy mainly includes immune checkpoint inhibitors, tumor antigen vaccines, and immune stimulating cytokines (4). These treatment methods can reshape the tumor microenvironment, enhance the immune function, strengthen anti-tumor immune responses, and thus suppress tumor growth and recurrence (5).
However, there are still some limitations and challenges in the application of immunotherapy in cancer at present (6). For example, the effectiveness and sustainability of immunotherapy are still not ideal, and individual differences are large. Some patients have poor tolerance to immunotherapy (7). In addition, some patients may also experience immune-related adverse reactions during immunotherapy, which may affect the treatment effect (8).
Acupuncture and moxibustion demonstrate bidirectional immune modulation (9). In cancer, these therapies synergistically boost anti-tumor immunity through distinct mechanisms. Electroacupuncture enhances lymphocyte populations and granzyme B secretion while activating interferon-mediated signaling pathways (10). Moxibustion suppresses adrenaline-driven signaling to activate natural killer (NK) cell activity and limit tumor growth, while also reducing regulatory T cell (Treg) infiltration in the tumor microenvironment—a strategy that curtails immune evasion and tumor progression (11, 12). Clinical observations further support their role in improving cancer patients’ immune function and prognosis, such as acupuncture at ST36 increasing NK cell counts and reducing tumor burden in cervical cancer (13, 14). Together, these findings underscore the capacity of acupuncture and moxibustion to reprogram immune responses, tipping the balance toward anti-tumor surveillance while mitigating immune dysregulation.
There is still a lack of systematic reviews of the effect of acupuncture and moxibustion on the immunity of patients with malignant tumors. This study aims to demonstrate and quantify the effect of acupuncture and moxibustion on the immune function of patients with malignant tumors, especially the number of T lymphocyte subsets, and to analyze the improvement of prognosis and quality of life of patients with malignant tumors.
Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis was performed according to the guideline of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 (15). Procedures and study inclusion criteria were registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023465759) (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/).
Data sources and search strategy
A systematic search for articles published in electronic databases (PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang database, VIP database and Chinese BioMedical Literature database) through December 31, 2024, was performed with no language or time restrictions. Medical subject headings (MeSH) terms and free text terms were used to obtain more comprehensive studies. The MeSH terms of “Acupuncture”, “Electroacupuncture”, “Moxibustion”, “Neoplasms”, “cancer”, “Immunity”, “T-Lymphocytes” were used to construct search Electroneedle, fire needle.
Eligible criteria
Inclusion criteria
1. The patients diagnosed with solid malignant tumor by histopathology;
2. Only RCTs were included;
3. The control group received conventional therapies (e.g., chemoradiotherapy, radiotherapy, surgical treatment, traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) treatment), and intervention groups received what control groups received plus acupuncture (including electroacupuncture, fire needle et.al) and/or moxibustion treatment;
4. The outcomes included immune function index (e.g., CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ or CD4+/CD8+).
Exclusion criteria
1. Repeated publication;
2. Outcome of interest not included;
3. Original data cannot be obtained by contacting the original author.
Study selection and data extraction
EndNote 21 was used to manage literature. Two researchers (YW and BLS) independently retrieved the titles and abstracts of all articles. Any disagreement in screening process should be consulted with another researchers (YZ) to make a decision. The relevant information were independently extracted and cross-checked by two researcher (YW and BLS) independently, which including: 1) basic information of the article: author’s name, year of publication, study type, and sample size; 2) patient characteristics: age, gender, cancer typology, pathological types and disease stage; and 3) treatment outcomes: clinical intervention, main points of acupuncture and/or moxibustionon, number of intervention, duration of intervention, and outcomes. Disagreements were solved by discussion or consulting third-party opinion (YZ). Imputing a change-from-baseline standard deviation (SD) and mean using a correlation coefficient. A SD of the change from baseline for the experimental intervention was input, using following formula:
(16)
Mean value of the change from baseline for the experimental intervention was input, using:
(17)
All data were rounded to two decimal places.
Outcomes of interest
The primary outcome of this study was immune function, mainly evaluated with the number of T lymphocyte subsets, including CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ or CD4+/CD8+. The secondary outcomes included the number of NK cell and clinical effective rate. The clinical effective rate = complete response (CR) + partial response(PR). CR and PR were defined by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST).
Assessment of study quality
Two researchers (YW and BLS) used the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool (RoB) (18) to evaluate the methodological quality of all included RCTs independently. The following seven domains were assessed: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting and other biases. The included RCTs were assessed as low, uncertain, or high risk of bias. The results were shown in RoB graph.
Statistical analysis
Review Manager software (version 5.4.1) was used to perform the meta-analysis. The random-effect model were used to synthesize evidence. Sensitivity or subgroup analysis were conducted to determine the cause of heterogeneity if it exists. The method of deleting studies one by one needed to be used to perform sensitivity analysis of the results to ensure stability. The subgroup analysis of the meta-analysis results for each outcome was required. The subgroup only includes items related to the comparison. Subgroup analysis was performed based on cancer typology and clinical interventions. For continuous variables, effect estimates were calculated as mean difference (MD); and for dichotomous variables, risk ratio (RR) were calculated. The effect estimates with their 95% confidence intervals (CI) were presented in the forest plots. If meta-analysis was not suitable, descriptive analysis was performed. Funnel plot was used to analyze potential publication bias. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 2610 articles were obtained by searching the database. There were 779 duplicate literature were found. After reading the title and abstract, 1582 articles were excluded. Then, after strict literature screening and reading the full-text articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 216 articles were eliminated as follows: 38 did not RCTs, 78 did not meet the inclusion criteria, 46 studies lack of outcome measures, 37 had incomplete data, thirteen articles were published in duplicate and four were non-solid tumors. Finally, a total of 33 eligible trials were included. The specific retrieval process is shown in Figure 1.
Study characteristics
Thirty-three RCTs were included with 2259 participants that divided into two groups that control group received conventional therapies (n=1130), and intervention groups received what control groups received plus acupuncture and/or moxibustion treatment (n=1129), including acupuncture, electroacupuncture, fire acupuncture and moxibustionon (19–51). Study characteristics of included studies was shown in Table 1. In participant, the average age of patients of the 33 studies were between 45 and 70 years old. There were 12 studies with lung cancer (20, 26, 29, 31, 33, 34, 37, 41, 46–49) and seven studies with gastrointestinal cancer (23, 30, 38, 39, 43–45). Nineteen studies used chemotherapy (19–28, 31, 33, 34, 37, 40–42, 46, 48), of which two studies combined with radiotherapy (24, 42) and two studies combined with TCM (20, 48). One study may have used one or more of the following: immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy (29). Eleven studies used acupuncture and moxibustion simultaneously (26, 28, 34, 36–38, 44, 45, 47, 48, 50). Fourteen studies used acupuncture only (19–24, 27, 31, 33, 39–42, 49), of which four studies used electroacupuncture (19, 22, 33, 39), two studies used fire acupuncture (31, 41). Moxibustion was used only in eight studies (25, 29, 30, 32, 35, 43, 46, 50). The most frequently used acupoints were: Zusanli (ST36), Qihai (CV6), Guanyuan (RN4), and Sanyinjiao (SP6). Study characteristics of included studies in Table 1.
Methodological quality of included studies
Twenty-seven RCTs were assessed as low risk for random sequence (21, 22, 24–34, 37–42, 44–51), including 24 RCTs used the random number table method (22, 24–32, 34, 37–40, 42, 44–51), one RCT used the simple randomization (41), two RCTs used the block randomization (21, 33) and the other six RCTs did not elaborate on specific methods of randomization (19, 20, 23, 35, 36, 43), so the risks were unclear. Due to the particularness of acupuncture and moxibustion, it is difficult to blind the practitioners of acupuncture and moxibustion. One study mentioned the blinding of researchers and patients (39), one study mentioned the blinding of statisticians and examiners (31), and one study mentioned the separation of researchers, data collection, and data statistical analysis (49), which considered low risk of bias. Three of the included studies achieved concealment by using sealed envelopes and were deemed to be at low risk of bias, which resulted in a low risk of bias in relative fields (28, 29, 39). None of the 33 studies had missing data or missing data that were comparable in each intervention group, and the reasons for missing data were similar, so they were rated as having a low attrition risk of bias. All 33 studies had a low risk of reporting bias. The quality assessment of the included trials risk of bias graph in Figure 2.
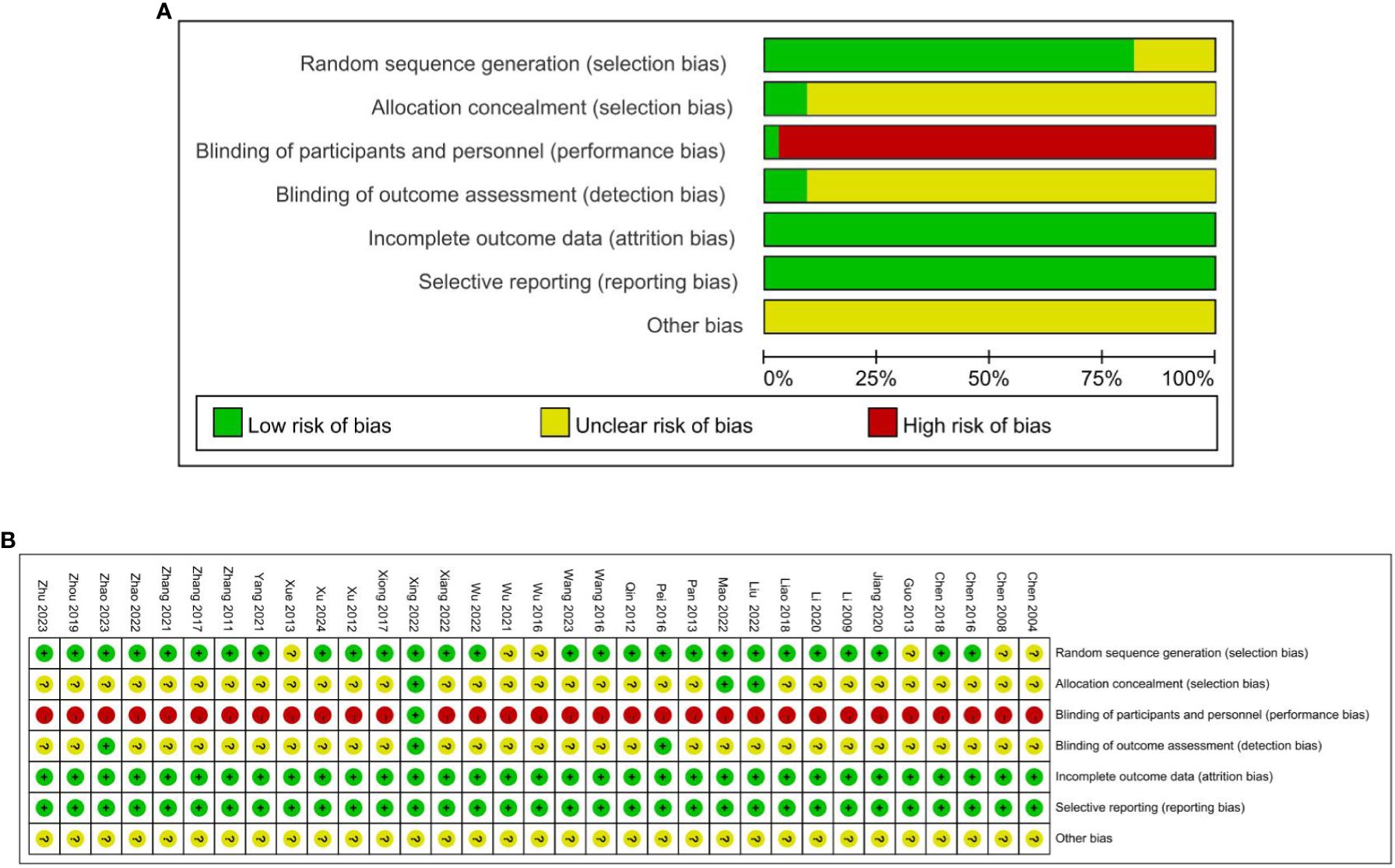
Figure 2. (A) Quality assessment of the included trials risk of bias graph. (B) Quality assessment of the included trials risk of bias graph.
Meta-analysis results
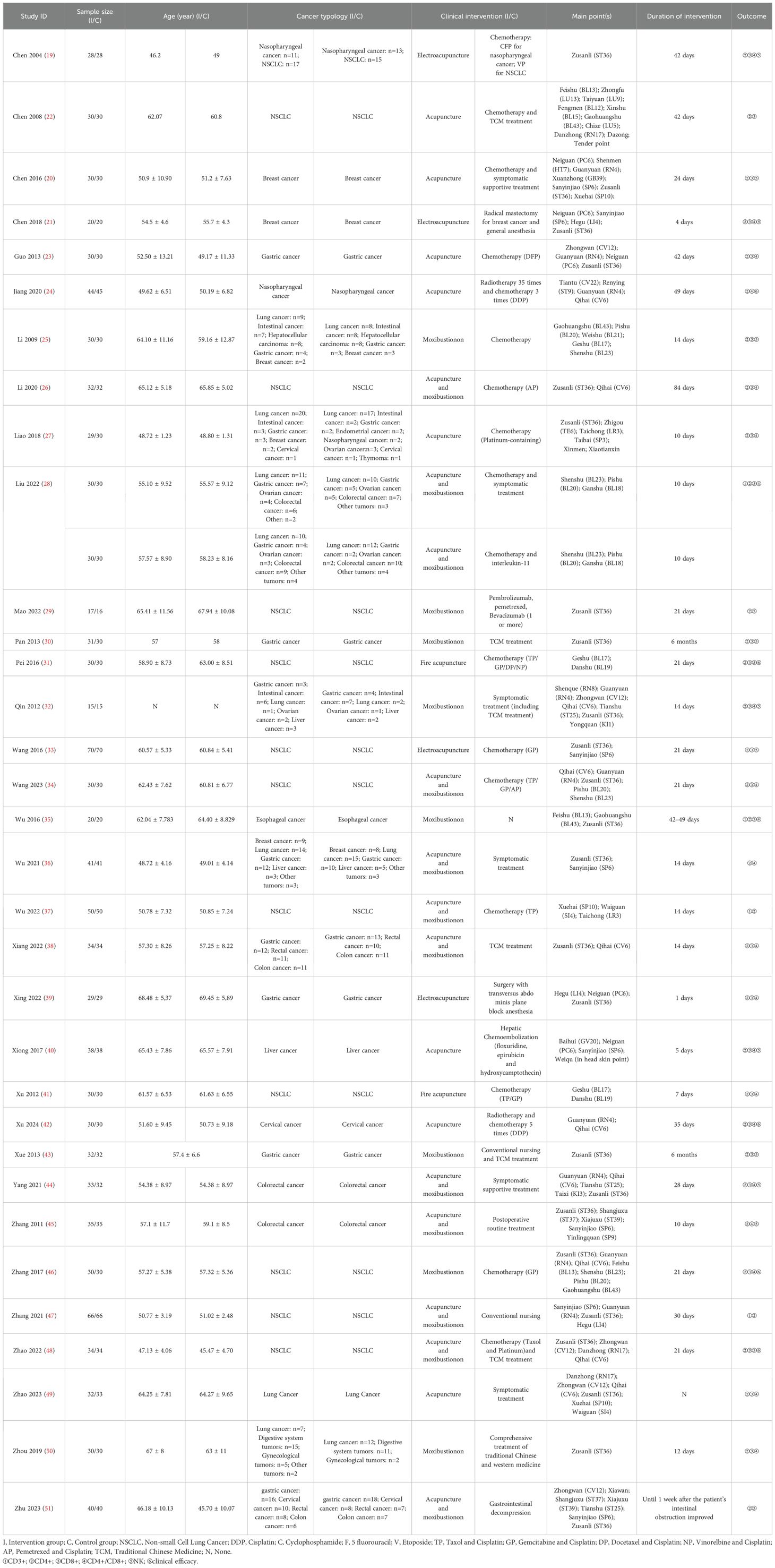
CD3+
All the included RCTs reported the CD3+ T lymphocyte counts of the patients. Meta-analysis results showed that: effect of the intervention group was significantly better than that of the control group in improving the CD3+ (MD = 4.97, 95% CI 3.81 to 6.13). Further subgroup analysis was conducted according to cancer typology, two groups clinical intervention (including combined chemotherapy, surgery, and other therapies), acupoint selection (according to whether the use of Zusanli (ST36) acupoint is divided), intervention group clinical treatment (according to the use of acupuncture, moxibustion, acupuncture and moxibustion divided) and duration of treatment (according to treatment duration of 30 days or more and less than 30 days divided). Subgroup analysis showed no statistical difference in cancer typology (P=1.00), control group clinical intervention (P=0.16), acupoint selection (P=0.64) and duration of treatment (P=0.53). The forest plot was shown in Supplementary Materials. (Supplementary Figures S1–S4).
The subgroup analysis revealed that the intervention group clinical treatment (P = 0.03) were the main source of heterogeneity in CD3+ and the forest plot was shown in Figure 3. No source of heterogeneity was identified by sensitivity analysis.
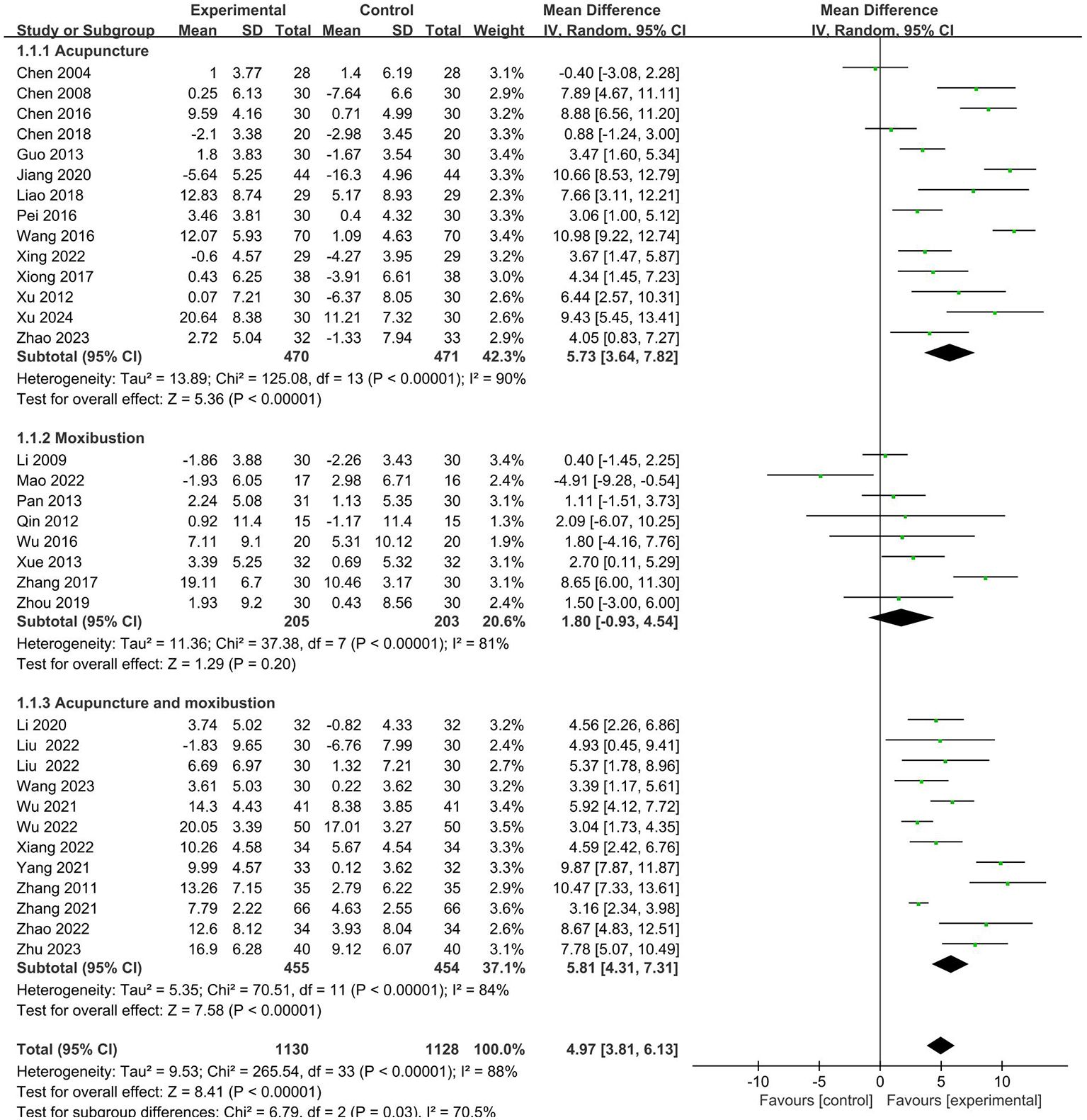
CD4+
A total of 33 studies (19–51) analyzed the effects of CD4+. The results showed that the intervention group had a more significant effect on increasing the CD4+ (MD = 4.25, 95% CI 2.80 to 5.69). Further subgroup analysis was conducted. It is shown that there is no statistical difference in cancer typology (P=0.23), two groups clinical intervention (P=0.80), acupoint selection (P=0.40) and duration of treatment (P=0.39). The forest plot was shown in Supplementary Materials. (Supplementary Figures S5–S8).
Similarly, the subgroup analysis revealed that the intervention group clinical treatment (P = 0.0001) were the main source of heterogeneity in CD4+. Forest plot was shown in Figure 4. No source of heterogeneity was identified by sensitivity analysis.
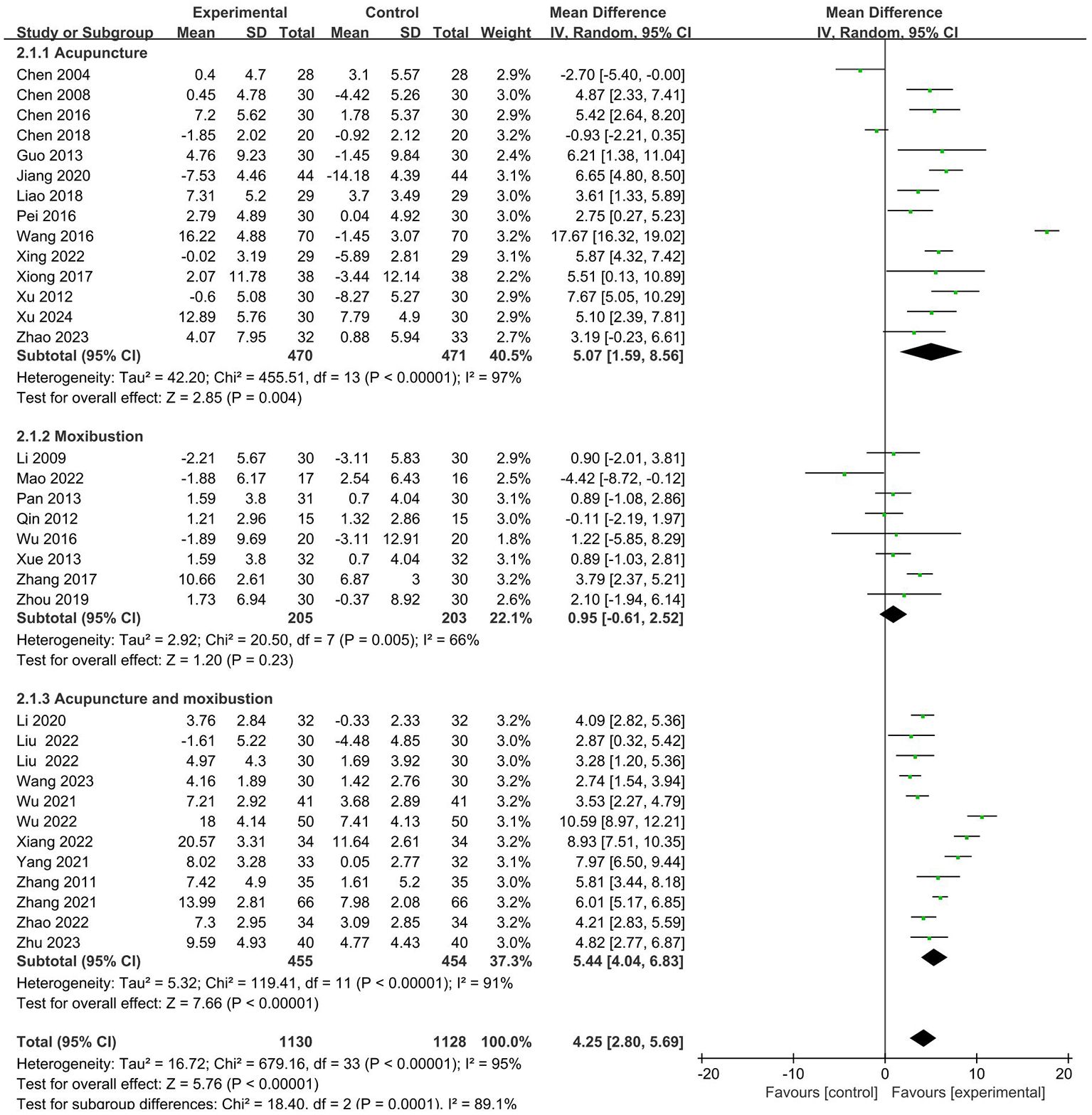
CD8+
26 RCTs with 1673 patients reported CD8+ index (19–23, 25–28, 30–35, 38–43, 45, 46, 48–50). Meta-analysis showed that the intervention group was decreased compared with the control group in CD8+ (MD = -1.56 95% CI -3.09– -0.03). The results are presented in Figure 5.
No sources of heterogeneity were identified by subgroup analysis in the intervention group clinical treatment (P = 0.07), cancer typology (P=0.37), two groups clinical intervention (P=0.48), acupoint selection (P=0.72) and duration of treatment (P=0.45). (Supplementary Figures S9–S13).
CD4+/CD8+
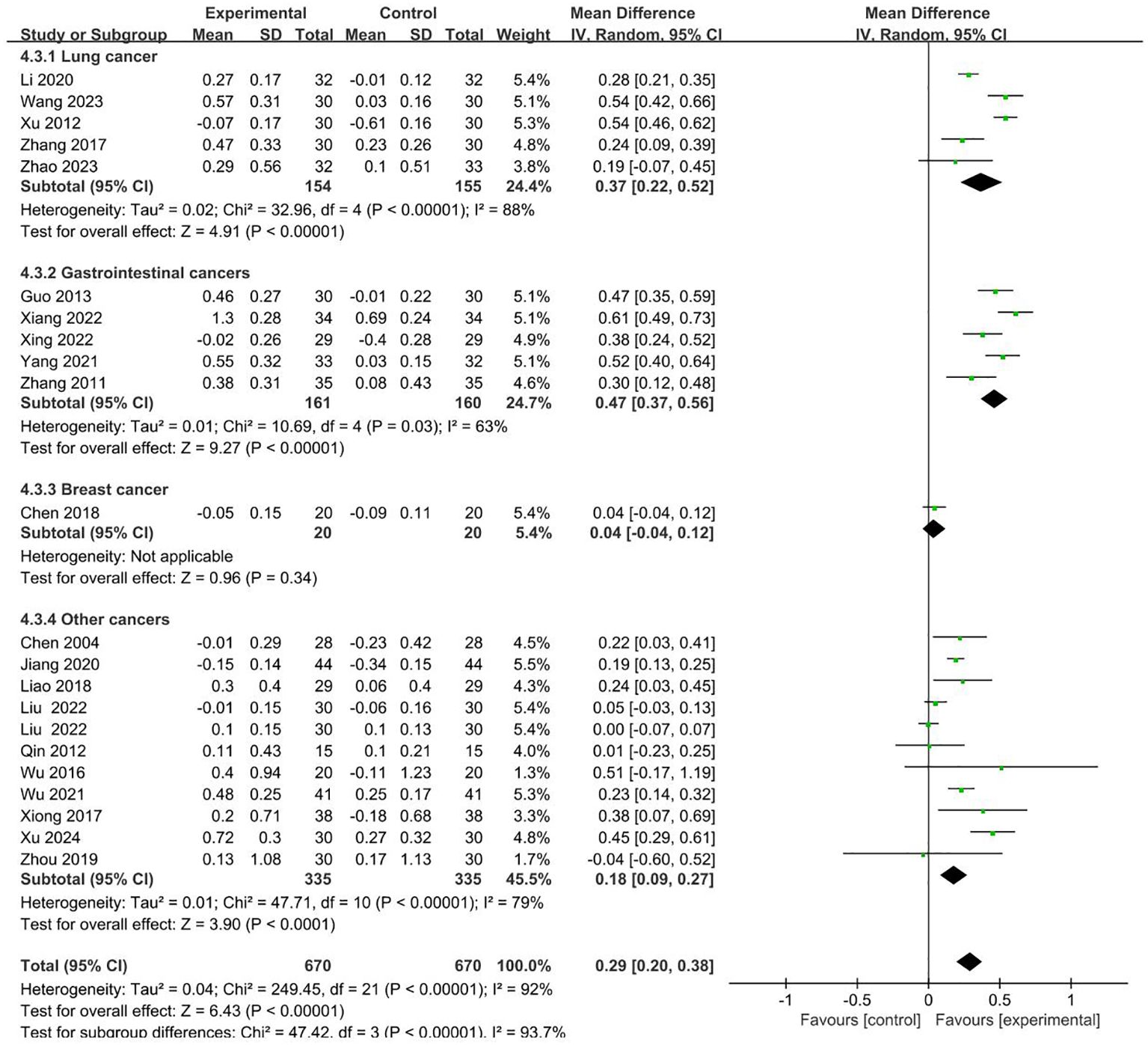
21 RCTs involving 670 cases in the intervention group and 670 cases in the control group reported CD4+/CD8+ in the outcome indicators (19, 22–24, 26–28, 32, 34–36, 38–42, 44–46, 49, 50). Meta-analysis showed that compared to control groups, intervention groups were significantly better in increasing the level of CD4+/CD8+ (MD = 0.29 95% CI 0.20–0.38). Subgroup analysis showed that the heterogeneity was associated with the cancer typology (P<0.00001). The results are presented in Figure 6.
No sources of heterogeneity were identified by subgroup analysis in the intervention group clinical treatment (P = 0.31), two groups clinical intervention (P=0.85), acupoint selection (P=0.63) and duration of treatment (P=0.65). (Supplementary Figures S14–S17).
NK
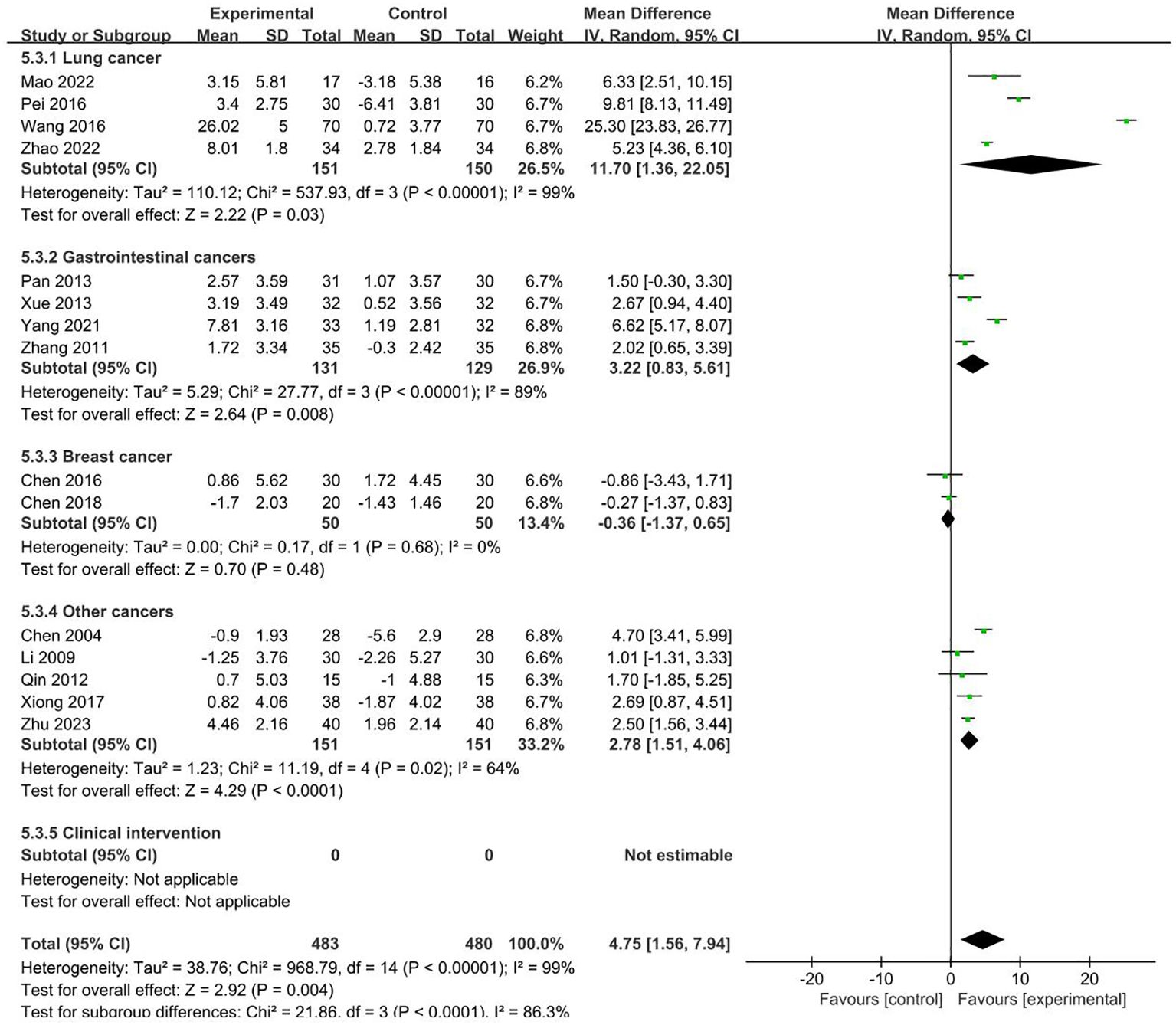
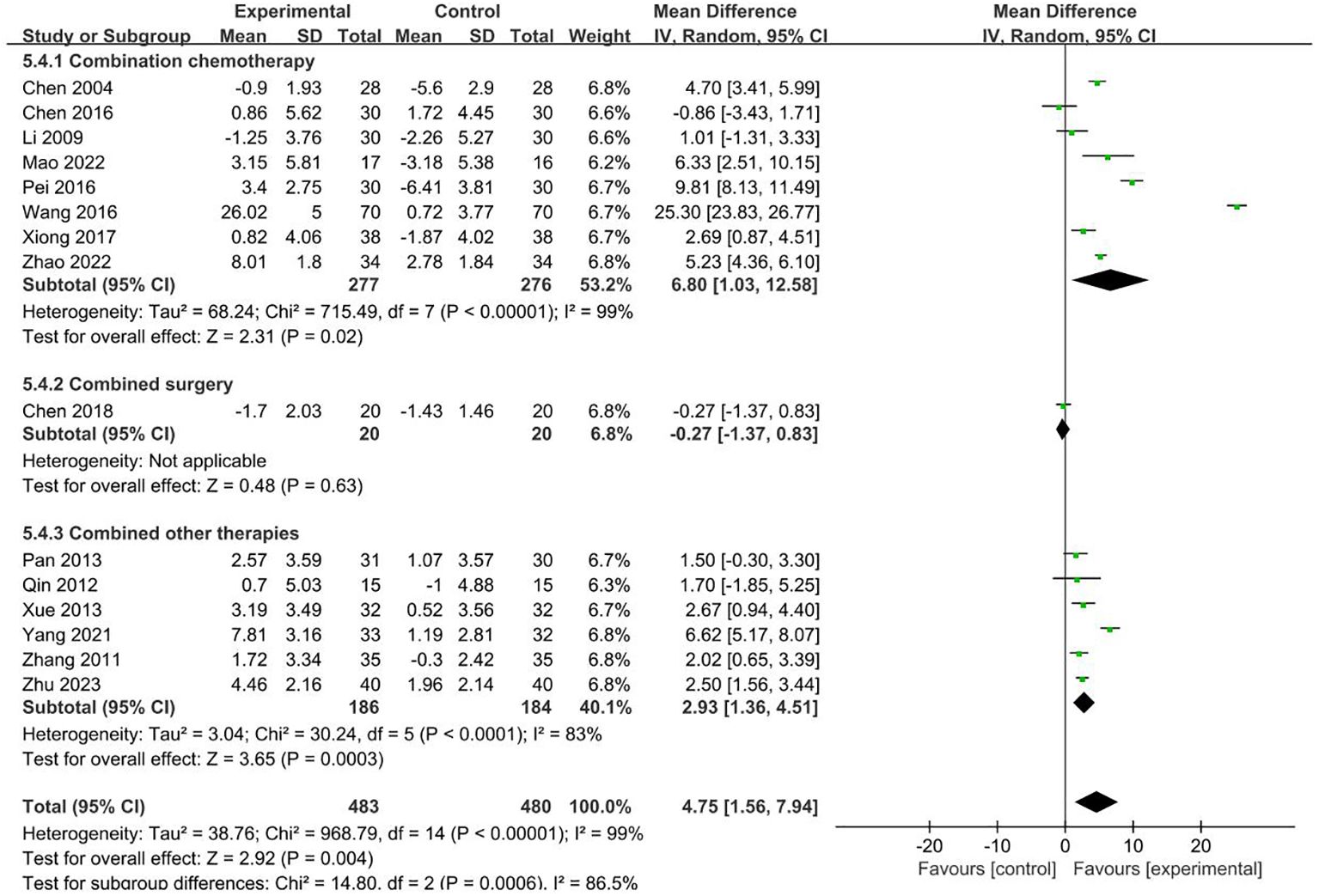
15 RCTs with 963 patients reported NK index (19, 21, 22, 25, 29–33, 40, 43–45, 48, 51). Meta-analysis showed that the intervention group was greatly improved compared with the control group in increasing NK (MD = 4.75, 95% CI 1.56–7.94). Subgroup analysis showed that the heterogeneity was associated with the cancer typology (P<0.0001) and two groups clinical intervention (P=0.0006). The results are presented in Figures 7, 8.
No sources of heterogeneity were identified by subgroup analysis in the intervention group clinical treatment (P = 0.21), acupoint selection (P=0.94) and duration of treatment (P=0.34). (Supplementary Figure S18–S20).
Clinical effective rate
Five RCTs with 337 patients reported clinical efficacy in outcome indicators (24, 31, 42, 46, 48). The results showed that compared to the patients who received conventional therapies, those who received acupuncture and moxibustion plus conventional therapies have a significantly better clinical efficacy (RR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.16–1.52). The forest plot is shown in Figure 9.
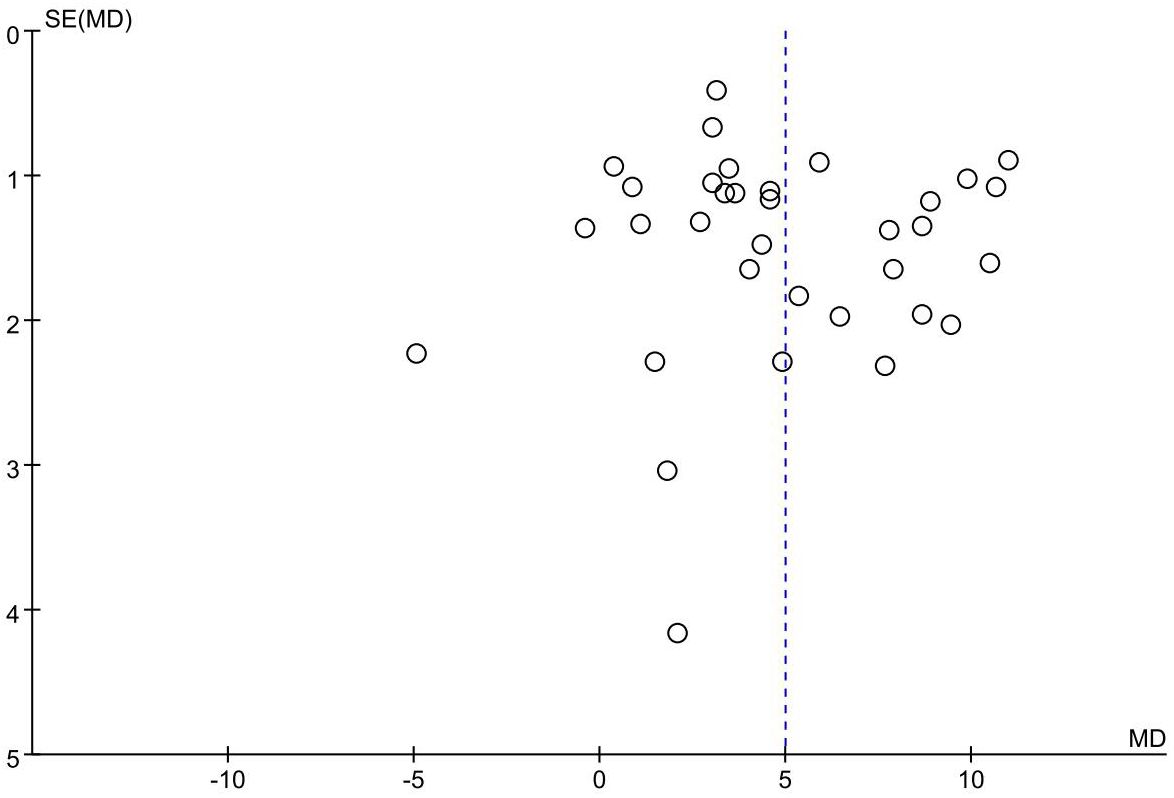
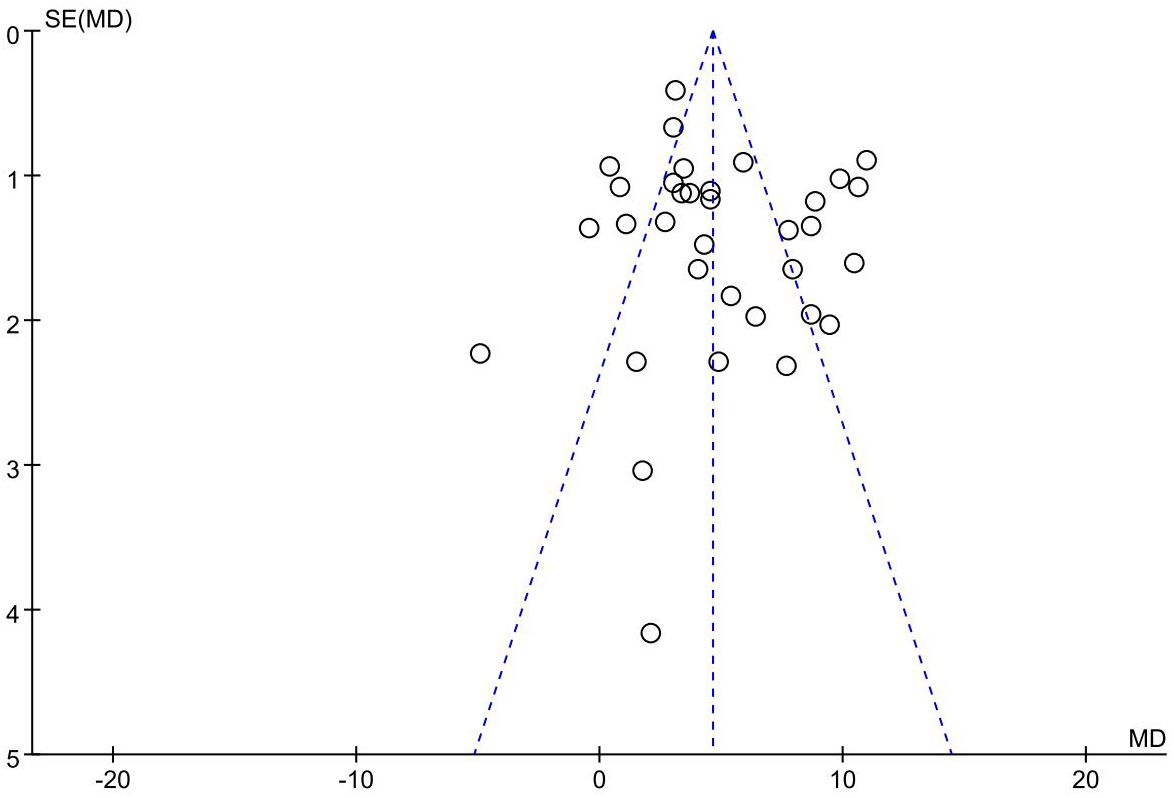
Publication bias
The funnel plot of the primary outcome (CD3+, CD4+) displayed an uneven distribution of studies, suggesting presence of publication bias. The result is presented in Figures 10, 11. The publication bias may be associated with negative results not being published and a part of studies had small sample sizes.
Discussion
The results showed that combined acupuncture and moxibustion, the levels of CD3+, CD4+, CD4+/CD8+, and NK cells increased, while the level of CD8+ cells decreased. Additionally, acupuncture and moxibustion indicated a positive effect on short-term clinical outcomes.
T lymphocytes cells are an important component of the immune system and are the main cellular component of the adaptive immune system, playing a crucial role in resisting pathogen invasion and suppressing tumorigenesis (52). A large number of studies have shown that T lymphocytes in the tumor microenvironment play an important role in the anti-tumor response. High levels of tumor-infiltrating T cells usually indicate a better prognosis for patients (53–55). CD3+ can effectively reflect the levels of CD4+ and CD8+. CD4+ directly reflects the immune function of the patient (56). CD8+ participates in the process of transmitting activation signals from T lymphocyte receptors recognizing antigens, and it belongs to cytotoxic T lymphocytes. CD8+ can produce negative regulation on T lymphocyte and B lymphocyte function through its own and related cytokines, inhibiting the formation of cellular immunity and antibodies, and its increased level can aggravate the immune dysregulation (57). CD4+/CD8+ balance is a key factor in maintaining the immune response (58). NK cells are an important component of tumor immune surveillance and play an important role in preventing tumor growth (59).
However, it has been proven that CD8+ T lymphocytes are associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients. As the tumor grows and develops, it can stimulate and induce the proliferation of CD8+ T lymphocytes, and the increase of CD8+ T lymphocytes can promote the growth of tumor cells to a certain extent, increase the risk of metastasis and recurrence, and is not conducive to the prognosis (60), and most patients exhibit a decrease in CD3+ and CD4+, leading to an imbalance of CD4+/CD8+ and a predominance of cell-mediated immune negative effects (61). The study by Muhammad Ramzan et al. showed that high infiltration of CD8+ cells in tumor tissue suggests a high recurrence rate and poor prognosis in HCC patients (62). Similarly, in colorectal cancer patients, studies have shown that high CD8+ T lymphocyte content may be associated with adverse clinical outcomes, and a decrease in CD4+ T lymphocyte content and a decrease in the CD4+/CD8+ ratio indicate that CRC is in a progressive state and undergoing accelerated proliferation (63). In lung cancer and melanoma patients, CD8+ T cell levels are low before treatment and ultimately derive a durable benefit from immunotherapy (64, 65).
The possible reasons for CD8+ cell elevation being associated with poor prognosis in patients are as follows: in the context of long-term suppressive tumor microenvironment, tumor-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes are prone to enter the “T lymphocyte exhaustion of function” stage (66–68), characterized by increased expression of immune inhibitory receptors such as lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3), cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4), and T cell immunoglobulin 3 (TIM-3) on the surface of lymphocytes, impaired production of cytokines such as IL-2, TNFα, and IFNγ, and impaired tumor killing ability (69, 70). Relevant studies show that the increase of CD8 +T cells may be related to the mechanism of tumor immune escape (71). This also suggests that in the future further researches on the effect of acupuncture on CD8+ cell function are needed.CD4+ cells and CD8+ cells are mutually inducing and restraining, forming a network of cells that is important for regulating immune responses and maintaining immune homeosta (72). When the CD8+ cells increases, the ratio of the CD4+ and CD8+ cells changes, it can cause the immune function of the body to decrease, thereby weakening the anti-tumor ability of the body (73). Meanwhile, CD8+ T cells have cytotoxic effects on antigen presenting cells, they can also inhibit the anti-tumor effect of CD4+ cells by producing inhibitory cytokines (74).
Furthermore, a compelling body of clinical evidence reveals that these traditional therapies can significantly improve the humoral immune levels and cytokine profiles of cancer patients. For instance, research has demonstrated that acupuncture and moxibustion can elevate key humoral immune markers such as IgM, IgG, C3, and C4 (48) and reduce TNF-α, TGF-β1 levels, increase IL-2 levels in tumor patients (24, 33, 41, 42), suggesting a potential mechanism for bolstering the body’s immune defenses against cancer.
Subgroup analysis showed that different acupuncture and moxibustion methods were one of the main sources leading to heterogeneity of CD3+ and CD4+. The heterogeneity of CD4+/CD8+ and NK cells is caused by different types of cancer, and the heterogeneity of NK cells is also caused by different stages of treatment.
In the field of clinical research, the selected acupoints and the determined treatment duration exhibit a relatively diverse range of characteristics. This study focuses on conducting subgroup analyses based on two key factors: whether the Zusanli acupoint is selected and whether the treatment duration exceeds 30 days. The analysis results indicate that these two factors are not the root causes of the heterogeneity in this study. However, the clinical issue of how to select the optimal acupoints and determine the optimal treatment duration to effectively enhance the immune function of cancer patients remains at a stage that requires in-depth research and exploration. More high-quality research results are needed to provide strong evidence and references.
Limitations
The meta-analysis has several limitations. Due to limited resources, this study only retrieved eight databases of published studies, which were all in Chinese or English. All included patients were from China. The single - source samples inevitably caused racial and genetic bias. They can’t adequately represent the diversity and complexity in disease features and genetic background across different races. This may limit the generalizability of the research findings. In addition, the majority of the included studies had small sample sizes, which may limit the persuasiveness of the results to some extent. Due to the uniqueness of acupuncture and moxibustion, all trials included in the study were not blinded to the acupuncturis. None of the 33 studies followed patients for a long time, so we cannot know the long-term effects of acupuncture and moxibustion on cancer patients. In the publication bias section, there was publication bias in CD3+ and CD4+ studies. This bias may be related to negative results not being published.
Implications for future research and clinical practice
In clinical practice, acupuncture and moxibustion can be used as an auxiliary therapeutic measure for patients who can accept it. Based on the above limitations, more large-sample, multi-center and more diverse participant recruitment clinical trials are needed in the future. By including individuals from various racial and ethnic backgrounds, researchers can obtain a broader and more representative dataset. In the study design, strict prospective design methods should be used to ensure the quality of outcomes, especially the blind setting and long-term follow-up of outcome indicators. Only one of the studies included partial patients who combined immunotherapy, and the clinical efficacy of acupuncture therapy to combine immunotherapy needs to be further confirmed by more research. In addition, the optimal acupuncture intervention duration and frequency for enhancing immune function need to be further explored in future studies.
Conclusion
In summary, in this systematic review and meta-analysis of 33 trials, including 1,378 patients with malignant tumors, acupuncture and moxibustion was found to have statistically significant and clinically meaningful effects on improving immune function compared to no acupuncture and moxibustion.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
YW: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. BS: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. LF: Writing – review & editing. YX: Writing – review & editing. YF: Writing – review & editing. RW: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by High Level Chinese Medical Hospital Promotion Project - Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Evidence-based Research Special Project - Clinical Efficacy Evaluation and Mechanism Research of Potential Advantage Diseases of Acupuncture (HLCMHPP2023089).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1685492.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1583522/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71(3):209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660, PMID: 33538338
2. Parkin J and Cohen B. An overview of the immune system. Lancet. (2001) 357(9270):1777–89. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04904-7, PMID: 11403834
3. Igarashi Y and Sasada T. Cancer vaccines: toward the next breakthrough in cancer immunotherapy. J Immunol Res. (2020) 2020:5825401. doi: 10.1155/2020/5825401, PMID: 33282961
4. Rui R, Zhou L, and He S. Cancer immunotherapies: advances and bottlenecks. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1212476. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1212476, PMID: 37691932
5. Riley RS, June CH, Langer R, and Mitchell MJ. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2019) 18(3):175–96. doi: 10.1038/s41573-018-0006-z, PMID: 30622344
6. Szeto GL and Finley SD. Integrative approaches to cancer immunotherapy. Trends Cancer. (2019) 5(7):400–10. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.05.010, PMID: 31311655
7. Simmons K, Kee BK, Raghav KPS, Johnson B, Kopetz S, Willis J, et al. Clinical outcomes following termination of immunotherapy due to long-term benefit in MSI-H colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:3585–5. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.3585
8. Kennedy LB and Salama AKS. A review of cancer immunotherapy toxicity. CA Cancer J Clin. (2020) 70(2):86–104. doi: 10.3322/caac.21596, PMID: 31944278
9. Liu F, Wang Y, Lyu K, Du X, Zhou M, Shi J, et al. Acupuncture and its ability to restore and maintain immune homeostasis. QJM. (2024) 117(3):167–76. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcad134, PMID: 37318994
10. Wang Y, Liu F, Du X, Shi J, Yu R, Li S, et al. Combination of anti-PD-1 and electroacupuncture induces a potent antitumor immune response in microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. (2024) 12(1):26–35. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0309, PMID: 37956404
11. Hu D, Shen W, Gong C, Fang C, Yao C, Zhu X, et al. Grain-sized moxibustion promotes NK cell antitumour immunity by inhibiting adrenergic signalling in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25(6):2900–8. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16320, PMID: 33506637
12. Li L, Shi Y, Luo M, and Zhao CL. Effects of moxibustion on Treg cells in sarcoma microenvironment. J Integr Med. (2021) 19(3):251–7. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2021.02.001, PMID: 33642209
13. Stone JA and Johnstone PA. Mechanisms of action for acupuncture in the oncology setting. Curr Treat Options Oncol. (2010) 11(3-4):118–27. doi: 10.1007/s11864-010-0128-y, PMID: 21108052
14. Saraswati W, Dahlan EG, Saputra K, and Sutrisno TC. Effect of electroacupuncture on natural-killer cells and tumor size in patients with cervical squamous-cell carcinoma: A randomized controlled trial. Med Acupunct. (2019) 31(1):29–36. doi: 10.1089/acu.2018.1316, PMID: 30805077
15. Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. (2015) 4(1):1. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-4-1, PMID: 25554246
16. Zhang L and Han K. How to analyze change from baseline: Absolute or percentage change. D-level Essay in Statistics. Dalarna, Sweden: Dalarna University (2009).
17. Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available online at: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-06.
18. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928, PMID: 22008217
19. Chuang C, Zuojun Z, Hanzhong L, Tan Z, Lu Y, Huang Z, et al. Clinical observation on the detoxification effect of electroacupuncture at zusanli (ST 36) in chemotherapy. New Chin Med. (2004) 03:46–7. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2004.03.024
20. Jun C, Naiqing F, Lei W, Wu X, Xiao H, Sun C, et al. Clinical study on the treatment of cancer-related fatigue in breast cancer patients with acupuncture. Jiangsu J Traditional Chin Med. (2016) 48(12):56–8.
21. Chen M, Lei H, Zheng S, and Wang J. Effects of acupuncture on analgesia and immune function in breast cancer patients during the perioperative period. J Int Traditional Chin Med. (2018) 40(1):22–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4246.2018.01.006
22. Delian C. Observation on the Short-term Therapeutic Effect of Acupuncture Combined with TCM Syndrome Differentiation and Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Stage Ⅲb and Ⅳ NSCLC. Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, PRC: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2008).
23. Yunqian G. Observation on the Therapeutic Effect of the Method of Consolidating the Root and Clearing the Source by Acupuncture on Gastric Cancer Patients Undergoing DCF Chemotherapy. Ji’nan, Shandong Province, PRC: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2013).
24. Shuai J, Ting W, and Guohong W. Effects of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with chemoradiotherapy on nasopharyngeal carcinoma and their impact on VEGF, TGF-β1 and immune function in patients. Gen Pract Clin Educ. (2020) 18(01):24–27+31. doi: 10.13558/j.cnki.issn1672-3686.2020.001.006
25. Xing L. Clinical Study on the Effects of Ginger-separated Moxibustion on Cellular Immunity and Quality of Life in Chemotherapy Patients. Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, PRC: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2009).
26. Li D, Yu J, Li R, Sun X, and Wang A. Analysis of the effects of warm acupuncture on gastrointestinal reactions and immune function in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Chin Med Innovation. (2020) 17(04):142–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2020.04.036
27. Liao G, Long S, Deng H, Li Q, Huang J, Gan Z, et al. Clinical study on the detoxification effect of spiral acupuncture on platinum-based chemotherapy regimens for Malignant tumors. Chin Med Herald. (2018) 15(19):117–20.
28. Wei L. Clinical Research on the Treatment of Chemotherapy-Related Thrombocytopenia in Tumors with Warm Acupuncture on Back-Shu Points. Hefei, Anhui Province, PRC: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (2022).
29. Jinfeng M. The Impact of Grain-Size Moxibustion on Zusanli (ST 36) on the Quality of Life and Immune Function of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, PRC: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (2022).
30. Pan C, Xue H, Shen K, Zhang H, Zhou H, Hu B, et al. Research on the improvement of immune function and quality of life in gastric cancer patients by moxibustion. Shanghai J Acupuncture Moxibustion. (2013) 32(09):726–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0957.2013.09.726
31. Wenyia P. Research on the Effects of Fire Needle at Sifahua Points on Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy Based on Th1/Th2 and MMPs/TIMPs. Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, PRC: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2016).
32. Xiaoyan Q. Clinical Research on the Treatment of Cancer-Related Fatigue with Warm Moxibustion. Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, PRC: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2012).
33. Wang X, Fang H, Wang Y, and Wang H. The effect of electroacupuncture on immune function in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer undergoing palliative Chemotherapy. Modern Pract Med. (2016) 28(08):1009–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2016.08.016
34. Jing W. Clinical Research on the Treatment of Cancer-Related Fatigue in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer After Chemotherapy with Warm Acupuncture. Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province, PRC: Hubei University of Chinese Medicine (2023).
35. Shuang W. Clinical Observation on the Prevention and Treatment of Radiation-Induced Lung Injury in Esophageal Cancer Patients After Radiotherapy with Leiho Moxibustion. Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, PRC: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (2016).
36. Xiaomin W. Clinical efficacy analysis of acupuncture and moxibustion in treating leukopenia after chemotherapy for Malignant tumors. Dis Surveillance Control. (2021) 15(03):207–9. doi: 10.19891/j.issn1673-9388.(2021)03-0207-03
37. Jun W. Observation on the therapeutic effect of tiaoyi sanjiao acupuncture and moxibustion on cancer-related fatigue in advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its impact on lymphocyte count. J Traditional Chin Med External Therapies. (2022) 31(02):96–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-978X.2022.02.043
38. Tingting X and Dan W. Analysis of the effect of warm acupuncture combined with weishu capsules on gastrointestinal Malignant tumors. Med Theory Pract. (2022) 35(03):426–8. doi: 10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2022.03.026
39. Xing R, Yang Y, Zhang M, Wang H, Tan M, Gao C, et al. Effect of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation combined with transversus abdominis plane block on postoperative recovery in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic gastric cancer surgery: A randomized controlled trial. Pain Ther. (2022) 11(4):1327–39. doi: 10.1007/s40122-022-00429-2, PMID: 36098938
40. Huisheng X and Qian L. The influence of acupuncture and moxibustion on TCM syndromes, quality of life and cellular immunity in patients with primary liver cancer undergoing transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Chin Community Doctor. (2017) 33(30):108–109+111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2017.30.65
41. Yanlin X. The effect of fire needle at Sifahua points on IL-2, TNF-a and T cell subsets in lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, PRC: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2012).
42. Xu Q, Luo L, Wang H, and Zeng C. The effect of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy on local advanced cervical cancer and its influence on patients' immune function. Contemp Med. (2024) 30(13):6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2024.13.02
43. Haiyan X. The effect of mild moxibustion at Zusanli on the immune function of patients with gastric cancer. Shanghai Nurs. (2013) 13(05):29–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8399.2013.05.007
44. Fan Y. Clinical research on the treatment of cancer-related fatigue in colorectal cancer patients with warm acupuncture and moxibustion. Hefei, Anhui Province, PRC: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (2021).
45. Shuangyan Z and Yeqin D. The effect of warm acupuncture and moxibustion on gastrointestinal function and immune function in patients after colorectal cancer surgery. Chin Acupuncture Moxibustion. (2011) 31(06):513–7. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2011.06.013
46. Bin Z. Clinical observation on the effect of Yang-strengthening and tonifying moxibustion on T lymphocyte subsets and quality of life in patients with advanced NSCLC. Jinzhong, Shanxi Province, PRC: Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine (2017).
47. Jinmei Z, Guojun Z, and Yingying L. The promoting effect of warm acupuncture and moxibustion nursing pathway on rapid recovery in patients undergoing lung cancer surgery. Tianjin J Traditional Chin Med. (2021) 38(05):638–41. doi: 10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2021.05.20
48. Zhao X, Qiao S, Liu X, Tong Y, Yan H, Liu H, et al. The effect of Xihuang Pill combined with acupuncture and moxibustion on immune function and quality of life in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. World J Chin Med. (2022) 17(14):2021–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2022.14.012
49. Gaofei Z. Clinical observation on the effect of Sanjiao acupuncture in improving cancer-related fatigue (Qi and blood deficiency type) in lung cancer patients. Tianjin, PRC: Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2023).
50. Zhou T, Li W, Yu J, and Jia Y. The effect of moxibustion at Zusanli on the quality of life of patients with advanced Malignant tumors. Chin Acupuncture Moxibustion. (2019) 39(02):133–136+146. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2019.02.005, PMID: 30942030
51. Li Z, Tianlong H, and Jinfeng J. The effect of warm acupuncture and moxibustion combined with conventional gastrointestinal decompression on intestinal obstruction during the chemotherapy interval after abdominal tumor surgery and its influence on immune function. Sichuan J Traditional Chin Med. (2023) 41(04):195–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3649.2023.4.sczy202304054
52. Quinn S, Lenart N, Dronzek V, Scurti G, Hossain NM, Nishimura MI, et al. Genetic modification of T cells for the immunotherapy of cancer. Vaccines. (2022) 10(3):10. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10030457, PMID: 35335089
53. Kagamu H, Kitano S, Yamaguchi O, Yoshimura K, Horimoto K, Kitazawa M, et al. CD4+ T-cell immunity in the peripheral blood correlates with response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Cancer Immunol Res. (2020) 8(3):334–44. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0574, PMID: 31871122
54. Zhang Z, Zhang S, Xu Y, Liu X, and Dong W. The differences in the distribution characteristics and prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocyte subsets between lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. Chin Clin Oncol. (2024) 13(6):83. doi: 10.21037/cco-24-62, PMID: 39806849
55. Yang B, Li Z, Li P, Liang B, Liu YH, Feng ES, et al. Role of T cell metabolism in brain tumor development: a genetic and metabolic approach. BMC Neurol. (2025) 25(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-04015-1, PMID: 39780065
56. Liu S, Meng Y, Liu L, Lv Y, Yu W, Liu T, et al. CD4+ T cells are required to improve the efficacy of CIK therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13(5):441. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04882-x, PMID: 35523765
57. Reina-Campos M, Scharping NE, and Goldrath AW. CD8+ T cell metabolism in infection and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21(11):718–38. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00537-8, PMID: 33981085
58. Salih MM, Almehmadi M, Shafie A, Alsharif A, Alsiwiehri N, El-Askary A, et al. Evaluation of CD4+:CD8+ Ratio in patients with cervical cancer and the levels of inflammatory markers. In Vivo. (2022) 36(5):2414–21. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12975, PMID: 36099148
59. Sun JC, Beilke JN, and Lanier LL. Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells. Nature. (2009) 457(7229):557–61. doi: 10.1038/nature07665, PMID: 19136945
60. Wu M, Lou J, Zhang S, Chen X, Huang L, Sun R, et al. Gene expression profiling of CD8+ T cells induced by ovarian cancer cells suggests a possible mechanism for CD8+ Treg cell production. Cell Prolif. (2016) 49(6):669–77. doi: 10.1111/cpr.2016.49.issue-6, PMID: 27641758
61. Zhang X and Jing J. Effect of peripheral blood lymphocytes on prognosis of multiple cancers. Cancer Control. (2023) 30:10732748231202921. doi: 10.1177/10732748231202921, PMID: 37815060
62. Ramzan M, Sturm N, Decaens T, Bioulac-Sage P, Bancel B, Merle P, et al. Liver-infiltrating CD8(+) lymphocytes as prognostic factor for tumour recurrence in hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. (2016) 36(3):434–44. doi: 10.1111/liv.2016.36.issue-3, PMID: 26215124
63. Yuan C, Huang J, Li H, Zhai R, Zhai J, Fang X, et al. Association of clinical outcomes and the predictive value of T lymphocyte subsets within colorectal cancer patients. Front Surg. (2023) 10:1102545. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1102545, PMID: 37206348
64. Nabet BY, Esfahani MS, Moding EJ, Hamilton EG, Chabon JJ, Rizvi H, et al. Noninvasive early identification of therapeutic benefit from immune checkpoint inhibition. Cell. (2020) 183(2):363–76. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.001, PMID: 33007267
65. Krieg C, Nowicka M, Guglietta S, Schindler S, Hartmann FJ, Weber LM, et al. High-dimensional single-cell analysis predicts response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat Med. (2018) 24(2):144–53. doi: 10.1038/nm.4466, PMID: 29309059
66. Poschke I, De Boniface J, Mao Y, and Kiessling R. Tumor-induced changes in the phenotype of blood-derived and tumor-associated T cells of early stage breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer. (2012) 131(7):1611–20. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v131.7, PMID: 22190148
67. Kim PS and Ahmed R. Features of responding T cells in cancer and chronic infection. Curr Opin Immunol. (2010) 22(2):223–30. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.02.005, PMID: 20207527
68. Zebley CC, Zehn D, Gottschalk S, and Chi H. T cell dysfunction and therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Immunol. (2024) 25(8):1344–54. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01896-9, PMID: 39025962
69. Sun LN, Su YH, Jiao AJ, Wang X, and Zhang B. T cells in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8(1):235. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01471-y, PMID: 37332039
70. Zhai Y, Liang X, and Deng M. Myeloid cells meet CD8+ T cell exhaustion in cancer: What, why and how. Chin J Cancer Res. (2024) 36(6):616–51. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.06.04, PMID: 39802897
71. Chen Y, Xu J, Wu X, Yao H, Yan Z, Guo, et al. CD147 regulates antitumor CD8+ T-cell responses to facilitate tumor-immune escape. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18(8):1995–2009. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00570-y, PMID: 33177695
72. Wolf D, Sopper S, Pircher A, Gastl G, Wolf AM, et al. Treg(s) in cancer: friends or foe? J Cell Physiol. (2015) 230(11):2598–605. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25016, PMID: 25913194
73. Yan Y, Wang X, Liu C, and Jia J. Association of lymphocyte subsets with efficacy and prognosis of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma: a retrospective study. BMC Pulm Med. (2022) 22(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01951-x, PMID: 35484541
Keywords: acupuncture, moxibustion, T lymphocyte cells, malignant tumors, meta-analysis
Citation: Wang Y, Sui B, Zhang Y, Fang L, Xie Y, Fang Y and Wang R (2025) Effect of acupuncture and moxibustion on the immune function of patients with malignant tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1583522. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1583522
Received: 26 February 2025; Accepted: 24 June 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025; Corrected: 10 October 2025.
Edited by:
Yi-Hung Chen, China Medical University, TaiwanReviewed by:
Paulo Sargento, Escola Superior de Saúde Ribeiro Sanches, PortugalYajie Ji, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Xuancheng Zhou, Southwest Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Sui, Zhang, Fang, Xie, Fang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Zhang, enlsenk1MDFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yan Wang
Yan Wang Bailu Sui1,2†
Bailu Sui1,2† Ying Zhang
Ying Zhang Yi Xie
Yi Xie Yuhang Fang
Yuhang Fang Runxi Wang
Runxi Wang
![Forest plot showing risk ratios for five studies comparing experimental and control groups. Most studies favor the experimental group with overall risk ratio 1.32 [1.16, 1.52]. Heterogeneity is low with I² = 0%.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1583522/fimmu-16-1583522-HTML-r1/image_m/fimmu-16-1583522-g009.jpg)