- 1Department of Biomedical, Surgical and Dental Sciences, University of Milan, Milan, Italy
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery, Fatebenefratelli Hospital, ASST Fatebenefratelli Sacco, Milan, Italy
- 3Department of Clinical Sciences and Community Health, University of Milan, Milan, Italy
- 4Internal Medicine Department, Fatebenefratelli Hospital, ASST Fatebenefratelli Sacco, Milan, Italy
- 5Department of Biomedical and Clinical Sciences, University of Milan, Fatebenefratelli Hospital, Milan, Italy
- 6Department of Otorhinolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery, ASST Grande Ospedale Metropolitano Niguarda, Milan, Italy
- 7Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, Italy
- 8Department of Otorhynolaringoiatry, ASPRagusa-Hospital Giovanni Paolo II, Ragusa, Italy
- 9Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Enna Kore, Enna, Italy
- 10Department of Pediatrics, Service of Pediatric Rheumatology, Fatebenefratelli Hospital, Milano, Italy
- 11Internal Medicine Department, Sacco Hospital, ASST Fatebenefratelli Sacco, Milan, Italy
- 12Clinical Immunology, ASST Grande Ospedale Metropolitano Niguarda, Milan, Italy
Introduction: Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA) is a rare necrotizing vasculitis characterized by eosinophilic inflammation that was traditionally treated with corticosteroids associated with other immunosuppressants. Over the last years different biological therapies targeting IL-5/IL-5 receptor have become available and have been employed to tackle this challenging condition. Aim of the present study is to synthesis the evidence on the clinical presentation of this disease and on the efficacy of the newly available therapeutic strategies.
Methods: In June 2024 PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane library were searched for studies reporting on EGPA patients being treated by means of different anti IL-5 or anti eosinophils biological therapies. Risk of bias was assessed through the ROBINS-I and RoB2 tools according to study design. Proportion meta-analysis was employed to synthetize data on EGPA clinical manifestations, while data on treatment outcomes was analyzed descriptively due to the high heterogeneity.
Results: The present systematic review included 25 studies on a total of 1131 patients. Asthma was present in 99.2% of the patients, Sinonasal involvement in 87.0% and ANCA positivity in 22.8%. The explored treatments consisted in Benralizumab 30 mg every 4 weeks, Mepolizumab 100 mg or 300 mg every 4 weeks and Reslizumab 3mg/Kg every 4 weeks. All the anti-IL-5/IL-5 receptor molecules proved efficacious in remission control and corticosteroid tapering.
Conclusion: The available data strongly suggests integrating anti IL-5/IL-5 receptor therapies into EGPA treatment strategies, to enhance patients’ outcomes and reduce the long term side effects of prolonged corticosteroid therapy.
Introduction
Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA), formerly known as Churg Strauss syndrome, is a rare form of necrotizing vasculitis with extravascular granulomas occurring in patients with asthma and tissue eosinophilia (1). Clinically, EGPA typically presents with asthma, peripheral eosinophilia, and sinonasal involvement, such as chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP). However, this condition is a multi-organ disease with a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations, leading to significant heterogeneity in presentation and severity. The pathogenesis of EGPA is still not fully understood, even if there is evidence suggesting the involvement of both environmental and genetic factors (2, 3). Organ damage in EGPA patients can occur with two different mechanisms: as a consequence of either vasculitis leading to ischemic effects and inflammation, which is prominent in myeloperoxidase anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (MPO-ANCA)-positive patients, or either eosinophil-associated vascular occlusion leading to ischemia and eosinophil-associated tissue damage, which is frequent in MPO-ANCA-negative patients (4). A clear distinction between vasculitis driven organ damage and eosinophilic mediated damage is not always possible. Only tissue biopsies allow to assess weather vasculitis is present or not and eosinophilic inflammation can trigger the vasculitis process and disease progression (3, 5).
EGPA may arise at any age but is more frequently diagnosed in adults. Indeed, due to its heterogeneous presentations and overlaps with other conditions, the diagnosis of EGPA is often delayed. Both remission induction and remission maintenance of disease activity traditionally require corticosteroids, the tapering of which is often challenging. Therefore, patients are typically treated with prolonged and excessive doses of corticosteroids, which, while controlling effectively the systemic inflammation, can lead to serious metabolic, cardiovascular, osteoporotic and infectious side effects (5). Other immunosuppressive agents such as cyclophosphamide, rituximab, mycophenolate, azathioprine and methotrexate can also be employed in EGPA therapy, especially for preventing disease relapses during OCS therapy. However, their efficacy is still debated and controversial, and no clear indication on which therapy is to be used was released at international level (3).
The recent development of humanized monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-5 or IL-5 receptor (IL-5R) marked a significant breakthrough in the treatment of EGPA, revolutionizing its management and achieving disease control while progressively reducing OCS intake, as shown in both phase III trials (6, 7) and real-life settings (8, 9). Although some systematic reviews (10, 11) have investigated the demographic and clinical characteristics of EGPA patients, previous studies (12, 13) on biological therapies directed against the IL-5 pathway have not considered all available molecules together but have analyzed them individually or have focused on specific combination of treatments. The present work aims to fill these gaps, by providing an up to date and comprehensive synthesis of the evidence on the topic.
Material and methods
This systematic review is written in accordance to the guidelines of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (14) and followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) 2020 statement (15).
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion in the present systematic review was restricted to studies that met all the following eligibility criteria: 1) Randomized or observational studies, 2) on a population of a minimum of 5 patients with EGPA, 3) receiving anti IL-5/IL-5R therapies. We excluded studies that did not report any clinical outcome. The cut-off of 5 patients was chosen to mitigate publication bias.
Search strategy
In June 2024 PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane library were consulted with combinations of the following search terms: Churg-Strauss Syndrome, Churg-Strauss, Churg Strauss, EGPA, Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis, Mepolizumab, Benralizumab, anti-IL-5 biologics, anti-IL-5. The full search strategies employed in the searched databases are reported in Supplementary File 1. No language restrictions were applied to be as complete as possible. Two authors (ML and VL) independently performed the abstract and full text screening of the retrieved articles through Rayyan (16), a free software specifically designed for screening of abstracts, titles and full texts through a process of semi-automation. Disagreements in any phase were resolved through discussion. If there was an overlap amongst studies populations, only the largest cohort was included in the present study.
Data extraction
Two reviewers (ML and VL) independently extracted relevant data from the selected articles: name of the first author and country of origin, year of publication, study design, sample size, age and sex of the enrolled patients. Data on clinical manifestations, signs, and organ damage at the time of disease diagnosis were collected, such as asthma, neuropathy, pulmonary infiltrates, sinonasal abnormalities, cardiac/renal/dermatological involvement, and ANCA positivity at baseline.
Pre-treatment data included, when described, the blood eosinophil count (BEC) and oral corticosteroid dose (OCS). For each study, treatment outcomes were recorded. These outcomes were diverse and included measures of disease remission, defined according to the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) as a Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) of 0 and an OCS dose ≤7.5 mg/day (17). Changes in the proportion of patients achieving remission over the study periods were analyzed, as well as variations in BEC, OCS dose and disease activity scores (BVAS). Additional outcomes were changes in the Asthma Control Test (ACT) scores, Sinonasal Outcome Test-22 (SNOT-22) scores, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and time to first disease relapse. Data extraction of numerical data from graphs was performed through WebPlotDigitizer.
Data synthesis
Proportion meta-analysis was used to analyze the demographic characteristics of the included EGPA patients effectively. Proportion meta-analysis is a statistical method usually employed to synthetize evidence, such as proportions or prevalence, from single group studies on rare conditions. A random effects model was chosen, as well as the Freeman–Tukey double-arcsine transformation. We assessed heterogeneity with I2 statistics and Cochrane Q test; p-values < 0.10 and I2 > 40% were considered significant for heterogeneity. R software (version 4.4.0, 2024-04-24) was used for the statistical analysis.
Due to the highly variable study designs, the lack of comparative studies, the highly heterogeneous follow up times and reported outcomes, meta-analytic synthesis was not deemed applicable to changes in remission rates and disease activity. Therefore, therapeutic outcomes were analyzed descriptively. Continuous variables are reported as means and standard deviations when normally distributed, or as medians and interquartile range when non-normally distributed. Categorical variables are reported as absolute frequencies and valid percentages.
Quality assessment
The risk of bias assessment of the included studies was performed with the Risk Of Bias In Non randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool (18) in case of observational, cohort studies or case series. While risk of bias for randomized studies was assessed through the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials (RoB-2) (19). Two authors (ML and VL) independently performed the quality assessment, resolving conflicts through discussion.
Results
Study selection
Figure 1 shows the PRISMA flowchart for the article selection process. A total of 791 records were retrieved from PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane library. After title and abstract screening, 95 studies remained and were assessed in their full text. Eventually, 25 studies (4, 6–9, 20–39) were included in the present systematic review. Two were randomized controlled trials (6, 7) and 23 observational studies (4, 8, 9, 20–39).
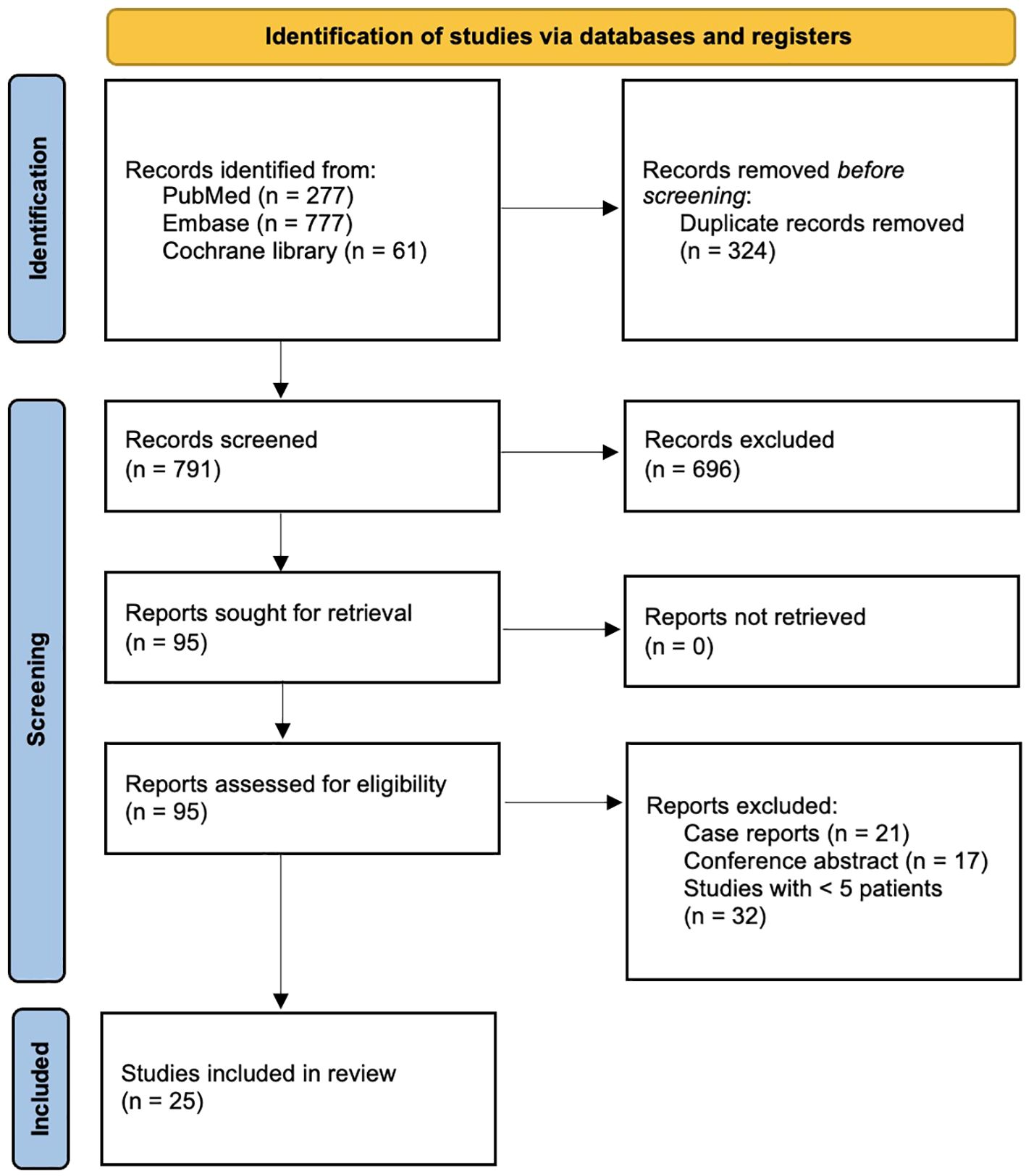
Figure 1. PRISMA flowchart of the study selection process for the present systematic review and meta-analysis.
Baseline characteristics
The present systematic review comprises a total of 1131 patients, of which 44% were male and 56% were female. These patients were mostly adult, being their age relatively homogeneous across studies. General baseline characteristics of the patients are presented in Table 1. The blood eosinophil count, however, showed significant variability: Wechsler et al. (6) reported mean BEC values of mean 177 ± 1.29, while Bostan et al. (20) a median BEC of 1000 (700-1800). The use of OCS among the included patients before starting their anti-IL-5/IL-5R therapies was consistently high, with values ranging from 8.75 (5-15) to 19.5 (5-40) mg.
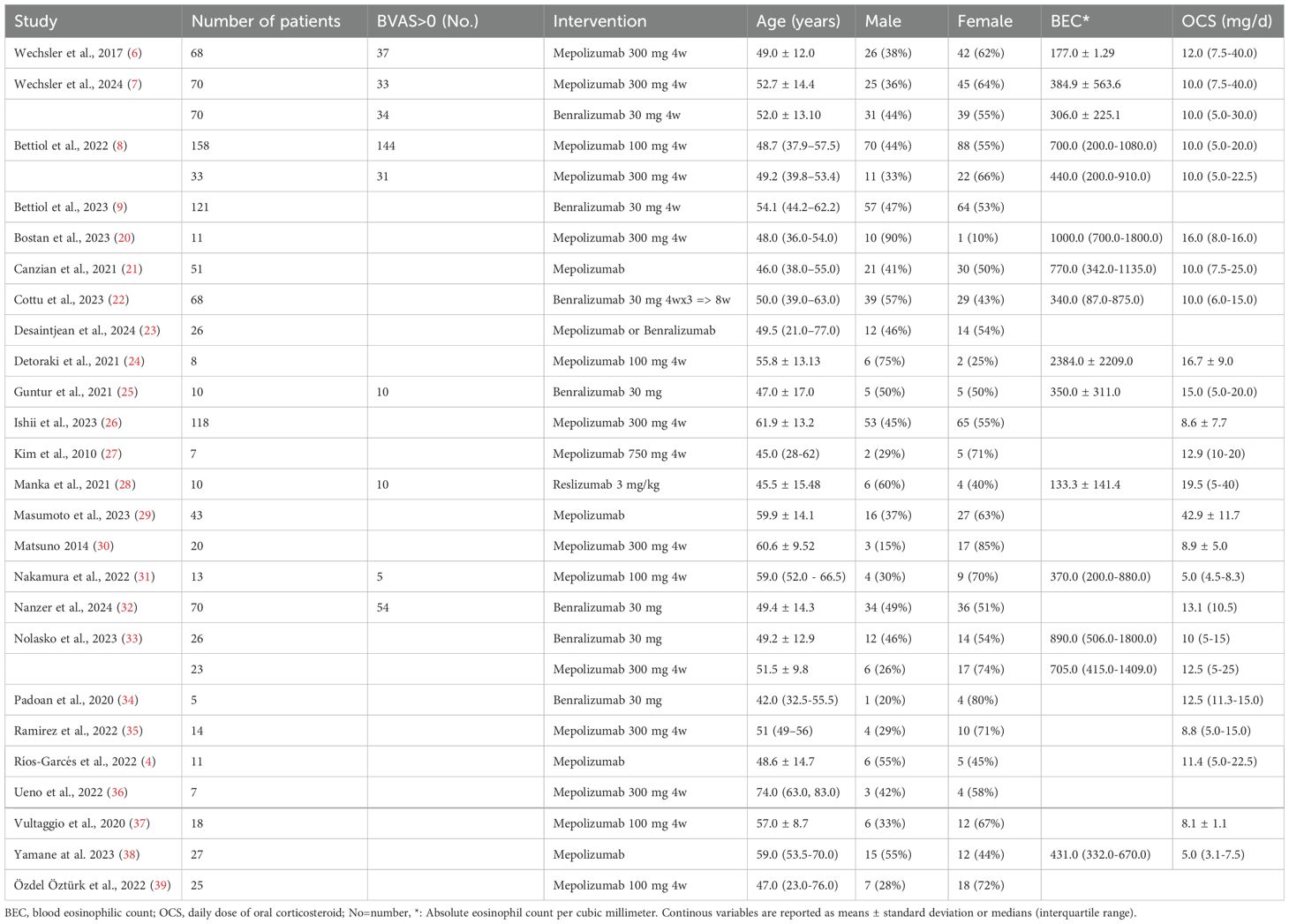
Table 1. baseline characteristics, each cohort of patients with EGPA of the included articles is described separately.
Disease manifestations
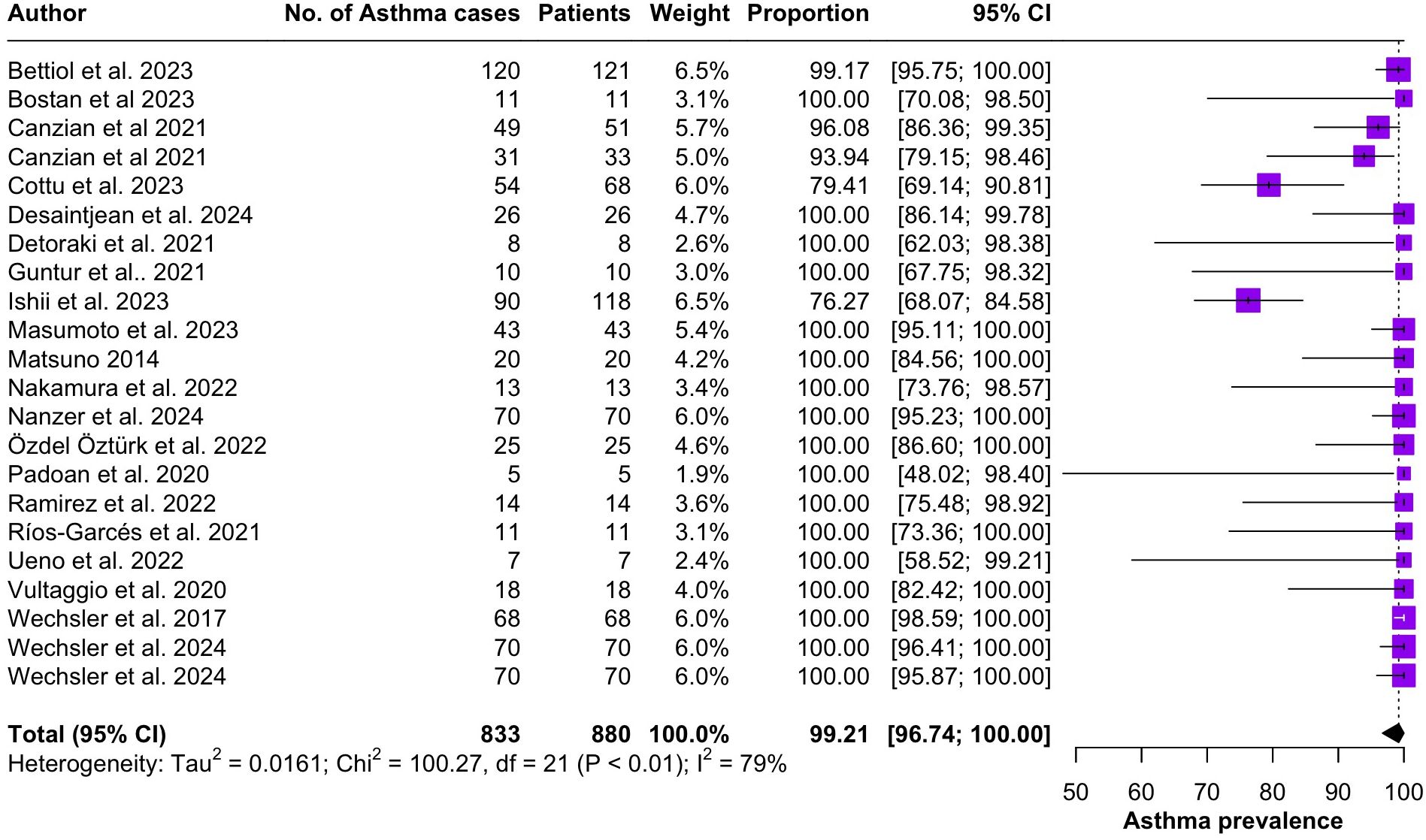
Regarding the clinical manifestations of EGPA, asthma was the most consistent feature with a pooled prevalence of 99.2% (95% CI 96.7-100.0, I2 = 79%) (Figure 2). Sinonasal involvement was also frequent, as marked by its pooled prevalence of 87.0% (95% CI 79.0-93.5, I2 = 87%)(Figure 3). Neuropathy was present in 36.9% of the patients (95% CI 23.3-51.5%, I2 = 95%), the I2 showing great heterogeneity between studies (Figure 4). Cardiac and cutaneous involvement were less commonly observed, with a pooled prevalence of 20.6% (95% CI 12.2-30.3%, I2 = 91%) and 17.7% (95% 8.5-29.2, I2 = 91%) respectively (Figures 5, 6). Renal involvement was even more rare, with a pooled prevalence of 3.4% (95% CI 0.9-7.0%, I2 = 73%) (Figure 7). Lastly, ANCA positivity was present in 22.8% of the patients (95% CI 16.7-29.5, I2 = 77%) (Figure 8).
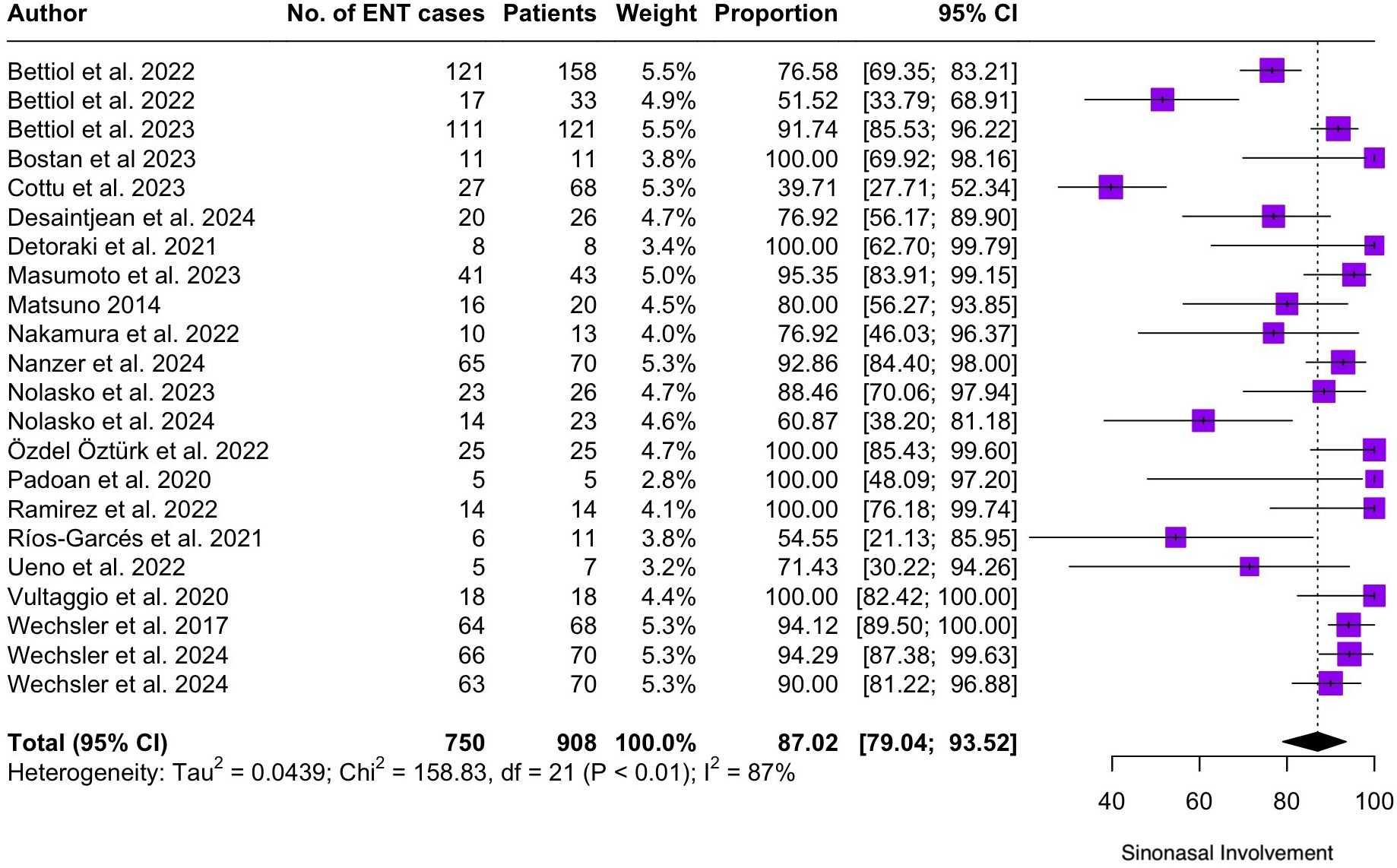
Figure 3. Forest plot reporting on the overall prevalence of sinonasal involvement among the included patients.
![Forest plot showing neuropathy prevalence from various studies, each represented by a purple square and horizontal line indicating 95% confidence intervals. The summary effect size is displayed as a diamond at the bottom. The vertical dashed line marks the overall prevalence, and study details like number of cases and weight are listed alongside. Total neuropathy prevalence is 36.86% with 95% CI [23.25, 51.51].](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1587158/fimmu-16-1587158-HTML/image_m/fimmu-16-1587158-g004.jpg)
Figure 4. Forest plot reporting on the overall prevalence of neuropathy among the included patients.
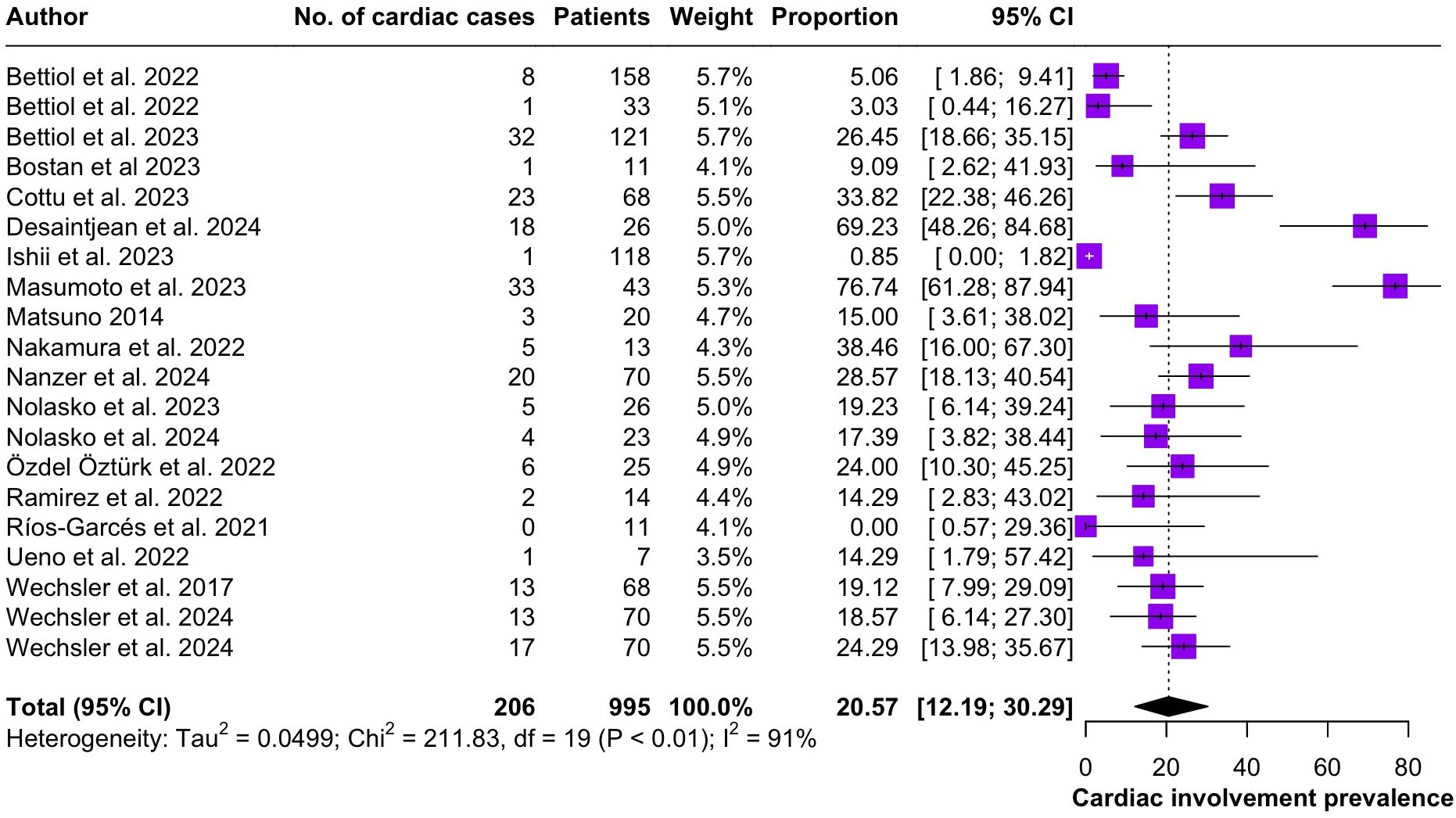
Figure 5. Forest plot reporting on the overall prevalence of cardiac involvement among the included patients.
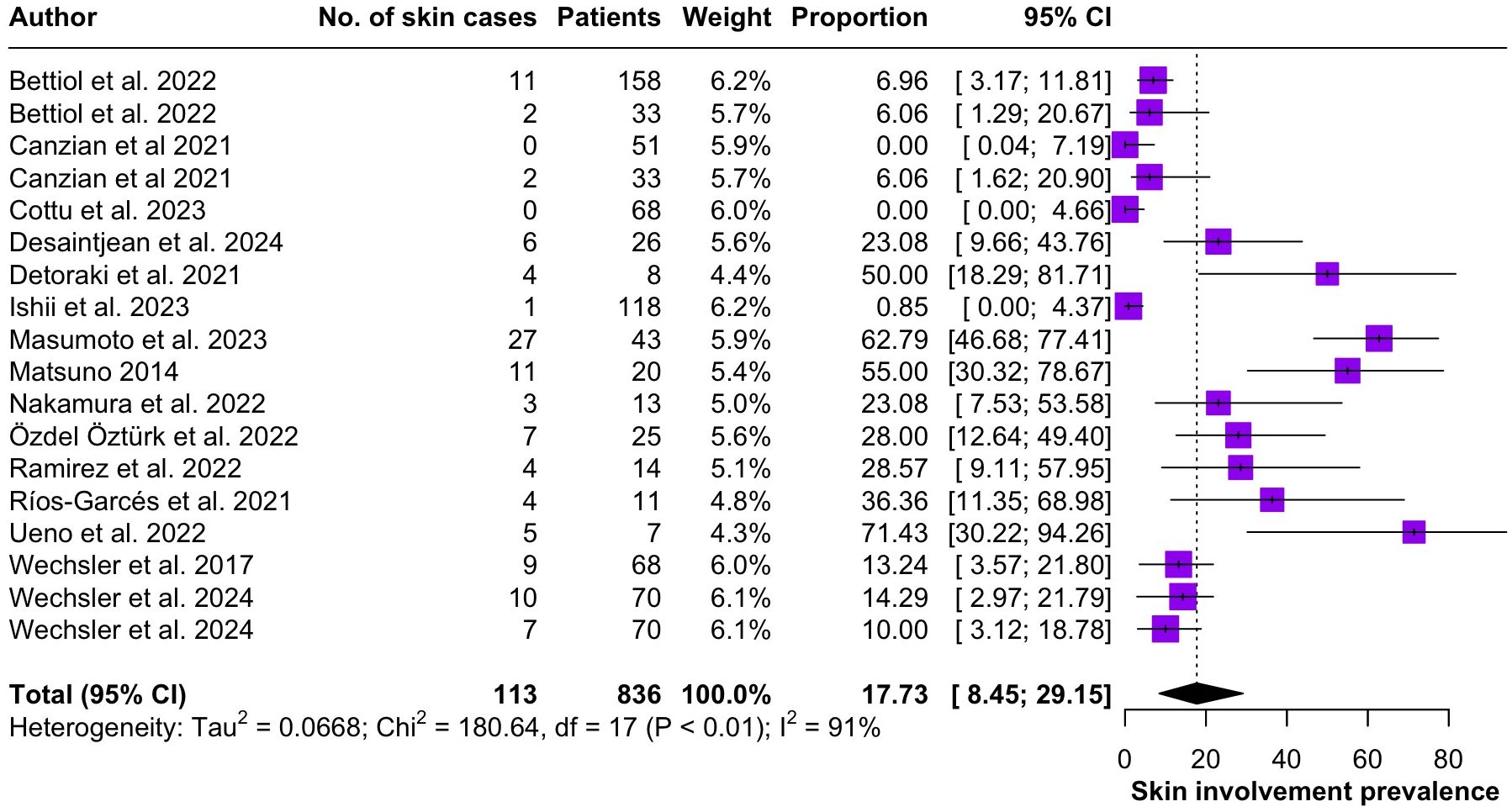
Figure 6. Forest plot reporting on the overall prevalence of cutaneous involvement among the included patients.
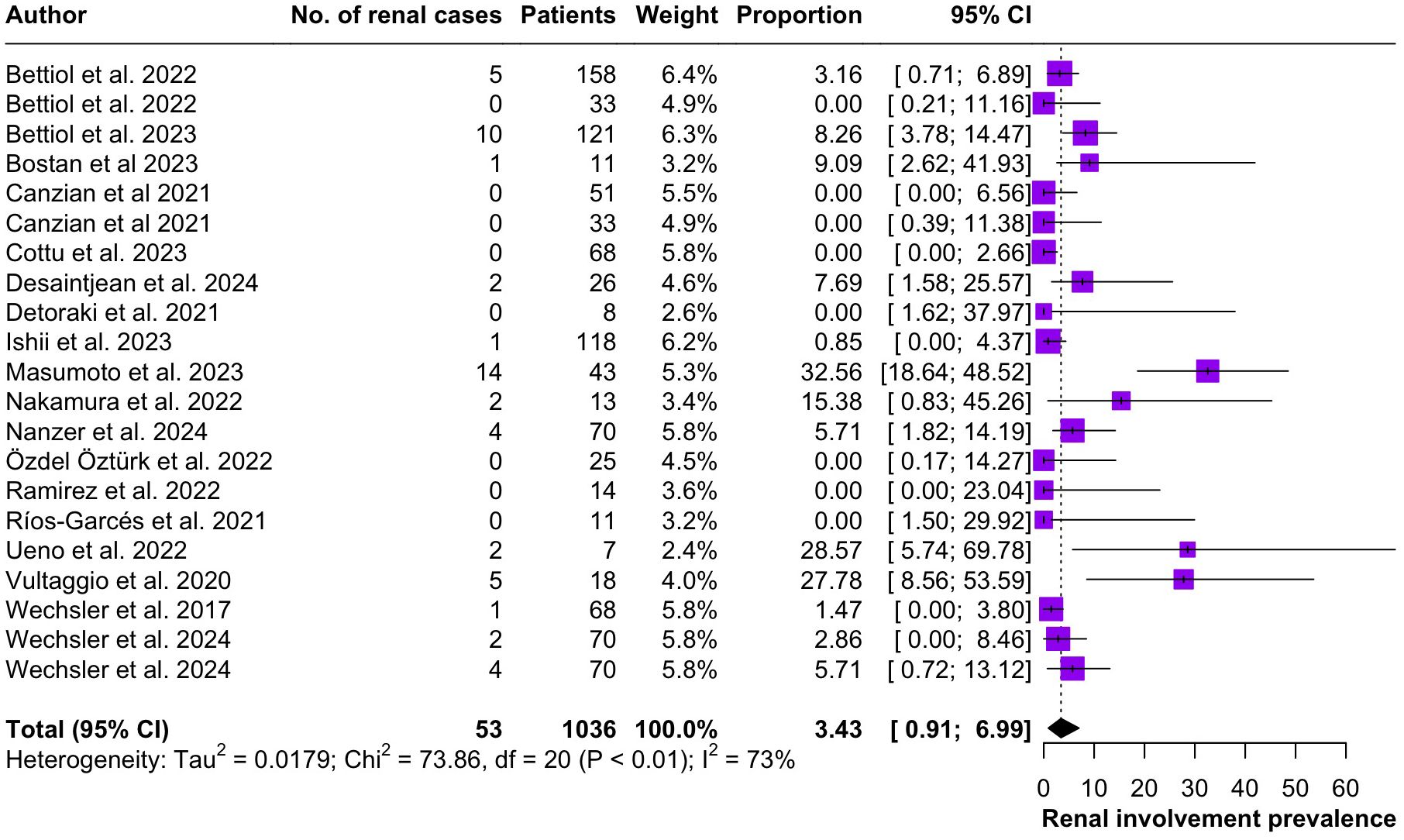
Figure 7. Forest plot reporting on the overall prevalence of renal involvement among the included patients.
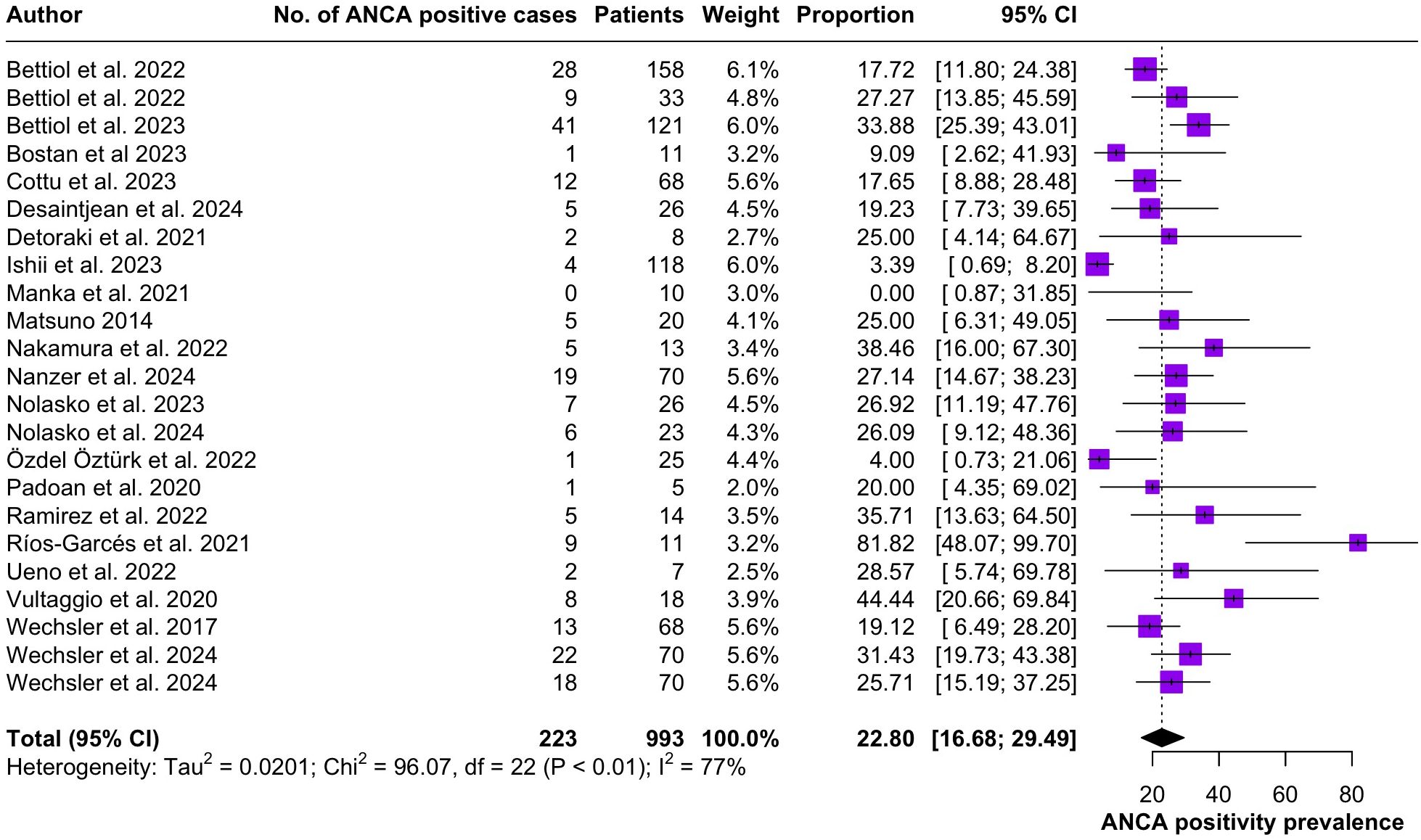
Figure 8. Forest plot reporting on the overall prevalence of ANCA positivity among the included patients.
Treatment
Among the included studies mepolizumab was the most frequently used anti IL-5 biologic in EGPA patients. The effects of different therapeutic doses were investigated, with several studies (6–8, 20, 26, 30, 33, 35, 36) evaluating its efficacy at a dose of 300 mg every 4 weeks, while others (8, 24, 31, 37) at 100 mg every 4 weeks. Notably, Kim et al. (27) treated their patients with 750 mg administered every 4 weeks. Benralizumab was also assessed in different studies, mostly prescribing it at the dosage of 30 mg every 4 weeks (7, 9, 25, 32–34). Cottu et al. (22) evaluated a regimen of 30 mg every 4 weeks for 3 doses, followed by administration every 8 weeks. Lastly, only one of the included articles (28) investigated the efficacy of Reslizumab (3 mg/kg).
The included studies followed different protocols for the timing of anti-IL-5/IL-5R therapy initiation. Bettiol et al. (8) and Cottu et al. (22) included patients who were already on long-term corticosteroid therapy. Similarly, the MIRRA and MANDARA trials (6, 7) evaluated IL-5/IL-5R antagonists as add-on agents in patients with relapsing or corticosteroid-dependent EGPA, rather than exploring their effect as induction therapy. However, studies such the ones of Nolasco et al. (33) and Ríos-Garcés et al. (4) do not indicate how long after being diagnosed with EGPA their patients were prescribed with anti-IL-5/IL-5R therapies.
The retrieved outcomes are presented in Supplementary File 1. Amongst this was the induction of disease remission according to the definition proposed by the European League against Rheumatism (17). Both mepolizumab and benralizumab showed promising results in this regard in all the 6 studies that included the information (6–9, 32, 33). The anti-IL-5/IL-5R therapies were also rapidly efficacious in controlling circulating eosinophils, being able to significantly reduce BEC already after the first 12 weeks of treatment (8, 9, 20, 22, 31, 34). Notably, Bettiol et al. (9), Cottu et al. (22) and Nolasko et al. (33) showed how benralizumab managed to reduce BECs to zero in their cohorts of patients. All the included studies showed how anti IL-5/IL-5R biological therapies are efficacious in obtaining sustained control of circulating eosinophils at 48 weeks (8, 9, 20, 22, 24, 31, 33, 34, 37, 39).
All the retrieved articles showed a significant reduction in OCS use by EGPA patients after all the anti-IL-5/IL-5R biological therapies. Bostan et al. (20) in particular showed how their patients were able to stop taking OCS, going from mean dosage of 16 (8-16) to 0 (0-4), similarly Nolasko et al. (33) cohort of patients taking Mepolizumab 300 mg 4w went from 12 (5-25) to 0 (0-5).
Lastly, the anti-IL-5/IL-5R biologics showed promising results in both rhinologic and pneumological domains. SNOT22 scores significantly decreased in EGPA patients after 24 weeks of therapy and continued to get lower until the end of the studies follow-up time at 48 weeks (20, 24, 37). The airflow measurements (FEV1) also homogeneously, progressively continued to improve in the retrieved studies (9, 20, 27, 32–34).
Quality assessment
According to the RoB-2 tool the risk of bias of the 2 randomized studies (6, 7) was deemed as “Low”, while According to the ROBINS-I tool the overall risk of bias of the 23 articles was “moderate” for 9 articles (8, 9, 21, 25, 31–33, 38, 39), “serious” for 3 (22, 26, 27) and “critical” for 11 (4, 23, 24, 28–30, 34–37).
Discussion
The present work represents the largest systematic review on EGPA, comprising 25 studies and a total of 1131 patients. It provides an updated overview of the demographic characteristics, clinical manifestations and therapeutic options for this rare condition.
Regarding organ involvement, upper and lower respiratory tracts are the most frequently affected sites (3). Indeed, our findings confirm that nearly all included patients had asthma (99.2%; 95% CI 96.7-100.0) and that the vast majority suffered from sinonasal involvement (87.0%; 95% CI 79.0-93.5). CRSwNP associated with late onset asthma in a patient with blood eosinophilia, undergoing chronic OCS treatment should be considered an important red flag for a possible EGPA (40). However, beyond CRSwNP, EGPA can manifest with a variety of ENT conditions, such as allergic rhinitis and hearing loss/otitis media. The latter has a prevalence that ranges between 10-20% according to the literature (41, 42) and typically falls under the category of eosinophilic otitis media: a type 2 inflammatory disease that is refractory to most conventional surgical and medical treatments (43).
Peripheral nerve involvement was observed in 36.9% of the patients included in the present systematic review. Neurological manifestations of EGPA most commonly present as multiple mononeuropathies, distal polyneuropathy or lumbar radiculopathy (3). The etiopathogenesis of neural involvement is thought to be directly linked to eosinophilic damage (44), as eosinophils play a pivoting role in driving disease progress. While EGPA has been classified as an anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, ANCA positivity is not a consistent finding in these patients. Cung et al. (45) reported that only 40% of EGPA patients produce detectable ANCA and our results indicate an even lower prevalence of 22.8% (95% CI 16.7-29.5).
EGPA treatment aims both at controlling the systemic vasculitis activity and progressively reduce corticosteroid dependence (46). OCS, either alone or in association with cyclophosphamide or rituximab, remains the cornerstone for remission induction in EGPA. Before the advent of anti-IL-5/IL-5R therapies, other immunosuppressants such as azathioprine, methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil were employed for remission maintenance (47).
The MIRRA trial showed that mepolizumab added to OCS, with or without conventional immunosuppressive drugs for induction, granted higher rates of sustained remission and OCS sparing in EGPA (6). Lastly, the MANDARA study later demonstrated the non-inferiority of benralizumab to mepolizumab in the induction of EGPA remission (7).
Our review further highlights the efficacy of anti-IL-5/IL-5R therapies in maintaining disease remission and OCS tapering, showing significant reduction OCS daily doses, as well as improved respiratory outcomes and marked reduction of circulating eosinophils throughout the follow up period.
Despite the extremely promising results reported in the registration studies of Mepolizumab and Benralizumab in Patients affected by EGPA, many aspects of therapy with anti-IL-5/IL-5R drugs still remain to be clarified.
First of all, there is no uniformity at an international level regarding the correct strategy for inducing remission in patients with EGPA; some Authors have proposed models of use of Rituximab associated with variable doses of OCS, other Authors have proposed the association of OCS with immunosuppressants of various nature, variable depending on the clinical characteristics of acute presentation. This is reflected in an uncertainty that often finds an answer in the experience and approach of the individual Center, therefore not contributing to guaranteeing uniformity of data in the evaluation of the different initial approaches.
In addition to this, EGPA itself can present with two different serological subsets, p-ANCA+ and p-ANCA-. As noted in a recent study by Piga et al. (48), therapy with anti-IL-5/IL-5R drugs may give rise to different results depending on the serological status of the Patient, underlining a possible pathogenic role of p-ANCA, which is still the subject of heated debate.
Furthermore, in the same paper the Authors emphasize how the different approaches used in the induction of remission can lead, both in p-ANCA- and p-ANCA+ patients, to different results, taking into account that p-ANCA may play a pathogenetic role once the eosinophilic response is ablated, which both drugs are demonstrably able to produce.
Both registration studies did not emphasize this possible serological difference nor did they evaluate any differences in the frequency of exacerbations or in the clinical manifestation of exacerbations, whose characteristics of organ involvement would be extremely important to attribute a possible pathogenic role to p-ANCA if the Patients who were carriers were more prone to developing relapses.
These data could be derived from phase IV studies if the right attention was paid both to the methods of induction of remission and to any differences in frequency and clinical characteristics of relapses.
Recent studies on large cohorts of patients are slowly highlighting peculiar aspects regarding the efficacy of Mepolizumab in maintaining remission and the retention rate of the drug in patients affected by EGPA (49–53), but to fully understand what is the best approach for inducing remission and how much the co-presence of p-ANCA affects the development of relapses, further studies on even larger case studies are needed, with targeted sub-analyses on the different subgroups of patients.
A recent post-hoc analysis has established that the need for high doses of OCS at baseline may represent a predictive factor of lower response to Mepolizumab, regardless of the type of immunosuppressant used in association with at baseline (54). These data seem to underline only that Mepolizumab may be less effective in cases where the disease has proven more aggressive and has required higher doses of OCS, but does not clearly establish whether the presence of p-ANCA represents a negative predictive factor nor does it specify the efficacy of the type of immunosuppressant used, together with OCS, in inducing remission before the use of Mepolizumab.
International multicenter studies are necessary, given the relative rarity of the disease, which allow case studies numerically sufficient to draw conclusions with statistical validity and able to direct clinicians to more targeted and informed therapeutic choices.
The present study has several limitations. Firstly, the included studies varied greatly in terms of study designs, treatments and outcomes. Due to the rarity of EGPA, there is a lack of comparative studies evaluating the success rates of different treatments and their combinations. Moreover, outcomes of different therapeutic strategies for EGPA were also reported heterogeneously between studies, some including organ specific parameters such as FEV1 and SNOT22 scores (24, 34), others focusing on the number of patients achieving disease remission (6–8). This great inconsistency prevented us from synthesizing available evidence through meta-analytic analysis. Furthermore, as remarked by our results, most included records are non-randomized, observational cohort studies that are at severe risk of bias, an issue that we have tackled through a rigorous quality assessment as indicated by the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (14). Studies with a high risk of bias are common when dealing with rare conditions, such as EGPA, since most records available on the topic will be simple case series with methodological issues such as the lack of a control group, incomplete outcome reporting, variability in definitions of treatment response. The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (14) doesn’t suggest to exclude these studies from systematic reviews, but rather to acknowledge their limitations in order to interpret the pooled findings with caution. Another limitation of the present study is that the results on clinical manifestations only apply to individuals receiving anti-IL-5/IL-5 receptor medications, therefore, while evaluating these findings, selection bias should be taken into account. However, our pooled analysis’s prevalence of important disease characteristics (such as asthma and sinonasal involvement) matches that of larger EGPA cohorts, indicating that any selection bias might not significantly skew the clinical picture presented by the present meta-analysis. Lastly, due to this variability in study designs, the precise timing of anti-IL5/IL-5R therapy initiation could not be uniformly assessed across the included studies, highlighting the need for phase IV trials focusing on induction strategies.
Author contributions
MLa: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. VL: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. PS: Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. EB: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AB: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. GG: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MB: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AD: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MG: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MLe: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AMan: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AMau: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AG: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JS: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. PC: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587158/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Greco A, Rizzo MI, De Virgilio A, Gallo A, Fusconi M, Ruoppolo G, et al. Churg-Strauss syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. (2015) 14:341–8.
2. Kouverianos I, Angelopoulos A, and Daoussis D. The role of anti-eosinophilic therapies in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. (2023) 43:1245–52. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05326-1
3. Furuta S, Iwamoto T, and Nakajima H. Update on eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Allergol Int. (2019) 68:430–6. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2019.06.004
4. Rios-Garces R, Prieto-Gonzalez S, Hernandez-Rodriguez J, Arismendi E, Alobid I, Penatti AE, et al. Response to mepolizumab according to disease manifestations in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Eur J Intern Med. (2022) 95:61–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2021.08.021
5. Berti A, Atzeni F, Dagna L, Del Giacco S, Emmi G, Salvarani C, et al. Targeting the interleukin-5 pathway in EGPA: evidence, uncertainties and opportunities. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:164–8. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223044
6. Wechsler ME, Akuthota P, Jayne D, Khoury P, Klion A, Langford CA, et al. Mepolizumab or placebo for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376:1921–32. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1702079
7. Wechsler ME, Nair P, Terrier B, Walz B, Bourdin A, Jayne DRW, et al. Benralizumab versus mepolizumab for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:911–21. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa2311155
8. Bettiol A, Urban ML, Dagna L, Cottin V, Franceschini F, Del Giacco S, et al. Mepolizumab for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A European multicenter observational study. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2022) 74:295–306.
9. Bettiol A, Urban ML, Padoan R, Groh M, Lopalco G, Egan A, et al. Benralizumab for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a retrospective, multicenter, cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5:e707–e15.
10. Solans-Laque R, Rua-Figueroa I, Blanco Aparicio M, Garcia Moguel I, Blanco R, Perez Grimaldi F, et al. Red flags for clinical suspicion of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). Eur J Intern Med. (2024) 128:45–52.
11. Redondo-Rodriguez R, Mena-Vazquez N, Cabezas-Lucena AM, Manrique-Arija S, Mucientes A, and Fernandez-Nebro A. Systematic review and meta analysis of worldwide incidence and prevalence of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis. J Clin Med. (2022) 11.
12. Pradhan RR, Nepal G, and Mandal S. Safety and efficacy of mepolizumab in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Pulm Med. (2019) 2019:4376380. doi: 10.1155/2019/4376380
13. Spataro F, Solimando AG, Di Girolamo A, Vacca A, and Ria R. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A meta-analysis of eight studies. Eur J Clin Invest. (2025) 55:e14333. doi: 10.1111/eci.14333
14. Higgins JPT. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. J T, editor. Chichester (UK: John Wiley & Sons (2019).
15. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71.
16. Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, and Elmagarmid A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. (2016) 5:210. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
17. Yates M, Watts RA, Bajema IM, Cid MC, Crestani B, Hauser T, et al. EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:1583–94. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209133
18. Sterne JA, Hernan MA, Reeves BC, Savovic J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomized studies of interventions. BMJ. (2016) 355:i4919.
19. Sterne JAC, Savovic J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898.
20. Bostan OC, Duran E, Tuncay G, Cihanbeylerden M, Karadag O, Damadoglu E, et al. Sinonasal and respiratory outcomes of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis patients receiving 100 mg mepolizumab in real-life clinical practice: 1-year follow up study. J Asthma. (2023) 60:931–7.
21. Canzian A, Venhoff N, Urban ML, Sartorelli S, Ruppert AM, Groh M, et al. Use of biologics to treat relapsing and/or refractory eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: data from a European collaborative study. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2021) 73:498–503. doi: 10.1002/art.41534
22. Cottu A, Groh M, Desaintjean C, Marchand-Adam S, Guillevin L, Puechal X, et al. Benralizumab for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:1580–6. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224624
23. Desaintjean C, Ahmad K, Traclet J, Gerfaud-Valentin M, Durel CA, Glerant JC, et al. Mepolizumab and benralizumab in patients with severe asthma and a history of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1341310. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1341310
24. Detoraki A, Tremante E, Poto R, Morelli E, Quaremba G, Granata F, et al. Real-life evidence of low-dose mepolizumab efficacy in EGPA: a case series. Respir Res. (2021) 22:185. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01775-z
25. Guntur VP, Manka LA, Denson JL, Dunn RM, Dollin YT, Gill M, et al. Benralizumab as a steroid-sparing treatment option in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2021) 9:1186–93 e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.09.054
26. Ishii T, Kunishige H, Kobayashi T, Hayashi E, Komatsubara M, Ishii T, et al. Real-world safety and effectiveness of mepolizumab for patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis in Japan: A 48-week interim analysis of the MARS study. Mod Rheumatol. (2024) 34:978–87.
27. Kim S, Marigowda G, Oren E, Israel E, and Wechsler ME. Mepolizumab as a steroid-sparing treatment option in patients with Churg-Strauss syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2010) 125:1336–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.03.028
28. Manka LA, Guntur VP, Denson JL, Dunn RM, Dollin YT, Strand MJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of reslizumab in the treatment of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2021) 126:696–701 e1. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2021.01.035
29. Masumoto N, Oshikata C, Nakadegawa R, Motobayashi Y, Osada R, Manabe S, et al. Long-term mepolizumab treatment reduces relapse rates in super-responders with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. (2023) 19:40. doi: 10.1186/s13223-023-00801-7
30. Matsuno O. Factors affecting the ability to discontinue oral corticosteroid use in patients with EGPA treated with anti-interleukin-5 therapy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2024) 185:116–23. doi: 10.1159/000533535
31. Nakamura Y, Fukutomi Y, Sekiya K, Kajiwara K, Kawasaki Y, Fujita N, et al. Low-dose mepolizumab is effective as an add-on therapy for treating long-lasting peripheral neuropathy in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Mod Rheumatol. (2022) 32:387–95. doi: 10.1093/mr/roab005
32. Nanzer AM, Maynard-Paquette AC, Alam V, Green L, Thomson L, Lam J, et al. Long-term effectiveness of benralizumab in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2024) 12:724–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.01.006
33. Nolasco S, Portacci A, Campisi R, Buonamico E, Pelaia C, Benfante A, et al. Effectiveness and safety of anti-IL-5/Ralpha biologics in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a two-year multicenter observational study. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1204444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1204444
34. Padoan R, Chieco Bianchi F, Marchi MR, Cazzador D, Felicetti M, Emanuelli E, et al. Benralizumab as a glucocorticoid-sparing treatment option for severe asthma in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2020) 8:3225–7 e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.05.033
35. Ramirez GA, Cariddi A, Noviello S, Campochiaro C, Canti V, Moroni L, et al. Real-Life efficacy and safety of mepolizumab for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Clin Immunol Commun. (2022) 2:23–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clicom.2022.01.002
36. Ueno M, Miyagawa I, Aritomi T, Kimura K, Iwata S, Hanami K, et al. Safety and effectiveness of mepolizumab therapy in remission induction therapy for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a retrospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2022) 24:159. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02845-3
37. Vultaggio A, Nencini F, Bormioli S, Vivarelli E, Dies L, Rossi O, et al. Low-dose mepolizumab effectiveness in patients suffering from eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. (2020) 12:885–93. doi: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.5.885
38. Yamane T and Hashiramoto A. Mepolizumab exerts crucial effects on glucocorticoid discontinuation in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a retrospective study of 27 cases at a single center in Japan. Arthritis Res Ther. (2023) 25:110. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03097-5
39. Ozdel Ozturk B, Yavuz Z, Aydin O, Mungan D, Sin BA, Demirel YS, et al. Effectiveness of low-dose mepolizumab in the treatment of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA): A real-life experience. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2022) 183:1281–90.
40. Coates ML and Martinez Del Pero M. Updates in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis for the ENT surgeon. Clin Otolaryngol. (2020) 45:316–26. doi: 10.1111/coa.13524
41. Krol RM, Remmelts HHF, Klaasen R, Frima A, Hagen EC, Kamalski DMA, et al. Systemic and local medical or surgical therapies for ear, nose and/or throat manifestations in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A systematic literature review. J Clin Med. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093173
42. Petersen H, Gotz P, Both M, Hey M, Ambrosch P, Bremer JP, et al. Manifestation of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis in head and neck. Rhinology. (2015) 53:277–85. doi: 10.4193/rhino14.074
43. Lazzeroni M, Elzinga H, Merkus P, van Spronsen E, Fokkens WJ, and Reitsma S. Management of eosinophilic otitis media in the era of biological therapy: systematic review and proportion meta-analysis. Rhinology. (2024).
44. Bagnasco D BA, Brembilla G, Canonica GW, Carpagnano GE, Caruso C, Crimi N, et al. The role of IL-5 in type 2 inflammatory diseases. EMJ. (2024).
45. Chung SA, Langford CA, Maz M, Abril A, Gorelik M, Guyatt G, et al. 2021 American college of rheumatology/Vasculitis foundation guideline for the management of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-Associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2021) 73:1366–83. doi: 10.1002/art.41773
46. Kumar N, Jett SD, Gomes PL, Marino MJ, Miglani A, and Lal D. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A real-world study of biologics and sinus surgery use for managing nasal polyposis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. (2025).
47. Sanchez-Alamo B, Schirmer JH, Hellmich B, Jayne D, Monti S, Tomasson G, et al. Systematic literature review informing the 2022 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV): Part 2 - Treatment of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis and diagnosis and general management of AAV. RMD Open. (2023) 9. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003083
48. Piga MA, Fraticelli P, Antonicelli L, Garritani MS, Ghirelli G, Martini M, et al. ANCA-negative EGPA: only eosinophils without vasculitis? Insights from anti-T2 biologics. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1325299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1325299
49. Kotani T, Matsuda S, Okazaki A, Nishioka D, Watanabe R, Gon T, et al. Risk prediction model for mortality in microscopic polyangiitis: multicenter REVEAL cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2023) 25:223. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03210-8
50. Matsuda S, Kotani T, Okazaki A, Nishioka D, Watanabe R, Gon T, et al. Prediction model for respiratory-related mortality in microscopic polyangiitis with interstitial lung disease: multicenter REVEAL cohort study. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2024) 63:1607–15. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead444
51. Shiomi M, Watanabe R, Matsuda S, Kotani T, Okazaki A, Masuda Y, et al. Factors associated with drug retention of mepolizumab in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A multicenter REVEAL cohort study. Mod Rheumatol. (2024) 35:126–33. doi: 10.1093/mr/roae044
52. Manabe A, Kadoba K, Hiwa R, Kotani T, Shoji M, Shirakashi M, et al. Risk factors for serious infections and infection-related mortality in patients with microscopic polyangiitis: Multicenter REVEAL cohort study. Mod Rheumatol. (2024) 34:1185–93. doi: 10.1093/mr/roae024
53. Shiomi M, Watanabe R, Matsuda S, Kotani T, Okazaki A, Masuda Y, et al. Long-term efficacy of mepolizumab in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a propensity score matching analysis in the multicenter REVEAL cohort study. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1457202. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1457202
Keywords: EGPA, IL5, eosinophil, mepolizumab, benralizumab
Citation: Lazzeroni M, Longoni V, Schiavo P, Bizzi E, Brucato A, Gramellini G, Borin M, Dragonetti A, Gaffuri M, Lentini M, Maniaci A, Mauro A, Gidaro A, Schroeder J and Capaccio P (2025) Anti-IL5/IL-5 receptor therapies for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: an updated Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 16:1587158. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587158
Received: 04 March 2025; Accepted: 04 July 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Lea Salamon, Clinical Hospital Dubrava, CroatiaReviewed by:
Marcella Visentini, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalySebastian Klapa, University of Lübeck, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Lazzeroni, Longoni, Schiavo, Bizzi, Brucato, Gramellini, Borin, Dragonetti, Gaffuri, Lentini, Maniaci, Mauro, Gidaro, Schroeder and Capaccio. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Emanuele Bizzi, Qml6emkuZW1hbnVlbGVAZ21haWwuY29t
 Matteo Lazzeroni
Matteo Lazzeroni Valeria Longoni3
Valeria Longoni3 Emanuele Bizzi
Emanuele Bizzi Antonio Brucato
Antonio Brucato Marco Borin
Marco Borin Michele Gaffuri
Michele Gaffuri Antonino Maniaci
Antonino Maniaci Angela Mauro
Angela Mauro Antonio Gidaro
Antonio Gidaro Pasquale Capaccio
Pasquale Capaccio