- 1Key Laboratory of Medical Science and Laboratory Medicine of Jiangsu Province, School of Medicine, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
- 2Institute of Hematology, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
- 3The People’s Hospital of Danyang, Affiliated Danyang Hospital of Nantong University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
The onset and progression of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which encompasses ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, are influenced by the immune system, environmental factors, genetics, and intestinal flora. Cell death is a biological phenomenon that occurs in all living organisms; nevertheless, excessive cell death has been linked to IBD, including increased immune and intestinal epithelial cell death and intestinal barrier abnormalities. Anti-tumor necrosis factor medication, which has made significant progress in treating IBD cell death, may fail in some individuals or lose effectiveness over time, necessitating the search for a safe and effective treatment. One of the novel and emerging areas in regenerative and nanomedicine used to regulate cell death is mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and their mediators (extracellular vesicles). MSCs and their mediators have been found to attenuate cell death in several illnesses, including IBD. This review explores cell death mechanisms and their implications in IBD, focusing on the potential ameliorative effects of MSCs and their mediators on cell death.
1 Introduction
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which encompasses Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is defined by persistent inflammation of the gastrointestinal system (1). The immune system, the environment, genetics, and gut microbiota all play a role in the onset and progression of IBD (2). The clinical symptoms in patients with IBD include weight loss, abdominal pain, diarrhea, weakness, blood in the stool, urgent bowel movements, and mucus in the stool (3). Since 1990, the incidence has risen in newly industrialized countries in Africa, Asia, and South America, notably Brazil (4). The burden of IBD is predicted to increase by 2050 due to population expansion and ageing, emphasizing how urgent it is to address the changing public health dilemma that IBD poses (5).
An important biological mechanism for all living creatures is cell death (6). In vivo, cell death leads to an inflammatory reaction (7). The ongoing hyperemia, plasma protein leakage, and white blood cell recruitment can be helpful for tissue healing and defense against pathogens (7). This reaction, however, could potentially damage tissue and contribute to the development of certain diseases (7). The emergence of IBDs in both humans and mice has been attributed to cell death mechanisms (8). Apoptosis, pyroptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, necroptosis, and neutrophil extracellular traps are typical of programmed cell death (PCD) mechanisms (9). These mechanisms are integral to the pathophysiology of IBD, as they lead to intestinal epithelial and immunological cell death (9). Other cell death forms include paraptosis (10), NETosis (11), immunogenic cell death (12), autosis (13), alkaliptosis (14), oxeiptosis (15), erebosis (15), mitoptosis (16), methuosis (17), cuproptosis (18), PANoptosis (19), and entosis (20). Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) medication is a significant breakthrough in IBD treatment, perhaps facilitating mucosal repair by mitigating elevated inflammation-related intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) death (21). On the other hand, some patients either do not react to anti-TNF therapy at all or their response diminishes with time (22). Therefore, comprehending the biology and ramifications of cell death in the intestinal epithelium is essential for developing novel strategies for IBD treatment (21). Furthermore, developing effective medicines to modulate immunological and IEC death pathways can help decrease the growing burden of IBD until 2050.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) demonstrate a broad range of therapeutic potential in treating IBD (23). MSCs are multipotent stem cells capable of self-renewal and possess various immunomodulatory properties, making them a promising option for treating IBDs (24). The sources of MSCs include dental tissues, menstrual blood, bone marrow, adipose tissue, endometrial polyps, and umbilical cord tissue (25, 26). Researchers have also discovered exosomes in MSCs derived from bone marrow (27, 28), adipose tissue (28, 29), dental pulp (28), menstrual blood (30), and the human umbilical cord (31). According to a recent study, exosomes are significant mediators of MSC function (32). Research shows that MSCs and their exosomes attenuate pyroptosis (31), apoptosis (33), and ferroptosis (34) in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced IBD. Thus, we review the cell death processes, such as apoptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis, and their role in IBD. We also review the potential of MSCs and their extracellular vesicle regulation in cell death to reduce IBD.
2 Cell death mechanisms and their implications in IBD
2.1 Apoptosis
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) initiates the extrinsic apoptotic cascade by forming the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) and activating effector caspases (35). Only death receptors (DR4 and DR5) induce apoptotic signaling among the many TRAIL receptors (35). Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) and fas (APO-1/CD95) initiate apoptosis by recruiting caspase-8 via the adaptor fas-associated death domain protein (FADD) (36). Fas directly binds FADD, while TNFR1 indirectly binds FADD through TNF receptor-associated death domain protein (TRADD) (36). TRADD additionally incorporates the RIP-NF-kappaB-inducing adapter (36). Thus, apoptosis communication via death receptors necessitates the acquisition of adaptor proteins (TRADD and FADD) and caspase-8 and caspase-10, which might serve comparable roles in apoptosis onset (37–40). There are two successive signaling networks involved in TNFR1-mediated apoptosis. The first plasma membrane-bound complex (complex I) comprises TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), receptor-interacting protein kinase(RIP1 kinase/RIPK1), TRADD, and TNFR1, which triggers NF-kappa B activation (39). Subsequently, FADD, caspase-8, TRADD, and RIP1 unite to create a cytoplasmic complex known as complex II (39).
BAK and BAX are proteins that trigger mitochondrial membrane permeabilization, releasing cytochrome C and activating apoptotic caspases, thereby facilitating mitochondrial apoptosis (41). BAK and BAX are essential regulators of apoptosis that mediate the critical process of permeabilization of the outer membrane of mitochondria (42). The recognized procurers of the death signal in this segment of the apoptotic cascade are caspase-8 and BID (43). The proapoptotic family members BAK or BAX oligomerize in response to activation of BID, a “BH3-domain-only” BCL-2 family member, releasing mitochondrial proteins into the cytosol (44). The activation of BAX/BAK is indirectly triggered by the deactivation of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins by BH3-only proteins (45). Cytochrome C is crucial for activating the apoptotic intrinsic pathway, which triggers the caspase cascade by connecting to apoptotic protease activating factor-1 (APAF-1) (46). Cytochrome C release causes APAF-1 to oligomerize, forming the huge complex known as an apoptosome (47). The apoptosome recruits and activates procaspase-9, which then triggers caspase-3 processing downstream (47). These processes are characteristics of the intrinsic pathway.
During the last stages of apoptosis, caspases-3,-6, and -7 are activated by the extrinsic (mediated by caspase-8) and intrinsic pathways (mediated by caspase-9), facilitating the cleavage of additional proteins (8). A powerful inhibitor of caspases 3, 7, and 9 is an x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP). During apoptosis, the release of mitochondrial SMAC (the second mitochondrial-derived activator of caspase) suppresses XIAP activity (48). Figure 1 shows the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. BCL-2 and BCL-XL do not affect TRAIL-induced apoptosis in lymphoid cells, but they can prevent or delay apoptosis in nonlymphoid cancer cells (49). BCL-XL and antioxidant enzymes prevent mitochondrial cytochrome C release and reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation in a cell-free reconstitution system caused by caspase-8-mediated BID cleavage and recombinant truncated Bid (tBid) (50).

Figure 1. Apoptosis pathway. Intrinsic stimuli like hypoxia, DNA damage, and ER stress all contribute to this pathway. Extrinsic stimuli like TNF alpha and FASL contribute to the extrinsic pathway. Ultimately, both routes activate the effector caspases, resulting in apoptosis. APAF1, apoptotic protease activating factor-1; BAX, bcl-2 associated x protein; BCL2, b-cell lymphoma-2; BH3, bcl2 homology domain 3; CIAPs, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins; FADD, fas-associated death domain protein; FASL/R, Fas ligand/receptor; PRC: procaspase; SMAC, second mitochondrial-derived activator of caspase; tBid, truncated bid; TNFα/R, tumor necrosis alpha/receptor; TRADD, TNF receptor-associated death domain protein; TRAF2, TNF receptor-associated factor 2; XIAP, x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.
2.1.1 Apoptosis in IBD
2.1.1.1 Apoptosis molecule expressions in IECs
Studies show higher levels of apoptotic molecules in the IEC, suggesting they may be implicated in the pathophysiology of IBD. For instance, current research found that IECs of DSS-induced animals produce more pro-apoptotic proteins (BAX and cleaved caspase-3) and fewer anti-apoptotic proteins (BCL2) (51). Similarly, Zhang and the team found that TNBS-treated mice’s IECs expressed more BAX and caspase 3 and less BCL2 (52). Also, Li and colleagues observed that mice given TNBS show increased caspase 3 and BAX expression in their IECs while reducing BCL2 (53). In a different study, only BCL-XL, one of the anti-apoptotic BCL2 proteins, is significantly elevated in human CRC tissues (54). After adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) loss, BCL2 is necessary for effective intestinal transformation and may be a target for chemoprevention (55). In acute lymphoblastic leukemia, elevated BCL2 expression has been noted (56). This may suggest that whereas BCL2/BCL-XL decreases in IBD, it is high in cancer; hence, elevated BCL2/BCL-XL may be required for tumor growth in cancer.
Clinical investigations have shown that apoptosis regulators can induce apoptosis in IECs. These regulators increase in patients with IBD. For instance, p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) expression was found to be higher in colitis-affected tissues in UC patient samples, and it is linked to apoptotic induction and colitis severity. PUMA activation promotes IEC apoptosis, which aids in the pathophysiology of colitis (57). Dirisina et al. (58) found that in patients with UC, levels of p53 and PUMA are elevated in inflamed mucosal tissues. This suggests human colon inflammation activates IEC apoptosis through p53-independent and p53-dependent pathways. Additionally, PUMA triggers an intrinsic apoptosis pathway associated with colitis.
2.1.1.2 Apoptosis, immune cells and intestinal barrier integrity
In crypts of affected and nearby uninvolved regions, apoptosis is the primary cause of epithelial cell death in active UC, with the Fas/Fas-L relationship acting as a mediator (59). Thus, investigations have revealed that the Fas/Fas-L connection may be present in immune cells, promoting apoptosis in IBD. For instance, a study revealed that FasL is present in CD3 lymphocytes penetrating UC lesions, suggesting Fas-FasL-induced apoptosis contributes to UC mucosal injury (60). According to separate research, immune cells such as T cells and macrophages may be less likely to suffer apoptosis when activated by Fas-FasL interaction. IBD patients with reduced Fas expression on intestinal lamina propria (LP) T-cells and macrophages may have a reduced susceptibility to Fas/FasL-mediated apoptosis (61). This suggests that higher Fas expression on LP T cells may enhance sensitivity to Fas/FasL apoptosis. Interestingly, the interstitial CD95L+ cell count and apoptosis frequency in the LP and epithelium are significantly elevated in UC. Subepithelial CD95L+ mononuclear cells are shown to be focally associated with epithelial apoptosis (62). In vitro studies indicate that activated T cells are the primary source of CD95L expression, suggesting that CD95L regulates immunological responses (63). As a result, T cells may be activated, increasing CD95L+ cells/mononuclear cells in the LP and epithelium.
Downregulation of specific proteins/enzymes has also been demonstrated to disrupt the intestinal barrier, resulting in inflammation and elevated apoptotic genes. A recent study found that downregulation of CRL4DCAF2 in IECs results in gut barrier dysfunction and inhibits IEC growth, increasing its susceptibility to inflammation. Inflamed colon tissues of mice lacking DCAF2 exhibited elevated levels of cleaved caspase 3 and other genes like p53, BAX, and Bid (64). Another study also found that the knockdown of 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase significantly increased the expression of cleaved caspase 3 and 8, decreased BCL-XL, and enhanced the experimental colitis induced by DSS. Intestinal epithelial damage and a ruptured barrier were also found (65). Zhang et al. (66) also found that the knockout of DJ-1 in mice significantly exacerbated colitis, resulting in increased intestinal inflammation and worsened IEC apoptosis. DJ-1−/− mice showed significantly higher cleaved, activated forms of caspase 3 and caspase 7 levels after DSS treatment than wild-type mice.
2.1.1.3 Apoptosis and the gut microbiome
The microbiota can either promote intestinal epithelial integrity or cause mucosal inflammation by causing or preventing intestinal epithelial cells from undergoing apoptosis (67). Therefore, studies have shown that the gut microbiota can induce apoptosis in the IEC. A study indicates that Cryptosporidium parvum (C. parvum) causes moderate apoptosis in human IECs, with the highest levels occurring 24 hours after infection (68). A recent study has shown that miR-3976, which targets BCL2A1, regulates cell apoptosis and parasite load in HCT-8 cells after C. parvum infection (69). This further reveals the role of C. parvum in regulating apoptosis in IECs.
3 Pyroptosis
Pyroptosis is an inflammatory PCD process triggered by mouse caspase-11, human caspase-4 and 5, or both human and mouse caspase-1 (70). Pyroptosis can be either canonical or noncanonical. The canonical pathway reacts to pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) during microbe infection, and the noncanonical pathway reacts to Gram-negative bacteria’s internal lipopolysaccharides (LPS) (71). In both pathways, pyroptosis occurs when inflammatory caspases cleave and activate the pore-forming effector protein gasdermin d (GSDMD) (70).
Canonical inflammasomes are produced by cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) in the presence of pathogen-related signals. This process activates pro-caspase-1 and results in pyroptotic cell death (72). The adaptor protein apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD (ASC) oligomerizes with inflammasome-forming PRRs, creating a massive cytosol structure that triggers dimerization, autoproteolysis, and pro-caspase-1 zymogen activation (72). A study found that cigarette smoke extracts (CSE) increase NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) and caspase-1 activity levels and improve the release of IL-1β and IL-18 in 16 bronchial epithelial cells (73). However, a recent study found that CSE enhances pro-IL-1β expression, activates caspase-1, and releases IL-1β and IL-18 without NLRP3 (74), implying that activation of caspase 1 may either be dependent or independent of NLRP3.
In the noncanonical pathway, Yang and the team found that LPS activation in the cytosol triggers caspase-11-dependent cleavage of the pannexin-1 channel, followed by ATP release, activating the purinergic P2X7 receptor, leading to cytotoxicity. These pathways are essential for initiating endotoxic shock in mice. The study finally found that caspase-11’s noncanonical inflammasome pathway triggers the pannexin-1 channel, leading to K+ efflux and NLRP3 activation (75). In response to microbial infection and cellular injury, the NLRP3 inflammasome plays a crucial role in the innate immune system by mediating caspase-1 activation and the release of proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1β, and IL-18 (76).
Pyroptosis’ final stage requires caspase 1 in the conventional pathway and caspase 4/5/11 (caspase 4/5 in humans, caspase 11 in mice) in the noncanonical pathway to cleave GSDMD at D275 into N- and C-termini. After cleavage, GSDMD’s N-terminus generates a transmembrane pore that leaks cytokines like IL-1β and IL-18 and messes with the water and ion balance, leading to severe inflammation and eventual cell death (71). Figure 2 depicts the mechanism of pyroptosis.

Figure 2. Mechanism of pyroptosis. PAMP and DAMP commence the canonical route, whereas bacteria and LPS synthesis initiate the non-canonical route. These two routes eventually cleave GSDMD, resulting in the GSDMD channel that leaks IL-1β and IL-18, causing pyroptosis. ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing card; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DAMP: damage-associated molecular patterns; GSDMD, gasdermin d; IL, interleukin; NLRP3: nod-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3; PRR, pattern-recognition receptor; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular patterns.
3.1 Pyroptosis in IBD
3.1.1 Intestinal epithelial barrier
Tight junction proteins, including occludins, zonula occludens (ZO), and claudins, are crucial for preserving the epithelial barrier integrity (77). Therefore, pyroptosis can weaken the intestinal barrier’s integrity by reducing tight junction proteins. A study found that mice treated with 5% DSS experienced mucin and occludin loss, increased inflammation, and NLRP3-related protein expression. The DSS group also showed increased levels of ASC, caspase-1, GSDMD, and IL-1β with decreased occludin protein levels (78). Similarly, Mahmoud and team also found increased IL-1β levels and elevated NLRP3, cleaved caspase-1, and ASC expressions in the colon tissues of DSS-induced mice. Additionally, DSS treatment decreased occludin gene expression and claudin-1 expression in immunohistochemistry (IHC) (79). Another study found that SP23 administration reduces ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 loss and downregulates STING and NLRP3 signaling pathways in intestinal inflammation caused by DSS (80). The study suggests that an increase in NLRP3 may lead to a decrease in tight junction proteins in DSS.
3.1.2 Pyroptosis and immune cells
In vitro, macrophages cultured with DSS secrete high amounts of IL-1β in a caspase-1-dependent manner (81). Macrophages lacking ASC, NLRP3, or caspase-1 show reduced IL-1β production, suggesting that DSS triggers caspase-1 via the NLRP3 inflammasome (81). Another study also found that Galectin-3 expression contributes to acute DSS-induced colitis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome and producing IL-1β in macrophages (82). Liu and the team revealed that salidroside skews macrophage pyroptosis and T helper 17 (Th17)/Treg balance to protect against experimental colitis (83). V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing 4 (VSIG4), a type I transmembrane receptor found in tissue-resident macrophages, has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects on immune-related illnesses (84). Liao and team found that VSIG4 is downregulated in IBD and negatively correlates with the NLRP3 inflammasome. The study reveals that M1 macrophages exhibit a greater NLRP3 inflammasome, pyroptosis, and inflammatory response than M2 macrophages (84). The study suggests that M1 macrophages may be involved in pyroptosis, while M2 may suppress it. In an alternative investigation, Shi and colleagues found that in macrophages, REGγ inhibition regulates members of the gasdermin family, promoting pyroptosis (85). Blocking REGγ can induce pyroptosis in macrophages.
A type of T cell and enzyme deletion has been shown to induce pyroptosis in tumor cells and IBD, respectively. For instance, Le Floch and team found that Vγ9Vδ2 T cells stimulated by 107G3B5 trigger caspase 3/7, leading to tumor cell death by pyroptosis. Therefore, using 107G3B5 to target BTN2A1 increases the Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell antitumor response by inducing immunogenic cell death through pyroptosis (86). Also, methyltransferase-like 13 (METTL3) deletion in IBD increases colonic epithelial cells’ vulnerability to pyroptosis and abnormal CD4+ T cell proliferation (87).
3.1.3 Other triggers of pyroptosis
Ma and the team found that long-term light exposure causes intestinal inflammation, which is linked to the gut microbiota and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. The study further found that the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is positively connected with gut microbiota dysbiosis. Bifidobacterium and unclassified Oscillospirales relative abundances were positively connected with NLRP3 mRNA expression levels. Additionally, the amount of caspase-1 and IL-1β mRNA expression was positively connected with the relative abundance of Family_XIII_UCG-001 (88).
Zhang and the team found that miR-223 promotes cell pyroptosis and contributes to the pathophysiology of IBD by activating the NF-κB pathway by targeting smad nuclear-interacting protein 1. Pyroptosis was reduced when miR-223 was knocked down. The IBD cell model’s ASC, NLRP3, and caspase-1/pro-caspase-1 levels were considerably lowered by miR-223 downregulation (89).
3.1.4 Pyroptosis markers in clinical study
Research in clinical settings has indicated that markers of pyroptosis, such as NLRP3 and its downstream pro-inflammatory cytokines, are present in patients with IBD. This leads to the release of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-18. For instance, Lazaridis and the team found that the NLRP3 inflammasome is active in CD patients. NLRP3 activation is only observed in UC patients with a long-standing history of the disease. CD patients exhibited a significantly higher mean maximal percentage increase in IL-1β release than controls and UC patients (90). Similarly, it was discovered that active UC and CD had higher levels of NLRP3 and IL-1β (91). However, NLRP3 and IL-1β were found in active UC, a neutrophil-dominated lamina propria cell population, indicating that IL-1β is processed independently of the inflammasome (91). Another study examined the potential link between NLRP3 and IBD in the Chinese Han community. It was discovered that the Chinese Han population’s NLRP3 polymorphisms rs10754558 and rs10925019 are strongly linked to UC susceptibility but not CD, suggesting NLRP3 may be crucial to UC pathophysiology (92).
CARD8 is a negative regulator of NLRP3 (93). It has been found that patients with missense mutation CARD8 CD have higher IL-1β levels than healthy controls, and when peripheral monocytes are stimulated with NLRP3 activators, they produce more IL-1β. The mutant T60 CARD8 could not bind to NLRP3 and prevent its oligomerization, undermining the NLRP3 inflammasome (94). This suggests that active NLRP3, a marker of pyroptosis, may be linked to CD patients.
3.1.5 Pyroptosis-related genes as biomarkers
Zhao and colleagues discovered potential genes such as AIM2, ZBP1, CASP1, IL1β, CASP11, and TLR4 in UC and CASP11, and TLR4 in active UC. To identify genes, the researchers employed a variety of analytical approaches such as binary logistic regression, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, random forest analysis, and artificial neural networks. Ultimately, the study found that these genes function well in differentiating between UC and determining if the condition is active (95). Another study found that AIM2 expression level could be a biomarker for predicting anti-TNF therapy efficacy. The hub genes found in the study were CAPS1, CASP5, GSDMD, AIM2, and NLRP3, with AIM2 being the best predictor of anti-TNF medication response. Immune function was greater, and anti-TNF medication was less effective in patients with a larger burden of the AIM2 inflammasome (96). A different research also identified ZBP1 and AIM2 as genes related to PANoptosis in atherosclerosis (97). Deep and machine-learning models have significantly improved the efficiency of IBD diagnosis and assessment by automating the accurate analysis of data from various diagnostic modalities (98). These techniques significantly reduce physicians’ time manually reviewing data for evaluation (98).
4 Necroptosis
Necroptosis, like other cell deaths such as apoptosis and necrosis, is a caspase-independent PCD mechanism that is believed to be a significant factor in the etiology of various illnesses (99). These include inflammatory conditions of the gut, skin, and lungs, in addition to kidney, heart, and brain ischemia-reperfusion injuries (100). The basic machinery that drives the route consists of the RIPK1 and RIPK3 kinases and the terminal effector pseudokinase mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL), which combine to create cytoplasmic necrosomes, leading to cell enlargement, plasma membrane rupture, intracellular component leakage, and cellular death and inflammation development (101, 102).
The canonical and noncanonical pathways make up this process. In the canonical pathway, it has been shown that RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL are the essential components when caspase-8 is deficient or inhibited (103). Necroptosis happens when the caspase activity necessary for apoptosis is inhibited in response to TNF, Fas, or TRAIL, as well as certain toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands (104). The primary mechanism of how necroptosis commences is the liberation of RIPK3 from caspase-8-induced repression (105). Also, Interferon (IFN)-β-induced macrophage necroptosis is triggered by tonic IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) signaling, resulting in the sustained expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1, STAT2, and interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) (106). Type I (mostly α/β) and type II (γ) IFNs both trigger pro-necrotic signaling through transcriptional activation of the latent kinase PKR that is dependent on Janus kinase (JAK)/STAT (107). Type I and type II IFNs trigger RIPK1/3 kinase-mediated necrosis when caspases (e.g., caspase 8) are inactivated or FADD is deleted or rendered inactive by phosphorylation (107).
The non-canonical route may not require the presence of all the kinases, such as RIPK1/3 and MLKL. For instance, the mouse cytomegalovirus infection results in necrosis that is RIPK3-dependent (108). Another study found that Influenza A virus (IAV) replication triggers Z-RNAs to activate ZBP1 in the nucleus, initiating RIPK3-mediated MLKL activation, leading to nuclear envelope rupture, DNA leakage, and necroptosis (109). Also, ZBP1 triggers RIPK3/MLKL signaling upon detecting cytosolic mitochondrial (mt)DNA (110). A recent study has shown that IAV-induced necroptosis requires RIPK3 in epithelial cells (111). These show that some viral infections may trigger necroptosis without RIPK1. Figure 3 depicts the fundamental machinery in these routes.

Figure 3. Necroptosis mechanism. The canonical and non-canonical paths lead to RIP3/MLKL activation, triggering the oligomerization of MLKL, resulting in the rupture of the plasma membrane, the release of intracellular chemicals, and cell death and inflammation promotion. FADD, fas-associated death domain protein; IFN, Interferon;IFNARI, ifn-α receptor type I; IRF9, interferon regulatory factor 9; ISGF3, ifn-stimulated gene factor 3; JAK1, janus kinase 1; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like; mt, mitochondrial; RIP/RIPK, receptor-interacting protein kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TLR3/4, toll-like receptor-3/4; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha; TRAIL/R, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/receptor; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β; ZBP1 (DAI), Z-DNA binding protein 1; VDNA, DNA viruses.
4.1 Necroptosis in IBD
4.1.1 Necroptosis and immune cells
Using confocal scanning, Lee and the team found that the development of UC is linked to CD4+ T cell necroptosis and inflammation. RIPK3, phosphorylated (p)-MLKL, and IL-17A are expressed more in CD4+ T cells in involved tissue from UC patients than in uninvolved tissue (112). Therefore, CD4+ T cell necroptosis may play a role in UC. Brasseit and team also found that colitogenic T lymphocytes are crucial for the initiation and progression of colitis. Colitogenic T-cell depletion decreases TNFα levels and inflammatory immune cell infiltration at inflammation sites (113).
It has been shown that once T-cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain-3 (Tim-3) knockdown macrophages attract neutrophils with their released chemokines, they emit TNF-α to cause neutrophil necroptosis. Consequently, this weakens the gut’s mucosal barrier and creates a vicious loop in colitis development (114). This suggests that macrophages may be involved in neutrophil necroptosis, which leads to colitis development.
4.1.2 Necroptosis and intestinal epithelial barrier
The intestinal epithelial barrier is crucial for maintaining host homeostasis (115). The intestinal epithelial barrier, composed of epithelial cells, tight junction proteins, and gut secretions, impedes the movement of antigens and luminal chemicals across the paracellular space (116). The stability of the epithelial barrier depends on tight junction proteins called occludins, claudins, and zonula occludens (77). Therefore, numerous harmful events that disrupt the tight junction complex can result in the loss of this homeostatic barrier (117).
A study by Liu and the team found that necroptosis disrupts the intestinal epithelial barrier by suppressing claudin-1 and occludin. However, Nec-1 inhibited necroptosis, which increased claudin-1 and occludin protein expression (118). Another study also showed that an RIPK1 inhibitor may reduce intestinal barrier damage by reducing tight junction breakdown and the oxidative stress that comes with it (119). This may imply that RIPK1, which is involved in necroptosis in IBD, may damage the intestinal barrier.
Negroni et al. (120) also revealed that necroptosis driven by RIPK3 significantly affects intestinal inflammation by increasing pMLKL, activating various cytokines and alarmins, and modifying epithelial permeability (E-cadherin, Occludin, Zonulin-1). The overexpression of RIPK3 leads to a reduction in the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier. In human intestinal epithelial cells, RIP3 inhibitor GSK872 or RIP3 knockdown reverses TNF-α’s promotion of necrosis and apoptosis and its negative influence on proliferation (121). This implies that RIP3 presence may lead to the disruption of the intestinal epithelial barrier.
Zhang et al. (122) found that non-littermate MLKL-deficient mice exhibit considerably better survival rates, clinical scores, intestinal damage, and intestinal mucosal barrier integrity than wild-type (non-littermate) mice. Schwarzer et al. (123) also found that MLKL loss only partially alleviated ileitis in animals lacking FADD in IECs, while it completely cured ileitis caused by epithelial caspase-8 ablation.
Notably, STATI has been demonstrated to cause necroptosis in IBD. Stolzer and team found that in IEC mice lacking caspase-8, an additional loss of STAT1 prevented cell death, barrier disruption, and systemic infection. When epithelial STAT1 is absent, epithelial cells are no longer lost, and caspase-8 activation is also decreased. Both caspase-8-dependent and -independent cell death are upstreamed by epithelial STAT1 (124). Controlling intestinal barrier penetration by beneficial and harmful microorganisms depends on Paneth cells (125). In IBD, it is common to observe a decrease in the number of Paneth cells (126). This suggests that in IBD, barrier breakdown may be caused by Paneth cell loss. Interestingly, IFNL (Interferon lambda) induces Paneth cell death in mice via MLKL and STAT1 activation (127). Also, TNF-α and IFN-γ, Th1-type cytokines, disrupt the gut epithelial barrier function and occupy crucial nodes within these networks. It is found that JAK1/2 kinases are the primary and nonredundant drivers of the synergistic death of human IECs induced by IFN-γ and TNF-α (128). These imply that STAT1/JAK1/2 may induce necroptosis in IEC, resulting in barrier breakdown.
4.1.3 Necroptosis in clinical studies
Necroptosis molecules may cause IBD, according to several clinical investigations. For instance, Duan et al. (121) found that as the severity of UC worsened, the expression levels of MLKL and RIP3 rose considerably. Similarly, in UC’s inflammatory tissues, RIP3 and MLKL are elevated (129). According to the study, intestinal inflammation in UC patients is closely linked to necroptosis (129).
Patients with IBD have higher levels of RIPK3 expression in inflammatory tissues than controls (130). Pierdomenico and the team also found that patients with IBD and allergic colitis have higher levels of RIP3 and MLKL in their inflammatory tissues, although caspase-8 was lower. Children with IBD have intestinal inflammation that is tightly linked to necroptosis, which exacerbates the inflammatory process (105).
5 Autophagy
Cells use autophagy to break down and recycle proteins and organelles to preserve intracellular homeostasis. Autophagy generally protects cells; nevertheless, excessive autophagic flux or disruption of autophagy pathways typically results in cell death (131).
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a crucial energy sensor that controls cellular metabolism to preserve energy homeostasis, stimulates autophagy. Nevertheless, the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a major regulator of cell development that combines signals from growth factors and nutrients, inhibits autophagy (132). AMPK phosphorylates Ser 317 and Ser 777 of unc-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) in response to a glucose shortage, hence inducing autophagy. High mTOR activity inhibits ULK1 activation when nutrients are sufficient by phosphorylating ULK1 Ser 757 and disrupting the ULK1-AMPK connection (132). Melatonin has been found to inhibit cancer cells by activating autophagy through ULK1 activation, following mTOR inhibition, which phosphorylates Beclin-1. Beclin-1 stimulates autophagy and phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate kinase (PI3K) complex I activity in cancer cells in conjunction with autophagy/beclin-1 regulator 1 (AMBRA1) and vacuolar protein sorting 34 (VPS34) (133). These show that AMPK, beclin-1, PI3K, and VPS34 may be involved in autophagy.
The autophagosome, a crucial initial step in autophagy, is a double-membrane organelle that absorbs cytosolic material for degradation. ULK1 mediates this phase by forming a complex with three protein partners: focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200 kDa (FIP200), autophagy-related protein (ATG) 13, and ATG101 (134). During this process, ATG8 is incorporated into the expanding phagophore via covalent attachment to phosphatidylethanolamine via the noncanonical ubiquitin-like conjugation cascade, including the E1 (ATG7), E2 (ATG3, ATG10), and E3 (ATG12-ATG5-ATG16 complex) enzymes (135). A study reveals that the ATG8 conjugation machinery, consisting of six ATG proteins, regulates the shape of the membrane during autophagosome development (136).
A popular marker for macroautophagy tests is LC3. Following translation, ATG4 processes pro-LC3 to reveal the glycine residue at the C-terminus to facilitate downstream conjugation events that convert LC3-I to LC3-II (137). Once autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes, autophagy consumes biological components in double membrane-bound autophagosomes for recycling and clearance (138). Transcription factor EB (TFEB) enhances autophagic flow by promoting lysosome formation, generating autophagosomes, and fusing with lysosomes, thereby aiding in the clearance of harmful protein structures (139). Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNAREs), RABs, and tethering complexes (homotypic fusion and protein sorting (HOPS)-tethering complex) are mainly responsible for controlling membrane fusion (140). Figure 4 illustrates the autophagy pathway.

Figure 4. Autophagy pathway. Nutrient starvation and energy depletion cause several cascades that alter the phagophore’s initiation and elongation to the autophagosome. During this process, ubiquitin-like conjugation cascade systems such as the LC3s and ATGs facilitate autophagosome formation. AMPK, amp-activated protein kinase; ATG, autophagy-related gene; FIP200, focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200 kDa; HOPS, homotypic fusion and protein sorting; LAMP-2, lysosome-associated membrane protein 2; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PI3P, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate; SNARE, soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor; ULK1, unc-51-like kinase 1; VPS 34, vacuolar protein sorting 34.
5.1 Autophagy in IBD
5.1.1 Autophagy genetic polymorphisms and risk of IBD
Multiple autophagy gene variants have been linked to an elevated risk of IBD. An elevated risk of CD is associated with the AG genotype for rs2241880 (ATG16L1) in Iraqi patients (141). Similarly, ATG16L1 rs2241880 (G allele) is a consistent risk factor for CD in Caucasian populations, according to a meta-analysis (142). In a different study, the T and G alleles of ATG16L1 rs2241880 polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of CRC (143) and esophageal cancer (144), respectively.
In Indian patients, the T allele at rs4663402 (ATG16L1) and the C allele at rs4663421 (ATG16L1) are positively associated with CD and UC (145). Among Iranians, there is a noteworthy correlation between the ATG16L1 gene rs2241879 and an elevated risk of IBD (146). These results show that genetic variations in the ATG16L1 may lead to an increased risk of IBD.
5.1.2 Expression levels of autophagy genes/proteins in IBD
Rezaie and colleagues discovered the downregulation of autophagy-related genes in the colon of the DSS group, including Beclin, ATG12, ATG5, ATG7, and ATG13 (147). Another study found that the colitis animals exhibit significantly increased autophagy-related proteins like mTOR, P62, and p-MTOR in IHC but substantially reduced LC3B levels (148). In western blot analysis, a similar pattern is seen. In the colon tissue of mice with DSS-induced colitis, the expressions of P62, mTOR, and p-mTOR increased, while ATG16L1 and LC3II/I decreased (148). Another study also showed that the DSS group exhibits an increase in p62 expression, while a decrease in the LC3II/I ratio and Beclin-1 expression is observed (149). Through western blot analysis, Shi and his team found increased levels of p62, p-mTOR/mTOR, and LC3-II/LC3-I in DSS-treated mice but decreased levels of Beclin-1 (150).
mTOR silencing significantly reduced inflammation and oxidative damage caused by LPS, but blocking ATG5 increased these effects. Experimental colitis and oxidative stress were significantly reduced in vivo by the pharmacological injection of mTOR inhibitors and autophagy stimulators (151). This further provides evidence that mTOR may contribute to IBD pathogenesis.
5.1.3 Autophagy regulators in clinical studies
Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) controls genes related to ER stress, autophagy, amino acid metabolism, and the inflammatory response. In patients with active CD or UC, the inflammatory intestinal mucosa has lower levels of ATF4. ATF4 loss in mice decreases Slc1a5 transcription, which decreases glutamine absorption by IECs and antimicrobial peptide expression. Therefore, ATF4 may be a target for IBD treatment (152).
CD-associated mutations alter the autophagy-mediated antibacterial pathway involving ATG16L1 and NOD2 in a manner specific to certain cells or functions (153). Studies have shown that NDO2 polymorphisms lead to IBD susceptibility. For instance, Watson et al. (154) found that patients with very early-onset IBD who have NOD2 polymorphisms (NOD2+) were substantially more likely than those in the NOD2 group to have arthropathy (60%) and a CD-like phenotype (90%), as well as linear growth impairment (90%).Horowitz et al. (155) found that a molecular driver of early onset IBD, specifically CD, is the recessive inheritance of NOD2 alleles, most likely a consequence of impaired NOD2 protein activity. Abdelnaby and the team also found that among Kuwaiti CD patients, NOD2/CARD15 gene variants were substantially linked to an elevated risk of illness and aggressive characteristics (156).
Human immunity-related GTP-binding protein M (IRGM) regulates mitophagy and xenophagy, two forms of selective autophagy (157). Lu and colleagues found that polymorphisms in the autophagy gene IRGM seem to increase the risk of CD but not UC, particularly among Europeans. This could help clarify the part autophagy plays in the pathophysiology of CD (158). IRGM participates in autophagy and mediates innate immune responses (159). It has been shown that the IRGM gene’s single-nucleotide polymorphism rs4958847 showed a highly significant correlation with the incidence of surgery in ileocolonic CD patients (159).
5.1.4 Polymorphisms in autophagy and gut microbiota
The risk allele ATG16L1 T300A, a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) linked to increased CD risk, leads to dysbiosis in mice, causing an increase in Bacteroides and amplifying the Th1 and Th17 immune responses in the gut lamina propria (160). These alterations occur before the start of illness in human stool microbiome-associated mice, indicating that microbiota modifications cause inflammatory cell population shifts in the gut (160). These findings clarify the genesis of CD and shed light on the connection between SNPs, dysbiosis, and the gut’s immune system (160). Another study revealed that ATG16L1T300A/T300A mice display several bacteria linked to IBD, including Tyzzerella, Mucispirillum, Ruminococcaceae, and Cyanobacteria. In the DSS colitis paradigm, ATG16L1T300A/T300A mice exhibited more severe inflammation than wild-type mice (161).
5.1.5 Autophagy and immune cells/immune response
Zhang and team found that ATG16L1 deficiency in dendritic cell (DC) mice displays elevated pro-inflammatory TNF-α and IL-1β levels, leading to intestinal inflammation. Thus, one of the unique causes of IBD is decreased ATG16L1 activity, resulting in elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines in vivo (162). Similarly, the deletion of ATGI6L1 in CD11c+ DCs exacerbates intestinal inflammation in DSS-induced colitis. The deletion of ATG16L1 enhances the co-expression of RAB5 and RAB7 with Salmonella typhimurium but doesn’t affect Beclin1 and suppresses the co-expression of LC3 and LAMP1 (163). The study indicates that ATGI6L1 deletion in the presence of Salmonella typhimurium can exacerbate colitis. This may suggest that ATGI6L1’s presence protects against colitis aggravation while its variants lead to IBD. As a result, ATGI6L1 and its variants may play distinct roles in immune system regulation during IBD progression.
Plantinga and team found that the ATG16L1 polymorphism in humans is linked to elevated IL-1β and IL-6 production, potentially influencing the inflammatory process in CD. Cells from ATG16L1 Thr300Ala (T300A) risk variants shown to affect ATG16L1 protein expression show enhanced NOD2-stimulated production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6 (164). In a different study, the ATG16L1 T300A is linked to better survival in gastric cancer individuals (165). The study found that tumors of individuals with T300A/T300A have downregulated PPAR, EGFR, and inflammatory chemokine pathways, while Wnt/β-catenin signaling is upregulated (165). This implies that the ATG16L1 T300A may have different roles in IBD and gastric cancer.
6 Ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is a controlled cell death influenced by iron and severe lipid peroxidation (LPO), affecting various physiological and pathological processes (166). An important component of ferroptosis is the transferrin receptor, which is essential for intracellular iron buildup and the development of ferroptosis (167). Iron is typically transported to endosomes by transferrin receptors, where the six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate family member 3 (STEAP3) converts it from Fe3+ to Fe2+ (168). The plasmalemma divalent metal ion transporter 1 (DMT1) facilitates the cellular uptake of Fe2+, while transferrin receptors carry transferrin-bound Fe3+ (169). Through poly r(C)-binding protein 1 (PCBP1), the labile iron pool (LIP) is coordinated, allowing the cell to effectively transport iron to non-heme iron enzymes, store iron in ferritin, and provide iron for the Fe-S cluster assembly/repair mechanism (170). Ferroportin (FPN), the only known iron exporter, is crucial for maintaining iron homeostasis (171). Ferritin is transported to autophagolysosomes for breakdown by nuclear receptor coactivator 4 during ferritinophagy (172). After autophagy degrades ferritin, iron ions are released, which trigger the LIP to initiate the fenton reaction, leading to lipid peroxidation (172). A study reveals that Z-Ligustilide’s excessive activation of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathway is responsible for the selective onset of ferroptosis in leukemia cells. The primary cause is the ROS-induced accumulation of LIP in acute myeloid leukemia cells (173).
An intracellular antioxidant called glutathione (GSH) is produced from glutamate, cysteine, and glycine (174). Free cystine enters cells via the cystine-glutamate antiporter xCT, while plasma glutathione-disulphide may be the main source of cystine throughout the body (175). A study in acute myeloid cells found that reduced cystine and glutamine levels disrupt GSH synthesis, leading to the malfunction of glutathione peroxidase-4 (GPX4), a co-factor used to maintain lipid peroxidation homeostasis (176). Small compounds that inhibit GPX4 generate a fatal buildup of lipid peroxides and promote ferroptosis cell death (177). A study by Cheng and the team found that Leonurine raises GPX4 and GSH, fixes ultrastructural defects in mitochondria effectively, and greatly lowers ferroptosis in acute kidney injury (AKI), both in vivo and in vitro. It also considerably reduces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by downregulating activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), CHOP, and Chac glutathione-specific γ−glutamylcyclotransferase 1 (CHAC1) (178). This may imply that in ER stress, the upregulation of ATF4, CHOP, and CHAC1 may suppress GSH and GPX4, leading to ferroptosis. Another study found that the GSH/glutathione disulphide ratio decreases when cells are exposed to dihydroartemisinin (DHA), a ferroptosis inducer. Treatment with DHA also inhibits GPX4 and increases CHAC1 expression levels (179). Lipid peroxidation, which may result from GPX4 activity suppression, can cause ferroptosis (180).
The long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthase 4 (ACSL4) esterifies coenzyme A (CoA) to produce certain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), including adrenic and arachidonic acid. The production of arachidonoyl-CoA, facilitated by ACSL4, plays a crucial role in ferroptosis execution by promoting phospholipid peroxidation (181). TPCI (photosensitizer) produces ROS when exposed to light, activating ALOX12 or resuscitating it through SLC7A11 downregulation. This leads to direct peroxidation of PUFAs into fatal lipid ROS, causing ferroptosis in cancer cells independent of ACSL4 (182). The study suggests lipid peroxidation may occur through arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase (ALOX12) activation when solute carrier family (SLC) 7A11 is down-regulated without ACSL4.
Recent research has revealed a connection between ferroptosis and p53 (183). Ren and colleagues found that the p53/spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 (SAT1)/arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase (ALOX15) signaling pathway induces ferroptosis, which is significantly suppressed by cerebroprotein hydrolysate-I in Alzheimer’s disease (184). The expression of SAT1 causes LPO and makes cells more susceptible to ferroptosis in response to stress caused by ROS. In xenograft tumor models, this results in tumor growth inhibition (185). However, in xenograft mouse models, inhibiting endogenous independent phospholipase A2β (iPLA2β) causes tumor cells to undergo p53-driven ferroptosis, increasing p53-dependent tumor suppression (186). This implies that the activation of iPLA2β may prevent p53-driven ferroptosis.
Certain elements have been found to trigger lipid peroxidation, leading to ferroptosis. Like erastin and RSL3, which block system XC- or directly target the reducing enzyme GPX4, respectively, FINO2 does not deplete GPX4 protein, unlike FIN56. Rather, FINO2 directly oxidizes iron and indirectly inhibits GPX4’s enzymatic activity, leading to widespread lipid peroxidation (187). However, GTP cyclohydrolase-1 (GCH1)-expressing cells synthesize tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)/dihydrobiopterin (BH2), which results in lipid remodeling and inhibits ferroptosis by blocking phospholipid loss with two acyl tails of polyunsaturated fats (188). BH4 is a strong antioxidant that sequesters radicals and, either by itself or in combination with vitamin E, prevents lipid membranes from undergoing autoxidation (189).The transsulfuration pathway, mevalonate pathway, ferroptosis inhibitory protein 1 (FSP1)-coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) pathway, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH)-dihydroubiquione (CoQH2) pathway, and GTP cyclohydrolase-1 (GCH1)-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) pathway are among the other antioxidant systems that have also been linked to the regulation of ferroptosis (190) (Figure 5).

Figure 5. Mechanism of ferroptosis. TFRI/TF, FAT/FATP/PUFAs, and other pathways influence ferroptosis formation. Lip-1, DFO, Fer-1, the GCH1/BH4 and GSH/GPX4 pathways, and FSP1 suppress ferroptosis. ACSL4, long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthase 4; ALOX12/5, arachidonate 12/5-lipoxygenase; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; BH2, dihydrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CHACI: chac glutathione specific γ−glutamylcyclotransferase 1; DFO, deferoxamine; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; DMT1, divalent metal ion transporter 1; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Fer-1, ferrostatin-1; FPN, ferroportin; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; GCH1, cyclohydrolase-1; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase-4; GSH, glutathione; GTP, guanosine 5′-triphosphate; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; iPLA2β, independent phospholipase A2β; LIP, labile iron pool; Lip-1, liproxstatin-1; MVA, Mevalonate; NADP+,nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SATI, spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1; SLC, solute carrier family; STEAP3, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate family member 3; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1; TS, transsulfuration.
6.1 Ferroptosis in IBD
6.1.1 Ferroptosis in IEC
The mammalian GIT, containing innate and adaptive immune cells and trillions of commensal microbes, requires barrier and regulatory systems to maintain tissue homeostasis and host-microbial relationships (191). Therefore, IECs are crucial mediators in maintaining intestinal homeostasis, promoting the formation of an immune environment conducive to commensal bacterial colonization (191). Notably, it has been shown that ferroptosis disrupts the IECs, which causes IBD. Xu and team found that IECs from UC patients and colitis-affected rats exhibit markedly increased ferroptosis, driven by ER stress signaling (192). Another study by Chen and colleagues also found that SLC6A14 uses the C/EBPβ-PAK6 axis to help epithelial cells undergo ferroptosis in UC (193). Mucosal inflammation, characterized by an impaired intestinal epithelial barrier, exposes the immune system to more luminal bacteria, leading to an ongoing inflammatory response (194).
According to in vitro studies, ACSL4 plays a significant role in the IEC impairment brought on by LPS stimulation. Using si-ACSL4 or RSG to inhibit ACSL4 can provide efficient defense against intestinal epithelial damage brought on by LPS (195). In Caco2 cells, ACSL4 siRNA significantly reduced the hypoxia-induced production of ACSL4, elevated the expression of GPx4, and reduced lipid peroxidation. By blocking ischemia-induced ACSL4, intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced cell damage and intestinal barrier dysfunction were lessened, and ferroptosis and lipid peroxidation were prevented (196). These findings suggest that ferroptosis can lead to IEC damage/disruption.
6.1.2 Ferroptosis in immune cells
6.1.2.1 Regulatory T cells
Tregs are crucial for sustaining immunological tolerance and homeostasis by regulating immune system activation (197). Treg cells are essential to the complex pathophysiology of IBD at the beginning or development of the disease (198). Preclinically, studies have shown that Tregs may undergo ferroptosis. Yan and their team found that a high-fat diet causes intestine Treg cells to undergo ferroptosis, which may be the primary first step in immunotolerance loss and colitis development (199). The reduction of Treg cells in necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is ascribed to ferroptosis caused by decreased expression of GPX4. Treg cells with GPX4 deficiency have reduced immunosuppressive activity and are prone to ferroptosis. In NEC, the ferroptosis of Treg cells worsens damage to the gut and increases the inflammatory cell response (200).According to Xu and the team, GPX4 controls immunological homeostasis and antitumor immunity by preventing Treg cells from ferroptosis and lipid peroxidation. GPX4 loss causes excessive lipid peroxide buildup and Treg cell ferroptosis in response to T cell receptor (TCR)/CD28 co-stimulation (201). These imply that Tregs may undergo ferroptosis.
6.1.2.2 Macrophages
As antigen-presenting cells, macrophages release molecules that modulate the immune system, such as chemokines and cytokines, essential for triggering other intestinal immune cells and influencing the gut’s immunological response (202). Macrophages, responsible for innate immunity, also play a role in the development of intestinal inflammation (203). Recent research indicates that ferroptosis in macrophages can lead to the development of colitis. Ye and colleagues found that combining ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) and 5-aminosalicylic acid reduces ferroptosis in colon tissue macrophages and increases M2 macrophages, suggesting targeting ferroptosis in M2 macrophages as a potential treatment for UC. This shows that macrophages may undergo ferroptosis. The study further demonstrated that M2 macrophages are more susceptible to ferroptosis than M1 macrophages, and this vulnerability is linked to the ERK-cPLA2-ACSL4-mediated activated arachidonic acid (AA) metabolism pathway (204). Another study also showed that mice with UC exhibit increased Fe2 accumulation in their colon macrophages, linked to increased production of inflammatory cytokines like NO, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 (205). Fe2+ accumulation is known to cause ferroptosis; therefore, increased Fe2 in macrophages may lead to macrophage ferroptosis. In a different study, ferroptotic macrophages facilitate the inflammatory bone resorption linked to apical periodontitis (206).
6.1.2.3 Group 3 innate lymphoid cells
ILC3 and intestinal T cells regulate gut immune responses and the microbiota’s makeup (207). ILC3s are vital for maintaining intestinal tissue integrity and defending against pathogens, and their dysfunction can increase vulnerability to gut inflammation. Intestinal mucosal ILC3s from patients with UC are shown to have elevated levels of ferroptosis-related genes, including GPX4, a crucial ferroptosis regulator (208). In a mouse model, when GPX4 was deleted, the number of NKp46+ILC3 cells decreased, IL-22 and IL-17A production was compromised, and intestinal inflammation worsened in a way that was independent of T cells (208). These findings suggest that ILC3 may undergo ferroptosis.
6.1.3 Ferroptosis-related genes as biomarkers
Biomarkers are utilized in various fields, such as diagnosing IBD, assessing disease activity, predicting treatment impact, and predicting relapse (209). Therefore, it is necessary to have biomarkers that combine environmental and genetic elements to forecast the course of complicated immunological illnesses like IBD (210). Certain genes involved in ferroptosis in IBD have been discovered. These genes may have diagnostic value for IBD. A study indicates that UC is linked to STAT3-mediated ferroptosis, suggesting that STAT3, a gene linked to ferroptosis, could serve as a valuable biomarker for diagnosis and treatment (211). Another study by Qian et al. (212) identified five hub genes (LCN2, MUC1, PARP8, PLIN2, and TIMP1) that can differentiate UC patients from controls and positively associate with ferroptosis in UC. These genes positively correlate with M1 macrophages and neutrophils. The logistic approach had an AUC value of 1.000 for the training cohort and 0.995 for the validation cohort. Therefore, these hub genes may be useful in diagnosing UC from controls. Similarly, five ferroptosis-related hub genes such as ALOX5, TIMP1, TNFAIP3, SOCS1, and DUOX2 have been identified as diagnostic markers to differentiate between UC and controls. SOCS1, TIMP1, DUOX2, and ALOX5 negatively correlate with M2 macrophages, while ALOX5 and TNFAIP3 are positively connected with neutrophils (213).
Other ferroptosis-related genes have been identified in CD. Ji and the team found five ferroptosis-related hub genes such as PTGS2, IL6, IL1B, NOS2, and IDO1. The expression of hub genes in CD patients and normal subjects showed significant changes upon external validation (214). The AUC values for all genes were above 0.8, suggesting they could serve as CD biomarkers (214). Zhang et al. (215) also discovered three upregulated ferroptosis genes (IL-6, DUOX2, and PTGS2) likely to modulate ferroptosis in CD and may be involved in its development and progression. Therefore, the findings could lead to new CD biomarkers and diagnostic and therapeutic indicators.
6.1.4 Gut microbiome and ferroptosis
Recently, the pathophysiology of IBD has been linked to the adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) pathotype of E. coli (216). Therefore, a recent study has shown that AIEC causes ferroptosis in IECs. AIE Ccolonisation in CD patients’ terminal ileum increases 4-hydroxynonenal levels and decreases ferritin heavy chain (FTH) and GPX4 levels in the intestinal epithelium (217). In vitro tests show that AIEC infection can lower FTH and GPX4 levels, elevate LPO, and cause IEC ferroptosis (217). So AIEC may modulate GPX4, FTH, and LPO to trigger ferroptosis.
7 Cell death in IBD pathophysiology
IEC passive shedding largely involves apoptosis at villi tips (218). In mice, shed IECs have been shown to persist for several hours, promoting the expression of antimicrobial genes at the tips of villi and helping to control the makeup of the gut microbiota (219).The rate of senescent epithelial monolayer cell clearance and the growth of stem cells in the crypts are both correlated with the shedding and renewal of IECs (21). It is unclear exactly how IEC death occurs in IBD (21). However, IEC shedding is elevated, and barrier integrity is compromised in the intestinal lamina propria due to a highly inflammatory environment rich in the proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α, which further fuels inflammation (21). Also, in IBD, IECs are continuously lost, and other immune cells are also continuously shed; this is most noticeable during the active stages of the disease. In IBD, the digestive tract experiences excessive cell death as a result of ongoing inflammation and recurring bouts. Increased cell death may stimulate the gut immune system, exacerbating intestinal inflammation in IBD (220, 221). Excessive IEC apoptotic cell death during the pathophysiological state causes a chronic inflammatory condition (222). Later, the necroptotic cell death takes over, bringing about more pathological features than apoptosis (222). It may also trigger other lytic cell death mechanisms, such as ferroptosis and pyroptosis, to increase the pathogenesis of intestinal diseases (222).These findings suggest that excessive cell death may destabilize the barrier and activate immune cells, resulting in additional inflammation. The commencement of apoptotic cell death may trigger the activation of other cell death mechanisms such as necroptosis, ferroptosis, and pyroptosis. As a result, cell death in IBD may activate other cell death processes, and in the presence of an inflammatory environment, the vicious cycle of cell death persists.
IBD-related necroptosis mostly affects IECs, and RIPK3 inhibition can somewhat reduce the chronic intestinal inflammation brought on by necroptosis (223, 224). In IBD, intestinal stem cells may also undergo necroptosis. The loss of the essential gene SETDB1 can cause necroptosis, which alters colon epithelial differentiation, compromises the mucosal layer, and increases intestinal inflammation (225, 226). According to a study on IBD patients, RIPK3-induced necroptosis modifies occludin, zonulin-1, and E-cadherin, which impacts membrane permeability (120). In the IBD gut, cell pyroptosis is caused by inflammasome activation (e.g., NLRP3), essential for innate immune reactions, and is vital for gut-brain balance and gut microbiota maintenance (227, 228). Cell pyroptosis, which is mostly carried out by proteins like GSDMB, GADMD, and GSDME, mediates several damage signals that result in chronic inflammation that persists in IBD (229). Additionally, GSDMB, a pyroptosis executor, is essential for preserving the function of the epithelial layer and reducing inflammation in IBD (230). Necroptosis and pyroptosis can cause lytic cell death, which is probably why they have the potential to spread disease. Distinct from apoptosis, this type of cell suicide permits the release of immunogenic cellular material, such as inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), to cause inflammation (231). Ferroptosis is seen in IECs of DSS animals and IBD patients, mostly due to endoplasmic reticulum stress and the NF-κB pathway (232). In IBD, the intestinal epithelium experiences excessive lipid peroxidation, elevated ferrous iron levels, and ROS buildup, contributing to chronic aberrant inflammation (232, 233). Ferroptosis inhibitors have demonstrated efficacious management of intestinal chronic inflammation, a finding extensively confirmed in both animal model and IBD patients (211, 234, 235).
Intestinal homeostasis and repair depend on autophagy and its regulatory mechanisms, promoting intestinal barrier function in response to cellular stress by regulating tight junctions and preventing cell death. Moreover, it has become evident that autophagy plays a part in intestinal stem cells as well as secretory cells, influencing their metabolism as well as their ability to proliferate and regenerate (236).
In addition, TNF-α can cause RIPK3-dependent necroptosis and extrinsic caspase-8 and executioner caspase-3-dependent apoptosis when caspase-8 or TNFAIP3 (A20, a ubiquitin editing enzyme) capabilities are compromised (223, 237–241). TNF-α can also cause IEC shedding (242–245). Unlike homeostatic IEC shedding where barrier integrity is maintained by rapid basolateral tight-junction protein redistribution and zipper-like replacement by neighboring cells (246, 247), necroptosis, in which several nearby IECs lose contact, has been documented to accompany TNF-α-induced shedding (243, 248). It would be challenging to discern cause from effect if greater IEC death and barrier integrity resulted in more inflammation, intestinal epithelial damage, and possibly even dysbiosis (21). Additional elements that might cause cell death include oxidative stress, hypoxia, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress (249). Cell death can result in aberrant IECs, which attract immune cells and promote inflammation. At the same time, inflammatory cytokines like TNF can trigger cell death, which leads to IEC abnormalities. As a result, cell death is bidirectional, making it difficult to discern the causal link between cell death and inflammation.
As previously documented, IEC cell death leads to IEC irregularity, which attracts immune cells and promotes inflammation. Meanwhile, inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α can cause cell death, resulting in IEC abnormality. Therefore, cell death is a bidirectional process, and it may be difficult to determine the causal relationship between cell death and inflammation. Therapies targeting the upstream cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β may be the best option for treating cell death, which can help reduce cell death at the IEC or immune cells. This may prevent proapoptotic signals. It is also known that excessive IEC apoptotic cell death leads to chronic inflammation, followed by necroptotic cell death. This causes more pathological features and potentially triggers other lytic cell death mechanisms like ferroptosis and pyroptosis, increasing the pathogenesis of intestinal diseases. Therefore, preventing the upstream signal TNF-α may prevent cell death. Some patients may not react to anti-TNF therapy or experience diminishing response over time. Targeting cell death markers with MSCs may prevent cell death, gut abnormalities, and inflammation, which may prevent further cell death processes. Therefore, exploring combination therapy with IBD medications and MSCs is recommended for better therapeutic outcomes.
8 MSCs and cell death modulation in IBD
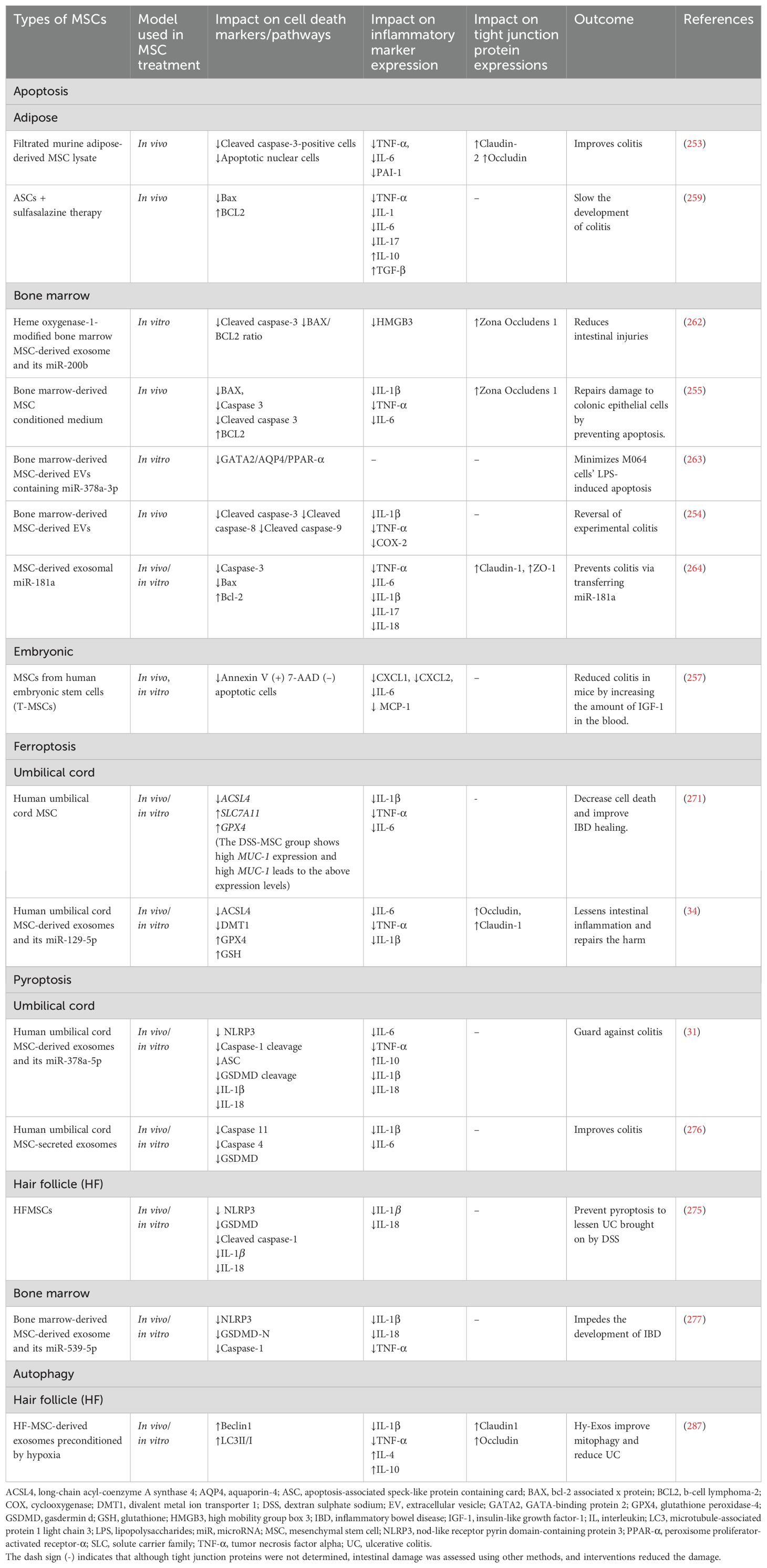
MSCs are a crucial alternative for tissue healing due to their differentiation capacity and paracrine characteristics. MSCs release extracellular vesicles (exosomes and microvesicles) and secrete soluble substances, fulfilling their paracrine roles. Extracellular vesicles, primarily endosomal in origin, carry proteins, mRNA, and miRNA from the cells of origin to target cells. Recent research indicates that MSCs’ therapeutic impact in animal disease models is solely due to these extracellular vesicles, suggesting they could replace MSC-based therapy in regenerative medicine (250). Nearly every tissue contains MSCs, which develop into specific cell types and perform immunomodulatory actions (251). MSCs primarily engage in immunomodulatory activities through cell-to-cell interactions with immune cells, including T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells (DCs), and neutrophils (252). Therefore, MSCs may regulate cell death through their extracellular vesicles (EVs) and interactions with immune cells. Major cell death markers in IBD lead to greater epithelial cell loss, decreased intestinal barrier integrity, and increased inflammatory cytokines and alarmins. DSS, 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS), and LPS have been utilized to create cell death models in tissues and cells. MSCs’ ability to regulate these markers, prevent epithelial cell loss, improve intestinal barrier integrity, and reduce inflammation may help prevent IBD. These will promote cell survival, tissue regeneration, immune cell modulation, and reduce inflammation.
8.1 MSC and apoptosis
Nishikawa and the team discovered that the DSS-induced colitis mouse model showed higher concentrations of caspase-3-positive cells and apoptotic nuclear cells in the colon sections and increased colon inflammatory cytokines, leading to decreased intestinal tight junction proteins such as claudin-2 and occludin (253). However, constant filtrated murine adipose-derived MSC lysate (FADSTL) administration prevented apoptosis, reduced inflammation, leading to preserved tight junction proteins (increased claudin-2 and occludin), and alleviated clinical symptoms (253). Yang et al. (254) found that rats that received TNBS enema experienced severe diarrhea, mucosal injury, weight and appetite loss, decreased colon length, elevated inflammatory markers, and even bloody stools. Additionally, there was an increase in the cleavage of apoptotic markers such as caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 (254). However, BMMSC-EVs reduced and averted all the colon pathologies and inhibited apoptosis in colitis rats by decreasing caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 cleavage (254). Liu and the team discovered that BMMSC-conditioned medium (CM) reduces cell apoptosis in DSS-induced experimental colitis. Proinflammatory cytokines, a shorter colon, weight loss, bloody diarrhea, lower expression of ZO-1, anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, and greater abundance of the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax, caspase 3, and cleaved caspase 3 were all seen in the DSS group. BMMSC-CM enema therapy increased ZO-1, prevented cell apoptosis, and reduced all histopathological characteristics (255). Additionally, MSC-CM decreased macrophage and neutrophil recruitment while augmenting the concentration of Foxp3 + Tregs (255). In a different study, the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio was higher in mice with colitis-associated cancer. However, treatment with intestinal MSCs reduced this ratio, providing protection against colitis-associated cancer and improving colitis symptoms (256). Xu and the team found that the infusion of human embryonic stem cells (T-MSCs) into mice reduced colitis by increasing the level of IGF-1 in the blood. Epithelium loss and inflammatory cell infiltration were increased, but T-MSC reversed these changes. The study found that 50 ng/mL TNF-α caused apoptosis in the human colon epithelial cell line (NCM 460 cells) in vitro, but rhIGF-1 stimulation reduced the proportion of early apoptotic cells, as per Annexin V and 7-AAD staining flow cytometry. Higher levels of IGF-1 helped to repair and regenerate epithelial cells while preserving their integrity. IGF-1-treated organoids were found to be larger and to have more buddings in an in vivo investigation that replicated the in vitro results. Additionally, on day 10, the number of organoids detected increased (257). It has been demonstrated that IGF-1 protects against apoptosis generated by intrinsic pathways but not by extrinsic pathways (258). Therefore, it is possible that T-MSC may have reduced apoptosis of epithelial cells, hence preventing colitis in vivo. Yousefi-Ahmadipour et al. (259) found that in the colitis rats, the expression level of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 was dramatically reduced, whereas that of the proapoptotic protein Bax was significantly elevated. Additionally, rats given TNBS experienced severe bloody diarrhea, an increased colon weight-to-length ratio, a macroscopic damage score, goblet cell loss, submucosal edema, increased inflammatory cell infiltration, and a marked weight loss (259). Nonetheless, concurrent administration of ASCs and sulfasalazine reversed all these changes. The combination also converted inflammatory M1 macrophages into anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages by increasing IL-10 and Arg-1 levels, decreasing MCP1 and CXCL9 levels, and promoting T reg cell development via Foxp3 gene activation (259). This shows the role of combination therapy with MSC and IBD medications. In a different study, adipose-derived MSCs reduce alveolar hemorrhage, thickening of the alveolar walls, and inflammatory infiltration caused by radiation in mice’s lung tissue. The MSCs increased lung tissue cell regeneration and decreased radiation-induced cell apoptosis (260). Yang and the team revealed that the number of apoptotic cardiomyocytes dropped in the BMMSCs exosome and BMMSCsDSY exosome groups. Cleaved caspase-3 expression levels decreased in the BMMSC and BMMSCsDSY exosome groups, with the latter group exhibiting lower expression levels (261). On days 7 and 28, the BMMSCs exosome group experienced an increase in the BAX/BCL2 ratio, while the BMMSCsDSY exosome group experienced a decrease (261).
Sun et al. (262) found that cell activity dropped, and early apoptosis happened following IEC-6 treatment with TNF-α and lymphocytes. ZO-1 concentrations dropped. The study found that treatment with HO-1/bone marrow (BM) MSC-derived exosomes significantly improves cell status and IEC-6 survival, reduces early apoptotic cells, and protects tight junction structures, demonstrated by increased ZO-1in an inflammatory environment. The HO-1/BMMSCs-exosomes group displayed a lower proportion of cleaved caspase-3 and BAX/BCL2 ratio compared to the BMMSCs co-culture group (262). Also, MSCs-EVs (from BM) release miR-378a-3p, which blocks GATA-binding protein 2 (GATA2), downregulating aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression, and disrupting the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) signaling pathway. This prevents the formation of IBD by suppressing the LPS-induced apoptosis of M064 cells (263). Results from an LPS-induced human colonic epithelial cell model show that the LPS group had higher levels of caspase-3 and Bax expression than the control group. While claudin-1 and ZO-1 expression declined in the LPS group, relative TNF-α expression rose (264). Nevertheless, the MSC-exosome and LPS-MSC-exosome groups increased the expression levels of claudin-1 and ZO-1 and decreased levels of caspase-3 and Bax compared to the LPS group. These outcomes aligned with the findings of the in vivo tests (264). In another study, Ock et al. (265) developed a model of alcoholic liver injury by exposing hepatocyte organoids (HOs) to alcohol, aiming to evaluate the effectiveness of HOs as a model for liver disease. Low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 and sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 were discovered to be elevated, along with BAK, BCL2L1, and caspase 8. Nevertheless, HO lipid accumulation is reduced and hepatocyte apoptosis is inhibited when HOs and adipose-derived MSCs are co-cultured (265). Yang and colleagues discovered that huc-MSC and human adipose tissue-derived MSC-conditioned media may significantly inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in the human U251 glioma cell line (266). This suggests that whereas MSCs inhibit apoptosis to mitigate IBD, they may stimulate apoptosis to prevent CRC. Liang and team also found that BMMSC-exosomes may contribute to the prevention of osteomyelitis by stimulating proliferation and osteogenic differentiation and controlling the inflammatory state of bone cells. Staphylococcal protein A (SPA) treated MC3T3-E1 cells to create an in vitro osteomyelitis model, and it was found that BCL2 and BCL-XL reduced, whereas BAX increased. Nonetheless, BMMSC-exosome combinations reduced the mRNA level of pro-apoptotic marker BAX in SPA-treated MC3T3-E1 cells while increasing the expression of anti-apoptotic marker genes (BCL2 and BCL-XL) (267).
8.2 MSCs and ferroptosis
Wei et al. (34) found that DSS-treated mice experienced diarrhea, bloody stools, weight loss, increased pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β), and decreased anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) and occludin and claudin-1. Nevertheless, exosomes produced from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSC-exosomes) corrected all of these alterations in mice. Additionally, DMT1, cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2), and ACSL4 showed substantial increases in mRNA expression levels, whereas GPX4 decreased in the DSS group. In contrast, hucMSC-exosome therapy elevated GPX4 and downregulated DMT1, COX2, and ACSL4. The study suggests that hucMSC-Ex plays a protective role in ferroptosis control, potentially preventing it in certain pathways linked to certain genes. In a different study, Li and team revealed that in the lung tissues of burn-induced acute lung injury (ALI) rats, hucMSCs-exosome and Fer-1 (inhibitor of ferroptosis) reduce lung inflammation and increase the levels of the proteins Nrf2 and HO-1. Burn-induced ALI significantly causes ferroptosis, as evidenced by elevated iron and Fe2+ concentrations and reduced SLC7A11 and GPX4 mRNA and protein levels (268). Thus, hucMSCs-exosome may have upregulated SLC7A11 and GPX4 mRNA and protein levels while decreasing iron and Fe2+ concentrations to reduce lung inflammation.
Moreover, Wang and the team found that the administration of LPS caused GPX4 to be down-regulated and ferroptosis-related molecules ACSL4, DMT1, and COX2 to be up-regulated. HucMSC-Ex therapy significantly recovered the depletion of GPX4 while inhibiting the levels of ACSL4, DMT1, and COX2, as observed in the in vivo investigation (34). The activation of LPO-related processes in IBD was confirmed by the upregulation of ACSL4 protein and mRNA expression in the LPS-induced inflammatory environment, while hucMSC-Ex therapy led to a decrease in this expression (34). Thus, this confirms hucMSC-Ex’s anti-inflammatory action in vitro and its capacity to block LPO, which lowers ferroptosis cell death and heals IBD (34). In a different study, in vitro, HucMSCs increased the abundance of SLC7A11 and GPX4 while lowering the expression of genes linked to lipid metabolism, including ACSL4, LPCAT3, and ALOX15, when corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells are exposed to elevated glucose (269). These demonstrated that HUCMSCs may prevent the ferroptosis signaling pathway in corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells, reducing erectile dysfunction in diabetes mellitus (269). Zhu et al. (270) found that hUCMSCs prevent type 2 diabetes mice from developing renal ferroptosis.
Wang et al. (271) illustrated the impact of MUC-1 on IEC-6 cell ferroptosis. In IEC-6 cells treated with erastin, it was discovered that when MUC-1 was overexpressed, SLC7A11 and GPX4 increased. Additionally, in cells treated with RSL3, the overexpression of MUC-1 results in the downregulation of ACSL4. This suggests that MUC-1 might be involved in MSCs’ mode of action in IBD treatment by reducing ferroptosis. MUC1 shields cells from bacterial genotoxins, indicating that cell surface mucins have expanded their functions beyond merely blocking bacterial toxins and are now also defending epithelial cells against xenobiotic toxins (272). It has also been shown that overexpression of MUC1 attenuates LPS-induced damage of BEAS-2B cells (human alveolar epithelial cell line) in vitro (273). While a previous study indicated that MUC1 could serve as a marker for ferroptosis in UC (274), it has also been demonstrated that the overexpression of MUC1 reduces LPS-induced damage in BEAS-2B cells (a human alveolar epithelial cell line) in vitro [258]. This finding supports the research conducted by Wang et al. (271), which revealed that increased levels of MUC1 lead to the downregulation of ACSL4 and the upregulation of GPX4 and SLC7A11.
8.3 MSC and pyroptosis
Chang et al. (275) found that the DSS group experienced higher mucosal injury, inflammatory infiltration, diarrhea, bloody stools, and decreased body weight and colon length. Increased levels of NLRP3 and GSDMD protein-positive cells were observed, along with increased levels of IL-1β and IL-18.However, these effects were reversed when MSCs generated from hair follicles (HFMSCs) were administered (275). Similarly, HFMSC exosomes prevented pyroptosis in DSS-treated mice by lowering NLRP3, GSDMD, cleaved caspase-1, and IL-1β proteins, reducing colon damage and the DAI in DSS animals (275). Cai et al. (31)discovered that the IBD mice group exhibited shorter colon length, intestinal injury (abnormality of the colorectal tissue without a typical intestinal gland),and increased pro-inflammatory cytokines and bloody stool; however, these changes were reversed by the administration of hucMSC exosomes. NLRP3 inflammasome-related molecules (NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, IL-18, and IL-1β) were significantly less expressed in the hucMSC-Ex group than in the IBD group. Mouse peritoneal macrophage IL-1β production was suppressed by hucMSC-derived exosomes even after NLRP3 inflammasome activation. A similar study by Xu and team revealed that the hucMSC-exosome relieves macrophage pyroptosis to ameliorate murine colitis by inhibiting caspase 11 activation and reducing the release of IL-1β, IL-6, and caspase 11.HucMSC exosomes repaired the distorted structure of the colon epithelium (276). These results (31, 276) suggest that hucMSC-exosomes suppressed M1 macrophages, which produce IL-1β.IBD mice’s weight loss, shorter colon, compromised structural integrity of colonic tissues, elevated pyroptosis-related proteins (NLRP3, GSDMD-N, and caspase-1), and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-18, and TNFα) were all reversed by BMSC-derived exosomes, according to another study (277). Bauer et al. (81) found that NLRP3(-/-) mice generated fewer proinflammatory cytokines in colonic tissue and experienced less severe colitis than wild-type mice after oral DSS administration. This implies that NLRP3 expression increases the susceptibility to colitis. Ruan and colleagues have identified pterostilbene analogs as novel NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors that may be used to treat mice’s DSS-induced colitis (278). Therefore, MSCs and their exosomes may be potential pyroptosis inhibitors.
Though Chang and the team investigated HFMSC exosome prevention of pyroptosis in animal models, similar findings were also observed in vitro. Additionally, the study discovered that exosomes significantly inhibited pyroptosis in a dose-dependent manner and somewhat aided in vitro regeneration. Western blotting showed that when exosome doses increased, the levels of the proteins NLRP3, GSDMD, cleaved caspase-1, and IL-1β dropped (275). Cai and the team found that HucMSC-derived exosomes improved cell viability in vitro following NLRP3 inflammasome activation in THP-1 and MPM cell counting kit-8 assays. They also decreased LDH release, a pyroptotic indicator. THP-1 cells stimulated with LPS and nigericin showed a statistically significant decrease in PI-positive THP-1 cells in the hucMSC-derived exosome-treated group compared to the untreated group, according to flow cytometry analysis. Western blot demonstrated that exosomes produced from hucMSCs prevented GSDMD from being cleaved to the active N-terminal fragment (31). Also, Wang and the team found that exosome treatment produced from BMMSCs decreases proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-18, and TNFα), ROS levels, and pyroptosis (NLRP3, GSDMD-N, and caspase-1) in mouse small IECs (mIECs) treated with LPS in a manner that is dependent on miR-539-5p (277). In a different study, the hucMSC-exosome has been found to target METTL14, effectively enhancing nucleus pulposus (NP) cell viability and protecting them against pyroptosis (279). Pei et al. (280) also found that exosomes generated from BMSCs prevented heat-stroke-induced pyroptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
8.4 MSCs and necroptosis
Figure 3 previously illustrated the identification of STAT1 and JAK1 as contributors to the development of necroptosis. Cao et al. (281) revealed that BMMSC-derived EVs significantly reduced the phosphorylation of JAK1 and STAT1 in DSS-induced UC. In a different study, adipose-derived MSCs and EVs treatment decreased JAK1 in DSS-induced colitis (282). These suggest that MSCs-EVs may help prevent necroptosis in IBD.
Although research on MSCs and their exosome modulation of necroptosis in IBD is sparse, previous studies have demonstrated that MSCs can regulate necroptosis. As a result, the involvement of MSCs and their EVs in controlling necroptosis in IBD is a developing topic that needs to be investigated. Yuan et al. (283) discovered that human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (hiPSC-MSCs)-EVs can reduce renal ischemia-reperfusion damage by activating sphingosine kinase 1 and inhibiting necroptosis. There was no discernible difference between the administration of hiPSC-MSCs-EVs alone and the necroptosis inhibitor necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) pretreatment. Studies have proven Nec-1’s ability to suppress necroptosis in IBD (118, 120, 284). Therefore, hiPSC-MSCs-EVs may regulate necroptosis molecules (RIPK1/3) and MLKL in IBD treatment. In pigs suffering from metabolic syndrome (metS) and renal artery stenosis (RAS), MSCs derived from adipose tissue and their EV improve the function of stenotic kidneys and lessen tissue damage (285). EV effectively preserved renal cellular integrity, while MSCs successfully protected the microcirculation (285). The metS + RAS group exhibited higher levels of RIPK1 and RIPK3, but the EV from MSC decreased these levels (285). Similar findings have been reported in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP), where miR-9 in BMMSCs decreased RIPK1, RIPK3, and p-MLKL (286). Notably, studies have shown that MSCs and their EVs can improve other diseases and possibly IBD. As a result, MSCs and their EVs may be able to modulate necroptosis during IBD therapy. We should further investigate this growing field.
8.5 Autophagy modulation by MSCs
Li et al. (287) found that mice treated with DSS showed infiltration of inflammatory cells, damaged colonic mucosa, missing glands, and decreased colon length and body weight. Nevertheless, all of these alterations were restored by hypoxia-preconditioned HF-MSC-derived exosomes (Hy-Ex)(i.e., reduced infiltration of inflammatory cells, improved colonic mucosa damage, and so on). Western blotting showed that after Hy-Exos therapy, the expression of p-mTOR/mTOR, p-AKT/AKT, and p-PI3K/PI3K decreased following an initial increase in the UC group (287). The autophagy process is mainly regulated by the kinase mTOR, which is affected by cellular stress, growth factors, and starvation (288). mTOR kinase regulates autophagy, while the PI3K/AKT survival pathway influences it indirectly (288). Therefore, MSCs’ ability to regulate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR route may be able to regulate autophagy. Studies have shown increased mTOR expressions in IBD (148, 150, 151). Therefore, Hy-Ex downregulating p-mTOR/mTOR may make it a potential autophagy regulator. In a different study, inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway reduces Piezo1 inhibition of chondrocyte autophagy (289), implying that PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation increases Piezo1 inhibition of chondrocyte autophagy. MSC-Exo-mediated KLF3-AS1 repressed autophagy and apoptosis of chondrocytes by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway (290). Additionally, research shows increased P62, mTOR, and p-mTOR levels in experimental colitis, while LC3B and ATG16L1 levels are reduced. However, rapamycin intervention improved colonic pathology in mice, reducing disease activity index score (148). Furthermore, the rapamycin group is revealed to have a significant abundance of Lactobacillus reuteri (L. reuteri) (148). Interestingly, a mouse model has shown that stem-cell-loaded hydrogel microcapsules (SC-HM) can enhance MSC (huc blood MSC) survival and retention in the stomach, promote tissue restoration, decrease colonic macrophage invasion, and significantly reduce the severity of IBD (291). SC-HM also enhanced L. reuteri in the inflammatory colon (291). These results show that SC-HM is a viable therapeutic option for IBD (291). L. reuteri aids in repairing intestinal diseases by protecting the gut barrier, inhibiting oxidative stress, regulating gut microbiota metabolism, and suppressing inflammation and immunological responses (292). As a result, MSCs may be able to modulate autophagy in IBD by regulating the gut flora.
In MODE-K cells, Hy-Ex reversed the LPS-induced reductions in Beclin1 and LC3II/I expression and raised in p62, HSP60, and TOMM20 expression (287). These show that Hy-Exos may regulate autophagy in IBD. Research has demonstrated decreased expressions of LC3II/I and beclin 1 in colitis (148, 149). Hence, Hy-Ex upregulates LC3II/I and beclin 1, making it a potential candidate for preventing colitis. MScs’ function in targeting IBD cell death markers is summarized in Figures 6, 7, and Table 1.

Figure 6. Summary of MSC + EV regulation on key cell death markers of IBD. The figure summarizes how MSC + EV regulates specific cell death markers to prevent or activate subsequent downstream signaling, as shown in Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. (A) Ferroptosis, (B) Pyroptosis, (C) Autophagy (D) Apoptosis. ACSL4, long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthase 4; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing card; ATG, autophagy-related gene; BAX, bcl-2 associated x protein; BH3, bcl2 homology domain 3; Casp, caspase; CIAPs, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins; DAMP, damage-associated molecular patterns; DMT1, divalent metal ion transporter 1; E, effector; FADD, fas-associated death domain protein; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase-4; GSDMD, gasdermin d; GSH, glutathione; IL, interleukin; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; NLRP3, nod-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PI3P, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate; PRC, procaspase; PRR, pattern-recognition receptor; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; TRADD, TNF receptor-associated death domain protein; TRAF2, TNF receptor-associated factor 2; VPS, vacuolar protein sorting.

Figure 7. Summary of the role of MSCs in targeting cell death markers of IBD. MSCs and their mediators target cell death indicators in vitro and in vivo to reduce inflammatory markers, disrupt tight junction proteins, and improve intestinal barrier integrity, thereby alleviating colitis. IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; miRNA, microRNA; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell.
9 Emerging research and potential therapeutic avenues
9.1 Clinical trials involving MSCs for IBD treatment
Several clinical trials have also demonstrated the usefulness of employing MSC to treat IBD.
For instance, a clinical trial found that patients with CD on a steady steroid dosage can greatly benefit and safely receive UC-MSC treatment (293). In this trial, 82 individuals with a CD diagnosis who had been on steroid maintenance medication for longer than six months were included. Every week, four times, patients in the UC-MSC group got an injection of 1×106 cells/kg. Patients were injected with 2,500 IU of low-molecular-weight heparin daily for three days to prevent thrombosis before surgery and then monitored for three, six, nine, and twelve months. The Harvey-Bradshaw index (HBI), corticosteroid dosage, adverse events, and CD activity index (CDAI) were evaluated at every follow-up visit (293). Colonoscopy results showed that the UC-MSC group’s CDAI decreased from 9.2 ± 1.5 before therapy to 3.4 ± 1.2 at the 12-month follow-up. The UC-MSC group experienced a decrease in CDAI, HBI, and corticosteroid dosage of 62.5 ± 23.2, 3.4 ± 1.2, and 4.2 ± 0.84 mg/day, respectively, while the control group experienced a drop of 23.6 ± 12.4, 1.2 ± 0.58, and 1.2 ± 0.35 mg/day (293). Four patients experienced fever after cell infusion, which subsided after symptomatic therapy, and seven patients experienced nine upper respiratory tract infection episodes within six months. There were no significant adverse effects noted (293). It is well established that MSCs can inhibit immune responses and have therapeutic promise for establishing transplant tolerance (294). This property may have caused infections and fever due to immune suppression. As a result, MSC might be more secure and useful in a medical context. A different trial showed that in patients with type 2 diabetes, administering UC-MSCs by intravenous infusion is a safe and efficient method that may lessen the need for exogenous insulin and improve insulin resistance (295). Transplanting UC-MSCs may be a viable treatment for type 2 diabetes (295). Zang et al. (296) revealed that the intravenous infusion of UC-MSCs is a successful strategy for reducing glycemic fluctuation and the time in range in type 2 diabetes. Bartolucci and the team found that in patients with stable heart failure and a lower ejection fraction receiving the best medical care, intravenous UC-MSC infusion proved safe (297). Patients treated with UC-MSCs showed improvements in their quality of life, functional status, and left ventricular function (297). Lanzoni et al. (298) found that UC-MSC infusions are safe for COVID-19 ARDS treatment, reducing inflammatory cytokines at day six and increasing patient survival rates.
Another study investigated the efficacy of allogeneic MSCs in patients with luminal CD (299). On day 42, the mean CDAI score for the 15 patients who finished the study dropped from 370 to 203. After every MSC infusion, the average CDAI scores dropped (299). Eight patients experienced clinical remission, while twelve experienced a clinical response. Seven patients (47%), whose mean CDEIS scores dropped from 21.5 to 11.0, experienced endoscopic improvement. Patients’ quality of life (QoL) was enhanced by MSC (299). IBD symptoms can include diarrhea, stomach pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, weight loss, malnourishment, and exhaustion. These symptoms may lead to lifestyle restrictions and significant psychosocial effects, ultimately impacting the QoL for those affected (300). Adults and children with IBD have lower QoL than healthy people, according to a meta-analysis review (301). Graff et al. (302) also found that those with active IBD experienced reduced social support, well-being, mastery, and disease-specific QoL, as well as higher levels of discomfort, health anxiety, and perceived stress. Therefore, MSC may enhance symptoms of IBD while also improving QoL.
Panés et al. (303) looked at the effectiveness and safety of using expanded, allogeneic, adipose-derived stem cells (Cx601) for CD patients’ treatment-refractory complicated perianal fistulas. Out of the 212 patients that took part, 107 were given Cx601 and 105 were given a placebo. The Cx601 group showed a higher percentage of patients experiencing total remission compared to the placebo group (303). Complex perianal fistulas in CD patients who did not react to biological, conventional, or both types of therapy can be safely and effectively treated with Cx601 (303). A related trial involving 212 individuals found that when Cx601 was administered once to patients with complex perianal fistulas who were not responding to treatment for CD, its effectiveness lasted for up to a year (304). Therefore, for difficult perianal fistulas, Cx601 offers a unique and least invasive substitute that might lessen the need for surgery or systemic immunosuppression (304). In a trial conducted by Furukawa and the team, it was found that 22 patients who received darvadstrocel (a suspension of expanded, allogeneic, adipose-derived MSCs) and completed the 52-week follow-up between March 6, 2019, and February 1, 2021, achieved a combined remission (magnetic resonance imaging-confirmed absence of collections more than 2 cm and clinically verified closure of all treated external holes that were draining during screening) rate of 59.1% by week 24 (305). At week 52, the effect persisted, with 68.2% of patients experiencing combined remission (305). Perianal illness is among the most incapacitating signs of CD and rarely in cases of UC (306, 307). Additionally, it might be challenging to treat pouch CD patients who develop perianal illness (such as fistula), which occasionally calls for pouch excision (308). Tan and colleagues discovered that while fistulas do not raise the risk of IBD, CD does inadvertently raise the chance of fistulas more than UC (309). De la Poza et al. (310) also found that surgical therapy is the most effective treatment for genital fistulas, which are a major issue for female CD patients. Consequently, MSC might be a possible remedy for perianal conditions (like fistula).A different trial also showed that in patients with COVID-19, nebulized exosomes made from human adipose-derived MSC (haMSC-Ex) enhanced computed tomography image scores and clinical symptoms (311). The haMSC-Ex nebulization was well tolerated by all COVID-19 patients, and neither the nebulization nor the immediate post-nebulization interval showed any signs of clinical instability or predicted adverse events (311). Table 2 highlights the use of MSCs in IBD in clinical trials.
9.2 Combination therapy using MSC, exosome, and IBD treatment drugs
Numerous studies have shown the effectiveness of conventional medicines in mitigating IBD. Additionally, a retrospective investigation discovered that 5-ASA was frequently utilized as a long-term CD therapy, and the usage of CD-related healthcare resources declined significantly in the year following the implementation of 5-ASA (312). According to Otkur et al. (313), aminosalicylates can prevent DSS-induced colitis by targeting GPR35. Other studies have shown the efficacy of aminosalicylates in treating IBD (314, 315). Moreover, the use of corticosteroids (316–318), immunomodulators (319–321), small molecule inhibitors (322, 323), and biologics (324–328) has also shown efficacy in IBD. Despite their therapeutic efficacy, some patients may not respond because of side effects and high costs (329, 330). However, the combination of these IBD medicines with MSCs and exosomes may be crucial in IBD treatment since these drugs have shown promise in reducing IBD alone. A study found that combining ASCs with traditional IBD treatment may be a far more effective way to delay the disease’s progression by lowering inflammatory and apoptotic indicators than either treatment alone (259). Interestingly, another study found that combination therapy with 5-ASA and MSC increases apoptosis and inflammation. The combined 5-ASA and MSC treatment had a detrimental impact on UC mice (331). 5-ASA can enhance inflammatory factors, cause cell death (apoptosis), and inhibit MSC development. 5-ASA considerably decreased the colon’s MSC content (331). As a result, combined therapy with MSC and IBD medicine may not be practical at this time, and further research is required to investigate this area due to limited data. While more research is being conducted, clinicians should exercise caution when considering combination therapy with MSCs, exosomes, and IBD drugs. Other IBD medicines with MSC should also be explored.
10 Challenges and limitations
The lack of confidence in MSC therapy stems from inconsistent pre-clinical and clinical outcomes and the mismatch between predicted and actual efficacy in various illnesses (332). Beyond safety, clinical effectiveness remains very diverse and contentious, with no evidence of a molecular explanation and conflicting therapeutic advantages (333). For instance, several clinical trials on MSC treatments in IBD (CD) reported fever (293), anal abscess and proctalgia (303), worsening of CD, diarrhea, increased blood bilirubin (305), and anal abscess/fistula (304). The trials suggest that while MSCs are safe and effective, their adverse effects may pose practical challenges. Interestingly, one study identified a major adverse event (2 dysplasia-related lesions) (299). Nonetheless, the study stated that MSCs most likely did not cause this. Research has indicated that MSCs might encourage the growth of tumors. For instance, the proangiogenic factors released by cancer cells to promote angiogenesis and tumor development may be enriched by IL-6 produced by MSCs; addressing this relationship may result in new preventative and therapeutic approaches (334). IL-6, secreted by MSCs, stimulates the growth of colorectal tumor-initiating cells and encourages tumor development through STAT3 signaling (335). In a different investigation, MSCs improved the capacity of lung cancer cells A549 and CL1–5 to grow tumors in immunocompromised mice (336). Another study has also demonstrated that MSC treatment has a protective effect on tumor development. For instance, Hu and colleagues discovered that late administration of MSCs promotes colitis-associated cancer (CAC) development, while early administration prevents CAC incidence (337). On the contrary, issues with EVs, the mediators of MSCs, have yet to be reported in IBD. As a result, further clinical studies with EVs should be considered. EVs, the mediators of MSCs, could be the new era of treating IBD-associated cell death.
Several limitations have been identified with the use of MSCs. Disease results vary significantly depending on the type of mesenchymal cells used, how the cells are preconditioned, how often treatments are administered, and how they are administered. Thus, a more thorough study of MSCs is required (255). According to the review, different MSC sources and conditioning methods are employed, which may influence the result of the MSCs. For instance, Nishikawa and colleagues found that while cell-free lysate injection produced a comparable improvement to the previously documented MSC treatment, the mechanism by which pleiotropic factors ameliorate DSS-induced colitis remains unknown. Also, what precisely makes up FADSTL and the process that underlies their apparent effectiveness is uncertain. Further research is needed to comprehend the mechanisms behind its anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties (253). Another study found that the mechanism of miR-378a-5p controlling NLRP3 is non-specific, highlighting the need for more research to gain clarification (31).
11 Conclusion and future directions
MSCs and their mediators have been shown to regulate cell death pathways in various diseases, including IBD. MSCs alleviate barrier defects and decrease immune cell infiltrations and inflammatory cytokine release. However, side effects may pose challenges in clinical settings. Clinical investigations show insufficient evidence to relate EVs to cell death in IBD, and EV use has not been associated with any preclinical negative effects. The diversity of extracellular vesicles (EVs) (338, 339) and the minimal uniformity regarding the methodologies for their isolation, purification, and characterization (340) make the application of EVs in the clinical setting challenging. Additionally, the wide range of methods utilizing unique biochemical characteristics of EVs and the lack of standardized protocols make data interpretation extremely challenging (341). The review’s findings showed evidence that may impede clinical research using EVs in IBD. For instance, regarding the appropriate dosage for EV use, different research studies have used varying amounts of EVs in colitis treatment; hence, there is no standardized dose when translating to clinical trials involving humans. Additionally, colitis induction to mimic the human model is created using different concentrations, making standardization of this model with EV treatment challenging for clinical studies. Frequent injections with EVs in animal models may also pose a challenge during clinical studies. Using different animal species for colitis model, different sources of EVs, and frequency of administration of EVs may also affect translation to clinical settings. Although these preclinical studies have shown the potential to explore the modulatory mechanism of EVs in IBD, the complete understanding of the mechanism in human IBD is lacking, therefore a study suggested the exploration of EVs in human model to better understand its mechanism (287). Notwithstanding these difficulties, EVs might one day be used to diagnose IBD, as is the case with CRC (342), given that IBD is a risk factor for CRC. Studies should focus on the standardization of protocols and the uniformity of EV extraction for IBD experiments, other routes of EV administration (oral) should be explored, and efforts to research larger sample sizes in clinical studies should be encouraged. Preclinical and clinical research should focus on MSCS and other cell death mechanisms with less evidence, such as cuproptosis. Cuproptosis, a type of cell death involving copper ions being delivered to lipoylated TCA cycle proteins, is a widely researched topic in cancer research. However, it is also linked to harmful processes like oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation (343, 344). Studies have also shown that cuproptosis genes may serve as biomarkers for IBD, and these genes have been associated with immune cell infiltration regulation in IBD (345–347). Nevertheless, the direct mechanism of MSCs targeting cuproptosis is novel and needs further exploration since cuproptosis may be implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD. Moreover, as cuproptosis represents a novel form of cellular death and has been insufficiently studied, further research will enhance the limited understanding of cuproptosis, offer innovative therapeutic strategies, elucidate disease variations, and furnish methodologies for assessing and identifying cell death pathways. Further exploration of MSCs and exosomes with other IBD medicines in cell death is warranted.
Author contributions
FA: Writing – original draft. CH: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. PC: Writing – review & editing. XW: Writing – review & editing. YW: Writing – review & editing. FM: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Zhenjiang Key Research and Development Plan (social development) (Grant No. SH2023050), the Henan Province 2024 science and technology development plan (Grant No. 242102310081), the open topic at the university level of Shangqiu Medical College in 2023 (Grant No. KFKT23005), and the Jiangsu Provincial Medical Key Discipline Cultivation Unit (Grant No. JSDW202241).
Acknowledgments
Figures 1, 4, 5, 6 and 7 are created in BioRender.com, while the others are in Adobe Illustrator.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Akrapovic Olic I, Vukovic J, Radic M, and Sundov Z. Enthesitis in IBD patients. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:4540. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154540
2. Akanyibah FA, Zhu Y, Wan A, Ocansey DKW, Xia Y, Fang AN, et al. Effects of DNA methylation and its application in inflammatory bowel disease (Review). Int J Mol Med. (2024) 53:55. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5379
3. Nóbrega VG, Silva INN, Brito BS, Silva J, Silva M, and Santana GO. THE ONSET OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE PATIENTS. Arq Gastroenterol. (2018) 55:290–5. doi: 10.1590/s0004-2803.201800000-73
4. Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet (London England). (2017) 390:2769–78. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0
5. Wang S, Dong Z, and Wan X. Global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease and its associated anemia, 1990 to 2019 and predictions to 2050: An analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019. Autoimmun Rev. (2024) 23:103498. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103498
6. Bertheloot D, Latz E, and Franklin BS. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:1106–21. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00630-3
7. Patankar JV, Müller TM, Kantham S, Acera MG, Mascia F, Scheibe K, et al. E-type prostanoid receptor 4 drives resolution of intestinal inflammation by blocking epithelial necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. (2021) 23:796–807. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00708-8
8. Nunes T, Bernardazzi C, and de Souza HS. Cell death and inflammatory bowel diseases: apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy in the intestinal epithelium. BioMed Res Int. (2014) 2014:218493. doi: 10.1155/2014/218493
9. Wang M, Wang Z, Li Z, Qu Y, Zhao J, Wang L, et al. Targeting programmed cell death in inflammatory bowel disease through natural products: New insights from molecular mechanisms to targeted therapies. Phytotherapy research: PTR. (2024) 39:1776–1807. doi: 10.1002/ptr.v39.4
10. Lee D, Kim IY, Saha S, and Choi KS. Paraptosis in the anti-cancer arsenal of natural products. Pharmacol Ther. (2016) 162:120–33. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.01.003
11. Yipp BG and Kubes P. NETosis: how vital is it? Blood. (2013) 122:2784–94. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-457671
12. Galluzzi L, Buqué A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L, and Kroemer G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:97–111. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.107
13. Depierre P, Ginet V, Truttmann AC, and Puyal J. Neuronal autosis is Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase alpha 3-dependent and involved in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:363. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06750-2
14. Liu J, Kuang F, Kang R, and Tang D. Alkaliptosis: a new weapon for cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. (2020) 27:267–9. doi: 10.1038/s41417-019-0134-6
15. Holze C, Michaudel C, Mackowiak C, Haas DA, Benda C, Hubel P, et al. Oxeiptosis, a ROS-induced caspase-independent apoptosis-like cell-death pathway. Nat Immunol. (2018) 19:130–40. doi: 10.1038/s41590-017-0013-y
16. Jangamreddy JR and Los MJ. Mitoptosis, a novel mitochondrial death mechanism leading predominantly to activation of autophagy. Hepat Mon. (2012) 12:e6159. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.6159
17. Maltese WA and Overmeyer JH. Methuosis: nonapoptotic cell death associated with vacuolization of macropinosome and endosome compartments. Am J Pathol. (2014) 184:1630–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.02.028
18. Liu L, Liang L, Yang C, and Chen Y. Machine learning-based solution reveals cuproptosis features in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1136991. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1136991
19. Yang Y, Hounye AH, Chen Y, Liu Z, Shi G, and Xiao Y. Characterization of PANoptosis-related genes in Crohn’s disease by integrated bioinformatics, machine learning and experiments. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:11731. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62259-w
20. Sun Q, Luo T, Ren Y, Florey O, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T, et al. Competition between human cells by entosis. Cell Res. (2014) 24:1299–310. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.138
21. Blander JM. Death in the intestinal epithelium-basic biology and implications for inflammatory bowel disease. FEBS J. (2016) 283:2720–30. doi: 10.1111/febs.2016.283.issue-14
22. Katsanos KH and Papadakis KA. Inflammatory bowel disease: updates on molecular targets for biologics. Gut Liver. (2017) 11:455–63. doi: 10.5009/gnl16308
23. Zhang Q, Zeng Z, Wei N, Su Y, Wang J, Ni Q, et al. Mesenteric lymph nodes: a critical site for the up-regulatory effect of hUC-MSCs on Treg cells by producing TGF-β1 in colitis treatment. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:190. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03809-x
24. Wu M, Li C, Zhou X, Wu Z, Feng J, Guo X, et al. Wogonin preconditioning of MSCs improved their therapeutic efficiency for colitis through promoting glycolysis. Inflammopharmacology. (2024) 32:2575–87. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01491-2
25. Peng Y, Jaar J, and Tran SD. Gingival mesenchymal stem cells: Biological properties and therapeutic applications. J Biol craniofacial Res. (2024) 14:547–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.07.003
26. Ding DC, Shyu WC, and Lin SZ. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. (2011) 20:5–14. doi: 10.3727/096368910X
27. Chen J, Ding C, Yang X, and Zhao J. BMSCs-derived exosomal miR-126-3p inhibits the viability of NSCLC cells by targeting PTPN9. J BUON: Off J Balkan Union Oncology. (2021) 26:1832–41. doi: none
28. Calligaris M, Zito G, Busà R, Bulati M, Iannolo G, Gallo A, et al. Proteomic analysis and functional validation reveal distinct therapeutic capabilities related to priming of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells with IFN-γ and hypoxia: potential implications for their clinical use. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1385712. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1385712
29. Heidari N, Abbasi-Kenarsari H, Namaki S, Baghaei K, Zali MR, Ghaffari Khaligh S, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-secreted exosome alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis by Treg cell induction and inflammatory cytokine reduction. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:5906–20. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v236.8
30. Robalo Cordeiro M, Roque R, Laranjeiro B, Carvalhos C, and Figueiredo-Dias M. Menstrual blood stem cells-derived exosomes as promising therapeutic tools in premature ovarian insufficiency induced by gonadotoxic systemic anticancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:8468. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158468
31. Cai X, Zhang ZY, Yuan JT, Ocansey DKW, Tu Q, Zhang X, et al. hucMSC-derived exosomes attenuate colitis by regulating macrophage pyroptosis via the miR-378a-5p/NLRP3 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:416. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02492-6
32. Zhang XY and He DM. Research progress in mesenchymal stem cell-related therapies in the treatment of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Zhonghua kou qiang yi xue za zhi = Zhonghua kouqiang yixue zazhi = Chin J stomatology. (2024) 59:732–7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20230817-00097
33. Yu H, Yang X, Xiao X, Xu M, Yang Y, Xue C, et al. Human adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect mice from DSS-induced inflammatory bowel disease by promoting intestinal-stem-cell and epithelial regeneration. Aging disease. (2021) 12:1423–37. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0601
34. Wei Z, Hang S, Wiredu Ocansey DK, Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhang X, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived exosome shuttling mir-129-5p attenuates inflammatory bowel disease by inhibiting ferroptosis. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:188. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01951-x
35. Woo SM and Kwon TK. E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases as modulators of TRAIL-mediated extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. BMB reports. (2019) 52:119–26. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.2.011
36. Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, and Ashkenazi A. Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity. (2000) 12:611–20. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80212-5
37. Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Tinel A, LeBlanc H, Virmani A, Schow P, et al. Death receptor recruitment of endogenous caspase-10 and apoptosis initiation in the absence of caspase-8. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:46639–46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105102200
38. Vanden Berghe T, van Loo G, Saelens X, Van Gurp M, Brouckaert G, Kalai M, et al. Differential signaling to apoptotic and necrotic cell death by Fas-associated death domain protein FADD. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279:7925–33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307807200
39. Micheau O and Tschopp J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell. (2003) 114:181–90. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00521-X
40. Wang J, Chun HJ, Wong W, Spencer DM, and Lenardo MJ. Caspase-10 is an initiator caspase in death receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2001) 98:13884–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.241358198
41. McArthur K, Whitehead LW, Heddleston JM, Li L, Padman BS, Oorschot V, et al. BAK/BAX macropores facilitate mitochondrial herniation and mtDNA efflux during apoptosis. Science. (2018) 359:eaao6047. doi: 10.1126/science.aao6047
42. Cosentino K, Hertlein V, Jenner A, Dellmann T, Gojkovic M, Peña-Blanco A, et al. The interplay between BAX and BAK tunes apoptotic pore growth to control mitochondrial-DNA-mediated inflammation. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:933–49.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.01.008
43. Kantari C and Walczak H. Caspase-8 and bid: caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2011) 1813:558–63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.026
44. Kandasamy K, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ, Bryant JL, et al. Involvement of proapoptotic molecules Bax and Bak in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced mitochondrial disruption and apoptosis: differential regulation of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO release. Cancer Res. (2003) 63:1712–21.
45. Huang K, O’Neill KL, Li J, Zhou W, Han N, Pang X, et al. BH3-only proteins target BCL-xL/MCL-1, not BAX/BAK, to initiate apoptosis. Cell Res. (2019) 29:942–52. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0231-y
46. Elena-Real CA, Díaz-Quintana A, González-Arzola K, Velázquez-Campoy A, Orzáez M, López-Rivas A, et al. Cytochrome c speeds up caspase cascade activation by blocking 14-3-3ϵ-dependent Apaf-1 inhibition. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:365. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0408-1
47. Shakeri R, Kheirollahi A, and Davoodi J. Apaf-1: Regulation and function in cell death. Biochimie. (2017) 135:111–25. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.02.001
48. Flanagan L, Sebastià J, Tuffy LP, Spring A, Lichawska A, Devocelle M, et al. XIAP impairs Smac release from the mitochondria during apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2010) 1:e49. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.26
49. Srivastava RK. TRAIL/Apo-2L: mechanisms and clinical applications in cancer. Neoplasia (New York NY). (2001) 3:535–46. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900203
50. Kim WS, Lee KS, Kim JH, Kim CK, Lee G, Choe J, et al. The caspase-8/Bid/cytochrome c axis links signals from death receptors to mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. Free Radical Biol medicine. (2017) 112:567–77. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.09.001
51. Geng Z, Zuo L, Li J, Yin L, Yang J, Duan T, et al. Ginkgetin improved experimental colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling. FASEB journal: Off Publ Fed Am Societies Exp Biol. (2024) 38:e23817. doi: 10.1096/fj.202400211RR
52. Zhang M, Song X, Liu S, Zhang N, Yang M, Gao P, et al. Magnolin inhibits intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis alleviating Crohn’s disease-like colitis by suppressing the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 134:112181. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112181
53. Li Q, Li J, Yin L, Huang J, Liu X, Shi J, et al. Sophoricoside improved Crohn’s disease-like colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through PI3K/AKT signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 131:111886. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111886
54. Scherr AL, Gdynia G, Salou M, Radhakrishnan P, Duglova K, Heller A, et al. Bcl-xL is an oncogenic driver in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2016) 7:e2342. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.233
55. van der Heijden M, Zimberlin CD, Nicholson AM, Colak S, Kemp R, Meijer SL, et al. Bcl-2 is a critical mediator of intestinal transformation. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10916. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10916
56. Kannan S, Li Y, Baran N, Yang X, Ghotbaldini S, Tatarata QZ, et al. Anti-leukemia efficacy of the dual BCL2/BCL-XL inhibitor AZD0466 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia preclinical models. Blood Adv. (2024) 9:473–487. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013423
57. Qiu W, Wu B, Wang X, Buchanan ME, Regueiro MD, Hartman DJ, et al. PUMA-mediated intestinal epithelial apoptosis contributes to ulcerative colitis in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121:1722–32. doi: 10.1172/JCI42917
58. Dirisina R, Katzman RB, Goretsky T, Managlia E, Mittal N, Williams DB, et al. p53 and PUMA independently regulate apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in patients and mice with colitis. Gastroenterology. (2011) 141:1036–45. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.05.032
59. Iwamoto M, Koji T, Makiyama K, Kobayashi N, and Nakane PK. Apoptosis of crypt epithelial cells in ulcerative colitis. J pathology. (1996) 180:152–9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199610)180:2<152::AID-PATH649>3.0.CO;2-Y
60. Ueyama H, Kiyohara T, Sawada N, Isozaki K, Kitamura S, Kondo S, et al. High Fas ligand expression on lymphocytes in lesions of ulcerative colitis. Gut. (1998) 43:48–55. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.1.48
61. Souza HS, Tortori CJ, Castelo-Branco MT, Carvalho AT, Margallo VS, Delgado CF, et al. Apoptosis in the intestinal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease: evidence of altered expression of FasL and perforin cytotoxic pathways. Int J colorectal disease. (2005) 20:277–86. doi: 10.1007/s00384-004-0639-8
62. Sträter J, Wellisch I, Riedl S, Walczak H, Koretz K, Tandara A, et al. CD95 (APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis in colon epithelial cells: a possible role in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. (1997) 113:160–7. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(97)70091-X
63. Sträter J, Mariani SM, Walczak H, Rücker FG, Leithäuser F, Krammer PH, et al. CD95 ligand (CD95L) in normal human lymphoid tissues: a subset of plasma cells are prominent producers of CD95L. Am J Pathol. (1999) 154:193–201. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65265-0
64. Zhang Y, Wang C, Wu L, Bai C, Huang K, Yao L, et al. Epithelial CRL4(DCAF2) is critical for maintaining intestinal homeostasis against DSS-induced colitis by regulating the proliferation and repair of intestinal epithelial cells. Digestive Dis Sci. (2024) 69:66–80. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08147-1
65. Zhang J, Cen L, Zhang X, Tang C, Chen Y, Zhang Y, et al. MPST deficiency promotes intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and aggravates inflammatory bowel disease via AKT. Redox Biol. (2022) 56:102469. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102469
66. Zhang J, Xu M, Zhou W, Li D, Zhang H, Chen Y, et al. Deficiency in the anti-apoptotic protein DJ-1 promotes intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and aggravates inflammatory bowel disease via p53. J Biol Chem. (2020) 295:4237–51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010143
67. Hausmann M. How bacteria-induced apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells contributes to mucosal inflammation. Int J inflammation. (2010) 2010:574568. doi: 10.4061/2010/574568
68. McCole DF, Eckmann L, Laurent F, and Kagnoff MF. Intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis following Cryptosporidium parvum infection. Infection immunity. (2000) 68:1710–3. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.3.1710-1713.2000
69. Li J, Sun L, Xie F, Shao T, Wu S, Li X, et al. MiR-3976 regulates HCT-8 cell apoptosis and parasite burden by targeting BCL2A1 in response to Cryptosporidium parvum infection. Parasites vectors. (2023) 16:221. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05826-w
70. Man SM, Karki R, and Kanneganti TD. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunological Rev. (2017) 277:61–75. doi: 10.1111/imr.2017.277.issue-1
71. Burdette BE, Esparza AN, Zhu H, and Wang S. Gasdermin D in pyroptosis. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2021) 11:2768–82. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.006
72. Ball DP, Taabazuing CY, Griswold AR, Orth EL, Rao SD, Kotliar IB, et al. Caspase-1 interdomain linker cleavage is required for pyroptosis. Life Sci alliance. (2020) 3. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000664
73. Zhang MY, Jiang YX, Yang YC, Liu JY, Huo C, Ji XL, et al. Cigarette smoke extract induces pyroptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells through the ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. Life Sci. (2021) 269:119090. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119090
74. Dino P, Giuffrè MR, Buscetta M, Di Vincenzo S, La Mensa A, Cristaldi M, et al. Release of IL-1β and IL-18 in human primary bronchial epithelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke is independent of NLRP3. Eur J Immunol. (2024) 54:e2451053. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451053
75. Yang D, He Y, Muñoz-Planillo R, Liu Q, and Núñez G. Caspase-11 requires the pannexin-1 channel and the purinergic P2X7 pore to mediate pyroptosis and endotoxic shock. Immunity. (2015) 43:923–32. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.10.009
76. Kelley N, Jeltema D, Duan Y, and He Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: an overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:3328. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133328
77. Chelakkot C, Ghim J, and Ryu SH. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med. (2018) 50:1–9. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0126-x
78. Wei YY, Fan YM, Ga Y, Zhang YN, Han JC, and Hao ZH. Shaoyao decoction attenuates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis, macrophage and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the MKP1/NF-κB pathway. Phytomedicine: Int J phytotherapy phytopharmacology. (2021) 92:153743. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153743
79. Mahmoud TN, El-Maadawy WH, Kandil ZA, Khalil H, El-Fiky NM, and El Alfy T. Canna x generalis L.H. Bailey rhizome extract ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via modulating intestinal mucosal dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and TLR4/NF-ҡB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 269:113670. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113670
80. Xu S, Peng Y, Yang K, Liu S, He Z, Huang J, et al. PROTAC based STING degrader attenuates acute colitis by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization and intestinal epithelial cells pyroptosis mediated by STING-NLRP3 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 141:112990. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112990
81. Bauer C, Duewell P, Mayer C, Lehr HA, Fitzgerald KA, Dauer M, et al. Colitis induced in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) is mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut. (2010) 59:1192–9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.197822
82. Simovic Markovic B, Nikolic A, Gazdic M, Bojic S, Vucicevic L, Kosic M, et al. Galectin-3 plays an important pro-inflammatory role in the induction phase of acute colitis by promoting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and production of IL-1β in macrophages. J Crohn’s colitis. (2016) 10:593–606. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw013
83. Liu X, Zhou M, Dai Z, Luo S, Shi Y, He Z, et al. Salidroside alleviates ulcerative colitis via inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis and repairing the dysbacteriosis-associated Th17/Treg imbalance. Phytotherapy research: PTR. (2023) 37:367–82. doi: 10.1002/ptr.v37.2
84. Liao Y, Deng C, and Wang X. VSIG4 ameliorates intestinal inflammation through inhibiting macrophages NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. Tissue Cell. (2024) 86:102285. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102285
85. Shi P, Du Y, Zhang Y, Yang B, Guan Q, Jing Y, et al. Ubiquitin-independent degradation of Bim blocks macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis-related tissue injury. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:703. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07072-z
86. Le Floch AC, Imbert C, Boucherit N, Gorvel L, Fattori S, Orlanducci F, et al. Targeting BTN2A1 enhances Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell effector functions and triggers tumor cell pyroptosis. Cancer Immunol Res. (2024) 12:1677–1690. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.27950788
87. Fang M, Yao J, Zhang H, Sun J, Yin Y, Shi H, et al. Specific deletion of Mettl3 in IECs triggers the development of spontaneous colitis and dysbiosis of T lymphocytes in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. (2024) 217:57–77. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae025
88. Ma D, Zhang M, and Feng J. Gut microbiota alleviates intestinal injury induced by extended exposure to light via inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in broiler chickens. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6695. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126695
89. Zhang LZ, Xue H, Qiao CX, You WL, Di AT, and Zhao G. MiR-223 promotes pyroptosis of enteritis cells through activating NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting SNIP1 in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmunity. (2021) 54:362–72. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1940973
90. Lazaridis LD, Pistiki A, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Georgitsi M, Damoraki G, Polymeros D, et al. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory bowel disease: differences between crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Digestive Dis Sci. (2017) 62:2348–56. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4609-8
91. Ranson N, Veldhuis M, Mitchell B, Fanning S, Cook AL, Kunde D, et al. NLRP3-dependent and -independent processing of interleukin (IL)-1β in active ulcerative colitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 20:57. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010057
92. Zhang HX, Wang ZT, Lu XX, Wang YG, Zhong J, and Liu J. NLRP3 gene is associated with ulcerative colitis (UC), but not Crohn’s disease (CD), in Chinese Han population. Inflammation research: Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc [et al]. (2014) 63:979–85. doi: 10.1007/s00011-014-0774-9
93. Ito S, Hara Y, and Kubota T. CARD8 is a negative regulator for NLRP3 inflammasome, but mutant NLRP3 in cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes escapes the restriction. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16:R52. doi: 10.1186/ar4483
94. Mao L, Kitani A, Similuk M, Oler AJ, Albenberg L, Kelsen J, et al. Loss-of-function CARD8 mutation causes NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Crohn’s disease. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:1793–806. doi: 10.1172/JCI98642
95. Zhao Y, Ma Y, Pei J, Zhao X, Jiang Y, and Liu Q. Exploring pyroptosis-related signature genes and potential drugs in ulcerative colitis by transcriptome data and animal experimental validation. Inflammation. (2024) 47:2057–2076. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02025-2
96. Gao X, Wang C, Shen XT, Li CY, Li YC, Gao H, et al. Pyroptosis burden is associated with anti-TNF treatment outcome in inflammatory bowel disease: new insights from bioinformatics analysis. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:15821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43091-0
97. Zheng Z, Li K, Yang Z, Wang X, Shen C, Zhang Y, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals molecular characterization and immune landscape of PANoptosis-related genes in atherosclerosis. Inflammation research: Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc [et al]. (2024) 73:961–78. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01877-6
98. Zulqarnain F, Rhoads SF, and Syed S. Machine and deep learning in inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin gastroenterology. (2023) 39:294–300. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000945
99. Li S, Ning LG, Lou XH, and Xu GQ. Necroptosis in inflammatory bowel disease and other intestinal diseases. World J Clin cases. (2018) 6:745–52. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.745
100. Chiou S, Al-Ani AH, Pan Y, Patel KM, Kong IY, Whitehead LW, et al. An immunohistochemical atlas of necroptotic pathway expression. EMBO Mol medicine. (2024) 16:1717–49. doi: 10.1038/s44321-024-00074-6
101. Samson AL, Fitzgibbon C, Patel KM, Hildebrand JM, Whitehead LW, Rimes JS, et al. A toolbox for imaging RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL in mouse and human cells. Cell Death differentiation. (2021) 28:2126–44. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00742-x
102. Long X, Zhu N, Qiu J, Yu X, Ruan X, Wang X, et al. Necroptosis in inflammatory bowel disease: A potential effective target. Zhong nan da xue xue bao Yi xue ban = J Cent South Univ Med Sci. (2022) 47:1289–98. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210501
103. Akanyibah FA, Zhu Y, Jin T, Ocansey DKW, Mao F, and Qiu W. The function of necroptosis and its treatment target in IBD. Mediators inflammation. (2024) 2024:7275309. doi: 10.1155/2024/7275309
104. Kearney CJ and Martin SJ. An inflammatory perspective on necroptosis. Mol Cell. (2017) 65:965–73. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.024
105. Pierdomenico M, Negroni A, Stronati L, Vitali R, Prete E, Bertin J, et al. Necroptosis is active in children with inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to heighten intestinal inflammation. Am J gastroenterology. (2014) 109:279–87. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.403
106. McComb S, Cessford E, Alturki NA, Joseph J, Shutinoski B, Startek JB, et al. Type-I interferon signaling through ISGF3 complex is required for sustained Rip3 activation and necroptosis in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2014) 111:E3206–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1407068111
107. Thapa RJ, Nogusa S, Chen P, Maki JL, Lerro A, Andrake M, et al. Interferon-induced RIP1/RIP3-mediated necrosis requires PKR and is licensed by FADD and caspases. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2013) 110:E3109–18. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301218110
108. Upton JW, Kaiser WJ, and Mocarski ES. Virus inhibition of RIP3-dependent necrosis. Cell Host Microbe. (2010) 7:302–13. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.03.006
109. Zhang T, Yin C, Boyd DF, Quarato G, Ingram JP, Shubina M, et al. Influenza virus Z-RNAs induce ZBP1-mediated necroptosis. Cell. (2020) 180:1115–29.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.050
110. Wang WY, Yi WQ, Liu YS, Hu QY, Qian SJ, Liu JT, et al. Z-DNA/RNA binding protein 1 senses mitochondrial DNA to induce receptor-interacting protein kinase-3/mixed lineage kinase domain-like-driven necroptosis in developmental sevoflurane neurotoxicity. Neuroscience. (2022) 507:99–111. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.11.005
111. Sun Y, Ji L, Liu W, Sun J, Liu P, Wang X, et al. Influenza virus infection activates TAK1 to suppress RIPK3-independent apoptosis and RIPK1-dependent necroptosis. Cell communication signaling: CCS. (2024) 22:372. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01727-2
112. Lee SH, Kwon JY, Moon J, Choi J, Jhun J, Jung K, et al. Inhibition of RIPK3 pathway attenuates intestinal inflammation and cell death of inflammatory bowel disease and suppresses necroptosis in peripheral mononuclear cells of ulcerative colitis patients. Immune Netw. (2020) 20:e16. doi: 10.4110/in.2020.20.e16
113. Brasseit J, Althaus-Steiner E, Faderl M, Dickgreber N, Saurer L, Genitsch V, et al. CD4 T cells are required for both development and maintenance of disease in a new mouse model of reversible colitis. Mucosal Immunol. (2016) 9:689–701. doi: 10.1038/mi.2015.93
114. Wang F, Zhou F, Peng J, Chen H, Xie J, Liu C, et al. Macrophage Tim-3 maintains intestinal homeostasis in DSS-induced colitis by suppressing neutrophil necroptosis. Redox Biol. (2024) 70:103072. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103072
115. Rios-Arce ND, Collins FL, Schepper JD, Steury MD, Raehtz S, Mallin H, et al. Epithelial barrier function in gut-bone signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2017) 1033:151–83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-66653-2_8
116. Yan H and Ajuwon KM. Butyrate modifies intestinal barrier function in IPEC-J2 cells through a selective upregulation of tight junction proteins and activation of the Akt signaling pathway. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0179586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179586
117. Slifer ZM and Blikslager AT. The integral role of tight junction proteins in the repair of injured intestinal epithelium. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:972. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030972
118. Liu Y, Xu Q, Wang Y, Liang T, Li X, Wang D, et al. Necroptosis is active and contributes to intestinal injury in a piglet model with lipopolysaccharide challenge. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:62. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03365-1
119. Lu H, Li H, Fan C, Qi Q, Yan Y, Wu Y, et al. RIPK1 inhibitor ameliorates colitis by directly maintaining intestinal barrier homeostasis and regulating following IECs-immuno crosstalk. Biochem Pharmacol. (2020) 172:113751. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113751
120. Negroni A, Colantoni E, Pierdomenico M, Palone F, Costanzo M, Oliva S, et al. RIP3 AND pMLKL promote necroptosis-induced inflammation and alter membrane permeability in intestinal epithelial cells. Digestive liver disease: Off J Ital Soc Gastroenterology Ital Assoc Study Liver. (2017) 49:1201–10. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.08.017
121. Duan C, Xu X, Lu X, Wang L, and Lu Z. RIP3 knockdown inhibits necroptosis of human intestinal epithelial cells via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling and ameliorates murine colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:137. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02208-x
122. Zhang J, Qin D, Yang YJ, Hu GQ, Qin XX, Du CT, et al. MLKL deficiency inhibits DSS-induced colitis independent of intestinal microbiota. Mol Immunol. (2019) 107:132–41. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.01.018
123. Schwarzer R, Jiao H, Wachsmuth L, Tresch A, and Pasparakis M. FADD and caspase-8 regulate gut homeostasis and inflammation by controlling MLKL- and GSDMD-mediated death of intestinal epithelial cells. Immunity. (2020) 52:978–93.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.002
124. Stolzer I, Schickedanz L, Chiriac MT, López-Posadas R, Grassl GA, Mattner J, et al. STAT1 coordinates intestinal epithelial cell death during gastrointestinal infection upstream of Caspase-8. Mucosal Immunol. (2022) 15:130–42. doi: 10.1038/s41385-021-00450-2
125. Vaishnava S, Behrendt CL, Ismail AS, Eckmann L, and Hooper LV. Paneth cells directly sense gut commensals and maintain homeostasis at the intestinal host-microbial interface. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2008) 105:20858–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808723105
126. Khaloian S, Rath E, Hammoudi N, Gleisinger E, Blutke A, Giesbertz P, et al. Mitochondrial impairment drives intestinal stem cell transition into dysfunctional Paneth cells predicting Crohn’s disease recurrence. Gut. (2020) 69:1939–51. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319514
127. Günther C, Ruder B, Stolzer I, Dorner H, He GW, Chiriac MT, et al. Interferon lambda promotes paneth cell death via STAT1 signaling in mice and is increased in inflamed ileal tissues of patients with crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. (2019) 157:1310–22.e13. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.031
128. Woznicki JA, Saini N, Flood P, Rajaram S, Lee CM, Stamou P, et al. TNF-α synergises with IFN-γ to induce caspase-8-JAK1/2-STAT1-dependent death of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:864. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04151-3
129. Wu T, Dai Y, Xue L, Sheng Y, Xu L, and Xue Y. Expression of receptor interacting protein 3 and mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein-key proteins in necroptosis is upregulated in ulcerative colitis. Ann Palliat Med. (2019) 8:483–9. doi: 10.21037/apm.2019.07.04
130. Panayotova E and Atanassova A. Expression of RIPK3 among a cohort of Bulgarian patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Varna Med Forum. (2022) 11:20–24. doi: 10.14748/vmf.v0i0.8451
131. Liu S, Yao S, Yang H, Liu S, and Wang Y. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Disease. (2023) 14:648. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06154-8
132. Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, and Guan KL. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. (2011) 13:132–41. doi: 10.1038/ncb2152
133. Pourbarkhordar V, Rahmani S, Roohbakhsh A, Hayes AW, and Karimi G. Melatonin effect on breast and ovarian cancers by targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. IUBMB Life. (2024) 76:1035–1049. doi: 10.1002/iub.v76.12
134. Zachari M and Ganley IG. The mammalian ULK1 complex and autophagy initiation. Essays Biochem. (2017) 61:585–96. doi: 10.1042/EBC20170021
135. Popelka H and Klionsky DJ. When an underdog becomes a major player: the role of protein structural disorder in the Atg8 conjugation system. Autophagy. (2024) 20:1–8. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2272233
136. Alam JM, Maruyama T, Noshiro D, Kakuta C, Kotani T, Nakatogawa H, et al. Complete set of the Atg8-E1-E2-E3 conjugation machinery forms an interaction web that mediates membrane shaping. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2024) 31:170–8. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01132-2
137. Wang W, Chen Z, Billiar TR, Stang MT, and Gao W. The carboxyl-terminal amino acids render pro-human LC3B migration similar to lipidated LC3B in SDS-PAGE. PloS One. (2013) 8:e74222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074222
138. Pino-Belmar C, Aguilar R, Valenzuela-Nieto GE, Cavieres VA, Cerda-Troncoso C, Navarrete VC, et al. An intrinsic host defense against HSV-1 relies on the activation of xenophagy with the active clearance of autophagic receptors. Cells. (2024) 13:1256. doi: 10.3390/cells13151256
139. Radbakhsh S, Kesharwani P, and Sahebkar A. Therapeutic potential of curcumin in autophagy modulation: Insights into the role of transcription factor EB. Mutat Res. (2024) 829:111879. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2024.111879
140. Jiang P, Nishimura T, Sakamaki Y, Itakura E, Hatta T, Natsume T, et al. The HOPS complex mediates autophagosome-lysosome fusion through interaction with syntaxin 17. Mol Biol Cell. (2014) 25:1327–37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e13-08-0447
141. Mushtaq Hashim Al-Bderee N, Faaz Nassir Al-Saad N, Jawad Al-Imari M, Mudhaher Habbeb S, and Mizal Azoz A. Genetic polymorphisms of NOD2 and ATG16L1 in different types of digestive tract inflammation. Arch Razi Institute. (2023) 78:493–8. doi: 10.22092/ARI.2022.359754.2473
142. Simovic I, Hilmi I, Ng RT, Chew KS, Wong SY, Lee WS, et al. ATG16L1 rs2241880/T300A increases susceptibility to perianal Crohn’s disease: An updated meta-analysis on inflammatory bowel disease risk and clinical outcomes. United Eur gastroenterology J. (2024) 12:103–21. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12477
143. Jamali L, Sadeghi H, Ghasemi MR, Mohseni R, Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E, Yassaee VR, et al. Autophagy ATG16L1 rs2241880 impacts the colorectal cancer risk: A case-control study. J Clin Lab analysis. (2022) 36:e24169. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24169
144. Bali JS, Sambyal V, Mehrotra S, Gupta P, Guleria K, Uppal MS, et al. Association of ATG10 rs1864183, ATG16L1 rs2241880 and miR-126 with esophageal cancer. Mol Biol reports. (2024) 51:231. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09012-0
145. Pugazhendhi S, Baskaran K, Santhanam S, and Ramakrishna BS. Association of ATG16L1 gene haplotype with inflammatory bowel disease in Indians. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0178291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178291
146. Baradaran Ghavami S, Kabiri F, Nourian M, Balaii H, Shahrokh S, Chaleshi V, et al. Association between variants of the autophagy related gene ATG16L1 in inflammatory bowel diseases and clinical statues. Gastroenterology hepatology bed to bench. (2019) 12:S94–s100.
147. Rezaie N, Ashrafian F, Shidvash F, Aghamohammad S, and Rohani M. The effect of novel paraprobiotic cocktail on dextran sodium sulfate induced acute colitis control focusing on autophagy signaling pathway. Eur J Nutr. (2024) 63:1797–805. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03376-0
148. Guo X, Xu J, Huang C, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Zhu M, et al. Rapamycin extenuates experimental colitis by modulating the gut microbiota. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 38:2130–41. doi: 10.1111/jgh.v38.12
149. Zhang H, Lang W, Liu X, Bai J, Jia Q, and Shi Q. Procyanidin A1 alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via regulating AMPK/mTOR/p70S6K-mediated autophagy. J Physiol Biochem. (2022) 78:213–27. doi: 10.1007/s13105-021-00854-5
150. Shi W, Peng K, Yu H, Wang Z, Xia S, Xiao S, et al. Autotaxin (ATX) inhibits autophagy leading to exaggerated disruption of intestinal epithelial barrier in colitis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis disease. (2023) 1869:166647. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166647
151. Zhou M, Xu W, Wang J, Yan J, Shi Y, Zhang C, et al. Boosting mTOR-dependent autophagy via upstream TLR4-MyD88-MAPK signaling and downstream NF-κB pathway quenches intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress injury. EBioMedicine. (2018) 35:345–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.08.035
152. Hu X, Deng J, Yu T, Chen S, Ge Y, Zhou Z, et al. ATF4 deficiency promotes intestinal inflammation in mice by reducing uptake of glutamine and expression of antimicrobial peptides. Gastroenterology. (2019) 156:1098–111. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.033
153. Homer CR, Richmond AL, Rebert NA, Achkar JP, and McDonald C. ATG16L1 and NOD2 interact in an autophagy-dependent antibacterial pathway implicated in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. (2010) 139:1630–41, 41.e1-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.07.006
154. Watson A, Forbes Satter L, Reiland Sauceda A, Kellermayer R, and Karam LB. NOD2 polymorphisms may direct a crohn disease phenotype in patients with very early-onset inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr gastroenterology nutrition. (2023) 77:748–52. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000003846
155. Horowitz JE, Warner N, Staples J, Crowley E, Gosalia N, Murchie R, et al. Mutation spectrum of NOD2 reveals recessive inheritance as a main driver of Early Onset Crohn’s Disease. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:5595. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84938-8
156. Abdelnaby H, Ndiaye NC, D’Amico F, Fouad AM, Hassan S, Elshafey A, et al. NOD2/CARD15 polymorphisms (P268S, IVS8(+158), G908R, L1007fs, R702W) among Kuwaiti patients with Crohn’s disease: A case-control study. Saudi J gastroenterology: Off J Saudi Gastroenterology Association. (2021) 27:249–56. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_613_20
157. Goswami AB, Karadarević D, and Castaño-Rodríguez N. Immunity-related GTPase IRGM at the intersection of autophagy, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Inflammation research: Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc. (2022) 71:785–95. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01595-x
158. Lu XC, Tao Y, Wu C, Zhao PL, Li K, Zheng JY, et al. Association between variants of the autophagy related gene–IRGM and susceptibility to Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. PloS One. (2013) 8:e80602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080602
159. Sehgal R, Berg A, Polinski JI, Hegarty JP, Lin Z, McKenna KJ, et al. Mutations in IRGM are associated with more frequent need for surgery in patients with ileocolonic Crohn’s disease. Dis colon rectum. (2012) 55:115–21. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0b013e31823ccea8
160. Lavoie S, Conway KL, Lassen KG, Jijon HB, Pan H, Chun E, et al. The Crohn’s disease polymorphism, ATG16L1 T300A, alters the gut microbiota and enhances the local Th1/Th17 response. Elife. (2019) 8:e39982. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39982
161. Liu H, Gao P, Jia B, Lu N, Zhu B, and Zhang F. IBD-associated atg16L1T300A polymorphism regulates commensal microbiota of the intestine. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:772189. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.772189
162. Zhang H, Zheng L, Chen J, Fukata M, Ichikawa R, Shih DQ, et al. The protection role of Atg16l1 in CD11c(+)dendritic cells in murine colitis. Immunobiology. (2017) 222:831–41. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2017.03.002
163. Zhang H, Wang D, Shihb DQ, and Zhang XL. Atg16l1 in dendritic cells is required for antibacterial defense and autophagy in murine colitis. IUBMB Life. (2020) 72:2686–95. doi: 10.1002/iub.v72.12
164. Plantinga TS, Crisan TO, Oosting M, van de Veerdonk FL, de Jong DJ, Philpott DJ, et al. Crohn’s disease-associated ATG16L1 polymorphism modulates pro-inflammatory cytokine responses selectively upon activation of NOD2. Gut. (2011) 60:1229–35. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.228908
165. Ma C, Storer CE, Chandran U, LaFramboise WA, Petrosko P, Frank M, et al. Crohn’s disease-associated ATG16L1 T300A genotype is associated with improved survival in gastric cancer. EBioMedicine. (2021) 67:103347. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103347
166. Li H, Sun Y, Yao Y, Ke S, Zhang N, Xiong W, et al. USP8-governed GPX4 homeostasis orchestrates ferroptosis and cancer immunotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2024) 121:e2315541121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315541121
167. Yu X, Guo Q, Zhang H, Wang X, Han Y, and Yang Z. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α can reverse the Adriamycin resistance of breast cancer adjuvant chemotherapy by upregulating transferrin receptor and activating ferroptosis. FASEB journal: Off Publ Fed Am Societies Exp Biol. (2024) 38:e23876. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401119R
168. Lomphithak T, Sae-Fung A, Sprio S, Tampieri A, Jitkaew S, and Fadeel B. Exploiting the ferroaddiction of pancreatic cancer cells using Fe-doped nanoparticles. Nanomedicine: nanotechnology biology medicine. (2024) 55:102714. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2023.102714
169. Guan W, Xia M, Ji M, Chen B, Li S, Zhang M, et al. Iron induces two distinct Ca(2+) signaling cascades in astrocytes. Commun Biol. (2021) 4:525. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02060-x
170. Philpott CC, Patel SJ, and Protchenko O. Management versus miscues in the cytosolic labile iron pool: The varied functions of iron chaperones. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2020) 1867:118830. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118830
171. Ćuk A, Rumora L, Mikulić I, Penava N, Cvetković I, Pušić A, et al. Serum concentration of ferroportin in women of reproductive age. Biochemia medica. (2024) 34:030701. doi: 10.11613/BM.2024.030701
172. Zhu Q, Zhai J, Chen Z, Guo Z, Wang N, Zhang C, et al. Ferritinophagy: Molecular mechanisms and role in disease. Pathol Res Pract. (2024) 262:155553. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155553
173. Chen Z, Zhu Q, Qi X, Yang LR, Rong YX, Wei Q, et al. Dual role of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in Z-ligustilide-induced ferroptosis against AML cells. Phytomedicine: Int J phytotherapy phytopharmacology. (2024) 124:155288. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155288
174. Whillier S, Garcia B, Chapman BE, Kuchel PW, and Raftos JE. Glutamine and α-ketoglutarate as glutamate sources for glutathione synthesis in human erythrocytes. FEBS J. (2011) 278:3152–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08241.x
175. Arnér ESJ and Schmidt EE. Unresolved questions regarding cellular cysteine sources and their possible relationships to ferroptosis. Adv Cancer Res. (2024) 162:1–44. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2024.04.001
176. Ma Z, Ye W, Wang J, Huang X, Huang J, Li X, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase 1: A novel metabolic target in inhibiting acute myeloid leukaemia progression. Br J haematology. (2023) 202:566–77. doi: 10.1111/bjh.v202.3
177. Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M, Shchepinov MS, and Stockwell BR. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2016) 113:E4966–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603244113
178. Cheng R, Wang X, Huang L, Lu Z, Wu A, Guo S, et al. Novel insights into the protective effects of leonurine against acute kidney injury: Inhibition of ER stress-associated ferroptosis via regulating ATF4/CHOP/ACSL4 pathway. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) 395:111016. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111016
179. Wang Z, Li M, Liu Y, Qiao Z, Bai T, Yang L, et al. Dihydroartemisinin triggers ferroptosis in primary liver cancer cells by promoting and unfolded protein response−induced upregulation of CHAC1 expression. Oncol Rep. (2021) 46:240. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8191
180. Forcina GC and Dixon SJ. GPX4 at the crossroads of lipid homeostasis and ferroptosis. Proteomics. (2019) 19:e1800311. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201800311
181. Ding K, Liu C, Li L, Yang M, Jiang N, Luo S, et al. Acyl-CoA synthase ACSL4: an essential target in ferroptosis and fatty acid metabolism. Chin Med J. (2023) 136:2521–37. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002533
182. Wang X, Chen Y, Yang X, Cheng L, He Z, Xin Y, et al. Activation of ALOX12 by a multi-organelle-orienting photosensitizer drives ACSL4-independent cell ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:1040. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05462-9
183. Xu R, Wang W, and Zhang W. Ferroptosis and the bidirectional regulatory factor p53. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:197. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01517-8
184. Ren X, Wen Y, Yuan M, Li C, Zhang J, Li S, et al. Cerebroprotein hydrolysate-I ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in APP/PS1 mice by inhibiting ferroptosis via the p53/SAT1/ALOX15 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. (2024) 979:176820. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176820
185. Ou Y, Wang SJ, Li D, Chu B, and Gu W. Activation of SAT1 engages polyamine metabolism with p53-mediated ferroptotic responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2016) 113:E6806–e12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1607152113
186. Chen D, Chu B, Yang X, Liu Z, Jin Y, Kon N, et al. iPLA2β-mediated lipid detoxification controls p53-driven ferroptosis independent of GPX4. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3644. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23902-6
187. Gaschler MM, Andia AA, Liu H, Csuka JM, Hurlocker B, Vaiana CA, et al. FINO(2) initiates ferroptosis through GPX4 inactivation and iron oxidation. Nat Chem Biol. (2018) 14:507–15. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0031-6
188. Kraft VAN, Bezjian CT, Pfeiffer S, Ringelstetter L, Müller C, Zandkarimi F, et al. GTP cyclohydrolase 1/tetrahydrobiopterin counteract ferroptosis through lipid remodeling. ACS Cent science. (2020) 6:41–53. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b01063
189. Soula M, Weber RA, Zilka O, Alwaseem H, La K, Yen F, et al. Metabolic determinants of cancer cell sensitivity to canonical ferroptosis inducers. Nat Chem Biol. (2020) 16:1351–60. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0613-y
190. Liu M, Kong XY, Yao Y, Wang XA, Yang W, Wu H, et al. The critical role and molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis in antioxidant systems: a narrative review. Ann Trans medicine. (2022) 10:368. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6942
191. Peterson LW and Artis D. Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:141–53. doi: 10.1038/nri3608
192. Xu M, Tao J, Yang Y, Tan S, Liu H, Jiang J, et al. Ferroptosis involves in intestinal epithelial cell death in ulcerative colitis. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:86. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2299-1
193. Chen Y, Yan W, Chen Y, Zhu J, Wang J, Jin H, et al. SLC6A14 facilitates epithelial cell ferroptosis via the C/EBPβ-PAK6 axis in ulcerative colitis. Cell Mol Life sciences: CMLS. (2022) 79:563. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04594-7
194. Lechuga S, Braga-Neto MB, Naydenov NG, Rieder F, and Ivanov AI. Understanding disruption of the gut barrier during inflammation: Should we abandon traditional epithelial cell lines and switch to intestinal organoids? Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1108289. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1108289
195. Lam IH, Chan CI, Han M, Li L, and Yu HH. ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation. Open Med (Warsaw Poland). (2024) 19:20240993. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-0993
196. Li Y, Feng D, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Sun R, Tian D, et al. Ischemia-induced ACSL4 activation contributes to ferroptosis-mediated tissue injury in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death differentiation. (2019) 26:2284–99. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0299-4
197. Oparaugo NC, Ouyang K, Nguyen NPN, Nelson AM, and Agak GW. Human regulatory T cells: understanding the role of tregs in select autoimmune skin diseases and post-transplant nonmelanoma skin cancers. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:1527. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021527
198. Yamada A, Arakaki R, Saito M, Tsunematsu T, Kudo Y, and Ishimaru N. Role of regulatory T cell in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. (2016) 22:2195–205. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2195
199. Yan J, Zeng Y, Guan Z, Li Z, Luo S, Niu J, et al. Inherent preference for polyunsaturated fatty acids instigates ferroptosis of Treg cells that aggravates high-fat-diet-related colitis. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114636. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114636
200. Luo S, Zeng Y, Chen B, Yan J, Ma F, Zhuang G, et al. Vitamin E and GPX4 cooperatively protect treg cells from ferroptosis and alleviate intestinal inflammatory damage in necrotizing enterocolitis. Redox Biol. (2024) 75:103303. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103303
201. Xu C, Sun S, Johnson T, Qi R, Zhang S, Zhang J, et al. The glutathione peroxidase Gpx4 prevents lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis to sustain Treg cell activation and suppression of antitumor immunity. Cell Rep. (2021) 35:109235. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109235
202. Ruder B and Becker C. At the forefront of the mucosal barrier: the role of macrophages in the intestine. Cells. (2020) 9:2162. doi: 10.3390/cells9102162
203. Han X, Ding S, Jiang H, and Liu G. Roles of macrophages in the development and treatment of gut inflammation. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:625423. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.625423
204. Ye Y, Liu L, Feng Z, Liu Y, Miao J, Wei X, et al. The ERK-cPLA2-ACSL4 axis mediating M2 macrophages ferroptosis impedes mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. Free Radical Biol medicine. (2024) 214:219–35. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.02.016
205. Ma H, Shu Q, Li D, Wang T, Li L, Song X, et al. Accumulation of intracellular ferrous iron in inflammatory-activated macrophages. Biol Trace element Res. (2023) 201:2303–10. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03362-9
206. Yang M, Shen Z, Zhang X, Song Z, Zhang Y, Lin Z, et al. Ferroptosis of macrophages facilitates bone loss in apical periodontitis via NRF2/FSP1/ROS pathway. Free Radical Biol medicine. (2023) 208:334–47. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.08.020
207. Rankin LC, Girard-Madoux MJ, Seillet C, Mielke LA, Kerdiles Y, Fenis A, et al. Complementarity and redundancy of IL-22-producing innate lymphoid cells. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:179–86. doi: 10.1038/ni.3332
208. Li X, He J, Gao X, Zheng G, Chen C, Chen Y, et al. GPX4 restricts ferroptosis of NKp46(+)ILC3s to control intestinal inflammation. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:687. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07060-3
209. Wagatsuma K, Yokoyama Y, and Nakase H. Role of biomarkers in the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Life (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 11:1375. doi: 10.3390/life11121375
210. Ma C, Haritunians T, Gremida AK, Syal G, Shah J, Yang S, et al. Ileal paneth cell phenotype is a cellular biomarker for pouch complications in ulcerative colitis. J Crohn’s colitis. (2024) 18:2010–2022. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae105
211. Huang F, Zhang S, Li X, Huang Y, He S, and Luo L. STAT3-mediated ferroptosis is involved in ulcerative colitis. Free Radical Biol medicine. (2022) 188:375–85. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.06.242
212. Qian R, Tang M, Ouyang Z, Cheng H, and Xing S. Identification of ferroptosis-related genes in ulcerative colitis: a diagnostic model with machine learning. Ann Trans medicine. (2023) 11:177. doi: 10.21037/atm-23-276
213. Chen C, Lan B, Xie G, and Liu Z. Analysis and identification of ferroptosis-related genes in ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. (2023) 58:1422–33. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2023.2240927
214. Ji X, Ma S, Sun X, Yu D, Song Y, and Li R. Analysis of ferroptosis-associated genes in Crohn’s disease based on bioinformatics. Front medicine. (2022) 9:1058076. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1058076
215. Zhang W, Li Z, Li H, and Zhang D. Identification of differentially expressed genes associated with ferroptosis in Crohn’s disease. Exp Ther medicine. (2024) 27:89. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12378
216. Palmela C, Chevarin C, Xu Z, Torres J, Sevrin G, Hirten R, et al. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. (2018) 67:574–87. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314903
217. Wen W, Xu Y, Qian W, Huang L, Gong J, Li Y, et al. PUFAs add fuel to Crohn’s disease-associated AIEC-induced enteritis by exacerbating intestinal epithelial lipid peroxidation. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2265578. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2265578
218. Iwanaga T and Takahashi-Iwanaga H. Disposal of intestinal apoptotic epithelial cells and their fate via divergent routes. Biomed Res (Tokyo Japan). (2022) 43:59–72. doi: 10.2220/biomedres.43.59
219. Bahar Halpern K, Korem Kohanim Y, Biram A, Harnik Y, Egozi A, Yakubovsky O, et al. The cellular states and fates of shed intestinal cells. Nat Metab. (2023) 5:1858–69. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00905-9
220. Günther C, Neumann H, Neurath MF, and Becker C. Apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis: cell death regulation in the intestinal epithelium. Gut. (2013) 62:1062–71. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301364
221. Dagenais M, Douglas T, and Saleh M. Role of programmed necrosis and cell death in intestinal inflammation. Curr Opin gastroenterology. (2014) 30:566–75. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000117
222. Subramanian S, Geng H, and Tan XD. Cell death of intestinal epithelial cells in intestinal diseases. Sheng li xue bao: [Acta physiologica Sinica]. (2020) 72:308–24. doi: 10.13294/j.aps.2020.0039
223. Günther C, Martini E, Wittkopf N, Amann K, Weigmann B, Neumann H, et al. Caspase-8 regulates TNF-α-induced epithelial necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature. (2011) 477:335–9. doi: 10.1038/nature10400
224. Welz PS, Wullaert A, Vlantis K, Kondylis V, Fernández-Majada V, Ermolaeva M, et al. FADD prevents RIP3-mediated epithelial cell necrosis and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nature. (2011) 477:330–4. doi: 10.1038/nature10273
225. Wang R, Li H, Wu J, Cai ZY, Li B, Ni H, et al. Gut stem cell necroptosis by genome instability triggers bowel inflammation. Nature. (2020) 580:386–90. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2127-x
226. Južnić L, Peuker K, Strigli A, Brosch M, Herrmann A, Häsler R, et al. SETDB1 is required for intestinal epithelial differentiation and the prevention of intestinal inflammation. Gut. (2021) 70:485–98. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321339
227. Chen X, Liu G, Yuan Y, Wu G, Wang S, and Yuan L. NEK7 interacts with NLRP3 to modulate the pyroptosis in inflammatory bowel disease via NF-κB signaling. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:906. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2157-1
228. Man SM. Inflammasomes in the gastrointestinal tract: infection, cancer and gut microbiota homeostasis. Nat Rev Gastroenterology hepatology. (2018) 15:721–37. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0054-1
229. Zhang S, Liang Y, Yao J, Li DF, and Wang LS. Role of pyroptosis in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): from gasdermins to DAMPs. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:833588. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.833588
230. Rana N, Privitera G, Kondolf HC, Bulek K, Lechuga S, De Salvo C, et al. GSDMB is increased in IBD and regulates epithelial restitution/repair independent of pyroptosis. Cell. (2022) 185:283–98.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.024
231. Frank D and Vince JE. Pyroptosis versus necroptosis: similarities, differences, and crosstalk. Cell Death differentiation. (2019) 26:99–114. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0212-6
232. Ocansey DKW, Yuan J, Wei Z, Mao F, and Zhang Z. Role of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis and as a therapeutic target of inflammatory bowel disease (Review). Int J Mol Med. (2023) 51:53. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5256
233. Chen Y, Zhang P, Chen W, and Chen G. Ferroptosis mediated DSS-induced ulcerative colitis associated with Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Immunol letters. (2020) 225:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.06.005
234. Arab HH, Eid AH, Mahmoud AM, and Senousy MA. Linagliptin mitigates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats by targeting inflammatory and redox signaling. Life Sci. (2021) 273:119295. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119295
235. Xu J, Liu S, Cui Z, Wang X, Ning T, Wang T, et al. Ferrostatin-1 alleviated TNBS induced colitis via the inhibition of ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res communications. (2021) 573:48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.08.018
236. Foerster EG, Mukherjee T, Cabral-Fernandes L, Rocha JDB, Girardin SE, and Philpott DJ. How autophagy controls the intestinal epithelial barrier. Autophagy. (2022) 18:86–103. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1909406
237. Gurung P, Man SM, and Kanneganti TD. A20 is a regulator of necroptosis. Nat Immunol. (2015) 16:596–7. doi: 10.1038/ni.3174
238. Onizawa M, Oshima S, Schulze-Topphoff U, Oses-Prieto JA, Lu T, Tavares R, et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 restricts ubiquitination of the kinase RIPK3 and protects cells from necroptosis. Nat Immunol. (2015) 16:618–27. doi: 10.1038/ni.3172
239. Vereecke L, Sze M, Mc Guire C, Rogiers B, Chu Y, Schmidt-Supprian M, et al. Enterocyte-specific A20 deficiency sensitizes to tumor necrosis factor-induced toxicity and experimental colitis. J Exp medicine. (2010) 207:1513–23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20092474
240. Blander JM. A long-awaited merger of the pathways mediating host defense and programmed cell death. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:601–18. doi: 10.1038/nri3720
241. Kaiser WJ, Upton JW, Long AB, Livingston-Rosanoff D, Daley-Bauer LP, Hakem R, et al. RIP3 mediates the embryonic lethality of caspase-8-deficient mice. Nature. (2011) 471:368–72. doi: 10.1038/nature09857
242. Neurath MF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:329–42. doi: 10.1038/nri3661
243. Leppkes M, Roulis M, Neurath MF, Kollias G, and Becker C. Pleiotropic functions of TNF-α in the regulation of the intestinal epithelial response to inflammation. Int Immunol. (2014) 26:509–15. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxu051
244. Brenner D, Blaser H, and Mak TW. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signaling: live or let die. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:362–74. doi: 10.1038/nri3834
245. Kiesslich R, Duckworth CA, Moussata D, Gloeckner A, Lim LG, Goetz M, et al. Local barrier dysfunction identified by confocal laser endomicroscopy predicts relapse in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. (2012) 61:1146–53. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300695
246. Madara JL. Maintenance of the macromolecular barrier at cell extrusion sites in intestinal epithelium: physiological rearrangement of tight junctions. J membrane Biol. (1990) 116:177–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01868675
247. Marchiando AM, Shen L, Graham WV, Edelblum KL, Duckworth CA, Guan Y, et al. The epithelial barrier is maintained by in vivo tight junction expansion during pathologic intestinal epithelial shedding. Gastroenterology. (2011) 140:1208–18.e1-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.004
248. Watson AJ and Hughes KR. TNF-α-induced intestinal epithelial cell shedding: implications for intestinal barrier function. Ann New York Acad Sci. (2012) 1258:1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06523.x
249. Cao SS. Cellular stress responses and gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2018) 2018:7192646. doi: 10.1155/2018/7192646
250. Keshtkar S, Azarpira N, and Ghahremani MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2018) 9:63. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0791-7
251. Zhou Y, Yamamoto Y, Xiao Z, and Ochiya T. The immunomodulatory functions of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells mediated via paracrine activity. J Clin Med. (2019) 8:1025. doi: 10.3390/jcm8071025
252. Song N, Scholtemeijer M, and Shah K. Mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 41:653–64. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2020.06.009
253. Nishikawa T, Maeda K, Nakamura M, Yamamura T, Sawada T, Mizutani Y, et al. Filtrated adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell lysate ameliorates experimental acute colitis in mice. Digestive Dis Sci. (2021) 66:1034–44. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06359-3
254. Yang J, Liu XX, Fan H, Tang Q, Shou ZX, Zuo DM, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect against Experimental Colitis via Attenuating Colon Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0140551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140551
255. Liu P, Xie XR, Wu H, Li H, Chi JS, Liu XM, et al. Conditioned medium of mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with H(2)O(2) promotes intestinal mucosal repair in acute experimental colitis. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:20772. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24493-y
256. Hidalgo-García L, Ruiz-Malagon AJ, Huertas F, Rodríguez-Sojo MJ, Molina-Tijeras JA, Diez-Echave P, et al. Administration of intestinal mesenchymal stromal cells reduces colitis-associated cancer in C57BL/6J mice modulating the immune response and gut dysbiosis. Pharmacol Res. (2023) 195:106891. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106891
257. Xu J, Wang X, Chen J, Chen S, Li Z, Liu H, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote colon epithelial integrity and regeneration by elevating circulating IGF-1 in colitis mice. Theranostics. (2020) 10:12204–22. doi: 10.7150/thno.47683
258. Guijarro LG, Cano-Martínez D, Toledo-Lobo MV, Salinas PS, Chaparro M, Gómez-Lahoz AM, et al. Relationship between IGF-1 and body weight in inflammatory bowel diseases: Cellular and molecular mechanisms involved. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2021) 144:112239. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112239
259. Yousefi-Ahmadipour A, Rashidian A, Mirzaei MR, Farsinejad A, PourMohammadi-Nejad F, Ghazi-Khansari M, et al. Combination therapy of mesenchymal stromal cells and sulfasalazine attenuates trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid induced colitis in the rat: The S1P pathway. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:11078–91. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v234.7
260. Zhai R, Tai F, Ding K, Tan X, Li H, Cao Z, et al. Comparative analysis of the therapeutic effects of MSCs from umbilical cord, bone marrow, and adipose tissue and investigating the impact of oxidized RNA on radiation-induced lung injury. Stem Cells Int. (2024) 2024:7419270. doi: 10.1155/2024/7419270
261. Yang Q, Zhong QM, Song MQ, Tong LG, and Bai CZ. Exosomes derived from Danshen decoction-pretreated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate myocardial infarction via anti-apoptosis and up-regulation of autophagy. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e38034. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38034
262. Sun D, Cao H, Yang L, Lin L, Hou B, Zheng W, et al. MiR-200b in heme oxygenase-1-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury of intestinal epithelial cells by targeting high mobility group box 3. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:480. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2685-8
263. Li P, Zhang HY, Gao JZ, Du WQ, Tang D, Wang W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles containing miR-378a-3p inhibit the occurrence of inflammatory bowel disease by targeting GATA2. J Cell Mol medicine. (2022) 26:3133–46. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.v26.11
264. Gu L, Ren F, Fang X, Yuan L, Liu G, and Wang S. Exosomal microRNA-181a derived from mesenchymal stem cells improves gut microbiota composition, barrier function, and inflammatory status in an experimental colitis model. Front medicine. (2021) 8:660614. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.660614
265. Ock SA, Kim SY, Kim YI, Ju WS, and Lee P. Enhanced in vitro recapitulation of in vivo liver regeneration by co-culturing hepatocyte organoids with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, alleviating steatosis and apoptosis in acute alcoholic liver injury. Cells. (2024) 13:1303. doi: 10.3390/cells13151303
266. Yang C, Lei D, Ouyang W, Ren J, Li H, Hu J, et al. Conditioned media from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells efficiently induced the apoptosis and differentiation in human glioma cell lines in vitro. BioMed Res Int. (2014) 2014:109389. doi: 10.1155/2014/109389
267. Liang W, Li Y, Ji Y, Kang R, Zhang K, Su X, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation and regulate the inflammatory state in osteomyelitis in vitro model. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. (2024) 398:1695–1705. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03357-4
268. Li L, Song QQ, Li SR, Jia ZG, Sun XC, Zhao YT, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuate burn-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. Acta histochemica. (2024) 126:152189. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2024.152189
269. Feng H, Liu Q, Deng Z, Li H, Zhang H, Song J, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate erectile dysfunction in rats with diabetes mellitus through the attenuation of ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:450. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03147-w
270. Zhu Y, Dong C, Xu Z, Lou Y, Tian N, Guan Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting ferroptosis via the JNK/KEAP1/NRF2 signaling pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2024). doi: 10.1089/ars.2024.0575
271. Wang H, Sun Y, Xiao FJ, Zhao X, Zhang WY, Xia YJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate DSS-induced experimental colitis by modulating the gut microbiota and MUC-1 pathway. J Inflammation Res. (2023) 16:2023–39. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S402592
272. McAuley JL, Linden SK, Png CW, King RM, Pennington HL, Gendler SJ, et al. MUC1 cell surface mucin is a critical element of the mucosal barrier to infection. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:2313–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI26705
273. Ye C, Xu B, Yang J, Liu Y, Zeng Z, Xia L, et al. Mucin1 relieves acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur J histochemistry: EJH. (2021) 65:3331. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2021.3331
274. Cui DJ, Chen C, Yuan WQ, Yang YH, and Han L. Integrative analysis of ferroptosis-related genes in ulcerative colitis. J Int Med Res. (2021) 49:3000605211042975. doi: 10.1177/03000605211042975
275. Chang Y, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Zhao L, Lv C, Huang Q, et al. From hair to colon: hair follicle-derived MSCs alleviate pyroptosis in DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by releasing exosomes in a paracrine manner. Oxid Med Cell longevity. (2022) 2022:9097530. doi: 10.1155/2022/9097530
276. Xu Y, Tang X, Fang A, Yan J, Kofi Wiredu Ocansey D, Zhang X, et al. HucMSC-Ex carrying miR-203a-3p.2 ameliorates colitis through the suppression of caspase11/4-induced macrophage pyroptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 110:108925. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108925
277. Wang D, Xue H, Tan J, Liu P, Qiao C, Pang C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes containing miR-539-5p inhibit pyroptosis through NLRP3/caspase-1 signaling to alleviate inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammation research: Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc. (2022) 71:833–46. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01577-z
278. Ruan B, Rong M, Ming Z, Wang K, Liu X, Deng L, et al. Discovery of pterostilbene analogs as novel NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors for potential treatment of DSS-induced colitis in mice. Bioorganic Chem. (2023) 133:106429. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106429
279. Yuan X, Li T, Shi L, Miao J, Guo Y, and Chen Y. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-26a-5p via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis through METTL14/NLRP3. Mol Med (Cambridge Mass). (2021) 27:91. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00355-7
280. Pei Y, Ma W, Wang H, Chen F, Xiao W, Fan M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-548x-3p inhibits pyroptosis of vascular endothelial cells through HMGB1 in heat stroke. Genomics. (2023) 115:110719. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110719
281. Cao L, Xu H, Wang G, Liu M, Tian D, and Yuan Z. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 72:264–74. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.020
282. Li Y, Altemus J, and Lightner AL. Mesenchymal stem cells and acellular products attenuate murine induced colitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11:515. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02025-7
283. Yuan X, Li D, Chen X, Han C, Xu L, Huang T, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (hiPSC-MSCs) protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via delivering specificity protein (SP1) and transcriptional activating of sphingosine kinase 1 and inhibiting necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:3200. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0041-4
284. Liu ZY, Wu B, Guo YS, Zhou YH, Fu ZG, Xu BQ, et al. Necrostatin-1 reduces intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. Am J Cancer Res. (2015) 5:3174–85.
285. Zhao Y, Zhu X, Zhang L, Ferguson CM, Song T, Jiang K, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and their extracellular vesicle progeny decrease injury in poststenotic swine kidney through different mechanisms. Stem Cells Dev. (2020) 29:1190–200. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0030
286. Song G, Ma Z, Liu D, Qian D, Zhou J, Meng H, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate severe acute pancreatitis via regulation of microRNA-9 to inhibit necroptosis in rats. Life Sci. (2019) 223:9–21. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.019
287. Li N, Zhao L, Geng X, Liu J, Zhang X, Hu Y, et al. Stimulation by exosomes from hypoxia-preconditioned hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells facilitates mitophagy by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to alleviate ulcerative colitis. Theranostics. (2024) 14:4278–96. doi: 10.7150/thno.96038
288. Heras-Sandoval D, Pérez-Rojas JM, Hernández-Damián J, and Pedraza-Chaverri J. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signaling. (2014) 26:2694–701. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.08.019
289. Chen W and Zhang H. Elucidating the mechanism of IL-1β-Mediated Piezo1 expression regulation of chondrocyte autophagy and apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling Pathway. Tissue Cell. (2024) 86:102291. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102291
290. Wen C, Lin L, Zou R, Lin F, and Liu Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome mediated long non-coding RNA KLF3-AS1 represses autophagy and apoptosis of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle (Georgetown Tex). (2022) 21:289–303. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.2019411
291. Kim DW, Jeong HS, Kim E, Lee H, Choi CH, and Lee SJ. Oral delivery of stem-cell-loaded hydrogel microcapsules restores gut inflammation and microbiota. J Controlled release: Off J Controlled Release Society. (2022) 347:508–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.028
292. Yu Z, Chen J, Liu Y, Meng Q, Liu H, Yao Q, et al. The role of potential probiotic strains Lactobacillus reuteri in various intestinal diseases: New roles for an old player. Front microbiology. (2023) 14:1095555. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1095555
293. Zhang J, Lv S, Liu X, Song B, and Shi L. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell treatment for crohn’s disease: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Gut Liver. (2018) 12:73–8. doi: 10.5009/gnl17035
294. Ding Y, Bushell A, and Wood KJ. Mesenchymal stem-cell immunosuppressive capabilities: therapeutic implications in islet transplantation. Transplantation. (2010) 89:270–3. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181c6ffbe
295. Zang L, Li Y, Hao H, Liu J, Cheng Y, Li B, et al. Efficacy and safety of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes: a single-center, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:180. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02848-6
296. Zang L, Li Y, Hao H, Liu J, Zhang Q, Gao F, et al. Efficacy of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of type 2 diabetes assessed by retrospective continuous glucose monitoring. Stem Cells Trans medicine. (2023) 12:775–82. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szad060
297. Bartolucci J, Verdugo FJ, González PL, Larrea RE, Abarzua E, Goset C, et al. Safety and efficacy of the intravenous infusion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in patients with heart failure: a phase 1/2 randomized controlled trial (RIMECARD trial [randomized clinical trial of intravenous infusion umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on cardiopathy]). Circ Res. (2017) 121:1192–204. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310712
298. Lanzoni G, Linetsky E, Correa D, Messinger Cayetano S, Alvarez RA, Kouroupis D, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome: A double-blind, phase 1/2a, randomized controlled trial. Stem Cells Trans medicine. (2021) 10:660–73. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0472
299. Forbes GM, Sturm MJ, Leong RW, Sparrow MP, Segarajasingam D, Cummins AG, et al. A phase 2 study of allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells for luminal Crohn’s disease refractory to biologic therapy. Clin gastroenterology hepatology: Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterological Association. (2014) 12:64–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.06.021
300. Ghosh S and Mitchell R. Impact of inflammatory bowel disease on quality of life: Results of the European Federation of Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis Associations (EFCCA) patient survey. J Crohn’s colitis. (2007) 1:10–20. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2007.06.005
301. Knowles SR, Graff LA, Wilding H, Hewitt C, Keefer L, and Mikocka-Walus A. Quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analyses-part I. Inflammation Bowel Dis. (2018) 24:742–51. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izx100
302. Graff LA, Walker JR, Lix L, Clara I, Rawsthorne P, Rogala L, et al. The relationship of inflammatory bowel disease type and activity to psychological functioning and quality of life. Clin gastroenterology hepatology: Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterological Association. (2006) 4:1491–501. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2006.09.027
303. Panés J, García-Olmo D, Van Assche G, Colombel JF, Reinisch W, Baumgart DC, et al. Expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in Crohn’s disease: a phase 3 randomised, double-blind controlled trial. Lancet (London England). (2016) 388:1281–90. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31203-X
304. Panés J, García-Olmo D, Van Assche G, Colombel JF, Reinisch W, Baumgart DC, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in patients with crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. (2018) 154:1334–42.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.12.020
305. Furukawa S, Mizushima T, Nakaya R, Shibata M, Yamaguchi T, Watanabe K, et al. Darvadstrocel for complex perianal fistulas in Japanese adults with crohn’s disease: A phase 3 study. J Crohn’s colitis. (2023) 17:369–78. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac144
306. Marzo M, Felice C, Pugliese D, Andrisani G, Mocci G, Armuzzi A, et al. Management of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s disease: an up-to-date review. World J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21:1394–403. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1394
307. Heimann TM, Swaminathan S, Slater GI, and Kurtz RJ. Perianal fistula after ileoanal pouch in patients with ulcerative colitis: A review of 475 patients operated on at a major IBD center. Dis colon rectum. (2022) 65:76–82. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000002114
308. Otero-Piñeiro AM, Hull T, Holubar S, Pedersen KE, Aykun N, Obi M, et al. Surgical options for the treatment of perianal and anovaginal fistulas in the setting of ileoanal pouch crohn’s disease: experience of a tertiary center. J gastrointestinal surgery: Off J Soc Surg Alimentary Tract. (2023) 27:2867–75. doi: 10.1007/s11605-023-05603-1
309. Tan Z, Zhu S, Liu C, Meng Y, Li J, Zhang J, et al. Causal link between inflammatory bowel disease and fistula: evidence from mendelian randomization study. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:2482. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072482
310. de la Poza G, López-Sanroman A, Taxonera C, Marín-Jimenez I, Gisbert JP, Bermejo F, et al. Genital fistulas in female Crohn’s disease patients.: clinical characteristics and response to therapy. J Crohn’s colitis. (2012) 6:276–80. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2011.08.015
311. Zhu YG, Shi MM, Monsel A, Dai CX, Dong X, Shen H, et al. Nebulized exosomes derived from allogenic adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with severe COVID-19: a pilot study. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:220. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02900-5
312. Hart A, Ng SC, Watkins J, Paridaens K, Edwards JO, Fullarton JR, et al. The use of 5-aminosalicylates in Crohn’s disease: a retrospective study using the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink. Ann gastroenterology. (2020) 33:500–7. doi: 10.20524/aog.2020.0521
313. Otkur W, Wang J, Hou T, Liu F, Yang R, Li Y, et al. Aminosalicylates target GPR35, partly contributing to the prevention of DSS-induced colitis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 949:175719. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175719
314. Murray A, Nguyen TM, Parker CE, Feagan BG, and MacDonald JK. Oral 5-aminosalicylic acid for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database systematic Rev. (2020) 8:Cd000543. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000543.pub5
315. Ford AC, Khan KJ, Sandborn WJ, Hanauer SB, and Moayyedi P. Efficacy of topical 5-aminosalicylates in preventing relapse of quiescent ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Clin gastroenterology hepatology: Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterological Association. (2012) 10:513–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2011.10.043
316. Ford AC, Bernstein CN, Khan KJ, Abreu MT, Marshall JK, Talley NJ, et al. Glucocorticosteroid therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J gastroenterology. (2011) 106:590–9; quiz 600. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.70
317. Sandborn WJ, Danese S, D’Haens G, Moro L, Jones R, Bagin R, et al. Induction of clinical and colonoscopic remission of mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with budesonide MMX 9 mg: pooled analysis of two phase 3 studies. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2015) 41:409–18. doi: 10.1111/apt.2015.41.issue-5
318. Masuda M, Fukata N, Sano Y, Nishimon S, Aoi M, Tomiyama T, et al. Analysis of the initial dose and reduction rate of corticosteroid for ulcerative colitis in clinical practice. JGH open: an Open Access J gastroenterology hepatology. (2022) 6:612–20. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12796
319. Gisbert JP, Niño P, Cara C, and Rodrigo L. Comparative effectiveness of azathioprine in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis: prospective, long-term, follow-up study of 394 patients. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2008) 28:228–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03732.x
320. Pugliese D, Aratari A, Festa S, Ferraro PM, Monterubbianesi R, Guidi L, et al. Sustained clinical efficacy and mucosal healing of thiopurine maintenance treatment in ulcerative colitis: A real-life study. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2018) 2018:4195968. doi: 10.1155/2018/4195968
321. Sequier L, Caron B, Loeuille D, Honap S, Jairath V, Netter P, et al. Systematic review: Methotrexate-A poorly understood and underused medication in inflammatory bowel disease. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2024) 60:686–700. doi: 10.1111/apt.18194
322. Weisshof R, Aharoni Golan M, Sossenheimer PH, El Jurdi K, Ollech JE, Pekow J, et al. Real-world experience with tofacitinib in IBD at a tertiary center. Digestive Dis Sci. (2019) 64:1945–51. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05492-y
323. Sandborn WJ, Ghosh S, Panes J, Schreiber S, D’Haens G, Tanida S, et al. Efficacy of upadacitinib in a randomized trial of patients with active ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:2139–49.e14. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.030
324. Colombel JF, Rutgeerts P, Reinisch W, Esser D, Wang Y, Lang Y, et al. Early mucosal healing with infliximab is associated with improved long-term clinical outcomes in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. (2011) 141:1194–201. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.054
325. Kamal ME, Werida RH, Radwan MA, Askar SR, Omran GA, El-Mohamdy MA, et al. Efficacy and safety of infliximab and adalimumab in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Inflammopharmacology. (2024) 32:3259–69. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01508-w
326. Sands BE, Sandborn WJ, Panaccione R, O’Brien CD, Zhang H, Johanns J, et al. Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. New Engl J medicine. (2019) 381:1201–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1900750
327. Sands BE, D’Haens G, Clemow DB, Irving PM, Johns JT, Hunter Gibble T, et al. Two-year efficacy and safety of mirikizumab following 104 weeks of continuous treatment for ulcerative colitis: results from the LUCENT-3 open-label extension study. Inflammation Bowel Dis. (2024) 30:2245–58. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izae024
328. Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, D’Haens G, Panés J, Kaser A, Ferrante M, et al. Induction therapy with the selective interleukin-23 inhibitor risankizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet (London England). (2017) 389:1699–709. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30570-6
329. Davila MM and Papada E. The role of plant-derived natural products in the management of inflammatory bowel disease-what is the clinical evidence so far? Life (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 13:1703. doi: 10.3390/life13081703
330. Cai Z, Wang S, and Li J. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: A comprehensive review. Front medicine. (2021) 8:765474. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.765474
331. Chen H, Wang H, Xu X, Hu Y, Su J, Li D, et al. The impact of 5-aminosalicylates on the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in a murine model of ulcerative colitis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 134:112255. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112255
332. Kim N and Cho SG. New strategies for overcoming limitations of mesenchymal stem cell-based immune modulation. Int J Stem Cells. (2015) 8:54–68. doi: 10.15283/ijsc.2015.8.1.54
333. Dunn CM, Kameishi S, Grainger DW, and Okano T. Strategies to address mesenchymal stem/stromal cell heterogeneity in immunomodulatory profiles to improve cell-based therapies. Acta biomaterialia. (2021) 133:114–25. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.03.069
334. Huang WH, Chang MC, Tsai KS, Hung MC, Chen HL, and Hung SC. Mesenchymal stem cells promote growth and angiogenesis of tumors in mice. Oncogene. (2013) 32:4343–54. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.458
335. Tsai KS, Yang SH, Lei YP, Tsai CC, Chen HW, Hsu CY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote formation of colorectal tumors in mice. Gastroenterology. (2011) 141:1046–56. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.05.045
336. Hsu HS, Lin JH, Hsu TW, Su K, Wang CW, Yang KY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance lung cancer initiation through activation of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2012) 75:167–77. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.07.001
337. Hu W, Wang W, Jiang X, Wang Z, and Lin R. Mesenchymal stem cells can prevent or promote the progression of colon cancer based on their timing of administration. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:227. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04028-3
338. van Niel G, D’Angelo G, and Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2018) 19:213–28. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.125
339. van de Wakker SI, Meijers FM, Sluijter JPG, and Vader P. Extracellular vesicle heterogeneity and its impact for regenerative medicine applications. Pharmacol Rev. (2023) 75:1043–61. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.123.000841
340. Salmond N and Williams KC. Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles for clinical applications in cancer - time for standardization? Nanoscale Adv. (2021) 3:1830–52. doi: 10.1039/d0na00676a
341. Konoshenko MY, Lekchnov EA, Vlassov AV, and Laktionov PP. Isolation of extracellular vesicles: general methodologies and latest trends. BioMed Res Int. (2018) 2018:8545347. doi: 10.1155/2018/8545347
342. Zhang H, Zhu M, Shan X, Zhou X, Wang T, Zhang J, et al. A panel of seven-miRNA signature in plasma as potential biomarker for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Gene. (2019) 687:246–54. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.11.055
343. Zu H, Wu Y, Meng H, Cheng X, Wang Y, Zhang LW, et al. Tumor metabolism aiming cu(2-x)S nanoagents mediate photothermal-derived cuproptosis and immune activation. ACS nano. (2024) 18:23941–23957. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c10588
344. Wang M, Zheng L, Ma S, Lin R, Li J, and Yang S. Cuproptosis: emerging biomarkers and potential therapeutics in cancers. Front oncology. (2023) 13:1288504. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1288504
345. Yuan Y, Fu M, Li N, and Ye M. Identification of immune infiltration and cuproptosis-related subgroups in Crohn’s disease. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1074271. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1074271
346. Zou M, Zhang W, Zhu Y, and Xu Y. Identification of 6 cuproptosis-related genes for active ulcerative colitis with both diagnostic and therapeutic values. Medicine. (2023) 102:e35503. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035503
Keywords: cell death, extracellular vesicles, exosome, IBD, MSc
Citation: Akanyibah FA, He C, Cai P, Wang X, Wang Y and Mao F (2025) Mechanism of cell death and its application in the repair of inflammatory bowel disease by mesenchymal stem cells. Front. Immunol. 16:1597462. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1597462
Received: 21 March 2025; Accepted: 19 May 2025;
Published: 04 June 2025.
Edited by:
Nicola Susca, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyReviewed by:
Maria del Carmen Domínguez Horta, Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (CIGB), CubaNayoun Kim, Catholic University of Korea, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Akanyibah, He, Cai, Wang, Wang and Mao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fei Mao, bWFvZmVpMjAwM0B1anMuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Francis Atim Akanyibah
Francis Atim Akanyibah Chang’e He3†
Chang’e He3† Fei Mao
Fei Mao