- 1Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 2School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 3Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen, China
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoscale particles secreted by cells, encapsulating a variety of biomolecules, and have emerged as significant players in the pathophysiology of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). These vesicles exhibit both detrimental and therapeutic effects. On one hand, EVs contribute to AMI progression by promoting apoptosis, exacerbating inflammatory responses, and impairing angiogenesis. On the other hand, they facilitate cardiac repair by enhancing neovascularization, mitigating programmed cell death, and inhibiting fibrosis. This review provides a comprehensive overview of EV biogenesis, release mechanisms, and their dual regulatory roles in AMI, emphasizing the complex interplay of EVs in myocardial injury. Additionally, it explores the potential of EVs as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic delivery vehicles, highlighting their importance in advancing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. By elucidating the multifaceted roles of EVs, this review aims to establish a foundation for their clinical translation, improve their applicability in precision medicine, and explore the promising potential in cardiovascular disease treatment.
1 Introduction
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) remains one of the leading causes of high mortality and disability in cardiovascular diseases. Despite significant advancements in medical technologies, such as timely thrombolysis, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for vascular reperfusion, and the standardized use of antithrombotic, antiplatelet, and prognostic-improving pharmacotherapies, AMI continues to be a significant cardiovascular disorder closely associated with global mortality (1). The continuing clinical need for innovative and effective treatment strategies highlights the urgency of exploring novel treatment options. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are naturally secreted, non-replicative, nucleus-free particles encased in a lipid bilayer. Depending on their biogenesis, biophysical properties, and receptor composition, EVs can be classified into various subtypes, including exosomes, microvesicles, apoptotic bodies, exosome-like vesicles, migrasomes, and ectosomes, with exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies being the most extensively studied (2). EVs encapsulate a broad array of biomolecules derived from their parent cells, such as proteins, mRNA, microRNA, lipids, and small-molecule metabolites. These biomolecules can be transferred to recipient cells, thereby mediating intercellular communication and regulation. Secreted by various cell types and tissues, EVs exhibit lower immunogenicity, reduced tumorigenic potential, and enhanced stability, making them promising candidates for therapeutic applications (3). Emerging research indicates that EVs play pivotal roles in regulating diverse physiological and pathological processes and act as key mediators of intercellular signaling, presenting a breakthrough avenue for disease treatment. Their potential application in AMI therapy has sparked increasing interest. This review provides an in-depth discussion of the therapeutic and biomarker potential of EVs derived from various cell types in AMI. By exploring their roles in promoting angiogenesis, alleviating myocardial fibrosis, improving cardiac function, modulating inflammation, and regulating immune responses, this review aims to offer insights into the mechanistic underpinnings of EVs in AMI and promote their clinical translation as a promising strategy for cardiovascular therapy.
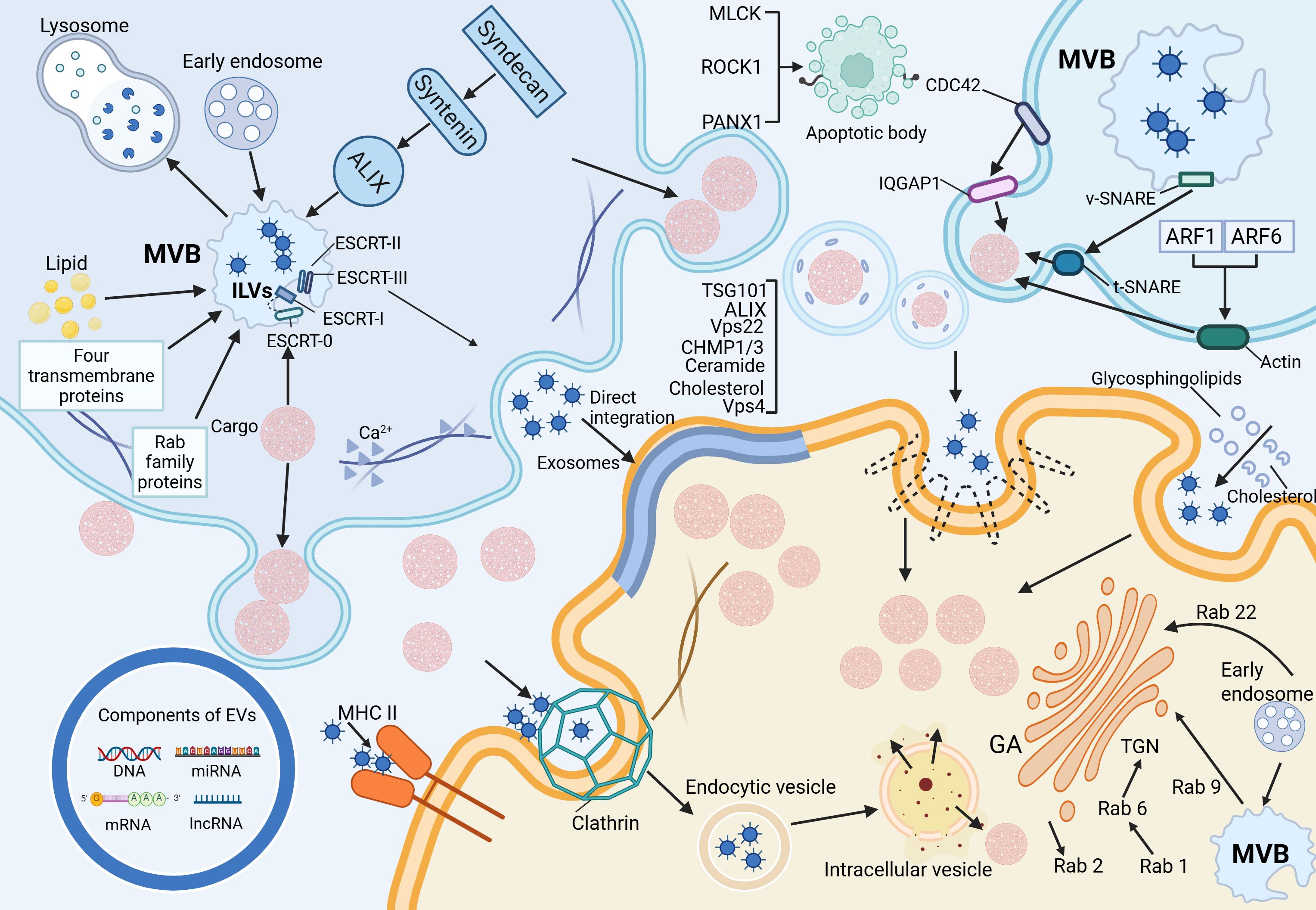
2 Biogenesis, release, and uptake of extracellular vesicles
As illustrated in Figure 1, the left figure summarizes the biogenesis pathways of exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies, as well as the regulatory mechanisms governing EV release, including cytoskeletal remodeling and membrane fusion events. The right figure illustrates the primary mechanisms by which recipient cells internalize EVs, such as membrane fusion, receptor–ligand interactions, and various endocytic pathways. By transporting bioactive molecules including proteins and nucleic acids, EVs play a pivotal role in mediating intercellular communication. The composition and functional properties of EVs can vary significantly, even when secreted by the same cell type under different environmental conditions. Moreover, different classes of EVs follow different biogenetic pathways, which further contributes to their heterogeneity and specific functions (4).
2.1 Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles and exosome formation
EVs are widely distributed across various biological fluids, including plasma, serum, saliva, amniotic fluid, breast milk, and urine, and are also secreted into cell culture media (5). Among the different EV subtypes, exosomes originate from intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) within multivesicular bodies (MVBs), which fuse with the plasma membrane to release ILVs into the extracellular space (6).
Exosome formation primarily occurs through the endosomal pathway. Early endosomes undergo inward budding of their limiting membrane, generating ILVs within MVBs. These MVBs may either fuse with lysosomes for degradation or the plasma membrane to release ILVs as exosomes (7). The biogenesis of ILVs is regulated by both endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) -dependent and ESCRT-independent mechanisms. The ESCRT-dependent pathway involves four protein complexes (ESCRT-0, -I, -II, and -III) along with accessory proteins that coordinate membrane remodeling and vesicle scission (8). ESCRT-0 recognizes and binds ubiquitinated cargo, recruiting ESCRT-I, which subsequently engages ESCRT-II to drive membrane invagination and ILV formation. ESCRT-III facilitates vesicle scission, a process that ALG-2-interacting protein X (ALIX)-mediated recruitment can further regulate. The ESCRT-independent pathway relies on alternative mechanisms, including the Syndecan-Syntenin-ALIX axis, lipid rafts, tetraspanins, and Rab family GTPases. Together, these factors regulate ILV formation and cargo sorting, reflecting the complexity and diversity of exosome biogenesis (9).
2.2 Mechanisms underlying the formation of microvesicles and apoptotic bodies
The biogenesis of microvesicles (MVs) fundamentally differs from that of exosomes, as MVs are formed through the direct outward budding of the plasma membrane, with a size range of 100–1000 nm (10). Their generation shares mechanistic similarities with ILV formation, involving both ESCRT-dependent and lipid-dependent pathways. Notably, the suppression of ESCRT-associated proteins, such as ALIX, TSG101, Vps22, CHMP1/3 (charged multivesicular body protein 1/3), and Vps4, results in a marked reduction in MV secretion (11). In addition, lipid components such as ceramides and cholesterol play regulatory roles in MV formation. A key driver of MV biogenesis is Ca²+-dependent cytoskeletal remodeling, which facilitates membrane deformation and vesicle budding. In contrast, apoptotic bodies (ABs) are distinct from other EV subtypes, as they are generated exclusively during programmed cell death and serve as hallmarks of apoptosis (12). Their size, ranging from 50 to 5000 nm, distinguishes them from the continuous release of EVs by viable cells. ABs emerge during the disassembly of apoptotic cells, wherein nuclear and cytoplasmic fragments are rapidly enclosed within densely packed membrane-bound vesicles of varying sizes (13). Studies have identified the involvement of specific kinases in AB formation, including myosin light chain kinase (MLCK), Rho-associated kinase (ROCK1), and pannexin 1 (PANX1), a plasma membrane channel protein. These molecular regulators orchestrate cytoskeletal reorganization and membrane dynamics required for AB biogenesis, further highlighting their mechanistic divergence from other EV subtypes (14).
2.3 Release of extracellular vesicles
Exosome secretion occurs following the fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane, a process that relies on the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complex (15). During this event, v-SNARE proteins on the MVB membrane interact with t-SNARE proteins on the plasma membrane, forming a functional SNARE complex that facilitates membrane fusion and subsequent release of ILVs. Key molecular regulators of exosome release include VAMP7, a v-SNARE-associated protein associated with membrane transport and cell migration, which modulates EV secretion in specific cell types (16). Additionally, SNAP23, a t-SNARE protein, and YKT6, a member of the SNARE family, serve as essential mediators of exosomal release. In contrast, the shedding of MVs is governed by the Rho family of small GTPases and Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) signaling pathways. Among these, CDC42, a key Rho-family GTPase, acts as a central hub integrating multiple regulatory signals for MV biogenesis (17). Activation of CDC42 by GTP promotes MV release via its downstream effector, IQGAP1 (IQ-domain GTPase-activating protein 1), which facilitates membrane budding. Simultaneously, CDC42 sustains epidermal growth factor (EGF) signaling by inhibiting receptor endocytosis, further enhancing MV secretion. Additionally, ARF1 and ARF6, small GTP-binding proteins, contribute to MV release by activating RhoA, which drives actomyosin contraction and promotes vesicle shedding (18).
2.4 Cargo, uptake, and intercellular communication of extracellular vesicles
EVs are critical mediators of intercellular communication, carrying a wide range of biomolecular “cargo,” including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids (such as DNA, mRNA, miRNA, and lncRNA) (19). The lipid bilayer encapsulating these molecules ensures their stability and integrity, allowing for the efficient transfer of information between cells (12). At the same time, this ability to reflect both physiological and pathological changes has led to the recognition of EVs as potential clinical diagnostic biomarkers. EVs interact with target cells through three primary mechanisms. First, exosomes and target cells directly interact via ligands and receptors (such as proteins, sugars, and lipids) on their respective membranes, initiating a cascade of signaling events (20). For instance, dendritic cells can transfer membrane proteins, like Major Histocompatibility Complex II (MHC II), to homologous T cells via exosomes, thereby playing a role in immune regulation (21). Second, the lipid bilayer of EVs can fuse directly with the target cell membrane, releasing their internal contents (such as proteins and RNA) into the cytoplasm, thus effectively transferring information. Third, EVs can be internalized by target cells through endocytosis, which includes clathrin-dependent endocytosis, caveolin-dependent endocytosis, macropinocytosis, phagocytosis, and lipid raft-mediated endocytosis (22). In clathrin-dependent endocytosis, clathrin assembles around membrane receptors to form a hexagonal and triangular lattice structure that encases the receptors and internalized substances, leading to the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles, which then fuse with intracellular vesicles to release their contents (23). Caveolin-mediated endocytosis, distinct from clathrin-mediated endocytosis, involves RhoA-dependent and Cdc42-mediated processes. These pathways are distinguished by their sensitivity to the biochemical properties of the cargo and the specificity of the involvement of adaptor proteins (11). External cholesterol and sphingolipids selectively stimulate caveolin-dependent endocytosis. Unlike the other two mechanisms, macropinocytosis and phagocytosis form larger vesicles (24). In macropinocytosis, the cell membrane undergoes folding to form large, irregular vesicles that engulf extracellular fluid and materials, whereas phagocytosis relies on receptor-ligand interactions to internalize particles. Lipid rafts, composed of cholesterol, sphingolipids, and receptor proteins, mediate endocytosis influenced by the lipid composition of these microdomains (25).
2.5 miRNA-mediated intercellular communication mechanisms: canonical and non-canonical pathways
Accumulating evidence indicates that exosome-associated miRNAs play crucial roles in various cardiac pathophysiological processes, particularly in myocardial repair and the regulation of fibrosis following ischemic injury, by modulating the function of recipient cells (26). Traditionally, miRNAs are thought to exert their effects via canonical mechanisms, primarily through complementary binding to the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of target mRNAs, thereby repressing translation or promoting mRNA degradation, ultimately influencing downstream signaling pathways and cellular functions (27). However, an increasing number of studies have revealed that certain miRNAs can also mediate biological effects through non-canonical pathways. For instance, miR-21, miR-29a, and members of the let-7 family have been shown to act as endogenous ligands for Toll-like receptors 7 and 8 (TLR7/8), triggering inflammatory or stress responses in recipient cells (28). These findings suggest that exosomal miRNA-mediated intercellular communication extends beyond the regulation of gene expression and may also involve immune recognition, apoptosis, and metabolic regulation, thus unveiling a broader and more complex spectrum of biological effects.
3 The dual role of extracellular vesicles in acute myocardial infarction
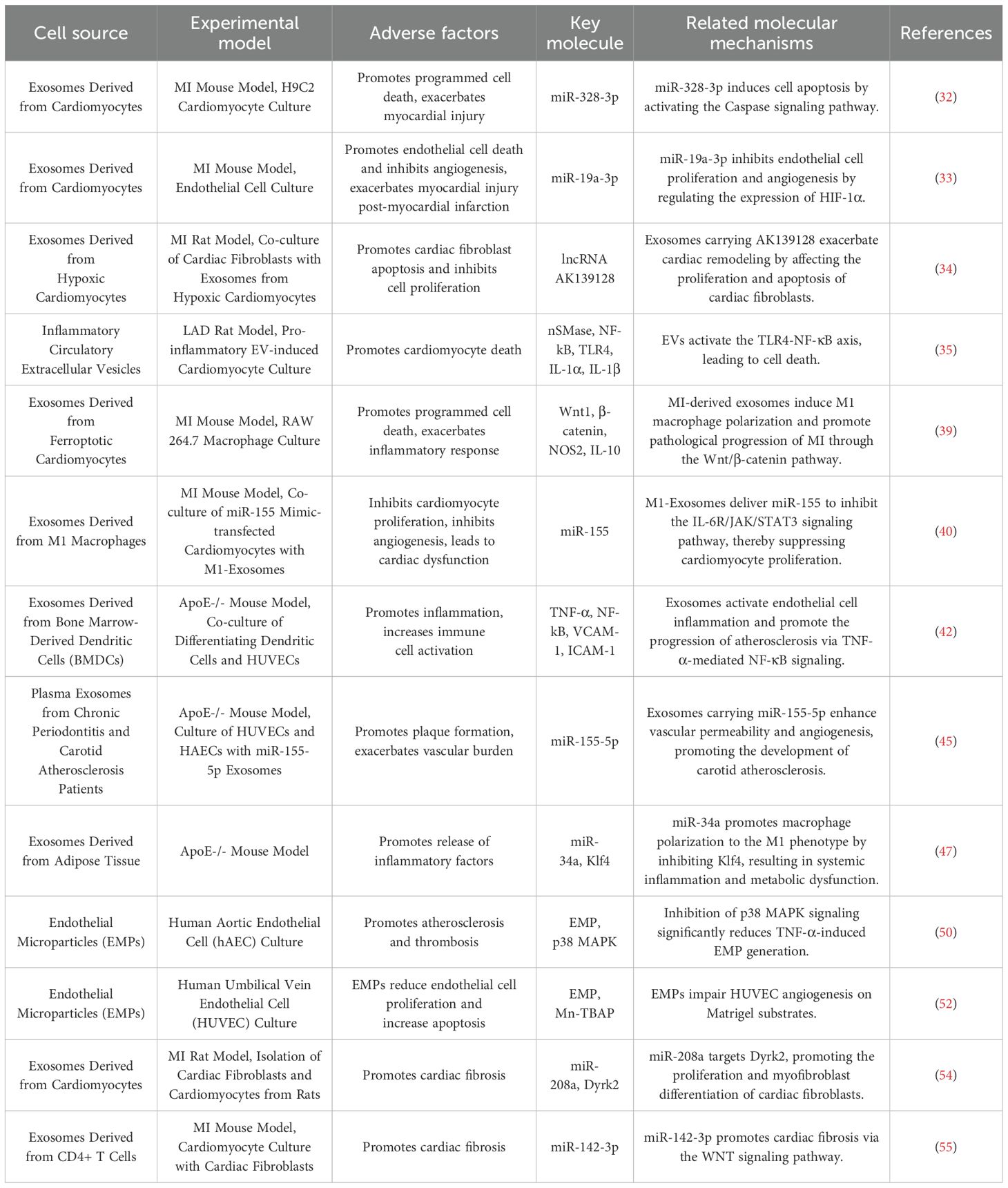
AMI is most commonly caused by intraluminal occlusion of the coronary artery due to atherosclerosis and the rupture and erosion of unstable plaques (29). When the blood supply is persistently reduced or completely interrupted, a large portion of the myocardium undergoes coagulative necrosis, accompanied by congestion, edema, and extensive infiltration of inflammatory cells in the myocardial interstitium (30). These pathological changes lead to a significant decline in myocardial contractility and a sudden reduction in cardiac output. Consequently, controlling excessive inflammatory responses, inhibiting myocardial apoptosis and necrosis, preventing ventricular fibrosis, and promoting vascular regeneration have emerged as potential therapeutic strategies to improve the prognosis of AMI patients. To gain a more comprehensive understanding of the negative effects of EVs in AMI, (Figures 2E–G) and Table 1 illustrate various detrimental impacts of EVs associated with myocardial injury, including their roles in promoting programmed cell death, exacerbating inflammatory responses, and enhancing cardiac fibrosis. In contrast, (Figures 2A–D) and Table 2 reveal the mechanisms through which EVs improve the prognosis of AMI. Exploring how to modulate the function of EVs to maximize their therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential negative effects is becoming an increasingly important focus of research.
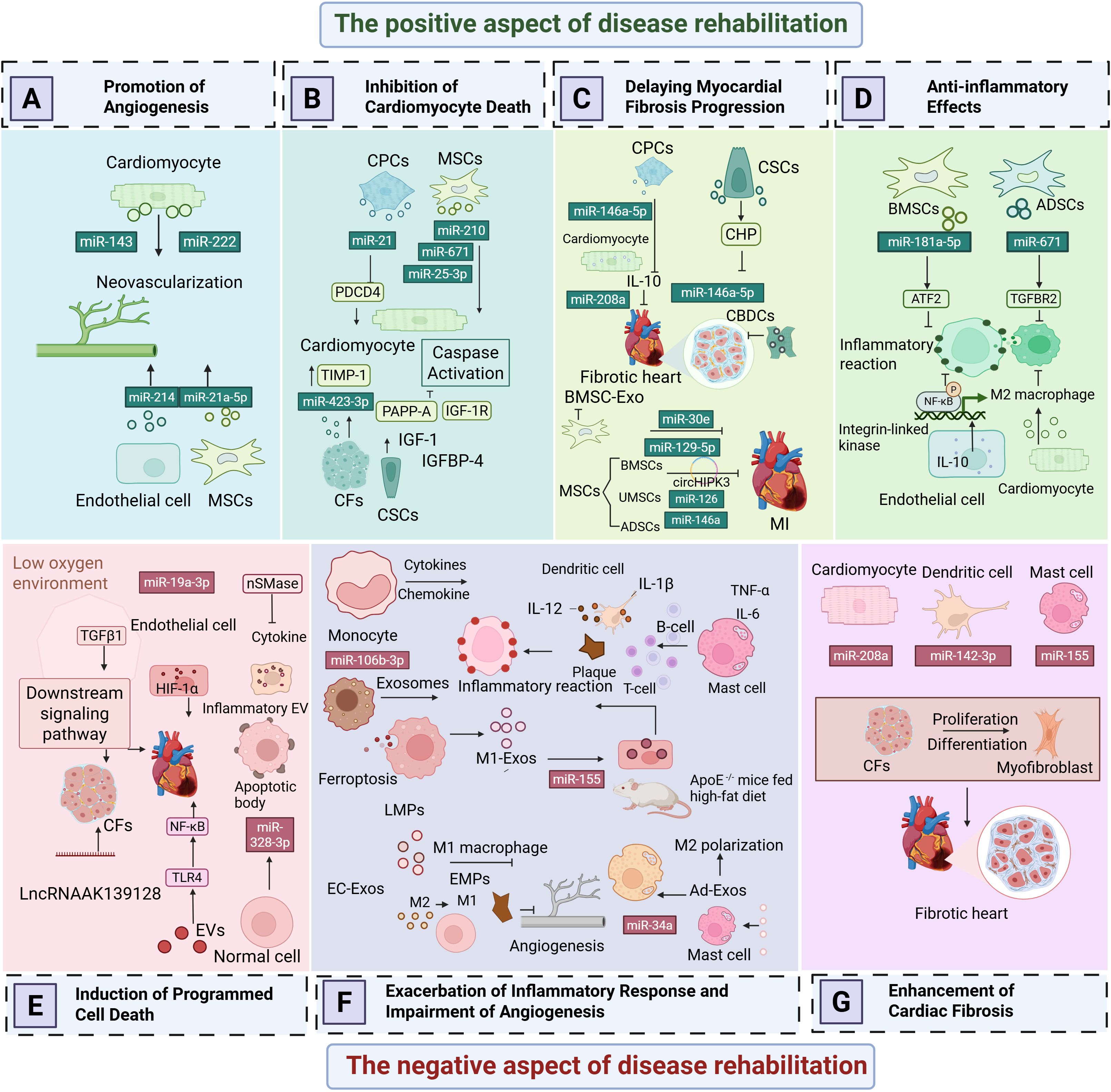
Figure 2. The dual role of extracellular vesicles in acute myocardial infarction. (A) Promotion of Angiogenesis. (B) Inhibition of Programmed Cardiomyocyte Death. (C) Delaying Myocardial Fibrosis Progression. (D) Anti-Inflammatory Effects. (E) Induction of Programmed Cell Death. (F) Exacerbation of Inflammatory Responses and Impairment of Angiogenesis. (G) Enhancement of Cardiac Fibrosis.
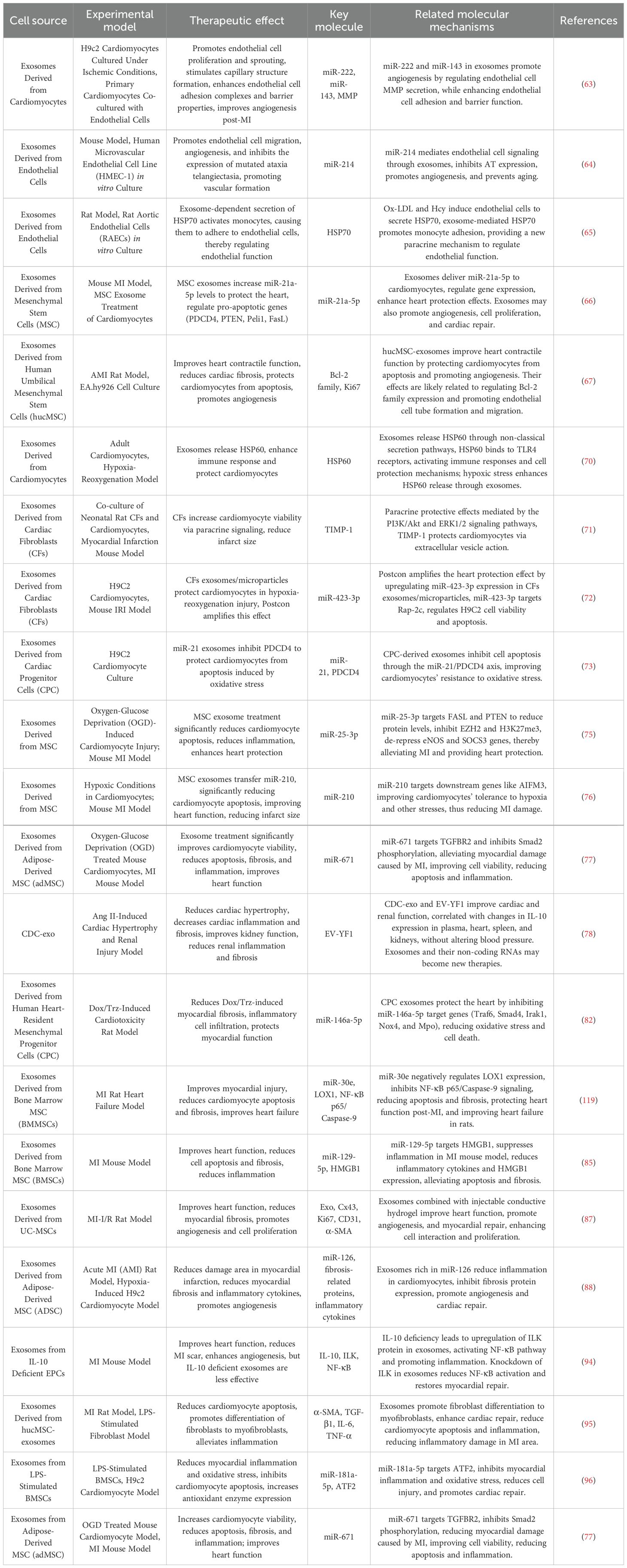
Table 2. An overview of the therapeutic implications of extracellular vesicles in myocardial infarction.
3.1 The negative aspect of disease rehabilitation
3.1.1 Induction of programmed cell death
Cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes contain a variety of non-coding RNAs, particularly miRNAs, which regulate apoptosis by targeting different apoptotic genes. As shown in Figure 2E, Following myocardial infarction, the secretion of certain paracrine factors in cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes increases, and when these exosomes are taken up by recipient cells, they may exacerbate myocardial injury. Caspases, a family of cysteine proteases, play a crucial role in programmed cell death and inflammation by selectively cleaving specific proteins, thereby inducing apoptosis (31). Research by Huang et al. (32) demonstrated that the levels of miR-328-3p in exosomes secreted by infarcted cardiomyocytes are significantly elevated. This miRNA activates intracellular caspase-related signaling pathways, promoting apoptosis. Infarcted cardiomyocytes can also directly transfer exosomes to adjacent cardiomyocytes, further inducing apoptosis and exacerbating MI. Similar studies have shown that miR-19a-3p is enriched in exosomes derived from infarcted cardiomyocytes. When taken up by endothelial cells, it inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and impairs cardiac function in post-MI mice by targeting the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) (33). Notably, hypoxia is a key factor contributing to cardiomyocyte apoptosis following MI. The hypoxic environment also activates transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) and its downstream signaling pathways, regulating the proliferation and apoptosis of cardiac fibroblasts (CFs). Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) also play an important role in exosomes. Hypoxic exposure upregulates the expression of lncRNA AK139128 in both cardiomyocytes and exosomes, which has been found to promote CF apoptosis and inhibit proliferation both in vitro and in vivo, thereby aggravating myocardial injury after MI (33, 34).
Additionally, circulating inflammatory EVs play a critical role in the acute and chronic phases of MI. One study found that inhibiting neutral sphingomyelinase (nSMase) significantly reduced inflammatory EVs and cytokines, improving left ventricular ejection fraction and enhancing cardiac function post-MI. Furthermore, EVs induce cardiomyocyte death by activating the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) -nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) axis, further contributing to myocardial damage (35).
3.1.2 Exacerbation of inflammatory responses and impairment of angiogenesis
After AMI, cardiomyocyte death triggers an inflammatory response, and excessive inflammation leads to extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and ventricular remodeling (36). From an inflammatory perspective, exosomes secreted by cardiomyocytes during AMI regulate various inflammatory cells. According to Figure 2F, AMI induces a transient increase in cardiac EVs, which, upon uptake by monocytes in the ischemic myocardium, modulate and enhance local inflammation (37, 38). Additionally, ferroptosis of cardiomyocytes during AMI reduces miR-106b-3p levels in secreted exosomes, activating the WNT signaling pathway, promoting M1 macrophage polarization, and exacerbating myocardial inflammation (39).
Macrophages play a critical role in the progression of inflammation. In the early phase of AMI, M1 macrophages are recruited to the infarcted myocardium, exhibiting strong phagocytic activity. Multiple factors regulate macrophage phenotype changes post-infarction (40). Liu et al. (41) found that M1-type macrophages release pro-inflammatory M1-derived exosomes (M1-Exos) after MI, which impair angiogenesis, accelerate myocardial damage, and are highly enriched in miR-155. miR-155 is transferred to endothelial cells, downregulating multiple target genes involved in inflammation, inhibiting angiogenesis, and leading to cardiac dysfunction. M1-Exos also suppresses related signaling pathways, reducing the angiogenic capacity of endothelial cells, exacerbating the myocardial injury and impeding recovery (40). Additionally, dendritic cell (DC)-derived exosomes recruit and activate immune cells post-MI, promoting the release of inflammatory factors. Advanced experiments have demonstrated that mature DCs contribute to endothelial inflammation via exosomes. DC-derived exosomes (DC-Exos) from bone marrow-derived DC culture medium stimulate human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and mature DC-Exos regulate the NF-κB pathway, increasing HUVEC inflammation (42). Mast cell-derived exosomes, containing pro-inflammatory factors, activate lymphocytes and may contribute to inflammation initiation and amplification. Mast cells can also promote atherosclerotic plaque rupture, leading to AMI (43, 44).
Moreover, endothelial cell-derived exosomes (EC-Exos), depending on their origin and miRNA composition, can have both protective and detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system. While they offer protective effects against vascular injury, they may also contribute to plaque formation, increasing vascular burden. Under oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) stimulation, HUVECs secrete miR-155-enriched exosomes, which promote the transition of monocytes/macrophages from the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype to the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, exacerbating atherosclerotic plaque formation (45).
Adipose-derived exosomes (Ad-Exos) are taken up by macrophages in adipose tissue. Triglycerides within Ad-Exos are hydrolyzed into fatty acids by macrophages and released to maintain systemic metabolic homeostasis. However, under conditions of excessive fat accumulation, this balance is disrupted, leading to macrophage activation, increased inflammatory cytokine release, and systemic insulin resistance. Studies have shown that exosomes isolated from visceral adipose tissue of high-fat diet-fed ApoE-/- mice downregulate ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABCA1 and ABCG1), impairing cholesterol efflux and significantly promoting M1 macrophage foam cell formation and pro-inflammatory factor (TNF-α and IL-6) expression, thereby exacerbating atherosclerosis (46). Another study identified miR-34a as a key regulatory miRNA in Ad-Exos, which transmits nutritional overload signals to resident adipose macrophages. By inhibiting the expression of the transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf4), miR-34a promotes macrophage polarization towards the inflammatory M1 phenotype, aggravating obesity-induced systemic inflammation and metabolic disorders (46, 47).
Beyond exosomes, microparticles also have pro-inflammatory effects and contribute to endothelial dysfunction, promoting atherosclerosis and thrombosis, which are closely associated with AMI progression (48). Endothelial microparticles (EMPs) express adhesion molecules on their surface, facilitating leukocyte aggregation and enhancing their transmigration across endothelial junctions. EMPs activate NF-κB, upregulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM-1) expression, a process that can be inhibited by NF-κB antagonists, suggesting a role in ICAM-1 upregulation via the NF-κB pathway (49). Microparticle release is linked to IL-6 production, with EMPs promoting inflammatory cytokine release in a positive feedback loop. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) pathway is critical in producing pro-inflammatory EMPs (50). Furthermore, EMPs inhibit nitric oxide production, impair endothelial relaxation, and increase oxidative stress in a dose-dependent manner (51). Mezentsev et al. (52) found that prolonged exposure to and higher concentrations of EMPs reduce endothelial cell proliferation, increase apoptosis, and impair repair capacity, ultimately leading to endothelial dysfunction. Additionally, leukocyte-derived microparticles (LMPs) participate in all stages of atherosclerosis, promoting inflammation and thrombosis, further contributing to AMI progression.
3.1.3 Enhancement of cardiac fibrosis
Cardiac fibrosis, primarily mediated by activated CFs, contributes to adverse cardiac remodeling and results from various forms of cardiac injury (53). As illustrated in Figure 2G, Cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes can influence cardiac fibrosis. Hypoxic cardiomyocytes secrete exosomes enriched with miR-208a into fibrotic cardiac tissue, where CF proliferation and differentiation are promoted into myofibroblasts, exacerbating cardiac fibrosis and further impairing cardiac function (54).
Dendritic cells, as key antigen-presenting cells, also play a role in fibrosis. Cai et al. discovered that CD4+ T cells release exosomes enriched with miR-142-3p, which aggravates cardiac fibrosis and leads to post-MI cardiac dysfunction (55). miR-142-3p directly targets and inhibits the WNT signaling pathway regulator APC, thereby activating the WNT pathway and stimulating CF activation. During cardiac injury, activated macrophages regulate fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts through miR-155-enriched exosomes, further driving fibrosis progression (56).
Fibroblast-derived exosomes are also implicated in cardiac fibrosis. These exosomes carry bioactive molecules, including miRNAs and proteins, that influence cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and immune cells, thereby accelerating fibrosis. They promote fibrosis by regulating CF proliferation, migration, and ECM protein synthesis and deposition (57). Additionally, fibroblast-derived exosomes may interact with cardiomyocytes, modulating their function, promoting apoptosis, or triggering cellular transformation, thereby worsening myocardial fibrosis (54). Endothelial cell-derived exosomes transmit signals related to vascular function, inflammation, or injury repair, influencing CF migration and proliferation (58). Macrophage-derived exosomes regulate local inflammation and tissue repair, further enhancing CF proliferation, migration, and secretion profile changes, thereby stimulating the secretion of fibroblast-derived exosomes (53).
3.2 The positive aspect of disease rehabilitation
In addition to the aforementioned detrimental effects, EVs have been shown to alleviate cardiac dysfunction effectively. Exosomes can be secreted by various cell types, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, cardiac fibroblasts, cardiac progenitor cells, and mesenchymal stem cells (59–61). These exosomes play a crucial role in cardioprotection by promoting angiogenesis, inhibiting myocardial fibrosis, reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis, suppressing inflammatory responses, and improving cardiac function. Furthermore, the miRNAs and proteins contained within exosomes regulate biological signaling pathways, thereby influencing various physiological and pathological processes in the body. Exosomes from different cellular sources have a wide range of biological functions, which offer great promise for their application in the prevention and treatment of AMI (62).
3.2.1 Promotion of angiogenesis
Cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells maintain close communication, as detailed in Figure 2A. Ribeiro-Rodrigues et al. (63) were the first to report that ischemic cardiomyocytes secrete exosomes that influence endothelial cell function and promote angiogenesis. One study confirmed that ischemic cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes protect the myocardium from oxidative damage while stimulating endothelial cell proliferation and sprouting, facilitating new blood vessel formation. Further analysis of miR-143 and miR-222 in exosomes revealed that exosomes from ischemic cardiomyocytes promote angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo, underscoring the significant role of intercellular signaling in vascular regulation. Van Balkom et al. (64) demonstrated that miR-214 plays a central role in endothelial cell-derived exosome-mediated signaling. Endothelial cells release miR-214-enriched exosomes, which suppress capillary dilation in target cells, regulate cell migration, and enhance angiogenesis. Zhan et al. (65) further confirmed that ox-LDL and homocysteine induce endothelial cells to release exosomes enriched with heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). These endothelial cell-derived exosomes activate monocyte-endothelial adhesion and upregulate HSP70 expression, providing a novel paracrine mechanism for maintaining vascular endothelial integrity and promoting neovascularization.
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSCs-Exos) play a crucial role in cardioprotection and angiogenesis. Luther et al. (66) identified miR-21a-5p as a cardioprotective miRNA transferred via exosomes from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) to cardiomyocytes, promoting angiogenesis. Zhao et al. (67) injected human umbilical cord-derived MSC exosomes (hUC-MSC-Exos) into AMI model rats via the tail vein and observed significant improvement in cardiac contractile function, inhibition of myocardial fibrosis, and enhanced cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Similarly, Ma et al. (68) used adenovirus-transfected hUC-MSCs to isolate and inject exosomes into an AMI model, confirming their ability to promote endothelial cell proliferation and significantly improve cardiac function. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes (ADSC-Exos) also contribute to angiogenesis by modulating miR-155 expression, improving endothelial cell function, promoting blood vessel formation, and protecting ischemic myocardium from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Additionally, platelet-derived microparticles (PMPs), released by activated platelets and enriched with coagulation-related proteins, promote coagulation, hemostasis, and thrombosis (24, 69). These microparticles interact with endothelial cells to facilitate vascular regeneration and repair, potentially playing a vital role in AMI vascular recovery, particularly restoring damaged vascular function and improving myocardial perfusion.
3.2.2 Inhibition of programmed cardiomyocyte death
Under ischemic and hypoxic stress conditions, cardiomyocytes actively secrete exosomes enriched with specific bioactive cargos, including miRNAs, lncRNAs, and stress-responsive proteins. These exosomes not only mediate intercellular transmission of stress signals but also exert cardioprotective effects by regulating apoptosis-related pathways and mitigating myocardial injury. Notably, certain proteins carried by exosomes, such as heat shock proteins and tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 10 (TNFSF10), play critical roles in modulating apoptosis and immune responses, and have increasingly been identified as promising targets in cardioprotection research (60). Gupta et al. (70) were the first to isolate exosomes containing heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) from adult rat cardiomyocytes. They found that under hypoxic conditions, HSP60 binds to the cardiomyocyte outer membrane, forming a protective barrier that sequesters excessive HSP60, thereby reducing cytotoxicity and inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Recently, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1)have emerged as a key regulator in cardiovascular disease research. Studies have explored the protective role of TIMP-1 in cardiac fibroblast-derived exosomes during MI. Abria et al. (71) injected cardiac fibroblast-derived exosomes into a rat MI model and observed a significant reduction in infarct size and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. This protective effect is thought to be mediated by TIMP-1, which exerts paracrine functions to inhibit fibrosis and mitigate myocardial injury. Luo et al. (72) conducted co-culture experiments and found that cardiac fibroblast proliferation significantly increased under hypoxia-reoxygenation conditions, effectively protecting cardiomyocytes from damage. Their study indicated that cardiac fibroblast-derived exosomes play a cardioprotective role during ischemia-reperfusion injury via the miR-423-3p/RAP2C signaling pathway, inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
As shown in Figure 2B, excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the ischemic region of AMI are a major cause of cardiomyocyte apoptosis and death. Xiao et al. (73) demonstrated that oxidative stress enhances the production of miR-21 in exosomes derived from cardiac progenitor cells. miR-21 inhibits PDCD4 expression, protecting cardiomyocytes from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis, thus providing a new molecular mechanism for cardioprotection. Additionally, Barile et al. (74) discovered that exosomes from cardiac stem cells contain pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A), which hydrolyzes IGFBP-4 to release insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). This activates IGF-1R signaling, leading to phosphorylation of intracellular Akt and ERK1/2, inhibition of caspase activation, and reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Their findings suggest that the cardioprotective effects of cardiac stem cell-derived exosomes are associated with PAPP-A-mediated IGF-1 release.
Peng et al. (75) found that in an AMI mouse model, mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes overexpressing miR-25-3p downregulate Fas Ligand (FASL) and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) expression, thereby suppressing cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Other studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce infarct size and improve post-AMI cardiac function (76). The underlying mechanism may involve miR-210, which targets AIFM3, pAKT, and p-p53, regulating apoptosis and enhancing hypoxic cardiomyocyte survival. Furthermore, in vivo studies on adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes revealed that they improve cardiomyocyte viability, reduce apoptosis, and attenuate both myocardial fibrosis and inflammation. This effect is believed to be mediated by exosomal miR-671, which targets TGFBR2, reducing Smad2 phosphorylation and thereby exerting anti-fibrotic and anti-apoptotic effects (77).
3.2.3 Delaying myocardial fibrosis progression
Elevated levels of angiotensin II induce heart failure and exacerbate the progression of cardiovascular diseases. Exosomes derived from cardiomyocytes can inhibit myocardial fibrosis by regulating the expression of inflammation-related factors, as detailed in Figure 2C. Cambier et al. (78) investigated the mechanistic role of cardiomyocyte-derived EVs using a long-term angiotensin II (Ang II) infusion-induced cardiac hypertrophy model established in C57BL/6J mice. Their study revealed that these exosomes modulate the expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10), thereby alleviating myocardial hypertrophy, reducing cardiac inflammation, and mitigating fibrosis. Additionally, miR-208a, found in cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes, is upregulated in MI models and redox enzyme-induced cardiomyopathy in rats, demonstrating its ability to inhibit myocardial fibrosis and improve cardiac function.
Beyond cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes, cardiac stem cells and progenitor cells (CPCs) play significant cardioprotective roles in AMI through multiple pathways. Cardiac homing peptides (CHPs) are a class of small peptides capable of specifically recognizing and binding to injured myocardial tissue, typically identified through in vivo phage display techniques. By targeting endothelial or stromal molecules associated with myocardial injury, CHPs enable the precise delivery of therapeutic agents to diseased cardiac regions. They have been widely employed to enhance the cardiac accumulation of exosomes, drugs, or nanocarriers, thereby improving therapeutic efficacy while minimizing off-target effects (79). Studies have shown that exosomes released by cardiac stem cells can bind to CHP, enhancing their targeted therapeutic effects and reducing post-infarction fibrosis and smaller infarct scars (80). CPC-derived exosomes are highly enriched with miR-146a-5p, which inhibits the deposition of collagen type I in the interstitial matrix, preventing anthracycline/trastuzumab-induced myocardial fibrosis and playing a crucial role in myocardial repair and regeneration (81, 82). He et al. (83) found that CPC-derived exosomes promote regulatory T cell (Treg) differentiation in MI mice, reducing myocardial damage, potentially through enhanced mTOR activity. Moreover, cardiosphere-derived cell (CDC)-secreted exosomes (CDCex) are also rich in miR-146a-5p and have been shown to reduce myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and transcription factors (84).
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), commonly derived from bone marrow, also exhibit anti-fibrotic effects through exosome secretion. Studies have demonstrated that exosomes derived from bone marrow MSCs (BMSC-Exo) overexpressing miR-30e can ameliorate myocardial infarction in rats by inhibiting LOX-1 expression and downregulating NF-κB p65/Caspase-9 signaling, thereby reducing myocardial pathological damage and fibrosis (85). Similarly, BMSC-Exo overexpressing miR-129-5p exerts cardioprotective and anti-fibrotic effects in MI models. Furthermore, BMSC-Exo stimulated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) reduces inflammatory factor expression, improves myocardial contractility, and decreases fibrosis in MI mice. Hypoxia-treated BMSC-Exo, with increased miR-210 expression, has been found to attenuate fibrosis (86). Exosomes from umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UMSC-Exo) delivering circHIPK3 have been shown to reduce infarct zone fibrosis in MI mice (87). Adipose-derived MSCs (ADSCs) overexpressing miR-126 decrease fibrosis-related protein expression in H9c2 cells, alleviating cardiac fibrosis in MI rats (88).
Exosomes derived from ADSCs-Exo have demonstrated superior cardioprotective and anti-fibrotic effects compared to exosomes from unspecified or other stem cell sources in multiple studies. At the molecular level, ADSCs-Exo exert their beneficial effects primarily by overexpressing miR-146a, which downregulates EGR1 expression and suppresses the activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway (89). This results in a marked reduction in post-infarction inflammation and cardiac fibrosis, thereby achieving better therapeutic outcomes than unmodified exosomes. At the pathological level, ADSCs-Exo significantly reduce the mRNA levels of multiple fibrosis-related markers, such as COL1A1 and α-SMA, in models of cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin and trastuzumab, indicating a more potent anti-fibrotic capacity (90, 91). In terms of immunomodulation, ADSCs-Exo promote macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype via activation of the S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling pathway, thereby contributing to myocardial microenvironmental remodeling, attenuating inflammation, and enhancing their anti-fibrotic and cardioprotective functions (91). Additionally, ADSCs-Exo have been shown to upregulate SIRT1 expression, leading to a reduction in infarct size and atrial fibrosis in AMI models, highlighting their greater potential in promoting tissue repair and functional recovery (92).
3.2.4 Anti-inflammatory effects
In the field of inflammation research, exosomes derived from HUVECs and human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) have been shown to modulate inflammatory responses and induce monocyte activation and migration (93). As shown in Figure 2D, recent studies have revealed that exosomes secreted by endothelial cells from IL-10 knockout mice lack pro-angiogenic and cardiac repair properties. These exosomes exhibit upregulated expression of integrin-linked kinase (ILK), which activates NF-κB-mediated inflammatory genes in recipient cells. Suppression of ILK expression can rescue the loss of repair activity caused by inflammation (94). In the later stages of MI, M2 macrophages play an anti-inflammatory and reparative role in myocardial tissue. Exosomes from hypoxic cardiomyocytes have been shown to polarize macrophages towards the M2 phenotype, thereby alleviating cardiomyocyte injury, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear and warrant further investigation. Research by Shi et al. (95) demonstrated that exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSCs) can suppress post-MI inflammatory responses and protect cardiomyocytes. Injection of these exosomes into an animal model of AMI resulted in increased myofibroblast density in the infarct zone, further alleviating inflammation. Additionally, studies have shown that exosomes derived from BM-MSCs overexpressing miRNA-181a-5p attenuate inflammation and oxidative stress by downregulating ATF2 expression (77, 96). Exosomes derived from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance cardiomyocyte viability, reduce apoptosis, and mitigate myocardial fibrosis and inflammation both in vitro and in vivo. These effects are potentially mediated by targeting TGFBR2 by exosome-carried miR-671, which reduces Smad2 phosphorylation (77).
4 Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles as multifunctional carriers in acute myocardial infarction
EVs have emerged as a promising therapeutic vehicle for AMI, attracting considerable research attention and yielding promising results. EVs have been validated as significant biomarkers for diagnosing and treating AMI. As illustrated in Figure 3, EVs have the capacity to transport a diverse array of nucleic acids and proteins into recipient cells, thereby influencing the phenotype and functionality of these cells. This unique characteristic positions EVs as a potentially advantageous drug delivery platform. However, the challenge of achieving precise targeting of EVs to specific recipient cells in vivo remains a critical issue that requires further investigation and innovation.
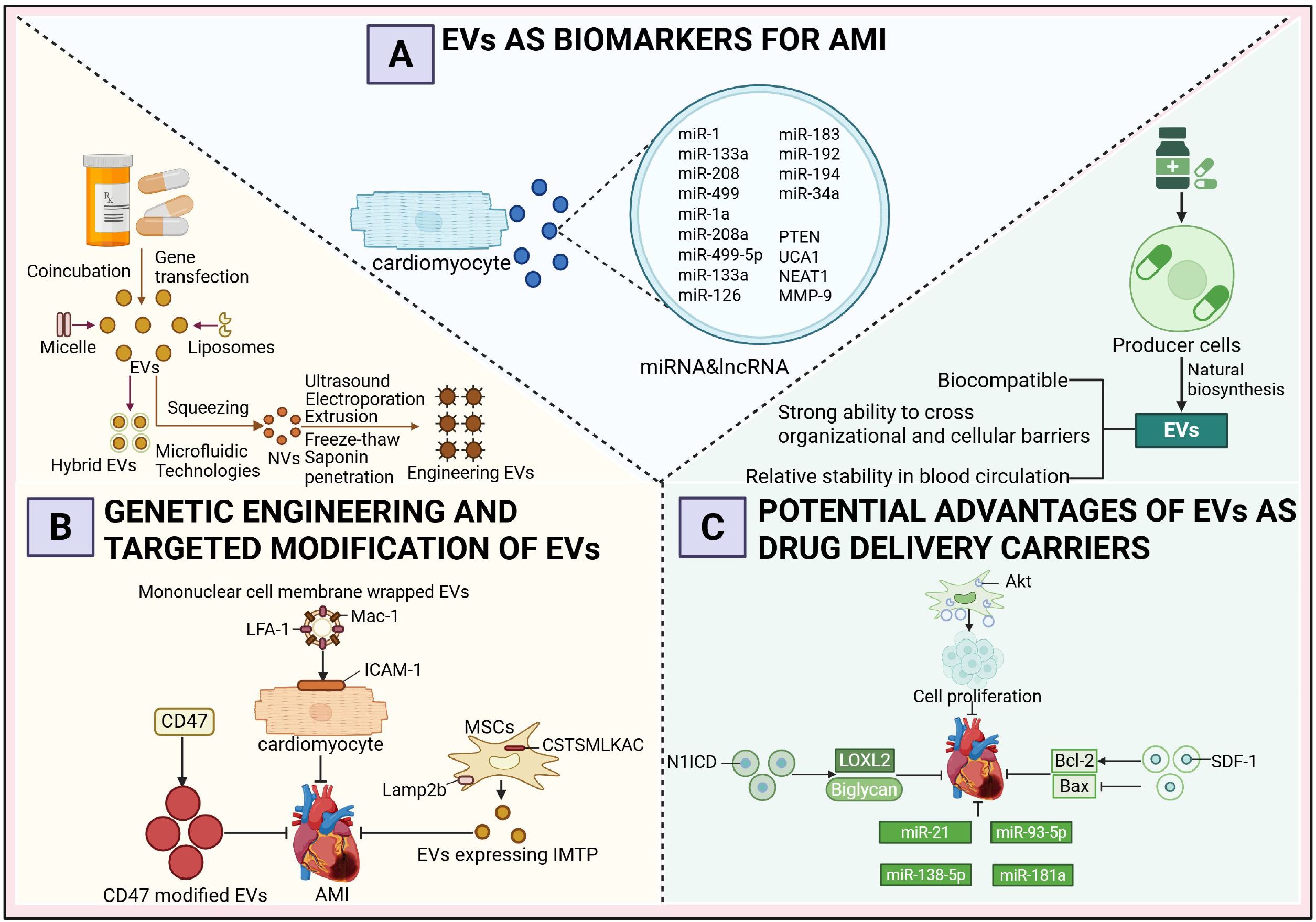
Figure 3. Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles as multifunctional carriers in acute myocardial infarction. (A) Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers of Acute Myocardial Infarction. (B) Genetic Engineering and Targeted Modification of Extracellular Vesicles. (C) The Prospective Advantages of Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Vehicles.
4.1 Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction
Extensive research has demonstrated that AMI patients treated within 12 hours exhibit a 50% reduction in mortality compared to those with delayed intervention, emphasizing the critical importance of early and accurate diagnosis to facilitate timely treatment, minimize myocardial damage, and prevent complications such as heart failure or sudden cardiac death (97, 98). Although cardiac troponin (cTn) is regarded as the gold standard for AMI diagnosis, its elevation in acute non-ACS conditions and chronic diseases highlights the need for more specific and sensitive biomarkers for early AMI detection (99, 100). In recent years, miRNAs and lncRNAs encapsulated within exosomes have emerged as promising biomarkers for the early diagnosis of AMI. Several miRNAs are presumed to originate predominantly from cardiomyocytes, a hypothesis primarily supported by data obtained from animal models. In AMI animal models, particularly in mice subjected to coronary artery ligation, researchers have employed cardiomyocyte-specific promoter-driven reporter systems or exosome-tracking techniques to successfully trace the myocardial origin of specific miRNAs (101). For instance, miR-1a, miR-208a, and miR-499-5p are markedly elevated in the circulation of mice following AMI and are known to be highly enriched in myocardial tissue under physiological conditions (102). Moreover, these miRNAs are rapidly released into the plasma within 2 to 4 hours after myocardial injury, with expression dynamics closely mirroring the progression of myocardial damage, further substantiating their cardiomyocyte-derived origin. Notably, miR-133a is predominantly detected in the non-exosomal fraction of plasma, suggesting a vesicle-independent release mechanism (103). In clinical studies, circulating exosomes from AMI patients have been found to contain elevated levels of miR-126, miR-183, and the PTEN gene, while lncRNAs such as UCA1, NEAT1, and MMP-9 are also significantly upregulated. In contrast, miR-21 and miR-204 exhibit downregulated expression patterns. Among these, the expression levels of miR-126 and miR-183 show a positive correlation with the severity of myocardial ischemia, indicating their potential utility in disease assessment. Therefore, exosomal miRNAs and lncRNAs not only hold promise for the early detection of AMI but may also serve as indicators of the extent of myocardial injury. Furthermore, recent findings suggest that in patients who progress to heart failure within one year following AMI, serum levels of miR-192 are significantly elevated, accompanied by a coordinated upregulation of miR-194 and miR-34a within serum exosomes (104). These three miRNAs may serve as potential biomarkers for predicting long-term heart failure risk after AMI.
4.2 Genetic engineering and targeted modification of extracellular vesicles
In addition to their role as biomarkers, EVs have been extensively explored for therapeutic applications in AMI through genetic engineering and targeted modification techniques. A growing body of research demonstrates that engineered EVs exhibit enhanced drug-loading efficiency, targeting precision, and tissue retention. Specifically, donor cells are often engineered via co-incubation or gene transfection to incorporate therapeutic agents, while techniques such as extrusion and microfluidics enable the fabrication of EV-like nanovesicles (NVs). Common methods for engineering EVs include ultrasonication, electroporation, freeze-thaw cycles, extrusion, and saponin permeabilization, all of which facilitate the encapsulation of therapeutic cargo into EVs. Furthermore, the anchoring of targeting ligands, peptides, or aptamers onto the EV membrane enhances their homing capabilities, while the fusion of EVs with lipid-based nanoparticles such as liposomes or micelles results in hybrid EVs with tailored properties (105).
In the context of AMI treatment, one study employed a fusion-extrusion technique to coat EVs with monocyte membranes. Following intravenous injection, these membrane-coated EVs exhibited increased interaction with ischemic cardiomyocytes, driven by the upregulation of ICAM-1 on the cardiomyocyte membrane and the enrichment of Mac-1 and LFA-1 on the EV surface. This interaction promoted EV homing to hypoxic myocardium, thereby improving therapeutic efficacy (106). Another study overexpressed IMTP and Lamp2b in mesenchymal stem cells, resulting in the display of IMTP on the membrane of secreted EVs. Intravenous administration of these IMTP-modified EVs in a murine myocardial infarction model led to enhanced accumulation in the infarcted region, prolonged cardiac retention, and superior therapeutic outcomes compared to unmodified EVs (107). Additionally, CD47-modified EVs, which bind to signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) to inhibit monocyte-macrophage phagocytosis, demonstrated extended cardiac retention and improved functional recovery in treated mice (108). While most studies focus on genetic engineering to modify EV surfaces, using techniques such as lentiviral transfection raises concerns regarding operational complexity, potential alterations in EV bioactivity, and safety issues such as tumorigenicity (109, 110). To address these limitations, alternative physical or chemical methods have been developed to achieve more precise surface modifications. For instance, chemical conjugation of tissue-specific antibodies or homing peptides onto the EV membrane in vitro has been shown to significantly enhance targeting efficiency, offering a safer and more controllable approach to EV engineering. These advancements underscore the transformative potential of engineered EVs in AMI therapy while addressing critical challenges in their development and application (110).
4.3 The prospective advantages of extracellular vesicles as drug delivery vehicles
EVs have emerged as promising nanocarriers for treating AMI due to their ability to transport a diverse array of therapeutic molecules, including proteins and miRNAs, which collectively enhance myocardial repair, promote angiogenesis, reduce apoptosis, and inhibit fibrosis. The intrinsic properties of EVs, such as excellent biocompatibility, robust tissue and cellular barrier penetration, and relative stability in the systemic circulation, have driven extensive research into their potential as drug delivery vehicles. Currently, two primary strategies are employed for drug loading into EVs: (1) integrating therapeutic agents into producer cells, utilizing their natural biogenesis pathways to yield drug-loaded EVs, and (2) isolating EVs from various sources (e.g., cultured cells, human blood, or milk) and subsequently incorporating therapeutic molecules using biotechnological methods (111, 112).
Studies have demonstrated the therapeutic efficacy of engineered EVs in AMI models. For instance, Xuan et al. (113) engineered MSCs to overexpress N1ICD, generating N1ICD-enriched EVs that, when injected into the peri-infarct zone of AMI mice, significantly reduced infarct size and fibrosis while improving cardiac function. This effect was attributed to N1ICD-mediated upregulation of LOXL2 and Biglycan, which promoted angiogenesis and attenuated cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Similarly, Ma et al. (68) enhanced the therapeutic potential of MSC-derived EVs by overexpressing Akt, increasing the enrichment of platelet-derived growth factor D (PDGF-D). These EVs facilitated endothelial cell proliferation and migration, angiogenesis in the peri-infarct region, and cardiomyocyte survival, ultimately improving myocardial regeneration and cardiac function. Another study reported that EVs derived from SDF-1-overexpressing MSCs outperformed unmodified EVs in treating myocardial infarction, as they upregulated Bcl-2, downregulated Bax, and inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis while promoting microvascular regeneration in the peri-infarct zone (114). The therapeutic utility of EVs has been further expanded by incorporating nucleic acids. Mao et al. (115) loaded MSC-derived EVs with KLF3-AS1, which sequestered miR-138-5p to alleviate its suppression of Sirt1, thereby reducing hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and enhancing therapeutic outcomes compared to unmodified EVs. Liu et al. (116) engineered adipose-derived MSC EVs to overexpress miR-93-5p, inhibiting Atg7 and TLR4 expression, and attenuating hypoxia-induced autophagy and inflammation. EVs loaded with miR-93-5p demonstrated superior therapeutic effects compared to unmodified EVs. Wei et al. (117) utilized MSC-derived EVs carrying miR-181a to treat AMI mice, resulting in reduced infarct size, improved cardiac function, and decreased inflammatory cell infiltration. Additionally, Song et al. (118) identified miR-21 as a critical cargo in MSC-derived EVs, which targeted the PDCD4/AP-1 pathway to inhibit apoptosis and activated the PTEN/Akt signaling pathway to stimulate VEGF expression, thereby promoting post-AMI functional recovery.
5 Discussion
5.1 Dual roles and research highlights of EVs in AMI
(1) EVs exhibit a dualistic role in AMI, capable of exacerbating disease progression by promoting apoptosis, amplifying inflammation, and reducing angiogenesis, while also potentially alleviating cardiac injury. Exosomes derived from various cell types have demonstrated cardioprotective effects, including promoting angiogenesis, inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis, repairing damaged myocardium, and suppressing fibrosis. Furthermore, intercellular communication mediated by EVs provides the molecular foundation for their diagnostic and therapeutic roles in cardiovascular diseases, as well as their cardioprotective effects. (2) Targeted modulation of the ratio of M1 to M2 macrophages in cardiac tissue through small exosomes may serve as a potential strategy for treating myocardial infarction. M1 macrophages, classically activated, and M2 macrophages, alternatively activated, exhibit pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory phenotypes, respectively, with their balance being critical for tissue inflammation, injury, and repair. Tissue cells and macrophages interact via EVs, with damaged tissue cells releasing exosomes that promote macrophage activation and polarization. Polarized macrophages, in turn, release exosomes and other factors that exacerbate cellular stress, tissue inflammation, and injury. (3) The role of EVs varies significantly across different phases of myocardial infarction, with the acute phase primarily characterized by repair and inflammation, while the chronic phase is more associated with fibrosis and tissue remodeling. Following AMI, cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and macrophages rapidly release EVs that carry bioactive molecules involved in inflammation, apoptosis, and repair. In the acute phase, EVs often carry pro-inflammatory factors such as miR-155 and miR-142-3p, which activate immune responses to promote inflammation and local repair, but they may also mediate cardiomyocyte apoptosis or exacerbate cardiac dysfunction. After the acute phase, the function of EVs shifts more towards cardiac remodeling and fibrosis, driving fibrosis by promoting fibroblast-related activities. In the chronic phase, EVs may carry immunomodulatory molecules such as miR-210 and miR-122 to regulate long-term immune responses. However, during chronic myocardial infarction, EVs may also further deteriorate cardiac structure and function due to persistent inflammation and fibrosis. (4) From a therapeutic perspective, the efficacy of stem cell therapy in cardiovascular diseases has been well-established, and exosome-based cell-free therapies are emerging as a new focus for treating conditions such as myocardial infarction and heart failure. With low toxicity, low immunogenicity and excellent biocompatibility, exosomes are a promising natural drug delivery carrier and are expected to become a new generation of nanoscale drug carriers.
5.2 Limitations and Prospects of EVs Involvement in the Progression of AMI
Despite the broad therapeutic prospects of EVs, several limitations are faced in current preclinical research: (1) The processes of exosome extraction and purification are complex, and targeted delivery of biologically active factors remains unresolved. Current isolation methods, such as ultracentrifugation, immunocapture, and density gradient centrifugation, exhibit limitations in efficiency, cost, and scalability. (2) There is no standardized method for drug loading into EVs. Although studies have successfully loaded small molecules such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs into EVs, current techniques, including electroporation, sonication, and incubation, require improved loading efficiency, stability, and targeting precision. (3) To date, no clinical trials are underway to investigate the use of exosomes for treating MI patients. Research on the long-term safety of EVs remains limited, particularly regarding their immunomodulatory effects across different disease states, which are not yet fully understood.To address these challenges, the roles of EVs in AMI should be further explored through the following strategies: (1) Development of EV isolation and purification technologies that comply with good manufacturing practice standards to ensure consistency and controllability in clinical applications. Establishment of quality control systems, including assessments of purity, composition, and bioactivity, to enhance safety and therapeutic predictability. (2) Investigation of the in vivo distribution and persistence of EVs to optimize dosing strategies. Exploration of mild yet efficient drug-loading techniques, such as bioengineering EV membrane proteins to enhance interactions with target cells, combined with nanotechnology, such as modifying specific ligands or antibodies to improve targeted delivery capabilities. (3) In-depth evaluation of the metabolic pathways, potential immune side effects, and long-term safety of different EVs in vivo. Simultaneously, large-scale animal experiments and clinical trials should be conducted across diverse disease models to validate their efficacy and identify optimal treatment windows.
6 Conclusion
EVs have emerged as pivotal tools for delivering essential biological molecules, demonstrating significant potential in the context of AMI. This review systematically summarizes the mechanisms through which EVs influence AMI, with a particular focus on their dual roles in both disease progression and therapeutic intervention. While EVs can exacerbate pathological processes such as programmed cell death and inflammation, they also hold considerable therapeutic potential by promoting angiogenesis and inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis. By comprehensively examining the biogenesis, release, and uptake mechanisms of EVs, as well as their applications in AMI, this review provides a solid foundation for utilizing EVs as biomarkers, drug delivery vehicles, and therapeutic targets. These insights are poised to advance the clinical translation of EVs in the diagnosis and treatment of myocardial infarction and other cardiovascular diseases, thus contributing to the development of precision medicine.
Author contributions
HW: Visualization, Writing – original draft. JX: Writing – original draft, Visualization. QL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Validation. ZW: Writing – review & editing, Visualization. LL: Writing – review & editing, Visualization. SS: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. PL: Visualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Validation. MC: Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Validation, Formal Analysis, Supervision. ML: Writing – review & editing, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82074378), the Project of Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2022YFS0618), the Project of Office of Science & Technology and talent work of Luzhou (No. 2023JYJ029, No. 2022JYJ104), 2024 Traditional Chinese Medicine Guangdong Provincial Laboratory Project (No. HQCML-C-2024005), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (No. JCYJ20230807094603007, No. JCYJ20240813152440051), Shenzhen Medical Research Fund (No. A2403028) and the Project of Southwest Medical University (No. 2023ZYYQ04, No. 2024ZKZ007, No. 202410632043). The funder had no role in the study design, data analysis, or decision to publish.
Acknowledgments
All authors would like to express their special thanks to MengNan Liu for his rigorous guidance, which serves as a lesson for all of us to steadily advance on our academic paths.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviation
EVs, extracellular vesicles; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; mRNA, messenger RNA; miRNA, microRNA; MVBs, multivesicular bodies; mTOR, mechanistic Target of Rapamycin; ESCRT, endosomal sorting complex required for transport; SNARE, soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor; ARF, ADP-ribosylation factor; ALIX, ALG-2-interacting protein XEGF, epidermal growth factor; MVs, microvesicles; CFs, cardiac fibroblasts; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor β1; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ox-LDL, oxidized low-density lipoprotein; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; M2 macrophages, anti-inflammatory macrophages; MSCs-Exos, mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes; BM-MSCs, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; HSP60, heat shock protein 60; ROS, reactive oxygen species; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; ICAM-1, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 Akt, protein kinase B; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2; FASL, Fas Ligand; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; IL-10, interleukin-10; CPCs, cardiac progenitor cells; BMSC-Exo, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes; LOX-1, lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; cTn, cardiac troponin; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
References
1. Zhu X, Wang Y, and Cheng J. Analysis of risk factors for complications after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Altern therapies Health Med. (2024) 30:152–5.
2. Melling GE, Carollo E, Conlon R, Simpson JC, and Carter DRF. The challenges and possibilities of extracellular vesicles as therapeutic vehicles. Eur J pharmaceutics biopharmaceutics. (2019) 144:50–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.08.009
3. Martin Perez C, Conceição M, Raz R, Wood MJA, and Roberts TC. Enhancing the therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles using peptide technology. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton N.J.). (2022) 2383:119–41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1752-6_8
4. Wang BZ, Luo LJ, and Vunjak-Novakovic G. RNA and protein delivery by cell-secreted and bioengineered extracellular vesicles. Advanced healthcare materials. (2022) 11:e2101557. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202101557
5. Wiklander OPB, Brennan M, Lötvall J, Breakefield XO, and El Andaloussi S. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci Trans Med. (2019) 11:15. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav8521
6. Takei Y, Yamada M, Saito K, Kameyama Y, Aihara T, Iwasaki Y, et al. Endothelium-derived extracellular vesicles expressing intercellular adhesion molecules reflect endothelial permeability and sepsis severity. Anesth analgesia. (2024) 139:385–96. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000006988
7. Villena-Rueda BE, Kajitani GS, Ota VK, Honorato-Mauer J, Santoro ML, Bugiga AVG, et al. miR-9-5p is downregulated in serum extracellular vesicles of patients treated with biperiden after traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 61:9595–607. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04194-5
8. Zou Y, Liao L, Dai J, Mazhar M, Yang G, Wang H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles/exosome: A promising therapeutic strategy for intracerebral hemorrhage. Regenerative Ther. (2023) 22:181–90. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2023.01.006
9. Weiss L, O’Doherty A, Uhrig W, Szklanna PB, Hong-Minh M, Wynne K, et al. Rivaroxaban, in combination with low-dose aspirin, is associated with a reduction in proinflammatory and prothrombotic circulating vesicle signatures in patients with cardiovascular disease. J Thromb haemostasis: JTH. (2025) 23:531–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2024.09.030
10. Zhu Z, Zhang X, Lin X, Wang Y, Han C, and Wang S. Research advances and application progress on miRNAs in exosomes derived from M2 macrophage for tissue injury repairing. Int J nanomedicine. (2025) 20:1543–60. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S508781
11. Zisser L and Binder CJ. Extracellular vesicles as mediators in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J Lipid Atheroscl. (2024) 13:232–61. doi: 10.12997/jla.2024.13.3.232
12. Zygmunciak P, Stróżna K, Błażowska O, and Mrozikiewicz-Rakowska B. Extracellular vesicles in diabetic cardiomyopathy-state of the art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6117. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116117
13. Zhou S, Huang J, Zhang Y, Yu H, and Wang X. Exosomes in action: unraveling their role in autoimmune diseases and exploring potential therapeutic applications. Immune network. (2024) 24:e12. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e12
14. Zhou W, Yang F, and Zhang X. Roles of M1 macrophages and their extracellular vesicles in cancer therapy. Cells. (2024) 13:1428. doi: 10.3390/cells13171428
15. Zhou X, Liu J, Wu F, Mao J, Wang Y, Zhu J, et al. The application potential of iMSCs and iMSC-EVs in diseases. Front bioengineering Biotechnol. (2024) 12:1434465. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1434465
16. Zhuang B, Zhong C, Ma Y, Wang A, Quan H, and Hong L. Innovative therapeutic strategies for myocardial infarction across various stages: non-coding RNA and stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 26:231. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010231
17. Zhou B, Chen Q, Zhang Q, Tian W, Chen T, and Liu Z. Therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles: from inflammation regulation to tissue repair. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:249. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03863-5
18. Zhou H, Hu S, and Yan W. Extracellular vesicles as modifiers of epigenomic profiles. Trends genetics: TIG. (2024) 40:797–809. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2024.05.005
19. Zheng B, Wang X, Guo M, and Tzeng CM. Current development of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Cell Transplant. (2025) 34:9636897241297623. doi: 10.1177/09636897241297623
20. Zheng X, Ai H, Qian K, Li G, Zhang S, Zou Y, et al. Small extracellular vesicles purification and scale-up. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1344681. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1344681
21. Zou C, Zhang Y, Liu H, Wu Y, and Zhou X. Extracellular vesicles: recent insights into the interaction between host and pathogenic bacteria. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:840550. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.840550
22. Zhao J, Zhu W, Mao Y, Li X, Ling G, Luo C, et al. Unignored intracellular journey and biomedical applications of extracellular vesicles. Advanced Drug delivery Rev. (2024) 212:115388. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2024.115388
23. Zhao S, Di Y, Fan H, Xu C, Li H, Wang Y, et al. Targeted delivery of extracellular vesicles: the mechanisms, techniques and therapeutic applications. Mol biomedicine. (2024) 5:60. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00230-x
24. Żmigrodzka M, Guzera M, Miśkiewicz A, Jagielski D, and Winnicka A. The biology of extracellular vesicles with focus on platelet microparticles and their role in cancer development and progression. Tumour biology: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. (2016) 37:14391–401. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5358-6
25. Zhao W, Li K, Li L, Wang R, Lei Y, Yang H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as drug delivery vehicles in disease therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:7715. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147715
26. Li G, Qiu Z, Li C, Zhao R, Zhang Y, Shen C, et al. Exosomal miR-29a in cardiomyocytes induced by angiotensin II regulates cardiac microvascular endothelial cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis by targeting VEGFA. Curr Gene Ther. (2022) 22:331–41. doi: 10.2174/1566523222666220303102951
28. Fabbri M, Paone A, Calore F, Galli R, Gaudio E, Santhanam R, et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2012) 109:E2110–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209414109
29. Zhang L, Ding H, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhu W, and Li P. Circulating microRNAs: biogenesis and clinical significance in acute myocardial infarction. Front Physiol. (2020) 11:1088. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.01088
30. Zhang S and Lin Y. Advancements, challenges, and innovative strategies in cardiac rehabilitation for patients with acute myocardial infarction: A systematic review. Curr problems Cardiol. (2025) 50:102934. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102934
31. Van Opdenbosch N and Lamkanfi M. Caspases in cell death. Inflammation Disease Immun. (2019) 50:1352–64. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.05.020
32. Huang J, Wang F, Sun X, Chu X, Jiang R, Wang Y, et al. Myocardial infarction cardiomyocytes-derived exosomal miR-328-3p promote apoptosis via Caspase signaling. Am J Trans Res. (2021) 13:2365–78.
33. Gou L, Xue C, Tang X, and Fang Z. Inhibition of Exo-miR-19a-3p derived from cardiomyocytes promotes angiogenesis and improves heart function in mice with myocardial infarction via targeting HIF-1α. Aging. (2020) 12:23609–18. doi: 10.18632/aging.103563
34. Wang L and Zhang J. Exosomal lncRNA AK139128 derived from hypoxic cardiomyocytes promotes apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation in cardiac fibroblasts. Int J nanomedicine. (2020) 15:3363–76. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S240660
35. Biemmi V, Milano G, Ciullo A, Cervio E, Dei Cas M, Paroni R, et al. P2585Cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction: role of pro-inflammatory extracellular vesicles. Eur Heart J. (2019) 40:2585. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz748.0911
36. Xiong YY, Gong ZT, Tang RJ, and Yang YJ. The pivotal roles of exosomes derived from endogenous immune cells and exogenous stem cells in myocardial repair after acute myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2021) 11:1046–58. doi: 10.7150/thno.53326
37. Loyer X, Zlatanova I, Devue C, Yin M, Howangyin KY, Klaihmon P, et al. Intra-cardiac release of extracellular vesicles shapes inflammation following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. (2018) 123:100–6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311326
38. Ben-Mordechai T, Palevski D, Glucksam-Galnoy Y, Elron-Gross I, Margalit R, and Leor J. Targeting macrophage subsets for infarct repair. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. (2015) 20:36–51. doi: 10.1177/1074248414534916
39. Sun S, Wu Y, Maimaitijiang A, Huang Q, and Chen Q. Ferroptotic cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes promote cardiac macrophage M1 polarization during myocardial infarction. PeerJ. (2022) 10:e13717. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13717
40. He X, Liu S, Zhang Z, Liu Q, Dong J, Lin Z, et al. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes inhibit cardiomyocyte proliferation through delivering miR-155. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2024) 24:365. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03893-0
41. Liu S, Chen J, Shi J, Zhou W, Wang L, Fang W, et al. M1-like macrophage-derived exosomes suppress angiogenesis and exacerbate cardiac dysfunction in a myocardial infarction microenvironment. Basic Res Cardiol. (2020) 115:22. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-0781-7
42. Gao W, Liu H, Yuan J, Wu C, Huang D, Ma Y, et al. Exosomes derived from mature dendritic cells increase endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis via membrane TNF-α mediated NF-κB pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2016) 20:2318–27. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.2016.20.issue-12
43. Elieh-Ali-Komi D, Bot I, Rodríguez-González M, and Maurer M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of mast cells in atherosclerotic plaque progression and destabilization. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2024) 66:30–49. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08981-9
44. Skenteris NT, Hemme E, Delfos L, Karadimou G, Karlöf E, Lengquist M, et al. Mast cells participate in smooth muscle cell reprogramming and atherosclerotic plaque calcification. Vasc Pharmacol. (2023) 150:107167. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107167
45. Yang WW, Li QX, Wang F, Zhang XR, Zhang XL, Wang M, et al. Exosomal miR-155-5p promote the occurrence of carotid atherosclerosis. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e70187. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.v28.21
46. Chen Y, Wen S, Jiang M, Zhu Y, Ding L, Shi H, et al. Atherosclerotic dyslipidemia revealed by plasma lipidomics on ApoE(-/-) mice fed a high-fat diet. Atherosclerosis. (2017) 262:78–86. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.05.010
47. Pan Y, Hui X, Hoo RLC, Ye D, Chan CYC, Feng T, et al. Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation. J Clin Invest. (2019) 129:834–49. doi: 10.1172/JCI123069
48. Zhang Y, Mei H, Chang X, Chen F, Zhu Y, and Han X. Adipocyte-derived microvesicles from obese mice induce M1 macrophage phenotype through secreted miR-155. J Mol Cell Biol. (2016) 8:505–17. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjw040
49. Dignat-George F and Boulanger CM. The many faces of endothelial microparticles. Arteriosclerosis thrombosis Vasc Biol. (2011) 31:27–33. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.218123
50. Curtis AM, Wilkinson PF, Gui M, Gales TL, Hu E, and Edelberg JM. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase targets the production of proinflammatory endothelial microparticles. J Thromb haemostasis: JTH. (2009) 7:701–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03304.x
51. Burger D and Touyz RM. Cellular biomarkers of endothelial health: microparticles, endothelial progenitor cells, and circulating endothelial cells. J Am Soc Hypertension: JASH. (2012) 6:85–99. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2011.11.003
52. Mezentsev A, Merks RM, O’Riordan E, Chen J, Mendelev N, Goligorsky MS, et al. Endothelial microparticles affect angiogenesis in vitro: role of oxidative stress. Am J Physiol. (2005) 289:H1106–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00265.2005
53. Thannickal VJ, Zhou Y, Gaggar A, and Duncan SR. Fibrosis: ultimate and proximate causes. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:4673–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI74368
54. Yang J, Yu X, Xue F, Li Y, Liu W, and Zhang S. Exosomes derived from cardiomyocytes promote cardiac fibrosis via myocyte-fibroblast cross-talk. Am J Trans Res. (2018) 10:4350–66.
55. Cai L, Chao G, Li W, Zhu J, Li F, Qi B, et al. Activated CD4(+) T cells-derived exosomal miR-142-3p boosts post-ischemic ventricular remodeling by activating myofibroblast. Aging. (2020) 12:7380–96. doi: 10.18632/aging.103084
56. Hu Q, Lyon CJ, Fletcher JK, Tang W, Wan M, and Hu TY. Extracellular vesicle activities regulating macrophage- and tissue-mediated injury and repair responses. Acta Pharm Sin. (2021) 11:1493–512. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.014
57. Ieda M, Tsuchihashi T, Ivey KN, Ross RS, Hong TT, Shaw RM, et al. Cardiac fibroblasts regulate myocardial proliferation through beta1 integrin signaling. Dev Cell. (2009) 16:233–44. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.12.007
58. Ranjan P, Kumari R, Goswami SK, Li J, Pal H, Suleiman Z, et al. Myofibroblast-derived exosome induce cardiac endothelial cell dysfunction. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:676267. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.676267
59. Barile L, Moccetti T, Marbán E, and Vassalli G. Roles of exosomes in cardioprotection. Eur Heart J. (2017) 38:1372–9. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw304
60. Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, and Bobryshev YV. Cardiac extracellular vesicles in normal and infarcted heart. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:63. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010063
61. Zhou Y, Li P, Goodwin AJ, Cook JA, Halushka PV, Chang E, et al. Exosomes from endothelial progenitor cells improve outcomes of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Crit Care (London England). (2019) 23:44. doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2339-3
62. Aminzadeh MA, Rogers RG, Fournier M, Tobin RE, Guan X, Childers MK, et al. Exosome-mediated benefits of cell therapy in mouse and human models of duchenne muscular dystrophy. Stem Cell Rep. (2018) 10:942–55. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.01.023
63. Ribeiro-Rodrigues TM, Laundos TL, Pereira-Carvalho R, Batista-Almeida D, Pereira R, Coelho-Santos V, et al. Exosomes secreted by cardiomyocytes subjected to ischaemia promote cardiac angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. (2017) 113:1338–50. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx118
64. van Balkom BW, de Jong OG, Smits M, Brummelman J, den Ouden K, de Bree PM, et al. Endothelial cells require miR-214 to secrete exosomes that suppress senescence and induce angiogenesis in human and mouse endothelial cells. Blood. (2013) 121:3997–4006. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-478925
65. Zhan R, Leng X, Liu X, Wang X, Gong J, Yan L, et al. Heat shock protein 70 is secreted from endothelial cells by a non-classical pathway involving exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2009) 387:229–33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.06.095
66. Luther KM, Haar L, McGuinness M, Wang Y, Lynch Iv TL, Phan A, et al. Exosomal miR-21a-5p mediates cardioprotection by mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2018) 119:125–37. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.04.012
67. Zhao Y, Sun X, Cao W, Ma J, Sun L, Qian H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells relieve acute myocardial ischemic injury. Stem Cells Int. (2015) 2015:761643. doi: 10.1155/2015/761643
68. Ma J, Zhao Y, Sun L, Sun X, Zhao X, Sun X, et al. Exosomes derived from akt-modified human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve cardiac regeneration and promote angiogenesis via activating platelet-derived growth factor D. Stem Cells Trans Med. (2017) 6:51–9. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0038
69. Windeløv NA, Ostrowski SR, Johansson PI, Wanscher M, Larsen CF, Sørensen AM, et al. Circulating levels of platelet α-granule cytokines in trauma patients. Inflammation research: Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc. (2015) 64:235–41. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0802-4
70. Gupta S and Knowlton AA. HSP60 trafficking in adult cardiac myocytes: role of the exosomal pathway. Am J Physiol. (2007) 292:H3052–6. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01355.2006
71. Abrial M, Da Silva CC, Pillot B, Augeul L, Ivanes F, Teixeira G, et al. Cardiac fibroblasts protect cardiomyocytes against lethal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 68:56–65. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.01.005
72. Luo H, Li X, Li T, Zhao L, He J, Zha L, et al. microRNA-423-3p exosomes derived from cardiac fibroblasts mediates the cardioprotective effects of ischaemic post-conditioning. Cardiovasc Res. (2019) 115:1189–204. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy231
73. Xiao J, Pan Y, Li XH, Yang XY, Feng YL, Tan HH, et al. Cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21 by targeting PDCD4. Cell Death Dis. (2016) 7:e2277. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.181
74. Barile L, Cervio E, Lionetti V, Milano G, Ciullo A, Biemmi V, et al. Cardioprotection by cardiac progenitor cell-secreted exosomes: role of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. Cardiovasc Res. (2018) 114:992–1005. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy055
75. Peng Y, Zhao JL, Peng ZY, Xu WF, and Yu GL. Exosomal miR-25-3p from mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial infarction by targeting pro-apoptotic proteins and EZH2. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:317. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2545-6
76. Cheng H, Chang S, Xu R, Chen L, Song X, Wu J, et al. Hypoxia-challenged MSC-derived exosomes deliver miR-210 to attenuate post-infarction cardiac apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11:224. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01737-0
77. Wang X, Zhu Y, Wu C, Liu W, He Y, and Yang Q. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carry microRNA-671 to alleviate myocardial infarction through inactivating the TGFBR2/smad2 axis. Inflammation. (2021) 44:1815–30. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01460-9
78. Cambier L, Giani JF, Liu W, Ijichi T, Echavez AK, Valle J, et al. Angiotensin II-induced end-organ damage in mice is attenuated by human exosomes and by an exosomal Y RNA fragment. Hypertension. (2018) 72:370–80. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11239
79. Ma C, Yang Z, Wang J, She H, Tan L, Ye Q, et al. Exosomes miRNA-499a-5p targeted CD38 to alleviate anthraquinone induced cardiotoxicity: experimental research. Int J Surg (London England). (2024) 110:1992–2006. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001118
80. Vandergriff A, Huang K, Shen D, Hu S, Hensley MT, Caranasos TG, et al. Targeting regenerative exosomes to myocardial infarction using cardiac homing peptide. Theranostics. (2018) 8:1869–78. doi: 10.7150/thno.20524
81. Bryl R, Kulus M, Bryja A, Domagała D, Mozdziak P, Antosik P, et al. Cardiac progenitor cell therapy: mechanisms of action. Cell bioscience. (2024) 14:30. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01211-x
82. Milano G, Biemmi V, Lazzarini E, Balbi C, Ciullo A, Bolis S, et al. Intravenous administration of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes protects against doxorubicin/trastuzumab-induced cardiac toxicity. Cardiovasc Res. (2020) 116:383–92. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz108
83. He Y, Li Z, Shen L, Shi D, and Li S. Cardiac progenitor cells-derived exosomes alleviate myocardial injury by regulating Treg cell differentiation through the mTOR pathway in mice with myocardial infarction. Nan fang yi ke da xue xue bao = J South Med Univ. (2023) 43:1644–50. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.09.24
84. Hirai K, Ousaka D, Fukushima Y, Kondo M, Eitoku T, Shigemitsu Y, et al. Cardiosphere-derived exosomal microRNAs for myocardial repair in pediatric dilated cardiomyopathy. Sci Trans Med. (2020) 12:573. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abb3336
85. Wang S, Dong J, Li L, Wu R, Xu L, Ren Y, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-129-5p modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells represses ventricular remolding of mice with myocardial infarction. J Tissue Eng regenerative Med. (2022) 16:177–87. doi: 10.1002/term.v16.2
86. Zhu J, Lu K, Zhang N, Zhao Y, Ma Q, Shen J, et al. Myocardial reparative functions of exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells are enhanced by hypoxia treatment of the cells via transferring microRNA-210 in an nSMase2-dependent way. Artif cells nanomedicine Biotechnol. (2018) 46:1659–70. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1388249
87. Zou Y, Li L, Li Y, Chen S, Xie X, Jin X, et al. Restoring Cardiac Functions after Myocardial Infarction-Ischemia/Reperfusion via an Exosome Anchoring Conductive Hydrogel. ACS Appl materials interfaces. (2021) 13:56892–908. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c16481
88. Luo Q, Guo D, Liu G, Chen G, Hang M, and Jin M. Exosomes from miR-126-overexpressing adscs are therapeutic in relieving acute myocardial ischaemic injury. Cell Physiol biochemistry: Int J Exp Cell physiology biochemistry Pharmacol. (2017) 44:2105–16. doi: 10.1159/000485949
89. Pan J, Alimujiang M, Chen Q, Shi H, and Luo X. Exosomes derived from miR-146a-modified adipose-derived stem cells attenuate acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage via downregulation of early growth response factor 1. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:4433–43. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v120.3
90. Ebrahim N, Al Saihati HA, Mostafa O, Hassouna A, Abdulsamea S, Abd El Aziz MEGE, et al. Prophylactic evidence of MSCs-derived exosomes in doxorubicin/trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: beyond mechanistic target of NRG-1/erb signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:5967. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115967
91. Deng S, Zhou X, Ge Z, Song Y, Wang H, Liu X, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2019) 114:105564. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105564
92. Huang H, Xu Z, Qi Y, Zhang W, Zhang C, Jiang M, et al. Exosomes from SIRT1-overexpressing ADSCs restore cardiac function by improving angiogenic function of EPCs, molecular therapy. Nucleic Acids. (2020) 21:737–50. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.07.007
93. Paone S, Baxter AA, Hulett MD, and Poon IKH. Endothelial cell apoptosis and the role of endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life sciences: CMLS. (2019) 76:1093–106. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2983-9
94. Yue Y, Wang C, Benedict C, Huang G, Truongcao M, Roy R, et al. Interleukin-10 deficiency alters endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosome reparative effect on myocardial repair via integrin-linked kinase enrichment. Circ Res. (2020) 126:315–29. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315829
95. Shi Y, Yang Y, Guo Q, Gao Q, Ding Y, Wang H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation in inflammatory environments and benefit cardioprotective effects. Stem Cells Dev. (2019) 28:799–811. doi: 10.1089/scd.2018.0242
96. Liu HY, Yu LF, Zhou TG, Wang YD, Sun DH, Chen HR, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes inhibit H2O2-induced cardiomyocyte inflammation and oxidative stress via regulating miR-181a-5p/ATF2 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:10069–77. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23224
97. Zimmermann M, Adamec R, and Ciaroni S. Reduction in the frequency of ventricular late potentials after acute myocardial infarction by early thrombolytic therapy. Am J Cardiol. (1991) 67:697–703. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90524-O
98. Zucker DR, Griffith JL, Beshansky JR, and Selker HP. Presentations of acute myocardial infarction in men and women. J Gen Internal Med. (1997) 12:79–87. doi: 10.1007/s11606-006-5001-0
99. Westwood M, van Asselt T, Ramaekers B, Whiting P, Thokala P, Joore M, et al. High-sensitivity troponin assays for the early rule-out or diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in people with acute chest pain: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess (Winchester England). (2015) 19:1–234. doi: 10.3310/hta19960
100. Wildi K, Twerenbold R, and Mueller C. How acute changes in cardiac troponin concentrations help to handle the challenges posed by troponin elevations in non-ACS-patients. Clin Biochem. (2015) 48:218–22. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.09.003
101. Wang K, Zhang S, Weber J, Baxter D, and Galas DJ. Export of microRNAs and microRNA-protective protein by mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. (2010) 38:7248–59. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq601
102. Gidlöf O, Smith JG, Miyazu K, Gilje P, Spencer A, Blomquist S, et al. Circulating cardio-enriched microRNAs are associated with long-term prognosis following myocardial infarction. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2013) 13:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-13-12
103. Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Zhang JT, Li Q, Li Y, He J, et al. Circulating microRNA: a novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur Heart J. (2010) 31:659–66. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq013
104. Cheng Y, Tan N, Yang J, Liu X, Cao X, He P, et al. A translational study of circulating cell-free microRNA-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Clin Sci (London Engl. (2010) 1979) 119:87–95. doi: 10.1042/CS20090645
105. Ziegler JN and Tian C. Engineered extracellular vesicles: emerging therapeutic strategies for translational applications. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:15206. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015206
106. Zhang N, Song Y, Huang Z, Chen J, Tan H, Yang H, et al. Monocyte mimics improve mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle homing in a mouse MI/RI model. Biomaterials. (2020) 255:120168. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120168
107. Wang X, Chen Y, Zhao Z, Meng Q, Yu Y, Sun J, et al. Engineered exosomes with ischemic myocardium-targeting peptide for targeted therapy in myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7:e008737. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008737
108. Wei Z, Chen Z, Zhao Y, Fan F, Xiong W, Song S, et al. Mononuclear phagocyte system blockade using extracellular vesicles modified with CD47 on membrane surface for myocardial infarction reperfusion injury treatment. Biomaterials. (2021) 275:121000. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121000
109. Zhu LP, Tian T, Wang JY, He JN, Chen T, Pan M, et al. Hypoxia-elicited mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates cardiac repair through miR-125b-mediated prevention of cell death in myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2018) 8:6163–77. doi: 10.7150/thno.28021
110. Tian T, Zhang HX, He CP, Fan S, Zhu YL, Qi C, et al. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials. (2018) 150:137–49. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.10.012
111. Zinger A, Brozovich A, Pasto A, Sushnitha M, Martinez JO, Evangelopoulos M, et al. Bioinspired extracellular vesicles: lessons learned from nature for biomedicine and bioengineering. Nanomaterials (Basel Switzerland). (2020) 10:2172. doi: 10.3390/nano10112172
112. Zou H, Zhu J, and Huang DS. Cell membrane capsule: a novel natural tool for antitumour drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug delivery. (2019) 16:251–69. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2019.1581762
113. Xuan W, Khan M, and Ashraf M. Extracellular vesicles from notch activated cardiac mesenchymal stem cells promote myocyte proliferation and neovasculogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:11. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00011
114. Gong XH, Liu H, Wang SJ, Liang SW, and Wang GG. Exosomes derived from SDF1-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit ischemic myocardial cell apoptosis and promote cardiac endothelial microvascular regeneration in mice with myocardial infarction. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:13878–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v234.8
115. Mao Q, Liang XL, Zhang CL, Pang YH, and Lu YX. LncRNA KLF3-AS1 in human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorates pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction through miR-138-5p/Sirt1 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10:393. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1522-4
116. Liu J, Jiang M, Deng S, Lu J, Huang H, Zhang Y, et al. miR-93-5p-containing exosomes treatment attenuates acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2018) 11:103–15. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.01.010
117. Wei Z, Qiao S, Zhao J, Liu Y, Li Q, Wei Z, et al. miRNA-181a over-expression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes influenced inflammatory response after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci. (2019) 232:116632. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116632
118. Song Y, Zhang C, Zhang J, Jiao Z, Dong N, Wang G, et al. Localized injection of miRNA-21-enriched extracellular vesicles effectively restores cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2019) 9:2346–60. doi: 10.7150/thno.29945
Keywords: extracellular vesicles, acute myocardial infarction, therapeutic targets, cardiac repair, biomarkers, immune modulation
Citation: Wu H, Xue J, Liu Q, Wan Z, Liang L, Sun S, Liu P, Chen M and Liu M (2025) Extracellular vesicles: molecular messengers and new therapeutic targets in acute myocardial infarction. Front. Immunol. 16:1598407. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1598407
Received: 23 March 2025; Accepted: 10 June 2025;
Published: 26 June 2025.
Edited by:
Ashwin Kotnis, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaReviewed by:
Carl Nelson, Nottingham Trent University, United KingdomCopyright © 2025 Wu, Xue, Liu, Wan, Liang, Sun, Liu, Chen and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ping Liu, aGVsbG9saXVwaW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Mingtai Chen, enl5Y2FyZGlvQGZveG1haWwuY29t; Mengnan Liu, bGl1bWVuZ25hbkBzd211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Hao Wu
Hao Wu Jinyi Xue1†
Jinyi Xue1† Qiuyu Liu
Qiuyu Liu Shihan Sun
Shihan Sun Ping Liu
Ping Liu Mingtai Chen
Mingtai Chen Mengnan Liu
Mengnan Liu