- 1Immunology Department, Dmitry Rogachev National Medical Research Center of Pediatric Hematology, Oncology and Immunology, Moscow, Russia
- 2Immunopathology Department, National Research Center Institute of Immunology Federal Medical and Biological Agency (FMBA), Moscow, Russia
- 3Moscow Center of Allergy and Immunology, Clinical City Hospital 52 Ministry of Healthcare of Moscow, Moscow, Russia
- 4Immunology Department, Children’s City Clinical Hospital №9, Moscow, Russia
- 5Immunology Department, Republican Children’s Clinical Hospital of the Ministry of Health of the Republic Bashkortostan, Ufa, Russia
- 6Immunology Department, Stavropol State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Stavropol, Russia
- 7Immunology Department, Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Rostov-on-Don, Russia
- 8Immunology Department, Altai State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Barnaul, Russia
- 9Immunology Department, Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Yaroslavl, Russia
- 10Immunology Department, Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Yekaterinburg, Russia
- 11Immunology Department, Arkhangelsk Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital named after P.G. Vyzhletsova, Arkhangelsk, Russia
- 12Immunology Department, Nizhny Novgorod Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia
- 13Immunology Department, First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after acad. I.P. Pavlova, Saint Petersburg, Russia
- 14Immunology Department, Voronezh Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Voronezh, Russia
- 15Immunology Department, Republican Children’s Clinical Hospital named after E.P. Glinka, Chechen Republic, Russia
- 16Immunology Department, Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Republic of Buryatia, Russia
- 17Immunology Department, Republican Children’s Clinical Hospital, Republic of Crimea, Russia
- 18Immunology Department, Research Institute of Fundamental and Clinical Immunology, Novosibirsk, Russia
- 19Immunology Department, Children’s Republican Clinical Hospital, Kazan, Russia
- 20Immunology Department, Chelyabinsk Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Chelyabinsk, Russia
- 21Immunology Department, Children’s Regional Hospital, Perm, Russia
- 22Immunology Department, Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital named after N.N. Silishchevoy, Astrakhan, Russia
- 23Immunology Department, Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital No. 1, Tyumen, Russia
- 24Immunology Department, City Children’s Clinical Hospital №2 named after V.P. Bisyarina, Omsk, Russia
- 25Immunology Department, Irkutsk State Regional Children’s Clinical Hospital, Irkutsk, Russia
- 26Immunology Department, Children’s City Clinical Hospital, Kaluga, Russia
Subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) preparations are widely used in patients with inborn errors of immunity (IEI), with proven efficacy and good tolerance. We assessed treatment efficacy, safety, and quality of life in a large cohort of IEI patients who switched from intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) to SCIG. Our observational study included 200 patients aged 1–65 years with IEI. SCIG Cutaquig (16.5%) was administered every 7–10 days for at least 12 months via the rapid push method. We assessed the rate of infection, immunoglobulin G (IgG) concentration, adverse events, and quality of life. A total of 8,787 SCIG doses were administered during the study. The rate of infections (per person/month) during SCIG treatment was 0.05, which was significantly lower compared to 0.19 during the IVIG period (p<0.001). The median trough IgG was 6.9 g/L on IVIG, compared to 9.0 g/L during the first six months, and 9.2 g/L during the next six months on SCIG. Systemic reactions occurred in 12.4% of the IVIG infusions and 1.9% of the SCIG infusions. The total scores on quality of life summary assessments of physical and mental health were higher on SCIG therapy compared with IVIG (p<0.001). At the end of the study, 85.6% of the patients chose to remain on SCIG. Our data suggest that SCIG infusion via the rapid push method is effective, well tolerated, and feasible in large groups of IEI patients, including those in large countries such as Russia.
Introduction
Inborn errors of immunity (IEI) is a group of genetic disorders that includes more than 550 different conditions (1). Immunoglobulin replacement therapy (IRT) using highly purified human immunoglobulin (IG) preparations is the standard of care for immunodeficiencies with impaired antibody production, which constitutes the majority of IEI (2). It is widely accepted that lifelong IRT substantially reduces the frequency and severity of infections by maintaining serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) concentrations close to physiological levels (3).
While the use of IG preparations for intravenous (IVIG) administration has been the most common type of IRT since the 1980s, subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) preparations are gaining popularity among physicians and patients due to their comparative ease of administration (4).
The conventional mode of SCIG administration uses a programmable infusion pump. More recently, subcutaneous push using a syringe and butterfly needle has emerged as an alternative and has been shown to be a comparable, if not a simpler and more convenient, method of administering SCIG (5). In countries where SCIG and infusion pumps are widely available, the choice of technique relies primarily on patient preference (5, 6).
SCIG preparations have not been easily accessible in Russia until recently. During the worldwide post-pandemic shortage of IVIG, 16.5% SCIG emerged as the preparation of choice for Russian IEI patients and presented an opportunity to assess real-life experience with SCIG delivered via the rapid push method in a large cohort of adult and pediatric patients with IEI.
Here we present the results of a multicenter observational study that evaluated the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of subcutaneous 16.5% immunoglobulin treatment as compared to previously used intravenous products.
Materials and methods
Study design and patients
Due to a plasma shortage following the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a significant shortage of IVIG supply in Russia. Beginning in 2022, 16.5% SCIG Cutaquig became available for all pediatric and some adult IEI patients due to a program of the nonprofit foundation Circle of Kindness, and a majority of IEI patients with antibody deficiencies were switched to SCIG. We conducted a prospective, non-interventional, open-label multicenter study of safety and feasibility with a retrospective phase (NCT05986734). The study subjects were recruited from patients who had been receiving IVIG treatment for at least six months prior and who had switched to SCIG treatment through the above-mentioned program. The main efficacy and safety parameters (see below) were assessed retrospectively for the six months of preceding IVIG treatment and prospectively for the first 12 months of SCIG treatment.
Pediatric and adult patients qualified for participation in the study if they had a documented diagnosis of IEI, required IgG replacement therapy, and had been receiving regular IVIG IRT for at least six months prior to inclusion in the study. Patients were ineligible if they had an active malignancy or had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
The study received Institutional Review Board approval, and prior to enrolling in the study, all patients or their legal guardians provided written informed consent.
The Russian IEI registry (7) was used as a platform for data collection, including the quality of life (QoL) questionnaires available to patients online through the registry.
A total of 233 IEI patients were originally enrolled in the study. During the prospective phase, 33 patients discontinued prematurely: 28 withdrew from the study but continued SCIG treatment, and five patients underwent HSCT. A total of 200 patients completed the study (Supplementary Table 1), and their data were analyzed. The median age of the patients was 11 years (1; 65), and the male/female ratio was 1.9:1. Patients were divided into the following age groups: <4 years, 4 to 7 years, 7 to 12 years, 12 to 18 years and over 18 years in accordance with the age groups of the quality of life questionnaires (PEDs-QL). (Supplementary Figure 1).
Immunoglobulin treatment
Prior to recruitment in the study (Period 1), eligible patients had received IVIG every month at a median dose of 0.52 g/kg/month (min 0.3; max 0.89). During SCIG treatment (Period 2), patients received SCIG 16.5% (Cutaquig 16.5%, Octapharma, Switzerland) at the same monthly dose as in Period 1, divided into 3–4 infusions per month. The SCIG was infused using the rapid push method and 21G–26G needles. The product was administered at one or multiple injection sites at mean estimated rates of about 1.5 mL/min. All patients or their caregivers received training in SCIG administration techniques, and the first SCIG infusions were performed under the supervision of a trained nurse or physician.
A total of 8,787 SCIG infusions were administered during the study, 90.3% of which were at home.
The mean single dose was 0,14 g/kg (min 0.05, max 0.33) in 1–6 month of therapy and 0,15 g/kg (min 0,1, max 0,4) in 7–12 month of therapy.
The mean single injection volume was 17.12 mL (min 6; max 48) in 1–6 month of therapy and 17,68 mL (min 4,5, max 60) in 7–12 month of therapy. The duration of administration was 31,78 min (min 6, max 120) min in 1–6 month of therapy and 27,67 min (min 2, max 120) in 7–12 month of therapy (Supplementary Table 2).
Efficacy assessment
The primary end-point was the rate of validated acute infections requiring additional antibiotic treatment, expressed as the average per person per month. Secondary end-points included frequency of hospitalizations, duration of inpatient hospital stays, days missed from school or work due to illness or infection, and duration of additional treatment with antibiotics. Trough levels of serum IgG were measured in serum samples taken immediately prior to immunoglobulin infusions at least three times during the specified IVIG and SCIG treatment periods.
Safety
All adverse events (AEs) during IVIG and SCIG therapy were recorded. The investigator provided guidance to the patient or caregiver on how to identify and document local and systemic AEs.
Measures of patient experience
QoL was surveyed in patients aged 2–18 years using the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory Russian, version 4.0 (PEDS‐QL) questionnaire and in patients older than 18 years using the SF‐36 survey. On all questionnaires, higher scores indicated higher satisfaction.
The treatment burden related to IG therapy was evaluated using a special questionnaire developed within the framework of this study (Supplementary Table 3).
The severity of pain was assessed using the Wong–Baker scale (8).
Statistical methods
Statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel 2019 and RStudio Server 1.3.959. Quantitative indices were described using the median, first and third quartiles, minimum, and maximum. The calculated data were described in absolute values and percentages. Null observations were described using averages and fraction of zero values. The significance of differences between patient indices at different stages of the study was established using the Mann–Whitney test for paired data with the Bonferroni–Holm correction, where necessary. The significance of the differences among the data was determined using the chi-square test.
In data sets where most of the values equaled zero, average values were given without standard error of mean deviations. The p values equal to or less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
Serum trough IgG levels
Trough levels of serum IgG were higher during SCIG therapy than during IVIG therapy (p<0.001). Serum IgG values measured for six consecutive months of IVIG treatment attained a median of 6.9 g/L (5.2; 9.1). During the first six months of SCIG treatment, the median serum IgG level was 9 g/L (7.3; 11.6). At the end of the SCIG treatment study period, the median serum IgG levels reached 9.2 g/L (7.8; 11.4) (Figure 1).
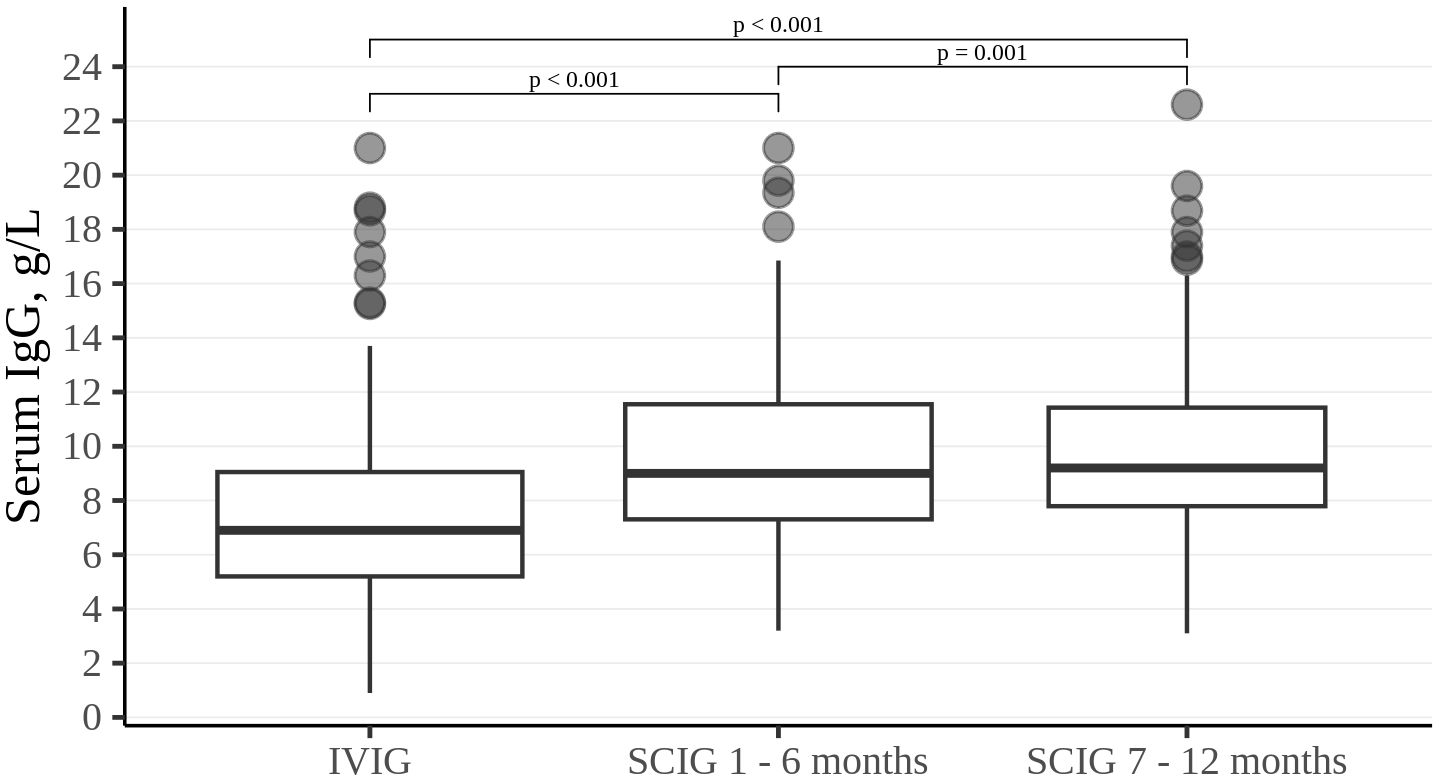
Figure 1. Trough IgG level in the study cohort. Thick lines represent median, boxes - the first and third quartiles.
Efficacy
The rate of infections during SCIG treatment was significantly lower than during IVIG treatment in adults and children (p<0.05) (Figure 2). The rate of infections during the entire SCIG treatment period was 0.05 per person/month, and 66% of the patients had no infections. The rate of infections during IVIG treatment was 0.19 per person/month, and 38% of the patients had no infections. Antibiotics used to treat infections were administered for a median of 1.53 days per person/month on IVIG, 0.49 days per person/month during the first six months of SCIG treatment, and 0.61 days per person/month during the next six months of SCIG treatment (p<0.001) (Figure 3). The median rates of hospitalization were 0.04 events per person/month during IVIG treatment and 0.01 events per person/month during SCIG treatment (p<0.001) (Figure 4). The durations of hospitalization were 0.44 days per person/month during IVIG treatment, 0.32 days per person/month during the first six months of SCIG treatment, and 0.045 days per person/month during the next six months of SCIG treatment (p<0.001) (Figure 4).
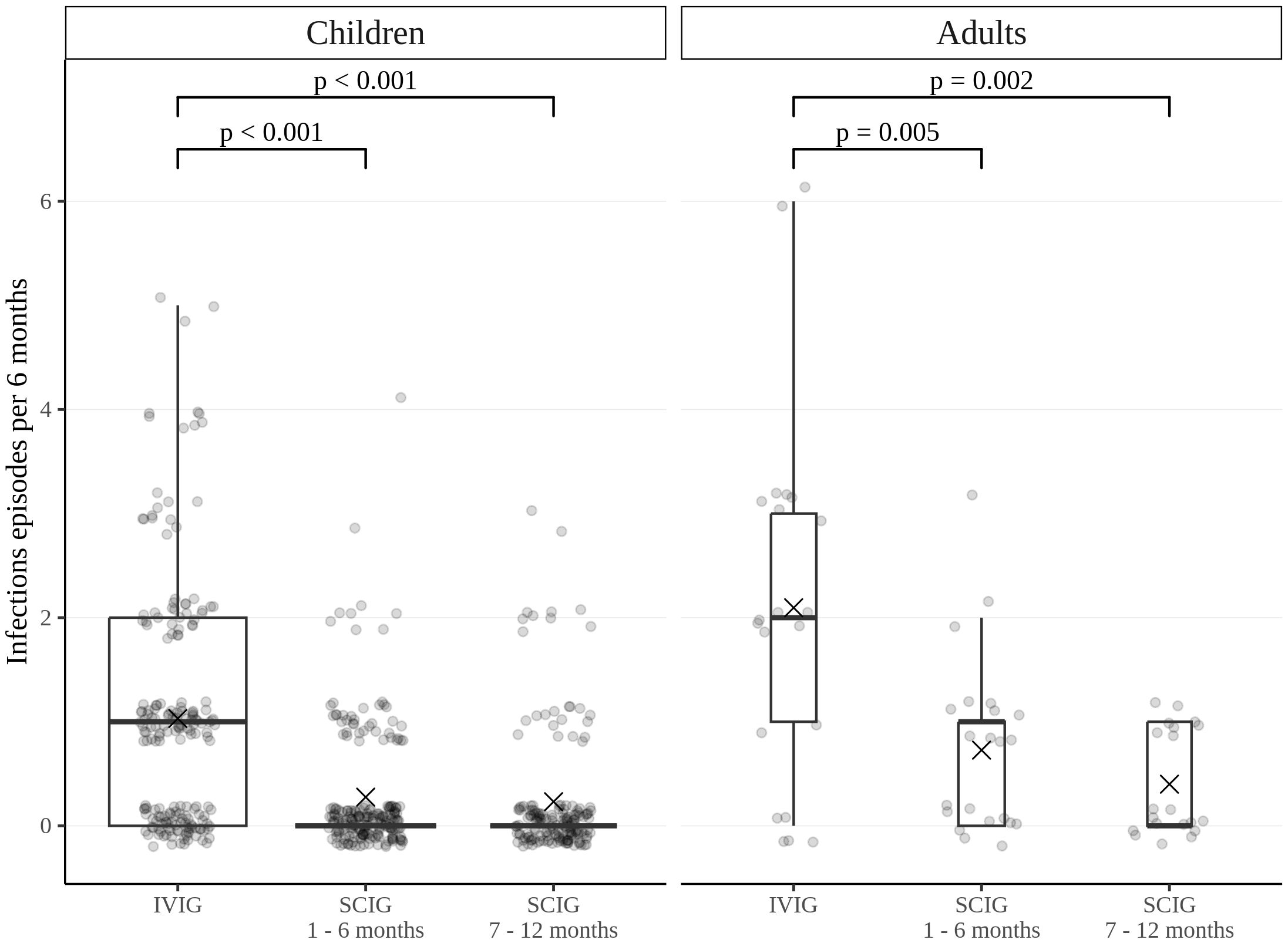
Figure 2. Frequency of infections in pediatric and adult patients. Infection rates are expressed as the number of episodes per six months. Thick lines represent the median, crosses represent the average, and boxes represent the first and third quartiles.
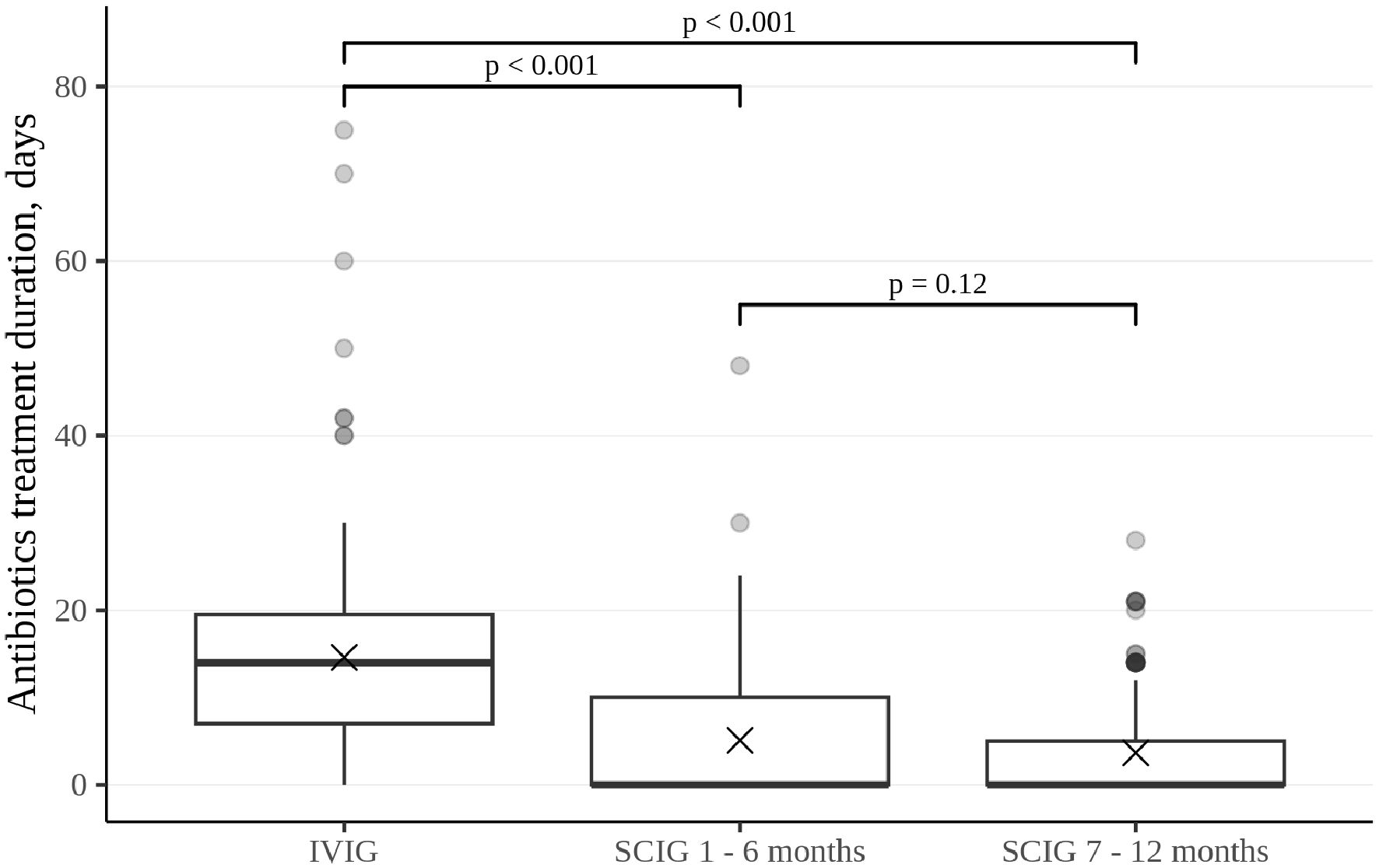
Figure 3. Duration of antibiotic treatment in patients who require it, presented as the total number of days per patient per each six-month interval. Thick lines represent the median, crosses represent the average, and boxes represent the first and third quartiles.
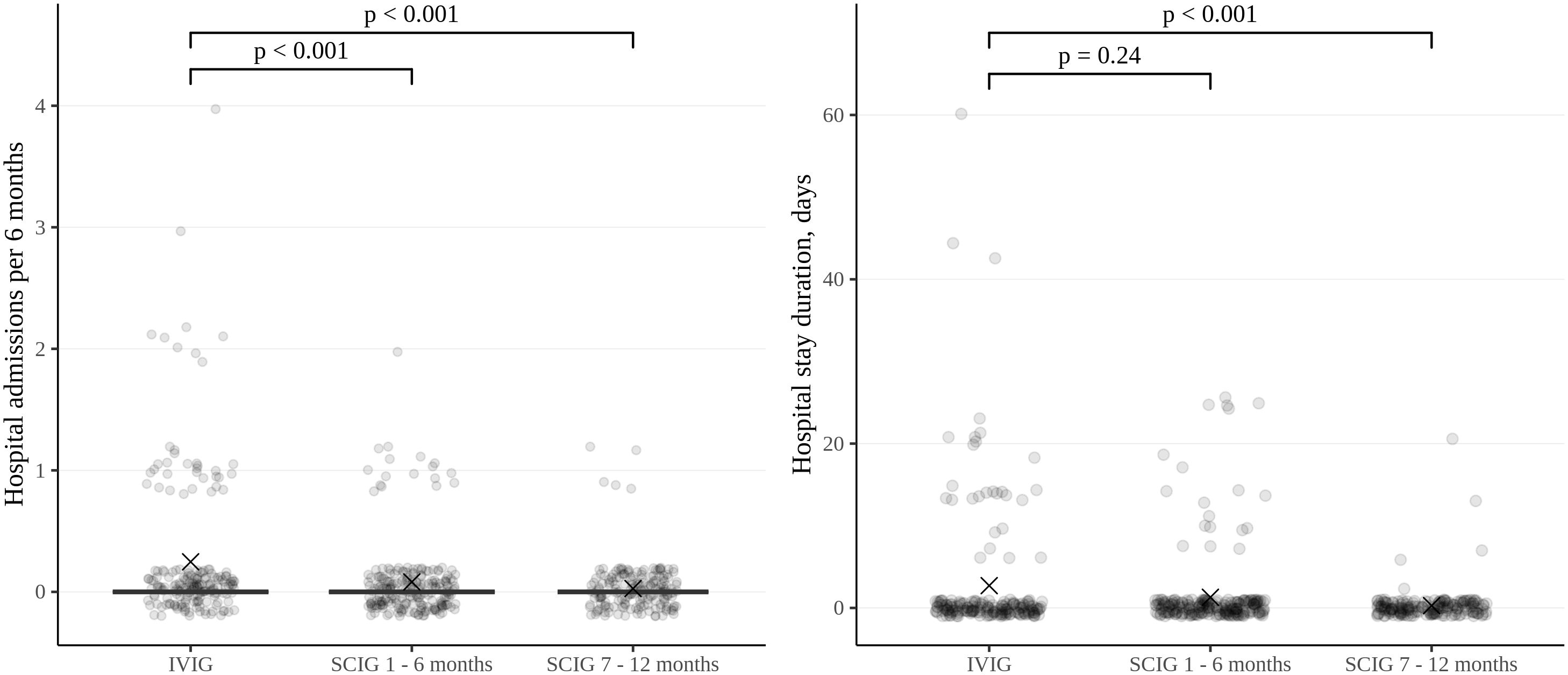
Figure 4. Frequency and duration of inpatient treatment of patients in the study cohort, expressed per patient per six-month period. Thick lines represent the median, crosses represent the average, and boxes represent the first and third quartiles.
While receiving SCIG treatment, patients missed school or work an average of 2.94 days per month as compared to 3.66 days per month during IVIG treatment (p<0.05).
Adverse events
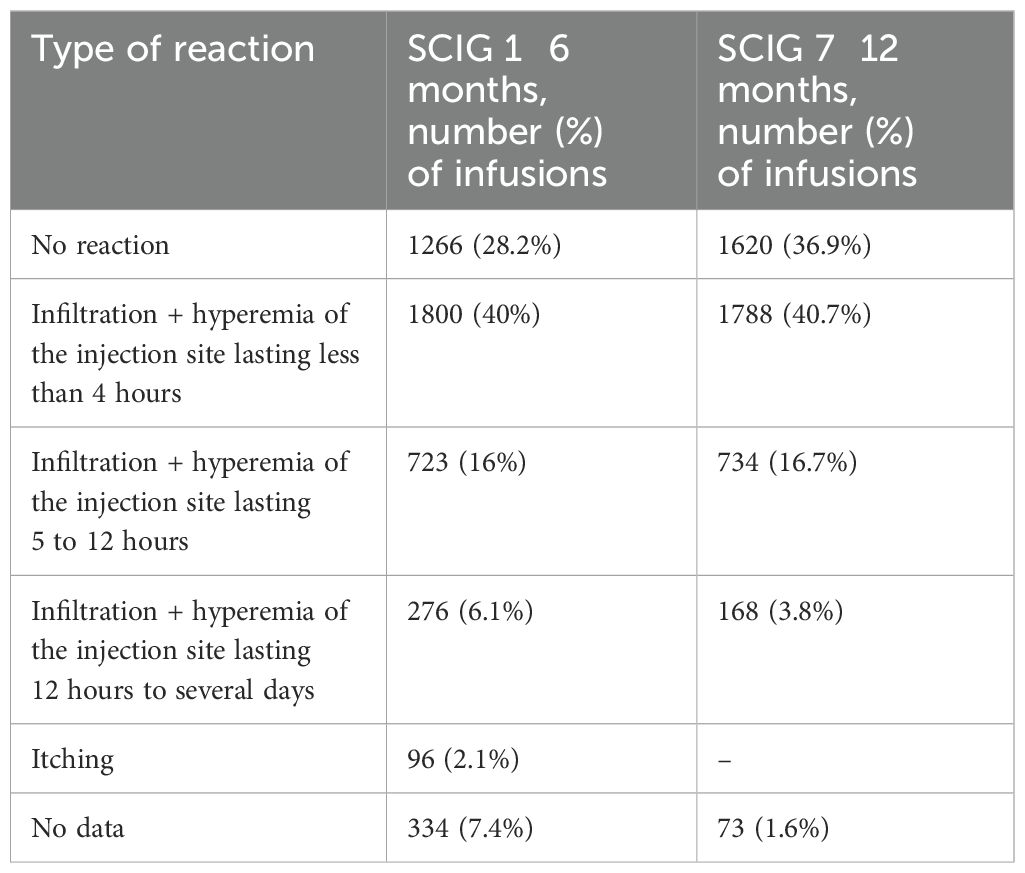
Local reactions were the most common AE during SCIG treatment (Table 1). The development of expected local reactions accompanied about 70% of infusions of SCIG over 12 months of treatment, and none led to discontinuation of treatment. The incidence of infusion site reactions decreased over time. The majority of these reactions were mild or moderate, and most were of short duration. In three patients, we documented the development of contact dermatitis related to the use of an aseptic patch to secure a needle at the SCIG injection site (Figures 5a, b).
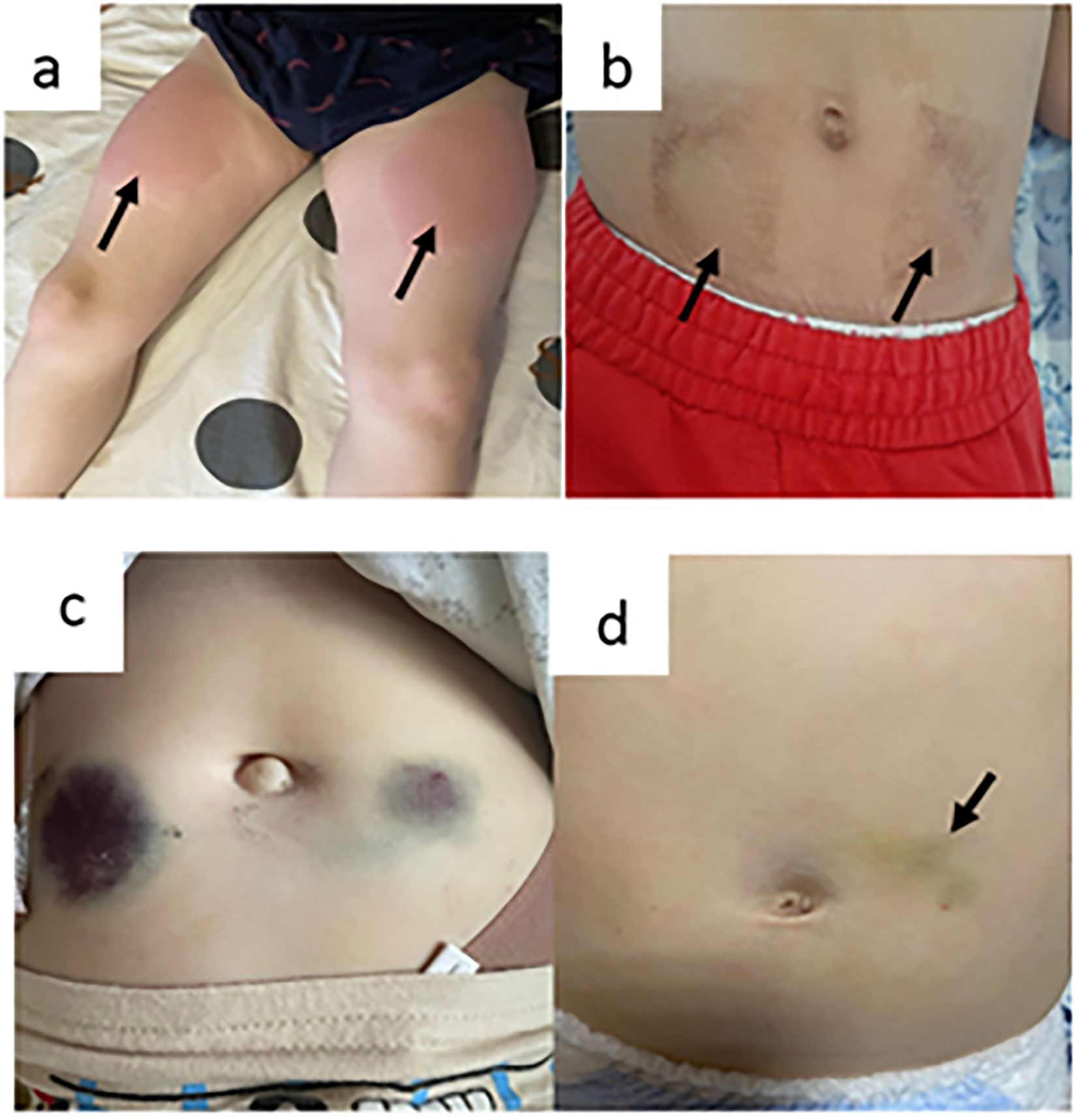
Figure 5. Local adverse events (a, b = contact dermatitis as a result of using an aseptic patch; c = hemorrhagic syndrome in a patient with a platelet count of 30,000 cells/µL; and d = hemorrhagic syndrome in patients with platelet counts of 3000 cells/µL).
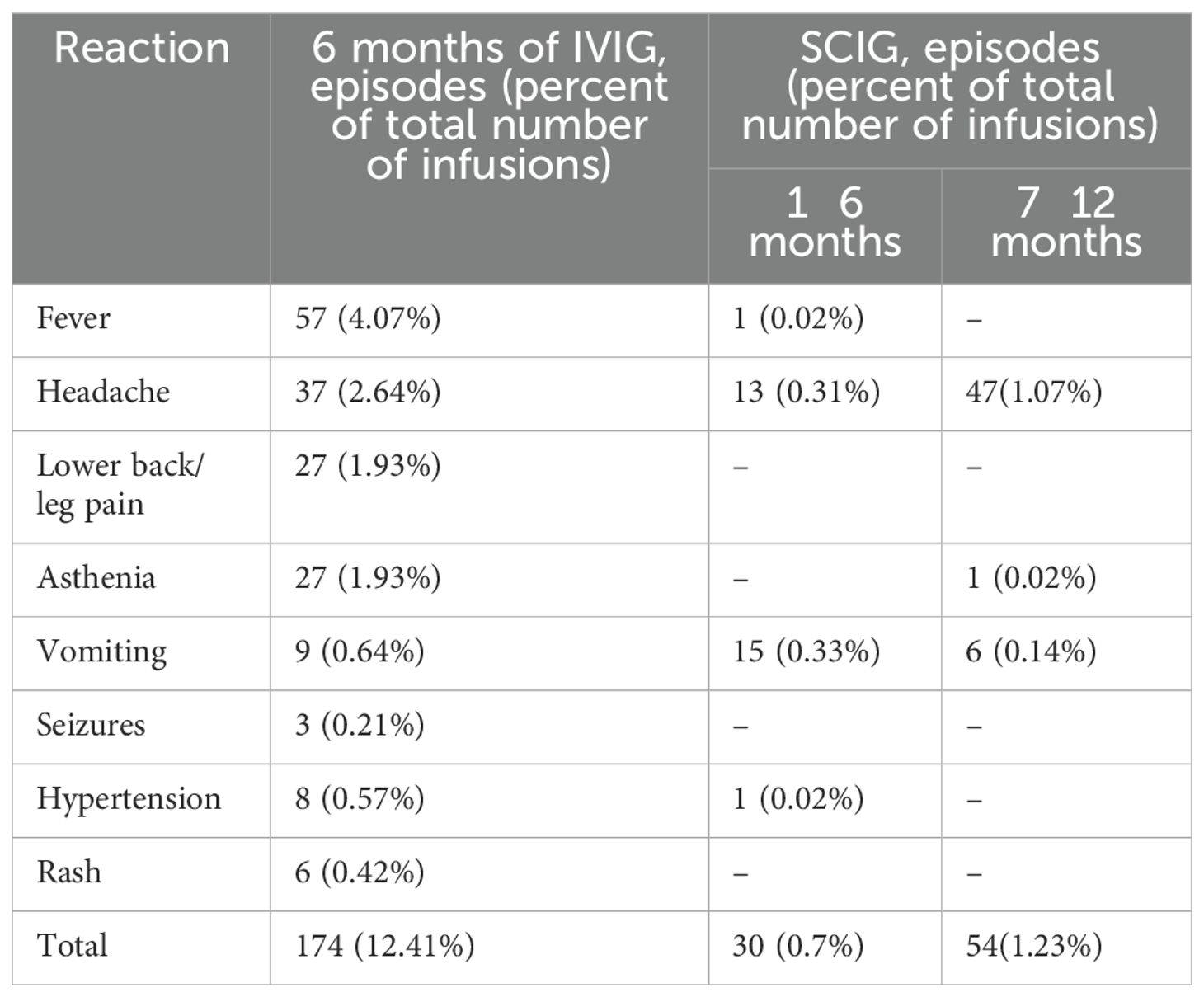
During the study, 7 (3.5%) patients (1.93% of infusions) experienced systemic reactions to SCIG, and none led to discontinuation of treatment. In addition, 39 (19.5%) patients (12.4% of infusions) experienced systemic reactions to IVIG (p<0.001). The most common systemic adverse reactions to IVIG were fever, headache, lower back/leg pain, asthenia, vomiting, seizures, hypertension, rash (Table 2).
SCIG treatment in special cohorts of patients
A total of 210 SCIG infusions were performed in eight patients with immune/other thrombocytopenia and the following IEI: Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome, 4; STAT1 gain-of-function defect, 2; LRBA defect, 1; and combined immunodeficiency without genetic verification, 1. The median platelet count in this patient group was 39,000 cells/µL (min 3000; max 130,000). The severity of skin hemorrhagic syndrome was correlated with platelet count. There was no cutaneous hemorrhagic syndrome in patients with platelet counts of 30,000 cells/µL or more (Figure 5c). In one patient with a platelet count of 3000 cells/µL, a hematoma of up to 4 cm in diameter developed at the injection site (Figure 5d).
In all, 278 infusions of SCIG were performed in patients with severe dermatitis: 134 in three patients with generalized specific dermatitis within the framework of Netherton syndrome and 144 infusions in four patients with atopic dermatitis (two with hyper-IgE syndrome and two with Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome). Local reactions in this group did not differ from those in the general cohort. Specifically, no infections at injection sites or worsening dermatitis were noted.
Patient experiences
In patients under 18 years of age, improvement in quality of life was observed in all age subgroups. Overall, on the pediatric cohort’s questionnaire, the median total score was 900 (0; 1475) at the end of the IVIG treatment period and 1075 (225; 1500) at the end of 12 months of SCIG treatment (p<0.001). On the parents’ questionnaire, the median summary score at the end of the IVIG treatment was 875 (0; 1475) and 1200 (100; 1500) at the end of 12 months of SCIG treatment (p<0.001) (Supplementary Table 4).
Interestingly, in adult patients, no significant changes in the quality of life were recorded between the IVIG and SCIG treatment periods (p>0.05), which can be explained by the small number of patients over age 18. At the end of IVIG treatment, the median score on the mental component was 35.67 (26.91; 50.69) and on the physical component, 44.93 (33.49; 62.04). After 12 months of SCIG treatment, the median score on the mental component was 42.18 (25.6; 51.26) and on the physical component, 48.73 (29.68; 62.11) (Supplementary Table 5).
At the end of the study, 83% of patients reported that they preferred SCIG self-infusions to IVIG. The remaining patients either had no preference or preferred IVIG therapy. According to the survey, 74% of patients wanted to continue the infusions using the rapid push method, which caused no technical difficulties in 84% of respondents (Figure 6a). Although 56.3% of the patients experienced some pain during subcutaneous administration of the drug, the severity of this pain in most cases (74.6%) was mild and ranged from 0–3 on the Wong–Baker scale (Figure 6b). The retrospective nature of the study’s IVIG treatment phase did not allow for the accurate assessment of pain during intravenous infusions, but many parents of the pediatric patients reported it to be significant.
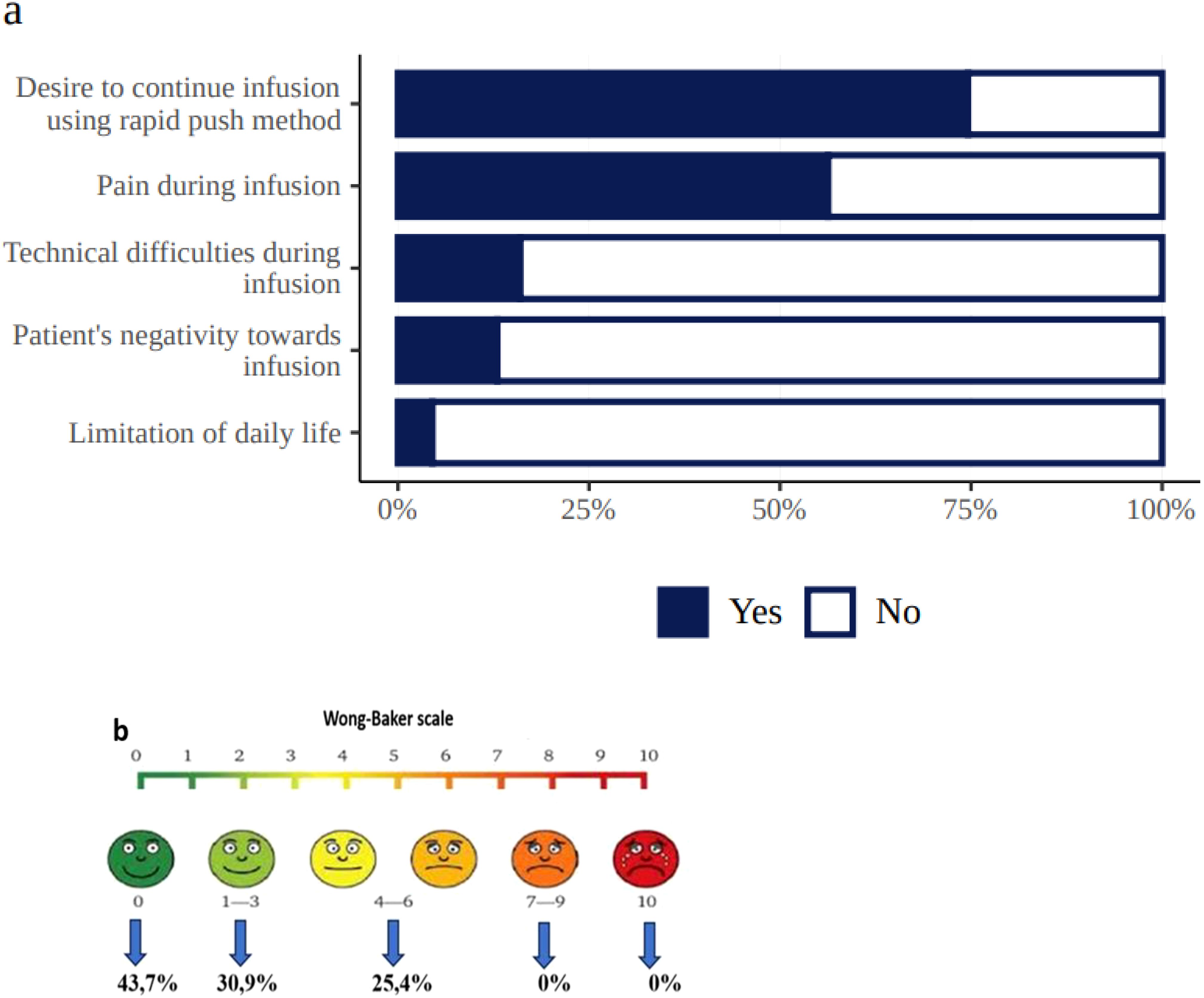
Figure 6. Patient experiences during SCIG treatment (a = treatment-related burden, b = Wong–Baker scale, demonstrating pain level distribution in 112 patients who experienced pain).
Discussion
This observational study is the first large-scale experience with SCIG in Russia, where more than 600 IEI patients currently receive SCIG, and 200 were recruited into and completed this study.
The results obtained with 16.5% SCIG substitution therapy in patients with IEI demonstrate efficacy and safety comparable or superior to that of the previously used IVIG.
SCIG at monthly doses equivalent to those of IVIG was more efficient in preventing infections, as previous studies have shown (9–11). During SCIG treatment in our study, the use of additional antibiotics to treat infections was low and comparable to the results obtained in other large studies (12, 13).
In our study infection frequency was 0.6 per patient/year. Previously published infection rates describe a yearly rate per patient of 5.18 (95% CI 4.305, 6.171) for IGSC 20% (14), 2.76 for IgPro20 (15), 3.95 for a 16% SCIG (11) and 4.1 for a 10% SCIG (12). Although it is difficult to compare efficacy results among studies due to differences in patient populations and study designs, infection rates observed in the our study are even lower than those reported for other SCIGs.
Another important parameter, the duration of antibiotics use is difficult to compare between the studies as practice of prophylactic antibiotics varies significantly between the countries and the patients’ groups. Our study demonstrates lower antibiotics use rate (12.12 days per person per year) in comparison with European centers (20.49 days per person per year) (16).
The retrospective nature of the IVIG treatment period assessment is a limitation of the present study due to the variability of the IVIG preparations used and the theoretical possibility of errors in recording the study’s parameters, yet the results and the outcomes of additional assessments (e.g., days missed from school or work, number and duration of hospitalizations) establish the high efficacy of SCIG 16.5% in the Russian cohort of IEI patients.
SCIG is administered every 3–14 days compared to every 21–28 days for IVIG. This method provides more consistent trough concentrations of serum IgG compared to the initial high peaks followed by low troughs that are associated with IVIG therapy (16, 17). In the present study, the median levels of serum IgG troughs remained above 8 g/L throughout the SCIG treatment, a result similar to that shown by Kobayashi et al. (16, 18) and one that explains the better control of the disease.
Compared to intravenous administration, subcutaneous administration of immunoglobulin is associated with a lower incidence of systemic side effects (18). Several studies have found similar low frequencies of systemic reactions to SCIG therapy in comparison with IVIG (19–21).
The incidence of systemic reactions to SCIG was also lower than reported by others (0.01 per infusion in our study vs 0.028 - 0.697 per infusion in meta-analysis by Orange et al) which yet again supports the fact that the majority of patients tolerate SCIG well (22).In the current study expected local AEs were mostly short-lived and easily managed by the patients. In addition, some local reactions at the injection site turned out to be unrelated to the injection or preparation but instead resulted from an allergic reaction to adhesive coverings used to cover the prick wound. Hence, it is important to treat atypical local reactions with this possibility in mind.
SCIG preparations have significant potential, particularly for Russian patients with IEI. In most countries, IVIG can be administered only in a hospital or outpatient clinic environment, although some centers do allow intravenous administration by nurses in the patient’s home. Russia is a vast country with some sparsely populated areas. As a result, many IEI patients must travel for many hours to reach an IVIG infusion clinic. This regular commute requires significant nonmedical expenses and time off from work or school, which in turn leads to decreased QoL and/or treatment compliance. In contrast, SCIG can be self-administered at home. As a result, SCIG administration does not interfere with daily activities and enables patients to maintain normal lifestyles.
Overall, patient‐centered outcomes showed that IEI patients preferred SCIG replacement therapy to IVIG, in line with the results of other studies (23–26). In the present study, 94% chose SCIG treatment to be conducted at home, and most were happy with the manual SCIG infusions via the rapid push method. Similarly, Shapiro showed that 71% of patients preferred the manual method compared to pump infusion (5).
In real-world practice, SCIG use in patients with thrombocytopenia of varying severity is important, yet underreported. The literature contains only very limited reports of SCIG injections in patients with thrombocytopenia (27). Pedini et al. safely used SCIG in three patients over the age of 18 with common variable immunodeficiency and immune thrombocytopenia (28). The present study demonstrates the safety of SCIG treatment—even in patients with severe thrombocytopenia—and a lack of skin AEs when platelet counts are higher than 30,000 cells/µL.
The present study also demonstrates the safety of using SCIG in patients with severe dermatitis. Skin lesions in patients with IEI are quite common, so these results are important.
In conclusion, the results of our study demonstrate that SCIG treatment was accompanied by a low frequency of infections and systemic adverse reactions and maintained protective trough levels of serum IgG. It also demonstrates the success of IRT in a hospital-free setting and a reduction in treatment-associated efforts. Importantly, it also demonstrates improvements in patients’ quality of life. The present study proves that it is possible to successfully switch from IVIG to SCIG in a large cohort of IEI patients in a country that has had very limited prior experience with SCIG therapy (29).
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics of Dmitry Rogachev National Medical Research Center of Pediatric Hematology, Oncology and Immunology, Immunology Department, Moscow, Russian Federation. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was obtained from the participants or the participants\' legal guardians/next of kin" and identifiable human data statement "Written informed consent for publication of potentially identifiable data was not obtained from the participants or the participants\' legal guardians/next of kin as no identifiable data are presented in this manuscript.
Author contributions
AA: Validation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Data curation, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Software, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Resources. ElD: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. YR: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. AMu: Data curation, Writing – original draft. EL: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. DY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. VBu: Writing – review & editing. NKa: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. DB: Validation, Writing – review & editing. AMo: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. NKu: Writing – review & editing, Validation. ZN: Writing – review & editing. EkD: Writing – review & editing. AO: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. VBl: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. AR: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DF: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. NZ: Writing – review & editing, Validation. YS: Writing – review & editing, Validation. LK: Validation, Writing – review & editing. DP: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LB: Validation, Writing – review & editing. ОS: Validation, Writing – review & editing. NS: Validation, Writing – review & editing. OL: Writing – review & editing, Validation. EV: Writing – review & editing. AG: Writing – review & editing, Validation. ETi: Validation, Writing – review & editing. OT: Writing – review & editing, Validation. MG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. NY: Validation, Writing – review & editing. EG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AI: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ZB: Writing – review & editing, Validation. DM: Writing – review & editing, Validation. SI: Validation, Writing – review & editing. AlS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ES: Writing – review & editing, Validation. TS: Validation, Writing – review & editing. EZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. IK: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. EK: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AMa: Validation, Writing – review & editing. SS: Validation, Writing – review & editing. TP: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ETy: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. PL: Software, Writing – review & editing. NG: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Software, Resources, Visualization, Project administration, Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation. AnS: Investigation, Software, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Project administration, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Octapharma grant.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and their families, as well as all the members of treating multidisciplinary teams.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1598491/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Age groups of the patients in the study.
Supplementary Table 1 | EI diagnosis.
Supplementary Table 2 | SCIG infusion parameters.
Supplementary Table 3 | Questionnaire for patients/parents of patients receiving regular immunoglobulin replacement therapy for subcutaneous administration.
Supplementary Table 4 | The results of the PEDS‐QL survey.
Supplementary Table 5 | The results of the SF-36 survey.
Abbreviations
AE, adverse events; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; IEI, inborn errors of immunity; IRT, immunoglobulin replacement therapy; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; PEDS‐QL, pediatric quality of life; SCIG, subcutaneous immunoglobulin; SF-36, short form-36; QoL, quality of life.
References
1. Poli MC, Aksentijevich I, Bousfiha AA, Cunningham-Rundles C, Hambleton S, Klein C, et al. Human inborn errors of immunity: 2024 update on the classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J Hum Immun. (2025) 1. doi: 10.70962/jhi.20250003, PMID: 31953710
2. Bonilla F, Khan D, Ballas Z, Chinen J, Frank M, Hsu J, et al. Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2015) 136:1186–205.e78. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.04.049, PMID: 26371839
3. Ochs H, Gupta S, Kiessling P, Nicolay U, and Berger M. Safety and efficacy of self-administered subcutaneous immunoglobulin in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases. J Clin Immunol. (2006) 26:265–73. doi: 10.1007/s10875-006-9021-7, PMID: 16783465
4. Peter J and Chapel H. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy for primary immunodeficiencies. Immunotherapy. (2014) 6:853–69. doi: 10.2217/imt.14.54, PMID: 25290417
5. Shapiro R. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin therapy by rapid push is preferred to infusion by pump: a retrospective analysis. J Clin Immunol. (2010) 30:301–7. doi: 10.1007/s10875-009-9352-2, PMID: 20082124
6. Shapiro RS. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin: rapid push vs. infusion pump in pediatrics. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2013) 24:49–53. doi: 10.1111/pai.2013.24.issue-1, PMID: 23331529
7. Available online at: https://data.rosmed.info/registers/patients/?id=100&type=common (Accessed July 2016).
8. Available online at: https://wongbakerfaces.org/ (Accessed August 2016).
9. Jolles S, Bernatowska E, Gracia J, Borte M, Cristea V, Peter H, et al. Efficacy and safety of Hizentra® in patients with primary immunodeficiency after a dose-equivalent switch from intravenous or subcutaneous replacement therapy. Clin Immunol. (2011) 141:90–102. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2011.06.002, PMID: 21705277
10. Krishnarajah G, Lehmann J, Ellman B, Bhak R, DerSarkissian M, Deane L Jr., et al. Evaluating dose ratio of subcutaneous to intravenous immunoglobulin therapy among patients with primary immunodeficiency disease switching to 20% subcutaneous immunoglobulin therapy. Am J Manag Care. (2016) 22:s475–81.
11. Borte M, Quinti I, Soresina A, Fernández-Cruz E, Ritchie B, Schmidt D, et al. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous Vivaglobin® replacement therapy in previously untreated patients with primary immunodeficiency: a prospective, multicenter study. J Clin Immunol. (2011) 31:952–61. doi: 10.1007/s10875-011-9588-5, PMID: 21932110
12. Wasserman RL, Melamed I, Kobrynski L, Strausbaugh SD, Stein MR, Sharkhawy M, et al. Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of a 10% liquid immune globulin preparation (GAMMAGARD LIQUID, 10%) administered subcutaneously in subjects with primary immunodeficiency disease. J Clin Immunol. (2011) 31:323–31. doi: 10.1007/s10875-011-9512-z, PMID: 21424824
13. Gupta S, DeAngelo J, Melamed I, JE W, Kobayashi A, Bridges T, et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin 16.5% (Cutaquig®) in primary immunodeficiency disease: safety, tolerability, efficacy, and patient experience with enhanced infusion regimens. J Clin Immunol. (2023) 43:1414–25. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01509-4, PMID: 37160610
14. Suez D, Stein M, Gupta S, Hussain I, Melamed I, Paris K, et al. Efficacy, Safety, and pharmacokinetics of a novel human immune globulin subcutaneous, 20 in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases in North America. J Clin Immunol. (2016) 36:700–12. doi: 10.1007/s10875-016-0327-9, PMID: 27582171
15. Hagan JB, Fasano MB, Spector S, Wasserman RL, Melamed I, Rojavin MA, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new 20 immunoglobulin preparation for subcutaneous administration, IgPro20, in patients with primary immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. (2010) 30:734–45. doi: 10.1007/s10875-010-9423-4, PMID: 20454851
16. Kobayashi RH, Gupta S, Melamed I, Mandujano JF, Kobayashi AL, Ritchie B, et al. Clinical efficacy, safety and tolerability of a new subcutaneous immunoglobulin 16.5% (Octanorm [Cutaquig®]) in the treatment of patients with primary immunodeficiencies. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:40. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00040 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1110388, PMID: 30778345
17. Latysheva E, Rodina Y, Sizyakina L, Totolian A, and Tuzankina I. Efficacy and safety of octanorm (cutaquig ®) in adults with primary immunodeficiencies with predominant antibody deficiency: aprospective, open-label study. Immunotherapy. (2020) 2:299–309. doi: 10.2217/imt-2020-0012, PMID: 32212944
18. Kobayashi RH, Litzman J, Melamed I, Mandujano JF, Kobayashi AL, Ritchie B, et al. Long-term efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a subcutaneous immunoglobulin 16.5% (cutaquig®) in the treatment of patients with primary immunodeficiencies. Clin Exp Immunol. (2022) 210:91–103. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac092, PMID: 36208448
19. Berger M. Adverse effects of IgG therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2013) 1:558–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2013.09.012, PMID: 24565701
20. Vultaggio А, Azzari Ch, Milito C, Finocchi A, Toppino C, Spadaro G, et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy in patients with primary immunodeficiency in routine clinical practice: the VISPO prospective multicenter study. Clin Drug Investig. (2015) 35:179–85. doi: 10.1007/s40261-015-0270-1, PMID: 25672929
21. Patel NC, Gallagher JL, Ochs HD, Atkinson TP, Wahlstrom J, Dorsey M, et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy with hizentra® is safe and effective in children less than 5 years of age. J Clin Immunol. (2015) 35:558–65. doi: 10.1007/s10875-015-0190-0, PMID: 26336818
22. Orange JS, Belohradsky BH, Berger M, Borte M, Hagan J, Jolles S, et al. Evaluation of correlation between dose and clinical outcomes in subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy. Clin Exp Immunol. (2012) 169:172–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04594.x, PMID: 22774992
23. Suez В, Kriván G, Jolles S, Stein M, Gupta S, Paris K, et al. Safety and tolerability of subcutaneous immunoglobulin 20% in primary immunodeficiency diseases from two continents. Immunotherapy. (2019) 11:1057–65. doi: 10.2217/imt-2019-0057, PMID: 31268374
24. Anterasian Ch, Duong R, Gruenemeier P, Ernst C, Kitsen J, and Geng B. Quality of life differences for primary immunodeficiency patients on home SCIG versus IVIG. J Clin Immunol. (2019) 39:814–22. doi: 10.1007/s10875-019-00705-5, PMID: 31673923
25. Al-Saud B, AlRumayyan N, Alfattani A, Awwad SA, Saud D, Mohammed R, et al. Quality of life evaluation in Saudi Arabian pediatric patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases receiving 20% Subcutaneous igG infusions at home. J Clin Immunol. (2023) 43:1360–6. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01507-6, PMID: 37145392
26. Warnatz K, Jolles S, Agostini C, Vianello F, Borte M, Bethune C, et al. Subcutaneous Gammanorm® by pump or rapid push infusion: Impact of the device on quality of life in adult patients with primary immunodeficiencies. Clin Immunol. (2022) 236:108938. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.108938, PMID: 35121105
27. Karastaneva A, Klobassa DS, Minkov M, Benesch M, and Seidel MG. Successful treatment with SCIG of a child with refractory chronic ITP. J Clin Immunol. (2019) 39:19–22. doi: 10.1007/s10875-018-0583-y, PMID: 30631990
28. Pedini V, Savore I, and Danieli MG. Facilitated subcutaneous immunoglobulin (fSCIg) in autoimmune cytopenias associated with common variable immunodeficiency. Isr Med Assoc J. (2017) 19:420–3., PMID: 28786256
29. Avedova A, Rodina Y, Yukhacheva D, Burlakov V, Deripapa E, and Shcherbina A. Experience with the use of immunoglobulin for subcutaneous administration (Hizentra) in the treatment of patients with primary immunodeficiency disease. Pediatr Hematology/Oncol Immunopathol. (2023) 22:92–7. doi: 10.24287/1726-1708-2023-22-2-92-97
Keywords: inborn errors of immunity, subcutaneous immunoglobulin, intravenous immunoglobulin, efficacy, safety, tolerability, quality of life, rapid push
Citation: Avedova A, Deripapa E, Rodina Y, Mukhina A, Latysheva E, Yukhacheva D, Burlakov V, Kan N, Bogdanova D, Moiseeva A, Kuzmenko N, Nesterenko Z, Deordieva E, Ogneva A, Bludova V, Roppelt A, Fomina D, Zinovieva N, Sevostyanova Y, Kalmeteva L, Prolygina D, Barycheva L, Selezneva O, Shakhova N, Laba O, Vlasova E, Gorenkova A, Timofeeva E, Trusova O, Guseva M, Yudina N, Grevtseva E, Ibisheva A, Bambaeva Z, Mashkovskaya D, Isakova S, Shakirova A, Selina E, Shilova T, Zubova E, Khabaeva I, Kitova E, Mandzhieva A, Starikova S, Pavlova T, Tyulyakova E, Levin P, Grachev N and Shcherbina A (2025) Рrospective multicenter study of treatment efficacy, safety, and quality of life in a large cohort of patients with inborn errors of immunity receiving subcutaneous immunoglobulin by the rapid push method. Front. Immunol. 16:1598491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1598491
Received: 23 March 2025; Accepted: 02 June 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Emily S. J. Edwards, Monash University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Ekaterini Simoes Goudouris, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilManuela Baronio, University of Brescia, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Avedova, Deripapa, Rodina, Mukhina, Latysheva, Yukhacheva, Burlakov, Kan, Bogdanova, Moiseeva, Kuzmenko, Nesterenko, Deordieva, Ogneva, Bludova, Roppelt, Fomina, Zinovieva, Sevostyanova, Kalmeteva, Prolygina, Barycheva, Selezneva, Shakhova, Laba, Vlasova, Gorenkova, Timofeeva, Trusova, Guseva, Yudina, Grevtseva, Ibisheva, Bambaeva, Mashkovskaya, Isakova, Shakirova, Selina, Shilova, Zubova, Khabaeva, Kitova, Mandzhieva, Starikova, Pavlova, Tyulyakova, Levin, Grachev and Shcherbina. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Asmik Avedova, YXN5YS5hdmVkb3ZhOTVAbWFpbC5ydQ==
†ORCID: Asmik Avedova, orcid.org/0000-0002-9399-6534
Elena Deripapa, orcid.org/0000-0002-9083-4783
Yulia Rodina, orcid.org/0000-0001-9857-4456
Anna Mukhina, orcid.org/0000-0002-3305-1694
Elena Latysheva, orcid.org/0000-0002-1606-205X
Daria Yukhacheva, orcid.org/0000-0001-9078-8206
Vasily Burlakov, orcid.org/0000-0003-1267-9957
Nellie Kan, orcid.org/0000-0003-3564-6496
Daria Bogdanova, orcid.org/0000-0003-2897-5208
Anna Moiseeva, orcid.org/0000-0002-6134-3811
Natalia Kuzmenko, orcid.org/0000-0002-1669-862
Zoya Nesterenko, orcid.org/0000-0003-4427-054X
Ekaterina Deordieva, orcid.org/0000-0002-8208-2075
Anna Ogneva, orcid.org/0000-0002-8697-4206
Victoria Bludova, orcid.org/0000-0003-0960-3089
Anna Roppelt, orcid.org/0000-0001-5132-1267
Daria Fomina, orcid.org/0000-0002-5083-6637
Natalia Zinovieva, orcid.org/0000-0002-6926-2055
Yulia Sevostyanova, orcid.org/0009-0004-4328-7803
Linara Kalmeteva, orcid.org/0000-0003-1866-0640
Dilara Prolygina, orcid.org/0000-0002-5797-4370
Lyudmila Barycheva, orcid.org/0000-0002-4069-0566
Olga Selezneva, orcid.org/0000-0003-1907-4168
Natalya Shakhova, orcid.org/0000-0002-7143-8259
Olga Laba, orcid.org/0000-0001-5784-1263
Elena Vlasova, orcid.org/0000-0002-6678-5360
Alla Gorenkova, orcid.org/0009-0008-2514-1594
Elena Timofeeva, orcid.org/0000-0003-3908-1947
Olga Trusova, orcid.org/0000-0002-0854-1536
Marina Guseva, orcid.org/0000-0002-3997-3390
Natalya Yudina, orcid.org/0009-0001-7498-0836
Evgeniya Grevtseva, orcid.org/0009-0004-9437-4851
Asya Ibisheva, orcid.org/0000-0003-4732-4515
Zema Bambaeva, orcid.org/0000-0002-7541-2793
Dina Mashkovskaya, orcid.org/0009-0000-4995-0427
Svetlana Isakova, orcid.org/0009-0007-8368-5250
Almazia Shakirova, orcid.org/0000-0001-9975-3632
Ekaterina Selina, orcid.org/0009-0003-6545-1435
Tatyana Shilova, orcid.org/0000-0001-9826-9654
Elena Zubova, orcid.org/0000-0002-9755-8929
Iman Khabaeva, orcid.org/0009-0008-7161-4540
Ekaterina Kitova, orcid.org/0009-0001-6004-2558
Anastasia Mandzhieva, orcid.org/0009-0002-7068-2601
Svetlana Starikova, orcid.org/0000-0002-4321-7301
Tatyana Pavlova, orcid.org/0000-0003-3403-4447
Elvira Tyulyakova, orcid.org/0009-0005-1642-4398
Pavel Levin, orcid.org/0000-0002-2410-1223
Nikolay Grachev, orcid.org/0000-0002-4451-3233
Anna Shcherbina, orcid.org/0000-0002-3113-4939
 Asmik Avedova
Asmik Avedova Elena Deripapa1†
Elena Deripapa1† Anna Mukhina
Anna Mukhina Elena Latysheva
Elena Latysheva Natalia Kuzmenko
Natalia Kuzmenko Zoya Nesterenko
Zoya Nesterenko Natalia Zinovieva
Natalia Zinovieva Linara Kalmeteva
Linara Kalmeteva Lyudmila Barycheva
Lyudmila Barycheva Olga Selezneva
Olga Selezneva Natalya Shakhova
Natalya Shakhova Olga Laba
Olga Laba Zema Bambaeva
Zema Bambaeva Anna Shcherbina
Anna Shcherbina