- Department of Dermatology, State Key Laboratory of Complex Severe and Rare Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Dermatologic and Immunologic Diseases, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of low-dose rituximab (RTX) in the treatment of pemphigus.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov to identify eligible studies. Primary efficacy outcomes included complete remission (CR), relapse rates, time to disease control (TDC), time to CR, and cumulative corticosteroid dose. Safety outcomes were assessed by meticulously documenting adverse events (AEs) and concomitant medications reported in each study.
Results: The final analysis incorporated five comparative studies and nine single-arm studies investigating the efficacy and safety outcomes of low-dose RTX. Comparative data revealed no statistically significant differences between the high-dose and low-dose RTX groups in CR, relapse rates, TDC, time to CR, and cumulative corticosteroid dose. In single-arm studies, pooled CR and relapse rates were 63.2% and 28.6%, respectively. No fatal events were reported; however, severe AEs, including pneumonia and sepsis, were documented in the low-dose RTX cohort.
Conclusion: Low-dose RTX exhibited comparable clinical efficacy to high-dose RTX regimens in pemphigus management. However, clinicians should remain vigilant for potential AEs associated with low-dose RTX infusion.
1 Introduction
Pemphigus is a group of rare, recurrent, and potentially life-threatening dermatological disorders characterized by flaccid blisters and erosions of the skin and/or mucous membranes. The pathogenesis of pemphigus is attributed to the abnormal production of autoantibodies targeting desmoglein 1 and/or 3, key components of desmosomal adhesion, leading to the loss of keratinocyte intercellular adhesion (1). Clinically, pemphigus can be categorized into two main types: pemphigus vulgaris (PV) and pemphigus foliaceus (PF) (2).
Systemic corticosteroids have long been the cornerstone of first-line therapy for pemphigus. However, the administration of high cumulative corticosteroids doses is associated with significant adverse events (AEs), including hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia, osteoporosis, and gastrointestinal complications such as bleeding and ulceration (3). To mitigate these risks, several immunosuppressants, including azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, and dapsone, are often used as steroid-sparing agents to reduce complications (4). Recently, biological therapies have emerged as a promising therapeutic option, particularly for refractory or severe cases in which conventional treatments fail to achieve adequate disease control (DC) (3).
Rituximab (RTX), a chimeric murine/human anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has been approved for refractory pemphigus due to its targeted depletion of pathogenic B lymphocytes, offering a promising therapeutic option (5). The landmark Ritux 3 study demonstrated superior outcomes in moderate-to-severe PV patients treated with a combination of RTX and short-term prednisone compared to prednisone alone (6). Despite its established efficacy, no consensus exists regarding the optimal RTX dosing regimen for pemphigus. Various regimens have been adopted in clinical practice. The most commonly used protocols include the lymphoma protocol (four weekly infusions of 375 mg/m2 RTX), and the rheumatoid arthritis (RA) protocol (two infusions of 1000 mg RTX 14 days apart) (7).
Unlike lymphoma patients, pemphigus patients exhibit significantly lower B-cell burden. Emerging evidence indicates that reduced RTX doses can achieve therapeutic efficacy, with studies reporting complete remission (CR) after a single 250 mg RTX dose and sustained B-cell depletion for up to 6 months (8). Pharmacodynamic studies in healthy volunteers have demonstrated that a single ultra-low dose of RTX (1 mg/m2) effectively depletes CD20+ cells (9), supporting the biological plausibility of dose reduction strategies. Low-dose RTX regimens appear to be safer and more affordable, driving growing clinical interest in their application. A meta-analysis conducted in 2015 examined the efficacy of different RTX regimens for pemphigus patients and found no significant difference in CR or relapse rates between high-dose and low-dose RTX protocols (10). However, new studies have emerged over the past decade, highlighting the need for an updated evaluation of low-dose RTX in the treatment of pemphigus. This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to provide an updated evidence synthesis on the efficacy and safety of low-dose RTX in patients with pemphigus. We anticipate that our findings will contribute to evidence-based practice, potentially facilitating more personalized, cost-effective therapeutic approaches while maintaining clinical efficacy.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
We conducted a systematic review of the literature by searching the following databases: PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov. The search spanned from the inception of each database to November 20, 2024, and was designed to identify eligible studies without restrictions on language, nationality, ethnicity, age, or cost. The search keywords were “low-dose RTX” and “pemphigus”, and the search strategy in PubMed was as follows: (“pemphigus” OR “pemphigus vulgaris” OR “pemphigus foliaceus”) AND (low-dose RTX).
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Our inclusion criteria for studies in this analysis were as follows: (1) Both prospective and retrospective studies, including comparative and single-arm designs; (2) Studies involving patients diagnosed with pemphigus who were treated with low-dose RTX; (3) Studies providing data on efficacy and/or safety endpoints, including CR, relapse rates, time to disease control (TDC), time to CR, cumulative corticosteroid dose and AEs; (4) Patients enrolled in clinical studies.
Studies were excluded if they met any of the following criteria: (1) Sample cohort size (<5 patients); (2) Significant baseline disease severity disparities between groups in comparative studies prior to RTX treatment; (3) Enrollment of pediatric patients (age<18 years); (4) Patients with concurrent bullous pemphigoid (BP), mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP), or other autoimmune bullous diseases (AIBDs), or those who transformed into BP, MMP, or other AIBDs; (5) Concurrent use of intravenous immunoglobulins with RTX; (6) Incomplete data or missing key efficacy/safety endpoints; (7) Non-original research (review, meta-analysis, case report) or preclinical studies (cell or animal-based research).
2.3 Quality assessment
Two investigators (SH L and SH W) independently conducted the quality assessment, with any discrepancies resolved through discussion and adjudication by a third author (YG Z). The quality of included randomized controlled trials was evaluated using the Modified Jadad scale (11), while the quality of non-randomized comparative studies and single-arm studies was assessed using the Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS) (12). The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach (13) was used to evaluate the quality of evidence for our meta-analysis outcomes. All assessments were independently conducted by two investigators, followed by discussion until consensus was reached. Publication bias was evaluated by visual inspection of funnel plot asymmetry.
2.4 Data extraction
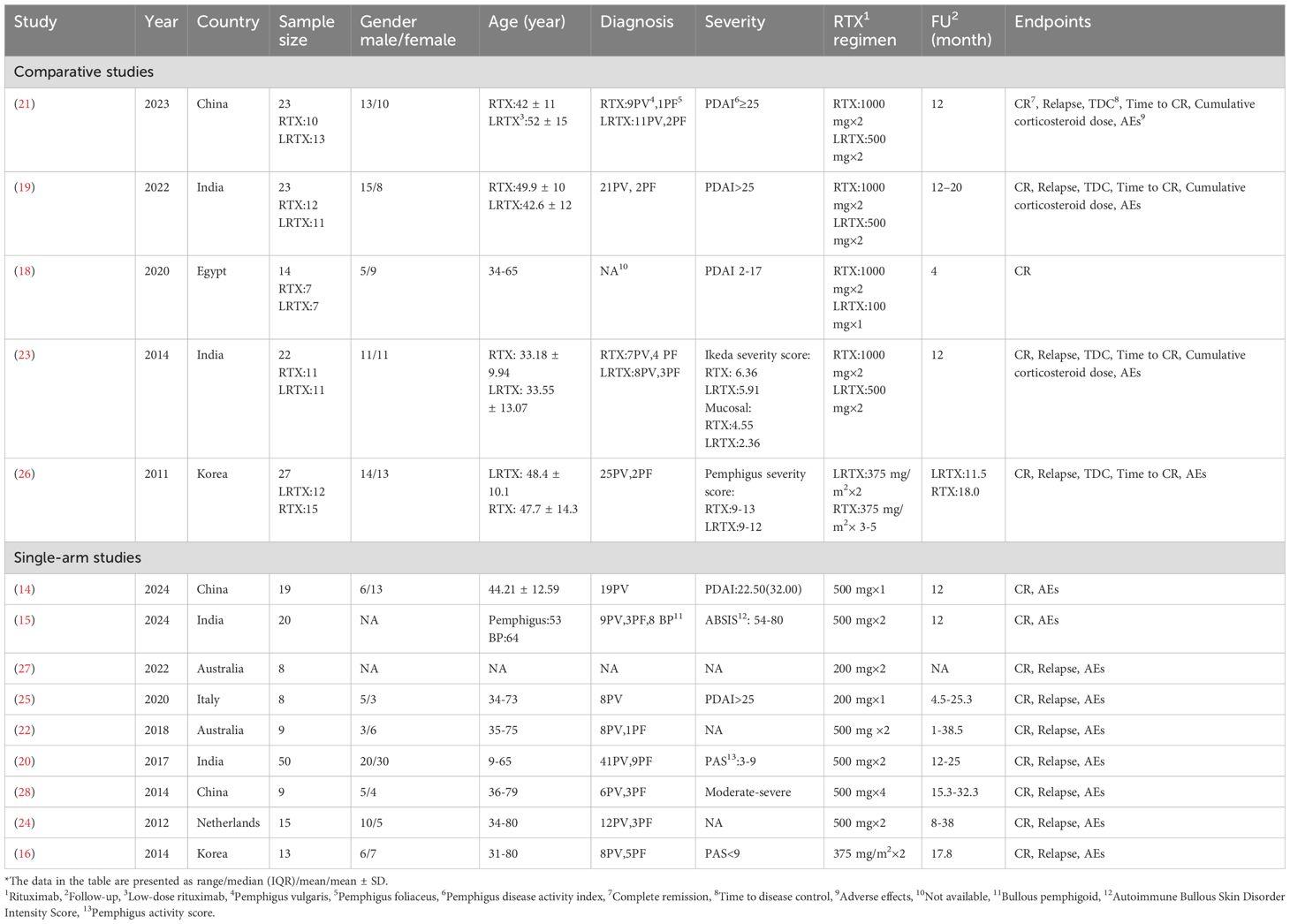
Study selection was independently performed by the first and second authors (SH L and SH W), with any discrepancies resolved by a third author (YG Z). The following details from the included studies were meticulously documented: authorship, publication year, country, sample size, gender, age, diagnosis, RTX therapeutic regimen, disease severity, follow-up duration, and endpoints. Efficacy outcomes (CR, relapse rates, TDC, time to CR, and cumulative corticosteroid dose) and safety outcomes (AEs) were captured in individually designed data sheets. Although Zhou X, et al. (14) reported outcomes for the low-dose RTX group, the comparative group did not receive high-dose RTX; therefore, it was classified as a single-arm study. In the study by Metta Parvathi et al. (15), which included both pemphigus and BP patients, data were extracted solely for the pemphigus patients. The study by Cho et al. (16) was treated as a single-arm study due to a significant difference in pemphigus severity between the high-dose and low-dose groups at baseline, rendering the comparative outcome unsuitable for our meta-analysis.
2.5 Definition
The definitions of DC, CR, and relapse were developed according to the consensus statement published in 2008 by the International Pemphigus Committee (17). DC was defined as the cessation of new lesion formation and the beginning of healing of established lesions. CR was defined as the absence of new or established lesions for at least two months. CR can be further subdivided into CR ON therapy and CR OFF therapy based on treatment status; however, these were not distinguished in this article. Relapse was defined as the appearance of three or more new lesions in a month that do not heal spontaneously within one week, or the extension of established lesions, in patients who previously achieved DC. Most included studies followed the definitions mentioned above, except for two studies. One study (18) didn’t provide a specific definition for CR in the original text, while another (19) defined relapse as CD19+ B-cell repopulation exceeding 1% of the total lymphocyte count (immunological relapse).
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Review Manager Version 5.4.1. For comparative studies, we calculated risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for dichotomous outcomes and the Standardized Mean difference (SMD) for continuous data. A two-tailed p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. In single-arm studies, data were transformed from Odds Ratio to obtain pooled results. Heterogeneity between studies was assessed using the I2 statistic. For pooled findings with low heterogeneity (I2 < 50%), a fixed-effects model was employed; otherwise, a random-effects model was employed. In cases of high heterogeneity (I² ≥50%), sensitivity analysis was conducted by excluding each study to evaluate its impact on the pooled results.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection and characteristics
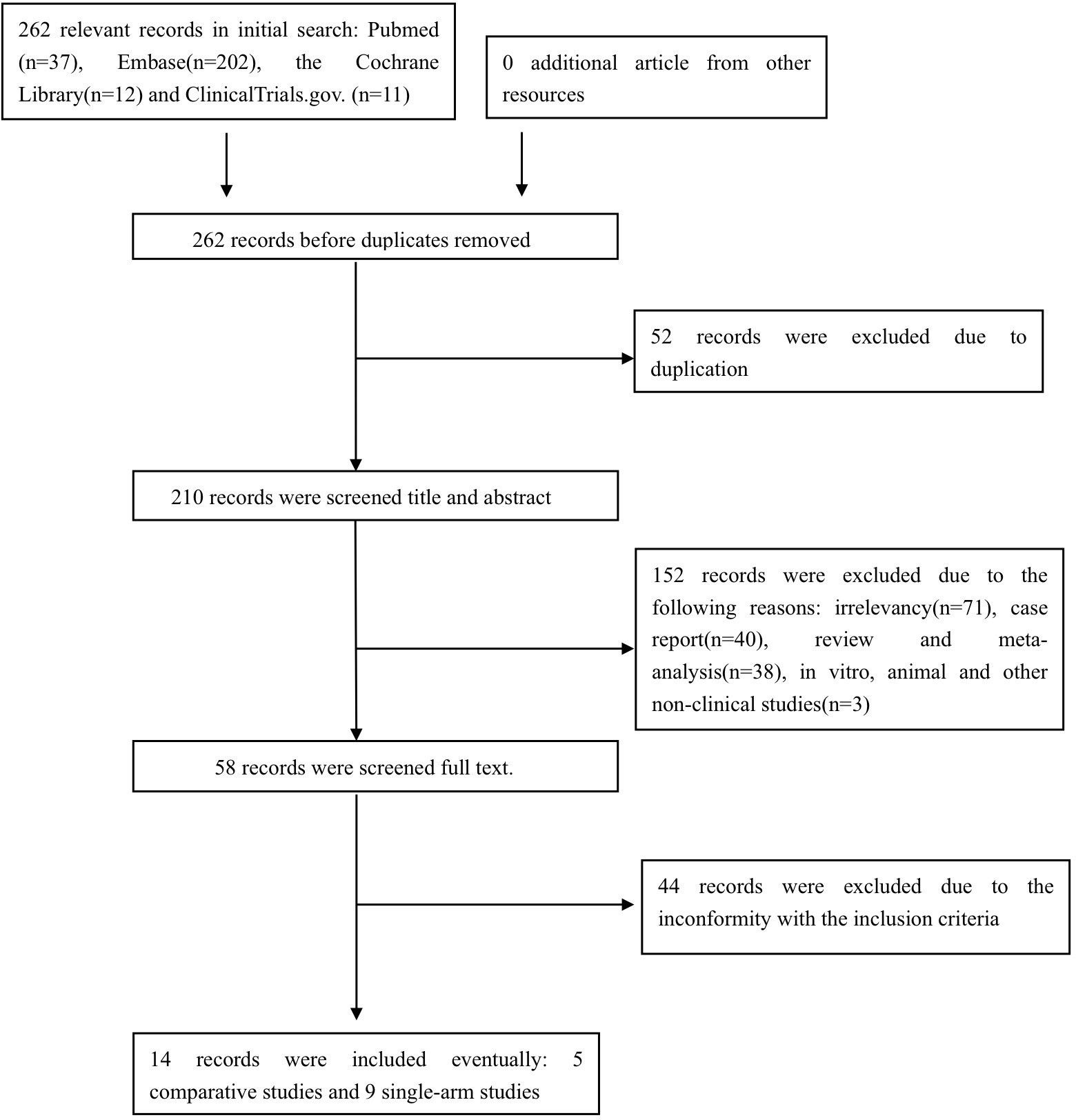
The preliminary search identified pertinent references in PubMed (n =37), Embase (n = 202), the Cochrane Library (n = 12), and ClinicalTrials.gov (n = 11). After excluding duplicated, irrelevant, or ineligible studies, a total of 14 studies (14–16, 18–28) comprising 252 pemphigus patients were included in the final analysis, comprising nine prospective and five retrospective studies, with five comparative and nine single-arm study designs. The study selection process is illustrated in Figure 1.
The studies originated from various countries: four from India, three from China, two each from Australia and Korea, and one each from the Netherlands, Egypt and Italy. It is important to note that the definition of low-dose RTX used in this analysis is distinct from the traditional RA and lymphoma protocols, with the most frequently used regimen being two infusions of 500 mg (adopted in seven studies: 15, 19–24). Alternative RTX regimens included single infusions of 1000 mg (18), 500 mg (14), or 200 mg (25), two infusions of 375 mg/m2 (16, 26), and double infusions of 200 mg (27). Although the total dose of the four-infusion 500 mg regimen (28) is equivalent to that of the RA protocol, its reduced per-infusion dosage qualified it as low-dose RTX in our analysis. The characteristics of the included studies are detailed in Table 1.
3.2 Quality assessment
Eleven studies (14–16, 20–22, 24–28) were evaluated using MINORS, with scores ranging from 11 to 14. These scores indicate satisfactory methodological quality, meeting the threshold for inclusion in this meta-analysis. Three randomized controlled trials (18, 19, 23) were assessed using the Modified Jadad scale, yielding scores of 4, 5, and 6, respectively, reflecting high quality methodology. Comprehensive quality assessment details are presented in Supplementary Table S1. The quality of evidence for our meta-analysis outcomes was evaluated and is presented in Supplementary Table S2. These results demonstrate high confidence in the findings on TDC, moderate confidence in the results on CR rate, time to CR, and cumulative corticosteroid dose, and limited confidence in the results on relapse rate. The funnel plots are presented in Supplementary Figures S1-S3.
3.3 Efficacy
3.3.1 CR
The CR rate was reported in five comparative studies (18, 19, 21, 23, 26) which included a total of 109 patients treated with low-dose (n=54) and high-dose RTX (n=55). Pooled analyses from comparative studies revealed no significant difference in CR rate between the low-dose and high-dose RTX groups (RR, 1.01, 95% CI: 0.78 to 1.31, I2 = 60%, P = 0.92) (Figure 2A). Further comparison of the CR rate between the subgroups receiving two infusions of 1000 mg and 500 mg RTX (19, 21, 23) also showed no significant difference (RR:1.12, 95% CI: 0.97 to 1.30, I2 = 26%, P = 0.13) (Figure 2B). In the pooled analysis of nine single-arm studies (14–16, 20, 22, 24, 25, 27, 28), the overall CR rate was 63.2% (95% CI: 54.3% to 71.3%, I2 = 48%, P = 0.04) (Figure 2C). Among these, four single-arm studies (15, 20, 22, 24) utilized the protocol of two infusions of 500 mg RTX, with a pooled CR rate of 63.1% (95% CI: 42.2% to 80.0%, I2 = 64%, P = 0.22) (Figure 2D).
![(A) Forest plot comparing low-dose and high-dose rituximab using risk ratios. Five studies are analyzed with overall risk ratio 1.01 [0.78, 1.31]. (B) Forest plot comparing low-dose and high-dose rituximab with fixed effects. Three studies are analyzed, showing a risk ratio of 1.12 [0.97, 1.30]. (C) Forest plot displaying odds ratios for various studies, exploring experimental versus control groups. The overall odds ratio is 1.72 [1.19, 2.49]. (D) Similar plot to (C) with random effects, showing an overall odds ratio of 1.71 [0.73, 4.01].](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1605243/fimmu-16-1605243-HTML/image_m/fimmu-16-1605243-g002.jpg)
Figure 2. Forest plot of CR rate. (A) Five comparative studies (B) Three comparative studies comparing 2 infusions of 1000mg versus 500mg RTX (C) Nine single-arm studies (D) Four single-arm studies using two infusions of 500mg RTX.
3.3.2 Relapse
The relapse rate was reported in four comparative studies (19, 21, 23, 26), which included a total of 95 patients treated with low-dose (n=47) and high-dose RTX (n=48). Pooled analyses from these comparative studies revealed no significant difference in the relapse rate between low-dose and high-dose RTX groups (RR: 2.06, 95% CI: 0.77 to 5.49, I2 = 60%, P =0.15) (Figure 3A). Further comparison of the relapse rate between the subgroups receiving two infusions of 1000 mg and 500 mg RTX (19, 21, 23) also showed no significant difference (RR: 1.54, 95% CI: 0.98 to 2.40, I2 = 0%, P = 0.06) (Figure 3B). In the pooled analysis of seven single-arm studies (16, 20, 22, 24, 25, 27, 28), the overall relapse rate was 28.6% (95% CI: 13.8% to 50.2%, I2 = 67%, P = 0.05) (Figure 3C). Among these, three single-arm studies (20, 22, 24) utilized the protocol of two infusions of 500 mg RTX, with a pooled relapse rate of 23.1% (95% CI: 7.4% to 53.5%, I2 = 76%, P = 0.08) (Figure 3D).
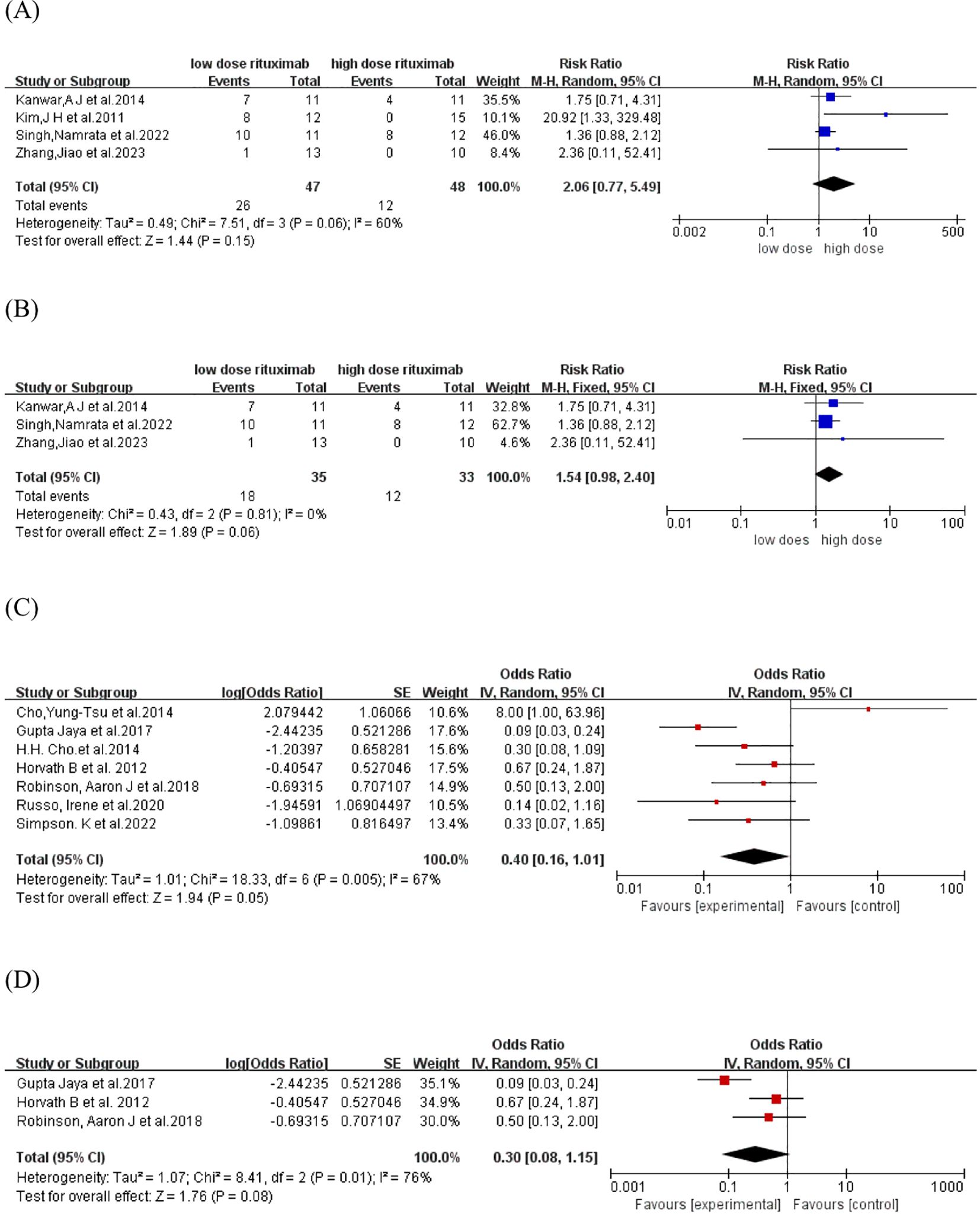
Figure 3. Forest plot of relapse rate. (A) Four comparative studies (B)Three comparative studies comparing 2 infusions of 1000mg versus 500mg RTX (C) Seven single-arm studies (D) Three single-arm studies using two infusions of 500mg RTX.
3.3.3 TDC, time to CR
TDC and time to CR were reported in four comparative studies (19, 21, 23, 26), which included 95 patients treated with low-dose RTX (n=47) and high-dose RTX (n=48). Pooled analyses from comparative studies revealed no significant difference in TDC or time to CR between the low-dose and high-dose RTX groups (SMD: -0.26, -0.09, 95% CI: -0.67 to 0.15, -1.14 to 0.95, I2 = 0%, 83%, P = 0.21, 0.86) (Figures 4A, B).
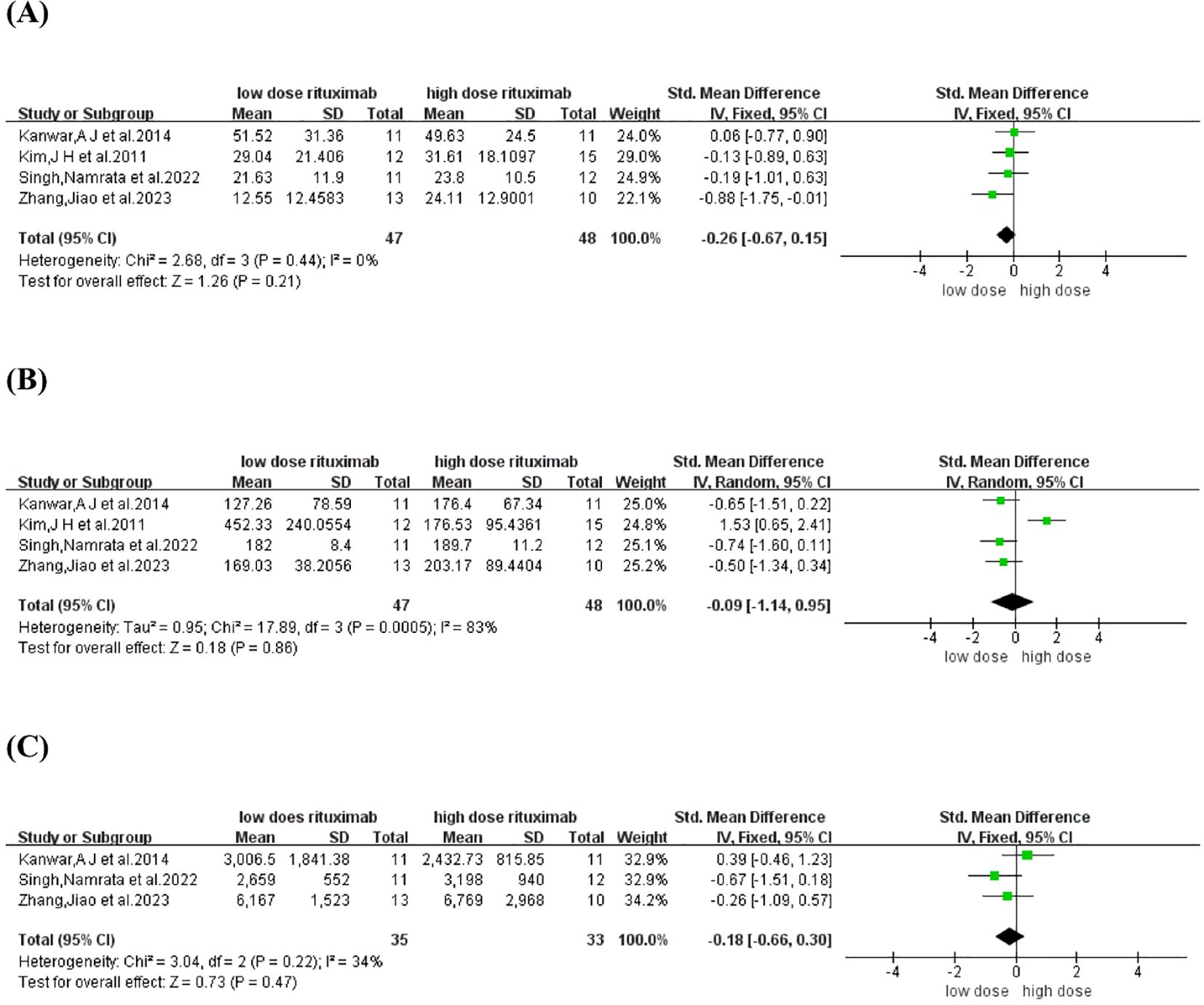
Figure 4. Forest plot of (A) time to disease control (B) time to CR (C) Cumulative corticosteroid dose.
3.3.4 Cumulative corticosteroid dose
Cumulative corticosteroid dose was reported in three comparative studies (19, 21, 23), which included 68 patients treated with low-dose (n=35) and high-dose RTX (n=33). Pooled analyses from these comparative studies revealed no significant difference in cumulative corticosteroid dose between low-dose and high-dose RTX groups (SMD: -0.18, 95% CI: -0.66 to 0.30, I2 = 34%, P = 0.47) (Figure 4C).
3.4 Safety
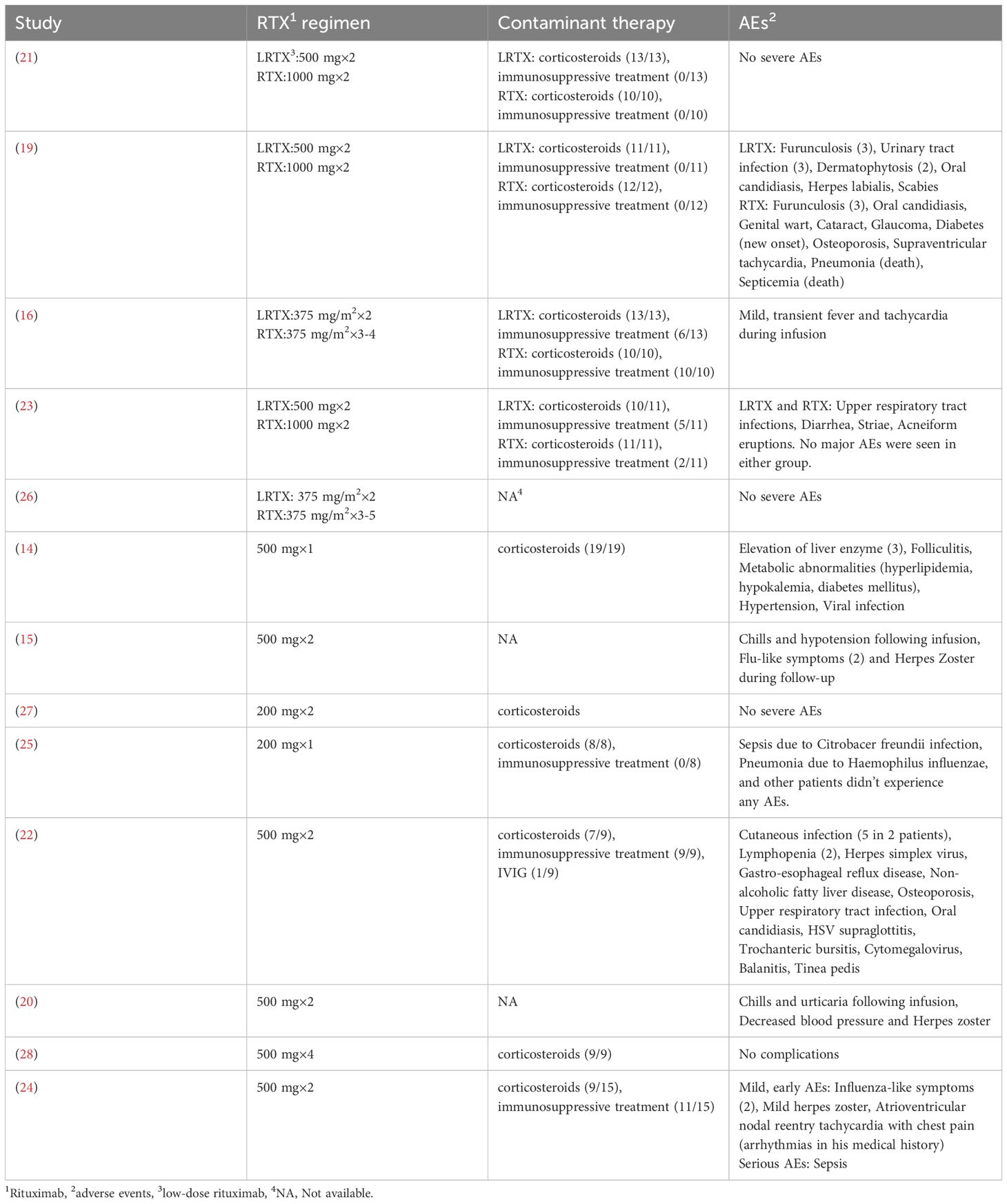
AEs related to RTX infusion were reported in thirteen studies. Two deaths due to pneumonia and sepsis occurred in patients who received two infusions of 1000 mg RTX. Additionally, three patients who received either a single infusion of 200 mg RTX or two infusions of 500 mg RTX survived episodes of pneumonia and sepsis. No deaths were reported in the low-dose RTX group. The most common AEs were infections, including viral, bacterial, and fungal. Infusion-related reactions, including transient fever, tachycardia, chills, hypotension, and urticaria, were also observed, emphasizing the need for close monitoring during administration. However, attributing all AEs solely to RTX remains challenging due to the concurrent use of other medications, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. The overlapping AE profiles complicate the identification of the primary causative agent. A summary of the reported AEs and concomitant medications from each included study is presented in Table 2.
4 Discussion
RTX has become increasingly pivotal in the treatment of pemphigus, though the optimal dosing regimen has not been fully established. Our meta-analysis demonstrated comparable clinical efficacy between low-dose and high-dose RTX regimens, with no statistically significant differences in CR or relapse rates, consistent with previous findings (10). Moreover, we innovatively demonstrated that the low-dose RTX cohort did not prolong TDC or time to CR, nor did it increase the overall cumulative corticosteroid dose compared to high-dose RTX. The pooled CR and relapse rates in single-arm studies were 63.2% and 28.6%, respectively. Importantly, while severe infections were documented in the low-dose RTX group, no treatment-related mortality was observed, supporting its overall safety profile when administered with appropriate monitoring.
Beyond pemphigus, low-dose RTX has been used to treat various autoimmune blistering diseases, including BP, MMP, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and linear IgA disease (29–32). Ultra-low dose RTX protocols have also been explored for pemphigus treatment. For instance, two PV patients were successfully treated with a single intravenous infusion of 200 mg RTX (33). A case report from China described a refractory PV patient who achieved total clearance of skin lesions three months after a single infusion of 100 mg RTX (34). Additionally, a large case series involving 16 PV patients reported a satisfactory CR rate (93.75%) after two infusions of 100 mg RTX (35). However, these preliminary findings require validation through controlled trials. Ongoing studies are exploring optimized administration schedules, such as a modified lymphoma protocol with extended infusion intervals, which has shown favorable outcomes with reduced side effects (36).
Relapse remains a common and challenging issue in clinical practice, imposing significant emotional and economic burden on patients. Mucosal involvement (37), anti-desmoglein3 IgG subclasses (particularly IgG3) (38), and delayed RTX initiation (39, 40) have been identified as key predictors of disease relapse in pemphigus patients treated with RTX.
Our study advances current understanding by incorporating novel single-arm meta-analyses and subgroup analyses while confirming previous conclusions (10). However, we acknowledge several limitations in our study. First, due to the rarity of pemphigus, only 14 articles comprising 252 patients were included in this meta-analysis. Second, the accuracy of the pooled outcomes may be affected by differences in disease severity, treatment regimens, and follow-up duration. Third, we were unable to directly compare the incidence of AEs between the low-dose and high-dose RTX groups due to insufficient detailed information in the original studies.
In the future, we anticipate more prospective, large-scale, randomized controlled trials to definitively establish dose-response relationships and compare protocol efficacy (RA vs. lymphoma regimens). Such efforts will facilitate the development of personalized, cost-effective treatment algorithms that maximize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing both clinical and economic burdens for pemphigus patients worldwide.
Author contributions
SL: Writing – original draft. SW: Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7232118), National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (2022-PUMCH-B-092) and National Key Clinical Specialty Project of China.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the supports from the Beijing Natural Science Foundation, National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding and National Key Clinical Specialty Project of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1605243/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Schmidt E, Kasperkiewicz M, and Joly P. Pemphigus. Lancet (London England). (2019) 394:882–94. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31778-7
2. Kasperkiewicz M, Ellebrecht CT, Takahashi H, Yamagami J, Zillikens D, Payne AS, et al. Pemphigus. Nat Rev Dis primers. (2017) 3:17026. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.26
3. Buonavoglia A, Leone P, Dammacco R, Di Lernia G, Petruzzi M, Bonamonte D, et al. Pemphigus and mucous membrane pemphigoid: An update from diagnosis to therapy. Autoimmun Rev. (2019) 18:349–58. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.02.005
4. Zhao W, Wang J, Zhu H, and Pan M. Comparison of guidelines for management of pemphigus: a review of systemic corticosteroids, rituximab, and other immunosuppressive therapies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2021) 61:351–62. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08882-1
5. Frampton JE. Rituximab: A review in pemphigus vulgaris. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2020) 21:149–56. doi: 10.1007/s40257-019-00497-9
6. Chen DM, Odueyungbo A, Csinady E, Gearhart L, Lehane P, Cheu M, et al. Rituximab is an effective treatment in patients with pemphigus vulgaris and demonstrates a steroid-sparing effect. Br J Dermatol. (2020) 182:1111–9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18482
7. Joly P, Horvath B, Patsatsi A, Uzun S, Bech R, Beissert S, et al. Updated S2K guidelines on the management of pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus initiated by the european academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol: JEADV. (2020) 34:1900–13. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16752
8. Lazzarotto A, Ferranti M, Meneguzzo A, Sacco G, and Alaibac M. Persistent B lymphocyte depletion after an ultralow dose of rituximab for pemphigus vulgaris. J investigational allergology Clin Immunol. (2018) 28:347–8. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0283
9. Schoergenhofer C, Schwameis M, Firbas C, Bartko J, Derhaschnig U, Mader RM, et al. Single, very low rituximab doses in healthy volunteers - a pilot and a randomized trial: implications for dosing and biosimilarity testing. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:124. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17934-6
10. Wang HH, Liu CW, Li YC, and Huang YC. Efficacy of rituximab for pemphigus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of different regimens. Acta dermato-venereologica. (2015) 95:928–32. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2116
11. Bañares R, Albillos A, Rincón D, Alonso S, González M, Ruiz-del-Arbol L, et al. Endoscopic treatment versus endoscopic plus pharmacologic treatment for acute variceal bleeding: a meta-analysis. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2002) 35:609–15. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31354
12. Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, and Chipponi J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J surgery. (2003) 73:712–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
13. Granholm A, Alhazzani W, and Møller MH. Use of the GRADE approach in systematic reviews and guidelines. Br J Anaesth. (2019) 123:554–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2019.08.015
14. Zhou X, Zhan T, Xu X, Lan T, Hu H, Zhou Y, et al. The efficacy and safety of low-dose rituximab in the treatment of pemphigus vulgaris: a cohort study. J Dermatol Treat. (2024) 35:2302071. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2024.2302071
15. Parvathi M, Rao DE, Kanthi B, Sagar GP, Rameesa A, and Guruprasad P. Efficacy and safety of low-dose rituximab in the treatment of immunobullous disorders. Int J Acad Med Pharmacy. (2024) 6:960–6. doi: 10.47009/jamp.2024.6.1.189
16. Cho HH, Jin SP, and Chung JH. Clinical experiences of different dosing schedules of rituximab in pemphigus with various disease severities. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol: JEADV. (2014) 28:186–91. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12080
17. Murrell DF, Dick S, Ahmed AR, Amagai M, Barnadas MA, Borradori L, et al. Consensus statement on definitions of disease, end points, and therapeutic response for pemphigus. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2008) 58:1043–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.01.012
18. Saleh MA and Saleh NA. A randomized study comparing full dose and half dose of rituximab in relapsing pemphigus patients. Dermatologic Ther. (2020) 33:e14349. doi: 10.1111/dth.14349
19. Singh N, Handa S, Mahajan R, Sachdeva N, and De D. Comparison of the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of an immunologically targeted low-dose rituximab protocol with the conventional rheumatoid arthritis protocol in severe pemphigus. Clin Exp Dermatol. (2022) 47:1508–16. doi: 10.1111/ced.15213
20. Gupta J, Raval RC, Shah AN, Solanki RB, Patel DD, Shah KB, et al. Low-dose rituximab as an adjuvant therapy in pemphigus. Indian J dermatology venereology leprology. (2017) 83:317–25. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_1078_14
21. Zhang J, Huang X, Zhang Z, Zhao P, Chen W, Liang Y, et al. Clinical observation of different doses of rituximab for the treatment of severe pemphigus: A single-center prospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2023) 88:500–2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2022.06.1187
22. Robinson AJ, Vu M, Unglik GA, Varigos GA, and Scardamaglia L. Low-dose rituximab and concurrent adjuvant therapy for pemphigus: Protocol and single-centre long-term review of nine patients. Australas J Dermatol. (2018) 59:e47–52. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12571
23. Kanwar AJ, Vinay K, Sawatkar GU, Dogra S, Minz RW, Shear NH, et al. Clinical and immunological outcomes of high- and low-dose rituximab treatments in patients with pemphigus: a randomized, comparative, observer-blinded study. Br J Dermatol. (2014) 170:1341–9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12972
24. Horváth B, Huizinga J, Pas HH, Mulder AB, and Jonkman MF. Low-dose rituximab is effective in pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. (2012) 166:405–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10663.x
25. Russo I, Miotto S, Saponeri A, and Alaibac M. Ultra-low dose rituximab for refractory pemghigus vulgaris: a pilot study. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2020) 20:673–8. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2020.1727440
26. Kim JH, Kim YH, Kim MR, and Kim SC. Clinical efficacy of different doses of rituximab in the treatment of pemphigus: a retrospective study of 27 patients. Br J Dermatol. (2011) 165:646–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10411.x
27. Simpson K, Low ZM, Yap T, Kern JS, and Scardamaglia L. Ultralow-dose rituximab in pemphigus: a single-centre experience. Br J Dermatol. (2022) 186:581–3. doi: 10.1111/bjd.20819
28. Cho YT, Lee FY, Chu CY, and Wang LF. First-line combination therapy with rituximab and corticosteroids is effective and safe for pemphigus. Acta dermato-venereologica. (2014) 94:472–3. doi: 10.2340/00015555-1746
29. Amir Dastmalchi D, Moslemkhani S, Bayat M, Balighi K, Abedini R, Mahmoudi H, et al. The efficacy of rituximab in patients with mucous membrane pemphigoid. J Dermatol Treat. (2022) 33:1084–90. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2020.1801974
30. Suárez-Carantoña C, Jiménez-Cauhé J, González-García A, Fernández-Guarino M, and Asunción Ballester M. Low-dose rituximab for bullous pemphigoid. Protocol and single-center experience. Actas dermo-sifiliograficas. (2023) 114:T62–t8. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2021.10.018
31. Lamberts A, Euverman HI, Terra JB, Jonkman MF, and Horváth B. Effectiveness and safety of rituximab in recalcitrant pemphigoid diseases. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:248. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00248
32. Chen Q, Hu B, Wan L, Hu L, Zhou X, Chen L, et al. Three cases of refractory bullous pemphigoid in the elderly treated successfully with ultra-low-dose rituximab. J Dermatol. (2023) 50:561–4. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16668
33. Ciolfi C, Tartaglia J, and Alaibac M. Is it time to reconsider rituximab dosing regimens for pemphigus vulgaris? Antibodies (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 13(1):4. doi: 10.3390/antib13010004
34. Wang YA, Lee JY, and Yang CC. Sustainable effect of ultra-low dose rituximab for mild-to-moderate pemphigus vulgaris: A case report. J Dermatol. (2021) 48:e583–e4. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16145
35. Patel NH, Padhiyar JK, Patel JR, Patel KA, Lakum MP, Oza YP, et al. A study of ultra-low dose rituximab as adjuvant to standard of care in treatment of significant and extensive pemphigus vulgaris: a case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2024) 91(6):1243–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2024.07.1506
36. Londhe PJ, Kalyanpad Y, and Khopkar US. Intermediate doses of rituximab used as adjuvant therapy in refractory pemphigus. Indian J dermatology venereology leprology. (2014) 80:300–5. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.136832
37. Cho SI, Kim JW, Lim JS, and Chung JH. Mucosal involvement is a risk factor for poor clinical outcomes and relapse in patients with pemphigus treated with rituximab. Dermatologic Ther. (2019) 32:e12814. doi: 10.1111/dth.12814
38. Golinski ML, Lemieux A, Maho-Vaillant M, Barray M, Drouot L, Schapman D, et al. The diversity of serum anti-DSG3 IgG subclasses has a major impact on pemphigus activity and is predictive of relapses after treatment with rituximab. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:849790. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849790
39. Balighi K, Daneshpazhooh M, Mahmoudi H, Badakhsh M, Teimourpour A, Ehsani AH, et al. Comparing early and late treatments with rituximab in pemphigus vulgaris: which one is better? Arch Dermatol Res. (2019) 311:63–9. doi: 10.1007/s00403-018-1881-1
40. Balighi K, Hatami P, Sheikh Aboli MJ, Daneshpazhooh M, Ghiasi M, Mahmoudi HR, et al. Multiple cycles of rituximab therapy for pemphigus: A group of patients with difficult- to-treat disease or a consequence of late rituximab initiation? Dermatologic Ther. (2022) 35:e15249. doi: 10.1111/dth.15249
Keywords: meta-analysis, pemphigus, rituximab, safety, treatment outcome
Citation: Liu S-H, Wang S-H and Zuo Y-G (2025) Efficacy and safety of low dose rituximab in pemphigus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1605243. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1605243
Received: 03 April 2025; Accepted: 20 June 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Animesh A. Sinha, University at Buffalo, United StatesReviewed by:
Xiaoguang Li, Daqing Oilfield General Hospital, ChinaXue Ruzeng, Southern Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Wang and Zuo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ya-Gang Zuo, enVveWFnYW5nQDI2My5uZXQ=
 Si-Han Liu
Si-Han Liu Si-Hang Wang
Si-Hang Wang Ya-Gang Zuo
Ya-Gang Zuo