- 1Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Emergency Department, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 3Emergency Department, Shanxi Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital, Shanxi, China
Atherosclerosis is a chronic vascular inflammatory disease in which macrophages play a pivotal role in modulating its pathology. In response to the intraplaque microenvironment, both pro-inflammatory M1 and anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes of macrophages have the polarization capability, each influencing the inflammatory state through the secretion of distinct cytokines. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification, the most prevalent internal chemical modification of RNA, significantly impacts various biological processes, including RNA transcription and protein expression. m6A modification acts as a critical determinant in macrophage polarization, with its molecular mechanisms intricately linked to the progression of atherosclerosis. This review aims to elucidate how different macrophage polarization phenotypes influence the progression of atherosclerosis while also exploring the significance of m6A modifications in this pathological context, thereby providing a theoretical foundation for identifying novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases represent a major category of disorders that pose a substantial threat to human health and life. Globally, approximately 16.7 million individuals die each year from cardiovascular diseases, making them the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Atherosclerosis (AS), recognized as the primary etiological factor for myocardial necrosis, ischemic stroke, coronary artery disease, and other cardiovascular condition (1), is characterized by arterial wall thickening and stiffening, elasticity loss, lumen narrowing, and yellow atheromatous plaques accumulation in the intima, qualifying as a chronic vascular inflammatory disease with complex pathophysiology. Theories including lipid infiltration, oxidation, and injury response have been proposed to elucidate its pathogenesis. Currently, it is widely accepted that endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, macrophages, and lymphocytes play crucial roles in the development of AS (2). In the pathogenesis of AS, macrophages play a pivotal role in driving AS progression. They prompt to plaque formation, degrade components of the fibrous cap and necrotic core, intensify inflammatory responses, and induce apoptosis of smooth muscle cells and leukocytes within the plaque (3). Additionally, macrophages are actively involved in lipid metabolism by regulating proliferation and migration, secreting various inflammatory factors, and phagocytosing lipids, dead cells, and other debris (4, 5). Shaped by a complex interplay of microbial factors and cytokine networks in their immediate microenvironment, macrophages, as one of the most plastic cell types in the immune system, exhibit diverse polarization states upon activation (6). These polarization states result in the classification of macrophages into various subtypes based on their functional characteristics and surface molecule expression. Specifically, M1 and Mox macrophages promote lesion development through the expression of pro-inflammatory factors (7), while M2 and Mhem macrophages mitigate disease progression by exerting anti-inflammatory effects (8). The pivotal role of macrophages in AS is closely tied to these diverse polarization subtypes, which are integral to all aspect of AS pathogenesis (9). Epigenetic modifications serve as regulatory mechanisms that influence gene expression without altering the fundamental DNA sequence, thereby shaping various biological processes such as gene expression, aging, and disease development (10). Among these modifications, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most prevalent and abundant epigenetic marks found in eukaryotic RNAs (11). Studies have demonstrated that m6A modification plays a crucial role in tissue and cellular metabolic processes associated with AS (12, 13). Specifically, m6A modification has been shown to promote endothelial inflammatory responses and facilitate the formation of AS plaque, whereas inhibiting m6A modification reduces endothelial inflammation and mitigates AS progression in mice (14). The established roles of m6A modification in regulating tissue cell metabolism and promoting atherosclerotic plaque formation highlight its potential to elucidate macrophage polarization as a critical frontier in atherosclerosis mechanism research. In this review, we investigate the association between distinct macrophage polarization subtypes and AS, as well as the impact of m6A modification on macrophage polarization in AS. This review aims to provide novel insights and solid evidence for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of AS.
2 Role of macrophage polarization in AS
2.1 Macrophage polarization
Macrophages undergo polarization into distinct subtypes in response to stimuli from the intraplaque microenvironment. These subtypes display characteristic gene and protein expression profiles (15, 16). Specifically, macrophages can polarize into two primary subpopulations: classically activated macrophages (M1) and alternatively activated macrophages (M2), each exhibiting distinct functional properties (17).
M1 macrophages originate from Ly6Chigh monocytes, establishing pro-inflammatory traits and marked by CD86 and CD16/32 surface markers (18). These cells are primarily triggered by TLR ligands such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and Th1-type cytokines like interferon-γ. LPS activates the canonical NF-κB pathway, leading to increased expression of inflammatory genes including TNF-α and interleukin-12 (IL-12), both of which are hallmarks of M1 polarization. Interferon-γ, on the other hand, activates signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), promoting the expression of downstream target genes in M1 macrophages, such as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and IL-12 (19). Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3), an inhibitor of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, is induced via interferon signaling and plays a role in suppressing the M1 pro-inflammatory phenotype (20). Actually, M1 macrophages exhibit potent antimicrobial and antitumor activities, while also contributing to ROS-induced tissue damage (21).
M2 macrophages originate from Ly6Clow monocytes, which exhibit anti-inflammatory properties (18). These monocytes are polarized into the M2 phenotype by Th2-type cytokines IL-4 or IL-13 through the activation of STAT6 via IL-4Rα (22). Additionally, these macrophages express mannose receptor, arginase 1, and dectin-1 on their surface (23, 24). The IL-4/STAT6 pathway induces ligand-dependent peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) expression, thereby facilitating M2 polarization (25). PPAR-γ upregulates various subsets of genes related to anti-inflammatory function, including arginase 1, cysteine-rich secretory proteins, and IL-10 (26), all of which are crucial for maintaining the M2 phenotype. M2 macrophages act as a pivotal factor in immune regulation, tissue remodeling, wound healing, and angiogenesis (27, 28).
2.2 Effects of different polarization states on AS
M1 and M2 macrophages exhibit distinct functions and are distributed in different regions within the atherosclerotic plaque. These differences influence the development of AS due to their varying protein expression patterns and levels. The progression of AS is characterized by a reduction in number of M2 macrophages within the plaque, a decreased M2/M1 ratio, and elevated levels of inflammatory factors and matrix metalloproteinases (29, 30). Furthermore, the diverse polarization phenotypes of macrophages can affect plaque regression by promoting plaque size reduction and enhancing stability (31, 32).
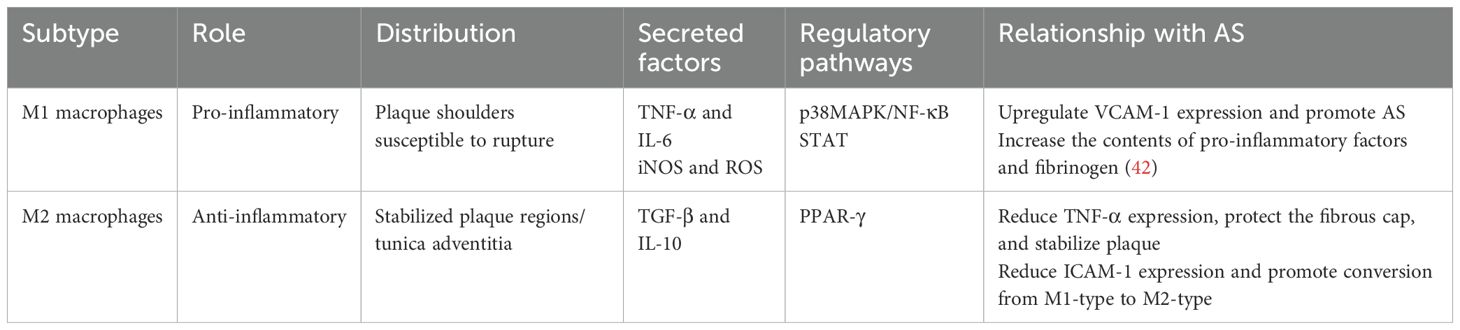
Atherosclerotic plaques can be categorized into stable and unstable types. Unstable plaques, also known as vulnerable plaques, are characterized by their rapid progression and higher risk of rupture and thrombus formation. M1 macrophages predominate in unstable plaques and secrete elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, inducible iNOS, and ROS (8). After lipid uptake, M1 macrophages produce and secrete high level of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, IL-15, IL-18, and TNF-α, through multiple complex mechanisms, thereby triggering a robust inflammatory response. The expression of TNF-α is regulated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK)/NF-κB pathway (33), which upregulates vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression and promotes atherogenesis (34, 35). In contrast, IL-6 expression is controlled by the STAT pathway (36) and influences nearly all cells involved in atherogenesis by enhancing cytokine and adhesion molecule expression, as well as promoting the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells (37).
M2 macrophages play a crucial role in plaque stabilization, comprising a substantial proportion of the plaque microenvironment. They secrete cytokines such as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and IL-10 (38). TGF-β not only inhibits natural killer cell activity and TNF-α production but also stimulates collagen synthesis and fibroblast proliferation, thereby reinforcing the fibrous cap and enhancing plaque stability (39) IL-10 reduces TNF-α production, downregulates the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) on endothelial cells, facilitates the polarization of M1-type macrophages towards the M2 phenotype, and exhibits anti-AS effects (Table 1) (40, 41).
The shoulder region of atherosclerotic plaques, being the thinnest part, is particularly susceptible to rupture (43) M1 macrophage markers are predominantly localized in the shoulders of rupture-prone plaques, while M2 macrophage markers are primarily observed in the tunica adventitia or stable plaque regions (44). Moreover, cytokines derived from both M1 and M2 macrophage induce osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of smooth muscles cells, thereby promoting arterial vascular calcification, which subsequently affects the stability of AS plaques (45). Calcification, a hallmark of AS, is considered one of the principal risk factors for plaque rupture (46). Both M1 and M2 macrophages play significant roles in vascular calcification. The initial calcium deposition in the necrotic core of the lesion by M1 macrophages is termed microcalcification (47), whereas calcium deposition associated with M2 macrophages is referred to as macrocalcification. Macrocalcification tends to stabilize plaque, while microcalcification increases the likelihood of plaque rupture (48).
Importantly, M1 and M2 macrophages exhibit plasticity and can interconvert. Feig et al. (49) utilized a transgenic approach to enhance lipid metabolism in mice, demonstrating that M2 macrophages are reprogrammed into M1 macrophages during plaque progression. Conversely, during atherosclerotic plaque regression, the expression of CD68+ inflammatory cells decreases within the plaque, while the expression of M2 macrophage marker genes increases, indicating a shift from M1-type to M2-type macrophages. These findings suggest that the balance between M2 to M1 macrophages may play a critical role in both the progression and regression of AS plaques.
Harmon et al. (50) induced the transformation of intraplaque macrophages toward the M2 macrophages in ApoE-/- mice and observed reduced intraplaque inflammatory factor activity and enhanced plaque stability, as evidenced by histological analysis. This indicates that M2 macrophages play a crucial role in mitigating the inflammatory response and stabilizing atherosclerotic plaques in hypercholesterolemic mice. Rahman et al. (51) compared M2 macrophages expression between chemokine receptor-deficient mice and normolipidemic controls, revealing significant plaque regression and increased M2 macrophage labeling in that chemokine receptor-deficient mice. These findings indicate that M2 macrophages are essential for reducing inflammation and promoting plaque regression.
However, M2 macrophages have been demonstrated to facilitate foam cell formation and augment the number of foam cells in atherosclerotic lesions (52), suggesting that their role in AS progression, particularly concerning foam cell formation, is still under debate. This paradoxical phenomenon can be attributed to the heterogeneity of M2 macrophages or disparities in the microenvironment. M2 macrophages can be further categorized into M2a, M2b, and M2c subtypes, each potentially exhibiting distinct functions in lipid metabolism and inflammatory modulation (53). Moreover, microenvironmental signals—such as plaque lipid composition, cytokine hyperactivation, or hypoxic stress—may steer their differentiation pathways (54), thereby enabling M2 macrophages to exhibit dual roles in both “promoting foam cell formation” and “facilitating plaque stabilization”. As a result, the role of M2 macrophages in atherosclerosis (AS) is not unidirectionally protective. Unraveling the mechanistic interplay between M2 macrophages and foam cell formation required more in-depth investigations, particularly focusing on the functional profiling of different M2 subtypes various pathological stages.
3 m6A modification and macrophage polarization
3.1 General molecular mechanisms processes of m6A modification
m6A is a reversible biological modification characterized by the methylation of the amino group at position 6 of adenosine. This modification predominantly localizes to the termination codon, the 3’untranslated region (UTR), and the exon RRACH sequence (55). m6A exhibits conservative, dynamic and reversible properties, which are regulated by various proteins and enzymes, including methyltransferase, demethylase, and m6A-specific binding proteins (56). This epigenetic modification influences multiple cellular processes such as RNA splicing, processing, mRNA stability, and gene expression regulation, thereby playing a crucial role in mammalian development and disease progression (57).
In the nucleus, the methyltransferase complex and demethylases collaboratively regulate the distribution and extent of m6A modification on RNA. Meanwhile, reader proteins control the selective splicing, nuclear export, translation, and degradation of m6A-modified RNA (58).
3.1.1 m6A methyltransferases
The methyltransferase complex, often referred to as the “writer”, plays a crucial role in catalyzing the transfer of methyl groups. This complex primarily comprises methyltransferase-like (METTL) enzymes such as METTL3, METTL14, and METTL16, along with the regulatory subunit Wilms’ tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) (59). METTL3 is the catalytically active subunit that utilizes S-adenosylmethionine to provide the methyl group, thereby playing a pivotal role in the methylation process (60). As the core enzyme of the methyltransferase complex, METTL3 not only catalyzes methyl transfer but also influences gene expression by stably recruiting the complex to specific gene loci and facilitating RNA transport to ribosomes (61). METTL14 provides an RNA-binging platform, that synergistically enhances the methytransferase’s affinity for RNA substrates, thereby stabilizing the complex (62). Although WTAP lacks methyltransferase activity, it interacts with the METTL3–METTL14 complex and plays a critical role in modulating the nuclear localization of the complex, thus influencing the efficiency of methylation (63, 64).
3.1.2 m6A demethylases
The primary function of m6A demethylases, also known as erasers, is to remove methyl groups from RNAs bearing m6A modification. These demethylases include the fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) and the alkylated DNA repair enzyme ALKB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) (65). Both proteins belong to the ALKB family but employ distinct mechanisms for demethylation. Specifically, ALKBH5 catalyzes demethylation in a single step without generating intermediate products (66), while FTO primarily catalyzes demethylation via an oxidation reaction that requires Fe (II) and 2-oxoglutarate (67). This process yields two intermediates, N6-hydroxymethyladenosine and N6-formyladenosine, which ultimately transform into adenine and formaldehyde (71). Moreover, FTO can demethylate various nucleotides, including m6A, whereas ALKBH5 specifically targets m6A (68).
3.1.3 m6A-binding proteins
m6A methylation sites are recognized by a variety of m6A-binding proteins, which play essential roles in regulating RNA metabolism, processing, translation, and stability. These m6A-binding proteins(readers), specifically recognize m6A modifications and predominantly comprise YTH domain-containing proteins, including the YTHDF family (YTHDF1, YTHDF2, and YTHDF3) and YTHDC family (YTHDC1 and YTHDC2) (69). These proteins bind to m6A modification sites on RNA molecules, regulating translation efficiency and stability of m6A-modified mRNAs to influence various physiological and pathological processes (70).
YTHDF2 was identified as the first m6A-binding protein that promotes mRNA degradation and destabilizes target transcripts (71). YTHDF1 enhances mRNA translation, thereby promoting protein synthesis. YTHDF3, which is closely related to YTHDF1 and YTHDF2, plays a crucial role in facilitating the specific binding of YTHDF1and YTHDF2 to RNA. Functionally, YTHDF3 collaborates with YTHDF1 to boost the translation of methylated mRNA, facilitate protein synthesis, and augment YTHDF2-mediated mRNA degradation and instability (72). By integrating and cooperating with m6A methylation modifications, YTHDF1–3 collectively regulate mRNA metabolism, processing, translation, and degradation. In contrast, YTHDC1 regulates nuclear mRNA splicing (73) and mediates nuclear export via RNA methylation (74). YTHDC2, featuring multiple RNA-binding domains, is a key m6A-binding protein in reproductive system development and maturation. It enhances mRNA translation efficiency by binding to m6A sites (75).
m6A modification significantly multiple facets of mRNA metabolism, including stability, translation efficiency, alternative splicing, and intracellular transport. This epigenetic mark serves an indispensable function in a broad spectrum of physiological and pathological processes, such as stem cell differentiation, immune response modulation, and tumorigenesis (Figure 1) (76, 77).
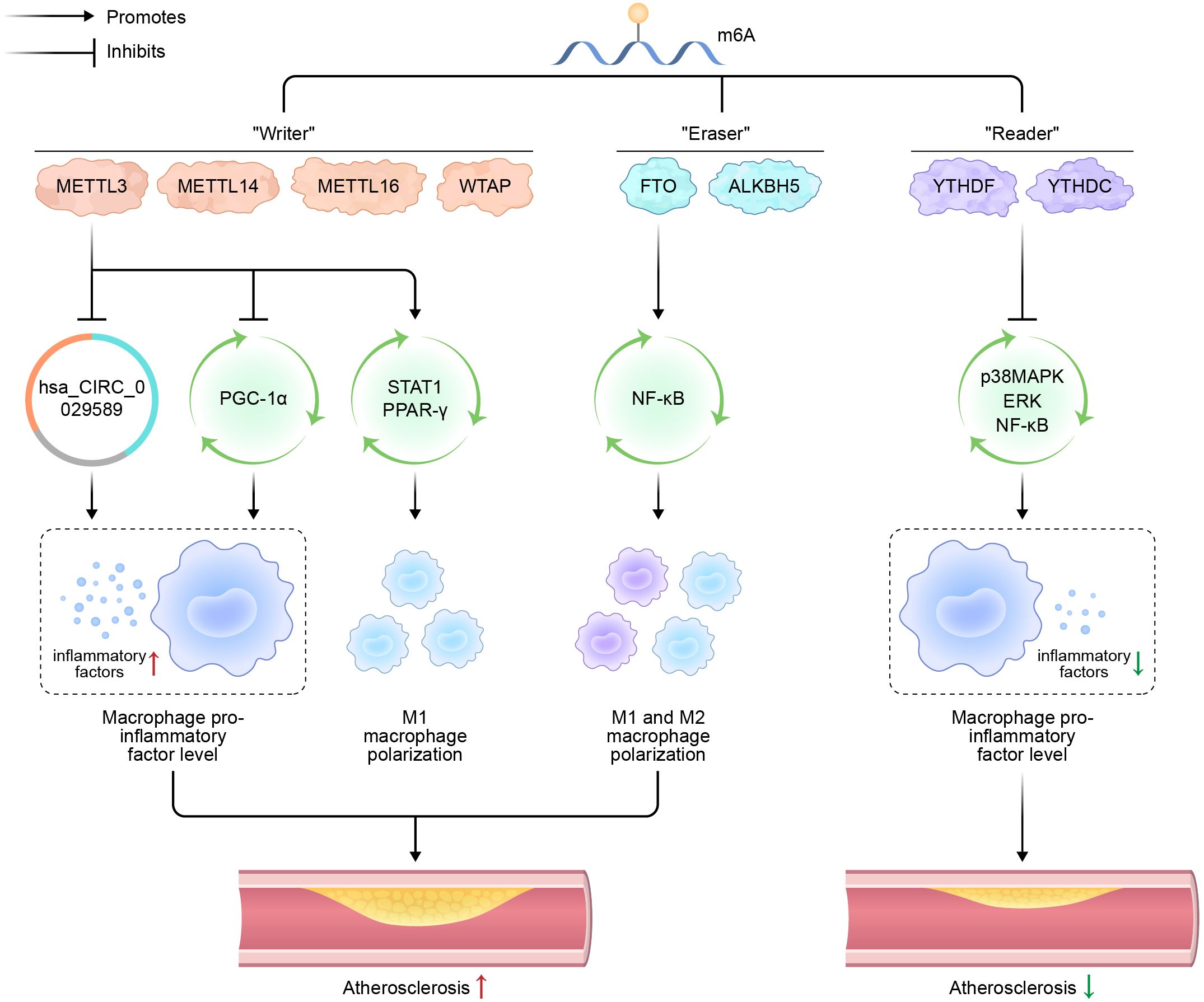
Figure 1. Schematic representation of m6A modification, macrophage polarization, and atherosclerosis.
N6-methyladenosine (m6A); methyltransferases-like (METTL); Wilms’ tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP); fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) protein; alkane hydroxylase homolog 5 (ALKBH5); circular RNA (hsa_CIRC_0029589); peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator (PGC)-1α; signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1); peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors (PPARs); nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB); p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK).
3.2 Effect of m6A modification on AS
Cellular structural damage and dysfunction caused by endothelial cell inflammation are pivotal mechanisms in the pathogenesis and progression of AS. D. Jian et al. (14) demonstrated through RNA co-immunoprecipitation experiments that METTL14 directly interacts with FOXO1 mRNA and recognizes its methylation sites via YTHDF1, thereby enhancing the translation efficiency of FOXO1 mRNA. The knockout of METTL14 reduces inflammation-induced FOXO1 expression and alleviates endothelial cells inflammation, consequently slowing the progression of AS. These findings suggest that m6A methylation plays a crucial role in vascular endothelial cell inflammation and the development of AS.
Moreover, it was observed that Atorvastatin reduced the expression of FTO in vascular endothelial cells. Knockdown of FTO led to upregulation of Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), while simultaneously downregulating endothelial expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, which are typically induced by inflammatory stimuli. By employing methylated RNA co-immunoprecipitation coupled with dual-luciferase reporter assays, researchers demonstrated that FTO directly interacts with KLF2 and eNOS. This interaction enables the modulation of their expression via an m6A modification-dependent mechanism (78).
X. Zhang et al. (79) demonstrated that ALKBH5 expression is downregulated in endothelial cells undergoing TNF-α-induced apoptosis. Upon upregulation of ALKBH5, the apoptotic rate of TNF-α-treated endothelial cells decreased, accompanied by an increase in BCL2 expression. Importantly, silencing BCL2 abolished the protective effect of ALKBH5 on TNF-α-induced apoptosis, indicating that ALKBH5 exerts its anti-apoptotic function in vascular endothelial cells through upregulation of BCL2.
Furthermore, it has been proved that m6A methylation is of crucial importance in regulating the angiogenesis of endothelial cells. Specifically, METTL3 knockdown continuously activates the Notch signal pathway, thereby significantly influencing endothelial cell angiogenesis (80). WTAP, another critical subunit of the methyltransferase complex, regulates desmosome protein expression through m6A methylation. Decreased WTAP expression can inhibit endothelial cell angiogenesis (81). Additionally, ALKBH5 has been shown to maintain endothelial cell angiogenesis under acute ischemic stress by reducing SPHK1 m6A methylation and modulating downstream eNOS-AKT signal transduction (82).
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) exhibit phenotypic and functional plasticity in response to vascular injury. Following vascular injury, VSMCs can transition from a quiescent, contractile phenotype to a synthetic state, which is marked by elevated rates of proliferation, migration, secretion and production of extracellular matrix components. Chronic inflammatory stimulation impairs the regulatory functions of VSMCs, leading to reduce contractile capacity and heightened secretory activity. This ultimately results in arterial wall thickening and stenosis (2).
The occurrence of AS is closely associated with post-angiogenesis restenosis. Intimal hyperplasia, primarily driven by the proliferation and migration of VSMCs, is one of the key factors contributing to arterial restenosis. Zhu et al. (83) investigated m6A methylation in the carotid arteries of rats following balloon injury. Their study demonstrated that both m6A methylation levels and WTAP expression were significantly reduced after injury. However, it was found that administration of total saponins extracted from Panax notoginseng increased WTAP expression, thereby enhancing the m6A methylation of the downstream target gene p16. This process concurrently suppressed the proliferation and migration of VSMCs. These findings suggest that WTAP regulates p16 expression via m6A methylation, consequently modulating the viability, proliferation, and migration of VSMCs.
Similarly, B.-F. Zhang et al. (84) demonstrated that m6A methylation plays a critical role in the insulin resistance-induced abnormal proliferation of VSMCs. Their study revealed elevated FTO levels in VSMCs treated with insulin and in type 2 diabetic mice with intimal injury. Furthermore, genetic ablation of FTO significantly suppressed the insulin-induced pathological proliferation and migration of VSMCs.
Y. Qin et al. (85)demonstrated that under hypoxic conditions resulted in elevated expression of METTL3 and YTHDF2 in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) as well as in a rodent model subjected to hypoxia. Silencing METTL3 was found to significantly reduce the proliferation and migratory capabilities of PASMCs. In another study, it was reported that hypoxia-induced adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) exhibited upregulated expression of METTL3, along with increased secretion of paracrine factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), which promoted their differentiation into VSMCs. These findings indicate that hypoxic stress not only promotes the differentiation of ASCs into VSMCs but also coordinates the expression of paracrine factors via METTL3 regulation consequently affecting cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation processes (86).
To sum up, existing studies have demonstrated that m6A methylation not only influences the biological functions of vascular endothelial cells but also modulates the activity, migration, and proliferation of VSMCs, thereby affecting the pathogenesis and progression of AS.
3.3 Effect of m6A on macrophage polarization
The role of m6A in the immune system is evident across three critical areas: immune recognition, activation of both innate and acquired immune responses, and differentiation immune cells. For example, specific deletion of METTL3 in CD4+ T cells disrupts their dynamic homeostasis and differentiation (87). Furthermore, viral infection in host cells leads to reduced expression of the m6A eraser ALKBH5, which subsequently modulates cellular metabolism to inhibit viral replication (88).
Regarding macrophage polarization, Liu et al. (89) induced M1 polarization in mouse peritoneal macrophages and observed a significant upregulation of METTL3 at both mRNA and protein levels, suggesting a robust correlation between METTL3 expression and M1 polarization in these cells. In subsequent experiments, METTL3 was either inhibited or overexpressed in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) using transfection techniques. The expression levels of key regulators of macrophage polarization, including interferon regulatory factor-5 (IRF5), STAT1, and NF-κB, were subsequently evaluated. The findings demonstrated that METTL3 mediates STAT1 mRNA methylation, thereby enhancing its mRNA stability, upregulating STAT1 expression, promoting M1 macrophage polarization, inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization, and participating in inflammatory responses.
Furthermore, a significant relationship has been established between the m6A demethylase FTO and macrophage polarization. Gu et al. (6) demonstrated that FTO expression was significantly downregulated during both M1 and M2 polarization of BMDMs, where M1 polarization was induced by E. coli LPS and interferon-γ, while M2 polarization was triggered by IL-4. Notably, the suppression of FTO expression impaired the polarization of both M1 and M2 macrophage. Further investigations revealed that FTO modulates the NF-κB signaling pathway and influences the stability of STAT1 and PPAR-γ. Specifically, FTO knockdown inhibits the NF-κB signaling cascade and destabilizes STAT1 and PPAR-γ, which are essential for macrophage polarization mediated by YTHDF2. These findings underscore the critical role of FTO in regulating macrophage polarization.
hsa_CIRC_0029589, a circular RNA, is upregulated in vascular smooth muscle cells of hyperlipidemia patients (90). Guo et al. (91) reported that in peripheral blood macrophages from patients with acute coronary syndrome, hsa_CIRC_0029589 expression is decreased while METTL3 expression is increased. Inhibition of METTL3 leads to a decrease in the methylation level of hsa_CIRC_0029589, resulting in its upregulation. Conversely, interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1) enhances METTL3 expression within macrophages, thereby suppressing hsa_CIRC_0029589 expression. These findings suggest that IRF-1 inhibits the expression of hsa_CIRC_0029589 via enhanced m6A modification, thereby subsequently facilitating macrophage pyroptosis and amplifying inflammatory responses in AS.
Cai et al. (92) recently demonstrated that in endotoxin-stimulated macrophages, the knockout of METTL3 leads to a significant reduction in its expression, along with an upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. Further experiments demonstrated that METTL3 deletion inhibits YTHDF2-mediated degradation of NOD1 and RIPK2 mRNA, resulting in upregulation of the NOD1 pathway and subsequent enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage inflammation. These findings suggest that METTL3 negatively regulates LPS-induced inflammation.
Additionally, Yu et al. (93) shown that inhibiting YTHDF2 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages enhances the stability of MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 mRNA. This stabilization subsequently enhances the activation of inflammatory pathways for instance p38MAPK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and the NF-κB pathway, resulting elevated levels of downstream inflammatory molecules, including IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-12. These findings indicate that YTHDF2 acts as a negative regulator of the LPS-induced inflammatory response in macrophages. Furthermore, X. Zhang et al. (94) Showed that METTL3 and YTHDF2 jointly suppress PGC-1α expression in THP-1 macrophages, leading to increased accumulation of cellular and mitochondrial ROS, and heightened expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
4 Summary and outlook
Macrophages exhibit significant heterogeneity in AS. As key components of the innate immune system, macrophages play a crucial role in regulating various physiological and pathological states through their M1 and M2 polarization, which substantially influences AS progression. Specifically, M1-type macrophages secrete pro-inflammatory factors, whereas M2-type macrophages produce anti-inflammatory factors. The dynamic shifts in the quantity and proportion of these two phenotypes within plaque tissue have a substantial impact on plaque development. m6A, a reversible RNA modification, plays a critical role in disease and treatment by modulating gene expression. Moreover, m6A profoundly affects macrophage polarization and cytokine secretion in AS. A thorough investigation into the interactions among polarization, m6A modification, and AS development is essential for identify novel targets for diagnosing and treating AS.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – original draft. ZY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YH: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Basic research expenditures for the Program for Outstanding Young Scientific and Technological Talents Special Training Program (innovation) at the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences: Project Code ZZ13-YQ-012.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation. (2020) 141:e139–596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757
2. Bennett MR, Sinha S, and Owens GK. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118:692–702. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306361
3. Tabas I and Bornfeldt KE. Intracellular and intercellular aspects of macrophage immunometabolism in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2020) 126:1209–27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315939
4. Jian X, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Zhao L, Wang D, and Liu Q. The role of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis through the regulation of macrophage activity. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 118:109375. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109375
5. Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB, and Ley K. Macrophage polarization: Different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively activated macrophages. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01084
6. Gu X, Zhang Y, Li D, Cai H, Cai L, and Xu Q. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes M1 and M2 macrophage activation. Cell Signalling. (2020) 69:109553. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109553
7. Serbulea V, Upchurch CM, Ahern KW, Bories G, Voigt P, DeWeese DE, et al. Macrophages sensing oxidized DAMPs reprogram their metabolism to support redox homeostasis and inflammation through a TLR2-syk-ceramide dependent mechanism. Mol Metab. (2018) 7:23–34. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.11.002
8. Gulay KCM, Aoshima K, Maekawa N, Suzuki T, Konnai S, Kobayashi A, et al. Hemangiosarcoma cells induce M2 polarization and PD-L1 expression in macrophages. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:2124. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06203-w
9. Yang S, Yuan H-Q, Hao Y-M, Ren Z, Qu S-L, Liu L-S, et al. Macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta; Int J Clin Chem. (2020) 501:142–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.10.034
10. Wu X, Sang L, and Gong Y. N6-methyladenine RNA modification and cancers. Am J Cancer Res. (2018) 8:1957–66. Available at: https://www.ajcr.us/ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0085006
11. Chen Y-S, Ouyang X-P, Yu X-H, Novák P, Zhou L, He P-P, et al. N6-adenosine methylation (m6A) RNA modification: An emerging role in cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2021) 14:857–72. doi: 10.1007/s12265-021-10108-w
12. Quiles-Jiménez A, Gregersen I, Mittelstedt Leal de Sousa M, Abbas A, Kong XY, Alseth I, et al. N6-methyladenosine in RNA of atherosclerotic plaques: An epitranscriptomic signature of human carotid atherosclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 533:631–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.057
13. Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, and Lewington S. Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res. (2016) 118:535–46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611
14. Jian D, Wang Y, Jian L, Tang H, Rao L, Chen K, et al. METTL14 aggravates endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis by increasing FOXO1 N6-methyladeosine modifications. Theranostics. (2020) 10:8939–56. doi: 10.7150/thno.45178
15. Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA, Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. (2014) 41:14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008
16. Hummitzsch L, Zitta K, Rusch R, Cremer J, Steinfath M, Gross J, et al. Characterization of the angiogenic potential of human regulatory macrophages (mreg) after ischemia/reperfusion injury in vitro. Stem Cells In. (2019) 2019:3725863. doi: 10.1155/2019/3725863
17. Cassetta L, Cassol E, and Poli G. Macrophage polarization in health and disease. Sci World J. (2011) 11:2391–402. doi: 10.1100/2011/213962
18. Robbins CS, Chudnovskiy A, Rauch PJ, Figueiredo J-L, Iwamoto Y, Gorbatov R, et al. Extramedullary hematopoiesis generates ly-6C(high) monocytes that infiltrate atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation. (2012) 125:364–74. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.061986
19. Porta C, Riboldi E, Ippolito A, and Sica A. Molecular and epigenetic basis of macrophage polarized activation. Semin Immunol. (2015) 27:237–48. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2015.10.003
20. Qin H, Holdbrooks AT, Liu Y, Reynolds SL, Yanagisawa LL, and Benveniste EN. SOCS3 deficiency promotes M1 macrophage polarization and inflammation. J Immunol. (2012) 189:3439–48. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201168
21. Li C, Xu MM, Wang K, Adler AJ, Vella AT, and Zhou B. Macrophage polarization and meta-inflammation. Transl Res. (2018) 191:29–44. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2017.10.004
22. Vats D, Mukundan L, Odegaard JI, Zhang L, Smith KL, Morel CR, et al. Oxidative metabolism and PGC-1beta attenuate macrophage-mediated inflammation. Cell Metab. (2006) 4:13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.011
23. Galván-Peña S and O’Neill LAJ. Metabolic reprograming in macrophage polarization. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:420. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00420
24. Young R, Bush SJ, Lefevre L, McCulloch MEB, Lisowski ZM, Muriuki C, et al. Species-specific transcriptional regulation of genes involved in nitric oxide production and arginine metabolism in macrophages. Immunohorizons. (2018) 2:27–37. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.1700073
25. Chawla A. Control of macrophage activation and function by PPARs. Circ Res. (2010) 106:1559–69. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.216523
26. Schultze JL and Schmidt SV. Molecular features of macrophage activation. Semin Immunol. (2015) 27:416–23. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.03.009
27. Jetten N, Verbruggen S, Gijbels MJ, Post MJ, De Winther MPJ, and Donners MMPC. Anti-inflammatory M2, but not pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo. Angiogenesis. (2014) 17:109–18. doi: 10.1007/s10456-013-9381-6
28. Italiani P and Boraschi D. From monocytes to M1/M2 macrophages: Phenotypical vs. Functional differentiation. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:514. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00514
29. Bisgaard LS, Mogensen CK, Rosendahl A, Cucak H, Nielsen LB, Rasmussen SE, et al. Bone marrow-derived and peritoneal macrophages have different inflammatory response to oxLDL and M1/M2 marker expression—Implications for atherosclerosis research. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:35234. doi: 10.1038/srep35234
30. Mueller PA, Zhu L, Tavori H, Huynh K, Giunzioni I, Stafford JM, et al. Deletion of macrophage low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) accelerates atherosclerosis regression and increases C-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CCR7) expression in plaque macrophages. Circulation. (2018) 138:1850–63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031702
31. Tajbakhsh A, Rezaee M, Kovanen PT, and Sahebkar A. Efferocytosis in atherosclerotic lesions: Malfunctioning regulatory pathways and control mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. (2018) 188:12–25. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.02.003
32. Zhang X, Li J, Luo S, Wang M, Huang Q, Deng Z, et al. IgE contributes to atherosclerosis and obesity by affecting macrophage polarization, macrophage protein network, and foam cell formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2020) 40:597–610. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313744
33. Chan KF, Siegel MR, and Lenardo JM. Signaling by the TNF receptor superfamily and T cell homeostasis. Immunity. (2000) 13:419–22. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00041-8
34. Ohta H, Wada H, Niwa T, Kirii H, Iwamoto N, Fujii H, et al. Disruption of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene diminishes the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. (2005) 180:11–7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.11.016
35. Mackesy DZ and Goalstone ML. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase-5: Novel mediator of insulin and tumor necrosis factor α-stimulated vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in vascular cells. J Diabetes. (2014) 6:595–602. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12132
36. Tousoulis D, Oikonomou E, Economou EK, Crea F, and Kaski JC. Inflammatory cytokines in atherosclerosis: Current therapeutic approaches. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:1723–32. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv759
37. Tyrrell DJ and Goldstein DR. Ageing and atherosclerosis: Vascular intrinsic and extrinsic factors and potential role of IL-6. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18:58–68. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0431-7
38. Rőszer T. Understanding the mysterious M2 macrophage through activation markers and effector mechanisms. Mediators Inflammation. (2015) 2015:816460. doi: 10.1155/2015/816460
39. Tabas I. Macrophage death and defective inflammation resolution in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) 10:36–46. doi: 10.1038/nri2675
40. Rajasingh J, Bord E, Luedemann C, Asai J, Hamada H, Thorne T, et al. IL-10-induced TNF-alpha mRNA destabilization is mediated via IL-10 suppression of p38 MAP kinase activation and inhibition of HuR expression. FASEB J. (2006) 20:2112–4. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-6084fje
41. Lisinski TJ and Furie MB. Interleukin-10 inhibits proinflammatory activation of endothelium in response to borrelia burgdorferi or lipopolysaccharide but not interleukin-1beta or tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Leukoc Biol. (2002) 72:503–11. doi: 10.1189/jlb.72.3.503
42. Huber SA, Sakkinen P, Conze D, Hardin N, and Tracy R. Interleukin-6 exacerbates early atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (1999) 19:2364–7. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.19.10.2364
43. Song Z-Z and Zhang Y-M. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of the vasa vasorum of carotid artery plaque. World J Radiol. (2015) 7:131–3. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i6.131
44. Stöger JL, Gijbels MJJ, van der Velden S, Manca M, van der Loos CM, Biessen EAL, et al. Distribution of macrophage polarization markers in human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2012) 225:461–8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.09.013
45. Chen Y, Zhao X, and Wu H. Arterial stiffness: A focus on vascular calcification and its link to bone mineralization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2020) 40:1078–93. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.313131
46. Babaniamansour P, Mohammadi M, Babaniamansour S, and Aliniagerdroudbari E. The relation between atherosclerosis plaque composition and plaque rupture. J Med Signals Sens. (2020) 10:267–73. doi: 10.4103/jmss.JMSS_48_19
47. Yang X, Liu H, Ye T, Duan C, Lv P, Wu X, et al. AhR activation attenuates calcium oxalate nephrocalcinosis by diminishing M1 macrophage polarization and promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Theranostics. (2020) 10:12011–25. doi: 10.7150/thno.51144
48. Shioi A and Ikari Y. Plaque calcification during atherosclerosis progression and regression. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2018) 25:294–303. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17020
49. Feig JE, Parathath S, Rong JX, Mick SL, Vengrenyuk Y, Grauer L, et al. Reversal of hyperlipidemia with a genetic switch favorably affects the content and inflammatory state of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation. (2011) 123:989–98. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.984146
50. Harmon EY, Fronhofer V, Keller RS, Feustel PJ, Zhu X, Xu H, et al. Anti-inflammatory immune skewing is atheroprotective: Apoe–/–FcγRIIb–/– mice develop fibrous carotid plaques. J Am Heart Assoc. (2014) 3:e001232. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001232
51. Rahman K, Vengrenyuk Y, Ramsey SA, Vila NR, Girgis NM, Liu J, et al. Inflammatory Ly6Chi monocytes and their conversion to M2 macrophages drive atherosclerosis regression. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:2904–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI75005
52. Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Baron M, Bouhlel MA, Vanhoutte J, Copin C, Sebti Y, et al. Human atherosclerotic plaque alternative macrophages display low cholesterol handling but high phagocytosis because of distinct activities of the PPARγ and LXRα pathways. Circ Res. (2011) 108:985–95. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.233775
53. Voloshyna I, Teboul I, Kasselman LJ, Salama M, Carsons SE, DeLeon J, et al. Macrophage lipid accumulation in the presence of immunosuppressive drugs mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporin a. Inflamm Res. (2019) . 68:787–99. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01262-8
54. Hou P, Fang J, Liu Z, Shi Y, Agostini M, Bernassola F, et al. Macrophage polarization and metabolism in atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis. (2023) . 14:691. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06206-z
55. Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. (2012) 485:201–6. doi: 10.1038/nature11112
56. Klungland A and Dahl JA. Dynamic RNA modifications in disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2014) 26:47–52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2014.05.006
57. Wang P, Doxtader KA, and Nam Y. Structural basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 methyltransferases. Mol Cell. (2016) 63:306–17. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.041
58. Zhang Z, Luo K, Zou Z, Qiu M, Tian J, Sieh L, et al. Genetic analyses support the contribution of mRNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification to human disease heritability. Nat Genet. (2020) 52:939–49. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0644-z
59. Shi H, Wei J, and He C. Where, when, and how: Context-dependent functions of RNA methylation writers, readers, and erasers. Mol Cell. (2019) 74:640–50. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.025
60. Śledź P and Jinek M. Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of the m(6)a writer complex. eLife. (2016) 5:e18434. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18434
61. Barbieri I, Tzelepis K, Pandolfini L, Shi J, Millán-Zambrano G, Robson SC, et al. Promoter-bound METTL3 maintains myeloid leukaemia by m6A-dependent translation control. Nature. (2017) 552:126–31. doi: 10.1038/nature24678
62. Gao R, Ye M, Liu B, Wei M, Ma D, and Dong K. m6A modification: A double-edged sword in tumor development. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:679367. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.679367
63. Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang L, et al. A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol. (2014) 10:93–5. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1432
64. Horiuchi K, Kawamura T, Iwanari H, Ohashi R, Naito M, Kodama T, et al. Identification of wilms’ tumor 1-associating protein complex and its role in alternative splicing and the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. (2013) 288:33292–302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.500397
65. Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang C-M, Li CJ, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. (2013) 49:18–29. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.015
66. Aik W, Scotti JS, Choi H, Gong L, Demetriades M, Schofield CJ, et al. Structure of human RNA N6-methyladenine demethylase ALKBH5 provides insights into its mechanisms of nucleic acid recognition and demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. (2014) 42:4741–54. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku085
67. Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung Y-CL, Webby CJ, Saudek V, Hewitson KS, et al. The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science. (2007) 318:1469–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1151710
68. Feng C, Liu Y, Wang G, Deng Z, Zhang Q, Wu W, et al. Crystal structures of the human RNA demethylase Alkbh5 reveal basis for substrate recognition. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:11571–83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.546168
69. Zhou B, Liu C, Xu L, Yuan Y, Zhao J, Zhao W, et al. N6 -methyladenosine reader protein YT521-B homology domain-containing 2 suppresses liver steatosis by regulation of mRNA stability of lipogenic genes. Hepatology. (2021) 73:91–103. doi: 10.1002/hep.31220
70. Zhao YL, Liu YH, Wu RF, Bi Z, Yao YX, Liu Q, et al. Understanding m6A function through uncovering the diversity roles of YTH domain-containing proteins. Mol Biotechnol. (2019) 61:355–64. doi: 10.1007/s12033-018-00149-z
71. Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M, et al. YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)a-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:12626. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12626
72. Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhao BS, Ma H, Hsu PJ, et al. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. (2017) 27:315–28. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.15
73. Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen Y-S, Hao Y-J, Sun B-F, et al. Nuclear m(6)a reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. (2016) 61:507–19. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.012
74. Roundtree IA, Luo G-Z, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhou T, Cui Y, et al. YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N6-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. eLife. (2017) 6:e31311. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31311
75. Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Guo Y, Shi X, Liu Y, et al. Ythdc2 is an N6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res. (2017) 27:1115–27. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.99
76. Dorn LE, Lasman L, Chen J, Xu X, Hund TJ, Medvedovic M, et al. The N6-methyladenosine mRNA methylase METTL3 controls cardiac homeostasis and hypertrophy. Circulation. (2019) 139:533–45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036146
77. Chen J and Du B. Novel positioning from obesity to cancer: FTO, an m6A RNA demethylase, regulates tumour progression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2019) 145:19–29. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2796-0
78. Mo W, Chen Z, Zhang X, Dai G, Ma D, Pan J, et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO (fat mass and obesity-associated protein) as a novel mediator of statin effects in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2022) 42:644–58. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.317295
79. Zhang X, Deng S, Peng Y, Wei H, and Tian Z. ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through bcl-2 pathway. Open Med (Wars). (2022) 17:1092–9. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0484
80. Wang L-J, Xue Y, Huo R, Yan Z, Xu H, Li H, et al. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 affects the phenotype of cerebral arteriovenous malformation via modulating notch signaling pathway. J BioMed Sci. (2020) 27:62. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00655-w
81. Wang L-J, Xue Y, Li H, Huo R, Yan Z, Wang J, et al. Wilms’ tumour 1-associating protein inhibits endothelial cell angiogenesis by m6A-dependent epigenetic silencing of desmoplakin in brain arteriovenous malformation. J BioMed Sci. (2020) 24:4981–91. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15101
82. Kumari R, Dutta R, Ranjan P, Suleiman ZG, Goswami SK, Li J, et al. ALKBH5 regulates SPHK1-dependent endothelial cell angiogenesis following ischemic stress. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:817304. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.817304
83. Zhu B, Gong Y, Shen L, Li J, Han J, Song B, et al. Total panax notoginseng saponin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration and intimal hyperplasia by regulating WTAP/p16 signals via m6A modulation. BioMed Pharmacother. (2020) 124:109935. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109935
84. Zhang B-F, Wu Z-H, Deng J, Jin H-J, Chen W-B, Zhang S, et al. M6A methylation-mediated elevation of SM22α inhibits the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells and ameliorates intimal hyperplasia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biol Chem. (2022) 403:317–29. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2021-0296
85. Qin Y, Qiao Y, Li L, Luo E, Wang D, Yao Y, et al. The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes hypoxic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Life Sci. (2021) 274:119366. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119366
86. Lin J, Zhu Q, Huang J, Cai R, and Kuang Y. Hypoxia promotes vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) differentiation of adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) by regulating Mettl3 and paracrine factors. Stem Cells Int. (2020) 2020:2830565. doi: 10.1155/2020/2830565
87. Li H-B, Tong J, Zhu S, Batista PJ, Duffy EE, Zhao J, et al. m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways. Nature. (2017) 548:338–42. doi: 10.1038/nature23450
88. Liu Y, You Y, Lu Z, Yang J, Li P, Liu L, et al. N 6-methyladenosine RNA modification-mediated cellular metabolism rewiring inhibits viral replication. Science. (2019) 365:1171–6. doi: 10.1126/science.aax4468
89. Liu Y, Liu Z, Tang H, Shen Y, Gong Z, Xie N, et al. The N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-forming enzyme METTL3 facilitates M1 macrophage polarization through the methylation of STAT1 mRNA. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2019) 317:C762–75. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00212.2019
90. Yang L, Yang F, Zhao H, Wang M, and Zhang Y. Circular RNA circCHFR facilitates the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle via miR-370/FOXO1/cyclin D1 pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2019) 16:434–41. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.02.028
91. Guo M, Yan R, Ji Q, Yao H, Sun M, Duan L, et al. IFN regulatory factor-1 induced macrophage pyroptosis by modulating m6A modification of circ_0029589 in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int Immunopharmaco. (2020) 86:106800. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106800
92. Cai Y, Yu R, Kong Y, Feng Z, and Xu Q. METTL3 regulates LPS-induced inflammatory response via the NOD1 signaling pathway. Cell Signal. (2022) 93:110283. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110283
93. Yu R, Li Q, Feng Z, Cai L, and Xu Q. m6A reader YTHDF2 regulates LPS-induced inflammatory response. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1323. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061323
Keywords: macrophage polarization, cytokines, atherosclerosis, N 6 -methyladenosine modification, inflammatory
Citation: Li X, Zhang H, Zhou Y, Zhang L and Huang Y (2025) m6A modification: a novel mechanism that regulates atherosclerosis via macrophage polarization. Front. Immunol. 16:1607932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1607932
Received: 08 April 2025; Accepted: 29 May 2025;
Published: 16 June 2025.
Edited by:
Vinay Kumar, The Pennsylvania State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Dharmendra Bhatt, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United StatesAnuradha Tyagi, Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Allied Sciences (DRDO), India
Copyright © 2025 Li, Zhang, Zhou, Zhang and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ye Huang, MjAxOTAyMjEwNzFAYnVjbS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiaying Li1,2†
Xiaying Li1,2† Yan Zhou
Yan Zhou Ye Huang
Ye Huang