- Department of Gastroenterology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Background: Behçet’s disease (BD), a multisystemic inflammatory disorder with genetic predisposition, is frequently complicated by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), particularly in cases harboring trisomy 8. Patients with refractory BD-MDS exhibit poor responses to conventional therapies, including glucocorticoids and TNF-α inhibitors, underscoring the need for novel therapeutic strategies. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which target cytokine-driven inflammation, represent a promising approach; however, clinical evidence in genetically complex BD-MDS cases remains limited.
Case presentation: We report a 29-year-old female with refractory intestinal BD, MDS, and dual trisomy 8/9, who presented with recurrent ulcers, thrombocytopenia, and ileocolonic resection due to perforation. Despite sequential therapies (thalidomide, prednisolone, and infliximab), disease progression persisted. Initiation of upadacitinib (45 mg/day), a selective JAK1 inhibitor, resulted in symptom resolution within one week and complete mucosal healing confirmed by colonoscopy at three months. Dose reduction to 15 mg/day led to disease relapse, while maintenance at 30 mg/day sustained remission over 12 months.
Methods: Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of intestinal specimens from the patient and three additional BD cases revealed robust phosphorylation of JAK1 and STAT3 in mucosal epithelium, stroma, and inflammatory infiltrates, particularly within occluded submucosal vessels. These findings mechanistically implicate JAK-STAT hyperactivation in BD-associated vascular pathology.
Conclusion: This study highlights the efficacy of upadacitinib in managing refractory BD with MDS and dual trisomy 8/9, a genetically complex phenotype. The dose-dependent response underscores the importance of tailored dosing strategies. Our mechanistic data further support JAK inhibition as a viable therapeutic alternative for TNF-α inhibitor-resistant BD. These results warrant validation through randomized controlled trials to optimize therapeutic protocols for similar high-risk populations.
1 Introduction
Behçet’s disease (BD), a chronic multisystemic inflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent mucocutaneous ulcers, ocular inflammation, and vascular involvement, exhibits a strong genetic predisposition, particularly among populations along the historic Silk Road (1). While its pathogenesis remains incompletely elucidated, dysregulated immune responses involving Th1/Th17 polarization and cytokine-driven inflammation are central to disease progression (1). Emerging evidence highlights a distinct clinical subset of BD complicated by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), a hematologic malignancy marked by cytopenias and clonal chromosomal abnormalities (2). Notably, trisomy 8—a karyotypic aberration observed in 7–9% of primary MDS cases—is present in over 80% of BD-MDS patients, suggesting a unique pathophysiologic interplay (3–5). These patients often present with severe gastrointestinal (GI) involvement, including deep ileocecal ulcers requiring surgical intervention, alongside hematologic abnormalities such as macrocytic anemia and thrombocytopenia (6–8). Despite aggressive management, BD-MDS patients exhibit poor responses to conventional therapies, including corticosteroids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors, with mortality rates exceeding 25% (6, 9). This underscores the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies targeting the underlying molecular drivers of refractory disease.
The JAK-STAT signaling pathway, a critical mediator of cytokine signaling, has emerged as a key contributor to BD pathogenesis. Upregulated JAK1 and STAT3 activation in monocytes and T cells drives the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6, IL-17, IFN-γ), perpetuating systemic inflammation and mucosal damage (10). Preclinical and clinical studies suggest that selective JAK inhibitors, such as upadacitinib, may attenuate Th1/Th17 responses and induce remission in refractory BD (10). However, evidence supporting their efficacy in genetically complex BD-MDS cases, particularly those with dual trisomy 8/9, remains scarce.
Here, we present a case of refractory intestinal BD complicated by MDS and dual trisomy 8/9, a rare karyotypic profile associated with heightened treatment resistance. Through immunohistochemical analysis of intestinal specimens, we further elucidate the role of JAK-STAT hyperactivation in BD-associated vascular pathology. Our findings highlight the therapeutic potential of upadacitinib in this challenging patient population and provide mechanistic rationale for JAK inhibition as a targeted strategy in TNF-α inhibitor-resistant BD.
2 Case presentation
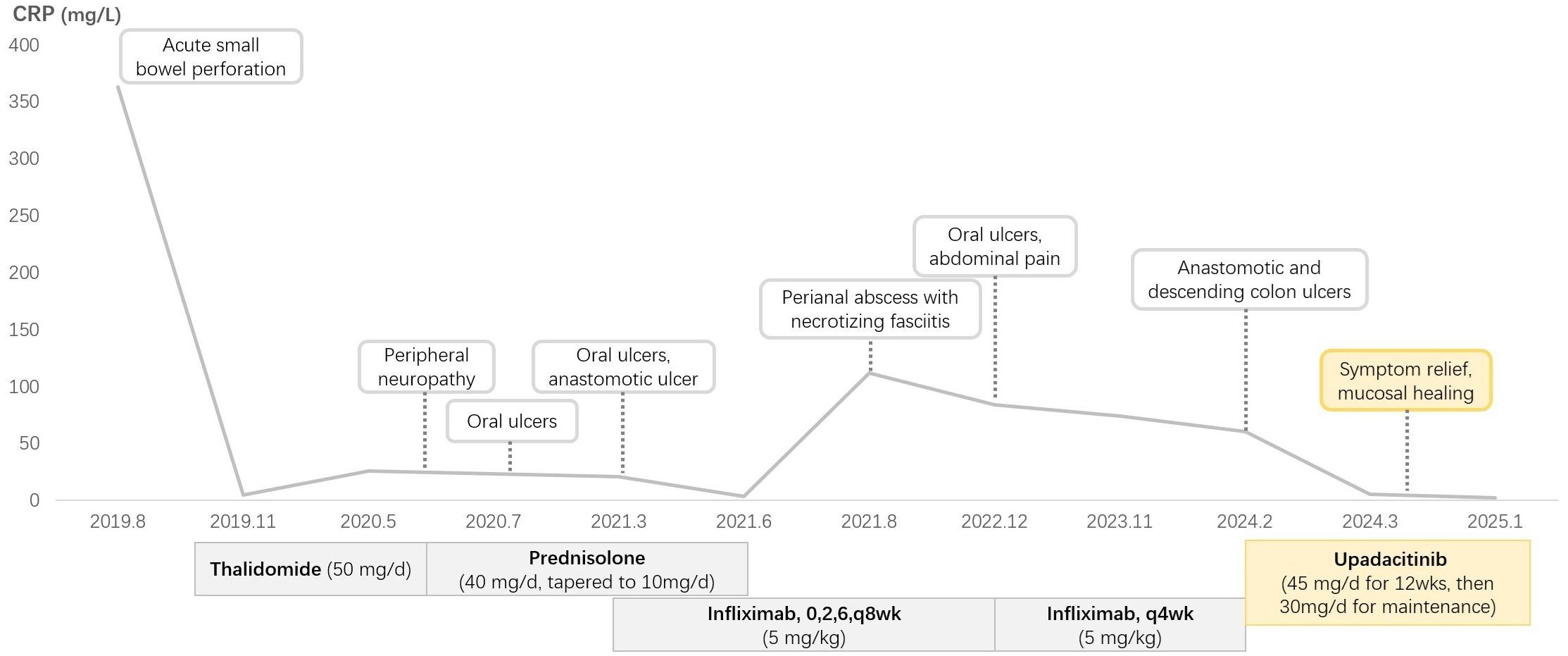
A 29-year-old female patient presented with a two-year history of recurrent oral ulcers and a one-year history of genital ulcers and thrombocytopenia. In August 2019, she was admitted due to acute small bowel perforation. Emergency laparotomy revealed a perforation 30 cm proximal to the ileocecal valve, accompanied by a deep ulcer in the terminal ileum (Figures 1A, B). Segmental resection of the ileum, ileocecal region, and ascending colon was performed, followed by end-to-end anastomosis. Histopathological examination of the resected specimen revealed submucosal vascular dilation, intimal hyperplasia of small arteries, and thrombi within the arterial and venous lumina. Postoperative diagnosis confirmed BD. A bone marrow biopsy performed due to persistent thrombocytopenia. Bone marrow biopsy was performed due to persistent thrombocytopenia. The biopsy revealed increased myeloblasts (1.6%), active erythroid hyperplasia (mainly intermediate/late-stage erythroblasts), and significant nuclear/cytoplasmic abnormalities in erythrocytes, with pathological cells comprising 38% of the erythroid lineage. Flow cytometry showed 1.1% CD34-positive immature myeloid cells. Karyotype analysis indicated trisomy 8 and trisomy 9 (Figure 1C). Although next-generation sequencing was recommended, the patient declined due to cost. The diagnosis of MDS was confirmed based on these findings. The patient was classified as International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) intermediate-2 (11) and revised IPSS (IPSS-R) high-risk (12). However, the patient refused allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation due to associated risks and costs. Initial treatment with thalidomide (50 mg/day) was discontinued after six months due to peripheral neuropathy. In July 2020, a recurrent oral ulcer prompted the initiation of prednisolone (40 mg/day), which was gradually tapered. However, disease relapse occurred in March 2021 (prednisone 10 mg/day), characterized by new oral ulcers and right mid-abdominal pain. Colonoscopy revealed an anastomotic ulcer, prompting infliximab induction (5 mg/kg) at weeks 0, 2, 6, and 8, followed by maintenance therapy every 8 weeks. A follow-up colonoscopy at three months confirmed ulcer healing, and maintenance infliximab therapy (every 8 weeks) was initiated.
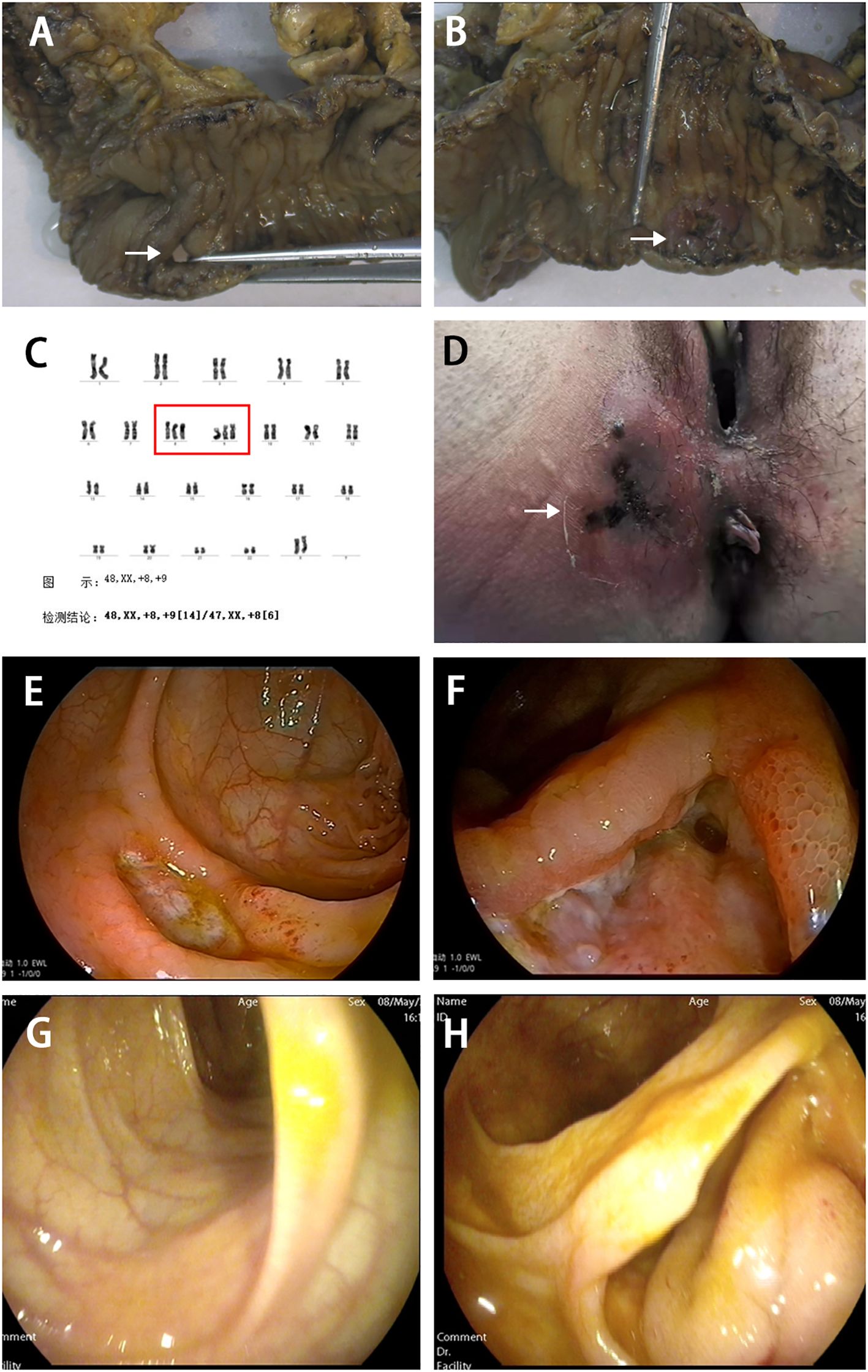
Figure 1. Surgical resection of intestinal specimens and clinical findings in this patient. (A) Resected intestinal specimen showing ileal perforation (indicated by white arrow). (B) Deep ulcer observed in the terminal ileum (indicated by white arrow). (C) Bone marrow chromosome examination showing trisomy 8 and 9 (indicated by red box). (D) In August 2021, the patient developed a perianal abscess with necrotizing fasciitis (indicated by white arrow). Colonoscopy showed ulcer at the descending colon (E) and the anastomotic site (F). After three months of treatment with upadacitinib, mucosal healing was observed in the descending colon (G) and the anastomotic site (H) after three months of treatment with upadacitinib.
In August 2021, the patient developed a perianal abscess with necrotizing fasciitis (Figure 1D). She recovered well after surgical drainage and continued regular infliximab therapy. Despite regular infliximab, disease activity recurred in December 2022, marked by oral ulcers, abdominal pain, and elevated CRP. Infliximab dosing was escalated to every 4 weeks, yet symptoms progressed. By February 2024, colonoscopy revealed recurrent anastomotic and descending colon ulcers (Figures 1E, F). Infliximab was discontinued, and upadacitinib (45 mg/day) was initiated.
Clinical improvement was noted within one week, with complete resolution of abdominal pain. A repeat colonoscopy performed three months after the initial procedure demonstrated mucosal healing (Figures 1G, H). The platelet count remained subnormal (95×10^9/L; reference range 150–450×10^9/L), but the CRP level normalized, and no active ulcers were observed. Dose reduction to 15 mg/day resulted in recurrent oral ulcers, necessitating maintenance therapy with 30 mg/day. At the last follow-up (March 2025), the patient remained asymptomatic on upadacitinib 30 mg/day. The patient’s clinical course is shown in Figure 2.
Based on these clinical observations, we performed IHC staining on surgically resected intestinal specimens from the patient. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (approval number: 2024PS1286K). The expression of phosphorylated JAK-1, JAK-2, JAK-3, STAT1, and STAT3 was detected in the mucosal epithelium, mucosal stroma, intrinsic glands, small blood vessels, and peripherally infiltrating inflammatory cells within the submucosal layer (Figures 3A-E). Notably, phosphorylated JAK-1 and STAT3 exhibited strong expression in the lumen of occluded small vessels in the submucosal layer, smooth muscle cells, and peripherally infiltrating inflammatory cells (Figures 3F, G). These findings suggest that upadacitinib may represent a promising therapeutic option for patients with Behçet’s disease (BD) who are refractory to TNF-α inhibitors.
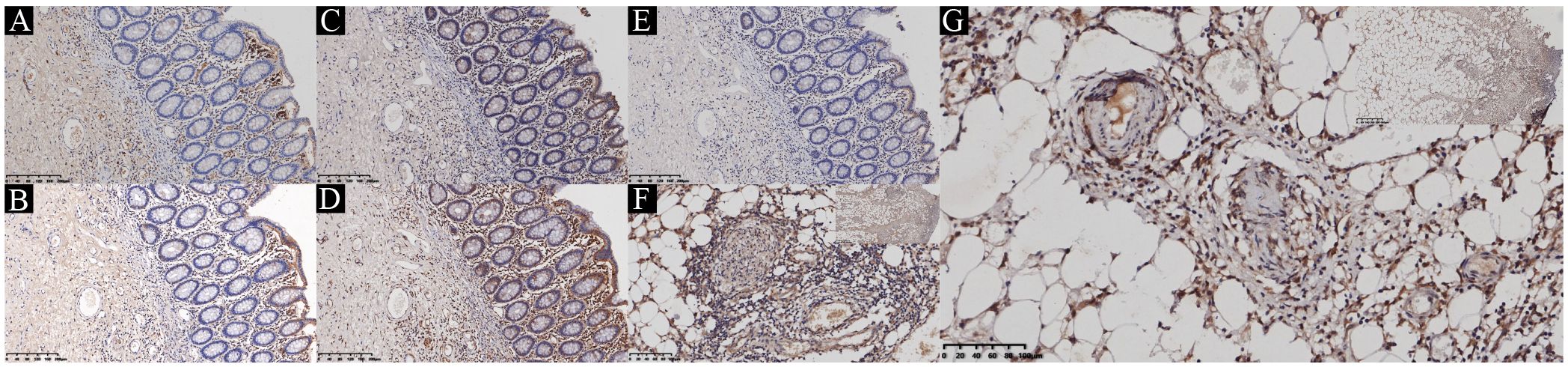
Figure 3. Immunohistochemical staining of JAK-STAT in the ileum. (A) Phosphorylated JAK-1. (B) Phosphorylated JAK-2. (C) Phosphorylated JAK-3. (D) Phosphorylated STAT1. (E) Phosphorylated STAT3. (F) Representative image of immunohistochemical staining of phosphorylated JAK-1 in typical vasculitic lesions. (G) Representative image of immunohistochemical staining of phosphorylated STAT3 in typical vasculitic lesions.
3 Literature review and discussion
The present case illustrates the sustained efficacy of upadacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, in achieving remission for refractory intestinal BD complicated by MDS and dual trisomy 8/9—a rare and genetically complex phenotype. MDS is increasingly recognized for its association with autoimmune and autoinflammatory manifestations, which significantly influence clinical trajectories and outcomes. These manifestations, ranging from mucocutaneous involvement to systemic inflammatory syndromes, are mechanistically linked to somatic mutations (e.g., RUNX1, TP53, TET2, ASXL1) and epigenetic alterations that disrupt immune cell homeostasis and promote dysregulated cytokine signaling (13). Aberrant innate immune activation, mediated by NLRP3 inflammasome hyperactivity and oxidative stress, further amplifies inflammatory cascades (14, 15). Additionally, dysfunction within the bone marrow microenvironment, including stromal cell abnormalities, contributes to chronic inflammation and hematopoietic failure (16). Notably, somatic mutations such as RUNX1 have been implicated in atypical inflammatory presentations preceding MDS progression, underscoring the interplay between clonal hematopoiesis and immune dysregulation (17). While genetic profiling was unavailable in our case due to patient refusal, the observed dual trisomy 8/9—a karyotype associated with aggressive disease phenotypes—likely exacerbates treatment resistance through undefined molecular mechanisms. This highlights the critical need for comprehensive genomic analyses in similar cases to elucidate genotype-phenotype correlations and identify actionable therapeutic targets.
Emerging evidence supports JAK inhibition as a promising strategy for cytokine-driven inflammatory disorders, particularly in cases refractory to conventional biologics. By reviewing the published literature associated with JAK inhibitors in treatment of BD, we identified 13 studies or case reports on BD treated with JAK inhibitors, including 3 pilot studies, 2 case series, and 8 case reports, totaling 69 cases. Among these, 32 patients received tofacitinib (18–23), 30 received baricitinib (24–26), and 7 received upadacitinib (27–32) (Table 1).
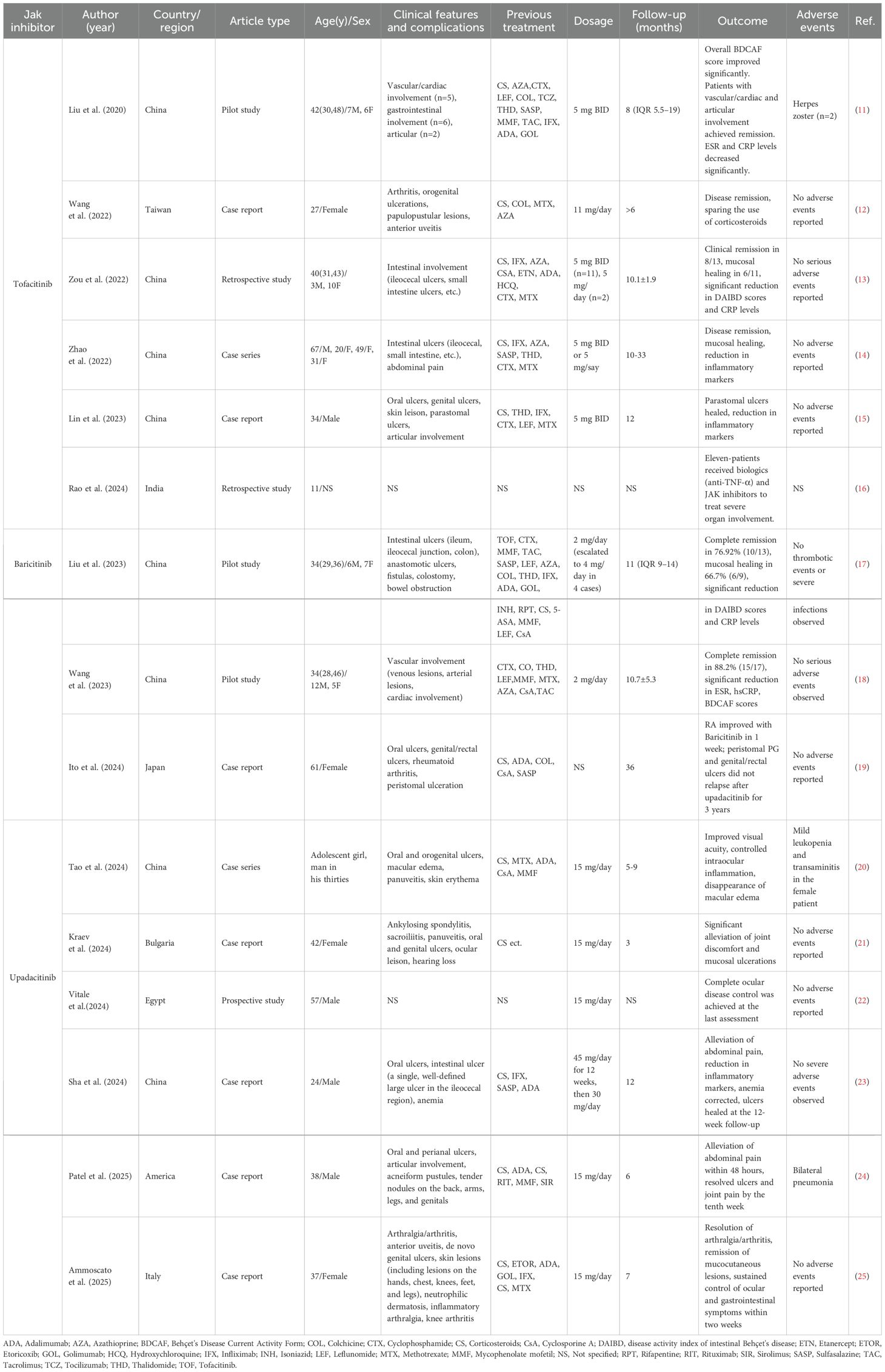
Table 1. Summary of JAK Inhibitor Therapies in Behçet's Disease: Clinical Features, Treatments, and Outcomes.
3.1 Role of the JAK-STAT pathway in Behçet’s disease
The JAK-STAT pathway is a critical signaling mechanism that mediates the effects of various cytokines and growth factors involved in immune responses, hematopoiesis, and cellular proliferation (33). This pathway comprises four members: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2, which are non-receptor tyrosine kinases that transmit signals from a wide range of cytokine receptors (34–36). The JAK-STAT pathway plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of BD. Studies have demonstrated upregulated JAK1 expression in CD14+ monocytes and CD4+ T cells of BD patients, with activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in these cells (37). Moreover, the expansion of Th1 and Th17 cell subsets in BD patients is closely associated with the activation of the JAK/STAT pathway (38, 39). In BD, the JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway is likely mediated by Th1/Th17-type cytokines, such as IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-17, and IL-23, which are central to the inflammatory response and disease activity (40–43). Additionally, BD patients exhibit significantly higher STAT3 expression compared to healthy controls, both under unstimulated and stimulated conditions (37). A study in Han Chinese BD patients identified three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the JAK1 gene—rs2780815, rs310241, and rs3790532—that are significantly associated with BD susceptibility (44). These SNPs may increase the risk of BD by altering the expression or function of the JAK1 gene. Furthermore, no gene-gene interaction was found between the JAK1 gene and HLA-B51, indicating that JAK1 is an independent risk factor for BD (44). Our IHC findings revealed robust expression of phosphorylated JAK-1 and STAT3 in occluded submucosal vessels and inflammatory infiltrates, further supporting the therapeutic rationale for JAK inhibitors in BD.
3.2 JAK inhibitors in refractory BD
JAK inhibitors, including tofacitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib, have emerged as promising therapeutic options for BD (18, 30). Clinical studies and case reports consistently demonstrate their ability to alleviate symptoms, improve laboratory markers, and achieve endoscopic remission in cases that are refractory to other treatments.
Tofacitinib, a pan-JAK inhibitor primarily targeting JAK1 and JAK3, has yielded mixed results in gastrointestinal Behçet’s disease (BD). A pilot study of tofacitinib (5 mg twice daily) in 13 patients with refractory BD reported mucosal healing in only one of six patients with gastrointestinal involvement. At the same time, vascular and articular manifestations responded more favorably (18). Conversely, a retrospective study of 13 patients with gastrointestinal BD found clinical remission in nine patients and mucosal healing in six of 11 patients after a mean treatment duration of 10 months (20). A case series reported successful outcomes in four patients with severe refractory intestinal BD treated with tofacitinib, highlighting its ability to induce remission in cases where other therapies had failed (21). Tofacitinib also demonstrated efficacy in refractory parastomal ulcers, a condition resistant to conventional therapies (22).
Baricitinib, a selective JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, has demonstrated promising efficacy in both intestinal and vascular Behçet’s disease (BD). In a pilot study of 13 patients with intestinal BD, baricitinib (2 mg daily, escalated to 4 mg in non-responders) achieved complete remission in 76.9% of patients and mucosal healing in 66.7%, with significant reductions in disease activity indices and CRP levels (24). Similarly, in vascular BD, 76.5% of patients achieved complete clinical and radiologic remission within three months of baricitinib therapy (25). Additionally, baricitinib has demonstrated efficacy in treating peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum associated with rheumatoid arthritis and Behçet’s disease (26).
Upadacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, has demonstrated rapid and sustained efficacy in patients with refractory BD, particularly in those resistant to TNF-α inhibitors. Six case reports (seven cases) highlight its ability to induce remission in patients with complex BD, including those with concurrent ankylosing spondylitis and macular edema (27, 28, 30–32). A recent prospective cohort study involving 12 patients with non-infectious inflammatory ocular diseases included one case of Behçet’s uveitis. This patient was treated with a combination of upadacitinib 15 mg/day and azathioprine 200 mg/day, achieving complete ocular disease control (29). In our case, considering the patient’s severe condition, including intestinal perforation, perianal abscesses, and refractory to TNF inhibitors, we chose an initial dose of 45 mg/day. Within three months on upadacitinib, the patient achieved rapid symptom resolution and mucosal healing. Unlike most reported cases where 15 mg/day sufficed, our patient required dose escalation to 30 mg/day for sustained control. This dosing strategy is similar to that reported by Sha et al., where upadacitinib was initiated at 45 mg/day for refractory intestinal BD in a patient who had previously failed corticosteroids and infliximab. The patient experienced rapid symptom improvement and mucosal healing within 12 weeks, after which the dose was tapered to 30 mg/day for maintenance therapy (30). The requirement for a higher initial dose in our patient may be attributed to the complexity of her disease profile, which included myelodysplastic syndrome with the extremely rare trisomy of chromosomes 8 and 9. This genetic abnormality likely contributed to the increased therapeutic challenge. Despite this, upadacitinib proved effective in managing her condition, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic option for complex BD cases.
3.3 Safety considerations
The safety data for JAK inhibitors primarily derive from patients with immune-mediated inflammatory disorders, highlighting risks such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary emboli, and herpes virus infections (45, 46). JAK inhibitors should be used cautiously in patients with a history of active malignancy, thromboembolic events, or cardiovascular disease (47). In a pilot study of tofacitinib for refractory BD, two patients with intestinal involvement developed herpes zoster infections, necessitating the discontinuation of the study medication (18). Mild leukopenia and transaminitis, as well as pneumonia, were reported in patients with Behçet’s uveitis treated with upadacitinib (27, 31). To date, no serious adverse events, such as thromboembolism, have been reported in patients with BD treated with JAK inhibitors.
3.4 Future directions
Ongoing clinical trials aim to evaluate further the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in BD. Notably, the DRIMID study is investigating filgotinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, in patients with refractory BD, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, and IgG4-related disease (48). This 26-week, open-label phase 2 trial will assess impacts on disease activity and quality of life. Results are eagerly awaited, as they may confirm JAK inhibitors as a viable therapeutic option for BD, a condition historically challenging to manage due to its heterogeneity.
4 Conclusion
This case reinforces JAK inhibition as a promising strategy for TNF-α inhibitor-resistant BD, even in the context of dual trisomy 8/9 and MDS. The dose-dependent response and mechanistic correlates underscore the importance of individualized therapy. While preliminary, these findings warrant further investigation through randomized controlled trials to establish standardized protocols for JAK inhibitor use in complex BD phenotypes.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
YW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FT: Writing – review & editing. HL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by a grant from the China Medical University Science and Technology Fund Project for High-quality Development (2023JH2/20200081).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Hong Shu for providing pathological intellectual support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Akbaba TH, Ekici M, Çolpak A, Brown KL, Karadağ Ö, and Balci-Peynircioglu B. Behçet’s syndrome: recent advances to aid diagnosis. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23:4079–90. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01226-7
2. Yilmaz U, Ar MC, Esatoglu SN, Bavunoglu I, Erzin YZ, Hatemi AI, et al. How to treat myelodysplastic syndrome with clinical features resembling Behçet syndrome: a case-based systematic review. Ann Hematol. (2020) 99:1193–203. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-03951-5
3. Bernasconi P, Klersy C, Boni M, Cavigliano PM, Calatroni S, Giardini I, et al. Incidence and prognostic significance of karyotype abnormalities in de novo primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a study on 331 patients from a single institution. Leukemia. (2005) 19:1424–31. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403806
4. Solé F, Espinet B, Sanz GF, Cervera J, Calasanz MJ, Luño E, et al. Incidence, characterization and prognostic significance of chromosomal abnormalities in 640 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Grupo Cooperativo Español de Citogenética Hematológica. Br J Haematol. (2000) 108:346–56. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.01868.x
5. Tada Y, Koarada S, Haruta Y, Mitamura M, Ohta A, and Nagasawa K. The association of Behçet’s disease with myelodysplastic syndrome in Japan: a review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2006) 24:S115–9.
6. Park JB, Han SJ, Lee SB, Kim DH, Cheon JH, Hwang SW, et al. Optimal treatment approaches to intestinal behçet’s disease complicated by myelodysplastic syndrome: the KASID and KSBD multicenter study. Yonsei Med J. (2024) 65:265–75. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0321
7. Ding Y, Hu W, Li L, Guan W, Guan K, He Y, et al. Clinical features and independent predictors of Behçet’s disease associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2023) 41:1823–30. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/04us5e
8. Liu Z, Yang C, Bai X, Shen K, Qiao L, Wang Q, et al. Clinical features and prognosis of patients with gastrointestinal Behçet’s disease-like syndrome and myelodysplastic syndrome with and without trisomy 8. Semin Arthritis Rheumatol. (2022) 55:152039. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152039
9. Wesner N, Fenaux P, Jachiet V, Ades L, Fain O, and Mekinian A. Behçet’s-like syndrome and other dysimmunitary manifestations related to myelodysplastic syndromes with trisomy 8. Rev Med Interne. (2021) 42:170–6. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2020.08.016
10. Bursi R, Cafaro G, Perricone C, Riccucci I, Calvacchi S, Gerli R, et al. Contribution of janus-kinase/signal transduction activator of transcription pathway in the pathogenesis of vasculitis: A possible treatment target in the upcoming future. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:635663. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.635663
11. Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. (1997) 89:2079–88.
12. Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Solé F, et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. (2012) 120:2454–65. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-420489
13. Watad A, Kacar M, Bragazzi NL, Zhou Q, Jassam M, Taylor J, et al. Somatic mutations and the risk of undifferentiated autoinflammatory disease in MDS: an under-recognized but prognostically important complication. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:610019. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.610019
14. Basiorka AA, McGraw KL, Eksioglu EA, Chen X, Johnson J, Zhang L, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome functions as a driver of the myelodysplastic syndrome phenotype. Blood. (2016) 128:2960–75. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-07-730556
15. Jo EK, Kim JK, Shin DM, and Sasakawa C. Molecular mechanisms regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Mol Immunol. (2016) 13:148–59. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.95
16. Kovtonyuk LV, Fritsch K, Feng X, Manz MG, and Takizawa H. Inflamm-aging of hematopoiesis, hematopoietic stem cells, and the bone marrow microenvironment. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:502. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00502
17. Okano T, Nishimura A, Inoue K, Naruto T, Tokoro S, Tomoda T, et al. Somatic mutation in RUNX1 underlies mucocutaneus inflammatory manifestations. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2021) 60:e429–e31. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab513
18. Liu J, Hou Y, Sun L, Li C, Li L, Zhao Y, et al. A pilot study of tofacitinib for refractory Behcet’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:1517–20. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217307
19. Wang CR, Wong TW, and Hsu SM. Extended-release tofacitinib for refractory Behçet disease: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2022) 101:e29189. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000029189
20. Zou J, Cai JF, Ye JF, and Guan JL. Tofacitinib as an alternative therapy for refractory intestinal Behçet’s syndrome. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. (2022) 14:1759720x221124014. doi: 10.1177/1759720x221124014
21. Zhao N, Tang Y, Wang S, Cui L, Sun X, Wang Z, et al. Case report: Refractory intestinal Behcet’s syndrome successfully treated with tofacitinib: A report of four cases. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:981502. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.981502
22. Lin M, Tang J, Huang Z, Gao X, and Chao K. Gastrointestinal: Refractory parastomal ulcers of Behcet's disease responsive to tofacitinib. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 38:485. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15997
23. Rao VK, Kodali RS, Patil A, Chebbi P, Subramanian R, Kumar S, et al. Clinical profiling, treatment characteristics and outcome in Behcet’s Disease (BD)-A retrospective cohort study from Karnataka Rheumatology Association (KRA). Clin Rheumatol. (2024) 43:3223–30. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07089-x
24. Liu J, Yu X, Wang Z, Liu W, Liu X, Wang X, et al. Baricitinib for the treatment of intestinal Behçet’s disease: A pilot study. Clin Immunol. (2023) 247:109241. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109241
25. Wang Z, Wang X, Liu W, Wang Y, Liu J, Zhang L, et al. Baricitinib for the treatment of refractory vascular Behçet’s disease. Clin Immunol. (2023) 250:109298. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109298
26. Ito H, Noda K, Saruta M, and Kurosaka D. Case report: Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum complicated by rheumatoid arthritis and Behçet’s disease successfully treated with baricitinib. Int J Rheum Dis. (2024) 27:e15275. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.15275
27. Tao T, He D, Peng X, Huang Z, and Su W. Successful remission with upadacitinib in two patients with anti-TNF-refractory macular edema associated with behcet’s uveitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. (2024) 32:1897–900. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2023.2263557
28. Kraev K, Uchikov P, Hristov B, Kraeva M, Basheva-Kraeva Y, Popova-Belova S, et al. Coexistence of ankylosing spondylitis and Behcet’s disease: Successful treatment with upadacitinib. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2024) 12:e1242. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1242
29. Vitale A, Palacios-Olid J, Caggiano V, Ragab G, Hernández-Rodríguez J, Pelegrín L, et al. Efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors in non-infectious inflammatory ocular diseases: a prospective cohort study from the international AIDA network registries. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1439338. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1439338
30. Sha S, Xu B, Wang K, Qiao C, Shi H, Jiang J, et al. Case report: Successful remission with upadacitinib in a young patient with anti-TNF-refractory intestinal Behcet’s disease. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1483993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483993
31. Patel A, Guenin S, Amara S, Lebwohl M, and Khattri S. Use of upadacitinib in refractory behcet’s disease: case report and systematic literature review. J Drugs Dermatol. (2025) 24:e1–6.
32. Ammoscato C, Gatti F, Iannone F, and Lopalco G. Targeting Janus kinase 1 in refractory Behcet’s disease: a case report on the clinical efficacy of upadacitinib. Intern Emerg Med. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s11739-025-03874-x
33. Leonard WJ and O'Shea JJ. Jaks and STATs: biological implications. Annu Rev Immunol. (1998) 16:293–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.293
34. Yamaoka K, Saharinen P, Pesu M, Holt VE 3rd, Silvennoinen O, and O’Shea JJ. The janus kinases (Jaks). Genome Biol. (2004) 5:253. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-12-253
35. Ihle JN and Kerr IM. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet. (1995) 11:69–74. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89000-9
36. O'Shea JJ and Plenge R. JAK and STAT signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated disease. Immunity. (2012) 36:542–50. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.014
37. Tulunay A, Dozmorov MG, Ture-Ozdemir F, Yilmaz V, Eksioglu-Demiralp E, Alibaz-Oner F, et al. Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in Behcet’s disease. Genes Immun. (2015) 16:170–5. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.64
38. Imamura Y, Kurokawa MS, Yoshikawa H, Nara K, Takada E, Masuda C, et al. Involvement of Th1 cells and heat shock protein 60 in the pathogenesis of intestinal Behcet’s disease. Clin Exp Immunol. (2005) 139:371–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02695.x
39. Annunziato F, Cosmi L, Liotta F, Maggi E, and Romagnani S. Type 17 T helper cells-origins, features and possible roles in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2009) 5:325–31. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.80
40. Hamzaoui K. Th17 cells in Behcet’s disease: a new immunoregulatory axis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2011) 29:S71–6.
41. Direskeneli H, Fujita H, and Akdis CA. Regulation of TH17 and regulatory T cells in patients with Behcet disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2011) 128:665–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.07.008
42. Chi W, Zhu X, Yang P, Liu X, Lin X, Zhou H, et al. Upregulated IL-23 and IL-17 in Behcet patients with active uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2008) 49:3058–64. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1390
43. Geri G, Terrier B, Rosenzwajg M, Wechsler B, Touzot M, Seilhean D, et al. Critical role of IL-21 in modulating TH17 and regulatory T cells in Behcet disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2011) 128:655–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.05.029
44. Hou S, Qi J, Zhang Q, Liao D, Li Q, Hu K, et al. Genetic variants in the JAK1 gene confer higher risk of Behcet’s disease with ocular involvement in Han Chinese. Hum Genet. (2013) 132:1049–58. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1312-5
45. Silverberg JI. Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2019) 123:144–51. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2019.04.020
46. Silverberg JI, Gelfand JM, Margolis DJ, Boguniewicz M, Fonacier L, Grayson MH, et al. Patient burden and quality of life in atopic dermatitis in US adults: A population-based cross-sectional study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2018) 121:340–7. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2018.07.006
47. Narla S and Silverberg JI. Efficacy and risk stratification of janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. (2024) 35:S24–s38. doi: 10.1089/derm.2023.0058
48. Geertsema-Hoeve BC, van Laar JAM, Raaphorst J, Tas SW, Welsing PMJ, Goekoop RJ, et al. Multicentre, 26-week, open-label phase 2 trial of the JAK inhibitor filgotinib in Behçet’s disease, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and IgG4-related disease: DRIMID study protocol. BMJ Open. (2025) 15:e089827. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-089827
Keywords: Behçet’s disease, myelodysplastic syndrome, trisomy 8, upadacitinib, JAK-STAT pathway, refractory disease
Citation: Wang Y, Tian F and Li H (2025) Upadacitinib for refractory Behçet’s disease with myelodysplastic syndrome and trisomy 8/9: a case report and mechanistic insights. Front. Immunol. 16:1609884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1609884
Received: 11 April 2025; Accepted: 06 May 2025;
Published: 27 May 2025.
Edited by:
Chris Wincup, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, United KingdomReviewed by:
Sara Bindoli, University of Padua, ItalyJinjing Liu, Peking Union Medical College Hospital (CAMS), China
Ana Basquiera, Private University Hospital of Córdoba, Argentina
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Tian and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Li, bGlodWljYW5nemkwMDdAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yukai Wang
Yukai Wang Feng Tian†
Feng Tian† Hui Li
Hui Li