- 1The Comprehensive Cancer Center of Drum Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University and Clinical Cancer Institute of Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Peking University, Beijing, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Epidemiology of Major Diseases (Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing, China
- 4Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Peking University, Beijing, China
- 5Department of Esophageal Surgery, Drum Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
by Ren W, Zhang H, Li Y, Sun W, Peng H, Guo H, Hou T, Wang M, Hu Z, Wu T and Liu B (2025). Front. Immunol. 16:1563300.doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1563300
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3 and Figure 4 as published. The trend line visualization in the original Figure 3 was incomplete. The hierarchical annotation in the original Figure 4 erroneously uses the symbol “=” instead of “≥” for stratification labels. The corrected Figure 3 and Figure 4 and its caption
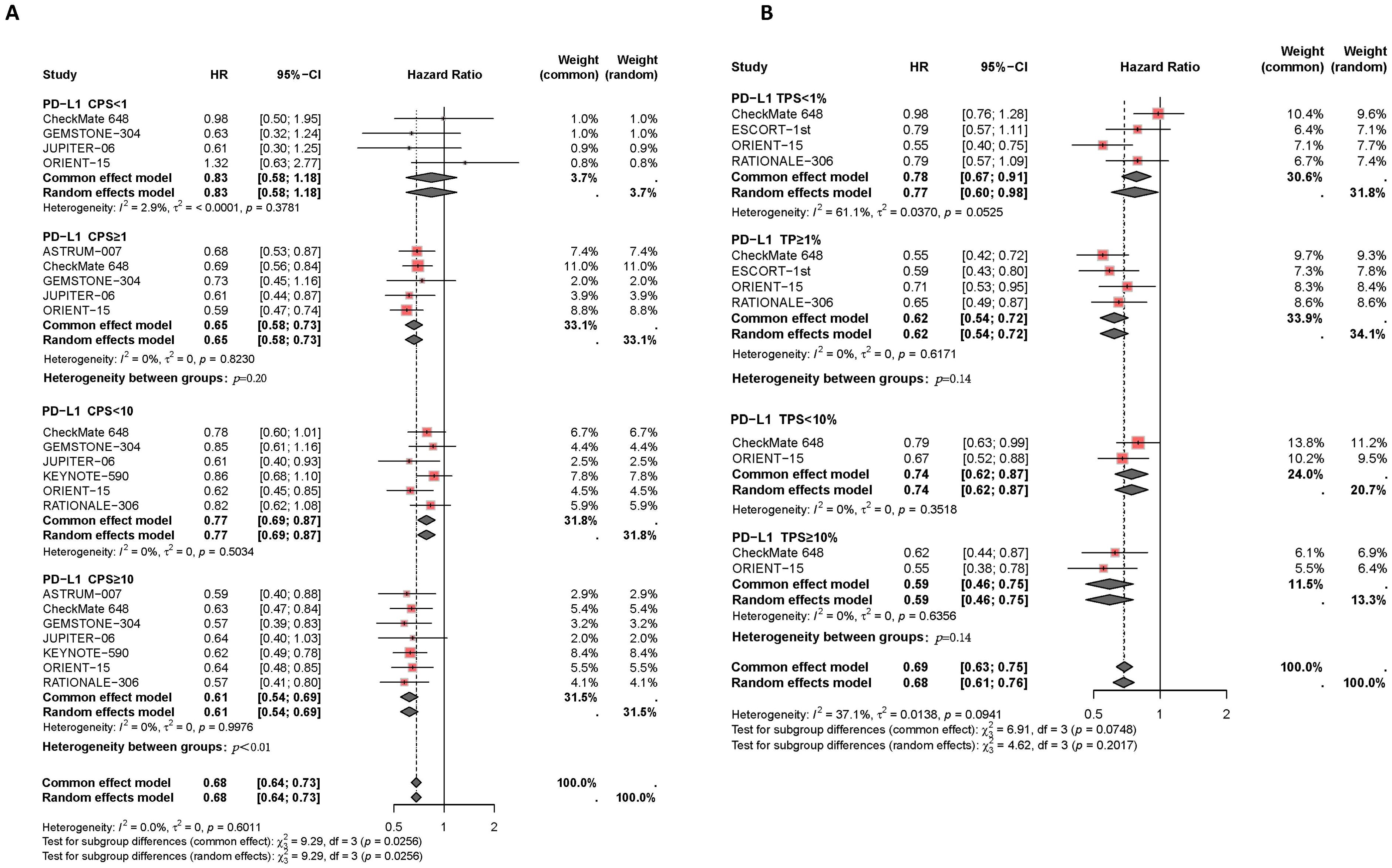
Figure 3. Forest plot of subgroup analysis comparing the overall survival HR in patients who received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-based therapy versus chemotherapy based on different PDL1 expression levels of CPS (A) and TPS (B).
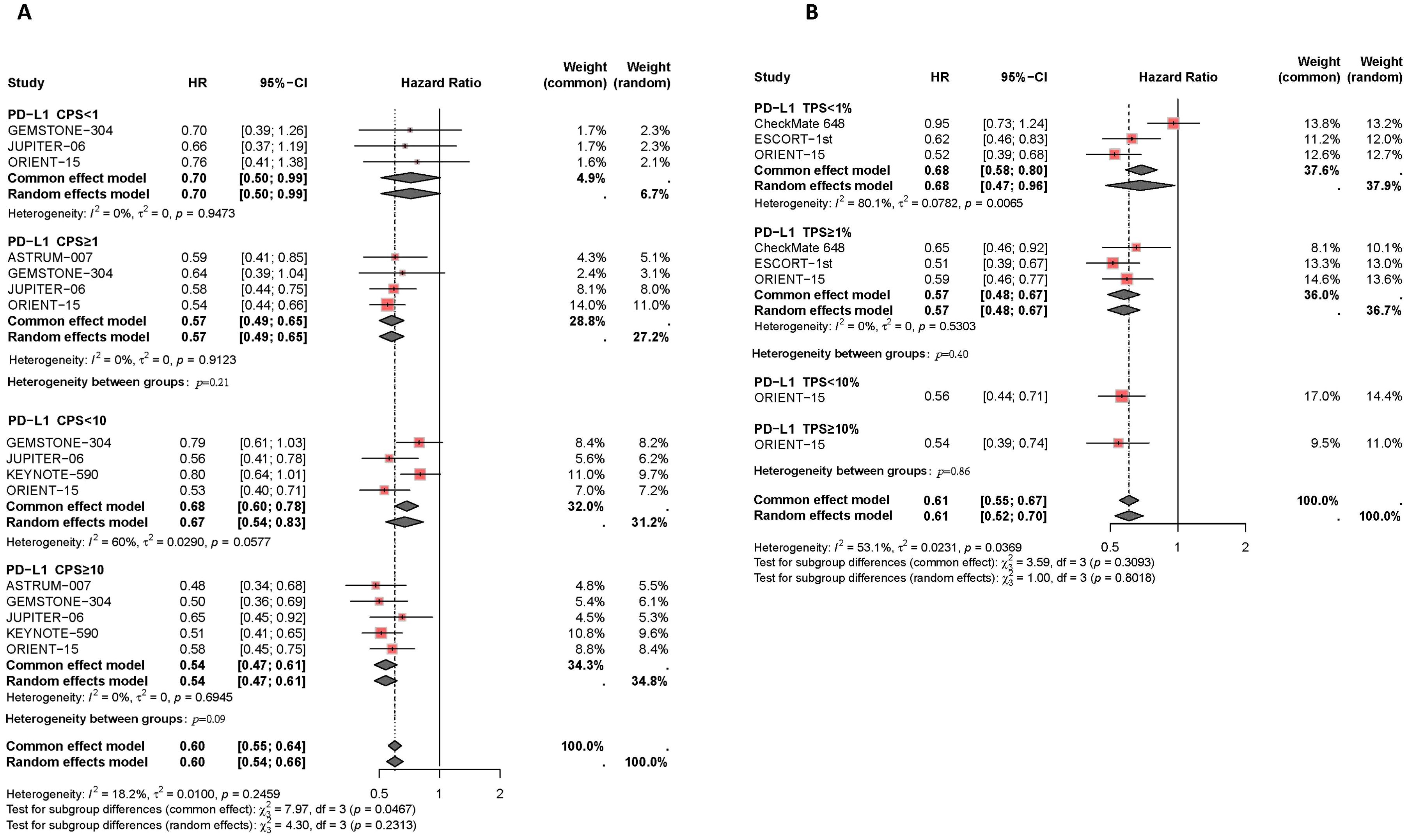
Figure 4. Forest plot of subgroup analysis comparing the progression-free survival HR in patients who received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-based therapy versus chemotherapy based on different PDL1 expression levels of CPS (A) and TPS (B).
“Figure 3 Forest plot of subgroup analysis comparing the overall survival HR in patients who received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-based therapy versus chemotherapy based on different PDL1 expression levels of CPS (A) and TPS (B).”
“Figure 4 Forest plot of subgroup analysis comparing the progression-free survival HR in patients who received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-based therapy versus chemotherapy based on different PDL1 expression levels of CPS (A) and TPS (B).” appear below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, meta-analysis, immunotherapy, combined positive score
Citation: Ren W, Zhang H, Li Y, Sun W, Peng H, Guo H, Hou T, Wang M, Hu Z, Wu T and Liu B (2025) Corrigendum: Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors as first-line treatment for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1611591. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1611591
Received: 14 April 2025; Accepted: 06 May 2025;
Published: 16 May 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Valentina De Falco, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyCopyright © 2025 Ren, Zhang, Li, Sun, Peng, Guo, Hou, Wang, Hu, Wu and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Baorui Liu, YmFvcnVpbGl1QG5qdS5lZHUuY24=; Tao Wu, dHd1QGJqbXUuZWR1LmNu; Zhendong Hu, aHVfemhlbmRvbmdAYWxpeXVuLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Wei Ren
Wei Ren Hanyu Zhang
Hanyu Zhang Yixin Li2†
Yixin Li2† Mengying Wang
Mengying Wang Tao Wu
Tao Wu Baorui Liu
Baorui Liu