- 1Clinical Medical College, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
- 2Dermatology Hospital of Jiangxi Province, Jiangxi Provincial Clinical Research Center for Skin Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Skin Diseases, The Affiliated Dermatology Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
- 3International Education College, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
Secukinumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that specifically targets and neutralizes interleukin (IL)-17A, a cytokine typically involved in the mucocutaneous defense against pathogens. Despite its favorable safety profile, serious adverse events such as inflammatory bowel disease, oral pemphigoid-like lesions, and lupus erythematosus have been reported. While widely used for psoriasis treatment, cytokine-based therapies carry a potential risk of triggering autoimmune responses. The precise mechanism by which secukinumab induces pemphigus erythematosus remains unclear but may involve immune dysregulation, autoantibody production, microbiota influences, and genetic susceptibility. We report a case of pemphigus erythematosus occurring in a psoriasis patient during secukinumab therapy, which improved after treatment with methylprednisolone sodium succinate injection, leading to clinical symptom resolution. Clinicians should remain vigilant for potential complications and develop individualized management strategies for patients receiving secukinumab.
1 Introduction
Pemphigus encompasses a group of chronic blistering diseases affecting mucous membranes and skin, including pemphigus vulgaris, pemphigus vegetans, pemphigus foliaceus, and pemphigus erythematosus, along with variants such as paraneoplastic pemphigus, IgA pemphigus, drug-induced pemphigus (DIP), and pemphigus herpetiformis. Pemphigus is triggered by IgG autoantibodies targeting keratinocyte adhesion proteins (desmogleins Dsg1 and Dsg3). Binding of IgG autoantibodies to desmosomal complexes causes intraepithelial adhesion loss (acantholysis), resulting in skin/mucosal blisters, bullae, and erosions (1). Although pemphigus erythematosus is recognized as an autoimmune disorder, the specific mechanism of desmosome destruction following autoantibody binding remains incompletely understood. Characteristic histopathological features include superficial epidermal acantholysis leading to subcorneal blisters, dermal edema, and perivascular inflammatory infiltrates; chronic lesions may show epidermal hyperplasia and parakeratosis. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) reveals the characteristic intercellular net-like deposition of IgG and C3 within the epidermis. Indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) detects serum-specific anti-intercellular epidermal antibodies (primarily anti-desmoglein 1 antibody), with titers correlating positively with disease activity. Notably, approximately 30%-80% of patients exhibit positive antinuclear antibodies (ANA), but concomitant cases meeting systemic lupus erythematosus diagnostic criteria remain rare (2). Herein, we report the case of a 54-year-old woman who developed pemphigus erythematosus three weeks after initiating secukinumab for psoriasis. Based on the temporal correlation between drug initiation and lesion onset, secukinumab-induced pemphigus erythematosus was suspected. While secukinumab has been reported to induce other autoimmune diseases (3), to the best of our knowledge, this represents the first documented global case of secukinumab-induced pemphigus erythematosus.
2 Case presentation
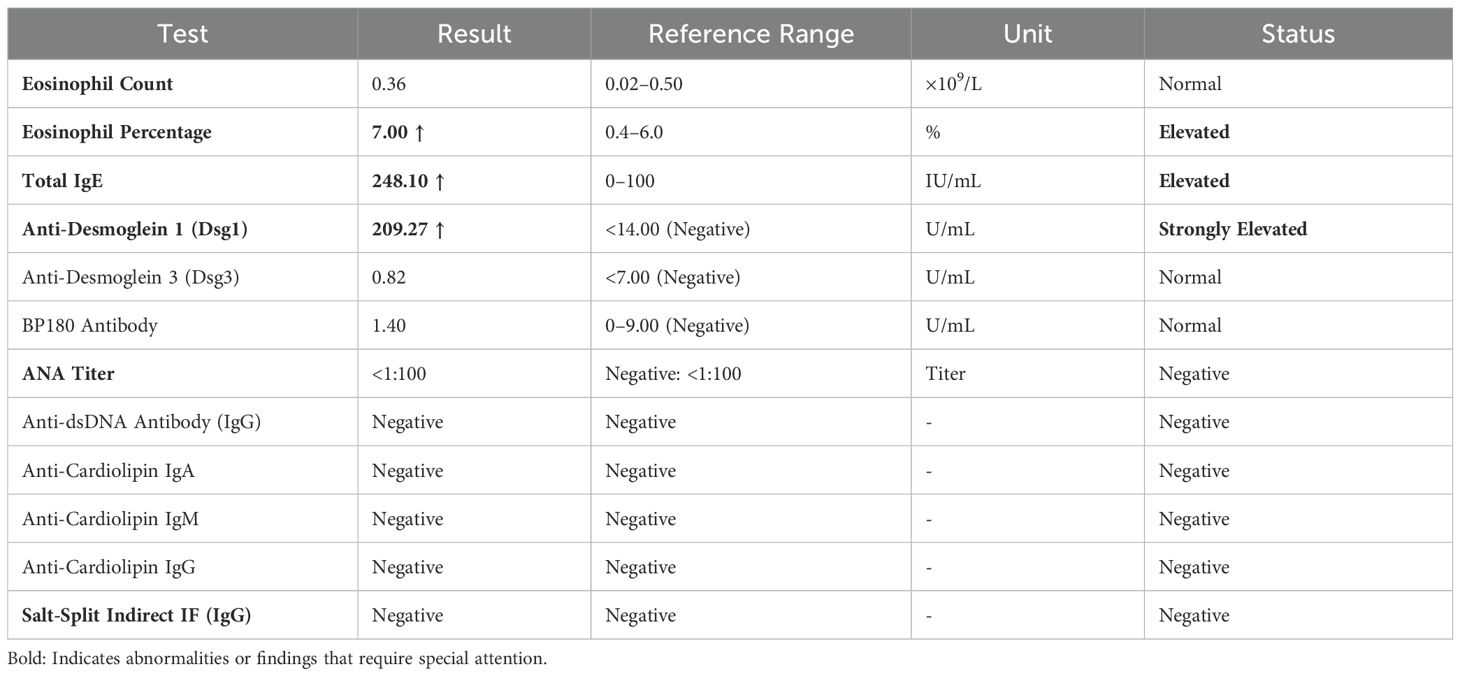
A 54-year-old woman with a 5-year history of psoriasis presented to our Department of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Histopathological examination revealed: extensive confluent parakeratotic foci containing neutrophilic microabscesses (Munro microabscesses); acanthosis with partial keratinocyte acantholysis and necrosis; spongiosis; club-shaped elongation of rete ridges; papillomatosis with overlying epidermal atrophy; and dilated, tortuous capillaries within the dermal papillae, accompanied by perivascular inflammatory cell infiltration in the superficial dermis (H&E, x100), confirming psoriasis (Figure 1A). Previous treatment with topical corticosteroids was ineffective. Due to widespread, recalcitrant lesions and the involvement of the IL-17A pathway in the disease pathology, the patient was initiated on secukinumab 300 mg subcutaneously. Three weeks post-initiation, erythematous plaques with pruritus appeared on her face. Suspecting a psoriasis flare, secukinumab was continued for two more doses. The rash progressively generalized, evolving into erythema and flaccid blisters, some of which ruptured forming yellow-crusted erosions (Figures 1B, C) that were slow to heal. Physical examination revealed widespread, round or oval red macules and patches on the face, trunk, and limbs. Some erythematous bases showed bright red erosions with yellow, greasy crusts, while others or adjacent normal skin exhibited flaccid vesicles/pustules with a positive Nikolsky sign. Scattered scaly plaques were also present. Mild facial edema and white ocular discharge were noted. No oral or genital blisters, erosions, or exudate were observed. Laboratory findings included: eosinophil count 0.36x10^9/L (↑), eosinophil percentage 7.00% (↑), IgE 248.10 IU/mL (↑). Autoantibodies: anti-Dsg1 antibody 209.27 U/mL (normal <14.00), anti-Dsg3 antibody 0.82 U/mL (normal <7.00), BP180 antibody 1.40 U/mL (normal 0-9.00). ANA titer <1:100. Anti-dsDNA (IgG), anticardiolipin antibodies (IgA, IgM, IgG) were negative. Salt-split skin IIF (IgG) was negative (Table 1). A skin biopsy from the right thigh showed hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, superficial crusting, acantholysis in the upper granular and spinous layers with intraepidermal cleft formation, and a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed predominantly of lymphocytes and eosinophils (Figures 1D, H&E, x40). DIF of the right thigh biopsy revealed linear deposition of IgG and C3 at the dermoepidermal junction (DEJ); IgA and IgM were negative (Figures 1E, F). Based on these findings, a diagnosis of pemphigus erythematosus was established. Secukinumab was discontinued. Treatment with methylprednisolone sodium succinate (32 mg IV daily) led to significant improvement, with resolution of psoriasis lesions observed during this period (Figures 2A, B). During follow-up, the patient was maintained on low-dose oral corticosteroids without new lesions. However, 10 months after discharge, she developed pea-sized red papules with silvery-white scales on her right axilla and lower abdomen (Figures 3A, B).
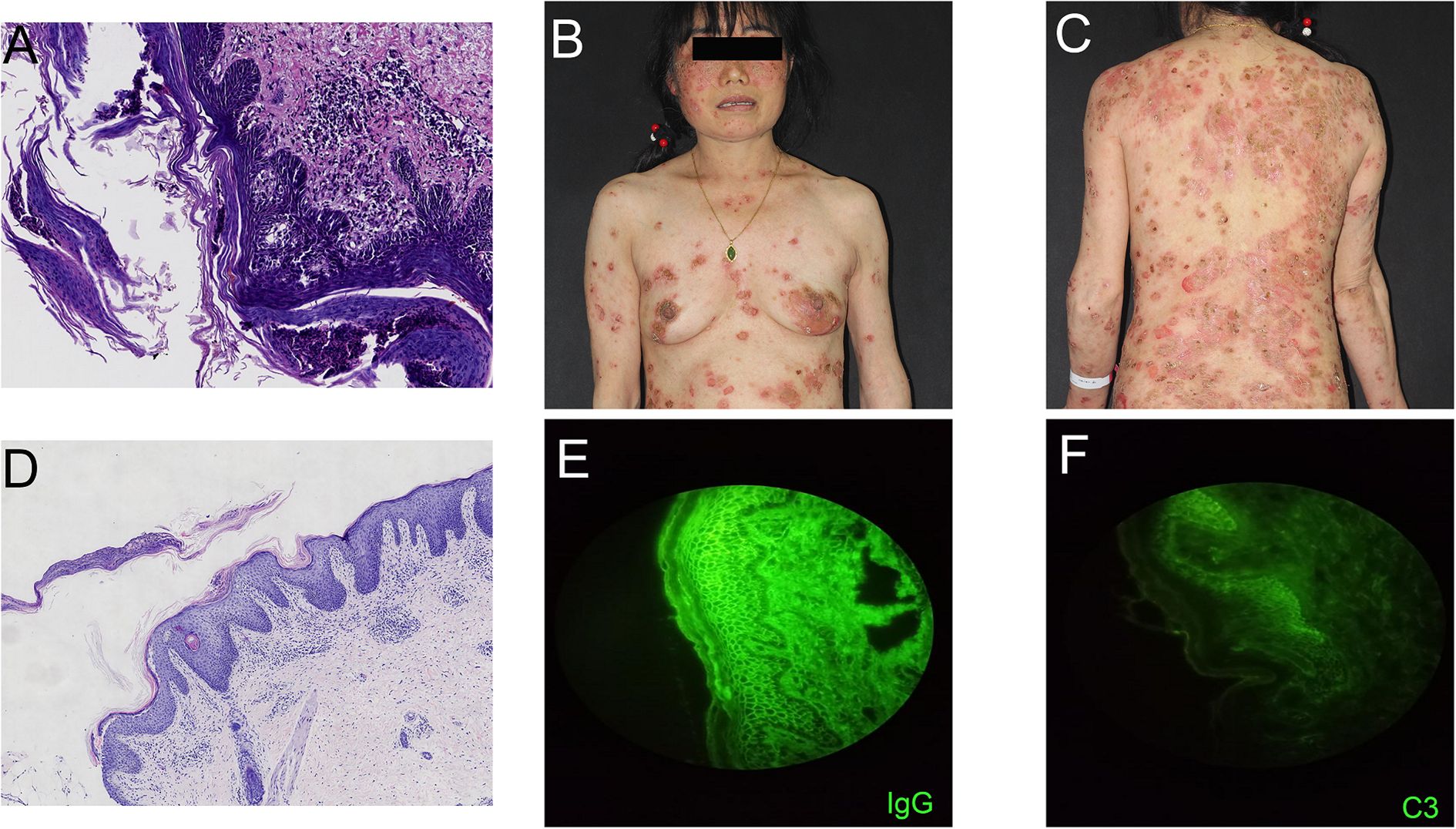
Figure 1. (A) Skin biopsy reveals extensive confluent hyperkeratotic lesions within the epidermis, accompanied by neutrophil infiltration forming Munro microabscesses; acanthocyte proliferation with partial acantholytic necrosis leading to spongiotic edema; rete ridges exhibit club-like elongation extending into the dermis. Dermal papillae project upward into the epidermis, with overlying epidermal atrophy; capillaries within the dermal papillae show proliferation, tortuosity, and dilation. Perivascular inflammatory cell infiltration is observed in the superficial dermis ((H&E; magnification, 100x). (B, C) Generalized bright red vesicles, thick yellow seborrheic crusts, as well as blisters and flaccid pustules on erythematous or normal skin are present. (D) Skin biopsy (right thigh) demonstrates hyperkeratosis, surface crusting, acantholysis in the granular layer and upper spinous layer, and intraepidermal cleft formation. Scattered perivascular inflammatory infiltrates composed predominantly of lymphocytes and eosinophils are seen in the superficial dermis ((H&E; magnification, 40x). (E, F) Direct immunofluorescence shows linear deposition of IgG and complement C3 at the dermoepidermal junction, while IgA and IgM are negative.
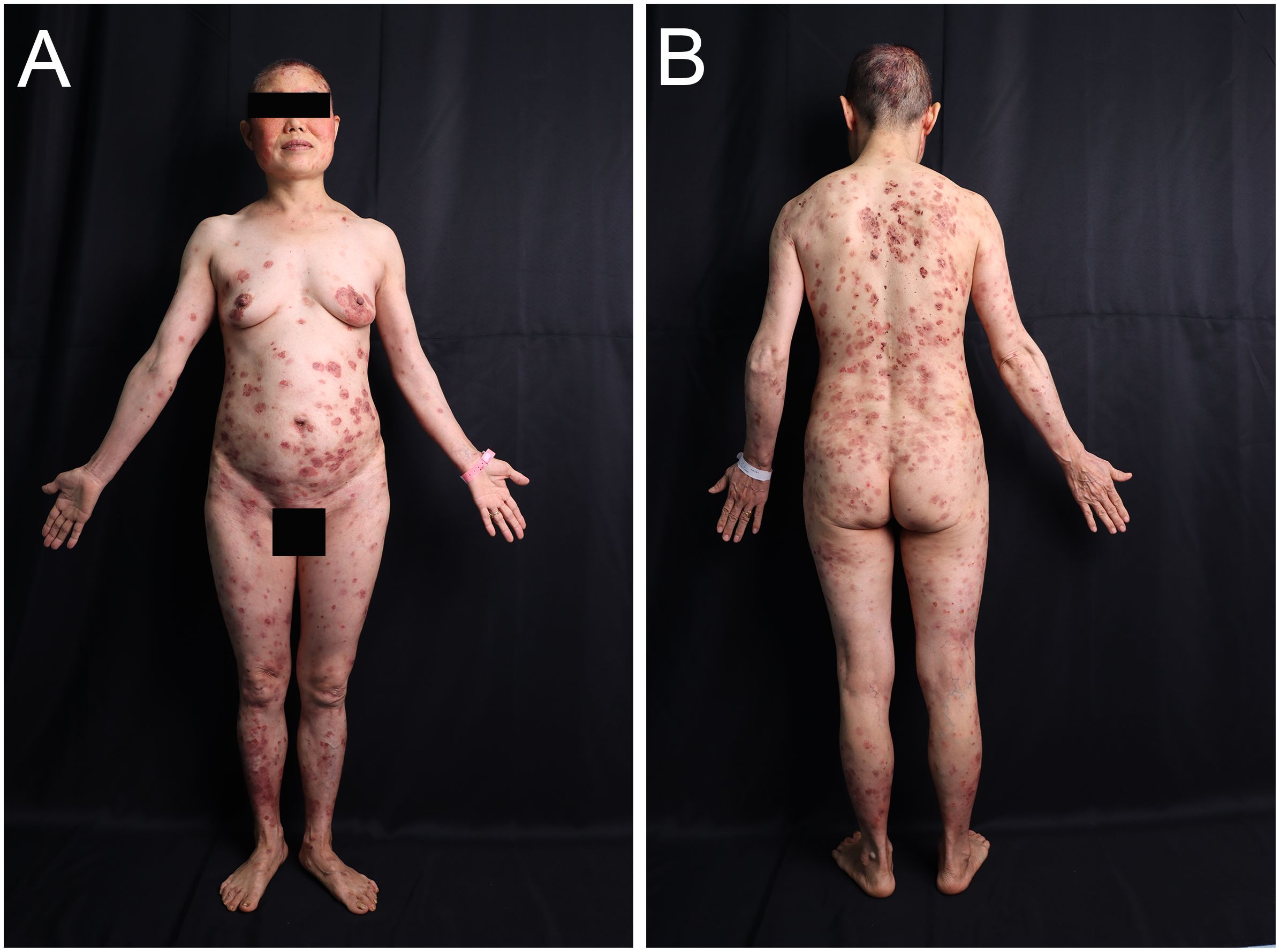
Figure 2. Images of the patient after treatment. (A, B) Significant improvement in lesions after glucocorticoid treatment.
Figure 3. Images of the patient relapsing. (A, B) Recurrence of psoriatic lesions 10 months after discharge when glucocorticoid administration was terminated.
3 Discussion
Pemphigus erythematosus, also known as Senear-Usher syndrome, is considered a subtype of pemphigus foliaceus. It predominantly affects elderly women, exhibiting overlapping clinical and immunological features of pemphigus foliaceus and cutaneous lupus erythematosus (4, 5). Lesions favor the seborrheic areas of the face, scalp, chest, and back, sometimes extending to the axillae and groin, but rarely involve the extremities. It primarily presents with erythema and scaling, requiring differentiation from lupus erythematosus and seborrheic dermatitis. The exact pathogenesis is unknown but may involve shared genetic markers and pathways regulating CD4+ T cells, such as IRF8 and STAT1 expression (6). Sun exposure has also been reported to exacerbate the condition (7). Senear and Usher proposed a potential link between pemphigus and lupus, possibly related to “shared autoimmunity,” with early mechanistic research focusing on the molecular level (8).
Drugs inducing DIP are categorized into thiol-containing drugs (e.g., penicillamine, captopril, bucillamine), phenol-containing drugs (e.g., aspirin, rifampicin, levodopa), and non-thiol/non-phenol drugs. Thiol drugs activate proteases and interfere with desmoglein function. Phenol drugs induce acantholysis via complement and protease modulation. Secukinumab, a non-thiol/non-phenol drug, may induce DIP through various mechanisms, such as activating autoantibodies or altering target antigen structures on keratinocytes (9). Thiol drugs typically induce pemphigus foliaceus, while non-thiol drugs often cause pemphigus vulgaris (10, 11). This case presented as pemphigus erythematosus, a phenotype not previously reported in the literature.
Reviewing prior literature, common adverse events associated with secukinumab include inflammatory bowel disease, eczematous drug eruptions, drug-associated vasculitis, and drug-induced lupus (12). Psoriasis is primarily driven by Th1/Th17 immunity, whereas pemphigus erythematosus is characterized by Th2 predominance. It is hypothesized that blocking the Th1/Th17 pathway may induce a counter-regulatory shift towards Th2 activation (13). In this case, the marked elevation of anti-Dsg1, eosinophilia, and dermal eosinophilic infiltrate suggest that IL-17A inhibition may have downregulated the Th1/Th17 axis, relieving inhibition of Th2 cells and promoting IL-4/IL-13 elevation. The eosinophilic infiltration and elevated IgE observed support Th2 predominance, potentially driving B cells to produce anti-Dsg1 autoantibodies and trigger pemphigus erythematosus. This highlights the close association between pemphigus erythematosus and type 2 inflammation involving eosinophils. The T helper 2 (Th2) pathway plays a crucial role in pemphigus. Anti-Dsg IgG production and disease severity correlate with Th2 activity. IL-4 induces Th2 proliferation, promotes isotype switching to IgG4 and IgE, and stimulates eosinophil and mast cell proliferation/degranulation (14).
Induction of pemphigus erythematosus may also involve dysregulated microbiota-immune interactions. Studies suggest IL-17 provides anti-inflammatory protection; its inhibition reduces antimicrobial peptides (e.g., β-defensins), disrupting microbial barrier balance and potentially promoting Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Superantigens from S. aureus could then activate autoreactive T/B cells (15). This inhibition might also induce polyclonal B-lymphocyte activation and autoantibody production (16). Murine studies show IL-17RA knockout leads to skin dysbiosis (e.g., increased Staphylococci and Corynebacteria), releasing antigens and activating autoimmune responses (17). Additionally, genetic susceptibility may play a role; specific HLA alleles (e.g., HLA-DRB1*04:02) could enhance susceptibility to biologic-induced autoimmunity by influencing antigen presentation efficiency (18).
4 Conclusion
As treatment needs for autoimmune diseases grow, the use of biologics has expanded significantly. However, associated adverse effects are increasingly recognized. With newer agents, predicting these side effects is challenging, and their underlying pathophysiology remains elusive. This case suggests secukinumab may trigger pemphigus erythematosus via Th2 immune deviation and skin dysbiosis. Clinicians using secukinumab should promptly investigate this adverse event if flaccid blisters appear on sun-exposed areas, even if DIF findings are atypical, by combining assessment with anti-Dsg1 antibody testing. Immune dysregulation induced by IL-17A inhibition likely contributed to this case. Clinicians must be aware of this potential adverse effect and consider the need for tailored management strategies and further investigation in patients receiving secukinumab.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
FH: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Resources. HP: Writing – original draft, Investigation. JG: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Supervision. XT: Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XW: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. JB: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. PH: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Resources. LD: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. ML: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. HY: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients for their cooperation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bystryn JC and Rudolph JL. Pemphigus. Lancet. (2005) 366:61–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66829-8
2. Oktarina DA, Poot AM, Kramer D, Diercks GF, Jonkman MF, and Pas HH. The IgG “lupus-band” deposition pattern of pemphigus erythematosus: association with the desmoglein 1 ectodomain as revealed by 3 cases. Arch Dermatol. (2012) 148:1173–8. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2012.1896
3. Ali AK, Torosian A, Porter C, Bloomfeld RS, and Feldman SR. New onset inflammatory bowel disease in patient treated with secukinumab: Case report and review of literature. Dermatol Ther. (2021) 34:e15151. doi: 10.1111/dth.15151
4. Makino T, Seki Y, Hara H, Mizawa M, Matsui K, Shimizu K, et al. Induction of skin lesions by ultraviolet B irradiation in a case of pemphigus erythematosus. Acta Derm Venereol. (2014) 94:487–8. doi: 10.2340/00015555-1781
5. Hobbs LK, Noland MB, Raghavan SS, and Gru AA. Pemphigus erythematosus: A case series from a tertiary academic center and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. (2021) 48:1038–50. doi: 10.1111/cup.13992
6. Sezin T, Vorobyev A, Sadik CD, Zillikens D, Gupta Y, and Ludwig RJ. Gene expression analysis reveals novel shared gene signatures and candidate molecular mechanisms between pemphigus and systemic lupus erythematosus in CD4(+) T cells. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01992
7. Malik M and Ahmed AR. Concurrence of systemic lupus erythematosus and pemphigus: coincidence or correlation. Dermatology. (2007) 214:231–9. doi: 10.1159/000099588
8. Pérez-Pérez ME, Avalos-Díaz E, and Herrera-Esparza R. Autoantibodies in senear-usher syndrome: cross-reactivity or multiple autoimmunity. Autoimmune Dis. (2012) 2012:296214. doi: 10.1155/2012/296214
9. Palleria C, Bennardo L, Dastoli S, Iannone LF, Silvestri M, Manti A, et al. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers induced pemphigus: A case series and literature review. Dermatol Ther. (2019) 32:e12748. doi: 10.1111/dth.12748
10. Saito Y, Hayashi S, Yamauchi A, Okamoto M, Kaminaga T, Hamasaki Y, et al. Tracing the origins of active amide group-positive drug-induced pemphigus vulgaris along the Silk Road: a case report of candesartan-induced pemphigus vulgaris and review of nonthiol drug-induced pemphigus. Int J Dermatol. (2018) 57:e131–4. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14108
11. Yoshimura K, Ishii N, Hamada T, Abe T, Ono F, Hashikawa K, et al. Clinical and immunological profiles in 17 Japanese patients with drug-induced pemphigus studied at Kurume University. Br J Dermatol. (2014) 171:544–53. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12925
12. Liang J, Zhang S, Li Q, Yu Y, Chen X, and Zhang X. Review of secukinumab-induced adverse events of special interest and its potential pathogenesis. Dermatol Ther. (2022) 35:e15599. doi: 10.1111/dth.15599
13. Eyerich S, Onken AT, Weidinger S, Franke A, Nasorri F, Pennino D, et al. Mutual antagonism of T cells causing psoriasis and atopic eczema. N Engl J Med. (2011) 365:231–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1104200
14. Chen J, Chen S, Wu X, Jiang X, Wang Y, and Cheng H. The complicated use of dupilumab in the treatment of atypical generalized pemphigus Erythematous: A report of two cases. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2023) 19:2151290. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2151290
15. Eken A, Erdem S, Haliloglu Y, Okus FZ, Cakir M, Yetkin MF, et al. Temporal overexpression of IL-22 and Reg3γ differentially impacts the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunology. (2021) 164:73–89. doi: 10.1111/imm.13340
16. Kolls JK, McCray PB Jr, and Chan YR. Cytokine-mediated regulation of antimicrobial proteins. Nat Rev Immunol. (2008) 8:829–35. doi: 10.1038/nri2433
17. Floudas A, Saunders SP, Moran T, Schwartz C, Hams E, Fitzgerald DC, et al. IL-17 receptor A maintains and protects the skin barrier to prevent allergic skin inflammation. J Immunol. (2017) 199:707–17. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1602185
Keywords: pemphigus erythematosus, secukinumab, adverse drug event, psoriasis, autoimmune disease
Citation: Hu F, Peng H, Gong J, Tao X, Wang X, Bao J, He P, Dirwanto L, Liu M and Yang H (2025) Induced pemphigus erythematosus after treatment for plaque psoriasis with secukinumab: a case report. Front. Immunol. 16:1612422. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1612422
Received: 28 April 2025; Accepted: 27 August 2025;
Published: 10 September 2025.
Edited by:
Hongjiang Qiao, Fourth Military Medical University, ChinaMihaela Georgescu, Dr. Carol Davila Central Military Emergency University Hospital, Romania
Reviewed by:
Ines Lakos Jukic, University Hospital Centre Zagreb, CroatiaCopyright © 2025 Hu, Peng, Gong, Tao, Wang, Bao, He, Dirwanto, Liu and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mingqiang Liu, MTA5OTU5MDAxMkBxcS5jb20=; Hongbing Yang, MTM3MDcwOTAzOThAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Mingqiang Liu, orcid.org/0000-0003-2404-8415
Hongbing Yang, orcid.org/0009-0009-6638-8486
 Fengming Hu1,2
Fengming Hu1,2 Hong Peng
Hong Peng Xiaohua Tao
Xiaohua Tao Mingqiang Liu
Mingqiang Liu Hongbing Yang
Hongbing Yang