- 1Central Laboratory, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
- 2Institute of Medical Genetics and Reproductive Immunity, School of Medical Science and Laboratory Medicine, Jiangsu College of Nursing, Huaian, Jiangsu, China
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory, Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-based cell therapies, initially designed for oncology, are rapidly advancing as a novel and highly targeted approach for the treatment of autoimmune diseases (AIDs). By harnessing engineered immune cells to eliminate autoreactive immune components or restore immune homeostasis, CAR-based strategies offer new avenues beyond conventional immunosuppression. In this review, we summarize current applications of CAR-T cells in autoimmune diseases, and discuss emerging approaches including CAR-Tregs, chimeric autoantibody receptor T (CAAR-T) cells, CAR-NK cells, and CAR-macrophages. We also describe advances in CAR design, including antigen selection, co-stimulatory domains, and safety control mechanisms, which are critical for improving therapeutic precision and reducing side effects. In addition, we highlight the role of synthetic biology in enabling more flexible and controllable CAR functions. Finally, we discuss the main challenges facing clinical translation, such as antigen specificity, long-term persistence, and manufacturing feasibility. These developments collectively support the potential of CAR-based therapies as a next-generation option for autoimmune disease treatment.
Introduction
Autoimmune diseases (AIDs) represent a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by impaired self/non-self-recognition, leading to immune system dysregulation and subsequent attacks on the body’s own tissues. These autoimmune responses involve the activation of autoreactive lymphocyte clones and the production of autoantibodies against self-antigens, resulting in immune-mediated damage that affects multiple organs. Notably, autoreactive B-cell clones and autoantibodies targeting self-antigens are present even before the onset of clinical symptoms (1).
AIDs exhibit significant complexity in both their underlying mechanisms and clinical manifestations, ranging from mild laboratory abnormalities to life-threatening acute organ failure. This heterogeneity poses substantial challenges in clinical management and therapeutic development. Currently, the primary therapeutic approach for AIDs relies on broad-spectrum immunosuppressants and neutralizing antibodies. While these agents can effectively control disease progression, complete remission is rarely achieved. For instance, although autoreactive B-cells play a critical role in autoantibody production in most AIDs, targeting them with monoclonal antibodies such as Rituximab and Inebilizumab has demonstrated only limited efficacy, largely due to the persistence of these cells in lymphoid organs and affected tissues (2).
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-based cell therapies—originally developed for B-cell malignancies, are now being repurposed for AIDs treatment. Specifically, autologous CAR-T cells targeting CD19 have shown rapid and sustained depletion of circulating autoreactive B-cells, leading to clinical and serological remission in RA (3). However, CAR-T therapy in patients with autoimmune diseases is not without adverse effects, most commonly presenting as transient B-cell aplasia and low-grade CRS. Importantly, the risks of lymphodepletion-induced immunosuppression and infectious complications appear to be markedly reduced in AIDs compared to oncologic contexts, likely due to the preservation of hematopoietic niches and accelerated immune reconstitution in non-malignant conditions (4). These risks raise concerns about the therapeutic index of CAR-T cells in non-malignant settings. To mitigate these issues, engineered CAR-T cells incorporating “safety switches” and immunomodulatory elements have been developed to allow for controlled activation, function, and persistence (5).
Recent studies have elucidated key characteristics of AIDs that distinguish them from cancers, including the pathological role of autoantibodies, the need for immune homeostasis reconstitution in solid tissues, and the poor quality of patient-derived immune cells. Such factors may limit the effectiveness of conventional CAR-T approaches. In response, researchers have pursued more tailored strategies, including in vivo gene delivery approaches to bypass the need for preconditioning lymphodepletion, the use of mRNA-based CARs for transient expression, and the design of chimeric autoantibody receptor T cells (CAAR-T) that express autoantigen epitopes in place of conventional scFvs to selectively eliminate autoreactive B-cell clones (6, 7). CAR-Tregs generated from CD4+ T cells are also being investigated to re-establish immune tolerance in affected tissues (8). Given the prolonged manufacturing timelines and substantial commercial costs of autologous CAR-T cells for AIDs treatment, allogeneic immune cells are being explored for the development of “off-the-shelf” CAR-T products (9). Additionally, CAR-macrophages have been designed for improved tissue infiltration, and CAR-NK, which are not restricted by major histocompatibility complex (MHC), offer potential for allogeneic application.
Beyond expanding cell platforms and refining CAR designs, advances in synthetic biology have introduced new possibilities for CAR-based therapies. For instance, the “OR-gate” design–such as CD19/BCMA bispecific CAR-T cells–enables targeting of either CD19+ B-cells or BCMA+ plasma cells, thereby enhancing therapeutic breadth (10). In contrast, “AND-gate” design requires dual-antigen recognition to activate the cell, thereby improving specificity and reducing off-target effects. In addition, the synthetic Notch (synNotch) system, a modified version of Notch signaling pathway, enables signal-dependent gene transcription by releasing natural or synthetic transcription factors upon antigen engagement (11).
In this review, we discuss recent advancements in CAR-based therapies for AIDs, focusing on improving efficacy and safety, selecting suitable cell platforms and CAR designs tailored to disease-specific characteristics, and leveraging synthetic biology to create innovative therapeutic strategies.
Current treatments of autoimmune disease
AIDs primarily result from inflammatory responses, cytolysis, and immune complex deposition, driven by the activation of autoreactive T and B-cells that continuously release excessive inflammatory factors, leading to tissue damage. Consequently, anti-inflammatory therapies have become a primary choice in AIDs treatment (12). Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (SAIDs), such as dexamethasone and prednisone, are widely used to inhibit the activation and infiltration of autoreactive T cells by suppressing prostaglandins and leukotrienes production. Although these hormonal treatments exhibit significant short-term efficacy, their long-term efficacy is limited by frequent disease relapse upon discontinuation and the emergence of adverse effects associated with chronic immunosuppression, including increased susceptibility to infections, hypertension, and osteoporosis (13). In addition to steroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and diclofenac, are commonly employed to alleviate localized joint inflammation in patients with RA. However, NSAIDs lack immunomodulatory properties and are ineffective in controlling the underlying disease progression. Moreover, prolonged NSAID use is associated with a wide range of adverse effects, including central nervous system abnormalities, cardiovascular complications, gastrointestinal disturbances, hematological alterations, and hepato-renal dysfunction (14). Given these limitations, concerns remain regarding the efficacy and safety of anti-inflammatory drugs in AIDs management.
To address these challenges, small-molecule drugs and neutralizing antibodies/receptors have become the alternative therapeutic strategies for AIDs. The Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) signaling pathway plays a crucial role in mediating inflammatory cytokines production, including interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), all of which contribute to AIDs pathogenesis (15). Tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor, has been clinically validated to relieve inflammation responses in AIDs by the inhibition of JAK1 and JAK3. However, the secretion of some key pro-inflammatory factors, including TNF-α, IL-1 and IL-17, is independent from the JAK pathway, necessitating the exploration of alternative therapeutic approaches (16). For patients exhibiting excessive TNF-α production who are resistant to Tofacitinib, neutralizing antibodies or soluble TNF-α receptors can serve as “traps” to neutralize and sequester free TNF-α, thereby mitigating tissue injury and inflammation. Beyond TNF-α, common neutralizing targets in AIDs include IL-1(targeted by Anakinra), IL-6 (targeted by Tocilizumab) and IL-17 (targeted by Secukinumab) (17–19). While these neutralizing antibodies provide effective symptomatic relief, they do not directly target the underlying immune dysregulation, such as the breakdown of immune tolerance and the persistent activation of autoreactive T and B-cells. IL-2, a pleiotropic cytokine, exhibits context-dependent immune regulatory functions (20). In the context of AIDs, CD4+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) prevent lethal autoimmunity in IL-2 receptor β-deficient mice, highlighting the critical role of IL-2 in Tregs-mediated immunosuppression (21). Subsequent studies revealed that IL-2 signaling through its high-affinity receptor, CD25 enhances Tregs function by promoting Forkhead box P3 (FoxP3) expression via the JAK3-STAT5 pathway (22). A 2016 clinical trial evaluating low-dose IL-2 therapy for SLE demonstrated selective modulation of Tregs, follicular helper T cells (Tfh), and IL-17-producing helper T cells (Th17) (23). To date, low-dose IL-2 therapy has achieved clinical remission in AIDs conditions such as primary Sjögre’n Syndrome and SLE with minimal adverse effects (24, 25).
Despite these promising findings, IL-2 therapy faces challenges, including a short half-life requiring frequent dosing and limited efficacy in suppressing autoantibody production (26). Given the essential roles of B-cells in autoantibody production, targeting B-cells remains a viable therapeutic strategy. Rituximab, a CD20-specific monoclonal antibody approved in 2004, facilitates B-cell depletion primarily through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and has demonstrated clinical benefits in RA. However, its broader application in other AIDs, such as SLE, has been constrained by the incomplete elimination of autoreactive B-cell reservoirs within lymphoid tissues (27). To address this limitation, Obinutuzumab—a humanized, glycoengineered anti-CD20 antibody which incorporates modifications that augment FcγRIII binding affinity—was developed with enhanced affinity for FcγRIII, resulting in stronger ADCC activity while attenuating complement-dependent cytotoxicity (28). In a phase II trial (NCT02550652) evaluating Obinutuzumab for the treatment of proliferative lupus nephritis, patients receiving standard therapy (mycophenolate and corticosteroids) combined with Obinutuzumab achieved a significantly higher complete renal response (CRR) rate (41%) compared to those receiving standard therapy alone (23%) at 104 weeks post-treatment (29). Another B-cell-targeting strategy involves inhibition of B cell survival and activation. Belimumab, a fully human recombinant IgG1 kappa monoclonal antibody that neutralizes B-cell-activating factor (BAFF), has demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing autoantibody titers and flare frequency, earning regulatory approval for the treatment of SLE in 2011 (30). Nevertheless, the need for repeated dosing and associated adverse effects, such as decreased IgG levels and heightened susceptibility to infections, have limited its widespread adoption (31).
Current therapies for AIDs primarily aim to inhibit inflammatory responses and restore immune tolerance. Although some treatments have achieved temporary clinical success in specific AIDs subtypes, they are often limited by immunosuppression-associated infection, incomplete depletion of autoreactive cell, and the requirement for repeat dosing. Moreover, inter-patient heterogeneity and the complex nature of these diseases mean that a substantial proportion of patients fail to respond adequately to existing therapies (32). Therefore, there remains an urgent need for a universal therapeutic approach that capable exerting precise immune modulation across multiple AIDs, while maintaining an optimal balance between therapeutic efficacy and safety.
CAR-T therapies in tumor and autoimmune diseases
Over the past decades, treatments for B-cell-driven malignancies have significantly benefitted from CAR-based strategies. CD19-targeted CAR-T cells, which induce potent B-cells depletion, have achieved remarkable success in clinical practice (33–35). The standard procedure involves isolating T cells from the patient’s peripheral blood, transducing them with a CAR construct specific to CD19, expanding the modified T cells in vitro, and reinfusing them into patients following lymphodepletion (36, 37).
The fundamental structure of CARs typically comprises three components: an extracellular single-chain variable fragment (scFv) that recognizes the target antigen, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain. In therapies for B-cell malignancies such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma or B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the scFv are typically designed to target CD19, a surface marker consistently expressed throughout B-cell development (38). The intracellular domain incorporates the CD3ζ signaling motif of the T-cell receptor (TCR)/CD3 complex, along with co-stimulatory domains such as 4-1BB or CD28, to provide activation signals for CAR-T cells. The CAR genes were usually delivered into patient-derived T cells via lentiviral vectors. However, the random integration feature of lentiviral vectors poses a theoretical risk for insertional mutagenesis, which could potentially contribute to secondary CAR-positive malignancies. Importantly, extensive clinical analyses indicate that such events are exceedingly rare and reveal no definite evidence directly linking CAR gene insertion to oncogenesis, despite case reports. In contrast, conventional cancer therapies such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation are well established contributors to secondary malignancies (39, 40). To mitigate this risk, the CRISPR-Cas9 system was employed to targeted insertion CAR gene with poly (A) sequences into the first exon of the TRAC gene, thereby replacing the endogenous TCRα constant region with the CAR (41). These CAR-positive T cells were expanded in vitro. Following infusion, CAR-T cells recognize cells expressing target antigen via their scFv, leading to activation and elimination of target cells through cytokine secretion (e.g., perforin and granzyme B) or engagement of apoptotic pathways such as factor associated suicide and its ligand (Fas/FasL) (42) (Figure 1).
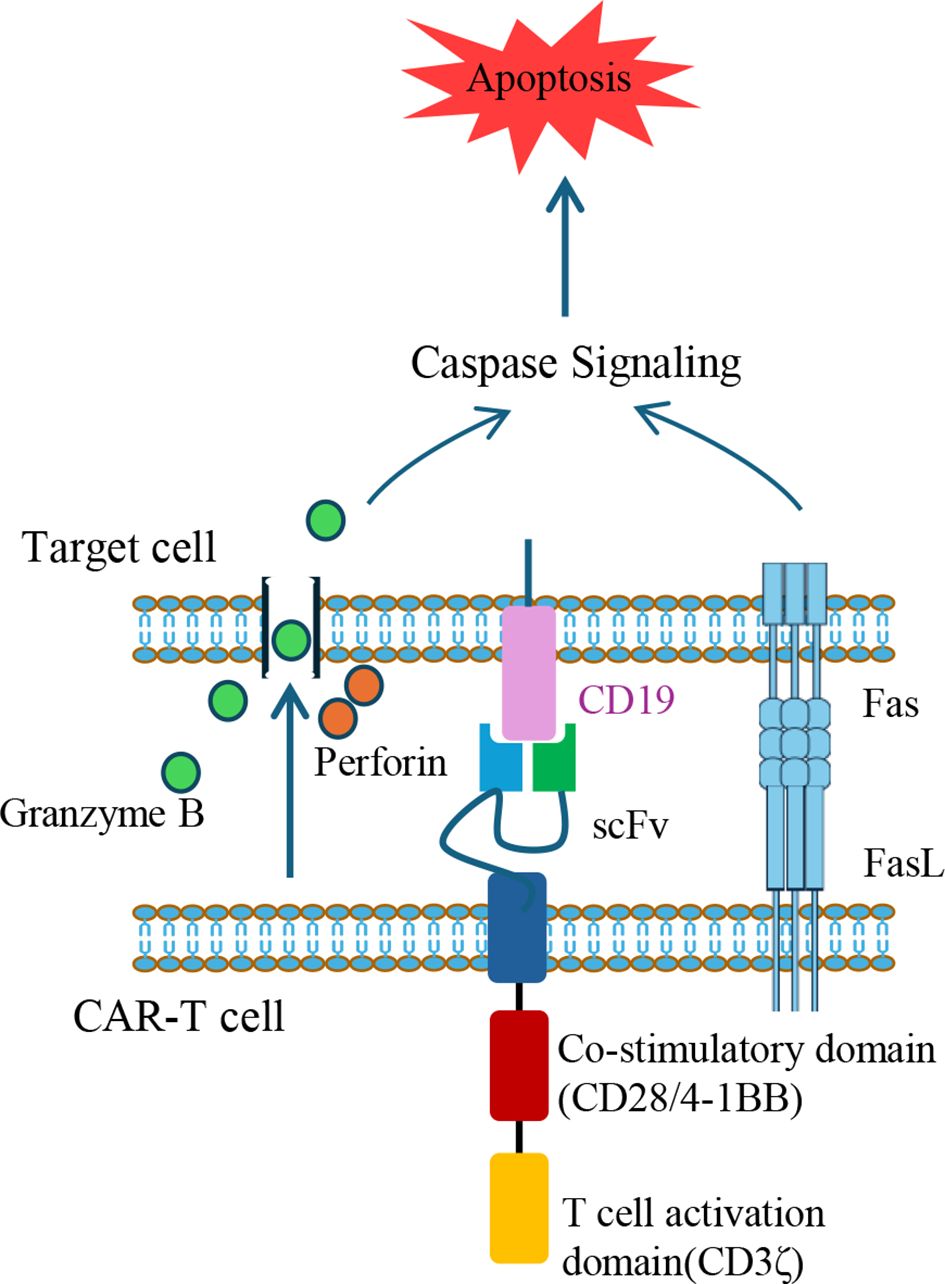
Figure 1. Mechanisms of target cell apoptosis induced by CAR-T cells. CAR-T cells eliminate target cells through two primary apoptotic pathways. One involves the secretion of perforin to create pores in the target cell membrane, allowing granzyme B to enter and activate caspase cascades. The second mechanism involves FasL expression on CAR-T cells, which engages Fas on target cells, triggering Caspase-dependent apoptotic signaling. The illustrated CAR construct contains a scFv targeting CD19, a co-stimulatory domain (e.g., CD28 or 4-1BB), and a T cell activation domain (CD3ζ). FasL, Fas ligand; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor.
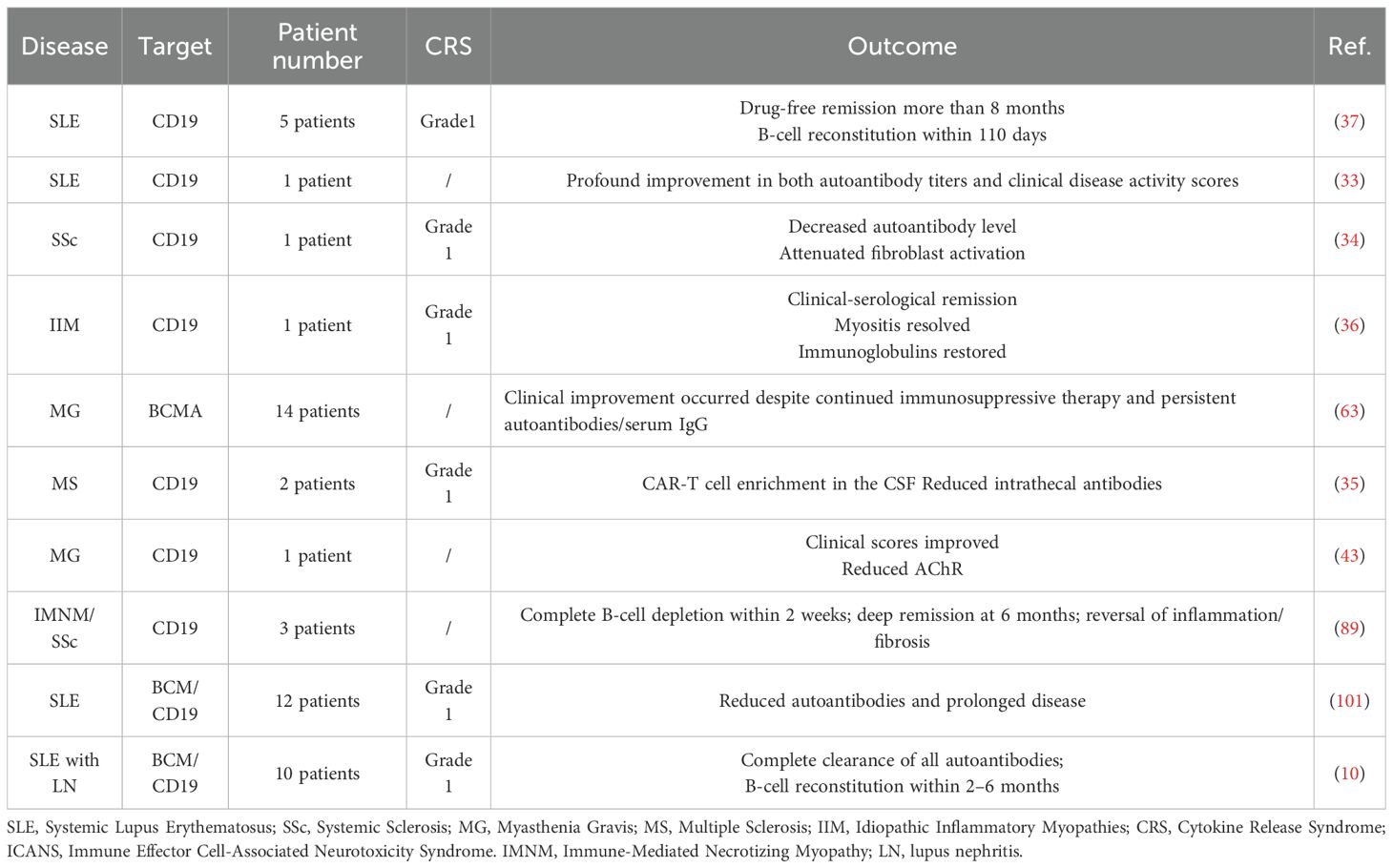
Beyond oncology, the application of CAR-T therapy has recently expanded into the field of AIDs, where it shows great promise as a novel immunomodulatory approach (43). Given the shared characteristics between B-cell-driven malignancies and AIDs, such as B-cell hyperactivation and excessive autoantibody production, CAR-T-mediated B-cell depletion may offer therapeutic benefits (Table 1). For instance, patients with SLE often exhibit elevated frequencies of CD19+CD20− B-cells, which are associated with autoantibody secretion (44). Moreover, animal studies have demonstrated that the infusion of anti-CD19 CAR-T cells effectively alleviates manifestations in murine SLE models (45).
However, regarding the differences in the mechanisms of AIDs and tumor, CAR-T strategies should be carefully evaluated before clinical use. In cancer patients, CRS and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) are major safety concerns, both arising from excessive cytokine release (e.g., IFN-γ, IL-6) by activated CAR-T cells. In a compassionate use report from Fabian Müller et al., 15 patients with severe AIDs—including 8 with SLE, 3 with idiopathic inflammatory myositis, and 4 with systemic sclerosis—were treated with anti-CD19 CAR-T cells. The treatment induced profound B-cell depletion and achieved sustained drug-free remission in all patients, with only one in each disease group experienced manageable grade 2 CRS and ICANS (46). This suggests a favorable safety profile of CAR-T therapy in AIDs compared to oncology settings. In cancer therapy, lymphodepletion is considered essential to enhance the efficacy of infused CAR-T cells. This conditioning regimen eliminates immunosuppressive cells such as Tregs and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), thereby creating a favorable microenvironment for CAR-T cell expansion and function (47). It also increases the bioavailability of homeostatic cytokines like IL-7 and IL-15, which are critical for T cell persistence and antitumor activity (48). For example, lymphodepletion significantly improved the therapeutic efficacy of Tisagenlecleucel, a commercial anti-CD19 CAR-T product, in treating refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, enhancing CAR-T cell expansion in vivo, prolonging patients’ progression-free survival, and increasing their remission rates (49).
Nevertheless, the role of lymphodepletion in AID treatment may differ from that in cancers, as the preservation of autologous immune cell subsets–particularly Tregs–is crucial for re-establishing immune homeostasis after CAR-T mediated depletion of pathogenic cells. Among available regimens, cyclophosphamide selectively depletes alloreactive T cells while sparing Tregs, facilitating the reconstitution of immune tolerance (50, 51). The combination of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine has proven effective in AIDs patients receiving anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy, with manageable adverse effects such as nausea, fatigue, and cytopenia (37, 46). However, the benefit-risk profile of cyclophosphamide requires carefully consideration—particularly in young female patients—due to its well-documented ovarian toxicity and the associated risk of infertility (52). To further obviate the need of lymphodepletion, in vivo CAR gene delivery approaches have been explored, such as target-specific lentiviral vectors that transduce T cells directly within the patients (53). These vectors introduce guide RNA (gRNA), Cas9 mRNA, and a CAR transgene flanked by homology arms (HA-CAR) into T cells. The targeting specificity is achieved through the display of anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 antibodies on the viral capsid (54). However, these approaches raise concerns regarding off-target transduction and limited control over CAR expression. To address these issues, engineered DNA-free virus-like particles (eVLPs) have emerged as promising vehicles, combining the key advantages of both viral and non-viral delivery. The eVLPs efficiently package and deliver macromolecules—such as base editor or Cas9 ribonucleoproteins (RNP, comprised Cas9 protein, crRNA and tracrRNA)—without integrating foreign DNA. Through the incorporation of pseudotyping glycoproteins with defined tropism, eVLPs allow for tissue- and cell-specific delivery, enabling precise, transient, and safe gene editing in vivo (55) (Figure 2).
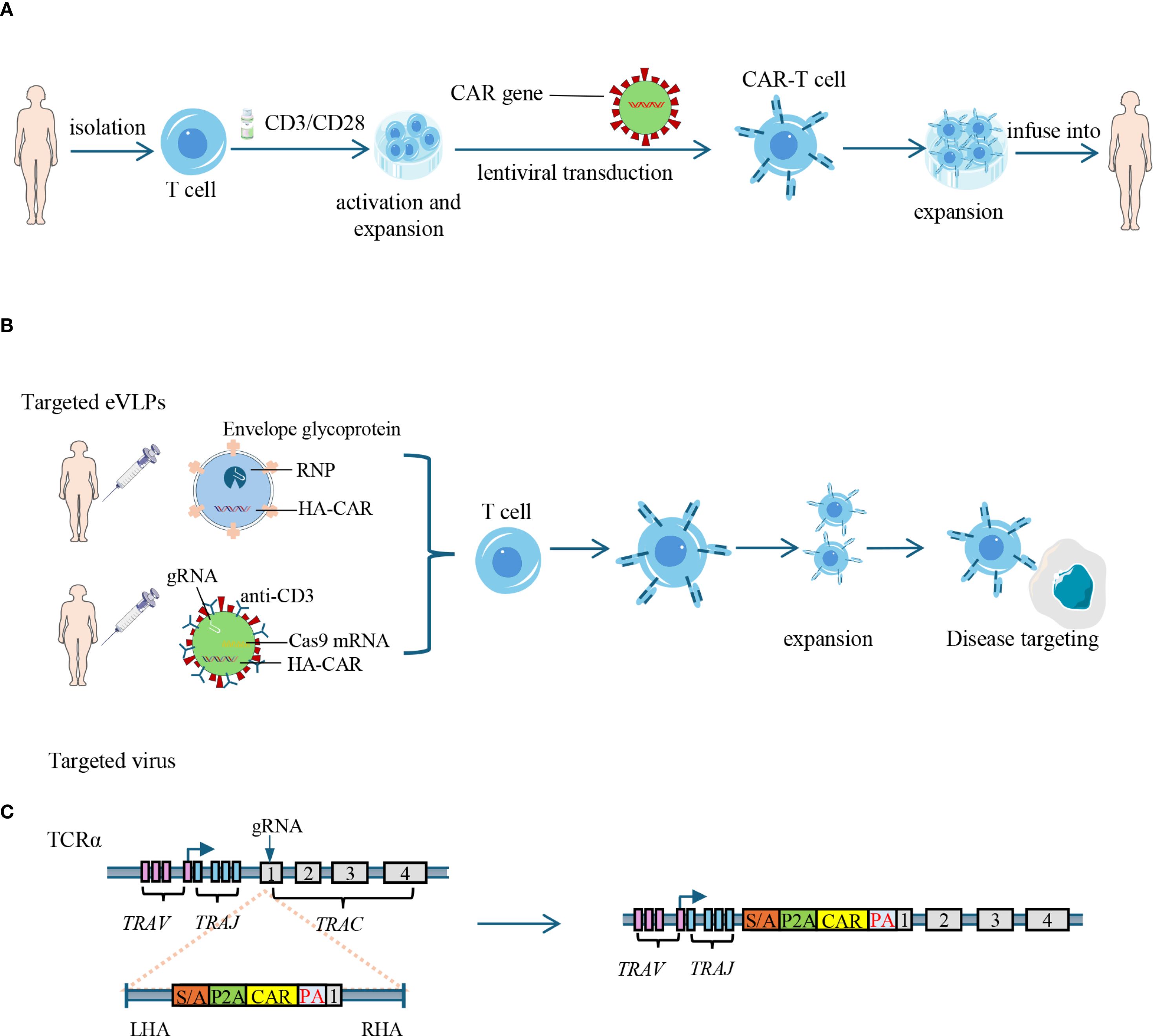
Figure 2. Strategies for CAR-T cell generation: in vitro engineering and in vivo delivery. (A) Ex vivo generation of CAR-T cells: T cells are isolated from peripheral blood and activated using CD3/CD28 stimulation. CAR genes are introduced via lentiviral transduction. The engineered CAR-T cells are then expanded in vitro and infused back into the patient. CAR: chimeric antigen receptor. (B) In vivo delivery of CAR constructs: engineered eVLPs carrying RNP (comprised Cas9 protein, crRNA and tracrRNA) and HA-CAR, or targeted virus carrying Cas9 mRNA, gRNAs, and HA-CAR are administered to directly transduce T cells in vivo, bypassing the need of lymphodepletion. eVLPs: engineered virus-like particles; RNP: ribonucleoprotein; HA-CAR: homology arms-flanking CAR sequence. (C) CRISPR-mediated targeted insertion of CAR into the TRAC locus: guide RNAs (gRNAs) and HA-CAR are used to disrupt the endogenous TCR and insert the CAR gene into the first exon of TCR α constant (TRAC) gene, reducing risks of graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic settings. RNP, ribonucleoprotein; TRAV, T cell receptor alpha variable region gene; TRAJ, T cell receptor alpha joining region gene; TRAC, T cell receptor alpha constant region gene; SA, splice acceptor; P2A, 2A peptide; PA, poly-A tail; LHA, left homology arm; RHA, right homology arm; eVLPs, Engineered virus-like particles.
Chronic B-cell aplasia is the most expected side effect in cancer patients treated with anti-CD19 CAR-T cells, often necessitate life-long immunoglobulin replacement therapy (IRT) to prevent infections (49). In contrast, B-cell aplasia in AIDs patients is typically transient, with B-cell counts recovering within a year—a median duration approximately 90 days—indicating different kinetics of CAR-T cells in the context of AIDs and malignancies (36). This difference was further confirmed by a recent comparative study by Muller et al, which demonstrated that CAR-T cell persistence in SLE patients (median: 110 days) is markedly shorter than that in B-cell lymphoma (median: 740 days). Likewise, immune reconstitution following CAR-T-induced B-cell depletion occurred significantly faster in SLE patients (155 days) compared to lymphoma patients (798 days) (4). These findings highlight the divergent behavior of CAR-T cells in malignant and autoimmune settings. Mechanistically, the continuous presence of CD19-expressing tumor cells provides sustained antigenic stimulation, driving prolonged CAR-T cell expansion and cytotoxic activity. This environment supports the generation of long-lived memory CAR-T cells—particularly CD45RO+CD27+CD8+ subsets—that can persist and rapidly regain effector function upon re-encounter with tumor antigens (56). Notably, tumor environment—particularly that in the bone marrow—provides a specialized survival niche with enriched cytokines such as IL-7 and IL-15, which are essential for the maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells and memory T cells (57). In contrast, CAR-T cells in AIDs primarily target autoreactive B-cells residing secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes and spleen. These anatomical compartments lack the specialized stromal and cytokine-rich milieu characteristic of the bone marrow, and thus do not support the establishment of long-lived CAR-T cell memory (58). Importantly, the inflammatory environment in AIDs typically resolves quickly following therapy, marked by rapid declines in cytokines like IL-6 and CXCL13. Simultaneously, homeostatic cytokines such as TGF-β1, CXCL12, and IL-7 rebound, promoting endogenous lymphocyte reconstitution. However, these factors are insufficient to support the prolonged survival of CAR-T cells, ultimately leading to a loss of therapeutic persistence (4). In addition, the antigenic burden in AIDs is generally lower and more transient than in malignancies, leading to rapid clearance of target cells. This results in an abrupt reduction in antigenic stimulation and subsequent contraction of the CAR-T cell (59). Moreover, leukapheresis products from SLE patients typically contain higher proportions of naïve T cells, which give rise to CAR-T cell products enriched in central memory phenotypes at their peak. These central-memory CAR-T cells exhibit shorter in vivo persistence than effector-dominant populations seen in B-cell lymphoma (4). Furthermore, AIDs patients typically retain an intact immune system, including functional hematopoietic niches that facilitate B-cell recovery once CAR-T activity subsides (37). CAR-T cells-associated immunodeficiency is more reversible and tolerable in AIDs, largely due to a combination of less supportive tissue microenvironments, lower antigen burden, intrinsic characteristics of the CAR-T cell products, and preserved hematopoietic function—all of which collectively favor their clinical applicability. However, a recently identified, AID-specific adverse effect of anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy—termed local immune effector cell-associated toxicity syndrome (LICATS)—garnered attention due to its high incidence (30 out of 39 patients affected). LICATS manifestations are strictly confined to organs previously affected by the underlying autoimmune pathology—for instance, skin and kidneys in SLE, or muscle in myositis— with skin (19 events) and renal (12 events) involvement being the most frequent among 54 reported events. These manifestations typically emerge at a median of 10 days post-infusion, during the phase of B-cell aplasia. They are generally self-limited, with a median duration of 11 days, and predominantly mild in severity (Grade 1–2). Distinct from CRS—which typically manifests within one day post-infusion and is characterized by elevated IL-6 levels—LICATS presents with a delayed onset, exhibits organ-specific localization, and lacks systemic IL-6 elevation. In parallel, LICATS also differs from classical autoimmune flares by the absence of characteristic serologic markers and its limited responsiveness to conventional immunosuppressive therapy. Rather than indicating disease relapse, LICATS is more likely a localized inflammatory reaction triggered by CAR-T-mediated clearance of tissue-resident autoreactive B cells. Nevertheless, its underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated in future studies (60).
CAR-engineered T cells tailored to the characteristics of autoimmune diseases
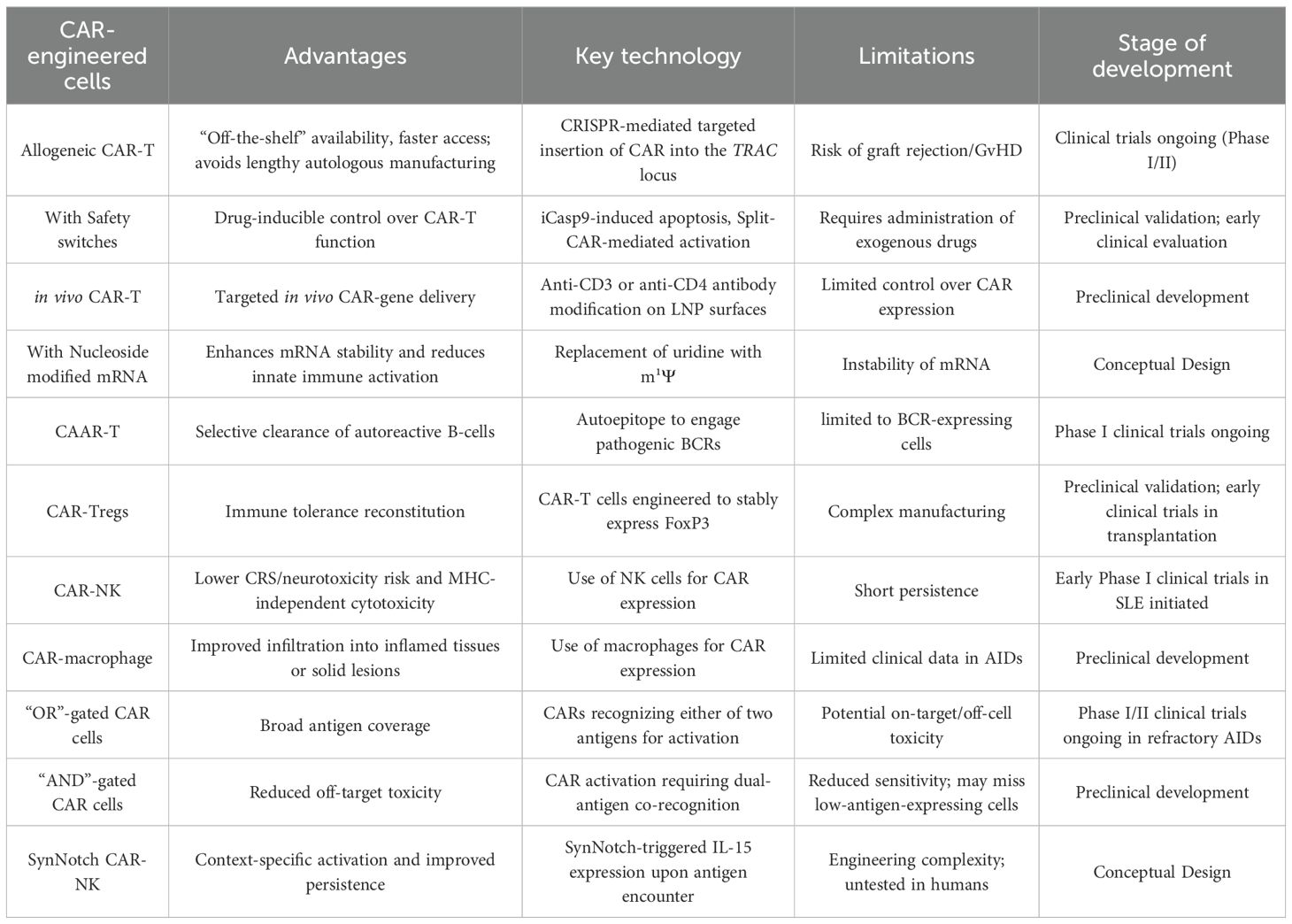
The applicability of CAR-T therapy needs to be carefully designed and evaluated to address the characteristics of AIDs. One prominent concern is the heightened risk of infection due to B-cell depletion, especially in patients previously exposed to immunosuppressive regimens. To mitigate potential safety issues, researchers have developed CAR constructs equipped with “safety switches” that allow for conditional control of CAR-T cell activation and persistence. For instance, inducible caspase-9 (iCasp9) functions as an “off switch”, triggering apoptosis of CAR-T cells upon administration of Rimiducid (61). In contrast, a drug-inducible “on switch” system has been designed using Rapamycin to dimerize FKBP-12 and FRB domains separately fused to the CAR scFv and intracellular signaling domains, thereby activating CAR-T cells only upon antigen binding and Rapamycin administration (62). These safety systems significantly enhance the controllability and safety of CAR-T therapy in non-malignant settings (Figure 3).
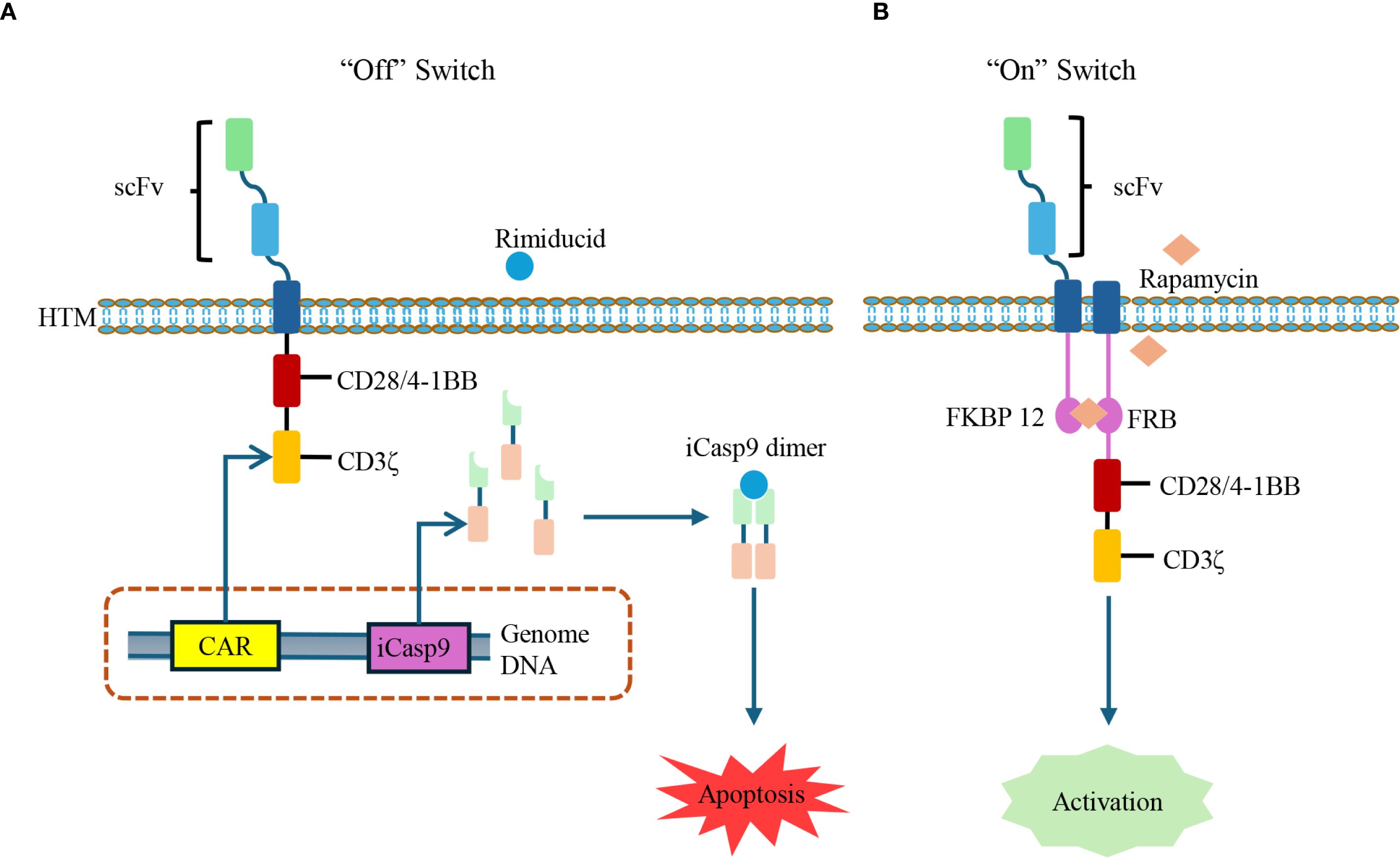
Figure 3. Controllable CAR-T cells with inducible safety switches. (A) Drug-inducible suicide switch: The iCasp-9 system is integrated into CAR-T cells. Upon administration of Rimiducid, iCasp-9 dimerizes and activates downstream caspase signaling, leading to CAR-T cell apoptosis and rapid termination of activity. iCasp-9: inducible caspase-9. (B) Drug-inducible activation switch: The CAR structure is split with FKBP12 and FRB domains, which can be dimerized in the presence of Rapamycin. This interaction restores CAR signaling, thereby enabling CAR-T cells activation in a ligand-dependent manner.
While long-term CAR expression is often essential in cancer therapy, time-dependent CAR expression has gained favor in the context of AIDs due to its improved safety profile. Transient CAR-T cells are generated by transfecting T cells with CAR-encoding mRNA, allowing temporary CAR expression and reducing the risk of prolonged off-target effects or cytokine storms. A recent clinical study in 14 patients with myasthenia gravis demonstrated that transient CAR-T cells induced clinical benefit with favorable safety and tolerability (63). Despite the advantages of transient CAR-T cells, challenges remain, including the inherent instability of mRNA and the notoriously low transfection efficiency of T cells by exogenous mRNA (64). Advances in nucleoside-modified mRNA technology have significantly improved mRNA stability and reduced activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), facilitating in vivo mRNA delivery (65). Furthermore, targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) have been engineered to specifically deliver this nucleoside-modified mRNA to T cells by surface-conjugated antibody, achieving effective and targeted gene expression in preclinical models (66, 67). These advances highlight the potential of tLNPs-mediated in vivo CAR-T generation as a promising non-viral approach for AIDs.
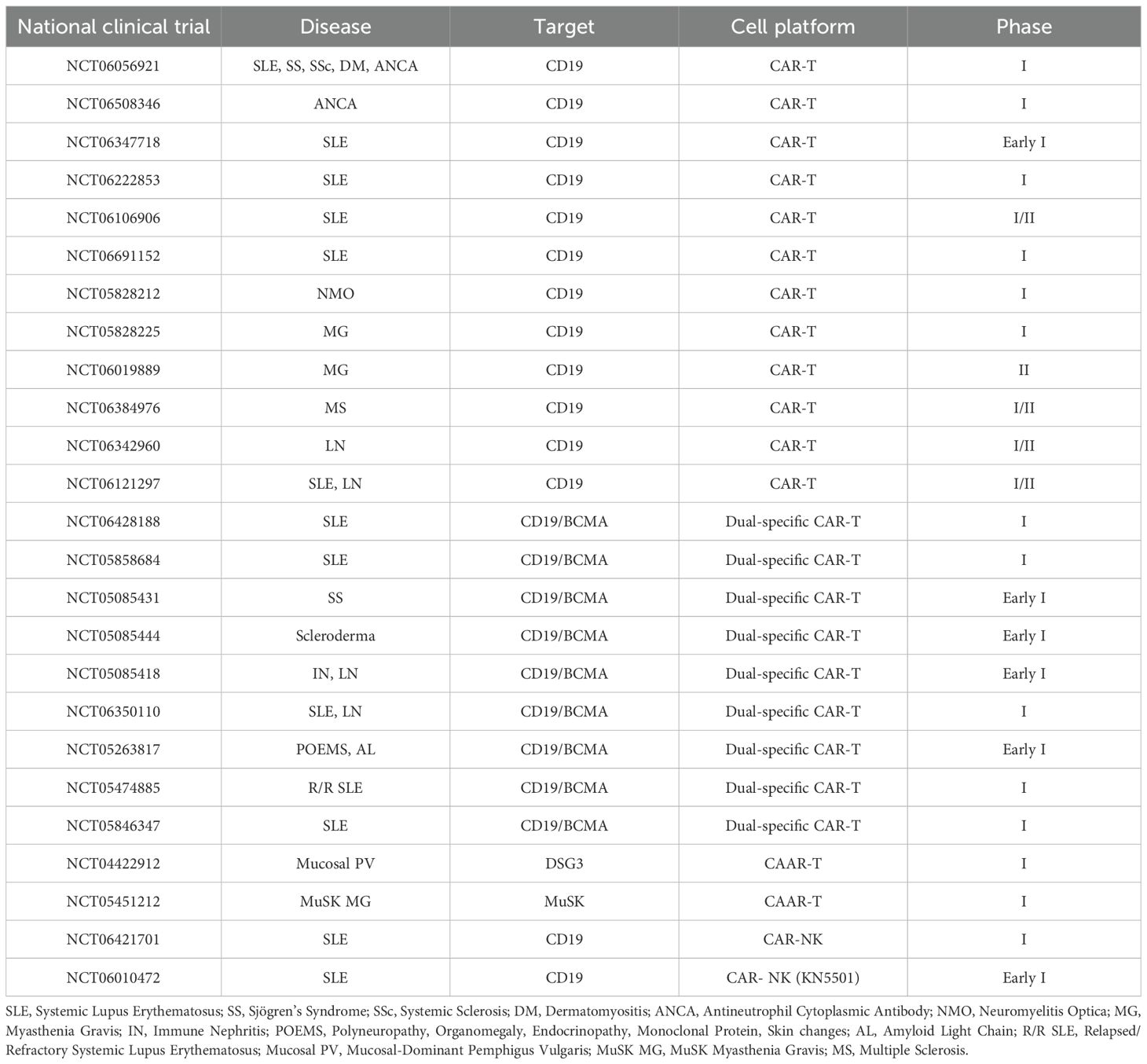
Unlike B-cell malignancies where CD19+ cells are abundant, the pathogenic B-cells in AIDs often represent a minor population expressing disease-specific B-cell receptors (BCRs). To selectively target these autoreactive B-cells, researchers have developed CAAR-T, in which the scFv is replaced with autoantigen epitopes (68). This modification enables “reverse targeting” of autoreactive B-cells that recognize these epitopes through their BCRs (69). Currently, Phase I clinical trials are evaluating CAAR-T therapies targeting mucosal pemphigoid (NCT04422912) and MuSK myasthenia gravis (NCT05451212). Additionally, CAAR-NK cells targeting La/SSB autoantigen-specific B-cells have been developed by incorporating lupus autoantigen sequences into NK-92MI cells, showing promise in preclinical models (70).
Given the critical role of Tregs in restoring immune homeostasis, their therapeutic use in AIDs is gaining attention. However, their low abundance in circulation poses a barrier to clinical applications. To overcome this, researchers have engineered Tregs (EngTregs) by transducing FoxP3 into CD4+ T cells (Figure 4). Buckner et al. pioneered an HDR-based gene editing approach to enforce stable FOXP3 expression in bulk CD4+ T cells, generating functional EngTregs with a durable phenotype and potent suppressive capacity (71). Beyond FoxP3 overexpression, alternative strategies have emerged, including the in vitro induction of Tregs through IL-2 stimulation (72), in vivo expansion using low-dose IL-2 (73), and epigenetic modifications—such as inhibition of histone deacetylases and selective demethylation of the Treg-specific demethylated region (TSDR)—to stabilize FoxP3 expression (74, 75). Recent findings also underscore the pivotal role of PI3Kδ signaling in Treg homeostasis, where gain-of-function mutations paradoxically impair suppressive activity despite expanding Treg numbers, positioning this pathway as a therapeutic target (76). For antigen-specific applications, TCR-modified EngTregs have been generated to recognize a novel PDC-E2 epitope in primary biliary cholangitis, allowing precise suppression of pathogenic T cell responses (77). To further enhance tissue specificity, these engineered Tregs have been equipped with antigen-specific receptors, giving rise to CAR-Tregs (78). Building on this concept, efforts are now directed toward optimizing CAR-Treg design and delivery. A representative advance is the dual HDR editing platform developed by the Rawlings group, which integrates FOXP3 stabilization, TRAC-targeted CAR insertion, and a chemical-inducible IL-2 system to improve EngTreg persistence and function (79). Complementing these cellular approaches, advances in nanomedicine have facilitated next-generation Treg therapies. Nanoparticle-based delivery systems enable targeted in vivo expansion of antigen-specific Tregs by encapsulating Treg-promoting cytokines or autoantigens, thereby enhancing local immune tolerance without systemic immunosuppression (80). Upon homing to inflamed tissues, these CAR-Tregs exert local immunosuppressive effects through cytokine secretion (TGF-β and IL-10) and induction of apoptosis in effector cells, with minimal systemic immune disruption (81). CAR-Tregs have shown promise in the field of transplantation, with HLA-A2-specific CAR-Tregs currently under clinical evaluation in renal (NCT04817774) and hepatic (NCT05234190) allograft recipients. In the context of AIDs, insulin-specific CAR-Tregs exhibited prolonged in vivo persistence—remaining detectable for approximately four months in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes—but did not improve disease outcomes (82). Preliminary data indicate myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-CAR-Tregs secrete remyelination-promoting factors, positioning them as a potential therapeutic approach for multiple sclerosis (MS) where neuroprotection is paramount (83). In inflammatory autoimmune conditions, CAR-Tregs targeting the interleukin-23 receptor (IL-23R) effectively suppressed pathogenic Th17 cell responses and attenuated colitis in preclinical models of Crohn’s disease (CD) (84). In addition, flagellin derived from Escherichia coli H18 (FliC)-specific CAR-Tregs preferentially home to the inflamed colon, suppress pathogenic T cells, and promote epithelial barrier integrity in preclinical models of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (85). More recently, a preclinical study evaluated Fox19CAR-Tregs—Mengineered by overexpressing FoxP3 and harboring an anti-CD19 CAR—for the treatment of SLE. The encouraging results showed that a single infusion of Fox19CAR-Tregs suppressed autoantibody production, delayed lymphopenia, and restored immune homeostasis within lymphoid organs in a humanized mouse model, all without detectable toxicity. Despite a limited survival duration, Fox19CAR-Tregs effectively protected SLE-affected organs with high efficacy and safety, supporting further exploration of this therapeutic approach (86).
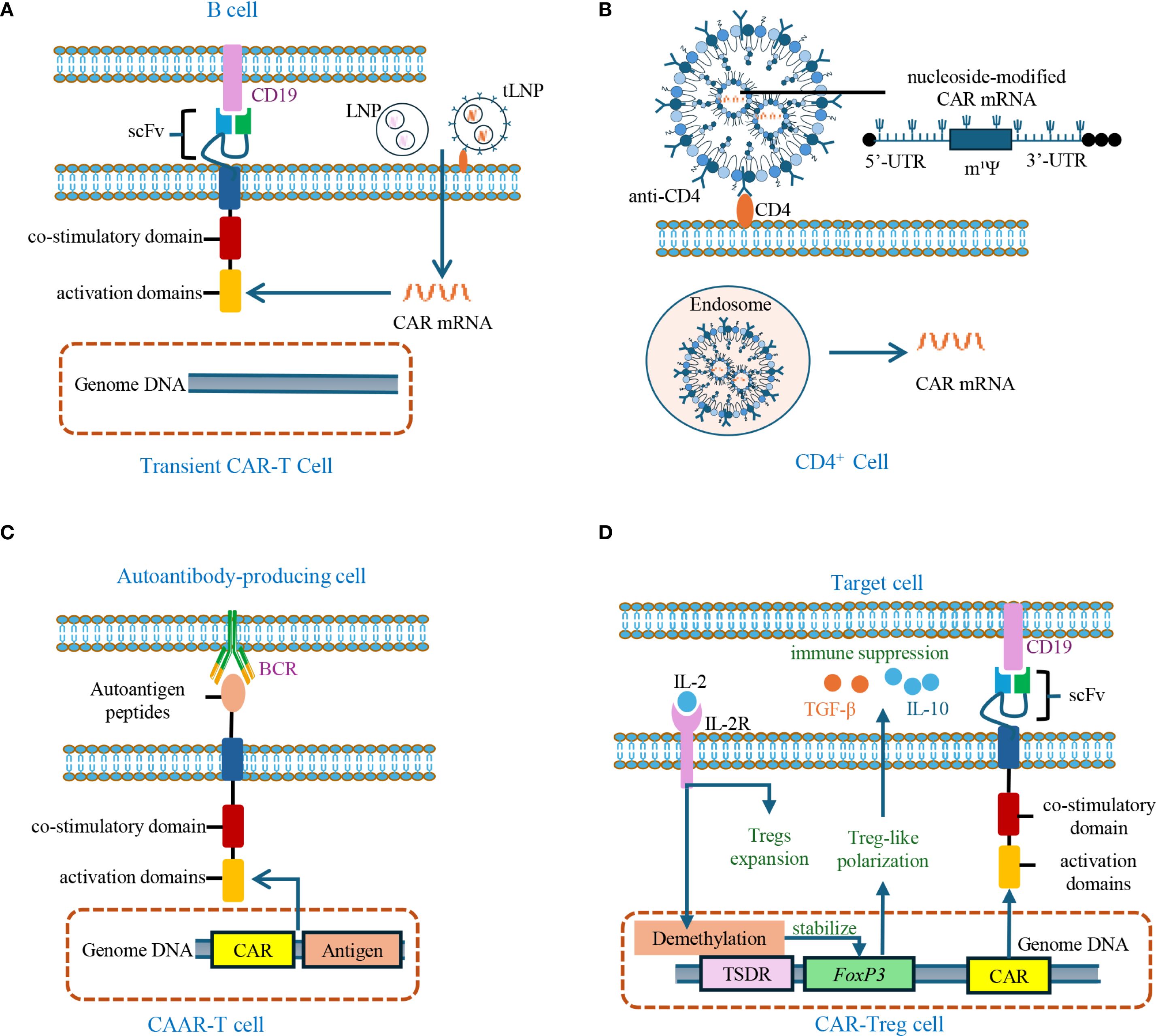
Figure 4. Engineered CAR-T cells and CAR-Tregs for autoimmune disease treatment. (A) Transient CAR-T cells are generated by delivering LNP or tLNP-encapsulated CAR mRNA targeting CD19 into T cells. Unlike conventional CAR-T cells, CAR expression here is transient and does not integrate into genomic DNA. LNP: lipid nanoparticle; tLNP: targeted lipid nanoparticle. (B) Schematic of tLNP-mediated CAR mRNA delivery: anti-CD4-targeted lipid nanoparticles encapsulating nucleoside-modified CAR mRNA (uridine replaced by 1-methylpseudouridine, m¹Ψ) are internalized by T cells through endocytosis, resulting in transient CAR expression. (C) CAAR-T cells are engineered to express autoantigen peptides in their extracellular domains, enabling selective targeting and depletion of autoantibody-producing cells via BCR engagement. CAAR: Chimeric autoantibody receptor; BCR: B-cell receptor. (D) CAR-Treg cells are engineered through FoxP3 overexpression or stabilization via TSDR demethylation in CD4+ T cells expressing tissue-specific CAR, thereby inducing a Treg-like phenotype. Upon antigen recognition, these CAR-Treg cells exert immunosuppressive functions, primarily by secreting IL-10 and TGF-β. FoxP3: Forkhead box P3; TSDR: Treg-specific demethylated region; CAR: chimeric antigen receptor; IL-2R: interleukin-2 receptor.
Nevertheless, the use of patient-derived autologous T cells for CAR-T manufacturing presents practical challenges, including prolonged production timelines and high commercial costs. These limitations have spurred interest in developing allogeneic, “off-the-shelf” CAR-T products to facilitate broader clinical application (87). Using CRISPR-Cas9, genes encoding HLA-A and HLA-B are knocked out from donor T cells to avoid host-versus-graft rejection (HvGR), while retention of HLA-C/E/G preserves NK cell tolerance (88). Additionally, deletion of the TCR α constant (TRAC) gene prevents graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) by eliminating native TCR expression (9). In a recent clinical trial, allogeneic anti-CD19 CAR-T cells with PDCD1 gene knockout achieved sustained B-cell depletion and drug-free remission for over six months in patients with myositis and systemic sclerosis, with no severe adverse events (89). This marked the first clinical application of PDCD1 knockout in allogeneic CAR-T therapy for AIDs, a strategy previously adopted in oncology to prolong CAR-T persistence. Moreover, a clinical trial evaluated allogeneic anti-CD19 CAR-T cells (TyU19), engineered using CRISPR/Cas9 to disrupt TRAC, HLA-A, HLA-B, CIITA, and PD-1 in patients with refractory SLE. This trial employed reduced-intensity lymphodepletion regimen that excluded anti-CD52 antibodies. TyU19 demonstrated robust expansion and persistence for over two months, with only grade 1 CRS observed. These results suggest that such genetic modifications effectively prevent immune rejection while preserving a favorable safety profile (90).
Utilizing innate immune cells for CAR-based therapies in autoimmune diseases
In malignancies, CAR-T therapy faces several limitations inherent to its mechanism and technical requirements. These include poor tissue infiltration, susceptibility to exhaustion, complex immune regulatory environments, and excessive cytokine release upon activation (91). Additionally, CAR-T cells preparation demands high-quality homogeneous T cells and involves substantial manufacturing costs, limiting its broader clinical applicability (92).
To address these challenges, alternative immune cell types have been investigated as potential platforms for CAR engineering. NK cells are MHC-unrestricted cytotoxic immune cells that are capable of lysing target cells by secreting granzyme B and perforin. Unlike T cells, NK cells derived from healthy donors can be readily prepared into off-the-shelf CAR-NK products, thereby avoiding the dysfunction or immunosuppression often seen in AIDs, meanwhile shortening patients’ waiting times and significantly lower treatment costs (93). Additionally, as target antigen loss is a major cause of CAR-T therapy failure, CAR-NK activation relies on the recognition of natural receptors, thus reducing the likelihood of target cell immune escape. CAR-NK therapy also induces less inflammatory cytokine release during cytotoxic activity, mitigating the risk of adverse effects including CRS and neurotoxicity compared to CAR-T therapy (94). Encouraging results support this approach: a trial using cryopreserved allogeneic CAR-NK cells in B-cell malignancies reported an overall response rate of 80% (95). Furthermore, clinical trials are exploring the use of CD19-targeted CAR-NK cells in SLE (NCT06010472, NCT06421701) (Table 2).
Macrophages have also emerged as another promising cell platform for CAR-based therapies, particularly for addressing the limited infiltration and immunosuppressive environments in solid tissues (96). In oncology, HER2-specific CAR-macrophages have demonstrated both robust tumor infiltration and anti-tumor activity in HER2-positive tumors, highlighting their potential utility in non-systemic AIDs that affect solid organs (97). Moreover, macrophages also play roles in tissue repair. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a reduction in TREM2+ tissue-resident macrophages is often observed, impairing phagocytic clearance and bone homeostasis, thereby exacerbating disease progression (98). These observations underscore the therapeutic potential of macrophages in modulating immune responses and promoting tissue repair in AIDs.
Synthetic biology expands the potential to CAR-based therapies for autoimmune diseases
Synthetic biology, a transformative discipline that emerged in the 21st century, focuses on constructing programmable biological circuits using fundamental biological elements such as DNA and genes. Its central objective is to engineer “artificial cells” that can sense their environment and respond to specific stimuli. This rapidly evolving field holds significant promise for advancing CAR-based cell therapies.
For instance, although anti-CD19 CAR-T cells have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in depleting B-cells, their utility in AIDs is limited by two main issues: off-target effects—since CD19 is not expressed on autoantibody-producing plasma cells, and the potential downregulation or loss of CD19 on B-cells after repeated interactions with anti-CD19 CAR-T cells (99). To address these challenges, researchers have drawn inspiration from “logic gates” in synthetic biology to achieve precise control over CAR-T cell activation (100). By engineering CAR-T cells to recognize multiple antigens—including CD19, CD20, and the plasma cell marker BCMA—via shared or independent intracellular signaling domains, these cells can be activated upon encountering any of the target antigens (101). This approach, known as an “OR gate,” expands antigen recognition and enhances therapeutic efficacy.
Another advanced design in CAR therapies involves the implementation of “AND gates” logic (88). Similar to rapamycin—inducible safety switches, AND gates assign intracellular signaling domains (e.g., CD3, 4-1BB, or CD28) downstream to distinct scFvs. Activation occurs only when all CARs simultaneously bind their target antigens, ensuring that only cells expressing all target markers trigger a full response. This design minimizes “on-target/off-cell” toxicity and enhances therapeutic precision by sparing healthy tissues that may share single antigens with pathogenic cells (102). For example, anti-CD19/BCMA bispecific CAR-T cells have been developed to selectively eliminate autoantibody-producing cells, allowing for targeted immune modulation while preserving broader immune function (103). Currently, seven ongoing Phase I/II clinical trials are evaluating anti-CD19/BCMA dual-targeting CAR-T in refractory AIDs (Figure 5).
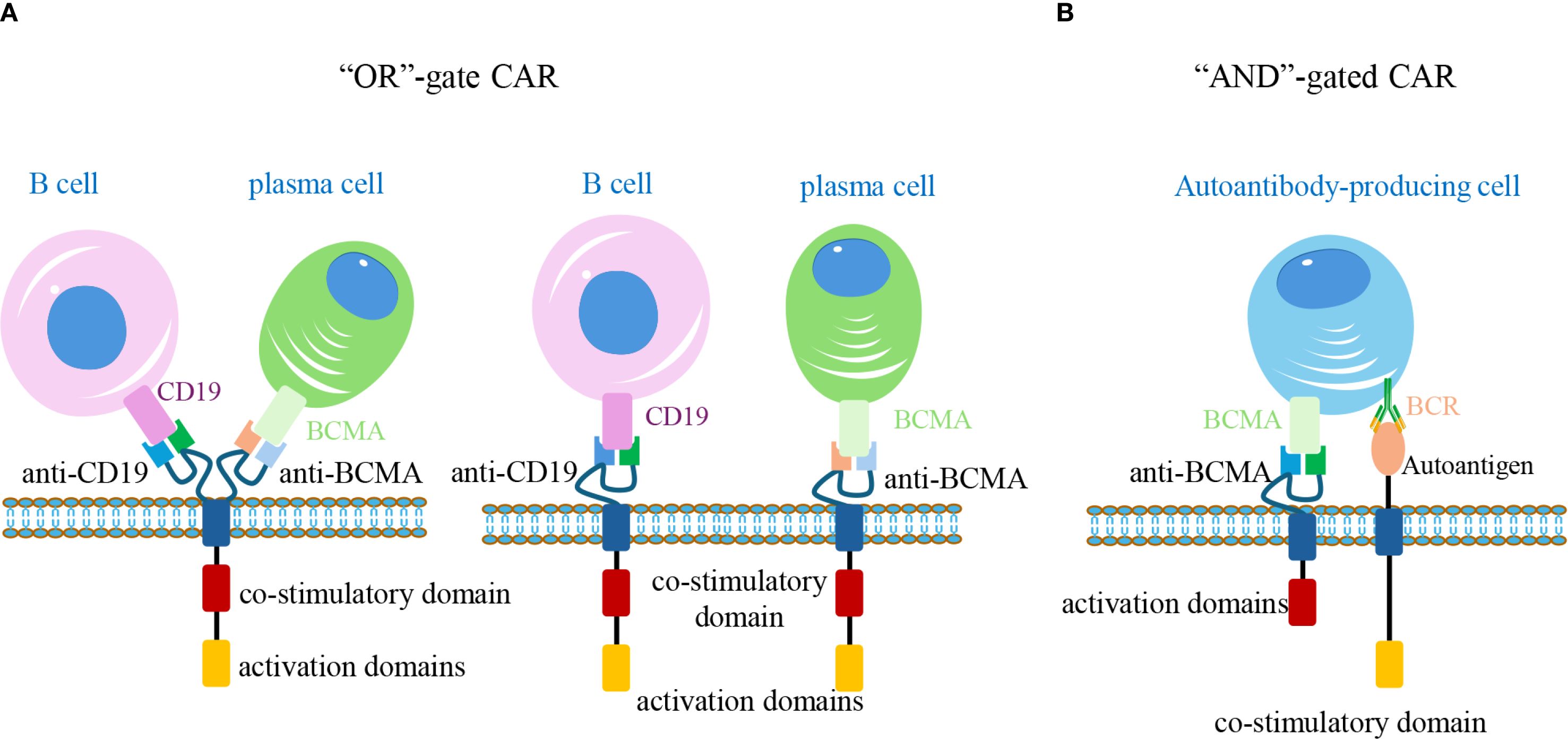
Figure 5. Logic-gated CAR-T cells for precise targeting of autoreactive cells. (A) “OR” gate design: CAR-T cells express tandem CARs recognizing CD19 and BCMA. Binding to either antigen (on B-cells or plasma cells, respectively) is sufficient to activate the cell, expanding the therapeutic coverage. (B) “AND” gate design: Two separate CARs are engineered with distinct intracellular signaling domains. Full activation occurs only when both BCMA and autoantigen-specific BCR are engaged on the same target cell, enabling selective elimination of pathogenic autoantibody-producing cells while sparing non-pathogenic counterparts. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; BCR, B-cell receptor.
Beyond logic gates, synthetic biology has also enabled the development of advanced artificial signaling systems, notably the synthetic Notch (SynNotch) platform. Modeled after endogenous Notch pathway, SynNotch system utilizes a mechanically activated extracellular domain—such as an scFv binding to an autoantigen—to initiate a proteolytic cascade. This results in the release of natural or artificial transcription factors, which subsequently drive the expression of specific gene or secondary regulators (104).
For instance, CAR-NK cells, while offering certain advantages over CAR-T cells, face challenges due to their short lifespan—typically less than 10 days—which necessitates frequent infusions to maintain sufficient cell number (105). To address this limitation, researchers have incorporated interleukin-15 (IL-15) mRNA into CAR constructs, given IL-15’s role in enhancing the proliferation, persistence, and homing capacity of CAR-NK cells. However, constitutive IL-15 expression also increases the risk of non-specific activation of host NK cells (106). The integration of SynNotch technology has provided an effective solution: upon recognition and binding of the CAR-NK scFv to its target antigen, the SynNotch signaling pathway is activated, thereby inducing the expression and release of IL-15 (107). Once target antigen engagement ceases, SynNotch signaling halts, leading to rapid IL-15 withdrawal and subsequent CAR-NK cell apoptosis. This dynamic regulation enhances both the specificity and safety of the therapy (108) (Figure 6).
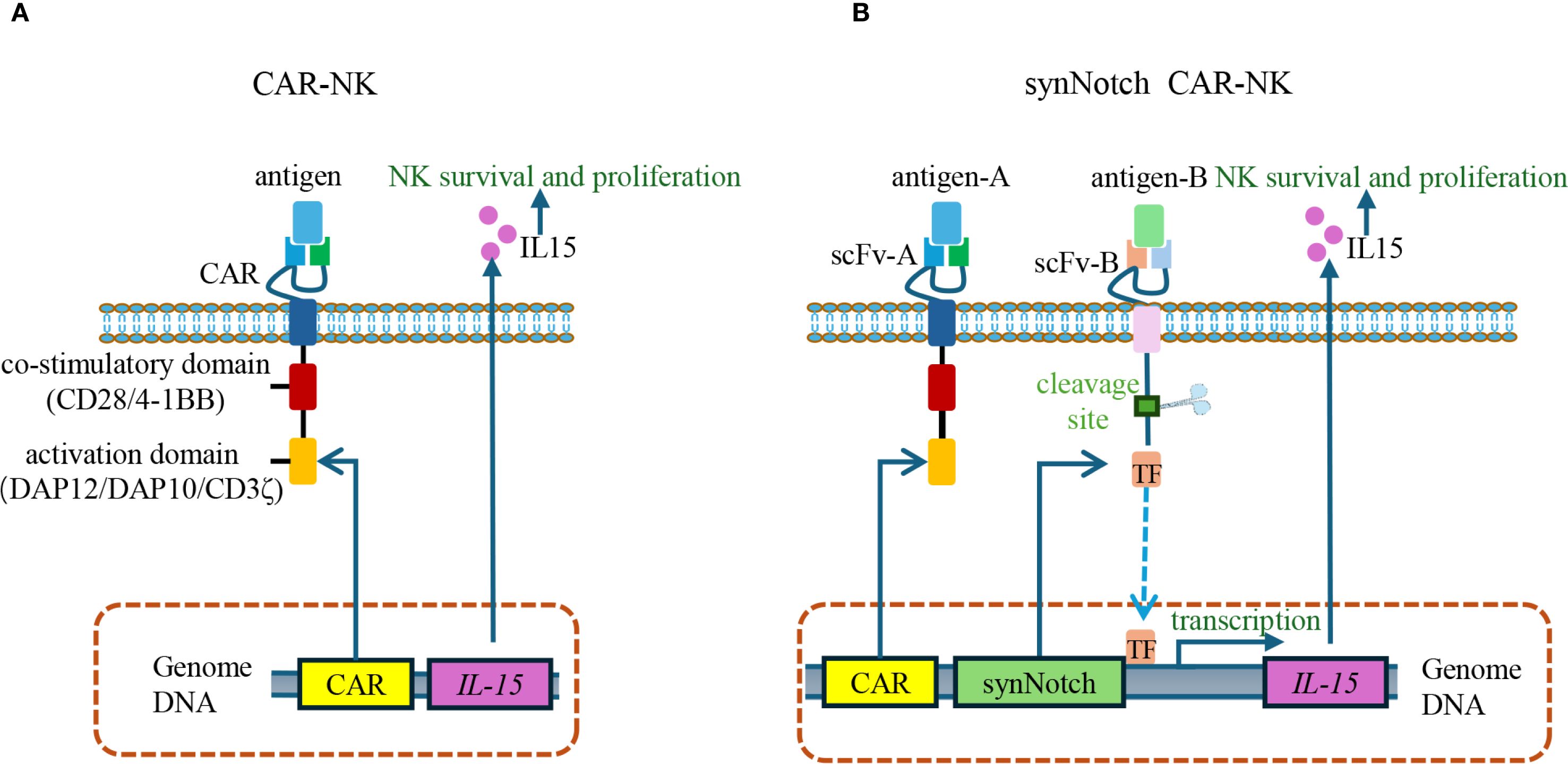
Figure 6. SynNotch-regulated CAR-NK cells for conditional IL-15 expression. (A) Conventional CAR-NK cells constitutively express IL-15 to promote NK cell survival, proliferation, and cytotoxic function. However, continuous IL-15 expression can induce off-target toxicity due to the undesired activation of host NK cells. (B) SynNotch CAR-NK cells use scFv-A to recognize antigen A and mediate cytotoxicity, while scFv-B detects antigen B to activate the SynNotch pathway. Upon antigen B binding, a transcription factor is released to induce IL-15 expression. Once antigen B is no longer present, IL-15 production stops, thereby enhancing safety by limiting cytokine release to dual-antigen recognition. scFv, single-chain variable fragment.
Conclusion and further thinkings
CAR-based cell therapy, which has demonstrated remarkable success in treating malignancies, has also made significant strides in the management of AIDs. Despite encouraging preclinical and early clinical findings, several challenges must be addressed to ensure its safe and effective application in the autoimmune setting.
First, AIDs patients often present with compromised immune cells due to long-term immunosuppressive treatment. Moreover, unlike in cancer, lymphodepletion may not be desirable in AIDs treatment, as preserving endogenous immune cells is essential for restoring immune homeostasis and preventing long-term immunodeficiency. Additionally, CAR-T cell therapy can induce acute B-cell aplasia, thereby increasing the risk of infections.
To overcome these limitations, researchers have developed refined CAR construction equipped with safety switches, and use mRNA-based transient CAR expression, enhancing the controllability of CAR activation and minimizing adverse effects. Therapeutic specificity has also been optimized using chimeric autoantibody receptor T (CAAR-T) cells and multi-antigen targeting CARs, such as CD19/BCMA bispecific constructs, to eliminate pathogenic B-cells while sparing normal immune components. Furthermore, CAR-Tregs have emerged as a strategy for restoring immune tolerance by delivering regulatory signals directly to inflamed tissues, thus achieving therapeutic effects with minimal systemic disruption.
In parallel, novel immune cell types such as NK cells and macrophages have been investigated as alternative platforms for CAR engineering. CAR-NK cells offer advantages including MHC-independent killing, reduced cytokine release, and the potential for “off-the-shelf” manufacturing, with promising results in early-stage trials. CAR-macrophages, on the other hand, demonstrate superior tissue infiltration and remodeling capacity, making them particularly attractive for targeting localized, organ-specific AIDs.
Synthetic biology has further expanded the potential of CAR-based therapies by introducing programmable logic and dynamic control systems. Logic gate-based CAR constructions allow for more precise discrimination of pathological cells, while the SynNotch signaling pathways enable context-dependent activation of therapeutic functions, such as inducible IL-15 production in CAR-NK cells (Table 3).
Moving forward, the successful clinical translation of CAR-engineered therapies for AIDs hinges on overcoming key challenges such as antigen escape, immune tolerance restoration, and scalability. Rigorous validation of safety, durability, and immunological outcomes is essential. Critical clinical design considerations include defining therapeutic windows, optimizing preconditioning regimens, and developing standardized trial protocols to account for disease heterogeneity. Ultimately, interdisciplinary collaboration across immunology, bioengineering, and clinical medicine will be vital to translate these therapies into effective treatments for AIDs.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – original draft. CH: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. KW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. GX: Writing – original draft. YX: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. XY: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82303559), Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission (H2023033), Research Project of Jiangsu Maternal and Child Health Association (FYX202402) and Medical Education Collaborative Innovation Project of Jiangsu University (JDY2023009) to C He, HuaiAn Basic Research Program (HABL2023034) to K Wang, Zhenjiang Social Development Project (SH2023025) to YC Xie and Medical and Health Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province (2025KY224) to XY Ying.
Acknowledgments
The authors are deeply grateful to the editor and reviewers for their invaluable contributions. The thorough review and thoughtful recommendations were instrumental in enhancing the quality and clarity of this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sokolove J, Bromberg R, Deane KD, Lahey LJ, Derber LA, Chandra PE, et al. Autoantibody epitope spreading in the pre-clinical phase predicts progression to rheumatoid arthritis. PloS One. (2012) 7:e35296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035296
2. Crickx E, Chappert P, Sokal A, Weller S, Azzaoui I, Vandenberghe A, et al. Rituximab-resistant splenic memory B cells and newly engaged naive B cells fuel relapses in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 13. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abc3961
3. Lidar M, Rimar D, David P, Jacoby E, Shapira-Frommer R, Itzhaki O, et al. CD-19 CAR-T cells for polyrefractory rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2025) 84:370–2. doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-226437
4. Müller F, Schwingen NR, Hagen M, Scholz JK, Aigner M, Wirsching A, et al. Comparison of the safety profiles of CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy in patients with SLE and B-cell lymphoma. Blood. (2025) 146:1088–95. doi: 10.1182/blood.2025028375
5. Sahillioglu AC and Schumacher TN. Safety switches for adoptive cell therapy. Curr Opin Immunol. (2022) 74:190–8. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2021.07.002
6. Baker DJ, Arany Z, Baur JA, Epstein JA, and June CH. CAR T therapy beyond cancer: the evolution of a living drug. Nature. (2023) 619:707–15. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06243-w
7. Zhou J, Xu Y, Shu J, Jiang H, Huang L, Xu M, et al. GPIbα CAAR T cells function like a Trojan horse to eliminate autoreactive B cells to treat immune thrombocytopenia. Haematologica. (2024) 109:2256–70. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283874
8. Arjomandnejad M, Kopec AL, and Keeler AM. CAR-T regulatory (CAR-Treg) cells: engineering and applications. Biomedicines. (2022) 10. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020287
9. Martínez Bedoya D, Dutoit V, and Migliorini D. Allogeneic CAR T cells: an alternative to overcome challenges of CAR T cell therapy in glioblastoma. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:640082. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.640082
10. Wang W, He S, Zhang W, Zhang H, DeStefano VM, Wada M, et al. BCMA-CD19 compound CAR T cells for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase 1 open-label clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) 83:1304–14. doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225785
11. Hyrenius-Wittsten A, Su Y, Park M, Garcia JM, Alavi J, Perry N, et al. SynNotch CAR circuits enhance solid tumor recognition and promote persistent antitumor activity in mouse models. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 13. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd8836
12. Song Y, Li J, and Wu Y. Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:263. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01952-8
13. Coutinho AE and Chapman KE. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2011) 335:2–13. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.04.005
14. Tachecí I, Bradna P, Douda T, Baštecká D, Kopáčová M, Rejchrt S, et al. Small intestinal injury in NSAID users suffering from rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int. (2016) 36:1557–61. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3552-x
15. Banerjee S, Biehl A, Gadina M, Hasni S, and Schwartz DM. JAK-STAT signaling as a target for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: current and future prospects. Drugs. (2017) 77:521–46. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0701-9
16. Benucci M, Bernardini P, Coccia C, De Luca R, Levani J, Economou A, et al. JAK inhibitors and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2023) 22:103276. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103276
17. Sebba A, Bingham CO, Bykerk VP, Fiore S, Ford K, Janak JC, et al. Comparative effectiveness of TNF inhibitor vs IL-6 receptor inhibitor as monotherapy or combination therapy with methotrexate in biologic-experienced patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An analysis from the CorEvitas RA Registry. Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 42:2037–51. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06588-7
18. Mihara M, Ohsugi Y, and Kishimoto T. Tocilizumab, a humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. (2011) 3:19–29. doi: 10.2147/oarrr.S17118
19. Adams R, Maroof A, Baker T, Lawson ADG, Oliver R, Paveley R, et al. Bimekizumab, a novel humanized IgG1 antibody that neutralizes both IL-17A and IL-17F. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1894. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01894
20. Boyman O and Sprent J. The role of interleukin-2 during homeostasis and activation of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. (2012) 12:180–90. doi: 10.1038/nri3156
21. Malek TR, Yu A, Vincek V, Scibelli P, and Kong L. CD4 regulatory T cells prevent lethal autoimmunity in IL-2Rbeta-deficient mice. Implications for the nonredundant function of IL-2. Immunity. (2002) 17:167–78. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00367-9
22. Burchill MA, Yang J, Vogtenhuber C, Blazar BR, and Farrar MA. IL-2 receptor beta-dependent STAT5 activation is required for the development of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. (2007) 178:280–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.1.280
23. von Spee-Mayer C, Siegert E, Abdirama D, Rose A, Klaus A, Alexander T, et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 selectively corrects regulatory T cell defects in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:1407–15. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207776
24. He J, Chen J, Miao M, Zhang R, Cheng G, Wang Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose interleukin 2 for primary Sjögren syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e2241451. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.41451
25. He J, Zhang R, Shao M, Zhao X, Miao M, Chen J, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose IL-2 in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:141–9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215396
26. Peterson LB, Bell CJM, Howlett SK, Pekalski ML, Brady K, Hinton H, et al. A long-lived IL-2 mutein that selectively activates and expands regulatory T cells as a therapy for autoimmune disease. J Autoimmun. (2018) 95:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.10.017
27. Cohen MD and Keystone E. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Ther. (2015) 2:99–111. doi: 10.1007/s40744-015-0016-9
28. Mössner E, Brünker P, Moser S, Püntener U, Schmidt C, Herter S, et al. Increasing the efficacy of CD20 antibody therapy through the engineering of a new type II anti-CD20 antibody with enhanced direct and immune effector cell-mediated B-cell cytotoxicity. Blood. (2010) 115:4393–402. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225979
29. Furie RA, Aroca G, Cascino MD, Garg JP, Rovin BH, Alvarez A, et al. B-cell depletion with obinutuzumab for the treatment of proliferative lupus nephritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) 81:100–7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220920
30. Siegel CH and Sammaritano LR. Systemic lupus erythematosus: A review. Jama. (2024) 331:1480–91. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.2315
31. Evans LS, Lewis KE, DeMonte D, Bhandari JG, Garrett LB, Kuijper JL, et al. Povetacicept, an enhanced dual APRIL/BAFF antagonist that modulates B lymphocytes and pathogenic autoantibodies for the treatment of lupus and other B cell-related autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2023) 75:1187–202. doi: 10.1002/art.42462
32. Kerschbaumer A, Sepriano A, Smolen JS, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, van Vollenhoven R, et al. Efficacy of pharmacological treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature research informing the 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:744–59. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216656
33. Mougiakakos D, Krönke G, Völkl S, Kretschmann S, Aigner M, Kharboutli S, et al. CD19-targeted CAR T cells in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:567–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2107725
34. Bergmann C, Müller F, Distler JHW, Györfi AH, Völkl S, Aigner M, et al. Treatment of a patient with severe systemic sclerosis (SSc) using CD19-targeted CAR T cells. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:1117–20. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-223952
35. Fischbach F, Richter J, Pfeffer LK, Fehse B, Berger SC, Reinhardt S, et al. CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in two patients with multiple sclerosis. Med. (2024) 5:550–8.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2024.03.002
36. Pecher AC, Hensen L, Klein R, Schairer R, Lutz K, Atar D, et al. CD19-targeting CAR T cells for myositis and interstitial lung disease associated with antisynthetase syndrome. Jama. (2023) 329:2154–62. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.8753
37. Mackensen A, Müller F, Mougiakakos D, Böltz S, Wilhelm A, Aigner M, et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Med. (2022) 28:2124–32. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02017-5
38. Jayaraman J, Mellody MP, Hou AJ, Desai RP, Fung AW, Pham AHT, et al. CAR-T design: Elements and their synergistic function. EBioMedicine. (2020) 58:102931. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102931
39. Verdun N and Marks P. Secondary cancers after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:584–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2400209
40. Baker DJ, Levine BL, and June CH. Assessing the oncogenic risk: the long-term safety of autologous chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Lancet. (2025) 405:751–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(25)00039-x
41. Eyquem J, Mansilla-Soto J, Giavridis T, van der Stegen SJ, Hamieh M, Cunanan KM, et al. Targeting a CAR to the TRAC locus with CRISPR/Cas9 enhances tumour rejection. Nature. (2017) 543:113–7. doi: 10.1038/nature21405
42. Loves R and Grunebaum E. FAS signalling pathway is crucial for CAR T cell persistence. Nat Rev Immunol. (2024) 24:380. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01038-0
43. Haghikia A, Hegelmaier T, Wolleschak D, Böttcher M, Desel C, Borie D, et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cells for refractory myasthenia gravis. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:1104–5. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(23)00375-7
44. Zhu Q, Li Y, Zhang L, Wang M, Chen Z, Shi J, et al. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus show increased proportions of CD19(+)CD20(-) B cells and secretion of related autoantibodies. Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 40:151–65. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05220-2
45. Jin X, Xu Q, Pu C, Zhu K, Lu C, Jiang Y, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR-T cells in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:1896–903. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0472-1
46. Müller F, Taubmann J, Bucci L, Wilhelm A, Bergmann C, Völkl S, et al. CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune disease - A case series with follow-up. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:687–700. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2308917
47. Dumitru CA, Moses K, Trellakis S, Lang S, and Brandau S. Neutrophils and granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells: immunophenotyping, cell biology and clinical relevance in human oncology. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2012) 61:1155–67. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1294-5
48. Gattinoni L, Finkelstein SE, Klebanoff CA, Antony PA, Palmer DC, Spiess PJ, et al. Removal of homeostatic cytokine sinks by lymphodepletion enhances the efficacy of adoptively transferred tumor-specific CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. (2005) 202:907–12. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050732
49. Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:45–56. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804980
50. Beyer M, Kochanek M, Darabi K, Popov A, Jensen M, Endl E, et al. Reduced frequencies and suppressive function of CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia after therapy with fludarabine. Blood. (2005) 106:2018–25. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0642
51. Kanakry CG, Ganguly S, Zahurak M, Bolaños-Meade J, Thoburn C, Perkins B, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase expression drives human regulatory T cell resistance to posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Sci Transl Med. (2013) 5:211ra157. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006960
52. Abdi M, Fadaee M, Jourabchi A, Karimzadeh H, and Kazemi T. Cyclophosphamide-induced infertility and the impact of antioxidants. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2024) 92:e70014. doi: 10.1111/aji.70014
53. Nawaz W, Huang B, Xu S, Li Y, Zhu L, Yiqiao H, et al. AAV-mediated in vivo CAR gene therapy for targeting human T-cell leukemia. Blood Cancer J. (2021) 11:119. doi: 10.1038/s41408-021-00508-1
54. Agarwal S, Hanauer JDS, Frank AM, Riechert V, Thalheimer FB, and Buchholz CJ. In vivo generation of CAR T cells selectively in human CD4(+) lymphocytes. Mol Ther. (2020) 28:1783–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.05.005
55. Banskota S, Raguram A, Suh S, Du SW, Davis JR, Choi EH, et al. Engineered virus-like particles for efficient in vivo delivery of therapeutic proteins. Cell. (2022) 185:250–65.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.021
56. Fraietta JA, Lacey SF, Orlando EJ, Pruteanu-Malinici I, Gohil M, Lundh S, et al. Determinants of response and resistance to CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat Med. (2018) 24:563–71. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0010-1
57. Di Rosa F and Pabst R. The bone marrow: a nest for migratory memory T cells. Trends Immunol. (2005) 26:360–6. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2005.04.011
58. Baker DJ and June CH. CAR T therapy extends its reach to autoimmune diseases. Cell. (2022) 185:4471–3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.026
59. Schett G, Mackensen A, and Mougiakakos D. CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Lancet. (2023) 402:2034–44. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01126-1
60. Hagen M, Müller F, Wirsching A, Kharboutli S, Spoerl S, Düsing C, et al. Local immune effector cell-associated toxicity syndrome in CAR T-cell treated patients with autoimmune disease: an observational study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2025) 7:e424–e33. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(25)00091-8
61. Guercio M, Manni S, Boffa I, Caruso S, Di Cecca S, Sinibaldi M, et al. Inclusion of the inducible caspase 9 suicide gene in CAR construct increases safety of CAR.CD19 T cell therapy in B-cell Malignancies. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:755639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.755639
62. Zheng Y, Nandakumar KS, and Cheng K. Optimization of CAR-T cell-based therapies using small-molecule-based safety switches. J Med Chem. (2021) 64:9577–91. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02054
63. Granit V, Benatar M, Kurtoglu M, Miljković MD, Chahin N, Sahagian G, et al. Safety and clinical activity of autologous RNA chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in myasthenia gravis (MG-001): a prospective, multicentre, open-label, non-randomised phase 1b/2a study. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:578–90. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(23)00194-1
64. Blache U, Tretbar S, Koehl U, Mougiakakos D, and Fricke S. CAR T cells for treating autoimmune diseases. RMD Open. (2023) 9:e002907. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002907
65. Karikó K, Buckstein M, Ni H, and Weissman D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity. (2005) 23:165–75. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.06.008
66. Tombácz I, Laczkó D, Shahnawaz H, Muramatsu H, Natesan A, Yadegari A, et al. Highly efficient CD4+ T cell targeting and genetic recombination using engineered CD4+ cell-homing mRNA-LNPs. Mol Ther. (2021) 29:3293–304. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.06.004
67. Szabó GT, Mahiny AJ, and Vlatkovic I. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: Platforms and current developments. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:1850–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.02.016
68. Protić-Rosić I, Sehgal ANA, Wrighton S, Heller B, and Pickl WF. Chimeric autoantibody receptor- and/or peptide-MHC-based CAR therapies for targeted elimination of antigen-specific B or T cells in hypersensitivity disorders such as allergies and autoimmune diseases. Cells. (2025) 14. doi: 10.3390/cells14100753
69. Flemming A. NMDAR-directed CAAR T cells show promise for autoimmune encephalitis. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:786. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00969-4
70. Meng H, Sun X, Song Y, Zou J, An G, Jin Z, et al. La/SSB chimeric autoantibody receptor modified NK92MI cells for targeted therapy of autoimmune disease. Clin Immunol. (2018) 192:40–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2018.04.006
71. Honaker Y, Hubbard N, Xiang Y, Fisher L, Hagin D, Sommer K, et al. Gene editing to induce FOXP3 expression in human CD4(+) T cells leads to a stable regulatory phenotype and function. Sci Transl Med. (2020) 12. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay6422
72. Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, Lei KJ, Li L, Marinos N, et al. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25- naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med. (2003) 198:1875–86. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030152
73. Ye C, Brand D, and Zheng SG. Targeting IL-2: an unexpected effect in treating immunological diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2018) 3:2. doi: 10.1038/s41392-017-0002-5
74. Arroyo-Olarte RD, Flores-Castelán JC, Armas-López L, Escobedo G, Terrazas LI, Ávila-Moreno F, et al. Targeted demethylation of FOXP3-TSDR enhances the suppressive capacity of STAT6-deficient inducible T regulatory cells. Inflammation. (2024) 47:2159–72. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02031-4
75. Requejo Cier CJ, Valentini N, and Lamarche C. Unlocking the potential of Tregs: innovations in CAR technology. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10:1267762. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1267762
76. Singh AK, Qureshah FA, Drow T, Hou B, and Rawlings DJ. Activated PI3Kδ specifically perturbs mouse Treg homeostasis and function leading to immune dysregulation. bioRxiv. (2023). doi: 10.1101/2023.12.21.569665
77. Tewari R, Yang SJ, McClain ED, Hu A, Mortensen E, DeSchmidt A, et al. Identification of a novel PDC-E2 epitope in primary biliary cholangitis: Application for engineered Treg therapy. J Autoimmun. (2024) 149:103327. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2024.103327
78. Tuomela K and Levings MK. Genetic engineering of regulatory T cells for treatment of autoimmune disorders including type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. (2024) 67:611–22. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-06076-2
79. Tripathi SK, Grimm A, Dahl NP, Honaker Y, Knebusch P, Chen Y, et al. HLA-A2 CAR/IL-2-CISC engineered Treg display robust in vitro and in vivo antigen-specific regulatory function. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. (2025) 33. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2025.101561
80. Wardell CM, Boardman DA, and Levings MK. Harnessing the biology of regulatory T cells to treat disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2025) 24:93–111. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01089-x
81. Henschel P, Landwehr-Kenzel S, Engels N, Schienke A, Kremer J, Riet T, et al. Supraphysiological FOXP3 expression in human CAR-Tregs results in improved stability, efficacy, and safety of CAR-Treg products for clinical application. J Autoimmun. (2023) 138:103057. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103057
82. Tenspolde M, Zimmermann K, Weber LC, Hapke M, Lieber M, Dywicki J, et al. Regulatory T cells engineered with a novel insulin-specific chimeric antigen receptor as a candidate immunotherapy for type 1 diabetes. J Autoimmun. (2019) 103:102289. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.05.017
83. Frikeche J, David M, Mouska X, Treguer D, Cui Y, Rouquier S, et al. MOG-specific CAR Tregs: a novel approach to treat multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflamm. (2024) 21:268. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03262-w
84. Cui Y, David M, Bouchareychas L, Rouquier S, Sajuthi S, Ayrault M, et al. IL23R-specific CAR Tregs for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis. (2025) 19:jjae135. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae135
85. Boardman DA, Wong MQ, Rees WD, Wu D, Himmel ME, Orban PC, et al. Flagellin-specific human CAR Tregs for immune regulation in IBD. J Autoimmun. (2023) 134:102961. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102961
86. Doglio M, Ugolini A, Bercher-Brayer C, Camisa B, Toma C, Norata R, et al. Regulatory T cells expressing CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor restore homeostasis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:2542. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46448-9
87. DiNofia AM and Grupp SA. Will allogeneic CAR T cells for CD19(+) Malignancies take autologous CAR T cells ‘off the shelf’? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:195–6. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00485-1
88. Chen X, Tan B, Xing H, Zhao X, Ping Y, Zhang Z, et al. Allogeneic CAR-T cells with of HLA-A/B and TRAC disruption exhibit promising antitumor capacity against B cell Malignancies. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2024) 73:13. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03586-1
89. Wang X, Wu X, Tan B, Zhu L, Zhang Y, Lin L, et al. Allogeneic CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy in patients with severe myositis and systemic sclerosis. Cell. (2024) 187:4890–904.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.06.027
90. Yang C, Sun C, Tan B, Hu C, Wan L, Wang C, et al. Allogeneic anti-CD19 CAR-T cells induce remission in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Res. (2025) 35:607–9. doi: 10.1038/s41422-025-01128-1
91. Neelapu SS, Tummala S, Kebriaei P, Wierda W, Gutierrez C, Locke FL, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy - assessment and management of toxicities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:47–62. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.148
92. Bui TA, Mei H, Sang R, Ortega DG, and Deng W. Advancements and challenges in developing in vivo CAR T cell therapies for cancer treatment. EBioMedicine. (2024) 106:105266. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105266
93. Arias J, Yu J, Varshney M, Inzunza J, and Nalvarte I. Hematopoietic stem cell- and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived CAR-NK cells as reliable cell-based therapy solutions. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2021) 10:987–95. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0459
94. Siegler EL, Zhu Y, Wang P, and Yang L. Off-the-shelf CAR-NK cells for cancer immunotherapy. Cell Stem Cell. (2018) 23:160–1. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.07.007
95. Liu E, Marin D, Banerjee P, Macapinlac HA, Thompson P, Basar R, et al. Use of CAR-transduced natural killer cells in CD19-positive lymphoid tumors. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:545–53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910607
96. Guan L, Wu S, Zhu Q, He X, Li X, Song G, et al. GPC3-targeted CAR-M cells exhibit potent antitumor activity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Rep. (2024) 39:101741. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101741
97. Klichinsky M, Ruella M, Shestova O, Lu XM, Best A, Zeeman M, et al. Human chimeric antigen receptor macrophages for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Biotechnol. (2020) 38:947–53. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0462-y
98. Rana AK, Li Y, Dang Q, and Yang F. Monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Circulating precursors of macrophages and osteoclasts and, their heterogeneity and plasticity role in RA pathogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2018) 65:348–59. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.10.016
99. Ruella M, Xu J, Barrett DM, Fraietta JA, Reich TJ, Ambrose DE, et al. Induction of resistance to chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy by transduction of a single leukemic B cell. Nat Med. (2018) 24:1499–503. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0201-9
100. Schett G, Müller F, Taubmann J, Mackensen A, Wang W, Furie RA, et al. Advancements and challenges in CAR T cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20:531–44. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01139-z
101. Yuan Y, He S, Zhang W, Zhang H, Destefano V, Wada M, et al. POS1134 novel approach to treat systemic lupus erythematosus, by targeting the “root cause”, B cells and plasma cells, using BCMA-CD19 compound CAR. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:895. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2023-eular.4161
102. Cheever A, Kang CC, O’Neill KL, and Weber KS. Application of novel CAR technologies to improve treatment of autoimmune disease. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1465191. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1465191
103. Li Z, Zheng Y, Wang H, Zhang C, Liu L, Lv L, et al. Development of allogeneic dual-targeting CD19/BCMA CAR-T cell therapeutics using ALL-in-one site-specific integration technology for autoimmune diseases. Blood. (2024) 144:4785. doi: 10.1182/blood-2024-199874
104. Shirzadian M, Moori S, Rabbani R, and Rahbarizadeh F. SynNotch CAR-T cell, when synthetic biology and immunology meet again. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1545270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1545270
105. Zhong Y and Liu J. Emerging roles of CAR-NK cell therapies in tumor immunotherapy: current status and future directions. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:318. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02077-1
106. Guo S, Lei W, Jin X, Liu H, Wang JQ, Deng W, et al. CD70-specific CAR NK cells expressing IL-15 for the treatment of CD19-negative B-cell Malignancy. Blood Adv. (2024) 8:2635–45. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023012202
107. Ji S, Jin C, and Cui X. Enhancing the physiological characteristics of chimeric antigen receptor natural killer cells by synthetic biology. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1592121. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1592121
Keywords: chimeric antigen receptor, autoimmune disease, cell therapy, synthetic biology, CAR-T cell
Citation: Li X, He C, Wang K, Xu G-Y, Xie Y-C and Ying X-Y (2025) CAR-based cell therapy for autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 16:1613622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1613622
Received: 17 April 2025; Accepted: 05 September 2025;
Published: 18 September 2025.
Edited by:
Subhash Kumar Tripathi, Seattle Children’s Research Institute, United StatesReviewed by:
Julia Sajman, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, IsraelLukasz Chlewicki, Eli Lilly, United States
Justin Spanier, University of Minnesota Twin Cities, United States
Daniel Baker, University of Pennsylvania, United States
Copyright © 2025 Li, He, Wang, Xu, Xie and Ying. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chao He, MTU5NTI4NTM4MDhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiu Li
Xiu Li Chao He1*†
Chao He1*†