- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Nanjing Jinling Hospital, Jinling School of Clinical Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
- 2Orthopedics Department, Wuxi 9th People’s Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
- 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Nanjing Jinling Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Backgrounds: Vitamin D insufficiency is usually seen in Crohn’s disease (CD). Our study aims to determine the risk factors for vitamin D insufficiency in CD patients.
Methods: Between May 2021 and December 2023, we enrolled 102 CD patients and 100 healthy people in our hospital who were eligible for the study. Changes in vitamin D levels were also analyzed. CD patients were divided into active and clinical remission, and further changes in micronutrient and vitamin D levels were analyzed. Lastly, risk factor analysis was conducted using univariate, multivariate, and LASSO regression analysis models.
Results: The average age of CD patients was 38.91 ± 3.31 years, whereas the average age of the healthy people was 38.64 ± 2.26 years. Vitamin D levels were significantly lower in CD patients than in healthy controls (19.62 ± 2.68 vs. 22.68 ± 4.61), especially for patients with active CD. In 11 patients treated with vedolizumab, compared to the pre-treatment Vedolizumab group, vitamin D levels improved more dramatically post-Vedolizumab therapy. According to univariate analysis, Age (OR: 0.95, 95% CI 0.26-1.33, p=0.01), sex (OR: 0.26, 95% CI 0.25-0.99, p=0.03), recent biologics (OR: 0.54, 95% CI 0.44-1.25, p=0.02), iron (OR: 0.89, 95% CI 0.72-1.62, p=0.02), and total 25-OH vitamin D (OR: 1.25, 95% CI 1.02-1.99, p=0.02) did significantly differ between patients with and without vitamin D deficiency. After controlling for several variables, multivariate analysis revealed that a lower odds ratio was linked to increasing age at diagnosis (OR: 0.12, 95% CI 0.03-0.85, p=0.02), sex (OR: 0.58, 95% CI 0.44-0.95, p=0.01), iron (OR: 0.44, 95% CI 0.11-0.62, p=0.01), and 25-OH vitamin D total (OR: 0.48, 95% CI 0.25-0.95, p=0.03). In addition, Age, time since illness onset, and 25-OH vitamin D were found to be helpful indicators for CD patients using LASSO regression.
Conclusion: According to this study, vitamin D insufficiency was often linked to CD patients with active status and pre-treatment Vedolizumab. Furthermore, Age, time since illness onset, and 25-OH vitamin D were found to be significant risk factors for CD.
Introduction
Abdominal discomfort, severe diarrhea, and exhaustion are clinical manifestations of Crohn’s disease (CD) (1), a chronic condition characterized by intestinal inflammation and gastrointestinal dysfunction (2). It has a significant impact on patients’ quality of life (3). Current treatment for CD includes biological agents, for example, vedolizumab is a gut-selective monoclonal anti-α4β7 integrin antibody treatment for Crohn’s disease (4). But there is still a risk of incomplete cure. Therefore, identifying potential risk factors for CD and alleviating symptoms while maintaining long-term remission are critical areas of research (5).
In the treatment of CD, inhibition of intestinal inflammation is key, and accurate assessment of disease severity is also essential (6, 7). Clinical symptoms, colonoscopy, gastroscopy, radiological imaging, and biopsy data from various gastrointestinal tract segments are usually used to evaluate disease activity (8). A full histological evaluation is performed to rule out chronic infectious bowel disease (9). However, endoscopic procedures for treatment and evaluation often carry risks such as high cost, complex surgery, and invasiveness (10, 11). Although different infections can alter their levels, the degree of CD has been assessed using fecal calprotectin and C-reactive protein (CRP) (12). Furthermore, CRP levels are influenced by hereditary variables, and fecal calprotectin is more effective when colonic mucosal inflammation is present (13). Finding trustworthy biomarkers for CD diagnosis and therapy is therefore still a top priority.
Vitamin D insufficiency, commonly defined as a blood 25(OH)D concentration below 50 nmol/L, is common in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) (14). Vitamin D has a significant impact on intestinal homeostasis and lowers serum levels of inflammatory factors (15). Compared to patients with adequate vitamin D, those with vitamin D deficiency are more likely to require surgery (16–18). In addition, vitamin D supplementation tends to have benign benefits (16). In the absence of evidence-based recommendations for vitamin D optimization in IBD, treatment at levels of at least, but ideally, 75 ng/mL is safe and may improve IBD disease activity (19–21). Research has indicated that vitamin D levels significantly affect immunological regulation (22). In human PBMCs infected with Mycobacterium TB, 1,25D dose-dependently suppresses the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and IFNγ (23). The intrasecretory synthesis of 1,25D by CDs results in a tolerogenic phenotype, which is typified by decreased expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II, costimulatory markers including CD40, CD83, and CD86, and decreased production of IL-10, IL-12, and IL-23 (24).
In order to better understand the function of trace elements in these alterations, our study examined variations in vitamin D levels in individuals with active and remission CD. Lastly, to ascertain the function of risk variables in CD patients and to give predictors for risk factors and therapy, univariate, multivariate, and LASSO regression models were employed.
Materials and methods
The institutional review board (IRB) and ethical committee of our hospital have authorized this single-center, controlled study (2021NZKY-001-01). After being informed, each patient signed an informed consent form. The CONSORT criteria state that these studies adhere to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Patients
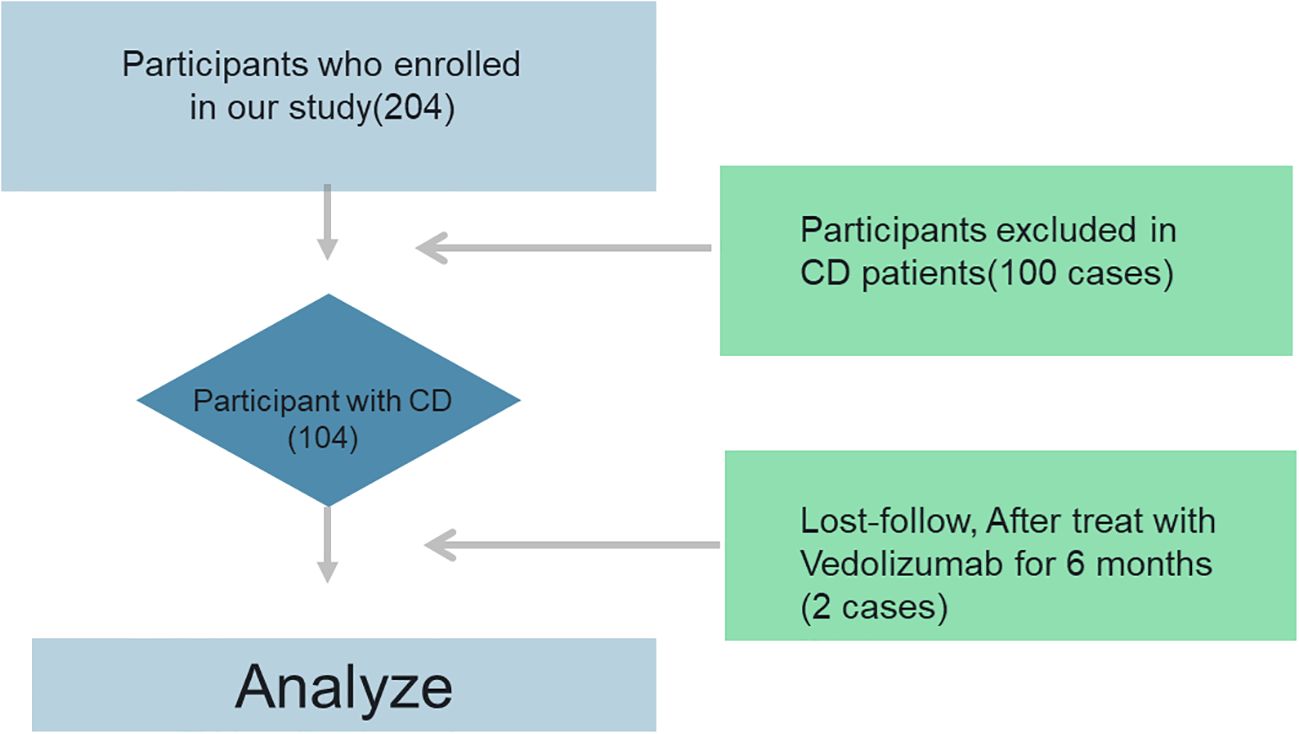
The study included both men and women aged 18 to 60 who were hospitalized for Crohn’s disease between May 2021 and December 2023. Measuring several parameters was the primary goal of the study. The healthy controls (n=100) were frequency-matched to CD patients by age (± 3 years) and sex (1:1 ratio).
Participants had to be between the ages of 18 and 60 and have a confirmed diagnosis of Crohn’s disease based on imaging, histology, endoscopy, and clinical symptoms (25). Data from gastrointestinal endoscopies and vitamin D availability. Individuals receiving vitamin D treatment were excluded, as were those with unclassified enterocolitis, pregnancy or lactation, alcohol or drug abuse, a history of mental or emotional disorders, or a history of severe or chronic cardiovascular, respiratory, urinary, endocrine, reproductive, skeletal, muscular, neurological, or other systemic disorders. Exclusion criteria for all participants (CD and controls) included: a) Vitamin D/calcium supplementation (>400 IU/day) within 3 months; b) Malabsorption syndromes (e.g., celiac disease, pancreatic insufficiency); c) Severe renal/liver impairment (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73m² or ALT >3× ULN); d) Pregnancy or lactation.
Patients who are thinking about stopping vedolizumab within the next four months or who have been taking it for less than six months. The study’s controls were healthy volunteers who did not have Crohn’s disease and who satisfied the inclusion requirements. Patients with vitamin D insufficiency (25-OH-D <30 ng/mL) received cholecalciferol 800 IU/day throughout vedolizumab therapy, aligning with ECCO guidelines on micronutrient repletion in active IBD. Supplementation commenced ≥4 weeks pre-treatment and was maintained during the 14-week observation period. Blood samples for vitamin D (25-OH-D) were drawn between 8–10 AM after overnight fasting. To account for seasonal variation: a) Sampling was balanced across seasons in both groups (CD: 26 spring, 28 summer, 25 autumn, 23 winter; controls: 25/26/25/24); b) Season-adjusted analysis was performed by assigning samples to ‘high-sunlight’ (May–October) or ‘low-sunlight’ (November–April) periods based on geographic latitude (32°N).
Determination of CD activity
CD activity was calculated using biochemical and clinical data. Endoscopic scores (SES-CD) and clinical scores (CDAI, HBI) were used to identify four types of disease activity: mildly active (SES-CD 3-6, HBI 5-7), moderately active (SES-CD 7-15, HBI 8-16), highly active (SES-CD > 15, HBI > 16), and remission (SES-CD < 2, HBI ≤ 4). A single physician performed each colonoscopy and assessed the endoscopic scores (26).
Clinical outcome
Before therapy, fasting blood was drawn between 7:00 and 8:00 in order to evaluate a number of biomarkers. After 20 to 30 minutes in a water bath at 37°C, the blood was centrifuged at 1580g for 5 minutes to collect serum. Using Synchron reagents from Leadmanbio (China), biochemical parameters, including hemoglobin (Hb; g/L), total protein (TP; g/L), albumin (ALB; g/L), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C; mmol/L), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C; mmol/L), were analyzed using a 7600–210 automatic biochemistry analyzer (Hitachi Inc., Japan). Serum 25(OH)D was measured using radioimmunoassay kits (Beijing North Institute of Biotechnology, China). Standardized methods were used for all biochemical measurements. The definitions of VD deficit, insufficiency, and sufficiency were 25(OH)D <20 ng/mL, 25(OH)D = 20–29 ng/mL, and 25(OH)D ≥30 ng/mL, respectively (27). Patients’ body weight was recorded to the closest 0.1 kg using an electronic scale while they were wearing very little clothes and no shoes. A stadiometer was used to measure height to the closest 0.1 cm, and BMI was computed as weight (kg) divided by height (m). According to WHO guidelines, BMI (kg/m2) values were classified as low (<18.5 kg/m2), eutrophic (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25-29.9 kg/m2), or obese (>30 kg/m2) (28, 29). The Harvey-Bradshaw index for CD was the clinical metric employed in this investigation.
Prognostic nomogram analysis
For multivariate logistic regression, we verified linearity between continuous predictors (age, disease duration) and the log-odds of vitamin D deficiency using the Box-Tidwell procedure (all p > 0.05), confirmed absence of multicollinearity through variance inflation factors (mean VIF = 1.7), and evaluated model fit with the Hosmer-Lemeshow test (p = 0.24). Multivariate data was reduced and risk factors were chosen using the LASSO approach. The variables in the training set were chosen using non-zero LASSO regression coefficients. LASSO regression was performed using R v4.3.1 (glmnet package), with 10-fold cross-validation repeated three times to determine the optimal penalization parameter (λ = 0.032). All continuous variables were standardized (mean = 0, SD = 1) before regularization to ensure coefficient comparability. Selected variables from the LASSO regression model were subjected to multiple logistic regression analysis to construct a prediction model. The non-stick coating nomogram’s calibration was evaluated using a calibration curve, and its discriminatory power was evaluated using the Harrell C index to determine if decision curve analysis is required in order to evaluate net benefit and find clinically relevant non-adherent nomograms. The clinical factor model’s diagnostic effectiveness was evaluated using the matching ROC curve (AUC) from the training and validation toolbox (30).
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was done using statistical tools. Each variable’s normality was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Measurements with a normal distribution are displayed as mean ± standard deviation (SD); groups were compared using independent samples t-tests. Groups were compared using non-parametric testing, and non-normal results are displayed as the median (Q1, Q3). Percentages were used to display categorical data. The index with P < 0.1 was added to the list of significant variables for logistic or linear regression analysis after each index completed univariate analysis. P < 0.05 was established as the cutoff point for statistical significance. To investigate the variation in treatment outcomes and influencing factors among various patient categories, subgroup analyses were conducted. The final multivariate model has a significant P value of 0.05.
Results
Clinical characteristics
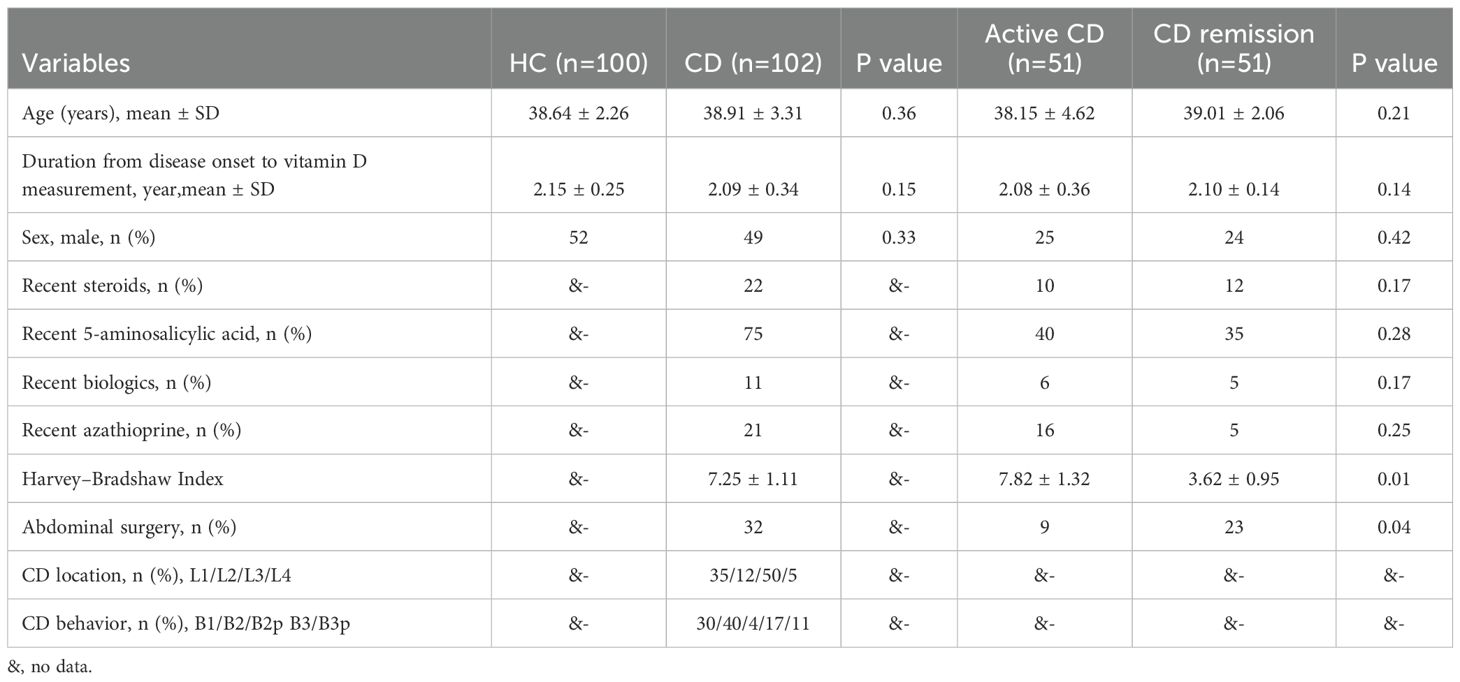
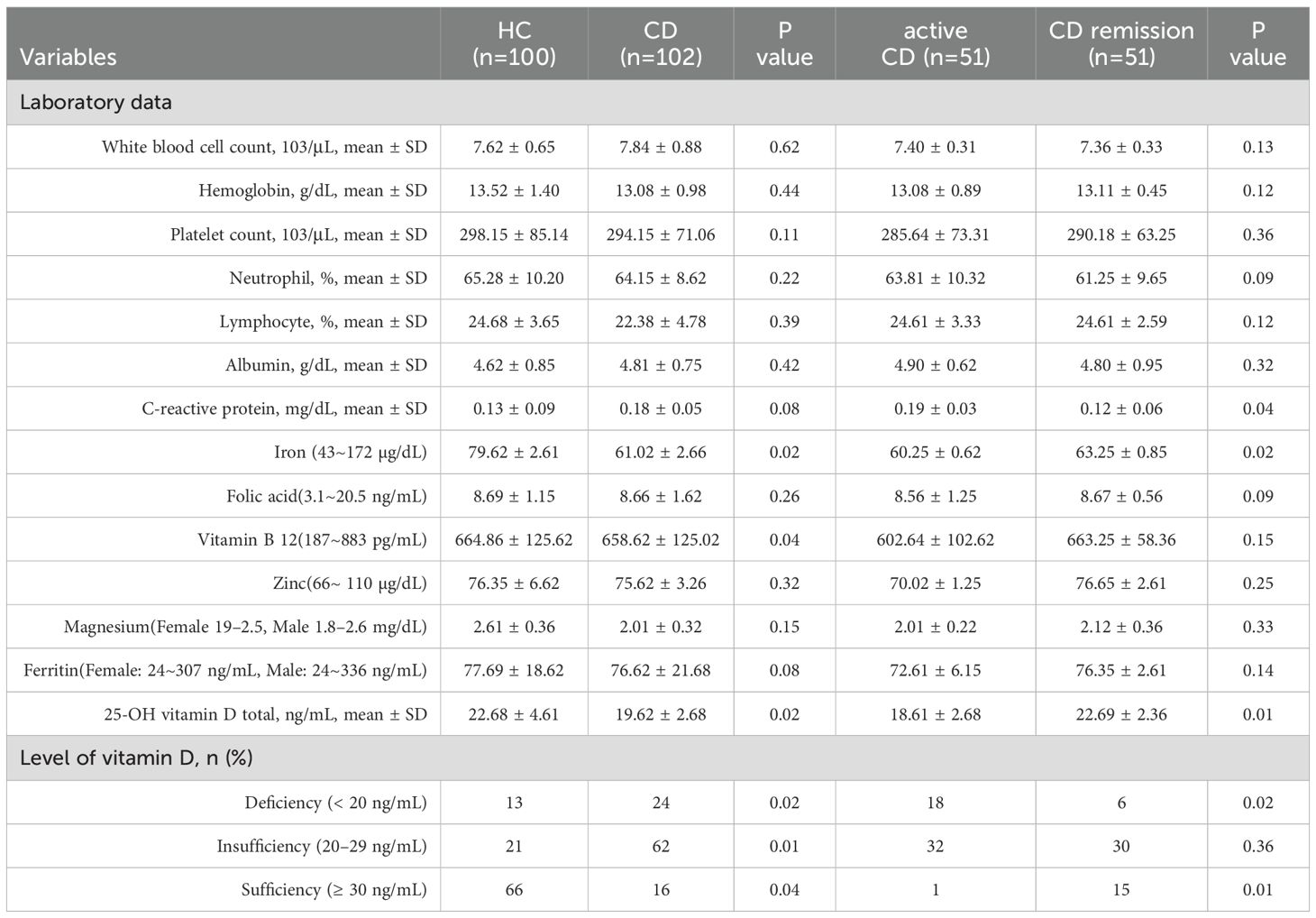
Our study comprised 102 patients with CD and 100 healthy volunteers, whose baseline characteristics are displayed in Table 1. Fifty-one of the 102 CD patients were in active CD, and fifty-one were in remission. The CD patients were 38.91 ± 3.31 years old, while the healthy volunteers were 38.64 ± 2.26 years old. The two groups’ levels of iron (p = 0.02) and vitamin B12 (p = 0.04) differed significantly. In addition, there were no significant statistical differences in white blood cell count, haemoglobin, platelet count, neutrophils, C-reactive protein, and trace elements (magnesium and ferritin) between the two groups. Lastly, we discovered that individuals with CD had significantly lower vitamin D levels (19.62 ± 2.68) than the healthy control group (22.68 ± 4.61) (Figure 1).
The median number of patients in the CD group had treatment before beginning vedolizumab. The difference in clinical outcomes between individuals with active CD and those in remission was next examined. Significant differences were seen between the CD remission and active CD groups in terms of C-reactive protein (p = 0.04), vitamin D deficiency (p=0.02) and vitamin D sufficiency (p=0.01), and abdominal surgery (p=0.04) (Table 2).
The role of vitamin D levels in CD patients
The similarities between the vitamin D-deficient and normal groups are displayed in Table 3. Compared to the group without vitamin D insufficiency, the vitamin D-deficient group had fewer instances of clinical remission (p=0.02) and more males (18 cases) (p=0.01). Regarding clinical medicine usage, the results indicated that the group with vitamin D insufficiency had significantly higher levels of current 5-aminosalicylic acid (p=0.04) and steroids (p=0.02) than the group without vitamin D deficiency. Clinical test results revealed that the vitamin D-deficient group had significantly lower 25-OH vitamin D totals (p=0.01) and significantly higher white blood cell counts (p=0.02) than the non-vitamin D-deficient group. The two groups did not vary substantially in terms of hemoglobin, platelet count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, albumin, C-reactive protein, or abdominal surgery.
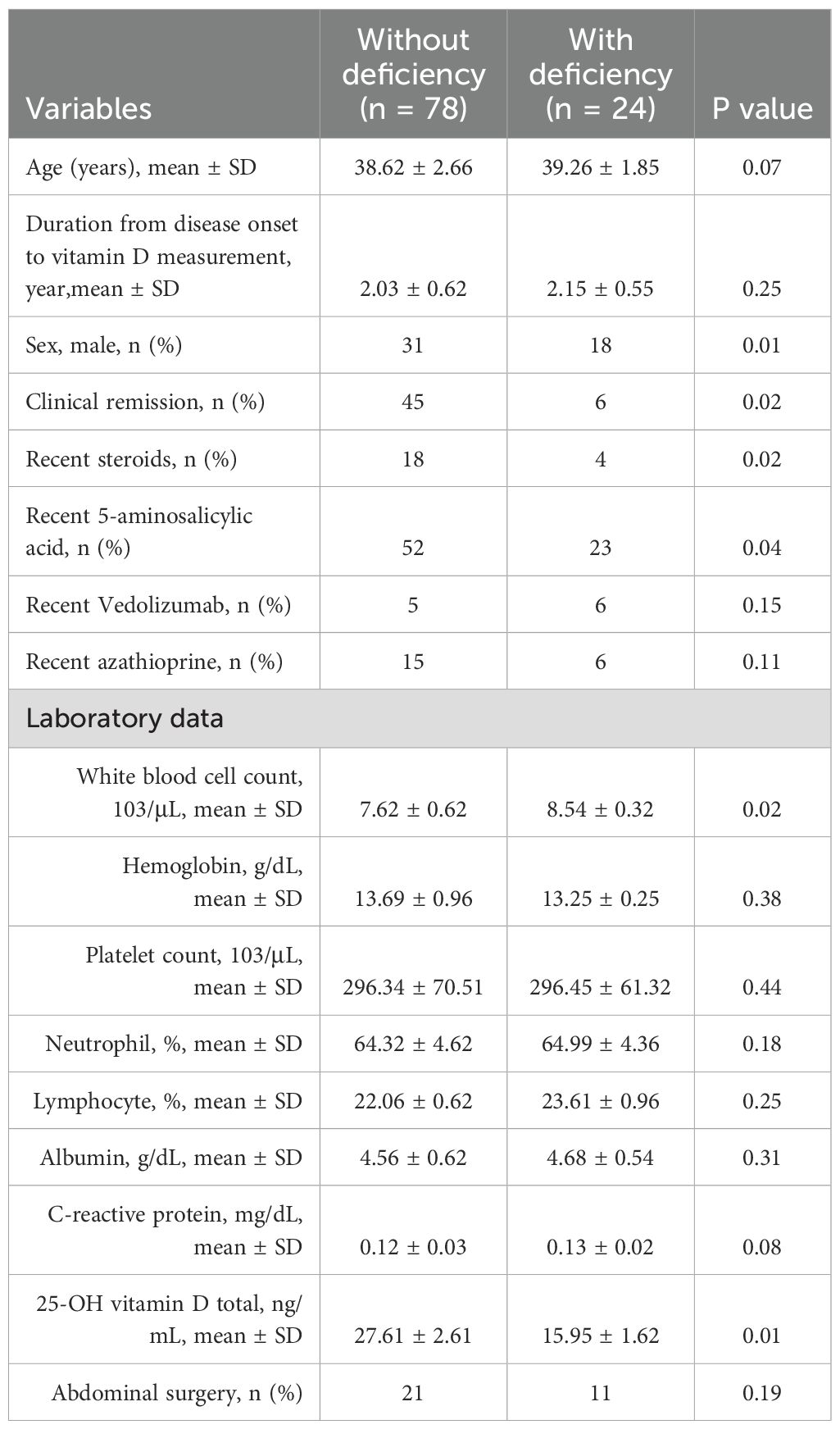
Table 3. Baseline characteristics of the CD population (comparisons between the groups with and without vitamin D deficiency).
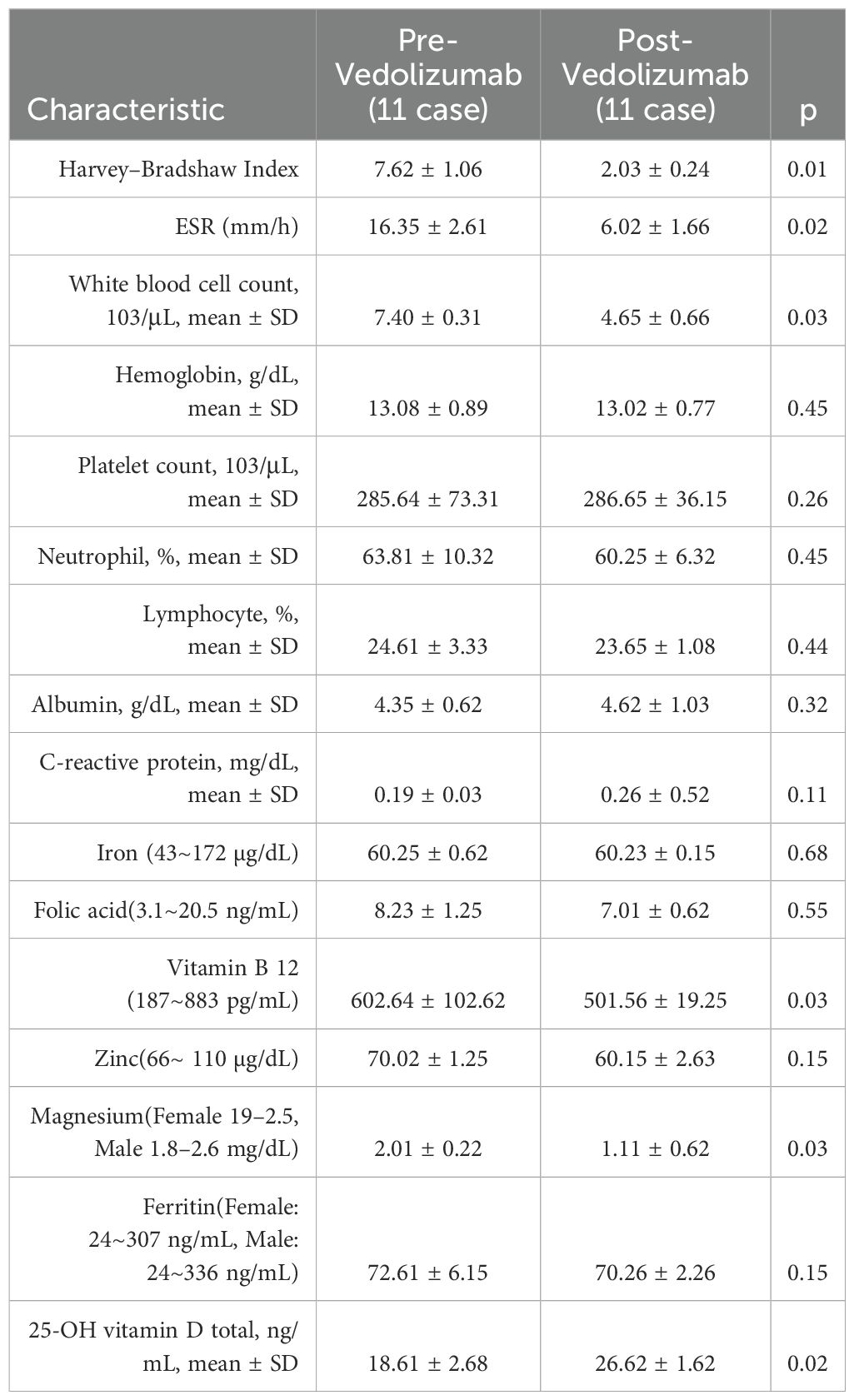
The results before and after using Vedolizumab were then compared in Table 4. After six months of vedolizumab treatment for Crohn’s disease, we found statistically significant improvements in the Harvey-Bradshaw index (p=0.01), ESR (p=0.02), white blood cell count (p=0.03), vitamin B12 (p=0.03), magnesium (p=0.03), and vitamin D (p=0.02).
Univariate, multivariate, and LASSO regression analysis models
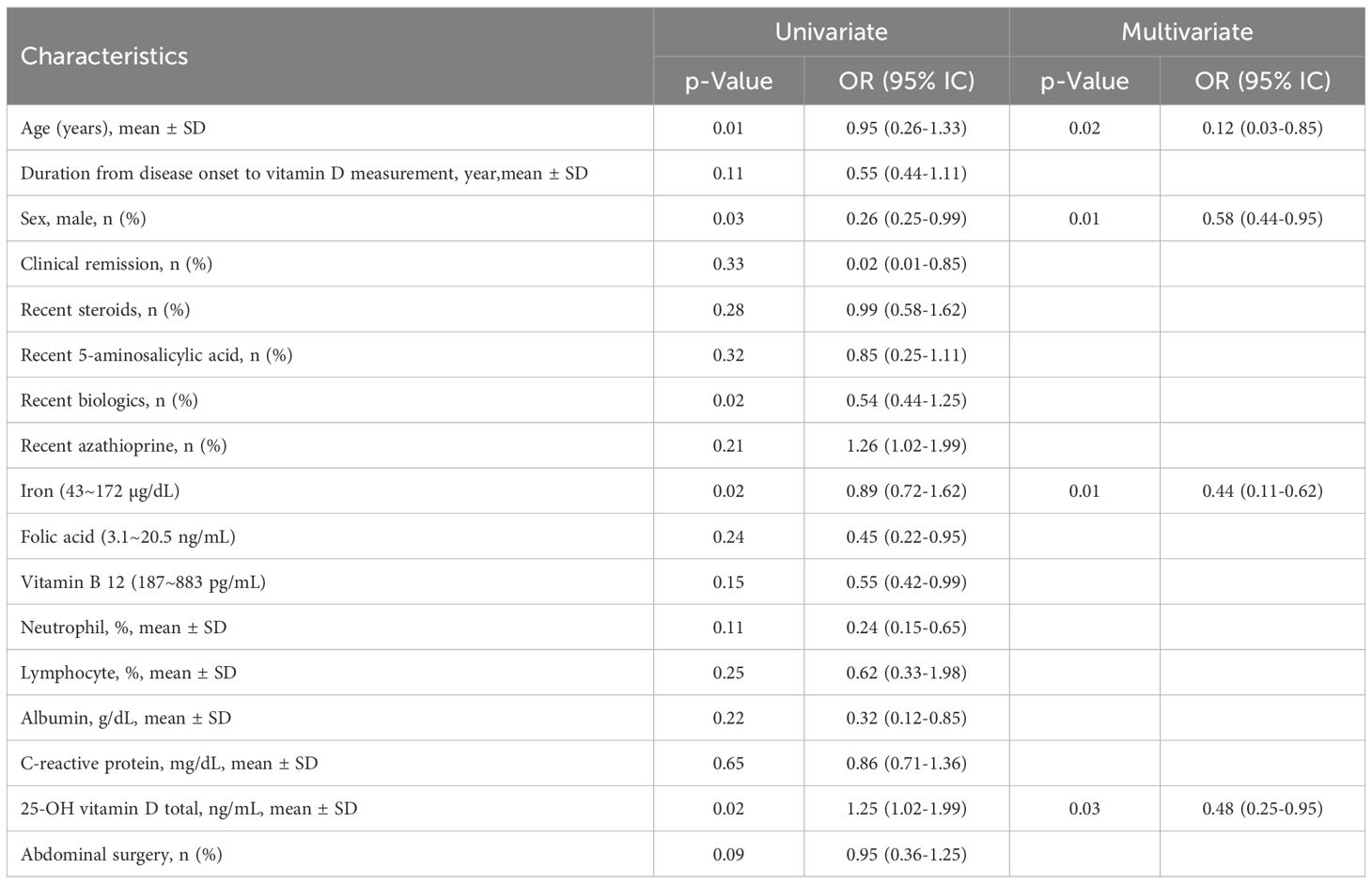
Table 5 lists the risk factors for vitamin D deficiency. Significant differences between patients with and without vitamin D deficiency were found in age (OR: 0.95, 95% CI 0.26-1.33, p=0.01), sex (OR: 0.26, 95% CI 0.25-0.99, p=0.03), newer biologics (OR: 0.54, 95% CI 0.44-1.25, p=0.02), iron (OR: 0.89, 95% CI 0.72-1.62, p=0.02), and total 25-OH vitamin D (OR: 1.25, 95% CI 1.02-1.99, p=0.02). Furthermore, multivariate analysis revealed that after multivariate adjustment, odds ratios were significantly lower for increasing age at diagnosis (OR: 0.12, 95% CI 0.03-0.85, p=0.02), sex (OR: 0.58, 95% CI 0.44-0.95, p=0.01), iron (OR: 0.44, 95% CI 0.11-0.62, p=0.01), and 25-OH vitamin D total (OR: 0.48, 95% CI 0.25-0.95, p=0.03).
Figure 2 illustrates the correlation between age, sex, iron, and the total amount of 25-OH vitamin D using several linear regression models. Based on CD patients in the vitamin D-positive and vitamin D-negative cohorts, the LASSO regression model reduced 15 components to 5 possible predictors with non-zero coefficients. Age, sex, iron, and total 25-OH vitamin D are some of these traits. The nomogram was created using a model that included the independent predictors previously described. In this cohort, there was significant agreement with the calibration curve of the risk of non-adherence nomogram, which is used to predict risk in patients with CD. The bootstrap validation of 0.912 and the C-index of the cohort-projected nomogram of 0.965 (95% CI, 0.33-2.67) demonstrate the great discriminativeness of the model. With an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.905, the CD linkage indicator nomogram’s decision curve analysis is displayed. In summary, 25-OH vitamin D levels, age, and the time between the development of the illness and vitamin D insufficiency may be helpful indicators for CD patients.
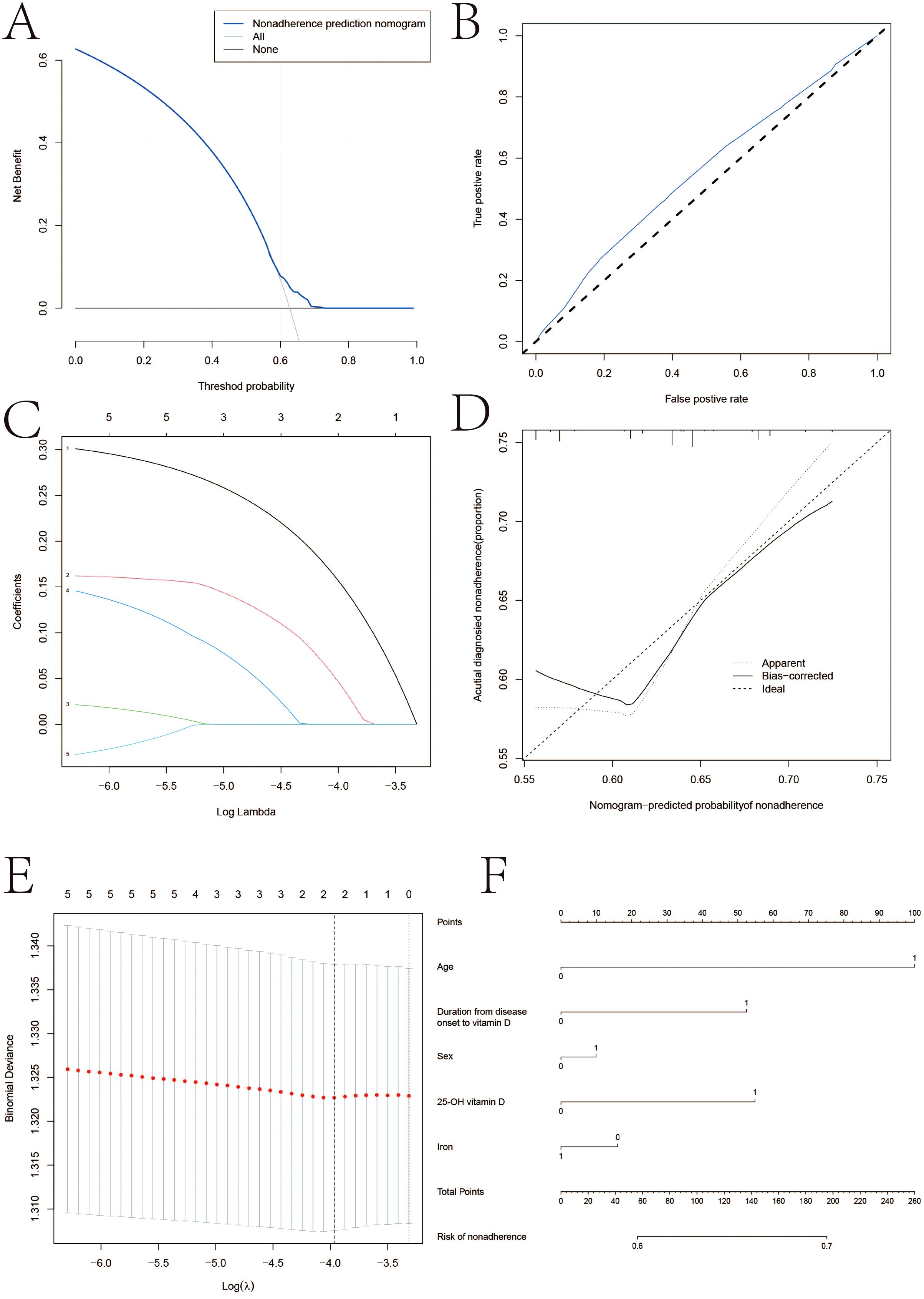
Figure 2. LASSO regression analysis. (A) Decision curve analysis for the nonadherence nomogram (B) Calibration curves of the nonadherence nomogram prediction in the cohort. (C) LASSO coefficient profiles of the 22 characteristics. (D) Acutial diagnosied nonadherence. (E) Optimal parameter (lambda) selection in the LASSO model uses fivefold cross‐validation using minimal criteria. (F) Vertical line was drawn at the value determined using fivefold cross‐validation, where optimum lambda resulted in five features with nonzero coefficients.
Discussion
Crohn’s disease (CD), a recurrent inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), is caused by innate immune dysregulation in the gut (31). Patients with CD may be at higher risk of developing the disease if they have a vitamin D deficit and the hazards that come with it. (32). According to our findings, vitamin D levels in CD patients significantly decreased. Among individuals with vitamin D insufficiency, there were statistically significant variations in white blood cell count, clinical remission, and gender. Following vedolizumab therapy, vitamin D levels considerably increased. In univariate, multivariate, and LASSO regression models, common characteristics, including age and vitamin D levels, may be risk factors for the advancement of CD illness.
With 20% coming from food, vitamin D is a steroid hormone with immunomodulatory properties that is mostly produced in the skin following sun exposure (33, 34). Prior research has demonstrated a substantial correlation between vitamin D insufficiency and the prevalence of CD in patients (32). Vitamin D production may be negatively impacted by darker-skinned Asian individuals’ decreased sun penetration (35, 36). Vertebral fractures are more frequent in CD patients than in healthy people, and they are crucial for children’s bone development (37). Prior to beginning steroid therapy, it is critical to ascertain the severity of vitamin D deficiency (38). While pan-hypovitaminosis occurred, vitamin D’s unique link to inflammation suggests its role as both a biomarker and pathophysiological mediator. For CD patients with active illness or undergoing steroid treatment, vitamin supplementation and monitoring are advised (38). It is still unknown, nevertheless, how precisely vitamin D levels relate to clinical remission or activity in CD patients.
Among our CD group, vedolizumab medication levels were significantly greater among those with higher vitamin D levels. From a therapeutic perspective, raising vitamin D levels might be one method of raising medication levels. However, due to enhanced absorption, mucosal healing, and general improvements in illness and nutritional condition, vedolizumab could have indirectly increased vitamin D levels (39). Compared to the low pre-treatment vedolizumab group, the vitamin D levels of the pre-treatment vedolizumab patients are lower (40). While our findings elucidate vitamin D pathophysiology in CD—particularly relevant given its ileal predominance—similar mechanisms may operate in UC through distinct pathways (e.g., epithelial barrier repair). Future studies should validate whether the identified risk factors (age, disease duration, baseline vitamin D) generalize across IBD subtypes.
Circulating 25D levels were determined using lifestyle surveys and direct measurements of plasma 25D, according to a large prospective cohort research of 72,719 women who participated in the Nurses’ Health Study, which was published in 2011 (41). Between 1986 and 2008, the ladies were monitored, and 122 CD cases were noted throughout that period. A combination of lifestyle surveys and direct measurements of plasma 25D was used to evaluate the levels of circulating 25D. The authors draw the conclusion that in this female group, a higher projected amount of circulating 25D considerably lowers the incidence of CD. Similarly, a retrospective cohort study of 403 patients with CD concluded that vitamin D deficiency is common in the patient population and is independently associated with lower health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and higher disease activity (42). Similarly, a retrospective cohort analysis of 403 CD patients found that vitamin D deficiency is common in the patient population and is independently associated with lower health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and greater disease activity (43). It should be highlighted, nonetheless, that in this particular demographic, vitamin D insufficiency may result from malabsorption and inactivity brought on by active illness before the clinical presentation (44). When vitamin D levels and indicators of inflammation and disease activity were analyzed in CD patients, fecal calprotectin assays revealed a substantial negative connection between 25D concentrations and intestinal inflammation (45). Patients in clinical remission are affected by this connection, whereas those with active CD are not. Moreover, the 25D level was not associated with either disease activity ratings or systemic inflammation as assessed by circulating C-reactive protein in this cohort (46). Our findings indicate that low vitamin levels are significantly associated with CD and active CD.
Age, gender, and vitamin D levels were the main risk factors for CD patients in our study. Previous studies have shown a considerable decrease in vitamin D levels in women. Han et al. found that vitamin D insufficiency was associated with Crohn’s disease (p=0.012) and female sex (p=0.012) (47). Women were 1.7 times more likely than men to have a 25-OH vitamin D level below 20 ng/ml, per Samantha et al.’s research (48). Women are a risk factor, according to our findings. Other investigations, however, have not demonstrated this correlation (49, 50). Vitamin D insufficiency is linked to longer age at diagnosis, according to research by Alex Ulitsky et al (42). According to our research, one risk factor for vitamin D insufficiency is being young when diagnosed. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that a younger age of onset is a poor prognostic factor for IBD and will need more future medical care (26, 51). Our results point to the necessity of screening our younger population for vitamin D (52, 53). Vitamin D supplementation is useful in raising vitamin D concentrations and lowering CRP levels in adults (54) and pediatric IBD patients (55). On the other hand, 82% of IBD patients had untreated vitamin D insufficiency, indicating a clinical disregard for the issue (56). While pan-hypovitaminosis occurred, vitamin D’s unique link to inflammation suggests its role as both biomarker and pathophysiological mediator (57, 58). While vedolizumab’s gut-specific action provides a unique model for studying mucosal healing-nutrient interactions, our results conceptually align with evidence for anti-TNF therapies. Future studies should directly compare vitamin D trajectories across biologic classes.
Furthermore, we discovered that vitamin D and iron ion levels can possibly be significant risk factors for CD patients. Moreover, disease activity is linked to vitamin D insufficiency. According to Søren et al., the median 25-OH vitamin D levels in slightly, moderately, and remission-stage Crohn’s disease were 64, 49, and 21 nmol/l (p<0.01) and 68, 76, and 35 nmol/l (p<0.05) by the Crohn’s disease activity index, respectively. Furthermore, low serum 25-OH vitamin D was linked to active Crohn’s disease. Regardless of disease activity, individuals who smoked had lower 25-OH vitamin D levels than nonsmokers (59). Vitamin D replenishment is linked to lower disease activity and higher quality of life in CD patients, according to Samantha et al. (48). A meta-analysis of 27 studies, including 8316 IBD patients, by Gubatan et al. found a significant correlation between low vitamin D levels and disease activity (OR: 1.53, 95% CI 1.32-1.77) (60). In addition to clinical evaluation, studies have demonstrated a negative correlation between vitamin D levels and inflammatory markers in CD populations, such as white blood cell count, CRP, and fecal calprotectin (61–64). Although standardized low-dose supplementation introduces uniformity, unmeasured individual factors (e.g., adherence, baseline deficiency severity) may contribute residual variability. The effect size and mechanistic plausibility support vedolizumab’s role, but prospective trials with controlled supplementation are warranted.
Limitations
The very limited number of instances in each group we examined is the first of many limitations of our research that should be addressed. Firstly, we mitigated recall bias via standardized electronic health record abstraction and sensitivity analyses excluding inconsistently documented cases. Secondly, the small size of our studies does not provide sufficient evidence to support clinical outcomes, and further expansion of the sample size for analysis data is needed in future studies. Residual effects of diet/sun exposure remain possible despite seasonal adjustment. Thirdly, we did not examine the effects of vitamin D supplementation in individuals with CD since our research was a retrospective observational study. Despite this, our research focuses on the connection between CD illness and vitamin D levels in local populations. But there is also a need to consider the effects of factors such as sunlight on vitamin D in future studies. Lastly, we examine the connection between CD and a few key clinical nutrients; nevertheless, we still need to investigate the association between vitamin D and nutrients.
Conclusion
According to this study, vitamin D insufficiency was often linked to CD patients with active status and pre-treatment Vedolizumab. Furthermore, Age, time since illness onset, and 25-OH vitamin D were found to be significant risk factors for CD. Our research serves as a reference for the connection between CD and vitamin D insufficiency on the Chinese mainland and might guide the clinical diagnosis and management of vitamin D-deficient CD patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XF: Writing – original draft, Project administration, Data curation, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Formal Analysis. QY: Writing – original draft, Resources, Software, Investigation, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Validation, Project administration, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis. YK: Investigation, Software, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Project administration. KJ: Project administration, Conceptualization, Validation, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. MX: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Investigation, Validation, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. FW: Writing – original draft, Software, Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all participants and our hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Wang Y, Lin Y, Feng J, Lin L, Liu L, Su J, et al. Correlation of serum trace elements with clinical features and gut microbiota in patients with Crohn’s disease. J Nutr Biochem. (2025) 142:109917. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2025.109917
2. Savin E, Sharif K, Amit S, and Ben Horin S. Walking the pathogenic tightrope: is mycobacterium simiae a benign colonizer or a potential threat in crohn’s disease? Israel Med Assoc J. (2025) 27:221–3.
3. Russell RK, Fagbemi A, Benyacoub J, Capobianco ME, Wells LE, Shergill-Bonner R, et al. Specialized and standard nutritional formulas for the dietary management of pediatric patients with Crohn’s disease: a systematic literature review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2025) 49(6):102591. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2025.2488887
4. Chen M, Gao X, Cao Q, Rossiter G, Kitagawa T, Sun Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of intravenous vedolizumab treatment in Chinese patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. linics Res Hepatol gastroenterology. (2025), 102591. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2025.102591
5. Chuang MC, Hsu TJ, Tsai FJ, Hsu JL, and Tsai TY. Crohn’s disease but not ulcerative colitis elevated risk of end-stage renal disease and mortality: A Taiwan retrospective cohort study. Medicine. (2025) 104:e42026. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000042026
6. Baronetto A, Fischer S, Neurath MF, and Amft O. Automated inflammatory bowel disease detection using wearable bowel sound event spotting. Front digital Health. (2025) 7:1514757. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1514757
7. Dong MD, Salwen-Deremer JK, and Siegel CA. Remote monitoring for patients with inflammatory bowel disease: current status and the future of the field. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 20:621–7. doi: 10.1211/pj.2017.20202316
8. Alsakarneh S, Al Ta’ani O, Aburumman R, Mikhail I, Hashash JG, and Farraye FA. Risk of de novo inflammatory bowel disease in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with IL-17A inhibitors: A population-based study. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2025) 62(1):72–6. doi: 10.1111/apt.70139
9. Vitello A, Maida M, Shahini E, Macaluso FS, Orlando A, Grova M, et al. Current approaches for monitoring of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: A narrative review. J Clin Med. (2024) 13(4):1008. doi: 10.3390/jcm13041008
10. Pruijt MJ, de Voogd FAE, Montazeri NSM, van Etten-Jamaludin FS, D’Haens GR, and Gecse KB. Diagnostic accuracy of intestinal ultrasound in the detection of intra-abdominal complications in crohn’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crohn’s colitis. (2024) 18:958–72. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad215
11. Dolinger MT and Kayal M. Intestinal ultrasound as a non-invasive tool to monitor inflammatory bowel disease activity and guide clinical decision making. World J gastroenterology. (2023) 29:2272–82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2272
12. Kopylov U, Rosenfeld G, Bressler B, and Seidman E. Clinical utility of fecal biomarkers for the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammatory bowel diseases. (2014) 20:742–56. doi: 10.1097/01.Mib.0000442681.85545.31
13. Wan J, Zhou J, Wang Z, Liu D, Zhang H, Xie S, et al. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: Insights from the past two years. Chin Med J. (2025) 138:763–76. doi: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000003542
14. Yediel Aras Ş, Gezer A, Mokhtare B, and Karadag Sari E. Effects of vitamin D and common nettle (Urtica dioica) extract administration on Mn-SOD and Catalase (CAT) secretion in the colon tissues of rats with experimentally induced Crohn’s disease. Biotechnic Histochem. (2025) 100:1–7. doi: 10.1080/10520295.2024.2434753
15. Wang K, Zhu S, Yao L, Cao Q, and Shao B. Association of vitamin D and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in treatment escalation risk for newly diagnosed Crohn’s disease adults. Nutr J. (2025) 24:49. doi: 10.1186/s12937-025-01115-7
16. O'Donnell JEM, Leach ST, Bowcock NL, Chen S, and Gupta N. Daily vitamin D3 versus stoss vitamin D3 for correction of 25OHD deficiency in children with inflammatory bowel disease, a randomised controlled trial. Digestive Dis Sci. (2025) 70(5):1844–53. doi: 10.1007/s10620-025-08913-3
17. Çakar S, Eren G, Erdur CB, Önder M, Pelek Ş, Demirtaş D, et al. Are vitamin D levels related to sarcopenia in children with inflammatory bowel disease? J Clin Med. (2025) 14(5):1548. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051548
18. Bagger-Jörgensen H, Thomsen C, Borrisholt M, Wanders A, and Sjöberg K. The colonic vitamin D receptor and inflammatory bowel disease: no correlation to histologic or endoscopic inflammation. APMIS. (2025) 133:e70000. doi: 10.1111/apm.70000
19. Liao YJ, Lin WT, Liao SC, Lin SJ, Huang YC, Wu MC, et al. Clinical application and feasibility of capsule endoscopy in children at a medical center in central Taiwan. J Formosan Med Assoc. (2024) 124(6):569–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2024.06.012
20. Lim JG, Ko JS, Ko JM, Kim HY, Kim MJ, Seong MW, et al. Characteristics of chronic enteropathy associated with SLCO2A1 gene (CEAS) in children, a unique type of monogenic very early-onset inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Pediatr. (2024) 24:396. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04877-x
21. Taş Ö, Aydın F, Kuloğlu Z, Kırsaçlıoğlu CT, Bahçeci O, Aydın BÖ, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease in paediatric rheumatological diseases. Clin Rheumatol. (2025) 44(5):2043–52. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07424-w
22. Artusa P and White JH. Vitamin D and its analogs in immune system regulation. Pharmacol Rev. (2025) 77:100032. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmr.2024.100032
23. Khoo AL, Chai LY, Koenen HJ, Oosting M, Steinmeyer A, Zuegel U, et al. Vitamin D(3) down-regulates proinflammatory cytokine response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis through pattern recognition receptors while inducing protective cathelicidin production. Cytokine. (2011) 55:294–300. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.04.016
24. Adorini L and Penna G. Dendritic cell tolerogenicity: a key mechanism in immunomodulation by vitamin D receptor agonists. Hum Immunol. (2009) 70:345–52. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2009.01.016
25. Maaser C, Sturm A, Vavricka SR, Kucharzik T, Fiorino G, Annese V, et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J Crohn’s colitis. (2019) 13:144–64. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy113
26. Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, and Kern F Jr. Development of a Crohn’s disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study. Gastroenterology. (1976) 70:439–44. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(76)80163-1
27. Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 96:1911–30. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0385
28. GBD 2021 Adolescent BMI Collaborators. Global, regional, and national prevalence of child and adolescent overweight and obesity, 1990-2021, with forecasts to 2050: a forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet (London England). (2025) 405:785–812. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(25)00397-6
29. Feingold KR. Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Cholesterol. Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, et al, editors. Am J Manag Care: Endotext. MDText.com, Inc. Copyright © 2000-2025, MDText.com, Inc (2000).
30. Guan Z, Jin X, Guan Z, Liu S, Tao K, and Luo L. The gut microbiota metabolite capsiate regulate SLC2A1 expression by targeting HIF-1α to inhibit knee osteoarthritis-induced ferroptosis. Aging Cell. (2023) 22:e13807. doi: 10.1111/acel.13807
31. Wilkins T, Jarvis K, and Patel J. Diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease. Am Family physician. (2011) 84:1365–75. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.97693
32. White JH. Vitamin D deficiency and the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2018) 175:23–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.12.015
33. Cui A, Zhang T, Xiao P, Fan Z, Wang H, and Zhuang Y. Global and regional prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in population-based studies from 2000 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 7.9 million participants. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1070808. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1070808
34. Duranton F, Rodriguez-Ortiz ME, Duny Y, Rodriguez M, Daurès JP, and Argilés A. Vitamin D treatment and mortality in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J nephrology. (2013) 37:239–48. doi: 10.1159/000346846
35. Joseph AJ, George B, Pulimood AB, Seshadri MS, and Chacko A. 25 (OH) vitamin D level in Crohn’s disease: association with sun exposure & disease activity. Indian J Med Res. (2009) 130:133–7. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132036
36. Shi S, Feng J, Zhou L, Li Y, and Shi H. Risk factors for vitamin D deficiency in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Turkish J Gastroenterol. (2021) 32:508–18. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2021.20614
37. Vázquez MA, Lopez E, Montoya MJ, Giner M, Pérez-Temprano R, and Pérez-Cano R. Vertebral fractures in patients with inflammatory bowel disease compared with a healthy population: a prospective case-control study. BMC gastroenterology. (2012) 12:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-230x-12-47
38. Bischoff SC, Escher J, Hébuterne X, Kłęk S, Krznaric Z, Schneider S, et al. ESPEN guideline: Clinical nutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutricion hospitalaria. (2022) 39:678–703. doi: 10.20960/nh.03857
39. Garg M, Hendy P, Ding JN, Shaw S, Hold G, and Hart A. The effect of vitamin D on intestinal inflammation and faecal microbiota in patients with ulcerative colitis. J Crohn’s colitis. (2018) 12:963–72. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy052
40. Valvano M, Magistroni M, Cesaro N, Carlino G, Monaco S, Fabiani S, et al. Effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation on disease course in inflammatory bowel disease patients: systematic review with meta-analysis. Inflammatory bowel diseases. (2024) 30:281–91. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izac253
41. Ananthakrishnan AN, Khalili H, Higuchi LM, Bao Y, Korzenik JR, Giovannucci EL, et al. Higher predicted vitamin D status is associated with reduced risk of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. (2012) 142:482–9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.11.040
42. Ulitsky A, Ananthakrishnan AN, Naik A, Skaros S, Zadvornova Y, Binion DG, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: association with disease activity and quality of life. JPEN J parenteral enteral Nutr. (2011) 35:308–16. doi: 10.1177/0148607110381267
43. Levin AD, Wadhera V, Leach ST, Woodhead HJ, Lemberg DA, Mendoza-Cruz AC, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Digestive Dis Sci. (2011) 56:830–6. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1544-3
44. El-Matary W, Sikora S, and Spady D. Bone mineral density, vitamin D, and disease activity in children newly diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease. Digestive Dis Sci. (2011) 56:825–9. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1380-5
45. Raftery T, Merrick M, Healy M, Mahmud N, O'Morain C, Smith S, et al. Vitamin D status is associated with intestinal inflammation as measured by fecal calprotectin in crohn’s disease in clinical remission. Digestive Dis Sci. (2015) 60:2427–35. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3620-1
46. Ananthakrishnan AN, Cheng SC, Cai T, Cagan A, Gainer VS, Szolovits P, et al. Association between reduced plasma 25-hydroxy vitamin D and increased risk of cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2014) 12:821–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.10.011
47. Han YM, Yoon H, Lim S, Sung MK, Shin CM, Park YS, et al. Zinc, and selenium deficiencies in Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut liver. (2017) 11:363–9. doi: 10.5009/gnl16333
48. Zullow S, Jambaulikar G, Rustgi A, Quezada S, and Cross RK. Risk factors for vitamin D deficiency and impact of repletion in a tertiary care inflammatory bowel disease population. Digestive Dis Sci. (2017) 62:2072–8. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4614-y
49. Blanck S and Aberra F. Vitamin d deficiency is associated with ulcerative colitis disease activity. Digestive Dis Sci. (2013) 58:1698–702. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2531-7
50. Fletcher J, Brown M, Hewison M, Swift A, and Cooper SC. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and modifiable risk factors in patients with Crohn’s disease: A prospective observational study. J advanced Nurs. (2023) 79:205–14. doi: 10.1111/jan.15476
51. Ha CY, Newberry RD, Stone CD, and Ciorba MA. Patients with late-adult-onset ulcerative colitis have better outcomes than those with early onset disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2010) 8:682–687.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.03.022
52. Wei SC, Chang TA, Chao TH, Chen JS, Chou JW, Chou YH, et al. Management of ulcerative colitis in Taiwan: consensus guideline of the Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Intestinal Res. (2017) 15:266–84. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.266
53. Wei SC, Chang TA, Chao TH, Chen JS, Chou JW, Chou YH, et al. Management of ulcerative colitis in Taiwan: consensus guideline of the Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease updated in 2023. Intestinal Res. (2024) 22:213–49. doi: 10.5217/ir.2023.00050
54. Guzman-Prado Y, Samson O, Segal JP, Limdi JK, and Hayee B. Vitamin D therapy in adults with inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflammatory bowel diseases. (2020) 26:1819–30. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaa087
55. Sohouli MH, Farahmand F, Alimadadi H, Rahmani P, Motamed F, da Silva Magalhães EI, et al. Vitamin D therapy in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Pediatr. (2023) 19:48–57. doi: 10.1007/s12519-022-00605-6
56. Domislović V, Vranešić Bender D, Barišić A, Brinar M, Ljubas Kelečić D, Rotim C, et al. High prevalence of untreated and undertreated vitamin d deficiency and insufficiency in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Acta clinica Croatica. (2020) 59:109–18. doi: 10.20471/acc.2020.59.01.13
57. Filgueiras MS, Rocha NP, Novaes JF, and Bressan J. Vitamin D status, oxidative stress, and inflammation in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 60:660–9. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1546671
58. Querfeld U. Vitamin D and inflammation. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin Germany). (2013) 28:605–10. doi: 10.1007/s00467-012-2377-4
59. Jørgensen SP, Hvas CL, Agnholt J, Christensen LA, Heickendorff L, and Dahlerup JF. Active Crohn’s disease is associated with low vitamin D levels. J Crohn’s colitis. (2013) 7:e407–13. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2013.01.012
60. Gubatan J, Chou ND, Nielsen OH, and Moss AC. Systematic review with meta-analysis: association of vitamin D status with clinical outcomes in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 50:1146–58. doi: 10.1111/apt.15506
61. Branco JC, Cardoso MF, Anapaz V, Lourenço LC, Oliveira AM, Rodrigues CG, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in a portuguese cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease: prevalence and relation to disease activity. GE Portuguese J gastroenterology. (2019) 26:155–62. doi: 10.1159/000488744
62. Caviezel D, Maissen S, Niess JH, Kiss C, and Hruz P. High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammatory intestinal diseases. (2018) 2:200–10. doi: 10.1159/000489010
63. Li J, Chen N, Wang D, Zhang J, and Gong X. Efficacy of vitamin D in treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. Medicine. (2018) 97:e12662. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000012662
Keywords: vitamin D, Crohn’s disease, vedolizumab, age, LASSO regression analysis
Citation: Feng X, Yin Q, Kang Y, Jiang K, Xu M and Wang F (2025) The role of vitamin D deficiency and modifiable risk factors in patients with Crohn’s disease. Front. Immunol. 16:1616924. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1616924
Received: 23 April 2025; Accepted: 10 July 2025;
Published: 30 July 2025.
Edited by:
Rocio Ferreiro-Iglesias, University Clinical Hospital of Santiago, SpainReviewed by:
Paul Rufo, Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United StatesAggelos Laliotis, The General Hospital of Heraklion “Venizeleio-Pananio”, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Feng, Yin, Kang, Jiang, Xu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fangyu Wang, d2FuZ2Z5NjVAbmp1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiaoyue Feng1†
Xiaoyue Feng1† Fangyu Wang
Fangyu Wang