- 1Department of Pathological Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, United States
- 2Department of Pathology, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS), Little Rock, AR, United States
- 3The Winthrop P. Rockefeller Cancer Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, United States
- 4Department of Pharmacology and Physiology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States
- 5Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum NCI Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States
- 6Department of Chemistry, Central Washington University, Ellensburg, WA, United States
- 7Department of Comparative Biological Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, United States
- 8Department of Biological Sciences and Chemistry, College of Sciences and Engineering, Southern University and A&M College, Baton Rouge, LA, United States
- 9Department of Molecular Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
- 10Division of Biomedical Sciences, Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine, Monroe, LA, United States
Oncolytic virotherapy (OVT) has emerged as a promising and innovative cancer treatment strategy that harnesses engineered viruses to selectively infect, replicate within, and destroys malignant cells while sparing healthy tissues. Beyond direct oncolysis, oncolytic viruses (OVs) exploit tumor-specific metabolic, antiviral, and immunological vulnerabilities to reshape the tumor microenvironment (TME) and initiate systemic antitumor immunity. Despite promising results from preclinical and clinical studies, several barriers, including inefficient intratumoral virus delivery, immune clearance, and tumor heterogeneity, continue to limit the therapeutic advantages of OVT as a standalone modality and hindered its clinical success. Recent advances in OV engineering have enhanced viral tropism, immune evasion, and transgene delivery, enabling better tumor targeting and penetration and sustained immune activation in malignant tumors. Moreover, rational combination strategies with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), chemotherapeutics, and immunometabolic modulators are reshaping OVT into a versatile strategy for precision oncology. This review highlights the mechanistic innovations driving next-generation OV engineering, explores emerging combination regimens, and discusses future directions to overcome resistance and maximize clinical efficacy.
1 Introduction
Oncolytic viruses (OVs), both naturally occurring and genetically engineered strains, are emerging as programmable immunotherapeutic that exploit tumor-intrinsic vulnerabilities, such as metabolic rewiring, impaired antiviral defenses, and immune evasion. By leveraging these characteristics, OVs remodel the tumor microenvironment (TME) and elicit systemic antitumor immune immunity (1). Through selective infection and replication, they induce direct oncolysis and immunogenic cell death (ICD), converting immunologically “cold” tumors into “hot” lesions that support T cell infiltration and activation (2).
The concept of oncolytic virotherapy (OVT) dates back to the early 20th-century when spontaneous tumor regressions were observed in patients with leukemia, Burkitt’s lymphoma, and Hodgkin’s disease following viral infections (3). Landmark therapies such as Onyx-015 [a genetically modified adenovirus (AdV)], H101 (AdV variant), and Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC), a herpes simplex virus-1 [HSV-1 expressing granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)], have since transformed viruses from pathogens into precision-targeted cancer therapeutics (4, 5)
OVs possess either DNA or RNA genomes, which may be single or double stranded. Among them, single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses are the most commonly used viruses for OV engineering. Notable exceptions include reovirus (a double-stranded RNA virus) and parvovirus (a single-stranded DNA virus). Examples of dsDNA viruses include AdV, vaccinia virus (VacV), and HSV-1. ssRNA viruses are further categorized by polarity into positive-sense (e.g., coxsackievirus, Seneca Valley virus, poliovirus), which are directly translated by host ribosomes, and negative-sense [(e.g., measles virus, Newcastle Disease virus, Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV)], which require transcription into positive-sense RNA before translation. OVs are also classified as either naturally attenuated strains or genetically modified vectors.
OVs may preferentially infect tumor cells due to overexpression of viral entry receptors, disrupted signaling pathways, and impaired antiviral defenses within both tumor cells and the TME. These conditions support viral replication and enable targeted virotherapy across diverse cancer types. Other OVs preferentially target rapidly-dividing, Ras-activated-tumors, IFN-deficient tumors, often of neuroendocrine origin (6). They also differ in their mechanism of egress. For example, HSV-1, AdV, and VacV typically induce rapid lytic egress, while measles and Maraba viruses use non-lytic egress, allowing prolonged survival in the infected cell. Non-lytic egress, is common in enveloped viruses where virions may bud from the plasma membranes or egress via vesicular-mediated pathways.
While not all OVs naturally induce ICD, many can be engineered to do so. Some viruses primarily cause non-immunogenic lysis, whereas others activate immunogenic pathways such as apoptosis, necroptosis, or pyroptosis (7). For example, wild-type AdVs and reoviruses may require genetic modification to trigger ICD effectively. To address this, OVs, notably T-VEC, Maraba virus, VacV and Ad-p53 have been engineered to deliver tumor-suppressor genes, which have been shown to induce hallmark features of ICD, including calreticulin exposure, ATP release, and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) secretion (8–10).
Despite their promising potential, OVT faces challenges as a standalone treatment. The TME presents physical and immunological barriers, such as dense extracellular matrix (ECM), hypoxia, and immunosuppressive cytokines [e.g. transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and interleukin-10 (IL-10)], that hinder viral entry, spread, replication, and antitumor immunity (11). Additionally, neutralizing antibodies and tumor heterogeneity further limit efficacy.
To overcome these limitations, next-generation OVs are being actively developed with enhanced delivery systems (e.g. stem cells, nanoparticles, cell-based carriers) and are being combined with other immunotherapies, including ICIs (e.g., anti-PD-1, anti-CTLA-4), chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, cancer vaccines, radiotherapy, and targeted inhibitors (12–14). OVs are also engineered to express immunomodulatory payloads [e.g. GM-CSF, IL-12, or tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)], incorporate tumor-specific promoters or delete oncogenes (e.g., E1B in AdV, ICP34.5 in HSV-1), to improve safety and selectivity (12–14).
Complementary strategies using epigenetic modifiers (e.g., HDAC inhibitors like valproic acid and vorinostat) and metabolic reprogramming bioactive molecules (e.g., PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors) can sensitize tumors to OV infection (15–17). Nutraceuticals such as curcumin, sulforaphane, and EGCG are also emerging as promising adjuvants that modulate immunity, reverse epigenetic silencing, and enhance viral selectivity (18–20). In this review, we will explore the evolving landscape of OVT, from viral tropism and payload engineering to immunometabolic reprogramming, highlighting its transformative potential in next-generation precision immunotherapy.
2 Reprogramming the tumor-OV-immune axis
The TME presents a paradoxical landscape where tumor-driven immune evasion, chronic inflammation, and impaired antiviral signaling support OV replication, while innate immune cells act as key barriers to viral spread. Understanding how OVs navigate and exploit this hostile yet permissive niche is essential for enhancing their efficacy in cancer immunotherapy. OVs reshape the tumor-immune microenvironment by releasing immunostimulatory signals, such as tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), during replication (21). These signals activate pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), including Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and RIG-I-like receptors, on innate immune cells, triggering type I IFN and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. This response promotes local inflammation and recruits antigen-presenting cells (APCs), particularly dendritic cells (DCs), to lymphoid tissues and the TME. Activated DCs capture TAAs and present them to T cells via MHC class I and II pathways, priming CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), CD4+ helper T cells, and activating natural killer (NK) cells through cytokine signaling and cross-talk with T cells. This cascade drives systemic antitumor immunity while reducing regulatory T cells (Tregs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) (22).
To enhance immune activation, engineered OVs are frequently designed to carry bispecific T-cell engagers that boost T-cell priming and cytotoxic function. Additionally, OVs can be modified to express checkpoint inhibitors, pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory molecules, or TAAS. Some OVs also activate innate immune pathways like STING or RIG-I, incorporate microRNA target sequences to improve tumor specificity, or disrupt tumor vasculature to facilitate immune infiltration.
Among these strategies, the expression of cytokines and costimulatory ligands plays a critical role in overcoming tumor-induced immune suppression by promoting cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) infiltration and activation. This can convert immunologically “cold” tumors into “hot,” inflamed lesions that are more responsive to immunotherapies, such as checkpoint blockade (22). Collectively, these strategies aim to enhance immune cell recruitment, activation, and tumor-specific responses, often acting synergistically with other forms of immunotherapy. In the following sections, we will examine the innate immune barriers that limit the efficacy of OVT.
2.1 Overview of the tumor-OV-immune system triad
The therapeutic outcome of OVT is shaped by the dynamic interplay between the tumor, immune system, and OVs. This triad determines whether OVs are neutralized, persist long enough to cause oncolysis, or successfully trigger systemic antitumor immunity. Upon infection, OVs induce immunogenic cell death (ICD), releasing tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), and pro-inflammatory cytokines that activate antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and prime cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), initiating abscopal effects that target metastatic lesions (23).
However, this therapeutic potential is often limited by antiviral immunity, tumor heterogeneity, and the immunosuppressive TME (24). Host defenses including PRR-mediated antiviral responses, type I IFN signaling, and neutralizing antibodies can limit OV replication and accelerate their clearance (25, 26). Simultaneously, tumors evade immune detection through MHC downregulation, checkpoint molecule upregulation (e.g., PD-L1, CTLA-4), impaired antigen presentation, and secretion of suppressive cytokines such as TGF-β and IL-10 (27, 28).
Paradoxically, the same immunosuppressive features can make tumors more permissive to OV infection. Many cancer cells harbor defects in antiviral sensing and apoptotic pathways, which help them evade immune surveillance but also create vulnerabilities that OVs can exploit. Factors such as hypoxia, metabolic stress, and acidity further impair IFN signaling, enhancing OV replication, particularly in “cold” tumors like pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), where VSV and Coxsackievirus A21 thrive (29, 30).
In contrast, healthy cells detect viral infections via pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as TLRs and RLRs (31), triggering interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) and pro-apoptotic pathways that restrict viral spread. Tumor cells often lose this capacity due to mutations or epigenetic silencing in key components like JAK-STAT, PKR, and OAS-RNase L, enabling selective OV replication (31–33). Additionally, overexpression of viral entry receptors [(e.g., Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor (CAR), nectin-1, EGFR)] enhances OV tropism (34). For example, glioblastoma and lung tumors with high CAR expression are particularly susceptible to AdV-based OVs, while PDAC with impaired IFN signaling supports VSV and Coxsackievirus A21 infection (34).
Navigating this triad requires balancing viral persistence and immune activation. While innate sensing and IFN responses are critical for systemic antitumor immunity, they can also prematurely eliminate therapeutic viruses. To overcome these barriers, next-generation OVs are engineered to evade or modulate immune detection, resist antiviral pathways, and express immunostimulatory payloads. These strategies convert “cold” tumors into “hot,” inflamed lesions that recruit and activate effector immune cells. Combination approaches further enhance efficacy by transiently suppressing innate antiviral defenses during OV administration and subsequently reactivating immune responses to promote tumor clearance (35–37).
2.2 TME creates immune suppression to favor OV infection
From the earliest stages of malignancy, cancer cells establish an immunosuppressive TME characterized by chronic inflammation, cell exhaustion and weak immunogenicity. While these conditions hinder immune surveillance, they paradoxically support selective OV infection and replication, and localized immune activation (38). As discussed in Section 2.1, the tumor-OV-immune triad shapes therapeutic outcomes. Here, we focus specifically on how the immunosuppressive TME and its inherent heterogeneity modulates to OV permissiveness and influences the outcome of OVT.
Tumors heterogeneity further influences immune engagement, giving rise to distinct immune phenotypes, immune-inflamed, immune-excluded, and immune-desert, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities for OVT (38). The TME contains immunosuppressive stromal cells, such as cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), lymphatic endothelial cells as well as infiltrating immunosuppressive cells, such as MDSCs, regulator T cells (Tregs), and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), all of which restrict CTL infiltration and function. CAFs secrete immunosuppressive cytokines (e.g., TGF-β, IL-10) and upregulate checkpoint molecules (e.g., PD-L1 and CTLA-4) (Figure 1), reinforcing immune escape. Although they express MHC-II and can present antigens to CD4+ T cells, their dominant role in the TME is suppressive. MHC-II expression is regulated by IFN-γ via Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway and the class II trans-activator (CIITA) (39). Lymphatic endothelial cells, while facilitating immune cell trafficking, also promote Treg expansion and local immune tolerance. These suppressive features impair IFN signaling and antiviral responses, creating metabolic stress that facilitates OV propagation. Engineered OVs expressing ICIs (e.g., anti-PD-1, anti-CTLA-4) or immunostimulatory cytokines (e.g., GM-CSF) can counteract these signals, reinvigorate T-cell function, and enhance both viral oncolysis and immune-mediated tumor clearance (40, 41).
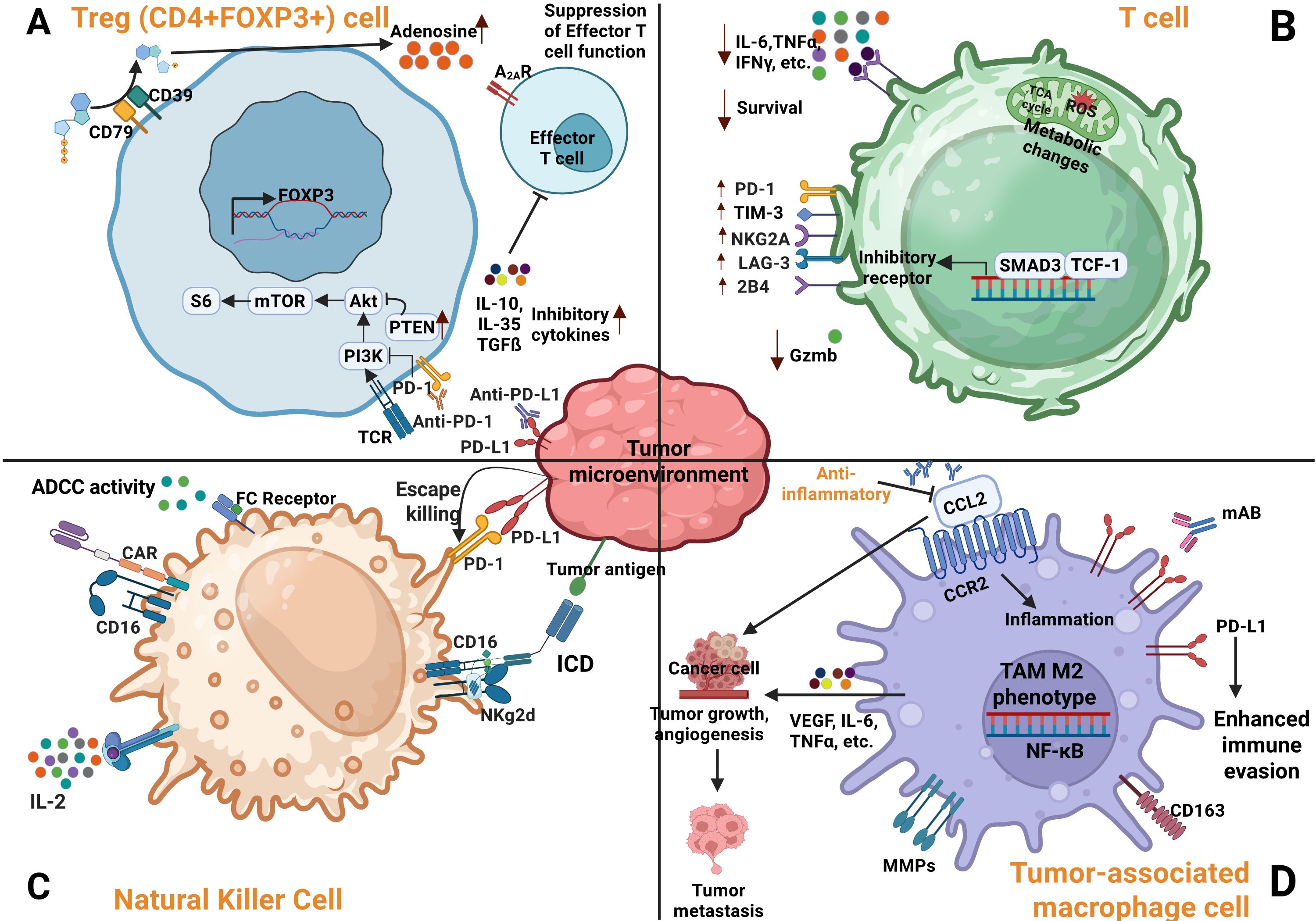
Figure 1. Regulation of immune cells activity within the TME. (A) Suppression of regulatory cells (Tregs) in the TME by anti PD-1/PD-L1 therapy leads to inhibition of PI3K signaling pathways and increased adenosine production. (B) T cell exhaustion within the TME is characterized by decreased cytokine production and elevated expression of inhibitory receptors. (C) Tumor cells evade NK cell mediated cytotoxicity through strong interactions between NK cell inhibitory receptors and their ligands expressed on cancer cells. (D) Immune evasion by cancer cells is further enhanced by TAMs, which contribute to angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis (38).
PD-L1 [also known as cluster of different (CD274) or B7 homology 1 (B7-H1)], expressed on APCs, macrophages, and tumor cells bind PD-1 on T cells, recruiting SHP-1 and SHP-2 phosphatases. This inhibits T cell receptor (TCR) signaling by dephosphorylating CD3 and Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70 (ZAP70) and suppress IL-2 secretion (42). This cascade not only blunts T-cell activation but also promotes regulatory T cell (Treg) differentiation and polarization of TAMs toward the immunosuppressive M2 phenotype. These M2-TAMs secrete pro-tumorigenic cytokines such as vascular endothelia growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor, and TNF-α, supporting angiogenesis and metastasis (43). PD-1 expression on NK cells also suppresses their cytotoxic activity, further aiding immune evasion.
CTLA-4, another key checkpoint, competes with CD28 for B7 binding, limiting T-cell co-stimulation and metabolic fitness. It also impairs APC function and nutrient uptake. LAG-3 exacerbates T-cell dysfunction by disrupting calcium signaling during TCR activation (44–46). In preclinical models, deletion of PD-1 or SHP-2 enhances antigen presentation and T-cell activation, underscoring the therapeutic potential of targeting these pathways to restore antitumor immunity.
In the TME, various cell types, including tumor cells, CAFs, TAMs, endothelial cells, and DCs, overexpress viral entry receptors, which can be exploited for OVT. Tumor cells frequently upregulate receptors such as CAR, heparan sulfate proteoglycans, and EGFR, due to oncogenic mutations or loss of tumor suppressors like p53 and RB. These changes are driven by tumor-intrinsic signaling, inflammatory cues, and epigenetic regulation. Similarly, CAFs express neuropilin-1 (NRP1) and integrins; TAMs may express DC-SIGN and ACE2; endothelial cells lining tumor vasculature express ACE2, NRP1, and integrins; and APCs like DCs express DC-SIGN (CD209) and L-SIGN, collectively enhancing OV tropism and entry (47–51).
Mutations in p53 and RB further shape the TME. p53 loss promotes immune evasion by downregulating antigen presentation, increasing secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines, and recruiting Tregs and MDSCs (52). It also weakens ISG expression in chemotherapy-resistant tumors like GBM, enabling oHSV-1 replication (53). RB inactivation, common in HPV-associated cancers, enhances E2F activity and S-phase entry, creating conditions favorable for replication of S-phase-dependent OVs like AdVs and HSV (53, 54). Overexpression of anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 also impairs OV-induced cell death, but this can be countered by engineering OVs to express pro-apoptotic transgenes or inhibitors of survival signaling pathways in tumor cells, thereby enhancing therapeutic oncolysis (55).
Chronic inflammation remodels the TME, promotes recruitment of suppressive population (Tregs, MDSCs, TAMs), and enhances OV infection by weakening antiviral defenses (56–60). Elevated cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 increase vascular permeability, facilitating OV delivery, but also inhibit immune cell function and upregulate immune checkpoints, further dampening antitumor immunity (56, 57).
Overall, the immunosuppressive, metabolically dysregulated, and chronically inflamed TME, while a barrier to immune surveillance, offers a strategic opportunity for OVT. By targeting impaired antiviral sensing, overexpressed viral entry receptors, and metabolic vulnerabilities, rationally engineered OVs can achieve enhanced selectivity and therapeutic efficacy. As our understanding of these mechanisms deepens, next-generation OVs are being designed with greater precision, reinforcing their role in the evolving landscape of cancer immunotherapy.
2.3 Overcoming immune barriers to optimize OVT
DCs play a central role by capturing tumor antigens released during OV-induced ICD. DAMPs and proinflammatory cytokines promote DC maturation, especially when combined with type I IFNs or innate agonists like STING or TLR ligands. Mature DCs migrate to lymph nodes, present antigens to naïve T cells, and initiate CTL responses limiting viral persistence. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), found in blood, lymphoid organs, and bone marrow, are specialized antiviral sentinels that detect viral RNA and CpG DNA via TLR7 and TLR9 (Figure 2). Upon activation, they secrete large quantities of type I IFNs that suppress OV replication and activate CTLs (61, 62). In addition to IFN production, DCs migrate to lymph nodes, present viral antigens via MHC I and II, and initiate adaptive immune responses by activating CD4+ helper T cells, CD8+ CTLs, and B cells, leading to antibody production and virus-specific cytotoxicity.
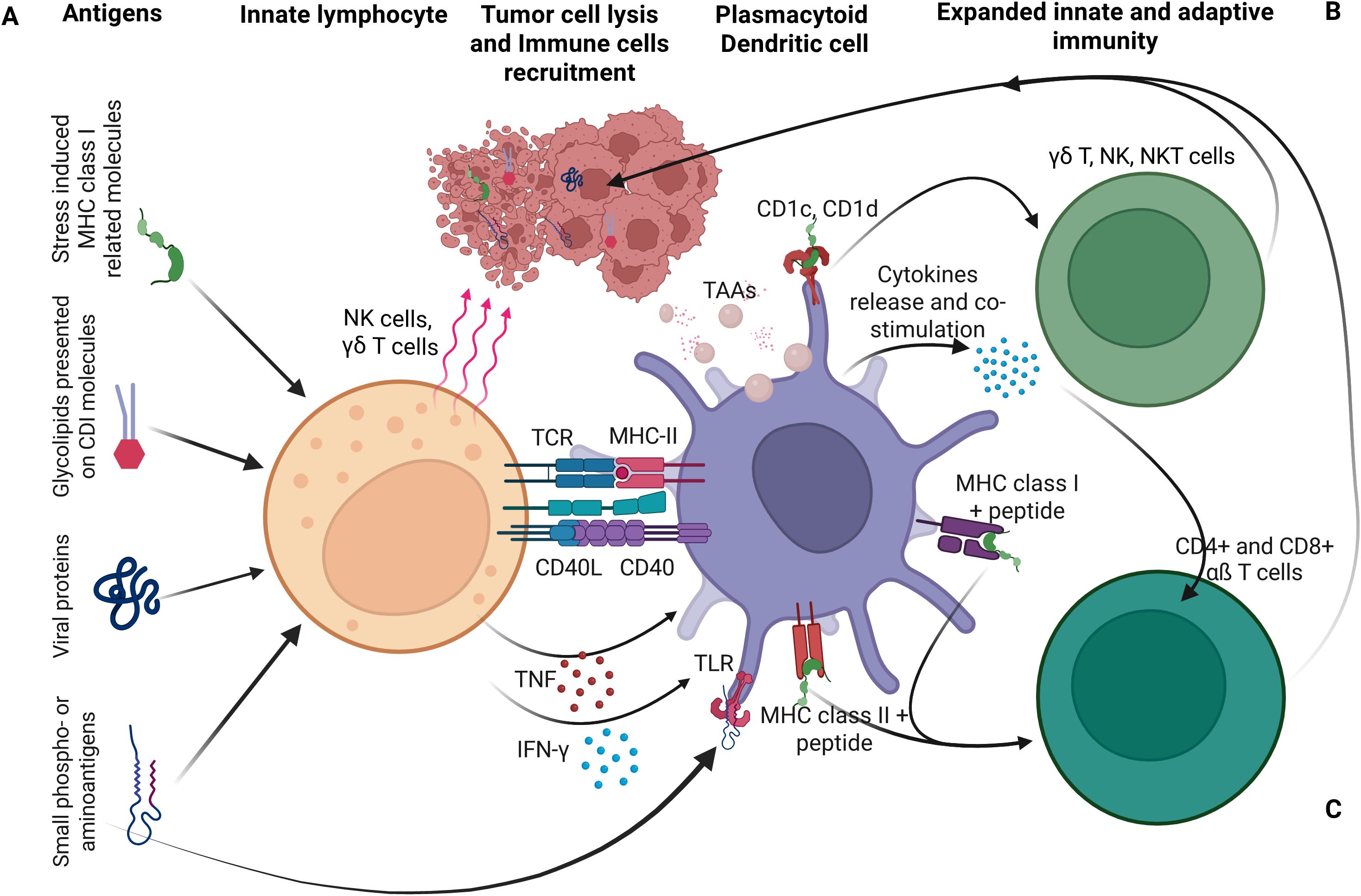
Figure 2. Dendritic cells (DCs) as a central link between innate and the adaptive immunity. (A) Innate lymphocytes, including T cells, NKT cells, and NK cells recognize pathogen-derived or self-antigens on infected cells, transform, or stressed cells. Their activation promotes DC maturation, particularly when DCs present activating ligands recognized by these lymphocytes. (B) Activated DCs in turn amplify innate immune responses. (C) DCs also stimulate adaptive immunity by processing and presenting antigens, including those from lysed cells, to naïve T cells. Cytokines and cell contact-dependent molecules interactions mediate DC activation by various innate lymphocytes. In turn, DC-derived cytokines support further expansion and differentiation of both innate and adaptive immune cells (61).
While these responses are essential for controlling natural infections, they can limit OV persistence and therapeutic efficacy, especially after systemic administration. To address this, recent strategies aim to transiently suppress pDC activation or reprogram their function, either to extend the window for OV replication or to harness their antigen-presenting capacity to enhance systemic antitumor immunity (63, 64). Other innate immune cells also restrict OV efficacy. NK cells rapidly recognize virus-infected tumor cells via stress ligands and missing-self signals, releasing cytotoxic granules and IFN-γ to recruit additional immune effectors (65). Macrophages, including Kupffer cells and splenic macrophages, efficiently clear circulating viral particles, while tissue-resident macrophages release antiviral cytokines like TNF-α and type I IFNs. Neutrophils further restrict viral spread through reactive oxygen species and neutrophil extracellular traps (66). The complement system adds another layer of defense. Activation of classical and alternative pathways leads to opsonization and lysis of viral particles, particularly in patients with pre-existing antiviral antibodies, posing a challenge for intravenous OV delivery (67).
Additional innate effectors, such as conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) and natural killer T (NKT) cells, bridge innate and adaptive immunity. cDCs detect viral PAMPs via TLRs and RLRs, produce type I IFNs and pro-inflammatory cytokines, and present antigens to T cells. NKT cells recognize lipid antigens via CD1d and amplify early cytokine responses that restrict viral propagation (68). Central to these defenses is type I IFN signaling. IFN-α/β binding activates the JAK-STAT pathway, inducing antiviral effectors like PKR, OAS-RNase L, and Mx proteins that degrade viral RNA, inhibit protein synthesis, and create a hostile environment for viral replication (69). While these mechanisms protect against opportunistic infections, they also limit the therapeutic window for OVs.
To overcome these barriers, innovative strategies are being developed, including transient immunosuppression, polymeric shielding of viral particles, and the use of carrier cells to deliver OVs to tumors. Balancing these approaches, by exploiting tumor-intrinsic vulnerabilities while fine-tuning host innate responses, offers a promising path to improving the durability and potency of oncolytic virotherapy (63, 64).
Despite the immune system’s capacity to detect and eliminate pathogens, many viruses have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to evade immune surveillance. These natural strategies form the basis for engineering OVs that can persist within tumors, avoid premature immune neutralization, and enhance therapeutic efficacy. RNA viruses like VSV, measles virus, and Newcastle Disease Virus naturally mutate their surface proteins to escape antibody recognition (70). Engineered OVs mimic this adaptability through immune cloaking strategies such as PEGylation, CD47 coating, or envelopment in extracellular vesicles. For example, CD47-coated AdVs, extracellular vesicle-shielded VacV, and measles virus with mutated envelope proteins evade phagocytic clearance and prolong persistence in the TME (71).
Critically, many tumors exhibit defects in innate antiviral defenses, particularly in the 2′-5′-OAS-RNase L and PKR pathways, key components of type I IFN-mediated responses. These sensors detect viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and initiate RNA degradation, translational arrest, or apoptosis to suppress viral replication (72, 73). However, dysfunction in these pathways allows OVs to evade immune detection and selectively replicate in malignant cells (73, 74).
To exploit this IFN-related vulnerabilities, introduced in section 2.1., OVs have evolved mechanisms to inhibit these antiviral sensors. Some encode proteins that directly block RNase L (e.g., HSV-1’s ICP34.5 and SKIV2L), while others produce decoy RNAs that bind OAS, preventing the synthesis of 2′-5′-linked oligoadenylates required for RNase L activation. Structural modifications in viral RNA can also reduce recognition by OAS, and some OVs minimize dsRNA production to avoid triggering both OAS-RNase L and PKR pathways. For instance, VacV uses E3 and K3 proteins to inhibit OAS and PKR, AdVs deploy VA RNA to block PKR activation, and Newcastle Disease Virus expresses a V protein that prevents PKR recognition of viral RNA (75–78). These adaptations enhance OV replication, tumor lysis, and immune activation, particularly in immune-cold tumors where antiviral defenses are already suppressed (79, 80). Tumors with impaired IFN signaling and MHC downregulation are particularly permissive to viruses like HSV and cytomegalovirus, which naturally evade immune detection. This principle has guided the development of engineered HSV strains (e.g., G207, G47Δ) with deletions in ICP34.5, enabling selective replication in IFN-deficient tumor cells while sparing healthy tissue (79, 81). Some OVs are further engineered to transiently suppress antigen presentation, delaying immune clearance and enhancing intratumoral replication (81).
3 Strategies to enhance OVs for tumor selectivity and potency
Reengineered as programmable immunotherapeutic agents, OVs can seamlessly breach complex tumor defenses with precision. Leveraging next-generation strategies, such as enhanced tumor tropism, improved intratumoral penetration, and immune-metabolic reprogramming, they mount a coordinated, multifaceted assault on cancer cells. When combined with checkpoint inhibitors, small molecule, radiotherapy, and metabolic modulators, OVT transcend monotherapy limitations and emerged as a cornerstone of multimodal cancer therapy.
3.1 Genetic manipulation strategies
3.1.1 Through directed evolution to enhance tumor selectivity and potency
Directed evolution emerged as a powerful strategy for optimizing OVs in the early 2000s, following its broader application in molecular biology and protein engineering in the 1990s. This iterative approach accelerates the natural selection of viral variants with enhanced tumor specificity, immune evasion, and replication efficiency in cancer cells. By subjecting large populations of recombinant precursor viruses to rounds of mutagenesis, selection, and amplification under tumor-like conditions, researchers have generated highly selective and potent oncolytic candidates with broad therapeutic potential. Unlike rational genetic engineering, which involves targeted modifications based on known viral mechanisms, directed evolution enables the discovery of superior tumor-killing variants while preserving safety and minimizing off-target effects (82).
A landmark application of directed evolution in OV development involved the optimization of HSV, VacV, and AdVs, where viral strains were subjected to selective pressures that enhanced their oncolytic potency. By the mid-to-late 2000s, this approach gained wider adoption in OV research, leading to significant advancements in viral adaptation. For instance, directed evolution was applied to engineered reoviruses and VacV capable of replicating more efficiently conditions characteristic of TME and aggressive cancers (83, 84). Among the most notable successes, ColoAd1, a chimeric AdV (Ad11p/Ad3), was developed through this process, demonstrating superior tumor selectivity. This virus exhibited up to 100-fold higher replication in human colon tumor tissues compared to normal tissues, underscoring the potential of directed evolution in generating highly effective oncolytic agents (85).
Further applications of this strategy in reovirus engineering resulted in variants with mutations in the λ2 and σ1 proteins, enhancing their infectivity and oncolytic efficacy in preclinical melanoma models (86). To expand host range, some reovirus variants evolved in Junctional Adhesion Molecule-A (JAM-A)-deficient cell lines, acquiring mutations in the σ1 and μ1 proteins that enabled binding to sialic acid coreceptors, thereby improving infection efficiency in a broader spectrum of cancer cells (87). Additional adapted variants exhibited enhanced tumor cell binding and apoptosis induction, though safety concerns remained (87). Efforts to refine IFN sensitivity led to reovirus variants that discriminated more effectively between malignant and normal cells, improving safety profiles. Similarly, attenuating JAM-A receptor binding yielded viruses with reduced pathogenicity but sustained oncolytic potential in preclinical models (82). Most of these modifications targeted the σ1 protein, which governs reovirus attachment to cellular receptors, highlighting the importance of fine-tuning viral entry mechanisms to balance infectivity and safety (88).
Despite its promise, directed evolution presents challenges. The emergence of unpredictable mutations poses a risk of generating variants with unintended pathogenicity or increased replication in normal cells. The selection process itself is labor-intensive and requires precise design of selective pressures and screening methodologies. Moreover, balancing multiple desirable traits, such as enhanced infectivity, robust oncolytic activity, and safety, remains a complex undertaking. While directed evolution has yielded promising preclinical results, translating these advances to human clinical applications is complicated by factors such as host immune responses, viral clearance, and the influence of the TME on viral efficacy (83). Nonetheless, the continued refinement of directed evolution strategies holds significant potential for developing next-generation OVs with improved therapeutic outcomes.
3.1.2 Through gene deleting and editing techniques to attenuate pathogenicity
A key challenge in OV engineering is achieving a balance between potent oncolytic efficacy and host safety. Attenuation strategies, particularly gene deletion and genome editing have emerged as key tools to restrict viral replication to tumor cells while minimizing off-target effects in normal tissues. Gene deletions are often designed to disable viral genes essential for replication in healthy cells but redundant in cancer cells, thereby enhancing tumor specificity. For instance, deletion of thymidine kinase (TK) gene in HSV restricts replication to rapidly dividing tumor cells while sparing normal cells (89). In T-VEC, deletions of γ34.5 and α47 gene combined with insertion of GM-CSF gene, enhances tumor selectivity and immune activation (55). Similarly, ONYX-015, an engineered AdV lacking E1B-55kDa gene, preferentially replicates in p53-deficient cancer cells (90). Deletion of the TK gene in JX-594/Pexa-Vec, an engineered VacV, likewise restricts replication to proliferative cancer cells, reducing systemic toxicity (55). Innovative synthetic chimeric viruses, such as vesiculovirus, incorporating Morreton virus glycoprotein with VSV genes, have shown promising safety and immunogenicity profiles in Ewing sarcoma and fibrosarcoma models, inducing potent CD8+ T-cell responses and tumor regression (91). Engineered strains like VSV-IFNβ and VSV- MΔ51-IFNβ encode IFNβ, to enhance immune stimulation while maintaining controlled replication and safety (92).
More recently, CRISPR-Cas9 technology has revolutionized OV genome engineering by enabling precise deletions, insertions, and modifications. In large-genome viruses such as HSV, AdV, and VACV, CRISPR has streamlined the process of creating recombinant constructs. In HSV-1, both non-homologous ends joining (NHEJ) and homology-directed repair (HDR) pathways have been used for gene knockouts and knock-ins in a single step (93). In VacV, CRISPR/Cas9 has facilitated simultaneous knockout of immunosuppressive genes (e.g., N1L, A46R) and insertion of TAA (e.g., TRP2), effectively transforming the virus into a therapeutic vaccine (94). In adenoviral systems, CRISPR-induced indels have shown tumor-selective replication and heritability.
3.1.3 Tumor-selective replication via miRNA and promoter engineering
miRNAs are key regulators of tumor progression, invasion, and immune evasion. Their dysregulation in cancer cells provide a unique opportunity for miRNA-guided OV selectivity. By incorporating miRNA response elements (MREs) into viral genomes, OVs can be programmed to replicate preferentially in cancer cells while being suppressed in normal tissues. For instance, Coxsackievirus B3 modified with MREs for miR-1, miR-216 (high in normal tissues), and miR-143, miR-145 (low in tumors) achieves selective replication and potent antitumor activity in breast cancer and melanoma models (95, 96). This selective targeting ensures preferential viral replication in cancer cells, minimizing off-target effects. When combined with melittin (a lytic peptide) and CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (TLR9 agonists), these modified viruses demonstrate potent antitumor activity in breast cancer and melanoma models (96).
Additionally, OVs can deliver tumor-suppressive miRNAs such as miR-143, which downregulates oncogenes like K-RAS and induces apoptosis. This has been demonstrated in both AdV and VSV platforms in colorectal and osteosarcoma models (97, 98). Tumor-specific miRNAs like miR-21 and miR-222 have also been exploited to regulate viral replication through engineered binding sites, ensuring selective activation in cancer cells (99, 100). For example, incorporation of miR-21-binding sites into the 3′ untranslated region of the UL9 gene allow oncogenic miR-21 (overexpressed in most cancers) to reactivate viral replication selectively in tumor cells (99). Similarly, miR-222, a key factor in viral propagation, has been targeted using oAdVs modified with miR-222-binding sites, sensitizing tumor cells to oncolysis (100). Complementing miRNA strategies, tumor-specific promoters (e.g., hTERT, PSA, alpha-fetoprotein, mucin-1, Oct4, Nanog, or Sox2) have been integrated into essential viral genes of OVs (like those for replication or lysis) to restrict gene expression to cancer cells, further refining selectivity (101).
Promoter engineering complements microRNA (miRNA) targeting strategies in a synergistic way. While promoter engineering ensures positive selectivity, activating viral replication only in CSCs, miRNA targeting provides negative selectivity by preventing replication in normal cells. This is achieved by inserting miRNA response elements (MREs) into the viral genome that are recognized by miRNAs highly expressed in normal tissues but downregulated in CSCs. When the virus enters a normal cell, these miRNAs bind to the MREs and suppress viral gene expression, effectively silencing replication. In contrast, in CSCs where these miRNAs are absent or low, the virus can replicate freely.
Promoter engineering is a powerful strategy in OVT and it involves modifying the viral genome so that key genes required for replication are placed under the control of CSC-specific promoters. These promoters are only active in cells expressing certain transcription factors, commonly found in CSCs, ensuring that the virus replicates selectively in malignant cells while sparing normal tissue. Promoters such as Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, and Nestin are frequently used because they are highly active in CSCs but largely inactive in normal differentiated cells.
Together, promoter engineering and miRNA targeting create a dual-layered safety and specificity system. This combination ensures that OVs are both activated in the right cells (via promoters) and inhibited in the wrong ones (via miRNAs), making them highly precise tools for targeting CSCs in solid tumors. Also, they have significantly enhanced OV specificity, reduced pathogenicity, and paved the way for safer, more effective OVTs. As precision genome editing continues to evolve, these tools are poised to accelerate the clinical translation of next-generation OVs (91).
3.2 Cancer stem cells therapeutic targeting
3.2.1 Receptor targeting
Successful OVT hinges on precise targeting of cancer stem cells (CSCs), which are known to drive tumor recurrence, metastasis, and resistance to conventional therapies, ensuring the selective destruction of cancer cells while sparing normal cells. This specificity is achieved through a combination of natural viral tropism, genetic engineering, and strategic exploitation of the TME (102).
CSCs often express unique or overexpressed surface receptors that distinguish them from normal stem cells and differentiated tumor cells. Some viruses naturally infect cancer cells due to the overexpression of specific receptors, while others can be engineered to exploit these differences, allowing for selective infection and destruction of CSCs. HSV-1, AdV, measles virus, and CVA21 exploit receptors such as nectin-1/HVEM, Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor (CAR), CD46/EGFR, and ICAM-1 to infect melanoma, epithelial, ovarian, and bladder cancers (103, 104). Reovirus, preferentially infects cells with activated Ras signaling through the junctional adhesion molecule-A (JAM-A) while vaccine-strain measles virus (MV-Edm) infect tumors overexpressing CD46, like GBM, lymphomas, and certain carcinomas, impairing the tumor-initiating capacity of their CSCs and enhancing their sensitivity to chemotherapy (105). CD133 is a well-established marker found on CSCs in glioblastoma, colorectal, and liver cancers. CD133-targeted oncolytic measles virus (MV-CD133) selectively target CSCs expressing CD133, helping prevent tumor reoccurrence (106). EpCAM, another surface marker prevalent in epithelial-derived CSCs, has also been used as a target for OV-mediated therapy. Additionally, integrins such as αvβ3 and αvβ5, which are upregulated in CSCs and tumor vasculature, have been exploited by AdVs and measles viruses to improve tumor selectivity and viral spread.
To enhance receptor targeting, OVs can be genetically modified through techniques such as pseudotyping, where viral envelope proteins are replaced with those from other viruses that naturally bind CSC-specific receptors. Ligand insertion is another approach, where peptides or single-chain antibodies (scFvs) are inserted into viral capsid proteins to direct binding to CSC markers.
These strategies collectively increase the specificity of OVs, reduce off-target effects, and enhance therapeutic efficacy. Moreover, targeting CSCs with OVs not only eliminates the root of tumor resistance but also promotes the release of TAAs, thereby stimulating a robust antitumor immune response. This makes receptor targeting a powerful and promising approach in the development of OV-based cancer therapies.
3.2.2 Suicide genes engineering
A major advancement in OVT is the integration of suicide genes, which enhance both therapeutic efficacy and safety by promoting tumor cell destruction while modulating the TME. These genetic modifications exploit cancer-specific vulnerabilities, such as defective antiviral responses and dysregulated signaling pathways, to achieve precise tumor targeting. Suicide genes function by encoding enzymes that convert non-toxic prodrugs into cytotoxic agents, selectively eliminating infected tumor cells. Among the most extensively studied is HSV-TK, which phosphorylates ganciclovir into a toxic nucleotide analog, leading to DNA chain termination and apoptosis. Another well-characterized enzyme is cytosine deaminase, which metabolizes 5-fluorocytosine into 5-fluorouracil, a potent inhibitor of DNA synthesis. Additionally, nitroreductase activates the prodrug CB1954, which induces DNA cross-linking and widespread tumor cell death (107).
Integrating suicide genes into OVs offers multiple therapeutic advantages. By combining viral oncolysis with prodrug activation, this approach enhances tumor specificity while minimizing systemic toxicity. The controlled administration of prodrugs enables spatiotemporal regulation of cytotoxicity, ensuring that tumor destruction remains highly targeted. A particularly valuable feature of suicide gene therapy is the bystander effect, in which toxic metabolites diffuse into adjacent cancer cells, amplifying the therapeutic impact beyond directly infected cells (108, 109).
Beyond direct tumor lysis, suicide gene-induced apoptosis also contributes to antitumor immune activation. The ICD triggered by these mechanisms enhances the recruitment and activation of immune cells, promoting a sustained systemic antitumor response. This dual approach, combining localized viral replication with systemic immune engagement, positions suicide gene therapy as a powerful strategy for durable tumor suppression (109). OVs expressing suicide genes are currently under extensive preclinical and clinical evaluation. HSV-1-based OVs encoding HSV-TK have shown promising results in GBM models, while AdVs and VacV engineered with suicide genes are being investigated for various solid malignancies. However, challenges remain, including optimization of delivery, enhancement of tumor specificity, and overcoming immune-mediated viral clearance. Advances in genetic engineering, such as combining OVs with ICIs, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, may further enhance therapeutic efficacy, bringing suicide gene-armed OVs closer to widespread clinical application (110).
Clinically, these targeting strategies pave the way for personalized OVT, enabling combination with chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy. Beyond precision, OVs can overcome resistance by lysing refractory tumor cells and exposing novel antigens, initiating broader immune responses (40). While immune clearance and delivery remain challenges, nanoparticle-based systems and carrier cell technologies are rapidly advancing toward clinical application.
4 Synergistic strategies to overcome TME barriers and boost OVT efficacy
4.1 Metabolic reprogramming
OVs represent a promising strategy to enhance T cell function and metabolism, particularly in tumors that are resistant to conventional therapies. By reshaping the metabolic landscape of T cells, OVs contribute to sustained antitumor immune responses and amplify the efficacy of existing immunotherapies (111).
A key mechanism involves metabolic reprogramming of tumor-infiltrating T cells. OVs interact with glycolytic enzymes in infected cells, increasing energy availability to support T cell expansion and function (112). Additionally, OV-induced ICD and release of tumor antigens and DAMPs activate and metabolically reprogram T cells to sustain a potent antitumor immune response (113). Some OVs are engineered to express metabolic regulators, such as leptin, to further enhance T cell fitness and tumor eradication (21).
OVs also improves T cell infiltration and activation within the TME. By disrupting immunosuppressive barriers, they enhance the trafficking and function of CAR T cells and endogenous T cells (114). When combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) or adoptive T cell therapies, OVs create synergistic effects that overcome the limitations of monotherapies and promote durable antitumor responses (102). Engineered OVs frequently express cytokines such as IL-2, IL-12, and TNF-α, which are essential for T cell proliferation, survival, and metabolic activation (115). IL-2 promotes clonal expansion, IL-12 enhances cytotoxicity, and TNF-α increases tumor vasculature permeability, facilitating deeper immune infiltration. These cytokines also stimulate glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation, supporting sustained CTL activity.
In parallel, OVs enhance antigen presentation by upregulating MHC molecules and recruiting DCs, which prime naïve T cells and reinforce metabolic reprogramming. This coordinated activation equips T cells with the energy and signaling support needed for long-term tumor control (41, 116). This effect is further strengthened by DC recruitment and activation, leading to increased T cell priming and metabolic reprogramming, equipping T cells with the necessary energy reserves to sustain a long-term antitumor response.
To further amplify T cell responses, OVs can be engineered to express costimulatory molecules such as OX40L, CD40L, CD137, ICAM-1, and GITR (117–120). For example, VALO-D102, an AdV encoding CD40L and OX40L, induces robust CD8+ T cell infiltration and tumor control in melanoma models, with enhanced efficacy when combined with anti-PD-1 therapy (119). Similarly, LOAd703, encoding CD40L and CD137, activates cytotoxic T cells and upregulates immunostimulatory molecules (CD80, CD86, CD70), MHC, and adhesion molecules like ICAM-1, improving tumor immunogenicity and therapeutic outcomes in multiple myeloma (120).
By integrating oncolysis, metabolic support, antigen presentation, costimulatory signaling, and checkpoint inhibition, OVs offer a powerful strategy for enhancing T cell-based cancer immunotherapy. These synergistic mechanisms collectively drive more effective and durable antitumor responses, offering renewed hope for patients with treatment-refractory malignancies.
4.2 Enhancing T Cell Function via TGF-β Payload and immune checkpoint blockade
TGF-β is a key regulator of immune homeostasis, but in cancer, it fosters an immunosuppressive TME by inhibiting T cell activation, proliferation, and cytotoxicity. This allows tumors to evade immune surveillance. Blocking TGF-β signaling within tumors is a promising strategy to restore T cell function and enhance cancer immunotherapy. OVs engineered to deliver TGF-β inhibitors offer a localized and potent approach to achieve this, converting immune-excluded tumors into highly inflamed tumors that are more responsive to immunotherapy (121).
Genetically modified OVs can express TGF-β inhibitors, including small molecules, decoy receptors, or neutralizing antibodies, ensuring targeted blockade of TGF-β signaling within the TME while minimizing systemic toxicity. TGF-β signaling suppresses CTLs and enhances the function of Tregs and MDSCs, all of which contribute to immune evasion (122). By disrupting this pathway, OVs enhance T cell metabolism, cytokine production, and effector function, while reducing immunosuppressive cell populations and promoting sustained antitumor immunity (123).
Several OV platforms incorporating TGF-β blockade are under investigation. Seneca Valley virus (SVV-001) induces tumor lysis and reprograms the immune microenvironment to enhance T cell infiltration. AdAPT-001, an oncolytic adenovirus (oAdV) expressing a TGF-β trap, has shown promising results in a Phase 1 trial, particularly when combined with ICIs, yielding durable responses in refractory tumors such as sarcomas and triple-negative breast cancer (124, 125). Jurona virus (JURV), in combination with anti-PD-1 therapy, improved survival and immune activation in hepatocellular carcinoma models, with favorable tolerability (14).
VacV engineered to express TGF-β receptor (TGF-βR) inhibitors represents another potent approach. By delivering these inhibitors directly into tumors, VacV suppresses TGF-β-mediated immune evasion, enhances T cell recruitment and cytotoxicity, and significantly improves ICI efficacy in preclinical models (126, 127).
Although early findings are encouraging, further research is needed to optimize delivery, specificity, and immune modulation. Ongoing clinical trials will be critical in determining the safety and efficacy of TGF-β-blocking OVs. Their ability to reshape the TME, synergize with ICIs (e.g., anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 therapies), and directly enhance T cell function positions them as powerful tools in the next generation of cancer immunotherapy (40, 128). While checkpoint blockade alleviates T cell exhaustion, OVs enhance T cell metabolic fitness and functional capacity, overcoming multiple layers of tumor-mediated immune suppression. This combination strategy has demonstrated enhanced tumor regression and prolonged survival in preclinical models, underscoring its potential for clinical translation (124, 125). In a Phase 1 clinical trial, AdAPT-001 exhibited encouraging responses, particularly when combined with ICIs, yielding a high objective response rate and durable clinical benefit in patients with refractory tumors, such as sarcomas and triple-negative breast cancer (124, 125). Jurona virus (JURV), a novel OV, in combination with anti-PD-1 antibody, enhanced immune response and improved survival in HCC models (14). The therapy demonstrated favorable tolerability, with most adverse events being mild and transient, further supporting its clinical potential.
4.3 Overcoming physical barriers in TME
4.3.1 Enhancing TME and cytoskeleton remodeling for OV penetration
The TME serves as a physical barrier that restricts viral diffusion and immune cell infiltration. To overcome this, OVs have been engineered to express matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and other proteolytic enzymes that degrade ECM components, facilitating deeper tumor penetration (129). For example, recombinant measles viruses expressing MMP-activated fusion proteins selectively target MMP-rich tumors, enhancing both safety and oncolytic activity (130, 131). Similarly, AdVs and VacVs modified to express MMPs or urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) improved viral dissemination and tumor infiltration (102, 132). A recombinant oVacV encoding hyaluronidase (OVV-Hyal1) was shown to degrade hyaluronic acid, a major ECM component, which significantly improved the intratumoral spread of the virus and enhanced the delivery of co-administered therapies like doxorubicin, gemcitabine, and CAR T cells. The virus also promoted the infiltration of immune cells such as CD8+ T cells and NK cells, amplifying the antitumor immune response (133).
OVs hijack intracellular transport and induce skeletal remodeling. They exploit the host cell’s microtubule transport system to reach the nucleus, where replication often occurs. African swine fever virus uses its p54 protein to bind to dynein light chain, DYNLL1, hijacking the dynein motor complex (134). Other OVs, such as oAdVs and oHSV similarly use dynein-mediated transport to move from the cell membrane to the nucleus. Some viruses have evolved proteases that cleave a dynein-activating adaptor protein, Ninein-like, disabling its function and making the tumor cells more permissive to OV infection (135).
In parallel, OVs can disrupt the cytoskeleton architecture of tumor cells by modulating signaling pathways such as Rho/ROCK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR, which regulate cytoskeletal dynamics. This disruption leads cytopathic effects such as cell rounding, detachment, and death, weakening the tumor’s structural integrity and promoting ICD. OVs like reovirus and AdVs can disrupt actin stress fibers and microtubule networks in infected tumor cells, enhancing viral spread and immune activation (55).
4.3.2 Hypoxia-responsive viral engineering
Hypoxia-responsive viral engineering is a promising strategy in OVT that exploits the oxygen deprivation in the TME to enhance selectivity and safety of OVs. Hypoxia, a hallmark of the TME, arises from rapid proliferation of tumor and inadequate vascularization, and it often impairs cell infiltration and reduces the efficacy of conventional therapies. However, this hostile environment can be leveraged to improve the precision of OV-based treatment. To exploit this feature, hypoxia-responsive elements (HREs), which are activated by hypoxia-inducible factors (e.g. HIF-1α), have been incorporated into essential viral genomes to regulate essential replication genes such as E1A in AdVs (130). These modifications enable OVs to replicate preferentially in hypoxic tumor regions, where immune defenses are often suppressed. In normoxic tissues, HIF-1α is rapidly degraded, keeping HRE-controlled genes inactive and thereby minimizing off-target viral replication. In contrast, in hypoxic tumor zones, HIF-1α binds to HREs and initiates the transcription of viral genes, enabling selective replication and oncolysis within the tumor. A well-characterized example of this approach involves AdVs engineered with the E1A gene under HRE control, allowing replication specifically in hypoxic tumor cells. Additionally, viruses like VSV naturally thrive in such environments, making them ideal candidates for hypoxia-adapted OVT (29). Beyond replication control, some OVs are designed to express therapeutic payloads, such as cytokines or prodrug-converting enzymes, only under hypoxic conditions, further enhancing tumor specificity and therapeutic impact.
Moreover, the integration of hypoxia-responsive elements with other engineering strategies, such as the expression of ECM-degrading enzymes, enables OVs to overcome both structural and molecular barriers within the TME. These combined modifications not only improve viral dissemination and tumor selectivity but also synergize with immunotherapies, offering a multifaceted approach to cancer treatment. Overall, hypoxia-responsive viral engineering represents a powerful tool in the development of next-generation OVs capable of targeting resistant tumor regions with high precision.
4.4 Enhancing OVT through physical modalities
To overcome challenges of OVT as monotherapy, such as tumor heterogeneity, immune evasion, and the immunosuppressive TME as discussed in section 2, combination strategies have emerged as a powerful means to potentiate OVT. The integration of OVs with ICIs, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or targeted agents, has amplified antitumor responses, improved viral delivery, and sustained immune activation, thus enhancing therapeutic outcomes of OVT across diverse cancer types. Combination of Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields) and radiation therapy with OVT offers an innovative therapeutic synergy to improve tumor targeting, viral spread, and immune engagement.
4.4.1 Tumor treating fields
TTFields represent a non-invasive treatment modality that delivers low-intensity, intermediate-frequency alternating electric fields to disrupt mitosis by interfering with microtubule polymerization, thereby inducing cell cycle arrest and (136). Clinically TTFields have demonstrated efficacy in GBM, malignant pleural mesothelioma, and mesothelioma, predominantly affecting actively dividing cells. When combined with OVs, which selectively infect both dividing and non-dividing tumor cells, this dual-targeting approach expands the therapeutic window and enhances cancer cell susceptibility. In addition to their direct antitumor effects, TTFields can modulate the TME by improving vascular perfusion, thereby facilitating viral dispersion and enhancing tumor tissue penetration. These effects, when coupled with the immunogenic potential of OVs, which promote the release of TAAs and danger signals (DAMPs), may synergistically amplify immune cell recruitment and foster durable antitumor immunity (136, 137). Nevertheless, further research is warranted to optimize treatment protocols, identify predictive biomarkers, and elucidate the precise molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic interactions between TTFields and OVs (138, 139).
4.4.2 Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy in combination with GL-ONC15 enhances OVT efficacy via DNA damage, ICD, and TME reprogramming (140, 141). The intersection of these mechanisms offers a powerful therapeutic synergy. The immune-stimulating effects of OVs augment radiation therapy (142). OVs facilitate antigen presentation and immune system activation when combined with radiation-induced immune priming, results in a more robust and sustained antitumor immune response (143) which triggered necroptotic cell death, releasing DAMPs and shifting the macrophage M1/M2 ratio, promoting a more pro-inflammatory and antitumor immune landscape (144). Radiation-induced cell stress and necrosis not only provide substrates for OV amplification but also upregulate viral entry receptors, rendering tumor cells more susceptible to infection. Furthermore, radiation primes the immune system by boosting antigen presentation and immune infiltration. Combined with the innate immune stimulation from OVs, this strategy significantly enhances antitumor responses. Preclinical models, the combination of high-dose hypo-fractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and oncolytic VacV in glioma and sarcoma, demonstrate increased infiltration of activated T cells (CD4+, CD8+), reduced Tregs, and improved survival outcomes (145). The combination of Delta-24-RGD and radiotherapy in pediatric gliomas and DIPG led to impaired DNA damage repair, increased immune cell trafficking, and prolonged survival (145). As ongoing trials continue to refine these combinations, this multimodal strategy represents a promising frontier for durable and effective cancer immunotherapy.
4.5 Enhancing OVT with inhibitors of aberrant signaling pathways
4.5.1 Combination with antagonist of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway plays a central role in cellular growth, proliferation, and survival, making its dysregulation a hallmark of various cancers and a critical target for therapeutic intervention (146–148). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mechanistic target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) inhibitors combined with OVs offers a promising strategy to enhance tumor susceptibility to oncolysis and modulate TME for better outcomes. Combination of OV ZD55-TRAIL with LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, in multiple myeloma, induces apoptosis via caspase activation, inhibits IGF-1R and NFκB and enhanced oncolysis (149). Also, combination of ZD55-TRAIL with MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, increased death receptor 5 expression, and enhanced oncolysis only in cancer cells (150).
The VC2, a novel oHSV-1, promoted long-lasting systemic anti-melanoma immune responses and improved survival in an immunocompetent B16F10-derived mouse melanoma model (151). Also, combination of reovirus and rapamycin enhanced viral oncolysis by inhibiting mTOR activity in B16F10 melanoma cells (152). Although rapamycin did not affect reovirus-neutralizing antibodies or cell cycle effects, it reduced viral replication and reovirus-induced apoptosis (152). Conversely, rapamycin enhanced autophagy, increased adenoviral E1A expression, and improved the replication of Ad-cycE, an oAdV, enhancing oncolysis than monotherapy (153).
Resistance to PI3K/AKT inhibitors often results from hyperactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Inhibition of tankyrase 1, regulates Wnt/β-catenin promotes replication of β- and γ-variants while suppressing wildtype of HSV-1, and offers promising OVT which warrants further exploration (154). Combination of HSVs with PI3K/AKT inhibitors, effectively target GBM and prostate cancer stem-like cells (139). AdV (150) and Newcastle Disease Virus (155, 156) in combination with inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway also enhanced oncolysis. However, temozolomide, gold standard of GBM treatment which activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling through the PI3K/AKT pathway (157), potentially counteract OVT in combination with G47Δ-mIL12 (an HSV-1 variant) (158). Combining Ovs with PI3K inhibition remodels the TME, and restores ICI sensitivity (159).
PI3Kδ inhibition enhances systemic OV delivery. IC87114 or idelalisib, clinically approved PI3Kδ inhibitor, improved the oncolysis of intravenously administered VacV by preventing sequestration of systemic macrophages, disrupting RhoA/ROCK, AKT, and Ras signaling, and promoting viral spread, in pancreatic cancer (160).
mTOR is a key regulator of cell proliferation and survival, making it a promising target for combination therapies with OVs (161). Everolimus (RAD001), an mTOR inhibitor, in combination with AdVs enhances oncolysis in colon cancer, inhibits tumor growth, mitigates angiogenesis, and suppresses immune responses (162). Combination of rapamycin with myxoma virus, VacV, HSV, VSVΔM51, and AdV enhances oncolysis and viral replication only in cancer cells by disrupting mTORC1-dependent type I IFN production and reducing macrophage infiltration in tumors (152, 163, 164). Interestingly, inhibitors targeting both mTORC1 and mTORC2, unlike rapamycin, enhance HSV1-dICP0 infection through the eIF4E/4E-BP pathway, further highlighting the potential of PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibition in OVT (164).
In summary, combining of OV with PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors, enhances viral replication, and reshapes the immune milieu. Further preclinical and clinical investigations are needed to optimize treatment protocols, identify predictive biomarkers, and address resistance mechanisms.
4.5.2 Combination with JAK/STAT pathway modulators
The JAK/STAT pathway is a key signaling cascade involved in cellular responses to cytokines and growth factors. Upon ligand binding, intracellular JAKs phosphorylate and activate STAT proteins that regulate gene expression (165). Hyperactivation of this pathway increases Tregs gene expression, fostering tumor tolerance and immune suppression (165). Tumors with defective IFN-β signaling are more susceptible to OV-mediated oncolysis, while those with intact IFN pathways mount antiviral response that hinders OV replication and efficacy (32, 166). Hence, JAK/STAT inhibitors have emerged as promising adjuncts to OVT (167). Ruxolitinib, a selective JAK1/2 inhibitor, enhances replication and efficacy of VSV-IFN-β and VSV-ΔM51 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and human PDACs, respectively, by inhibiting STAT1/2 phosphorylation and reducing antiviral responses that restrict viral replication (167, 168). Similarly, TPCA-1, a dual inhibitor of JAK1 and IκB kinase, boost HSV replication in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) cells, amplifying OV-mediated cytotoxicity (169).
Beyond the JAK/STAT axis, RNA viruses and poxviruses encounter additional barriers such as protein kinase R (PKR), which activates stress responses via the NF-κB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways (170). JNK’s role in viral replication is context-dependent; its inhibition can enhance viral replication in some cases. For instance, combining the JNK inhibitor SP600125 with VacV significantly increased viral titers and induced apoptosis in murine fibroblast cells (171). Further research is needed to optimize these and improve their outcomes in oncology.
4.5.3 Targeting p53 and MDM2 pathways to sensitize tumors to oncolytic viruses
The tumor suppressor, p53 protein, maintains genomic stability by inducing cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, senescence, and apoptosis in response to cellular stress (172). Its mutation found in about 50% of cancers subtypes, contribute to tumor growth and progression (173). ONYX-015, an oAdV, combined with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil enhances oncolysis in p53-deficient cancer cells, particularly recurrent head and neck tumors (174).
Also, targeting MDM2-p53 interaction restore p53 function in tumors with wild-type p53, making them more susceptible to OVT (175–177). MDM2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, negatively regulates p53 by promoting its degradation. Combining an MDM2 inhibitor with Ad-delE1B, an AdV lacking the E1B-55kDa gene, enhanced viral replication and oncolysis in mesothelioma cells with wild-type p53. This approach increased nuclear factor 1 expression and amplified oncolysis (175) offering a promising strategy for treating p53-mutant or -deficient cancers by restoring p53’s tumor-suppressive functions.
4.5.4 Combination with inhibitors of EGFR/K-RAS/MAPK signaling pathway
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are essential enzymes involved in cellular processes such as growth, motility, differentiation, inflammation, and metabolism. Their dysregulation is a hallmark of many cancers, making them attractive therapeutic targets (178). Combining oncolytic viruses (OVs) with RTK inhibitors offers a synergistic strategy to enhance tumor selectivity, viral replication, and immune activation.
EGFR-targeted therapies have shown promise in combination with OVs. For instance, erlotinib combined with canerpaturev (C-REV) enhances viral replication and reduces tumor burden in colorectal cancer models. Similarly, cetuximab, an EGFR inhibitor, improves C-REV distribution and inhibits angiogenesis, leading to tumor regression in HT-29 xenografts (179). In EGFR-driven tumors such as malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs), combining oncolytic HSV (oHSV) with erlotinib enhances viral biodistribution and therapeutic efficacy (79).
Multi-target RTK inhibitors like sorafenib and sunitinib, which block VEGF, PDGF, and ERK pathways, have demonstrated synergistic effects with OVs. Sorafenib, approved for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), enhances OV efficacy by sensitizing tumor vasculature and inhibiting angiogenesis (180, 181). When combined with VSV, sunitinib suppresses antiviral enzymes (PKR, RNase L), boosting viral replication and tumor clearance in prostate, breast, and kidney cancer models. Similar synergy has been observed with VacV and reovirus in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and RCC (182, 183).
A notable example is the sequential use of Pexa-Vec (JX-594) followed by sorafenib in HCC, where Pexa-Vec primes the tumor for VEGF/VEGFR inhibition, enhancing sorafenib efficacy (184, 185). Likewise, combining axitinib (a VEGFR inhibitor) with G47Δ-mIL12 improves antitumor responses in glioblastoma models. CSF-1R inhibitors like PLX3397 also synergize with OVs by reprogramming the TME, increasing CD8+ T cell infiltration, and enhancing anti-PD-1 therapy (43, 186).
In RAS-mutated tumors, combining OVs with RAS/BRAF/MEK inhibitors enhances viral replication and overcomes resistance. Examples include combinations of reovirus (TR3D) and PLX4720, T-VEC and trametinib, and VacV and trametinib, which have shown improved outcomes in melanoma, ovarian cancer, and BRAF-mutant tumors (187–190).
Together, these combination strategies not only suppress tumor growth but also overcome resistance mechanisms, enhance immune responses, and improve viral delivery. The growing body of evidence supports RTK inhibitor, OV combinations as a powerful approach for treating aggressive and treatment-resistant cancers.
4.6 Combination with drugs, nutraceuticals, and their synthetic analogs
The combination of OVs with drugs, nutraceuticals, and their synthetic analogs, has emerged as a promising strategy in cancer therapy. Over the past decade, these small molecules have been explored for their ability to modulate key signaling pathways, enhance immune responses, and reshape the immunosuppressive TME (191). Their potential to augment OVT has opened new avenues for combination therapies, offering enhanced therapeutic efficacy and improved patient outcomes. They work synergistically with OVs by complementing and enhancing OV-mediated tumor destruction (192). They can modulate intracellular signaling, increase viral replication, improve tumor selectivity, and promote ICD, thereby maximizing the antitumor effects of OVs. Immune-modulating agents can also counteract the immunosuppressive TME, making it more susceptible to OV infection and immune activation. Additionally, these agents may sensitize tumor cells to OV-induced apoptosis or inhibit pathways that allow cancer cells to evade viral oncolysis.
The structure of anticancer drugs directly contributes to their capacity to enhance OVT by targeting complementary pathways in cancer cells and the TME (Table 1). HDAC inhibitors such as valproic acid and trichostatin A use their zinc-chelating functional groups to disrupt chromatin condensation and restore expression of viral entry receptors and immunostimulatory genes, sensitizing tumors to viral infection and immune-mediated clearance (193, 194). Multi-kinase inhibitors like sunitinib, whose indolinone scaffold allows ATP-site binding across receptor tyrosine kinases, suppress angiogenesis and impair antiviral signaling pathways such as IFN responses, thereby promoting viral replication within tumors (182, 183, 195). Lenalidomide’s phthalimide core enables targeted degradation of transcription factors critical for tumor survival and immune evasion, indirectly boosting antiviral immunity and modulating the TME to favor OVT (196–199). Bortezomib’s boronic acid moiety blocks proteasomal degradation of pro-apoptotic proteins, increasing virus-induced cell death. Doxorubicin, through its planar anthracycline core intercalation and free radical generation, compromises DNA integrity and heightens susceptibility to viral oncolysis (200). Everolimus leverages its macrocyclic lactone structure to inhibit mTORC1, a pathway critical both for tumor growth and for type I interferon production, thereby enhancing viral replication and spread (201–203). Platinum-based drugs like cisplatin and carboplatin, with their reactive platinum coordinated to reactive ligands that form intra- and interstrand DNA crosslinks ultimately triggering apoptosis and synergizing with viral lytic activity (204–206). Taxanes and camptothecin derivatives such as paclitaxel, docetaxel, and irinotecan, possess complex diterpenoid cores that stabilize microtubules and prevent their depolymerization, arresting mitosis or topoisomerase function, sensitizing dividing cancer cells to virus-induced apoptosis. Antimetabolites like 5-fluorouracil and gemcitabine, by depleting nucleotide pools and incorporating into nucleic acids, create replication stress that increases tumor permissiveness to viral infection (207, 208). Collectively, the unique structural features of these agents not only define their primary anticancer mechanisms but also strategically prime tumors to respond more robustly to oncolytic viruses, offering a rational basis for combination therapies that exploit vulnerabilities in cancer cell survival, antiviral defense, and immune regulation.
Recent studies have identified several successful OV-small molecule combinations, highlighting both therapeutic potential and challenges (209). As cancer immunotherapy evolves, the strategic development of these small molecule as next-generation immunotherapeutic may redefine cancer treatment paradigms (210). The synergy between OVs and pharmacological small molecules can be categorized into distinct mechanisms that enhance tumor targeting and immune activation (Figure 3). However, further research and clinical trials are essential to optimize dosing regimens, identify predictive biomarkers, and address potential resistance mechanisms, ensuring this combinatorial strategy achieves its full therapeutic potential in oncology.
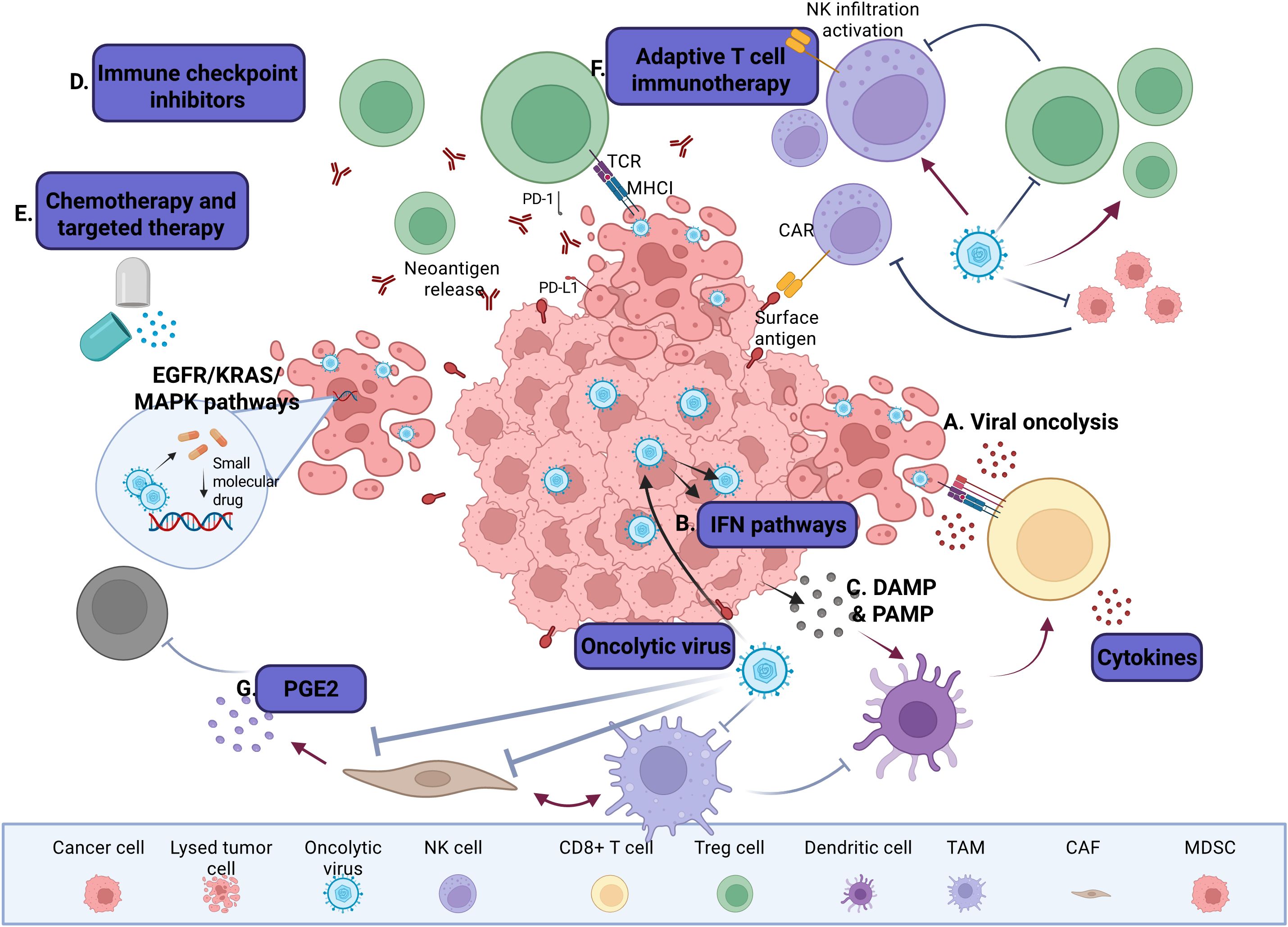
Figure 3. Interactions between OV and small molecules on tumors and TME. (A) OVs selectively replicate within tumor cells and mediate direct oncolysis. (B) Enhancement of OV-mediated release of DAMPs, PAMPs and proinflammatory cytokines promotes the infiltration of CTLs into the tumor beds and supports their cytolytic activity. (C) OVs activate IFN signaling pathways and stimulate innate and adaptive immune responses, leading to broader and more durable antitumor immunity. D) OV infection increases the expression of immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1 and CTLA-4 on tumor and stromal cells, rendering tumors more susceptible to ICIs. (E) Cytotoxic chemotherapies promote tumor cell death, often via ICD, while targeted therapies disrupt oncogenic signaling pathways and potentially tumor cell death. These treatments can elicit weak to moderate antitumor immune responses. (F) Relevant cells in the TME, such as TAMs, DCs, CAFs, and MDSCs, secrete ECM components, growth factors, and immunomodulatory cytokines, which can contribute to the regulation of tumor progression and therapeutic response in unique ways. For instance, CAFs suppress T and NK cell activity through secretion of factors such as PGE2 and TGF-β. Some OVs are engineered to target not only cancer cells, but also stromal cells and components such as CAFs. (G) OVs can reshape the TME by converting immunologically “cold” tumors into “hot” tumors, thereby enhancing immune cell recruitment and effector function (288).
4.6.1 Combination with epigenetic modulators
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) regulate transcription regulation and immune responses, particularly in IFN signaling (211). HDAC inhibitors are emerging as enhancers of OV replication in tumor cells, providing a novel therapeutic avenue. Among them, HDAC6 plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses and autophagy, especially in TLR-mediated signaling by intracellular bacteria (212). Targeting HDACs, can significantly improve OVs efficacy. For example, combining oncolytic G47Δ with the HDAC inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA) showed strong synergy against endothelial and various cancer cell lines, but not normal cells. This synergy depends on viral replication and high cyclin D1 levels in tumor cells, amplifying inhibition of cyclin D1 levels in tumour and VEGF to enhance treatment efficacy (212). In HCT116 colon tumor xenograft models, combining TSA and VacV improved survival compared to using either agent alone (79).
Valproic acid (VPA), an FDA-approved antiepileptic with HDAC-inhibitory properties has shown independent anticancer effects (213). With its carboxylic acid moiety to chelate the zinc ion within the HDAC catalytic pocket, thereby reactivating silenced tumor suppressor genes. In GBM models, VPA reduced NK cell and macrophage recruitment shortly after HSV infection, although infiltration increased over time. VPA also suppressed NK cell cytotoxicity in vitro. Conversely, combining VPA with H-1Protoparvovirus synergistically enhanced cytotoxicity and NS1-mediated transcription and cytotoxicity. This combination induced oxidative stress and increased apoptosis, leading to better therapeutic outcomes (214). Silent Mating Type Information Regulation 2 Homolog 1 (SIRT1), a NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase, has been linked to increased cancer cell susceptibility to OVT. For example, SIRT1 enhanced replication and oncolytic efficacy of VSVΔM51 in prostate cancer cells (PCC) (215). HDAC inhibitors like suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (vorinostat), and resminostat upregulate miR-34a, which regulates SIRT1 levels, enhancing OV efficacy. Inhibiting or silencing SIRT1 also sensitizes prostate cancer cells to VSVΔM51, promoting viral replication and spread (215). The hydroxamic acid group of vorinostat is essential for its function, as it coordinates the zinc ion located in the catalytic site of HDAC enzymes, effectively inhibiting deacetylase activity while the suberoyl linker, an eight-carbon chain, allows the molecule to reach deep into the enzyme’s tubular pocket and position the zinc-binding moiety precisely. The terminal phenyl ring of the anilide functions as a capping group that sits at the rim of the active site, where it contributes important hydrophobic and π–π stacking interactions that stabilize binding. Resminostat shares the same fundamental pharmacophore with reminostat, a combination of a zinc-binding hydroxamic acid, a linker region, and an aromatic cap, but differs in key structural refinements that enhance its pharmacologic profile.
5 Clinical applications of OVs and vaccines
Clinical trials have extensively evaluated various OVs, both as monotherapies and in combination with ICIs and other treatments, demonstrating their significant potential in oncology (216, 217). Among the most well-characterized OVs, T-VEC has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in melanoma. As the only FDA-approved OV for melanoma, T-VEC has also approved in Australia and Europe for treating unresectable stages IIIB, IIIC, and IV melanoma (217, 218). The pivotal OPTiM Phase III trial revealed a durable response rate (DRR) of 25.2% for T-VEC-treated patients versus 1.2% for GM-CSF alone, with a median overall survival of 41.1 months versus 21.5 months in the control group (219, 220). Retrospective analyses in European cohorts reported an objective response rate of 63.7% and complete remission in 43.2% of treated patients (217).
Combinatorial strategies with T-VEC have also shown promise. A Phase II trial combining T-VEC with the anti-CTLA4 monoclonal antibody ipilimumab improved durable response rate to 29.6%, surpassing ipilimumab monotherapy (13%) (221, 222). Additionally, T-VEC combined with pembrolizumab, an anti-PD-1 drug, showed a twofold increase in response rates compared to T-VEC monotherapy (219, 223). Beyond T-VEC, other OVs have demonstrated clinical promise. AdVs, like AdV-p53, when combined with chemotherapy and radiotherapy, achieved an 82% response rate in malignant pleural effusion patients receiving cisplatin (224, 225). In China, Oncorine (H101), a AdV, was approved for nasopharyngeal carcinoma, showing a response rate exceeding 78% when combined with chemotherapy (226). Our group has made significant contributions to OVT and vaccine development, particularly in genetic engineering. Inactivating the UL37 deamidase in the VC2 (an HSV-1 variant) enhanced viral replication, spread, and GM-CSF secretion, boosting its immunogenic potential (227). Preclinical studies show that the VC2 increases immune activation, converts immunosuppressive “cold” tumors into immunostimulatory “hot” tumors and improves survival in mouse models of melanoma and breast cancer (151, 227, 228). This underscores the importance of targeted viral modifications to optimize OV vaccines.
In addition, we have explored live-attenuated HSV vaccines for genital and ocular HSV infections, focusing on their ability to elicit robust immune responses. Preclinical studies are ongoing to advance these vaccines into human clinical trials (229). Notably, several HSV-based OVs have progressed into clinical testing. In a Phase 1b trial for recurrent GBM, G207, administered into resected tumor cavities, demonstrated a strong safety profile and significant CD8+ T-cell and macrophage infiltration. In a first-in-human trial for pediatric malignant pediatric cerebellar tumors, 11 out of 12 patients showed positive clinical responses, with four surviving beyond 18 months, significantly exceeding the median survival of 5.6 months with standard therapies (230).
Another novel oHSV, HSV1716, has been investigated for melanoma, mesothelioma, and solid tumors. In mesothelioma patients treated intrapleurally, Th1 cytokines (IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α) were elevated, and antitumoral antibody responses were detected. Intravenous HSV1716 was well tolerated in young patients with extracranial solid tumors, with some achieving stable disease (231). Similarly, HF10, an attenuated HSV-1, has shown safety and efficacy in pancreatic cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, and breast cancer, increasing immune cell infiltration and inducing immune responses. Our group has also worked on other types of OVs, including those based on measles virus and VSV (1). A Phase I/II trial of MV-NIS (an engineered measles virus encoding the sodium iodide symporter) in ovarian, primary peritoneal, and fallopian tube cancer patients, showed promising results. The virus replicated, induced antitumor responses, and was well-tolerated, with some patients experiencing grade 3–4 adverse events, like neutropenia and leukopenia. One patient achieved a complete response that lasted for more than 10 years (232),.
Additionally, our team has also pioneered the development of Jurona virus (JURV), demonstrating its therapeutic potential in HCC. In preclinical models, JURV monotherapy led to significant tumor regression, while its combination with anti-PD-1 therapies improved survival outcomes by reshaping the immune landscape within the TME (14). The trivalent live-attenuated measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine also have similar oncolytic applications (33). Other OVs under clinical evaluation include Pexa-Vec, a poxvirus-based OV tested in HCC. High-dose Pexa-Vec in combination with sorafenib extended median OS to 14.1 months compared to 6.7 months in the low-dose cohorts. However, the Phase III PHOCUS trial was discontinued due to insufficient survival benefits (233). In contrast, G47Δ, a third-generation HSV-1 derivative, has received conditional approval in Japan for GBM, demonstrating an 84.2% one-year survival rate and robust tumor-infiltrating CD4+/CD8+ T-cell responses (234). Reovirus-based therapy, particularly pelareorep, has shown tumor stabilization in 86% of metastatic cancer patients, although few have progressed beyond early-phase trials. The VacVDD, a VacV with double TK gene deletion, exhibits systemic tumor targeting in advanced solid tumors but shows a median survival of 4.8 months underscoring the need for further optimization (235). While OVs have shown promise in early-phase clinical trials, translating these results into consistent survival benefits in late-phase trials remain challenging. However, novel engineering strategies, such as arming OVs with ICIs, suicide genes, and tumor-specific promoters, continue to enhance their therapeutic potential. Our ongoing research into OV-TME interactions, in combination with established immunotherapies like CART cells and checkpoint blockade, represents a crucial step in improving OV efficacy and solidifying their role as mainstays in cancer immunotherapy (14, 227, 236).
6 New immune and metabolic classification of tumors to guide oncolytic virotherapy
To optimize the clinical application OVs, we propose a new classification system for OV-responsive tumors based on their immune, metabolic, and genetic landscapes. This framework is designed to guide OV selection and engineering therapeutic efficacy (Table 2).
Table 2. Classification Model for OV-Responsive Tumors: This model enables personalized OV therapies by aligning the tumor's unique features with optimized viral engineering strategies.
6.1 A new classification system for OV-responsive tumors
As the field of OVT advances toward precision medicine, there is a growing need for systematic frameworks that can stratify tumors based on their molecular characteristics. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of genomic and epigenomic alterations in shaping tumor susceptibility to OV infection, replication, and immune activation. This section introduces a molecular classification system that categorizes tumors according to their genetic, epigenetic, and immunologic profiles, providing a foundation for tailoring OVT strategies to individual tumor vulnerabilities. By aligning therapeutic design with tumor-intrinsic features, this approach aims to enhance treatment efficacy and expand the clinical applicability of OVT.
Tumors with specific genetic alterations, such as loss-of-function mutations in tumor suppressor genes like p53 or RB1, exhibit impaired antiviral responses, rendering them highly permissive to OV replication. For instance, GBM, frequently harboring these mutations, represent ideal candidates for OVs engineered to exploit such vulnerabilities, particularly when paired with synthetic lethal agents that further sensitize tumor cells to oncolysis (116, 237, 238). Tumors characterized by chromosomal instability, such as ovarian cancer, often display defective DNA repair mechanisms. These tumors are highly responsive to OVs armed with interferon-stimulatory transgenes, which trigger innate immune activation. The therapeutic efficacy of these OVs is further amplified when combined with ICIs, promoting durable antitumor immunity. This genetic-based classification system offers a structured framework for designing personalized OVT, optimizing treatment by targeting the unique immune, metabolic, and genetic traits of tumors. Ultimately this approach aims to improve patient outcomes and drive greater clinical success.
In contrast, epigenetically driven tumors, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, exhibit widespread DNA hypermethylation and histone modifications that repress immune-related gene expression. In such tumors, OV responsiveness can be enhanced through epigenetic reprogramming using hypomethylating agents or histone deacetylase inhibitors, which restore immune surveillance pathways. Moreover, CRISPR-based genome editing strategies offer promising avenues to augment OV replication and restore tumor suppressor activity, further improving therapeutic outcomes.
This molecularly guided classification system allows for precision-matched OVT, tailored to the genetic, metabolic, and immunologic profiles of individual tumors. By integrating OVs with co-therapies that address the specific vulnerabilities of each tumor subtype, this strategy holds the potential to revolutionize personalized cancer immunotherapy and significantly improve patient prognosis.
6.2 Immune-based classification: targeting tumor immune profiles
Tumors exhibit distinct immune profiles that influence OV efficacy. Immune-hot tumors, such as melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer, feature high T-cell infiltration and an inflamed TME, responding well to OVs, especially when combined with ICI and immune-stimulatory cytokines (204, 239). Immune-cold tumors, like pancreatic adenocarcinoma, have low T-cell infiltration and abundant immunosuppressive cells (240). OVs targeting these tumors should be engineered to reprogram the TME into an immune-permissive state, with combination therapies to modulate immune cell recruitment and activity (240). Immune-excluded tumors, such as colorectal cancer, present additional challenge as T cells is confined to the stroma, limiting tumor infiltration (33). OVs for these tumors should incorporate matrix-degrading enzymes to break down physical barriers, and VEGF blockade may further enhance penetration and therapeutic effectiveness (241).
6.3 Metabolism-based classification: targeting tumor metabolic vulnerabilities
Tumor metabolism significantly impacts OV replication and therapeutic efficacy. Glycolytic tumors, like TNBC, rely on aerobic glycolysis, creating an acidic, hypoxic environment (124, 125). OVs targeting these tumors should include pH-adaptive envelope proteins to survive in acidic conditions, with metabolic inhibitors to disrupt glycolytic pathways (207, 208). Oxidative tumors, such as ovarian cancer, primarily depend on oxidative phosphorylation and exhibit high ROS levels (187–190). OVs can exploit this oxidative stress to enhance replication, potentially combined with NADPH oxidase inhibitors to increase tumor susceptibility. Metabolically plastic tumors, like colorectal cancer, can switch between glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation, complicating treatment. OVs targeting these tumors should disrupt metabolic flexibility, potentially combined with dual metabolic inhibitors to restrict the tumor’s ability to adapt to metabolic stress.
7 Future perspectives
While OVs have demonstrated notable promise, several biological, immunological, and delivery-related hurdles continue to limit their efficacy. Overcoming these challenges will be key to realizing their full therapeutic potential. Hence the future success of OVT depends on refining delivery methods, identifying predictive biomarkers, and combining OVs with other therapies to enhance efficacy and mitigate limitations.
7.1 Addressing delivery, immune, and personalization challenges in OV monotherapy
To overcome the dense ECMs, hypovascularity, and high interstitial fluid pressure that restrict intratumoral spread of OVs integration of tumor-penetrating peptides, enzymatic ECM degradation (e.g., hyaluronidase co-expression), and stromal remodeling agents to improve viral distribution within solid tumors, become pertinent (13). Nanoparticle- and hydrogel-based delivery platforms may also enhance OV retention and diffusion at tumor sites. immune cloaking techniques using polymer coatings or ex vivo OV-loaded immune cells, such as monocytes or DCs, to stealthily deliver the virus to tumors could be used to overcome pre-existing antiviral immunity in the host. Moreover, tumor-tropic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown promise in shielding OVs from immune detection and improving delivery to immune-privileged sites like the brain. Sites such as the brain, eyes, and testes present natural obstacles to immune access. Nanoparticle-based delivery (for example encapsulating viruses in nanoliposomes), modular capsid engineering, and BBB-penetrating vectors can enhance OV access to these areas. Additionally, ultrasound-mediated delivery and convection-enhanced delivery are promising strategies to physically drive OVs into solid masses or across tight barriers (242, 243). To personalize OVT, robust biomarkers are needed to predict treatment response. Promising candidates include PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden, and deficiencies in antiviral pathways (e.g., STING, JAK) that facilitate OV replication. The development of imaging-based viral tracking, liquid biopsies, and RNA signatures may further guide patient selection and treatment monitoring.
7.2 Repositioning live vaccines as immunovirotherapy in cancer treatment and prevention
Live vaccines represent a groundbreaking approach in cancer immunovirotherapy, repurposing viral vaccines as powerful tools to combat cancer. Originally developed to prevent infectious diseases and some cancers, live vaccines are now being explored for their ability to activate both immune responses, directly targeting and eliminating cancer cells (243). This approach leverages the unique immunogenic properties of attenuated or engineered viruses, stimulating broad immune responses capable of targeting tumor cells throughout the body.
Oncolytic virus live vaccines are also used preventively to protect high-risk individuals from cancers driven by oncogenic pathogens. Unlike therapeutic live viruses, which are administered after malignancy develops, to convert tumors into in situ vaccines, preventive vaccines prime the immune system to recognize and eradicate cancer-causing infections before tumorigenesis occurs. They deliver viral antigens or virus-like particles that elicit neutralizing antibodies and durable memory responses. The HPV vaccine, which prevents cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers by targeting high-risk HPV strains, and the hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccine, which lowers hepatocellular carcinoma risk by preventing chronic HBV infection, are among the most successful examples. These interventions have demonstrated high efficacy in reducing infection rates and associated cancer incidence, underscoring their pivotal role in global cancer prevention strategies (244, 245).
However, the concept of prophylactic administration of OVs to prevent non-virus-induced cancers remains clinically unexploited. Also, in the absence of tumor tissue, OVs lack a target substrate for infection and lysis, precluding the release of TAAs necessary to prime an effective immune response. Furthermore, non-virus-driven malignancies do not share uniform pre-existing antigens that could be targeted in advance. Administering OVs to healthy individuals therefore poses safety risks without conferring the needed immunologic benefit. Consequently, OVs such as T-VEC and VV are reserved for therapeutic use in established cancers, where they convert tumors into in situ vaccines and synergize with other immunotherapies to drive robust antitumor immunity (244, 245).
Our group has investigated the potential of repurposing the live attenuated trivalent measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine as a cost-effective cancer immunotherapy (33). In murine models of HCC and colorectal cancer, intratumoral MMR vaccine injections resulted in significant tumor growth inhibition and improved survival. The vaccine activated a robust CTL response and reduced TAMs, enhancing the antitumor immune response and offering a promising option for cancer immunotherapy. Additionally, the recombinant HSV-1 vaccine vector has shown promise for personalized cancer vaccines (151). A recombinant engineered oHSV-1 called VC2-OVA, expressing a fragment of ovalbumin fused with the VP26 viral capsid protein, demonstrated specific antitumor immunity in a murine melanoma model, significantly reducing tumor cell colonization in the lungs and extending survival (228). The effects of HSV-1 vaccine strain VC2 in a mouse model of stage four breast cancer was investigated, and VC2 treatment resulted in significant intratumor infiltration of functionally active T cells, inhibited tumor metastasis and reduced the expression of pro-tumor genes VEGF and PD-L1 (246). Similarly, intramuscular injection of mice with live attenuated VC2 vaccine strain protected against ocular challenges, which was associated with enhanced intracorneal infiltration of γδ T cells, which helped control ocular immunopathogenesis (246). These live vaccines mimic viral infections, stimulating immune responses that target tumor cells directly and generating systemic antitumor effects. They activate CTL, NK cells, and other immune effectors, which infiltrate the TME, promote tumor cell destruction and can address distant metastases. Notably, live vaccines can generate long-lasting immune memory, providing protection against tumor recurrence (233).
One of the key advantages of repurposing live vaccines for cancer is their ability to be readily available for cancer treatment without the need for extensive production or toxicology testing (247). Certain live vaccines, including those based on VSV, reoviruses, and engineered measles viruses, exhibit natural oncolytic activity. These viruses selectively infect and replicate within tumor cells, exploiting the unique characteristics of cancer, such as defective in antiviral responses and altered cellular machinery. This replication process causes tumor cell death, releasing viral particles that spread to adjacent cancer cells, amplifying the therapeutic effect.
In addition to their oncolytic properties, live vaccines also enhance immune responses against tumors that are typically resistant to immune attack. The viral infection itself acts as a “danger signal” that alerts the immune system to the presence of tumor cells, converting “cold” tumors (poorly infiltrated by immune cells) into “hot” tumors that are more receptive to immune-based therapies, including ICIs (248).
Several live vaccines are currently undergoing clinical trials for cancer treatment. The modified VacV used in the oncolytic vaccine Pexa-Vec has shown promise in treating melanoma and colorectal cancer. Similarly, engineered oncolytic measles viruses have demonstrated efficacy in tumor regression across multiple cancers, including GBM and ovarian cancer. The reovirus, with its selective oncolytic properties, has also shown potential when combined with chemotherapy and ICIs.
Despite these promising results, challenges remain, particularly concerning safety. Although engineered to minimize risks, live viral vectors may still pose potential threats, particularly for immunocompromised patients. However, OVs are often modified to attenuate their effects or selectively target cancer cells, reducing these risks. Rigorous monitoring during clinical application is crucial to detect and manage potential side effects, such as viral shedding or immune-related reactions (247).
One of the significant advantages of live vaccines is their ability to enhance other cancer therapies. When combined with ICIs, live vaccines have shown synergistic effects by boosting T-cell activity and improving immune cell infiltration, making tumors more susceptible to checkpoint blockade. Additionally, live vaccines can be combined with targeted therapies or chemotherapy, offering a multifaceted approach to overcoming tumor heterogeneity and resistance mechanisms.
Looking forward, live vaccines are poised to play an increasingly critical role in cancer treatment. As research deepens our understanding of immune responses and the TME, and as new viral vectors and delivery systems, e.g. are developed, live vaccine-based therapies will likely become a cornerstone of cancer immunotherapy. The potential of these vaccines to induce lasting immune responses, treat a broad range of malignancies, and prevent cancer recurrence offers new hope for patients facing challenging cancers. Ongoing research and clinical trials will continue to refine their applications, making live vaccine-based therapies a promising avenue for future cancer treatments.
7.3 Leveraging nutraceuticals to reprogram immunosuppressive cells and enhance OVs efficacy
Nutraceuticals, bioactive food-derived compounds, are emerging as promising adjuncts to OVT, particularly through their ability to reprogram immunosuppressive cells within the TME. By modulating immune pathways, these compounds can reduce populations of Tregs and MDSCs, shift TAMs from a pro-tumor M2 phenotype to an antitumor M1 phenotype, and enhance the infiltration and activity of CTLs and NK cells, all of which are critical for effective OVT. Curcumin, exhibit potent immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties. It enhances both innate and adaptive immunity by activating CTLs and NK cells, inhibiting immunosuppressive cytokines and enzymes via NF-κB suppression, reprogramming M2-like TAMs into M1-like antitumor phenotypes, and reducing Treg and MDSC activity.
By modulating multiple biological pathways, nutraceuticals can improve immune responses, modify the TME, and increase cancer cells’ susceptibility to viral infection, thus improving the potency of OVT. Combining nutraceuticals with OVs holds great promise in optimizing treatment outcomes, overcoming resistance mechanisms, and improving patient survival (40). A primary mechanism through which nutraceuticals support OVs is by boosting the immune responses, as OVs rely heavily on the host’s immune system to effectively target and eliminate tumor cells.
Several nutraceuticals, including curcumin from turmeric, possess immunomodulatory properties that can activate immune cells such as CTLs and NK cells, key players in immune-mediated tumor destruction. Curcumin has been shown to enhance both innate and adaptive immunity by promoting immune cell activation, reducing immunosuppressive signaling or cytokines and enzymes by inhibiting NF-κB binding, and creating a more favorable environment for viral replication within the TME (256). Additionally, curcumin possesses anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory qualities (249). Moreover, curcumin’s potential to enhance chemotherapy and ICIs suggests that it could increase the effectiveness of OVT. Curcumin has been shown to influence the proliferation and function of different immune cells, such as CTL and NK cells, potentially enhancing the immune system’s response to the tumor (249). Yet, curcumin might also suppress certain antiviral mechanisms that typically restrict OV replication. It can reduce the expression of ISGs, a critical component of the body’s antiviral defense (250). Furthermore, curcumin can trigger apoptosis in cancer cells, rendering them more vulnerable to OV-induced infection and destruction (251). Curcumin can inhibit angiogenesis within tumors, potentially starving them of nutrients and enhancing their vulnerability to OVT. Preclinical studies have shown that curcumin enhances cancer therapy (18), however, further clinical trials are needed to validate that curcumin could be a beneficial supplement to OVT, partly addressing some of the limitations of single use of OVs.
Other nutraceuticals, like resveratrol (from grapes and berries), epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a polyphenol in green tea), have both demonstrated the ability to boost NK cell activity and promote immune responses, thereby enhancing viral-induced tumor regression (18, 252). These compounds can improve OVT efficacy by modulating immune checkpoint molecules and promoting a more favorable immune environment within the TME.
In addition to modulating the immune system, nutraceuticals can help overcome TME barriers that limit OVT efficacy. The TME is often characterized by hypoxia, dense extracellular matrices, and immunosuppressive factors, all of which hinder viral replication and spread. Nutraceuticals, such as sulforaphane, found in cruciferous vegetables, can downregulate factors like VEGF and MMPs. However, upregulation of VEGF increases angiogenesis which facilitate the entry of oncolytic viruses like HSV-1, in cancer cells (253). Antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, known for reducing oxidative stress, help optimize the TME, promoting viral replication and immune function. These antioxidants also activate immune cells, fostering a more favorable environment and enhancing the overall efficacy of OVTs. Clinical trials exploring the use of vitamins C and E as adjuncts to cancer therapy have shown promising results, particularly in melanoma and head and neck cancers, indicating improved viral replication and immune response (254).
Nutraceuticals can also sensitize cancer cells to OVs by modulating cellular pathways critical for viral entry and replication. For example, quercetin, a flavonoid abundantly found in apples and onions, enhances oAdV therapy by influencing autophagy and apoptosis, which regulate cancer cells’ responses to viral infection (255). While autophagy facilitates viral particle degradation, apoptosis promotes viral-induced cell death. In liver cancer models, quercetin improved OVT efficacy, resulting in more effective tumor cell lysis (114). Similarly, berberine, an alkaloid derived from various herbs, has been shown to exhibit direct antiviral properties, complementing OV activity by enhancing viral replication and tumor cell killing (256). In combination with HSV-1, berberine has been shown to enhance viral replication and tumor cell killing in pancreatic and liver cancer models by modulating cellular stress responses and promoting viral entry (256).
Certain nutraceuticals also possess inherent antiviral properties that can boost OVT efficacy. For example, garlic extract, rich in sulfur compounds such as allicin, has demonstrated antiviral activity that supports viral replication and spread within tumors (257). In combination with oncolytic VSV, garlic extract could improve viral particle production and oncolytic activity in lung cancer models. By stimulating innate immune responses and inhibiting viral clearance, garlic extract can complement OV therapies. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil, known for their anti-inflammatory properties (257), can modify the TME to promote OV activity by suppressing inflammatory pathways like NF-κB and promoting resolution molecules such as resolvins and protectins, which reduce inflammation and boost OV efficacy (258).
Despite the promise of combining nutraceuticals with OVs, challenges remain in optimizing this strategy. The timing, dosage, and selection of nutraceuticals must be tailored to maximize their synergistic effects with OVs. Also, not all nutraceuticals are suitable for every cancer type or OVT. Moreover, patient-specific factors such as genetic background, tumor type, and disease stage must be considered to ensure the best therapeutic outcomes.
Integrating nutraceuticals into OVT represents a novel approach to overcoming barriers in cancer treatment (Figure 4). By enhancing the immune responses, modifying the TME, and boosting viral replication and sensitivity, nutraceuticals and other small molecular scaffolds inspired from the latter can significantly amplify OVs efficacy. Ongoing preclinical and clinical studies continue to explore these combinations, with promising early results suggesting that nutraceuticals may overcome some limitations of monotherapy. Combining nutraceuticals with OVs is not without challenges. The timing, dosage, and selection of nutraceuticals must be tailored to maximize their synergistic effects with OVs. Also, not all nutraceuticals are suitable for every cancer type or OVT. Moreover, patient-specific factors such as genetic background, tumor type, and disease stage must be considered to ensure the best therapeutic outcomes. As research advances, this integrated approach has the potential to transform cancer therapy, providing a more robust and personalized treatment strategy for patients with hard-to-treat cancers.
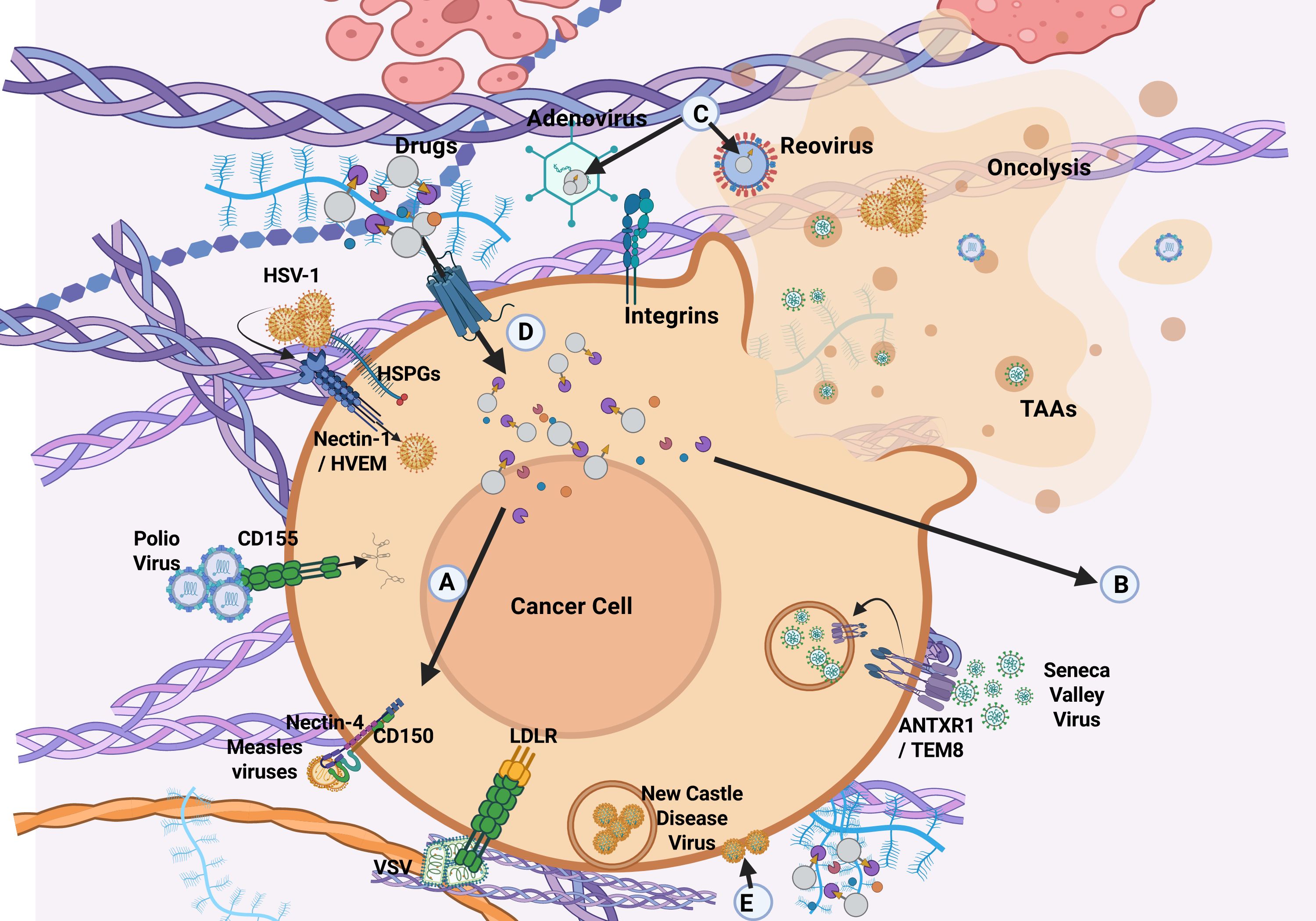
Figure 4. A proposed hypothesis for the pharmacological potentiation of OVT. HVEM = Herpesvirus Entry Mediator; CAR = Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor; ICAM-1 = Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1; DAF = Decay-Accelerating Factor; SARs = Sialic Acid Receptors; SLAM = Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule (A) Pharmacologically active natural or synthetic small molecules (drugs) can enhance the entry of OVs into solid tumors by upregulating the expression of viral entry receptors on the surface of cancer cells. (B) Certain therapeutic molecules promote vascular normalization within the TME, thereby facilitating endocytosis of viral particles and enhancing both oncolysis and immune modulation. (C) Biologically active small molecules can also be encapsulated within OV particles, enabling targeted delivery into the TME. (D) Upregulation of glucose or amino acid transporters on cancer cells supports increased uptake of biologically active compounds by cancer cells. (E) Some bioactive molecules, such as hyaluronidase and collagenase, disrupt the extracellular matrix or increase vascular permeability, enhancing OV penetration into tumor tissues (289).
8 Conclusion
OVT is an emerging field that works both locally and systemically, stimulating adaptive antitumor immunity. Small-molecule inhibitors derived from natural products or synthetic scaffolds targeting key signaling pathways are gaining momentum in immuno-oncology; however, their therapeutic impact as monotherapies has been modest, often requiring combination with other modalities to achieve durable clinical responses. Combining OVs with these inhibitors, guided by mechanistic insights, presents a promising strategy to enhance cancer treatment. Preclinically, small molecules boost OV efficacy. However, those inhibiting PI3K-AKT-mTOR and KRAS-ERK/MAPK oncogenic pathways may suppress cancer and immune cells alike, leading to unintended consequences, like impaired T-cell function, and weakened immune responses. Managing toxicity to normal cells is important, and treatment timing plays a key role. If cancer cells die too early, it can reduce OV replication. In HCC, administering Pexa-Vec before sorafenib improves outcomes, but reduces OV effectiveness when administered together.
Nutraceuticals, such as curcumin, resveratrol, green tea polyphenols, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and selenium, further enhance OVT by modulating immunity, improving TME, and promoting viral replication. These natural bioactives, along with their synthetic scaffolds, offer the potential to make cancer therapies more effective and less toxic. The synergy between OVs, small molecules, and nutraceuticals offers a dual approach to boost viral oncolysis and immune responses. Clinical trials will be pivotal in optimizing combinations and dosages, paving the way for personalized and innovative cancer treatments that improve outcomes and quality of life.
Author contributions
TO: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Visualization, Data curation, Validation. JF: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation. MT: Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology. HM: Visualization, Software, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Validation. ODu: Resources, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. LR: Writing – review & editing. KF: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RG: Writing – review & editing. AC: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. TB: Visualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft. JF: Visualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. ODa: Resources, Visualization, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration. MB: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Software, Visualization, Validation. KK: Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. SD: Visualization, Validation, Conceptualization, Supervision, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft. BN: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Conceptualization, Validation, Formal analysis, Visualization. JC: Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Supervision, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Data curation, Visualization, Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Research work in the Chamcheu laboratories at Southern University and A&M College and at Louisiana State University (LSU), School of Veterinary Medicine, Baton Rouge were partially supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Cancer Institute (NCI) grant 1R15CA290568-01, full project awards from LSU COBRE NIH/NIGMS grant 1P20 GM135000-01A1, and LBRN NIH/NIGMS grant P20 GM103424–21 awards. Additionally, the Kousoulas laboratory is partially supported by NIH GM110760 grant. The DiGuiseppe laboratory was partly supported by LSU COBRE NIH/NIGMS grant 5P2-GM134974. The Nagalo laboratory work is partially supported by the NIH/NCI through a K01 award (CA234324), an American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) grant, a Seed of Science Award from the Winthrop P. Rockefeller Cancer Institute, and NIH DP2CA301099 grant. Additional support was provided by the Development Enhancement Awards for Proposals (DEAP) from the UAMS Research Committee and the College of Medicine’s intramural grant Barton Pilot Award Program. We would also like to thank Jessica Muller, MA at Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine, for her assistance in editing the manuscript. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or in the decision to submit the work for publication. Scientific images were portrayed with BioRender.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Nagalo BM, Breton CA, Zhou Y, Arora M, Bogenberger JM, Barro O, et al. Oncolytic virus with attributes of vesicular stomatitis virus and measles virus in hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancers. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2020) 18:546–55. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.08.007
2. Santos Apolonio J, Lima de Souza Goncalves V, Cordeiro Santos ML, Silva Luz M, Silva Souza JV, Rocha Pinheiro SL, et al. Oncolytic virus therapy in cancer: A current review. World J Virol. (2021) 10:229–55. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v10.i5.229
3. Jin KT, Du WL, Liu YY, Lan HR, Si JX, and Mou XZ. Oncolytic virotherapy in solid tumors: the challenges and achievements. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:588. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040588
4. Parmar HS, Nayak A, Kataria S, Tripathi V, Jaiswal P, Gavel PK, et al. Restructuring the ONYX-015 adenovirus by using spike protein genes from SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV: Possible implications in breast cancer treatment. Med Hypotheses. (2022) 159:110750. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2021.110750
5. Babiker HM, Riaz IB, Husnain M, and Borad MJ. Oncolytic virotherapy including Rigvir and standard therapies in malignant melanoma. Oncolytic Virother. (2017) 6:11–8. doi: 10.2147/OV.S100072
6. Poirier JT, Dobromilskaya I, Moriarty WF, Peacock CD, Hann CL, and Rudin CM. Selective tropism of Seneca Valley virus for variant subtype small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2013) 105:1059–65. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt130
7. Ma J, Ramachandran M, Jin C, Quijano-Rubio C, Martikainen M, Yu D, et al. Characterization of virus-mediated immunogenic cancer cell death and the consequences for oncolytic virus-based immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:48. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2236-3
8. Kohlhapp FJ and Kaufman HL. Molecular Pathways: Mechanism of Action for Talimogene Laherparepvec, a New Oncolytic Virus Immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:1048–54. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2667
9. El-Shemi AG, Ashshi AM, Na Y, Li Y, Basalamah M, Al-Allaf FA, et al. Combined therapy with oncolytic adenoviruses encoding TRAIL and IL-12 genes markedly suppressed human hepatocellular carcinoma both in vitro and in an orthotopic transplanted mouse model. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 35:74. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0353-8
10. Kaliberov SA, Kaliberova LN, Yan H, Kapoor V, and Hallahan DE. Retargeted adenoviruses for radiation-guided gene delivery. Cancer Gene Ther. (2016) 23:303–14. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2016.32
11. Shen Z, Liu X, Fan G, Na J, Liu Q, Lin F, et al. Improving the therapeutic efficacy of oncolytic viruses for cancer: targeting macrophages. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:842. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04709-z
12. Lv P, Liu X, Chen X, Liu C, Zhang Y, Chu C, et al. Genetically engineered cell membrane nanovesicles for oncolytic adenovirus delivery: a versatile platform for cancer virotherapy. Nano Lett. (2019) 19:2993–3001. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00145
13. Chen Y, Chen X, Bao W, Liu G, Wei W, and Ping Y. An oncolytic virus-T cell chimera for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Biotechnol. (2024) 42:1876–87. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-02118-7
14. Tesfay MZ, Zhang Y, Ferdous KU, Taylor MA, Cios A, Shelton RS, et al. Enhancing immune response and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma with novel oncolytic Jurona virus and immune checkpoint blockade. Mol Ther Oncol. (2024) 32:200913. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200913
15. Park J, Thomas S, and Munster PN. Epigenetic modulation with histone deacetylase inhibitors in combination with immunotherapy. Epigenomics. (2015) 7:641–52. doi: 10.2217/epi.15.16
16. Lekshmi VS, Asha K, Sanicas M, Asi A, Arya UM, and Kumar B. PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 mediated cellular signaling and virus-host interactions: latest updates on the potential therapeutic management of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10:1158133. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1158133
17. Wang L, Zhang X, Xiong X, Zhu H, Chen R, Zhang S, et al. Nrf2 Regulates Oxidative Stress and Its Role in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:2377. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122377
18. Della Via FI, Shiraishi RN, Santos I, Ferro KP, Salazar-Terreros MJ, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis and differentiation in leukaemia by targeting reactive oxygen species and PIN1. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:9103. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88478-z
19. Sita G, Hrelia P, Graziosi A, and Morroni F. Sulforaphane from cruciferous vegetables: recent advances to improve glioblastoma treatment. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1755. doi: 10.3390/nu10111755
20. Mansouri K, Rasoulpoor S, Daneshkhah A, Abolfathi S, Salari N, Mohammadi M, et al. Clinical effects of curcumin in enhancing cancer therapy: A systematic review. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:791. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07256-8
21. Rivadeneira DB, DePeaux K, Wang Y, Kulkarni A, Tabib T, Menk AV, et al. Oncolytic Viruses Engineered to Enforce Leptin Expression Reprogram Tumor-Infiltrating T Cell Metabolism and Promote Tumor Clearance. Immunity. (2019) 51:548–560 e544. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.07.003
22. Zhao J, Hu S, Qi Z, Xu X, Long X, Huang A, et al. Mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming of macrophages and T cells enhances CD47 antibody-engineered oncolytic virus antitumor immunity. J Immunother Cancer. (2024) 12:e009768. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009768
23. Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Hett E, Kroemer G, and Marincola FM. Immunogenic cell death in cancer: concept and therapeutic implications. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:162. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04017-6
24. Fend L, Yamazaki T, Remy C, Fahrner C, Gantzer M, Nourtier V, et al. Immune Checkpoint Blockade, Immunogenic Chemotherapy or IFN-alpha Blockade Boost the Local and Abscopal Effects of Oncolytic Virotherapy. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:4146–57. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2165
25. Jennings VA, Scott GB, Rose AMS, Scott KJ, Migneco G, Keller B, et al. Potentiating Oncolytic Virus-Induced Immune-Mediated Tumor Cell Killing Using Histone Deacetylase Inhibition. Mol Ther. (2019) 27:1139–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.04.008
26. Bourgeois-Daigneault MC, Roy DG, Falls T, Twumasi-Boateng K, St-Germain LE, Marguerie M, et al. Oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus expressing interferon-gamma has enhanced therapeutic activity. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2016) 3:16001. doi: 10.1038/mto.2016.1
27. Tie Y, Tang F, Wei YQ, and Wei XW. Immunosuppressive cells in cancer: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:61. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01282-8
28. Li J, Yu J, Shen A, Lai S, Liu Z, and He TS. The RNA-binding proteins regulate innate antiviral immune signaling by modulating pattern recognition receptors. Virol J. (2024) 21:225. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02503-x
29. Bishnoi S, Tiwari R, Gupta S, Byrareddy SN, and Nayak D. Oncotargeting by vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV): advances in cancer therapy. Viruses. (2018) 10:90. doi: 10.3390/v10020090
30. Abdelmageed AA, Dewhurst S, and Ferran MC. Employing the Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus in Cancer Virotherapy: Resistance and Clinical Considerations. Viruses. (2024) 17:16. doi: 10.3390/v17010016
31. Swaraj S. Interference without interferon: interferon-independent induction of interferon-stimulated genes and its role in cellular innate immunity. mBio. (2024) 15:e0258224. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02582-24
32. Nguyen TT, Ramsay L, Ahanfeshar-Adams M, Lajoie M, Schadendorf D, Alain T, et al. Mutations in the IFNgamma-JAK-STAT Pathway Causing Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Melanoma Increase Sensitivity to Oncolytic Virus Treatment. Clin Cancer Res. 27:3432–42. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3365
33. Zhang Y and Nagalo BM. Immunovirotherapy Based on Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus: Where Are We? Front Immunol. (2022) 13:898631. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.898631
34. Reeh M, Bockhorn M, Gorgens D, Vieth M, Hoffmann T, Simon R, et al. Presence of the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) in human neoplasms: a multitumour array analysis. Br J Cancer. (2013) 109:1848–58. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.509
35. Mealiea D and McCart JA. Cutting both ways: the innate immune response to oncolytic virotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther. (2022) 29:629–46. doi: 10.1038/s41417-021-00351-3
36. Delwar ZM, Kuo Y, Wen YH, Rennie PS, and Jia W. Oncolytic virotherapy blockade by microglia and macrophages requires STAT1/3. Cancer Res. (2018) 78:718–30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0599
37. Liu J, Piranlioglu R, Ye F, Shu K, Lei T, and Nakashima H. Immunosuppressive cells in oncolytic virotherapy for glioma: challenges and solutions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1141034. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1141034
38. Mellman I, Chen DS, Powles T, and Turley SJ. The cancer-immunity cycle: Indication, genotype, and immunotype. Immunity. (2023) 56:2188–205. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.09.011
39. Cho KJ, Ishido S, Eisenlohr LC, and Roche PA. Activation of dendritic cells alters the mechanism of MHC Class II antigen presentation to CD4 T Cells. J Immunol. (2020) 204:1621–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901234
40. Yan Z, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Xu J, Wang J, and Wang Z. Enhancing cancer therapy: the integration of oncolytic virus therapy with diverse treatments. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24:242. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03424-z
41. Fu R, Qi R, Xiong H, Lei X, Jiang Y, He J, et al. Combination therapy with oncolytic virus and T cells or mRNA vaccine amplifies antitumor effects. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:118. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01824-1
42. Sun X, Zhang T, Li M, Yin L, and Xue J. Immunosuppressive B cells expressing PD-1/PD-L1 in solid tumors: a mini review. QJM. (2022) 115:507–12. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcz162
43. Shi G, Yang Q, Zhang Y, Jiang Q, Lin Y, Yang S, et al. Modulating the tumor microenvironment via oncolytic viruses and csf-1r inhibition synergistically enhances anti-PD-1immunotherapy. Mol Ther. (2019) 27:244–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.010
44. Xia C, Yin S, To KKW, and Fu L. CD39/CD73/A2AR pathway and cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:44. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01733-x
45. Li C, Jiang P, Wei S, Xu X, and Wang J. Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: new mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:116. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01234-1
46. Ma X, Bi E, Lu Y, Su P, Huang C, Liu L, et al. Cholesterol induces CD8(+) T Cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. (2019) 30:143–156 e145. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.04.002
47. Chen C, Zhang R, Ma L, Li Q, Zhao YL, Zhang GJ, et al. Neuropilin-1 is up-regulated by cancer-associated fibroblast-secreted IL-8 and associated with cell proliferation of gallbladder cancer. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:12608–18. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15825
48. Li Q, Hasan N, Zhao F, Xue Y, Zhu S, Lv Y, et al. DC-SIGN (CD209)-mediated interactions between bacteria, lung cancer tissues, and macrophages promote cancer metastasis. Infect Agent Cancer. (2025) 20:40. doi: 10.1186/s13027-025-00667-x
49. Sarabipour S and Mac Gabhann F. Tumor and endothelial cells collaborate via transcellular receptor complexes. J Pathol. (2019) 247:155–7. doi: 10.1002/path.5185
50. Del Prete A, Salvi V, Soriani A, Laffranchi M, Sozio F, Bosisio D, et al. Dendritic cell subsets in cancer immunity and tumor antigen sensing. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:432–47. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-00990-6
51. Guven-Maiorov E, Tsai CJ, and Nussinov R. Oncoviruses Can Drive Cancer by Rewiring Signaling Pathways Through Interface Mimicry. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:1236. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01236
52. Liu S, Liu T, Jiang J, Guo H, and Yang R. p53 mutation and deletion contribute to tumor immune evasion. Front Genet. (2023) 14:1088455. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1088455
53. Hu J, Cao J, Topatana W, Juengpanich S, Li S, Zhang B, et al. Targeting mutant p53 for cancer therapy: direct and indirect strategies. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:157. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01169-0
54. Krump NA and You J. Molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis in humans. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2018) 16:684–98. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0064-6
55. Lin D, Shen Y, and Liang T. Oncolytic virotherapy: basic principles, recent advances and future directions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:156. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01407-6
56. Burgos-Molina AM, Tellez Santana T, Redondo M, and Bravo Romero MJ. The crucial role of inflammation and the immune system in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis: a comprehensive perspective. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6188. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116188
57. Landwehr LS, Altieri B, Sbiera I, Remde H, Kircher S, Olabe J, et al. Expression and prognostic relevance of PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 immune checkpoints in adrenocortical carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2024) 109:2325–34. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae109
58. Labani-Motlagh A, Ashja-Mahdavi M, and Loskog A. The Tumor Microenvironment: A Milieu Hindering and Obstructing Antitumor Immune Responses. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:940. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00940
59. Hartupee C, Nagalo BM, Chabu CY, Tesfay MZ, Coleman-Barnett J, West JT, et al. Pancreatic cancer tumor microenvironment is a major therapeutic barrier and target. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1287459. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1287459
60. Ren Z, Ding T, Zuo Z, Xu Z, Deng J, and Wei Z. Regulation of MAVS Expression and signaling function in the antiviral innate immune response. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01030
61. Ngo C, Garrec C, Tomasello E, and Dalod M. The role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) in immunity during viral infections and beyond. Cell Mol Immunol. (2024) 21:1008–35. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01167-5
62. Musumeci A, Lutz K, Winheim E, and Krug AB. What Makes a pDC: Recent Advances in Understanding Plasmacytoid DC Development and Heterogeneity. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1222. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01222
63. Zhou B, Lawrence T, and Liang Y. The role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in cancers. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:749190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.749190
64. Lawler SE, Speranza MC, Cho CF, and Chiocca EA. Oncolytic viruses in cancer treatment: a review. JAMA Oncol. (2017) 3:841–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.2064
65. Bjorkstrom NK, Strunz B, and Ljunggren HG. Natural killer cells in antiviral immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2012) 22:112–23. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00558-3
66. Silva MT and Correia-Neves M. Neutrophils and macrophages: the main partners of phagocyte cell systems. Front Immunol. (2012) 3:174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00174
67. Wang SSY, Tang H, Loe MWC, Yeo SC, and Javaid MM. Complements and their role in systemic disorders. Cureus. (2024) 16:e52991. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52991
68. Zhao L and Yang X. Cross Talk Between Natural Killer T and Dendritic Cells and Its Impact on T Cell Responses in Infections. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:837767. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.837767
69. Biron CA. Interferons alpha and beta as immune regulators–a new look. Immunity. (2001) 14:661–4. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00154-6
71. Kuang L, Wu L, and Li Y. Extracellular vesicles in tumor immunity: mechanisms and novel insights. Mol Cancer. (2025) 24:45. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02233-w
72. von Locquenghien M, Rozalen C, and Celia-Terrassa T. Interferons in cancer immunoediting: sculpting metastasis and immunotherapy response. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e143296. doi: 10.1172/JCI143296
73. Drappier M, Jha BK, Stone S, Elliott R, Zhang R, Vertommen D, et al. A novel mechanism of RNase L inhibition: Theiler's virus L* protein prevents 2-5A from binding to RNase L. PloS Pathog. (2018) 14:e1006989. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006989
74. Wang B, Han Y, Zhang Y, Zhao Q, Wang H, Wei J, et al. Overcoming acquired resistance to cancer immune checkpoint therapy: potential strategies based on molecular mechanisms. Cell Biosci. (2023) 13:120. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01073-9
75. Yang R, Han Y, Guan X, Hong Y, Meng J, Ding S, et al. Regulation and clinical potential of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT/hTERT) in breast cancer. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:218. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01244-8
76. Sundaramoorthy E, Ryan AP, Fulzele A, Leonard M, Daugherty MD, and Bennett EJ. Ribosome quality control activity potentiates vaccinia virus protein synthesis during infection. J Cell Sci. (2021) 134:jcs257188. doi: 10.1242/jcs.257188
77. Meade N, DiGiuseppe S, and Walsh D. Translational control during poxvirus infection. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. (2019) 10:e1515. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1515
78. de Graaf JF, van Nieuwkoop S, Bestebroer T, Groeneveld D, van Eijck CHJ, Fouchier RAM, et al. Optimizing environmental safety and cell-killing potential of oncolytic Newcastle Disease virus with modifications of the V, F and HN genes. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0263707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263707
79. Tian Y, Xie D, and Yang L. Engineering strategies to enhance oncolytic viruses in cancer immunotherapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:117. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00951-x
80. Watters CR, Barro O, Gabere M, Masuda MY, Elliott NM, Raupach EA, et al. Resistance signatures to oncolytic vesiculoviruses in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Ther Oncol. (2025) 33:200937. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2025.200937
81. Erickson NJ, Stavarache M, Tekedereli I, Kaplitt MG, and Markert JM. Herpes Simplex Oncolytic Viral Therapy for Malignant Glioma and Mechanisms of Delivery. World Neurosurg. (2025) 194:123595. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.123595
82. Zainutdinov SS, Kochneva GV, Netesov SV, Chumakov PM, and Matveeva OV. Directed evolution as a tool for the selection of oncolytic RNA viruses with desired phenotypes. Oncolytic Virother. (2019) 8:9–26. doi: 10.2147/OV.S176523
83. Shayan S, Arashkia A, and Azadmanesh K. Modifying oncolytic virotherapy to overcome the barrier of the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Where do we stand? Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22:370. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02774-w
84. Raguram A, An M, Chen PZ, and Liu DR. Directed evolution of engineered virus-like particles with improved production and transduction efficiencies. Nat Biotechnol. (2024), 1–17. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02467-x
85. Illingworth S, Di Y, Bauzon M, Lei J, Duffy MR, Alvis S, et al. Preclinical safety studies of enadenotucirev, a chimeric group b human-specific oncolytic adenovirus. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2017) 5:62–74. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2017.03.003
86. Bourhill T, Mori Y, Rancourt DE, Shmulevitz M, and Johnston RN. Going (Reo)Viral: Factors Promoting Successful Reoviral Oncolytic Infection. Viruses. (2018) 10:421. doi: 10.3390/v10080421
87. Diller JR, Halloran SR, Koehler M, Dos Santos Natividade R, Alsteens D, Stehle T, et al. Reovirus sigma1 Conformational Flexibility Modulates the Efficiency of Host Cell Attachment. J Virol. (2020) 94:e01163–01120. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01163-20
88. Sandekian V and Lemay G. Amino acids substitutions in sigma1 and mu1 outer capsid proteins of a Vero cell-adapted mammalian orthoreovirus are required for optimal virus binding and disassembly. Virus Res. (2015) 196:20–9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.11.002
89. Xie Y, Wu L, Wang M, Cheng A, Yang Q, Wu Y, et al. Alpha-Herpesvirus Thymidine Kinase Genes Mediate Viral Virulence and Are Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front Microbiol. (2019) 10:941. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00941
90. O'Shea CC, Johnson L, Bagus B, Choi S, Nicholas C, Shen A, et al. Late viral RNA export, rather than p53 inactivation, determines ONYX-015 tumor selectivity. Cancer Cell. (2004) 6:611–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.11.012
91. Watters CR, Barro O, Elliott NM, Zhou Y, Gabere M, Raupach E, et al. Multi-modal efficacy of a chimeric vesiculovirus expressing the Morreton glycoprotein in sarcoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2023) 29:4–14. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.02.009
92. Felt SA and Grdzelishvili VZ. Recent advances in vesicular stomatitis virus-based oncolytic virotherapy: a 5-year update. J Gen Virol. (2017) 98:2895–911. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000980
93. Lin C, Hao HM, Xiong D, Luo Y, Huang C, et al. Increasing the Efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Precise Genome Editing of HSV-1 Virus in Human Cells. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:34531. doi: 10.1038/srep34531
94. Bhujbal S, Bhujbal R, and Giram P. An overview: CRISPR/Cas-based gene editing for viral vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines. (2022) 21:1581–93. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2022.2112952
95. Liu Y, Cai J, Liu W, Lin Y, Guo L, and Liu X. al.Intravenous injection oncolytic Virus M1 awakens antitumor T Cells overcomes resistance to checkpoint blockade. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:1062. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03285-0
96. Bahreyni A, Liu H, Mohamud Y, Xue YC, Fan YM, Zhang YL, et al. A combination of genetically engineered oncolytic virus and melittin-CpG for cancer viro-chemo-immunotherapy. BMC Med. (2023) 21:193. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02901-y
97. Luo, Song QH, Deng X, Li J, Jian W, Zhao J, et al. A triple-regulated oncolytic adenovirus carrying microrna-143 exhibits potent antitumor efficacy in colorectal cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2020) 16:219–29. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.01.005
98. Sakuda T, Kubo T, Johan MP, Furuta T, Sakaguchi T, and Adachi N. Development of an oncolytic recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus encoding a tumor-suppressor microRNA. Anticancer Res. (2020) 40:6319–25. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14652
99. Marzulli M, Mazzacurati L, Zhang M, Goins WF, Hatley ME, Glorioso JC, et al. A Novel Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Design based on the Common Overexpression of microRNA-21 in Tumors. J Gene Ther. (2018) 3:10.13188/12381–13326.1000007. doi: 10.13188/2381-3326.1000007
100. Raimondi G, Gea-Sorli S, Otero-Mateo M, and Fillat C. Inhibition of miR-222 by oncolytic adenovirus-encoded miRNA sponges promotes viral oncolysis and elicits antitumor effects in pancreatic cancer models. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:3233. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133233
101. Montano-Samaniego M, Bravo-Estupinan DM, Mendez-Guerrero O, Alarcon-Hernandez E, and Ibanez-Hernandez M. Strategies for targeting gene therapy in cancer cells with tumor-specific promoters. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:605380. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.605380
102. Ferdous KU, Tesfay MZ, Cios A, Shelton RS, Hartupee C, Urbaniak A, et al. Enhancing neoadjuvant virotherapy's effectiveness by targeting stroma to improve resectability in pancreatic cancer. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:1596. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071596
103. Knebel-Morsdorf D. Nectin-1 and HVEM: cellular receptors for HSV-1 in skin. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:19087–8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8340
104. Agelidis AM and Shukla D. Cell entry mechanisms of HSV: what we have learned in recent years. Future Virol. (2015) 10:1145–54. doi: 10.2217/fvl.15.85
105. Msaouel P, Opyrchal M, Dispenzieri A, Peng KW, Federspiel MJ, Russell SJ, et al. Clinical trials with oncolytic measles virus: current status and future prospects. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. (2018) 18:177–87. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666170222125035
106. Kleinlutzum D, Hanauer JDS, Muik A, Hanschmann KM, Kays SK, Ayala-Breton C, et al. Enhancing the Oncolytic Activity of CD133-Targeted Measles Virus: Receptor Extension or Chimerism with Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Are Most Effective. Front Oncol. (2017) 7:127. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00127
107. Singleton DC, Mowday AM, Guise CP, Syddall SP, Bai SY, Li D, et al. Bioreductive prodrug PR-104 improves the tumour distribution and titre of the nitroreductase-armed oncolytic adenovirus ONYX-411(NTR) leading to therapeutic benefit. Cancer Gene Ther. (2022) 29:1021–32. doi: 10.1038/s41417-021-00409-2
108. Jeong SN and Yoo SY. Novel Oncolytic Virus Armed with Cancer Suicide Gene and Normal Vasculogenic Gene for Improved Anti-Tumor Activity. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12:1070. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051070
109. Thoidingjam S, Sriramulu S, Freytag S, Brown SL, Kim JH, Chetty IJ, et al. Oncolytic virus-based suicide gene therapy for cancer treatment: a perspective of the clinical trials conducted at Henry Ford Health. Transl Med Commun. (2023) 8:11. doi: 10.1186/s41231-023-00144-w
110. Shokoohi M, Sedaghatshoar S, Arian H, Mokarami M, Habibi F, and Bamarinejad F. Genetic advancements in breast cancer treatment: a review. Discovery Oncol. (2025) 16:127. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01884-x
111. Gan M, Liu N, Li W, Chen M, Bai Z, et al. Metabolic targeting of regulatory T cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma: new horizons in immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:273. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02193-7
112. Goyal P and Rajala MS. Reprogramming of glucose metabolism in virus infected cells. Mol Cell Biochem. (2023) 478:2409–18. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04669-4
113. Wu YY, Sun TK, Chen MS, Munir M, and Liu HJ. Oncolytic viruses-modulated immunogenic cell death, apoptosis and autophagy linking to virotherapy and cancer immune response. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1142172. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1142172
114. Zhang Z, Yang N, Xu L, Lu H, Chen Y, Wang Z, et al. Systemic delivery of oncolytic herpes virus using CAR-T cells enhances targeting of antitumor immuno-virotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2024) 73:173. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03757-8
115. Packiriswamy N, Upreti D, Zhou Y, Khan R, Miller A, Diaz RM, et al. Oncolytic measles virus therapy enhances tumor antigen-specific T-cell responses in patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia. (2020) 34:3310–22. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0828-7
116. Zhong Y, Le H, Zhang X, Dai Y, Guo F, Ran X, et al. Identification of restrictive molecules involved in oncolytic virotherapy using genome-wide CRISPR screening. J Hematol Oncol. (2024) 17:36. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01554-5
117. Eriksson E, Milenova I, Wenthe J, Stahle M, Leja-Jarblad J, Ullenhag G, et al. Shaping the tumor stroma and sparking immune activation by CD40 and 4-1BB signaling induced by an armed oncolytic virus. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:5846–57. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0285
118. Eriksson E, Moreno R, Milenova I, Liljenfeldt L, Dieterich LC, Christiansson L, et al. Activation of myeloid and endothelial cells by CD40L gene therapy supports T-cell expansion and migration into the tumor microenvironment. Gene Ther. (2017) 24:92–103. doi: 10.1038/gt.2016.80
119. Ylosmaki E, Ylosmaki L, Fusciello M, Martins B, Ahokas P, Cojoc H, et al. Characterization of a novel OX40 ligand and CD40 ligand-expressing oncolytic adenovirus used in the PeptiCRAd cancer vaccine platform. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2021) 20:459–69. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.02.006
120. Wenthe J, Naseri S, Hellstrom AC, Wiklund HJ, Eriksson E, and Loskog A. Immunostimulatory oncolytic virotherapy for multiple myeloma targeting 4-1BB and/or CD40. Cancer Gene Ther. (2020) 27:948–59. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-0176-9
121. Chowaniec H, Slubowska A, Mroczek M, Borowczyk M, Braszka M, Dworacki G, et al. New hopes for the breast cancer treatment: perspectives on the oncolytic virus therapy. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1375433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1375433
122. Ghahremanifard P, Chanda A, Bonni S, and Bose P. TGF-beta mediated immune evasion in cancer-spotlight on cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12:3650. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123650
123. Conley AP, Roland CL, Bessudo A, Gastman BR, Villaflor VM, Larson C, et al. BETA prime: a first-in-man phase 1 study of AdAPT-001, an armed oncolytic adenovirus for solid tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. (2024) 31:517–26. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00720-0
124. Kesari S, Bessudo A, Gastman BR, Conley AP, Villaflor VM, Nabell LM, et al. BETA PRIME: Phase I study of AdAPT-001 as monotherapy and combined with a checkpoint inhibitor in superficially accessible, treatment-refractory solid tumors. Future Oncol. (2022) 18:3245–54. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0481
125. Eriksson E, Milenova I, Wenthe J, Moreno R, Alemany R, and Loskog A. IL-6 signaling blockade during CD40-mediated immune activation favors antitumor factors by reducing TGF-beta, collagen Type I, and PD-L1/PD-1. J Immunol. (2019) 202:787–98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800717
126. DePeaux K, Rivadeneira DB, Lontos K, Dean VG, Gunn WG, Watson MJ, et al. An oncolytic virus-delivered TGFbeta inhibitor overcomes the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. J Exp Med. (2023) 220:e20230053. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230053
127. Yu F, Wang X, Guo ZS, Bartlett DL, Gottschalk SM, and Song XT. T-cell engager-armed oncolytic vaccinia virus significantly enhances antitumor therapy. Mol Ther. (2014) 22:102–11. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.240
128. Gao W, Zhao Z, Bi Y, Li J, Tian N, Zhang C, et al. 4-1BBL-Armed Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Exerts Antitumor Effects in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Vaccines (Basel). (2024) 12:1309. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121309
129. Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Wang X, Wang X, Ren S, He X, et al. The investigation of oncolytic viruses in the field of cancer therapy. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1423143. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1423143
130. Bhattacharjee S and Yadava PK. Measles virus: Background and oncolytic virotherapy. Biochem Biophys Rep. (2018) 13:58–62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.12.004
131. Jing Y, Zaias J, Duncan R, Russell SJ, and Merchan JR. In vivo safety, biodistribution and antitumor effects of uPAR retargeted oncolytic measles virus in syngeneic cancer models. Gene Ther. (2014) 21:289–97. doi: 10.1038/gt.2013.84
132. Cristi F, Gutierrez T, Hitt MM, and Shmulevitz M. Genetic Modifications That Expand Oncolytic Virus Potency. Front Mol Biosci 9. (2022). doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.831091
133. Wang S, Li Y, Xu C, Dong J, and Wei J. An oncolytic vaccinia virus encoding hyaluronidase reshapes the extracellular matrix to enhance cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. (2024) 12:e008431. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008431
134. Hernaez B, Tarrago T, Giralt E, Escribano JM, and Alonso C. Small peptide inhibitors disrupt a high-affinity interaction between cytoplasmic dynein and a viral cargo protein. J Virol. (2010) 84:10792–801. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01168-10
135. Stevens DA, Beierschmitt C, Mahesula S, Corley MR, Salogiannis J, Tsu BV, et al. Antiviral function and viral antagonism of the rapidly evolving dynein activating adaptor NINL. Elife. (2022) 11:e81606. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81606
136. Carrieri FA, Smack C, Siddiqui I, Kleinberg LR, and Tran PT. Tumor treating fields: at the crossroads between physics and biology for cancer treatment. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:575992. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.575992
137. Marchini A, Daeffler L, Pozdeev VI, Angelova A, and Rommelaere J. Immune conversion of tumor microenvironment by oncolytic viruses: the protoparvovirus H-1PV case study. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1848. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01848
138. Xiao T, Zheng H, Zu K, Yue Y, and Wang Y. Tumor-treating fields in cancer therapy: advances of cellular and molecular mechanisms. Clin Transl Oncol. (2025) 27:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03551-z
139. Wang Y, Pandey M, and Ballo MT. Integration of tumor-treating fields into the multidisciplinary management of patients with solid malignancies. Oncologist. (2019) 24:e1426–36. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0603
140. Mell LK, Brumund KT, Daniels GA, Advani SJ, Zakeri K, Wright ME, et al. Phase i trial of intravenous oncolytic vaccinia virus (GL-ONC1) with cisplatin and radiotherapy in patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:5696–702. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3232
141. Soldozy S, Skaff A, Soldozy K, Sokolowski JD, Norat P, Yagmurlu K, et al. From Bench to Bedside, the Current State of Oncolytic Virotherapy in Pediatric Glioma. Neurosurgery. (2020) 87:1091–7. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyaa247
142. Jhawar SR, Wang SJ, Thandoni A, Bommareddy PK, Newman JH, Marzo AL, et al. Combination oncolytic virus, radiation therapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment in anti-PD-1-refractory cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006780. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-006780
143. Zhang Z, Liu X, Chen D, and Yu J. Radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy: the dawn of cancer treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:258. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01102-y
144. Chen WY, Chen YL, Lin HW, Chang CF, Huang BS, Sun WZ, et al. Stereotactic body radiation combined with oncolytic vaccinia virus induces potent anti-tumor effect by triggering tumor cell necroptosis and DAMPs. Cancer Lett. (2021) 523:149–61. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.09.040
145. Martinez-Velez N, Marigil M, Garcia-Moure M, Gonzalez-Huarriz M, Aristu JJ, Ramos-Garcia LI, et al. Delta-24-RGD combined with radiotherapy exerts a potent antitumor effect in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and pediatric high grade glioma models. Acta Neuropathol Commun. (2019) 7:64. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0714-6
146. Omolekan TO, Chamcheu JC, Buerger C, and Huang S. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Network in Human Health and Diseases. Cells. (2024) 13:1500. doi: 10.3390/cells13171500
147. Roy T, Boateng ST, Uddin MB, Banang-Mbeumi S, Yadav RK, Bock CR, et al. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR and associated signaling pathways as molecular drivers of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases: update on therapeutic strategy using natural and synthetic compounds. Cells. (2023) 12:1671. doi: 10.3390/cells12121671
148. Chamcheu JC, Roy T, Uddin MB, Banang-Mbeumi S, Chamcheu RN, Walker AL, et al. Role and therapeutic targeting of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in skin cancer: a review of current status and future trends on natural and synthetic agents therapy. Cells. (2019) 8:803. doi: 10.3390/cells8080803
149. Sarwar A, Hashim L, Faisal MS, Haider MZ, Ahmed Z, Ahmed TF, et al. Advances in viral oncolytics for treatment of multiple myeloma - a focused review. Expert Rev Hematol. (2021) 14:1071–83. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2021.1972802
150. Tong Y, Zhu W, Huang X, You L, Han X, Yang C, et al. PI3K inhibitor LY294002 inhibits activation of the Akt/mTOR pathway induced by an oncolytic adenovirus expressing TRAIL and sensitizes multiple myeloma cells to the oncolytic virus. Oncol Rep. (2014) 31:1581–8. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3020
151. Uche IK, Fowlkes N, Vu L, Watanabe T, Carossino M, Nabi R, et al. Novel Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus 1 VC2 Promotes Long-Lasting, Systemic Anti-melanoma Tumor Immune Responses and Increased Survival in an Immunocompetent B16F10-Derived Mouse Melanoma Model. J Virol. (2021) 95:e01359–01320. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01359-20
152. Comins C, Simpson GR, Rogers W, Relph K, Harrington K, Melcher A, et al. Synergistic antitumour effects of rapamycin and oncolytic reovirus. Cancer Gene Ther. (2018) 25:148–60. doi: 10.1038/s41417-018-0011-8
153. Stavrakaki E, Dirven CMF, and Lamfers MLM. Personalizing oncolytic virotherapy for glioblastoma: in search of biomarkers for response. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:614. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040614
154. Ahmadi A, Najafi M, Farhood B, and Mortezaee K. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling: Tumorigenesis and targeting for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:12173–87. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27955
155. Ye T, Jiang K, Wei L, Barr MP, Xu Q, Zhang G, et al. Oncolytic newcastle disease virus induces autophagy-dependent immunogenic cell death in lung cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. (2018) 8:1514–27.
156. Jiang K, Li Y, Zhu Q, Xu J, Wang Y, Deng W, et al. Pharmacological modulation of autophagy enhances Newcastle disease virus-mediated oncolysis in drug-resistant lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer. (2014) 14:551. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-551
157. Tomar VS, Patil V, and Somasundaram K. Temozolomide induces activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in glioma cells via PI3K/Akt pathway: implications in glioma therapy. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2020) 36:273–8. doi: 10.1007/s10565-019-09502-7
158. Saha D, Rabkin SD, and Martuza RL. Temozolomide antagonizes oncolytic immunovirotherapy in glioblastoma. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e000345. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000345
159. Xing F, Xiao J, Wu J, Liang J, Lu X, Guo L, et al. Modulating the tumor microenvironment via oncolytic virus and PI3K inhibition synergistically restores immune checkpoint therapy response in PTEN-deficient glioblastoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6:275. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00609-0
160. Marelli G, Chard Dunmall LS, Yuan M, Di Gioia C, Miao J, Cheng Z, et al. A systemically deliverable Vaccinia virus with increased capacity for intertumoral and intratumoral spread effectively treats pancreatic cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e001624. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001624
161. Zou Z, Tao T, Li H, and Zhu X. mTOR signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer: progress and challenges. Cell Biosci. (2020) 10:31. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00396-1
162. Alexopoulos A, Karanikiotis C, Ardavanis A, Boukovinas I, Makrantonakis P, Papadimitriou C, et al. Safety and efficacy of RAD001 (Everolimus) administered upon relapse during or after adjuvant treatment in post-menopausal women with hormone receptor positive, her2/neu negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer (CRAD001JGR08 "MELPOMENI" study). Anticancer Res. (2022) 42:1031–41. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15564
163. Rahman MM and McFadden G. Oncolytic virotherapy with myxoma virus. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:171. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010171
164. Zakaria C, Sean P, Hoang HD, Leroux LP, Watson M, Workenhe ST, et al. Active-site mTOR inhibitors augment HSV1-dICP0 infection in cancer cells via dysregulated eIF4E/4E-BP axis. PloS Pathog. (2018) 14:e1007264. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007264
165. Gutierrez-Hoya A and Soto-Cruz I. Role of the JAK/STAT pathway in cervical cancer: its relationship with HPV E6/E7 oncoproteins. Cells. (2020) 9:2297. doi: 10.3390/cells9102297
166. Yan Z, Gibson SA, Buckley JA, Qin H, and Benveniste EN. Role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in regulation of innate immunity in neuroinflammatory diseases. Clin Immunol. (2018) 189:4–13. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.09.014
167. Patel MR, Dash A, Jacobson BA, Ji Y, Baumann D, Ismail K, et al. JAK/STAT inhibition with ruxolitinib enhances oncolytic virotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer models. Cancer Gene Ther. (2019) 26:411–8. doi: 10.1038/s41417-018-0074-6
168. Cataldi M, Shah NR, Felt SA, and Grdzelishvili VZ. Breaking resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to an attenuated vesicular stomatitis virus through a novel activity of IKK inhibitor TPCA-1. Virology. (2015) 485:340–54. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.08.003
169. Jackson JD, Markert JM, Li L, Carroll SL, and Cassady KA. STAT1 and NF-kappaB inhibitors diminish basal interferon-stimulated gene expression and improve the productive infection of oncolytic HSV in MPNST Cells. Mol Cancer Res. (2016) 14:482–92. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0427
170. Mahjoor M, Mahmoudvand G, Farokhi S, Shadab A, Kashfi M, and Afkhami H. Double-edged sword of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in viral infections: novel insights into virotherapy. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:272. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01240-y
171. Zhang P, Liu Y, Jia L, Ci Z, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. SP600125, a JNK-specific inhibitor, regulates in vitro auricular cartilage regeneration by promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting extracellular matrix metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:630678. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.630678
172. Hafner A, Bulyk ML, Jambhekar A, and Lahav G. The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 20:199–210. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0110-x
173. Marei HE, Althani A, Afifi N, Hasan A, Caceci T, Pozzoli G, et al. p53 signaling in cancer progression and therapy. Cancer Cell Int. (2021) 21:703. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02396-8
174. Spirito F, Nocini R, Mori G, Albanese M, Georgakopoulou EA, Sivaramakrishnan G, et al. The potential of oncolytic virotherapy in the treatment of head and neck cancer: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:12990. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312990
175. Zhu H, Gao H, Ji Y, Zhou Q, Du Z, Tian L, et al. Targeting p53-MDM2 interaction by small-molecule inhibitors: learning from MDM2 inhibitors in clinical trials. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:91. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01314-3
176. Yao Y, Zhang Q, Li Z, and Zhang H. MDM2: current research status and prospects of tumor treatment. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24:170. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03356-8
177. Konopleva M, Martinelli G, Daver N, Papayannidis C, Wei A, Higgins B, et al. MDM2 inhibition: an important step forward in cancer therapy. Leukemia. (2020) 34:2858–74. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0949-z
178. Du Z and Lovly CM. Mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cancer. Mol Cancer 17. (2018). doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0782-4
179. Wu Z, Ichinose T, Naoe Y, Matsumura S, Villalobos IB, Eissa IR, et al. Combination of cetuximab and oncolytic virus canerpaturev synergistically inhibits human colorectal cancer growth. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2019) 13:107–15. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2019.04.004
180. Deng H, Liu W, He T, Hong Z, Yi F, Wei Y, et al. Comparative efficacy, safety, and costs of sorafenib vs. sunitinib as first-line therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:479. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00479
181. Zhu Z, McGray AJR, Jiang W, Lu B, Kalinski P, and Guo ZS. Improving cancer immunotherapy by rationally combining oncolytic virus with modulators targeting key signaling pathways. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:196. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01664-z
182. Lawson KA, Mostafa AA, Shi ZQ, Spurrell J, Chen W, Kawakami J, et al. Repurposing sunitinib with oncolytic reovirus as a novel immunotherapeutic strategy for renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:5839–50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0143
183. Kim M, Nitschke M, Sennino B, Murer P, Schriver BJ, Bell A, et al. Amplification of oncolytic vaccinia virus widespread tumor cell killing by sunitinib through multiple mechanisms. Cancer Res. (2018) 78:922–37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3308
184. Moehler M, Heo J, Lee HC, Tak WY, Chao Y, Paik SW, et al. Vaccinia-based oncolytic immunotherapy Pexastimogene Devacirepvec in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after sorafenib failure: a randomized multicenter Phase IIb trial (TRAVERSE). Oncoimmunology. (2019) 8:1615817. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1615817
185. Abou-Alfa GK, Galle PR, Chao Y, Erinjeri J, Heo J, et al. PHOCUS: a phase 3, randomized, open-label study of sequential treatment with pexa-vec (JX-594) and sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. (2024) 13:248–64. doi: 10.1159/000533650
186. Fujiwara T, Yakoub MA, Chandler A, Christ AB, Yang G, Ouerfelli O, et al. CSF1/CSF1R signaling inhibitor pexidartinib (PLX3397) reprograms tumor-associated macrophages and stimulates t-cell infiltration in the sarcoma microenvironment. Mol Cancer Ther. (2021) 20:1388–99. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0591
187. Cai J, Lin K, Cai W, Lin Y, Liu X, Guo L, et al. Tumors driven by RAS signaling harbor a natural vulnerability to oncolytic virus M1. Mol Oncol. (2020) 14:3153–68. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12820
188. Roulstone V, Pedersen M, Kyula J, D. Mansfield AA, McEntee G, et al. BRAF- and MEK-targeted small molecule inhibitors exert enhanced antimelanoma effects in combination with oncolytic reovirus through er stress. Mol Ther 23. (2015). doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.15
189. Bommareddy PK, Aspromonte S, Zloza A, Rabkin SD, and Kaufman HL. MEK inhibition enhances oncolytic virus immunotherapy through increased tumor cell killing and T cell activation. Sci Transl Med. (2018) 10:eaau0417. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau0417
190. Lee S, Yang W, Kim DK, Kim H, Shin M, Choi KU, et al. Inhibition of MEK-ERK pathway enhances oncolytic vaccinia virus replication in doxorubicin-resistant ovarian cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2022) 25:211–24. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.04.006
191. Osipov A, Saung MT, Zheng L, and Murphy AG. Small molecule immunomodulation: the tumor microenvironment and overcoming immune escape. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:224. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0667-0
192. Spiesschaert B, Angerer K, Park J, and Wollmann G. Combining Oncolytic Viruses and Small Molecule Therapeutics: Mutual Benefits. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:3386. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143386
193. Andreu S, Ripa I, Bello-Morales R, and Lopez-Guerrero JA. Valproic Acid and Its Amidic Derivatives as New Antivirals against Alphaherpesviruses. Viruses. (2020) 12:1356. doi: 10.3390/v12121356
194. Gotfryd K, Skladchikova G, Lepekhin EA, Berezin V, Bock E, and Walmod PS. Cell type-specific anti-cancer properties of valproic acid: independent effects on HDAC activity and Erk1/2 phosphorylation. BMC Cancer. (2010) 10:383. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-383
195. Roskoski R Jr.. Sunitinib: a VEGF and PDGF receptor protein kinase and angiogenesis inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2007) 356:323–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.156
196. Oku M, Ishino R, Uchida S, Imataki O, Sugimoto N, Todo T, et al. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) in combination with lenalidomide for plasma cell neoplasms. Br J Haematol. (2021) 192:343–53. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17173
197. Fink EC and Ebert BL. The novel mechanism of lenalidomide activity. Blood. (2015) 126:2366–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-567958
198. Hsu AK, Quach H, Tai T, Prince HM, Harrison SJ, Trapani JA, et al. The immunostimulatory effect of lenalidomide on NK-cell function is profoundly inhibited by concurrent dexamethasone therapy. Blood. (2011) 117:1605–13. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-278432
199. Kater AP, Tonino SH, Egle A, and Ramsay AG. How does lenalidomide target the chronic lymphocytic leukemia microenvironment? Blood. (2014) 124:2184–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-578286
200. Thorn CF, Oshiro C, Marsh S, Hernandez-Boussard T, McLeod H, Klein TE, et al. Doxorubicin pathways: pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet Genomics. (2011) 21:440–6. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e32833ffb56
201. Bartee E. Potential of oncolytic viruses in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Oncolytic Virother. (2017) 7:1–12. doi: 10.2147/OV.S136644
202. Lane HA and Lebwohl D. Future directions in the treatment of hormone-sensitive advanced breast cancer: the RAD001 (Everolimus)-letrozole clinical program. Semin Oncol. (2006) 33:S18–25. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.03.024
203. Zhou X, Wang Y, Metselaar HJ, Janssen HL, Peppelenbosch MP, and Pan Q. Rapamycin and everolimus facilitate hepatitis E virus replication: revealing a basal defense mechanism of PI3K-PKB-mTOR pathway. J Hepatol. (2014) 61:746–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.026
204. Kampan NC, Madondo MT, McNally OM, Quinn M, and Plebanski M. Paclitaxel and its evolving role in the management of ovarian cancer. BioMed Res Int. (2015) 2015:413076. doi: 10.1155/2015/413076
205. Noonan AM, Farren MR, Geyer SM, Huang Y, Tahiri S, Ahn D, et al. Randomized phase 2 trial of the oncolytic virus pelareorep (reolysin) in upfront treatment of metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mol Ther. (2016) 24:1150–8. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.66
206. Liew YX, Karen-Ng LP, and Vincent-Chong VK. A comprehensive review of natural products as therapeutic or chemopreventive agents against head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells using preclinical models. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:2359. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092359
207. Ciccolini J, Serdjebi C, Peters GJ, and Giovannetti E. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics of Gemcitabine as a mainstay in adult and pediatric oncology: an EORTC-PAMM perspective. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2016) 78:1–12. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3003-0
208. Jazowiecka-Rakus J, Sochanik A, Hadrys A, Fidyk W, Chmielik E, Rahman MM, et al. Combination of LIGHT (TNFSF14)-Armed Myxoma Virus Pre-Loaded into ADSCs and Gemcitabine in the Treatment of Experimental Orthotopic Murine Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:2022. doi: 10.3390/cancers14082022
209. Falzone L, Salomone S, and Libra M. Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the third millennium. Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:1300. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01300
210. Kerr WG and Chisholm JD. The next generation of immunotherapy for cancer: small molecules could make big waves. J Immunol. (2019) 202:11–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800991
211. Bahl S and Seto E. Regulation of histone deacetylase activities and functions by phosphorylation and its physiological relevance. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 78:427–45. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03599-4
212. Moreno-Gonzalo O, Ramirez-Huesca M, Blas-Rus N, Cibrian D, Saiz ML, Jorge I, et al. HDAC6 controls innate immune and autophagy responses to TLR-mediated signalling by the intracellular bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. PloS Pathog. (2017) 13:e1006799. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006799
213. Sinha P, Cree SL, Miller AL, Pearson JF, and Kennedy MA. Transcriptional analysis of sodium valproate in a serotonergic cell line reveals gene regulation through both HDAC inhibition-dependent and independent mechanisms. Pharmacogenomics J. (2021) 21:359–75. doi: 10.1038/s41397-021-00215-x
214. Bretscher C and Marchini A. H-1 parvovirus as a cancer-killing agent: past, present, and future. Viruses. (2019) 11:562. doi: 10.3390/v11060562
215. Muscolini M, Castiello L, Palermo E, Zevini A, Ferrari M, Olagnier D, et al. SIRT1 modulates the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to vesicular stomatitis virus oncolysis. J Virol. (2019) 93:e00626–00619. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00626-19
216. LaRocca CJ and Warner SG. Oncolytic viruses and checkpoint inhibitors: combination therapy in clinical trials. Clin Transl Med. (2018) 7:35. doi: 10.1186/s40169-018-0214-5
217. Ressler JM, Karasek M, Koch L, Silmbrod R, Mangana J, Latifyan S, et al. Real-life use of talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC) in melanoma patients in centers in Austria, Switzerland and Germany. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e001701. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001701
218. Zhang T, Jou TH, Hsin J, Wang Z, Huang K, Ye J, et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC): A Review of the Recent Advances in Cancer Therapy. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1098. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031098
219. Andtbacka RH, Kaufman HL, Collichio F, Amatruda T, Senzer N, Chesney J, et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec Improves Durable Response Rate in Patients With Advanced Melanoma. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:2780–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.3377
220. Rehman H, Silk AW, Kane MP, and Kaufman HL. Into the clinic: talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC), a first-in-class intratumoral oncolytic viral therapy. J Immunother Cancer. (2016) 4:53. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0158-5
221. Chesney J, Puzanov I, Collichio F, Singh P, Milhem MM, Glaspy J, et al. Randomized, Open-Label Phase II Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Talimogene Laherparepvec in Combination With Ipilimumab Versus Ipilimumab Alone in Patients With Advanced, Unresectable Melanoma. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:1658–67. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.7379
222. Chesney JA, Puzanov I, Collichio FA, Singh P, Milhem MM, Glaspy J, et al. Talimogene laherparepvec in combination with ipilimumab versus ipilimumab alone for advanced melanoma: 5-year final analysis of a multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase II trial. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006270. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006270
223. Zhou Y, Wei Y, Tian X, and Wei X. Cancer vaccines: current status and future directions. J Hematol Oncol. (2025) 18:18. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01670-w
224. Dong H, Li M, Yang C, Wei W, He X, Cheng G, et al. Combination therapy with oncolytic viruses and immune checkpoint inhibitors in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: an approach of complementary advantages. Cancer Cell Int. (2023) 23:1. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02846-x
225. Zhang QN, Li Y, Zhao Q, Tian M, Chen LL, Miao LY, et al. Recombinant human adenovirus type 5 (Oncorine) reverses resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor in a patient with recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: A case report. Thorac Cancer. (2021) 12:1617–9. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13947
226. Zhang Y, Gabere M, Taylor MA, Simoes CC, Dumbauld C, Barro O, et al. Repurposing live attenuated trivalent MMR vaccine as cost-effective cancer immunotherapy. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:1042250. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1042250
227. Clark CM, Jambunathan N, Collantes TMA, and Kousoulas KG. Inactivation of the UL37 Deamidase Enhances Virus Replication and Spread of the HSV-1(VC2) Oncolytic Vaccine Strain and Secretion of GM-CSF. Viruses. (2023) 15:367. doi: 10.3390/v15020367
228. Nabi R, Musarrat F, Menk PLJC, Langohr IM, Chouljenko VN, and Kousoulas KG. The Oncolytic herpes simplex virus type-1 (HSV-1) vaccine strain VC2 causes intratumor infiltration of functionally active T cells and inhibition of tumor metastasis and pro-tumor genes VEGF and PDL1 expression in the 4T1/Balb/c mouse model of stage four breast cancer. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10:1199068. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1199068
229. Stanfield B and Kousoulas KG. Herpes simplex vaccines: prospects of live-attenuated hsv vaccines to combat genital and ocular infections. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. (2015) 2:125–36. doi: 10.1007/s40588-015-0020-4
230. Chang C, Chavarro VS, Gerstl JVE, Blitz SE, Spanehl L, Dubinski D, et al. Recurrent glioblastoma-molecular underpinnings and evolving treatment paradigms. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6733. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126733
231. Streby KA, Geller JI, Currier MA, Warren PS, Racadio JM, Towbin AJ, et al. Intratumoral injection of HSV1716, an oncolytic herpes virus, is safe and shows evidence of immune response and viral replication in young cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:3566–74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2900
232. Dispenzieri A, Tong C, LaPlant B, Lacy MQ, Laumann K, Dingli D, et al. Phase I trial of systemic administration of Edmonston strain of measles virus genetically engineered to express the sodium iodide symporter in patients with recurrent or refractory multiple myeloma. Leukemia. (2017) 31:2791–8. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.120
233. Vandeborne L, Pantziarka P, and Van Nuffel AMT. Repurposing Infectious Diseases Vaccines Against Cancer. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:688755. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.688755
234. Bommareddy PK, Wakimoto H, Martuza RL, Kaufman HL, Rabkin SD, and Saha D. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus expressing IL-2 controls glioblastoma growth and improves survival. J Immunother Cancer. (2024) 12:e008880. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-008880
235. Downs-Canner S, Guo ZS, Ravindranathan R, Breitbach CJ, O'Malley ME, Jones HL, et al. Phase 1 study of intravenous oncolytic poxvirus (vvDD) in patients with advanced solid cancers. Mol Ther. (2016) 24:1492–501. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.101
236. Zhang Y, Qian L, Chen K, Gu S, Wang J, Meng Z, et al. Intraperitoneal oncolytic virotherapy for patients with malignant ascites: Characterization of clinical efficacy and antitumor immune response. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2022) 25:31–42. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.03.003
237. Kardani K, Sanchez Gil J, and Rabkin SD. Oncolytic herpes simplex viruses for the treatment of glioma and targeting glioblastoma stem-like cells. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1206111. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1206111
238. Ortega JA, Liang Z, Xu JK, and Gottwein E. Retargeting target-directed microRNA-decay sites to highly expressed viral or cellular miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. (2024) 52:14171–83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1103
239. Villalona-Calero MA, Lam E, Otterson GA, Zhao W, Timmons M, Subramaniam D, et al. Oncolytic reovirus in combination with chemotherapy in metastatic or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer patients with KRAS-activated tumors. Cancer. (2016) 122:875–83. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29856
240. Yoo JY, Jaime-Ramirez AC, Bolyard C, Dai H, Nallanagulagari T, Wojton J, et al. Bortezomib treatment sensitizes oncolytic HSV-1-treated tumors to nk cell immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:5265–76. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1003
241. Soko GF, Kosgei BK, Meena SS, Ng YJ, Liang H, Zhang B, et al. Extracellular matrix re-normalization to improve cold tumor penetration by oncolytic viruses. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1535647. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1535647
242. Garcia-Carbonero R, Salazar R, Duran I, Osman-Garcia I, Paz-Ares L, Bozada JM, et al. Phase 1 study of intravenous administration of the chimeric adenovirus enadenotucirev in patients undergoing primary tumor resection. J Immunother Cancer. (2017) 5:71. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0277-7
243. Koske I, Rossler A, Pipperger L, Petersson M, Barnstorf I, Kimpel J, et al. Oncolytic virotherapy enhances the efficacy of a cancer vaccine by modulating the tumor microenvironment. Int J Cancer. (2019) 145:1958–69. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32325
244. Bartlett DL, Liu Z, Sathaiah M, Ravindranathan R, Guo Z, He Y, et al. Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Mol Cancer. (2013) 12:103. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-103
245. Li M, Zhang M, Ye Q, Liu Y, and Qian W. Preclinical and clinical trials of oncolytic vaccinia virus in cancer immunotherapy: a comprehensive review. Cancer Biol Med. (2023) 20:646–61. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0202
246. Nabi R, Lewin AC, Collantes TM, Chouljenko VN, and Kousoulas KG. Intramuscular vaccination with the HSV-1(VC2) live-attenuated vaccine strain confers protection against viral ocular immunopathogenesis associated with gammadeltaT cell intracorneal infiltration. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:789454. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.789454
247. Index. A Comprehensive Guide to Toxicology in Nonclinical Drug Development (Second Edition) Vol. pp. Ali Said F, editor. Boston: Academic Press (2017) p. 939–71.
248. Shekarian T, Sivado E, Jallas AC, Depil S, Kielbassa J, Janoueix-Lerosey I, et al. Repurposing rotavirus vaccines for intratumoral immunotherapy can overcome resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Sci Transl Med. (2019) 11. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat5025
249. Allegra A, Mirabile G, Ettari R, Pioggia G, and Gangemi S. The impact of curcumin on immune response: an immunomodulatory strategy to treat sepsis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:14710. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314710
250. Nicoliche T, Bartolomeo CS, Lemes RMR, Pereira GC, Nunes TA, Oliveira RB, et al. Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin and curcuminoids in SH-SY5Y cells infected by SARS-CoV-2. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:10696. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61662-7
251. Mortezaee K, Salehi E, Mirtavoos-Mahyari H, Motevaseli E, Najafi M, Farhood B, et al. Mechanisms of apoptosis modulation by curcumin: Implications for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:12537–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28122
252. Liao MT, Wu CC, Wu SV, Lee MC, Hu WC, Tsai KW, et al. Resveratrol as an Adjunctive Therapy for Excessive Oxidative Stress in Aging COVID-19 Patients. Antioxidants (Basel). (2021) 10:1440. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091440
253. Alkharsah KR. VEGF upregulation in viral infections and its possible therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:1642. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061642
254. Barnhart AS, Anthony AL, Conaway KR, Sibbitt BG, Delaney E, Haluschak J, et al. Safety and efficacy of Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and selenium supplementation in the oncology setting: A systematic review. J Oncol Pharm Pract. (2024) 30:678–96. doi: 10.1177/10781552231182362
255. Zou H, Zheng YF, Ge W, Wang SB, and Mou XZ. Synergistic Anti-tumour Effects of Quercetin and Oncolytic Adenovirus expressing TRAIL in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:2182. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20213-7
256. Warowicka A, Nawrot R, and Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A. Antiviral activity of berberine. Arch Virol. (2020) 165:1935–45. doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04706-3
257. Giacobbe J, Benoiton B, Zunszain P, Pariante CM, and Borsini A. The anti-inflammatory role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolites in pre-clinical models of psychiatric, neurodegenerative, and neurological disorders. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:122. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00122
258. Nabavi SF, Bilotto S, Russo GL, Orhan IE, Habtemariam S, Daglia M, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cancer: lessons learned from clinical trials. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2015) 34:359–80. doi: 10.1007/s10555-015-9572-2
259. Soliman H, Hogue D, Han H, Mooney B, Costa R, Lee MC, et al. A phase i trial of talimogene laherparepvec in combination with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for the treatment of nonmetastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:1012–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3105
260. Bourgeois-Daigneault MC, St-Germain LE, Roy DG, Pelin A, Aitken AS, Arulanandam R, et al. Combination of Paclitaxel and MG1 oncolytic virus as a successful strategy for breast cancer treatment. Breast Cancer Res. (2016) 18:83. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0744-y
261. Garofalo M, Saari H, Somersalo P, Crescenti D, Kuryk L, Aksela L, et al. Antitumor effect of oncolytic virus and paclitaxel encapsulated in extracellular vesicles for lung cancer treatment. J Control Release. (2018) 283:223–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.05.015
262. Chen W, Fan W, Ru G, Huang F, Lu X, Zhang X, et al. Gemcitabine combined with an engineered oncolytic vaccinia virus exhibits a synergistic suppressive effect on the tumor growth of pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep. (2019) 41:67–76. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6817
263. Jung KH, Choi IK, Lee HS, Yan HH, Son MK, Ahn HM, et al. Oncolytic adenovirus expressing relaxin (YDC002) enhances therapeutic efficacy of gemcitabine against pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. (2017) 396:155–66. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.009
264. Hirooka Y, Kasuya H, Ishikawa T, Kawashima H, Ohno E, Villalobos IB, et al. A Phase I clinical trial of EUS-guided intratumoral injection of the oncolytic virus, HF10 for unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. (2018) 18:596. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4453-z
265. Garcia-Carbonero R, Bazan-Peregrino M, Gil-Martin M, Alvarez R, Macarulla T, Riesco-Martinez MC, et al. multicenter, open-label study of intravenous VCN-01 oncolytic adenovirus with or without nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e003255. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003255
266. Cheng PH, Lian S, Zhao R, Rao XM, McMasters KM, and Zhou HS. Combination of autophagy inducer rapamycin and oncolytic adenovirus improves antitumor effect in cancer cells. Virol J. (2013) 10:293. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-293
267. Mahalingam D, Wilkinson GA, Eng KH, Fields P, Raber P, Moseley JL, et al. Pembrolizumab in combination with the oncolytic virus pelareorep and chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a phase ib study. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:71–81. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2078
268. Tchounwou PB, Dasari S, Noubissi FK, Ray P, and Kumar S. Advances in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of action of cisplatin in cancer therapy. J Exp Pharmacol. (2021) 13:303–28. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S267383
269. Nounamo B, Liem J, Cannon M, and Liu J. Myxoma virus optimizes cisplatin for the treatment of ovarian cancer in vitro and in a syngeneic murine dissemination model. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2017) 6:90–9. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2017.08.002
270. Mooney R, Majid AA, Batalla-Covello J, Machado D, Liu X, Gonzaga J, et al. Enhanced delivery of oncolytic adenovirus by neural stem cells for treatment of metastatic ovarian cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2019) 12:79–92. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2018.12.003
271. Lv Y, Zhang CD, Wang YL, Zhou DM, Zhu MY, Hao XQ, et al. Synergism of rMV-Hu191 with cisplatin to treat gastric cancer by acid sphingomyelinase-mediated apoptosis requiring integrity of lipid raft microdomains. Gastric Cancer. (2021) 24:1293–306. doi: 10.1007/s10120-021-01210-8
272. Igase M, Shibutani S, Kurogouchi Y, Fujiki N, Hwang CC, Coffey M, et al. Combination therapy with reovirus and ATM inhibitor enhances cell death and virus replication in canine melanoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2019) 15:49–59. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2019.08.003
273. Davern M, RM OB, McGrath J, Donlon NE, Melo AM, Buckley CE, et al. PD-1 blockade enhances chemotherapy toxicity in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:3259. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07228-x
274. Mao L, Yu H, Ma S, Xu Z, Wei F, Yang C, et al. Combination of oncolytic adenovirus targeting SATB1 and docetaxel for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Cancer. (2021) 12:1846–52. doi: 10.7150/jca.46868
275. Dobson CC, Naing T, Beug ST, Faye MD, Chabot J, St-Jean M, et al. Oncolytic virus synergizes with Smac mimetic compounds to induce rhabdomyosarcoma cell death in a syngeneic murine model. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:3495–508. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13849
276. Dona AA, Tandoh T, Nigam L, Singer M, Caserta E, Murtadha M, et al. Proteasome inhibition enhances oncolytic reovirus therapy in multiple myeloma independently of its direct cytotoxic effects. J Hematol Oncol. (2025) 18:1. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01645-3
277. Thirukkumaran CM, Shi ZQ, Neri P, Bahlis N, and Morris D. Reovirus synergy with proteosome inhibitor carfilzomib and Akt inhibitor perifisone overcomes therapy resistance of multiple myeloma: promising preclinical activity. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:1709–9.
278. Gulla A, Morelli E, Samur MK, Botta C, Hideshima T, Bianchi G, et al. Bortezomib induces anti-multiple myeloma immune response mediated by cGAS/STING pathway activation. Blood Cancer Discovery. (2021) 2:468–83. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-21-0047
279. Aspirin AP, de Los Reyes VA, and Kim Y. Polytherapeutic strategies with oncolytic virus-bortezomib and adjuvant NK cells in cancer treatment. J R Soc Interface. (2021) 18:20200669. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2020.0669
280. Yoo JY, Hurwitz BS, Bolyard C, Yu JG, Zhang J, Selvendiran K, et al. Bortezomib-induced unfolded protein response increases oncolytic HSV-1 replication resulting in synergistic antitumor effects. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20:3787–98. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0553
281. Berghauser Pont LM, Kleijn A, Kloezeman JJ, van den Bossche W, Kaufmann JK, de Vrij J, et al. The HDAC Inhibitors Scriptaid and LBH589 Combined with the Oncolytic Virus Delta24-RGD Exert Enhanced Anti-Tumor Efficacy in Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Cells. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0127058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127058
282. Smalley Rumfield C, Roller N, Pellom ST, Schlom J, and Jochems C. Therapeutic Vaccines for HPV-Associated Malignancies. Immunotargets Ther. (2020) 9:167–200. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S273327
283. Chodkowska A, Bienkowska A, Slyk Z, Giebultowicz J, and Malecki M. Anticancer activity of topical ointments with histone deacetylase inhibitor, trichostatin A. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2020) 29:1039–49. doi: 10.17219/acem/124439
284. Liu TC, Castelo-Branco P, Rabkin SD, and Martuza RL. Trichostatin A and oncolytic HSV combination therapy shows enhanced antitumoral and antiangiogenic effects. Mol Ther. (2008) 16:1041–7. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.58
285. Katsura T, Iwai S, Ota Y, Shimizu H, Ikuta K, and Yura Y. The effects of trichostatin A on the oncolytic ability of herpes simplex virus for oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. (2009) 16:237–45. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2008.81
286. Santaguida S. Two decades of chromosomal instability and aneuploidy. Chromosome Res. (2024) 32:4. doi: 10.1007/s10577-024-09748-w
287. Chianese A, Santella B, Ambrosino A, Stelitano D, Rinaldi L, Galdiero M, et al. Oncolytic Viruses in Combination Therapeutic Approaches with Epigenetic Modulators: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:2761. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112761
288. White LG, Goy HE, Rose AJ, and McLellan AD. Controlling cell trafficking: addressing failures in CAR T and NK cell therapy of solid tumours. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:978. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040978
Keywords: oncolytic viruses, engineered viruses, cancer immunotherapy, combination therapy, immune evasion, pharmacological treatment, tumor targeting, cancer therapy
Citation: Omolekan TO, Folahan JT, Tesfay MZ, Mohan H, Dutta O, Rahimian L, Ferdous KU, Ghavimi R, Cios A, Beng TK, Francis J, D'Auvergne O, Borad MJ, Kousoulas KG, DiGiuseppe S, Nagalo BM and Chamcheu JC (2025) Viral warfare: unleashing engineered oncolytic viruses to outsmart cancer’s defenses. Front. Immunol. 16:1618751. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1618751
Received: 26 April 2025; Accepted: 30 July 2025;
Published: 25 August 2025.
Edited by:
Tilman Sanchez-Elsner, University of Southampton, United KingdomReviewed by:
Jia Yao, Emory University, United StatesYanhua Gao, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Copyright © 2025 Omolekan, Folahan, Tesfay, Mohan, Dutta, Rahimian, Ferdous, Ghavimi, Cios, Beng, Francis, D'Auvergne, Borad, Kousoulas, DiGiuseppe, Nagalo and Chamcheu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jean Christopher Chamcheu, amVhbmNocmlzdG9waGVyLmNAc3Vici5lZHU=; amNoYW1jaGV1QGxzdS5lZHU=
†ORCID: Jean Christopher Chamcheu, orcid.org/0000-0002-3927-5664
 Tolulope O. Omolekan
Tolulope O. Omolekan Joy T. Folahan
Joy T. Folahan Mulu Z. Tesfay
Mulu Z. Tesfay Harikrishnan Mohan
Harikrishnan Mohan Ojasvi Dutta1
Ojasvi Dutta1 Leila Rahimian
Leila Rahimian Reza Ghavimi
Reza Ghavimi Joseph Francis
Joseph Francis Mitesh J. Borad
Mitesh J. Borad Konstantin G. Kousoulas
Konstantin G. Kousoulas Stephen DiGiuseppe
Stephen DiGiuseppe Bolni Marius Nagalo
Bolni Marius Nagalo Jean Christopher Chamcheu
Jean Christopher Chamcheu