- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Common Infectious Disease Prevention and Control in Ningxia, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 3School of Inspection, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 4School of Basic Medical Sciences, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
- 5General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
Introduction: Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is a globally distributed zoonotic disease caused by Echinococcus granulosus (Eg) that often presents with insidious onset and asymptomatic progression. Although several Eg-based recombinant vaccines have been developed for the prevention of CE, our previous study demonstrated that recombinant Eg.P29 (rEg.P29) is a potent immunogen that induces a robust Th1 immune response. Furthermore, microarray data from miRNA profiling of CD4+T cells isolated from mouse spleens showed that miR-378a-5p was significantly upregulated one week after immunization with rEg.P29.
Methods: In this context, bioinformatics predictions and dual-luciferase reporter assays identified BRAF as a direct miR-378a-5p target, with downstream signaling involving the MAPK/ERK pathway.
Results: Our research demonstrated that rEg.P29 immunization increased miR-378a-5p expression in naïve CD4+T cells, reduced BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 expression, and promoted Th1 differentiation while inhibiting Th2 differentiation. Overexpression of miR-378a-5p in naïve CD4+T cells yielded similar results, whereas knockdown of miR-378a-5p had the opposite effect.
Conclusion: In summary, our findings reveal that under the induction of rEg.P29, miR-378a-5p targeted to BRAF regulation and initiated the differentiation of CD4+T cells in mouse spleen to Th1 direction, and MAPK/ERK pathway may be involved in this process, identifying miR-378a-5p as apotential biomarker and immunomodulatory target in CE.
1 Introduction
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is a zoonotic parasitic disease caused by the larval forms of Echinococcus tapeworms. It is common in livestock-raising regions such as Central Asia, North and Central Africa, and southwestern Latin America (1). In China, it is primarily found in the western regions, including Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu, Ningxia, and Tibet (2, 3). This disease leads to significant health and economic losses for both humans and animals (4–6).
The life cycle of Echinococcus spp. involves two types of mammals. CE often causes no apparent symptoms in its early stages and can remain undetected in the host for extended periods (7–9). Current clinical diagnoses of cystic CE largely rely on imaging techniques, which hinders early diagnosis, as hydatid cysts in the liver are slow growing (10). Therapeutic strategies for cystic CE primarily involve surgical intervention and pharmacological treatment; however, complete clinical recovery remains difficult due to the high recurrence rate and potential complications associated with both modalities (11–13). Therefore, vaccine development is essential for preventing CE. For example, Eg95 provides 96%–98% protection in sheep (14), and rEg.P29 shows 96.6% and 94.5% protective rates in mice and sheep, respectively (15–17). rEg.P29 induces both humoral and cellular immune responses, stimulating high levels of specific antibodies and promoting Th1 differentiation, which produces IFN-γ and other cytokines to eliminate pathogens (18, 19). However, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying rEg.P29-mediated immunomodulation remain unknown. This study aimed to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying CD4+T cells differentiation and the associated signaling pathways involved in this immunomodulatory process.
When infected by Echinococcus larvae, the host mounts a sophisticated immunological response. CD4+T cells are crucial in the interaction between Echinococcus and its host (20–23). In response to pathogen invasion, naïve CD4+T cells develop into Th1 and Th2 cells, with Th cell differentiation and activation having a substantial influence on the outcome of the immune response (24–26).
MicroRNAs, single-stranded non-coding RNAs approximately 22 nucleotides long, are widely expressed in cells. They mainly bind to the 3’ untranslated region of target genes to degrade mRNA or inhibit translation, thereby regulating gene expression (27–31). Recent studies have demonstrated that miRNAs are involved in various diseases (32–36), including host responses to parasitic infections, by modulating gene expression to evade immune defenses (37–40). They also regulate CD4+T cells development, proliferation, and differentiation during viral and parasitic infections (41, 42).
Previous laboratory studies established both hydatid infection and rEg.P29 immunization models, and next-generation sequencing identified miR-378a-5p as significantly upregulated. To further investigate this, target gene prediction tools such as TargetScan, miRDB, and miRWALK suggested that miR-378a-5p may regulate BRAF. Further exploration using the online STRING platform revealed that BRAF is an upstream molecule in the MAPK/ERK pathway. Based on these findings, this study explores the regulation of the miR-378a-5p/BRAF/MAPK-ERK axis in Th1 differentiation of naïve CD4+T cells in response to rEg.P29-induced immune reactions and identifies miR-378a-5p as a potential biomarker and immunomodulatory target for CE.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animals
Female BALB/c mice measuring 18–25 g at 6–8 weeks of age were acquired from Ningxia Medical University’s Experimental Animal Centre. The mice were kept at 22°C in a specialized pathogen-free (SPF) environment. All experimental protocols, including euthanasia (Sodium pentobarbital (≥100 ug/kg IP) combo followed by exsanguination), were strictly carried out in accordance with the Ningxia Medical University’s Animal Welfare Guidelines.
2.2 Expression, purification, and endotoxin removal of rEg.P29
Our laboratory was able to effectively synthesize and recombine the Eg.P29 gene from Echinococcus granulosus obtained from Escherichia coli (16). The recombinant strain harboring the Eg.P29 gene was initially streaked onto LB agar plates supplemented with kanamycin and incubated overnight at 37°C to obtain single colonies. A single colony was inoculated into kanamycin-containing LB broth and cultured at 37°C with shaking at 200 rpm for approximately 12 h until visible turbidity was observed. The culture was scaled up until the bacterial cells reached the logarithmic growth phase, as indicated by an OD600 value of 0.6, at which point isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added to induce Eg.P29 expression. Following induction, the cells were harvested by centrifugation, treated with lysozyme and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), and lysed by sonication. A pre-equilibrated resin suspension was combined with the supernatant and incubated overnight at 4 °C under mild agitation. The recombinant Eg.P29 protein was purified using affinity chromatography. Subsequently, endotoxins were eliminated from purified protein and used in animal immunization experiments.
2.3 Establishment of a mouse model immunization of rEg.P29
In the rEg.P29 vaccination experiment, 21 female BALB/c mice (6–8 weeks old) were randomly assigned to three groups: phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA), and rEg.P29+FCA. The mice in the PBS group received 100 uL of PBS, the FCA group received 20 μg of FCA diluted with 100 uL of PBS, and the rEg.P29+FCA group received 20 μg rEg.P29 and 20 μg of FCA in 100 uL of PBS. To minimize protein degradation during emulsification, the adjuvant and PBS were pre-emulsified briefly before adding the proteins, and the protocol was conducted on ice. The emulsified mixture was then loaded into a 1 mL syringe for immunization. The immunization protocol consisted of two stages, primary and booster immunizations. For booster immunization, Freund’s incomplete adjuvant (FIA) was used instead of FCA. Both primary and booster immunizations were administered via a subcutaneous three-point injection.
2.4 Isolation of CD4+T cells and naive CD4+T cells
Mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation and soaked in 75% alcohol. Sterile spleens were then obtained by removing the epidermis. Lymphocytes were isolated from the spleen using a mouse spleen lymphocyte separation medium kit (Tianjin HaoYang Biological Manufacture Co., Ltd., China). Subsequently, CD4+T cells were purified from the lymphocytes using a mouse Cells isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Inc., Cologne, Germany), briefly, lymphocytes (1×107 cells) were labeled with Biotin-Antibody Cocktail in 40 μL MACS buffer (4°C, 5 min), followed by incubation with Anti-Biotin MicroBeads (20 μL in 20 μL buffer; 4°C, 10 min). Cells were separated through pre-wetted MS columns mounted on a magnetic stand over ice. After centrifugation (350 × g, 10 min, 4°C), purified cells were resuspended in complete RPMI-1640 medium for subsequent experiments. Naive CD4+T cells were further purified using a mouse naive CD4+T cells isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Inc., Cologne, Germany), specifically, lymphocytes (1×107 cells) were first labeled with Naive CD4+ T Cell Biotin-Antibody Cocktail in 40 μL MACS buffer (4°C, 5 min). Subsequently, 20 μL Anti-Biotin MicroBeads and 10 μL CD44 MicroBeads were added in 20 μL buffer (4°C, 12 min). Cells were separated through ice-cooled MS columns pre-rinsed with MACS buffer, with sequential loading of cell suspension interrupted by buffer washes. Target cells were collected by centrifugation (350 × g, 10 min, 4°C) and resuspended in complete RPMI-1640 medium”.
2.5 Differentiation of naive CD4+T cells
The naive CD4+T cells were cultured in 24-well plates with 5 × 105 cells, (precoated with anti-CD3, 1 μg/ml, Thermo Fisher Scientific Co., Ltd, Xian,USA) and were then transfected with miR-378a-5p mimics (60 nM, Shanghai GenePharma Co.,Ltd) and inhibitor (150 nM, QIAGEN, Shanghai GenePharma Co.,Ltd) using HiPerFect transfection reagent (QIAGEN, USA). After 6 h, soluble anti-CD28 (0.2 μg/ml, Thermo Fisher Scientific Co., Ltd, USA) was added along with cytokines that differentiate naive CD4+T cells into different T-cell subtypes. For Th1 cells, IL-2 (20 ng/ml, BioLegend, Inc, California, USA.), IL-12 (50 ng/ml, BioLegend, Inc, California, USA.), and anti-IL-4 antibody (10 ng/ml, BioLegend, Inc, California, USA) were added to the well plates for 48 h. To differentiate the cells into Th2 cells, IL-2 (20 ng/ml, BioLegend, Inc, California, USA), IL-4 (10 ng/ml, BioLegend, Inc, California, USA.), and anti-IL-IFN-γ antibody (10 ng/ml, BioLegend, Inc, California, USA.) were added to the well plates for 48 h.
2.6 Bioinformatics prediction of target genes
Three miRNA target prediction databases were used, namely miRWALK (version 3.0), miRDB (http://mirdb.org/miRDB/), and TargetScan (version 8.0).The analysis was conducted with the species parameter set to Mus musculus (mouse) and the miRNA sequence of interest was used as the query. The predicted target genes from each database were subsequently analyzed for common targets using the Venn diagram approach implemented in the Draw Venn Diagram tool. The overlapping target genes identified by all three prediction platforms were considered high-confidence candidates and visualized using a Venn diagram representation.
2.7 Dual-luciferase reporter assay
293T (Key Laboratory of Common Infectious Disease Prevention and Control in Ningxia) cells were reconstituted and cultivated in full media. Wild-type and mutant BRAF plasmids, in conjunction with miR-378a-5p mimics or negative controls (NC), were prepared for transfection. At 70% cellular confluence, transfection complexes were formulated by combining 10 μL DMEM with 0.3 μL transfection reagent and incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. Concurrently, 10 μL of DMEM was combined with 0.1 μg of plasmid DNA (either wild-type or mutant BRAF) and miR-378a-5p mimics/negative control, followed by a 5-minute incubation at ambient temperature. The transfection reagent was amalgamated with the DNA solution, gently agitated by tapping the tube, and incubated for 10 minutes at an ambient temperature. The completed transfection complexes were uniformly placed into 293T cell culture plates and incubated in a humidified environment (37°C, 5% CO2) for 48 hours. After incubation, cells were lysed by the addition of 100 μL of Passive Lysis Buffer (PLB) each well in a 96-well plate. Following careful pipetting, the plates were agitated at an ambient temperature for 15 minutes. Cell lysates were aliquoted into 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes and subjected to centrifugation at 13,400 ×g for 8 minutes at 4 °C. Supernatants were obtained for further analysis. To quantify luciferase activity, 100 μL of Luciferase Assay Reagent II was mixed with 20 μL of cell lysate in each well. The activity of firefly luciferase was quantified as an internal reference. Subsequently, 100 μL of Stop & Glo® Reagent was administered to each well for the assessment of Renilla luciferase activity. Relative luciferase activity was determined by the ratio of Renilla luciferase activity to firefly luciferase activity.
2.8 Prediction of interaction pathways with target gene
Log in to the STRING(https://cn.string-db.org/) online database and enter the target gene and species source to obtain the proteins or signaling pathways interacting with the target gene.
2.9 qRT-PCR
TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) was used to extract total RNA from CD4+T cells and naïve CD4+T cells. The First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) was used to synthesis cDNA for mRNA analysis. An ABI 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) was used to conduct quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). The Bestar® Sybr Green qPCR Master Mix (DBI® Bioscience) was used to assess the levels of mRNA expression. Both mRNA and miRNA were normalized using U6 and GAPDH as endogenous controls. The 2−ΔΔCT technique was used to determine the relative expression levels of genes. Table 1 lists the primer sequences utilized in this investigation.
2.10 Western blot
Whole-cell lysis buffer (KeyGen Biotech, Jiangsu, China) was used to extract the total protein from the treated cells. A BCA protein quantification assay (KeyGen Biotech, Jiangsu, China) was used to measure the protein content. Protein samples were denatured for eight minutes at 100°C after being combined with 5X SDS-PAGE loading buffer (Shanghai Epizyme Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd). After being separated using 12% SDS-PAGE, the denatured proteins were put onto 0.2 μm PVDF membranes. For two hours at room temperature, the membranes were blocked using 5% skim milk in PBST. The membranes were incubated with primary antibodies against Phospho-B-Raf (Ser445), Phospho-MEK1/2, Phospho-p44/42(Erk1) (Tyr204)/(Erk2) (Tyr187) (D1H6G) Mouse mAb, (Cell Signaling Technology, USA)(1:1000), and β-actin, IFN-γ, IL-4 (Bioworld Biotech, Nanjing, China)(1:1000) overnight at 4°C. Following PBST washing, membranes were incubated for two hours at room temperature with secondary antibodies conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (HRP) (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA)(1:10000). The ChemiDoc Touch Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Shanghai, China) and an ECL detection kit (KeyGen Biotech, Jiangsu, China) were used to observe protein bands. To normalize the results, β-actin was employed as an internal loading control.
2.11 Staining and flow cytometry
To evaluate the purity of magnetically isolated naive CD4+ T cells, surface staining was performed using the following antibodies: FITC-anti-CD4, PE-anti-CD44, APC-anti-CD25, and PerCP-Cy5.5-anti-CD62L antibodies (all from BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.12 Statistical analysis
The data was analyzed using GraphPad Prism software and given as mean ± SD. Student’s t-test was used to compare two groups. P-values < 0.05 were deemed statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 The expression, purification, and identification of rEg.P29, as well as its effects on miR-378a-5p and the BRAF-MAPK/ERK pathway in CD4+T cells
A His-tag purification kit was used to purify the rEg.P29 protein, and endotoxins were then eliminated (Figure 1A). The purified protein solution was sterilized by filtration through a 0.22-μm filter to meet experimental standards. Spleen lymphocytes were isolated from mice, and CD4+T cells. with >95% purity were obtained via magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS). (Supplementary Figure 1A). Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) quantified miR-378a-5p expression in purified CD4+T cells. Comparative analysis revealed that rEg.P29, when administered with FCA or FIA, significantly upregulated miR-378a-5p expression in mouse splenic CD4+T cells compared with the PBS and adjuvant-only control groups (Figure 1B). These results suggest that miR-378a-5p was may involved in the differentiation of CD4+T cells in mouse spleen induced by rEg.P29.
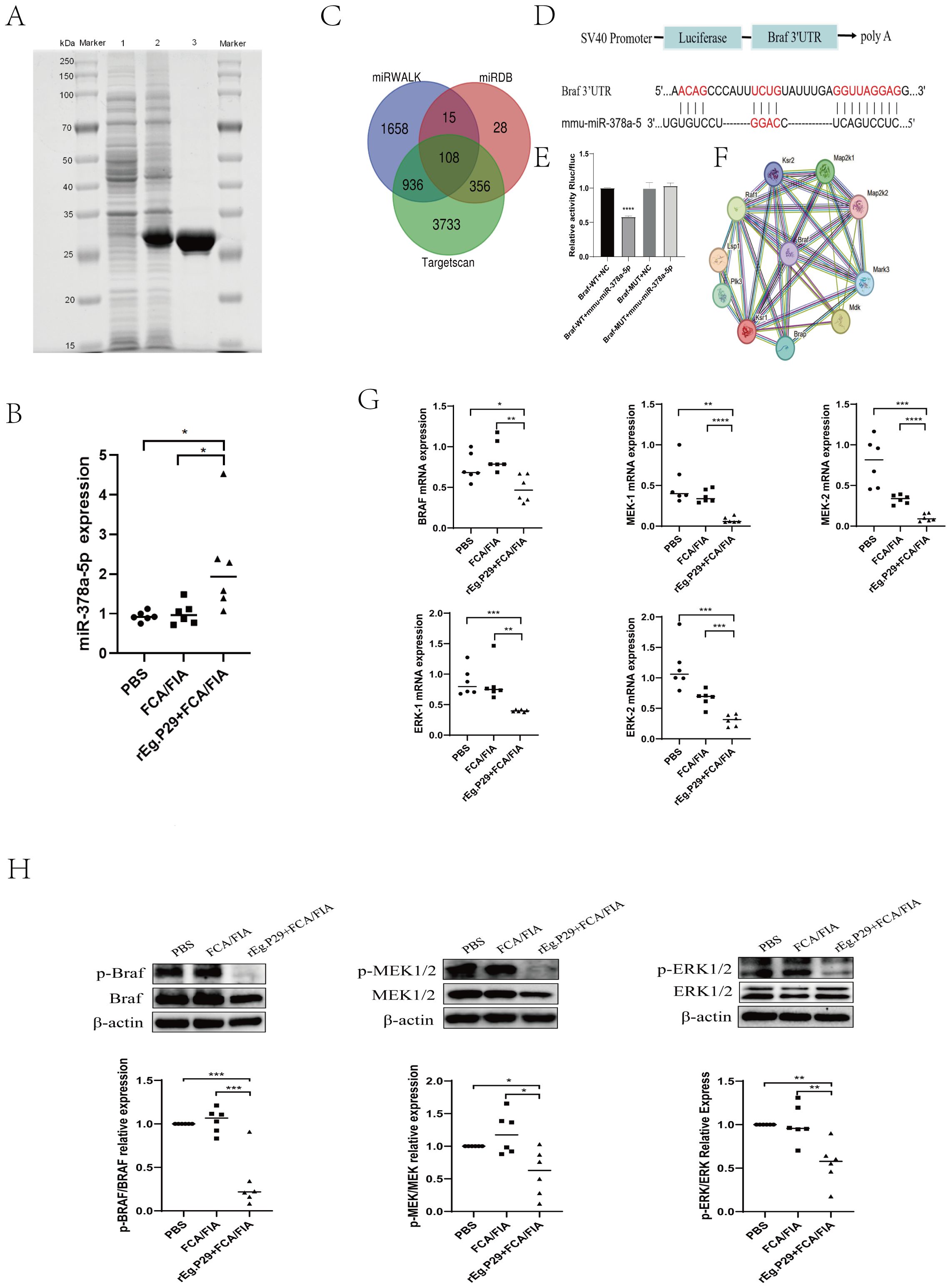
Figure 1. (A) SDS-PAGE Analysis of rEg.P29 after induction, expression, and purification: line 1. Bacterial culture without IPTG induction; line 2. Bacterial culture after IPTG induction; line 3. Purified and endotoxin-free rEg.P29 protein. (B) Expression of miR-378a-5p after rEg.P29 immunization. (C) Venn diagram of miR-378a-5p target gene predictions from three databases. (D, E) The constructs used in the double luciferase assay were psiCHECK-2 vectors, the binding sites of miR-378a-5p and BRAF were illustrated, and the double luciferase reporter assay was statistically analyzed. (F) Protein-protein interaction network of target gene BRAF. (G) Effects of rEg.P29 Immunization on the mRNA Expression of Key Molecules in the BRAF and MAPK/ERK Pathway in Mice. (H) Effects of rEg.P29 Immunization on the Protein Expression of Key Molecules in the BRAF and MAPK/ERK Pathway in Mice. ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05; ns, not significant.
To elucidate the specific mechanism by which rEg.P29-induced miR-378a-5p modulates CD4+T cells differentiation into Th1 cells, we used three databases (miRWalk, miRDB, and TargetScan) to predict miR-378a-5p target genes. Intersecting the target genes from these databases identified 108 overlapping genes (Figure 1C). Dual luciferase results showed that co-transfection of miR-378a-5p mimics in 293T cells significantly inhibited the luciferase activity of Braf wild-type 3’-UTR, validated BRAF as a target gene regulated by miR-378a-5p (Figures 1D, E). Using the STRING online database, we analyzed BRAF-interacting proteins and found a significant association between BRAF and the MAPK pathway (Figure 1F). Extensive research emphasizes BRAF’s crucial function in regulating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, which is critical for cell division and differentiation in many disorders (43–50). One week after using rEg.P29 immunized mice, spleen lymphocytes were isolated from mice, and CD4+T cells with >95% purity were obtained using magnetic bead sorting. mRNA and protein expression levels of BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 in CD4+T cells were quantified by qRT-PCR and western blotting, respectively. The results demonstrated that rEg.P29 combined with FCA/FIA significantly downregulated BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 expression in mouse splenic CD4+T cells compared to the PBS and adjuvant groups (Figures 1G, H). These findings suggest that the BRAF and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways are may involved in miR-378a-5p-mediated regulation of CD4+T cells differentiation induced by rEg.P29.
3.2 Effect of miR-378a-5p on the differentiation of naïve CD4+T Cells towards Th1 and Th2 subsets
First, the optimal concentration of miR-378a-5p mimics or miR-378a-5p inhibitors were screened. (Supplementary Figure 1B). Then, Magnetic bead sorting was used to separate naïve CD4+T cells from mouse splenic lymphocytes, Naïve CD4+T cells were transfected with miR-378a-5p mimics, miR-mimics negative control (miR-mimics-NC), miR-378a-5p inhibitors, or miR-inhibitor negative control (miR-inhibitor-NC),following transfection, cells were polarized towards either the Th1 or Th2 lineage using lineage-specific cytokine cocktails. After 48 hours of stimulation, total RNA and total protein were extracted for downstream analyses. We found that miR-378a-5p mimics substantially increased Th1-associated cytokine IFN-γ and transcription factor T-bet expression compared to the control group, according to qRT-PCR analysis. In contrast, miR-378a-5p inhibitors drastically decreased these indicators. In contrast, miR-378a-5p mimics decreased the production of the Th2-associated cytokine IL-4 and transcription factor GATA-3, whereas miR-378a-5p inhibitors boosted their levels. (Figures 2A, B). Western blot analyses confirmed these findings, showing that miR-378a-5p mimics increased IFN-γ levels and decreased IL-4 levels, whereas miR-378a-5p inhibition had the opposite effects (Figures 2C, D).
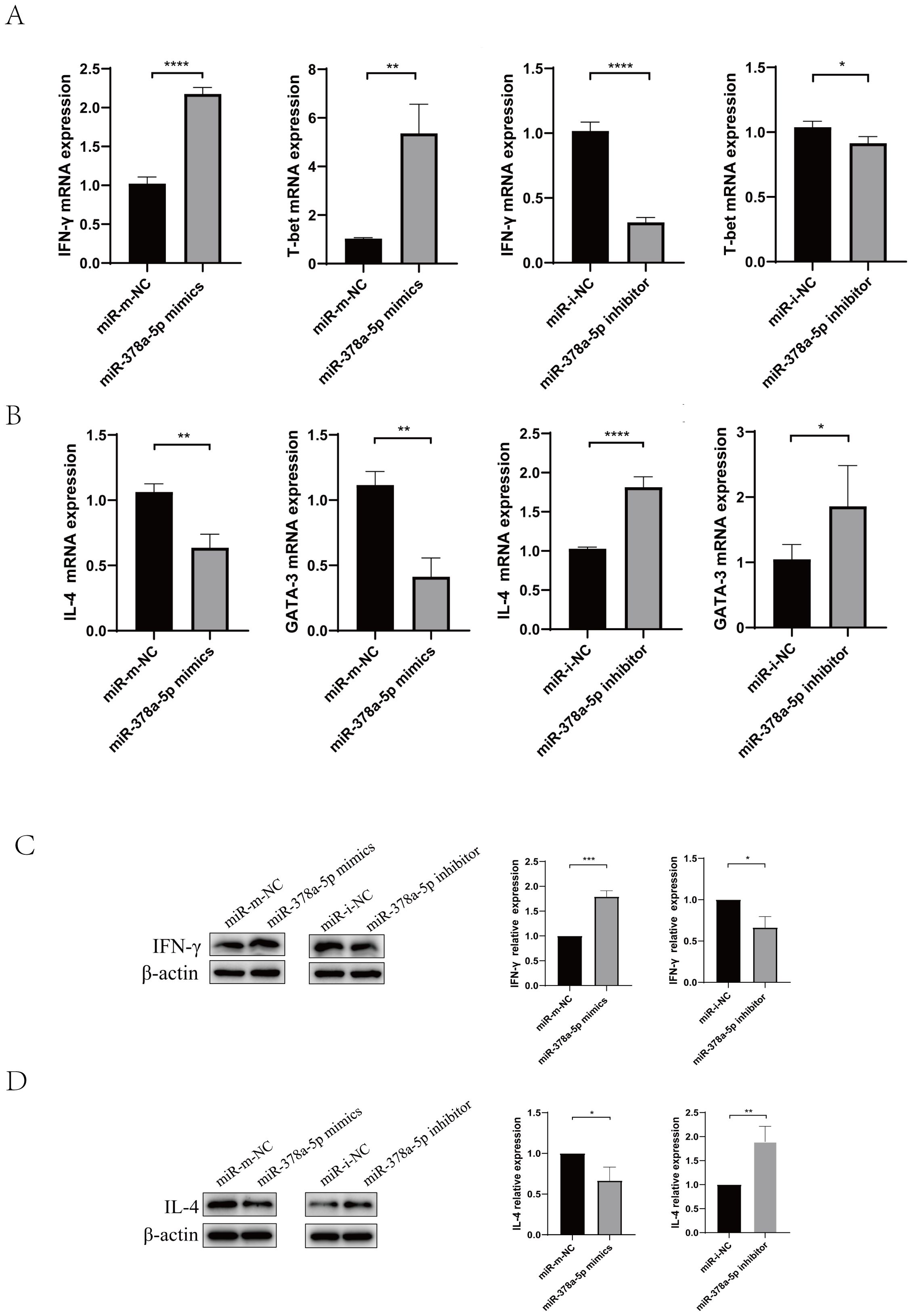
Figure 2. Naïve CD4+T cells were transfected with miR-378a-5p mimics, miR-mimics negative control (miR-mimics-NC), miR-378a-5p inhibitors, or miR-inhibitor negative control (miR-inhibitor-NC),following transfection, cells were polarized towards either the Th1 or Th2 lineage using lineage-specific cytokine cocktails. (A) Following Th1 polarization, mRNA expression levels of IFN-γ and T-bet were quantified using RT-qPCR. (B) Following Th2 polarization, mRNA expression levels of IL-4 and GATA-3 were quantified using RT-qPCR (C) Following Th1 polarization, protein expression levels of IFN-γ was analyzed by Western blotting. (D) Following Th2 polarization, protein expression levels of IL-4 was analyzed by Western blotting. ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05; ns, not significant.
3.3 Evaluation of miR-378a-5p on BRAF and the MAPK/ERK pathway
To determine the mechanism by which rEg.P29 induces miR-378a-5p to regulate CD4+T cells differentiation toward the Th1 phenotype, we examined the expression of key molecules in the BRAF and MAPK/ERK pathways at the mRNA and protein levels using qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses. The results demonstrated that overexpression of miR-378a-5p significantly decreased the mRNA and protein expression levels of BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2. Conversely, miR-378a-5p inhibition significantly increased the expression of these molecules (Figures 3A–D). These findings suggest that under the induction of rEg.P29, miR-378a-5p targeted to BRAF regulation and initiated the differentiation of CD4+T cells in mouse spleen to Th1 direction, and MAPK/ERK pathway may be involved in this process.
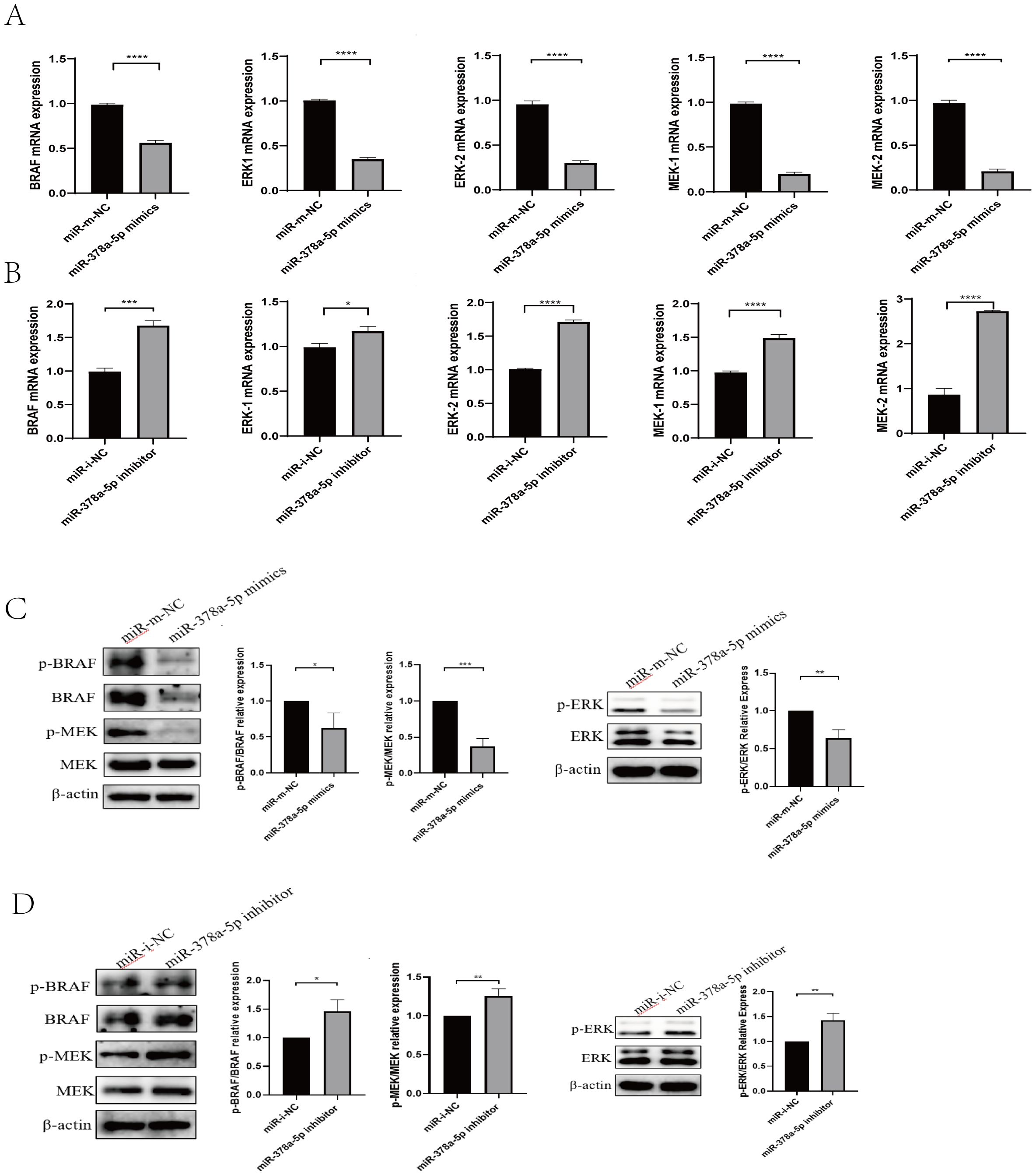
Figure 3. (A) qRT-PCR was used to analyze BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with miR-378a-5p mimics and miR- m-NC (miR- mimics-NC). (B) qRT-PCR was used to analyze BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with miR-378a-5p inhibitor and miR- i-NC (miR- inhibitor-NC). (C) Western blot was used to analyze BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with miR-378a-5p mimics and miR- m-NC (miR- mimics-NC). (D) Western blot was used to analyze BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2 levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with miR-378a-5p inhibitor and miR- i-NC (miR- inhibitor-NC). ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05; ns, not significant.
3.4 Effect of BRAF on differentiation of naïve CD4+T cells towards Th1 and Th2
Magnetic bead-based cell sorting was used to extract naïve CD4+T cells from mouse splenic lymphocytes. To elucidate the regulatory function of BRAF in CD4+T cells differentiation, we first Screened of OE-BRAF (overexpression - BRAF) via Recombinant Lentivirus Packaging (Supplementary Figure 2A),.and synthesized siRNA-BRAF (siRNA-induced BRAF silencing) by GenePharma company, then, determined the optimal transfection about OE-BRAF and siRNA-BRAF. we performed qRT-PCR to assess the effects of OE-BRAF and siRNA-BRAF. Our findings revealed that OE-BRAF significantly suppressed the expression of Th1-associated cytokine IFN-γ and its key transcription factor T-bet relative to control groups. In contrast, siRNA-BRAF significantly enhanced the expression of Th1 markers (Figures 4A). Conversely, OE-BRAF promoted the expression of the Th2-associated cytokine IL-4 and its transcription factor GATA-3, whereas siRNA-BRAF significantly attenuated their expression (Figures 4B). These observations were further corroborated by Western blot analysis, which demonstrated that OE-BRAF reduced IFN-γ production while augmenting IL-4 expression (Figures 4C, D). Taken together, these data indicate that OE-BRAF inhibits Th1 differentiation in primary CD4+T cells, whereas siRNA-BRAF promote Th1 differentiation.
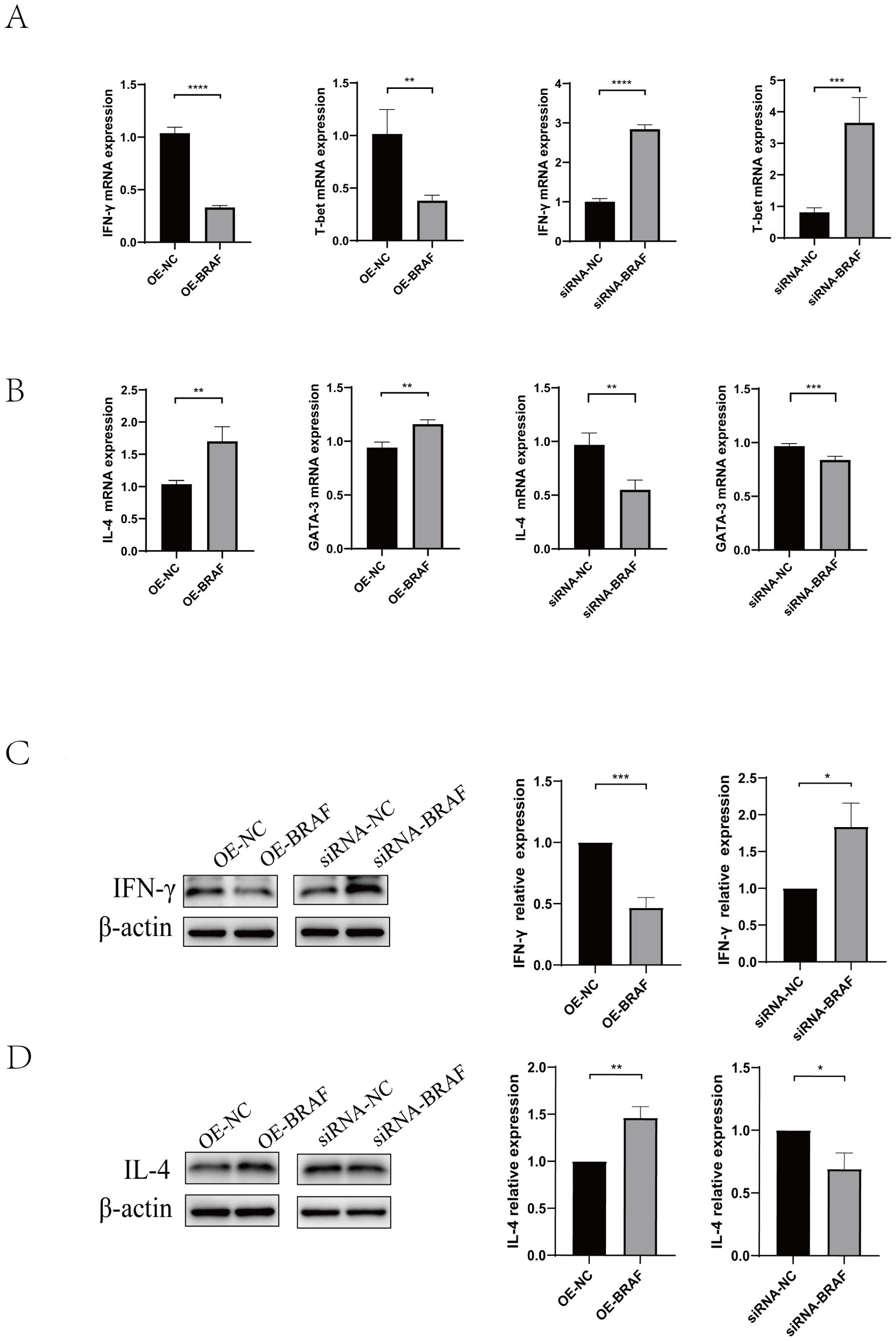
Figure 4. (A) qRT-PCR was used to analyze IFN-γ and T-bet levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with OE-BRAF or siRNA-BRAF. (B) qRT-PCR was used to analyze IL-4 and GATA-3 levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with OE-BRAF or siRNA-BRAF (C) Western blot was used to analyze IFN-γ levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with OE-BRAF or siRNA-BRAF. (D) Western blot was used to analyze IL-4 levels in naïve CD4+T cells transfected with OE-BRAF or siRNA-BRAF. ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05; ns, not significant.
3.5 Impact of co-transfection with miR-378a-5p and BRAF on Th1 and Th2 differentiation
Using qRT-PCR, the impact of co-transfection BRAF and miR-378a-5p on Th1/Th2 differentiation was evaluated. Th1-associated cytokine IFN-γ and transcription factor T-bet levels in CD4+T cells co-transfected with OE-BRAF and miR-378a-5p mimics were greater than those in cells transfected with OE-BRAF alone, but considerably lower than those in cells transfected with miR-378a-5p mimics alone. Contrastingly, when cells were co-transfected with the miR-378a-5p inhibitor and siRNA-BRAF, Th1 cytokineTh1-associated cytokine IFN-γ and transcription factor T-bet levels significantly decreased in comparison to cells transfected with siRNA-BRAF alone, but they did significantly rise in comparison to cells transfected with the miR-378a-5p inhibitor alone. (Figures 5A–D). Moreover, Th2-associated cytokine IL-4 and transcription factor GATA-3 levels were considerably increased by co-transfection with miR-378a-5p mimics and OE-BRAF in comparison to cells transfected with miR-378a-5p mimics alone but decreased in comparison to cells transfected with OE-BRAF alone. Conversely, Th2-associated cytokine IL-4 and transcription factor GATA-3 levels were significantly lower after co-transfection with the miR-378a-5p inhibitor and siRNA-BRAF, than after cells transfected with the miR-378a-5p inhibitor alone, but higher after co-transfection with siRNA-BRAF (Figures 5E–H).
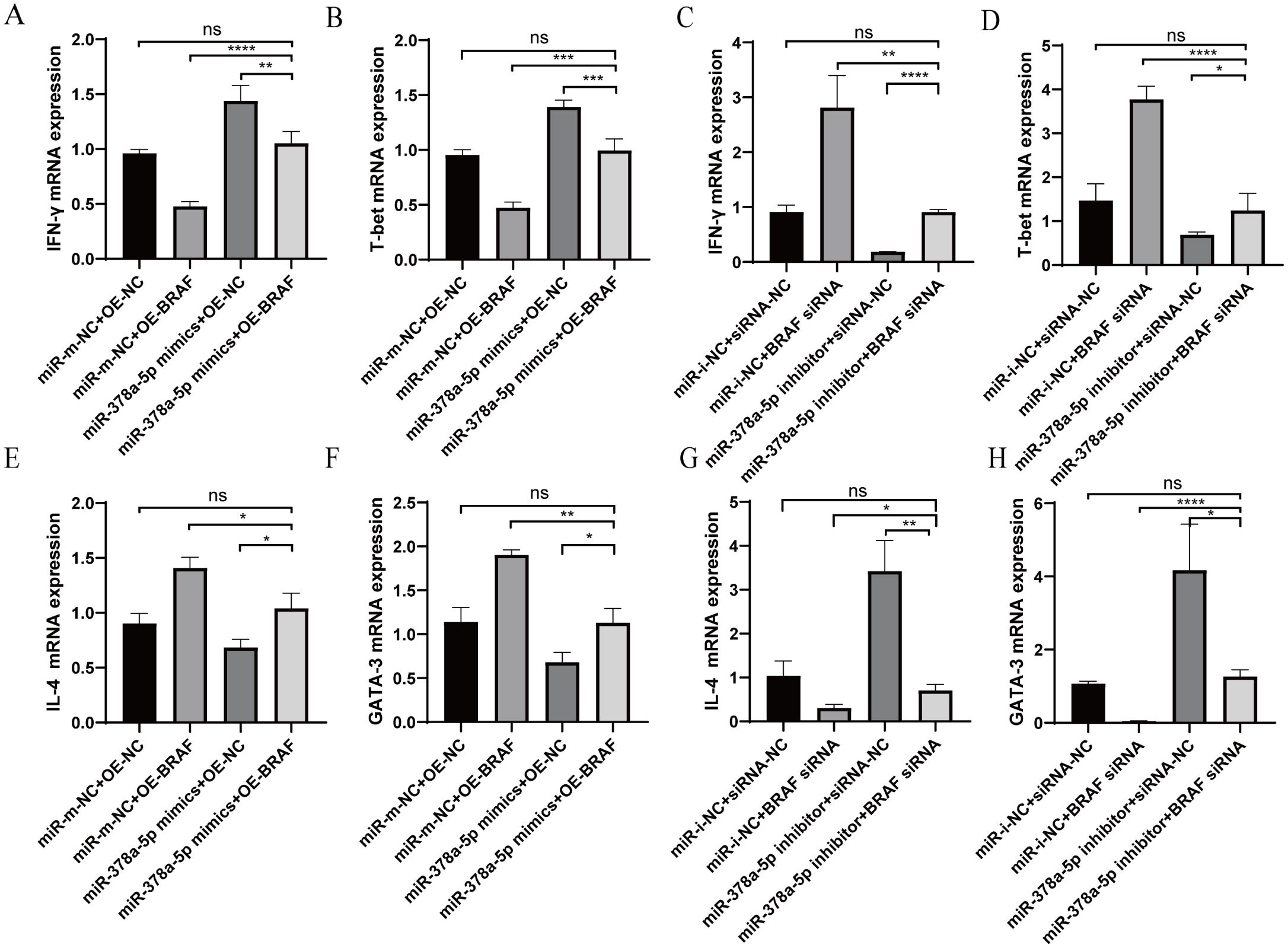
Figure 5. (A–D) qRT-PCR was used to analyze IFN-γ and T-bet levels in naïve CD4+T cells after Co-Transfection with miR-378a-5p and BRAF. (E–H) qRT-PCR was used to analyze IL-4 and GATA-3 levels in naïve CD4+T cells after Co-Transfection with miR-378a-5p and BRAF. ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05; ns, not significant.
4 Discussion
Recent research has shown that vaccinating intermediate hosts is a viable technique for preventing the spread of CE. Vaccines such as Eg95, Eg29, and EgN123 have shown promising immune protection (51–53). However, their high costs hinder their widespread use. Therefore, investigating immunological mechanisms is essential to guide the development of more effective vaccines.
CD4+T cells are crucial to immunological responses, and their differentiation is directly influences by E. granulosus infection. Th1 immune differentiation is associated with immunological protection, whereas Th2 immunity is linked to parasite growth in later stages of infection (24, 54).
Previous investigations have indicated that rEg.P29 provides strong immunological protection in both sheep and mice. Additionally, miRNA microarray analysis of immunized and infected mice suggested upregulation of miR-378a-5p. Although research on the role of the miR-378 family in T cell immune regulation is limited, most studies focus on its involvement in cancer. The miR-378 family is highly expressed in normal tissues and exerts protective effects, including guarding the heart from ischemic injury, inhibiting cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, and preventing liver fibrosis (55). Mice lacking miR-378 or with a conditional knockout, exhibit impaired maintenance of muscle mass, reduced exercise capacity, autophagy dysfunction, mitochondrial accumulation, and severe apoptosis in skeletal muscle cells. In contrast, miR-378 overexpression promotes autophagy and prevents skeletal muscle cell death (56–60). In light of these findings, we examined miR-378a-5p expression to explore its potential role in rEg.P29-induced immune regulation. Our findings demonstrated that in naïve CD4+T cells, miR-378a-5p inhibited Th2 development while promoting Th1 differentiation.
To further understand the molecular mechanism behind miR-378a-5p-mediated CD4+T cells differentiation, we utilized miRNA target prediction algorithms, bioinformatics analysis, and literature review to identify BRAF as a potential target. A dual-luciferase reporter gene assay confirmed that BRAF is a direct target of miR-378a-5p. Functional studies showed that miR-378a-5p overexpression significantly reduced BRAF mRNA levels and protein phosphorylation, whereas miR-378a-5p inhibition had the opposite effect. To further investigate this, we generated lentiviral constructs for BRAF overexpression and RNA interference, which were transfected into naïve CD4+T cells from mouse spleens. These experiments confirmed that miR-378a-5p promotes Th1 differentiation by inhibiting BRAF. Using the STRING database for protein interaction analysis, we found that BRAF is closely linked to the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. ERK activation in T-cell precursors promotes CD4+T cells differentiation (61), and ERK-mediated regulation of the IL-4 receptor (IL-4R) influences Th2 differentiation by increasing IL-10 production (62, 63). Our data demonstrated that miR-378a-5p overexpression significantly reduced the mRNA levels and phosphorylation of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2, while miR-378a-5p inhibition produced the opposite effect. These results suggest that miR-378a-5p-mediated Th1 differentiation via BRAF inhibition may involve the MAPK/ERK pathway.
In conclusion, our in vivo and in vitro experiments demonstrated that rEg.P29 induction leads to miR-378a-5p targeting BRAF, which regulates the differentiation of naïve CD4+T cells from mouse spleens toward Th1 cells, potentially via the MAPK/ERK pathway. This study offers new insights and a theoretical foundation for the development of anti-Echinococcosis vaccines.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Ethics Committee of Ningxia Medical University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
TZ: Validation, Software, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Investigation. HM: Investigation, Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Software. CW: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. BQ: Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. MZ: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Software, Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Methodology, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Ningxia Natural Science Foundation 2025A0790 and Open Research Projects of the Key Laboratory for Prevention and Control of Common Infectious Diseases in Ningxia (2023-KF003, 2024-KF003).
Acknowledgments
We thank all those who contributed to this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1620225/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | (A) Purity evaluation of first CD4+T lymphocytes sorted using magnetic beads. (B) Evaluation of various transfection concentrations of miR-378a-5p mimics and inhibitors.
Supplementary Figure 2 | (A) Lentivirus Packaging in 293T cells. OE-NC: Fluorescence image of cells transduced with the empty lentiviral vector showing baseline fluorescence; OE-BRAF: Fluorescence image of cells transduced with the BRAF overexpression lentiviral vector (OE-BRAF) showing enhanced fluorescence. (B) BRAF Overexpression Lentivirus: the effect of BRAF overexpression lentivirus on BRAF expression. (C) BRAF Interference Fragments: The impact of different BRAF interference fragments on BRAF expression.
References
1. Tamarozzi F, Legnardi M, Fittipaldo A, Drigo M, and Cassini R. Epidemiological distribution of Echinococcus granulosus s.l. infection in human and domestic animal hosts in European Mediterranean and Balkan countries: A systematic review. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2020) 14:e8519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008519
2. Romig T. Epidemiology of echinococcosis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. (2003) 388:209–17. doi: 10.1007/s00423-003-0413-3
3. Larrieu E, Gavidia CM, and Lightowlers MW. Control of cystic echinococcosis: Background and prospects. Zoonoses Public Health. (2019) 66:889–99. doi: 10.1111/zph.12649
4. Woolsey ID and Miller AL. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato and Echinococcus multilocularis: A review. Res Vet Sci. (2021) 135:517–22. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.11.010
5. Wang X, Kui Y, Xue CZ, Wang Q, Zheng CJ, Zhao JS, et al. Past, present and future epidemiology of echinococcosis in China based on nationwide surveillance data 2004-2022. J Infect. (2025) 90:106445. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2025.106445
6. Wang L, Quzhen G, Qin M, Liu Z, Pang H, Frutos R, et al. Geographic distribution and prevalence of human echinococcosis at the township level in the Tibet Autonomous Region. Infect Dis Poverty. (2022) 11:10. doi: 10.1186/s40249-022-00933-9
7. Pourseif MM, Moghaddam G, Daghighkia H, Nematollahi A, and Omidi Y. A novel B- and helper T-cell epitopes-based prophylactic vaccine against Echinococcus granulosus. Bioimpacts. (2018) 8:39–52. doi: 10.15171/bi.2018.06
8. McManus DP, Gray DJ, Zhang W, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of echinococcosis. BMJ. (2012) 344:e3866. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e3866
9. Díaz Á, Fernández C, Pittini Á, Seoane PI, Allen JE, Casaravilla C, et al. The laminated layer: Recent advances and insights into Echinococcus biology and evolution. Exp Parasitol. (2015) 158:23–30. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2015.03.019
10. Brunetti E, Kern P, and Vuitton DA. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop. (2010) 114:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.11.001
11. Ma J, Wei Y, Zhang L, Wang X, Yao D, Liu D, et al. Identification of a novel linear B-cell epitope as a vaccine candidate in the N2N3 subdomain of Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin-binding protein A. J Med Microbiol. (2018) 67:423–31. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000633
12. Zhao Z, Sun HQ, Wei SS, Li B, Feng Q, Zhu J, et al. Multiple B-cell epitope vaccine induces a Staphylococcus enterotoxin B-specific IgG1 protective response against MRSA infection. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:12371. doi: 10.1038/srep12371
13. Baykan AH, Aydin E, Koc M, Sahin H, Karul A, Baykan ME, et al. Hydatid disease: imaging, treatment, and beyond. Clin Radiol. (2025) 80:106748. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2024.106748
14. Johnson KS, Harrison GB, Lightowlers MW, O'Hoy KL, Cougle WG, Dempster RP, et al. Vaccination against ovine cysticercosis using a defined recombinant antigen. Nature. (1989) 338:585–7. doi: 10.1038/338585a0
15. González G, Spinelli P, Lorenzo C, Hellman U, Nieto A, Willis A, et al. Molecular characterization of P-29, a metacestode-specific component of Echinococcus granulosus which is immunologically related to, but distinct from, antigen 5. Mol Biochem Parasitol. (2000) 105:177–84. doi: 10.1016/S0166-6851(99)00166-8
16. Shi Z, Wang Y, Li Z, Li Z, Bo Y, Ma R, et al. Cloning, expression, and protective immunity in mice of a gene encoding the diagnostic antigen P-29 of Echinococcus granulosus. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2009) 41:79–85. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmn009
17. Wang H, Li Z, Gao F, Zhao J, Zhu M, He X, et al. Immunoprotection of recombinant Eg.P29 against Echinococcus granulosus in sheep. Vet Res Commun. (2016) 40:73–9. doi: 10.1007/s11259-016-9656-7
18. Lv Y, Li S, Zhang T, Zhu Y, Tao J, Yang J, et al. Identification of B-cell dominant epitopes in the recombinant protein P29 from Echinococcus granulosus. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2022) 10:e611. doi: 10.1002/iid3.611
19. Du X, Zhu M, Zhang T, Wang C, Tao J, Yang S, et al. The Recombinant Eg.P29-Mediated miR-126a-5p Promotes the Differentiation of Mouse Naive CD4(+) T Cells via DLK1-Mediated Notch1 Signal Pathway. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:773276. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.773276
20. Baz A, Ettlin GM, and Dematteis S. Complexity and function of cytokine responses in experimental infection by Echinococcus granulosus. Immunobiology. (2006) 211:3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2005.09.001
21. Zhang W, Ross AG, and McManus DP. Mechanisms of immunity in hydatid disease: implications for vaccine development. J Immunol. (2008) 181:6679–85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.6679
22. Pang N, Zhang F, Li S, Zhu Y, Zhang C, An M, et al. TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway positively up-regulates the differentiation of Interleukin-9-producing CD4(+) T cells in human Echinococcus granulosus infection. J Infect. (2018) 76:406–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2018.01.005
23. Petrone L, Vanini V, Petruccioli E, Ettorre GM, Schininà V, Busi Rizzi E, et al. Polyfunctional specific response to echinococcus granulosus associates to the biological activity of the cysts. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2015) 9:e4209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004209
24. Rostami-Rad S, Jafari R, and Yousofi DH. Th1/Th2-type cytokine profile in C57 black mice inoculated with live Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. J Infect Public Health. (2018) 11:834–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.06.007
25. Zhu M, Wang X, Wang H, Wang Z, Zhao J, Wang Y, et al. Mechanism of protective immunity by vaccination with recombinant Echinococcus granulosus glutathione S-transferase (Chinese strain) in mice. Exp Ther Med. (2015) 10:1127–32. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2582
26. Wang J, Lin R, Zhang W, Li L, Gottstein B, Blagosklonov O, et al. Transcriptional profiles of cytokine/chemokine factors of immune cell-homing to the parasitic lesions: a comprehensive one-year course study in the liver of E. multilocularis-infected mice. PloS One. (2014) 9:e91638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091638
27. Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Mostafavi E, Aref AR, Sethi G, Wang L, et al. Non-coding RNA-based regulation of inflammation. Semin Immunol. (2022) 59:101606. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101606
28. West KA and Lagos D. Long non-coding RNA function in CD4(+) T cells: what we know and what next? Noncoding RNA. (2019) 5:43. doi: 10.3390/ncrna5030043
29. Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. (2011) 12:99–110. doi: 10.1038/nrg2936
30. Sayed D and Abdellatif M. MicroRNAs in development and disease. Physiol Rev. (2011) 91:827–87. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00006.2010
31. Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, and Bartel DP. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. (2009) 19:92–105. doi: 10.1101/gr.082701.108
32. Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. (2011) 12:861–74. doi: 10.1038/nrg3074
33. Lin S and Gregory RI. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2015) 15:321–33. doi: 10.1038/nrc3932
34. Liu N and Olson EN. MicroRNA regulatory networks in cardiovascular development. Dev Cell. (2010) 18:510–25. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.03.010
35. Olson EN. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers of cardiovascular disease. Sci Transl Med. (2014) 6:233p–239. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009008
36. Issler O and Chen A. Determining the role of microRNAs in psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2015) 16:201–12. doi: 10.1038/nrn3879
37. Zheng Y, Cai X, and Bradley JE. microRNAs in parasites and parasite infection. RNA Biol. (2013) 10:371–9. doi: 10.4161/rna.23716
38. Zeng X, Shen J, Li D, Liu S, Feng Y, Yuan D, et al. CEBPalpha/miR-101b-3p promotes meningoencephalitis in mice infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis by promoting microglial pyroptosis. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:31. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01038-y
39. Geraci NS, Tan JC, and McDowell MA. Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in Leishmania-infected human phagocytes. Parasite Immunol. (2015) 37:43–51. doi: 10.1111/pim.12156
40. Alizadeh Z, Mahami-Oskouei M, Spotin A, Kazemi T, Ahmadpour E, Cai P, et al. Parasite-derived microRNAs in plasma as novel promising biomarkers for the early detection of hydatid cyst infection and post-surgery follow-up. Acta Trop. (2020) 202:105255. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.105255
41. Ferreira LRP, Ferreira FM, Laugier L, Cabantous S, Navarro IC, da Silva Cândido D, et al. Integration of miRNA and gene expression profiles suggest a role for miRNAs in the pathobiological processes of acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:17990. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18080-9
42. Ramaswamy R, Maier LM, Mueller C, Lee Y, Korioth-Schmitz B, Hedley ML, et al. Correction to: Identification of miRNA-mRNA crosstalk in CD4(+) T cells during HIV-1 infection by integrating transcriptome analyses. J Transl Med. (2020) 18:312. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02479-6
43. Moon H and Ro SW. MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13(12):3026. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123026
44. Peng J, Guo J, Huang J, Zhang W, Ai W, He Y, et al. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. (2015) 35:600–4. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2015.1030412
45. Zhang J, Sun B, Ruan X, Hou X, Zhi J, Meng X, et al. Oncoprotein HBXIP promotes tumorigenesis through MAPK/ERK pathway activation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Med. (2021) 18:105–19. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0098
46. El Ridi R, Tallima H, Salah M, Aboueldahab M, Fahmy OM, Al-Sherbiny M, et al. MEK inhibitors for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:1. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01025-7
47. Dong C, Davis RJ, and Flavell RA. MAP kinases in the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. (2002) 20:55–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.091301.131133
48. Ahmed SA, Gad MZ, Dessouki O, El-Tantawi M, Tallima H, El Ridi R, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase activation by oncogenes, serum, and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate requires Raf and is necessary for transformation. J Biol Chem. (1994) 269:7030–5. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37478-1
49. Fang JY and Richardson BC. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. (2005) 6:322–7. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70168-6
50. Pearce EJ, James SL, Hieny S, Lanar DE, and Sher A. Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein: structure, function, regulation of cell signaling, and pivotal role in apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res. (2004) 91:169–200. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(04)91005-6
51. Larrieu E, Herrero E, Mujica G, Labanchi JL, Araya D, Grizmado C, et al. Pilot field trial of the EG95 vaccine against ovine cystic echinococcosis in Rio Negro, Argentina: early impact and preliminary data. Acta Trop. (2013) 127:143–51. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.04.009
52. Amarir F, Rhalem A, Sadak A, Raes M, Oukessou M, Saadi A, et al. Control of cystic echinococcosis in the Middle Atlas, Morocco: Field evaluation of the EG95 vaccine in sheep and cesticide treatment in dogs. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2021) 15:e0009253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009253
53. Zhang ZZ, Guo G, Li J, Shi BX, Zhao L, Guo BP, et al. Dog vaccination with EgM proteins against Echinococcus granulosus. Infect Dis Poverty. (2018) 7:61. doi: 10.1186/s40249-018-0425-4
54. Vuitton DA. Echinococcosis and allergy. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2004) 26:93–104. doi: 10.1007/s12016-004-0004-2
55. Qin Y, Liang R, Lu P, Lai L, and Zhu X. Depicting the implication of miR-378a in cancers. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 21:15330338221134385. doi: 10.1177/15330338221134385
56. Eichner LJ, Perry MC, Dufour CR, Bertos N, Park M, St-Pierre J, et al. miR-378(∗) mediates metabolic shift in breast cancer cells via the PGC-1β/ERRγ transcriptional pathway. Cell Metab. (2010) 12:352–61. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.09.002
57. Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH, and Yang BB. MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2007) 104:20350–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706901104
58. Lightowlers MW. Hepatic miR-378 targets p110alpha and controls glucose and lipid homeostasis by modulating hepatic insulin signalling. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:5684. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6684
59. Gauci CG, Jenkins DJ, and Lightowlers MW. miR-378 activates the pyruvate-PEP futile cycle and enhances lipolysis to ameliorate obesity in mice. EBioMedicine. (2016) 5:93–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.01.035
60. Li Y, Jiang J, Liu W, Wang H, Zhao L, Liu S, et al. microRNA-378 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2018) 115:E10849–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803377115
61. Sharp LL, Schwarz DA, Bott CM, Marshall CJ, and Hedrick SM. The influence of the MAPK pathway on T cell lineage commitment. Immunity. (1997) 7:609–18. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80382-9
62. Yamashita M, Kimura M, Kubo M, Shimizu C, Tada T, Perlmutter RM, et al. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway controls interleukin 4 receptor function and type-2 helper T cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (1999) 96:1024–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.3.1024
Keywords: Echinococcus granulosus P29, miR-378a-5p, BRAF, CD4+T cells differentiation, MAPK/ERK pathway
Citation: Zhang T, Mu H, Wang C, Qian B and Zhu M (2025) miR-378a-5p targeting BRAF regulates CD4+T cells differentiation to Th1 under rEg.P29 induction. Front. Immunol. 16:1620225. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1620225
Received: 29 April 2025; Accepted: 15 August 2025;
Published: 04 September 2025.
Edited by:
Herbert Leonel de Matos Guedes, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilReviewed by:
Oscar Badillo-Godinez, Uppsala University, SwedenLisa Kronstad, Midwestern University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Mu, Wang, Qian and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mingxing Zhu, emh1bWluZ3hpbmdAbnhtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Tingting Zhang
Tingting Zhang Hu Mu
Hu Mu Chuan Wang
Chuan Wang Bingshuo Qian
Bingshuo Qian Mingxing Zhu
Mingxing Zhu