- 1Department of Pharmacy, Daping Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Southwest Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 3Frontier Medical Training Brigade, Army Medical University, Xinjiang, China
Myeloid leukemia (ML) is a clonal malignant disease with abnormal hematopoietic stem cells. With the emergence of novel immunotherapies, such as CAR-T, therapeutic outcomes in ML patients have improved, while significant challenges persist, including severe adverse events and disease recurrence. Natural killer cells (NK cells) are “natural killers” of the immune system that do not require antigen presentation and responsible for recognizing and destroying tumor cells. Some NK cells-based clinical experiments have been carried out and achieved remarkable results with lower side effects in ML. Crucially, within the ML microenvironment, NK cells frequently exhibit more severe functional exhaustion compared with T cells, characterized by impaired cytotoxicity, cytokine production, and proliferative capacity which limits anti-ML efficacy of NK cells. However, clinical studies utilizing NK cell-based therapies (e.g., adoptive transfer, CAR-NK cells) have demonstrated promising results with favorable safety profiles, underscoring their therapeutic potential. Therefore, developing more strategies based on NK cell is of great clinical significance for the treatment of ML. In this review, we systematically analysed the relationship between ML and NK cells, aiming to propose more novel protocols for NK cell expansion and persistence enhancement, establish evidence-based guidelines for next-generation NK cell-based immunotherapies in ML treatment.
1 Introduction
Hematological malignancies (HMs), including four subtypes (non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), leukemia (with several subtypes), multiple myeloma (MM), and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL)), are the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths, which contribute approximately 7% of global cancer incidence with an upward trend in prevalence (1–3). Among HMs, leukemia is a hematologic neoplasm with the characteristic of the excessive production of immature or mature blood cells. Despite advances in understanding disease pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions, leukemia remains a significant global health burden, ranking as the 13th most common malignancy (2.4% of all cancer cases) and the 10th leading cause of cancer-related mortality (3.1%) in 2022 (1–3).
Haematopoiesis is governed by haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that produce all lineages of blood and immune cells (4). These HSCs maintain blood homeostasis through dynamic stress-response mechanisms, whose dysregulation can trigger leukaemia (4). Leukaemogenesis involves chromosomal abnormalities (5, 6), gene mutation (7), and immune system disorders in leukemia stem cells (LSCs) (8), leading to abnormal proliferation and differentiation of LSCs, principally in the BM, and disrupting normal hematopoietic genesis (9, 10). Leukemia is classified into myeloid leukemia (ML) and lymphocytic leukemia (LL) based on lineage commitment and cellular maturation (11). ML results from acquired driver and cooperating mutations within HSCs or myeloid progenitors (12). Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by accumulation of 20% or more abnormal leukemic blast cells, principally in the bone marrow (BM), and impaired normal blood cell production, leading to anemia and thrombocytopenia (12). In contrast, chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) exhibits accumulation of abnormally mature leukocyte, with clinical feature such as severe blood granulocytosis, granulocytic immaturity, basophilia, frequent thrombocytosis, anemia, and splenomegaly (12). LL can originate from cells across a wide spectrum of stages of T-, NK-, or B-lymphocyte differentiation (13). While acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) arises from early lymphoid progenitors expressing pre-B or pre-T cell phenotypes (14), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) derives from a more mature B-lymphocyte progenitor, characterized by accumulation of apoptosis-resistant B-cells (15).
Mounting evidence demonstrates that the tumor microenvironment (TME), the complex cellular ecosystem in which malignant cells emerge, plays a pivotal role in cancer pathogenesis (16). Within secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs) and BM, the TME comprises a heterogeneous population of stromal cells, including fibroblasts, cells of the innate and adaptive immune response, and vascular endothelial cells (ECs) (16). NK cells, as potent cytotoxic effectors of innate immunity, serve as a primary surveillance system against leukemia transformation (17, 18).
Unlike T cells and B cells, NK cells are the “rapid reaction forces” in the immune system (19), exhibiting pronounced exhaustion phenotype during early-stage leukemic progression (20–22). CAR-NK cells have shown a relatively low incidence of off-target effect and CRS, almost no ICANS in clinical applications, significantly reducing the risk of GvHD (23–25). Emerging clinical evidence validates the therapeutic efficacy of CAR-NK cells in CD19+ B-cell leukemia (26), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma or CLL (27), and MM (28). Therefore, NK cells may play a more direct and important role in tumorigenesis, ML treatment strategies based on NK cells would be an effective immunotherapy strategy. In this review, we will summarize NK cell immunobiology and potential targets or strategies for ML treatment systematically in the aspect of NK cell-based immunotherapy.
2 NK cell immunobiology in cancer
Both human and murine NK cells differentiate from HSCs in BM before migrating to peripheral tissues (29, 30). For murine NK cells, HSCs are lineage negative (Lin-) stem cells (31), which can differentiate into NK progenitor cells (NKPs) (32). Acquisition of CD122 is a crucial step in NK cell specification (33). After specification, NK cells sequentially acquire the expression of cytokine receptors (e.g., CD27, CD122, CD127, CD244) (34, 35), activation and inhibitory receptor, adhesion molecules (e.g., integrin) (36), and chemotactic receptors (37). The activation receptor, NKG2D,which is widely expressed on NK cells, serves as a critical determinant in the initial transition of NKPs into immature NK cells (iNKs) (38), while the characteristic of NK cells mature to the DX5+ stage is the acquisition of the Ly49 family receptors (39). The expression of CD43 or CD11b determines the ultimate maturation of NK cells via PYK-2 signaling or Src/β-catenin pathway (40, 41). Mature NK cells (mNKs) can acquire inhibitory Ly49 receptors, including Ly49A/C/I/G and NKG2A, which could attenuate NK cell responses to normal cells expressing MHC-I molecules, thereby enabling more robust responses to infected or cancerous cells lacking MHC-I on the cell surface (42–44).
Human NK cells develop along a continuum of progressively down-regulated CD34 and up-regulated CD56 in common lymphoid progenitor cells (CLPs) (45). HSCs differentiate into multipotent progenitor cells and then transform into CLPs (46). CLPs differentiate into NKPs through transcriptional regulation mediated by key factors including GATA2 and E4bp4 (47). And then, NKPs differentiate into iNKs (48), characterized by high expression of IL-1R1 (49) and the appearance of NKG2D (38), NKp30/46 (50, 51) and CD161 (52). The next stage is the emergence of CD56bright NK cells exhibiting potent cytokine production (53, 54). Finally, CD56bright NK cells transform into CD56dim NK cells (55, 56), which have higher CD16 expression and cytotoxicity (57). NK cell subsets could be used to stratify patients for NK-based therapies. For example, for NK cells exhibiting CD16+ expression or elevated NKG2A+ NK cell infiltration in the TME, personalized therapeutic approaches may include: combination with monoclonal antibodies (e.g., anti-CD20) (58) or co-administration with NKG2A inhibitors (e.g., monalizumab) (59).
After differentiation, iNKs and some mNKs migrate from the parenchyma to the blood sinuses and eventually into the bloodstream, and then into secondary lymphoid tissue to further differentiate (60, 61). Some special subpopulations of NK cells return to BM to perform specific functions, such as monitoring and controlling infected cells (62). In mice, CD62L is necessary for NK cell homing (63). Factors that control NK cell trafficking and homing include integrins (64), selectin (65, 66), chemokine receptors and ligands (67, 68). For example, during NK cell maturation, the up-regulation of S1P5 and CX3CR1, concurrent with down-regulation of CXCR4, facilitates NK cells egress from BM into the bloodstream (69) (Figure 1a). Integrin and chemokine receptors, along with corresponding ligands or chemokines (e.g., VLA-4, CCL3, CXCR6, CCR5, CCL25-CCR9), are typically responsible for recruiting NK cells into peripheral tissues (37, 70, 71).
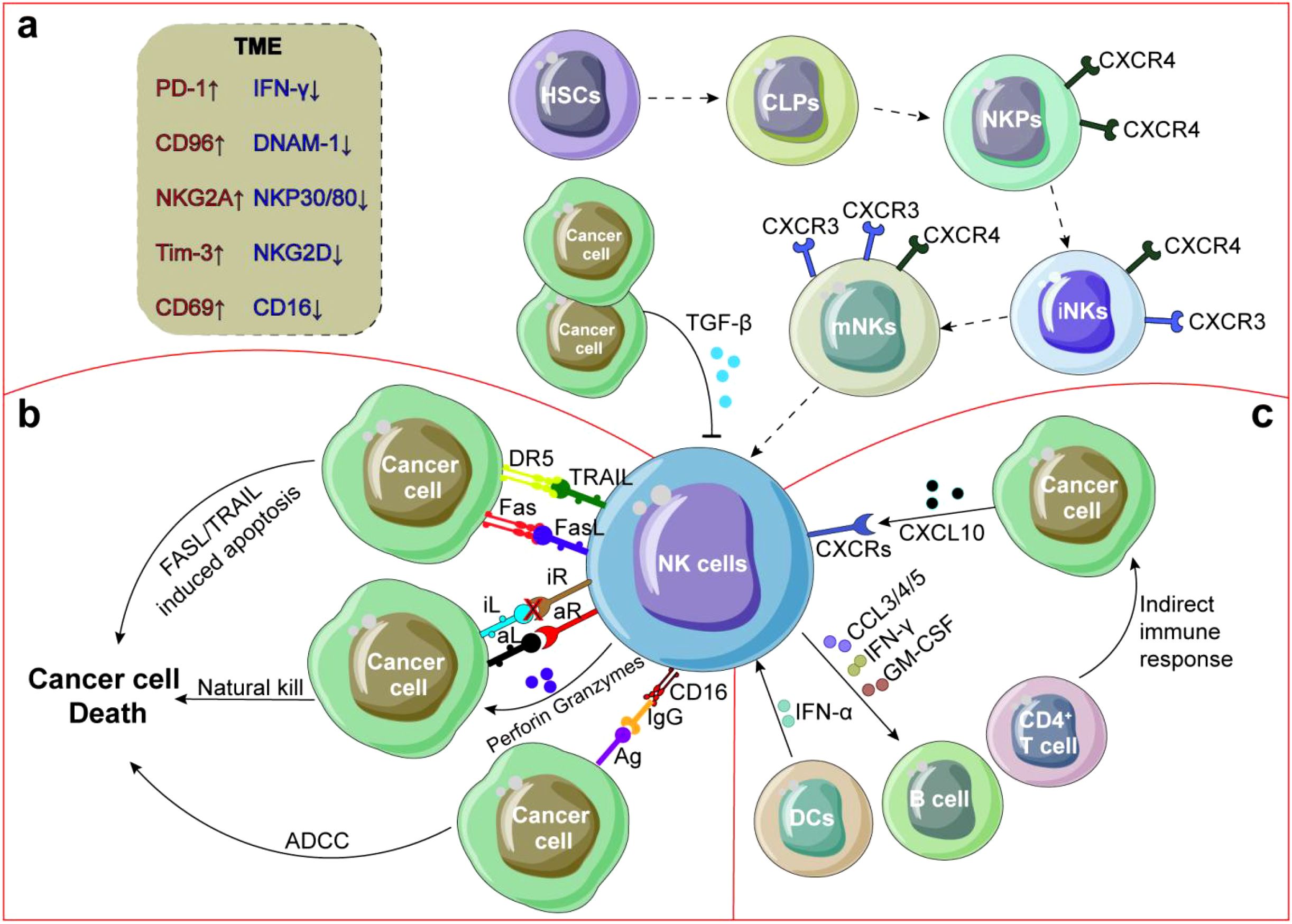
Figure 1. Crosstalk between NK cells and TME. (a) NK cells develop from HSCs in BM, with down-regulation of CXCR4 expression, upregulation of CXCR3 expression, NK cells mature and enter PB and tissues. (b) After exudation from PB, NK cells are recruited to TME by integrins, chemokine receptors and selectins, and secrete cytokines or chemokines to recruit other immune cells and improve anti-tumor response through degranulation, ADCC or FASL/TRAIL induced tumor cell apoptosis. (c) NK cell function is often inhibited by suppressors secreted by tumor cells and DCs or by direct interaction with CD4+ T cells. In addition, NK cells can also secrete angiogenic factors to promote tumor angiogenesis.
NK cell activation is governed by the dynamic equilibrium between activating and inhibitory signals (72), mediated through the engagement of their respective receptors with cognate ligands expressed on target cells (73, 74). In addition to their direct cytotoxic functions, NK cells can execute antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) through the membrane receptor CD16 (75), inducing tumor cell apoptosis pathways via Fas ligands (FasL) or TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligands (TRAIL) (76, 77) (Figure 1b). However, NK cell-based immunotherapy has not yet achieved optimal clinical outcomes due to NK cell exhaustion-a double-edged sword involving the homeostasis disorder dysregulation among NK cells, cytokines and TME (Figure 1c). This review highlights NK cells as dynamic integrators of TME signals, with combinatorial approaches targeting metabolic, epigenetic, and stromal factors offering new therapeutic avenues.
3 The relation between NK cells and AML
3.1 Characteristics of AML
AML arises from sequential somatic mutations in a primitive multipotential hematopoietic cell, which is a leukemia subtype with the highest incidence rate, poor outcomes (78, 79). The primary risk factors for AML include obesity, radiation exposure, prolonged exposure to high concentrations of benzene, and chronic tobacco smoke inhalation (80). A small but increasing proportion of AML cases (7% ~ 8%) develop after a patient with lymphoma, or an autoimmune disorder undergoing intensive chemotherapy, especially with alkylating agents platinum derivatives, or topoisomerase II inhibitors (81). According to French-American-British (FAB) classification (82), due to the origin and maturity of the leukemia cells, AML is generally divided into eight subtypes (M0-M7) (82).
LSCs are the initiation cells of AML, which have the ability of self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation to maintain the growth and recurrence of AML (83). LSCs are highly dependent on oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis contributing to the aggressiveness of AML and are more drug-resistant (83–85). The onset of AML is closely related to gene mutations, such as NPM1, FLT3, IDH1/2, TP53 (86–88), as well as chromosomal rearrangements such as t(8;21) and inv16 (89, 90). AML development and progression are associated with dysregulated immune responses and induction of an immunosuppressive TME (91). Furthermore, AML blasts can hide from immune recognition by promoting T cell exhaustion and expansion of T regulatory cells (Tregs) (91). AML blasts have been found to increase the number of myeloid suppressor cells (MDSCs), polarize macrophages toward a pro-tumoral phenotype, and hamper NK cell effector functions (91). Moreover, AML cells can dysregulate the innate immune response by releasing cytokines and soluble factors or through direct contact with innate immune cells (92). In short, conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) are diminished in the AML BM compared to healthy donors, which may contribute to the lack of CD8+ T cells in the TME (93, 94) and increase the proportion of Tregs, MDSCs (95), which promotes the proliferation and metastasis of AML cells. BM stromal cells (BMSCs), specifically, CD73+CD105+CD271+ BMSCs subgroup in AML TME can promote the survival and proliferation of AML cells by secreting growth factors, thereby reducing treatment efficacy (96, 97).
Despite significant advances in conventional therapeutic approaches, including chemotherapy (e.g., cytarabine, anthracycline antibiotic doxorubicin) (98), targeted therapy (e.g., gilteritinib targeting FLT3 mutations) (99), radiation therapy (100), and HSCs transplantation (HSCT) have acquired great success in AML treatment (101), the overall survival rate of AML patients remain suboptimal, with 5-year survival rates ranging from 30% to 40% according to different studies (102–104). Moreover, while T cell-based immunotherapeutic approaches have shown promise in other hematologic malignancies, their efficacy in adult AML has been disappointingly limited, with pediatric trials only in the initial phases (105, 106).
Taken together, the treatment of AML is a long-term and complex process, and the current treatment plan has a certain effect on the alleviation of AML, but is far from achieving the goal of preventing recurrence or even complete cure. Therefore, the development of novel AML treatment methods have important clinical significance.
3.2 Treatment of AML based on NK cells
DNA hypomethylation drugs, currently FDA-approved for AML treatment, demonstrate interesting mechanistic effects: treatment with azacytidine and decitabine for 48 hours could decrease shedding of MICA, MICB, and ULBP2, consequently restoring NK cell function (107). Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta (GSK3β) expression is elevated in AML-NK cells and GSK3β pharmacological inhibition promotes conjugator formation by up-regulating LFA expression on NK cells and inducing ICAM-1 expression on AML cells, thereby enhancing the cytotoxic activity of AML-NK cells. This process only requires a short ex vivo exposure (16 hours) to 30 μM GSK3β inhibitors (SB415286, LY-2090314, Tideglusib) (108). Overactivation of NK cells by targeting GSK3β may be a novel strategy for the treatment of AML.
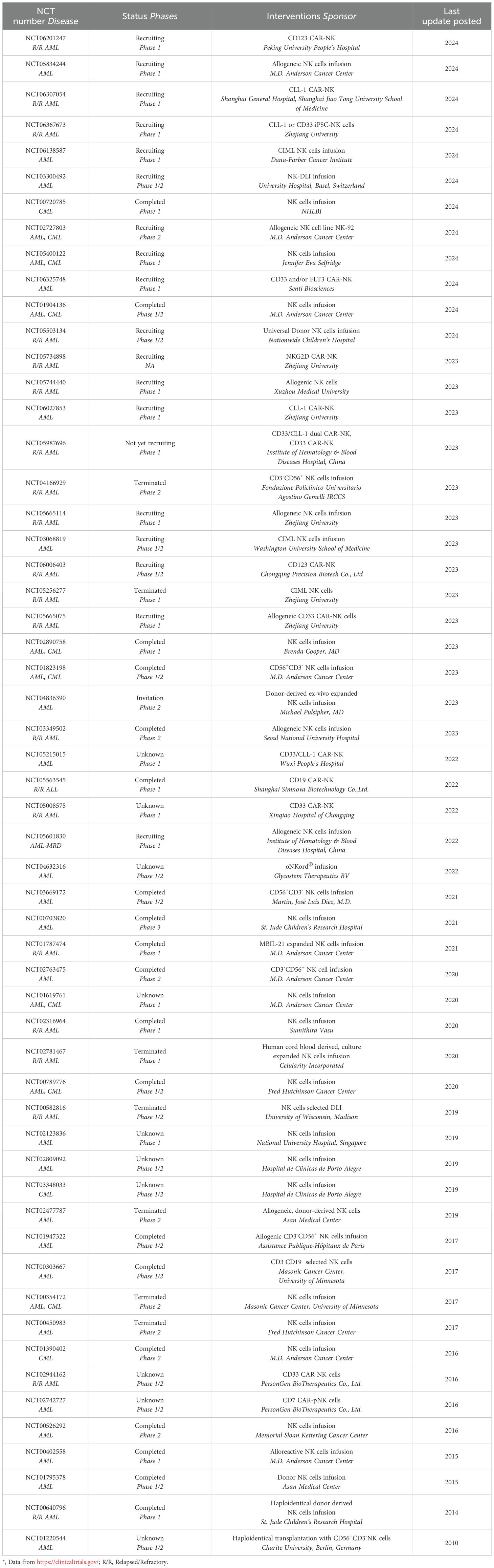
The recovery of NK cell functions after allo-HCT has been associated with protection against AML relapse (109) and NK cells have been identified as crucial players in the eradication of AML (110). Furthermore, donor NK cells, along with T cells, play a role in the graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect following HSCT for AML (111). In a phase I clinical trial (NCT01898793) (Table 1), adoptive transfer cytokine induced memory like NK (CIML-NK) cells (dose range: 0.5 ~ 10×107 cells/kg) proliferated and expanded in patients with AML and observed in 5 of 9 evaluable patients, including 4 complete responses (112). Another recent phase II clinical study (NCT02782546) (Table 1) involved 15 AML patients who received consolidation therapy, followed by haploidentical HSCT and infusion of CIML-NK cells (dose level: 0.5 ~ 10×106 cells/kg) and 13 patients (87%) achieved composite complete response after 28 days, the median event-free survival for all patients was 3.2 months, and 29% of the participants remained alive after 1 year (113). Another clinical trial (NCT03068819) conducted in 2021 (Table 1), Jeffrey J Bednarski used donor derived CIML-NK cell to treat 8 pediatric and young adult AML patients with HSCT recurrence found that 4 patients achieved complete response CIML-NK cell (dose level: 4 ~ 6×106 cells/kg) infusion. Interestingly, a patient showed sustained remission during a 2-year follow-up after CIML-NK cell infusion without any subsequent treatment (114).
CAR-NK cell therapy offers a promising therapeutic approach for treating AML. Primary CD33-targeting CAR-NK cells strongly reduce the burden of leukemia and prevents BM transplantation of leukemia cells without significant side effects (115, 116) (Figure 2b). For example, AML clearance in OCI-AML2-engrafted NSG-SGM3 mice was enhanced by injecting a total of three doses of 1 × 107 of CD33 CAR-NK cells (115). The clinical trial, NCT05008575, currently underway at the Hematology Department of Chongqing Xinqiao Hospital in China targets leukemia cells expressing CD33, employing CAR-NK cells in combination with chemotherapy drugs (Table 1). Among the 10 evaluated patients, only 1 developed grade II CRS and no higher grade CRS occurred. Regarding anti-leukemia efficacy, 60% (6/10) of patients achieved complete remission 28 days after CAR-NK cell infusion (117, 118). In a preclinical study, CD123 CAR-NK cells (5-day OS: 100%) also showed lower acute toxicity than CD123 CAR-T cells (5-day OS: 0%) in a mouse model of transplanted artificial blood cells, while their anti-leukemia efficacy was comparable in a mouse model of AML (119).
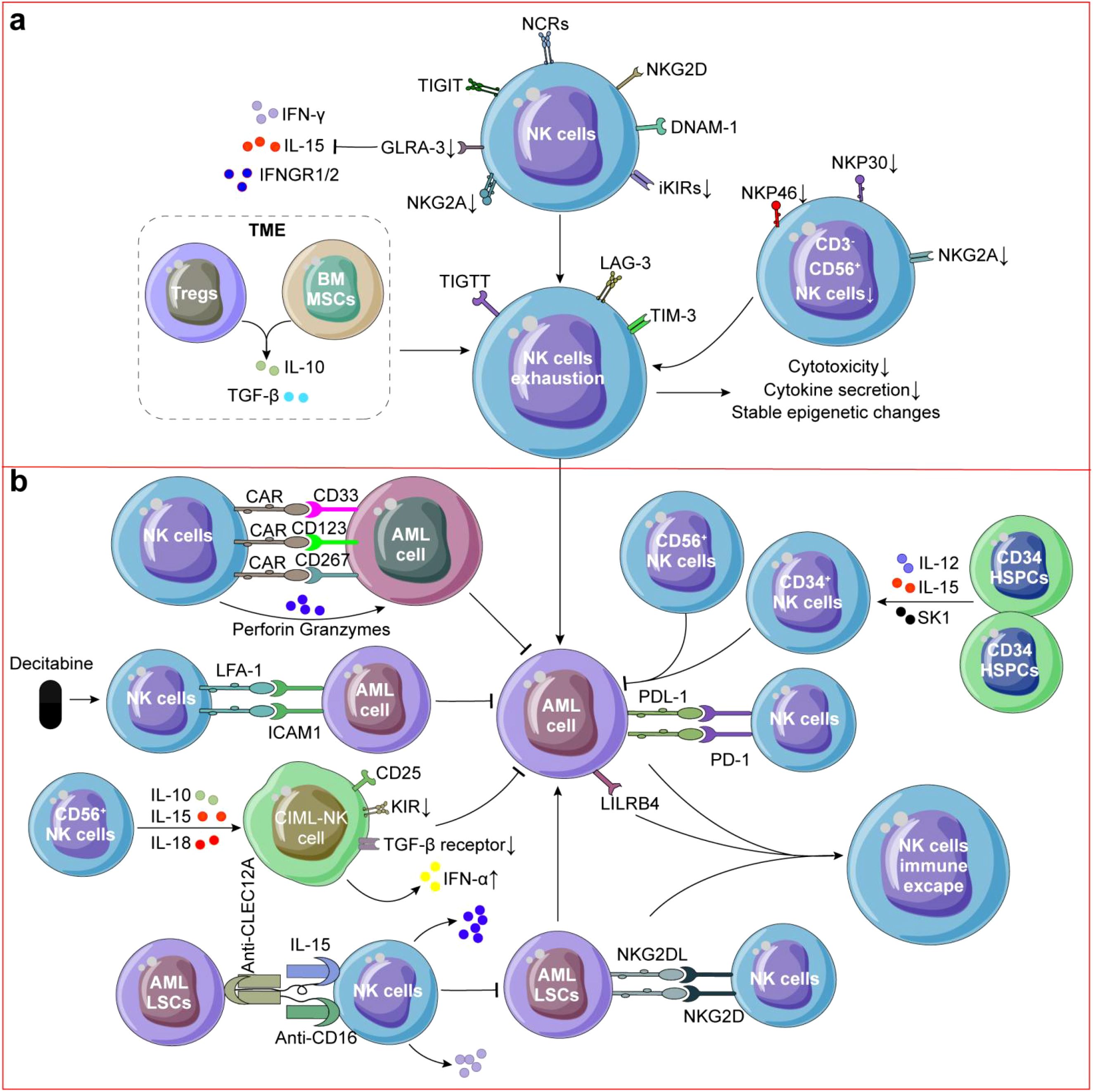
Figure 2. NK cells in AML. (a) NK cells exhibited impaired killing ability and exhausted phenotype. CD3-CD56+ NK cells in AML was decreased and Tregs or BMSCs secreting IL-10 or TGF-β also contributed to NK cell exhaustion in AML. (b) Decitabine could upregulating LFA expression on NK cells and inducing ICAM-1 expression on AML cells, thereby enhancing the cytotoxic activity of AML-NK cells. CD34+ NK cells, CD56+ NK cells or CIML-NK cells could directly kill AML cells. CD33/CD123/CD267 CAR-NK cells and TriKE molecules targeting CLEC12A were also used to reactive NK cells for killing AML cells and LSCs. Immune escape of NK cells is caused by residual LSCs and binding of PD-L1 on the surface of AML cells to PD-1 on the surface of NK cells, which results in AML recurrence.
Other studies have investigated novel therapeutic strategies to kill AML cells by combination of NK cells, and trispecific killer engager (TriKE) molecules targeting CLEC12A, the AML mice treated with CLEC12A TriKE had significantly less tumor burden compared to tumor alone or tumor with NK cells (120) (Figure 2b). Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor-human leukocyte antigen (KIR-HLA) mismatched NK cells (median, 29 × 106/kg NK cells) infusions shown a significant expansion of KIR-mismatched NK cells (median, 5,800/mL of blood on day 14) could decrease relapse rates without increasing mortality in children with AML (121). CD276 (B7-H3) is highly expressed in leukemia cells of AML patients, FC optimized CD276 mAb specifically binds to CD276 on primary AML cells, promoting activation and enhancing anti-AML effects of NK cells (122).
On the whole, preclinical studies using NK cells to treat AML have shown encouraging results. However, challenges remain in ensuring long-term sustainability and mitigating potential off-target toxicity. Future clinical trials will determine the true potential of NK cells to revolutionize the AML treatment landscape.
3.3 NK cell exhaustion in AML
NK cells in AML patients mainly exhibit impaired killing ability and overall functional impairment of exhausted phenotype (Figure 2a) that indicates poor prognosis and high recurrence (123). On the one hand, the content of resident CD3-CD56+ NK cells in AML was decreased compared to healthy donors (124) (Figure 2a). NK cells from AML patients typically express more NCRs/NKG2D/DNAM-1, down-regulated NKG2A/iKIRs (113) and the ability of NK cells secreting IFN-γ is significantly reduced which may limit their ability to recognize and clear AML cells and patients with NK cell spectrum defects increased recurrence risk (p = 0.03) without regard for their cytogenetic classification (125). Turk et al. found that down-regulation of renin-angiotensin system (Ras) genes and neurotransmitter genes were involved in NK cell dysfunction in AML (126). For example, ATP6AP2 may modulate NK cell responses through regulation of pH homeostasis, autophagic flux, and NLRP3 inflammasome activation (127, 128). And, down-regulation of arginine may also impair cytokine secretion capacity of NK cells (129). Transcriptomic analysis of BM NK cells from AML patients reveals stress-induced inhibition of NK cell effector function. While CD160 expression is down-regulated in these NK cells, patients with CD160high NK cells demonstrate significantly improved survival rates (130).
On the other hand, reduction in the number and function, high expression of T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT) of NK cells has been implicated in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), a condition that can progress to AML (131, 132). Through intercellular contact or secrete IL-10 or TGF-β by Tregs in AML TME contributed to NK cell exhaustion, which accelerates the occurrence of AML (22) (Figure 2a). And, AML development has been linked to impairing the BM homing capacity of infused NK cells (133). Unconventional CD56-CD16+ NK cells which decreased expression of NKG2A/NKp30/NKp46 in AML has been observed, indicating adverse clinical outcome (134, 135) (Figure 2a), and high expression of NKp46 contribute to the prognosis of AML patients after allo-HSCT (135). Similarly, the results were also found in animal experiments, in the MLL-AF9-induced mouse AML model, more mNKs were detected, but their mature state may not be sufficient to fully exert their anti-AML effects (136).
In summary, NK cell exhaustion promotes the occurrence, progression, and recurrence of AML. Increasing the number of NK cells or activating their function can contribute to the treatment and prognosis of AML. Therefore, NK cell-based treatment strategies for AML show theoretical promise and warrant further investigation.
3.4 Immune evasion of NK cells in AML
Significant challenges persist in maximizing the therapeutic potential of NK cells in AML treatment, particularly as AML cells have developed sophisticated mechanisms to evade NK cell-mediated immunosurveillance (137). Claudia Lengerke et al. demonstrated that NKG2D ligands are generally expressed on most of AML cells but not on LSCs, potentially explaining their resistance to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity and their role in therapeutic resistance (138). In AML, the function of NK cells can be inhibited by various factors, including the presence of multiple immunosuppressive factors in the TME, such as TGF-β and IL-10 (Figure 2a), which inhibit the activity and proliferation of NK cells (139). In AML, Tregs and BMSCs typically expand and secrete inhibitory cytokines to reduce the anti-AML activity of NK cells (140, 141). AML cells may express inhibitory ligands such as PD-L1 (Figure 2b), which can bind to receptors on the surface of NK cells and inhibit their activity (142, 143). Some AML cells can induce NK cell death by activating the apoptotic pathway (144, 145) and overexpressing inhibitory immune molecules LILRB4 (Figure 2b), directly inhibiting the activity of NK cells (137, 146). AML cells can alter TME, for example, tumor associated fibroblasts may suppress NK cell function by secreting inhibitory factors (147, 148). One study suggested that combination of hypomethylating agents and NK cell infusion could be a promising strategy to overcome AML immune escape (137). Although there has been progress in understanding the immune escape mechanism of NK cells in AML, there are still some unknown areas.
Future research directions in AML should prioritize: i) elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying AML-mediated NK cell dysfunction; ii) characterizing the dynamic interactions between NK cells and the leukemic microenvironment; iii) developing patient-stratified NK cell-based immunotherapeutic approaches to optimize clinical outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
4 The relation between NK Cells And CML
4.1 Characteristics of CML
CML is a multipotential hematopoietic stem cell disease (149). The hematopoietic cells contain a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 in more than 90% of patients with classic morphologic findings, which leads to an overtly foreshortened long arm of one of the pair of chromosome 22, referred to as the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) (150). The most iconic change in CML is Ph, caused by the reciprocal translocation t(9;22) (q34;q11.2), resulting in the formation of BCR-ABL fusion gene which was a clinical diagnostic marker (151). The chronic myelogenous leukemias (CMLs) include BCR rearrangement-positive CML, atypical CML, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, chronic neutrophilic leukemia, chronic eosinophilic leukemia, and chronic basophilic leukemia (152).
Similar to AML, LSCs are the main cause of CML occurrence and recurrence. CML is caused by activation of BCR-ABL in HSCs and converting them into LSCs defined as CD34+CD38- lead to expansion of myeloid progenitors (153). For example, in a phase 2 pilot study of 46 CML patients, patients who did not achieve major molecular response (MMR) at 18 months of treatment with imatinib or dasatinib had Ph+ cells (> 75%) in the CD34+CD38- fraction (154). Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) induce up-regulation of N-cadherin in LSCs and adhesion to MSCs leads to activation in typical Wnt signaling, protects LSCs from apoptosis and promotes relapse (155). LSCs may also avoid eradication by modulating host immune surveillance in TME, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) fail to induce an appropriate immune response against CML cells through CTLs exhaustion due to the interaction of the PD-1 receptor expressed on CTLs with the inhibitory ligand PD-L1 expressed on CML cells (156). Meanwhile, the number and activity of CD4+ helper T cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are decreased in CML patients, manifested by up-regulation of surface markers such as PD-1 and CTLA-4, ultimately leading to a weakened immune response to CML cells (157). The expression of Lin-CD11b+CD33+ MDSCs was increased at diagnosis (38.6 ± 6.5%) compared with MMR (11.8 ± 2.5%, p = 0.0004) and CD4+CD25highCD127-Foxp3+ Tregs was higher at diagnosis (2.3 ± 0.2%) compared with MMR (1.8 ± 0.2%, p = 0.02) (158) indicating the treatment of CML may require a combination of TKI and immunotherapy.
TKIs significantly improve patient outcomes by specifically inhibiting the activity of BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase such as asciminib, imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, etc (159). The advancement of TKIs has substantially prolonged the survival time of most CML patients, with 5-year survival rates reaching approximately 65% to 70% (160). Patients taking imatinib showed that about 86% to 93% were still alive 5 years (161). However, long-term TKI therapy may result in drug resistance in approximately 15 ~ 17% of cases, primarily due to T315I mutations and LSCs activation, presenting an urgent clinical challenge (162). HSCT, interferon therapy (Pegylated interferon), hormone treatment, radiation therapy were also used to treat CML patients, but recurrence of CML still occur because the immune system of patient is not durably reactivated. In order to solve the above problems, CD19 (163), CD26 (164) or CD38 (165) CAR-T was used to overcome TKIs and chemotherapy resistance which achieved satisfactory results. However, it is worth noting that there was some extratumoral cytotoxicity towards activated lymphocytes (164).
As described above, for the clinical treatment of CML and the reversal of chemotherapy resistance, it is a feasible strategy to combination of chemotherapy novel immunotherapies with high efficiency and low toxicity.
4.2 Treatment of CML based on NK cells
NK cell-based therapeutic strategies for CML have garnered increasing attention in recent years (166). To enhance NK cell expansion and cytotoxicity, modified dendritic cell-derived exosomes activated NK cells could improve anti-CML effects via NKG2D/NKG2D-L pathway (167). K562 cells were modified by expressing a membrane-bound form of IL-15 which could induce higher expansion of CD56+CD3- NK cells from PB (168, 169) (Figure 3b). Modification effects of IL-15 are also used in MM (170), MDS (171), colon cancer (CRC) and pancreatic cancer (PDAC) (172). Qi Li also reported that IL-21(50 ng/mL) could increase the number of CD56+CD3+ NK cells among PBMCs (173) revealing the feasibility of IL-15 or 21-secreting CAR-NK in treating CML. At present, CAR-NK based CML therapy is in the animal experimental stage (Figure 3b), Jusuf Imeri found that CD25 CAR-NK92 cells can effectively treat NSG mice transplanted with K562-CD25 cells and significantly increased the survival rate as compared to the untreated and NK92 WT treated cohorts (p < 0.01) (174) indicating that it is feasible to treat CML with CAR-NK.
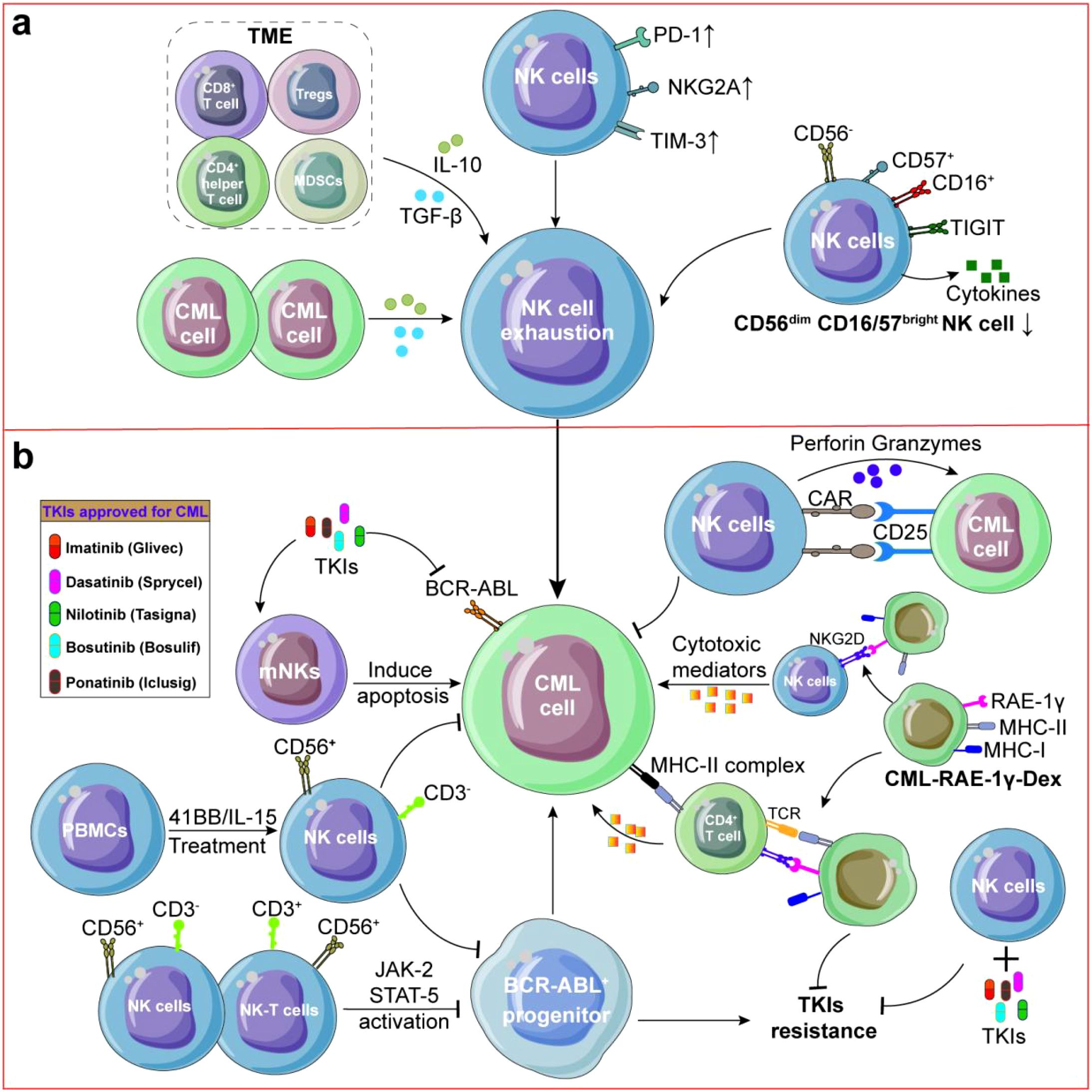
Figure 3. NK cells in CML. (a) Immune cell subpopulations and CML cells secreted IL-10 or TGF-β which contributed to dysfunction of NK cells. Meanwhile, Mature CD56dimCD16/57bright NK cells and circulating NK cells were reduced which could promote CML occurence and recrudescence. (b) NK cells could demonstrate direct cytotoxicity against CML cells and both CD56+CD3- NK cells and CD56+CD3+ NK-T cells suppress proliferation of BCR-ABL+ progenitors through JAK-2/STAT-5 pathway activation. To enhance NK cell expansion and cytotoxicity, PBMCs cells were treated with IL-15 and 41-BB could increase the number of CD56+CD3+ NK cells, CD25 CAR-NK92 cells can effectively kill CML cells. In reversing TKIs resistance, CML-RAE-1γ-Dex activate both NK cells and T lymphocytes, and inhibit the proliferation of TKIs-resistant CML cells.
Multiple clinical trials have been conducted exploring NK cell-based treatments for CML. For example, the clinical trial (NCT00720785) conducted in 2021 (Table 1b) verified the anti-CML effects by combination of Bortezomib and NK cells infusion. In another phase I/II study (NCT03348033) assessing the safety and feasibility of autologous activated and expanded NK cells in CML, infusion of NK cells significantly reduced BCR-ABL gene expression compared to untreated controls (Table 1). NCT02727803 and NCT02727803, both CML clinical trials, similarly demonstrated that infusion of the allogeneic NK cell line NK92 or primary CD56+CD3- NK cells, respectively, significantly reduced BCR-ABL gene expression compared to controls (Table 1). These results provided a clinical reference for NK cell-based CML therapy and further confirmed its feasibility.
NK cells can be also used to reverse TKIs resistance. For reversing TKIs resistance, NK cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) exhibit stronger cytotoxicity against imatinib resistant cells than parental ones by reducing the CD34+/CD38- sub-populations (166). In advanced EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer, Ye Fei et al. found that combination of CD8+CD56+ NKT cells with gefitinib can overcome EGFR-TKIs resistance, revealing the universality of NK cells in reversing TKIs resistance (175). NK92-CD16 cells preferally kill TKIs-resistant cells by targeting ICAM-1, especially combination with cetuximab (an EGFR-targeted mab), the effect of reversing resistance is further enhanced (176, 177). CML-specific Dendritic cell-derived exosomes (CML-RAE-1γ-Dex) rich in RAE-1γ activate both NK cells and T lymphocytes (Figure 3b), and inhibit the proliferation of imatinib-resistant CML cells with T315I mutations (167).
Future directions in CML should prioritize: i) optimization of NK cell expansion and activation protocols; ii) advancement of CAR-NK development and clinical validation; iii) longitudinal assessment of NK cell therapy safety and efficacy in CML patients through rigorous clinical trials.
4.3 NK cell exhaustion in CML
Most NK cells in CML were active CD56dim cluster in PB and interacted with leukemia cells through inhibitory LGALS9-TIM3 and PVR-TIGIT interactions (178). Other studies also found the expression of TIGIT was increased on CD56dim NK cells in CML PB while CD57 was increased on CD56dim NK cells in CML BM (179), indicating that reversing immune suppression of PB NK cells by blocking TIGIT while improving proliferation of BM NK cells via targeting CD57 may be more effective in anti-CML (Figure 3a). Similar to AML, the absolute number of mature CD56dimCD16/57bright NK cells and circulating NK cells in PB were significantly reduced in CML patients (180). For example, the percentage of CD56+ NK subset in total circulating NK pool was significantly reduced in 21 CML patients (2.5% ± 0.5%) compared with normal donors (5.7% ± 0.8%) (p < 0.001) (181). Meanwhile, NK cells were dysfunctional during CML progression from chronic phase to blast crisis because BCR-ABL decreased the natural cytotoxicity of NK cells and the acquisition of KIRs (182). BCR-ABL could also interference with NK cell differentiation and exogenous addition of BCR-ABL transduced autologous CD34+ cells could inhibit NK cell differentiation of normal umbilical cord blood CD34+ and CD38- cells (183). Another study found that CML cells could effectively inhibit the cytotoxicity of baseline and IL-2-induced NK cells to K562 cells through reducing NADPH oxidase-mediated formation of ROS (184) revealing the complexity of interrelation between CML and NK cells.
NK cell exhaustion could promote CML recrudescence (Figures 3a, b). Firstly, inhibition of ROS can restore NK cell numbers and enhance their cytotoxicity against CML (185). And, knockout of CXCR4 leads to NK cell depletion and TKIs resistance (186, 187). Secondly, both CD56+CD3-NK cells and CD56+CD3+ NK-T cells suppress granulocyte-macrophage colony formation in BCR-ABL+ progenitors through JAK-2/STAT-5 pathway activation, while sparing normal CD34+ cells (188). Meanwhile, CML cells may release MICA into plasma, leading to NKG2D down-regulation on CD56+ NK cells and subsequent NK cell dysfunction (188). Thirdly, hyper-functional adaptive-like NK cells in CML MMR patients exhibited a 56-fold expansion of a normally rare subset (p < 0.01) which diminished following TKIs resistance (189). Degranulation of NK cells can be partially saved by inhibiting CIS or TNF-β to overcome NK cell suppression (190). Consistent with these findings, Amandine Decroos et al. found that high frequencies of perforin-expressing NK cells is associated with treatment-free remission (191), and these results suggest that targeting inflammatory signals can enhance NK cell-based CML immunotherapy.
Clinical evidence demonstrates that CML patients with favorable responses to imatinib exhibit elevated levels of CD3-CD56+ NK cells (p = 0.0043), CD16+ NK cells (p = 0.0046) and CD57+ NK cells (p = 0.0208) (192). Moreover, NK cells from TKIs-treated CML patients show enhanced expression of NKp30/NKp46/NKp80 (193), suggesting that NK cell maturation status correlates with TKIs response. The clinical trial, NCT03239886, revealed that patients experiencing relapse after 6-month imatinib discontinuation demonstrated significantly lower NK cell proportions compared to non-relapsing patients, indicating NK cell levels as potential predictive biomarkers for molecular relapse risk (Table 1). In the context of allo-HSCT, patients receiving HLA-matched but KIR3DL1-mismatched transplants showed reduced BCR-ABL transcription levels and enhanced NK cell activity (194). Notably, KIR3DL1+ NK cells exhibited rapid recovery (17.1% median at days 28-56, increasing to 41.7-86.0% by days 28-41), suggesting that KIR3DL1-HLA-B interactions may modulate anti-tumor immunity.
The above studies indicate that NK cells play an important role in the occurrence and recurrence of CML and can be used as an effective weapon in the treatment of CML. Next, we will further summarize the mechanism of NK cell immune escape in CML.
4.4 Immune evasion of NK cells in CML
Immune escape represents a critical barrier to NK cell-based immunotherapy. The CML microenvironment is characterized by abundant MDSCs and Tregs (Figure 3a), which suppress NK cell activity and proliferation, facilitating immune evasion (195, 196). Changes in receptors on the surface of NK cells also mediate immune escape. Ya-Ching Hsieh et al. found that up-regulation of inhibitory receptors NKG2A on NK cells leads to loss of effective recognition of CML cells by NK cells (197), Meanwhile, the CML cells themselves can secrete a variety of cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, which could inhibit the function and proliferation of NK cells (107). CML cells may also evade NK cell attacks by altering surface antigens, such as down-regulating the expression of NKG2DL or MHC, to inhibit the action of NK cells by secreting soluble MICA (sMICA) and reduce NK cell recognition (198). CML cells also inhibited NK cell activation signals by up-regulating TIM-3 or PD-1 that interact with receptors on the NK cell surface (178). Many CML cells exhibit a deficiency of the HLA-DR antigen, which is an important molecule for NK cells to recognize target cells (199). When HLA antigen expression decreases, the recognition ability of NK cells is limited (199). Future studies need to focus on how to restore the function of NK cells and prevent immune escape of NK cells and treatment failure.
5 Comparative analysis of CAR-T and CAR-NK cell therapy in AML/CML
NK cells present several advantages over T cells, including reduced toxicity (200), superior scalability in manufacturing (201), and an intrinsic ability of CAR-NK to differentiate between malignant and non-malignant cells (202). CAR-T cells mediate cytotoxicity through T-cell receptor (TCR) activation via CD3ζ signaling domains and costimulatory domains (e.g., 4-1BB/CD28), targeting specific antigens (e.g., CD19, CD22), but AML/CML lack ideal tumor-specific antigens, leading to on-target/off-tumor toxicity against normal HSCs (23, 203). The limitations of CAR-T cells in AML/CML mainly include: shared expression of targets (e.g., CD33, CD123, FLT3) on normal hematopoietic progenitors causes myelosuppression (203), and high antigen escape rates (> 60% in heterogeneous AML) (23, 203). The mechanisms of CAR-NK cells include: scFv-mediated antigen recognition (e.g., CD19, CD70), innate cytotoxicity (“missing-self” recognition of low MHC-I cells), CD16-mediated ADCC, and IFN-γ/TNF-α secretion (204–206). CAR-NK cells can eliminate AML HSCs with low MHC-I expression (feature of advanced CML) (207) and target CD70 (highly expressed on AML blasts and CML blast crisis), while also clearing alloreactive T cells to prolong persistence (208). The advantages of CAR-T cells in AML/CML are long persistence (> 12 months) and efficacy against high tumor burden (23). However, CAR-T cells require prolonged manufacturing (3–5 weeks), and the antigen density was low (23). In contrast, iPSC-derived CD70 CAR-NK cells have demonstrated > 90% AML cell clearance while suppressing alloreactive T-cell rejection (208). In short, compared with CAR-T cells, CAR-NK cells exhibit higher clinical efficacy and translational potential.
6 Conclusions
In the past 15 years, clinical trials of NK cell-based therapy for ML have expanded significantly with promising outcomes. Nevertheless, significant challenges remain, particularly in optimizing NK cell expansion, variability in response, circumventing immune surveillance mechanisms and manufacturing scalability. The future directions or therapeutic strategies of NK cell-based therapeutics in ML depends on the following critical factors. First, the diversification of cell sources, encompassing both autologous and allogeneic NK cells, along with established cell lines such as NK92, offers more therapeutic options. Next, concurrent advances in genetic engineering platforms, particularly CRISPR/Cas9 technology, are expected to enhance targeting specificity and anti-ML efficacy. Last, the integration of NK cell therapy with conventional treatments, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy, as well as other immunotherapeutic approaches, could yield superior therapeutic outcomes. Additionally, the development of patient-tailored NK cell products based on individual ML characteristics presents an opportunity to optimize therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. In conclusion, the NK cell-based therapeutic strategy for ML demonstrates both theoretical soundness and clinical feasibility, warranting further research focused on advancing NK cell product development and clinical translation.
Author contributions
LZ: Writing – original draft. YZ: Writing – original draft. YD: Writing – review & editing. XJ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KJQN202412805) and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region “Tingzhou talents” support program (Grant No.2024-75).
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to all the editors and reviewers for their hard work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
3. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, and Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2018) 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
4. Yamashita M, Dellorusso PV, Olson OC, and Passegue E. Dysregulated haematopoietic stem cell behaviour in myeloid leukaemogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. (2020) 20:365–82. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0260-3
5. Cayssials E and Guilhot F. The -7 chromosomal abnormalities with signs of myelodysplasia in chronic myeloid leukemia as a major red signal. Haematologica. (2019) 104:1096–98. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.217034
6. Rubin CM, Arthur DC, Woods WG, Lange BJ, Nowell PC, Rowley JD, et al. Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia in children: correlation between chromosomal abnormalities and prior therapy. Blood. (1991) 78:2982–88. doi: 10.1182/blood.V78.11.2982.2982
7. Duncavage EJ, Abel HJ, Szankasi P, Kelley TW, and Pfeifer JD. Targeted next generation sequencing of clinically significant gene mutations and translocations in leukemia. Mod Pathol. (2012) 25:795–804. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.29
8. Rutella S, Vadakekolathu J, Mazziotta F, Reeder S, Yau TO, Mukhopadhyay R, et al. Immune dysfunction signatures predict outcomes and define checkpoint blockade-unresponsive microenvironments in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:e159579. doi: 10.1172/JCI159579
9. Wu Y, Zhu H, and Wu H. PTEN in regulating hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2020) 10:a036244. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036244
10. Tsiftsoglou AS, Bonovolias ID, and Tsiftsoglou SA. Multilevel targeting of hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal, differentiation and apoptosis for leukemia therapy. Pharmacol Ther. (2009) 122:264–80. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.03.001
11. Whiteley AE, Price TT, Cantelli G, and Sipkins DA. Leukaemia: a model metastatic disease. Nat Rev Cancer. (2021) 21:461–75. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00355-z
12. Shroff GS, Truong MT, Carter BW, Benveniste MF, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Rauch G, et al. Leukemic involvement in the thorax. Radiographics. (2019) 39:44–61. doi: 10.1148/rg.2019180069
13. Luca DC. Update on lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Clin Lab Med. (2021) 41:405–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2021.04.003
14. Faderl S, O’Brien S, Pui CH, Stock W, Wetzler M, Hoelzer D, et al. Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: concepts and strategies. Cancer. (2010) 116:1165–76. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24862
15. Quijada-Alamo M, Hernandez-Sanchez M, Robledo C, Hernandez-Sanchez JM, Benito R, Montano A, et al. Next-generation sequencing and FISH studies reveal the appearance of gene mutations and chromosomal abnormalities in hematopoietic progenitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. (2017) 10:83. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0450-y
16. Hopken UE and Rehm A. Targeting the tumor microenvironment of leukemia and lymphoma. Trends Cancer. (2019) 5:351–64. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.05.001
17. Guillerey C. NK cells in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1273:69–90. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49270-0_4
18. Xie J, Liu XF, Zhou T, Liu L, Hou RQ, Yu XX, et al. Overexpressing natural killer group 2 member A drives natural killer cell exhaustion in relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2025) 10:143. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02228-5
19. Mujal AM, Delconte RB, and Sun JC. Natural killer cells: from innate to adaptive features. Annu Rev Immunol. (2021) 39:417–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-101819-074948
20. Barshidi A, Ardeshiri K, Ebrahimi F, Alian F, Shekarchi AA, Hojjat-Farsangi M, et al. The role of exhausted natural killer cells in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of leukemia. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:59. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01428-2
21. Sivori S, Vacca P, Del ZG, Munari E, Mingari MC, and Moretta L. Human NK cells: surface receptors, inhibitory checkpoints, and translational applications. Cell Mol Immunol. (2019) 16:430–41. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0206-4
22. Zhang Z, Deng C, Zhu P, Yao D, Shi J, Zeng T, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals a microenvironment and an exhaustion state of T/NK cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:3873–83. doi: 10.1111/cas.15932
23. Peng L, Sferruzza G, Yang L, Zhou L, and Chen S. CAR-T and CAR-NK as cellular cancer immunotherapy for solid tumors. Cell Mol Immunol. (2024) 21:1089–108. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01207-0
24. Ebrahimiyan H, Tamimi A, Shokoohian B, Minaei N, Memarnejadian A, Hossein-Khannazer N, et al. Novel insights in CAR-NK cells beyond CAR-T cell technology; promising advantages. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 106:108587. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108587
25. Xie G, Dong H, Liang Y, Ham JD, Rizwan R, and Chen J. CAR-NK cells: A promising cellular immunotherapy for cancer. Ebiomedicine. (2020) 59:102975. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102975
26. Marin D, Li Y, Basar R, Rafei H, Daher M, Dou J, et al. Safety, efficacy and determinants of response of allogeneic CD19-specific CAR-NK cells in CD19(+) B cell tumors: a phase 1/2 trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:772–84. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02785-8
27. Liu E, Marin D, Banerjee P, Macapinlac HA, Thompson P, Basar R, et al. Use of CAR-transduced natural killer cells in CD19-positive lymphoid tumors. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:545–53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910607
28. Jiang H, Zhang W, Shang P, Zhang H, Fu W, Ye F, et al. Transfection of chimeric anti-CD138 gene enhances natural killer cell activation and killing of multiple myeloma cells. Mol Oncol. (2014) 8:297–310. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.12.001
29. Ma S, Caligiuri MA, and Yu J. A four-stage model for murine natural killer cell development in vivo. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:31. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01243-1
30. Kim EM, Lee EH, Lee HY, Choi HR, Ji KY, Kim SM, et al. Axl signaling induces development of natural killer cells in vitro and in vivo. Protoplasma. (2017) 254:1091–101. doi: 10.1007/s00709-016-1016-5
31. Flores CT, Wildes TJ, Drake JA, Moore GL, Dean BD, Abraham RS, et al. Lin(-)CCR2(+) hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells overcome resistance to PD-1 blockade. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:4313. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06182-5
32. Wang X and Zhao XY. Transcription factors associated with IL-15 cytokine signaling during NK cell development. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:610789. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.610789
33. Li D, Wang Y, Yang M, and Dong Z. mTORC1 and mTORC2 coordinate early NK cell development by differentially inducing E4BP4 and T-bet. Cell Death Differ. (2021) 28:1900–09. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00715-6
34. Reyes RM, Zhang C, Deng Y, Ji N, Mukherjee N, Padron AS, et al. CD122-targeted interleukin-2 and alphaPD-L1 treat bladder cancer and melanoma via distinct mechanisms, including CD122-driven natural killer cell maturation. Oncoimmunology. (2021) 10:2006529. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.2006529
35. Luther C, Warner K, and Takei F. Unique progenitors in mouse lymph node develop into CD127+ NK cells: thymus-dependent and thymus-independent pathways. Blood. (2011) 117:4012–21. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-298901
36. Maenpaa A, Jaaskelainen J, Carpen O, Patarroyo M, and Timonen T. Expression of integrins and other adhesion molecules on NK cells; impact of IL-2 on short- and long-term cultures. Int J Cancer. (1993) 53:850–55. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530524
37. Bernardini G, Gismondi A, and Santoni A. Chemokines and NK cells: regulators of development, trafficking and functions. Immunol Lett. (2012) 145:39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.04.014
38. Mukherjee S, Jensen H, Stewart W, Stewart D, Ray WC, Chen SY, et al. In silico modeling identifies CD45 as a regulator of IL-2 synergy in the NKG2D-mediated activation of immature human NK cells. Sci Signal. (2017) 10:eaai9062. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aai9062
39. Gordon SM, Chaix J, Rupp LJ, Wu J, Madera S, Sun JC, et al. The transcription factors T-bet and Eomes control key checkpoints of natural killer cell maturation. Immunity. (2012) 36:55–67. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.016
40. Dang N, Lin Y, Waer M, and Sprangers B. Donor lymphocyte-derived natural killer cells control MHC class I-negative melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res. (2020) 8:756–68. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0666
41. Zhang T, Liu S, Yang P, Han C, Wang J, Liu J, et al. Fibronectin maintains survival of mouse natural killer (NK) cells via CD11b/Src/beta-catenin pathway. Blood. (2009) 114:4081–88. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-219881
42. Zhang X, Feng J, Chen S, Yang H, and Dong Z. Synergized regulation of NK cell education by NKG2A and specific Ly49 family members. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:5010. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13032-5
43. Millan AJ, Hom BA, Libang JB, Sindi S, and Manilay JO. Evidence for prescribed NK cell Ly-49 developmental pathways in mice. J Immunol. (2021) 206:1215–27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000613
44. Lindberg J, Martin-Fontecha A, and Hoglund P. Natural killing of MHC class I(-) lymphoblasts by NK cells from long-term bone marrow culture requires effector cell expression of Ly49 receptors. Int Immunol. (1999) 11:1239–46. doi: 10.1093/intimm/11.8.1239
45. Freud AG, Becknell B, Roychowdhury S, Mao HC, Ferketich AK, Nuovo GJ, et al. A human CD34(+) subset resides in lymph nodes and differentiates into CD56bright natural killer cells. Immunity. (2005) 22:295–304. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.01.013
46. Cordeiro GA, Hara T, Lim VY, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Nevius E, Sugiyama T, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell niches produce lineage-instructive signals to control multipotent progenitor differentiation. Immunity. (2016) 45:1219–31. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.11.004
47. Male V, Nisoli I, Kostrzewski T, Allan DS, Carlyle JR, Lord GM, et al. The transcription factor E4bp4/Nfil3 controls commitment to the NK lineage and directly regulates Eomes and Id2 expression. J Exp Med. (2014) 211:635–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.20132398
48. Rosmaraki EE, Douagi I, Roth C, Colucci F, Cumano A, and Di Santo JP. Identification of committed NK cell progenitors in adult murine bone marrow. Eur J Immunol. (2001) 31:1900–09. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200106)31:6<1900::aid-immu1900>3.0.co;2-m
49. Hughes T, Becknell B, Freud AG, McClory S, Briercheck E, Yu J, et al. Interleukin-1beta selectively expands and sustains interleukin-22+ immature human natural killer cells in secondary lymphoid tissue. Immunity. (2010) 32:803–14. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.06.007
50. Song S, Zhi Y, Tian G, Sun X, Chen Y, Qiu W, et al. Immature and activated phenotype of blood NK cells is associated with acute rejection in adult liver transplant. Liver Transpl. (2023) 29:836–48. doi: 10.1097/LVT.0000000000000139
51. Liu B, Yang GX, Sun Y, Tomiyama T, Zhang W, Leung P, et al. Decreased CD57 expression of natural killer cells enhanced cytotoxicity in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:912961. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.912961
52. Montaldo E, Vitale C, Cottalasso F, Conte R, Glatzer T, Ambrosini P, et al. Human NK cells at early stages of differentiation produce CXCL8 and express CD161 molecule that functions as an activating receptor. Blood. (2012) 119:3987–96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-379693
53. Poli A, Michel T, Theresine M, Andres E, Hentges F, and Zimmer J. CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells: an important NK cell subset. Immunology. (2009) 126:458–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03027.x
54. Michel T, Poli A, Cuapio A, Briquemont B, Iserentant G, Ollert M, et al. Human CD56bright NK cells: an update. J Immunol. (2016) 196:2923–31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502570
55. Chan A, Hong DL, Atzberger A, Kollnberger S, Filer AD, Buckley CD, et al. CD56bright human NK cells differentiate into CD56dim cells: role of contact with peripheral fibroblasts. J Immunol. (2007) 179:89–94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.89
56. Cichocki F, Grzywacz B, and Miller JS. Human NK cell development: one road or many? Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02078
57. Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, and Caligiuri MA. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol. (2001) 22:633–40. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(01)02060-9
58. Capuano C, Pighi C, Maggio R, Battella S, Morrone S, Palmieri G, et al. CD16 pre-ligation by defucosylated tumor-targeting mAb sensitizes human NK cells to gamma(c) cytokine stimulation via PI3K/mTOR axis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2020) 69:501–12. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02482-2
59. Vietzen H, Staber PB, Berger SM, Furlano PL, Kuhner LM, Lubowitzki S, et al. Inhibitory NKG2A(+) and absent activating NKG2C(+) NK cell responses are associated with the development of EBV(+) lymphomas. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1183788. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183788
60. Caligiuri MA. Human natural killer cells. Blood. (2008) 112:461–69. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-077438
61. Ran GH, Lin YQ, Tian L, Zhang T, Yan DM, Yu JH, et al. Natural killer cell homing and trafficking in tissues and tumors: from biology to application. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:205. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01058-z
62. van Helden MJ, de Graaf N, Boog CJ, Topham DJ, Zaiss DM, and Sijts AJ. The bone marrow functions as the central site of proliferation for long-lived NK cells. J Immunol. (2012) 189:2333–37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200008
63. Mishra HK, Dixon KJ, Pore N, Felices M, Miller JS, and Walcheck B. Activation of ADAM17 by IL-15 limits human NK cell proliferation. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:711621. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.711621
64. Shannon MJ and Mace EM. Natural killer cell integrins and their functions in tissue residency. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:647358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.647358
65. Perfilyeva YV, Kustova EA, Urazalieva NT, Baisheva SA, Aubakirova AT, Tleulieva RT, et al. Effects of L-selectin stimulation of the expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 on NK cells of healthy donors and tumor patients. Bull Exp Biol Med. (2012) 153:86–8. doi: 10.1007/s10517-012-1650-7
66. Lin SJ, Chang LY, Yan DC, Huang YJ, Lin TJ, and Lin TY. Decreased intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (CD54) and L-selectin (CD62L) expression on peripheral blood natural killer cells in asthmatic children with acute exacerbation. Allergy. (2003) 58:67–71. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.2003.t01-1-23697.x
67. Santos J, Wang P, Shemesh A, Liu F, Tsao T, Aguilar OA, et al. CCR5 drives NK cell-associated airway damage in pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury. JCI Insight. (2023) 8:e173716. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.173716
68. Yao X and Matosevic S. Chemokine networks modulating natural killer cell trafficking to solid tumors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2021) 59:36–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.12.003
69. Bernardini G, Sciume G, and Santoni A. Differential chemotactic receptor requirements for NK cell subset trafficking into bone marrow. Front Immunol. (2013) 4:12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00012
70. Peng H and Tian Z. NK cell trafficking in health and autoimmunity: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2014) 47:119–27. doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8400-0
71. Bernardini G, Sciume G, Bosisio D, Morrone S, Sozzani S, and Santoni A. CCL3 and CXCL12 regulate trafficking of mouse bone marrow NK cell subsets. Blood. (2008) 111:3626–34. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-106203
72. Chen Y, Lu D, Churov A, and Fu R. Research progress on NK cell receptors and their signaling pathways. Mediators Inflamm. (2020) 2020:6437057. doi: 10.1155/2020/6437057
73. Kucuksezer UC, Aktas CE, Esen F, Tahrali I, Akdeniz N, Gelmez MY, et al. The role of natural killer cells in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:622306. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.622306
74. Scarno G, Pietropaolo G, Di Censo C, Gadina M, Santoni A, and Sciume G. Transcriptional, epigenetic and pharmacological control of JAK/STAT pathway in NK cells. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02456
75. Park JE, Kim SE, Keam B, Park HR, Kim S, Kim M, et al. Anti-tumor effects of NK cells and anti-PD-L1 antibody with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in PD-L1-positive cancer cell lines. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e000873. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000873
76. Zhang Y, Cheng G, Xu ZW, Li ZL, Song CJ, Li Q, et al. Down regulation of TRAIL and FasL on NK cells by Cyclosporin A in renal transplantation patients. Immunol Lett. (2013) 152:1–07. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.03.002
77. Belizario JE, Neyra JM, and Setubal DRM. When and how NK cell-induced programmed cell death benefits immunological protection against intracellular pathogen infection. Innate Immun. (2018) 24:452–65. doi: 10.1177/1753425918800200
78. Rahmani S, Yazdanpanah N, and Rezaei N. Natural killer cells and acute myeloid leukemia: promises and challenges. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2022) 71:2849–67. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03217-1
79. Alsulami HA, Alnashri MM, Bawazir AF, Alrashid LT, Dly RA, Alharbi YA, et al. Prognostics and clinical outcomes in patients diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in a teaching hospital. Cureus. (2021) 13:e18915. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18915
80. Yi M, Li A, Zhou L, Chu Q, Song Y, and Wu K. The global burden and attributable risk factor analysis of acute myeloid leukemia in 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017: estimates based on the global burden of disease study 2017. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:72. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00908-z
81. Strickland SA and Vey N. Diagnosis and treatment of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2022) 171:103607. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103607
82. Lejman M, Dziatkiewicz I, and Jurek M. Straight to the point-the novel strategies to cure pediatric AML. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1968. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041968
83. Stelmach P and Trumpp A. Leukemic stem cells and therapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. (2023) 108:353–66. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.280800
84. Zhang Y, Jiang S, He F, Tian Y, Hu H, Gao L, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals multiple chemoresistant properties in leukemic stem and progenitor cells in pediatric AML. Genome Biol. (2023) 24:199. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03031-7
85. Zhou H, Jiang Y, Huang Y, Zhong M, Qin D, Xie C, et al. Therapeutic inhibition of PPARalpha-HIF1alpha-PGK1 signaling targets leukemia stem and progenitor cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Lett. (2023) 554:215997. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215997
86. Nong T, Mehra S, and Taylor J. Common driver mutations in AML: biological impact, clinical considerations, and treatment strategies. Cells. (2024) 13:1392. doi: 10.3390/cells13161392
87. Kramer MH, Zhang Q, Sprung R, Day RB, Erdmann-Gilmore P, Li Y, et al. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic landscapes of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. (2022) 140:1533–48. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022016033
88. Rose D, Haferlach T, Schnittger S, Perglerova K, Kern W, and Haferlach C. Subtype-specific patterns of molecular mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. (2017) 31:11–7. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.163
89. Han SY, Mrozek K, Voutsinas J, Wu Q, Morgan EA, Vestergaard H, et al. Secondary cytogenetic abnormalities in core-binding factor AML harboring inv(16) vs t(8;21). Blood Adv. (2021) 5:2481–89. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003605
90. Bolis M, Terao M, Pattini L, Garattini E, and Fratelli M. The ATRA-21 gene-expression model predicts retinoid sensitivity in CEBPA double mutant, t(8;21) and inv(16) AML patients. Blood Cancer J. (2019) 9:76. doi: 10.1038/s41408-019-0241-5
91. Perzolli A, Koedijk JB, Zwaan CM, and Heidenreich O. Targeting the innate immune system in pediatric and adult AML. Leukemia. (2024) 38:1191–201. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02217-7
92. Baragano RA, Martin-Palanco V, Fernandez AF, Rodriguez RM, Fraga MF, Lopez-Larrea C, et al. Methylation of NKG2D ligands contributes to immune system evasion in acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Immun. (2015) 16:71–82. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.58
93. Fink A, Hung E, Singh I, and Ben-Neriah Y. Immunity in acute myeloid leukemia: Where the immune response and targeted therapy meet. Eur J Immunol. (2022) 52:34–43. doi: 10.1002/eji.202048945
94. Bruck O, Dufva O, Hohtari H, Blom S, Turkki R, Ilander M, et al. Immune profiles in acute myeloid leukemia bone marrow associate with patient age, T-cell receptor clonality, and survival. Blood Adv. (2020) 4:274–86. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000792
95. Vadakekolathu J, Minden MD, Hood T, Church SE, Reeder S, Altmann H, et al. Immune landscapes predict chemotherapy resistance and immunotherapy response in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Transl Med. (2020) 12:eaaz0463. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz0463
96. Weickert MT, Hecker JS, Buck MC, Schreck C, Riviere J, Schiemann M, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells from MDS and AML patients show increased adipogenic potential with reduced Delta-like-1 expression. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:5944. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85122-8
97. Zhang L, Chi Y, Wei Y, Zhang W, Wang F, Zhang L, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in patients with acute myeloid leukemia reveal transcriptome alterations and deficiency in cellular vitality. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:365. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02444-0
98. Xu J, Zong S, Sheng T, Zheng J, Wu Q, Wang Q, et al. Rapamycin increases leukemia cell sensitivity to chemotherapy by regulating mTORC1 pathway-mediated apoptosis and autophagy. Int J Hematol. (2024) 119:541–51. doi: 10.1007/s12185-024-03732-0
99. Ramdas B, Dayal N, Pandey R, Larocque E, Kanumuri R, Pasupuleti SK, et al. Alkynyl nicotinamides show antileukemic activity in drug-resistant acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134:e169245. doi: 10.1172/JCI169245
100. Brooks J, Zuro D, Song JY, Madabushi SS, Sanchez JF, Guha C, et al. Longitudinal preclinical imaging characterizes extracellular drug accumulation after radiation therapy in the healthy and leukemic bone marrow vascular microenvironment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2022) 112:951–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.10.146
101. Cornelissen JJ and Blaise D. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with AML in first complete remission. Blood. (2016) 127:62–70. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-604546
102. Kantarjian HM, Kadia TM, DiNardo CD, Welch MA, and Ravandi F. Acute myeloid leukemia: Treatment and research outlook for 2021 and the MD Anderson approach. Cancer. (2021) 127:1186–207. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33477
103. Zarychta J, Kowalczyk A, Krawczyk M, Lejman M, and Zawitkowska J. CAR-T cells immunotherapies for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia-recent advances. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:2944. doi: 10.3390/cancers15112944
104. Richard-Carpentier G, Rausch CR, Sasaki K, Hammond D, Morita K, Takahashi K, et al. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients with acute myeloid leukemia with inv(3)(q21q26.2) or t(3;3)(q21;q26.2). Haematologica. (2023) 108:2331–42. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.282030
105. Isidori A, Cerchione C, Daver N, DiNardo C, Garcia-Manero G, Konopleva M, et al. Immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia: where we stand. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:656218. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.656218
106. Koedijk JB, van der Werf I, Calkoen FG, Nierkens S, Kaspers G, Zwaan CM, et al. Paving the way for immunotherapy in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: current knowledge and the way forward. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:4364. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174364
107. Carlsten M and Jaras M. Natural killer cells in myeloid Malignancies: immune surveillance, NK cell dysfunction, and pharmacological opportunities to bolster the endogenous NK cells. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2357. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02357
108. Parameswaran R, Ramakrishnan P, Moreton SA, Xia Z, Hou Y, Lee DA, et al. Repression of GSK3 restores NK cell cytotoxicity in AML patients. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:11154. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11154
109. Kim S and Choi J. Restoring NK cell functions in AML relapse. Blood. (2022) 140:2765–66. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022018079
110. Pende D, Spaggiari GM, Marcenaro S, Martini S, Rivera P, Capobianco A, et al. Analysis of the receptor-ligand interactions in the natural killer-mediated lysis of freshly isolated myeloid or lymphoblastic leukemias: evidence for the involvement of the Poliovirus receptor (CD155) and Nectin-2 (CD112). Blood. (2005) 105:2066–73. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3548
111. Stringaris K, Adams S, Uribe M, Eniafe R, Wu CO, Savani BN, et al. Donor KIR Genes 2DL5A, 2DS1 and 3DS1 are associated with a reduced rate of leukemia relapse after HLA-identical sibling stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia but not other hematologic Malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. (2010) 16:1257–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.03.004
112. Romee R, Rosario M, Berrien-Elliott MM, Wagner JA, Jewell BA, Schappe T, et al. Cytokine-induced memory-like natural killer cells exhibit enhanced responses against myeloid leukemia. Sci Transl Med. (2016) 8:123r–357r. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf2341
113. Bakhtiyaridovvombaygi M, Yazdanparast S, Mikanik F, Izadpanah A, Parkhideh S, Shahbaz GA, et al. Cytokine-Induced Memory-Like NK Cells: Emerging strategy for AML immunotherapy. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115718. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115718
114. Bednarski JJ, Zimmerman C, Berrien-Elliott MM, Foltz JA, Becker-Hapak M, Neal CC, et al. Donor memory-like NK cells persist and induce remissions in pediatric patients with relapsed AML after transplant. Blood. (2022) 139:1670–83. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021013972
115. Albinger N, Pfeifer R, Nitsche M, Mertlitz S, Campe J, Stein K, et al. Primary CD33-targeting CAR-NK cells for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. (2022) 12:61. doi: 10.1038/s41408-022-00660-2
116. Stefanczyk SA, Hagelstein I, Lutz MS, Muller S, Holzmayer SJ, Jarjour G, et al. Induction of NK cell reactivity against acute myeloid leukemia by Fc-optimized CD276 (B7-H3) antibody. Blood Cancer J. (2024) 14:67. doi: 10.1038/s41408-024-01050-6
117. Wlodarczyk M and Pyrzynska B. CAR-NK as a rapidly developed and efficient immunotherapeutic strategy against cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 15:117. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010117
118. Huang R, Wen Q, and Zhang X. CAR-NK cell therapy for hematological Malignancies: recent updates from ASH 2022. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:35. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01435-3
119. Caruso S, De Angelis B, Del BF, Ciccone R, Donsante S, Volpe G, et al. Safe and effective off-the-shelf immunotherapy based on CAR.CD123-NK cells for the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:163. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01376-3
120. Arvindam US, van Hauten P, Schirm D, Schaap N, Hobo W, Blazar BR, et al. A trispecific killer engager molecule against CLEC12A effectively induces NK-cell mediated killing of AML cells. Leukemia. (2021) 35:1586–96. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01065-5
121. Rubnitz JE, Inaba H, Ribeiro RC, Pounds S, Rooney B, Bell T, et al. NKAML: a pilot study to determine the safety and feasibility of haploidentical natural killer cell transplantation in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:955–59. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.4590
122. Tan X and Zhao X. B7-H3 in acute myeloid leukemia: From prognostic biomarker to immunotherapeutic target. Chin Med J (Engl). (2024) 137:2540–51. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003099
123. Kumar B, Singh A, Basar R, Uprety N, Li Y, Fan H, et al. BATF is a major driver of NK cell epigenetic reprogramming and dysfunction in AML. Sci Transl Med. (2024) 16:p4. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adp0004
124. Ho X, Fook-Chong S, and Linn YC. Natural killer cell receptor repertoire is comparable amongst newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia of different French-American-British subtypes, risk categories and chemosensitivities. Leuk Lymphoma. (2014) 55:342–48. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.791986
125. Khaznadar Z, Boissel N, Agaugue S, Henry G, Cheok M, Vignon M, et al. Defective NK cells in acute myeloid leukemia patients at diagnosis are associated with blast transcriptional signatures of immune evasion. J Immunol. (2015) 195:2580–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500262
126. Turk S, Baesmat AS, Yilmaz A, Turk C, Malkan UY, Ucar G, et al. NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin-angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes. Open Med (Wars). (2022) 17:1495–506. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0551
127. Li W, Kawaguchi K, Tanaka S, He C, Maeshima Y, Suzuki E, et al. Cellular senescence triggers intracellular acidification and lysosomal pH alkalinized via ATP6AP2 attenuation in breast cancer cells. Commun Biol. (2023) 6:1147. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05433-6
128. Li L, Cui YJ, Liu Y, Li HX, Su YD, Li SN, et al. ATP6AP2 knockdown in cardiomyocyte deteriorates heart function via compromising autophagic flux and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:161. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00967-w
129. Oberlies J, Watzl C, Giese T, Luckner C, Kropf P, Muller I, et al. Regulation of NK cell function by human granulocyte arginase. J Immunol. (2009) 182:5259–67. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803523
130. Crinier A, Dumas PY, Escaliere B, Piperoglou C, Gil L, Villacreces A, et al. Single-cell profiling reveals the trajectories of natural killer cell differentiation in bone marrow and a stress signature induced by acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:1290–304. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00574-8
131. Arellano-Ballestero H, Sabry M, and Lowdell MW. A killer disarmed: natural killer cell impairment in myelodysplastic syndrome. Cells. (2023) 12:633. doi: 10.3390/cells12040633
132. Liu Z, Guo Y, Huang L, Jia Y, Liu H, Peng F, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate the dysfunction of NK cells via the T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Cell Commun Signal. (2022) 20:169. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00985-2
133. Sanz-Ortega L, Andersson A, and Carlsten M. Harnessing upregulated E-selectin while enhancing SDF-1alpha sensing redirects infused NK cells to the AML-perturbed bone marrow. Leukemia. (2024) 38:579–89. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-02126-1
134. Chretien AS, Devillier R, Granjeaud S, Cordier C, Demerle C, Salem N, et al. High-dimensional mass cytometry analysis of NK cell alterations in AML identifies a subgroup with adverse clinical outcome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2021) 118:e2020459118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2020459118
135. Gauthier L, Virone-Oddos A, Beninga J, Rossi B, Nicolazzi C, Amara C, et al. Control of acute myeloid leukemia by a trifunctional NKp46-CD16a-NK cell engager targeting CD123. Nat Biotechnol. (2023) 41:1296–306. doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01626-2
136. Yang F, Wang R, Feng W, Chen C, Yang X, Wang L, et al. Characteristics of NK cells from leukemic microenvironment in MLL-AF9 induced acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Immunol. (2018) 93:68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.11.003
137. Xiao Y, Chen J, Wang J, Guan W, Wang M, Zhang L, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia epigenetic immune escape from nature killer cells by ICAM-1. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:751834. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.751834
138. Paczulla AM, Rothfelder K, Raffel S, Konantz M, Steinbacher J, Wang H, et al. Absence of NKG2D ligands defines leukaemia stem cells and mediates their immune evasion. Nature. (2019) 572:254–59. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1410-1
139. Teague RM and Kline J. Immune evasion in acute myeloid leukemia: current concepts and future directions. J Immunother Cancer. (2013) 1:1. doi: 10.1186/2051-1426-1-13
140. Sauerer T, Velazquez GF, and Schmid C. Relapse of acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: immune escape mechanisms and current implications for therapy. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:180. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01889-6
141. Lion E, Willemen Y, Berneman ZN, Van Tendeloo VF, and Smits EL. Natural killer cell immune escape in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. (2012) 26:2019–26. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.87
142. Restelli C, Ruella M, Paruzzo L, Tarella C, Pelicci PG, and Colombo E. Recent advances in immune-based therapies for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer Discov. (2024) 5:234–48. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0202
143. Taghiloo S and Asgarian-Omran H. Immune evasion mechanisms in acute myeloid leukemia: A focus on immune checkpoint pathways. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2021) 157:103164. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.103164
144. D’Silva SZ, Singh M, and Pinto AS. NK cell defects: implication in acute myeloid leukemia. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1112059. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1112059
145. Khaldoyanidi S, Nagorsen D, Stein A, Ossenkoppele G, and Subklewe M. Immune biology of acute myeloid leukemia: implications for immunotherapy. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:419–32. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00475
146. Nair R, Salinas-Illarena A, and Baldauf HM. New strategies to treat AML: novel insights into AML survival pathways and combination therapies. Leukemia. (2021) 35:299–311. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01069-1
147. Tettamanti S, Pievani A, Biondi A, Dotti G, and Serafini M. Catch me if you can: how AML and its niche escape immunotherapy. Leukemia. (2022) 36:13–22. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01350-x
148. Kaito Y and Imai Y. Evolution of natural killer cell-targeted therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol. (2024) 120:34–43. doi: 10.1007/s12185-024-03778-0
149. Era T and Witte ON. Regulated expression of P210 Bcr-Abl during embryonic stem cell differentiation stimulates multipotential progenitor expansion and myeloid cell fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2000) 97:1737–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.4.1737
150. Ahmad F, Shah A, Angi M, Narmawala Q, Gupta I, Chaudhary P, et al. Identification of a novel cryptic variant chromosomal rearrangement involving 9q34, 22q11.2, and 5q22 resulting in ins(9;22) and t(5;22) in chronic myeloid leukemia: a case report. Ann Hematol. (2024) 103:5963–71. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05966-8
151. Houshmand M, Simonetti G, Circosta P, Gaidano V, Cignetti A, Martinelli G, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Leukemia. (2019) 33:1543–56. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0490-0
152. Tefferi A, Elliott MA, and Pardanani A. Atypical myeloproliferative disorders: diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc. (2006) 81:553–63. doi: 10.4065/81.4.553
153. Soverini S, De Santis S, Monaldi C, Bruno S, and Mancini M. Targeting leukemic stem cells in chronic myeloid leukemia: is it worth the effort? Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:7093. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137093
154. Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G, Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF, et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. (2013) 122:872–84. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-501569
155. Holyoake TL and Vetrie D. The chronic myeloid leukemia stem cell: stemming the tide of persistence. Blood. (2017) 129:1595–606. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-696013
156. Riether C, Gschwend T, Huguenin AL, Schurch CM, and Ochsenbein AF. Blocking programmed cell death 1 in combination with adoptive cytotoxic T-cell transfer eradicates chronic myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia. (2015) 29:1781–85. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.26
157. Ureshino H, Shindo T, and Kimura S. Role of cancer immunology in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Res. (2020) 88:106273. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2019.106273
158. Hughes A, Clarson J, Tang C, Vidovic L, White DL, Hughes TP, et al. CML patients with deep molecular responses to TKI have restored immune effectors and decreased PD-1 and immune suppressors. Blood. (2017) 129:1166–76. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-745992
159. Hochhaus A, Rea D, Boquimpani C, Minami Y, Cortes JE, Hughes TP, et al. Asciminib vs bosutinib in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia previously treated with at least two tyrosine kinase inhibitors: longer-term follow-up of ASCEMBL. Leukemia. (2023) 37:617–26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01829-9
160. Sasaki K, Haddad FG, Short NJ, Jain N, Issa G, Jabbour E, et al. Outcome of Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in the United States since the introduction of imatinib therapy-The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, 2000-2019. Cancer. (2023) 129:3805–14. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35038
161. Cojbasic I, Macukanovic-Golubovic L, Vucic M, and Cojbasic Z. Generic imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia treatment: long-term follow-up. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. (2019) 19:e526–31. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.05.006
162. Jiang Y, Zhang D, He X, Chen C, Xie L, Liu L, et al. BCAT1 contributes to the development of TKI-resistant CML. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2024) 48:411–24. doi: 10.1007/s13402-024-01003-y
163. Venkataraman V, Casey KS, Onozato M, Cin PD, Nardi V, Amrein PC, et al. Long: molecular tracking of CML with bilineal inv(16) myeloid and del(9) lymphoid blast crisis and durable response to CD19-directed CAR-T therapy. Leukemia. (2020) 34:3050–54. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0983-x
164. Zhou S, Li W, Xiao Y, Zhu X, Zhong Z, Li Q, et al. A novel chimeric antigen receptor redirecting T-cell specificity towards CD26(+) cancer cells. Leukemia. (2021) 35:119–29. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0824-y
165. Cui Q, Liang P, Dai H, Cui W, Cai M, Ding Z, et al. Case report: CD38-directed CAR-T cell therapy: A novel immunotherapy targeting CD38- positive blasts overcomes TKI and chemotherapy resistance of myeloid chronic myeloid leukemia in blastic phase. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1012981. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012981
166. McCune A and Kornbluth J. NK3.3-derived extracellular vesicles penetrate and selectively kill treatment-resistant tumor cells. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 16:90. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010090
167. Du Z, Huang Z, Chen X, Jiang G, Peng Y, Feng W, et al. Modified dendritic cell-derived exosomes activate both NK cells and T cells through the NKG2D/NKG2D-L pathway to kill CML cells with or without T315I mutation. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2022) 11:36. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00289-8
168. Vidard L, Dureuil C, Baudhuin J, Vescovi L, Durand L, Sierra V, et al. CD137 (4-1BB) engagement fine-tunes synergistic IL-15- and IL-21-driven NK cell proliferation. J Immunol. (2019) 203:676–85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801137
169. Oberoi P, Kamenjarin K, Ossa J, Uherek B, Bonig H, and Wels WS. Directed Differentiation of Mobilized Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells into Functional NK cells with Enhanced Antitumor Activity. Cells. (2020) 9:811. doi: 10.3390/cells9040811
170. Zhang C, Kadu S, Xiao Y, Johnson O, Kelly A, O’Connor RS, et al. Sequential exposure to IL21 and IL15 during human natural killer cell expansion optimizes yield and function. Cancer Immunol Res. (2023) 11:1524–37. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0151
171. Gandhi M, Sharma B, Nair S, and Vaidya A. Current insights into CAR T-cell-based therapies for myelodysplastic syndrome. Pharm Res. (2024) 41:1757–73. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03761-8
172. Van den Eynde A, Gehrcken L, Verhezen T, Lau HW, Hermans C, Lambrechts H, et al. IL-15-secreting CAR natural killer cells directed toward the pan-cancer target CD70 eliminate both cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. J Hematol Oncol. (2024) 17:8. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01525-w
173. Li Q, Ye LJ, Ren HL, Huyan T, Li J, Shi JL, et al. Multiple effects of IL-21 on human NK cells in ex vivo expansion. Immunobiology. (2015) 220:876–88. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.01.009
174. Imeri J, Marcoux P, Huyghe M, Desterke C, Fantacini D, Griscelli F, et al. Chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) engineered natural killer cells in a chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) blast crisis model. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1309010. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1309010
175. Yu W, Ye F, Yuan X, Ma Y, Mao C, Li X, et al. A phase I/II clinical trial on the efficacy and safety of NKT cells combined with gefitinib for advanced EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:877. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08590-1
176. Park HR, Ahn YO, Kim TM, Kim S, Kim S, Lee YS, et al. NK92-CD16 cells are cytotoxic to non-small cell lung cancer cell lines that have acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cytotherapy. (2019) 21:603–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.03.312
177. Mallmann-Gottschalk N, Sax Y, Kimmig R, Lang S, and Brandau S. EGFR-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor modifies NK cell-mediated antitumoral activity against ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:4693. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194693
178. Huuhtanen J, Adnan-Awad S, Theodoropoulos J, Forsten S, Warfvinge R, Dufva O, et al. Single-cell analysis of immune recognition in chronic myeloid leukemia patients following tyrosine kinase inhibitor discontinuation. Leukemia. (2024) 38:109–25. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-02074-w
179. Yao D, Xu L, Liu L, Zeng X, Zhong J, Lai J, et al. Increased expression of TIGIT/CD57 in peripheral blood/bone marrow NK cells in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:9531549. doi: 10.1155/2020/9531549
180. Aggarwal N, Swerdlow SH, TenEyck SP, Boyiadzis M, and Felgar RE. Natural killer cell (NK) subsets and NK-like T-cell populations in acute myeloid leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. (2016) 90:349–57. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21349
181. Pierson BA and Miller JS. CD56+bright and CD56+dim natural killer cells in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia progressively decrease in number, respond less to stimuli that recruit clonogenic natural killer cells, and exhibit decreased proliferation on a per cell basis. Blood. (1996) 88:2279–87. doi: 10.1182/blood.V88.6.2279.bloodjournal8862279
182. Chiorean EG, Dylla SJ, Olsen K, Lenvik T, Soignier Y, and Miller JS. BCR/ABL alters the function of NK cells and the acquisition of killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs). Blood. (2003) 101:3527–33. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1172
183. Nakajima H, Zhao R, Lund TC, Ward J, Dolan M, Hirsch B, et al. The BCR/ABL transgene causes abnormal NK cell differentiation and can be found in circulating NK cells of advanced phase chronic myelogenous leukemia patients. J Immunol. (2002) 168:643–50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.2.643
184. Mellqvist UH, Hansson M, Brune M, Dahlgren C, Hermodsson S, and Hellstrand K. Natural killer cell dysfunction and apoptosis induced by chronic myelogenous leukemia cells: role of reactive oxygen species and regulation by histamine. Blood. (2000) 96:1961–68. doi: 10.1182/blood.V96.5.1961
185. Aurelius J, Martner A, Riise RE, Romero AI, Palmqvist L, Brune M, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemic cells trigger poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-dependent inactivation and cell death in lymphocytes. J Leukoc Biol. (2013) 93:155–60. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0512257
186. Lyu F, Burzynski C, Fang YY, Tal A, Chen AY, Kisa J, et al. Maternal CXCR4 deletion results in placental defects and pregnancy loss mediated by immune dysregulation. JCI Insight. (2023) 8:e172216. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.172216
187. Herrmann AB, Muller ML, Orth MF, Muller JP, Zernecke A, Hochhaus A, et al. Knockout of LASP1 in CXCR4 expressing CML cells promotes cell persistence, proliferation and TKI resistance. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:2942–55. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14910
188. Sconocchia G, Lau M, Provenzano M, Rezvani K, Wongsena W, Fujiwara H, et al. The antileukemia effect of HLA-matched NK and NK-T cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia involves NKG2D-target-cell interactions. Blood. (2005) 106:3666–72. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0479
189. Krishnan V, Schmidt F, Nawaz Z, Venkatesh PN, Lee KL, Ren X, et al. A single-cell atlas identifies pretreatment features of primary imatinib resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. (2023) 141:2738–55. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022017295
190. Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Rossi GR, Dagley LF, Foroutan M, McCulloch TR, Yousef J, et al. TGFbeta and CIS inhibition overcomes NK-cell suppression to restore antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Res. (2022) 10:1047–54. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-21-1052
191. Decroos A, Meddour S, Demoy M, Piccirilli N, Rousselot P, Nicolini FE, et al. The CML experience to elucidate the role of innate T-cells as effectors in the control of residual cancer cells and as potential targets for cancer therapy. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1473139. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1473139
192. Sanchez MB, Vasconcelos CB, Pavlovsky C, Moiraghi B, Varela A, Custidiano R, et al. In-depth characterization of NK cell markers from CML patients who discontinued tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1241600. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1241600
193. Rodrigues-Santos P, Lopez-Sejas N, Almeida JS, Ruzickova L, Couceiro P, Alves V, et al. Effect of age on NK cell compartment in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2587. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02587
194. Ureshino H, Shindo T, Sano H, Kubota Y, Ando T, Kidoguchi K, et al. Reconstitution of NK cells expressing KIR3DL1 is associated with reduced NK cell activity and relapse of CML after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. (2020) 111:733–38. doi: 10.1007/s12185-019-02809-5
195. Camacho V, Kuznetsova V, and Welner RS. Inflammatory cytokines shape an altered immune response during myeloid Malignancies. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:772408. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.772408
196. Hughes A and Yong A. Immune effector recovery in chronic myeloid leukemia and treatment-free remission. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00469
197. Hsieh YC, Kirschner K, and Copland M. Improving outcomes in chronic myeloid leukemia through harnessing the immunological landscape. Leukemia. (2021) 35:1229–42. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01238-w
198. Shang J, Hu S, and Wang X. Targeting natural killer cells: from basic biology to clinical application in hematologic Malignancies. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2024) 13:21. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00481-y
199. Fei F, Rong L, Jiang N, Wayne AS, and Xie J. Targeting HLA-DR loss in hematologic Malignancies with an inhibitory chimeric antigen receptor. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:1215–26. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.013
200. Cao Y, Wang LY, and Wang L. CAR-NK, a splendid strategy for cancer, especially for gynecologic tumor. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2025) 13:e70210. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70210
201. Guo J, Afzal A, Ahmad S, Saeed G, Rehman A, Khan UA, et al. Novel strategies to overcome tumor immunotherapy resistance using CAR NK cells. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1550652. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550652
202. Stransky N, Ji R, Prause L, Ganser K, Wels WS, Ruth R, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor NK-92 cell function is modulated by HLA class I expression of target cells. iScience. (2025) 28:112523. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112523
203. Ikeda S, Hasegawa K, Kogue Y, Arimori T, Kawamoto R, Wibowo T, et al. CAR T or NK cells targeting mismatched HLA-DR molecules in acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Nat Cancer. (2025) 6:595–611. doi: 10.1038/s43018-025-00934-1
204. Bahramloo M, Shahabi SA, Kalarestaghi H, Rafat A, Mazloumi Z, Samimifar A, et al. CAR-NK cell therapy in AML: Current treatment, challenges, and advantage. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 177:117024. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117024
205. Zhu X, Xue J, Jiang H, and Xue D. CAR-NK cells for gastrointestinal cancer immunotherapy: from bench to bedside. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:237. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02151-3
206. Daher M and Rezvani K. Outlook for new CAR-based therapies with a focus on CAR NK cells: what lies beyond CAR-engineered T cells in the race against cancer. Cancer Discov. (2021) 11:45–58. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0556
207. Rodriguez-Sevilla JJ, Ganan-Gomez I, Kumar B, Thongon N, Ma F, Chien KS, et al. Natural killer cells’ functional impairment drives the immune escape of pre-malignant clones in early-stage myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Commun. (2025) 16:3450. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58662-0
Keywords: myeloid leukemia, NK cell, exhaustion, therapeutic potential, immunobiology
Citation: Zhang L, Zhao Y, Dong Y and Jiang X (2025) NK cell-based immunotherapy strategies for myeloid leukemia. Front. Immunol. 16:1621885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1621885
Received: 02 May 2025; Accepted: 26 June 2025;
Published: 14 July 2025.
Edited by:
Avishek Bhuniya, Wistar Institute, United StatesReviewed by:
Nadia El Khawanky, Technical University of Munich, GermanyDivanshu Shukla, University of Pennsylvania, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhao, Dong and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Dong, eWFuZG9uZ0B0bW11LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiuxing Jiang, anh4MDUyMUB0bW11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share senior authorship
 Lin Zhang1†
Lin Zhang1† Yibo Zhao
Yibo Zhao Yan Dong
Yan Dong Xiuxing Jiang
Xiuxing Jiang