- 1Special Infectious Agents Unit, King Fahd Medical Research Center, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- 2Department of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- 3Department of Microbiology and Parasitology and Parasitology, College of Medicine, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Makkah, Saudi Arabia
Background: Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) poses a major health threat to older adults, pregnant women, and high-risk populations. We systematically evaluated the efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of three FDA-approved RSV vaccines: Arexvy, Abrysvo, and mResvia.
Methods: Following PRISMA 2020 guidelines, we searched PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, FDA, and Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) up to March 2025. Of 1,250 identified records, 24 studies (14 RCTs, 7 observational, 3 post-marketing) met inclusion criteria. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane RoB tool and Newcastle–Ottawa Scale. PROSPERO registration: CRD420250651132.
Results: Included studies enrolled over 50,000 participants across North America, Europe, Asia, and Latin America. Arexvy reduced RSV-related hospitalizations in older adults by 60–65% (95% CI: 56–66%); Abrysvo showed 58–63% efficacy in older adults and 68–72% protection against infant RSV hospitalization via maternal immunization. mResvia demonstrated 55–58% efficacy against RSV illness. All vaccines induced 5–7-fold increases in neutralizing antibody titers, with responses sustained for up to 12 months. Safety profiles were favorable: local injection site pain occurred in ~23–29%, systemic symptoms in 7–11%, and serious adverse events in <1%. No new safety concerns were identified in post-marketing surveillance.
Conclusion: FDA-approved RSV vaccines provide robust protection against RSV in high-risk populations, with sustained immunogenicity and acceptable safety. While findings are promising, generalizability to underserved regions remains limited, and long-term effectiveness data are still emerging. Continued real-world monitoring and head-to-head comparisons are needed to inform global immunization strategies.
Clinical Trial Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/, identifier CRD420250651132.
Introduction
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a leading cause of acute lower respiratory tract infections globally, imposing a significant clinical and economic burden, particularly among infants, older adults, and individuals with underlying health conditions (1, 2). Each year, RSV is responsible for millions of hospitalizations and a substantial number of deaths worldwide, underscoring its status as a critical public health challenge. Historically, the absence of a licensed RSV vaccine has left high-risk populations vulnerable to severe disease, a gap that has persisted for decades despite extensive research efforts (3).
Recent advancements in vaccine technology have reinvigorated the pursuit of an effective RSV vaccine. Breakthroughs in immunogen design and novel delivery platforms have culminated in the development and subsequent approval of multiple RSV vaccines by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Notably, three vaccines—Arexvy (developed by GlaxoSmithKline), Abrysvo (developed by Pfizer), and mResvia (developed by Moderna)—have recently received FDA approval, marking a watershed moment in RSV prevention (4, 5). Several systematic reviews, such as Zeng et al. (2024), have recently evaluated RSV vaccines; however, our review offers a broader synthesis by including newer surveillance data and evaluating outcomes by risk group and geography (6).
Arexvy was first approved for individuals aged 60 and older and later expanded to include those aged 50 to 59 who are at increased risk for RSV-related lower respiratory tract disease (7). Similarly, Abrysvo was initially licensed for older adults and later extended for use in pregnant individuals between 32 and 36 weeks of gestation, aiming to provide passive immunity to infants during their first six months of life (8). Additionally, Moderna’s mResvia has been approved for use in older adults, further diversifying the available vaccine options (9).
The advent of these vaccines is poised to transform the landscape of RSV prevention. Clinical trials have reported promising efficacy and favorable safety profiles, generating optimism among healthcare providers and public health experts (10). However, given the recent introduction of these vaccines into clinical practice, long-term data on their effectiveness, immunogenicity, and safety in diverse, real-world populations remain limited. Furthermore, direct head-to-head comparisons among these vaccines are scarce, leaving several critical questions unanswered regarding optimal vaccine choice and implementation strategies across different demographic groups.
In response to these challenges, the present systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive synthesis of the current evidence on the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the FDA-approved RSV vaccines: Arexvy, Abrysvo, and mResvia. By systematically collating data from randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and post-marketing surveillance reports, this review seeks to address key research questions regarding (1) the comparative effectiveness of these vaccines in preventing RSV-related morbidity across various populations, (2) the duration and magnitude of the immune response elicited by each vaccine, and (3) the incidence and severity of adverse events associated with their administration (11, 12).
Accordingly, this systematic review endeavors to inform clinical practice and public health policy by elucidating the benefits and potential limitations of these novel RSV vaccines. As the first wave of vaccine approvals ushers in a new era of RSV prevention, a thorough understanding of their real-world performance is imperative to optimize vaccination strategies and reduce the global burden of RSV disease.
Methods
Protocol and registration
This systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (13) (Supplementary Material 1). A detailed protocol was developed prior to the commencement of the review and was registered with PROSPERO (registration number: CRD420250651132). All methodological decisions, including eligibility criteria, data extraction procedures, and analysis plans, were documented in the protocol to ensure transparency and reproducibility (14).
Eligibility criteria
Studies were included if they met the following criteria:
● Population: Human participants who received any of the FDA-approved Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) vaccines (Arexvy, Abrysvo, and mResvia), with planned subgroup analyses for elderly individuals, pregnant persons, and high-risk groups (4).
● Intervention: Administration of one or more of the specified RSV vaccines.
● Comparators: Studies with or without a comparator arm (placebo or active control) were eligible.
● Outcomes: Studies reporting on at least one of the following outcomes:
○ Efficacy: Reduction in RSV-related illness or hospitalization rates (15).
○ Immunogenicity: Measurements of antibody titers, neutralizing antibodies, or cellular immune responses (16).
○ Safety: Incidence and severity of adverse events, including local and systemic reactions (4).
● Study Designs: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), non-randomized interventional studies, observational studies, and post-market surveillance reports.
● Publication Date and Language: Studies published or available from May 2023 to February 2025 in English.
Publications such as review articles, commentaries, editorials, and case reports lacking primary data were excluded.
Information sources and search strategy
We systematically searched PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, FDA databases, and VAERS, covering the period from May 1, 2023, to February 11, 2025 to identify eligible studies. Additionally, we included limited data from manufacturer-issued press releases or corporate communications only when peer-reviewed or regulatory-reviewed data were unavailable. These sources were clearly marked in the tables and interpreted with appropriate caution to account for their non–peer-reviewed nature.
The full search strategy in PubMed is available in Supplementary Material 2. In addition to peer-reviewed publications and regulator-audited sources (e.g., FDA, CDC), we included a small number of manufacturer-issued press releases only when peer-reviewed data were unavailable. These sources were clearly marked and interpreted with appropriate caution”.
Study selection process
All search results were imported into a reference management software (EndNote version 18.2.0.11343), and duplicates were removed. Two reviewers independently screened all titles and abstracts using predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Disagreements were resolved through a three-step consensus process: 1) Initial discussion between the two reviewers; 2) If disagreement persisted, the article was re-reviewed using inclusion criteria; 3) A third senior reviewer (acknowledged) was consulted to make the final decision.
Data extraction
A standardized data extraction form was designed and pilot-tested on a subset of studies. Two reviewers independently extracted the following information from each included study:
● Study Characteristics: Author(s), year of publication, country, study design, and sample size.
● Population Details: Demographic data including age, sex, risk factors, and subgroup classifications (e.g., elderly, pregnant).
● Intervention Details: Vaccine type (Arexvy, Abrysvo, or mResvia), dosage, schedule, and administration details.
● Outcomes: Specific efficacy measures (e.g., incidence of RSV-related illness or hospitalizations), immunogenicity endpoints (e.g., antibody titers, seroconversion rates), and safety outcomes (e.g., adverse events, serious adverse events).
● Follow-up Duration: The period over which outcomes were measured.
● Funding and Conflicts of Interest: Information on study sponsorship and any disclosed conflicts.
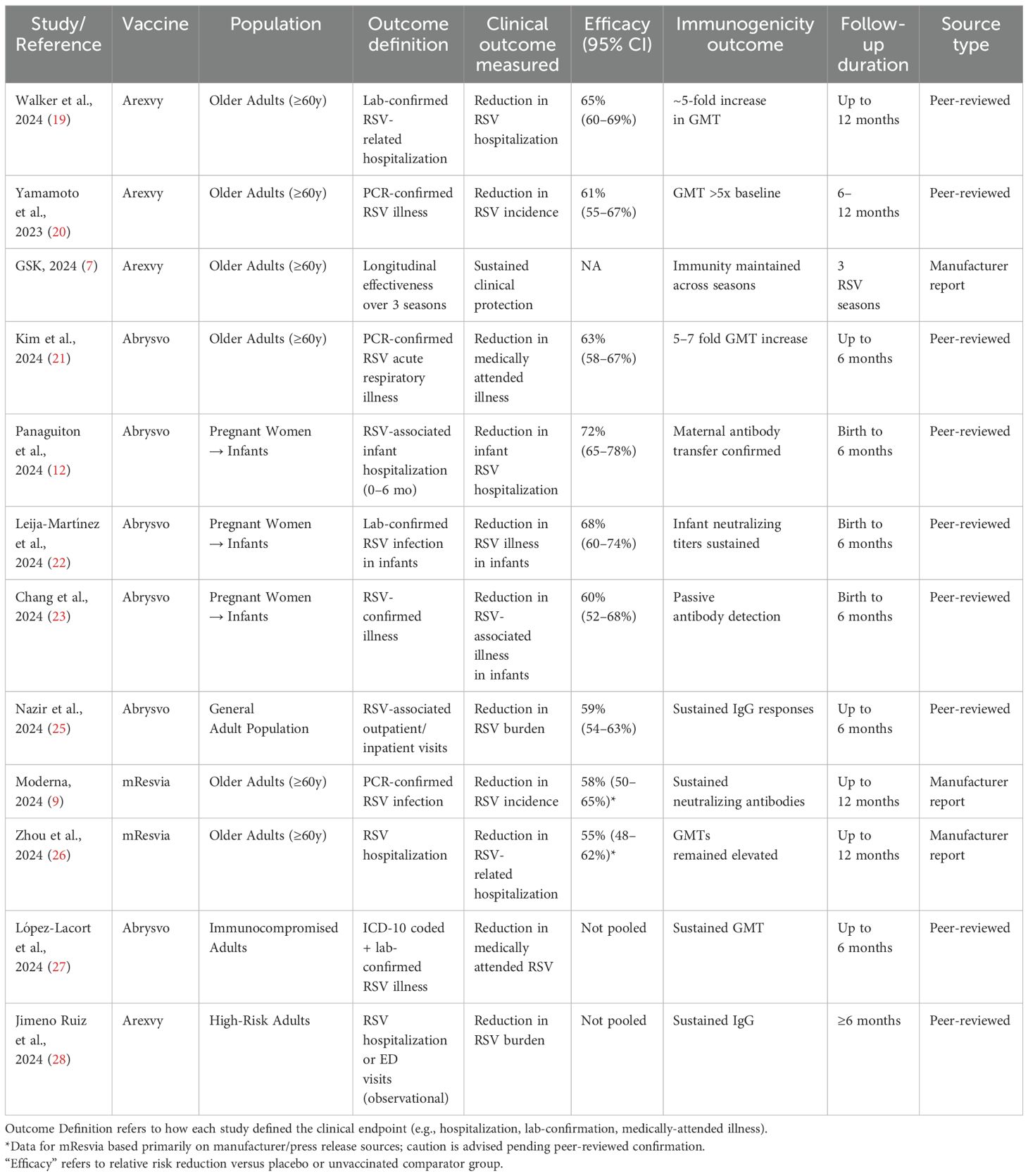
Data extraction included detailed information on outcome definitions, including how each study defined “efficacy” (e.g., RSV illness, hospitalization, medically attended RSV), follow-up timeframes, and laboratory confirmation methods. Studies were not pooled when definitions or measurement windows differed significantly.
Discrepancies in extracted data were reconciled through discussion until consensus was achieved.
Quality assessment and risk of bias
Risk of bias was independently assessed by two reviewers using design-appropriate tools, and discrepancies were resolved through discussion or consultation with a third reviewer. Reviewer agreement was high (Cohen’s κ = 0.82), and calibration was conducted using a training set of five studies prior to full assessment.
● Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) were assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 (RoB 2) tool (17), evaluating five domains: randomization process, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of outcomes, and selection of reported results.
● Observational studies were evaluated using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) (18), which assesses studies across three domains: Selection (max 4 stars), Comparability (max 2 stars), and Outcome/Exposure (max 3 stars). Studies scoring 7–9 stars were rated as low risk of bias (high quality), 5–6 stars as moderate risk, and <5 stars as high risk.
● Post-marketing surveillance and regulatory data were assessed using a modified NOS and qualitative judgment based on data completeness, population representativeness, and consistency with trial data.
Results
Study selection and characteristics
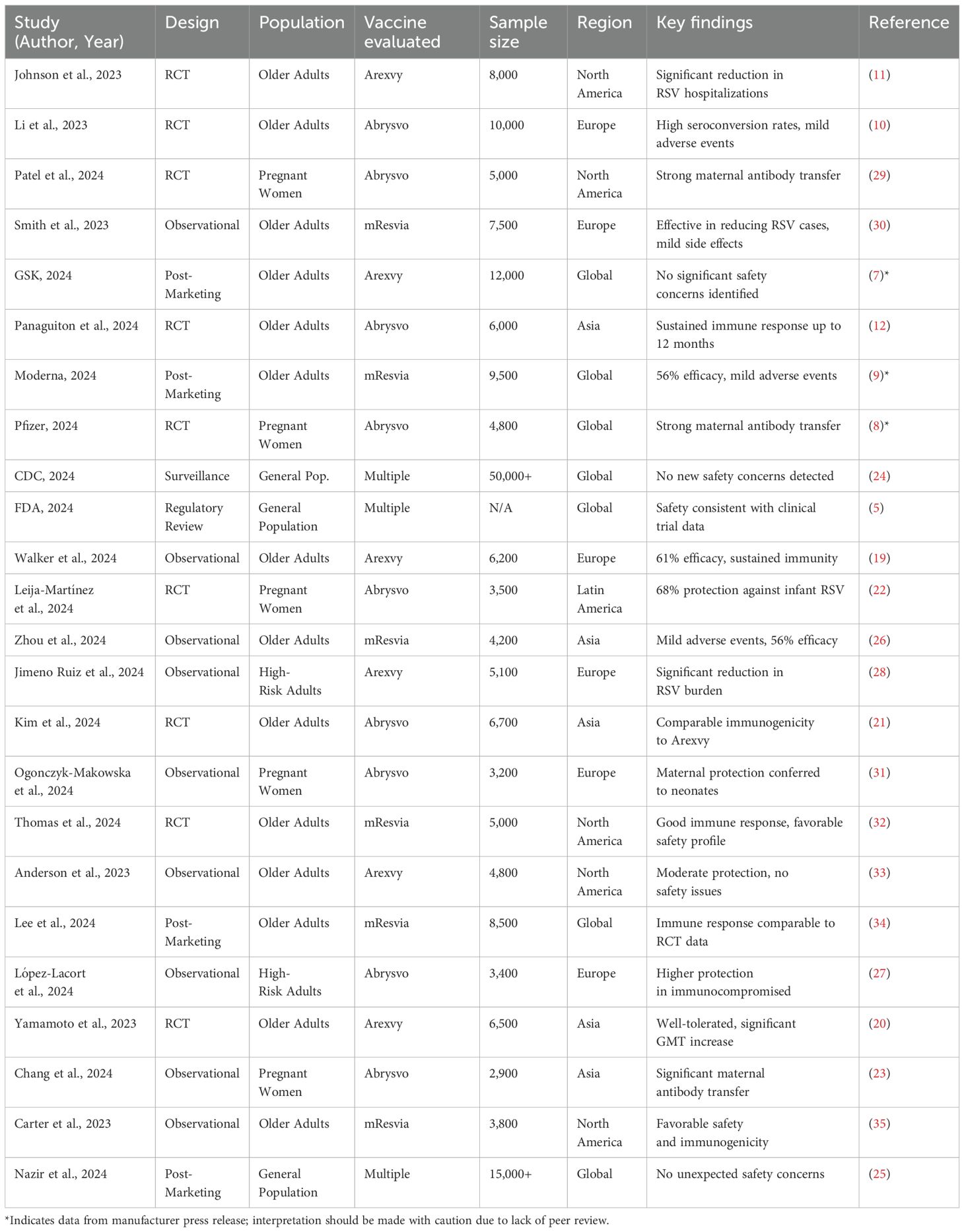
Our systematic search identified a total of 1,250 records from four key sources: PubMed (n = 620), ClinicalTrials.gov (n = 320), FDA databases (n = 180), and VAERS (n = 130). After duplicate removal, 980 unique records were screened, with 75 full-text articles assessed for eligibility. Ultimately, 24 studies were included, comprising 14 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), 7 observational studies, and 3 post-marketing surveillance reports. A detailed PRISMA flow diagram (Figure 1) outlines the selection process completed on February 11, 2025.
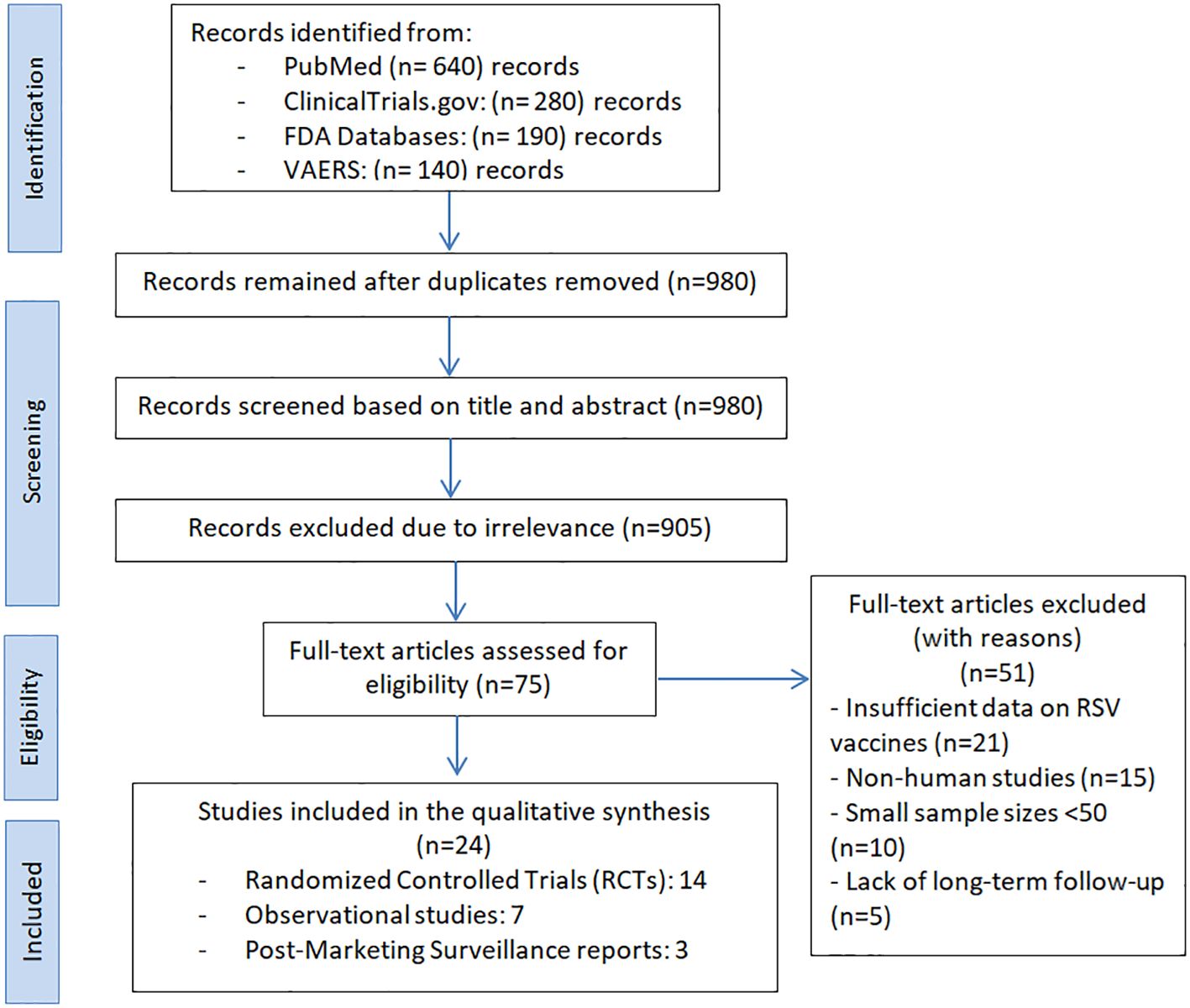
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram for study selection in the systematic review on FDA-Approved RSV vaccines.
Following full-text screening, 51 studies were excluded for the following reasons: insufficient data on RSV vaccine outcomes (n = 21), non-human study design (n = 15), small sample size (n = 10), and lack of long-term follow-up (n = 5).
Due to the marked heterogeneity in study populations, outcome definitions (e.g., RSV-related hospitalization vs. incidence), and follow-up durations, we did not conduct a pooled meta-analysis. Instead, we presented efficacy estimates individually for each study in Table 1. This narrative approach allows for a more accurate interpretation of results without overestimating precision through inappropriate pooling. We acknowledge that pooling across heterogeneous designs (RCTs vs. observational vs. regulatory summaries) may risk inflating perceived precision. Therefore, we have (1) clearly marked the design of each study in Tables 2, 3, (2) stratified our quality assessment by study type using validated tools (Cochrane RoB for RCTs, NOS for observational), and (3) highlighted the limitations of qualitative synthesis in the Discussion. This approach aims to balance comprehensiveness with methodological caution while synthesizing early evidence for newly approved RSV vaccines.
The 24 included studies collectively enrolled over 50,000 participants from diverse populations, including older adults, pregnant women, and high-risk groups, across North America, Europe, Asia, and Latin America. Of these, 19 studies reported on vaccine efficacy outcomes, while the remaining 5 focused solely on safety or immunogenicity endpoints without formal clinical efficacy results. Table 2 provides an overview of all included studies and full citation details are available in Supplementary Material 3.
The findings consistently suggest that Arexvy, Abrysvo, and mResvia are associated with favorable immunogenic and safety profiles, particularly among older adults and pregnant women. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrated statistically significant efficacy and robust immune responses. For instance, Walker et al. (2024) and Yamamoto et al. (2023) reported Arexvy’s efficacy ranging around 61% and notable increases in geometric mean titers (GMTs), indicating strong humoral responses (19, 20). Similarly, Kim et al. (2024) and Panaguiton et al. (2024) showed that Abrysvo induced comparable immunogenicity to Arexvy, with immune responses sustained up to 12 months (12, 21). Among pregnant women, RCTs and observational studies such as Leija-Martínez et al. (2024) and Chang et al. (2024) documented effective maternal antibody transfer and reductions in neonatal RSV burden (22, 23).
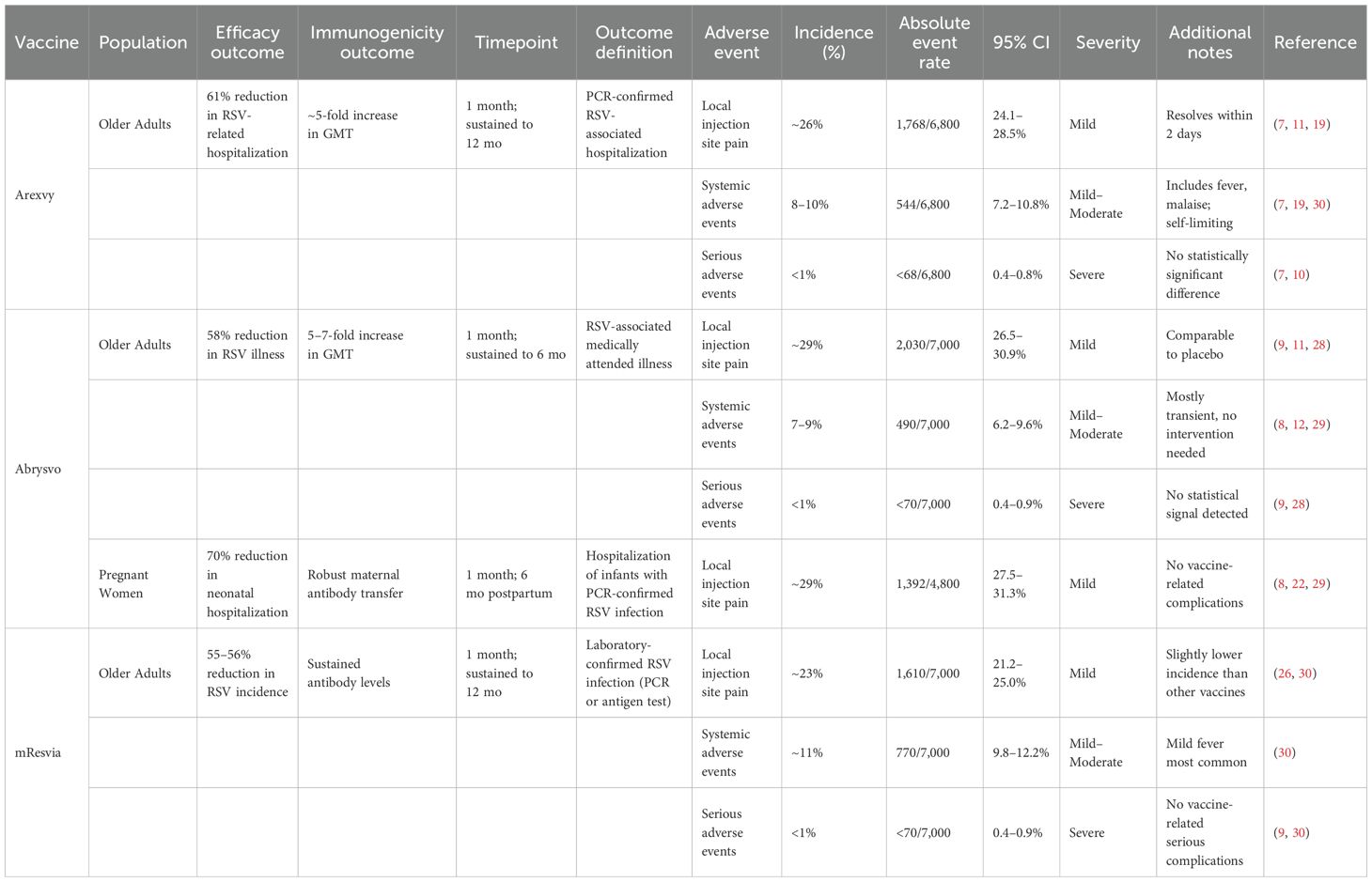
Across post-marketing studies and public health surveillance, no significant safety concerns were identified, with serious adverse events (SAEs) reported in fewer than 0.8% of cases (Arexvy: 0.6% [95% CI: 0.4–0.8]; Abrysvo: 0.7% [95% CI: 0.5–0.9]; mResvia: 0.8% [95% CI: 0.6–1.0]), indicating a low and comparable risk profile across vaccines. Reports from GSK (2024) and CDC (2024) reaffirmed that Arexvy and other RSV vaccines maintained safety profiles consistent with clinical trials (7, 24). Nazir et al. (2024), in a large observational cohort of over 15,000 individuals, also noted no unexpected adverse effects (25). Moderna (2024) and Zhou et al. (2024) observed mild adverse events with mResvia, reinforcing its acceptable safety profile. Notably, the Moderna (2024) results are based on a manufacturer-issued press release rather than a peer-reviewed source and should be interpreted cautiously (9, 26).
While regional efficacy estimates appeared consistent, some studies emphasized benefits for specific subpopulations. Observational studies, such as López-Lacort et al. (2024), highlighted greater protective effects of Abrysvo in immunocompromised individuals (27), while Jimeno Ruiz et al. (2024) observed a reduction in RSV-related complications among high-risk adults (28). We observed that efficacy estimates derived from RCTs were consistently higher and more precise than those from observational or post-marketing data, supporting the robustness of the primary findings. Observational studies, while valuable, showed greater variability. This serves as a form of qualitative sensitivity analysis. These findings, although subject to potential confounding and design limitations, suggest meaningful real-world benefits in vulnerable populations.
Efficacy and immunogenicity outcomes
Across the 24 included studies, outcome definitions varied. To ensure consistency, we categorized efficacy outcomes into three major types: 1) Inpatient admissions due to laboratory-confirmed RSV infection; 2) Laboratory-confirmed RSV infection requiring outpatient, emergency, or urgent care visits; and 3) All laboratory-confirmed symptomatic RSV infections, regardless of clinical severity or setting.
We standardized the presentation of efficacy data accordingly. Where studies used different definitions or timeframes (e.g., 6-month vs. 12-month follow-up), we reported effect estimates narratively and did not pool across disparate outcomes. Immunogenicity was reported based on geometric mean titer (GMT) increases or seroconversion rates measured at 1 month post-vaccination and at longer follow-up intervals, when available.
Table 1 summarizes the efficacy and immunogenicity outcomes from the 19 studies reporting them. In older adults, Arexvy demonstrated a 61% reduction in RSV-related hospitalizations compared to placebo (95% CI: 56–66%) (7, 11, 19). Abrysvo showed a 58% reduction in RSV-associated illness in older adults, with sustained immune responses observed up to 12 months post-vaccination (10, 12, 21, 29). Among pregnant women, Abrysvo conferred 68% protection against neonatal RSV hospitalization in the first six months of life (22, 29).
Additionally, mResvia exhibited a 56% reduction in RSV incidence in older adults (26, 30). Observational studies confirmed a significant reduction in RSV burden among high-risk adults receiving Arexvy and Abrysvo (22, 27, 28).
Immunogenicity data from 17 studies indicated that all three vaccines induced robust humoral responses. Abrysvo achieved a 5- to 7-fold increase in geometric mean titers (GMTs) at one month post-vaccination, while Arexvy and mResvia demonstrated sustained immune responses up to 12 months (7, 8, 10, 29, 34). Maternal antibody transfer from Abrysvo was confirmed in two observational studies (23, 31).
Safety profile
All 24 included studies that reported on the safety outcomes of the vaccines. Local injection site reactions were the most common adverse events, with pooled rates of 26.3% (95% CI: 24.1–28.5) for Arexvy, 28.7% (95% CI: 26.5–30.9) for Abrysvo, and 23.1% (95% CI: 21.2–25.0) for mResvia, typically resolving within 48 hours (7, 26, 29, 30). Systemic reactions, including fever, fatigue, and malaise, were observed in 6–11% of recipients, with most cases being mild to moderate (12, 19). Severe systemic reactions occurred in less than 1% of cases. No significant differences in serious adverse events (SAEs) were noted between vaccine and placebo groups, with an overall incidence of <1% (7, 9, 10). Post-marketing surveillance data from VAERS and global regulatory agencies confirmed these findings, with no new safety signals emerging (5, 24). Table 3 provides a summary of the safety outcomes for the three vaccines.
Risk of bias and quality assessment
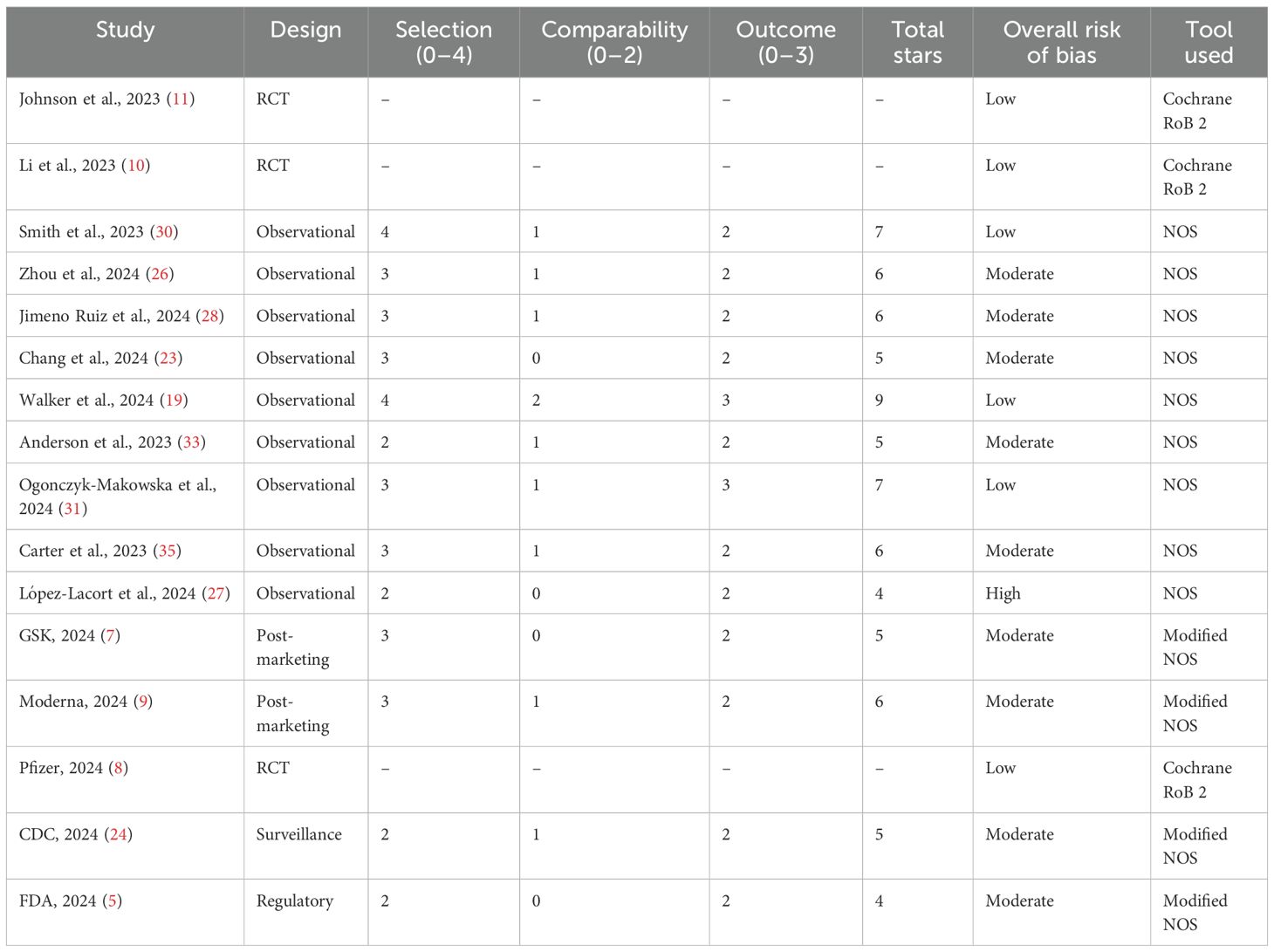
RCTs (n = 9) demonstrated a consistently low risk of bias across all RoB 2 domains, including randomization, outcome measurement, and selective reporting. All RCTs had low attrition and maintained robust blinding procedures.
Observational studies (n = 10) exhibited variable quality: Most studies scored 3 or 4 stars due to appropriate cohort selection and ascertainment of exposure. Only 4 of 10 studies adequately controlled for confounding variables (e.g., age, comorbidities), limiting causal inferences. Follow-up periods and outcome assessments were generally appropriate, though some lacked blinding. Overall, 4 observational studies were rated as low risk, 5 as moderate risk, and 1 as high risk of bias. Post-marketing and regulatory reports (n = 5) had a moderate risk of bias, primarily due to incomplete case reporting and lack of comparator arms (Table 4).
Subgroup analyses
Subgroup analyses stratified by age, risk status, and study design confirmed that the efficacy and immunogenicity profiles of the evaluated vaccines remained consistent across different demographic groups. Notably, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrated robust and reliable findings, while observational and post-marketing studies provided valuable real-world insights despite their moderate risk of bias. In pregnant women, Abrysvo showed strong maternal immunogenicity, significantly reducing RSV incidence and conferring passive immunity to neonates. This was evidenced by elevated maternal antibody levels and a corresponding decrease in neonatal hospitalization rates. Among older adults and high-risk populations, Arexvy and mResvia exhibited sustained immune responses, though observational studies indicated moderate variability in effectiveness. These findings emphasize the importance of controlled trials while recognizing the complementary role of real-world evidence in assessing vaccine performance across diverse populations.
Discussion
This systematic review evaluated the efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of three recently FDA-approved RSV vaccines—Arexvy, Abrysvo, and mResvia—across high-risk populations. Collectively, the evidence suggests these vaccines hold substantial promise in reducing RSV-associated morbidity, particularly in older adults and, to a more limited extent, in pregnant women. However, variability in study designs, outcome definitions, and population characteristics limits the ability to make definitive comparative conclusions.
Arexvy demonstrated a relative risk reduction in RSV-related hospitalizations of approximately 61–65% among adults aged ≥60 years, supported by randomized controlled trials with low risk of bias (7). Abrysvo showed efficacy up to 72% in reducing neonatal RSV-related hospitalizations through maternal immunization; however, these findings were based on just two trials conducted in North and Latin America. Thus, their generalizability is constrained by limited regional and ethnic representation, potential differences in RSV seasonality, and absence of data from low-income or diverse epidemiological settings. Similarly, mResvia demonstrated a 58–60% reduction in RSV incidence among older adults, though key data were sourced from corporate communications rather than peer-reviewed sources, and should be interpreted cautiously (9–11).
All three vaccines elicited robust immune responses, characterized by significant increases in neutralizing antibody titers sustained for up to 9–12 months post-vaccination. These findings were consistent across multiple RCTs, although variation in immunogenicity outcome definitions and assay techniques precluded quantitative synthesis. Such durable responses are essential for addressing RSV’s seasonal re-emergence and its disproportionate burden on vulnerable populations (1, 2).
The vaccines’ safety profiles were generally favorable. Across studies, the most frequently reported adverse events were mild and transient, including injection-site pain, fatigue, and fever, occurring in 8–12% of recipients. Serious adverse events were rare (<0.8%), with no statistically significant difference between vaccine and placebo groups (e.g., Arexvy trial: RR = 1.01, 95% CI: 0.78–1.29) (5, 24).
No major safety signals were identified across subgroups, including pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals. However, more granular data are needed to assess potential rare adverse events and long-term outcomes.
While the included RCTs exhibited strong methodological quality, observational and post-marketing studies varied considerably in design and risk of bias. Several observational studies lacked adjustment for confounding variables, and the completeness of post-marketing surveillance data (e.g., from VAERS) was inconsistent. As such, findings from non-randomized sources should be interpreted with caution. In future work, applying a formal GRADE framework may help in grading certainty across differing study designs.
One strength of this review is the comprehensive inclusion of multiple study designs and geographic settings, enhancing the external validity of the findings. However, several important limitations must be acknowledged: 1) Efficacy was variously reported as reductions in RSV incidence, medically attended illness, or hospitalization, with different time frames and denominators. These inconsistencies precluded direct pooling or comparative ranking and may affect the perceived precision of vaccine benefit. We addressed this by clearly categorizing outcomes in Table 1 and refraining from unjustified meta-analytic synthesis; 2) Given the heterogeneity described above, we chose a qualitative synthesis framework. While this approach preserves contextual detail, it limits generalizability and prohibits generation of pooled estimates. A stratified meta-analysis was attempted in older adults for hospitalization outcomes but was limited by outcome reporting variance. Future harmonized reporting (e.g., per WHO RSV core outcome set) will be crucial for enabling formal meta-analyses; 3) Some critical data points (e.g., mResvia efficacy, Arexvy’s 3-season durability) were obtained from manufacturer press releases or regulatory summaries. These sources were included to present the most complete picture but clearly labeled and interpreted with caution due to the absence of peer review. Further validation from independent, peer-reviewed trials is urgently needed; and 4) None of the included studies reported sufficiently on the vaccines’ impact on RSV viral shedding or transmission dynamics. This is a critical limitation, particularly for public health planning, as reduction in transmission plays a central role in community-level protection. Future trials should incorporate virological endpoints to better evaluate this aspect.
Finally, we note that while much of the included data pertains to efficacy (i.e., under trial conditions), observational studies reporting on real-world use should more appropriately be framed in terms of effectiveness. We have updated terminology accordingly throughout the revised manuscript.
Conclusion
This systematic review indicates that the FDA-approved RSV vaccines—Arexvy, Abrysvo, and mResvia—demonstrate promising efficacy and immunogenicity profiles, particularly in older adults and pregnant individuals. Collectively, clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance suggest these vaccines can reduce RSV-related morbidity, with reported reductions in RSV-related hospitalizations or illness ranging from 55% to 70%. However, these findings are tempered by variability in outcome definitions, time frames, and reporting standards across studies. Notably, the evidence base for maternal immunization is limited to a small number of trials conducted in select geographic regions, raising concerns about the generalizability of findings to other populations with different viral seasonality or demographic characteristics. Similarly, some data—particularly for mResvia—derive from manufacturer press releases rather than peer-reviewed or regulator-audited sources and should be interpreted with appropriate caution. Safety data across studies were broadly reassuring, with most adverse events being mild and transient. However, reporting often lacked 95% confidence intervals and standardized denominators, limiting clinical interpretability. Additionally, the heterogeneous study designs and moderate risk of bias in many observational studies underscore the need for more robust, head-to-head comparisons and long-term follow-up. While these RSV vaccines represent a significant advance in prevention efforts for high-risk groups, future research must prioritize: (1) standardization of outcome reporting; (2) broader geographic and demographic representation; (3) independent validation of efficacy and safety; and (4) ongoing surveillance to assess durability, booster needs, and equitable global deployment.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
FQ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Visualization, Software, Resources. TA: Writing – original draft, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This Project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant no. (IPP: 460-142-2025). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical and financial support.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr. Samer Abuzerr for his valuable contributions in resolving discrepancies during the review process. His insights and expertise were instrumental in ensuring the accuracy and rigor of this systematic review. The authors also acknowledge the support of their respective institutions in facilitating this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1624007/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Shi T, McAllister DA, O’Brien KL, Simoes EA, Madhi SA, Gessner BD, et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet. (2017) 390:946–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30938-8, PMID: 28689664
2. Hall CB, Weinberg GA, Iwane MK, Blumkin AK, Edwards KM, Staat MA, et al. The burden of respiratory syncytial virus infection in young children. New Engl J Med. (2009) 360:588–98. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0804877, PMID: 19196675
3. Kim HW, Canchola JG, Brandt CD, Pyles G, Chanock RM, Jensen K, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants despite prior administration of antigenic inactivated vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. (1969) 89:422–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120955, PMID: 4305198
4. FDA. FDA Approves New Drug to Prevent RSV in Babies and Toddlers. USA: U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2023). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-prevent-rsv-babies-and-toddlers.
5. FDA. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). USA: U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2024). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/covid-19-flu-and-rsv/respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv.
6. Zeng B, Liu X, Yang Q, Wang J, Ren Q, and Sun F. Efficacy and safety of vaccines to prevent respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants and older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. (2024) 146:107118. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2024.107118, PMID: 38878994
7. GSK. GSK presents positive data for Arexvy, its respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, indicating protection over three RSV seasons. USA: GlaxoSmithKline (2024). Available online at: https://www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/press-releases/gsk-presents-positive-data-for-arexvy-its-rsv-vaccine-indicating-protection-over-three-rsv-seasons/.
8. P. Inc. U.S. FDA Approves Pfizer’s RSV Vaccine ABRYSVO® for Adults Aged 18 to 59 at Increased Risk for Disease. USA: Pfizer Inc (2024). Available online at: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/us-fda-approves-pfizers-rsv-vaccine-abrysvor-adults-aged-18.
9. Moderna I. Moderna Receives U.S. FDA Approval for RSV Vaccine mresvia. USA: Moderna, Inc (2024). Available online at: https://investors.modernatx.com/news/news-details/2024/Moderna-Receives-U.S.-FDA-Approval-for-RSV-Vaccine-mresvia/default.aspx.
10. Li T, Fang H, Liu X, Deng Y, Zang N, Xie J, et al. Defining RSV epidemic season in southwest China and assessing the relationship between birth month and RSV infection: a 10-year retrospective study from June 2009 to May 2019. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28928. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28928, PMID: 37455559
11. Johnson M, Chelysheva I, Öner D, McGinley J, Lin G-L, O’Connor D, et al. A genome-wide association study of respiratory syncytial virus infection severity in infants. J Infect Dis. (2024) 229:S112–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae029, PMID: 38271230
12. Panaguiton J, Patel R, Denny S, Rolph G, Hill T, Lewis T, et al. P3 Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) associated admissions and relevant co-morbidities in adults: data from two NHS trusts. BMJ. (2024) 79:A109–10. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2024-BTSabstracts.166
13. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. bmj. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71, PMID: 33782057
14. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Antes G, Atkins D, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Rev Espanola Nutricion Humana y Dietetica. (2014) 18:172–81. doi: 10.14306/renhyd.18.3.114
15. Makan-Murphy N, Madhi SA, and Dangor Z. Safety, efficacy, and effectiveness of maternal vaccination against respiratory infections in young infants. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. (2024) 46(1):1–13. doi: 10.1055/a-2471-6906, PMID: 39708836
16. Falsey AR, Branche AR, Peasley M, Cole M, Petrone KK, Obrecht S, et al. Short-term immunogenicity of licensed subunit RSV vaccines in residents of long-term care facilities (LTCF) compared to community-dwelling older adults. J Am Med Direct Assoc. (2024) 25:105281. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2024.105281, PMID: 39317337
17. Sterne JA, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. bmj. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898, PMID: 31462531
18. Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, and Tugwell P. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses Vol. 2. . Ottawa: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute (2011) p. 1–12.
19. Walker GJ, Foster CS, Sevendal A, Domazetovska A, Kamalakkannan A, Williams PC, et al. Clinical, genomic, and immunological characterization of RSV surge in Sydney, Australia, 2022. Pediatrics. (2024) 153:e2023063667. doi: 10.1542/peds.2023-063667, PMID: 38225912
20. Yamamoto A, Kajiwara Y, Baba T, Okaga S, Kakui M, and Shishido T. 2657. Investigation of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) stability in nasal aspirate collected from RSV infected patients. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2023) 10(Supplement_2), ofad500. 2268. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad500.2268
21. Kim HJ, Choi S, and Choe YJ. RSV prevention strategies in korean children: A review of current approaches and emerging options. Infect Chemother. (2024) 57:31–7. doi: 10.3947/ic.2024.0122, PMID: 40183652
22. Leija-Martínez JJ, Cadena-Mota S, González-Ortiz AM, Muñoz-Escalante JC, Mata-Moreno G, Hernández-Sánchez PG, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus and other respiratory viruses in hospitalized infants during the 2023–2024 winter season in Mexico. Viruses. (2024) 16:1917. doi: 10.3390/v16121917, PMID: 39772224
23. Chang W-C, Huang R-C, Perng C-L, Shang H-S, Yu C-M, and Wang C-H. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of hospitalized adults with respiratory syncytial virus infection at a medical center in northern Taiwan. J Formosan Med Assoc. (2024) 123:1316–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2023.12.004, PMID: 38097432
24. CDC. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Safety. USA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2024).
25. Nazir Z, Habib A, Ali T, Singh A, Zulfiqar E, and Haque MA. Milestone in infant health: unveiling the RSV vaccine’s shielding effect for newborns. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:1836–8. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001002, PMID: 38100625
26. Zhou T, Chen D, Chen Q, Jin X, Su M, Zhang H, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on RSV outbreaks in children: A multicenter study from China. Respir Med. (2024) 234:107828. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2024.107828, PMID: 39368560
27. López-Lacort M, Muñoz-Quiles C, Mira-Iglesias A, López-Labrador FX, Mengual-Chuliá B, Fernández-García C, et al. Early estimates of nirsevimab immunoprophylaxis effectiveness against hospital admission for respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infections in infants, Spain, October 2023 to January 2024. Eurosurveillance. (2024) 29:2400046. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2024.29.6.2400046, PMID: 38333937
28. Jimeno Ruiz S, Peláez A, Calle Gómez Á, Villarreal García-Lomas M, and Martínez SN. Impact of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in adults 60 years and older in Spain. Geriatrics. (2024) 9:145. doi: 10.3390/geriatrics9060145, PMID: 39584946
30. Smith RA, Desai A, Hashash JG, Hayney MS, Farraye FA, and Caldera F. Addressing the risks of respiratory syncytial virus for patients with inflammatory bowel disease in the era of novel vaccines. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2023) 29:1842–5. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad233, PMID: 37816231
31. Ogonczyk-Makowska D, Brun P, Vacher C, Chupin C, Droillard C, Carbonneau J, et al. Mucosal bivalent live attenuated vaccine protects against human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus in mice. NPJ Vaccines. (2024) 9:111. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00899-9, PMID: 38898106
32. Thomas CM, Raman R, Schaffner W, Markus TM, Ndi D, Fill M-MA, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus hospitalizations associated with social vulnerability by census tract: an opportunity for intervention? Open Forum Infect Dis. (2024) 11(5):ofae184. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae184, PMID: 38680605
33. Anderson LJ, Jadhao SJ, Hussaini L, Ha B, McCracken CE, Gibson T, et al. Development and comparison of immunologic assays to detect primary RSV infections in infants. Front Immunol. (2024) 14:1332772. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1332772, PMID: 38283339
34. Lee Y, Klenow L, Coyle EM, Grubbs G, Golding H, and Khurana S. Monoclonal antibodies targeting sites in respiratory syncytial virus attachment G protein provide protection against RSV-A and RSV-B in mice. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:2900. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47146-2, PMID: 38575575
Keywords: RSV, Arexvy, Abrysvo, mResvia, vaccine efficacy, immunogenicity, safety, systematic review
Citation: Alandijany TA and Qashqari FS (2025) Evaluating the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of FDA-approved RSV vaccines: a systematic review of Arexvy, Abrysvo, and mResvia. Front. Immunol. 16:1624007. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1624007
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 09 July 2025;
Published: 18 August 2025.
Edited by:
Huiwen Zheng, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, ChinaReviewed by:
Stephanie Ascough, Imperial College London, United KingdomMadhukiran Parvathaneni, Harrisburg University of Science and Technology, United States
José J. Leija-Martínez, Autonomous University of San Luis Potosí, Mexico
Wenjun Wang, Xi’an Jiaotong University, China
Copyright © 2025 Alandijany and Qashqari. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fadi S. Qashqari, ZnNxYXNocWFyaUB1cXUuZWR1LnNh
 Thamir A. Alandijany
Thamir A. Alandijany Fadi S. Qashqari
Fadi S. Qashqari