- 1Department of Pediatrics, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Obstetric and Gynecologic and Pediatric Diseases and Birth Defects, Sichuan University, Ministry of Education, Chengdu, China
- 3West China School of Clinical Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, West China Second University Hospital, Chengdu, China
- 5Department of Pharmacy/Evidence-Based Pharmacy Center, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 6Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children, Sichuan University, Ministry of Education, Chengdu, China
- 7West China School of Pharmacy, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 8NHC(National Health Commission) Key Laboratory of Chronobiology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Immune-mediated cytopenias (IMCs) following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) can lead to substantial morbidity and mortality, presenting a major therapeutic obstacle. Here, we report a case of a pediatric patient with acquired aplastic anemia. Nine months after HSCT, this patient developed severe, refractory hemolytic anemia and immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (IMT). Despite treatment with corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), rituximab, along with avatrombopag, romiplostim, acetylcysteine, and decitabine, the patient’s platelet count showed no signs of improvement. Subsequently, daratumumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CD38, was administered. This treatment induced a rapid and sustained response. Four months after initial daratumumab administration, the percentage of CD38-positive immune cells in the patient’s peripheral blood increased, which was concurrent with another decline in platelet levels. After re-initiating daratumumab therapy, the patient’s platelet count returned to normal levels. The only significant adverse effect noted was a delayed recovery of humoral immunity. Daratumumab, by targeting antibody-producing plasma cells, shows promise as a therapeutic alternative for refractory IMCs in post-HSCT patients.
Introduction
The incidence of immune-mediated cytopenias (IMCs) following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in patients with non-malignant conditions varies significantly across different studies. In pediatric cases, this incidence ranges from 1.5% to 22% as reported in several studies (1–3). These complications can manifest as immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (IMHA), immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (IMT), or immune-mediated neutropenia (IMN). They may occur independently or in combination, as seen in Evans syndrome, where immune hemolytic anemia coexists with thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. Among these, hemolytic anemia is the most common form of IMCs (4–6). Immune thrombocytopenia has been observed in 0.5-2% of pediatric HSCT patients (1, 7). Typically, IMCs develop within a median time frame of 2 to 40 months after HSCT, regardless of the continuous use of immunosuppressive therapy aimed at preventing or managing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (3, 8).
The pathophysiology of IMCs following HSCT remains incompletely understood. Risk factors for IMCs include conditioning regimen type, anti-T-cell serotherapy, recipient’s cytomegalovirus serostatus, umbilical cord blood stem cells, unrelated donor source, and GVHD development (9–11). The pathophysiology of IMCs involves humoral and cellular immune dysfunctions: autoreactive CD4+ (e.g., T follicular helper cells) and CD8+ T cells drive autoantibody production (e.g., anti-GPIIb/IIIa, GPIb/IX) and direct cytotoxicity against platelets/megakaryocytes. Autoantibodies trigger antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis and complement-mediated cytotoxicity via the membrane attack complex, with the spleen (macrophages) and liver (desialylation via the Ashwell-Morell receptor) as key sites of platelet destruction. Regulatory T/B cell deficiencies and complement activation amplify immune responses. Genetic factors, such as human leukocyte antigen (HLA) and FcγR polymorphisms, and clonal hematopoiesis may influence susceptibility and treatment resistance, while impaired thrombopoietin signaling and megakaryocyte dysfunction reduce platelet production (12).
Although prednisolone and other immunosuppressive agents can control most cases of IMCs, up to 60% of patients with post-transplant IMT do not respond fully to first- or second-line therapies, including rituximab (13). The relapse mechanism is likely due to the re-emergence or continuous production of platelet auto-antibodies by pathogenic platelet-specific B cells, potentially long-lived plasma cells and plasma blasts that reside in the bone marrow, liver, and spleen. Plasma blasts and plasma cells strongly express CD38 rather than CD20, allowing them to evade CD20-directed therapy. Daratumumab, an anti-CD38 antibody designed for the treatment of multiple myeloma and approved by the FDA in 2015 (14), has the ability to target these antibody-producing plasma cells. It has shown promise in treating patients with refractory IMCs. Recently, there have been reports of successful use of daratumumab in managing resistant IMHA or IMT (15–19). Here, we present our experience of treating a pediatric patient with autoimmune cytopenias secondary to very severe aplastic anemia (VSAA) following allogeneic HSCT using daratumumab at our pediatric facility.
Case presentation
The child in this case was a 9-year-old female. At 8 years old, she presented with recurrent skin ecchymosis, petechiae, and anemia. A routine blood test revealed pancytopenia. After bone marrow and genetic examinations, she was diagnosed with VSAA and harbored a heterozygous ANKRD26 gene mutation (c.3544A>C/p.S1182R) of paternal origin, with uncertain clinical significance. As the patient was transfusion-dependent, she received a HSCT 3 months after diagnosis, and the HLA matching result was 7/12. Based on our prior experience, we employed a myeloablative conditioning regimen. This regimen consisted of busulfan (0.8mg/kg/day × 2 days, from - 9d to - 8d), cyclophosphamide (60 mg/kg/dose × 2 doses, from - 3d to - 2d), fludarabine (40mg/m2/day × 5 days, from - 7d to - 3d), Anti-thymocyte globulin (5 mg/kg/day × 3 days, from - 4d to - 2d). Tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil were used for GVHD prophylaxis. The child achieved neutrophil engraftment on day +11 and platelet engraftment on day +17, with 100% donor cells detected in peripheral blood chimerism assessment tests. The hematopoietic reconstruction proceeded smoothly. Subsequently, the patient suffered a pulmonary infection but was discharged after receiving antibacterial treatment.
On day +75, the child was diagnosed with rhinoorbito-cerebral mucormycosis (ROCM), presenting with right ocular swelling, pain, headache, and vision loss. MRI revealed significant right orbital inflammation. Initial empiric therapy (meropenem/vancomycin/voriconazole) was escalated to liposomal amphotericin B (L-AmB) and posaconazole after CSF NGS detected Mucor spp. Due to persistent fever and rising hs-CRP, posaconazole was switched to isavuconazole with L-AmB. Follow-up MRI showed progression to the left orbit and frontal/temporal lobes. On day +145, tacrolimus was discontinued due to severe infection, and bilateral endoscopic debridement confirmed fungal hyphae histopathologically. Infection resolved with negative follow-up NGS (CSF/blood) and resolved MRI lesions, but resulted in permanent bilateral blindness requiring chronic posaconazole suppression.
On day +269 post-HSCT, the patient developed pallor, tachycardia, and lower limb ecchymoses/petechiae after household cold exposure, without other symptoms or GVHD signs. Full donor chimerism was confirmed (day +270). Labs showed macrocytic anemia (Hgb 71g/L, MCV 100fL), marked reticulocytosis (0.086×1012/L; normal 0.024-0.084×1012/L), and severe thrombocytopenia (nadir 1×109/L). Direct Antiglobulin Test(DAT) was positive, while lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and indirect bilirubin remained normal. Rhinovirus was detected, while tests for M. pneumoniae, fungal markers (G/GM), platelet antibodies, and evidence of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC), as well as urine/stool/sputum cultures, were negative. All other tests negative including TA-TMA exclusion criteria: normal ADAMTS13 (Thrombospondin Type 1 Motif, Member 13) activity/antibodies, CFH(Complement Factor H), C5b-9(Complement Component 5b-9), CH50(50% Hemolytic Complement). Bone marrow demonstrated hypercellularity with megakaryocytosis (127 MKs), indicating intact thrombopoiesis. Serum anti-platelet antibodies positive, specific to platelet membrane protein IX(GPIX) and granule membrane protein (GMP140), confirming post-HSCT IMCs.
Initially, thrombocytopenia presented solely with cutaneous hematomas, petechiae, and mild oral mucosal bleeding. Progressively, recurrent epistaxis developed, requiring packed red blood cell (PRBC) transfusions. Despite repeated platelet transfusions, the child exhibited platelet transfusion refractoriness (PTR). Hemostatic interventions included oral etamsylate, Yunnan Baiyao (a traditional Chinese hemostatic agent), gargling with diluted norepinephrine-thrombin solution, and prothrombin complex concentrate administration. Concurrent antimicrobial therapy involved cefoperazone-sulbactam for bacterial infection and posaconazole for fungal prophylaxis.
Prednisolone was initiated (2mg/kg/day for 14 days, tapered to 0.4mg/kg/day maintenance) with weekly IVIG (1g/kg ×12 doses). GVHD prophylaxis continued with cyclosporine A (150-200ng/ml) or sirolimus (8-12ng/ml troughs). Platelets remained critically low (2-19×109/L) despite irradiated platelet transfusions. Multiple agents were trialled: eltrombopag (50-75mg/day ×19d) (20), avatrombopag (30mg/day ×1m) (21), romiplostim (10μg/kg/week ×8 doses) (22), oseltamivir (75mg bid ×8d) (23), acetylcysteine (200mg bid ×1m) (24), and decitabine (3mg/m² ×3 doses) (25). Following steroid failure, donor lymphocyte infusion was administered at day +292 (CD3+ cells 1.156x106/Kg, MNC 2.7x107/Kg) with rituximab from day +297 (375 mg/m2/w x 4w). Hemoglobin stabilized at 98-116g/L, but platelet counts showed no improvement (Figure 1).
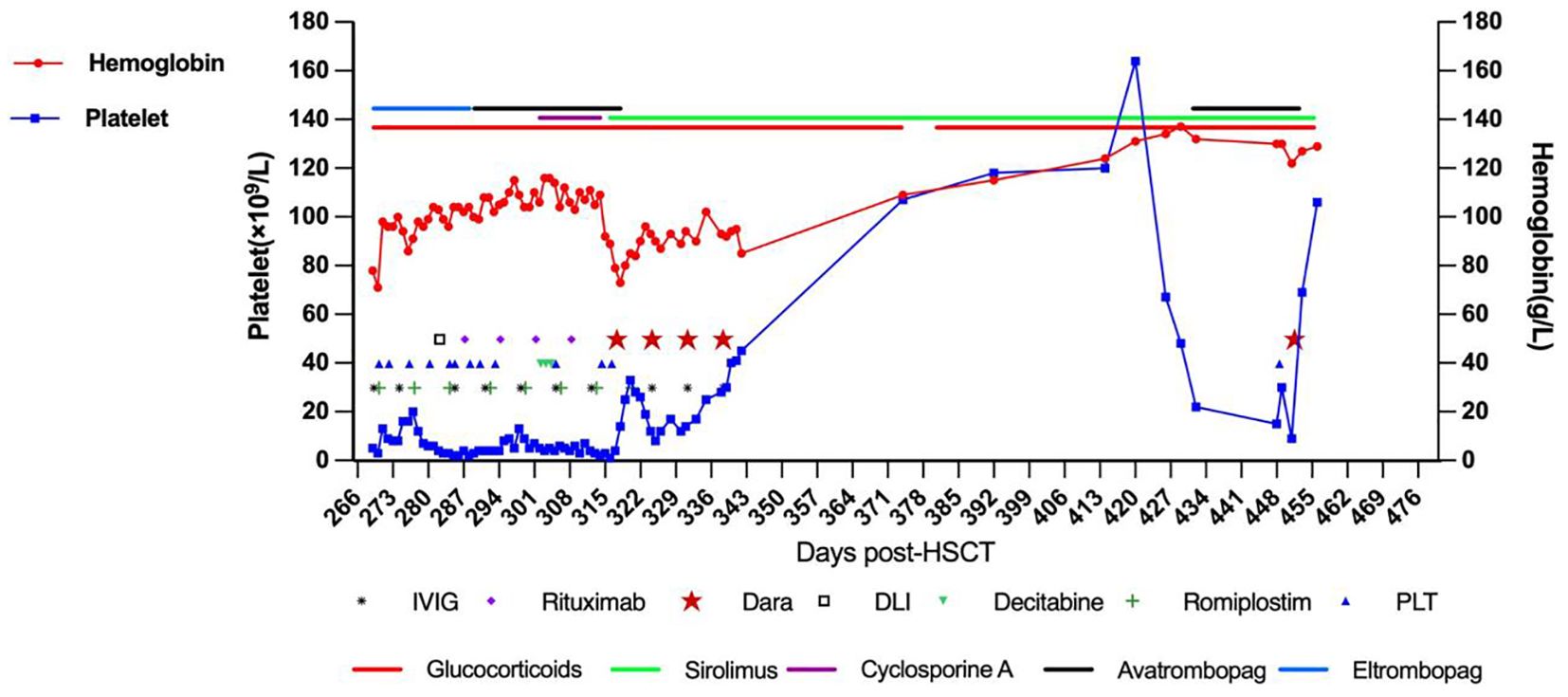
Figure 1. The treatment timeline is presented, demonstrating the patient’s hemoglobin levels, platelet counts, and the various treatments administered over time.
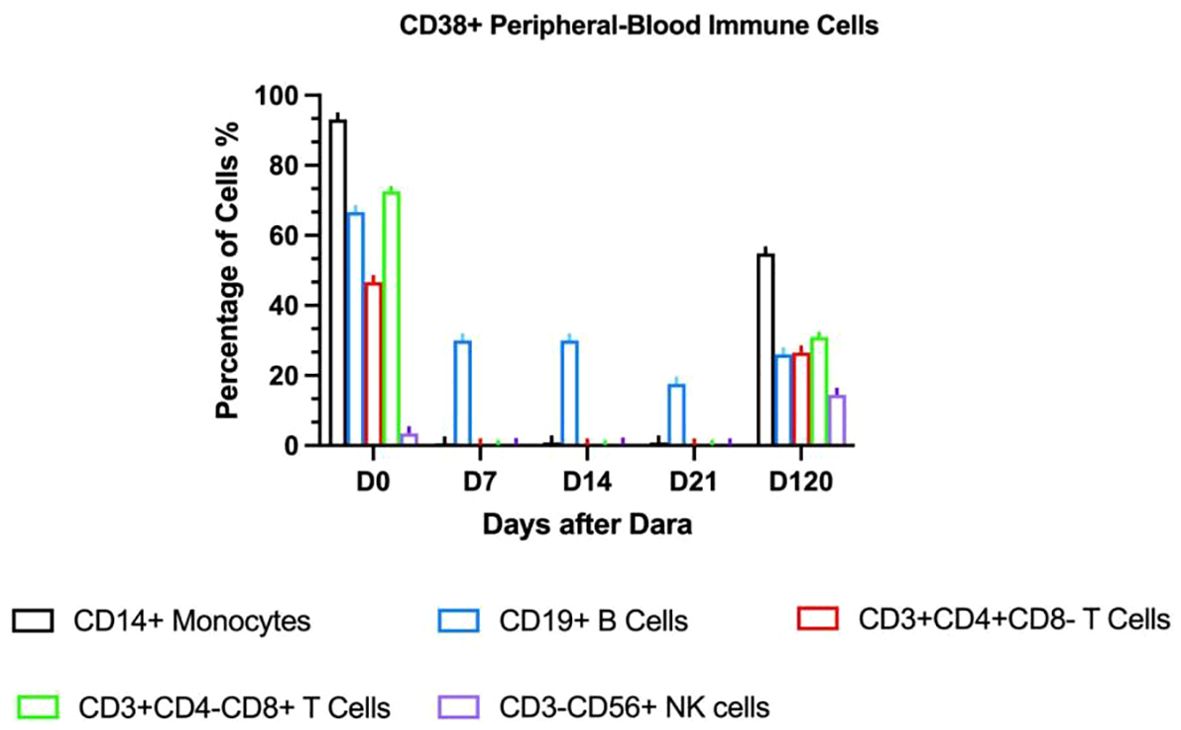
Given persistent severe thrombocytopenia despite rituximab-induced B-cell depletion, plasma cell-derived anti-platelet antibodies were suspected. Daratumumab (16mg/kg IV weekly) was initiated On day +317 (day +49 after onset of IMT). Platelets rose to 33×109/L post-first dose but declined to a nadir of 8×109/L. After the second dose, counts progressively increased. Four total doses were completed per protocol. Discharge labs showed hemoglobin (Hb) 85g/L and platelets 45×109/L; all infusions were well-tolerated. Pre-treatment peripheral blood revealed elevated CD38 expression on immune cells (T lymphocytes, monocytes, natural killer cells) and increased antibody-secreting cells. Post-CD38-targeting, CD38 expression markedly decreased (Figure 2). Platelet (120×109/L) and Hb (120g/L) normalized by day +85. At 3-month follow-up, the child maintained normal hematologic parameters.
On day +426, recurrent fever coincided with rhinovirus infection and methylprednisolone tapering. Progressive thrombocytopenia prompted prednisone escalation and avatrombopag initiation. Despite this, platelets fell to 15×109/L with recurrent epistaxis, requiring transfusion; post-transfusion levels only rose marginally to 30×109/L. CD38 expression analysis revealed significant upregulation on immune cells (Figure 2), suggesting recurrent plasma cell-derived anti-platelet antibodies. A subsequent daratumumab dose (16mg/kg) on day +451 achieved platelet recovery to 106×109/L within six days. At last follow-up (Dara+341), hemoglobin and platelets normalized without medications, though delayed cellular immunity recovery necessitated IVIG substitution (Figure 3). IVIG was administered weekly×12 consecutive weeks, then biweekly×3 months, transitioning to monthly until 12 months post-daratumumab after confirming normalized immunoglobulins.
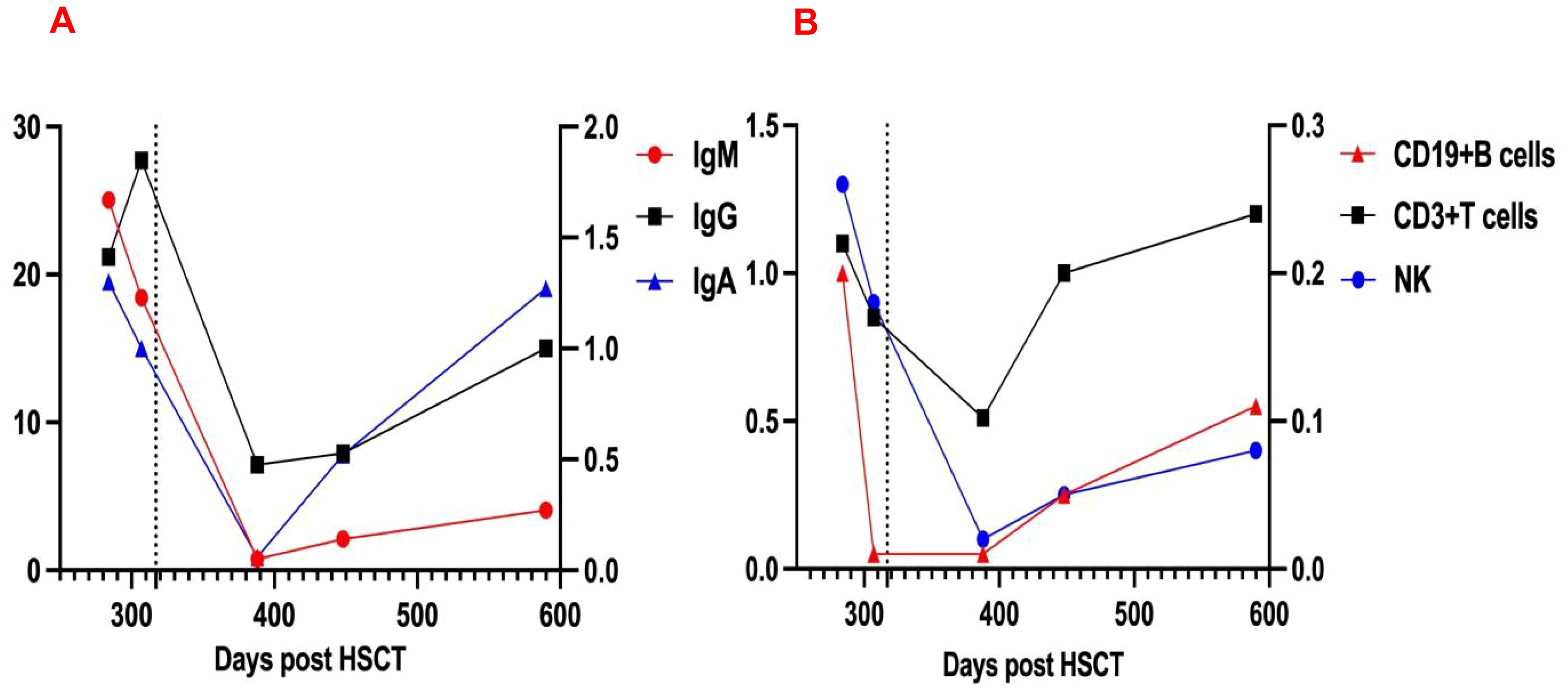
Figure 3. Changes in immunoglobulin (A) and lymphocyte counts (B) Levels Pre- and Post-Dara, dashed line indicates initiation of daratumumab therapy. IgG and T-lymphocyte counts correspond to the left vertical axis; IgM, IgA, B-lymphocyte, and NK-cell counts are scaled to the right vertical axis.
Review of literature
To our knowledge, five previous reports have presented data on six patients with post-HSCT IMT (13, 15, 19, 26, 27). A search for additional cases of IMCs was conducted through PubMed, using the keyword “daratumumab” combined with “HSCT, AIC, AIHA, hemolytic, Evans syndrome, ITP, thrombocytopenia, immune dysregulation, and autoimmunity (excluding multiple myeloma)”. Prior to dara initiation, the patient’s hemoglobin had normalized, but refractory immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (IMT) persisted, prompting our review of previous IMT diagnostic cases. The identified articles were screened to exclude duplicate patients and verify cross-references.
To date, including the patient in this study, a total of 7 cases of IMT following HSCT have been reported. Among these, 3 presented with isolated IMT, while 4 were diagnosed with IMT concomitant with autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA). Of the 7 patients, 4 were children (all <12 years of age) with the youngest aged 2 years, and 3 were adults (age 23–60 years, median 25). The primary disease leading to HSCT was myelodysplastic syndrome (n=1), severe aplastic anemia (n=2), primary myelofibrosis (n=1), or a primary immunodeficiency disease (n=3). Two patients received peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC), three whole bone marrow, and in one case the stem cell source was not reported. The child in our case received bone marrow and peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells. Two patients were transplanted from a 10/10 and two from a 9/10 unrelated donor. One patient was transplanted from a family donor. The child in our case received the transplatation from her father with 7/12 HLA-matched. Chimerism was 100% donor in four and >90% in one patient. The onset of IMT was at a median of day +151 (range +61 to +359), and the first dose of daratumumab was administered at a median of 68 days (range 8–223 days) after IMCs diagnosis. One patient recieved single dose of daratumumab, and daratumumab was administered once weekly at a dose of 16mg/kg in the other cases. The median number of infusions was 4 (range 1-6). Patients had previously zero to nine different therapies, most commonly corticosteroids, rituximab, and IVIG (Table 1). In six patients, at least one concomitant treatment was given during daratumumab therapy. Following daratumumab administration, one patient experienced no adverse reactions, while one developed hypertension and chest pain. Two patients exhibited bronchial obstruction, and three developed hypogammaglobulinemia-two of whom concurrently presented with lymphopenia (Table 2). No severe adverse events occurred, indicating favorable tolerability. Among these, three patients received regular intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) infusions post-daratumumab therapy for infection prophylaxis. Five patients reached transfusion independency and normal blood count. One patient did not respond to daratumumab and proceeded to second HSCT 9 days from first dose of daratumumab. Another one did not respond to daratumumab and deceased from cardiac arrest due to acute heart failure most likely related to pulmonary embolism. The median follow-up time after daratumumab treatment among the six patients who reached transfusion independency was 4 months (range 1–16 months), and six patients were alive without severe long-term toxicities (Table 2).
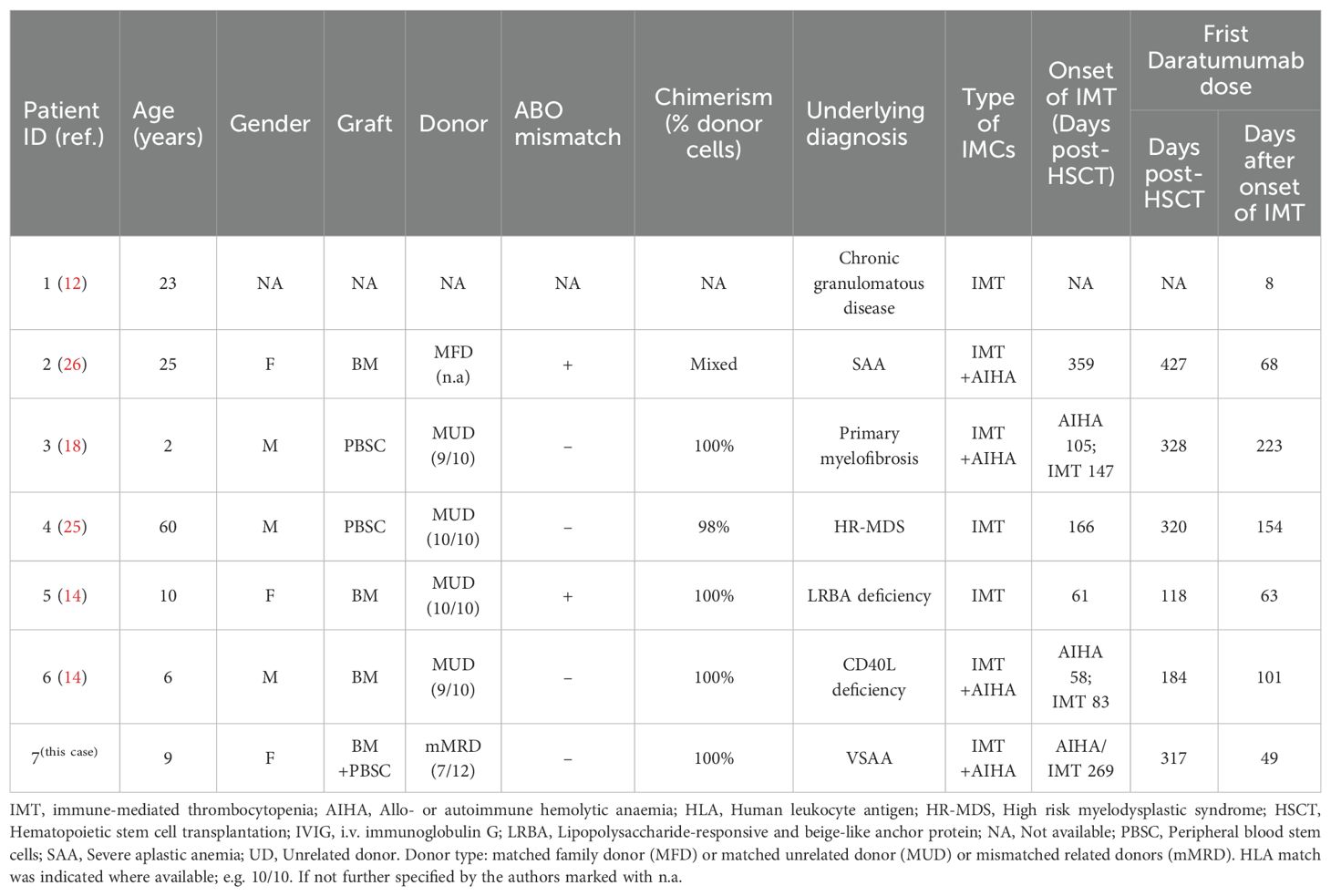
Table 1. Clinical summary of seven patients with IMT following HSCT who received daratumumab treatment.
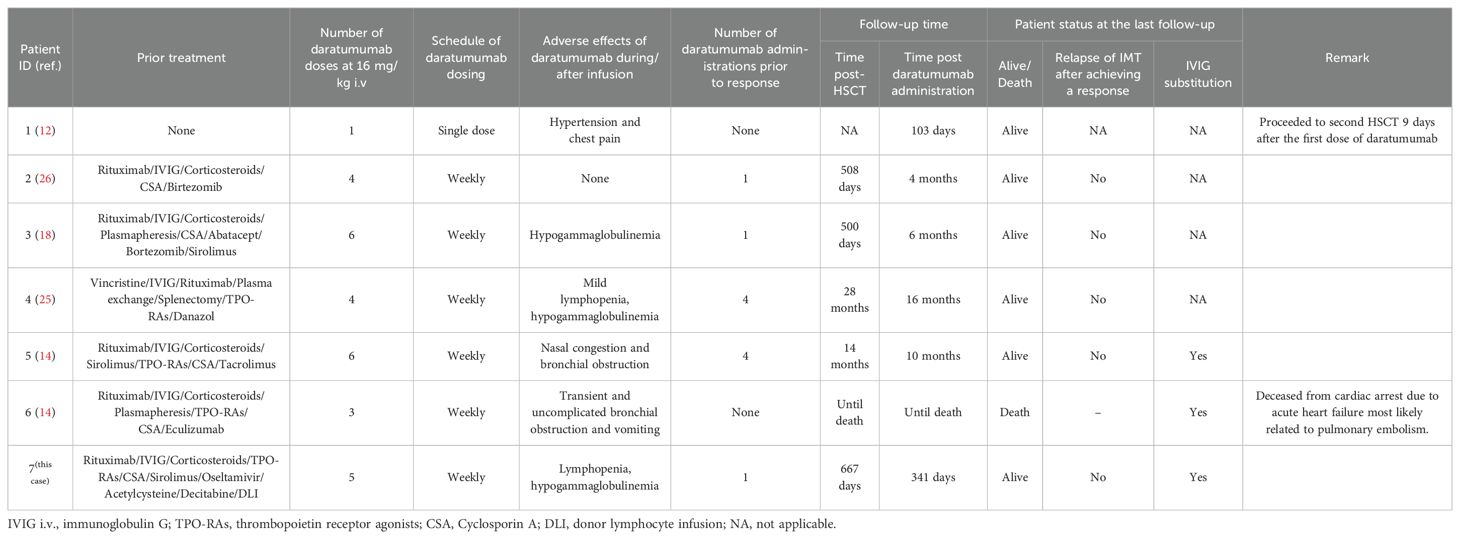
Table 2. Details of daratumumab schedule, durability of response and patients’ status at the last follow-up.
Discussion
HSCT-associated IMCs pose a substantial threat to patient health and are often extremely challenging to manage. In non-malignant disease settings, several risk factors for developing IMCs post-HSCT have been identified (7). Moreover, environmental factors may play a role. In murine models, inflammatory states have been shown to trigger and promote autoreactive T-cell populations (28), and infections may be linked to lymphodepletion and homeostatic expansion that favor autoreactive clones. The standard first-line treatment for post-HSCT IMCs usually involves corticosteroids and IVIG. For cases unresponsive to steroids and IVIG, rituximab is commonly used as second-line therapy (29). Other treatment approaches reported in the literature include calcineurin inhibitors, sirolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, abatacept, and bortezomib (8). Additional therapeutic strategies include plasmapheresis; chemotherapeutic agents such as 6-mercaptopurine, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, and vincristine; and in some refractory cases, splenectomy or a second stem cell transplant may be considered (30).
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) can be particularly challenging after allogeneic HSCT due to multifactorial causes of thrombocytopenia: GVHD, disease relapse, viral infections, thrombotic microangiopathy, or drug reactions (31). Approximately 40-60% and 20-40% of ITP patients harbor platelet-bound autoantibodies targeting platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa (integrin αIIbβ3) and the GPIb/IX/V complex, respectively (32), with meta-analyses confirming high GP-specific antibody specificity in ITP (33). These antibodies drive platelet destruction via phagocytosis and complement activation (34). To confirm the immunological mechanism underlying thrombocytopenia, detecting glycoprotein-specific anti-platelet antibodies is very useful. In this case, we identified GP IX-specific antibodies and Granule Membrane Protein 140 (GMP140) in the patient without P-selectin (CD62P), which helped diagnose allo-HSCT-related secondary IMT. Reported response rates for post-HSCT IMT are 30-50% after first-line and second-line therapies (15). Similar to literature, our patient showed hemoglobin improvement after multiple interventions (corticosteroids/IVIG/rituximab/oseltamivir/acetylcysteine/decitabine/TPO-RAs), yet thrombocytopenia persisted.
Crickx et al. found that daratumumab may provide clinical benefit in some patients with severe refractory ITP or warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) (35). Koo et al. used daratumumab to treat three patients with relapsing, refractory AIHA following allo-HSCT. Two of the three patients achieved remission and were able to discontinue steroid therapy concurrently (36), Among six reported post-HSCT IMT cases, five failed first-/second-line and multiple interventions therapies (including plasmapheresis), but four achieved complete hematologic remission after 3–6 daratumumab doses, supporting its efficacy in refractory IMT with or without AIHA. This provides further evidence for the potential of daratumumab in treating post- HSCT IMT,similar to our findings in the present case. One patient showed no response and developed severe AIHA one week after the first daratumumab administration. He received salvage therapy with high-frequency plasmapheresis, methylprednisolone pulses, three doses of IVIG, and one dose of eculizumab. Without any response to this therapy, this patient deceased from cardiac arrest due to acute heart failure most likely related to pulmonary embolism (15). Another patient, upon diagnosis of IMT, bypassed first- and second-line therapies and directly proceeded to a single infusion of daratumumab, but exhibited no therapeutic response. He had previously undergone allogeneic HSCT for chronic granulomatous disease with secondary graft failure. It is possible that the lack of observed response could have been due to a low bone marrow reserve following secondary graft failure (13). However, treatment of IMT with daratumumab warrants caution given the lack of long-term experience, the off-label use, and the fact that daratumumab may not always be the best suitable therapy since IMCs can derive from different forms of immune dysregulation (37), not all of which involve plasma cells. Compared to other IMT patients, our case underwent haploidentical transplantation and was diagnosed with ROCM post-transplant. Immunosuppressants were discontinued prematurely, followed by long-term antifungal therapy. This may have contributed to immune dysregulation, potentially triggering IMT development.
Post-HSCT IMT recurrence arises from CD38+ pathogenic plasma cells in spleen/bone marrow that evade CD20-targeted therapies (38). CD38, a receptor widely expressed on plasmablasts, short-lived, and long-lived plasma cells, is an attractive target for the therapeutic antibody daratumumab in IMT treatment (39). Daratumumab has been approved for multiple myeloma (40) and is effective in refractory ITP that have failed second-line treatments (41). Along with the rapid increase in platelet count, the number of CD38+ immune cells, including T lymphocytes, monocytes, CD56dimCD16+ NK (Natural Killer) cells, decreased rapidly within a week after the first daratumumab treatment. Daratumumab infusion effectively suppressed lymphocyte proliferative function (Figure 2), indicating its ability to down-regulate autoantibody production by eliminating plasma cells and maintaining a long-term response. Reducing platelet destruction and restoring platelet count may gradually bring the immune activation state back to equilibrium. We observed a significant decrease in CD56+ NK cells, which are important effector cells in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. In another study, daratumumab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone (D-Rd) downregulated CD38 expression in multiple myeloma (MM) patients compared to Rd, especially in NK cells, B cells, basophils, monocytes, and CD4+ T cells, with no significant change in CD8+ T cells. Daratumumab-CD38 complex transfer (trogocytosis) reduces surface CD38 levels (42). Effector and memory CD8+ T cells increased, especially in deep responders, showing an activated phenotype with upregulated GrB and HLA-DR (43). Here, we observed decreased CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proportions after daratumumab treatment, potentially related to the non-neoplastic nature of the disease. We hypothesize that daratumumab may lead to rapid platelet recovery by down- regulating antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Daratumumab shows promise as a treatment option, especially in patients with secondary IMT following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Four months after the initial daratumumab administration, the percentage of CD38-positive immune cells in the patient’s peripheral blood increased again, coinciding with another drop in platelet levels. Despite this setback, daratumumab treatment was effective once more, highlighting its continued efficacy. This recurrence pattern is a common challenge in managing other forms of immune thrombocytopenia (44). In this study, flow cytometry revealed elevated CD38+ cells, guiding successful daratumumab use. Pre-treatment and intra-treatment assessment of CD38+ cell proportions may help guide the successful use of daratumumab.
CD38 promotes pro-inflammatory phenotypes in innate immune cells, regulates leukocyte recruitment to infected tissues, modulates macrophage phagocytosis and dendritic cell migration to lymph nodes, thereby impairing T/B cell activity. Combined with direct depletion of CD38-expressing NK cells and other immune cells crucial for pathogen control, these features may explain daratumumab-induced immunosuppression in some patients (45). An integrated safety analysis of data pooled from 5 completed phase III, randomized, controlled studies in comparator-treated patients with MM as a first-line in both transplant-eligible and transplant-ineligible patients, and for relapsed/refractory disease, identified high rates of neutropenia, lymphopenia, and pneumonia as common grade 3/4 adverse events with daratumumab compared with comparators (46). In this case, no serious adverse events were observed, and the therapy was well-tolerated, which is consistent with previous research reports (15, 16, 19, 36, 37). Although generally considered a well-tolerated therapy, daratumumab has a significant risk of infectious complications, and this risk has not been fully evaluated in pediatric populations (47). Therefore, its potential hazards should not be ignored in immunocompromised transplant patients. Due to the typically short follow-up periods, it is difficult to determine long-term outcomes, infection frequencies, and potential chronic toxicities, such as impaired humoral immunity. Therefore, we recommend periodic monitoring of cellular and humoral immunity in post-transplant IMT patients receiving daratumumab, alongside tailored immunoglobulin replacement regimens to prevent severe infections.
In conclusion, we present a case study of a pediatric patient with post-HSCT IMCs who achieved complete recovery after treatment with daratumumab. Notably, the treatment was well-tolerated, with the only significant adverse event being prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia. Our findings suggest that daratumumab could be considered as a potential treatment option for managing refractory post-HSCT IMCs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by West China Second University Hospital Ethical Committee. Written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the participants’legal guardian/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
X-YJ: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. D-JL: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. S-NL: Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. Q-KD: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. S-WS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LH: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YA: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. JG: Writing – review & editing. Y-PZ: Writing – review & editing. J-QN: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. X-XL: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2025JDKP0108), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (YJ202339), and the Sichuan University Research Funds for Graduate Education and Teaching Reform (GSSCU2023120).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Miller PDE, Snowden JA, De Latour RP, Iacobelli S, Eikema D-J, Knol C, et al. Autoimmune cytopenias (AIC) following allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant for acquired aplastic anaemia: a joint study of the Autoimmune Diseases and Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Parties (ADWP/SAAWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Bone Marrow Transplant. (2020) 55:441–51. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0680-4
2. Page KM, Mendizabal AM, Prasad VK, Martin PL, Parikh S, Wood S, et al. Posttransplant autoimmune hemolytic anemia and other autoimmune cytopenias are increased in very young infants undergoing unrelated donor umbilical cord blood transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant. (2008) 14:1108–17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.07.006
3. Hwang-Bo S, Kim S-K, Lee JW, Jang P-S, Chung N-G, Jeong D-C, et al. Treatment and response of autoimmune cytopenia occurring after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in children. Blood Res. (2017) 52:119–24. doi: 10.5045/br.2017.52.2.119
4. Bhatt V, Shune L, Lauer E, Lubin M, Devlin SM, Scaradavou A, et al. Autoimmune hemolysis and immune thrombocytopenic purpura after cord blood transplantation may be life-threatening and warrants early therapy with rituximab. Bone Marrow Transplant. (2016) 51:1579–83. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2016.228
5. Daikeler T and Tyndall A. Autoimmunity following haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. (2007) 20:349–60. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2006.09.008
6. Ueki H, Igarashi S, Kimura S, Tsuchimochi T, Furudate K, Sakurai A, et al. Evans syndrome after unrelated bone marrow transplantation for refractory cytopenia of childhood. Pediatr Transplant. (2014) 18:E246–251. doi: 10.1111/petr.12323
7. Faraci M, Zecca M, Pillon M, Rovelli A, Menconi MC, Ripaldi M, et al. Autoimmune hematological diseases after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children: an Italian multicenter experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant. (2014) 20:272–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.11.014
8. Gupta AO, Jan Boelens J, Ebens CL, Kurtzberg J, Lund TC, Smith AR, et al. Consensus opinion on immune-mediated cytopenias after hematopoietic cell transplant for inherited metabolic disorders. Bone Marrow Transplant. (2021) 56:1238–47. doi: 10.1038/s41409-020-01179-5
9. Szanto CL, Langenhorst J, De Koning C, Nierkens S, Bierings M, Huitema ADR, et al. Predictors for autoimmune cytopenias after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. (2020) 26:114–22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.07.022
10. Daikeler T, Labopin M, Ruggeri A, Crotta A, Abinun M, Hussein AA, et al. New autoimmune diseases after cord blood transplantation: a retrospective study of EUROCORD and the Autoimmune Disease Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood. (2013) 121:1059–64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-445965
11. Deambrosis D, Lum SH, Hum RM, Poulton K, Ogden W, Jones S, et al. Immune cytopenia post-cord transplant in Hurler syndrome is a forme fruste of graft rejection. Blood Adv. (2019) 3:570–4. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018026963
12. Moulinet T, Moussu A, Pierson L, and Pagliuca S. The many facets of immune-mediated thrombocytopenia: Principles of immunobiology and immunotherapy. Blood Rev. (2024) 63:101141. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2023.101141
13. Khandelwal P, Teusink-Cross A, Kumar AR, Bleesing JJ, Mehta PA, Jordan MB, et al. Daratumumab for the management of autoimmune cytopenias in children and young adults: a case series. Br J Haematol. (2021) 194:e84–9. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17565
14. Lokhorst HM, Plesner T, Laubach JP, Nahi H, Gimsing P, Hansson M, et al. Targeting CD38 with daratumumab monotherapy in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1207–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1506348
15. Driouk L, Schmitt R, Peters A, Heine S, Girschick HJ, Strahm B, et al. Daratumumab therapy for post-HSCT immune-mediated cytopenia: experiences from two pediatric cases and review of literature. Mol Cell Pediatr. (2021) 8:5. doi: 10.1186/s40348-021-00114-y
16. Schuetz C, Hoenig M, Moshous D, Weinstock C, Castelle M, Bendavid M, et al. Daratumumab in life-threatening autoimmune hemolytic anemia following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Adv. (2018) 2:2550–3. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018020883
17. Chapuy CI, Kaufman RM, Alyea EP, and Connors JM. Daratumumab for delayed red-cell engraftment after allogeneic transplantation. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:302. doi: 10.1056/NEJMx180048
18. Bathini S, Holtzman NG, Koka R, Singh Z, Wilding E, Zou Y, et al. Refractory postallogeneic stem cell transplant pure red cell aplasia in remission after treatment with daratumumab. Am J Hematol. (2019) 94:E216–9. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25515
19. Even-Or E, Naser Eddin A, Shadur B, Dinur Schejter Y, Najajreh M, Zelig O, et al. Successful treatment with daratumumab for post-HSCT refractory hemolytic anemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2020) 67:e28010. doi: 10.1002/pbc.28010
20. Giammarco S, Sica S, Chiusolo P, Laurenti L, Sorá F, Martino M, et al. Eltrombopag for the treatment of poor graft function following allogeneic stem cell transplant: a retrospective multicenter study. Int J Hematol. (2021) 114:228–34. doi: 10.1007/s12185-021-03153-3
21. Ruan Y, Cao W, Luo T, Liu X, Liu Q, Xiao Y, et al. Avatrombopag for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in children’s patients following allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: A pilot study. Front Pediatr. (2023) 11:1099372. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1099372
22. Bussel JB, Soff G, Balduzzi A, Cooper N, Lawrence T, and Semple JW. A review of romiplostim mechanism of action and clinical applicability. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2021) 15:2243–68. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S299591
23. Colunga-Pedraza PR, Peña-Lozano SP, Sánchez-Rendón E, de la Garza-Salazar F, Colunga-Pedraza JE, Gómez-De León A, et al. Oseltamivir as rescue therapy for persistent, chronic, or refractory immune thrombocytopenia: a case series and review of the literature. J Thromb Thrombolysis. (2022) 54:360–6. doi: 10.1007/s11239-022-02651-3
24. Wang Y, Kong Y, Zhao H-Y, Zhang Y-Y, Wang Y-Z, Xu L-P, et al. Prophylactic NAC promoted hematopoietic reconstitution by improving endothelial cells after haploidentical HSCT: a phase 3, open-label randomized trial. BMC Med. (2022) 20:140. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02338-9
25. Shao X, Xu P, Ji L, Wu B, Zhan Y, Zhuang X, et al. Low-dose decitabine promotes M2 macrophage polarization in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia via enhancing KLF4 binding to PPARγ promoter. Clin Transl Med. (2023) 13:e1344. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1344
26. Migdady Y, Ediriwickrema A, Jackson RP, Kadi W, Gupta R, Socola F, et al. Successful treatment of thrombocytopenia with daratumumab after allogeneic transplant: a case report and literature review. Blood Adv. (2020) 4:815–8. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001215
27. Blennerhassett R, Sudini L, Gottlieb D, and Bhattacharyya A. Post-allogeneic transplant Evans syndrome successfully treated with daratumumab. Br J Haematol. (2019) 187:e48–51. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16171
28. Lang KS, Recher M, Junt T, Navarini AA, Harris NL, Freigang S, et al. Toll-like receptor engagement converts T-cell autoreactivity into overt autoimmune disease. Nat Med. (2005) 11:138–45. doi: 10.1038/nm1176
29. Spadea M. Immune-mediated cytopenias (IMCs) after HSCT for pediatric non-malignant disorders: epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, and treatment. Eur J Pediatr. 182(6):2471–83. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-04912-6
30. Hess J, Su L, Nizzi F, Beebe K, Magee K, Salzberg D, et al. Successful treatment of severe refractory autoimmune hemolytic anemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplant with abatacept. Transfusion (Paris). (2018) 58:2122–7. doi: 10.1111/trf.14907
31. Yuan C, Boyd AM, Nelson J, Patel RD, Varela JC, Goldstein SC, et al. Eltrombopag for treating thrombocytopenia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant. (2019) 25:1320–4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.01.027
32. Li J, van der Wal DE, Zhu G, Xu M, Yougbare I, Ma L, et al. Desialylation is a mechanism of Fc-independent platelet clearance and a therapeutic target in immune thrombocytopenia. Nat Commun. (2015) 6. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8737
33. Vrbensky JR, Moore JE, Arnold DM, Smith JW, Kelton JG, and Nazy I. The sensitivity and specificity of platelet autoantibody testing in immune thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of a diagnostic test. J Thromb Haemost JTH. (2019) 17:787–94. doi: 10.1111/jth.14419
34. Li J, Sullivan JA, and Ni H. Pathophysiology of immune thrombocytopenia. Curr Opin Hematol. (2018) 25:373–81. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000447
35. Crickx E, Audia S, Robbins A, Boutboul D, Comont T, Cheminant M, et al. Daratumumab, an original approach for treating multi-refractory autoimmune cytopenia. Haematologica. (2021) 106:3198–201. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.279232
36. Koo J, Giller RH, Quinones R, McKinney CM, Verneris MR, and Knight-Perry J. Autoimmune cytopenias following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant in pediatric patients: Response to therapy and late effects. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2020) 67:e28591. doi: 10.1002/pbc.28591
37. Barcellini W, Fattizzo B, and Zaninoni A. Current and emerging treatment options for autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2018) 14:857–72. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2018.1521722
38. Akuta K, Fukushima K, Nakata K, Hayashi S, Toda J, Shingai Y, et al. Autoimmune-mediated thrombocytopenia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: significance of detecting reticulated platelets and glycoprotein-specific platelet autoantibodies. Int J Hematol. (2022) 115:322–8. doi: 10.1007/s12185-021-03272-x
39. Vernava I and Schmitt CA. Daratumumab as a novel treatment option in refractory ITP. Blood Cells Mol Dis. (2023) 99:102724. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2023.102724
40. McKeage K. Daratumumab: first global approval. Drugs. (2016) 76:275–81. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0536-1
41. Al-Samkari H and Neufeld EJ. Novel therapeutics and future directions for refractory immune thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. (2023) 203:65–78. doi: 10.1111/bjh.19078
42. Krejcik J, Frerichs KA, Nijhof IS, van Kessel B, van Velzen JF, Bloem AC, et al. Monocytes and granulocytes reduce CD38 expression levels on myeloma cells in patients treated with daratumumab. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2017) 23:7498–511. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2027
43. Casneuf T, Xu XS, Adams HC, Axel AE, Chiu C, Khan I, et al. Effects of daratumumab on natural killer cells and impact on clinical outcomes in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. (2017) 1:2105–14. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017006866
44. Chen Y, Cao X, Liu X, Wang W, Ju M, and Zhang L. A novel anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody for treating immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390(23):2178–190. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2400409
45. Glaría E and Valledor AF. Roles of CD38 in the immune response to infection. Cells. (2020) 9:228. doi: 10.3390/cells9010228
46. Al Hadidi S, Miller-Chism CN, Kamble R, and Mims M. Safety analysis of five randomized controlled studies of daratumumab in patients with multiple myeloma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. (2020) 20:e579–89. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.04.004
Keywords: immune-mediated cytopenias, post-HSCT, daratumumab, pediatric, immune-mediated thrombocytopenia
Citation: Jing X-y, Li D-j, Su S-n, Dai Q-k, Sun S-w, Huang L, Ai Y, Gao J, Zhu Y-P, Ni J-q and Lu X-x (2025) Effective treatment with daratumumab in post-HSCT refractory immune-mediated cytopenias: a case report and literature review. Front. Immunol. 16:1625365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1625365
Received: 08 May 2025; Accepted: 14 July 2025;
Published: 01 August 2025.
Edited by:
Liang Huang, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, ChinaReviewed by:
Thomas Pincez, CHU Sainte-Justine, CanadaManuela Spadea, University of Turin, Italy
Selin Küçükyurt, Istanbul University Cerrahpasa, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Jing, Li, Su, Dai, Sun, Huang, Ai, Gao, Zhu, Ni and Lu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiao-xi Lu, bHVfaGVsZW5hQHNpbmEuY29t; Jia-qi Ni, amlhcWluaTAwN0AxNjMuY29t
 Xiao-yu Jing
Xiao-yu Jing Dong-jun Li1,2
Dong-jun Li1,2 Ju Gao
Ju Gao Jia-qi Ni
Jia-qi Ni