- 1Clinical Medical College, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
- 2Department of Graduate School, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, China
- 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Yangzhou, China
Moonlighting enzymes perform multiple distinct functions under different conditions without relying on gene fusion, splicing, or polymerization. Many classical metabolic enzymes, beyond their involvement in pathways like glycolysis and glutamine metabolism, also function as transcription factors, RNA-binding proteins, or signaling molecules. These dual roles are crucial in processes such as cancer metabolic reprogramming, immune evasion, and drug resistance. Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 2 (GOT2), a key example, is located in the mitochondria and catalyzes the transamination of aspartate and glutamate. Apart from its metabolic function, GOT2 also influences nuclear fatty acid metabolism and immune-related gene expression, affecting the tumor microenvironment. By integrating metabolic and signaling roles, GOT2 supports tumor cell adaptation to stress, promoting growth, survival, and immune escape. This multifunctionality positions GOT2 as a potential target for cancer diagnosis and therapy. This review discusses GOT2’s moonlighting roles and its clinical potential.
1 Introduction
Moonlighting enzymes refer to single polypeptide chains that perform two or more distinct functions under different microenvironmental conditions through conformational changes or subcellular localization shifts. This phenomenon does not rely on gene fusion, alternative splicing, or protein multimerization mechanisms (1, 2). Recent studies have increasingly shown that many classical metabolic enzymes are not limited to their traditional roles, such as glycolysis or glutamine metabolism, but also possess non-classical functions like transcriptional regulation, RNA binding, and signal transduction. These functions play crucial roles in tumor metabolic reprogramming, immune evasion, and drug resistance, challenging the traditional concept of “one enzyme, one function” (3–6). GOT2, a classical mitochondrial metabolic enzyme, has recently become a major research focus in the field of moonlighting enzymes due to its significant temporal and spatial dynamic regulation characteristics in tumor microenvironments and metabolic remodeling processes (7–10). GOT2 plays a particularly notable moonlighting role during malignant tumor progression. It regulates tumor cell lipid metabolism and immune-related gene expression by altering its subcellular localization, shaping the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, GOT2 integrates metabolic and signaling pathways, enabling tumor cells to adapt to stress conditions and facilitating their proliferation, survival, and immune escape (11–13). This review systematically summarizes the molecular mechanisms underlying the moonlighting functions of GOT2 (Figure 1), provides an in-depth analysis of interactions between metabolic networks and signaling pathways mediated by GOT2 during tumor progression (Table 1), and discusses the potential application prospects of its functional plasticity in developing targeted cancer therapies.
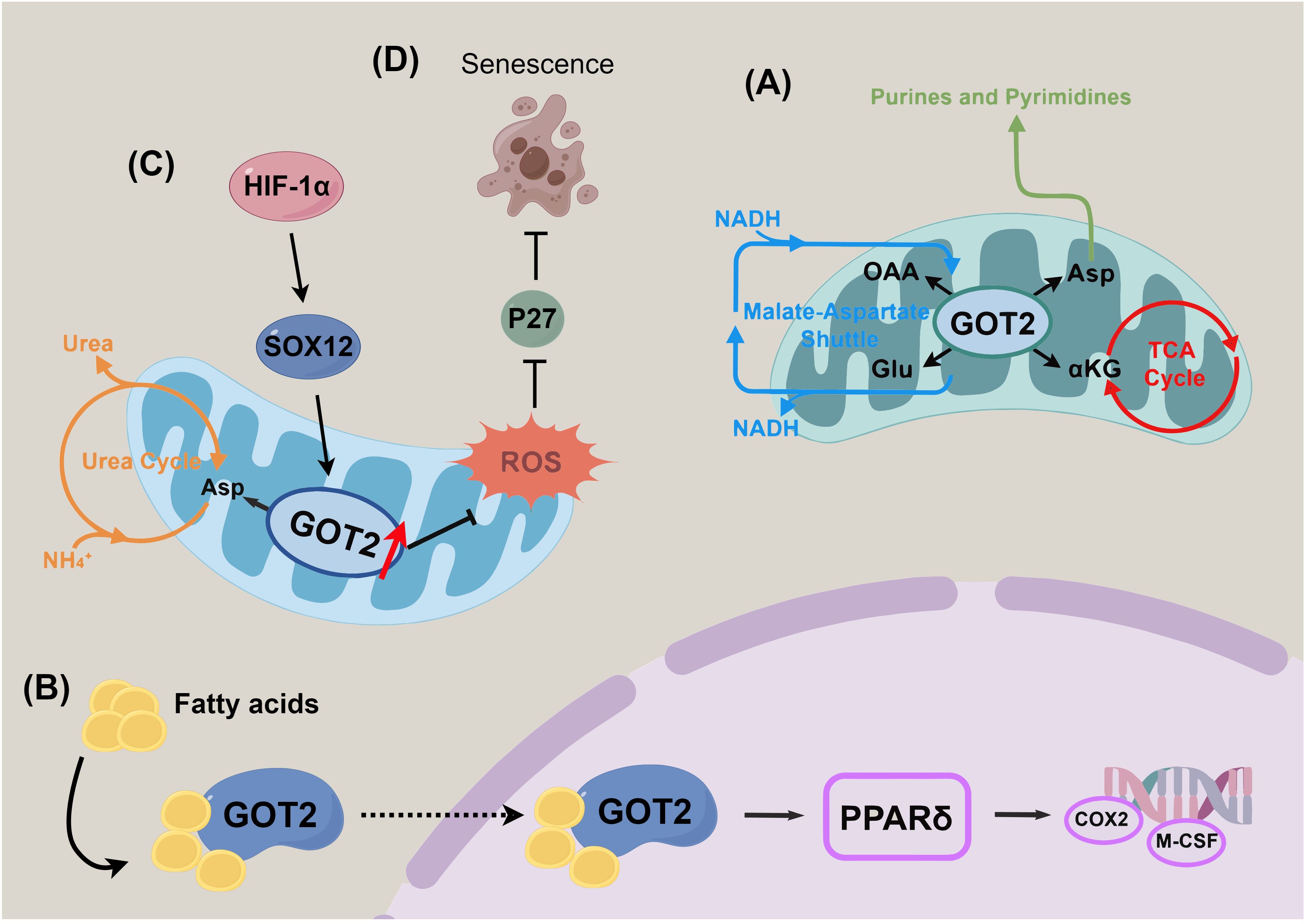
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the moonlighting functions of GOT2 in tumor biology. (A) Canonical metabolic roles of GOT2 in cellular energy production and redox balance. (B) Non-classical fatty acid-binding and membrane-associated activities contributing to cellular signaling and membrane dynamics. (C) Regulation of nitrogen homeostasis and metabolic reprogramming in response to tumor microenvironmental cues. (D) Involvement in cellular senescence and maintenance of antioxidant defense mechanisms.
2 Genetic features and mutations of GOT2
The human GOT2 gene is located on chromosome 16q21 (chr16:58,526,874–58,561,638), spans approximately 34.7 kb, and consists of 10 exons and 9 introns (14). It encodes a 430-amino-acid mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase, with exon 2 at the 5’ end responsible for the mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) and exons 4–6 forming the highly conserved PLP (Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate)-dependent catalytic core. The gene exhibits strong evolutionary conservation among vertebrates. Although multiple rare nonsynonymous variants have been identified in population databases such as gnomAD, pathogenic mutations are predominantly observed in homozygous or compound heterozygous states and mainly affect key residues in the PLP-binding sites (e.g., Lys259, Arg387) or the dimer interface (e.g., Leu146, Phe322, Arg262) (15–17). Such mutations commonly result in severe loss of GOT2 enzymatic activity, disruption of aspartate shuttling, developmental delay, and epilepsy, with their deleterious mechanisms validated by genetic, biochemical, and structural studies (9, 18).
3 Structural dynamics and functional versatility of GOT2
As shown in Figure 2, the yellow domain represents a typical type I PLP-dependent aspartate aminotransferase-like major domain. This domain is essential for maintaining transaminase activity by stabilizing the active site and facilitating the binding of the coenzyme PLP. The active site of GOT2 is deeply embedded within the PLP-binding pocket at the homodimer interface. Lys259 forms a Schiff base (internal aldimine bond) with PLP, while conserved residues such as His260, Trp261, and Ser262 collaboratively stabilize its spatial orientation and electronic environment. Arg387 and Asp223 further anchor the PLP phosphate group through salt bridges and hydrogen bonds, shaping the local proton-transfer microenvironment. During the catalytic cycle, the substrate aspartate is recognized by residues including Glu177, Arg246, and Thr130 upon entering the active site (17, 19). Its α-amino group undergoes transamination with PLP, forming an external aldimine intermediate. In this process, electrons are transiently delocalized through a polarized network toward His260 and Arg387, enabling amino group transfer and cleavage of the covalent bond, ultimately generating α-ketoglutarate and glutamate. Conformational changes involving the gating helix (residues 168–176) and substrate recognition loops regulate substrate entry and product release. Dynamic adjustments in the volume and polarity of the active pocket ensure substrate specificity. GOT2 functions as a homodimer, with dimerization stabilized by interface residues such as Leu146, Phe322, and Arg387. These residues are critical for maintaining the structural integrity of the catalytic core and the proper opening of the substrate channel. Disruption of the dimer interface—such as by Leu146Pro or Phe322Ser mutations—leads to exposure of the active site, impaired PLP binding, and near-complete loss of catalytic activity, ultimately resulting in disturbances in energy and amino acid metabolism. These molecular mechanisms have been validated through X-ray crystallography and site-directed mutagenesis studies (17, 20).
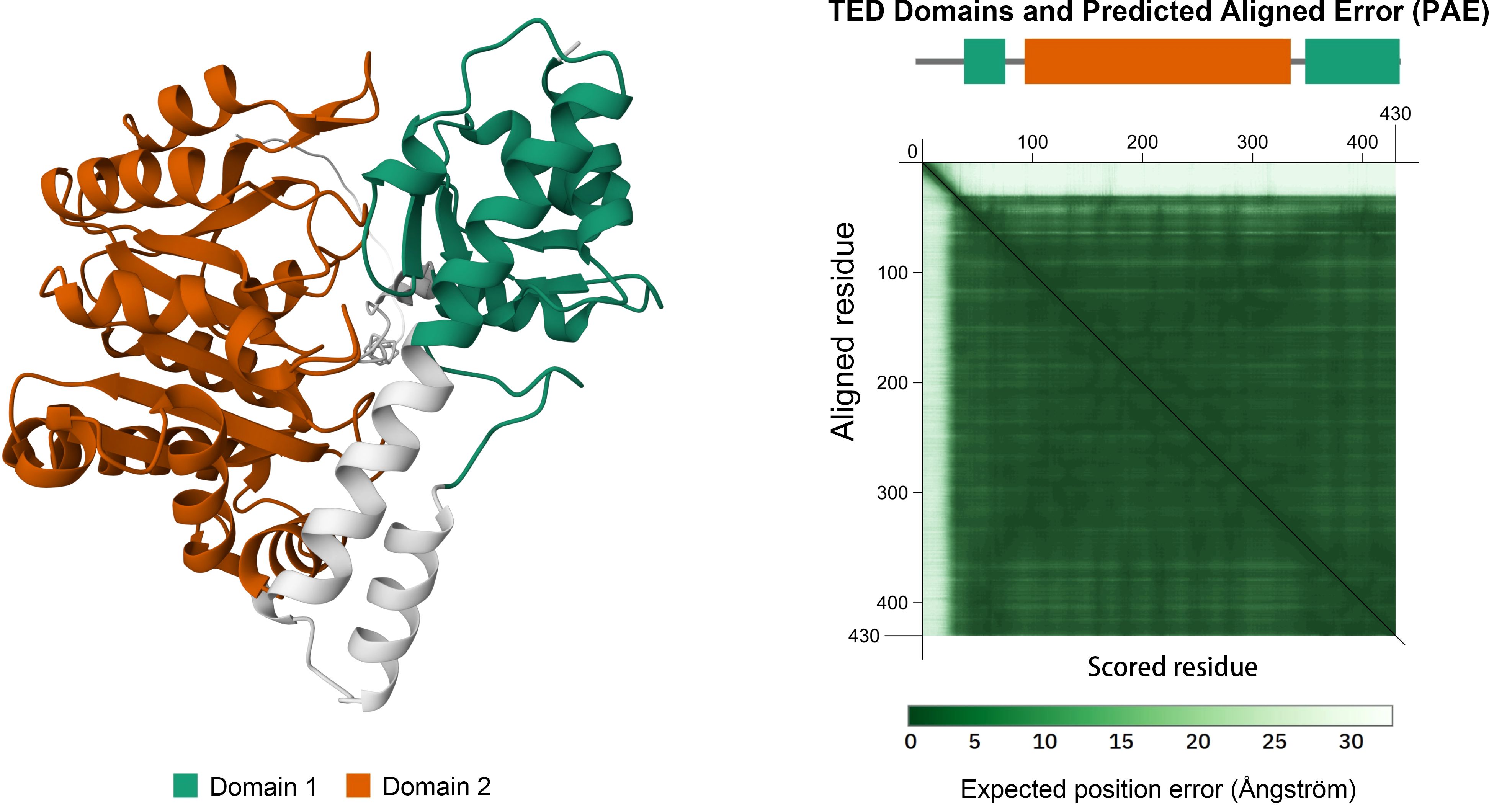
Figure 2. Domain architecture of the human GOT2 protein. The orange region (Hex: #BF5700) denotes the PLP-dependent aminotransferase domain responsible for its catalytic activity. Structure obtained from the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database (UniProt: P00505).
4 Canonical metabolic functions of GOT2
GOT2 is a key mitochondrial aminotransferase that links amino acid metabolism to central carbon flux and redox balance in both normal and malignant cells. By catalyzing the transamination of glutamate and oxaloacetate to produce aspartate and α-ketoglutarate, GOT2 ensures the availability of aspartate—essential for nucleotide biosynthesis and tumor cell proliferation—and supports the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle via α-ketoglutarate anaplerosis, thereby sustaining mitochondrial energy metabolism (21–26). As a key component of the malate–aspartate shuttle (MAS), GOT2 facilitates the transfer of reducing equivalents from cytosolic NADH into the mitochondrial matrix, maintaining the NAD+/NADH balance required for oxidative phosphorylation and redox homeostasis (12, 22, 27–29). Disruption of GOT2 or MAS results in redox imbalance and impaired metabolic flux, which may cause neurological deficits or constrain tumor growth due to aspartate depletion and elevated oxidative stress (18, 30, 31). Beyond cancer, GOT2 activity is also critical for cellular differentiation and viability in multiple normal tissues, underscoring its fundamental role in maintaining physiological homeostasis (32, 33).
5 Moonlighting functions of GOT2 in cancer
5.1 Fatty acid-binding and membrane-associated functions
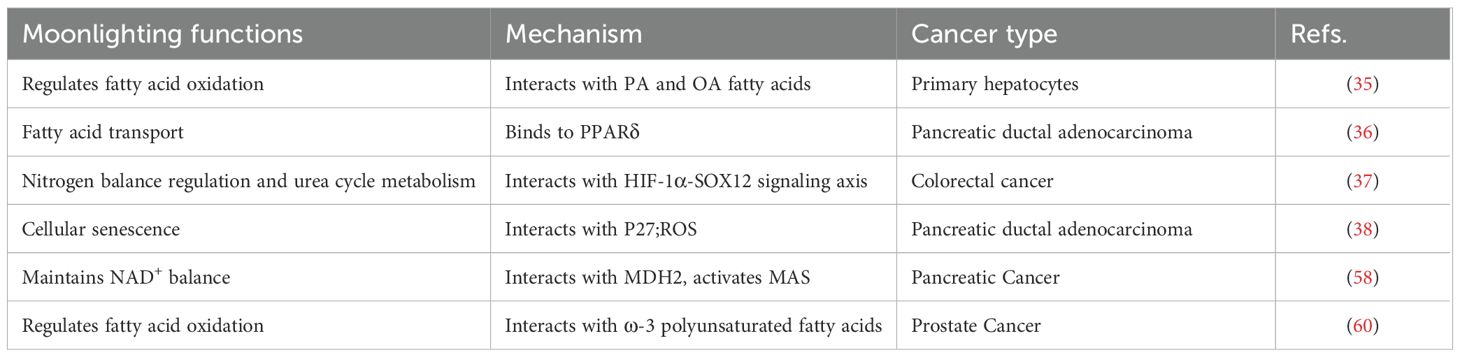
Besides its mitochondrial role, GOT2 has been identified as a plasma membrane-associated fatty acid-binding protein (FABPpm). Under conditions of cellular stress, organ injury, or lipid accumulation, GOT2/FABPpm regulates fatty acid oxidation and energy metabolism by mediating transmembrane transport of free fatty acids (34). While the role of GOT2 in fatty acid transport is well-established in normal tissues, its biological function in cancer has only recently been uncovered. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma models, Abrego et al. found that GOT2 predominantly localizes to the nucleus, enhancing the transport of fatty acids such as arachidonic acid, thereby facilitating their binding to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ (PPARδ) and significantly activating the PPARδ signaling pathway (35). These findings reveal a novel mechanism by which GOT2 drives tumor progression through regulating fatty acid oxidation and lipid signaling pathways, especially under conditions of stress or metabolic dysregulation (Table 2).
5.2 Nitrogen balance and metabolic reprogramming
As a key enzyme in the glutamine-aspartate shuttle, GOT2 participates in nitrogen balance regulation and urea cycle metabolism. By directing the transfer of aspartate into the urea cycle, GOT2 promotes excretion and recycling of excess intracellular nitrogen, maintaining nitrogen metabolic homeostasis. Studies have shown that in colorectal cancer (CRC), the HIF-1α–SOX12 signaling axis activates GOT2 expression, driving asparagine biosynthesis, thereby simultaneously regulating the urea cycle and amino acid synthesis pathways. Specific inhibition of this signaling axis significantly reduces asparagine levels, thereby suppressing tumor cell proliferation through metabolic reprogramming (36). In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), Li et al. further demonstrated that GOT2 knockdown reprograms glutamine metabolism by enhancing glutaminolysis, nucleotide biosynthesis, and glutathione production, maintaining redox balance and promoting tumor progression via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway (37). Notably, the molecular mechanisms by which cancer cells dynamically allocate aspartate flux between the urea cycle and nucleotide synthesis pathways through GOT2 remain to be systematically elucidated.
5.3 Cellular senescence and antioxidant homeostasis
GOT2 has a dual role in regulating cellular senescence. During glutamine catabolism, it promotes aspartate production, dynamically modulating glutamate and glutathione synthesis, thereby maintaining ROS homeostasis and preventing lipid peroxidation damage. Abnormal GOT2 expression significantly alters the cellular response to senescence signals, and the resulting disruption of redox homeostasis directly impacts tumor cell proliferation and survival. Yang et al. revealed that mitochondrial GOT2 participates in the regulation of cellular senescence in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by finely controlling ROS levels. Further studies indicated that GOT2 knockdown increases ROS levels in PDAC cells, triggering p27-mediated cellular senescence, a protective effect potentially closely related to chemotherapy resistance (38).
5.4 Other potentially associated metabolic pathways
As a mitochondrial transaminase with broad substrate specificity, GOT2 catalyzes the transamination of cysteine sulfinate to generate 3-sulfinylpyruvate, which can subsequently decompose into pyruvate and sulfur dioxide. This reaction potentially links GOT2 to the biosynthesis of taurine and suggests a role in maintaining cellular sulfur metabolic homeostasis (39, 40). Previous studies have shown that aberrant GOT2 expression—such as decreased tissue levels or elevated serum levels—is closely associated with dysregulation of the sulfur oxidation pathway in certain patients with myocardial injury or cardiovascular diseases. This may involve mitochondrial sulfur compound metabolism and lead to oxidative stress and cellular dysfunction (41). Although current research on GOT2-related sulfur metabolism has primarily focused on non-cancerous diseases, whether a similar mechanism operates in tumor cells to affect taurine synthesis or modulate sulfur oxidation remains to be determined. Given the potential roles of taurine and sulfur dioxide in regulating apoptosis, redox balance, and the immune microenvironment, investigating GOT2-mediated sulfur metabolism may offer new insights into cancer metabolic reprogramming.
6 GOT2 and the tumor microenvironment
6.1 Expression and function across multiple cell types
The multicellular expression pattern and functional heterogeneity of GOT2 within the tumor ecosystem have been progressively elucidated. GOT2 is not only highly expressed in cancer cells but is also broadly expressed in immune cells (such as T cells and macrophages) and stromal cells (such as fibroblasts and endothelial cells) within the tumor microenvironment. For instance, in a spontaneous pancreatic cancer transgenic model (KPC mice), quantitative immunohistochemical analyses revealed that although GOT2 protein expression is markedly downregulated in tumor epithelial cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) retain high levels of GOT2 expression, suggesting a compensatory role in stromal remodeling (12). Single-cell transcriptomic analysis further confirmed that GOT2 is widely expressed in non-malignant cells within the pancreatic tumor microenvironment, including macrophages, CD8+ T cells, and endothelial cells, with expression levels positively correlated with metabolic activity (42). Bioinformatic analyses also revealed broad GOT2 expression in immune and stromal compartments of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (43). Moreover, fourth-generation CAR-T cells engineered to stably overexpress GOT2 via lentiviral vectors demonstrated enhanced cytotoxicity against hepatocellular carcinoma cells in both in vitro and in vivo models (44).
6.2 Metabolic competition and immune microenvironment modulation
By catalyzing glutamine metabolism to produce aspartate and its derivatives, GOT2 not only maintains intracellular nitrogen metabolism and TCA cycle function but also supplies key metabolic substrates for immune cells. Aspartate is essential not only for pyrimidine and nucleotide biosynthesis but also plays an irreplaceable role in the activation, proliferation, and effector function of CD8+ T cells. Studies have shown that activated T cells are highly dependent on aspartate; insufficient aspartate availability leads to mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction, suppression of mTOR signaling, and reduced expression of cytotoxic molecules such as granzyme B (GZMB) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ), ultimately impairing T cell cytotoxicity (45). Tumor cells often upregulate GOT2 and associated metabolic pathways to enhance aspartate synthesis and uptake, thereby establishing metabolic competition with immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. Given the nutrient-restricted nature of the tumor microenvironment, preferential aspartate acquisition by tumor cells exacerbates its scarcity, severely limiting the metabolic adaptability and functional status of CD8+ T cells. This compromises their antitumor activity and facilitates immune evasion (46). Therefore, GOT2 not only participates in cancer cell metabolic reprogramming but also plays a pivotal role in shaping an immunosuppressive microenvironment.
6.3 Metabolic coupling with cancer-associated fibroblasts
CAFs support GOT2-mediated metabolic reactions by secreting nutrient substrates such as glutamine, thereby facilitating the production of energy and biosynthetic intermediates in tumor cells. In turn, aspartate or α-KG generated by tumor cell metabolism can regulate CAF metabolism, for example, by enhancing their lactate production capacity, establishing a bidirectional metabolic coupling. This cooperative interaction significantly enhances tumor cell proliferation and invasiveness (35, 47). A study by Kerk et al. further revealed this microenvironment-dependent metabolic complementation. In PDAC, while GOT2 knockdown significantly suppresses tumor cell proliferation in vitro, it does not impair tumor growth in xenograft or orthotopic mouse models. Mechanistically, CAFs—an essential component of the PDAC microenvironment—secrete redox-active pyruvate that provides alternative metabolic support to GOT2-deficient cells. When cultured in CAF-conditioned medium (CM), the proliferation of GOT2-deficient cells is partially restored. However, when pyruvate uptake is blocked or its conversion to lactate is inhibited, neither CAF CM nor exogenous pyruvate can rescue the proliferative capacity of GOT2-deficient cells (12). These findings underscore a functionally complementary metabolic interaction between tumor cells and CAFs, in which GOT2 serves as a critical mediator linking cancer and stromal metabolism.
6.4 Vesicle-mediated long-range effects and metastasis
In addition to interacting with neighboring cells in the local microenvironment through metabolic and signaling pathways, tumor cells can also engage in long-range communication via extracellular vesicles, particularly exosomes (48). Exosomes not only carry bioactive molecules such as miRNAs, proteins, and lipids, but may also encapsulate metabolic enzymes like GOT2 and their associated metabolites for delivery to adjacent or distant recipient cells. Through this mechanism, GOT2 may contribute to the formation of the pre-metastatic niche. For example, GOT2 transferred via exosomes to distant tissues may modulate the intracellular balance of glutamate and aspartate through its transamination activity, thereby influencing glutamine utilization, supporting aspartate biosynthesis, and promoting metabolic reprogramming to enhance the adaptability of recipient cells to new microenvironments. In metastatic lesions, this vesicle-mediated metabolic support mechanism facilitates cancer cell proliferation and survival, enhancing their competitive advantage and accelerating colonization and malignant progression at distant sites (49). Moreover, GOT2-associated metabolites may further modulate immune cell function and stromal remodeling within metastatic sites, contributing to the optimization of the metastatic microenvironment. Collectively, GOT2 not only maintains metabolic homeostasis within primary tumors but also functions as both a bridge and an amplifier of long-range metabolic regulation through exosome-mediated intercellular communication during metastasis.
7 Multi-level regulation of GOT2 in cancer
7.1 Transcriptional regulation
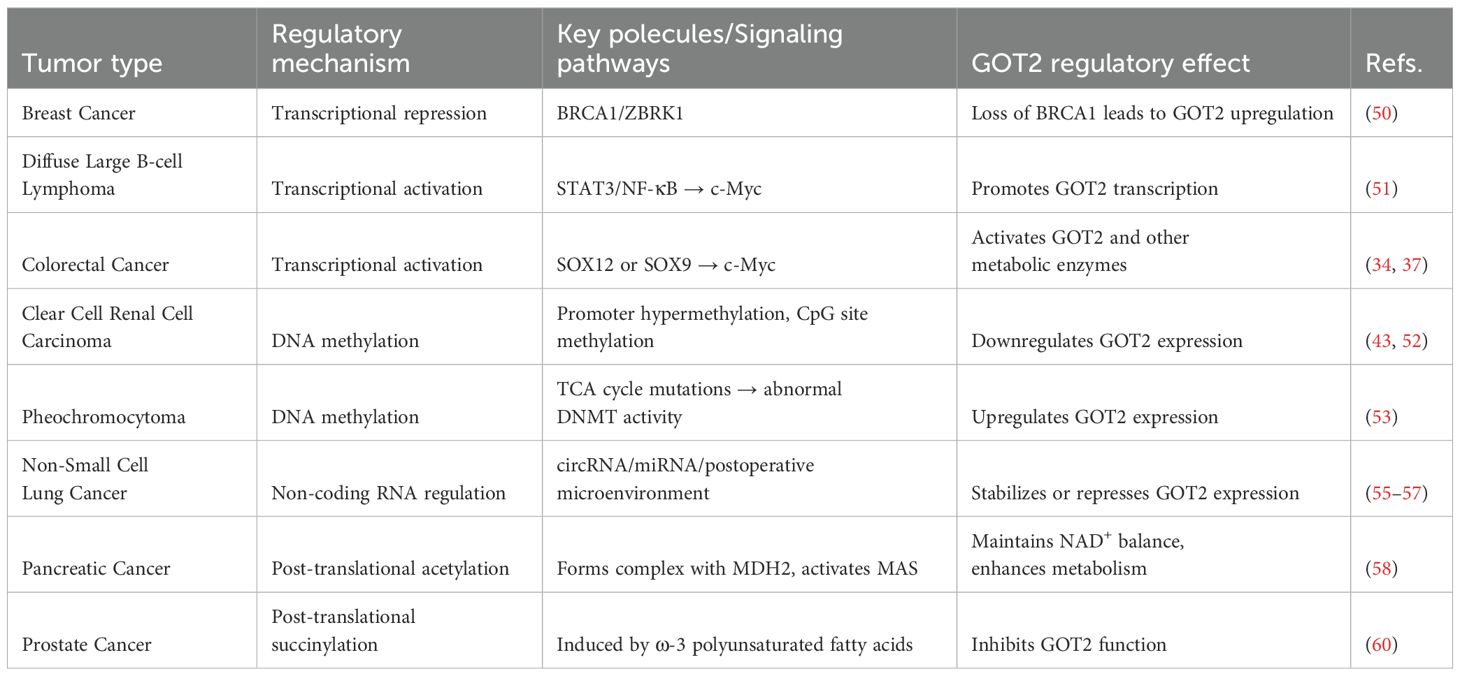
Various transcription factors dynamically regulate GOT2 transcription by binding to its promoter or enhancer regions. In breast cancer, the BRCA1/ZBRK1 complex represses GOT2 promoter activity, suggesting that BRCA1 loss-of-function may upregulate GOT2 by removing this repression (50). Notably, in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, inflammation-related signaling pathways (e.g., STAT3 and NF-κB) indirectly enhance GOT2 transcription by upregulating c-Myc, thus meeting the high metabolic demands of tumor cells (51). Further studies revealed that SOX12 forms a metabolic regulatory network in CRC by activating glutaminase (GLS), GOT2, and asparagine synthetase (ASNS). Downregulation of GLS, GOT2, and ASNS effectively blocks SOX12-mediated CRC cell proliferation and metastasis, while ectopic expression of these enzymes reverses the inhibitory effects of SOX12 knockdown on tumor progression (36). Additionally, Stegen et al. identified a novel mechanism by which SOX9 regulates glutamine metabolism through c-MYC, simultaneously increasing expression levels of GLUD1, GLS1, and GOT2 (33).
7.2 DNA methylation regulation
GOT2 expression is dynamically regulated by epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation, but this regulation shows significant disease- and environment-dependent variability. In clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), reduced GOT2 expression is directly associated with abnormally high methylation of its promoter region (43). Another study indicated that GOT2 expression in ccRCC patients is significantly correlated with methylation levels at multiple CpG sites, suggesting that epigenetic silencing of GOT2 may be a critical factor driving tumorigenesis (52). Notably, DNA methylation exerts opposite effects on GOT2 expression in different tumors. In pheochromocytoma, Remacha et al. found that high GOT2 expression correlates with abnormal accumulation of TCA cycle metabolites. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that mutations in TCA cycle-related genes in this tumor might alter DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) activity, inducing hypermethylation of promoter regions of multiple metabolic enzyme genes, including GOT2 (53).
7.3 Non-coding RNAs and post-transcriptional regulation
GOT2 mRNA levels are precisely regulated by a multi-layered network of non-coding RNAs. At the direct interaction level, Runtsch et al. found that ACOD1 lncRNA enhances GOT2 enzymatic activity by directly binding to the GOT2 protein, thereby driving tumor metabolic reprogramming (54). At the competitive regulation level, circRNAs function through a “molecular sponge” mechanism: Tang et al. demonstrated that Circ_0006220 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) stabilizes GOT2 mRNA and enhances its translation by sequestering miR-342-3p, thus promoting tumor angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis (55). Jin’s study showed that silencing circSEC31A releases miR-520a-5p, targeting and inhibiting GOT2, significantly reducing MAS function in NSCLC cells (56). Notably, clinical research has indicated the reversibility of this regulation—Prystupa et al. observed a dramatic decrease in GOT2 mRNA levels in peripheral blood leukocytes of NSCLC patients after radical surgery, highlighting the critical role of the tumor microenvironment in post-transcriptional regulation (57).
7.4 Post-translational modifications
GOT2 functions are dynamically regulated by post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylation, and succinylation, with modification patterns showing significant tumor type specificity. Among metabolism-enhancing modifications, acetylation has been identified as a critical regulatory mechanism. In pancreatic cancer, GOT2 acetylation promotes its interaction with malate dehydrogenase 2, forming a functional complex that activates MAS to maintain NADH/NAD+ homeostasis, thus driving tumor proliferation (58). In an inflammatory liver microenvironment, inflammation-induced GOT2 acetylation enhances its catalytic activity, promoting adaptive metabolic remodeling (59). Conversely, ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid-induced succinylation inhibits GOT2-mediated aspartate synthesis, disrupting essential metabolic pathways in prostate cancer cells and ultimately suppressing their proliferation (60). Notably, phosphorylation also participates in this regulatory network: activation-induced phosphorylation of GOT2 by protein kinase C epsilon significantly enhances its enzymatic activity, suggesting this modification acts as a key molecular switch regulating MAS functions (61). Although these findings underscore the importance of post-translational modifications in tumor metabolic reprogramming, the specificity and biological effects of these modification patterns across different tumor types still require systematic elucidation.
8 Potential and challenges of GOT2 as a theranostic target
By simultaneously regulating tumor metabolic reprogramming (maintaining aspartate supply) and redox homeostasis (regulating NAD+ regeneration), GOT2 has emerged as a promising anticancer target. However, clinical translation faces two major challenges (1): Target specificity—current inhibitors (e.g., amino acid analogs) struggle to distinguish between GOT1 and GOT2 isoenzymes; (2) Metabolic compensation risk—tumor cells may activate alternative pathways, such as pyruvate carboxylase, to compensate for GOT2 inhibition, leading to failure of single-target therapies (12, 62). Nevertheless, studies have proposed targeted interventions, including downregulating GOT2 via MYC/HIF-1α inhibition, developing allosteric inhibitors targeting the acetylation site K159 to induce tumor oxidative stress, and combining GOT2 inhibitor AOA with anti-GPC3 CAR-T therapy (such as BOXR1030) to enhance T-cell activity by depleting aspartate in the tumor microenvironment (36, 44, 58). Notably, the theranostic potential of GOT2 has expanded into dynamic monitoring. Combining plasma α-KG/aspartate ratio with ¹8F-FDG PET/CT imaging can establish a dynamic “metabolic biomarker-molecular imaging” system. This approach enables real-time monitoring of tumor metabolic activity (e.g., correlations between decreased glucose uptake and restored aspartate levels), achieving an integrated diagnostic-therapeutic loop. This development marks GOT2’s progression from basic research toward a unified “detection-intervention-monitoring” platform (37).
9 Conclusion and perspectives
As a recently identified “moonlighting enzyme,” GOT2 not only regulates classical metabolic pathways (e.g., the MAS-TCA cycle) but also profoundly influences the tumor metabolic-immune microenvironment through changes in subcellular localization and remodeling of protein interaction networks, exhibiting remarkable functional diversity and tumor-type specificity. Future studies should focus on developing precise GOT2-targeted drugs and combined metabolic-immunotherapy strategies, constructing multimodal platforms for dynamic diagnosis and treatment monitoring, and utilizing systems biology approaches to comprehensively understand the dynamic roles of GOT2 in the tumor microenvironment. These efforts will drive the transformation of cancer treatment from single-target interventions towards a novel therapeutic paradigm involving coordinated metabolic-immune network modulation.
Author contributions
JXH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. QR: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WH: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JQH: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. YS: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Yangzhou Social Development and Clinical Frontier Technology Project (Grant No. YZ2023084). Yusheng Shu served as the principal investigator, and Xiaolin Wang was the project administrator.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the use of the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database (entry: P00505) for data and visualization resources in Figures 2.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lin C, Yu M, Wu X, Wang H, Wei M, and Zhang L. Targeting moonlighting enzymes in cancer. Molecules. (2024) 29:1573. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071573
2. Jeffery CJ. An introduction to protein moonlighting. Biochem Soc Trans. (2014) 42:1679–83. doi: 10.1042/BST20140226
3. Huang CK, Sun Y, Lv L, and Ping Y. ENO1 and cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2022) 24:288–98. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.12.026
4. Krieg S, Fernandes SI, Kolliopoulos C, Liu M, and Fendt SM. Metabolic signaling in cancer metastasis. Cancer Discov. (2024) 14:934–52. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0174
5. Rahaman H, Herojit K, Singh LR, Haobam R, and Fisher AB. Structural and functional diversity of the peroxiredoxin 6 enzyme family. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2024) 40:759–75. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0287
6. Coffey NJ and Simon MC. Metabolic alterations in hereditary and sporadic renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2024) 20:233–50. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00800-2
7. Yang R, Cheng S, Xiao J, Pei Y, Zhu Z, Zhang J, et al. GLS and GOT2 as prognostic biomarkers associated with dendritic cell and immunotherapy response in breast cancer. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e24163. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24163
8. Zhang JN, Zhang Z, Huang ZL, Guo Q, Wu ZQ, Ke C, et al. Isotoosendanin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by reducing mitochondrial fission and lamellipodia formation regulated by the Smad2/3-GOT2-MYH9 signaling axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2024) 45:2672–83. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01335-3
9. Soon JW, Manca MA, Laskowska A, Starkova J, Rohlenova K, and Rohlena J. Aspartate in tumor microenvironment and beyond: metabolic interactions and therapeutic perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167451. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167451
10. Yao Q, Wang C, Wang Y, Xiang W, Chen Y, Zhou Q, et al. STXBP3 and GOT2 predict immunological activity in acute allograft rejection. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1025681. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1025681
11. Newsom OJ and Sullivan LB. Targeting PDAC metabolism: environment determines what has GOT2 give. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:1617–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.027
12. Kerk SA, Lin L, Myers AL, Sutton DJ, Andren A, Sajjakulnukit P, et al. Metabolic requirement for GOT2 in pancreatic cancer depends on environmental context. Elife. (2022) 11:e73245. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73245
13. Song L, Wei X, Zhang X, and Lu Y. Combining single-cell and transcriptomic analysis revealed the immunomodulatory effect of GOT2 on a glutamine-dependent manner in cutaneous melanoma. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1241454. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1241454
14. Bradbury MW and Berk PD. Mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase: direction of a single protein with two distinct functions to two subcellular sites does not require alternative splicing of the mRNA. Biochem J. (2000) 345:423–7. doi: 10.1042/bj3450423
15. Çapan ÖY, Türkdoğan D, Atalay S, and Çağlayan HS. Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 82 (DEE82) with novel compound heterozygous mutations of GOT2 gene. Seizure. (2024) 116:126–32. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2023.11.003
16. Vagaggini C, D’Ursi P, Poggialini F, Fossa P, Francesconi V, Trombetti G, et al. Deciphering the landscape of allosteric glutaminase 1 inhibitors as anticancer agents. Bioorg Chem. (2025) 161:108523. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108523
17. Kirsch JF, Eichele G, Ford GC, Vincent MG, Jansonius JN, Gehring H, et al. Mechanism of action of aspartate aminotransferase proposed on the basis of its spatial structure. J Mol Biol. (1984) 174:497–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90333-4
18. van Karnebeek CDM, Ramos RJ, Wen XY, Tarailo-Graovac M, Gleeson JG, Skrypnyk C, et al. Bi-allelic GOT2 mutations cause a treatable malate-aspartate shuttle-related encephalopathy. Am J Hum Genet. (2019) 105:534–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.07.015
19. Liu Z, Xiang P, Zeng S, Weng P, Wen Y, Zhang W, et al. N-acetylneuraminic acid triggers endothelial pyroptosis and promotes atherosclerosis progression via GLS2-mediated glutaminolysis pathway. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:467. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02233-7
20. Jiang X, Wang J, Chang H, and Zhou Y. Recombinant expression, purification and crystallographic studies of the mature form of human mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase. Biosci Trends. (2016) 10:79–84. doi: 10.5582/bst.2015.01150
21. Altea-Manzano P, Vandekeere A, Edwards-Hicks J, Roldan M, Abraham E, Lleshi X, et al. Reversal of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase 2 enables anaplerosis via redox rescue in respiration-deficient cells. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:4537–47. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.10.008
22. Wang Y, Stancliffe E, Fowle-Grider R, Wang R, Wang C, Schwaiger-Haber M, et al. Saturation of the mitochondrial NADH shuttles drives aerobic glycolysis in proliferating cells. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:3270–83. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.07.007
23. Birsoy K, Wang T, Chen WW, Freinkman E, Abu-Remaileh M, and Sabatini DM. An essential role of the mitochondrial electron transport chain in cell proliferation is to enable aspartate synthesis. Cell. (2015) 162:540–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.016
24. Garcia-Bermudez J, Baudrier L, La K, Zhu XG, Fidelin J, Sviderskiy VO, et al. Aspartate is a limiting metabolite for cancer cell proliferation under hypoxia and in tumours. Nat Cell Biol. (2018) 20:775–81. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0118-z
25. Sullivan LB, Gui DY, Hosios AM, Bush LN, Freinkman E, and Vander Heiden MG. Supporting aspartate biosynthesis is an essential function of respiration in proliferating cells. Cell. (2015) 162:552–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.017
26. Sullivan LB, Luengo A, Danai LV, Bush LN, Diehl FF, Hosios AM, et al. Aspartate is an endogenous metabolic limitation for tumour growth. Nat Cell Biol. (2018) 20:782–8. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0125-0
27. Altman BJ, Stine ZE, and Dang CV. From Krebs to clinic: glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2016) 16:619–34. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.71
28. Broeks MH, van Karnebeek CDM, Wanders RJA, Jans JJM, and Verhoeven-Duif NM. Inborn disorders of the malate aspartate shuttle. J Inherit Metab Dis. (2021) 44:792–808. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12402
29. Borst P. The malate-aspartate shuttle (Borst cycle): how it started and developed into a major metabolic pathway. IUBMB Life. (2020) 72:2241–59. doi: 10.1002/iub.2367
30. Chakrabarti G, Moore ZR, Luo X, Ilcheva M, Ali A, Padanad M, et al. Targeting glutamine metabolism sensitizes pancreatic cancer to PARP-driven metabolic catastrophe induced by ß-lapachone. Cancer Metab. (2015) 3:12. doi: 10.1186/s40170-015-0137-1
31. Garcia-Bermudez J, Badgley MA, Prasad S, Baudrier L, Liu Y, La K, et al. Adaptive stimulation of macropinocytosis overcomes aspartate limitation in cancer cells under hypoxia. Nat Metab. (2022) 4:724–38. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00583-z
32. Qi L, Martin-Sandoval MS, Merchant S, Gu W, Eckhardt M, Mathews TP, et al. Aspartate availability limits hematopoietic stem cell function during hematopoietic regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. (2021) 28:1982–99. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.07.011
33. Stegen S, Rinaldi G, Loopmans S, Stockmans I, Moermans K, Thienpont B, et al. Glutamine metabolism controls chondrocyte identity and function. Dev Cell. (2020) 53:530–44. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.05.001
34. Chabowski A, Żendzian-Piotrowska M, Konstantynowicz K, Pankiewicz W, Mikłosz A, Łukaszuk B, et al. Fatty acid transporters involved in the palmitate and oleate induced insulin resistance in primary rat hepatocytes. Acta Physiol (Oxf). (2013) 207:346–57. doi: 10.1111/apha.12022
35. Abrego J, Sanford-Crane H, Oon C, Xiao X, Betts CB, Sun D, et al. A cancer cell-intrinsic GOT2-PPARδ axis suppresses antitumor immunity. Cancer Discov. (2022) 12:2414–33. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0661
36. Du F, Chen J, Liu H, Cai Y, Cao T, Han W, et al. SOX12 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating asparagine synthesis. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:239. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1481-9
37. Li Y, Li B, Xu Y, Qian L, Xu T, Meng G, et al. GOT2 silencing promotes reprogramming of glutamine metabolism and sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to glutaminase inhibitors. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:3223–35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0042
38. Yang S, Hwang S, Kim M, Seo SB, Lee JH, and Jeong SM. Mitochondrial glutamine metabolism via GOT2 supports pancreatic cancer growth through senescence inhibition. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:55. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0089-1
39. Jiang H, Stabler SP, Allen RH, Abman SH, and Maclean KN. Altered hepatic sulfur metabolism in cystathionine β-synthase-deficient homocystinuria: regulatory role of taurine on competing cysteine oxidation pathways. FASEB J. (2014) 28:4044–54. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-253633
40. Sies H, Mailloux RJ, and Jakob U. Fundamentals of redox regulation in biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2024) 25:701–19. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00730-2
41. Sookoian S, Castaño GO, Scian R, Fernández Gianotti T, Dopazo H, Rohr C, et al. Serum aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are a signature of liver metabolic perturbations at the amino acid and Krebs cycle level. Am J Clin Nutr. (2016) 103:422–34. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.118695
42. Steele NG, Carpenter ES, Kemp SB, Sirihorachai VR, The S, Delrosario L, et al. Multimodal mapping of the tumor and peripheral blood immune landscape in human pancreatic cancer. Nat Cancer. (2020) 1:1097–112. doi: 10.1038/s43018-020-00121-4
43. Ferreira WAS and de Oliveira EHC. Expression of GOT2 is epigenetically regulated by DNA methylation and correlates with immune infiltrates in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Curr Issues Mol Biol. (2022) 44:2472–89. doi: 10.3390/cimb44060169
44. Hickman TL, Choi E, Whiteman KR, Muralidharan S, Pai T, Johnson T, et al. BOXR1030, an anti-GPC3 CAR with exogenous GOT2 expression, shows enhanced T cell metabolism and improved anti-cell line derived tumor xenograft activity. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0266980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266980
45. Chang HC, Tsai CY, Hsu CL, Tai TS, Cheng ML, Chuang YM, et al. Asparagine deprivation enhances T cell antitumour response in patients via ROS-mediated metabolic and signal adaptations. Nat Metab. (2025) 7:918–27. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01245-6
46. Wang B, Pei J, Xu S, Liu J, and Yu J. System analysis based on glutamine catabolic-related enzymes identifies GPT2 as a novel immunotherapy target for lung adenocarcinoma. Comput Biol Med. (2023) 165:107415. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107415
47. Zhang H, Li S, Wang D, Liu S, Xiao T, Gu W, et al. Metabolic reprogramming and immune evasion: the interplay in the tumor microenvironment. biomark Res. (2024) 12:96. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00646-1
48. Han QF, Li WJ, Hu KS, Gao J, Zhai WL, Yang JH, et al. Exosome biogenesis: machinery, regulation, and therapeutic implications in cancer. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:207. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01671-0
49. Rai A, Fang H, Claridge B, Simpson RJ, and Greening DW. Proteomic dissection of large extracellular vesicle surfaceome unravels interactive surface platform. J Extracell Vesicles. (2021) 10:e12164. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12164
50. Hong R, Zhang W, Xia X, Zhang K, Wang Y, Wu M, et al. Preventing BRCA1/ZBRK1 repressor complex binding to the GOT2 promoter results in accelerated aspartate biosynthesis and promotion of cell proliferation. Mol Oncol. (2019) 13:959–77. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12466
51. Feist M, Schwarzfischer P, Heinrich P, Sun X, Kemper J, von Bonin F, et al. Cooperative STAT/NF-κB signaling regulates lymphoma metabolic reprogramming and aberrant GOT2 expression. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:1514. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03803-x
52. Ahmmed R, Hossen MB, Ajadee A, Mahmud S, Ali MA, Mollah MMH, et al. Bioinformatics analysis to disclose shared molecular mechanisms between type-2 diabetes and clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma, and therapeutic indications. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:19133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69302-w
53. Remacha L, Comino-Méndez I, Richter S, Contreras L, Currás-Freixes M, Pita G, et al. Targeted exome sequencing of Krebs cycle genes reveals candidate cancer-predisposing mutations in pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:6315–24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2250
54. Runtsch MC and O’Neill LA. GOTcha: lncRNA-ACOD1 targets metabolism during viral infection. Cell Res. (2018) 28:137–8. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.153
55. Tang J, Li X, Zhao L, Hui J, and Ding N. Circ_0006220 contributes to NSCLC progression through miR-342-3p/GOT2 axis. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2023) 29:11–22. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.22-00090
56. Jin M, Shi C, Hua Q, Li T, Yang C, Wu Y, et al. High circ-SEC31A expression predicts unfavorable prognoses in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the miR-520a-5p/GOT-2 axis. Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12:10381–97. doi: 10.18632/aging.103264
57. Prystupa TK, Sagan D, Kocki J, Kocki T, Szymanowski R, and Bogucki J. Surgical resection of lung cancer inhibits mRNA expression of GOT2 gene encoding kynurenine aminotransferase in leukocytes. Ann Agric Environ Med. (2023) 30:755–62. doi: 10.26444/aaem/176813
58. Yang H, Zhou L, Shi Q, Zhao Y, Lin H, Zhang M, et al. SIRT3-dependent GOT2 acetylation status affects the malate-aspartate NADH shuttle activity and pancreatic tumor growth. EMBO J. (2015) 34:1110–25. doi: 10.15252/embj.201591041
59. Wang T, Yao W, Li J, He Q, Shao Y, and Huang F. Acetyl-CoA from inflammation-induced fatty acids oxidation promotes hepatic malate-aspartate shuttle activity and glycolysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 315:E496–510. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00061.2018
60. Jiang Y, He C, Ye H, Xu Q, Chen X, Chen Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the lysine succinylome in fish oil-treated prostate cancer cells. Life Sci Alliance. (2023) 6:e202302131. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302131
61. Xu J, Khoury N, Jackson CW, Escobar I, Stegelmann SD, Dave KR, et al. Ischemic neuroprotectant PKCϵ restores mitochondrial glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase in the neuronal NADH shuttle after ischemic injury. Transl Stroke Res. (2020) 11:418–32. doi: 10.1007/s12975-019-00729-4
Keywords: moonlighting enzymes, GOT2, cancer metabolism, tumor microenvironment, immunotherapy
Citation: Hu J, Liu Q, Ren Q, He W, Hou J, Wang X and Shu Y (2025) GOT2: a moonlighting enzyme at the crossroads of cancer metabolism and theranostics. Front. Immunol. 16:1626914. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1626914
Received: 12 May 2025; Accepted: 19 July 2025;
Published: 06 August 2025.
Edited by:
Rongzhang Dou, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, United StatesReviewed by:
William Sivitz, The University of Iowa, United StatesDecai Yu, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China
Yunzheng Li, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Liu, Ren, He, Hou, Wang and Shu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaolin Wang, MTgwNTEwNjM5MDlAeXp1LmVkdS5jbg==; Yusheng Shu, c2h1eXVzaGVuZzM0QDE2My5jb20=
 Junxi Hu
Junxi Hu Qingwen Liu2
Qingwen Liu2