- 1Department of Pediatric Cardiology, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Pediatrics, The Affiliated Taian City Central Hospital of Qingdao University, Tai’an, Shandong, China
- 3School of Medicine, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 4Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan, Shandong, China
Introduction: Myocarditis is an inflammatory injury to the myocardium characterized by disrupted intercellular communication, involving macrophages and cardiomyocytes as key players. However, the interactions between macrophages and cardiomyocytes during myocarditis remain inadequately explored. Emerging evidence indicated that extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a crucial role in intercellular communication.
Methods: In our study, LPS- or PBS-preconditioned cardiomyocytes derived large EVs (C-lEVLPS/C-lEVPBS) were isolated. qPCR, ROS and flow cytometry assays were employed to evaluate their impact on macrophages and in the in vivo experiments, C-lEVLPS was administered to mice with viral myocarditis. Cardiac function was assessed through echocardiography and cTnT levels, while inflammatory responses were analyzed via histopathological examination and cytokine profiling. Then mechanistic investigations were performed using integrated transcriptomic and proteomic profiling to characterize EV-mediated regulatory networks. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-test or ANOVA, with significance set at p < 0.05.
Results: We demonstrated C-lEVLPS exhibited anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages and alleviated cardiac inflammation and dysfunction in a mouse model of CVB3-induced myocarditis. Additionally, C-lEVLPS facilitated macrophage polarization toward the M2-like phenotype and inhibits M1 polarization, both in vitro and in vivo. Notably, compared to C-lEVPBS, C-lEVLPS was enriched in the phosphatase 2 scaffold subunit alpha protein (PP2AA), which can recruit other subunits to form the PP2A complex, ultimately leading to the dephosphorylates of p38.
Discussion: This study highlights the effect of C-lEVLPS in myocarditis and uncovers the potential mechanism that modulates macrophage polarization by delivering PP2AA from cardiomyocytes to macrophages and regulating the p38 MAPK pathway. These findings provide a promising therapeutic strategy for myocarditis.
1 Introduction
Myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle, presents a range of symptoms from mild fatigue and chest discomfort to severe complications such as arrhythmias, heart failure, cardiogenic shock, and sudden death (1, 2). The etiology of myocarditis is multifactorial, with common infectious agents including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. In developed countries, viral infections (such as Coxsackie virus B3 and adenovirus) are the most prevalent causes (1); whereas in tropical and subtropical regions, parasitic infections such as Chagas disease, toxoplasmosis, and schistosomiasis contribute significantly to the incidence of myocarditis (3). These pathogens can induce myocardial inflammation through direct invasion or immune-mediated mechanisms. Due to the incomplete understanding of myocarditis pathogenesis, specific treatment strategies are currently unavailable (1, 2).
Cardiomyocytes, the primary cellular components of the heart, are targeted during myocarditis by pathogens like viruses, leading to their replication within the host cells (1, 2, 4, 5). This results in direct damage characterized by swelling, apoptosis, and necrosis (4). Additionally, macrophages—the main immune cells in the heart (1, 5, 6)—accumulate at injury sites during myocarditis and exhibit significant phenotypic plasticity (6, 7). They are generally classified into M1 and M2 macrophages, where M1 macrophages enter injury sites and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines that block tissue repair, while M2 macrophages aid in later healing stages by eliminating pathogens and encouraging the repair of inflammatory sites (8–10). Given the dynamic and heterogeneous nature of macrophages, targeting macrophage heterogeneity may offer new therapeutic avenues for myocarditis.
Communication between macrophages and cardiomyocytes usually occurs via direct contact, paracrine factors, or extracellular vesicles (EVs) (11). EVs are now recognized as critical modulators in both physiological and pathological processes, especially in contexts such as cardiovascular diseases (12–17). Notably, EVs serve as key mediators by transferring cellular substances like miRNA and proteins (18, 19). For instance, hypoxic cardiomyocytes release small EVs rich in TNF-α (20), while exosomes originating from M2 macrophages containing miRNA-148a and miRNA-378a-3p mitigate cardiomyocyte apoptosis and pyroptosis following cardiac injury (19, 21). In the context of heart failure and myocardial infarction, EVs play crucial roles in cardiac repair, especially when triggered by cell therapy (22–24).
According to the MISEV 2023 recommendations, EVs are classified into small EVs (sEVs) and large EVs (lEVs, also referred to as microvesicles) based on size (25). Although sEVs might generally refer to EVs <200 nm in diameter and lEVs typically ranging from 150 nm to over 1,000 nm, there is no strict consensus on upper and lower size cut-offs (25, 26). And it has become clear that many separation methods, such as dUC, yield EV subpopulations with overlapping size distributions (25). Critically, compared with sEVs, lEVs carry unique bioactive molecules, such as specific protein signatures (27–29) and potentially distinct sets of miRNAs (30). These cargo molecules often fulfilling roles that differ from those attributed to sEVs (29), contributing significantly to processes like immunomodulation (31, 32) and tissue repair (9), Meanwhile, their larger size confers greater cargo capacity, enabling them to transport complex molecular or larger volumes of bioactive cargo for enhanced functional effects upon fusion with recipient cells (33) and larger membrane area enhancing their fusion ability with recipient cells (34). However, in myocarditis—an immune-mediated myocardial injury—the signaling functions and pathological regulatory mechanisms of EVs, particularly cardiomyocyte-derived lEVs (C-lEVs) with unique large cargo transport capacity, remain significantly understudied. Urgent multi-dimensional investigations are needed to uncover their potential value, thus offering new opportunities for the accurate diagnosis and targeted therapy of myocarditis.
This research investigated the impact of C-lEVs on myocarditis, focusing on the interaction between cardiomyocytes and macrophages. In our study, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used solely as an in vitro tool to simulate the inflammatory environment experienced by cardiomyocytes during infection or injury. The purpose was to dissect the molecular composition and function of C-lEVs secreted under defined stress conditions. Our findings revealed that lEVs derived from LPS-preconditioned cardiomyocytes (C-lEVLPS) regulated macrophage polarization by altering M1/M2 macrophage marker expression and suppressing inflammatory cytokine production. Further investigation demonstrated that C-lEVLPS influenced macrophage polarization by interacting with the p38 MAPK pathway. Proteomic analysis showed that C-lEVLPS delivers PP2AA to macrophages, thereby modulating the p38 MAPK pathway. Essentially, this research specifically looks into the involvement of C-lEVs in myocarditis, providing new insights into its pathogenesis and potential therapeutic approaches.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Cell culture
The cardiomyocyte cell line H9C2, murine macrophage cell line RAW264.7, and human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma Hep2 cells were purchased from Yanyi Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shandong, China). Cells were maintained in high-glucose DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Solarbio, Shanghai, China) under conditions of 37 °C and 5% CO2. H9C2 cells were starved for 12 hours and then exposed to 1.5 μg/mL LPS for 24 hours, while RAW264.7 cells received a 12-hour treatment with 1 μg/mL LPS to stimulate polarization. Following this, the therapeutic impact of C-lEVs was examined by introducing 1 × 107 C-lEVs particles to the culture medium. 100 nM Anisomycin(AM, MCE, #22862-76-6) was introduced into the culture medium to stimulate the MAPK signaling pathway.
2.2 Isolation and characterization of C-lEVs
The culture medium of H9C2 cardiomyocytes treated with PBS or LPS was collected, and the C-lEVs were obtained by differential centrifugation as previous described (9). Briefly, the cell culture medium was collected and centrifuged at 300× g at 4 °C for 10 minutes, followed by additional centrifugation steps at 2,000× g and 10,000× g at 4 °C for 20 and 30 minutes, respectively. Following resuspension with PBS, the pelleted C-lEVs were washed by recentrifugation at 10,000× g for 30 minutes at 4 °C.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses were performed by the 120 kV transmission electron microscope (Hitachi HT-7800, Tokyo, Japan). In brief, 10 μL C-lEVs were loaded on a copper grid placed on ice for 1 minute. 10 μL of phosphotungstic acid was applied to the copper grid for 1 minute for negative staining. The grid was air-dried for several minutes before TEM imaging at 120 kV.
The size and concentration of C-lEVs were analyzed using nanoparticle tracking analysis (NS300, Malvern, UK). Following the manufacturer’s instructions, the NTA instrument was set up. The C-lEV samples were diluted to 1 mL with PBS and analyzed at room temperature.
2.3 RT-qPCR
RNA was isolated from cells or heart tissue by adding Trizol Reagent (AG21101, Accurate Biology), then separated by adding chloroform and centrifugation. With a reverse transcription kit Evo M-MLV RT (AG11707, Accurate Biology), 1 μg total RNA was converted into cDNA. RT-qPCR reactions were performed on a ROCHE 480II using the SYBR® Green qPCR Kit (AG11701, Accurate Biology) and appropriate primers. Primer sequences are provided in Supplementary Table S1.
2.4 Western blot analysis
The cell and C-lEV proteins were obtained by adding RIPA lysis buffer supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Beyotime Biotechnology, CN). Proteins were quantified by a BCA assay kit. After adding loading buffer, the sample was heated to 95 °C for 10 minutes to induce denaturation. Identical protein amounts were resolved using SDS-PAGE and then transferred to PVDF membranes (Millipore, USA). The membrane was blocked with 5% non-fat milk for 1–2 hours at room temperature, followed by overnight incubation at 4 °C with specific antibodies on a skaker. Membranes were then incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies, and immunoblots were visualized using Pierce ECL reagent (Thermo Fisher) through chemiluminescence. Antibodies used included Calnexin (A15631, ABclonal, 1:1000), TSG101 (ab125011, Abcam, 1:2000), β-actin (#sc47778, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, 1:3000), CD63 (ab217345, Abcam, 1:1000), Tubulin (ab6160, Abcam, 1:5000), p-p38 (4511T, Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000), p38 (ab170099, Abcam, 1:2000), GAPDH (10494-1-AP, Proteintech, 1:5000), and PP2A (81G5, Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000).
2.5 In vitro cellular uptake of C-lEVs
Following the manufacturer’s instructions, C-lEVs labeled with Dil fluorochrome (C1991S, Byotime) were prepared. RAW264.7 cells were stained with Actin-Tracker Green-488 (C2201S, Byotime) for 10 minutes at 37 °C and incubated with fluorescently labeled C-lEVs for 30 minutes. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with DAPI (Sigma-Aldrich, #D9542). Using an EVOS M7000 fluorescence microscope (Invitrogen, Massachusetts, USA), images were observed.
2.6 Flow cytometry
RAW264.7 cells were collected and counted using an automated cell counter (CountessTM3, Thermo Fisher). 106 cells were blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA, Gibco) to prevent non-specific binding, followed by incubating at 4 °C for 30 minutes with PE-CD86 monoclonal antibody (1:100; 561963, BD Biosciences). To stain with the CD206 antibody, cells were fixed and permeabilized with the intracellular staining kit (00-5523-00, eBioscience) after blocking Fc receptors, as the epitope is located in the medial segment of the cell membrane. Subsequently, PE-CD206 (1:400; 2535977, eBioscience™) staining was performed. Following staining, the cells were rinsed twice with 1% BSA and examined using a flow cytometer (ATTUNE NXT, Thermo Fisher).
2.7 Cell proliferation assay
Cell proliferation was assessed with a CCK-8 kit. Briefly, 2 × 104 cells/well per 100 µL was seeded into 96-well plates. 24 hours after the plates were planted, each group of cells was subjected to fluid exchange with the treatment of PBS, LPS, and LPS+C-lEVs, respectively. Following a 10-hour treatment, each well received 10 µL of CCK8 reagent (Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) and was further incubated for 2 hours. Absorbance measurements at 450 nm were performed on a TECAN Spark microplate reader.
2.8 Detection of reactive oxygen species
The intracellular ROS level was measured with dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) green dye. RAW264.7 cells subjected to various treatments were incubated at 37 °C for 45 min with 20 μM DCFH-DA (Beyotime Biotechnology, China; #S0033S) for staining, followed by PBS washing. Then the fluorescent intensity of cells was detected with a flow cytometer (AttuneNxT, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA) and analyzed using FlowJo 10.8.1 software.
2.9 Animal experiment
The Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3, Nancy strain, USA) was amplified in Hep2 cells with titter measured via the 50% tissue culture infection dose (TCID50) method. The Animal Experimental Ethics Committee of Shandong Provincial Hospital approved the study’s animal experimental protocols (NSFC: 2024-178). SPF grade BALB/c male mice (18–20 g, 4 weeks old) were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. and kept in a specific pathogen-free conditions. After a 3-day adaptive feeding period, mice were randomly assigned to one of three groups: the normal control group (NC), the CVB3 group, or the CVB3+C-lEVLPS group. A dose of 200 µL 104 TCID50 CVB3 was given to mice by intraperitoneal injection to set up viral myocarditis model, whereas the NC group received 200 µL PBS administration intraperitoneally. To investigate the effect of C-lEVLPS, a dose of 150 µL C-lEVLPS (1 × 108 particles/mL) was administered via the tail vein day 1 and day 3 following the establishment of the viral myocarditis model. Seven days after virus or PBS injection, echocardiography was performed on the mice in each group using M-mode ultrasound (SiliconWave 60, Kolo Medical Co., Ltd., Suzhou, China) to measure the ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) of the left ventricle. Then all mice were anesthetized, blood samples were collected in EDTA tubes, and myocardial tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde.
2.10 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
ELISA analysis was conducted to evaluate the level of cardiac biomarker cardiac troponin (cTnT) in mice plasma. Plasma samples were centrifuged at 1,000× g at 4 °C for 15 minutes within 30 minutes of collection, and the supernatant was collected. cTnT detection was performed using a mouse ELISA kit (ReedBiotech, RE1358M) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.11 Hematoxylin-eosin and immunohistochemistry staining
Heart samples fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde were embedded in paraffin and sectioned into 5 µm white pieces. After staining with hematoxylin-eosin, samples were observed under an optical microscope. Immunohistochemistry staining was performed as previously described (35), the paraffin-embedded heart tissue was cut into 5 µm thick sections, dewaxed and rehydrated, and after antigen repair, the endogenous catalase was blocked. The slide was sealed with 1% BSA for 30 minutes, incubated with CD86 primary antibody overnight, washed, treated with a biotin-coupled secondary antibody for 30 minutes, and observed under a microscope following DAB staining. The CD206 antibody, targeting an epitope in the medial cell membrane segment, was incubated with 0.2% Triton X-100 following BSA blocking to permeabilize the membrane for antibody staining for 15 minutes. Myocardial lesion severity was scored as follows: 0 = no inflammation; 1 = 1–5 inflammatory foci (≤5% area); 2 = >5 foci or >5-20% area involvement; 3 = diffuse inflammation (>20% area), no necrosis; 4 = diffuse inflammation with necrosis.
2.12 PolyA-Selected mRNA-Seq
RNA was isolated by adding chloroform followed by centrifugation. Quality assessment involved agarose gel electrophoresis, Nanodrop spectrophotometry, and Qubit fluorometry. Library preparation was streamlined using a kit that combined double-strand synthesis, end repair, and dA-tailing. mRNA was enriched with VAHTS mRNA Capture Beads, fragmented, and then reverse transcribed into cDNA (9, 36). The cDNA was purified, and sequencing adapters were ligated. Library quality was assessed using the Agilent Bioanalyzer and Qubit fluorometer. Sequencing was conducted on an Illumina Novaseq6000 platform in paired-end 150 mode. This protocol generated high-quality sequencing data suited for subsequent bioinformatic analysis.
Raw data was processed with fastp (version 2.0), which removed adapter sequences, trimmed low-quality bases (quality score < 20), and filtered out reads containing more than 10% ambiguous nucleotides (N). The resulting data was referred to as clean data. These clean reads were mapped to the reference genome with HISAT2 (version 2.1.0), and the alignment quality was evaluated with RSeQC (version 3.0.1). Gene expression levels were quantified with StringTie, and differentially expressed genes were identified through DESeq2 analysis (9).
2.13 NanoLC-MS/MS analysis
Peptides (200 ng) were analyzed using a nano-UPLC (nanoElute2) coupled with a timsTOF Pro2 mass spectrometer (Bruker) equipped with a nano-electrospray ion source. A PePSep C18 reversed-phase column (1.9 µm, 75 µm × 15 cm, Bruker, Germany) was used for the separation. The mobile phases were H2O with 0.1% FA (phase A) and ACN with 0.1% FA (phase B). The sample was separated using a 60-minute gradient at a flow rate of 300 nL/min. Gradient B: 2% for 0 minutes, increasing to 22% over 45 minutes, then to 37% over 5 minutes, further to 80% over another 5 minutes, and maintained at 80% for 5 minutes (37).
Data acquisition is performed in DDA PaSEF mode, with an MS1 scanning range between 100 and 1700 m/z. In PASEF MS/MS scanning, the impact energy rises linearly with ion mobility, starting at 20 eV for 1/K0 = 0.6 Vs/cm2 and reaching 59 eV for 1/K0 = 1.6 Vs/cm2.
2.14 Protein identification and quantification
The vendor’s raw MS files were analyzed with SpectroMine software (v4.2.230428.52329) with the integrated Pulsar search engine. MS spectra were searched against a species-specific UniProt FASTA database (Rattus.fasta) with fixed carbamidomethylation and variable oxidation and N-terminal acetylation. Trypsin was utilized as a protease. A maximum of 2 missed cleavages was permitted. Both PSM and peptide levels were set at 0.01 false discovery rate. Peptide identification was conducted with an initial precursor and fragment mass deviation of up to 20 ppm. All other parameters were kept as default.
2.15 Statistical analysis
The data were statistically analyzed and plotted by GraphPad Prism9 software. p-values were calculated using Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA. p < 0.05 was deemed statistically significant. All experiments were conducted a minimum of three times.
3 Results
3.1 Characterization of C-lEVs
The rat cardiomyocyte cell line H9C2 was used for the isolation of C-lEVs. Following LPS treatment, there was a significant increase in inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α, accompanied by a decrease in cell viability (Supplementary Figure S1). Differential centrifugation was used to isolate C-lEVPBS and C-lEVLPS from the culture medium (Figure 1A). Western blot analysis confirmed the presence of C-lEV markers TSG101, CD63, and Actin, while Calnexin was absent (Figure 1B). TEM revealed the typical membranous cup-shaped morphology of both C-lEVPBS and C-lEVLPS (Figures 1C, D). NTA-determined particle sizes predominantly ranged from 100 to 500 nm, with peak sizes of 158 nm for C-lEVPBS and 171.6 nm for C-lEVLPS (Figures 1E, F). Additionally, the particle numbers of C-lEVLPS per milliliter of culture medium were significantly elevated compared to C-lEVPBS (Figure 1G).
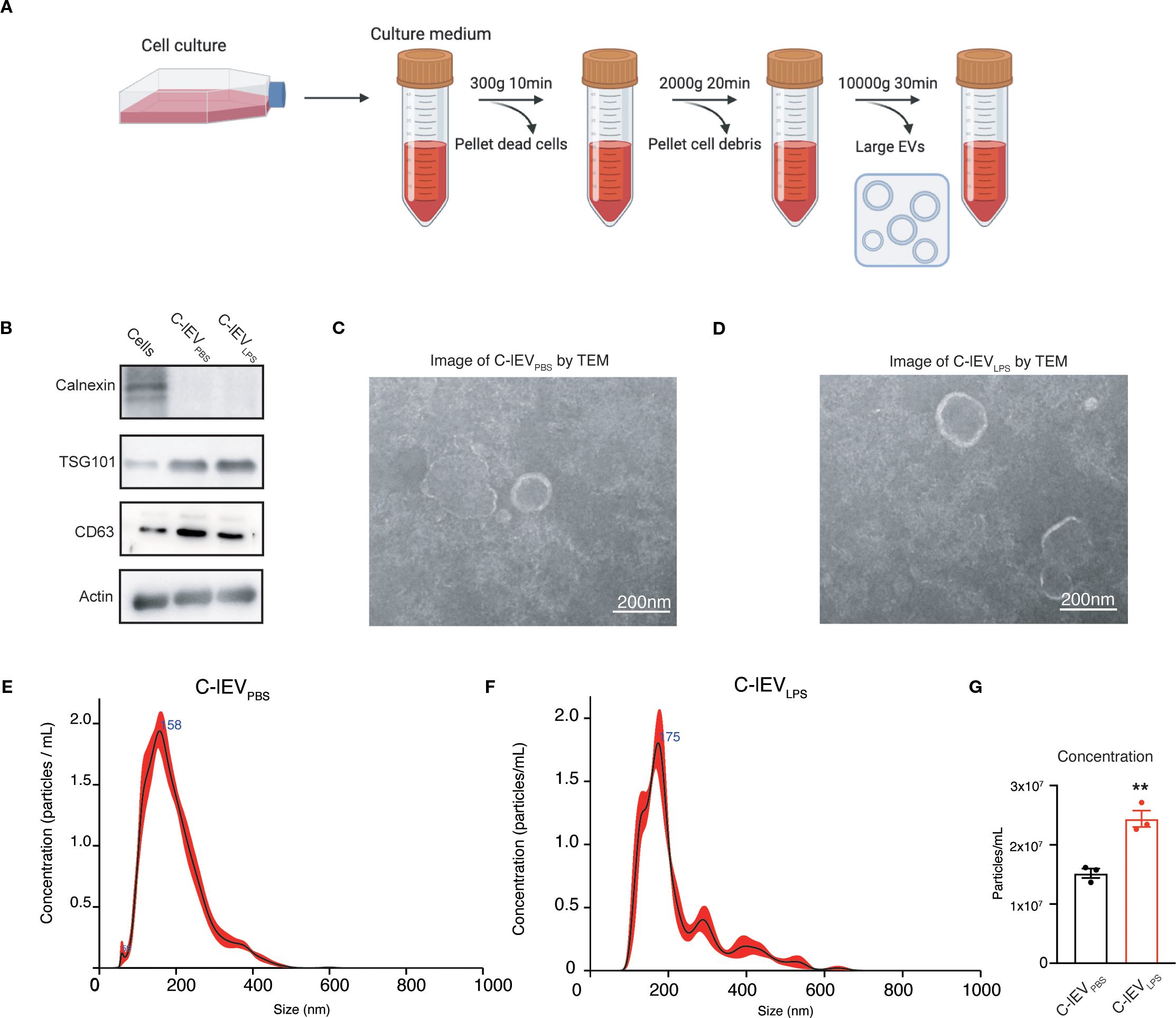
Figure 1. Isolation and characterization of C-lEVs. (A) Workflow schematic for the isolation of C-lEVs. (B) Western blot analysis of Calnexin and C-lEVs markers of TSG101, CD63, and Actin. (C, D) Representative images of C-lEVPBS and C-lEVLPS by TEM, scale bars: 200 nm. (E, F) Size distribution of C-lEVPBS and C-lEVLPS. (G) Particle concentration of C-lEVPBS and C-lEVLPS. **p < 0.01 vs. C-lEVPBS group.
3.2 In vitro studies demonstrate the anti-inflammatory properties of C-lEVLPS
The in vitro effects of C-lEVLPS were examined with the murine macrophage cell line RAW264.7. The internalization of C-lEVLPS by RAW264.7 cells was evaluated first. Dil fluorescent dye-labeled C-lEVLPS were incubated with RAW264.7 cells for 6 hours. As depicted in Figure 2A, C-lEVLPS could be taken up by RAW264.7 cells. Emerging evidence indicated that activated macrophages can release ROS and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (38). Herein, RAW264.7 cells were treated with LPS and subsequently exposed to varying concentrations of C-lEVPBS or C-lEVLPS. Flow cytometry results indicated that ROS levels were significantly elevated upon treatment with LPS, while C-lEVLPS reversed the LPS-induced increase in ROS (p=0.000034, Figure 2B). The expression levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β were significantly elevated in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells (Figures 2C-E). Different C-lEVLPS concentrations resulted in varying decreases in inflammatory cytokine expression. Notably, the 107 particles/mL C-lEVLPS group exerted the most potent effect, significantly suppressing the expression of all inflammatory cytokines tested (Figures 2C-E). Additionally, increased cell proliferation was observed following LPS stimulation, which was suppressed by C-lEVLPS treatment (Supplementary Figure S2). In contrast, different concentrations of C-lEVPBS did not influence the expression of inflammatory cytokines (Supplementary Figure S3). Taken together, C-lEVLPS decreased the expression of inflammatory cytokines compared to C-lEVPBS (Figures 2F-H). These data indicate that C-lEVLPS treatment exerts anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages.
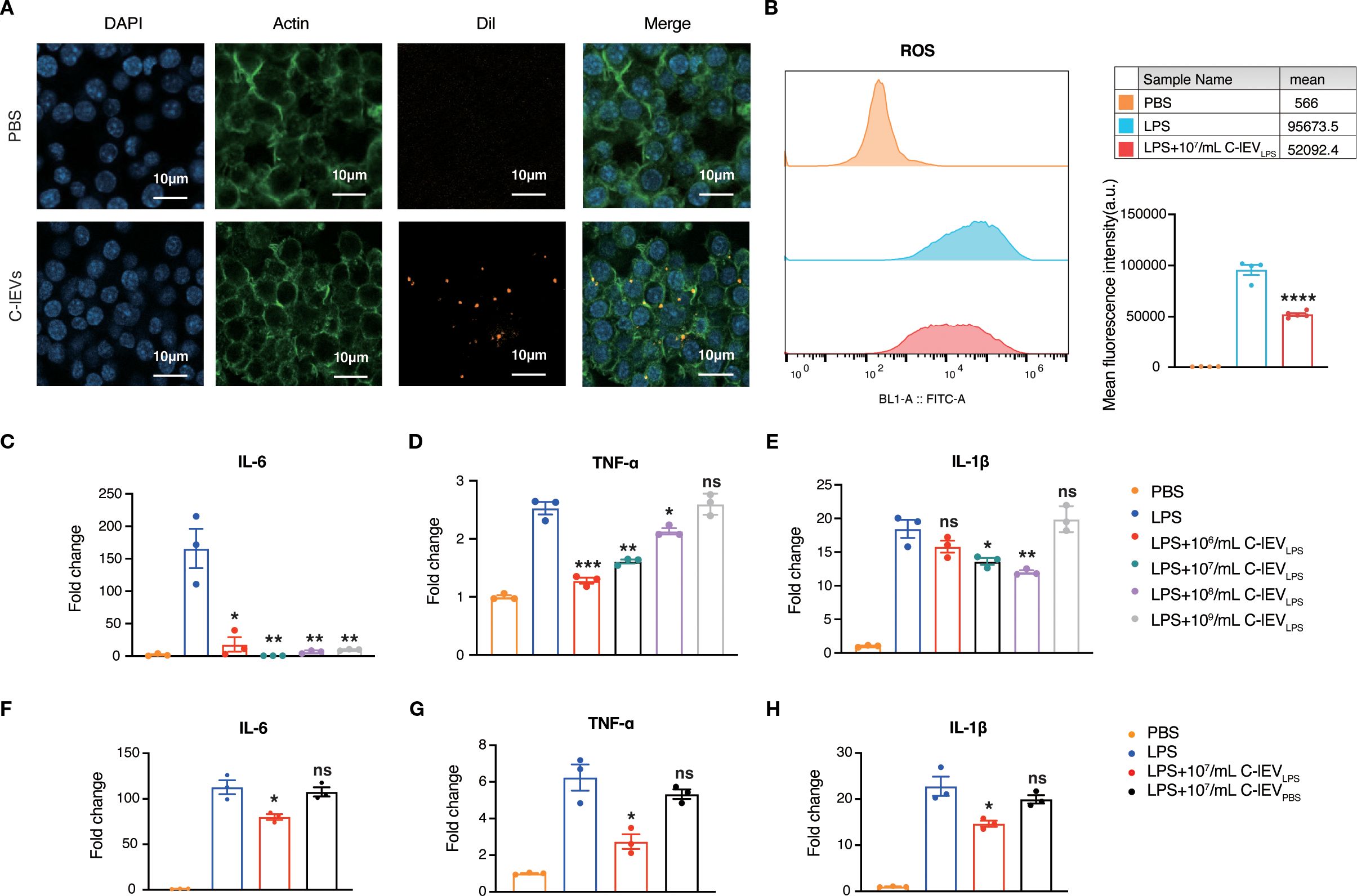
Figure 2. C-lEVLPS suppressed LPS-stimulated inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells. (A) Representative images of RAW 264.7 cells internalizing C-lEVLPS, scale bar: 10 µm. (B) ROS production in RAW264.7 cells. (C-H) The expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β in RAW264.7 cells determined by RT-qPCR under different treatments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns, nonsignificant difference vs. PBS group.
3.3 C-lEVLPS alleviated CVB3-induced myocarditis in mice
To evaluate the role of C-lEVLPS in myocarditis, BALB/c mice were injected with CVB3 to induce viral myocarditis. On days 1 and 4 post-CVB3 injection, the mice were administered 150 μL of C-lEVLPS (108 particles/mL) or PBS (carrier solution) via tail vein injection (Figure 3A). As expected, C-lEVLPS accumulated in the mouse hearts after tail vein injection (Supplementary Figure S4). On day 7, C-lEVLPS mildly reversed the weight loss observed after CVB3 infection (Figure 3B). Thus, cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography. As expected, mice induced by CVB3 exhibited cardiac dysfunction, as evidenced by decreased ejection fraction (EF) (p=0.0003) and fractional shortening (FS) (p=0.0005). Strikingly, the cardiac dysfunction was remarkably attenuated upon treatment with C-lEVLPS (Figure 3C). However, there were no significant differences in left ventricular posterior wall thickness (LVPW) or left ventricular mass (LV mass Cor) between the CVB3 group and the C-lEVLPS group (Supplementary Figure S5). In addition, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed no statistically significant differences in survival rates among these groups during the observation period (Supplementary Figure S5).

Figure 3. C-lEVLPS treatment relieved CVB3-induced myocarditis in vivo. (A) Animal treatment illustration. (B) Appearance of the heart after different treatments. (C) Changes in mice body weight among different treatment groups. (D) Left panel, representative echocardiographic images of the mice. Right panel, statistical analysis results of left ventricular EF and FS. (E) HE staining images and pathological scores of myocardial tissues, scale bar: 20 µm. (F-H) Analysis of immunohistochemical staining for inflammatory cytokines expression and semiquantitative histological analysis, scale bar: 20 µm. (I-K) The expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in mice myocardial tissue. (L) The serum levels of cTnT in mice. (n = 5) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. CVB3 group.
Then the myocardial tissue was collected. The myocardial surfaces of mice in the NC group appeared smooth, while mice with viral myocarditis showed patch-like lesions in the heart. Notably, upon treatment with C-lEVLPS, the area of patch-like lesions was significantly reduced in the heart (Figure 3D). H&E staining indicated significantly higher pathology scores in the CVB3 group of mice compared to the NC group, while the CVB3 + C-lEVLPS group exhibited notably reduced scores relative to the CVB3 group (Figure 3E). IHC staining and RT-qPCR analysis showed that TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β expressions were significantly elevated in the hearts of the mice in the CVB3 group compared to the NC group. Conversely, these cytokine expressions were reduced significantly in the CVB3 + C-lEVLPS group compared to the CVB3 group (Figures 3F-K). Additionally, ELISA analysis revealed that plasma cTnT levels were significantly elevated in CVB3-infected mice and markedly decreased in the CVB3 with C-lEVLPS group (Figure 3L). Collectively, these results indicate that C-lEVLPS treatment reduces the inflammatory response in myocarditis.
3.4 C-lEVLPS induces macrophage polarization from M1 toward M2
Macrophages are crucial in the early development of myocarditis as the main inflammatory and infiltrating cells (5, 7). They can differentiate into pro-inflammatory M1 or anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes based on the cardiac environment (39). Flow cytometry was used to evaluate macrophage phenotypes and determine if C-lEVLPS reduces inflammation by influencing macrophage polarization. The results indicated that the proportion of CD86-positive M1 macrophages significantly increased after LPS treatment, whereas C-lEVLPS treatment reduced this proportion (p=0.008, Figures 4A, B). Conversely, the proportion of CD206-positive M2 macrophages increased after LPS treatment and was further elevated with C-lEVLPS treatment (p=0.0049, Figures 4C, D).
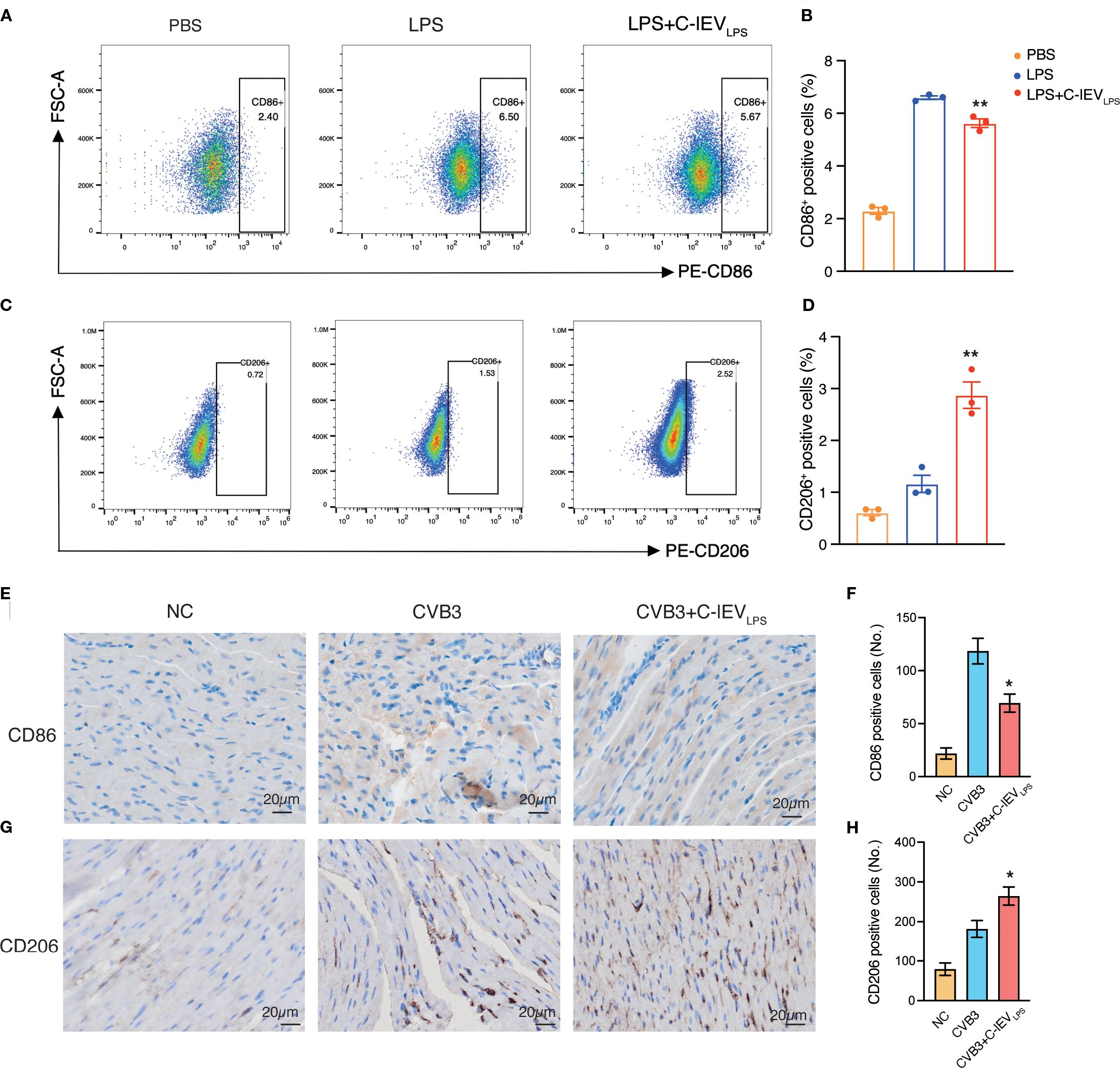
Figure 4. C-lEVLPS treatment regulated macrophage polarization both in vitro and in vivo. (A, B) Flow cytometry analysis of CD86 positive RAW 264.7 cells and quantitative data analysis. (C, D) Flow cytometry analysis of CD206 positive RAW 264.7 cells and quantitative data analysis. (E, F) Analysis of immunohistochemical staining for CD86 and semiquantitative histological analysis (n=5), scale bar: 20 µm. (G, H) Analysis of immunohistochemical staining for CD206 and semiquantitative histological analysis (n=5), scale bar: 20 µm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. LPS or CVB3 group.
Additionally, to verify whether C-lEVLPS could influence macrophage polarization in vivo, we performed IHC staining of CD86 and CD206 on the myocardial tissues in the mice. C-lEVLPS treatment modulated macrophage infiltration, reducing the presence of M1 macrophages while enhancing the recruitment of M2 macrophages (Figures 4E-H). These findings suggest that C-lEVLPS treatment induced macrophage polarization toward an M2-like phenotype while inhibiting M1 polarization.
3.5 C-lEVLPS regulates macrophage polarization via the p38 MAPK pathway
To elucidate the mechanism by which C-lEVLPS regulates macrophage polarization, RNA sequencing was conducted to identify gene expression differences in macrophages upon treatment with or without C-lEVLPS. The volcano plot analysis revealed 941 upregulated genes (p < 0.05, log2FC > 0.5) and 1048 downregulated genes (p < 0.05, log2FC < −0.5) (Figure 5A).

Figure 5. C-lEVLPS regulates macrophage polarization by the p38 MAPK pathway. (A, B) Transcriptomic alterations in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells following treatment with C-lEVLPS revealed by RNA-seq analysis. (C, D) Representative bands of p-p38/p38 levels by Western blot, with semiquantitative analysis, in RAW 264.7 cells subjected to various treatments. (E-G) Expression levels of pro-inflammatory gene profiles in RAW 264.7 cells. (H, I) Flow cytometry analysis of CD86-positive RAW 264.7 cells and quantitative data analysis. (J, K) Flow cytometry analysis of CD206-positive RAW 264.7 cells and quantitative data analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Notably, gene ontology (GO) analysis of differentially expressed genes indicated significant enrichment of the MAPK pathway (Figure 5B). Given that the p38 MAPK pathway is involved in macrophage polarization (40, 41), we hypothesized that C-lEVLPS modulates macrophage polarization through the p38 MAPK pathway. Blot analysis demonstrated that LPS increased p38 phosphorylation, an effect reversed by C-lEVLPS, pointing to C-lEVLPS-mediated inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway (Figures 5C, D).
To confirm that C-lEVLPS influences macrophage polarization through the p38 MAPK pathway, LPS-preconditioned RAW264.7 cells were co-cultured with C-lEVLPS and the p38 MAPK agonist AM. RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that treatment with C-lEVLPS significantly reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α compared to the LPS group. However, co-treatment with AM eliminates the anti-inflammatory effects of C-lEVLPS (Figures 5E–G). Flow cytometry analysis showed that treatment with C-lEVLPS significantly increased the proportion of CD206-positive M2 macrophages and decreased the proportion of CD86-positive M1 macrophages compared to the LPS group. Notably, the addition of AM reversed the effects of C-lEVLPS, which reduced the proportion of M2 macrophages and increased M1 macrophages (Figures 5H–K). Collectively, these findings suggest that C-lEVLPS modulates macrophage polarization, at least in part, through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
3.6 PP2AA serves a potential regulator from C-lEVLPS mediating macrophage polarization
EVs are known to contain multiple proteins relevant to various biological processes (34). Based on label-free proteomics analysis, C-lEVLPS and C-lEVPBS exhibited distinct protein compositions, with 824 and 580 proteins identified, respectively (Figure 6A). Then GO analyses of biological processes and reactome gene set analysis were performed. GO biological process analysis (Figure 6B) revealed that the “peptide metabolic process” was enriched in C-lEVLPS proteins significantly. Reactome gene set analysis revealed that these proteins are associated with several signaling pathways, particularly those involved in regulating the inflammatory response, including the “RAF/MAPK kinase cascade”, “Adaptive immune system”, “TCR signaling”, “MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling”, and “NIK-noncanonical NF-κB signaling” pathways (Figure 6C).
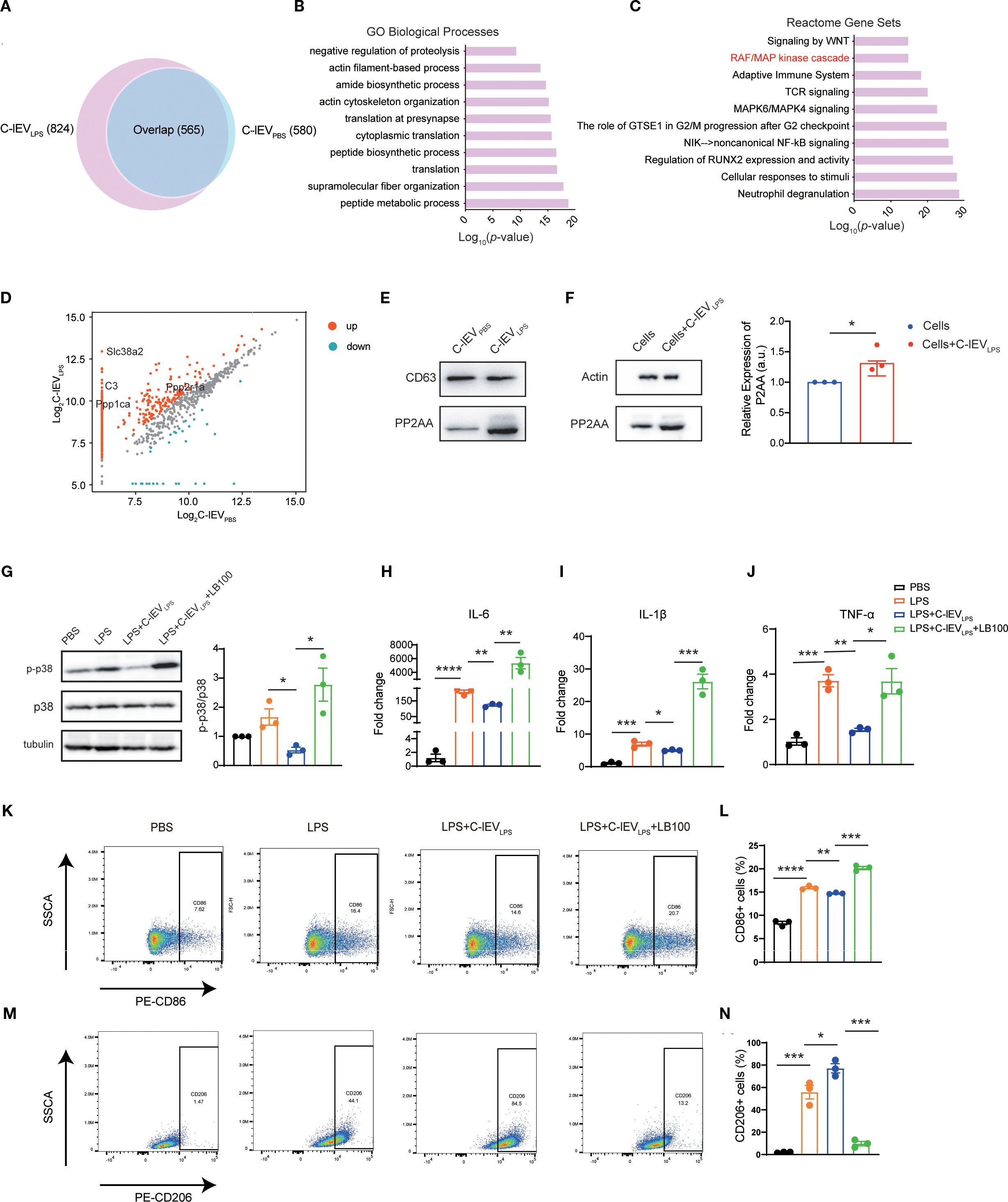
Figure 6. C-lEVLPS encapsulates PP2AA and regulates the p38-MAPK pathway of macrophage by synthesizing PP2A. (A) Venn diagram depicting the common and total proteins in C-lEVLPS vs. C-lEVPBS. (B) Gene ontology analysis of proteins enriched in C-lEVLPS focused on biological processes. (C) Reactome pathway analysis conducted on proteins enriched in C-lEVLPS. (D) Volcano plot illustrating the differentially enriched proteins in C-lEVLPS vs C-lEVPBS. (E) Representative bands of PP2A and CD63 in C-lEVLPS and C-lEVPBS by Western blot. (F) Western blot showing PP2A and actin expression in RAW264.7 cells. (G) Representative bands of p-p38/p38 levels by Western blot, with semiquantitative analysis, in RAW 264.7 cells subjected to various treatments. (H-J) Expression levels of pro-inflammatory gene profiles in RAW 264.7 cells. (K, L) Flow cytometry analysis of CD86-positive RAW 264.7 cells and quantitative data analysis. (M, N) Flow cytometry analysis of CD206-positive RAW 264.7 cells and quantitative data analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Among the proteins associated with the “RAF/MAPK kinase cascade”, Ppp2r1a was identified as upregulated in C-lEVLPS (Figure 6D), which was validated by Western blot analysis (Figure 6E). Ppp2r1a encodes PP2AA, a subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), an important serine-threonine phosphatase capable of dephosphorylating p38 MAPK. It has been reported that PP2AA can recruit other subunits of PP2A (42). Therefore, we hypothesized that the upregulated PP2AA in C-lEVLPS is delivered to macrophages, where it recruits additional PP2A subunits to dephosphorylate p38 MAPK.
To confirm that C-lEVLPS transports PP2AA to macrophages, RAW264.7 cells were incubated with C-lEVLPS for 12 hours. Western blot showed a significant increase in PP2AA expression in RAW264.7 cells treated by C-lEVLPS (Figure 6F). Overall, these data indicate that C-lEVLPS has the capability to deliver PP2AA to macrophages, thereby promoting the formation of PP2A complexes, which may subsequently dephosphorylate p38 MAPK.
To further confirm that the effects of C-lEVLPS are mediated through PP2A, LPS-preconditioned RAW264.7 cells were co-cultured with C-lEVLPS and the PP2A inhibitor LB-100. Western blot analysis revealed that C-lEVLPS reduced the phosphorylation level of p38 after LPS stimulation, while the use of LB-100 diminished this effect (Figure 6G). Meanwhile, RT-qPCR analysis revealed that treatment with C-lEVLPS significantly reduced the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells compared to the LPS group. Importantly, co-treatment with LB-100 eliminates the anti-inflammatory effects of C-lEVLPS (Figures 6H–J).
Flow cytometry results showed that treatment with C-lEVLPS decreased the proportion of CD86-positive M1 macrophages (Figures 6K, L) and increased the proportion of CD206-positive M2 macrophages (Figures 6M, N) relative to the LPS group. However, the addition of LB-100 reversed these effects resulting in increased percentage of M1 macrophages and reduced percentage of M2 macrophages (Figures 6K-N).
Overall, these data indicate that C-lEVLPS has the capability to deliver PP2AA to macrophages, which may subsequently dephosphorylate p38 MAPK and exert anti-inflammatory effects.
4 Discussion
Myocarditis is characterized by the infiltration of various inflammatory cells into myocardial tissue (43, 44), with macrophages being the primary immune cells (5). Viral infections are the main cause of myocarditis (45, 46), where viruses enter cardiomyocytes via virus-specific receptors, activating innate immune responses that include macrophage infiltration (47). However, the fundamental mechanisms underlying the crosstalk between cardiomyocytes and macrophages in myocarditis remain largely unexplored.
Existing literature has shown that EVs can alter the polarization state of macrophages during cardiac injury. For example, sEVs secreted by M2 macrophages promote the conversion of macrophages toward the M2 phenotype in viral myocarditis (48), while sEVs secreted by ischemic cardiomyocytes act on macrophages, modulating their inflammatory cytokine expression profile and enhancing their adhesion to fibronectin (49). However, the effects of lEVs secreted by cardiomyocytes under inflammatory conditions on macrophages remain unexplored. In contrast to previous studies, our research fills this gap by revealing how lEVs derived from inflamed cardiomyocytes influence macrophages in myocarditis.
In this study, the in vitro model employed LPS to stimulate inflammatory signaling, primarily activating the TLR4-NF-κB pathway (50); the in vivo model used CVB3 infection, which triggers cytoplasmic RIG-I-like receptors (51) and, to a lesser extent, TLR4 signaling (52). Although the upstream receptors that initiate the two models differ, the literature has reported that the capsid protein of CVB3 can crosstalk with TLR4 and induce inflammasome activation (52, 53). The choice of LPS for in vitro work was indeed due to CVB3 infection causing extensive cell death and abundant viral release, making it almost impossible to obtain pure, virus-free C-lEVs, whereas LPS-induced sterile inflammation can be readily washed out of C-lEV preparations.
We found that certain doses of C-lEVLPS but not C-lEVPBS inhibited the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in macrophages and ameliorated myocardial inflammation in mice. In addition, our findings indicate that the culture medium of LPS-induced H9C2 cells contained approximately 2–3 × 107 C-lEVs per milliliter. Similarly, the most effective concentration for macrophages is 107 particles per milliliter, which is comparable to the concentration secreted by cardiomyocytes. Based on our experimental results and current literature, we speculate that only C-lEVLPS at near-physiological concentrations exhibits the expected anti-inflammatory effects, while excessively high doses (e.g., 109/mL) may lose their regulatory capacity. This indicates that the amount of large EVs released by cardiomyocytes under inflammatory conditions is sufficient to alter macrophage polarization. Although these findings provide valuable insights, more detailed mechanistic investigation is needed to thoroughly explain this observation. Considering that the normal blood volume of a mouse is approximately 72 mL/kg, a 20 g mouse has a blood volume of approximately 1.44 mL (54). To achieve a concentration of 107 particles/mL in mouse blood, we injected 150 µL of C-lEVLPS at 108 particles/mL, which alleviated myocarditis in mice.
Besides, in this study we found that C-lEVLPS altered the M1/M2 macrophage ratio both in vivo and in vitro. RNA sequencing suggested that the effects of C-lEVLPS may be mediated through the p38 MAPK pathway, and this was further confirmed by Western blot analysis, which demonstrated that C-lEVLPS could regulate the phosphorylation level of p38. Additionally, proteomic analysis identified an increase in PP2AA, a subunit of PP2A, in C-lEVLPS. PP2A is a crucial serine-threonine phosphatase capable of dephosphorylating p38 MAPK. PP2AA exhibits a horseshoe-shaped structure that facilitates the recruitment of other PP2A subunits (42). In addition, the PP2A inhibitor abrogated the anti-inflammatory effects of C-lEVLPS. These results suggest that C-lEVLPS regulates the p38 MAPK pathway through PP2A (Figure 7). Taken together, these results suggest that C-lEVLPS regulates the p38 MAPK pathway through PP2A.
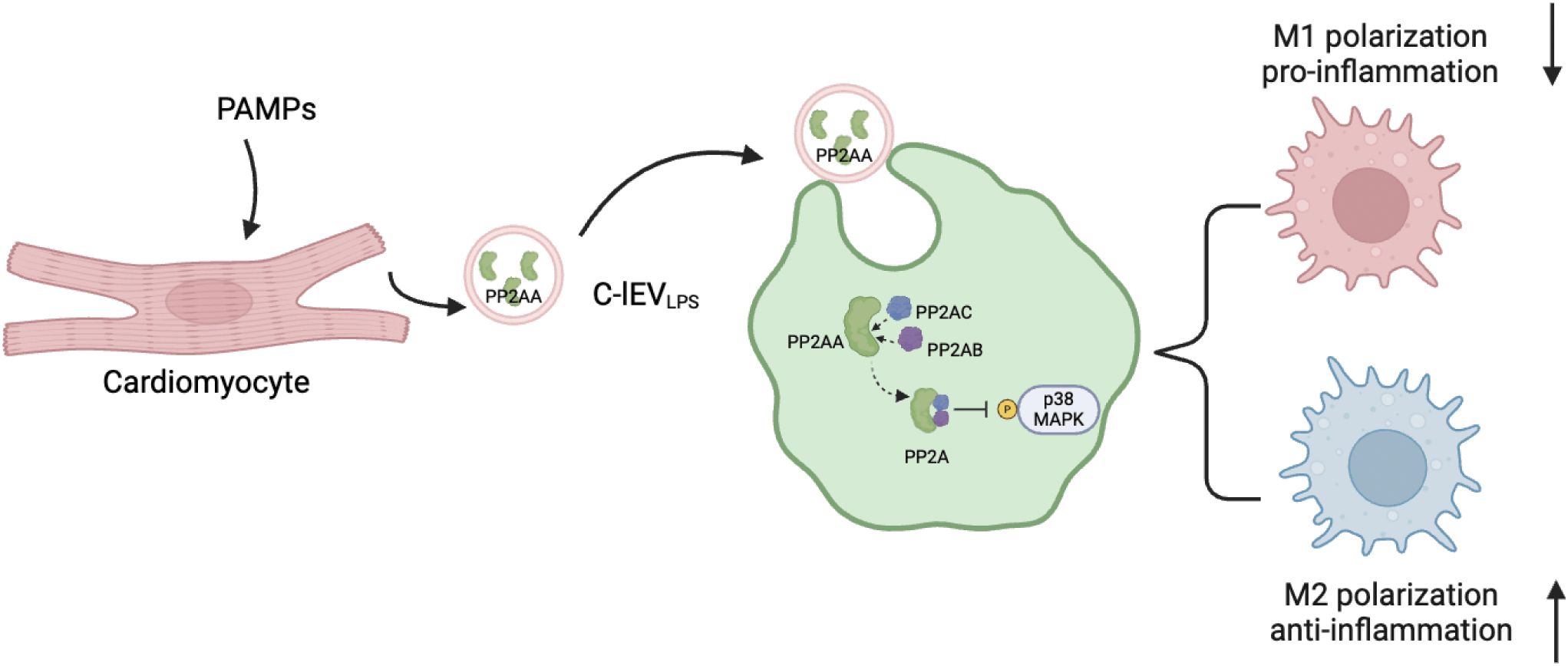
Figure 7. Proposed model explaining how C-lEVLPS derived from inflammatory cardiomyocytes regulate macrophage polarization via MAPK pathway. The diagram is created by Biorender.
Nevertheless, our study has some limitations that should be addressed in future research. First, our study uses LPS to stimulate H9C2 cardiomyocytes in vitro and CVB3 to induce myocarditis in vivo. Despite possible mechanistic differences, it is technically challenging to obtain C-lEVs completely free of infectious viral particles following CVB3 exposure. Moreover, the recent evidence indicates that CVB3 may also engage TLR4 signaling (52, 53), suggesting an overlap in the downstream pathways activated by CVB3 and LPS. Nonetheless, we recognize that viral myocarditis is more clinically relevant, and our current approach represents a compromise to balance experimental feasibility and mechanistic insight. Future studies employing advanced virus inactivation methods and refined cell models will be necessary to distinguish these mechanisms more clearly.
Second, macrophage polarization is an extremely complex process that is regulated by multiple signaling pathways (49, 55). While our data indicate that the regulatory function of C-lEVLPS is mediated through the MAPK signaling pathway, we acknowledge the potential involvement of additional pathways and do not discount their significance. RNA sequencing revealed that C-lEVLPS modulates numerous pathways, including the NF-κB signaling pathway, which may influence macrophage polarization. Therefore, the immune regulatory mechanisms of C-lEVLPS require further investigation.
Third, we did not assess the long-term effects of C-lEVLPS on myocarditis progression. Myocarditis is a dynamic disease that progresses through three distinct phases: the acute phase (characterized by viral infection and initial inflammatory response), the subacute phase (involving immune-mediated myocardial injury), and the chronic phase (which may lead to fibrosis and dilated cardiomyopathy). Our study focused solely on the acute phase, leaving open the question of whether C-lEVLPS administration could influence later stages, particularly fibrosis and cardiac remodeling. Future studies should evaluate the impact of C-lEVLPS at different disease stages to determine its full therapeutic potential.
Currently, there is no specific therapy for myocarditis, and symptomatic management remains the primary method. Research indicates that lncRNA AK083884 from M2 macrophage exosomes safeguards mice against CVB3-induced viral myocarditis (48). Besides, a recent study suggests that large EVs contain higher levels of cargo molecules, including proteins and RNAs, and have segregated plasma membrane domains compared to small EVs (34). This enhances their likelihood of fusing with target cells. In a study about myocardial infarction, cardiomyocyte-derived large EVs, but not small EVs, modulate the release of CCL2, CCL7, and IL-6 from cardiac monocytes (56). Leveraging a controllable in vitro LPS-induced inflammatory model, we found that inflammation-induced C-lEVs can modulate macrophage polarization and attenuate inflammation both in vitro and in vivo. This suggests that specific cargo proteins within C-lEVs (e.g., PP2A-A) could be extracted and employed as novel intercellular signaling vehicles, providing a potential therapeutic avenue for the treatment of myocarditis.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, GSE279575 http://www.proteomexchange.org/, PXD057460.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the animal experimental ethics committee of Shandong Provincial Hospital. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YJ: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation. YY: Software, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Project administration, Formal analysis. YX: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Visualization. SZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. MM: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. BH: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Software, Funding acquisition, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was funded by Special Expert of Taishan Scholars (no.201511099), Jinan Science and Technology Development Plan (no.202134015), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Youths (ZR2023QH310), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Provincial (ZR2023MH052).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our heartfelt gratitude to Kai Guo from the Shandong Provincial Hospital for the technical help and to Qiuyao Jiang from Shandong First Medical University for the guidance. We also thank Lingjun Tong from Shandong First Medical University for his valuable advice, as well as Haidan Wang and Yutong Wei for their assistance in the experiments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1629676/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Law YM, Lal AK, Chen S, Čiháková D, Cooper LT Jr., Deshpande S, et al. Diagnosis and management of myocarditis in children: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. (2021) 144:e123–e35. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001001
2. Sagar S, Liu PP, and Cooper LT Jr. Myocarditis. Lancet (London England). (2012) 379:738–47. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60648-X
3. Nunes MC, Guimarães Júnior MH, Diamantino AC, Gelape CL, and Ferrari TC. Cardiac manifestations of parasitic diseases. Heart (British Cardiac Society). (2017) 103:651–8. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2016-309870
4. Francone M, Chimenti C, Galea N, Scopelliti F, Verardo R, Galea R, et al. CMR sensitivity varies with clinical presentation and extent of cell necrosis in biopsy-proven acute myocarditis. JACC Cardiovasc imaging. (2014) 7:254–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.10.011
5. Lasrado N, Borcherding N, Arumugam R, Starr TK, and Reddy J. Dissecting the cellular landscape and transcriptome network in viral myocarditis by single-cell RNA sequencing. iScience. (2022) 25:103865. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103865
6. Epelman S, Lavine KJ, Beaudin AE, Sojka DK, Carrero JA, Calderon B, et al. Embryonic and adult-derived resident cardiac macrophages are maintained through distinct mechanisms at steady state and during inflammation. Immunity. (2014) 40:91–104. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.019
7. Nahrendorf M and Swirski FK. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity in the heart. Circ Res. (2013) 112:1624–33. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300890
8. Mosser DM and Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2008) 8:958–69. doi: 10.1038/nri2448
9. Ye T, Chen Z, Zhang J, Luo L, Gao R, Gong L, et al. Large extracellular vesicles secreted by human iPSC-derived MSCs ameliorate tendinopathy via regulating macrophage heterogeneity. Bioactive Materials. (2023) 21:194–208. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.08.007
10. Taufalele PV, Wang W, Simmons AJ, Southard-Smith AN, Chen B, Greenlee JD, et al. Matrix stiffness enhances cancer-macrophage interactions and M2-like macrophage accumulation in the breast tumor microenvironment. Acta Biomaterialia. (2023) 163:365–77. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.04.031
11. Yang P, Chen Z, Huang W, Zhang J, Zou L, and Wang H. Communications between macrophages and cardiomyocytes. Cell Communication Signaling: CCS. (2023) 21:206. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01202-4
12. Kumar MA, Baba SK, Sadida HQ, Marzooqi SA, Jerobin J, Altemani FH, et al. Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct targeted Ther. (2024) 9:27. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01735-1
13. Memon MA and Shahidan WNS. Evaluating the feasibility of exosome technologies in COVID-19 treatment: navigating the intersection of reality and fantasy perspectives. (2024) 9:amj-23-204. doi: 10.21037/amj-23-204
14. Amirzadeh Gougheri K, Ahmadi A, Ahmadabadi MG, Babajani A, Yazdanpanah G, Bahrami S, et al. Exosomal Cargo: Pro-angiogeneic, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative effects in ischemic and non-ischemic heart diseases - A comprehensive review. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115801. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115801
15. Jadli AS, Parasor A, Gomes KP, Shandilya R, and Patel VB. Exosomes in cardiovascular diseases: pathological potential of nano-messenger. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:767488. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.767488
16. Yaghoobi A, Rezaee M, Behnoush AH, Khalaji A, Mafi A, Houjaghan AK, et al. Role of long noncoding RNAs in pathological cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction: An emerging insight into molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 172:116248. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116248
17. Caño-Carrillo S, Castillo-Casas JM, Franco D, and Lozano-Velasco E. Unraveling the signaling dynamics of small extracellular vesicles in cardiac diseases. Cells. (2024) 13:265. doi: 10.3390/cells13030265
18. Wang Y, Qiu Z, Yuan J, Li C, Zhao R, Liu W, et al. Hypoxia-reoxygenation induces macrophage polarization and causes the release of exosomal miR-29a to mediate cardiomyocyte pyroptosis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Animal. (2021) 57:30–41. doi: 10.1007/s11626-020-00524-8
19. Dai Y, Wang S, Chang S, Ren D, Shali S, Li C, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry microRNA-148a to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TXNIP and the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2020) 142:65–79. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.02.007
20. Yu X, Deng L, Wang D, Li N, Chen X, Cheng X, et al. Mechanism of TNF-α autocrine effects in hypoxic cardiomyocytes: initiated by hypoxia inducible factor 1α, presented by exosomes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2012) 53:848–57. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.10.002
21. Yuan W, Liang X, Liu Y, and Wang H. Mechanism of miR-378a-3p enriched in M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles in cardiomyocyte pyroptosis after MI. Hypertension Res: Off J Japanese Soc Hypertension. (2022) 45:650–64. doi: 10.1038/s41440-022-00851-1
22. Gallet R, Dawkins J, Valle J, Simsolo E, de Couto G, Middleton R, et al. Exosomes secreted by cardiosphere-derived cells reduce scarring, attenuate adverse remodelling, and improve function in acute and chronic porcine myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. (2017) 38:201–11. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw240
23. Kervadec A, Bellamy V, El Harane N, Arakélian L, Vanneaux V, Cacciapuoti I, et al. Cardiovascular progenitor-derived extracellular vesicles recapitulate the beneficial effects of their parent cells in the treatment of chronic heart failure. J Heart Lung Transplant: Off Publ Int Soc Heart Transplant. (2016) 35:795–807. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2016.01.013
24. El Harane N, Kervadec A, Bellamy V, Pidial L, Neametalla HJ, Perier MC, et al. Acellular therapeutic approach for heart failure: in vitro production of extracellular vesicles from human cardiovascular progenitors. Eur Heart J. (2018) 39:1835–47. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy012
25. Welsh JA, Goberdhan DCI, O’Driscoll L, Buzas EI, Blenkiron C, Bussolati B, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13:e12404. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12404
26. Cheng L and Hill AF. Therapeutically harnessing extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2022) 21:379–99. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00410-w
27. Durcin M, Fleury A, Taillebois E, Hilairet G, Krupova Z, Henry C, et al. Characterisation of adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicle subtypes identifies distinct protein and lipid signatures for large and small extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. (2017) 6:1305677. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2017.1305677
28. Lim HJ, Yoon H, Kim H, Kang YW, Kim JE, Kim OY, et al. Extracellular vesicle proteomes shed light on the evolutionary, interactive, and functional divergence of their biogenesis mechanisms. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:734950. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.734950
29. Gavinho B, Sabatke B, Feijoli V, Rossi IV, da Silva JM, Evans-Osses I, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibition abolishes the production of large extracellular vesicles from giardia intestinalis, affecting host-pathogen interactions by hindering adhesion to host cells. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2020) 10:417. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00417
30. Sproviero D, Gagliardi S, Zucca S, Arigoni M, Giannini M, Garofalo M, et al. Different miRNA profiles in plasma derived small and large extracellular vesicles from patients with neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:2737. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052737
31. Scuteri A and Donzelli E. Dual role of extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative diseases. World J Stem Cells. (2024) 16:1002–11. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i12.1002
32. Krishnamachary B, Cook C, Kumar A, Spikes L, Chalise P, and Dhillon NK. Extracellular vesicle-mediated endothelial apoptosis and EV-associated proteins correlate with COVID-19 disease severity. J Extracell Vesicles. (2021) 10:e12117. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12117
33. Jimenez L, Yu H, McKenzie AJ, Franklin JL, Patton JG, Liu Q, et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis of small and large extracellular vesicles (EVs) reveals enrichment of adhesion proteins in small EVs. J Proteome Res. (2019) 18:947–59. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00647
34. Cocucci E and Meldolesi J. Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. (2015) 25:364–72. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.01.004
35. Liu X, Li M, Chen Z, Yu Y, Shi H, Yu Y, et al. Mitochondrial calpain-1 activates NLRP3 inflammasome by cleaving ATP5A1 and inducing mitochondrial ROS in CVB3-induced myocarditis. Basic Res Cardiol. (2022) 117:40. doi: 10.1007/s00395-022-00948-1
36. Liu Z, Weng T, Cheng M, Lei T, Xiao D, Deng Q, et al. KRT14 knockdown reduces cisplatin resistance by lowering LRP11 expression levels in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Trans Cancer Res. (2025) 14:1786–98. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1795
37. Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yin R, Fang X, Miao R, Guan H, et al. Multi-omics characterization of type 2 diabetes mellitus-induced gastroenteropathy in the db/db mouse model. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1417255. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1417255
38. Sha W, Zhao B, Wei H, Yang Y, Yin H, Gao J, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates vascular endothelial dysfunction by stimulating macrophage M2 polarization via potentiating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacology. (2023) 112:154667. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154667
39. Dong J, Lu J, Cen Z, Tang Q, Li Y, Qin L, et al. Cardiac macrophages undergo dynamic changes after coxsackievirus B3 infection and promote the progression of myocarditis. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e29004. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29004
40. Liu L, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Jin L, Xiang N, Zhang M, et al. Eosinophils attenuate arthritis by inducing M2 macrophage polarization via inhibiting the IκB/P38 MAPK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 508:894–901. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.010
41. Zhou F, Mei J, Han X, Li H, Yang S, Wang M, et al. Kinsenoside attenuates osteoarthritis by repolarizing macrophages through inactivating NF-κB/MAPK signaling and protecting chondrocytes. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2019) 9:973–85. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.01.015
42. Seshacharyulu P, Pandey P, Datta K, and Batra SK. Phosphatase: PP2A structural importance, regulation and its aberrant expression in cancer. Cancer Letters. (2013) 335:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.02.036
43. Tschöpe C, Ammirati E, Bozkurt B, Caforio ALP, Cooper LT, Felix SB, et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: current evidence and future directions. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18:169–93. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00435-x
44. Caforio ALP, Adler Y, Agostini C, Allanore Y, Anastasakis A, Arad M, et al. Diagnosis and management of myocardial involvement in systemic immune-mediated diseases: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Disease. Eur Heart J. (2017) 38:2649–62. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx321
45. Trachtenberg BH and Hare JM. Inflammatory cardiomyopathic syndromes. Circ Res. (2017) 121:803–18. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310221
46. McCarthy RE 3rd, Boehmer JP, Hruban RH, Hutchins GM, Kasper EK, Hare JM, et al. Long-term outcome of fulminant myocarditis as compared with acute (nonfulminant) myocarditis. New Engl J Med. (2000) 342:690–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003093421003
47. Pollack A, Kontorovich AR, Fuster V, and Dec GW. Viral myocarditis–diagnosis, treatment options, and current controversies. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2015) 12:670–80. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.108
48. Zhang Y, Zhu L, Li X, Ge C, Pei W, Zhang M, et al. M2 macrophage exosome-derived lncRNA AK083884 protects mice from CVB3-induced viral myocarditis through regulating PKM2/HIF-1α axis mediated metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Redox Biol. (2024) 69:103016. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.103016
49. Almeida Paiva R, Martins-Marques T, Jesus K, Ribeiro-Rodrigues T, Zuzarte M, Silva A, et al. Ischaemia alters the effects of cardiomyocyte-derived extracellular vesicles on macrophage activation. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:1137–51. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14014
50. Xiong T, Zheng X, Zhang K, Wu H, Dong Y, Zhou F, et al. Ganluyin ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by inhibiting the enteric-origin LPS/TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 289:115001. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115001
51. Han-Wei Y, Ying-Da F, Na T, Feng-Chuan C, Ying-Feng L, Wei C, et al. Viral myocarditis: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic prospects. (2024) 982:176935. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176935
52. Satoh M, Nakamura M, Akatsu T, Shimoda Y, Segawa I, and Hiramori K. Toll-like receptor 4 is expressed with enteroviral replication in myocardium from patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol. (2004) 84:173–81. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700031
53. Bao J, Sun T, Yue Y, and Xiong S. Macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome activated by CVB3 capsid proteins contributes to the development of viral myocarditis. Mol Immunol. (2019) 114:41–8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.07.012
54. Lee W, Lee S, Choi J, Park JH, Kim KM, Jee JG, et al. Antithrombotic properties of JJ1, a potent and novel thrombin inhibitor. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:14862. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13868-1
55. Chen C, Cai S, Wu M, Wang R, Liu M, Cao G, et al. Role of cardiomyocyte-derived exosomal microRNA-146a-5p in macrophage polarization and activation. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:2948578. doi: 10.1155/2022/2948578
Keywords: myocarditis, cardiomyocytes, macrophages, large extracellular vesicles, MAPK
Citation: Jiang Y, You Y, Xie Y, Zhou S, Ma M and Han B (2025) Large extracellular vesicles derived from LPS-preconditioned cardiomyocytes alleviate myocarditis via mediating macrophage polarization and modulating p38 MAPK pathway. Front. Immunol. 16:1629676. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1629676
Received: 16 May 2025; Accepted: 14 August 2025;
Published: 09 September 2025.
Edited by:
Dong-Yun Ouyang, Jinan University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Jiang, You, Xie, Zhou, Ma and Han. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bo Han, YmhhbkBlbWFpbC5zZGZtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yanjie Jiang
Yanjie Jiang Yingnan You
Yingnan You Yaxue Xie
Yaxue Xie Shan Zhou
Shan Zhou Mengjie Ma4
Mengjie Ma4