- Department of Colorectal Surgery, Cancer Hospital of China Medical University, Liaoning Cancer Hospital & Institute, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally and the third most commonly diagnosed malignancy, posing a major threat to public health. Clinical manifestations such as altered bowel habits (e.g., constipation, diarrhea, or pencil-thin stools), rectal bleeding, and abdominal pain or bloating may indicate CRC. A hallmark of CRC is metabolic reprogramming, which enables tumor cells to meet the bioenergetic and biosynthetic demands of rapid proliferation and survival. This reprogramming encompasses dysregulated glycolysis, amino acid metabolism, and lipid metabolism, collectively driving tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and therapeutic resistance. Targeting metabolic reprogramming has emerged as a promising strategy in CRC therapy. Inhibitors of key metabolic enzymes and signaling pathways involved in glycolysis have demonstrated efficacy in preclinical and early clinical studies. Additionally, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has attracted increasing interest for its potential to modulate tumor metabolism. This review examines current evidence on marketed drugs, TCM, and the underlying metabolic mechanisms implicated in CRC treatment. While TCM shows promise as a complementary therapeutic approach, further research is essential to validate its clinical utility and mechanistic underpinnings.
1 Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a major global health challenge, ranking among the most commonly diagnosed malignancies and leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide (1, 2). In 2020, Asia accounted for over half of global CRC cases, with 51.8% of incidence and 52.4% of deaths occurring in the region, as reported by Global Cancer Statistics 2020 (3, 4). CRC is typically diagnosed at advanced stages due to the absence of symptoms in its early phases. The prognosis for stage IV CRC is particularly poor, with a 5-year survival rate of approximately 14% (5). Consequently, elucidating the mechanisms underlying CRC progression and drug resistance is crucial for improving therapeutic outcomes.
Metabolic reprogramming is a hallmark of CRC, enabling cancer cells to meet elevated bioenergetic and biosynthetic demands required for rapid proliferation, survival, and metastasis (6). This reprogramming encompasses multiple metabolic pathways—including those involved in glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism—which collectively support tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and resistance to therapy (7–9). Key genetic mutations frequently observed in CRC, such as those in APC, KRAS, TP53, MYC, and SMAD4, have been shown to drive global metabolic alterations by modulating the expression and activity of critical metabolic enzymes (10–12). These insights provide valuable opportunities to curb metastasis and recurrence, thereby enhancing patient survival and quality of life.
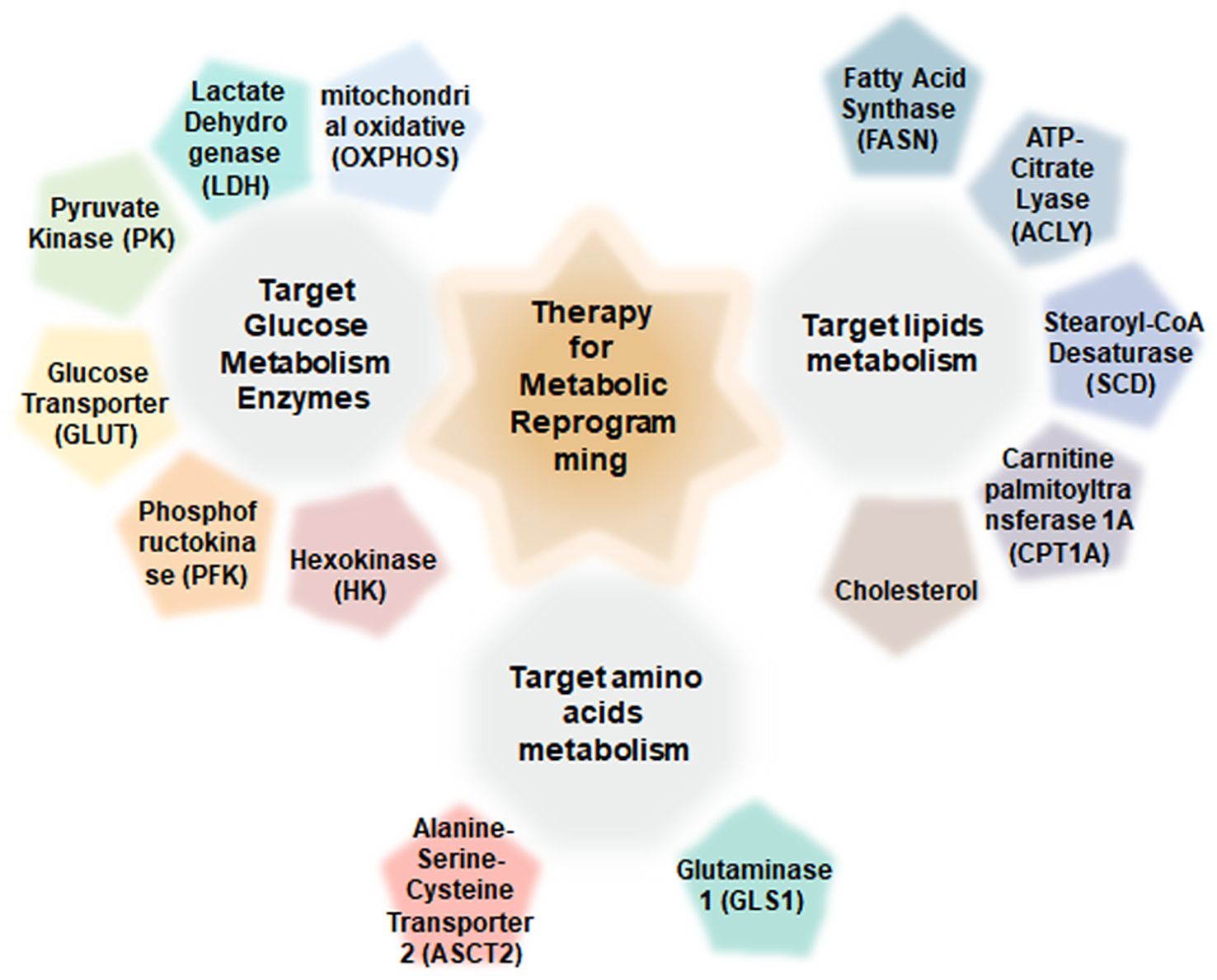
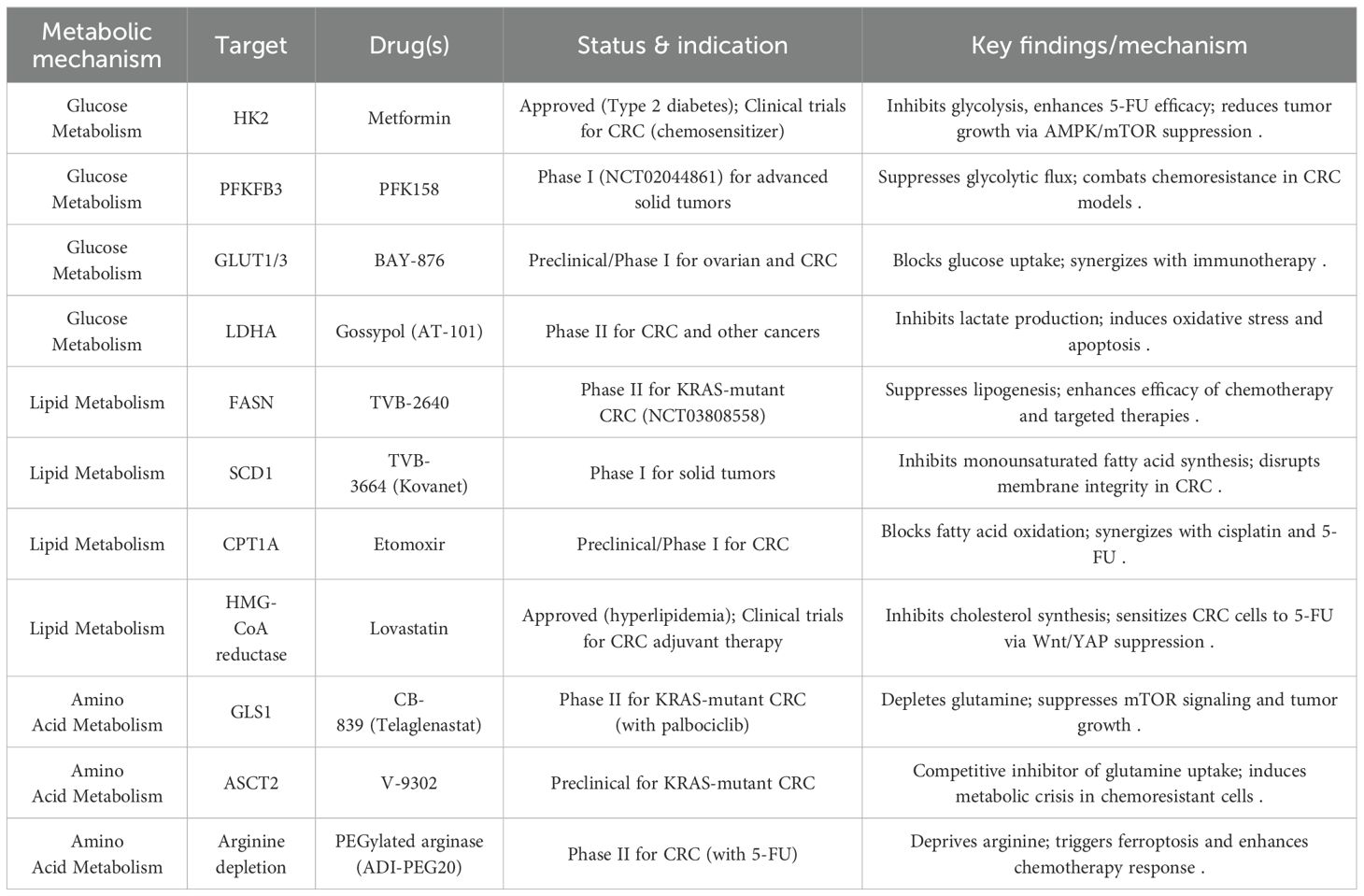
The current therapeutic landscape for CRC includes conventional chemotherapies, targeted agents, and immunotherapies (13). A deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying metabolic dysregulation in CRC may reveal novel therapeutic targets and foster the development of more effective treatments (14). Inhibitors targeting key metabolic enzymes are emerging as promising anticancer agents (15) (Figure 1).
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers compelling potential for CRC management, with several advantages over conventional therapies. Numerous chemotherapeutic agents derived from botanical sources—such as vinca alkaloids, taxanes, and camptothecins—exert their anticancer effects through disruption of metabolic pathways (16, 17). However, current research on TCM is predominantly conducted in China and often lacks diversity in cell line models, underscoring the need for broader, more inclusive studies (18). TCM not only suppresses tumor growth but also enhances the efficacy of standard chemotherapeutics by modulating cancer cell metabolism. Furthermore, due to its multi-targeted (polypharmacological) properties, TCM may alleviate cancer- and chemotherapy-induced symptoms and improve patient quality of life. Although TCM holds promise as an adjunct and chemosensitizer in CRC treatment, comprehensive research is essential to fully realize its clinical potential.
This review explores the roles of chemical and plant-derived drugs in targeting metabolic reprogramming in CRC, emphasizing their unique mechanisms of action, and outlining current challenges and future directions. A systematic search of electronic databases—including PubMed (Medline) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)—was conducted using predefined keywords such as “Traditional Chinese Medicine,” “Regulatory drugs,” “Colorectal cancer,” “Chemotherapeutic,” and “Metabolic reprogramming.” A total of 539 English-language publications were identified and synthesized. This study aims to advance the therapeutic application of plant-derived and regulatory drugs in CRC by elucidating their mechanisms of metabolic regulation and highlighting their potential to target critical metabolic pathways.
2 Conventional drugs and natural compounds that target glucose metabolism enzymes
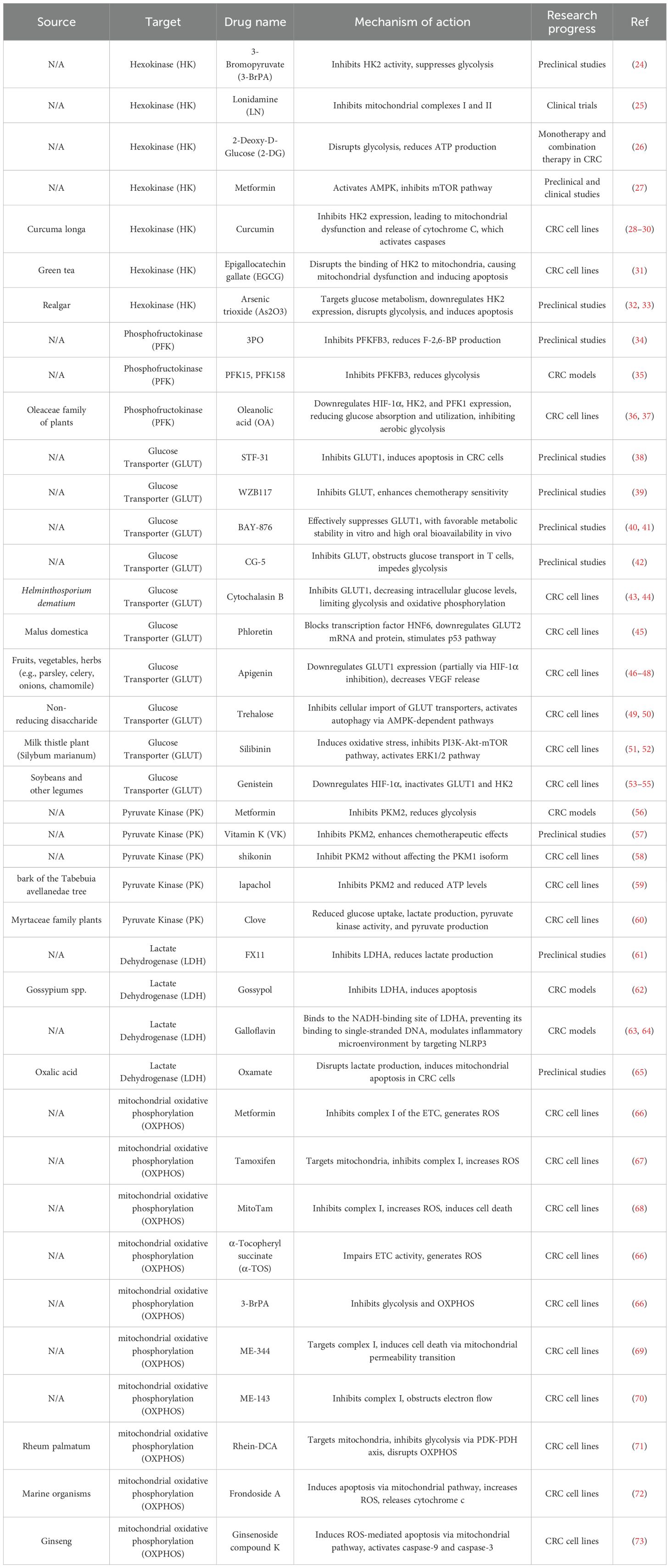
Glucose is a primary energy source and biosynthetic substrate for cancer cells. Reprogrammed glucose metabolism ensures a continuous supply of ATP and metabolic intermediates required for the synthesis of essential macromolecules—including lipids, amino acids, and nucleic acids—thus supporting rapid tumor cell proliferation (19). Simultaneously, lactate, a glycolytic byproduct, interacts with the tumor microenvironment to facilitate immune evasion and promote tumor progression (20). Mechanistically, key oncogenes and their associated enzymes—such as hexokinase (HK), phosphofructokinase (PFK), lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), and pyruvate kinase isoforms M1/2 (PKM1/2) (21)—play central roles in enhancing glycolysis, thereby driving tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis (22). Conversely, inhibition of glycolysis has been shown to suppress tumor growth in various cancers (23). Recent studies have identified several antineoplastic agents that modulate glucose metabolism by targeting key metabolic enzymes and proteins, as summarized in Table 1.
2.1 Targeting hexokinase
Hexokinase (HK), the first rate-limiting enzyme in glycolysis, catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate [G-6-P (23, 74)], a pivotal intermediate in glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and glycogen synthesis. Among glycolytic enzymes, HK is considered the most critical regulatory node in glucose metabolism. Mammalian cells express four HK isoforms: HK1, HK2, HK3, and HK4 (24).
Several HK inhibitors have demonstrated anticancer activity, with the most extensively studied being 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA), lonidamine (LN), 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG), and metformin. 3-BrPA directly inhibits HK2, thereby suppressing glycolytic flux in cancer cells (75). In addition to its glycolytic inhibition, 3-BrPA enhances the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents and mitigates multidrug resistance (MDR), a major mechanism of therapeutic failure in cancer by promoting drug efflux (25, 76). Lonidamine (LN), an adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT) ligand, inhibits mitochondrial complexes I and II and promotes the formation of mitochondrial permeability transition pores (77, 78). It is a novel glycolysis-targeting agent currently undergoing clinical evaluation for the treatment of various cancers, including ovarian, breast, and lung malignancies (26). 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG), a glucose analog, interferes with glycolysis and ATP synthesis, leading to energy depletion and cancer cell death. In CRC, 2-DG has shown antitumor efficacy both as monotherapy and in combination with chemotherapy and radiotherapy (26, 27). Metformin, another HK2 inhibitor, exerts its effects primarily by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which subsequently suppresses the mTOR pathway, thereby reducing glycolysis and cell proliferation (79). In CRC models, metformin decreases glucose uptake and lactate production, ultimately inhibiting tumor growth and enhancing chemosensitivity (28).
Several natural compounds also inhibit HK2 and exert pro-apoptotic effects in cancer cells. Curcumin, a polyphenolic compound derived from Curcuma longa, has been widely investigated for its anticancer potential (29, 30). By downregulating HK2, curcumin induces mitochondrial dysfunction and the release of cytochrome c, activating caspases and promoting apoptosis in CRC cells (31). Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a major polyphenol in green tea, inhibits the anchorage-independent growth of CRC cells by disrupting the interaction between HK2 and mitochondria. This mitochondrial disruption impairs energy metabolism and induces apoptosis (32). Arsenic trioxide (As2O3), an established therapeutic agent for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) (33), has also been shown to inhibit HK2 expression and glycolysis in cancer cells. By downregulating glucose metabolism and inducing apoptosis, As2O3 offers a unique mechanism for suppressing tumor growth (80).
2.2 Targeting phosphofructokinase
PFK, the second major rate-limiting enzyme in glycolysis, catalyzes the conversion of fructose-6-phosphate (F-6-P) to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-BP) (81). PFKFB3 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3) is a critical glycolytic regulator that promotes the synthesis of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP), a potent allosteric activator of PFK1. PFKFB3 is frequently overexpressed in various cancers and is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor survival outcomes (34).
Several PFKFB3 inhibitors—including 3PO, PFK15, and PFK158—have been identified as potential therapeutic agents. Administration of 3PO leads to a rapid reduction in glucose uptake, lactate production, and ATP synthesis. Additionally, 3PO can reprogram the metabolic profile of patient-derived tumor organoids to favor oxidative phosphorylation. In vivo, neoadjuvant treatment with 3PO promotes vascular normalization, alleviates hypoxia, and enhances tumor necrosis (35). PFK15 and PFK158, derivatives of 3PO, have also demonstrated efficacy in attenuating glycolytic activity and suppressing tumor growth in colorectal cancer (CRC) models. Notably, PFK15 exhibits approximately 100-fold greater inhibitory potency against PFKFB3 compared to 3PO (82). PFK15 significantly reduces F-2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP) levels in xenograft tumors and induces apoptosis in transformed cancer cells in both in vivo and in vitro settings (82). PFK158 is currently being evaluated in a Phase I, dose-escalation, multicenter clinical trial (NCT02044861) aimed at assessing its safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics in patients with advanced solid tumors. Preliminary findings revealed antitumor activity in 6 of 19 evaluable patients. Although the trial did not meet the desired efficacy endpoints, it underscored the therapeutic potential of targeting PFKFB3 in cancer treatment (36, 83).
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), oleanolic acid (OA) has emerged as a potential therapeutic candidate for gastric cancer (37). OA, a triterpenoid compound abundant in plants of the Oleaceae family, modulates aerobic glycolysis and tumor cell proliferation. Specifically, OA inhibits gastric cancer cell growth and reduces intracellular lactate levels by suppressing glucose uptake and utilization through downregulation of HIF-1α, HK2, and PFK1 expression (84).
2.3 Targeting glucose transporter
Glucose transporters (GLUTs) are integral membrane proteins responsible for facilitating glucose entry into cells. Among the best-characterized subtypes are GLUT1, GLUT2 (SLC2A2), GLUT3 (SLC2A3), and GLUT4 (SLC2A4), each exhibiting distinct regulatory mechanisms and kinetic properties, thereby playing specialized roles in maintaining cellular and systemic glucose homeostasis (85, 86). GLUT1 is implicated in chemoresistance via its regulation of glycolysis (87), while elevated expression of GLUT2 and GLUT3 correlates with poor prognosis in CRC (38). Consequently, GLUTs represent attractive therapeutic targets for disrupting glucose metabolism in CRC.
Several small-molecule inhibitors targeting GLUTs have shown preclinical promise, including STF-31, WZB117, BAY-876, and CG-5. STF-31 selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells without affecting normal tissues, thereby reducing CRC cell viability and proliferation (39). WZB117 triggers CRC cell death, particularly when delivered via hypoxia-responsive nanoparticles (88), and has also been shown to resensitize 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-resistant colon cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents, supporting its potential as an adjuvant for overcoming drug resistance (40). BAY-876 is a potent and selective GLUT1 inhibitor with high metabolic stability in vitro and favorable oral bioavailability in vivo; it has demonstrated antitumor efficacy in several cancers, including ovarian and triple-negative breast cancer (41, 42). CG-5, a thiazolidinedione derivative, inhibits GLUT-mediated glucose transport in T cells, disrupts glycolysis, and impairs Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation while promoting Treg cell development and reducing CD4+ T cell proliferation (43).
Natural compounds have emerged as promising GLUT inhibitors with potential anticancer effects in CRC. Key examples include cytochalasin B, phloretin, apigenin, trehalose, silibinin, and genistein. Cytochalasin B, the first identified GLUT1 inhibitor, has provided critical insights into CRC metabolism (44). By inhibiting GLUT1, it reduces intracellular glucose availability, thereby limiting substrates for glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (45). Phloretin, a natural GLUT2 inhibitor, suppresses GLUT2 expression by blocking the transcription factor HNF6. It also activates the p53 pathway, promoting cell cycle arrest and apoptosis—mechanisms that collectively inhibit tumor progression and enhance CRC cell sensitivity to other therapies (46). Apigenin, a flavonoid found in parsley, celery, onions, and chamomile (47), inhibits CRC cell proliferation and induces apoptosis through downregulation of GLUT1, partially via HIF-1α inhibition (48). Furthermore, Apigenin reduces VEGF secretion under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions, highlighting its anti-metastatic potential (49). Trehalose, a non-reducing disaccharide composed of two glucose units linked via an α,α-1,1-glycosidic bond (50), impedes glucose transporter activity and induces a starvation-like state characterized by ATP depletion. This metabolic stress activates autophagy through AMPK-dependent signaling, contributing to its anticancer effects (51). Silibinin, a flavonoid derived from Silybum marianum (52) (milk thistle), rapidly induces oxidative stress in CRC cells. It disrupts energy homeostasis by inhibiting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway and activating ERK1/2, leading to metabolic reprogramming (53). Genistein, an isoflavone abundant in soybeans and legumes (54), suppresses GLUT1 and HK2 by downregulating HIF-1α (55). It also induces cell cycle arrest and reduces invasion capacity in CRC cells (54).
2.4 Targeting pyruvate kinase
The third rate-limiting step in glycolysis is catalyzed by pyruvate kinase (PK), which converts phosphoenolpyruvate to (89)pyruvate. In mammals, PK exists in four isoforms: PKM1, PKM2, PKR, and PKL (56), among which PKM2 is predominant in cancer cells. Inhibition of PKM2 disrupts glycolysis and promotes apoptosis.
Three principal classes of PKM2 inhibitors have been identified: metformin, vitamin K, and shikonin. Metformin suppresses PKM2 expression and inhibits tumor growth (90) by modulating AMPK and mTOR signaling. In CRC xenograft models, metformin significantly reduces tumor volume through these pathways (57). Vitamin K (VK), a lipophilic naphthoquinone, exhibits isoform-specific inhibition, with VK3 and VK5 more potently targeting PKM2 over PKM1 (91). The combination of VK3 and vitamin C has shown enhanced anticancer efficacy, and clinical studies suggest VK3 can overcome resistance to chemotherapeutics such as doxorubicin and adriamycin (92). VK2 has also been reported to inhibit CRC cell proliferation by suppressing NF-κB signaling and inducing pro-apoptotic proteins (58).
Shikonin, a naturally occurring compound, selectively inhibits PKM2 without affecting PKM1. It reduces glucose uptake and lactate production, underscoring its therapeutic promise in cancer metabolism (59). Similarly, lapachol, a naphthoquinone derived from the bark of Tabebuia avellanedae, inhibits PKM2 activity and reduces ATP levels (60). An active fraction from clove (Eugenia caryophyllata or Syzygium aromaticum), referred to as AFC, has been shown to decrease glucose uptake, lactate production, PK activity, and pyruvate synthesis in CRC cells via PKM2 downregulation, ultimately attenuating aerobic glycolysis (93).
2.5 Targeting lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) catalyzes the final step of glycolysis by reversibly converting pyruvate to lactate. The human genome encodes four LDH isoforms—LDHA, LDHB, LDHC, and LDHD (61). Among these, LDHA and LDHB are highly expressed in malignancies, with LDHA predominantly converting pyruvate to lactate and LDHB catalyzing the reverse reaction. Elevated LDHA expression is associated with poor prognosis across multiple tumor types.
FX11, a small-molecule LDHA inhibitor, binds directly to its active site, blocking pyruvate-to-lactate conversion and thereby reducing cancer cell invasiveness and metastatic potential (94). In preclinical xenograft models of human lymphoma and pancreatic cancer, FX11 exhibited significant antitumor activity (95).
The natural compound gossypol, a nonselective LDHA inhibitor, has demonstrated potent anticancer effects in vitro and in animal models (62). In CRC cells, gossypol suppresses LDHA activity, lowering lactate production and glycolytic flux. This metabolic disruption induces bioenergetic and oxidative stress, resulting in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (96). In CRC xenograft models, gossypol markedly inhibited tumor growth and progression (63). Galloflavin, another LDHA inhibitor, binds to the enzyme’s NADH-binding site, blocking its activity and impeding CRC proliferation (64). Additionally, Galloflavin modulates the tumor inflammatory microenvironment by targeting NLRP3 and downregulating oncogenic c-Myc and P21, further enhancing its antitumor efficacy (65). Oxamate, an LDHA inhibitor, induces mitochondrial apoptosis in CRC cells by suppressing lactate synthesis. In combination with metformin or mTOR inhibitors, it shows synergistic antitumor effects in preclinical models (97).
2.6 Targeting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
To meet increased energy and biosynthetic demands, cancer cells often augment oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) (98).Inhibiting OXPHOS suppresses proliferation and tumorigenicity even in glycolysis-competent CRC cells, both in vitro and in patient-derived xenografts (66). Proper electron transport chain (ETC) function is essential for OXPHOS and ATP production, both critical for carcinogenesis. ETC inhibitors—such as metformin, tamoxifen, α-tocopheryl succinate (α-TOS), 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA), and ME-series inhibitors—disrupt respiratory complex activity, increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and trigger apoptosis (67). Tamoxifen, traditionally used as a selective estrogen receptor modulator in breast cancer, also targets mitochondria (68). Its derivative, MitoTam, localizes to mitochondria, inhibits complex I, elevates ROS, and induces cell death in breast cancer cells (69). The small-molecule inhibitor ME-344 effectively inhibits complex I and multiple pro-death signaling pathways associated with mitochondrial permeability transition in CRC (70). Both ME-143 and ME-344 disrupt NADH oxidation at complex I, blocking electron flow through the ETC. ME-344 further induces Bax translocation to the mitochondrial outer membrane, triggering mitochondrial permeability transition and releasing pro-apoptotic molecules (71).
The natural product Rhein, known for its mitochondrial-targeting properties, has been conjugated with dichloroacetate (DCA) to create Rhein-DCA, a dual glycolysis and OXPHOS inhibitor. Rhein-DCA accumulates in mitochondria, inhibits glycolysis via the PDK-PDH axis, and disrupts the respiratory chain. In CRC models, it induces oxidative stress, decreases lactate levels, and promotes immunogenic cell death (72). Frondoside A, a triterpene glycoside derived from marine organisms, induces mitochondrial apoptosis by decreasing antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and survivin, increasing ROS production, and promoting cytochrome c release (73). Similarly, ginsenoside compound K, a natural derivative of ginseng, activates ROS-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis, leading to cytochrome c release and caspase-9/-3 activation (99). These natural compounds offer promising avenues for CRC therapy by targeting mitochondrial function and enhancing oxidative stress-induced cell death.
3 Conventional drugs and natural compounds that target lipid metabolism
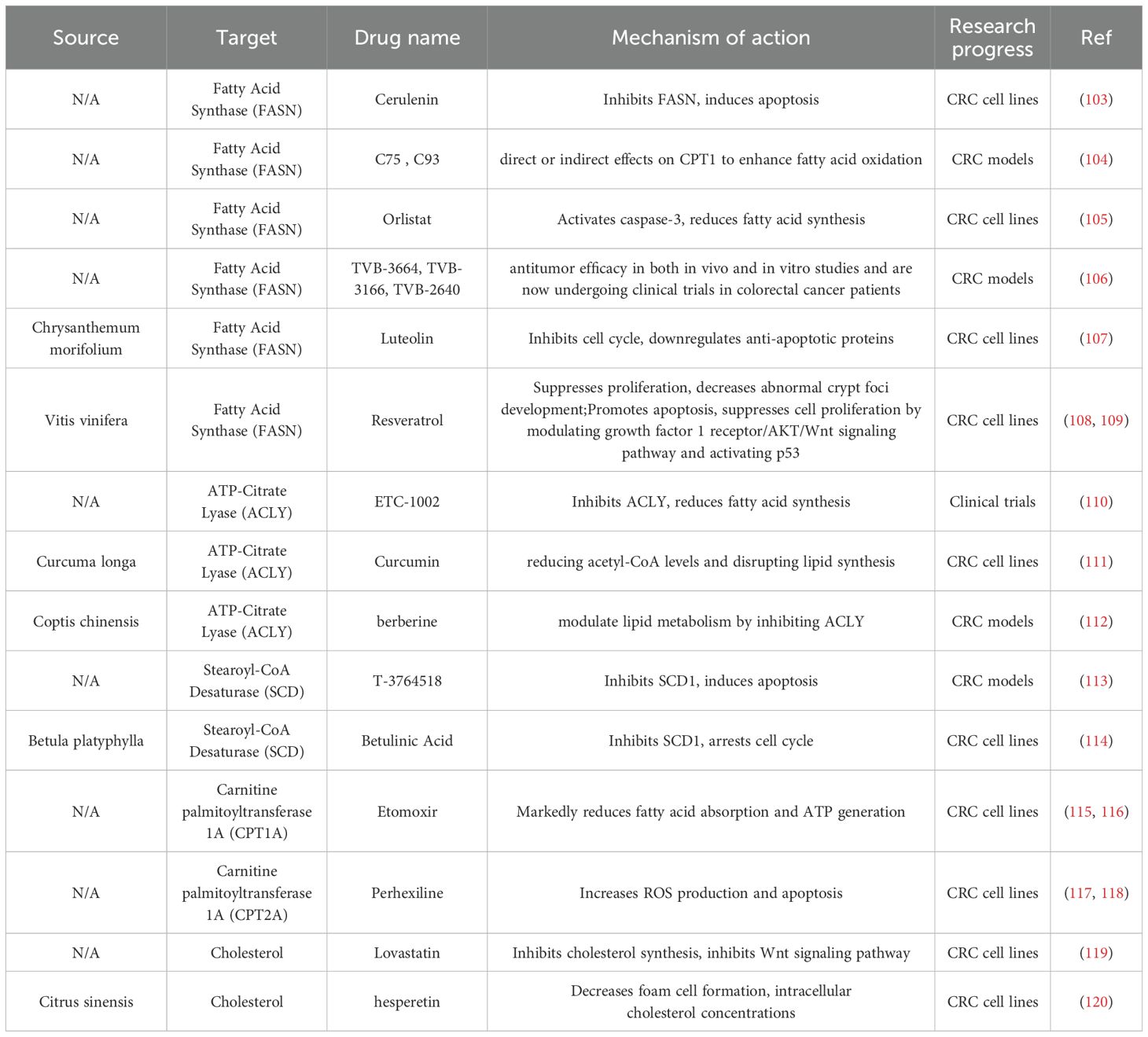
Modulating key regulators of lipid metabolism represents a promising strategy to counteract metabolic reprogramming in malignancies, underscoring the urgent need for novel therapeutic targets to improve cancer treatment and prognosis (100, 101). Although no lipid-targeting therapeutics are currently approved for CRC, numerous small-molecule inhibitors that interfere with lipid metabolism have shown preclinical efficacy and may enhance therapeutic outcomes when used in combination regimens (102)(Table 2).
3.1 Targeting fatty acid synthase
Fatty acid synthase (FASN), a pivotal enzyme in de novo lipogenesis, is inversely correlated with CRC prognosis (102, 121). Several FASN-specific inhibitors—such as cerulenin, C75, Orlistat, and TVB-series compounds—have demonstrated pro-apoptotic activity and therapeutic potential across various cancer types (103).
Cerulenin induces apoptosis in CRC cell lines by activating the caspase cascade and inhibiting DNA replication and S-phase progression (122). In HT-29 and LoVo cells, cerulenin also disrupts energy metabolism and inhibits mTOR signaling, thereby suppressing the malignant phenotype of CRC (123). Combination therapy with cerulenin and oxaliplatin may attenuate oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity, reduce required dosages, and improve long-term chemotherapeutic tolerance in clinical trials (124). C75 and C93 structurally related to cerulenin, also target FASN (105). Both compounds, including cerulenin, influence carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), thereby enhancing fatty acid oxidation (104, 105). Notably, treatment with C75 and cerulenin significantly reduces food intake and body weight in murine models (105). Orlistat, another FASN inhibitor, activates caspase-3 in a dose-dependent manner, induces G1 cell cycle arrest, and reduces both proliferation and lipid synthesis in HT-29 cells (106). Second-generation FASN inhibitors—TVB-3664, TVB-3166, and TVB-2640—exhibit potent antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo and are currently undergoing clinical evaluation in CRC patients (107).
In addition to synthetic compounds, natural products such as luteolin and resveratrol also exhibit FASN-inhibitory and anticancer properties. In HT-29 cells, luteolin downregulates anti-apoptotic proteins and induces cell cycle arrest (108). Resveratrol inhibits proliferation in Caco-2 cells, suppresses aberrant crypt foci formation (109), and induces apoptosis by modulating the IGF1R/AKT/Wnt pathway and activating p53 (125).
3.2 Targeting ATP‐citrate lyase
ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), which catalyzes the conversion of citrate to acetyl-CoA, acts as a rate-limiting enzyme in early lipid biosynthesis. ACLY has been implicated in promoting CRC progression in both in vitro and in vivo models (110). ETC-1002, a potent ACLY inhibitor, activates the AMPK pathway and suppresses lipid and cholesterol synthesis, although its clinical efficacy has been predominantly observed in cholesterol regulation (126). Nonetheless, co-administration of ETC-1002 with the IGF1R inhibitor linsitinib has demonstrated significant synergistic effects in inhibiting CRC metastasis (111). Curcumin, a natural compound, also inhibits ACLY activity, lowering acetyl-CoA levels and disrupting lipid synthesis essential for tumor growth (112). Other natural agents, such as berberine, similarly suppress ACLY activity, thereby attenuating tumor progression and metastatic potential (127).
3.3 Targeting stearoyl‐CoA desaturase
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD), an endoplasmic reticulum membrane enzyme, catalyzes the conversion of saturated fatty acids to monounsaturated fatty acids, thus facilitating lipid biosynthesis (128). Elevated expression of SCD1, the predominant isoform, is negatively associated with CRC prognosis (113). The novel oral SCD inhibitor T-3764518 has been shown to promote apoptosis by disrupting lipid raft integrity and inhibiting oncogenic signaling in CRC xenograft models (114). Betulinic acid, a natural SCD1 inhibitor derived from birch bark, induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and inhibits CRC growth (129). Furthermore, it reduces clonogenicity and induces apoptosis in CRC stem-like cells, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent targeting cancer stemness (130).
3.4 Targeting carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A (CPT1A) is a key rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid oxidation. CPT1A-mediated β-oxidation supports reactive oxygen species (ROS) detoxification and enhances reduced glutathione synthesis by increasing intracellular NADPH levels (115). Etomoxir, an irreversible CPT1 inhibitor, significantly impairs fatty acid uptake and ATP production without affecting tumor cell stemness or angiogenesis (115, 116). Notably, combining etomoxir with cisplatin enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in HCT116 colorectal cancer (CRC) cells in a dose-dependent manner (117). Another CPT1 inhibitor, perhexiline, induces ROS accumulation and apoptosis, thereby suppressing gastrointestinal tumor progression (118). Co-treatment with perhexiline and oxaliplatin further promotes apoptosis and sensitizes HCT116 cells to oxaliplatin (131).
3.5 Targeting cholesterol
Numerous studies have established a positive correlation between elevated dietary and plasma cholesterol levels and increased CRC risk, whereas statin-mediated inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis is associated with reduced risk (119, 132). Lovastatin inhibits both canonical Wnt signaling and alternative oncogenic pathways, such as YAP/TAZ, thereby suppressing CRC progression (133). At low doses, lovastatin promotes CRC cell differentiation and significantly increases their sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) (120). Hesperetin, a cholesterol-lowering flavonoid found in citrus juices, reduces foam cell formation, intracellular cholesterol levels, and cholesterol esterification, while enhancing cholesterol efflux in THP-1 macrophages (134). These findings suggest that hesperetin may also regulate cholesterol metabolism and inhibit CRC progression.
4 Conventional drugs and natural compounds that target amino acid metabolism
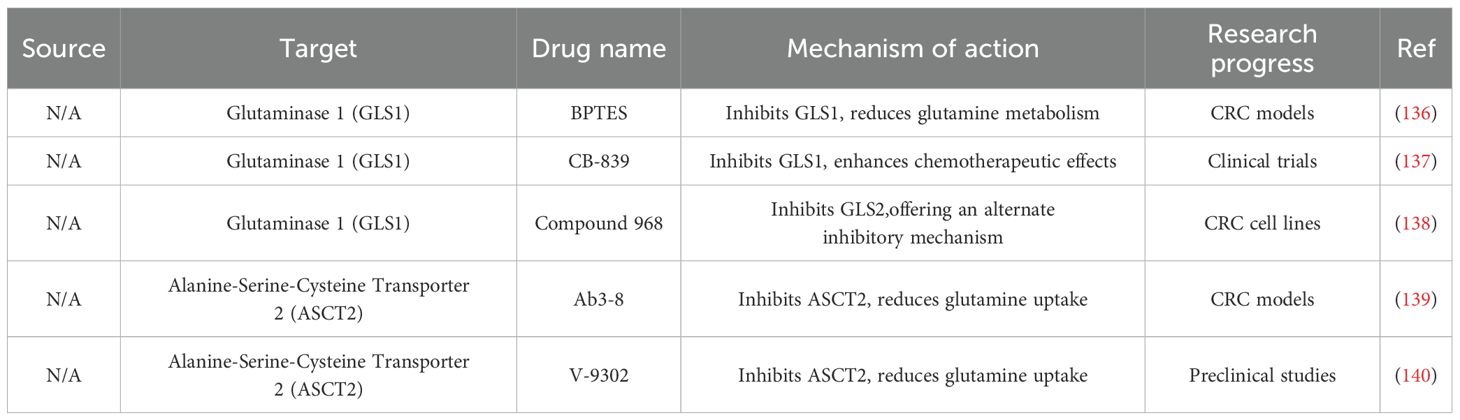
Amino acids serve as critical metabolic intermediates linking glucose and lipid metabolism. Under glutamine-deprived conditions, CRC cells activate autophagy to maintain amino acid homeostasis and intracellular metabolic balance (135)(Table 3).
4.1 Targeting glutaminase 1
Glutaminase 1 (GLS1) catalyzes the conversion of glutamine to glutamate, and its overexpression is strongly associated with poor prognosis in multiple cancers. Inhibiting GLS1 may disrupt glutamine metabolism and hinder tumor progression (136). BPTES (Bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,2,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide), a potent GLS1 inhibitor, suppresses glutamine utilization and inhibits CRC growth (141), although its clinical development is limited by poor solubility and metabolic instability (137). CB-839, a selective and clinically advanced GLS1 inhibitor, has demonstrated promising results. In a phase II trial, CB-839 combined with 5-FU extended progression-free survival beyond 6 months in 21.8% of patients, potentially through modulation of neutrophil extracellular traps (142). Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating CB-839 in combination with palbociclib for KRAS-mutant CRC and with nivolumab for melanoma and renal cell carcinoma (138). Compound 968, another GLS1 inhibitor with a distinct mechanism of action, has shown broad anticancer efficacy across multiple cell lines (143).
4.2 Targeting alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2
The amino acid transporter ASCT2 has emerged as a critical pro-tumorigenic factor, with elevated expression linked to poor prognosis in various cancers (139). In CRC, ASCT2 overexpression is strongly associated with KRAS mutations. Given the therapeutic resistance commonly observed in KRAS-mutant tumors, ASCT2 represents a promising target for this CRC subset (144, 145).
A monoclonal antibody against ASCT2, Ab3-8, significantly reduced glutamine uptake and inhibited AKT and ERK phosphorylation in SW1116 and HCT116 CRC cells in vitro. In vivo, Ab3–8 treatment markedly suppressed tumor growth in KRAS-mutant CRC xenografts. Additionally, V-9302, a small-molecule ASCT2 inhibitor, competitively blocks glutamine transport. Combined with ASCT2 gene silencing, V-9302 further impairs glutamine uptake and significantly inhibits tumor progression in preclinical models (140).
5 Current clinical status of the metabolic mechanisms in CRC
Based on the metabolic mechanisms of glucose, lipid, and amino acid pathways in CRC discussed in our previous dialogue and further supported by recent research, we present a comprehensive overview of drugs currently under clinical investigation or already approved for CRC treatment. These are categorized by metabolic targets in Table 4.
A systematic review of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in CRC identified 1,778 RCTs published from database inception through August 1, 2023 (146). The publication volume has steadily increased, reflecting growing interest and research activity in this area. However, most trials feature small sample sizes, typically ranging from 60 to 100 participants, and intervention durations commonly span 4, 8, or 12 weeks. Interventions include various TCM modalities such as decoctions, injections, patent medicines, and acupuncture.
Despite this growing body of work, several critical limitations remain in current TCM-CRC RCTs. First, the quality of randomization is generally poor. Only a minority of trials adequately report random sequence generation methods, increasing the risk of selection bias and undermining result validity. Second, blinding is rarely implemented effectively. The proportion of trials reporting blinding procedures is low and has declined in recent years, raising concerns about performance and detection biases due to participants and investigators being aware of treatment assignments (147). Third, small sample sizes limit statistical power, making many studies unable to detect clinically meaningful differences. Fourth, outcome measures are typically based on Western medical evaluation systems, which are complex and lack standardization. Moreover, TCM-specific indicators are rarely incorporated, and important aspects such as long-term efficacy, anxiety, and depression are insufficiently addressed.
To overcome these limitations, future TCM-CRC RCTs should adopt rigorous methodologies. This includes robust randomization techniques (e.g., computer-generated sequences, centralized randomization), effective blinding strategies (e.g., placebo controls, double-blind designs), and sample size determinations based on a priori power analyses. Multicenter collaborations may be necessary to achieve adequate recruitment. Studies should also incorporate long-term follow-up to assess the durability of TCM effects and evaluate both clinical and psychosocial outcomes, including quality of life. Furthermore, adherence to reporting standards such as the CONSORT guidelines will enhance transparency and reproducibility. Optimizing study protocols based on the shortcomings of prior research will be essential for improving trial quality.
In conclusion, although the number of TCM-CRC RCTs is increasing, substantial improvements in study design—particularly in randomization, blinding, sample size, and outcome measurement—are necessary to strengthen the reliability and credibility of evidence. Future research should aim to generate high-quality data to support the safety and efficacy of TCM in CRC prevention and treatment.
6 Major setbacks of TCMs in CRC management
Despite technological advancements, the application of TCM in CRC management still faces significant challenges. First, the inherent complexity of botanical mixtures in TCM complicates standardization, especially in multi-component formulations. This complexity also impedes the identification and quantification of bioactive constituents, which is essential for quality control. Second, mechanistic ambiguity remains a major obstacle; the multi-target interactions of TCM components are poorly defined, limiting our understanding of their pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles in clinical settings. Third, regulatory barriers persist due to the absence of harmonized guidelines for the approval of botanical drugs. These factors collectively hinder the clinical translation and widespread integration of TCM in CRC treatment. Addressing these challenges will require the application of advanced analytical technologies, multi-omics approaches, and the development of cohesive regulatory frameworks. As research progresses, the mechanisms of action of TCMs and their individual components will become increasingly well-characterized. While TCM holds considerable promise as an adjunctive therapy in CRC, further investigation is needed to fully elucidate its therapeutic potential and establish its role in evidence-based oncology.
7 Discussion
CRC is the third most common malignancy globally, posing significant challenges due to its high morbidity and mortality. Over the past two decades, research into CRC pathogenesis has highlighted the pivotal role of somatic genetic alterations acquired during tumorigenesis. Increasing evidence also underscores the critical influence of epigenetic modifications, which alter transcriptional programs and consequently affect gene expression and cellular behavior in CRC. Among the hallmarks of cancer, metabolic reprogramming has emerged as a defining feature and a promising therapeutic target in solid tumors. In CRC, enzymes involved in altered metabolic pathways are frequently dysregulated to support tumor progression and enhance resistance to cellular stress. Targeting these metabolic enzymes has transformed the therapeutic landscape and improved clinical outcomes in various cancers. Given the prevalence of metabolic enzyme modifications, a deeper understanding of the downstream effector mechanisms involved in metabolic reprogramming is essential for the development of targeted therapies (148–150). This review explores key metabolic alterations in CRC and their associated therapeutic agents. Exploiting genetic and metabolic vulnerabilities offers novel avenues for the development of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Although several pathway-specific inhibitors have demonstrated promising anticancer effects, most remain in preclinical stages, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive prospective studies to validate their clinical efficacy.
Traditional chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of CRC treatment, offering notable benefits such as the ability to suppress or eliminate proliferating cancer cells. Combination regimens such as FOLFOX and FOLFIRI have significantly improved overall survival rates. However, chemotherapy is often accompanied by substantial drawbacks. Adverse effects—including nausea, fatigue, and immunosuppression—can markedly impair patients’ quality of life (151, 152). Moreover, therapeutic efficacy is often limited in advanced or metastatic CRC, and drug resistance frequently emerges over time (153). Despite these limitations, chemotherapy continues to play a vital role in CRC management, particularly when combined with targeted therapies (154).
The integration of TCMs into CRC treatment presents several challenges that hinder their broader clinical application. The inherent complexity of multi-component botanical formulations complicates standardization and quality control, as the identification and quantification of active ingredients remain difficult. Additionally, the mechanisms of action for many TCM components are poorly defined, and their multi-target interactions are inadequately characterized. This mechanistic ambiguity impairs the elucidation of their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles in clinical contexts. Regulatory barriers further complicate clinical translation, as there is a lack of harmonized approval pathways for botanical drugs. Together, these factors limit the widespread adoption of TCMs in CRC therapy. Overcoming these challenges will require advances in analytical methodologies, multi-omics integration, and more adaptive regulatory frameworks to fully harness the therapeutic potential of TCMs in CRC management.
The interplay between tumor metabolism and immune regulation is pivotal in cancer progression and therapeutic response. Lactate, a key byproduct of aerobic glycolysis, plays a central role in establishing an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Beyond acidifying the extracellular milieu—thereby impairing T-cell function—lactate also acts as a signaling molecule, promoting angiogenesis and enhancing the immunosuppressive activities of MDSCs and Tregs (155).
Glucose metabolism is equally critical for T-cell activation. Effector T cells depend on glucose uptake via GLUT1 to sustain their functions. However, glucose competition within the tumor microenvironment—driven by the Warburg effect in cancer cells—can severely restrict T-cell activity (156). Metabolic reprogramming further supports the immunosuppressive functions of MDSCs and Tregs, with MDSCs exhibiting elevated arginine metabolism and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (157), while Tregs preferentially utilize fatty acid oxidation and specific amino acids (158). Notably, tumor metabolic activity has been linked to PD-L1 expression (159), suggesting that metabolic interventions could enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade. Early clinical trials are currently evaluating combinations of metabolic inhibitors—such as CA-170, YPD-30, MAX-10181, GS-4224, and BMS-986189 (160)—with immune checkpoint inhibitors across multiple cancer types, including lung cancer, melanoma, and CRC (161). While these approaches show promise, further studies are necessary to optimize therapeutic efficacy and mitigate adverse effects.
Author contributions
ZL: Writing – original draft, Investigation. XG: Investigation, Writing – original draft. XD: Writing – original draft, Data curation. TX: Investigation, Writing – original draft. SM: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. YL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was financially supported by the Project of Department of Science & Technology of Liaoning Province (No. 2023-MSLH-159 and 2024JH2/102600173).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung J, Chiu HM, Jung KW, Jun JK, Sekiguchi M, Matsuda T, et al. Increasing trend in young-onset colorectal cancer in asia: more cancers in men and more rectal cancers. Am J Gastroenterol. (2019) 114:322–29. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000133
2. Keum N and Giovannucci E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:713–32. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0189-8
3. Schreuders EH, Ruco A, Rabeneck L, Schoen RE, Sung JJ, Young GP, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: a global overview of existing programmes. Gut. (2015) 64:1637–49. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-309086
4. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
5. Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, and Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:233–54. doi: 10.3322/caac.21772
6. Hanahan D and Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. (2011) 144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
7. Qin R, Fan X, Huang Y, Chen S, Ding R, Yao Y, et al. Role of glucose metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer progression and drug resistance. Transl Oncol. (2024) 50:102156. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102156
8. Wu L, Yang B, Sun Y, Fan G, Ma L, Ma Y, et al. Isoprenaline inhibits histone demethylase LSD1 to induce cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2025) 25:34–47. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09937-3
9. Qian L, Fei Q, Zhang H, Qiu M, Zhang B, Wang Q, et al. lncRNA HOTAIR promotes DNA repair and radioresistance of breast cancer via EZH2. DNA Cell Biol. (2020). doi: 10.1089/dna.2020.5771
10. Sjoblom T, Jones S, Wood LD, Parsons DW, Lin J, Barber TD, et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. (2006) 314:268–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1133427
11. Satoh K, Yachida S, Sugimoto M, Oshima M, Nakagawa T, Akamoto S, et al. Global metabolic reprogramming of colorectal cancer occurs at adenoma stage and is induced by MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2017) 114:E7697–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710366114
12. Wang L, Qiu M, Wu L, Li Z, Meng X, He L, et al. Construction and validation of prognostic signature for hepatocellular carcinoma basing on hepatitis B virus related specific genes. Infect Agent Cancer. (2022) 17:60. doi: 10.1186/s13027-022-00470-y
13. Wang Q, Wang Y, Du L, Xu C, Sun Y, Yang B, et al. shRNA-mediated XRCC2 gene knockdown efficiently sensitizes colon tumor cells to X-ray irradiation in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. (2014) 15:2157–71. doi: 10.3390/ijms15022157
14. Yoshida GJ. Metabolic reprogramming: the emerging concept and associated therapeutic strategies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2015) 34:111. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0221-y
15. Wang Q, Sun Z, Du L, Xu C, Wang Y, Yang B, et al. Melatonin sensitizes human colorectal cancer cells to gamma-ray ionizing radiation in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123974
16. Demain AL and Vaishnav P. Natural products for cancer chemotherapy. Microb Biotechnol. (2011) 4:687–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2010.00221.x
17. Wang S, Fu JL, Hao HF, Jiao YN, Li PP, and Han SY. Metabolic reprogramming by traditional Chinese medicine and its role in effective cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 170:105728. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105728
18. Zamani M, Safari F, Siri M, Igder S, Khatami N, Dastghaib S, et al. Epigenetic modulation of autophagy pathway by small molecules in colorectal cancer: a systematic review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150:474. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05982-1
19. Hong X, Song R, Song H, Zheng T, Wang J, Liang Y, et al. PTEN antagonises Tcl1/hnRNPK-mediated G6PD pre-mRNA splicing which contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis. Gut. (2014) 63:1635–47. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305302
20. Zhang T, Suo C, Zheng C, and Zhang H. Hypoxia and metabolism in metastasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2019) 1136:87–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12734-3_6
21. Burns JS and Manda G. Metabolic pathways of the warburg effect in health and disease: perspectives of choice, chain or chance. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122755
22. Zhang J, Wang S, Jiang B, Huang L, Ji Z, Li X, et al. c-Src phosphorylation and activation of hexokinase promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:13732. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13732
23. Kim SM, Yun MR, Hong YK, Solca F, Kim JH, Kim HJ, et al. Glycolysis inhibition sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutation to irreversible EGFR inhibitors via translational suppression of Mcl-1 by AMPK activation. Mol Cancer Ther. (2013) 12:2145–56. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1188
24. Wilson JE. Isozymes of mammalian hexokinase: structure, subcellular localization and metabolic function. J Exp Biol. (2003) 206:2049–57. doi: 10.1242/jeb.00241
25. Cao X, Jia G, Zhang T, Yang M, Wang B, Wassenaar PA, et al. Non-invasive MRI tumor imaging and synergistic anticancer effect of HSP90 inhibitor and glycolysis inhibitor in RIP1-Tag2 transgenic pancreatic tumor model. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2008) 62:985–94. doi: 10.1007/s00280-008-0688-8
26. Berruti A, Bitossi R, Gorzegno G, Bottini A, Alquati P, De Matteis A, et al. Time to progression in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with epirubicin is not improved by the addition of either cisplatin or lonidamine: final results of a phase III study with a factorial design. J Clin Oncol. (2002) 20:4150–59. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.08.012
27. Lei X, Li K, Liu Y, Wang ZY, Ruan BJ, Wang L, et al. Co-delivery nanocarriers targeting folate receptor and encapsulating 2-deoxyglucose and alpha-tocopheryl succinate enhance anti-tumor effect in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. (2017) 12:5701–15. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S135849
28. Jia Y, Ma Z, Liu X, Zhou W, He S, Xu X, et al. Metformin prevents DMH-induced colorectal cancer in diabetic rats by reversing the warburg effect. Cancer Med. (2015) 4:1730–41. doi: 10.1002/cam4.521
29. Johnson SM, Gulhati P, Arrieta I, Wang X, Uchida T, Gao T, et al. Curcumin inhibits proliferation of colorectal carcinoma by modulating Akt/mTOR signaling. Anticancer Res. (2009) 29:3185–90.
30. Li W, Bai J, Fu L, Zhu Y, Fan G, Yang B, et al. Effects of curcumin on uterine leiomyoma in a rat model by inhibiting β-catenin/Wnt signaling pathway. Precis Med Res. (2023) 5:6. doi: 10.53388/PMR20230006
31. Ismail NI, Othman I, Abas F, LN H, and Naidu R. Mechanism of apoptosis induced by curcumin in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102454
32. Gao F, Li M, Liu WB, Zhou ZS, Zhang R, Li JL, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits human tongue carcinoma cells via HK2−mediated glycolysis. Oncol Rep. (2015) 33:1533–39. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3727
33. Yilmaz M, Kantarjian H, and Ravandi F. Acute promyelocytic leukemia current treatment algorithms. Blood Cancer J. (2021) 11:123. doi: 10.1038/s41408-021-00514-3
34. Han J, Meng Q, Xi Q, Wang H, and Wu G. PFKFB3 was overexpressed in gastric cancer patients and promoted the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Cancer biomark. (2017) 18:249–56. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160143
35. Edelmann M, Fan S, De Oliveira T, Goldhardt T, Sartorius D, Midelashvili T, et al. Tumor Vessel Normalization via PFKFB3 Inhibition Alleviates Hypoxia and Increases Tumor Necrosis in Rectal Cancer upon Radiotherapy. Cancer Res Commun. (2024) 4:2008–24. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0077
36. Zheng JB, Wong CW, Liu J, Luo XJ, Zhou WY, Chen YX, et al. Glucose metabolism inhibitor PFK-015 combined with immune checkpoint inhibitor is an effective treatment regimen in cancer. Oncoimmunology. (2022) 11:2079182. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2079182
37. Feng A, Yang S, Sun Y, Zhang L, Bo F, and Li L. Development and evaluation of oleanolic acid dosage forms and its derivatives. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:1308749. doi: 10.1155/2020/1308749
38. Guo Z, Cheng Z, Wang J, Liu W, Peng H, Wang Y, et al. Discovery of a potent GLUT inhibitor from a library of rapafucins by using 3D microarrays. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. (2019) 58:17158–62. doi: 10.1002/anie.201905578
39. Stine ZE, Schug ZT, Salvino JM, and Dang CV. Targeting cancer metabolism in the era of precision oncology. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2022) 21:141–62. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00339-6
40. Liu W, Fang Y, Wang XT, Liu J, Dan X, and Sun LL. Overcoming 5-Fu resistance of colon cells through inhibition of Glut1 by the specific inhibitor WZB117. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2014) 15:7037–41. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.17.7037
41. Wu Q, Ba-Alawi W, Deblois G, Cruickshank J, Duan S, Lima-Fernandes E, et al. GLUT1 inhibition blocks growth of RB1-positive triple negative breast cancer. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:4205. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18020-8
42. Ma Y, Wang W, Idowu MO, Oh U, Wang XY, Temkin SM, et al. Ovarian cancer relies on glucose transporter 1 to fuel glycolysis and growth: anti-tumor activity of BAY-876. Cancers (Basel). (2018) 11. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010033
43. Li W, Qu G, Choi SC, Cornaby C, Titov A, Kanda N, et al. Targeting T cell activation and lupus autoimmune phenotypes by inhibiting glucose transporters. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:833. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00833
44. Tilekar K, Upadhyay N, Iancu CV, Pokrovsky V, Choe JY, and Ramaa CS. Power of two: combination of therapeutic approaches involving glucose transporter (GLUT) inhibitors to combat cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2020) 1874:188457. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188457
45. Ulanovskaya OA, Cui J, Kron SJ, and Kozmin SA. A pairwise chemical genetic screen identifies new inhibitors of glucose transport. Chem Biol. (2011) 18:222–30. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.12.015
46. Lin ST, Tu SH, Yang PS, Hsu SP, Lee WH, Ho CT, et al. Apple Polyphenol Phloretin Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth via Inhibition of the Type 2 Glucose Transporter and Activation of p53-Mediated Signaling. J Agric Food Chem. (2016) 64:6826–37. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02861
47. Salehi B, Venditti A, Sharifi-Rad M, Kregiel D, Sharifi-Rad J, Durazzo A, et al. The therapeutic potential of apigenin. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061305
48. Bao YY, Zhong JT, Shen LF, Dai LB, Zhou SH, Fan J, et al. Effect of Glut-1 and HIF-1alpha double knockout by CRISPR/CAS9 on radiosensitivity in laryngeal carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2022) 26:2881–94. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17303
49. Fang J, Bao YY, Zhou SH, and Fan J. Apigenin inhibits the proliferation of adenoid cystic carcinoma via suppression of glucose transporter-1. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 12:6461–66. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4233
50. Opielka M, Sobocki B, Mierzejewska P, and Smolenski RT. The effect of trehalose on intracellular and extracellular nucleotide metabolism. A pilot study. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. (2020) 39:1400–09. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2020.1772492
51. Mardones P, Rubinsztein DC, and Hetz C. Mystery solved: Trehalose kickstarts autophagy by blocking glucose transport. Sci Signal. (2016) 9:fs2. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf1937
52. Bijak M. Silybin, a major bioactive component of milk thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaernt.)-chemistry, bioavailability, and metabolism. Molecules. (2017) 22. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111942
53. Raina K, Agarwal C, Wadhwa R, Serkova NJ, and Agarwal R. Energy deprivation by silibinin in colorectal cancer cells: a double-edged sword targeting both apoptotic and autophagic machineries. Autophagy. (2013) 9:697–713. doi: 10.4161/auto.23960
54. Pavese JM, Farmer RL, and Bergan RC. Inhibition of cancer cell invasion and metastasis by genistein. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2010) 29:465–82. doi: 10.1007/s10555-010-9238-z
55. Tuli HS, Tuorkey MJ, Thakral F, Sak K, Kumar M, Sharma AK, et al. Molecular mechanisms of action of genistein in cancer: recent advances. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:1336. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01336
56. Noguchi T, Yamada K, Inoue H, Matsuda T, and Tanaka T. The L- and R-type isozymes of rat pyruvate kinase are produced from a single gene by use of different promoters. J Biol Chem. (1987) 262:14366–71. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)47947-1
57. Geagea AG, Rizzo M, Jurjus A, Cappello F, Leone A, Tomasello G, et al. A novel therapeutic approach to colorectal cancer in diabetes: role of metformin and rapamycin. Oncotarget. (2019) 10:1284–305. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26641
58. Xv F, Chen J, Duan L, and Li S. Research progress on the anticancer effects of vitamin K2. Oncol Lett. (2018) 15:8926–34. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8502
59. Rathod B, Chak S, Patel S, and Shard A. Tumor pyruvate kinase M2 modulators: a comprehensive account of activators and inhibitors as anticancer agents. Rsc Med Chem. (2021) 12:1121–41. doi: 10.1039/d1md00045d
60. Alquraishi M, Puckett DL, Alani DS, Humidat AS, Frankel VD, Donohoe DR, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2: A simple molecule with complex functions. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 143:176–92. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.08.007
61. Doherty JR and Cleveland JL. Targeting lactate metabolism for cancer therapeutics. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:3685–92. doi: 10.1172/JCI69741
62. Feng Y, Xiong Y, Qiao T, Li X, Jia L, and Han Y. Lactate dehydrogenase A: A key player in carcinogenesis and potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. (2018) 7:6124–36. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1820
63. Masci D, Puxeddu M, Silvestri R, and La Regina G. Metabolic rewiring in cancer: small molecule inhibitors in colorectal cancer therapy. Molecules. (2024) 29. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092110
64. Kozal K, Jozwiak P, and Krzeslak A. Contemporary perspectives on the warburg effect inhibition in cancer therapy. Cancer Control. (2021) 28:1399508005. doi: 10.1177/10732748211041243
65. Guo L, Yang Y, Sheng Y, Wang J, Li W, Zhou X, et al. Galloflavin relieves the Malignant behavior of colorectal cancer cells in the inflammatory tumor microenvironment. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:752118. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.752118
66. Zhao XH, Han MM, Yan QQ, Yue YM, Ye K, Zhang YY, et al. DNA replication stress underpins the vulnerability to oxidative phosphorylation inhibition in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2025) 16:16. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07334-4
67. Dong L and Neuzil J. Targeting mitochondria as an anticancer strategy. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2019) 39:63. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0412-6
68. Bielcikova Z, Werner L, Stursa J, Cerny V, Krizova L, Spacek J, et al. Mitochondrially targeted tamoxifen as anticancer therapy: case series of patients with renal cell carcinoma treated in a phase I/Ib clinical trial. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2023) 15:2642693. doi: 10.1177/17588359231197957
69. Rohlenova K, Sachaphibulkij K, Stursa J, Bezawork-Geleta A, Blecha J, Endaya B, et al. Selective disruption of respiratory supercomplexes as a new strategy to suppress her2(high) breast cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2017) 26:84–103. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6677
70. Huang Q, Chen Z, Cheng P, Jiang Z, Wang Z, Huang Y, et al. LYRM2 directly regulates complex I activity to support tumor growth in colorectal cancer by oxidative phosphorylation. Cancer Lett. (2019) 455:36–47. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.04.021
71. Lim SC, Carey KT, and McKenzie M. Anti-cancer analogues ME-143 and ME-344 exert toxicity by directly inhibiting mitochondrial NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase (Complex I). Am J Cancer Res. (2015) 5:689–701.
72. Zhang Z, Tang S, Qi M, Zhao H, Wu M, and Huang SW. Mitochondria-targeting natural product rhein conjugated with dichloroacetate as the dual inhibitor of glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation to off energize cancer cells and induce ROS storm. Theranostics. (2025) 15:4909–29. doi: 10.7150/thno.107812
73. Al SJ, Mensah-Brown E, Parekh K, Thomas SA, Attoub S, Hellman B, et al. Frondoside A enhances the antiproliferative effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer. Eur J Cancer. (2014) 50:1391–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.01.002
74. Zhong X, He X, Wang Y, Hu Z, Huang H, Zhao S, et al. Warburg effect in colorectal cancer: the emerging roles in tumor microenvironment and therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:160. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01358-5
75. Geschwind JF, Georgiades CS, Ko YH, and Pedersen PL. Recently elucidated energy catabolism pathways provide opportunities for novel treatments in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. (2004) 4:449–57. doi: 10.1586/14737140.4.3.449
76. Ihrlund LS, Hernlund E, Khan O, and Shoshan MC. 3-Bromopyruvate as inhibitor of tumour cell energy metabolism and chemopotentiator of platinum drugs. Mol Oncol. (2008) 2:94–101. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2008.01.003
77. Belzacq AS, El HC, Vieira HL, Cohen I, Haouzi D, Metivier D, et al. Adenine nucleotide translocator mediates the mitochondrial membrane permeabilization induced by lonidamine, arsenite and CD437. Oncogene. (2001) 20:7579–87. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204953
78. Nath K, Guo L, Nancolas B, Nelson DS, Shestov AA, Lee SC, et al. Mechanism of antineoplastic activity of lonidamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2016) 1866:151–62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.08.001
79. Ma T, Tian X, Zhang B, Li M, Wang Y, Yang C, et al. Low-dose metformin targets the lysosomal AMPK pathway through PEN2. Nature. (2022) 603:159–65. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04431-8
80. Zhang HN, Yang L, Ling JY, Czajkowsky DM, Wang JF, Zhang XW, et al. Systematic identification of arsenic-binding proteins reveals that hexokinase-2 is inhibited by arsenic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:15084–89. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521316112
81. Chesney J. 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase and tumor cell glycolysis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2006) 9:535–39. doi: 10.1097/01.mco.0000241661.15514.fb
82. Clem BF, O’Neal J, Tapolsky G, Clem AL, Imbert-Fernandez Y, Kerr DN, et al. Targeting 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3) as a therapeutic strategy against cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. (2013) 12:1461–70. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0097
83. Chelakkot C, Chelakkot VS, Shin Y, and Song K. Modulating glycolysis to improve cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032606
84. Li Y, Xu Q, Yang W, Wu T, and Lu X. Oleanolic acid reduces aerobic glycolysis-associated proliferation by inhibiting yes-associated protein in gastric cancer cells. Gene. (2019) 712:143956. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.143956
85. Mueckler M and Thorens B. The SLC2 (GLUT) family of membrane transporters. Mol Aspects Med. (2013) 34:121–38. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.001
86. Thorens B and Mueckler M. Glucose transporters in the 21st century. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 298:E141–45. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00712.2009
87. Bukkuri A, Gatenby RA, and Brown JS. GLUT1 production in cancer cells: a tragedy of the commons. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. (2022) 8:22. doi: 10.1038/s41540-022-00229-6
88. Yang K, Yue L, Yu G, Rao L, Tian R, Wei J, et al. A hypoxia responsive nanoassembly for tumor specific oxygenation and enhanced sonodynamic therapy. Biomaterials. (2021) 275:120822. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120822
89. Yang W and Lu Z. Pyruvate kinase M2 at a glance. J Cell Sci. (2015) 128:1655–60. doi: 10.1242/jcs.166629
90. Kamarudin M, Sarker M, Zhou JR, and Parhar I. Metformin in colorectal cancer: molecular mechanism, preclinical and clinical aspects. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:491. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1495-2
91. Ivanova D, Zhelev Z, Getsov P, Nikolova B, Aoki I, Higashi T, et al. Vitamin K: Redox-modulation, prevention of mitochondrial dysfunction and anticancer effect. Redox Biol. (2018) 16:352–58. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.03.013
92. Chen J, Jiang Z, Wang B, Wang Y, and Hu X. Vitamin K(3) and K(5) are inhibitors of tumor pyruvate kinase M2. Cancer Lett. (2012) 316:204–10. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.039
93. Liu L, Xing G, Guo X, Chen H, Li J, Wang J, et al. Inhibition of colorectal cancer cell growth by downregulation of M2-PK and reduction of aerobic glycolysis by clove active ingredients. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1552486. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1552486
94. Granchi C, Roy S, Giacomelli C, Macchia M, Tuccinardi T, Martinelli A, et al. Discovery of N-hydroxyindole-based inhibitors of human lactate dehydrogenase isoform A (LDH-A) as starvation agents against cancer cells. J Med Chem. (2011) 54:1599–612. doi: 10.1021/jm101007q
95. Le A, Cooper CR, Gouw AM, Dinavahi R, Maitra A, Deck LM, et al. Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A induces oxidative stress and inhibits tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2010) 107:2037–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914433107
96. Ha MS, Han CW, Jeong MS, Cheon S, Ha KT, Kim HY, et al. Structural basis of lactate dehydrogenase A-gossypol complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2024) 733:150721. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150721
97. Yu H, Yin Y, Yi Y, Cheng Z, Kuang W, Li R, et al. Targeting lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) exerts antileukemic effects on T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2020) 40:501–17. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12080
98. Xu Y, Xue D, Bankhead AR, and Neamati N. Why all the fuss about oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS)? J Med Chem. (2020) 63:14276–307. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01013
99. Oh JM, Kim E, and Chun S. Ginsenoside compound K induces ros-mediated apoptosis and autophagic inhibition in human neuroblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174279
100. Bleve A, Durante B, Sica A, and Consonni FM. Lipid metabolism and cancer immunotherapy: immunosuppressive myeloid cells at the crossroad. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165845
101. Zaytseva Y. Lipid metabolism as a targetable metabolic vulnerability in colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020301
102. Mozolewska P, Duzowska K, Pakiet A, Mika A, and SledziNski T. Inhibitors of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation as potential anticancer agents in colorectal cancer treatment. Anticancer Res. (2020) 40:4843–56. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14487
103. Fhu CW and Ali A. Fatty acid synthase: an emerging target in cancer. Molecules. (2020) 25. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173935
104. Tu Y, Thupari JN, Kim EK, Pinn ML, Moran TH, Ronnett GV, et al. C75 alters central and peripheral gene expression to reduce food intake and increase energy expenditure. Endocrinology. (2005) 146:486–93. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0976
105. Orita H, Coulter J, Tully E, Abe M, Montgomery E, Alvarez H, et al. High levels of fatty acid synthase expression in esophageal cancers represent a potential target for therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. (2010) 10:549–54. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.6.12727
106. Chuang HY, Chang YF, and Hwang JJ. Antitumor effect of orlistat, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, is via activation of caspase-3 on human colorectal carcinoma-bearing animal. BioMed Pharmacother. (2011) 65:286–92. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2011.02.016
107. Falchook G, Infante J, Arkenau HT, Patel MR, Dean E, Borazanci E, et al. First-in-human study of the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of first-in-class fatty acid synthase inhibitor TVB-2640 alone and with a taxane in advanced tumors. Eclinicalmedicine. (2021) 34:100797. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100797
108. Lim DY, Jeong Y, Tyner AL, and Park JH. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells by the dietary compound luteolin. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2007) 292:G66–75. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00248.2006
109. Schneider Y, Vincent F, Duranton B, Badolo L, Gosse F, Bergmann C, et al. Anti-proliferative effect of resveratrol, a natural component of grapes and wine, on human colonic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. (2000) 158:85–91. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00511-5
110. Wen J, Min X, Shen M, Hua Q, Han Y, Zhao L, et al. ACLY facilitates colon cancer cell metastasis by CTNNB1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:401. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1391-9
111. Qiao C, Huang W, Chen J, Feng W, Zhang T, Wang Y, et al. IGF1-mediated HOXA13 overexpression promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through upregulating ACLY and IGF1R. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:564. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03833-2
112. Ramasamy TS, Ayob AZ, Myint HH, Thiagarajah S, and Amini F. Targeting colorectal cancer stem cells using curcumin and curcumin analogues: insights into the mechanism of the therapeutic efficacy. Cancer Cell Int. (2015) 15:96. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0241-x
113. Piccinin E, Cariello M, and Moschetta A. Lipid metabolism in colon cancer: Role of Liver X Receptor (LXR) and Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1). Mol Aspects Med. (2021) 78:100933. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2020.100933
114. Nishizawa S, Sumi H, Satoh Y, Yamamoto Y, Kitazawa S, Honda K, et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor activities of T-3764518, a novel and orally available small molecule stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. (2017) 807:21–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.03.064
115. Qu Q, Zeng F, Liu X, Wang QJ, and Deng F. Fatty acid oxidation and carnitine palmitoyltransferase I: emerging therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2016) 7:e2226. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.132
116. Hossain F, Al-Khami AA, Wyczechowska D, Hernandez C, Zheng L, Reiss K, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation modulates immunosuppressive functions of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhances cancer therapies. Cancer Immunol Res. (2015) 3:1236–47. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0036
117. Hernlund E, Ihrlund LS, Khan O, Ates YO, Linder S, Panaretakis T, et al. Potentiation of chemotherapeutic drugs by energy metabolism inhibitors 2-deoxyglucose and etomoxir. Int J Cancer. (2008) 123:476–83. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23525
118. Dhakal B, Tomita Y, Drew P, Price T, Maddern G, Smith E, et al. Perhexiline: old drug, new tricks? A summary of its anti-cancer effects. Molecules. (2023) 28. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083624
119. Jun SY, Brown AJ, Chua NK, Yoon JY, Lee JJ, Yang JO, et al. Reduction of squalene epoxidase by cholesterol accumulation accelerates colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:1194–207. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.009
120. Kodach LL, Jacobs RJ, Voorneveld PW, Wildenberg ME, Verspaget HW, van Wezel T, et al. Statins augment the chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells inducing epigenetic reprogramming and reducing colorectal cancer cell ‘stemness’ via the bone morphogenetic protein pathway. Gut. (2011) 60:1544–53. doi: 10.1136/gut.2011.237495
121. Lu T, Sun L, Wang Z, Zhang Y, He Z, and Xu C. Fatty acid synthase enhances colorectal cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway. Onco Targets Ther. (2019) 12:3339–47. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S199369
122. Huang PL, Zhu SN, Lu SL, Dai ZS, and Jin YL. Inhibitor of fatty acid synthase induced apoptosis in human colonic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. (2000) 6:295–97. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i2.295
123. Chang L, Wu P, Senthilkumar R, Tian X, Liu H, Shen X, et al. Loss of fatty acid synthase suppresses the Malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells by down-regulating energy metabolism and mTOR signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2016) 142:59–72. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2000-8
124. Wils J. Adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: past, present and future. J Chemother. (2007) 19:115–22. doi: 10.1179/joc.2007.19.2.115
125. Vanamala J, Reddivari L, Radhakrishnan S, and Tarver C. Resveratrol suppresses IGF-1 induced human colon cancer cell proliferation and elevates apoptosis via suppression of IGF-1R/Wnt and activation of p53 signaling pathways. BMC Cancer. (2010) 10:238. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-238
126. Bilen O and Ballantyne CM. Bempedoic acid (ETC-1002): an investigational inhibitor of ATP citrate lyase. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2016) 18:61. doi: 10.1007/s11883-016-0611-4
127. Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, Khalil AA, Imran M, Shah ZA, Emran TB, et al. Berberine as a potential anticancer agent: A comprehensive review. Molecules. (2021) 26. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237368
128. Ran H, Zhu Y, Deng R, Zhang Q, Liu X, Feng M, et al. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis in response to glucose by suppressing PTEN. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 37:54. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0711-9
129. Wang S, Zhang Y, Yang X, Wang K, Yang X, Zhang B, et al. Betulinic acid arrests cell cycle at G2/M phase by up-regulating metallothionein 1G inhibiting proliferation of colon cancer cells. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e23833. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23833
130. Potze L, di Franco S, Kessler JH, Stassi G, and Medema JP. Betulinic acid kills colon cancer stem cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2016) 11:427–33. doi: 10.2174/1574888x11666151203223512
131. Wang Y, Lu JH, Wang F, Wang YN, He MM, Wu QN, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid catabolism augments the efficacy of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Lett. (2020) 473:74–89. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.12.036
132. Poynter JN, Gruber SB, Higgins PD, Almog R, Bonner JD, Rennert HS, et al. Statins and the risk of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:2184–92. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043792
133. Li J, Pan J, Wang L, Ji G, and Dang Y. Colorectal cancer: pathogenesis and targeted therapy. Medcomm (2020). (2025) 6:e70127. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70127
134. Chen X, Zou D, Chen X, Wu H, and Xu D. Hesperetin inhibits foam cell formation and promotes cholesterol efflux in THP-1-derived macrophages by activating LXRalpha signal in an AMPK-dependent manner. J Physiol Biochem. (2021) 77:405–17. doi: 10.1007/s13105-020-00783-9
135. Li J, Song P, Zhu L, Aziz N, Zhou Q, Zhang Y, et al. Synthetic lethality of glutaminolysis inhibition, autophagy inactivation and asparagine depletion in colon cancer. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:42664–72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16844
136. Nan D, Yao W, Huang L, Liu R, Chen X, Xia W, et al. Glutamine and cancer: metabolism, immune microenvironment, and therapeutic targets. Cell Commun Signal. (2025) 23:45. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-02018-6
137. Gross MI, Demo SD, Dennison JB, Chen L, Chernov-Rogan T, Goyal B, et al. Antitumor activity of the glutaminase inhibitor CB-839 in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. (2014) 13:890–901. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0870
138. Jin J, Byun JK, Choi YK, and Park KG. Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. Exp Mol Med. (2023) 55:706–15. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00971-9
139. Hassanein M, Hoeksema MD, Shiota M, Qian J, Harris BK, Chen H, et al. SLC1A5 mediates glutamine transport required for lung cancer cell growth and survival. Clin Cancer Res. (2013) 19:560–70. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2334
140. Zhang Z, Liu R, Shuai Y, Huang Y, Jin R, Wang X, et al. ASCT2 (SLC1A5)-dependent glutamine uptake is involved in the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. (2020) 122:82–93. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0637-9
141. Liu HY, Zhang HS, Liu MY, Li HM, Wang XY, and Wang M. GLS1 depletion inhibited colorectal cancer proliferation and migration via redox/Nrf2/autophagy-dependent pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2021) 708:108964. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2021.108964
142. Li Y, Wu S, Zhao Y, Dinh T, Jiang D, Selfridge JE, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps induced by chemotherapy inhibit tumor growth in murine models of colorectal cancer. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134. doi: 10.1172/JCI175031
143. Choi YK and Park KG. Targeting glutamine metabolism for cancer treatment. Biomol Ther (Seoul). (2018) 26:19–28. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2017.178
144. Toda K, Nishikawa G, Iwamoto M, Itatani Y, Takahashi R, Sakai Y, et al. Clinical role of ASCT2 (SLC1A5) in KRAS-mutated colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081632
145. Liu WS, Yang B, Wang RR, Li WY, Ma YC, Zhou L, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of pyridine derivatives as selective SHP2 inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. (2020) 100:103875. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103875
146. Zhang D, Ni MX, Wei XM, Geng XC, Li L, and Cheng HB. Evidence map for randomized controlled trials of traditional Chinese medicine in prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2024) 49:6512–20. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240812.501
147. Li J, Liu Z, Chen R, Hu D, Li W, Li X, et al. The quality of reports of randomized clinical trials on traditional Chinese medicine treatments: a systematic review of articles indexed in the China National Knowledge Infrastructure database from 2005 to 2012. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2014) 14:362. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-362
148. Yang B, Li X, He L, and Zhu Y. Computer-aided design of temozolomide derivatives based on alkylglycerone phosphate synthase structure with isothiocyanate and their pharmacokinetic/toxicity prediction and anti-tumor activity. vitro. BioMed Rep. (2018) 8:235–40. doi: 10.3892/br.2018.1051
149. Yang B, Tang Q, Post J, Zhou H, Huang XB, Zhang XD, et al. Effect of radiation on the Notch signaling pathway in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. (2013) 31:698–706. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1255
150. Hou S, Tan J, Yang B, He L, and Zhu Y. Effect of alkylglycerone phosphate synthase on the expression profile of circRNAs in the human thyroid cancer cell line FRO. Oncol Lett. (2018) 15:7889–99. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8356
151. Ou SI, Janne PA, Leal TA, Rybkin II, Sabari JK, Barve MA, et al. First-in-human phase I/IB dose-finding study of adagrasib (MRTX849) in patients with advanced KRAS(G12C) solid tumors (KRYSTAL-1). J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:2530–38. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02752
152. Ballhausen A, Karthaus M, Fruehauf S, Graeven U, Muller L, Konig AO, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with fluorouracil and folinic acid with or without panitumumab as maintenance therapy: a prespecified secondary analysis of the PanaMa (AIO KRK 0212) trial. Eur J Cancer. (2023) 190:112955. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.112955
153. Napolitano S, Martini G, Ciardiello D, Del TS, Martinelli E, Troiani T, et al. Targeting the EGFR signalling pathway in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 9:664–76. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00479-X
154. Weng J, Li S, Zhu Z, Liu Q, Zhang R, Yang Y, et al. Exploring immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:95. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01294-4
155. Sun Q, Hong Z, Zhang C, Wang L, Han Z, and Ma D. Immune checkpoint therapy for solid tumours: clinical dilemmas and future trends. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:320. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01522-4
156. Courtnay R, Ngo DC, Malik N, Ververis K, Tortorella SM, and Karagiannis TC. Cancer metabolism and the Warburg effect: the role of HIF-1 and PI3K. Mol Biol Rep. (2015) 42:841–51. doi: 10.1007/s11033-015-3858-x
157. Gu XY, Yang JL, Lai R, Zhou ZJ, Tang D, Hu L, et al. Impact of lactate on immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1563303. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1563303
158. Li Q and Xiang M. Metabolic reprograming of MDSCs within tumor microenvironment and targeting for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2022) 43:1337–48. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00776-4
159. San-Millan I, Julian CG, Matarazzo C, Martinez J, and Brooks GA. Is lactate an oncometabolite? Evidence supporting a role for lactate in the regulation of transcriptional activity of cancer-related genes in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:1536. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01536
160. Zamani MR and Sacha P. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy: what lies beyond monoclonal antibodies? Med Oncol. (2025) 42:273. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02822-1
Keywords: metabolic reprogramming, colorectal cancer, clinical applications, regulatory therapy, traditional Chinese medicine, complementary treatment
Citation: Zhexian L, Xingqi G, Xinxin D, Tong X, Siping M and Yanxi L (2025) Clinical application prospects of traditional Chinese medicine as adjuvant therapy for metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer. Front. Immunol. 16:1630279. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1630279
Received: 17 May 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 15 July 2025.
Edited by:
Bing Yang, Krirk University, ThailandReviewed by:
Xi Yu, Macau University of Science and Technology, ChinaXin Hu, National Center for Child Health and Development (NCCHD), Japan
Jingchun Shi, Hong Kong Baptist University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhexian, Xingqi, Xinxin, Tong, Siping and Yanxi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ma Siping, bWFzaXBpbmdAY2FuY2VyaG9zcC1sbi1jbXUuY29t; Li Yanxi, bGl5YW54aUBjYW5jZXJob3NwLWxuLWNtdS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Liu Zhexian
Liu Zhexian Guo Xingqi†
Guo Xingqi† Ma Siping
Ma Siping Li Yanxi
Li Yanxi