- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Shandong Second Medical University, Weifang, China
- 2The Affiliated Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital of Qingdao University, Yantai, China
- 3Second Clinical Medical College of Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, China
- 4Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai, China
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that exerts diverse effects on immune regulation. It alleviates excessive inflammatory responses in the body by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the activation of antigen-presenting cells. In recent years, the therapeutic potential of IL-10 in various pulmonary inflammatory diseases has attracted extensive attention, including acute lung injury (ALI), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), asthma, and pulmonary fibrosis. IL-10 has also been studied in lung transplantation to improve the pro-inflammatory cytokine profile of donor lungs that do not meet conventional criteria. Nonetheless, its limited bioavailability, short half-life and potential for systemic adverse effects constrain its clinical application. To enhance its therapeutic efficacy and lung tissue targeting, intranasal administration and nebulized inhalation are the earliest methods applied in pulmonary diseases. Recombinant proteins, engineered mesenchymal stem cells, nanoparticle delivery systems, and gel delivery systems have also been developed and are undergoing preclinical trials. Many drug delivery platforms and pulmonary-targeted approaches have been shown to effectively increase the drug’s accumulation in the lungs and sustain its release, thus minimizing systemic toxicity. These IL-10-based therapies for pulmonary diseases can be broadly categorized into two main strategies: prolonging the half-life of exogenous IL-10 and enhancing the secretion of endogenous IL-10. The former mainly includes the development of IL-10 fusion proteins, nanoparticle delivery systems, and hydrogel delivery systems. The latter primarily involves IL-10 expression plasmids and IL-10-expressing adenoviruses. Despite its therapeutic potential, the clinical translation of IL-10 remains challenging. Its narrow therapeutic window constrains efficacy, and factors such as patient heterogeneity, disease stage, and the dynamic regulation of IL-10 signaling complicate the establishment of optimal dosing regimens. Emerging targeted delivery strategies provide opportunities to overcome these limitations by enabling precise spatial and temporal modulation of IL-10 activity. In light of these opportunities and challenges, this review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of current IL-10 delivery systems and to highlight strategies for their optimization to facilitate clinical translation in pulmonary diseases.
1 Introduction
Inflammation-associated lung diseases are pulmonary conditions in which inflammation plays a central role in the pathogenesis, progression, or exacerbation of the disease. These diseases often involve immune cell infiltration, cytokine production, tissue remodeling, and impaired gas exchange (1). Pneumonia remains a major global cause of illness and mortality, with particularly high death rates among children under five and adults over seventy. In 2021, excluding COVID-19, the global mortality rate from lower respiratory tract infections across all age groups was 27.7 per 100,000 population, resulting in a total of 2.18 million deaths (2). ALI is a critical condition characterized by neutrophil infiltration in the lung tissue, damage to the alveolar-capillary barrier, and pulmonary edema. These manifestations can lead to severe arterial hypoxemia and impaired carbon dioxide clearance (3). ARDS, a critical form of ALI, is associated with hospital mortality rates exceeding 40%, with major contributors including persistent pulmonary inflammation, disruption of the vascular endothelial barrier, continuous alveolar edema, and the progression to multiple organ dysfunction (4). The annual incidence of ARDS ranges from 3.65 to 78.9 cases per 100,000 population. The mortality rate of non-COVID-related ARDS remains relatively stable, at approximately 30%–35% for mild ARDS and 45%–50% for severe ARDS (5). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is commonly associated with an increase in B cell numbers, specifically in the small airway lymphoid follicles (6). It is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by persistent airflow obstruction and respiratory symptoms, and it is the third leading cause of death worldwide. As of 2017, the number of people with chronic respiratory diseases worldwide reached 544.9 million, of which approximately 55% of cases were attributed to COPD (7). Asthma is a chronic respiratory inflammation caused by intermittent bronchospasm, leading to dyspnea and wheezing, affecting approximately 300 million people globally. As of 2023, the prevalence of asthma is approximately 10% among children and adolescents worldwide, and around 6%–7% among adults (8). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the leading type of interstitial lung disease. IPF typically leads to respiratory failure, with a median survival of only 2.5 to 3.5 years (9). A major challenge in the treatment of IPF is diagnostic delay, with the typical time from symptom onset to IPF diagnosis being 1.7 years (10). The abnormal deposition of collagen and other extracellular matrix (ECM) components within the lung parenchyma is a pathological hallmark of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), released during epithelial cell injury, and its downstream mediator connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), contribute to the increased ECM accumulation, which often leads to impaired gas exchange and altered lung function (11).
IL-10 is a multifunctional anti-inflammatory cytokine that plays a crucial role in inhibiting excessive immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis (12). However, the therapeutic use of IL-10 encounters multiple obstacles in clinical settings, such as its short half-life in vivo (13), pro-inflammatory side effects due to its pleiotropic effects (14), and the need for precise delivery to the site of pulmonary inflammation. To overcome these limitations, researchers have developed various IL-10 therapeutic strategies, including IL-10 gene therapy, fusion proteins, and nanoparticle delivery systems.
This article provides a concise overview of the immunomodulatory functions of IL-10 and its therapeutic potential in a variety of lung diseases. We discuss current IL-10-based therapeutic modalities and emphasize recent advancements in lung-targeted delivery strategies, with the goal of offering theoretical and technical insights to support the further development of IL-10 as an effective treatment for lung inflammation-associated disorders. Figure 1 summarizes the core arguments of this review in a graphical abstract.
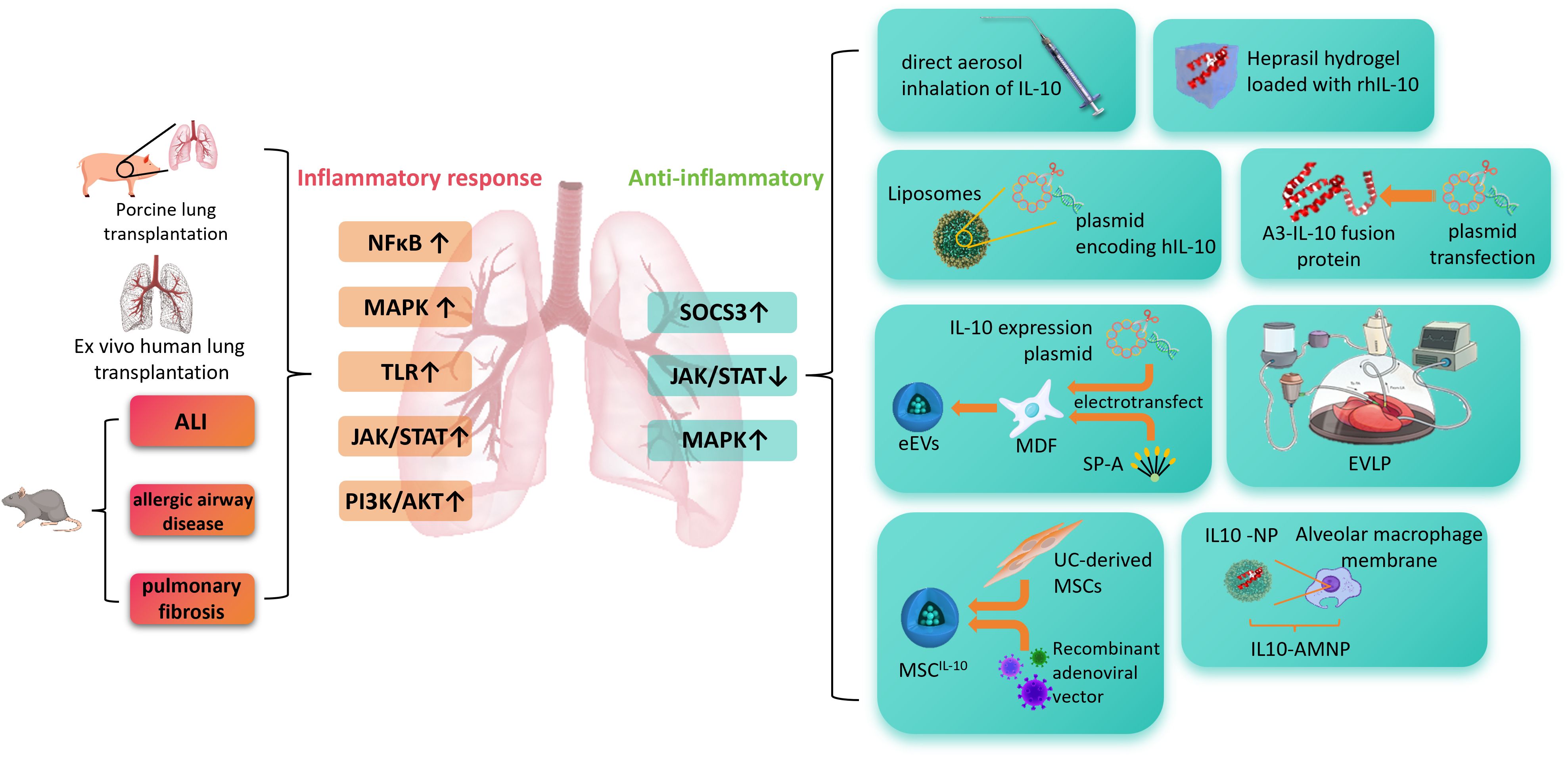
Figure 1. This figure illustrates the role of IL-10 in pulmonary inflammation-related diseases and its delivery strategies. In pathological conditions such as acute lung injury, allergic airway disease, and pulmonary fibrosis, signaling pathways including NF-κB, MAPK, TLR, JAK/STAT, and PI3K/AKT are excessively activated, leading to inflammatory responses. IL-10 exerts anti-inflammatory effects by activating SOCS3 and modulating JAK/STAT and MAPK pathways. Various IL-10 delivery approaches are shown on the right, including aerosol inhalation, hydrogel-based release, liposome/plasmid delivery, A3-IL-10 fusion protein, electroporation with ex vivo lung perfusion, mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-based vectors, and nanoparticle systems combined with macrophage membranes, which enhance its stability and targeting efficiency. ALI, acute lung injury; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TLR, Toll-like receptor; JAK/STAT, Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription; PI3K/AKT, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; rIL-10, recombinant interleukin-10; hIL-10, human interleukin-10; A3-IL-10, von Willebrand factor A3 domain–interleukin-10 fusion protein; MDF, mouse dermal fibroblasts; SP-A, surfactant protein A; eEVs, engineered extracellular vesicles; EVLP, ex vivo lung perfusion; UC-MSCs, umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells; MSCIL-10, mesenchymal stem cells expressing interleukin-10; NP, nanoparticle; IL10-AMNP, interleukin-10–alveolar macrophage membrane nanoparticle.
2 Therapeutic effects of IL-10
Since the identification of the IL-10 family, researchers have been working to design IL-10-based therapeutic approaches for a range of conditions, including autoimmune disorders, infections, tissue damage and cancer (15). IL-10 is widely expressed in various cells from both the innate and adaptive immune systems. Macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells (DCs), natural killer (NK) cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, as well as B cells, all express IL-10 (16). IL-10 is the first cytokine identified in the major three subfamilies of the IL-10 family (17) and is initially named cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF). It is secreted by activated CD4+ T helper (Th) 2 cells and is known to inhibit the synthesis of Th1 cytokines (18).
2.1 Regulation of immune inflammation by IL-10
IL-10 and its receptors are expressed in vertebrates, forming an ancient anti-infection mechanism that constitutes the inflammation resolution phase of host defense (19). IL-10 primarily targets antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as monocytes and macrophages, inhibiting their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This mainly includes tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1β, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), MCP-1, and IP-10 (20). IL-10’s inhibitory effects on IL-1 and TNF are crucial for its anti-inflammatory activity, as these cytokines synergize in inflammation and amplify the inflammatory response by inducing secondary mediators such as chemokines, prostaglandins, and platelet-activating factor (PAF, 16). IL-10 interferes with antigen presentation primarily by reducing the expression of major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II), co-stimulatory molecules, and adhesion molecules (21, 22). When directly acting on T cells, IL-10 can induce their anergy, suppressing T cell proliferation and cytokine production (23). IL-10 can also inhibit IL-12 and IL-23, which are required for CD4+ T cell differentiation (24).
Figure 2 provides a simplified illustration of the downstream pathways involving IL-10 and its anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
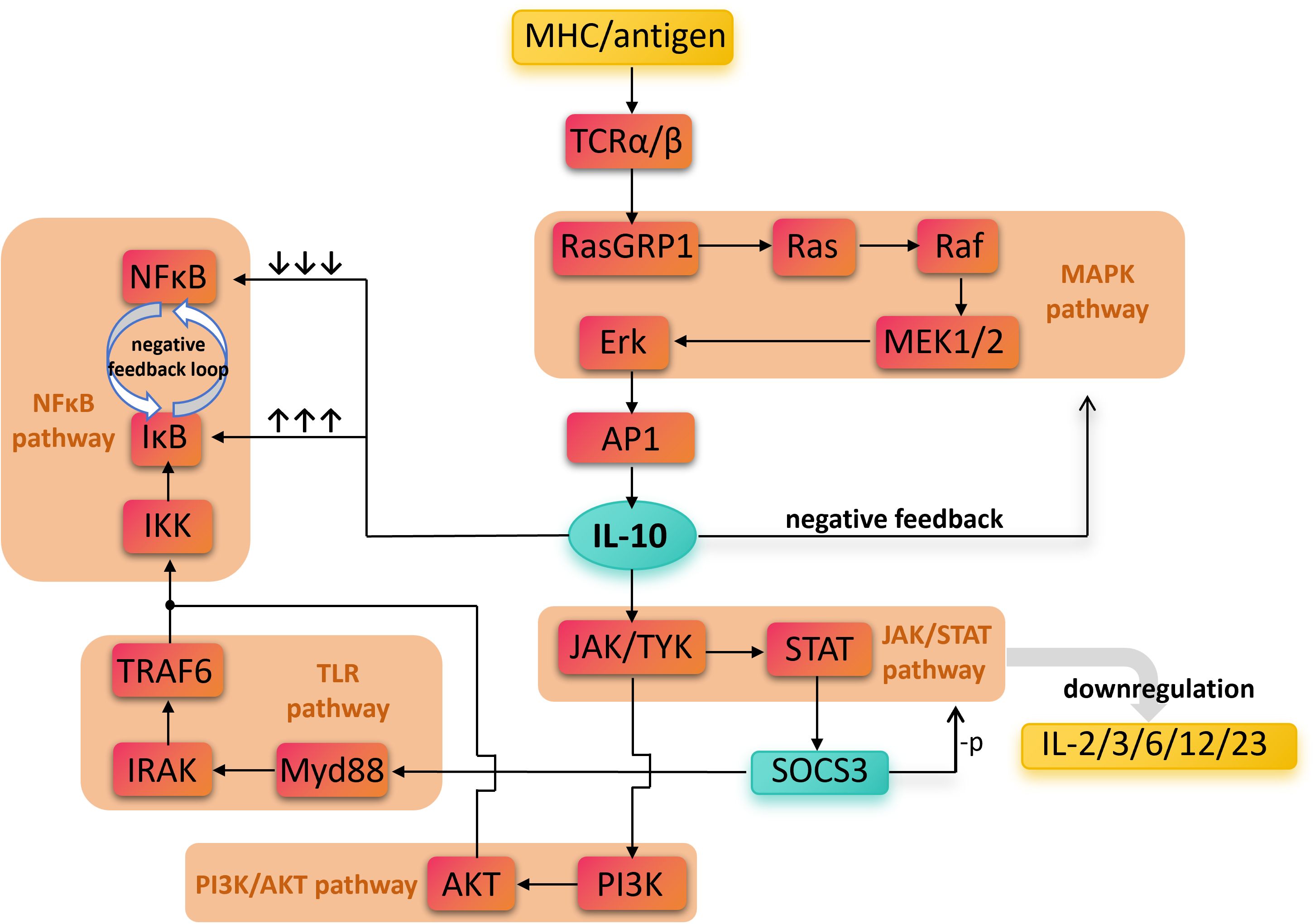
Figure 2. The direct and indirect biochemical pathways involved in IL-10’ s anti-inflammatory effects. Antigen recognition activates multiple pro-inflammatory pathways, including TCR, NF-κB, TLR, and PI3K/AKT, leading to inflammatory responses. In contrast, IL-10 signals through the JAK/STAT pathway to induce SOCS3 expression, which suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2, IL-3, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-23. Overall, the figure emphasizes IL-10 as a key anti-inflammatory mediator that negatively regulates inflammatory signaling, maintains immune homeostasis, and prevents excessive immune damage. Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, NF-κB; Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, MAPK; Toll-Like Receptor, TLR; Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B, PI3K/AKT; Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription, JAK/STAT; Major Histocompatibility Complex, MHC; T Cell Receptor alpha/beta, TCRα/β; Ras Guanyl Releasing Protein 1, RasGRP1; Rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog, Ras; Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma kinase, Raf; Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 1/2, MEK1/2; Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase, Erk; Activator Protein 1, AP-1; IκB Kinase, IKK; Inhibitor of κB, IκB; TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6, TRAF6; Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase, IRAK; Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response 88, Myd88; Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase, PI3K; Protein Kinase B (also called PKB), AKT; Janus Kinase/Tyrosine Kinase, JAK/TYK; Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription, STAT; Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3, SOCS3; Interleukin, IL.
2.2 Therapeutic potential of IL-10 in pulmonary diseases
In a study using a mouse ALI model, Huan Qin and colleagues (25) demonstrated that direct inhalation of rhIL-10 effectively ameliorated pulmonary cytokine storm. Interventions using placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (pMSCs, 26), human fetal lung-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hFL-MSCs, 27), or carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1A, 28) have all found that the suppression of the ALI inflammatory response is IL-10-mediated, and blocking the IL-10 signaling pathway exacerbates the inflammatory response in ALI (29). ARDS is the most severe form of ALI, often caused by pulmonary infections, trauma, inflammation, or hemorrhagic shock (30). IL-10 also shows strong therapeutic potential in ARDS caused by COVID-19 (31).
COPD is a classic example of chronic pulmonary inflammation. The reduced numbers of IL-10-secreting regulatory B cells (IL-10+ B-reg, 32) and IL-10-secreting regulatory T cells (IL-10+ T-reg, 33) in COPD patients indicate that IL-10 expression is negatively correlated with the progression of COPD. In a rat model of COPD, the alleviation of pulmonary inflammation induced by allopurinol was mediated through the enhancement of endogenous IL-10 (34). In a cell-based study simulating chronic airway inflammation, fish oil intervention reduced cellular oxidative stress by enhancing the expression of IL-10 (35). These findings suggest that IL-10 could serve as a biomarker for assessing the severity of COPD. The exact mechanism of IL-10 in human asthma remains unclear, but a decrease in IL-10 expression has been closely linked to the exacerbation of asthma in clinical patients, as well as increased eosinophils and circulating IgE levels (36). A study on viral infections leading to childhood asthma also confirmed the correlation between decreased IL-10 levels and asthma incidence (37). Insufficient IL-10 production by T cells is considered a contributing factor to allergic asthma, as it impairs the regulation of the Th2 response (38). Current clinical antifibrotic treatments are unable to reverse disease progression (39). IL-10 delivery can inhibit bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the production of TGF-β1 from alveolar macrophages, lung fibroblasts, and myofibroblasts (40). Conversely, IL-10 deficiency accelerates the progression of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice (41). The combination of IL-10 with rapamycin has been shown to inhibit the progression of pulmonary fibrosis with greater efficiency (42). These findings suggest that IL-10 has the potential to become a new antifibrotic agent.
According to conventional criteria for lung transplantation, donor lungs with high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines are often excluded from transplantation (43), as transplanting such lungs significantly increases the 30-day mortality rate of recipients (44). In the context of donor lung shortages and the increasing maturity of ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) technology (45), researchers conducted EVLP using porcine donor lungs and administered adenovirus-mediated IL-10 (AdhIL-10) into the bronchi. This strategy significantly improved donor lung function, with no apparent adverse effects observed at the multi-organ level (46).
2.3 IL-10 formulations
Endogenously secreted IL-10 plays a crucial role in limiting excessive inflammatory responses, but its plasma concentration is influenced by multiple factors such as pathological states, its half-life, and signal regulation. Like many cytokines, IL-10 faces key limitations in therapeutic applications, including signaling redundancy, pleiotropic effects, and a narrow therapeutic window resulting from its short half-life (47). Therefore, relying solely on endogenous IL-10 is often insufficient to meet therapeutic needs, and exogenous IL-10 formulations are necessary for treatment.
2.3.1 Recombinant human IL-10
Recombinant human IL-10 (rhIL-10) is produced in Escherichia coli that has been transfected with plasmids carrying the rhIL-10 gene. The produced IL-10 protein is identical to natural human IL-10, except for one methionine residue at the N-terminus. Recombinant mouse IL-10 (rmuIL-10) shares about 73% amino acid sequence homology with rhIL-10 (48). While rhIL-10 still retains some activity in mouse cells, rmuIL-10 does not exhibit significant effects in human cells (49). Therefore, rhIL-10 is the most commonly used form in current research. However, unmodified rhIL-10 has a terminal half-life of only 2.3 to 3.7 hours in vivo (13), which severely limits its sustained therapeutic effects in clinical practice. In a psoriasis treatment study, only high-dose and frequent administration regimens could maintain a relatively ideal therapeutic effect (50).
2.3.2 IL-10 gene therapy strategies
IL-10 gene therapy strategies often use plasmids, lentiviruses, or adeno-associated viruses (AAV) as vectors to deliver the IL-10 encoding gene into host cells, with the primary goal of increasing endogenous IL-10 expression. Recombinant adenoviruses are typically constructed using standard homologous recombination methods (51). To generate recombinant adenoviral vectors expressing rhIL-10, a common approach is to isolate the cDNA sequence encoding IL-10 from the pDSRG-IL-10 plasmid (52). The safety of adenovirus gene therapy has been confirmed by several studies (46, 53). Lentiviruses, a type of retrovirus, can also be used to mediate IL-10 gene therapy (54). To construct a lentivirus that drives human IL-10 expression, IL-10 cDNA is amplified by PCR and inserted into the lentiviral backbone vector, followed by packaging using a classic three-plasmid system (55). The clinical safety of lentiviral gene therapy has also been established (56). Plasmids, which are double-stranded circular DNA molecules with autonomous replication capabilities, are commonly used as high-efficiency expression vectors for transient transfection (57) and to mediate IL-10 gene expression (58).
2.3.3 IL-10 fusion proteins
These modified cytokines typically have a longer half-life and can enhance the efficacy of IL-10 in specific disease models. Vascular leakage in fibrotic tissue exposes extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins that are typically found in the blood circulation (59, 60), and von Willebrand factor A3 (VWF-A3) can bind to type I and type III collagen (61). Figure 3 illustrates how the VWF-A3 domain enables VWF dimers to target collagen exposed at sites of vascular injury.
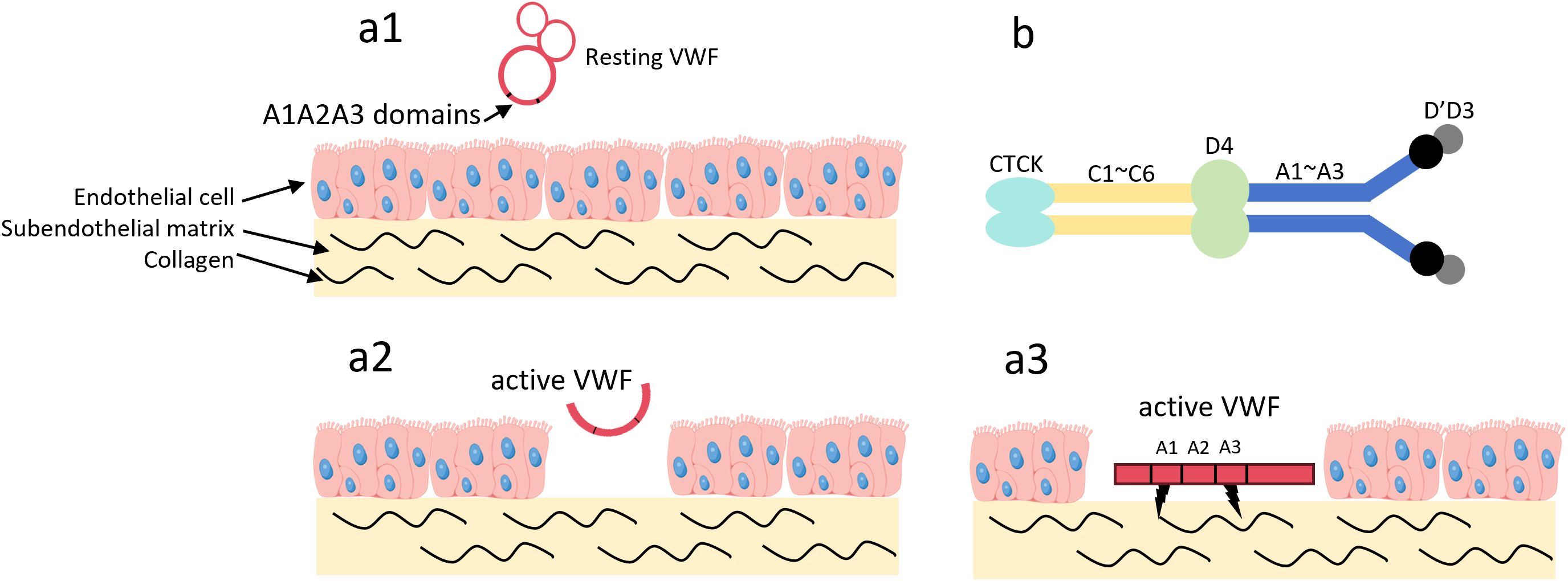
Figure 3. The VWF A3 domain can target type I and type III collagen. (a1) In the absence of vascular wall injury, VWF circulates in the blood in its resting state. In this state, VWF adopts a globular conformation, and the A1 and A3 domains are not exposed; (a2) Upon vascular wall injury, high shear stress activates VWF, and collagen in the subendothelial matrix becomes exposed; (a3) The A1 and A3 domains of VWF bind to the exposed collagen; (b) VWF exists as a dimer. Among these domains, the A1 domain can target type I, IV, VI collagen, while the A3 domain can target type I, III collagen. Von Willebrand Factor, VWF; C-terminal Cysteine Knot domain, CTCK.
Michael J. V. White and his team (42) designed a recombinant protein by re-engineering the VWF-A3 domain and fusing it with IL-10. This A3–IL-10 fusion protein can target the leaky vasculature within fibrotic tissue. Using fluorescent labeling as a tracking method, the presence of VWF-A3 increased drug targeting to fibrotic lungs by approximately 3%, with a statistically significant difference compared to the non-fibrotic control group. Based on histological image analysis, the ratio of fibrotic to healthy tissue area in the A3–IL-10 treatment group improved by about 30% compared with the model group, the absolute collagen content was significantly reduced, and the Ashcroft score decreased by 2 points. The covalent attachment of polymers to proteins can enhance their bio-distribution when applied to tissues, and maintain their bioactivity over a longer period (62). Polyethylene glycol (PEG), formed by linking ethylene glycol molecules through ether bonds, is a neutral linear polyether with a broad range of molecular weights. The repeated ethylene groups in the PEG chain create hydrophobicity, while the oxygen atoms strongly interact with water (63). PEG conjugation prolongs the retention time of proteins in the lungs by promoting mucosal adhesion, increasing protein loading, and maximizing inhaled doses. It also reduces the uptake of PEG-conjugates by alveolar macrophages, significantly extending the protein’s half-life (64). High molecular weight PEG conjugated with drugs in a polymer-drug coupling can further extend the drug’s retention time in the lungs (65–67). PEG can be covalently linked to IL-10 to form PEGylated IL-10 (PEG-IL-10). PEG-IL-10 can mediate CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity and promote IFN-γ expression in CD8+ T-cells, mediating tumor rejection and sustained tumor immunity (68). This mechanism shows promise for IL-10 in anti-inflammatory therapies as well. Immunoglobulin fragment crystallizable (Fc) fusion is another method to extend IL-10’s half-life. Mutations in the Fc domain can reduce antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. By linking the C-terminus of the Fc domain to wild-type IL-10 via a glycine-serine-rich peptide linker, IL-10 activity can be preserved (69). The non-target-mediated clearance of Fc-rhIL-10 is estimated to be approximately 200 times slower than that of rhIL-10, leading to target-mediated drug disposition (TMDD) phenomena in the pharmacokinetics of the fusion protein (70). Current studies on the efficacy of IL-10 fusion proteins mainly focus on cancer (71), but their ability to mediate CD8+ T-cell proliferation, activation, and metabolic reprogramming (72) also gives IL-10 fusion proteins significant potential in the anti-inflammatory field.
3 IL-10 delivery systems
Based on past experiences with the failure of using rhIL-10 to treat diseases such as Crohn’s disease (73), rheumatoid arthritis (74), and sepsis (75), the systemic administration of IL-10 faces numerous challenges, necessitating the development of more effective delivery systems. Given the cytokine nature of IL-10, an ideal delivery system should be capable of extending its half-life, improving its bioavailability, and reducing the pleiotropic effects of the cytokine, thereby enhancing its anti-inflammatory effects and clinical application potential in the treatment of pulmonary diseases.
3.1 Nanoparticle delivery systems
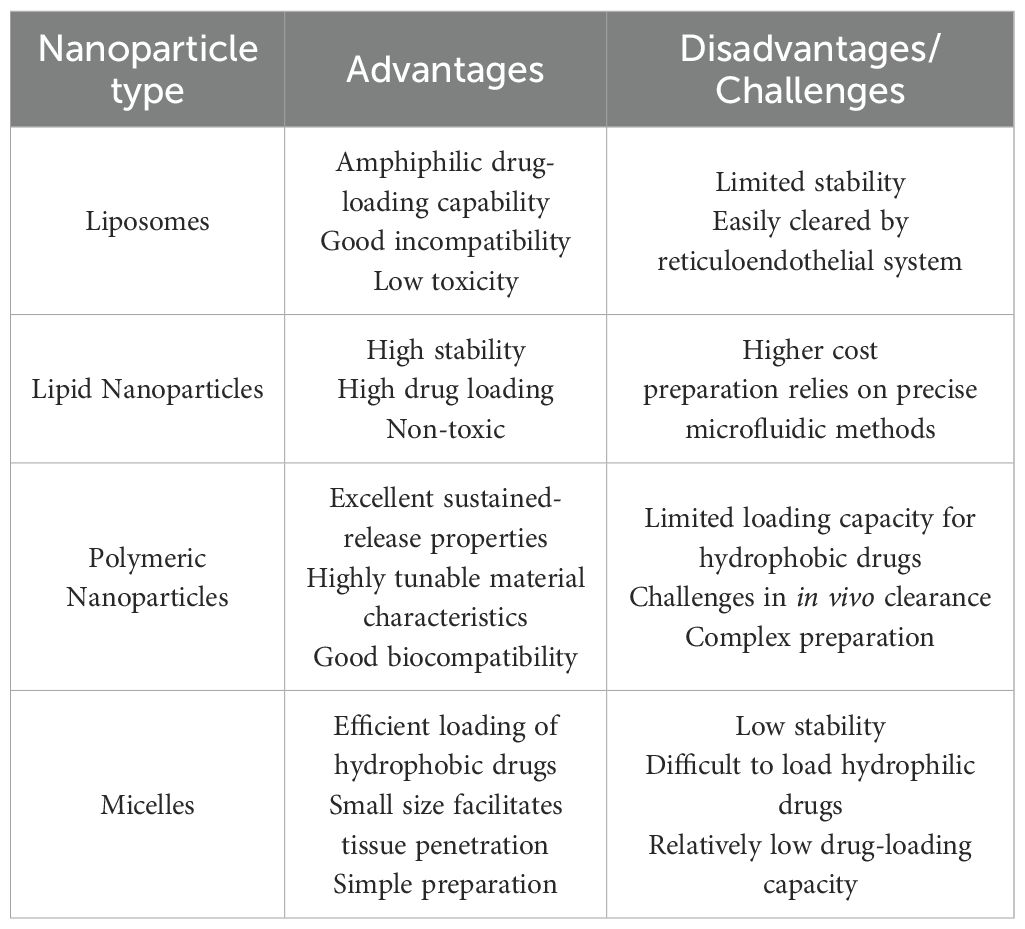
Polymeric nanoparticles (PNPs), liposomes and lipid-based nanoparticles are widely used as typical nanocarrier systems (76). Liposomes are spherical vesicles composed of at least one layer of lipid bilayers. They vary in size from nanometers to micrometers and are primarily composed of phosphatidylcholine or lipids (77). Liposomes offer excellent biocompatibility, can encapsulate both hydrophilic and lipophilic agents, and exhibit minimal toxicity (78). In the treatment of pulmonary diseases, they can extend the local effect and reduce irritation to lung tissue (79). Inhalation administration is a more effective method for delivering liposomes to the lungs; however, intraperitoneal injection of liposomes carrying IL-10 gene expression plasmids can still alleviate lung injury in a mesenteric ischemia-induced ALI mouse model. In the study by Burhan Kabay et al. (80), mice injected with liposome-encapsulated hIL-10 plasmid DNA exhibited an increase in plasma hIL-10 concentration to 12.8 ± 1.28 ng/ml at the time of sacrifice. The lung wet-to-dry weight ratio in animals receiving the empty vector was significantly elevated to 7.47 ± 0.35, whereas the ratio in the treatment group was 4.26 ± 0.47. This indicates that the therapeutic intervention markedly improved pulmonary edema in ALI mouse. The activity of myeloperoxidase (MPO) was determined using a spectrophotometric method, and the treatment group exhibited approximately a twofold reduction in MPO activity compared with the empty vector group. The 2-hour survival rate in the treatment group was increased by 30% compared with the empty vector group. Lipid nanoparticles (LNs) are lipid-based nanocarriers. LNs are colloidal carriers made of biodegradable lipid matrices that are considered Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) and are stabilized by surfactants (81). LNs offer advantages such as high stability, large drug loading capacity, and non-toxicity (82), and although some LN-based platforms have been developed to enable targeted delivery to the lung (83–86), no studies have yet explored their use in IL-10 delivery or pulmonary disease treatment. Poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid, PLGA) copolymers emphasize biocompatibility and biodegradability (87), which can extend the in situ retention time of drugs and enhance mucosal penetration (88). IL-10 encapsulated in PLGA-chitosan can inhibit IL-6 and TNF-mediated inflammatory responses (89). Inhalation of PLGA-encapsulated MSC-derived exosomes has been shown to inhibit airway inflammatory responses (90). Poly-lactic acid-polyethylene glycol (PLA-PEG) is an amphiphilic polymer, and the use of PLA-PEG to encapsulate IL-10 in polymer nanoparticles significantly extends the half-life of IL-10 and improves its thermal stability (91). Micelles are relatively less common in IL-10 delivery; they are colloidal particles composed of amphiphilic block copolymers or surfactants (92), typically ranging in size from 5 nm to 100 nm. Micelles can prevent alveolar macrophage uptake and prolong drug release (93). In a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis, intravenous injection of collagen-conjugated micelles carrying VWF-A3 fused IL-10 (A3-IL-10) significantly improved the degree of pulmonary fibrosis. Table 1. compares the advantages and disadvantages of the nanoparticles discussed in this section.
3.2 Gel delivery systems
Hydrogels are a class of non-Newtonian fluids composed of three-dimensional hydrophilic networks that store large amounts of water (94). With over 75% water content, hydrogels exhibit excellent biocompatibility (95) and are ideal materials for mimicking the extracellular matrix (ECM). In the context of chronic inflammation induced by surgical tissue damage, polyethylene glycol (PEG) hydrogel systems delivering IL-10 can promote the recruitment and functional re-education of monocytes in the damaged area, demonstrating potential for regulating regenerative cell subpopulations and promoting wound healing (96). Hyaluronic acid hydrogels can enhance the targeting and bioavailability of IL-10, demonstrating significant anti-inflammatory effects both locally and systemically (97, 98). In a bleomycin-induced mouse pulmonary fibrosis model (40), a hyaluronic acid–heparin hydrogel was used as a carrier for IL-10 (HH-10), and intranasal administration ensured its sustained release. IL-10 inhibited transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-driven collagen production in pulmonary fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, effectively reducing collagen deposition in the lungs and significantly improving both the degree of fibrosis and the 21-day survival rate in the treatment group. In the model group, approximately 1800 μg of collagen per gram of lung tissue was detected, whereas this value decreased to 1000 μg in the HH-10 treatment group. The Ashcroft score was reduced from 6 in the model group to 2 in the HH-10 treatment group. Self-assembling peptides (SAPs) represent another form of hydrogel, capable of spontaneously forming cross-linked nanofibers in aqueous solution, which then transition into three-dimensional hydrogels in physiological saline environments (99). IL-10 encapsulated in SAP hydrogels can also significantly reduce systemic pro-inflammatory cytokine levels (100). Similar to hydrogels, nanogels are submicron colloidal formulations obtained by micronizing the three-dimensional hydrogel network (94), and they can also be used as carriers for drug delivery (101). Research has shown that β-glucan nanogels carrying rhIL-10 can maintain a stable IL-10 concentration in mice for at least 4 hours (102), though no studies have yet explored the use of nanogel delivery systems for pulmonary anti-inflammatory therapy.
3.3 Extracellular vesicles and other delivery systems
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are naturally derived carriers that play a key role in mediating intercellular communication, sharing molecular cues with their donor cells (103, 104). EVs can directly cross biological barriers to deliver various active biomolecules, with no significant size limitations (105). This allows EVs to overcome challenges faced by other delivery systems, such as nanoparticles. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived EVs are the most common type, and even without carrying anti-inflammatory cytokines or therapeutic drugs, EVs and their derived nanovesicles (NVs) can suppress systemic inflammation (106, 107). MSC-EVs have demonstrated good efficacy in ALI (108, 109), lung transplantation (110), and asthma (111), with the anti-inflammatory effects being mediated by IL-10. When EVs are used as carriers for IL-10, they fully retain its immunomodulatory function (112), allowing IL-10 to penetrate biological barriers that it would not normally cross (113). Chitosan/alginate-modified EVs can protect IL-10 from premature degradation by the body’s environment (114). These findings make EVs direct as carriers for IL-10 in the treatment of pulmonary inflammation highly promising. In studies using a porcine lung transplantation model (115) and an ex vivo human lung model (116), Antti I. Nykänen and his team developed engineered mesenchymal stem cells capable of expressing IL-10, designated as MSCIL-10. This engineered MSC technology involves adenoviral transduction of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) to produce higher levels of human IL-10 (hIL-10). These cells maintained high levels of IL-10 secretion for at least six days even after cryopreservation and thawing, and are able to stably express IL-10 in ex vivo human lungs. When MSCIL-10 was used during EVLP, IL-10 levels in the perfusate increased significantly without negatively affecting lung function. In EVLP, a single administration of 20×106 MSCIL-10 markedly reduced pulmonary apoptosis, whereas increasing the dose to 40 × 106 promoted apoptosis. However, the therapeutic effect remained limited. This was mainly due to the difficulty in reversing elevated pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in poor-quality donor lungs, the detrimental impact of impaired donor lung metabolism on MSCIL-10 function, the challenge of maintaining IL-10 levels in a low-pH environment (pH < 6.4), and the inability of MSCIL-10 to survive for more than 3 days after administration via EVLP and subsequent lung transplantation. Overall, these studies open new avenues for IL-10-based cell delivery and the treatment of post–lung transplantation complications.
4 Targeting approaches
4.1 Nasal administration
Nasal administration, whether by nasal drops or aerosol inhalation, is the most direct targeting method. It offers advantages such as reducing drug dosage, improving patient compliance, and avoiding first-pass metabolism in the liver (117). This non-invasive route is particularly suitable for drug delivery platforms like polymer nanoparticles, liposome carriers (118), and gel carriers (40), which do not have intrinsic targeting functions. Although IL-10 is a pleiotropic cytokine, in an ALI mouse model, Huan Qin and colleagues (25) demonstrated that direct inhalation of exogenous IL-10 could markedly ameliorate pulmonary cytokine storm, lung edema, and histopathological damage. Two different doses of rhIL-10 (100 μg/kg and 200 μg/kg) were used for treatment, and the results showed that the high-dose group could reduce plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines to nearly those of the blank control group. Compared with the model group, in the high-dose treatment group, IL-1β decreased from 500 pg/mL to 100 pg/mL, IL-6 from 1200 pg/mL to 200 pg/mL, IL-8 from 800 pg/mL to 100 pg/mL, and TNFα from 1300 pg/mL to 100 pg/mL. The potential mechanism of this treatment is that rhIL-10 promotes the interaction between neutrophils and platelets through the STAT/SOCS–IκB/NFκB–CD40 signaling pathway, thereby facilitating the differentiation of neutrophils into an anti-inflammatory phenotype. While safety verification is still lacking for this approach, its simple administration method and efficacy make IL-10 aerosol inhalation a promising candidate for clinical translation. In a mouse model of asthma induced by ovalbumin sensitization (119), intratracheal administration of IL-10 significantly suppressed the infiltration of eosinophils and neutrophils as well as the development of airway hyperresponsiveness. This effect may occur through the suppression of proliferation in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells that express vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Although IL-10 did not improve airway remodeling in this model, it effectively attenuated airway hyperresponsiveness in corticosteroid-insensitive asthmatic mice. This alternative therapy may hold clinical potential for treating corticosteroid-insensitive asthma.
4.2 Immunogenic reutilization
Some immune cells or cell-derived materials naturally have the ability to target inflammatory regions or the lungs. Certain IL-10 delivery methods directly exploit this capability for targeted lung delivery. One such method is macrophage membrane coating, which targets pulmonary diseases. The innate immune system mediates the initial response to infection, with immune cells primarily composed of macrophages, which have a lifespan of several months, and neutrophils, which live for about 48 hours (120). Macrophages possess active targeting capabilities, high immunocompatibility, and long circulation times. They primarily recognize pathogens and respond to infection and injury through pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) (121) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) (122). Macrophage membranes express P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1), L-selectin, lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), integrins, and very late antigen-4 (VLA-4), facilitating adhesion to inflammatory cells (123). These immune mechanisms make the macrophage membrane an ideal material for coating IL-10 and IL-10 carriers. In fact, macrophage membranes, as targeting materials, were initially used for targeting lung cancer rather than pulmonary inflammation (124). Figure 4 illustrates the recruitment of pulmonary macrophages in response to pulmonary inflammation.
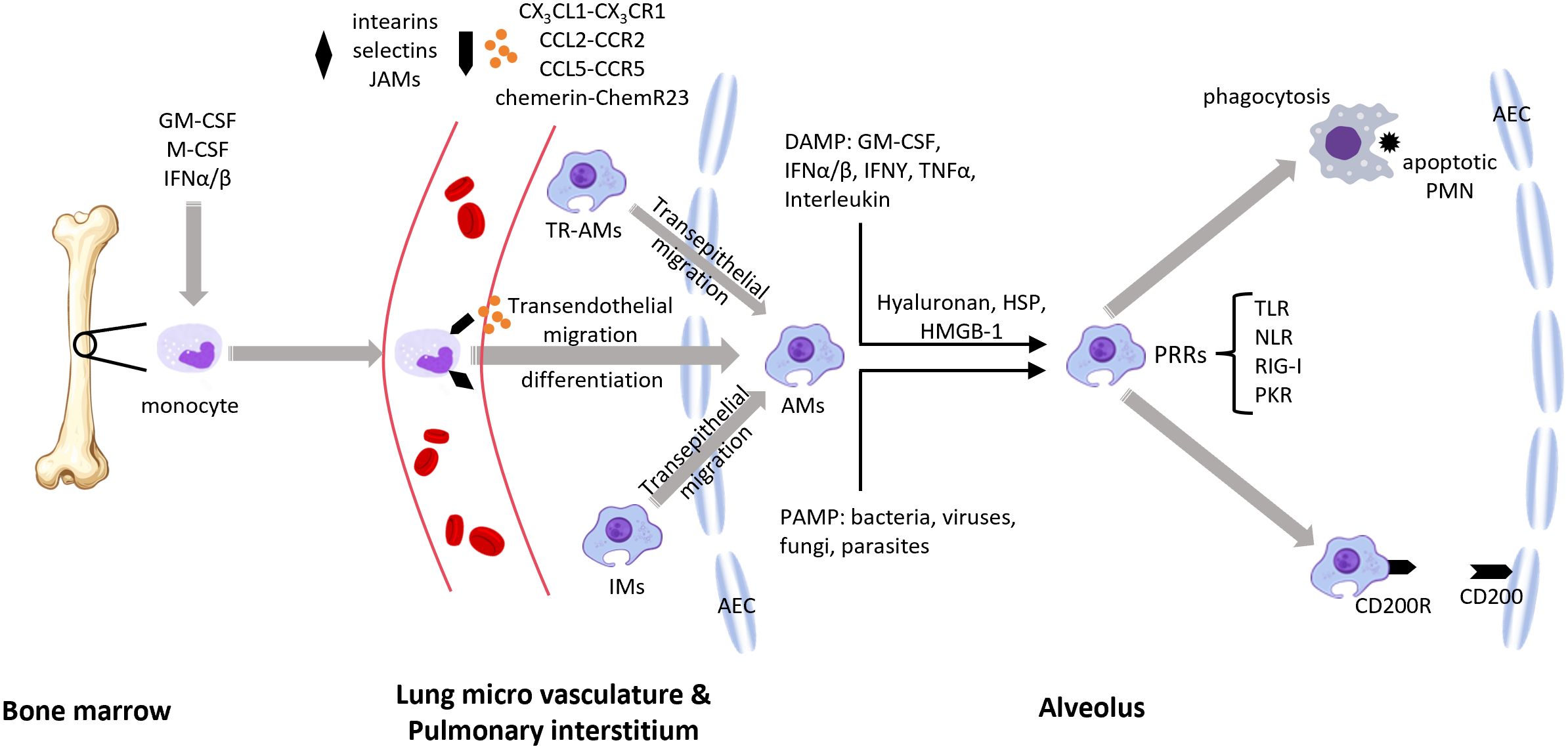
Figure 4. During pulmonary inflammation, lung macrophages from different origins can be recruited to the site of inflammation (1). Growth factors such as GM-CSF, M-CSF, and IFNs drive the differentiation and activation of macrophage progenitors (e.g., monocytes), which then enter the bloodstream (2). Macrophages are recruited to the alveoli under the influence of chemokines and their receptors, the ChemR23–chemerin axis, and adhesion molecules (3). Resident alveolar macrophages and interstitial macrophages are also recruited to the alveolar space (4). Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMP) transmit signals through (PRRs) (5). Macrophages phagocytose apoptotic neutrophils and promote an anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotype via the CD200–CD200R interaction. GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN, interferon; JAMs, junctional adhesion molecules; TR-AMs, tissue-resident alveolar macrophages; AMs, alveolar macrophages; IMs, interstitial macrophages; DAMP, damage-associated molecular patterns; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; HSP, heat shock proteins; HMGB-1, high-mobility group box 1; PRRs, pattern recognition receptors; TLR, toll-like receptor; NLR, NOD-like receptor; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; PKR, protein kinase R; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophils; AEC, alveolar epithelial cell.
However, Jun-Da Li and colleagues (125) demonstrated in a mouse model of house dust mite (HDM)-induced allergic airway inflammation that IL-10-loaded alveolar macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles (IL-10-AMNPs) significantly reduced Th2 and Th17 cytokine levels, increased airway compliance and markedly reduced airway resistance, compared to IL-10-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid, PLGA) nanoparticles. IL-10-AMNPs reduced the total number of inflammatory cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid by approximately 3.5-fold, from 3.5×106 in the model group to 1×106 in the treatment group. This therapeutic effect was significantly superior to that of the IL-10-PLGA nanoparticles (IL-10-NP) group without encapsulated pulmonary macrophage membranes. In terms of inflammatory factor improvement, IL-10-AMNPs showed significantly superior effects on IL-10, IL-13, IL-17A, TNFα, and IFNγ levels compared with both the model group and the IL-10-NP group. This confirmed that alveolar macrophage membranes could effectively target drug delivery to areas of pulmonary inflammation, significantly enhancing the overall therapeutic efficacy. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) have been shown in numerous studies to be effective for treating pulmonary inflammation (126–128). MSCs can be derived from various cell types, and exosomes derived from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AdMSCs-Exos, 108) and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs-Exos, 129) naturally accumulate in the lungs, making them ideal natural targeted lung carriers. The mechanism behind the targeting ability of exosomes remains unclear, but it may be related to the homing effect of MSCs (130). MSC-EVs have been used in several studies for IL-10 delivery (112–114, 131), making exosome-mediated IL-10 delivery for pulmonary diseases a promising approach. Figure 5 illustrates the homing mechanism of MSCs. MSC-derived exosomes are likely to inherit this homing mechanism to target sites of inflammation.
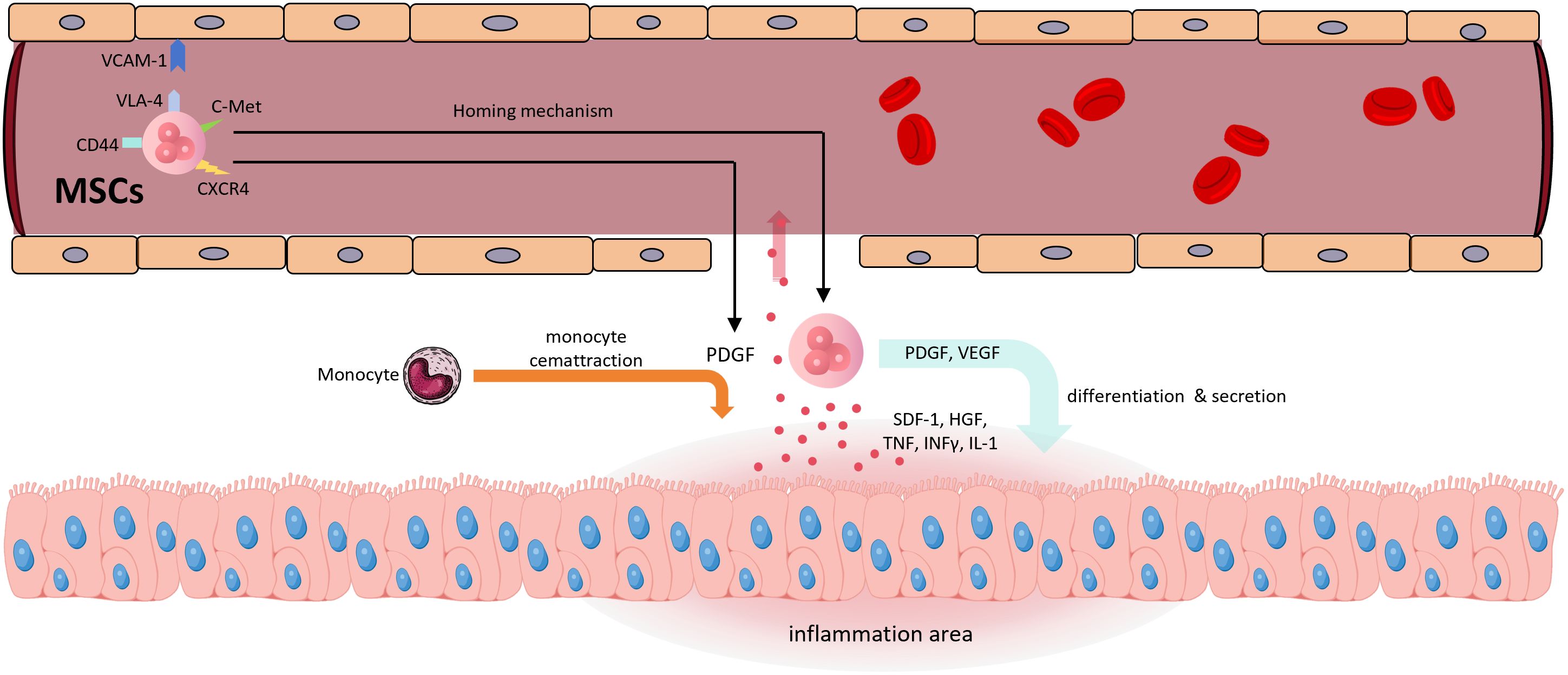
Figure 5. The homing mechanism of MSCs (1) Inflammatory regions release pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF, IFN-γ, and IL-1, as well as chemokines like SDF-1 and HGF, which enter the bloodstream (2). CXCR4 recognizes SDF-1, and c-Met recognizes HGF, initiating the homing mechanism (3). VCAM-1, VLA-4, and CD44 are involved in cell rolling, adhesion, and transendothelial migration (4). MSCs secrete PDGF and VEGF; the former promotes monocyte recruitment, while both contribute to the transition of inflamed tissue toward regeneration (5). MSCs themselves participate in tissue differentiation. SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; c-Met, mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor; VLA-4, very late antigen-4.
4.3 Engineered modifications
The targeted engineering modifications of IL-10 carriers primarily depend on the specificity of the target organ and disease. In earlier animal experiments (132, 133), pulmonary surfactant protein A (SP-A) was confirmed to have targeting abilities for the lungs. SP-A helps maintain pulmonary homeostasis by acting as an innate immune scavenger receptor, regulating the expression of receptors, including the mannose receptor, on macrophages, which is a key receptor for mediating phagocytosis (134). SP-A can bind to the SP-R210 receptors on pulmonary macrophage, which are critical regulatory targets in pulmonary inflammation (135). Figure 6 illustrates how SP-A facilitates pathogen clearance in the lung.
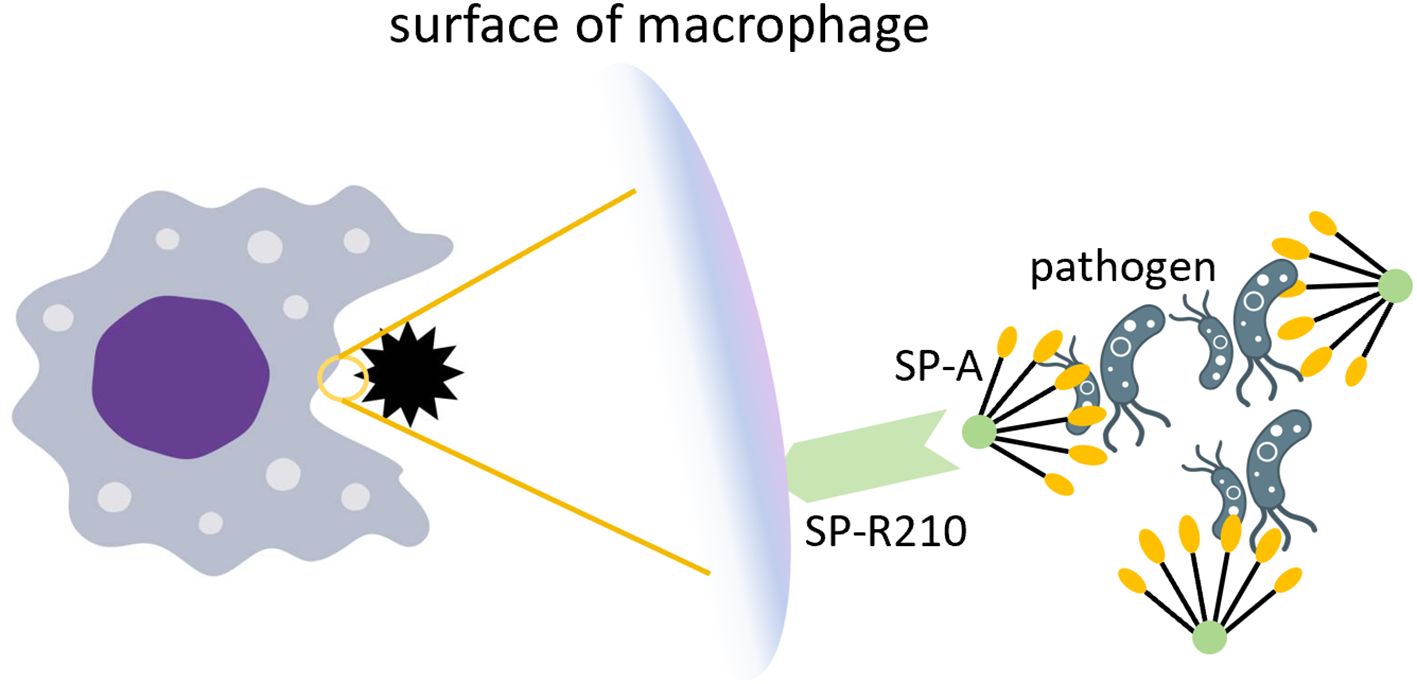
Figure 6. The role of SP-A in pathogen clearance. SP-A recognizes and aggregates pathogens by relying on the COOH-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain. The SP-R210 receptor on the surface of macrophages recognizes SP-A and enhances phagocytosis of pathogens.
In fact, Ana I. Salazar-Puerta and her team (131) successfully electroporated a plasmid encoding SP-A into murine-derived skin fibroblasts (MDF), thereby generating EVs capable of targeting lung tissue. These MDF-derived engineered EVs (MDF-eEVs) delivered IL-10 via intranasal administration. The ability of SP-A-functionalized eEVs to preferentially accumulate in the lungs in vivo was evaluated by intranasal delivery of fluorescently labeled IL-10 + SP-A eEVs. Biodistribution analysis performed 12 hours post-delivery using an in vivo imaging system (IVIS) showed that, compared with non-functionalized eEVs, SP-A-functionalized eEVs exhibited significantly enhanced retention in the lungs. Compared with the model group, the treatment group showed significant improvement in the inflammatory factors interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), as well as in pulmonary inflammatory cell infiltration. Miji Kim and colleagues (136) combined SP-A with alveolar macrophages to develop a more powerful drug delivery carrier with enhanced targeting capabilities. Table 2 summarizes IL-10-based therapeutic approaches and advanced delivery systems for pulmonary inflammatory disease.
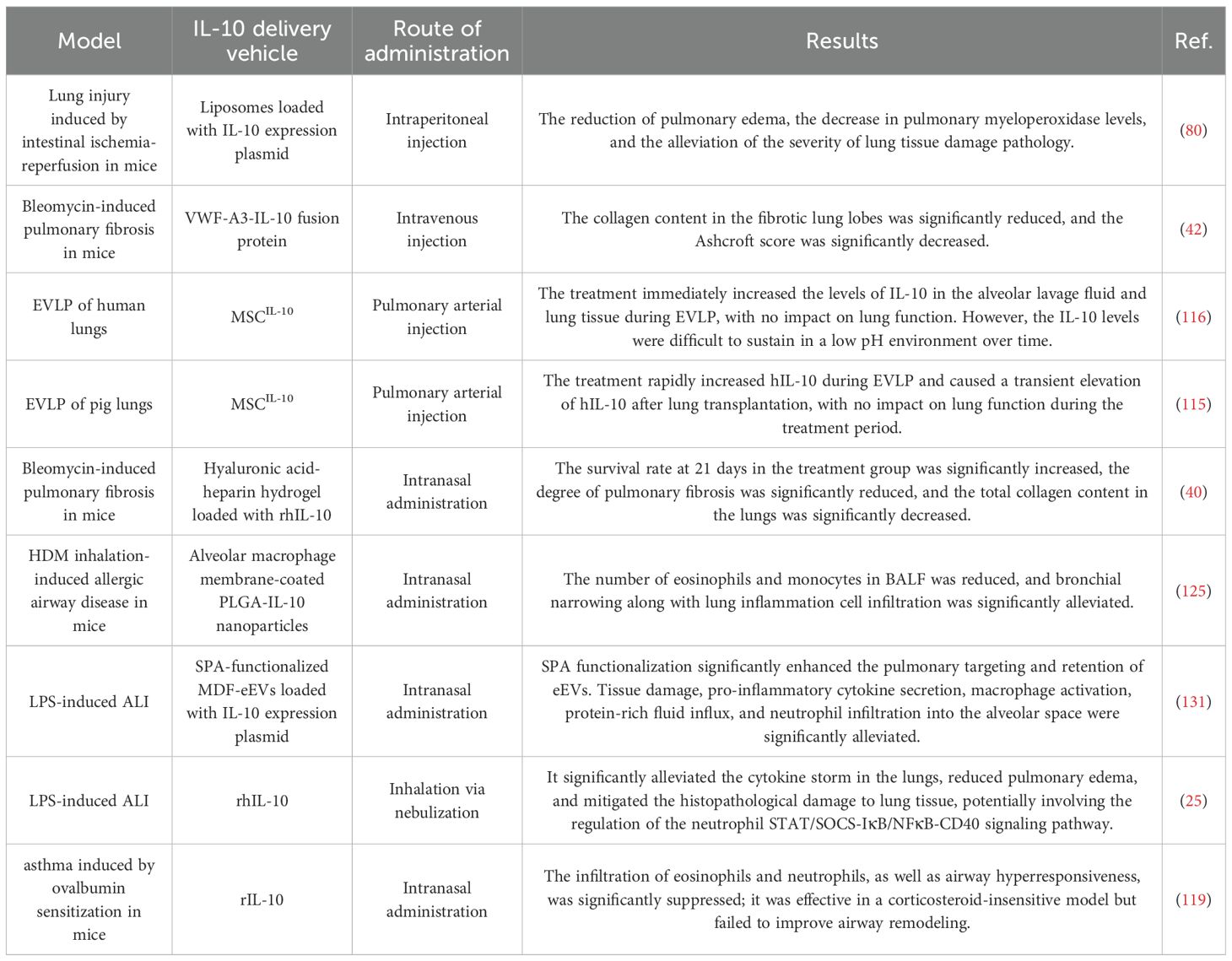
Table 2. Overview of IL-10-Based Therapeutic Strategies and Delivery Systems for Pulmonary Diseases”.
5 Challenges in IL-10 delivery
5.1 Good manufacturing practice challenges of IL-10 vectors
MSC-based products, as living cells that undergo continuous changes over time, require more sophisticated risk management strategies to ensure product quality. Owing to the heterogeneity of MSCs themselves and their preparation methods, variations in extracellular vesicle (EV) production, and limited reproducibility of in vitro and in vivo functional assays, the efficacy and safety of MSCs remain highly controversial (137). As derivatives of MSCs, MSC-EVs are most commonly isolated and concentrated by differential ultracentrifugation. However, this method still faces several challenges, including low EV yield, reduced recovery following purification and washing, spontaneous aggregation of vesicles making resuspension difficult, structural disruption, and difficulty in scaling up production (138).
In the European Union, Regulation No. 1394/2007, introduced in December 2008, classified advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs), including MSCs, as medicinal products for regulatory oversight. Since 2018, guidelines for Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) in ATMPs have been implemented (139). Recently, fully automated, closed Ficoll-based systems have been applied for harvesting bone marrow (BM) cells. Furthermore, a novel GMP-compliant non-woven filter system has shown promise in increasing cell yield without altering MSC characteristics (140). To meet large-scale expansion requirements, multilayered adherent culture systems that comply with GMP standards have been employed for MSC production (141). For MSC-EV production, size-based fractionation strategies, such as size exclusion chromatography and tangential flow filtration (TFF), are increasingly recognized as GMP-compatible and scalable technologies (142).
Lentiviral vectors play a crucial role in gene-modified cell therapies. Human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 and its derivative 293T cell lines are the most widely used systems for lentivirus production. The first and still most commonly used lentiviral production system is based on transient production via multiplasmid cotransfection of 293T cells, which enables rapid and efficient vector generation (143). However, transient systems require large amounts of highly purified DNA and transfection reagents, making them unsuitable for large-scale, high-titer production. Stable producer cell lines (PCLs) remain the preferred choice for large-scale lentivirus manufacturing, though current limitations include batch-to-batch variability and elevated production costs (144).
Due to the clinical development of pegilodecakin and its completion of Phase III clinical trials, PEGylation of IL-10 no longer faces major GMP-related challenges (145). In contrast, PLGA-based systems present distinct obstacles. PLGA nanoparticles are primarily administered by injection (146). Given the physicochemical properties of PLGA, sterilization methods such as steam autoclaving or gamma irradiation often result in polymer degradation, making sterile filtration the optimal choice for PLGA nanoparticles (147). Moreover, as self-assembling drug delivery systems, PLGA nanoparticles require separation of free active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from successfully assembled nanoparticles, for which diafiltration is the preferred method (148). This must be performed in conjunction with sterile filtration to comply with GMP standards.
5.2 Optimization of IL-10 therapeutic strategies
The therapeutic response to IL-10 is highly dependent on variations within the patient’s immune microenvironment, making individualized treatment a critical unmet need in clinical translation. The IL-10 gene comprises five exons (149). Numerous single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and microsatellite polymorphisms have been reported in IL-10, including IL-10-1082G/A, IL-10-819C/T, IL-10-592C/A, IL-10.R, and IL-10.G (150). Interindividual variation in IL-10 levels is largely determined by SNPs within its promoter regionv (151). Thus, attention to IL-10 promoter and receptor SNPs provides direction for developing personalized therapeutic strategies.
Another major clinical translational challenge lies in IL-10’s pleiotropic effects on downstream signaling pathways. Formation of the IL-10/IL-10 receptor complex induces phosphorylation of STAT3 in macrophages, which can paradoxically activate pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and prevent PI3K recruitment (47). IL-10 has also been implicated in the induction of human leukocyte antigen-G (HLA-G), an immune checkpoint molecule (152). HLA-G, by interacting with killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs), protects target cells from NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity (153), thereby attenuating innate immunity. Profiling cytokine networks downstream of IL-10 signaling may help clarify differences in patient immune environments.
Balancing IL-10’s anti-inflammatory efficacy with its potential immunosuppressive risks remains a critical challenge. c-MAF, a member of the MAF transcription factor family and part of the AP-1 superfamily, binds directly to the MAF recognition element (MARE) sequence within the IL-10 promoter in human macrophages (154). c-MAF regulates IL-10 expression directly and mediates the M2 macrophage polarization program induced by IL-10 (155). Interestingly, in cases of mild pulmonary inflammation (e.g., low-dose LPS), pulmonary macrophages exhibit low c-MAF expression, and IL-10 is not induced under these conditions (156). β-glucan curdlan, a c-MAF antagonist (157), has shown potential in mitigating immunosuppression arising from missed IL-10 therapeutic windows.
Moreover, engineered strategies provide novel approaches to optimizing IL-10 therapy. In one study, conventional CD4+ T cells were engineered with synthetic Notch (synNotch) regulatory circuits to respond to specific antigens (158). Upon antigen recognition, synNotch activation locally induced the production of customized anti-inflammatory payloads, including IL-10. These engineered T cells exhibited dual-antigen recognition of tumor cells: in the presence of Her2 alone, T cells exerted cytotoxic effects, whereas co-expression of Her2 and CD19 abrogated killing in favor of local immunomodulation. To effectively implement such promoter-driven localized expression systems, identification of unique antigenic epitopes in the target organ or tissue must precede payload selection.
5.3 Potential risks of the vector
Adeno-associated virus (AAV), a non-enveloped parvovirus, is currently one of the most widely studied gene delivery vectors. More than 255 clinical trials involving AAV-mediated gene therapy are ongoing, and seven AAV-based products have received regulatory approval (159). Lentiviruses, belonging to the Retroviridae family, are enveloped viruses with high transduction efficiency and the ability to confer stable, long-term transgene expression, making them advantageous in gene therapy. For instance, lentiviral delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) genes enables T cells to recognize and target tumor cells, and CAR-T therapies have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA, 160).
The primary challenges for viral vectors lie in the complexity of viral-receptor interactions, as the mechanisms by which enveloped viruses engage their receptors remain incompletely understood. Some viruses can bind multiple receptors or utilize alternative entry pathways, complicating engineering strategies. For AAV vectors, issues of delivery efficiency, packaging optimization, and host immune responses—particularly at high therapeutic doses—remain obstacles in clinical development (161).
Overall, hydrogel-based products hold great promise for advancing medical technologies, but further progress is required to facilitate translation from bench to bedside. Current challenges include material-associated immune-mediated foreign body responses (FBRs), leading to fibrosis around the hydrogel, impaired cellular infiltration, and ultimately therapeutic failure (162). Fortunately, modified alginate analogs demonstrate excellent biocompatibility, with negligible fibrosis observed (163).
6 Conclusions and future directions
Recent advances in IL-10 delivery strategies have significantly improved its therapeutic potential. Particularly promising are lung-targeted approaches, which enhance IL-10 accumulation in lung tissues while minimizing systemic exposure. Despite these advances, several hurdles remain. These include the need to optimize lung-specific targeting, extend the duration of IL-10 activity, ensure consistent therapeutic outcomes across disease models, and better understand potential long-term effects. Additionally, balancing IL-10’s immunosuppressive functions without compromising host defense or promoting tumorigenesis remains critical. Future study should prioritize: 1) Developing precision delivery systems: Next-generation delivery platforms should integrate prolonged bioactivity, biodegradability, and minimal immunogenicity to optimize IL-10’s therapeutic efficacy. LNs, polymeric nanoparticles (e.g., PLGA, PLA-PEG), and engineered EVs are promising candidates for delivering IL-10, as well as other anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, or gene-editing agents, directly to lung tissue. 2) Personalized medicine approaches: Leveraging omics data (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics) and artificial intelligence (AI)-based predictive models can enable tailored IL-10 therapies based on individual disease phenotypes and drug response profiles. By identifying biomarkers such as baseline IL-10 expression, immune cell signatures, or genetic variants, personalized dosing and delivery strategies can be developed to optimize efficacy and minimize adverse effects. AI-driven models could also predict patient-specific inflammatory dynamics, guiding the selection of IL-10 formulations or combination therapies for conditions like COPD or pulmonary fibrosis. 3) Targeting specific lung cell types: Precise targeting of IL-10 to specific lung cell populations - such as alveolar macrophages, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, or endothelial cells - can enhance therapeutic specificity and reduce systemic side effects. Emerging strategies include exploiting ligand-receptor interactions (e.g., SP-A binding to P63/CKAP4 receptors on type II alveolar cells) or cell-specific promoters to drive IL-10 expression in target cells. With continuous innovation in biomaterials and targeted delivery technologies, IL-10 is poised to become a key component of next-generation therapies for pulmonary inflammation. By addressing the remaining challenges, IL-10-based treatments have the potential to move from promising experimental strategies to effective clinical solutions for patients suffering from debilitating lung diseases.
Author contributions
WT: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Methodology. XW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JZ: Writing – review & editing. YG: Writing – review & editing. ST: Writing – review & editing. CM: Writing – review & editing. LY: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Project administration. XT: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Savin IA, Zenkova MA, and Sen’kova AV. Pulmonary fibrosis as a result of acute lung inflammation: molecular mechanisms, relevant in vivo models, prognostic and therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:14959. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314959
2. Ching PR and Pedersen LL. Severe pneumonia. Med Clin North Am. (2025) 109:705–20. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2024.12.011
3. Nadeem A, Al-Harbi NO, Ahmad SF, Ibrahim KE, Siddiqui N, and Al-Harbi MM. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase inhibition attenuates acute lung injury through reduction in NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Clin Exp Immunol. (2018) 191:279–87. doi: 10.1111/cei.13097
4. Price DR and Garcia JGN. A razor’s edge: vascular responses to acute inflammatory lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Annu Rev Physiol. (2024) 86:505–29. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-042222-030731
5. Wick KD, Ware LB, and Matthay MA. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ. (2024), 387. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076612
6. Faner R, Cruz T, Casserras T, López-Giraldo A, Noell G, Coca I, et al. Network analysis of lung transcriptomics reveals a distinct B-cell signature in emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2016) 193:1242–53. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201507-1311OC
7. Christenson SA, Smith BM, Bafadhel M, and Putcha N. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. (2022) 399:2227–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00470-6
8. Porsbjerg C, Melén E, Lehtimäki L, and Shaw D. Asthma. Lancet. (2023) 401:858–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02125-0
9. Maher TM. Interstitial lung disease: A review. JAMA. (2024) 331:1655. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.3669
10. Nathan SD and Lee JS. Real-world data on the course of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Manag Care. (2024) 30:S107–13.
11. Libra A, Sciacca E, Muscato G, Sambataro G, Spicuzza L, and Vancheri C. Highlights on future treatments of IPF: clues and pitfalls. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:8392. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158392
12. Carlini V, Noonan DM, Abdalalem E, Goletti D, Sansone C, Calabrone L, et al. The multifaceted nature of IL-10: regulation, role in immunological homeostasis and its relevance to cancer, COVID-19 and post-COVID conditions. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1161067. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161067
13. Huhn RD, Radwanski E, O’Connell SM, Sturgill MG, Clarke L, Cody RP, et al. Pharmacokinetics and immunomodulatory properties of intravenously administered recombinant human interleukin-10 in healthy volunteers. Blood. (1996) 87:699–705.
14. Qian G, Jiang W, Sun D, Sun Z, Chen A, Fang H, et al. B-cell-derived IL-10 promotes allergic sensitization in asthma regulated by Bcl-3. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:1313–27. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01079-w
15. Wang X, Wong K, Ouyang W, and Rutz S. Targeting IL-10 family cytokines for the treatment of human diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2019) 11:a028548. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028548
16. Moore KW, De Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, and O’Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. (2001) 19:683–765. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.683
17. Ouyang W, Rutz S, Crellin NK, Valdez PA, and Hymowitz SG. Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. (2011) 29:71–109. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101312
18. Fiorentino DF, Bond MW, and Mosmann TR. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. Exp Med. (1989) 170:2081–95. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2081
19. Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, and Fisher PB. Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. (2004) 22:929–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104622
20. de Waal Malefyt R, Abrams J, Bennett B, Figdor CG, and de Vries JE. Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med. (1991) 174:1209–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1209
21. Creery WD, Diaz-Mitoma F, Filion L, and Kumar A. Differential modulation of B7-1 and B7-2 isoform expression on human monocytes by cytokines which influence the development of T helper cell phenotype. Eur J Immunol. (1996) 26:1273–7. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260614
22. Willems F, Marchant A, Delville J, Gérard C, Delvaux A, Velu T, et al. Interleukin-10 inhibits B7 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. (1994) 24:1007–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240435
23. Groux H, Bigler M, de Vries JE, and Roncarolo MG. Interleukin-10 induces a long-term antigen-specific anergic state in human CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. (1996) 184:19–29. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.19
24. Schuetze N, Schoeneberger S, Mueller U, Freudenberg MA, Alber G, and Straubinger RK. IL-12 family members: differential kinetics of their TLR4-mediated induction by Salmonella Enteritidis and the impact of IL-10 in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Int Immunol. (2005) 17:649–59. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh247
25. Qin H, Wang J, Bai L, Ding H, Ding H, Zhang F, et al. Aerosol inhalation of rhIL-10 improves acute lung injury in mice by affecting pulmonary neutrophil phenotypes through neutrophil-platelet aggregates. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 147:113948. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113948
26. Nie Z, Fan Q, Jiang W, Wei S, Luo R, Hu H, et al. Placental mesenchymal stem cells suppress inflammation and promote M2-like macrophage polarization through the IL-10/STAT3/NLRP3 axis in acute lung injury. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1422355. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422355
27. Golmohammadi M, Sheikhha MH, Ganji F, Shirani A, Barati M, Kalantar SM, et al. Human fetal lung mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate lung injury in an animal model. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:6433. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91406-0
28. Wang M, Wu D, Liao X, Hu H, Gao J, Meng L, et al. CPT1A-IL-10-mediated macrophage metabolic and phenotypic alterations ameliorate acute lung injury. Clin Transl Med. (2024) 14:e1785. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1785
29. Sun Z, Chen A, Fang H, Sun D, Huang M, Cheng E, et al. B cell-derived IL-10 promotes the resolution of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:418. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05954-2
30. Rajasekaran S, Pattarayan D, Rajaguru P, Sudhakar Gandhi PS, and Thimmulappa RK. MicroRNA regulation of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Cell Physiol. (2016) 231:2097–106. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25316
31. Shih LJ, Yang CC, Liao MT, Lu KC, Hu WC, and Lin CP. An important call: Suggestion of using IL-10 as therapeutic agent for COVID-19 with ARDS and other complications. Virulence. (2023) 14:2190650. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2190650
32. Jacobs M, Verschraegen S, Salhi B, Anckaert J, Mestdagh P, Brusselle GG, et al. IL-10 producing regulatory B cells are decreased in blood from smokers and COPD patients. Respir Res. (2022) 23:287. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02208-1
33. Alves LHV, Ito JT, Almeida FM, Oliveira LM, Stelmach R, Tibério LFLC, et al. Phenotypes of regulatory T cells in different stages of COPD. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 140:112765. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112765
34. Cai SY, Liu A, Xie WX, Zhang XQ, Su B, Mao Y, et al. Esketamine mitigates mechanical ventilation-induced lung injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats via inhibition of the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway and reduction of oxidative stress. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) :139:112725. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112725
35. Distefano A, Orlando L, Giallongo S, Tropea E, Spampinato M, Santisi A, et al. Fish oil containing pro-resolving mediators enhances the antioxidant system and ameliorates LPS-induced inflammation in human bronchial epithelial cells. Pharmaceuticals. (2024) 17:1066. doi: 10.3390/ph17081066
36. Branchett WJ, Saraiva M, and O’Garra A. Regulation of inflammation by Interleukin-10 in the intestinal and respiratory mucosa. Curr Opin Immunol. (2024) 91:102495. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2024.102495
37. Melgaard ME, Jensen SK, Eliasen A, Pedersen CT, Thorsen J, Mikkelsen M, et al. Asthma development is associated with low mucosal IL -10 during viral infections in early life. Allergy. (2024) 79:2981–92.
38. Hawrylowicz CM and O’Garra A. Potential role of interleukin-10-secreting regulatory T cells in allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. (2005) 5:271–83. doi: 10.1038/nri1589
39. Knüppel L, Ishikawa Y, Aichler M, Heinzelmann K, Hatz R, Behr J, et al. A novel antifibrotic mechanism of nintedanib and pirfenidone. Inhibition of collagen fibril assembly. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2017) 57:77–90. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0217OC
40. Shamskhou EA, Kratochvil MJ, Orcholski ME, Nagy N, Kaber G, Steen E, et al. Hydrogel-based delivery of Il-10 improves treatment of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Biomaterials. (2019) 203:52–62.
41. Li Y, Yin H, Yuan H, Wang E, Wang C, Li H, et al. IL-10 deficiency aggravates cell senescence and accelerates BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis in aged mice via PTEN/AKT/ERK pathway. BMC Pulm Med. (2024) 24:443. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03260-x
42. White MJV, Raczy MM, Budina E, Solanki A, Shim HN, Zhang ZJ, et al. Engineering IL-10 and rapamycin to bind collagen leads to improved anti fibrotic efficacy in lung and kidney fibrosis. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:13279. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94073-3
43. Cypel M, Kaneda H, Yeung JC, Anraku M, Yasufuku K, De Perrot M, et al. Increased levels of interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α in donor lungs rejected for transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. (2011) 30:452–9. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2010.11.012
44. Kaneda H, Waddell TK, De Perrot M, Bai XH, Gutierrez C, Arenovich T, et al. Pre-implantation multiple cytokine mRNA expression analysis of donor lung grafts predicts survival after lung transplantation in humans. Am J Transplant. (2006) 6:544–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01204.x
45. Chilvers NJS, Gilmour J, Brown ML, Bates L, Pang CY, Pauli H, et al. A split-lung ex vivo perfusion model for time- and cost-effective evaluation of therapeutic interventions to the human donor lung. Transpl Int. (2024) 37:12573. doi: 10.3389/ti.2024.12573
46. Machuca TN, Cypel M, Bonato R, Yeung JC, Chun YM, Juvet S, et al. Safety and efficacy of ex vivo donor lung adenoviral IL-10 gene therapy in a large animal lung transplant survival model. Hum Gene Ther. (2017) 28:757–65. doi: 10.1089/hum.2016.070
47. Rallis KS, Corrigan AE, Dadah H, Stanislovas J, Zamani P, Makker S, et al. IL-10 in cancer: an essential thermostatic regulator between homeostatic immunity and inflammation – a comprehensive review. Future Oncol. (2022) 18:3349–65. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0063
48. Rosenblum IY, Johnson RC, and Schmahai TJ. Preclinical safety evaluation of recombinant human interleukin-10. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. (2002) 35:56–71. doi: 10.1006/rtph.2001.1504
49. Moore KW, O’Garra A, de Waal Malefyt R, Vieira P, and Mosmann TR. Interleukin-10. Annu Rev Immunol. (1993) 11:165–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001121
50. Asadullah K, Sterry W, Stephanek K, Jasulaitis D, Leupold M, Audring H, et al. IL-10 is a key cytokine in psoriasis. Proof of principle by IL-10 therapy: a new therapeutic approach. J Clin Invest. (1998) 101:783–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI1476
51. Graham FL and Prevec L. Methods for construction of adenovirus vectors. Mol Biotechnol. (1995) 3:207–20. doi: 10.1007/BF02789331
52. Vieira P, De Waal-Malefyt R, Dang MN, Johnson KE, Kastelein R, Fiorentino DF, et al. Isolation and expression of human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor cDNA clones: homology to Epstein-Barr virus open reading frame BCRFI. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (1991) 88:1172–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1172
53. Nemunaitis J, Cunningham C, Buchanan A, Blackburn A, Edelman G, Maples P, et al. Intravenous infusion of a replication-selective adenovirus (ONYX-015) in cancer patients: safety, feasibility and biological activity. Gene Ther. (2001) 8:746–59. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301424
54. Hirayama S, Sato M, Loisel-Meyer S, Matsuda Y, Oishi H, Guan Z, et al. Lentivirus IL-10 gene therapy down-regulates IL-17 and attenuates mouse orthotopic lung allograft rejection. Am J Transplant. (2013) 13:1586–93. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12230
55. Hirayama S, Sato M, Liu M, Loisel-Meyer S, Yeung JC, Wagnetz D, et al. Local long-term expression of lentivirally delivered IL-10 in the lung attenuates obliteration of intrapulmonary allograft airways. Hum Gene Ther. (2011) 22:1453–60. doi: 10.1089/hum.2010.225
56. Liu M, Juvet SC, Medin JA, Martinu T, Oishi H, and Keshavjee S. Lentiviral interleukin-10 gene therapy: Safety and questions. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2019) 157:818–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.10.082
57. Hitoshi N, Ken-ichi Y, and Jun-ichi M. Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene. (1991) 108:193–9.
58. Nakagome K. In vivo IL-10 gene delivery attenuates bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the production and activation of TGF- in the lung. Thorax. (2006) 61:886–94. doi: 10.1136/thx.2005.056317
59. Mei Q, Liu Z, Zuo H, Yang Z, and Qu J. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an update on pathogenesis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 12:797292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.797292
60. Liu G, Philp AM, Corte T, Travis MA, Schilter H, Hansbro NG, et al. Therapeutic targets in lung tissue remodelling and fibrosis. Pharmacol Ther. (2021) :225:107839. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107839
61. Ishihara J, Ishihara A, Sasaki K, Lee SSY, Williford JM, Yasui M, et al. Targeted antibody and cytokine cancer immunotherapies through collagen affinity. Sci Transl Med. (2019) 11:eaau3259. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau3259
62. Roberts MJ, Bentley MD, and Harris JM. Chemistry for peptide and protein PEGylation. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2002) 54:459–76. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00022-4
63. Veronese FM. PEGylated protein drugs: basic science and clinical applications. Basel, Boston: Birkhäuser (2009). 287 p.
64. Chapman AP. PEGylated antibodies and antibody fragments for improved therapy: a review. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2002) 54:531–45. doi: 10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00026-1
65. Freches D, Patil HP, MaChado Franco M, Uyttenhove C, Heywood S, and Vanbever R. PEGylation prolongs the pulmonary retention of an anti-IL-17A Fab’ antibody fragment after pulmonary delivery in three different species. Int J Pharm. (2017) 521:120–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.02.021
66. Gursahani H, Riggs-Sauthier J, Pfeiffer J, Lechuga-Ballesteros D, and Fishburn CS. Absorption of polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymers: the effect of PEG size on permeability. J Pharm Sci. (2009) 98:2847–56. doi: 10.1002/jps.21635
67. Guo Y, Bera H, Shi C, Zhang L, Cun D, and Yang M. Pharmaceutical strategies to extend pulmonary exposure of inhaled medicines. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2021) 11:2565–84. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.015
68. Oft M. IL-10: master switch from tumor-promoting inflammation to antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Res. (2014) 2:194–9. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0214
69. Yang Z, Loy J, Poirson B, Dai Y, Rajendran S, Xu S, et al. Application of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling to bridge mouse antitumor efficacy and monkey toxicology data for determining the therapeutic index of an interleukin-10 fc fusion protein. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:829063. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.829063
70. Yang Z, Rajendran S, Spires V, Poirson B, Gururajan M, Lin Z, et al. Target-mediated drug disposition affects the pharmacokinetics of interleukin-10 fragment crystallizable fusion proteins at pharmacologically active doses. Drug Metab Dispos. (2022) 50:898–908. doi: 10.1124/dmd.121.000799
71. Boersma B, Poinot H, and Pommier A. Stimulating the antitumor immune response using immunocytokines: A preclinical and clinical overview. Pharmaceutics. (2024) 16:974. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16080974
72. Chang YW, Hsiao HW, Chen JP, Tzeng SF, Tsai CH, Wu CY, et al. A CSF-1R-blocking antibody/IL-10 fusion protein increases anti-tumor immunity by effectuating tumor-resident CD8+ T cells. Cell Rep Med. (2023) 4:101154. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101154
73. Buruiana FE, Solà I, and Alonso-Coello P. Recombinant human interleukin 10 for induction of remission in Crohn’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2010) 2012. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005109.pub3
74. van Roon J, Wijngaarden S, Lafeber FP, Damen C, van de Winkel J, and Bijlsma JW. Interleukin 10 treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis enhances Fc gamma receptor expression on monocytes and responsiveness to immune complex stimulation. J Rheumatol. (2003) 30:648–51.
75. Kumar A, Zanotti S, Bunnell G, Habet K, Añel R, Neumann A, et al. Interleukin-10 blunts the human inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide without affecting the cardiovascular response. Crit Care Med. (2005) 33:331–40. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000152229.69180.2
76. Santonocito D and Puglia C. Nanotechnological systems and lung: A perfect combination for lung pharmaceutical applications. Curr Med Chem. (2023) 30:725–43. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220829092323
77. Abu Lila AS and Ishida T. Liposomal delivery systems: design optimization and current applications. Biol Pharm Bull. (2017) 40:1–10. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b16-00624
78. Bassetti M, Vena A, Russo A, and Peghin M. Inhaled liposomal antimicrobial delivery in lung infections. Drugs. (2020) 80:1309–18.
79. Swaminathan J and Ehrhardt C. Liposomes for pulmonary drug delivery. In: Smyth HDC and Hickey AJ, editors. Controlled pulmonary drug delivery. Springer New York, New York, NY (2011). p. 313–34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9745-6_14
80. Kabay B, Aytekin FO, Aydin C, Ozer A, Kabay N, Tekin K, et al. Interleukin-10 gene therapy attenuates pulmonary tissue injury caused by mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion in a mouse model. Tohoku J Exp Med. (2005) 207:133–42. doi: 10.1620/tjem.207.133
81. Santonocito D and Puglia C. Applications of lipid-based nanocarriers for parenteral drug delivery. Curr Med Chem. (2022) 29:4152–69. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220104111949
82. Puglia C, Santonocito D, Romeo G, Intagliata S, Romano GL, Strettoi E, et al. Lipid nanoparticles traverse non-corneal path to reach the posterior eye segment: in vivo evidence. Molecules. (2021) 26:4673. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154673
83. Massaro M, Wu S, Baudo G, Liu H, Collum S, Lee H, et al. Lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA delivery in lung fibrosis. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2023) 183:106370. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106370
84. Kim J, Jozic A, Lin Y, Eygeris Y, Bloom E, Tan X, et al. Engineering Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhanced Intracellular Delivery of mRNA through Inhalation. ACS Nano. (2022) 16:14792–806. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c05647
85. Li Q, Chan C, Peterson N, Hanna RN, Alfaro A, Allen KL, et al. Engineering caveolae-targeted lipid nanoparticles to deliver mRNA to the lungs. ACS Chem Biol. (2020) 15:830–6. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00003
86. Popoola DO, Cao Z, Men Y, Li X, Viapiano M, Wilkens S, et al. Lung-specific mRNA delivery enabled by sulfonium lipid nanoparticles. Nano Lett. (2024) 24:8080–8. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01854
87. Bonaccorso A, Pellitteri R, Ruozi B, Puglia C, Santonocito D, Pignatello R, et al. Curcumin loaded polymeric vs. Lipid nanoparticles: antioxidant effect on normal and hypoxic olfactory ensheathing cells. Nanomaterials. (2021) 11:159. doi: 10.3390/nano11010159
88. Mundargi RC, Babu VR, Rangaswamy V, Patel P, and Aminabhavi TM. Nano/micro technologies for delivering macromolecular therapeutics using poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) and its derivatives. J Controlled Release. (2008) 125:193–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.09.013
89. Yilma A, Sahu R, Subbarayan P, Villinger F, Coats M, Singh S, et al. PLGA-chitosan encapsulated IL-10 nanoparticles modulate chlamydia inflammation in mice. Int J Nanomedicine. (2024), 1287–301. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S432970
90. Shahzad KA, Wang Z, Li X, Li J, Xu M, and Tan F. Immunomodulatory effect of PLGA-encapsulated mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1429442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429442
91. Duncan SA, Dixit S, Sahu R, Martin D, Baganizi DR, Nyairo E, et al. Prolonged release and functionality of interleukin-10 encapsulated within PLA-PEG nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. (2019) 9:1074.
92. Torchilin VP. Micellar nanocarriers: pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharm Res. (2006) 24:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s11095-006-9132-0
93. Patton JS and Byron PR. Inhaling medicines: delivering drugs to the body through the lungs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2007) 6:67–74. doi: 10.1038/nrd2153
94. Diaferia C, Rosa E, Accardo A, and Morelli G. Peptide-based hydrogels as delivery systems for doxorubicin. J Pept Sci. (2022) 28:e3301. doi: 10.1002/psc.3301
95. Du X, Zhou J, Shi J, and Xu B. Supramolecular hydrogelators and hydrogels: from soft matter to molecular biomaterials. Chem Rev. (2015) 115:13165–307. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00299
96. Sok MCP, Baker N, McClain C, Lim HS, Turner T, Hymel L, et al. Dual delivery of IL-10 and AT-RvD1 from PEG hydrogels polarize immune cells towards pro-regenerative phenotypes. Biomaterials. (2021) 268:120475.
97. Soranno DE, Rodell CB, Altmann C, Duplantis J, Andres-Hernando A, Burdick JA, et al. Delivery of interleukin-10 via injectable hydrogels improves renal outcomes and reduces systemic inflammation following ischemic acute kidney injury in mice. Am J Physiol-Ren Physiol. (2016) 311:F362–72. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00579.2015
98. Wang Z, Li D, Wang Y, Yuan P, Zhang W, Zhang Y, et al. Hyaluronic acid methacryloyl hydrogel with sustained IL-10 release promotes macrophage M2 polarization and motor function after spinal cord injury. J Biomater Appl. (2025), 08853282251329302. doi: 10.1177/08853282251329302
99. Liu J and Zhao X. Design of self-assembling peptides and their biomedical applications. Nanomed. (2011) 6:1621–43.
100. Wang C, Li T, Zeng X, Wu L, Gao M, Tong N, et al. Sustained delivery of IL-10 by self-assembling peptide hydrogel to reprogram macrophages and promote diabetic alveolar bone defect healing. Dent Mater. (2023) 39:418–29. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2023.03.014
101. Li L, Fu L, Ai X, Zhang J, and Zhou J. Design and fabrication of temperature-sensitive nanogels with controlled drug release properties for enhanced photothermal sterilization. Chemistry. (2017) 23:18180–6.
102. Carvalho V, Castanheira P, Madureira P, Ferreira SA, Costa C, Teixeira JP, et al. Self-assembled dextrin nanogel as protein carrier: Controlled release and biological activity of IL-10. Biotechnol Bioeng. (2011) 108:1977–86. doi: 10.1002/bit.23125
103. Kwok ZH, Ni K, and Jin Y. Extracellular vesicle associated non-coding RNAs in lung infections and injury. Cells. (2021) 10:965.
104. Kalluri R and LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. (2020) 367:eaau6977. doi: 10.1126/science.aau6977
105. Hisey CL, Artuyants A, Guo G, Chang V, Reshef G, Middleditch M, et al. Investigating the consistency of extracellular vesicle production from breast cancer subtypes using CELLine adherent bioreactors. J Extracell Biol. (2022) 1:e60. doi: 10.1002/jex2.60
106. Park KS, Svennerholm K, Shelke GV, Bandeira E, Lässer C, Jang SC, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived nanovesicles ameliorate bacterial outer membrane vesicle-induced sepsis via IL-10. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10:231. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1352-4
107. Arabpour M, Saghazadeh A, and Rezaei N. Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 97:107823. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107823
108. Xia L, Zhang C, Lv N, Liang Z, Ma T, Cheng H, et al. AdMSC-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury via transferring mitochondrial component to improve homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Theranostics. (2022) 12:2928–47.
109. Meng Q, Winston T, Ma J, Song Y, Wang C, Yang J, et al. INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM CELL-DERIVED MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS-DERIVED EXTRACELLULAR VESICLES ATTENUATE LPS-INDUCED LUNG INJURY AND ENDOTOXEMIA IN MICE. Shock. (2024) 62:294–303. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002381
110. Stone ML, Zhao Y, Robert Smith J, Weiss ML, Kron IL, Laubach VE, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury and enhance reconditioning of donor lungs after circulatory death. Respir Res. (2017) 18:212. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0704-9
111. Ren J, Liu Y, Yao Y, Feng L, Zhao X, Li Z, et al. Intranasal delivery of MSC-derived exosomes attenuates allergic asthma via expanding IL-10 producing lung interstitial macrophages in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 91:107288. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107288
112. Saleh NA, Gagea MA, Vitija X, Janovic T, Schmidt JC, Deng CX, et al. Harnessing extracellular vesicles for stabilized and functional IL-10 delivery in macrophage immunomodulation. Immunology. (2025). doi: 10.1101/2025.01.14.633016
113. Kammala AK, Mosebarger A, Radnaa E, Rowlinson E, Vora N, Fortunato SJ, et al. Extracellular Vesicles-mediated recombinant IL-10 protects against ascending infection-associated preterm birth by reducing fetal inflammatory response. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1196453. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1196453
114. Liu J, Ren H, Zhang C, Li J, Qiu Q, Zhang N, et al. Orally-delivered, cytokine-engineered extracellular vesicles for targeted treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Small. (2023) 19:2304023.
115. Nykänen AI, Mariscal A, Duong A, Ali A, Takahagi A, Bai X, et al. Lung transplant immunomodulation with genetically engineered mesenchymal stromal cells—Therapeutic window for interleukin-10. Cells. (2024) 13:859.
116. Nykänen AI, Mariscal A, Duong A, Estrada C, Ali A, Hough O, et al. Engineered mesenchymal stromal cell therapy during human lung ex vivo lung perfusion is compromised by acidic lung microenvironment. Mol Ther - Methods Clin Dev. (2021) 23:184–97.
117. Li Z, Qiao W, Wang C, Wang H, Ma M, Han X, et al. DPPC-coated lipid nanoparticles as an inhalable carrier for accumulation of resveratrol in the pulmonary vasculature, a new strategy for pulmonary arterial hypertension treatment. Drug Deliv. (2020) 27:736–44. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1760962
118. Ghadiri M, Young PM, and Traini D. Strategies to enhance drug absorption via nasal and pulmonary routes. Pharmaceutics. (2019) 11:113.
119. Matsuda M, Inaba M, Hamaguchi J, Tomita H, Omori M, Shimora H, et al. Local IL-10 replacement therapy was effective for steroid-insensitive asthma in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) :110:109037. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109037
120. Gomez Perdiguero E, Schulz C, and Geissmann F. Development and homeostasis of “resident” myeloid cells: The case of the microglia. Glia. (2013) 61:112–20. doi: 10.1002/glia.22393
121. Newton K and Dixit VM. Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2012), a006049–a006049. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006049
122. Zindel J and Kubes P. DAMPs, PAMPs, and LAMPs in immunity and sterile inflammation. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis. (2020) 15:493–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032847
123. Wu Y, Wan S, Yang S, Hu H, Zhang C, Lai J, et al. Macrophage cell membrane-based nanoparticles: a new promising biomimetic platform for targeted delivery and treatment. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:542. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01746-6
124. Oroojalian F, Beygi M, Baradaran B, Mokhtarzadeh A, and Shahbazi M. Immune cell membrane-coated biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Small. (2021) 17:2006484.
125. Li JD and Yin J. Interleukin-10-alveolar macrophage cell membrane-coated nanoparticles alleviate airway inflammation and regulate Th17/regulatory T cell balance in a mouse model. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1186393. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186393
126. Chu M, Wang H, Bian L, Huang J, Wu D, Zhang R, et al. Nebulization therapy with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for COVID-19 pneumonia. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2022) 18:2152–63. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10398-w
127. Matsuzaka Y and Yashiro R. Therapeutic strategy of mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles as regenerative medicine. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:6480. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126480
128. Wang S, Lei B, Zhang E, Gong P, Gu J, He L, et al. Targeted therapy for inflammatory diseases with mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes: from basic to clinics. Int J Nanomedicine. (2022) 17:1757–81. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S355366
129. Tao Y, Xu X, Yang B, Zhao H, and Li Y. Mitigation of sepsis-induced acute lung injury by BMSC-derived exosomal miR-125b-5p through STAT3-mediated suppression of macrophage pyroptosis. Int J Nanomedicine. (2023) 18:7095–113. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S441133
130. Nitzsche F, Müller C, Lukomska B, Jolkkonen J, Deten A, and Boltze J. Concise review: MSC adhesion cascade—Insights into homing and transendothelial migration. Stem Cells. (2017) 35:1446–60. doi: 10.1002/stem.2614
131. Salazar-Puerta AI, Rincon-Benavides MA, Cuellar-Gaviria TZ, Aldana J, Vasquez Martinez G, Ortega-Pineda L, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles derived from dermal fibroblasts attenuate inflammation in a murine model of acute lung injury. Adv Mater. (2023) 35:2210579. doi: 10.1002/adma.202210579
132. Li N, Weng D, Wang SM, Zhang Y, Chen SS, Yin ZF, et al. Surfactant protein-A nanobody-conjugated liposomes loaded with methylprednisolone increase lung-targeting specificity and therapeutic effect for acute lung injury. Drug Deliv. (2017) 24:1770–81. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1402217
133. Li H, Wang S, He X, Li N, Yu F, Hu Y, et al. A novel nanobody specific for respiratory surfactant protein A has potential for lung targeting. Int J Nanomedicine. (2015), 2857. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S77268
134. Watson A, Madsen J, and Clark HW. SP-A and SP-D: dual functioning immune molecules with antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. Front Immunol. (2021) 11:622598. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.622598
135. Yang L, Carrillo M, Wu YM, DiAngelo SL, Silveyra P, Umstead TM, et al. SP-R210 (Myo18A) isoforms as intrinsic modulators of macrophage priming and activation. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0126576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126576
136. Kim M, Park S, Lee N, Kim D, Kim D, Jin Y, et al. Advanced MicroRNA delivery for lung inflammatory therapy: surfactant protein A controls cellular internalisation and degradation of extracellular vesicles. Thorax. (2025) 80:322–34. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2024-221793
137. Ma C, Zhai Y, Li CT, Liu J, Xu X, Chen H, et al. Translating mesenchymal stem cell and their exosome research into GMP compliant advanced therapy products: Promises, problems and prospects. Med Res Rev. (2024) 44:919–38. doi: 10.1002/med.22002
138. Witwer KW, Van Balkom BWM, Bruno S, Choo A, Dominici M, Gimona M, et al. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J Extracell Vesicles. (2019) 8:1609206. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1609206
139. McGowan NWA, Campbell JDM, and Mountford JC. Good manufacturing practice (GMP) translation of advanced cellular therapeutics: lessons for the manufacture of erythrocytes as medicinal products. In: Lloyd JA, editor. Erythropoiesis. Springer New York, New York, NY (2018). p. 285–92. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7428-3_18
140. Spohn G, Witte AS, Kretschmer A, Seifried E, and Schäfer R. More human BM-MSC with similar subpopulation composition and functional characteristics can be produced with a GMP-compatible fabric filter system compared to density gradient technique. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:638798. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.638798
141. Cherian DS, Bhuvan T, Meagher L, and Heng TSP. Biological considerations in scaling up therapeutic cell manufacturing. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:654. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00654
142. Chen YS, Lin EY, Chiou TW, and Harn HJ. Exosomes in clinical trial and their production in compliance with good manufacturing practice. Tzu Chi Med J. (2020) 32:113. doi: 10.4236/cm.2020.113007
143. Ferreira MV, Cabral ET, and Coroadinha AS. Progress and perspectives in the development of lentiviral vector producer cells. Biotechnol J. (2021) 16:2000017. doi: 10.1002/biot.202000017
144. Park J, Inwood S, Kruthiventi S, Jenkins J, Shiloach J, and Betenbaugh M. Progressing from transient to stable packaging cell lines for continuous production of lentiviral and gammaretroviral vectors. Curr Opin Chem Eng. (2018) 22:128–37. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2018.09.007
145. Cavallazzi Sebold B, Ni G, Li J, Li H, Liu X, and Wang T. PEGylated IL-10: clinical development in cancer immunotherapy, where to go? Curr Oncol Rep. (2023) 25:115–22.
146. Park K, Skidmore S, Hadar J, Garner J, Park H, Otte A, et al. Injectable, long-acting PLGA formulations: Analyzing PLGA and understanding microparticle formation. J Controlled Release. (2019) 304:125–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.05.003
147. Zhi K, Raji B, Nookala AR, Khan MM, Nguyen XH, Sakshi S, et al. PLGA nanoparticle-based formulations to cross the blood–brain barrier for drug delivery: from R&D to cGMP. Pharmaceutics. (2021) 13:500. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040500
148. Wasalathanthri DP, Feroz H, Puri N, Hung J, Lane G, Holstein M, et al. Real-time monitoring of quality attributes by in-line Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic sensors at ultrafiltration and diafiltration of bioprocess. Biotechnol Bioeng. (2020) 117:3766–74. doi: 10.1002/bit.27532
149. Eskdale J, Kube D, Tesch H, and Gallagher G. Mapping of the human IL10 gene and further characterization of the 5’ flanking sequence. Immunogenetics. (1997) 46:120–8.
150. Świątek BJ. Is interleukin-10 gene polymorphism a predictive marker in HCV infection? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2012) 23:47–59.
151. Suárez A, Castro P, Alonso R, Mozo L, and Gutiérrez C. Interindividual variations in constitutive interleukin-10 messenger RNA and protein levels and their association with genetic polymorphisms1. Transplantation. (2003) 75:711–7.
152. Thellin O, Coumans B, Zorzi W, Igout A, and Heinen E. Tolerance to the foeto-placental ‘graft’: ten ways to support a child for nine months. Curr Opin Immunol. (2000) 12:731–7. doi: 10.1016/S0952-7915(00)00170-9
153. Urosevic M and Dummer R. HLA-G and IL-10 expression in human cancer—different stories with the same message. Semin Cancer Biol. (2003) 13:337–42. doi: 10.1016/S1044-579X(03)00024-5
154. Cao S, Liu J, Song L, and Ma X. The protooncogene c-maf is an essential transcription factor for IL-10 gene expression in macrophages. J Immunol. (2005) 174:3484–92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.6.3484
155. Michée-Cospolite M, Boudigou M, Grasseau A, Simon Q, Mignen O, Pers JO, et al. Molecular mechanisms driving IL-10- producing B cells functions: STAT3 and c-MAF as underestimated central key regulators? Front Immunol. (2022) 13:818814. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.818814
156. Lim PN, Cervantes MM, Pham LK, Doherty SR, Tufts A, Dubey D, et al. Absence of c-Maf and IL-10 enables type I IFN enhancement of innate responses to LPS in alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. (2025) 214:551–64. doi: 10.1093/jimmun/vkae029
157. Kawashima S, Hirose K, Iwata A, Takahashi K, Ohkubo A, Tamachi T, et al. β-glucan curdlan induces IL-10–producing CD4+ T cells and inhibits allergic airway inflammation. J Immunol. (2012) 189:5713–21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201521
158. Reddy NR, Maachi H, Xiao Y, Simic MS, Yu W, Tonai Y, et al. Engineering synthetic suppressor T cells that execute locally targeted immunoprotective programs. Science. (2024) 386:eadl4793. doi: 10.1126/science.adl4793
159. Wang JH, Gessler DJ, Zhan W, Gallagher TL, and Gao G. Adeno-associated virus as a delivery vector for gene therapy of human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:78. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01780-w
160. Albelda SM. CAR T cell therapy for patients with solid tumours: key lessons to learn and unlearn. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2024) 21:47–66. doi: 10.1038/s41571-023-00832-4
161. He B, Wilson B, Chen SH, Sharma K, Scappini E, Cook M, et al. Molecular engineering of virus tropism. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:11094. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011094
162. Cao H, Duan L, Zhang Y, Cao J, and Zhang K. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6:426. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00830-x
Keywords: interleukin-10, pulmonary inflammation, anti-inflammatory, targeted delivery, nanoparticles, hydrogels, extracellular vesicles, cell-based delivery
Citation: Tian W, Wang X, Zeng J, Gao Y, Tang S, Ma C, Ye L and Tian X (2025) Advances in interleukin-10-based therapies for pulmonary diseases: focus on targeted lung delivery systems. Front. Immunol. 16:1630990. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1630990
Received: 19 May 2025; Accepted: 28 October 2025;
Published: 12 November 2025.
Edited by:
Leandro J. Carreno, University of Chile, ChileReviewed by:
Rohit Sharma, University of California, Berkeley, United StatesHadi Rajabi, Koç University Hospital, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Wang, Zeng, Gao, Tang, Ma, Ye and Tian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liping Ye, NTMxNTAzNTQ3QHFxLmNvbQ==; Xinghan Tian, dGFuZmVuZ2VyNzhAZ21haWwuY29t
 Weikun Tian
Weikun Tian Xu Wang1
Xu Wang1