- Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Hengyang, China
Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum (T. pallidum) is the causative agent of syphilis, a chronic sexually transmitted disease that leads to widespread organ damage. The pathogenesis of syphilis involves crucial functional proteins that facilitate bacterial adhesion to host cells, invasion, dissemination, immune evasion, and inflammatory responses. Investigating these proteins is crucial for the development of innovative diagnostic tools, vaccines, and therapies. However, the intricate nature of T. pallidum and the inability to culture in vitro hinder our comprehensive understanding of these proteins. This review article presents innovative understandings of the pathogenesis of T. pallidum functional proteins, building upon existing knowledge. This paper establishes a foundation for comprehending the current knowledge landscape and outlining future research avenues.
1 Introduction
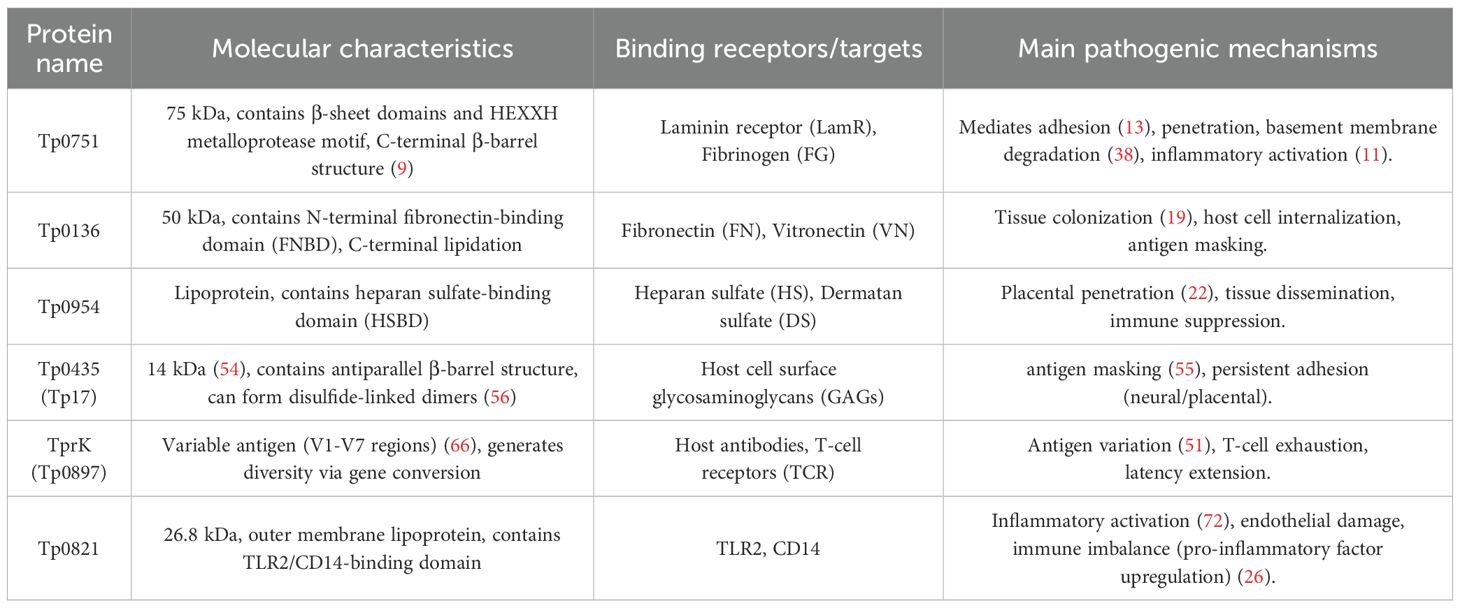
Syphilis, a chronic sexually transmitted disease caused by Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum (T. pallidum), poses a significant threat to human health due to its potential for multi-organ damage (1). Syphilis treatment and clinical management must adhere to the principles of “early diagnosis, prompt treatment, and adequate standardized medication.” Penicillin-based regimens are the first-line therapy, adjusted according to disease stage and individual circumstances. This approach emphasizes synchronized partner screening and treatment, along with rigorous serological monitoring (early and sufficient penicillin treatment can achieve cure). Maternal and neonatal management constitutes a critical component for blocking mother-to-child transmission (2). Global efforts are intensifying screening and expanding accessible services to curb the epidemic. According to the latest data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021, there were approximately 18.696 million incident cases of syphilis globally in 2021, with an age-standardized incidence rate of 235.47 per 100,000 population (3). Recent epidemiological data in China indicate a notable rise in syphilis incidence (4). However, the inability to cultivate and genetically manipulate T. pallidum in the laboratory has impeded the elucidation of its molecular pathogenic mechanisms. T. pallidum, a member of the genus Treponema within the family Treponema, features a structure comprising a cylindrical protoplasm, a flagella-like structure, a plasma membrane, a peptidoglycan layer, a periplasmic space, and an outer membrane arranged from inner to outer layers (5). Notably, the outer membrane lacks lipopolysaccharides typical of Gram-negative bacteria and does not secrete lytic or cytotoxic toxins; nevertheless, it exhibits robust tissue invasion capabilities. During the initial stages of infection, T. pallidum can breach the placental and blood-brain barriers, leading to congenital syphilis and neurosyphilis, respectively (6). Previous investigations have outlined the pathogenic cascade of T. pallidum, encompassing adhesion, invasion, immune evasion, dissemination, and tissue damage. Numerous studies have delved into the functional proteins’ roles in T. pallidum pathogenesis. This review will summarize advancements in understanding the pathogenic mechanisms of the agent’s functional proteins across these processes (Table 1).
2 Adhesion and colonization
T. pallidum, as a microaerophilic bacterium, is compelled to adhere to and colonize host cells due to its severe biosynthetic deficiencies and ineffective reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging mechanisms. This strategy serves dual purposes: direct nutrient acquisition and dependence on host antioxidant systems (e.g., catalase) to mitigate oxidative stress for survival. By employing specific adhesion facilitated by functional proteins, T. pallidum establishes targeted attachment to mucopolysaccharide-rich tissues such as the skin and aorta (7). This adhesion and colonization process represents the initial stages of T. pallidum infection, where surface proteins of T. pallidum interact with the host extracellular matrix (ECM) and receptors through various mechanisms, setting the stage for subsequent invasion.
2.1 Tp0751
Tp0751 comprises an N-terminal disordered region (IDR) and a C-terminal lipocalin fold (8). The C-terminal domain is composed of eight beta chains that create an unconventional lipid vesicle protein fold. This domain features multiple short conserved regions scattered on its surface, establishing an interface with extracellular matrix (ECM) components (9). Moreover, the C-terminus of this domain harbors a zinc ion-catalyzed HEXXH metalloprotease activity motif responsible for degrading host proteins like fibrinogen and laminin (10). Recent studies further reveal that Tp0751 contributes to blood-brain barrier disruption by altering tight junction protein expression (e.g., ZO-1, occludin) and inducing pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6) in endothelial cells (11). Tp0751 is situated external to the plasma membrane of T. pallidum, rather than on the outer membrane surface, leading to its limited immunogenicity. Heterogeneous expression studies demonstrate its capacity to mimic adhesion functions on the surface of Borrelia burgdorferi, affirming its potential for surface exposure (12). The adhesion mechanism of the Tp0751 protein involves utilizing multiple domains to collectively recognize host extracellular matrix (ECM) components such as laminin, fibronectin. It facilitates electrostatic binding through arginine/lysine-rich regions and generates a multivalent anchoring effect (13). Critically, Tp0751 disrupts endothelial integrity by targeting VE-cadherin junctions, thereby facilitating bacterial transmigration across endothelial barriers (14). Under shear stress conditions, Tp0751 facilitates adhesion through a two-stage mechanism: an initial deceleration stage, wherein it extensively binds to extracellular matrix (ECM) components, thereby reducing helicoid movement speed; and a subsequent specific binding stage, during which it interacts with endothelial receptors (e.g., ICAM-1) via the p10 region to establish stable adhesion. Experimental evidence has demonstrated that synthetic peptides derived from the lipocalcin domain of Tp0751 can impede its adhesion capacity (9). Vaccination studies in rabbits demonstrate that antibody-mediated blockade of Tp0751’s adhesive functions significantly inhibits T. pallidum dissemination, highlighting its pivotal role in systemic spread without invoking thrombin degradation (15). Tp0751 has been demonstrated to bind multiple extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. The aberrant deposition of these proteins within the tumor microenvironment provides a foundation for its targeting potential (16). Future research should explore Tp0751-functionalized nanoparticles to enhance tumor-targeted delivery efficiency through specific ECM binding. Integrating imaging probes with therapeutic payloads could facilitate the development of theranostic nanoplatforms.
2.2 Tp0136
Tp0136, a 495-amino-acid protein with a molecular weight of approximately 50 kDa, is encoded by a 1,488 bps gene. Tp0136 exhibits significant sequence heterogeneity among different strains (17). This manifests as nucleotide mismatches, insertions, or deletions in the coding gene, leading to amino acid sequence diversity, and such differences remain stable across different isolates (18). In the pathogenesis of T. pallidum adhesion, the Tp0136 protein utilizes a complex molecular mechanism. It selectively binds to host extracellular matrix (ECM) components in the conserved N-terminal region and variable C-terminal regions (18). Particularly, its binding affinity for cellular fibronectin (cFn) exceeds that for plasma fibronectin (pFn), highlighting its essential function in tissue penetration (18). In human dermal vascular smooth muscle cells (HDVSMCs), Cai et al. demonstrated that recombinant Tp0136 protein activates the PI3K, MAPK (JNK, p38), and NF-κB signaling pathways. This activation led to a significant, concentration-dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP1) at both mRNA and protein levels, while TIMP1 and TIMP2 expression remained largely unchanged. Consequently, the MMP1/TIMP1 and MMP1/TIMP2 ratios were significantly increased. Pharmacological inhibition of these pathways suppressed MMP1 induction and restored the MMP/TIMP balance. These findings suggest that Tp0136 promotes ECM degradation and facilitates T. pallidum dissemination by disrupting the MMP/TIMP equilibrium via PI3K/MAPK/NF-κB signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells (19). Djokic et al. (20) observed that when Borrelia burgdorferi expressed Tp0136 heterologously (B314 strain), it displayed varying affinities for different host cell lines, with the highest affinity observed for epidermal cells (HEK293) and glial cells (C6). Furthermore, the protein disrupts vascular endothelial cell-to-cell junctions, including VE-cadherin, in a dose-dependent manner. This disruption results in a threefold increase in endothelial permeability above baseline levels within 24 hours, promoting spirochete hematogenous dissemination (21). The mechanisms mentioned above work together to anchor pathogens to infection sites and facilitate systemic dissemination by altering host microenvironments, providing essential molecular targets for targeted intervention strategies to inhibit pathogen adhesion.
2.3 Tp0954
Tp0954, a surface lipoprotein of T. pallidum, plays a pivotal role as a placenta-targeted adhesin (22). Its pathogenic role is associated with its tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain, which mediates specific interactions with host tissues and forms oligomers, significantly enhancing the pathogen’s adherence to host tissues, particularly glycosaminoglycans like dermatan sulfate, heparin, and heparan sulfate (23). This interaction facilitates the binding of spirochetes to placental trophoblast cells. In experimental models, the adhesion efficiency of Tp0954 increases by more than 50%. This targeted adhesion not only assists in the traversal of the pathogen through the placental barrier but also promotes vertical transmission from mother to child by disrupting intercellular junction structures, a fundamental mechanism in the pathogenesis of congenital syphilis (22). He et al. demonstrated through heterologous expression of Tp0954 that this protein significantly enhances adhesion to epithelial, endothelial, neuronal, and placental cells in heterologous hosts such as the Borrelia burgdorferi B314 strain (22, 24). Their findings indicate that Tp0954 mediates T. pallidum adhesion to host cells, thereby promoting initial pathogen colonization and transplacental transmission. Future studies should focus on elucidating the specific interaction mechanisms between Tp0954 and host cell surface receptors, as well as exploring how its adhesion functionality regulates immune evasion and systemic dissemination. In vitro studies have shown that overexpression of Tp0954 significantly enhances spirochete colonization in placental tissues, highlighting its potential as a critical target for preventing mother-to-child transmission.
2.4 Tp0155
Tp0155, consisting of 371 amino acids and has a molecular weight of approximately 43 kDa, is cell surface localized (25). It plays a crucial role in the adhesion process of T. pallidum due to its distinctive domain structure and dynamic expression profile. The protein facilitates the pathogenicity of T. pallidum by utilizing two key domains, namely LysM and M23. The LysM domain specifically interacts with fibronectin (FN) present on the surface of host cells. The M23 domain acts as a peptidase that degrades peptidoglycans, thereby facilitating tissue invasion (26). Similarly, studies suggest that the M23 domain in Treponema denticola may degrade extracellular matrix components to support bacterial colonization. Tp0155 collaborates with Tp0483 to establish an adhesion system where Tp0155 anchors matrix FN for direct adhesion, while Tp0483 facilitates indirect binding of soluble FN (27). Throughout the infection process, Tp0155 demonstrates a dual-phase expression pattern during the chancre and immune clearance phases. It maintains high expression levels to evade host defenses effectively. Moreover, its coordinated action with the metalloproteinase Tp0751, which enhances adhesion and degrades the matrix, accelerates the dissemination of the pathogen. Targeting the LysM domain with small-molecule inhibitors presents a promising approach to impede FN binding, offering a novel avenue for anti-adhesion therapy.
3 Invasion and dissemination
T. pallidum exhibits a robust capacity for invasion and infection, leading to various clinical presentations throughout the course of syphilis, which is characterized by three stages: primary syphilitic chancre, secondary syphilis with mucocutaneous lesions, and tertiary syphilis involving gummatous lesions and cardiovascular/neurological complications (28). This pathogen can disseminate systemically via blood and lymphatic routes, breaching the blood-brain, blood-testis, and placental barriers (29). Upon successful colonization, the pathogen employs a sophisticated “molecular drilling system” comprising multiple protein modules to facilitate systemic dissemination by simultaneously dismantling physical barriers and modulating the immune microenvironment.
3.1 Tp0965
Tp0965 protein, with a molecular weight of approximately 35.5 kDa, is a periplasmic membrane fusion protein encoded by the tp34 gene cluster (30). Its robust immunogenicity and interactions with host cells are pivotal in the pathogenesis process (31). Generally, this protein can facilitate pathogen dissemination by disrupting vascular barriers through a multifaceted mechanism. Specifically, Tp0965 activates endothelial cells, leading to a substantial upregulation of adhesion molecules such as ICAM-1, E-selectin, and the chemokine MCP-1 (30). Moreover, it enhances monocyte mobility by 34.8%. Additionally, Tp0965 induces F-actin reorganization in endothelial cells, resulting in the formation of intracellular stress fibers and a 50% reduction in the expression of the tight junction protein Claudin-1. Consequently, vascular permeability is significantly increased, as evidenced by a 130% rise in HRP flux, thereby expediting pathogen infiltration into deeper tissues. Studies on the molecular mechanisms have revealed that Tp0965 facilitates cytoskeletal remodeling and barrier damage via the RhoA/ROCK pathway, with partial reversal of its effects by a ROCK inhibitor (30). Furthermore, it triggers the activation of the ERK/JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway depending on the TLR2/Chemerin-ChemR23 axis (32). This leads to the upregulation of Cemerin-dependent inflammatory factors, such as MMP-2, thereby exacerbating endothelial damage and immunopathological effects. The structural characteristics of Tp0965, including its membrane fusion properties and regulation of signaling cascades, collectively disturb vascular barrier homeostasis. As a highly sensitive antigen and a critical signaling target (e.g., RhoA/ROCK), Tp0965 serves as a crucial molecular determinant for understanding the mechanisms underlying syphilitic vascular injury and for devising targeted intervention strategies (30).
3.2 TpF1
TpF1, a 17.2 kDa monomer forming a 206 kDa dodecamer (33), shares structural homology with Helicobacter pylori HP-NAP and exhibits pro-inflammatory properties (34). It serves as an early serological marker, though diagnostic sensitivity data requires validation (35). In human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), TpF1 activates the CREB/NF-κB signaling, elevating IL-8 expression 3-fold. Consequently, endothelial proliferation, migration, and microangiogenesis are significantly enhanced in an IL-8-dependent manner, as evidenced by 50% more vessel branches in zebrafish (34). This process is crucial in secondary syphilis, where IL-8-mediated neovascularization facilitates pathogen dissemination and neutrophil recruitment, exacerbating local inflammation. Conversely, TpF1 suppresses microglial migration by impairing actin polymerization via TLR4/PI3K/AKT/Rac1 inhibition, reducing F-actin/G-actin ratio and impairing cytoskeletal dynamics. This dual modulation of host responses—enhancing vascularization while disabling microglial motility—may facilitate systemic dissemination (36). Theoretical targeting of IL-8 pathways could attenuate angiogenic effects (34). The dual functionality of TpF1 as both a diagnostic marker and a pathogenic factor, along with its conserved structural characteristics, lays the groundwork for the development of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
3.3 Tp0751 (pallilysin)
Tp0751 is a bifunctional outer membrane protein with the capacity to bind laminin (LN), fibronectin (FN), and fibrinogen (FG), which are present on endothelial cell surfaces and in the underlying basement membrane (37). Additionally, it exhibits metalloproteinase activity, known as pallilysin, enabling the degradation of bound laminin and fibrinogen (38). Structurally, the C-terminal region of Tp0751 features a predicted beta-barrel structure composed of eight beta-strands, belonging to the OmpA-OmpF porin-like superfamily (9). This region harbors the HEXXH metalloproteinase motif, facilitating Zn²+ binding and functioning as a zinc-dependent membrane-bound metalloproteinase (10). Studies by Houston et al. (38) demonstrated that mutations in the HEXXH motif do not impact Tp0751’s adhesion function, suggesting a structural and functional independence between its adhesion and protease activities. The proteolytic action of pallilysin on fibrin clots promotes the dissemination of T. pallidum within the host, aiding in the establishment of chronic infection. Recent work by Lithgow et al. (14) revealed that both live T. pallidum and recombinant Tp0751 can disrupt VE-cadherin without altering vascular barrier permeability. This finding, along with supporting data on cholesterol dependence, led Lithgow et al. to propose a model where T. pallidum traverses the endothelial barrier via cholesterol-dependent endocytosis.
3.4 Tp0750
Tp0750, a serine protease located at out membrane in T. pallidum, functions in adhesion. The gene encoding it spans 672 bp, translating into a 223-amino-acid protein with a molecular weight of approximately 26 × 10³. Structurally and functionally akin to Tp0751, Tp0750 serves as a pivotal virulence factor in T. pallidum, facilitating host barrier penetration and systemic dissemination. Noteworthy features of this protein include vWFA domains and metal ion-dependent adhesion sites (MIDAS), enabling interactions with host proteins like annexin A2 through calcium ion binding (39). Moreover, Tp0750 modulates the coagulation-fibrinolytic system by exhibiting dual enzymatic properties (serine protease and metalloproteinase-like activities). Functionally, Tp0750 impedes thrombosis by degrading fibrinogen (Fg) and fibronectin (Fn), while its interaction with annexin A2 promotes plasminogen activation, hastening pathogen release. Additionally, its metalloproteinase-like activity collaborates with pallilysin (Tp0751) to degrade ECM components like laminin and collagen, instigating a sequence of events termed “basement membrane degradation-deep invasion” (39). Moreover, Tp0750 orchestrates an intricate “invasion-lysis” cycle by modulating endothelial hemostasis equilibrium, suppressing anticoagulant factors, and stimulating the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors, which significantly enhances vascular permeability, thereby facilitating the penetration of spirochetes through endothelial barriers. The concurrent transcription and functional synergy with pallilysin’s genome, involving enzyme activity division and collaboration in thrombus inhibition, further intensifies the destructive impact on tissues. The regulation of targeting through its structural configuration and the coordination within a multi-enzyme network establishes the molecular underpinning for the widespread dissemination of T. pallidum. Additionally, in the view of its highly conserved pivotal functional domains, Tp0750 may serve as a promising candidate for vaccine development (40).
4 Immune evasion
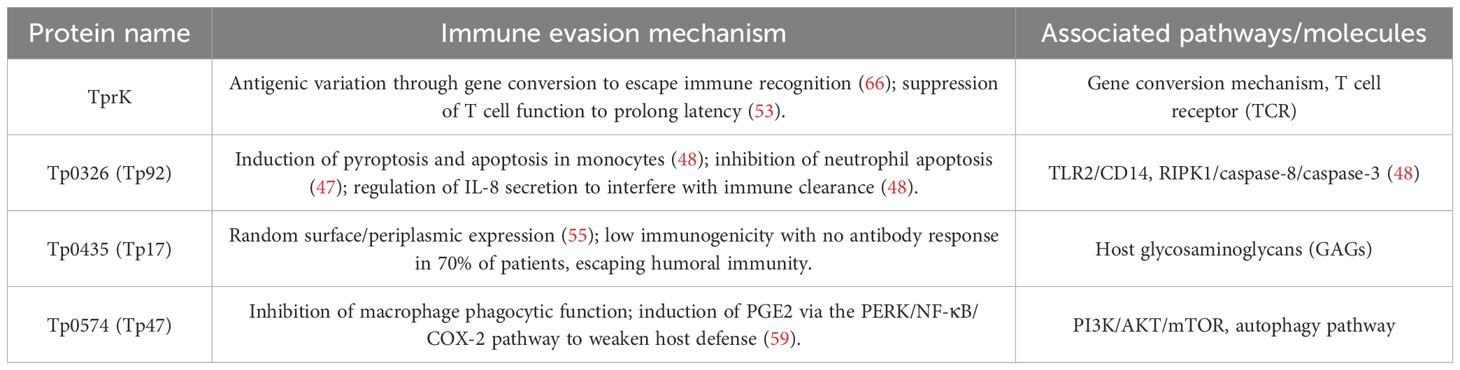
T. pallidum has exhibited robust immune evasion capabilities, capacitating it to withstand host immune responses, with functional proteins playing a pivotal role in this phenomenon. Specifically, the pathogen evades individual immune defense and elimination through the generation of numerous antigenic variations. Additionally, certain functional proteins impede the activation and replication of host immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and macrophages, facilitating the establishment of prolonged latency and sustaining transmission (41) (Table 2).
4.1 Tp0326 (Tp92)
Tp0326 (Tp92) is the sole outer membrane protein (OMP) within the T. pallidum family that shares homology with Escherichia coli’s BamA (42). It is the singular protein in the genome exhibiting sequence similarity to OMPs found in known Gram-negative bacteria (43). Belonging to the Omp85 superfamily, Tp0326 features a β-barrel structure and is characterized by low expression levels (44). Its structural attributes encompass the N-terminal POTRA domain, which facilitates outer membrane protein folding, and the C-terminal 18-strand β-barrel transmembrane structure. This structure exposes functional epitopes on the cell surface, albeit its limited abundance (approximately 100 copies/cell) and variations in the conformation of recombinant proteins hinder host immune recognition (45). Notably, It reveals that T. pallidum evades immune attacks by restricting the immunogenicity of surface antigens (such as β-barrels) and preferentially exposing non-surface regions (such as POTRA domains) (43). Furthermore, Tp92 not only contributes to immune evasion by restricting the immunogenicity of surface epitopes, but also actively promotes inflammation; for instance, it has been shown to activate endothelial cells and induce the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators. Tp92 induces apoptosis in monocytic cells (THP-1) through the RIPK1/caspase-8/caspase-3 pathway, promotes IL-8 secretion, resulting in depletion of immune cells (46). Conversely, it suppresses apoptosis in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (hPMNs) via activation of ERK MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB signaling pathways, thereby prolonging neutrophil survival (47). This anti-apoptotic effect is mediated by upregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1, inhibition of caspase-3/8/9 activity, and maintenance of mitochondrial membrane potential. Furthermore, Tp92 activates endothelial cells through the chemerin/CMKLR1 axis, inducing TNF-α and ICAM-1 expression to promote macrophage migration (48). The imbalanced “pro-inflammatory-anti-apoptotic” strategy exacerbates vascular permeability and tissue damage by inducing excessive IL-8 levels. Moreover, it creates a conducive environment for pathogen dissemination across physiological barriers like the blood-brain barrier by depleting immune cell populations.
4.2 TprK (Tp0897)
TprK (Tp0897) serves as the primary immune evasion factor in T. pallidum (49). Its structure comprises 20 β-barrel pore proteins with 10 surface-exposed loops, including 7 variable regions (V1-V7) that undergo sequence diversification via gene conversion mechanisms (50). Meanwhile, conserved regions (C1-C3) ensure structural stability. This dynamic variability enables host antibodies to target variable epitopes within the V region, promoting immune evasion. For instance, the SS14-DCKO strain exhibits reduced virulence in vivo due to its inability to generate new variants, underscoring the importance of antigenic diversity for pathogen survival (51). Pre-existing antibodies, such as anti-V6 antibodies, can drive specific sequence remodeling in corresponding regions, initiating an “immune selection-escape” cycle (52). Furthermore, the segregation of B and T cell epitopes in TprK (with B cell epitopes predominantly in variable regions and T cell epitopes primarily in conserved regions) hinders effective immune clearance (53). Although its outer membrane transport function is dispensable for in vitro growth, it serves as a virulence factor under immune pressure in vivo. The substantial variability of TprK presents significant obstacles to vaccine development; however, approaches that focus on conserved regions or utilize multivalent antigens have the potential to overcome protective constraints, offering novel avenues for managing the chronicity and transmission of syphilis.
4.3 Tp0435 (Tp17)
Tp0435 (Tp17), a 14 kDa periplasmic lipoprotein antigen of Treponema pallidum encoded by one of the pathogen’s most highly expressed genes (54), is characterized by an antiparallel beta-barrel structure comprising eight beta chains (55). Unlike conventional transmembrane proteins, Tp0435 lacks a central channel and is filled with amino acid side chains, suggesting a distinct function in mediating adhesion through membrane organization or ligand binding (55). Regarding immune evasion mechanisms, it undergoes lipidation (e.g., palmitoylation) generating multiple isoforms, as observed in heterologous expression systems like Borrelia burgdorferi (56). These isomers are partially exposed on the surface while mostly concealed in the periplasmic space, effectively evading antibody recognition. Keane et al. reported antibody reactivity to dominant Tp0435 epitopes (peptides 1,4,5) in 95-100% of primary/secondary syphilis sera versus 67-83% in late latent stage, indicating temporal downregulation to evade adaptive immunity (57). Subsequently, its expression is down-regulated to evade adaptive immunity, thereby supporting the long-term latency of spirochetes in immune-privileged sites such as the central nervous system. Furthermore, the preferential colonization of immune-privileged tissues contributes to attenuating the systemic immune response of the host. These mechanisms demonstrate how Tp0435 contributes to the chronicity of syphilis by adapting structurally and evading the immune system, thus offering a fundamental molecular foundation for specific interventions.
4.4 Tp0574 (Tp47)
Tp47, a 367-amino acid hydrophobic outer membrane protein anchored via N-terminal lipidation, mediates immune evasion through multifaceted mechanisms. In macrophages, Tp47 triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways (PERK/ATF4 and IRE1/XBP1), inducing autophagy and promoting prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthesis (58). PGE2 suppresses phagosome maturation via autocrine EP2 receptor signaling, impairing bacterial clearance—an effect reversible by COX-2 inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib) (59). Concurrently, Tp47 competitively binds to pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), inhibiting its ubiquitin-dependent degradation. This stabilizes phosphorylated PKM2-Y105, enhancing glycolytic flux (3-fold increase in lactate) and activating EIF2AK2 phosphorylation, which drives NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and caspase-1-mediated IL-1β release (60). The resulting inflammatory storm causes tissue damage and depletes anti-inflammatory resources (e.g., IL-1RA). For promoting leukocyte adhesion and endothelial activation, Tp47 stimulates monocytes to secrete MMP-2-enriched microvesicles (Tp47-MVs). These activate the ERK1/2-NF-κB cascade in endothelial cells, upregulating ICAM-1/VCAM-1 to promote monocyte transendothelial migration, while MMP-2 degrades tight junction proteins (occludin/claudin-5) (61). Additionally, in fibroblasts, Tp47 induces proinflammatory mediators via the PI3K/Akt-p38MAPK-NF-κB axis (62), recruiting monocytes and promoting leukocyte adhesion to promote inflammatory vasculopathy. Furthermore, by blocking PKM2 ubiquitination, Tp47 exacerbates lactate-driven EIF2AK2-NLRP3 activation, inducing pyroptotic inflammatory senescence in macrophages (60). Tp47 inhibits the mTOR pathway, provoking autophagy-dependent microglial death (63). Collectively, while its high immunogenicity establishes it as a core serodiagnostic marker (64), Tp47 orchestrates immune evasion by suppressing phagocytosis, inciting inflammatory cascades, disrupting vascular integrity, reprogramming immunometabolism, and facilitating neural invasion.
5 Inflammation induction
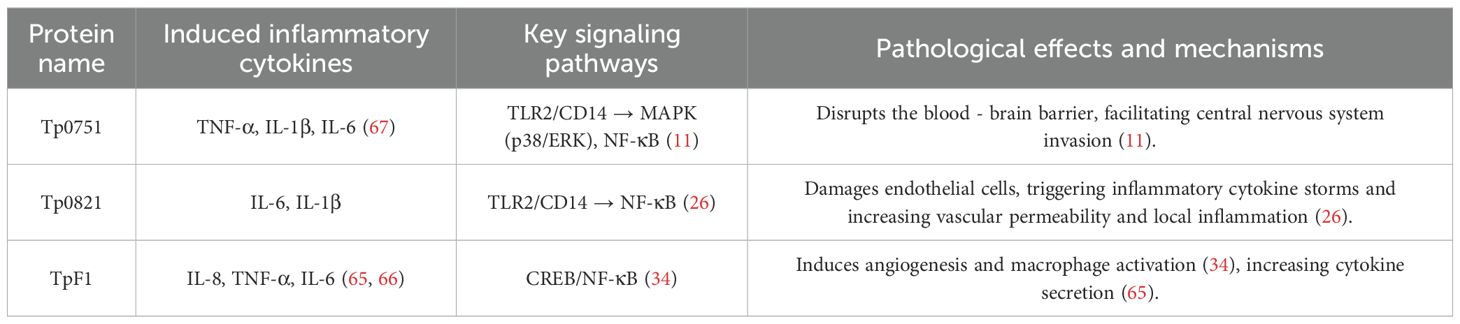
Following infection with T. pallidum, local tissue inflammation ensues, facilitated by the release of toxins and enzymes, including plasminogen activator and hyaluronidase, which directly harm the extracellular matrix and intercellular connections of host cells, leading to tissue structural deterioration and functional impairment. Moreover, the infection can trigger apoptosis and necrosis of host cells, exacerbating tissue injury. The pathogenic proteins of T. pallidum contribute to tissue damage and the persistence of infection by orchestrating a delicate interplay between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signaling pathways (Table 3).
5.1 TpF1
TpF1 is an iron ion-binding oligoferritin with a monomeric molecular weight of approximately 42 kDa. As the core pathogenic antigen of T. pallidum, it drives host tissue damage and chronic infection through the multi-target immune regulation mechanism. The core functions of TpF1 are as follows: By activating the cAMP-CREB/NF-κB signaling pathway in endothelial cells (e.g., HUVECs), TpF1 potently induces high expression of IL-8/CXCL8, which subsequently mediates pathological angiogenesis and aberrant endothelial proliferation through an IL-8-dependent (VEGF-independent) mechanism. This pro-angiogenic effect mechanistically relies on IL-8 binding to CXCR1/CXCR2 receptors and has been validated in vivo: TpF1 injection significantly promotes angiogenesis concomitant with elevated IL-8 levels in a zebrafish model (34). Concurrently, TpF1 triggered IL-8 acts as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant, driving neutrophil infiltration into the vascular endothelium. This process induces characteristic vascular inflammation (vasculitis) and vessel wall damage, consequently resulting in vascular leakage; furthermore, TpF1 targeted activation of macrophage NLRP3 inflammatory body promotes IL-1β release, and synergistically stimulates T lymphocytes to secrete IL-8, TGF-β and other pro-inflammatory factors, forming persistent inflammatory cascade reaction (65, 66). In addition, TpF1 inhibits host immune clearance ability by inducing regulatory T cell differentiation and activates pathogen-specific T cells to produce pro-inflammatory mediators (66), constructing a pathological network with “pro-inflammatory-immunosuppression” bi-directional imbalance. This multi-dimensional regulatory mechanism not only leads to vascular leakage, central nervous system injury, and other tissue lesions but also provides a key molecular basis for T. pallidum to establish chronic infection by evading immune surveillance and maintaining intracellular latency, highlighting its central position in disease progression.
5.2 Tp0751
Tp0751 activates MAPK/p38 and NF-κB pathways by binding to TLR2 and CD14 molecules on the surface of monocytic THP-1 cells, induces monocytes THP-1 to release pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (67). Lu et al. (11) further clarified that Tp0751 induces apoptosis of bEnd3 cells in a concentration-dependent and time-dependent manner, accompanied by caspase-8 activation. It also downregulates tight junction proteins (such as ZO-1 and occludin), and destroys the blood-brain barrier to promote T. pallidum invasion into the central nervous system. The dual apoptosis-barrier disruption mechanism exhibits functional complementarity with the pathogenic strategy of Leptospira LipL32 protein: LipL32 triggers endothelial cell apoptosis by binding to host fibronectin (68), yet its action is independent of the TLR2 signaling pathway (69), thereby highlighting the pathway-specific selectivity of Tp0751. Meanwhile, Tp0751 significantly promoted IL-6 secretion by bEnd3 cells and exacerbated the inflammatory response by upregulating TNF-α. This multidimensional pathogenic network of “receptor activation–inflammatory cascade–barrier disruption” not only elucidates the core mechanism underlying T. pallidum neuroinvasion but also unveils novel avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions.
5.3 Tp0821
Tp0821 is an outer membrane lipoprotein of T. pallidum, encoding an 749 bp gene containing 249 amino acids, with high immunogenicity and immunoreactivity (70). Tp0821 drives host inflammatory damage and chronic infection through a multi-pathway synergistic mechanism. Its core functions include: Activation of ERK1/2-p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling axis significantly induced IL-6, IL-8 and IL-1β secretion by monocytes/macrophages. The pro-inflammatory mechanism of Tp0821 shares homology with the NF-κB activation strategy employed by Helicobacter pylori CagA protein, yet differs in its mode of action: while CagA relies on a type IV secretion system (T4SS) to invade host cells, Tp0821 directly triggers signal transduction through outer membrane contact (71). Direct cytotoxicity to macrophages, causing LDH leakage and NO release in a dose-dependent manner. This mechanism exhibits functional overlap with Mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT-6 protein-induced pyroptosis, though Tp0821-induced cytotoxicity primarily involves membrane damage and inflammatory mediator release rather than canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation (72); Immune escape (late antibody titer decay) is achieved through low adventitial exposure, CD14/TLR2 interaction, and epitope variation; synergistic activation of endothelial ICAM-1/E-selectin and IL-8 increases vascular leakage and neuroinflammatory risk (26). This “inflammation activation-immunosuppression-tissue destruction” multidimensional network not only clarifies the molecular mechanism of syphilis vasculitis and neuropathy but also provides a core strategy for the chronicity of pathogens, highlighting its key value as a diagnostic target.
6 Conclusion and perspective
Despite the advancements made in understanding the pathogenic functions of T. pallidum proteins, several challenges impede further progress (73). One major obstacle is the bacterium’s intricate growth requirements, which hinder comprehensive analyses of its proteome (74). The demanding nature of these growth conditions presents a barrier to in-depth studies of T. pallidum proteins. In recent years, the increasingly severe problem of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in syphilis treatment has further compounded research challenges — 76.2% of globally circulating SS14 strain isolates harbor the TP0705(A1873G) mutation conferring partial resistance to β-lactam antibiotics (e.g., penicillin G and ceftriaxone) (75), while 99.2% of strains in North America exhibit genotypic resistance to the macrolide azithromycin (76). Moreover, the diverse clinical manifestations of syphilis, combined with individual variations among patients, complicate investigations into the mechanisms underlying the disease (77). The multifaceted roles of T. pallidum proteins and their intricate interactions with each other further add layers of complexity to mechanistic studies, making it challenging to unravel the precise pathways involved in disease progression.
To overcome these challenges, upcoming technological advancements such as CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene editing, Activity-Based Protein Profiling, single-cell sequencing, and metabolomics are poised to play a crucial role. CRISPR-Cas9 technology can create T. pallidum strains with specific gene modifications, enabling researchers to conduct more precise evaluations of virulence factors like the adhesin Tp0751 or the metalloprotease Tp0926. Single-cell sequencing and metabolomics approaches hold promise in providing detailed insights into the dynamic interactions between hosts and pathogens, including host-specific metabolic reprogramming during infection (78). Additionally, emerging computational tools—such as Alpha Fold-driven structural predictions and deep learning-based functional annotation—are revolutionizing the decoding of enigmatic proteins like the Tpr family adhesins or the proposed “stealth factor” Tp0435, bridging gaps left by experimental limitations. Collaborative efforts that span disciplines and geographic boundaries are essential to accelerate progress in this field. By fostering interdisciplinary and global initiatives, researchers can collectively address the challenges posed by T. pallidum pathogenesis and drive advancements in understanding the roles of its functional proteins.
In conclusion, the functional proteins of T. pallidum play a central role in its pathogenicity. Unraveling the specific functions of these proteins not only advances our knowledge of syphilis pathogenesis but also paves the way for the development of innovative diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics. Given the escalating threat of drug resistance confronting current first-line therapeutics, the pursuit of proteomics-driven vaccine development and the exploration of novel antibacterial targets have become an urgent imperative. Proteome-wide interaction network modeling, for instance, may uncover novel virulence complexes such as the Tp0136-Tp0326 membrane synergy, while CRISPR-validated studies could clarify the oligomeric pore-forming capacity of Tp0453. Despite the biological complexity of T. pallidum and the limitations in laboratory cultivation, the integration of predictive technologies (e.g., comparative genomics-guided domain mapping) with single-cell host-pathogen profiling holds great promise for yielding transformative insights into T. pallidum pathogenesis. Notably, breakthroughs have emerged in host-targeted therapeutics: microRNA-based intervention strategies demonstrate therapeutic potential by modulating immune pathways. Specifically, Long et al. demonstrated that miR-223-3p suppresses Tp17-induced pyroptosis through direct targeting of the NLRP3 inflammasome (79). Concurrently, Huang’s team revealed that miR-101-3p downregulates TLR2 expression via direct binding to its 3’ untranslated region (3’UTR), thereby suppressing both transcriptional and translational expression of TLR2 (80). This mechanism subsequently inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine production (e.g., IL-1β, TNF-α) in Treponema pallidum-stimulated macrophages, thus offering novel avenues for immune pathology containment.
As studies continue to deepen, it is reasonable to anticipate that the synergistic application of predictive modeling and cutting-edge experimentation will not only demystify antigenic variation mechanisms but also catalyze breakthroughs in structure-guided vaccine design and host-directed therapies. Ultimately, enhanced global collaboration and technological convergence may turn the tide against this ancient yet persistently enigmatic pathogen.
Author contributions
WZ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. YJX: Writing – review & editing. QX: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. SX: Writing – review & editing. YFX: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project was supported by Hunan Province Clinical Medical Technology Innovation Guidance Project (grant number: 2021SK51716).
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank my supervisor, Professor Yongjian Xiao, for his meticulous guidance throughout this study. We are also deeply grateful to all the faculty members in the Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, for their technical support and invaluable suggestions during the experimental design and data analysis. Finally, we extend our heartfelt appreciation to the volunteers who participated in this research and the reviewers for their dedicated efforts and insightful feedback.
Conflict of interest
The research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Peeling RW, Mabey D, Chen X-S, and Garcia PJ. Syphilis. Lancet. (2023) 402:336–46. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02348-0
2. Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, Johnston CM, Muzny CA, Park I, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. (2021) 70:1. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
3. Yu W, You X, and Luo W. Global, regional, and national burden of syphilis, 1990–2021 and predictions by Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Front Med. (2024) 11:1448841. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1448841
4. Tao Y, Chen MY, Tucker JD, Ong JJ, Tang W, Wong NS, et al. A nationwide spatiotemporal analysis of syphilis over 21 years and implications for prevention and control in China. Clin Infect Dis. (2020) 70:136–9. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz331
5. Liu J, Howell JK, Bradley SD, Zheng Y, Zhou ZH, and Norris SJ. Cellular architecture of treponema pallidum: novel flagellum, periplasmic cone, and cell envelope as revealed by cryo-electron tomography. J Mol Biol. (2010) 403:546–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.09.020
6. LaFond RE and Lukehart SA. Biological basis for syphilis. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2006) 19:29–49. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.29-49.2006
7. Fitzgerald TJ. Pathogenesis and immunology of treponema pallidum. Annu Rev Microbiol. (1981) 35:29–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.000333
8. Luthra A, Montezuma-Rusca JM, Vake CJL, LeDoyt M, Delgado KN, Davenport TC, et al. Evidence that immunization with TP0751, a bipartite Treponema pallidum lipoprotein with an intrinsically disordered region and lipocalin fold, fails to protect in the rabbit model of experimental syphilis. PloS Pathog. (2020) 16:e1008871. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008871
9. Parker ML, Houston S, Pětrošová H, Lithgow KV, Hof R, Wetherell C, et al. The structure of treponema pallidum Tp0751 (Pallilysin) reveals a non-canonical lipocalin fold that mediates adhesion to extracellular matrix components and interactions with host cells. PloS Pathog. (2016) 12:e1005919. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005919
10. Houston S, Hof R, Francescutti T, Hawkes A, Boulanger MJ, and Cameron CE. Bifunctional role of the treponema pallidum extracellular matrix binding adhesin Tp0751. Infect Immun. (2011) 79:1386–98. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01083-10
11. Lu S, Wang J, He Z, He S, Zheng K, Xu M, et al. Treponema pallidum Tp0751 alters the expression of tight junction proteins by promoting bEnd3 cell apoptosis and IL-6 secretion. Int J Med Microbiol. (2022) 312:151553. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2022.151553
12. Kao W-CA, Pětrošová H, Ebady R, Lithgow KV, Rojas P, Zhang Y, et al. Identification of Tp0751 (Pallilysin) as a Treponema pallidum Vascular Adhesin by Heterologous Expression in the Lyme disease Spirochete. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01589-4
13. Lithgow KV, Church B, Gomez A, Tsao E, Houston S, Swayne LA, et al. Identification of the neuroinvasive pathogen host target, LamR, as an endothelial receptor for the treponema pallidum adhesin Tp0751. mSphere. (2020) 5:e00195–20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00195-20
14. Lithgow KV, Tsao E, Schovanek E, Gomez A, Swayne LA, and Cameron CE. Treponema pallidum disrupts VE-cadherin intercellular junctions and traverses endothelial barriers using a cholesterol-dependent mechanism. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:691731. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.691731
15. Lithgow KV, Hof R, Wetherell C, Phillips D, Houston S, and Cameron CE. A defined syphilis vaccine candidate inhibits dissemination of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:14273. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14273
16. Naba A, Clauser KR, Ding H, Whittaker CA, Carr SA, and Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: tools and insights for the “Omics” Era. Matrix Biol J Int Soc Matrix Biol. (2016) 49:10–24. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.06.003
17. Brinkman MB, McGill MA, Pettersson J, Rogers A, Matějková P, Šmajs D, et al. A novel treponema pallidum antigen, TP0136, is an outer membrane protein that binds human fibronectin. Infect Immun. (2008) 76:1848–57. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01424-07
18. Ke W, Molini BJ, Lukehart SA, and Giacani L. Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum TP0136 Protein Is Heterogeneous among Isolates and Binds Cellular and Plasma Fibronectin via its NH2-Terminal End. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2015) 9:e0003662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003662
19. Cai C-X, Li S-L, Lin H-L, Wei Z-H, Xie L, Lin L-R, et al. Treponema pallidum protein Tp0136 promoting MMPs/TIMPs imbalance via PI3K, MAPK and NF-κB signalling pathways in HDVSMCs. Heliyon. (2022) 8:e12065. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12065
20. Djokic V, Giacani L, and Parveen N. Analysis of host cell binding specificity mediated by the Tp0136 adhesin of the syphilis agent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2019) 13:e0007401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007401
21. Tang Y, Zhou Y, He B, Cao T, Zhou X, Ning L, et al. Investigation of the immune escape mechanism of Treponema pallidum. Infection. (2023) 51:305–21. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01939-z
22. Primus S, Rocha SC, Giacani L, and Parveen N. Identification and functional assessment of the first placental adhesin of treponema pallidum that may play critical role in congenital syphilis. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:621654. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.621654
23. Ávila-Nieto C, Pedreño-López N, Mitjà O, Clotet B, Blanco J, and Carrillo J. Syphilis vaccine: challenges, controversies and opportunities. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1126170. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1126170
24. He Y, Chen D, Fu Y, Huo X, Zhao F, Yao L, et al. Immunization with Tp0954, an adhesin of Treponema pallidum, provides protective efficacy in the rabbit model of experimental syphilis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1130593. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130593
25. Bamford CV, Francescutti T, Cameron CE, Jenkinson HF, and Dymock D. Characterization of a novel family of fibronectin-binding proteins with M23 peptidase domains from Treponema denticola. Mol Oral Microbiol. (2010) 25:369–83. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2010.00584.x
26. Kubanov A, Runina A, and Deryabin D. Novel treponema pallidum recombinant antigens for syphilis diagnostics: current status and future prospects. BioMed Res Int. (2017) 2017:1436080. doi: 10.1155/2017/1436080
27. Dickerson MT, Abney MB, Cameron CE, Knecht M, Bachas LG, and Anderson KW. Fibronectin Binding to the Treponema pallidum Adhesin Protein Fragment rTp0483 on Functionalized Self-Assembled Monolayers. Bioconjug Chem. (2012) 23:184–95. doi: 10.1021/bc200436x
28. Tuddenham S, Hamill MM, and Ghanem KG. Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections: A review. JAMA. (2022) 327:161–72. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.23487
29. Kaminiów K, Kiołbasa M, and Pastuszczak M. The significance of the cell-mediated host immune response in syphilis. Microorganisms. (2024) 12:2580. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122580
30. Zhang R-L, Zhang J-P, and Wang Q-Q. Recombinant treponema pallidum protein tp0965 activates endothelial cells and increases the permeability of endothelial cell monolayer. PloS One. (2014) 9:e115134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115134
31. McGill MA, Edmondson DG, Carroll JA, Cook RG, Orkiszewski RS, and Norris SJ. Characterization and serologic analysis of the treponema pallidum proteome. Infect Immun. (2010) 78:2631–43. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00173-10
32. Zhang R-L, Wang Q-Q, and Yang L-J. Chemerin induced by Treponema pallidum predicted membrane protein Tp0965 mediates the activation of endothelial cell via MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:19621–34. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29269
33. Thumiger A, Polenghi A, Papinutto E, Battistutta R, Montecucco C, and Zanotti G. Crystal structure of antigen TpF1 from Treponema pallidum. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinforma. (2006) 62:827–30. doi: 10.1002/prot.20828
34. Pozzobon T, Facchinello N, Bossi F, Capitani N, Benagiano M, Di Benedetto G, et al. Treponema pallidum (syphilis) antigen TpF1 induces angiogenesis through the activation of the IL-8 pathway. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:18785. doi: 10.1038/srep18785
35. Jiang J, Xu L, Wang X, Wang M, Cao Y, Li R, et al. A comprehensive strategy for the development of a multi-epitope vaccine targeting Treponema pallidum, utilizing heat shock proteins, encompassing the entire process from vaccine design to in vitro evaluation of immunogenicity. Front Microbiol. (2025) 16:1551437. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1551437
36. Zhao Y-Y, Xie L, Wang R-Y, Yan Y, and Liu L-L. Treponema pallidum Protein TpF1 Inhibits Migration by Impairing Actin Polymerization via Toll-Like Receptor 4/PI3K/AKT in Microglia. ACS Infect Dis. (2025) 11:1104–13. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00868
37. Cameron CE, Brouwer NL, Tisch LM, and Kuroiwa JMY. Defining the interaction of the treponema pallidum adhesin Tp0751 with laminin. Infect Immun. (2005) 73:7485–94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7485-7494.2005
38. Houston S, Hof R, Honeyman L, Hassler J, and Cameron CE. Activation and proteolytic activity of the treponema pallidum metalloprotease, pallilysin. PloS Pathog. (2012) 8:e1002822. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002822
39. Houston S, Russell S, Hof R, Roberts AK, Cullen P, Irvine K, et al. The multifunctional role of the pallilysin-associated treponema pallidum protein, tp0750, in promoting fibrinolysis and extracellular matrix component degradation. Mol Microbiol. (2014) 91:618–34. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12482
40. Houston S, Taylor JS, Denchev Y, Hof R, Zuerner RL, and Cameron CE. Conservation of the Host-Interacting Proteins Tp0750 and Pallilysin among Treponemes and Restriction of Proteolytic Capacity to Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. (2015) 83:4204–16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00643-15
41. Radolf JD, Deka RK, Anand A, Šmajs D, Norgard MV, and Yang XF. Treponema pallidum, the syphilis spirochete: making a living as a stealth pathogen. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2016) 14:744–59. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.141
42. Cox DL, Luthra A, Dunham-Ems S, Desrosiers DC, Salazar JC, Caimano MJ, et al. Surface immunolabeling and consensus computational framework to identify candidate rare outer membrane proteins of treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. (2010) 78:5178–94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00834-10
43. Desrosiers DC, Anand A, Luthra A, Dunham-Ems SM, LeDoyt M, Cummings MAD, et al. TP0326, a treponema pallidum β-barrel assembly machinery A (BamA) ortholog and rare outer membrane protein. Mol Microbiol. (2011) 80:1496–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07662.x
44. Luthra A, Anand A, Hawley KL, LeDoyt M, La Vake CJ, Caimano MJ, et al. A homology model reveals novel structural features and an immunodominant surface loop/opsonic target in the treponema pallidum BamA ortholog TP_0326. J Bacteriol. (2015) 197:1906–20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00086-15
45. Ferguson MR, Delgado KN, McBride S, Orbe IC, La Vake CJ, Caimano MJ, et al. Use of Epivolve phage display to generate a monoclonal antibody with opsonic activity directed against a subdominant epitope on extracellular loop 4 of Treponema pallidum BamA (TP0326). Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1222267. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1222267
46. Luo X, Zhang X, Gan L, Zhou C, Zhao T, Zeng T, et al. The outer membrane protein Tp92 of Treponema pallidum induces human mononuclear cell death and IL-8 secretion. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 22:6039–54. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13879
47. Li W, Li S, Wang J, Yu M, Yang H, He Z, et al. The outer membrane protein Tp92 of Treponema pallidum delays human neutrophil apoptosis via the ERK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB pathways. Mol Microbiol. (2023) 120:684–701. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15164
48. Zhang R-L and Wang Q-Q. The Treponema pallidum outer membrane protein Tp92 activates endothelial cells via the chemerin/CMKLR1 pathway. Int J Med Microbiol. (2020) 310:151416. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2020.151416
49. Centurion-Lara A, LaFond RE, Hevner K, Godornes C, Molini BJ, Van Voorhis WC, et al. Gene conversion: a mechanism for generation of heterogeneity in the tprK gene of Treponema pallidum during infection. Mol Microbiol. (2004) 52:1579–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04086.x
50. Giacani L, Molini BJ, Kim EY, Godornes BC, Leader BT, Tantalo LC, et al. Antigenic variation in Treponema pallidum: TprK sequence diversity accumulates in response to immune pressure during experimental syphilis. J Immunol Baltim Md 1950. (2010) 184:3822–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902788
51. Reid TB, Molini BJ, Fernandez MC, and Lukehart SA. Antigenic variation of TprK facilitates development of secondary syphilis. Infect Immun. (2014) 82:4959–67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02236-14
52. Parveen N, Fernandez MC, Haynes AM, Zhang R-L, Godornes BC, Centurion-Lara A, et al. Non-pathogenic Borrelia burgdorferi expressing Treponema pallidum TprK and Tp0435 antigens as a novel approach to evaluate syphilis vaccine candidates. Vaccine. (2019) 37:1807–18. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.02.022
53. Morgan CA, Molini BJ, Lukehart SA, and Van Voorhis WC. Segregation of B and T cell epitopes of treponema pallidum repeat protein K to variable and conserved regions during experimental syphilis infection1. J Immunol. (2002) 169:952–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.952
54. De Lay BD, Cameron TA, De Lay NR, Norris SJ, and Edmondson DG. Comparison of transcriptional profiles of Treponema pallidum during experimental infection of rabbits and in vitro culture: Highly similar, yet different. PloS Pathog. (2021) 17:e1009949. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009949
55. Brautigam CA, Deka RK, Liu WZ, and Norgard MV. Insights into the potential function and membrane organization of the TP0435 (Tp17) lipoprotein from Treponema pallidum derived from structural and biophysical analyses. Protein Sci Publ Protein Soc. (2015) 24:11–9. doi: 10.1002/pro.2576
56. Chan K, Nasereddin T, Alter L, Centurion-Lara A, Giacani L, and Parveen N. Treponema pallidum Lipoprotein TP0435 Expressed in Borrelia burgdorferi Produces Multiple Surface/Periplasmic Isoforms and mediates Adherence. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:25593. doi: 10.1038/srep25593
57. Keane JL, Bose M, Molini BJ, Konda KA, Vargas SK, Reyes Diaz M, et al. B-cell epitope mapping of the treponema pallidum tp0435 immunodominant lipoprotein for peptide-based syphilis diagnostics. Diagnostics. (2025) 15:1443. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111443
58. Li W, Xie L, Li Q-L, Xu Q-Y, Lin L-R, Liu L-L, et al. Treponema pallidum membrane protein Tp47 promotes angiogenesis through ROS-induced autophagy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2023) 37:558–72. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18728
59. Yi D-Y, Xu Q-Y, He Y, Zheng X-Q, Yang T-C, and Lin Y. Treponema pallidum protein Tp47 induced prostaglandin E2 to inhibit the phagocytosis in human macrophages. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2024) 38:1166–78. doi: 10.1111/jdv.19809
60. Xie J-W, Guo Y-F, Fan S-H, Zheng Y, Zhang H-L, Zhang Y, et al. Treponema Pallidum protein Tp47 triggers macrophage inflammatory senescence via PKM2-mediated metabolic reprogramming. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 283:137991. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137991
61. Wang M, Xie J-W, Zheng Y-W, Wang X-T, Yi D-Y, Lin Y, et al. Tp47-induced monocyte-derived microvesicles promote the adherence of THP-1 cells to human umbilical vein endothelial cells via an ERK1/2–NF-κB signaling cascade. Microbiol Spectr. (2023) 11:e01888-23. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01888-23
62. Zheng X-Q, Kong X-Q, He Y, Wang Y-J, Xie L, Liu L-L, et al. Treponema pallidum recombinant protein Tp47 enhanced interleukin-6 secretion in human dermal fibroblasts through the toll-like receptor 2 via the p38, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB signalling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Cell Res. (2023) 1870:119540. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2023.119540
63. Liu W-N, Jiang X-Y, JunRen, Zhuang J-C, Chen M-H, Zhu S-G, et al. Tp47 induces cell death involving autophagy and mTOR in human microglial HMO6 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 74:105566. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.013
64. Deka RK, Machius M, Norgard MV, and Tomchick DR. Crystal structure of the 47-kDa lipoprotein of treponema pallidum reveals a novel penicillin-binding protein *. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:41857–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207402200
65. Lu D-P, Jia J, Wei S-F, Zhang W-L, Liang R, Liu T, et al. Treponema pallidum (Syphilis) antigen tpF1 induces activation of macrophages and accelerates P2X7R-induced NLRP3-dependent release of IL-1β. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. (2022) 22:425–32. doi: 10.2174/1871530321666211015091109
66. Babolin C, Amedei A, Ozoliņš D, Žileviča A, D’Elios MM, and de Bernard M. TpF1 from treponema pallidum activates inflammasome and promotes the development of regulatory T cells. J Immunol. (2011) 187:1377–84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100615
67. Liu S, Wang S, Wu Y, Zhao F, Zeng T, Zhang Y, et al. Production of proinflammatory cytokines in the human THP-1 monocyte cell line following induction by Tp0751, a recombinant protein of Treponema pallidum. Sci China Life Sci. (2010) 53:229–33. doi: 10.1007/s11427-010-0038-z
68. Sun Z, Bao L, Li D, Huang B, and Wu B. Effect of Leptospira interrogans outer membrane proteins LipL32 on HUVEC. Microb Pathog. (2010) 49:116–21. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2010.05.006
69. Hsu S-H, Yang H-Y, Chang C-C, Tsai S-K, Li C, Chang M-Y, et al. Blocking pathogenic Leptospira invasion with aptamer molecules targeting outer membrane LipL32 protein. Microbes Infect. (2024) 26:105299. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2024.105299
70. Wu N, Li N, Hu L, He J, Li J, Zhao F, et al. Immunogenicity and immunoreactivity of Tp0821 recombinant protein from Treponema pallidum. Mol Med Rep. (2017) 16:851–6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6675
71. Brandt S, Kwok T, Hartig R, König W, and Backert S. NF-κB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2005) 102:9300–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409873102
72. Sun F, Li J, Cao L, and Yan C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence protein ESAT-6 influences M1/M2 polarization and macrophage apoptosis to regulate tuberculosis progression. Genes Genomics. (2024) 46:37–47. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01469-4
73. Radolf JD and Kumar S. The treponema pallidum outer membrane. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. (2018) 415:1–38. doi: 10.1007/82_2017_44
74. Houston S, Gomez A, Geppert A, Eshghi A, Smith DS, Waugh S, et al. Deep proteome coverage advances knowledge of Treponema pallidum protein expression profiles during infection. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:18259. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45219-8
75. Pospíšilová P, Bosák J, Hrala M, Krbková L, Vrbová E, and Šmajs D. Resistance to ceftriaxone and penicillin G among contemporary syphilis strains confirmed by natural in vitro mutagenesis. Commun Med. (2025) 5:224. doi: 10.1038/s43856-025-00948-x
76. Lieberman NAP, Reid TB, Cannon CA, Nunley BE, Berzkalns A, Cohen SE, et al. Near-universal resistance to macrolides of treponema pallidum in North America. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:2127–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2314441
77. Morshed MG and Singh AE. Recent trends in the serologic diagnosis of syphilis. Clin Vaccine Immunol CVI. (2015) 22:137–47. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00681-14
78. Liu L-L, Lin Y, Chen W, Tong M-L, Luo X, Lin L-R, et al. Metabolite profiles of the cerebrospinal fluid in neurosyphilis patients determined by untargeted metabolomics analysis. Front Neurosci. (2019) 13:150. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00150
79. Long F, Kou C, Li K, Wu J, and Wang Q. MiR-223-3p inhibits rTp17-induced inflammasome activation and pyroptosis by targeting NLRP3. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:14405–14. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16061
Keywords: Treponema pallidum, functional protein, interaction, pathogenesis, immune evasion
Citation: Zuo W, Xiao Y, Xiang Q, Xiao S and Xie Y (2025) Participants in Treponema pallidum pathogenesis: progress in functional proteins. Front. Immunol. 16:1632677. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1632677
Received: 21 May 2025; Accepted: 08 August 2025;
Published: 26 August 2025.
Edited by:
Syamal Roy, Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (CSIR), IndiaReviewed by:
Allan Pillay, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), United StatesShantanabha Das, Diamond Harbor Women’s University, India
Copyright © 2025 Zuo, Xiao, Xiang, Xiao and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongjian Xiao, eGlhb3lvbmdqaWFuQHVzYy5lZHUuY24=
 Wei Zuo
Wei Zuo Yongjian Xiao
Yongjian Xiao Qing Xiang
Qing Xiang Yafeng Xie
Yafeng Xie