- 1Jilin Ginseng Academy, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
- 2College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
- 3The Affiliated Hospital to Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease caused by many factors, with a high disability rate, unsatisfactory clinical treatment effect, and unclear pathogenesis. The oxygen level in the joint cavity is significantly reduced, and the hypoxic microenvironment has become a key factor in the pathogenesis and progression of RA. Based on the latest research developments, this review delves into the structure and main functions of the key factor HIF in the hypoxic microenvironment, and expounds the main regulatory mechanisms of HIF. The effect of the hypoxic microenvironment on the pathological changes of RA was analyzed, especially how hypoxia affects the signal transduction of related molecules and cells, thus aggravating the occurrence and development of RA. In addition, the review also discusses emerging therapeutic strategies aimed at targeting the hypoxic pathways, including HIF-1α inhibitors, Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and the application of traditional Chinese medicine. By providing a comprehensive overview of the interplay between RA and the hypoxic microenvironment, this review aims to provide new perspectives on the underlying mechanisms of RA and provide a theoretical basis for the development of therapeutic drugs to improve the hypoxic microenvironment of RA.
1 Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease characterized by synovitis and destructive arthropathy, affecting approximately 1% of the population worldwide (1). The pathological changes of RA are chronic inflammation and abnormal hyperplasia of synovial tissue in the joints, which promote the pannus formation around the joints and then erode the articular cartilage, bone, and surrounding tissues, eventually leading to joint injury, deformity, dysfunction, and even permanent disability (2). According to WHO statistics, with the progression of the disease, RA patients not only experience joint deformity and limited activity but also have an impact on their heart, lung, and nervous system, significantly increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and infection, and seriously affect the quality of life of patients (3, 4). At present, the pathogenesis and biomarkers of RA are not completely clear, involving many aspects, including genetic factors and environmental factors, immune disorders and microbiome-gut-brain axis (Figure 1). Therefore, it is of great theoretical significance to deeply understand its disease mechanism and improve the pathological links of RA.
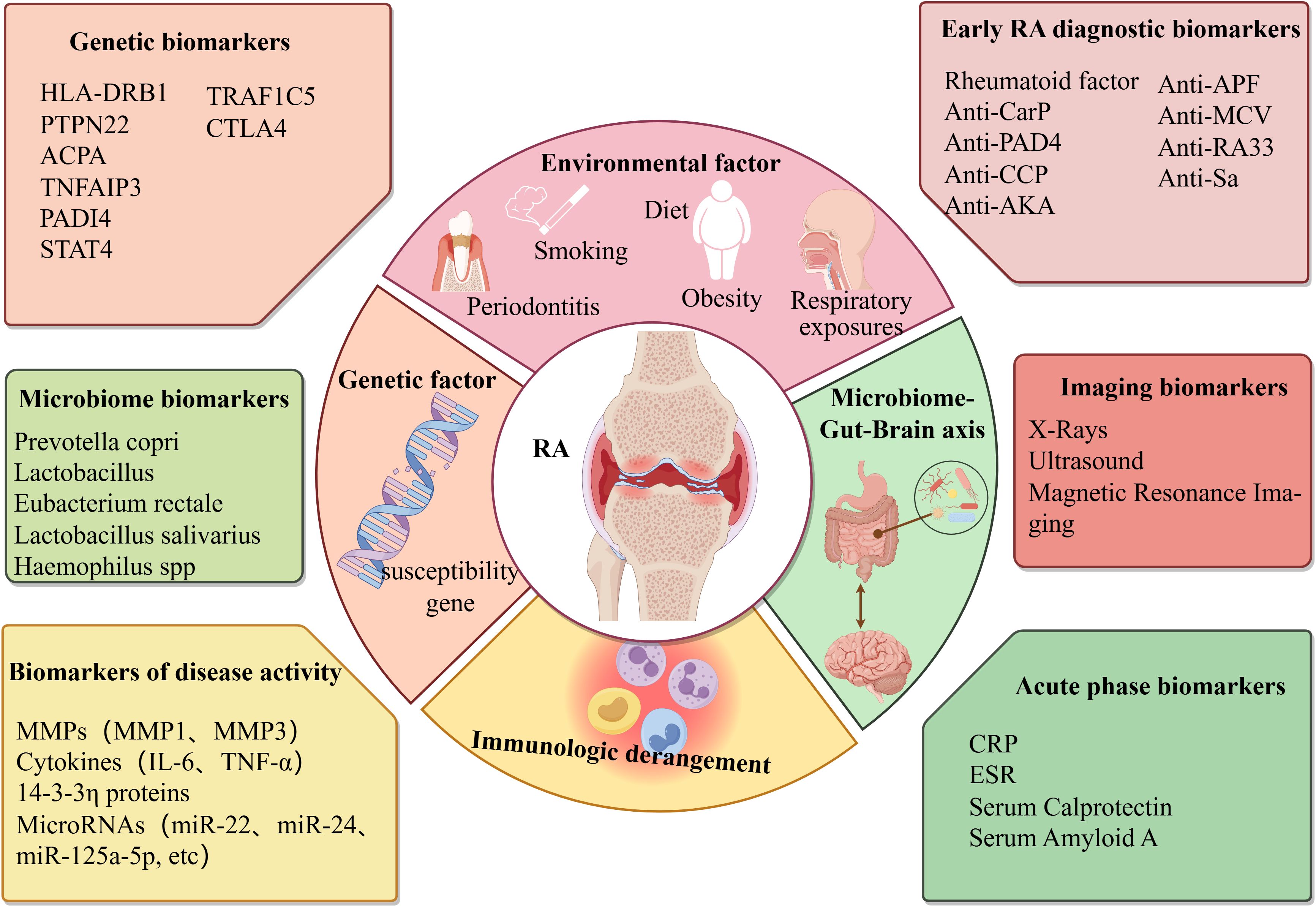
Figure 1. Triggering factors and biomarkers in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Created with figdraw.com.
Hypoxia refers to the oxygen content in the air, blood and tissues is being lower than the normal level. At present, it has been reported in the literature that compared with the synovial tissue of healthy people, the oxygen partial pressure in the joint cavity of RA patients is significantly reduced. The oxygen partial pressure is only 2-4%, and even less than 1%, suggesting that there is an hypoxic microenvironment in the synovial tissue of RA patients (5). There are two main factors in the formation of hypoxic microenvironment in RA. Firstly, In the pathological state of RA, fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) shows abnormal biological behavior similar to tumor cells, including strong invasiveness and migration ability, excessive proliferation and anti-apoptosis, resulting in active metabolism and decreased blood flow in synovial tissue, resulting in a large increase in oxygen consumption and aggravation of local tissue hypoxia, thus forming an hypoxic microenvironment (6). The second reason is that hypoxia induces FLS to secrete pro-angiogenic factors continuously, promotes the proliferation and remodeling of blood vessels in the synovium, further aggravates local blood circulation disorders, and the oxygen supply mechanism is seriously blocked, eventually causing hypoxia in the joint cavity (7). In 2016, Quiñonez-Flores et al. reviewed the effects of hypoxic microenvironment on RA angiogenesis, inflammatory response, apoptosis, cartilage erosion, abnormal energy metabolism and oxidative damage, and believed that synovial hypoxia is a potential pathogenic factor of RA (8). However, recent studies have found that hypoxic microenvironment can affect mitochondrial function, FLS activity, and the phenotype and function of immune cells by activating HIFs and downstream signaling pathways (9). Based on previous studies, this paper systematically reviews and updates the effects of hypoxic microenvironment on the pathological changes of RA and related molecular mechanisms, and discusses the emerging treatment strategies of hypoxic pathway, aiming to provide a theoretical reference for the in-depth study of the pathogenesis of RA and the development of targeted intervention strategies (Figure 2).
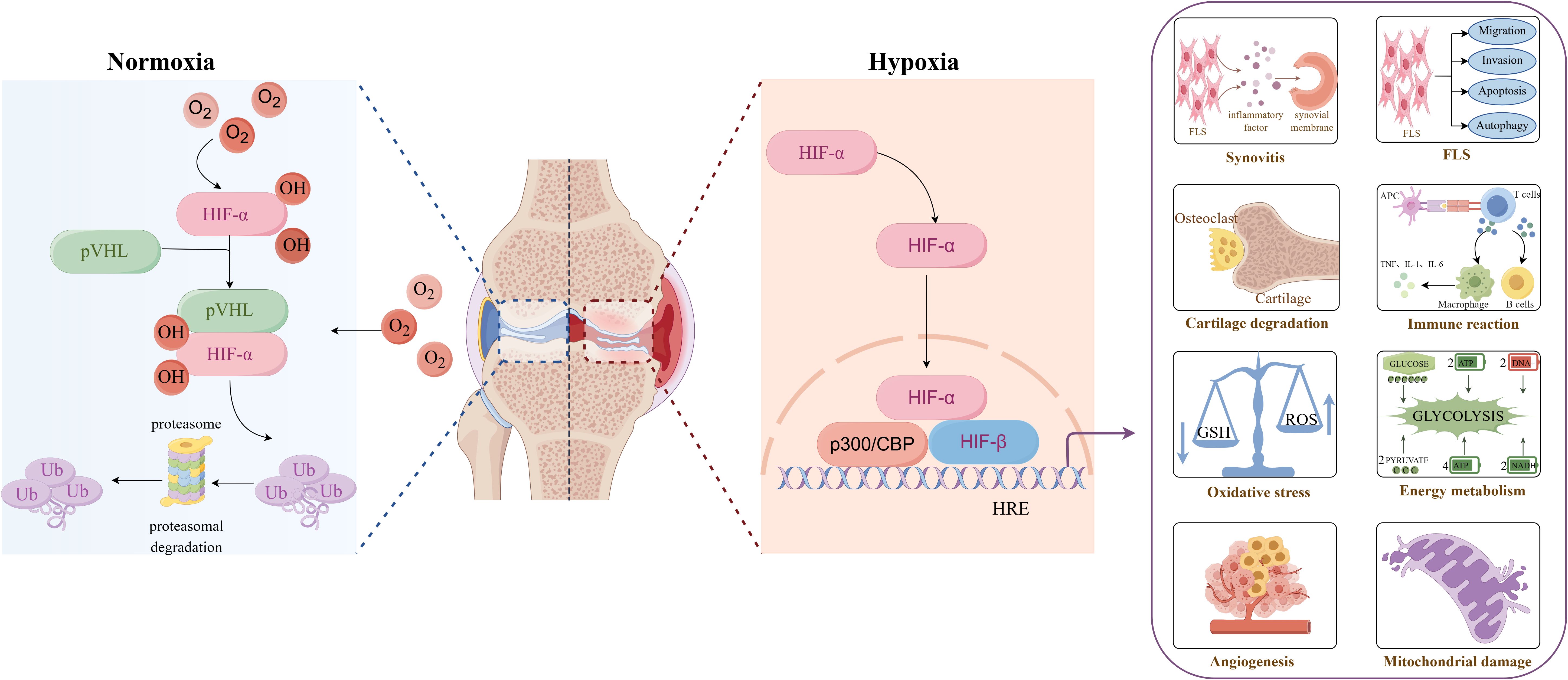
Figure 2. Overview of hypoxic microenvironment on the pathological changes of rheumatoid arthritis. Created with figdraw.com.
2 Hypoxia inducible factor in hypoxic microenvironment
2.1 Source and structure of HIF
In 1992, Semenza et al. discovered the transcription factor HIF associated with hypoxic stress under low-oxygen conditions (10). HIF is a heterodimer, which is composed of an N-terminal helix-loop-helix domain (binding to DNA), an intermediate Per-AHR/ARNT-Sim (PAS) domain (promoting heterodimer formation), and a C-terminal transcriptional activation region (binding to transcriptional cofactors and promoting transcriptional regulation). At present, it is found in the human genome that the HIF family is mainly composed of HIF-1,2,3 subtypes and α and β subunits. Among them, the oxygen-insensitive β subunit is constitutively expressed and is stably expressed in cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions, mainly responsible for the stability of the HIF complex. The oxygen-sensitive α subunit is a functional subunit, and its expression is tightly regulated by cellular oxygen concentration, which is mainly responsible for regulating the activity of HIF. Among the three subtypes of HIF-α, HIF-1α and HIF-2α have great similarities in structure and function (Figure 3). They are rapidly stable under hypoxic conditions and induce the transcription of similar target genes (11). However, studies have shown that HIF-1α is activated in strong hypoxia or early hypoxia (<24 hours), while HIF-2α is activated in mild or chronic hypoxia (>24 hours) (12). In addition, differential expression studies have shown that HIF-1α is expressed in all cell types, while HIF-2α is mainly expressed in specific cell types such as endothelial cells, glial cells, and type II lung cells (13). At present, there are few studies on HIF-3α. Some studies suggest that HIF-3α may act as an inhibitory element to regulate HIF-1α and HIF-2α negatively (14, 15).
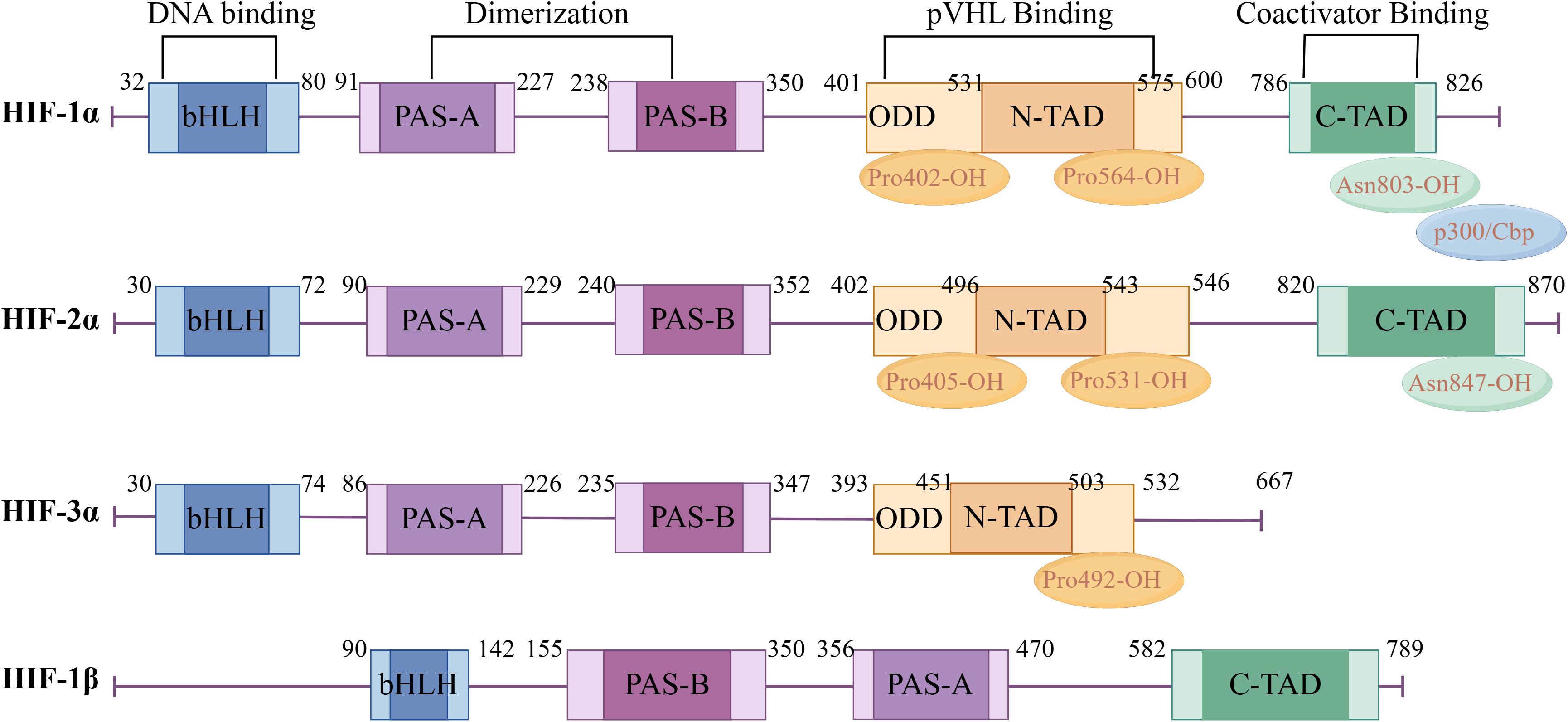
Figure 3. Hypoxia-inducible factor α and β subunit domain structure diagram. Created with figdraw.com.
In the hypoxic microenvironment, HIF dimers can bind to the co-activator p300/CBP (CREB-binding protein) to form a complex, which binds to the promoter region of the target gene containing the hypoxia response element (HRE) to promote its transcriptional expression (16). Although the oxygen level regulates three HIF-α subtypes (HIF-1α, HIF-2α, HIF-3α), and they all form a complex with HIF-1β to recognize and bind to the hypoxia response element HRE with a conserved sequence G/ACGTG upstream of the hypoxia-related gene promoter, HIF-1α is highly sensitive to hypoxia. When the oxygen concentration is lower than 6.0%, the cell HIF-1α level increases exponentially and reaches its highest when the oxygen concentration is 0.5% (equivalent to PO210~15mmHg, 1mmHg =0.133kPa) (17). Therefore, HIF-1α is considered to be the main factor regulating hypoxia response under hypoxic conditions.
2.2 Regulation mechanism of HIF expression
HIF-1α is a key regulator of the response of cells to hypoxia in the body, and its expression is regulated in both oxygen-dependent and non-oxygen-dependent ways. Under normoxic conditions, HIF-1α is hydroxylated by prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins (PHDs). The hydroxylated HIF-1α binds to von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) and is rapidly degraded through VHL-mediated ubiquitination modification and the 26S proteasome pathway (18). In addition, the factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) can also specifically modify the Asn803 of HIF-1α to weaken the binding ability of HIF-1α to its transcription cofactor p300/CBP (19). Therefore, HIF-1α is structurally unstable under normoxic conditions, with a half-life of less than 5 min, and its expression is undetectable. Under hypoxic conditions, the activity of PHDs and FIH is inhibited, HIF-1α protein accumulates in the cell, translocates to the nucleus from the cytoplasm, and binds to HIF-1β to form a heterodimer, which binds to the HRE in the promoter region of its target gene to initiate the transcription of related target genes, and participates in various physiological and pathological processes such as erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, autophagy and energy metabolism (20). In addition to oxygen-dependent regulation, the expression of HIF-1α is also affected by non-oxygen-dependent factors such as mechanical stress, hormones, cytokines, growth factors, and low pH. Therefore, HIF-1α, as a core transcription factor in the hypoxic microenvironment, its level continues to rise in RA and plays an important role in the pathological progression of RA (21).
3 The mechanism of hypoxic microenvironment in the pathogenesis of RA
3.1 Synovitis
Hypoxia is part of the inflammatory microenvironment in RA joints. Under normal circumstances, a dynamic equilibrium state of mutual regulation is maintained between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors. When the cells are in a hypoxic state, the expression levels of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in the synovial tissue of RA patients increase, which promotes the secretion of inflammatory factors by FLS, leading to the imbalance of pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokines and aggravates the inflammatory response (22, 23). At the same time, inflammatory factors act on FLS, increase HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression levels, and aggravate tissue hypoxia. A closed loop of self-amplification is formed between the two, resulting in the persistence of RA synovial inflammation. Studies have shown that the expression levels of HIF-1α and HIF-2α are increased in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats. Blocking the HIF pathway by injecting lentiviral vector shRNA plasmid (pLVX-shRNA-conHIF-1α) and HIF-1α gene knockout (lysm-cre/HIF-1α) into CIA rats can reduce the inflammatory response of CIA rat model, reduce the expression levels of TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6 in serum, and reduce the pathological damage of joints, including bone destruction, synovitis and synovial formation (24, 25).
In the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, HIF-1α promotes FLS to produce more IL-33 by activating p38 and acting on the ERK signaling pathway. In addition, IL-33 can reversely induce the expression of HIF-1α in FLS, thereby forming a HIF-1α/IL-33 regulatory circuit and aggravating the inflammation of RA (26). NF-κB is considered the prominent pro-inflammatory family of transcription factors. Under normoxic conditions, activated PHD1 can reduce the expression of NF-κB, thereby inhibiting the transcription of inflammatory factors. Under hypoxic conditions, PHD1 is inactivated, and NF-κB up-regulates the expression of inflammatory factors involved in RA inflammatory response (27, 28). Studies have shown that hypoxia regulates the activity of NF-κB stimulated by classical signaling pathways, and the activation of NF-κB pathway is positively correlated with hypoxia level (29, 30). Under a hypoxic microenvironment, the synergistic effect of the TAK1/NF-κB/HIF-1α signaling pathway was enhanced, and the expression of inflammatory factors IL-6 and IL-8 in FLS cells was induced (31). Hu et al. (32). found that hypoxia and HIF-1α can promote the inflammatory response mediated by the TLR signaling pathway by simulating the hypoxic environment of RA with Na2S2O4. Other studies have shown that HIF-1α can promote the intercellular contact between FLS and T cells and B cells by up-regulating the expression of intercellular contact media and enhancing the secretion of inflammatory factors such as IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and IL-1β, thus exacerbating synovial inflammation (33–35). In addition, under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α can also interact with Notch-3 and STAT-1 to jointly regulate the inflammatory mechanism of RA synovial fibroblasts (36, 37).
In summary, the transcription of related downstream target genes can be initiated under the hypoxic microenvironment through the above-mentioned series of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways (Figure 4). The expression of cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-15, IL-17, IL-33, TNF-α, IFN-γ), thrombospondin-1, chemokines (CXCL12, CXCL8, CCL20), etc. can be increased, leading to the aggregation of inflammatory cells, further exacerbating the synovial inflammation and other pathological reactions of RA.
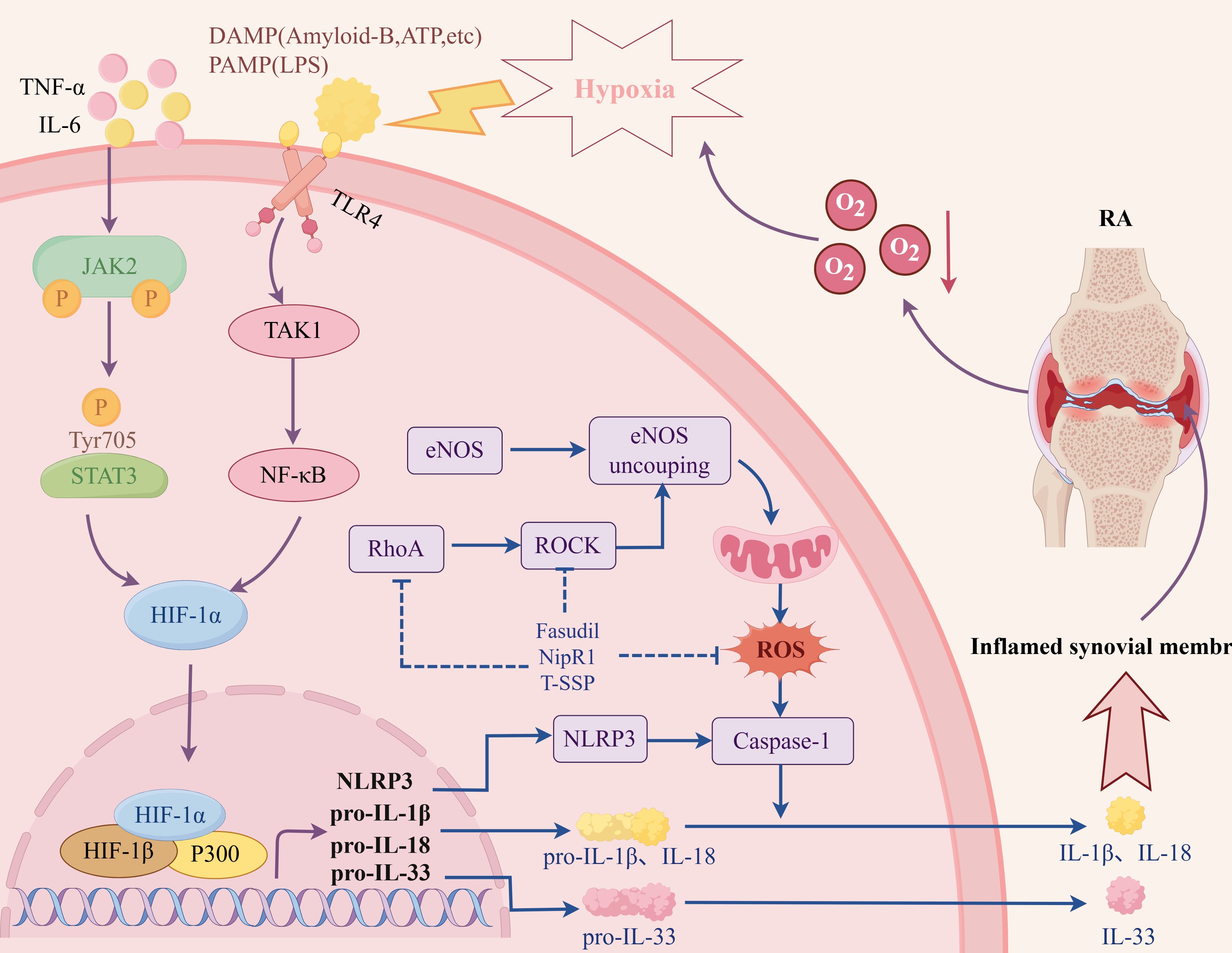
Figure 4. The related mechanism of RA synovitis induced by hypoxic microenvironment. Created with figdraw.com.
3.2 Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis, a complex process of new blood vessel formation and expression of multiple genes, is a typical characteristic of RA and is generally connected to hypoxia in both physiological and pathological states. In the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, the continuous accumulation of HIF-1α is a key driving molecule to induce angiogenesis, and the number of HIF-1α positive cells is positively correlated with the infiltration of synovial inflammatory cells and the number of neovascularization (38). Studies have shown that VEGF is a typical hypoxia response gene. When the joint cavity is continuously hypoxic, the activity of PHD is reduced, and HIF-1α and HIF-2α are accumulated in large quantities. The high expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α increases the expression levels of downstream target genes VEGF and VEGF receptors, induces the release of Angiopoietin-2 from the Weibel-Palade body in vascular endothelial cells, and promotes angiogenesis (39, 40). In addition, VEGF is also a target gene of VHL. Under hypoxia, VHL is disabled, unable to recognize and hydrolyze HIF, resulting in a significant accumulation of HIF, which makes VHL and HIF cooperate, further amplifying the effect, promoting the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells and inducing angiogenesis (41). Notch3 is also a key regulator of pathological angiogenesis. Under hypoxic conditions, Notch3 and HIF-1α synergistically regulate Angiopoietin-2 expression and neovascularization (42). Another study has shown that under hypoxic conditions, the S1P/S1PR1 signaling pathway is activated, and S1PR1 coupled with only inhibited type G protein on EPCs can mediate vasodilation and promote neovascularization (43). Hypoxia can also induce RASFs and SM to increase the expression of MMP, IL-8, and SDF-1 through HIF-1α, degrade extracellular matrix components, and promote angiogenesis (44). Shen K et al. found that Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR/P70S6K pathways were activated under hypoxic conditions in the articular cavity of RA, regulating the activation of HIF-1α and the transcription and expression of VEGF, and promoting angiogenesis (45). High mobility group protein B1 (HMGB-1) is a non-histone nuclear protein, which belongs to the endogenous TLR ligand. HMGB1 up-regulates HIF-1α transcription through the TLR4/NF-kB pathway, increases VEGF levels, and leads to angiogenesis (46).
In summary, Angiogenesis, a complex process of new blood-vessel formation as well as expression of multiple genes, is closely related to hypoxia in both physiological and pathological conditions. Hypoxia increases microvascular density in the inflammatory area of synovial tissue by up-regulating pro-angiogenic factors, activating endothelial cells and promoting their migration, while remodeling and degrading extracellular matrix, enabling endothelial cells to invade and form new blood vessels (Figure 5). However, the formation rate of new blood vessels is usually unable to catch up with the speed of synovial hyperplasia, and the structure of these new blood vessels is incomplete and cannot effectively provide oxygen. Therefore, despite the formation of new blood vessels, the oxygen supply in the joint cavity is not enough to alleviate the hypoxia of the joint cavity, so that the joint cavity is still in a state of hypoxia, which further aggravates the pathological process of RA.
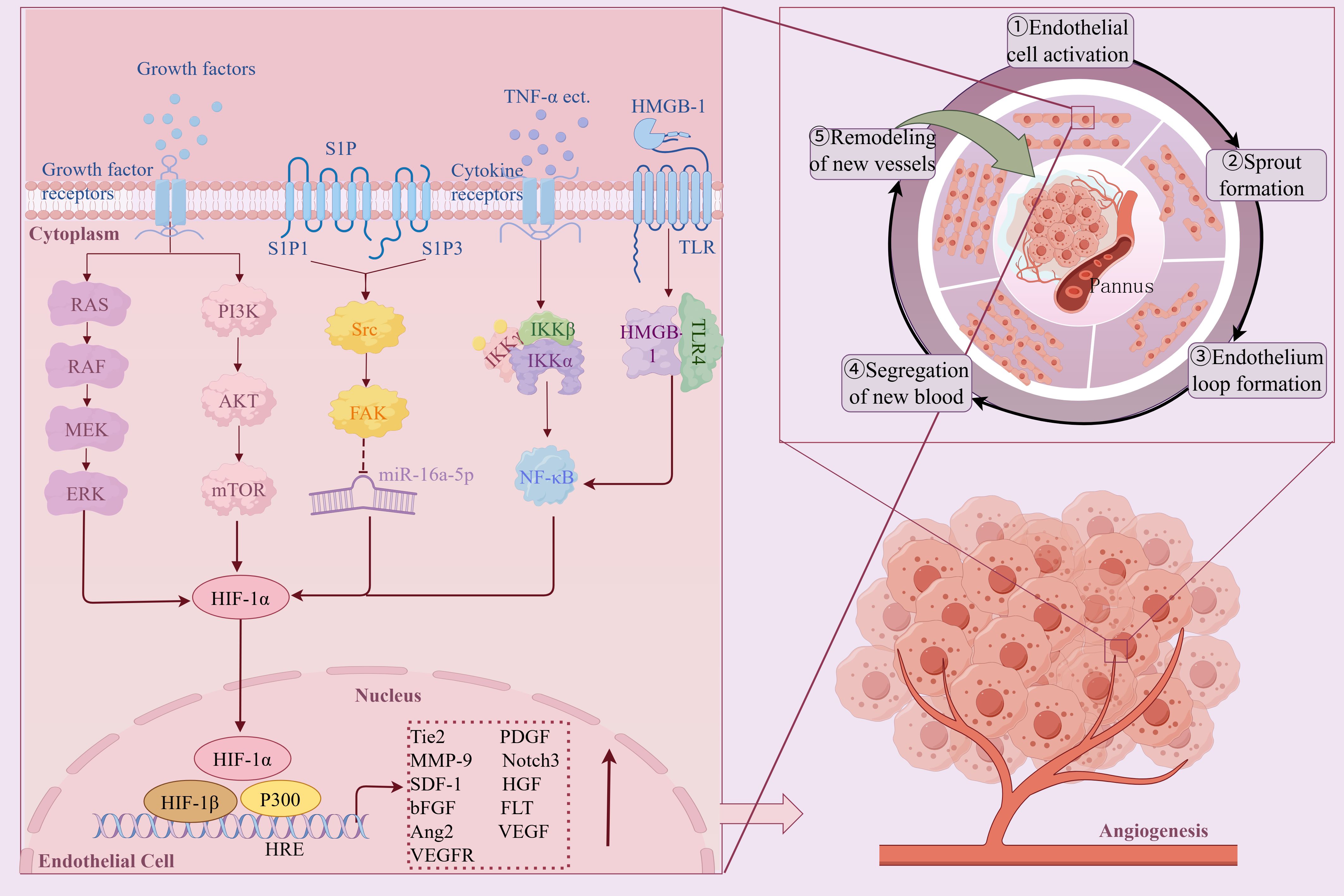
Figure 5. The mechanism and pathway of hypoxic microenvironment induced RA angiogenesis. Created with figdraw.com.
3.3 Cartilage degradation
The destruction of articular cartilage and bone erosion are essential factors for RA dysfunction and disability. The hypoxic microenvironment of RA will lead to an increase in the number of osteoclasts, increased bone resorption, and increased activity of osteolytic enzymes, thereby accelerating bone destruction (47). HIF-1α is a regulator of chondrocyte survival and osteoclast differentiation (48). The continuous hypoxia of the joint cavity can continuously inhibit the activity of PHD. High levels of HIF-1α can directly induce mature osteoclasts to enhance bone resorption and destroy bone and cartilage (49, 50). On the contrary, HIF-1α siRNA can block hypoxia-induced effects (51).
The expression of MMP is increased during tissue damage and remodeling, and the cartilage destruction of the joint is related to the increased activity of MMPs. Under hypoxic conditions, high expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α can induce chondrocytes to secrete MMPs and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-4, promote chondrocyte apoptosis, inhibit chondrocyte autophagy, and aggravate articular cartilage destruction (52, 53). The expression of MMP is induced by Ets-1, which is involved in the invasion and destruction of RA cartilage and bone. The study found that in the AIA rat model, hypoxia can induce the expression of Ets-1 and co-localize with HIF-1α in the synovial inflammatory infiltration site (54). Angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) stimulates osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. Under hypoxic conditions in RA, ANGPLT4 is overexpressed in RA osteoclasts in a HIF-1α-dependent manner (55, 56). Highly expressed HIF-1α activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, induces excessive proliferation, migration, and adhesion of FLS to cartilage tissue, and ultimately destroys bone and cartilage, resulting in joint deformity (57–60). Other studies have found that hypoxia and proinflammatory cytokines can play a synergistic role in enhancing osteoclast-mediated bone erosion and MMPs expression, thereby aggravating RA bone destruction, mainly through IL-1β/HIF-1α, IL-17/HIF-1α and other pathways (61, 62). RANKL is a central osteoclastogenic molecule. HIF-1α directly increases the osteoclast differentiation of RANKL-mediated RAW264.7 cells in vitro by upregulating the MAPK and JAK/STAT pathway under hypoxic conditions in the RA joint cavity (63, 64) (Figure 6).
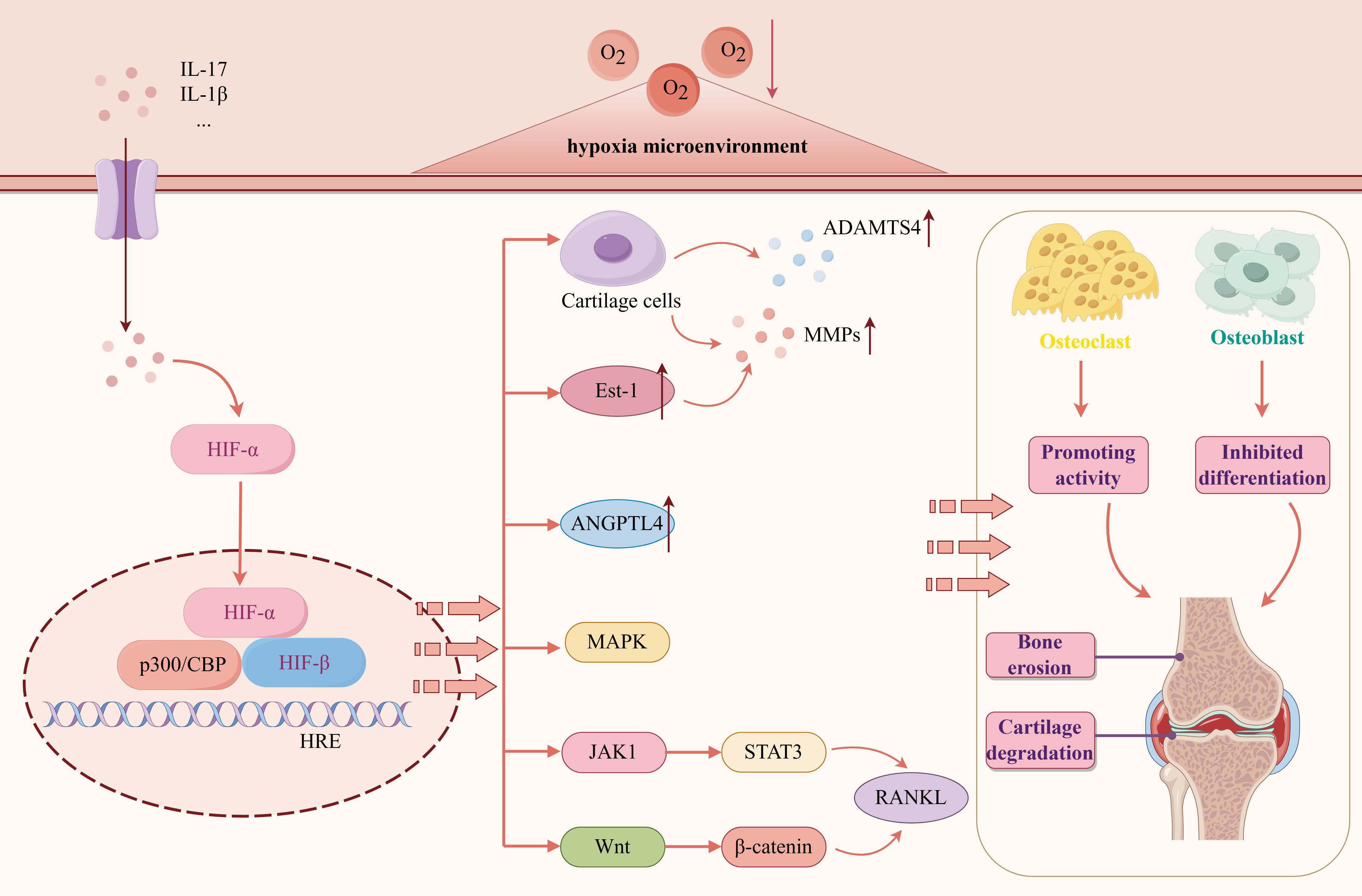
Figure 6. The mechanism and pathway of RA bone destruction induced by hypoxic microenvironment. Created with figdraw.com.
RA bone homeostasis depends on the balance between osteoclast bone resorption and osteoblast bone formation. The above studies reveal that hypoxia can lead to the imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation and promote bone destruction, and HIF plays an essential role in it.
3.4 HFLS-RA invasion and metastasis
The tumor-like migration and invasion characteristics of FLS are the basis of pathological processes such as RA bone destruction and invasive pannus formation. In the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, the migration and invasion of FLS are significantly enhanced, resulting in FLS penetrating the vascular wall and eroding articular cartilage and bone, further aggravating joint injury and inflammatory response. Compared with normoxia, the activity and invasiveness of RA-FLS under hypoxic conditions were significantly enhanced, and their invasiveness was positively correlated with the expression level of HIF-1α (65, 66). In addition, high expression of HIF-2α can also promote the proliferation and migration of FLS (67).
In the hypoxic microenvironment, the PI3K signaling pathway is activated, and the activated Akt increases the expression of HIF-1α, MMP-2, and MMP-9 and promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of RA-FLS resulting in enhanced migration and invasion (68). This indicates that hypoxia-induced changes in migration and invasion activity of RA-FLS are closely related to the activation of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Fascin-1 can regulate the reconstruction of cytoskeleton and is a key protein to promote cell migration and invasion. In the hypoxic microenvironment, the STAT3 signaling pathway participated in promoting the expression of high accumulation of HIF-1α. Subsequently, the activated HIF-α pathway facilitated the expression of fascin-1, which ultimately contributed to the migration and invasion of FLS (69, 70). Other studies have shown that under hypoxia, IL-17A can up-regulate the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by activating the NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway and promoting the migration and invasion of RA-FLS (71). The hypoxic state of RA can also affect epigenetic factors. Hypoxia-induced ALKBH5 regulates m6A modification of CH25H and aggravates synovial invasion and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (72, 73). C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) is a vital chemokine receptor widely involved in cell migration and invasion. Under hypoxic conditions, high levels of HIF-1α up-regulate CXCR4 due to the inhibition of PHD2. CXCR4 binds to its ligand SDF-1 and promotes RA-FLS activation, migration, and proliferation (74). The above studies have shown that the hypoxic microenvironment of RA synovium may be an essential reason for the increase of FLS migration and invasion ability.
3.5 Mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular stress
Mitochondria, as the ‘ energy factory ‘ of cells, are the main place for aerobic respiration of cells and are very sensitive to changes in oxygen concentration. In the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, mitochondria are mainly characterized by swelling, cristae disappearance, and membrane rupture, causing extensive changes in mitochondrial structure and genomic stability, leading to mitochondrial respiration reduction, oxidative damage, and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutation accumulation (75–77). Under hypoxic conditions, the expression of mitochondrial marker COX IV in RA-FLS was significantly up-regulated, indicating that hypoxia not only caused mitochondrial damage but also increased the number of damaged mitochondria (78). BNIP3 is a mitochondrial outer membrane protein. The accumulation of HIF-1α under hypoxic conditions promotes BNIP3-mediated mitophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis, which jointly promote the inflammatory response of FLS (79, 80). Under the condition of joint hypoxia, HIF-1α targets ALKBH7 and down-regulates the expression of UQCRC2 by binding to the ALKBH7 promoter, resulting in mitochondrial damage (81). After mitochondrial damage, the mitochondrial matrix escapes into the cytoplasm, activates cGAS-STING, TLR9, and other signaling pathways, affects the differentiation and function of FLS, OBS, and OCS, destroys the homeostasis of bone metabolism, promotes the secretion of inflammatory factors, and promotes the development of RA (82).
In RA synovial tissue, the persistent hypoxic microenvironment activates cell stress through multiple molecular mechanisms, thereby aggravating the abnormal proliferation of RA-FLS and inhibiting its programmed cell death. Studies have shown that in the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, HIF-1α can inhibit the degradation of wild-type p53 binding protein and increase the expression of p53 by inhibiting the function of Mdm2. However, hypoxia can promote the mutation of p53, which weakens the pro-apoptotic effect of HIF-1α through p53 (83, 84). Another study showed that the level of miR-191-C/EBPβ was negatively correlated with hypoxic stimulation (85, 86). In the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, reducing the expression of miR-191 relieves the inhibition of C/EBPβ, thereby activating its expression and promoting the proliferation of RA-FLS cells while preventing apoptosis (87).
In the early stages of RA disease, FLS can initiate autophagy through various mechanisms, remove denatured proteins and metabolites, and contribute to cell survival (88). However, with the progression of RA disease, with long-term or severe hypoxia, excessive autophagy of FLS triggers autophagy stress, induces damage to cell structure, and then causes continuous damage to cells, leading to RA pathological conditions such as maintaining synovial inflammation, promoting bone destruction, and destroying immune system homeostasis (89). It was found that the expression of autophagy-related proteins p62 and LC-3 in FLS treated with hypoxia was higher than that in normal FLS, indicating that the hypoxic microenvironment in RA joints could induce autophagy in FLS (90). PAD is involved in the post-translational transformation of arginine residues to citrulline, and the expression of citrullinated proteins and antigen presentation induced by PAD are closely related to FLS autophagy (91). In the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, the expression of PAD2 and PADI4 can be increased by regulating HIF-1α, and the production of citrullinated protein can be promoted, thereby inducing FLS autophagy and promoting FLS proliferation (92, 93).
In summary, the hypoxic microenvironment in RA synovial tissue induces mitochondrial damage, activates cell stress and autophagy procedures, and affects the survival status and functional behavior of RA-FLS by regulating HIF-1α and its downstream multi-pathways (Figure 7). This ‘hypoxia-stress-apoptosis escape and autophagy regulation‘ related response is not only a driving factor for RA chronic inflammation maintenance and bone destruction, but also provides a theoretical basis and potential intervention target for the future development of new therapeutic strategies such as targeting HIF-1α, mitochondrial function protection, and autophagy regulation.
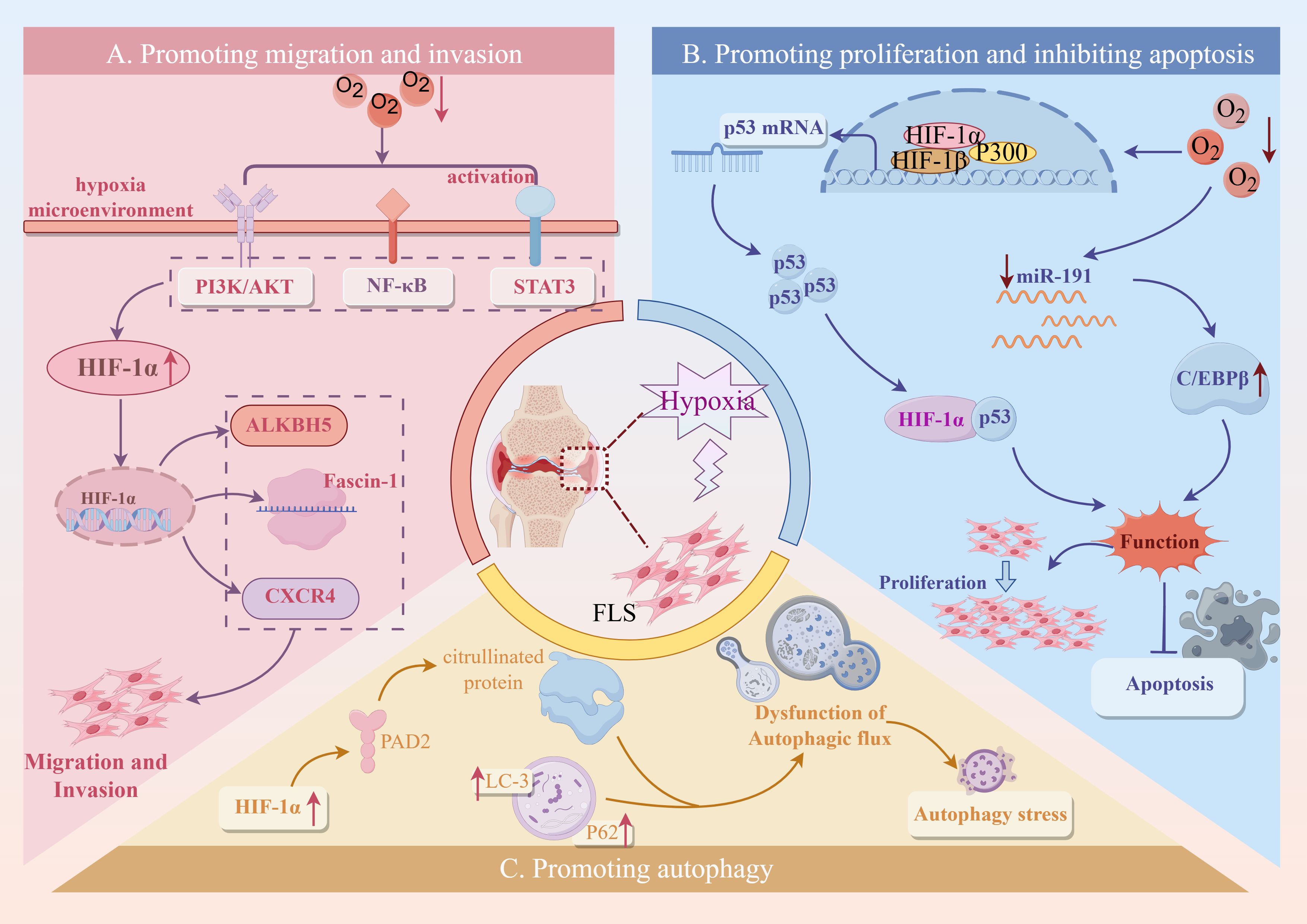
Figure 7. The mechanism and pathway of FLS-RA induced by hypoxic microenvironment. Created with figdraw.com.
3.6 Changes of immune cells
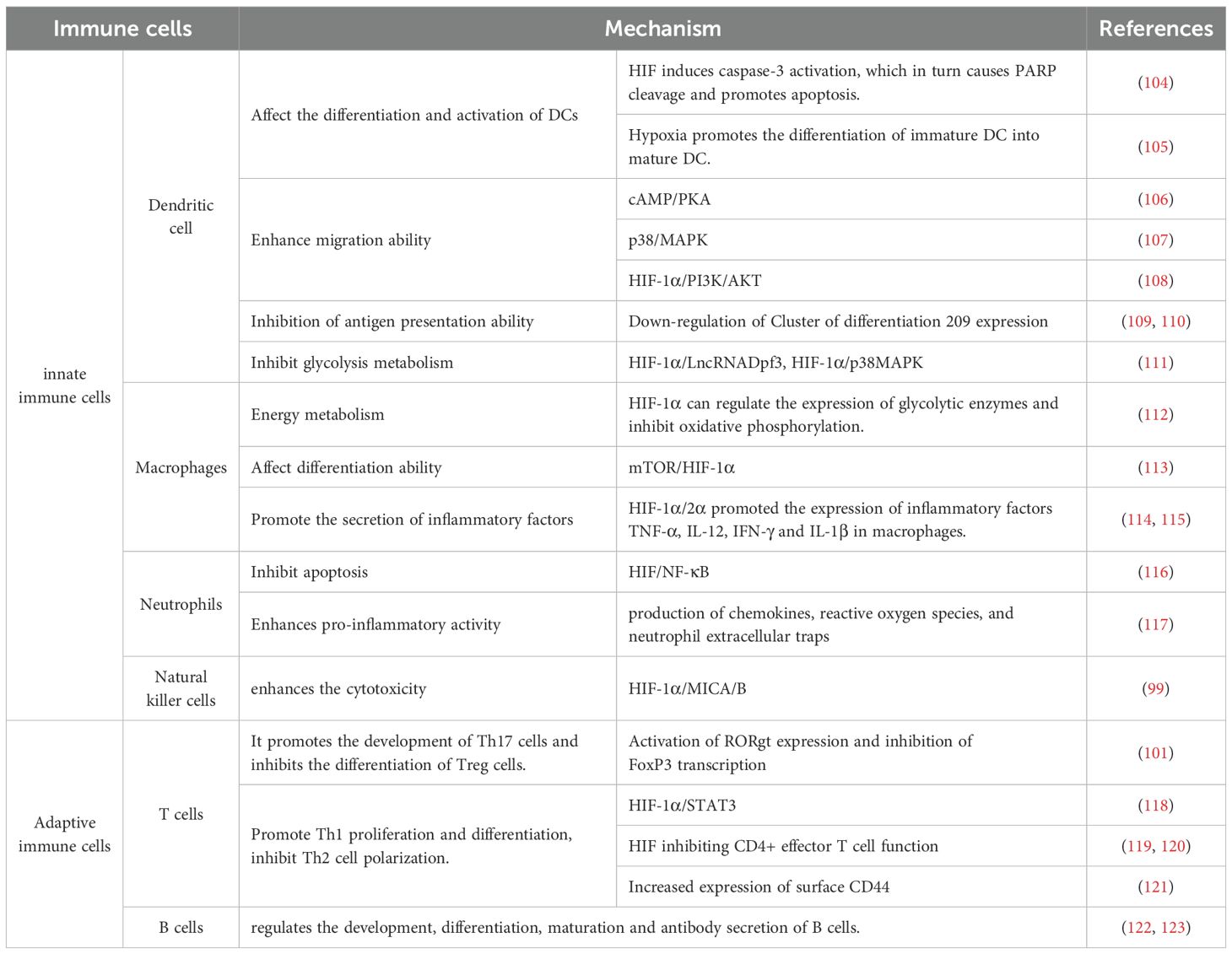
Immune cells are usually the first cells to reach RA lesions and are directly exposed to the stimulation of the hypoxic microenvironment. Hypoxia not only affects the function of innate immune cells (such as macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells) but also regulates the differentiation of adaptive immune cells (such as T cells and B cells), which promotes the inflammatory state of RA disease and affects the pathological process of RA.
Innate immune cells show heterogeneous responses in function and metabolism in the hypoxic microenvironment of RA. Dendritic cells (DCs) are powerful antigen-presenting cells. Hypoxia can activate HIF-1α, regulate downstream p38/MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and other signaling pathways, affect DCs’ maturation and apoptosis, migration ability, glucose metabolism, antigen presentation ability, promote infiltration in synovial fluid and synovial tissue, aggravate immune response, and promote the continuous activity and pathological progress of RA (94, 95). The infiltration of a large number of macrophages in synovial tissue is an early marker of active RA. The hypoxic microenvironment can upregulate inflammatory factors, such as TNF-α, IL-12, and IL-1β, by activating HIF-1α and HIF-2α. At the same time, it regulates the expression of glycolytic enzymes, promotes the metabolic shift to aerobic glycolysis, and enhances its pro-inflammatory polarization ability (96). Neutrophils are the core cells of innate immunity. The hypoxic microenvironment enhances the pro-inflammatory activity of neutrophils. It inhibits their apoptosis, produces ROS, activates proteases of soluble proteins, induces innate and adaptive immune responses, releases neutrophil extracellular traps, mediates gene expression and cell signal transduction, cell metabolism, and ultimately leads to joint damage (97). In the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, HIF-1α leads to abnormal function of natural killer cells (NK) by inducing MICA/B expression, prompting the immune system to attack its healthy cells indiscriminately, causing tissue damage (98, 99). Other studies have shown that NK function is abnormal, and the ability to release IFN-γ is reduced, thereby losing the inhibitory effect on Th17 cells and exacerbating the inflammatory response (100).
In terms of adaptive immunity, HIF-1α, as a metabolic sensor, plays a core regulatory role in CD4+ T cell differentiation. Studies have shown that in the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, HIF-1α can promote the development of Th17 cells by activating RORγt expression and inhibiting FoxP3 transcriptional activity, thereby inhibiting the differentiation of Treg cells and significantly biasing the Th17/Treg balance in a pro-inflammatory direction (101). This HIF-1α-mediated lineage bias is critical for the persistent immune activation of RA. In addition, under the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, HIF-1α not only promotes the polarization of B cells to the IL-6 phenotype, enhances the secretion of inflammatory factors, and activates the STAT3 signaling pathway, but also maintains the survival and function of IL-10-regulated B cell subsets by regulating glycolysis and co-transcriptional regulation of STAT3 (102). The results suggest that B cells are not only antibody producers, but also metabolically dependent inflammatory regulatory hubs in the hypoxic microenvironment of RA. Interestingly, these immune cells do not operate in isolation from each other. Under hypoxic conditions, activated B cells can enhance Th17 response through antigen presentation. Th17 cells secrete IL-17 to stimulate FLS to release IL-6 and chemokines, further recruiting neutrophils and macrophages, thus forming a positive feedback inflammatory loop between cells (103). The regulation and mechanism of hypoxia on various immune cells are shown in Table 1.
Although existing studies have revealed the regulatory mechanisms of hypoxic microenvironment on the function of various immune cells, the systematic understanding of how these mechanisms intertwine in intercellular interactions and drive RA progression is still insufficient. Therefore, an in-depth study of the interweaving of these mechanisms in a hypoxic microenvironment and elucidating the dynamic regulation map of the immune cell network under hypoxic conditions may provide new perspectives and research directions for understanding the occurrence and development of RA.
3.7 Energy metabolism
Energy metabolism has become an essential field in the study of RA. A hypoxic environment significantly affects the metabolic pathway of RA synovial tissue. Under hypoxic conditions, chondrocytes exhibit higher glycolytic activity, increasing glucose consumption and lactate production and increasing the expression of glycolytic genes such as LDHA and PGK1. In addition, hypoxia induces RA tissue to switch from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis by activating HIF-1α, reprogramming the energy metabolism pathway of cells (124, 125). Further studies have shown that under hypoxic conditions, up-regulation of HIF-1α leads to an increase in glucose transporter GLUT1 and GLUT3 in RA synovial tissue, thereby promoting glucose uptake and further enhancing the process of glycolysis by regulating the activities of hexokinase II, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase (126, 127).
Based on the above studies, it is found that the direct effect of hypoxia on RA energy metabolism is mainly reflected in two aspects: On the one hand, cells in RA synovium often rely on anaerobic glycolysis to maintain energy supply. This metabolic change not only leads to a decrease in the efficiency of ATP production, which makes cells face energy shortage but also increases the accumulation of local lactic acid, which leads to the formation of a local acidic environment and further aggravates the inflammatory response. On the other hand, hypoxia changes the metabolic pathway of cells by activating HIF, increases glycolysis and glucose uptake, reduces oxidative phosphorylation, and leads to metabolic reprogramming. Long-term hypoxia not only leads to a decrease in the efficiency of energy generation but also further aggravates RA tissue damage (Figure 8). Therefore, hypoxia directly affects the energy metabolism of synovial and intra-articular cells in RA patients, aggravating the inflammatory response and promoting the process of joint injury.
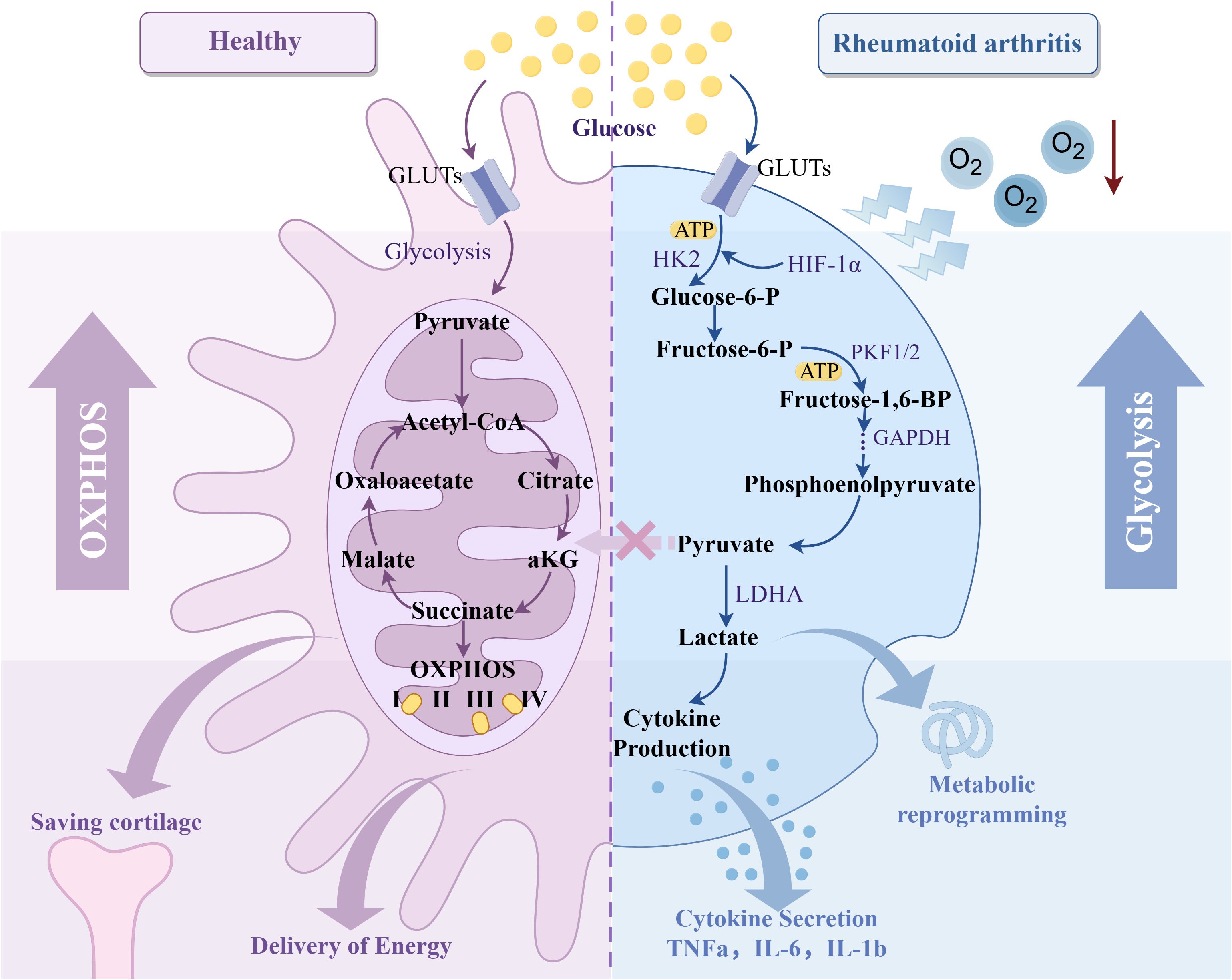
Figure 8. Effect of hypoxic microenvironment on RA glycolysis. Created with figdraw.com.
3.8 Oxidative stress
Under the normal physiological state, the body’s oxidation-antioxidation function maintains a dynamic balance within a specific range. When subjected to hypoxic stimulation, the oxidation system becomes unbalanced, and the oxygen molecules in the cell’s mitochondrial electron transport chain, serving as the final electron acceptor, are insufficient (128). The supply of oxygen molecules leads to the production of a large amount of ROS and accumulation in the cell, which causes damage to the macromolecules and organelles in the cell, activates the inflammatory response, and aggravates the clinical symptoms of RA (129).
Under hypoxic conditions, nitric oxide synthase and NADPH oxidase activity in FLS are upregulated, which promotes the formation of harmful oxidizing substances, such as peroxynitrite, thereby exacerbating inflammation and oxidative damage to joints (130). HIF-1α is the core regulator of the hypoxia response, which can activate redox-related enzymes, such as NADPH oxidase, and increase the production of ROS, thereby inducing oxidative stress (131). Additionally, Nrf2 is a vital antioxidant transcription factor that regulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase, to protect cells from oxidative damage (132). Under hypoxic conditions, the activation of Nrf2 may be inhibited, leading to a decrease in the antioxidant defense system, which in turn exacerbates oxidative stress and inflammatory responses (133, 134). The above studies suggest that hypoxic environment is not only the cause of oxidative stress but also may be a key node in the interaction between oxidative damage and inflammatory response in the pathological process of RA. Therefore, oxidative stress is closely related to hypoxia, and the two work together to promote inflammatory pathways and aggravate disease progression.
4 Drugs improving hypoxic microenvironment in the RA
4.1 Regulating hypoxia response pathway
4.1.1 HIF inhibitors
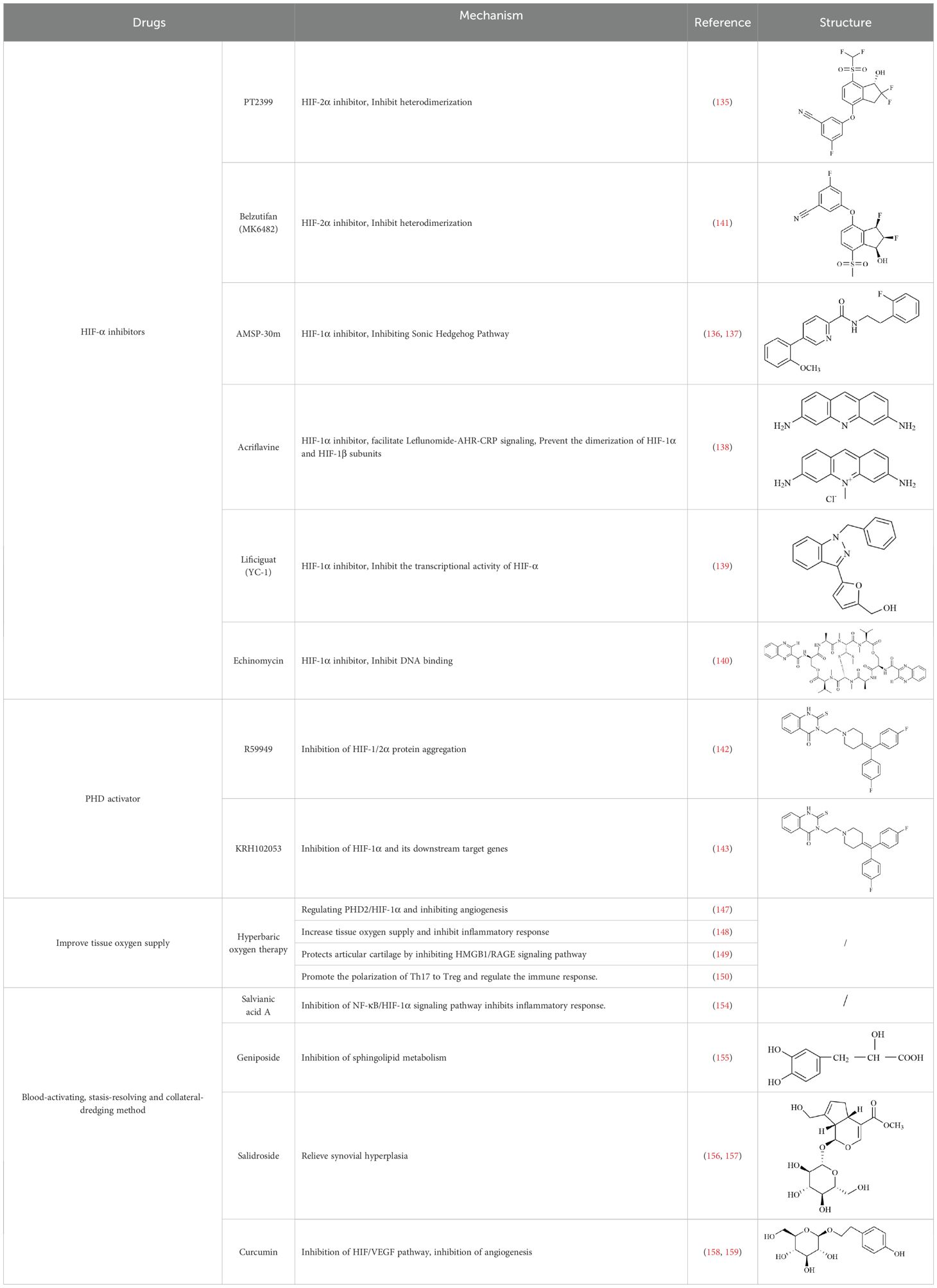
HIF is the main transcription factor to adapt to hypoxia, which can regulate the downstream gene spectrum and participate in the pathological process of RA. The existing HIF inhibitors mainly improve the hypoxic microenvironment by reducing the expression of HIF-α protein, inhibiting the transcriptional activity of HIF-α, inhibiting the dimerization of HIF-α and HIF-β, accelerating the degradation of HIF-α, and inhibiting the binding pathway of HIF-α and downstream target genes. It has been found that HIF-2α antagonist PT2399 can change its molecular structure by binding to the PASB domain of HIF-2α, interfere with or inhibit the expression of HIF-2α, and thus play a role in cartilage protection (135). Recent studies have found that HIF-1α inhibitor AMSP-30m can improve the hypoxic microenvironment of RA, inhibit the proliferation of MH7A cells, and improve the symptoms of arthritis in CIA rats by inhibiting Sonic Hedgehog Pathway (136, 137). Other studies have shown that in RA patients with higher CRP levels, the expression of HIF-1α is increased, and HIF-1α competes with AHR to bind to ARNT, which limits the efficacy of Leflunomide. The combination with HIF inhibitor Acriflavine can reduce the binding of ARNT with HIF-1α, promote Leflunomide activating AHR to inhibit CRP production, and inhibit bone erosion in CIA rats with no obvious toxicity. In the future, through in-depth exploration of the pathological mechanisms of RA, the combined application of traditional drugs and targeted agents has led to the development of more targeted therapeutic drugs with a precise mechanism of action. This provides a new direction for RA in precision medicine, combined therapy, and targeted therapy (138). In addition, Other inhibitors of HIF, such as Belzutifan, anti-platelet aggregation agent YC-1, and echinomycin, mainly focus on improving the hypoxic state of tumors (139–141). However, since the hypoxic microenvironment and HIF-1α overexpression in RA synovium are similar to those in solid tumors, these HIF-1α inhibitors are expected to become a new strategy for the treatment of RA.
4.1.2 Prolyl hydroxylase activator
In the hypoxic microenvironment, PHD activity is inhibited, resulting in high expression of HIF-α and participating in pathological processes such as RA inflammatory response, angiogenesis, and bone destruction by affecting downstream target genes. Therefore, by using a PHD activator, the activity of PHD in a hypoxic environment can be increased, and the degradation of HIF-α can be accelerated, thus playing a role in the treatment of RA. It has been found that diacylglycerol kinase inhibitors can activate PHD and inhibit the aggregation of HIF-1/2α protein under high and low oxygen concentrations, thereby inhibiting the activity of HIF-1/2α (142). HJ Choi et al. found a PHD2 activator KRH102053. They proved that KRH102053 can inhibit hypoxia-induced angiogenesis, cell migration and invasion, and glycolysis by measuring the levels of HIF-1α and its downstream target genes (143).
In summary, HIF inhibitors and PHD activity regulate the hypoxic response pathway by directly or indirectly regulating HIF gene expression, and have the potential to improve the hypoxic microenvironment and treat RA and other related diseases. Despite their promise, they are still experimental agents, primarily used in animal and cell studies, and have not yet been officially marketed for clinical treatment of RA. Its clinical transformation faces multiple challenges related to pharmacokinetics and resistance mechanisms, and further research and verification are urgently needed.
4.2 Improving tissue oxygen supply
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) refers to the method of inhaling pure oxygen to treat diseases under more than one atmospheric pressure, which can provide more O2 for damaged tissues, improve the physiological function of tissues and accelerate the recovery of tissues (144). At present, HBOT has been used as a treatment for arthritis. It can increase the oxygen transport and uptake of tissues, significantly reduce the expression of HIF-1α, and improve the hypoxic microenvironment of joints (145). Dulberger et al. confirmed the effectiveness of HBOT in the treatment of RA through the standard method of MRI quantification of inflammation and injury (146). Studies have found that HBOT can improve the common pathological angiogenesis of RA, and its mechanism is mainly through promoting the expression of PHD2, accelerating the degradation of HIF-1α, and inhibiting the production of angiogenic factor VEGFA (147). In addition, HBOT can also effectively increase the oxygenation of RA tissues, reduce inflammatory cell infiltration and inhibit the production of inflammatory factors (148). HBOT can inhibit HMGB-1/RAGE signaling pathway in chondrocytes and restore cartilage damage (149). HBOT can promote the transformation of Th17 cells to Treg cells in RA mouse model, which helps to restore the balance of the immune system and reduce the immune injury of RA (150). However, clinical studies have found that the benefits of HBOT are not permanent, and pain symptoms reappear within weeks to months after the last HBOT (151). Therefore, HBOT can be used as an adjuvant therapy, combined with other drugs for the treatment of RA as a new treatment method.
4.3 Blood-activating, stasis-resolving and collateral-dredging method
RA belongs to the ‘arthralgia syndrome’ category in traditional Chinese medicine. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that RA is closely related to the disorder of qi and blood and the obstruction of collaterals. When qi and blood are not running well, local tissues do not get enough oxygen and nutrition, resulting in increased hypoxia and inflammatory response in joint tissues. Therefore, traditional Chinese medicine, with the effects of promoting blood circulation, removing blood stasis, and dredging meridians and collaterals, can be used to restore the qi and blood flow of RA, inhibit the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells, thereby inhibiting vascular proliferation and neovascularization, improving the blood supply of joints, and alleviating local hypoxia (152, 153). Salvianic acid A, the active ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine, can down-regulate the expression of inflammatory factors by inhibiting NF-κB/HIF-1α and HIF-1α/STAT3/NLRP3 signaling pathways, inhibit cell excessive proliferation, and improve hypoxia-induced FLS injury (154). Geniposide restored the abnormal sphingolipid metabolism induced by the FLS hypoxic microenvironment (155). Salidroside can effectively alleviate the hypoxic state of CIA model mice and alleviate the hyperplasia of synovial tissue, angiogenesis, and inflammatory symptoms of RA (156, 157). Curcumin can inactivate HIF-α, down-regulate VEGF expression, and reduce RA angiogenesis and inflammatory response (158, 159). Therefore, some compound Buyang Huanwu decoctions with the effects of Yiqi Huoxue and Tongjing Huoluo can inhibit the BNIP3-PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby inhibiting hypoxia-induced mitophagy in FLS (160). Traditional Chinese medicine has shown certain potential in improving the hypoxic microenvironment of joint tissue in RA patients through its unique efficacy in promoting blood circulation, removing blood stasis, and dredging meridians.
In summary, these therapeutic implications of drugs on RA (Table 2), are designed to optimize the hypoxic microenvironment through multifaceted pathways, ultimately curbing inflammation and mitigating tissue damage, thereby achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes for autoimmune diseases. In the future, combining traditional Chinese medicine, components, and compound prescriptions with modern molecular biology technology will further enrich the contemporary connotation of arthralgia, more accurately reveal its mechanism of action, and give full play to the characteristic advantages of traditional Chinese medicine in intervening hypoxic microenvironment.
5 Discussion
The relationship between hypoxic microenvironment and RA pathological process is a two-way interaction. A large number of proliferating FLS and infiltrating inflammatory cells increased local oxygen consumption (161). At the same time, the proliferation and remodeling of blood vessels in the synovium cause the new blood vessels to extend into the articular cavity, resulting in increased intra-articular pressure and intermittent collapse of the articular capsule capillary network, limiting the effective supply of oxygen (162). The synergistic effect of the above multiple factors leads to long-term hypoxia of synovial tissue and the formation of a RA hypoxic microenvironment. By activating HIFs and downstream signaling pathways, promoting angiogenesis factors, and increasing the recruitment of immune cells, the hypoxic microenvironment itself aggravates the pathological processes of synovitis, angiogenesis, cartilage destruction, mitochondrial damage, cell migration, and invasion of RA. In addition, the hypoxic microenvironment also regulates the differentiation of immune cells, promotes the inflammatory state of RA disease, and interacts with other signaling pathways, thereby promoting the persistence of RA pathology. Therefore, the hypoxic microenvironment is not only the result of the pathological process of RA but also plays a role in promoting the progress of RA.
This article summarizes the literature and finds that HIF, as the main factor regulating hypoxia response under hypoxic conditions, plays multiple roles in different stages of RA. In the stage of RA disease, HIF is usually activated under strong hypoxia or acute hypoxia. As a driving factor, it promotes the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus promoting the formation of immune response and inflammatory response and the pathogenesis of RA. In addition, HIF also provides basic conditions for angiogenesis and joint injury. In the progression of RA, HIF is an intermediary factor, which is involved in the destruction of articular cartilage, angiogenesis, and the proliferation and migration of FLS cells by maintaining the hypoxic environment, and promotes the continuous deterioration of the disease. With the extension of the course of RA, the expression of HIF may no longer directly drive the disease, but as a result of pathological reactions, reflecting the persistence of inflammation and cell damage, and enhancing the immune response to promote the recurrence of the disease. Therefore, in the future, we can focus on the mechanism of HIF in different stages of RA, and provide new perspectives and strategies for its targeted therapy.
Currently, the potential drugs to improve the hypoxic microenvironment for treating RA mainly include HIF inhibitors, prolyl hydroxylase catalysts, traditional Chinese medicines, active ingredients, and compounds that promote blood circulation and remove blood stasis. Its mechanism of action is mainly to improve the hypoxic microenvironment by regulating the hypoxic response pathway, improving tissue oxygen supply, and promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis and dredging collaterals, and then to intervene in various pathological changes of RA, which provides a new strategy for RA treatment.
However, the research on the hypoxic microenvironment of RA is still in its infancy. First, RA is a process of multi-mechanism and multi-signal pathway regulation. There are many cross-effects and influencing factors in multiple pathways regulated by hypoxia-mediated HIF-1α transcription factors. Whether HIF-1α has spatiotemporal dynamics in different links of RA pathological progression, how these signaling pathways coordinate and interact with each other, and the complex relationship with other immune responses or synovial hyperplasia still need further study. Secondly, the potential drugs for improving the hypoxic microenvironment primarily focus on pharmacological inhibitors. However, research on HIF inhibitors at home and abroad has focused mainly on the field of tumors. Its application in RA is still in the preclinical research stage, involving animal experiments or in vitro models, and has not been approved for the clinical treatment of RA patients. It is necessary to explore its mechanism of action further and promote clinical transformation. Traditional Chinese medicine and active ingredients can effectively improve the hypoxic microenvironment due to their multi-target and safety advantages, showing certain potential in the treatment of RA. However, at present, it only focuses on a particular pathological link of RA. Still, it ignores the unique advantages of traditional Chinese medicine in improving multiple pathological changes of RA and reducing joint damage of RA.
Therefore, the future will focus on the following aspects. 1) Reveal the hypoxia mechanism of RA tissues and cells: Through single-cell sequencing, proteomics, and gene knockout technology, the interaction mechanism of HIF-1α on downstream signaling pathways and its temporal and spatial dynamic changes in the hypoxic microenvironment of RA was deeply explored, which provided a new perspective and new ideas for the development of new diagnostic biomarkers and the determination of new therapeutic targets. 2) Enhance the targeting efficiency of inhibitors and reduce side effects: Because of the pharmacokinetics of HIF inhibitors, liposomes, and other technologies are used to improve the stability and biocompatibility of HIF inhibitors, and more clinical trials and animal-related studies are carried out to evaluate their efficacy, accurately control the drug dose and time, and reduce the development of side effects and drug resistance. 3) Give full play to the advantages and clinical transformation of traditional Chinese medicine: Based on the thought of syndrome differentiation and treatment of traditional Chinese medicine, classical clinically effective traditional Chinese medicine was selected as the research object, focusing on its main active components, and using modern scientific and technological methods and means to develop traditional Chinese medicine nano-preparations and other pharmaceutical products with independent intellectual property rights, and further develop the unique advantages of improving the hypoxic microenvironment and slowing down joint damage.
In conclusion, the research on the role of hypoxic microenvironment in the occurrence and development of RA has, on a theoretical level, deepened the scientific understanding of the interaction between oxygen, microenvironment, HIF-1α, and multiple receptor expressions and, on the practical level, promoted the research and development of new hypoxic microenvironment regulators. Combining RA drug therapy with hypoxia biomarkers is not only beneficial to the application of hypoxic microenvironment regulation strategy in modern clinical practice but also contributes to the discovery of new drug targets for the treatment of RA and provides scientific prospects for the development of targeted therapy for other immune diseases.
Author contributions
QZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82074324), Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department Project of China (No. 20230508065RC), the Science and Technology Research Project of Jilin Provincial Department of Education (No. JJKH20250645KJ).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
ACPA: Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies
AHR-CRP: Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-C-reactive Protein
AKT: Ak Strain Transforming
ANGPTL4: Angiopoietin-like 4
Anti-CarP: Anti-Carbamylated Protein Antibodies
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate
BNIP3: BCL2/Adenovirus e1B 19 kDa Protein-in-teracting Protein 3
C/EBPβ: CCAAT/enhancer binding pro tein 尾
cGAS: Cyclic GMP–AMP synthase
CIA: Collagen-induced arthritis
COX: Cyclooxygenase
CRP: C-reactive protein
CXCL: Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand
CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4
DCs: Dendritic cells
EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
EPCs: Endothelial progenitor cells
ERK: Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase
ESR: Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
FIH: Factor inhibiting HIF
FLS: Fibroblast-like synoviocyte
GLUT: Glucose transporters
HBOT: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor
HMGB-1: High mobility group protein B1
HRE: Hypoxia response element
IFN-γ: Interferon-γ
IL: Interleukin
JAK: Janus-activated kinase
LC-3: Microtubule-Associated Protein 1 Light Chain 3
LDHA: Lactate dehydrogenase
MAPK: Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase
MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
MMP: Metalloproteinases
MTOR: Mammalian Target of Rapamycin
NF-κB: Nuclear Factor Kappa B
NK: Natural Killer Cells
NLRP3: Nod-like Receptor Pyrin Domain Containing 3
Notch-3: Neurogenic Locus Notch Homolog Protein 3
Nrf2: Nuclear Factor-erythroid 2-related Factor-2
OBS: Osteoblast
OCS: Osteoclast
PAD: Peptidylarginine deiminases
PGK1: Phosphoglycerate kinase 1
PHDs: Prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins
PI3K: Phoshatidylinositol-3 Kinase
PTPN22: Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22
RA: Rheumatoid Arthritis
Raf: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
RANKL: Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-β
ROR γt: Retinoic Acid-related Orphan Receptor Gamma t
ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species
S1P: Sphingosine-1-phosphate
S1PR1: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1
SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor 1
STAT: Signal Transducer and Activator and Transcription
STING: stimulator of interferon genes
TAK1: Transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1
Th17: T Helper Cell 17
TLR: Toll-like Receptor
TNF α: Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha
VEGF: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
VHL: Von Hippel-Lindau
Th17: T Helper Cell 17.
References
1. Finckh A, Gilbert B, Hodkinson B, Bae SC, Thomas R, Deane KD, et al. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:591–602. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00827-y
2. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2018) 4:18001. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.2
3. Weber BN, Giles JT, and Liao KP. Shared inflammatory pathways of rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2023) 19:417–28. doi: 10.1038/s41584-023-00969-7
4. Ito Y, Ichikawa Y, Murashima S, Sakuma H, and Nakajima A. Rheumatoid arthritis disease activity significantly impacts on the severity of interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Res Ther. (2024) 26:95. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03333-6
5. Fearon U, Canavan M, Biniecka M, and Veale DJ. Hypoxia mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:385–97. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.69
6. Gan P, Sun M, Wu H, Ke J, Dong X, and Chen F. A novel mechanism for inhibiting proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes: geniposide suppresses HIF-1α accumulation in the hypoxic microenvironment of synovium. Inflammation Res. (2022) 71:1375–88. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01636-5
7. Li Q, Chen Y, Liu H, Tian Y, Yin G, and Xie Q. Targeting glycolytic pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes for rheumatoid arthritis therapy: challenges and opportunities. Inflammation Res. (2023) 72:2155–67. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01807-y
8. Quiñonez-Flores CM, González-Chávez SA, and Pacheco-Tena C. Hypoxia and its implications in rheumatoid arthritis. J BioMed Sci. (2016) 23:62. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0281-0
9. McGettrick AF and O'Neill LAJ. The role of HIF in immunity and inflammation. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:524–36. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.002
10. Semenza GL and Wang GL. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. (1992) 12:5447–54. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5447-5454.1992
11. Lee SY, Kim SJ, Park KH, Lee G, Oh Y, Ryu JH, et al. Differential but complementary roles of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in the regulation of bone homeostasis. Commun Biol. (2024) 7:892. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06581-z
12. Bakleh MZ and Al Haj Zen A. The distinct role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in hypoxia and angiogenesis. Cells. (2025) 14:673. doi: 10.3390/cells14090673
13. Hu CJ, Wang LY, Chodosh LA, Keith B, and Simon MC. Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. (2003) 23:9361–74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.24.9361-9374.2003
14. López-Mejía A, Briseño-Díaz P, and Robles-Flores M. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-3α in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2025) 11:120007. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2025.120007
15. Semenza GL. Pharmacologic targeting of hypoxia-inducible factors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2019) 59:379–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010818-021637
16. Javan B and Shahbazi M. Hypoxia-inducible tumour-specific promoters as a dual-targeting transcriptional regulation system for cancer gene therapy. Ecancermedicalscience. (2017) 11:751. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2017.751
17. Ahn JK, Koh EM, Cha HS, Lee YS, Kim J, Bae EK, et al. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in hypoxia-induced expressions of IL-8, MMP-1 and MMP-3 in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2008) 47:834–9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken086
18. Sim J, Cowburn AS, Palazon A, Madhu B, Tyrakis PA, Macías D, et al. The factor inhibiting HIF asparaginyl hydroxylase regulates oxidative metabolism and accelerates metabolic adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab. (2018) 27:898–913.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.020
19. Malkov MI, Lee CT, and Taylor CT. Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cells. (2021) 10:2340. doi: 10.3390/cells10092340
20. Dong P, Li Q, and Han H. HIF−1α in cerebral ischemia (Review). Mol Med Rep. (2022) 25:41. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12557
21. Guo X and Chen G. Hypoxia-inducible factor is critical for pathogenesis and regulation of immune cell functions in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1668. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01668
22. Jiang Y, Zhou Y, Peng G, Liu N, Tian H, Pan D, et al. Topotecan prevents hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension and inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and TRPC channels. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2018) 104:161–70. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.09.010
23. Wang YQ, Tang YF, Yang MK, and Huang XZ. Dexmedetomidine alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:7834–44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28058
24. Hu Y, Zhang T, Chen J, Cheng W, Chen J, Zheng Z, et al. Downregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by RNA interference alleviates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 19:1330–42. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.014
25. Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Förster I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, et al. HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation. Cell. (2003) 112:645–57. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00154-5
26. Hu F, Shi L, Mu R, Zhu J, Li Y, Ma X, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and interleukin 33 form a regulatory circuit to perpetuate the inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. PloS One. (2013) 8:e72650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072650
27. Song XL, Su J, Liu CY, Zhang GY, and Zhang X. Expression and significance of prolyl hydroxylase and von-Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein in the synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. (2019) 23:3623–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1305
28. Oliver KM, Taylor CT, and Cummins EP. Hypoxia. Regulation of NFkappaB signalling during inflammation: the role of hydroxylases. Arthritis Res Ther. (2009) 11:215. doi: 10.1186/ar2575
29. Oliver KM, Garvey JF, Ng CT, Veale DJ, Fearon U, Cummins EP, et al. Hypoxia activates NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression through the canonical signaling pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2009) 11:2057–64. doi: 10.1089/ars.2008.2400
31. Wang G, Wang J, Li X, Wu Q, Yao R, and Luo X. Hypoxia and TNF-α Synergistically induce expression of IL-6 and IL-8 in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes via enhancing TAK1/NF-κB/HIF-1α Signaling. Inflammation. (2023) 46:912–24. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01779-x
32. Hu F, Mu R, Zhu J, Shi L, Li Y, Liu X, et al. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α provoke toll-like receptor signalling-induced inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73:928–36. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202444
33. Hu F, Liu H, Xu L, Li Y, Liu X, Shi L, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α perpetuates synovial fibroblast interactions with T cells and B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. (2016) 46:742–51. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545784
34. Sabi EM, Singh A, Althafar ZM, Behl T, Sehgal A, Singh S, et al. Elucidating the role of hypoxia-inducible factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology. (2022) 30:737–48. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00974-4
35. Korbecki J, Kojder K, Kapczuk P, Kupnicka P, Gawrońska-Szklarz B, Gutowska I, et al. The effect of hypoxia on the expression of CXC chemokines and CXC chemokine receptors-A review of literature. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:843. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020843
36. Gao W, McCormick J, Connolly M, Balogh E, Veale DJ, and Fearon U. Hypoxia and STAT3 signalling interactions regulate pro-inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:1275–83. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204105
37. Zhang F, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Cai Y, Li Z, Sun J, et al. Metabolic effects of quercetin on inflammatory and autoimmune responses in rheumatoid arthritis are mediated through the inhibition of JAK1/STAT3/HIF-1α signaling. Mol Med. (2024) 30:170. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00929-1
38. Zhang X, Liu J, Wan L, Sun Y, Wang F, Qi Y, et al. Up-regulated expressions of HIF-1α, VEGF and CD34 promote synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol. (2015) 31:1053–6. doi: 10.13423/j.cnki.cjcmi.007483
39. Li Y, Liu Y, Wang C, Xia WR, Zheng JY, Yang J, et al. Succinate induces synovial angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis through metabolic remodeling and HIF-1α/VEGF axis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 126:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.07.009
40. Befani C and Liakos P. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha in angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:9087–98. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26805
41. Zimna A and Kurpisz M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in physiological and pathophysiological angiogenesis: applications and therapies. BioMed Res Int. (2015) 2015:549412. doi: 10.1155/2015/549412
42. Wei K, Korsunsky I, Marshall JL, Gao A, Watts GFM, Major T, et al. Notch signalling drives synovial fibroblast identity and arthritis pathology. Nature. (2020) 582:259–64. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2222-z
43. Huang CC, Tseng TT, Liu SC, Lin YY, Law YY, Hu SL, et al. S1P Increases VEGF Production in Osteoblasts and Facilitates Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-16-5p Expression via the c-Src/FAK Signaling Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. (2021) 10:2168. doi: 10.3390/cells10082168
44. Kiriakidis S, Henze AT, Kruszynska-Ziaja I, Skobridis K, Theodorou V, Paleolog EM, et al. Factor-inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH-1) is required for human vascular endothelial cell survival. FASEB J. (2015) 29:2814–27. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-252379
45. Shen K, Ji L, Gong C, Ma Y, Yang L, Fan Y, et al. Notoginsenoside Ft1 promotes angiogenesis via HIF-1α mediated VEGF secretion and the regulation of PI3K/AKT and Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. (2012) 84:784–92. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.05.024
46. Park SY, Lee SW, Kim HY, Lee WS, Hong KW, and Kim CD. HMGB1 induces angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis via HIF-1alpha activation. Eur J Immunol. (2015) 45:1216–27. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444908
47. Dandajena TC, Ihnat MA, Disch B, Thorpe J, and Currier GF. Hypoxia triggers a HIF-mediated differentiation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells into osteoclasts. Orthod Craniofac Res. (2012) 15:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-6343.2011.01530.x
48. Chang Z, Huo L, Wu Y, and Zhang P. HIF-1 α had pivotal effects on downregulation of miR-210 decreasing viability and inducing apoptosis in hypoxic chondrocytes. Sci World J. (2014) 2014:876363. doi: 10.1155/2014/876363
49. Knowles HJ and Athanasou NA. Acute hypoxia and osteoclast activity: a balance between enhanced resorption and increased apoptosis. J Pathol. (2009) 218:256–64. doi: 10.1002/path.2534
50. Wolf D, Muralidharan A, and Mohan S. Role of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins in bone metabolism. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. (2022) 8:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2022.03.001
51. Kaihara K, Nakagawa S, Arai Y, Inoue H, Tsuchida S, Fujii Y, et al. Sustained hypoxia suppresses joint destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis via negative feedback of hypoxia inducible factor-1α. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:3898. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083898
52. Zhang FJ, Luo W, and Lei GH. Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. (2015) 82:144–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.10.003
53. Yang S, Kim J, Ryu JH, Oh H, Chun CH, Kim BJ, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Nat Med. (2010) 16:687–93. doi: 10.1038/nm.2153
54. Peters CL, Morris CJ, Mapp PI, Blake DR, Lewis CE, and Winrow VR. The transcription factors hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and Ets-1 colocalize in the hypoxic synovium of inflamed joints in adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2004) 50:291–6. doi: 10.1002/art.11473
55. Swales C, Athanasou NA, and Knowles HJ. Angiopoietin-like 4 is over-expressed in rheumatoid arthritis patients: association with pathological bone resorption. PloS One. (2014) 9:e109524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109524
56. Knowles HJ, Cleton-Jansen AM, Korsching E, and Athanasou NA. Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates osteoclast-mediated bone resorption: role of angiopoietin-like 4. FASEB J. (2010) 24:4648–59. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-162230
57. Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y, and Vallée JN. The key role of the WNT/β-catenin pathway in metabolic reprogramming in cancers under normoxic conditions. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:5557. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215557
58. Zhou Y, Wang T, Hamilton JL, and Chen D. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in osteoarthritis and in other forms of arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2017) 19:53. doi: 10.1007/s11926-017-0679-z
59. Lories RJ, Corr M, and Lane NE. To Wnt or not to Wnt: the bone and joint health dilemma. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2013) 9:328–39. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2013.25
60. Huang P, Yan R, Zhang X, Wang L, Ke X, and Qu Y. Activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway for disease therapy: Challenges and opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 196:79–90. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.11.008
61. Lee YA, Choi HM, Lee SH, Hong SJ, Yang HI, Yoo MC, et al. Hypoxia differentially affects IL-1β-stimulated MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in an HIF-1α-dependent manner. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2012) 51:443–50. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker327
62. Samarpita S, Doss HM, Ganesan R, and Rasool M. Interleukin 17 under hypoxia mimetic condition augments osteoclast mediated bone erosion and expression of HIF-1α and MMP-9. Cell Immunol. (2018) 332:39–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.07.005
63. Hu L, Liu R, and Zhang L. Advance in bone destruction participated by JAK/STAT in rheumatoid arthritis and therapeutic effect of JAK/STAT inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 111:109095. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109095
64. Wang D, Liu L, Qu Z, Zhang B, Gao X, Huang W, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α enhances RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by upregulating the MAPK pathway. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:1227. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-4603
65. Zhao X, Yue Y, Cheng W, Li J, Hu Y, Qin L, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor: a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Drug Targets. (2013) 14:700–7. doi: 10.2174/1389450111314060010
66. Zhang Y and Zhang B. Trichostatin A,an inhibitor of histone deacetylase,inhibits the viability and invasiveness of hypoxic rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via PI3K/Akt signaling. JBiochem Mol Toxicol. (2016) 30:163–9. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21774
67. Ryu JH, Chae CS, Kwak JS, Oh H, Shin Y, Huh YH, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α is an essential catabolic regulator of inflammatory rheumatoid rethritis. PloS Biol. (2014) 12:1001881. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001881
68. Li GQ, Zhang Y, Liu D, Qian YY, Zhang H, Guo SY, et al. PI3 kinase/Akt/HIF-1α path way is associated with hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Cell Biochem. (2013) 372:221–31. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1463-z
69. Yang W, Wei X, Jiao Y, Bai Y, Sam WN, Yan Q, et al. STAT3/HIF-1α/fascin-1 axis promotes RA FLSs migration and invasion ability under hypoxia. Mol Immunol. (2022) 142:83–94. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.12.004
70. Ma K, Zhang C, and Li W. Fascin1 mediated release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and invasion/migration in rheumatoid arthritis via the STAT3 pathway. Cell Cycle. (2025) 26:1. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1974790
71. Li G, Zhang Y, Qian Y, Zhang H, Guo S, Sunagawa M, et al. Interleukin-17A promotes rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes migration and invasion under hypoxia by increasing MMP2 and MMP9 expression through NF-κB/HIF-1αpathway. Mol Immunol. (2013) 53:227–36. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.08.018
72. Fan D, Geng Q, Wang B, Wang X, Xia Y, Yang L, et al. Hypoxia-induced ALKBH5 aggravates synovial aggression and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the m6A modification of CH25H. Clin Immunol. (2024) 261:109929. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2024.109929
73. Kuang Y, Li R, Wang J, Xu S, Qiu Q, Lin S, et al. ALKBH5-mediated RNA m6 A methylation regulates the migration, invasion, and proliferation of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2024) 76:192–205. doi: 10.1002/art.42676
74. Li GQ, Liu D, Zhang Y, Qian YY, Zhu YD, Guo SY, et al. Anti-invasive effects of celastrol in hypoxia-induced fibroblast-like synoviocyte through suppressing of HIF-1α/CXCR4 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2013) 17:1028–36. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.10.006
75. Hao T, Yu J, Wu Z, Jiang J, Gong L, Wang B, et al. Hypoxia-reprogramed megamitochondrion contacts and engulfs lysosome to mediate mitochondrial self-digestion. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:4105. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39811-9
76. Thankam FG, Ayoub JG, Ahmed MMR, Siddique A, Sanchez TC, Peralta RA, et al. Association of hypoxia and mitochondrial damage associated molecular patterns in the pathogenesis of vein graft failure: a pilot study. Transl Res. (2021) 229:38–52. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.08.010
77. Biniecka M, Canavan M, McGarry T, Gao W, McCormick J, Cregan S, et al. Dysregulated bioenergetics: a key regulator of joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:2192–200. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208476
78. Ma C, Wang J, Hong F, and Yang S. Mitochondrial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:1216. doi: 10.3390/biom12091216
79. Deng R, Wang Y, Bu Y, and Wu H. BNIP3 mediates the different adaptive responses of fibroblast-like synovial cells to hypoxia in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med. (2022) 28:64. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00490-9
80. Hong Z, Wang H, Zhang T, Xu L, Zhai Y, Zhang X, et al. The HIF-1/BNIP3 pathway mediates mitophagy to inhibit the pyroptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 127:111378. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111378
81. Wang H, Zhao YC, Xu L, Zhang TJ, Liu LH, Zhou MQ, et al. HIF-1α mediates mitochondrial damage by down-regulating ALKBH7 expression to promote the aberrant activation of FLS in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2025) 46:2225–36. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01520-y
82. Li P, Zhou M, Wang J, Tian J, Zhang L, Wei Y, et al. Important role of mitochondrial dysfunction in immune triggering and inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. J Inflammation Res. (2024) 17:11631–57. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S499473
83. Li M, Su Y, Gao X, Yu J, Wang Z, and Wang X. Transition of autophagy and apoptosis in fibroblasts depends on dominant expression of HIF-1α or p53. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2022) 23:204–17. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2100187
84. Obacz J, Pastorekova S, Vojtesek B, and Hrstka R. Cross-talk between HIF and p53 as mediators of molecular responses to physiological and genotoxic stresses. Mol Cancer. (2013) 12:93. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-93
85. Camps C, Saini HK, Mole DR, Choudhry H, Reczko M, Guerra-Assunção JA, et al. Integrated analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression and association with HIF binding reveals the complexity of microRNA expression regulation under hypoxia. Mol Cancer. (2014) 13:28. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-28
86. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. (2004) 116:281–97. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5
87. Yu S, Lu Y, Zong M, Tan Q, and Fan L. Hypoxia-induced miR-191-C/EBPβ signaling regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2019) 21:78. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1861-7
88. Rockel JS and Kapoor M. Autophagy: controlling cell fate in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:517–31. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.92
89. Karami J, Masoumi M, Khorramdelazad H, Bashiri H, Darvishi P, Sereshki HA, et al. Role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: Latest evidence and therapeutic approaches. Life Sci. (2020) 254:117734. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117734
90. Yang R, Zhang Y, Wang L, Hu J, Wen J, Xue L, et al. Increased autophagy in fibroblast-like synoviocytes leads to immune enhancement potential in rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:15420–30. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14331
91. Durrant LG, Metheringham RL, and Brentville VA. Autophagy, citrullination and cancer. Autophagy. (2016) 12:1055–6. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1166326
92. Fan T, Zhang C, Zong M, and Fan L. Hypoxia−induced autophagy is inhibited by PADI4 knockdown, which promotes apoptosis of fibroblast−like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17:5116–24. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8501
93. Yu R, Li C, Sun L, Jian L, Ma Z, Zhao J, et al. Hypoxia induces production of citrullinated proteins in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes through regulating HIF1α. Scand J Immunol. (2018) 87:e12654. doi: 10.1111/sji.12654
94. Naldini A, Morena E, Pucci A, Miglietta D, Riboldi E, Sozzani S, et al. Hypoxia affects dendritic cell survival: role of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and lipopolysaccharide. J Cell Physiol. (2012) 227:587–95. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22761
95. Yang M, Ma C, Liu S, Shao Q, Gao W, Song B, et al. HIF-dependent induction of adenosine receptor A2b skews human dendritic cells to a Th2-stimulating phenotype under hypoxia. Immunol Cell Biol. (2010) 88:165–71. doi: 10.1038/icb.2009.77
96. Staples KJ, Sotoodehnejadnematalahi F, Pearson H, Frankenberger M, Francescut L, Ziegler-Heitbrock L, et al. Monocyte-derived macrophages matured under prolonged hypoxia transcriptionally up-regulate HIF-1α mRNA. Immunobiology. (2011) 216:832–9. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2010.12.005
97. Elks PM, Van Eeden FJ, Dixon G, Wang X, Reyes-Aldasoro CC, Ingham PW, et al. Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a (Hif-1a) delays inflammation resolution by reducing neutrophil apoptosis and reverse migration in a zebrafish inflammation model. Blood. (2011) 118:712–22. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-324186
98. Yamin R, Berhani O, Peleg H, Aamar S, Stein N, Gamliel M, et al. High percentages and activity of synovial fluid NK cells present in patients with advanced stage active Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:1351. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37448-z
99. Wei L, Lu J, Feng L, Long D, Shan J, Li S, et al. HIF-1alpha accumulation upregulates MICA and MICB expression on human cardiomyocytes and enhances NK cell cytotoxicity during hypoxia-reoxygenation. Life Sci. (2010) 87:111–9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.05.012
100. Lo CK, Lam QL, Sun L, Wang S, Ko KH, Xu H, et al. Natural killer cell degeneration exacerbates experimental arthritis in mice via enhanced interleukin-17 production. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2008) 58:2700–11. doi: 10.1002/art.23760
101. Dang EV, Barbi J, Yang HY, Jinasena D, Yu H, Zheng Y, et al. Control of T(H)17/T(reg) balance by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell. (2011) 146:772–84. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.033
102. Meng X, Grötsch B, Luo Y, Knaup KX, Wiesener MS, Chen XX, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02683-x
103. Fan C, Li J, Li Y, Jin Y, Feng J, Guo R, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulates the interleukin-6 production by B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Transl Immunol. (2023) 12:e1447. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1447
104. Mancino A, Schioppa T, Larghi P, Pasqualini F, Nebuloni M, Chen IH, et al. Divergent effects of hypoxia on dendritic cell functions. Blood. (2008) 112:3723–34. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-142091
105. Bosco MC, Pierobon D, Blengio F, Raggi F, Vanni C, Gattorno M, et al. Hypoxia modulates the gene expression profile of immunoregulatory receptors in human mature dendritic cells: identification of TREM-1 as a novel hypoxic marker. Vitro vivo Blood. (2011) 117:2625–39. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-292136
106. Zhao P, Li XG, Yang M, Shao Q, Wang D, Liu S, et al. Hypoxia suppresses the production of MMP-9 by human monocyte-derived dendritic cells and requires activation of adenosine receptor A2b via cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. Mol Immunol. (2008) 45:2187–95. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.12.002
107. Paardekooper LM, Bendix MB, Ottria A, de Haer LW, Ter Beest M, Radstake TRDJ, et al. Hypoxia potentiates monocyte-derived dendritic cells for release of tumor necrosis factor α via MAP3K8. Biosci Rep. (2018) 38:BSR20182019. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182019
108. Filippi I, Morena E, Aldinucci C, Carraro F, Sozzani S, and Naldini A. Short-term hypoxia enhances the migratory capability of dendritic cell through HIF-1α and PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Physiol. (2014) 229:2067–76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24666
109. Liu J, Zhang X, Cheng Y, and Cao X. Dendritic cell migration in inflammation and immunity. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:2461–71. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00726-4
110. Monaci S, Aldinucci C, Rossi D, Giuntini G, Filippi I, Ulivieri C, et al. Hypoxia shapes autophagy in LPS-activated dendritic cells. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:573646. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.573646
111. Liu J, Zhang X, Chen K, Cheng Y, Liu S, Xia M, et al. CCR7 chemokine receptor-inducible lnc-dpf3 restrains dendritic cell migration by inhibiting HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis. Immunity. (2019) 50:600–615.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.01.021
112. Kelly B and O'neill LA. Metabolic reprogramming in macrophages and dendritic cells in innate immunity. Cell Res. (2015) 25:771–84. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.68
113. Cheng SC, Quintin J, Cramer RA, Shepardson KM, Saeed S, Kumar V, et al. mTOR-and HIF-1 alphamediated aerobic glycolysis as metabolic basis for trained immunity. Science. (2014) 345:1250684. doi: 10.1126/science.1250684
114. Imtiyaz HZ, Williams EP, Hickey MM, Patel SA, Durham AC, Yuan LJ, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha regulates macrophage function in mouse models of acute and tumor inflammation. J Clin Invest. (2010) 120:2699–714. doi: 10.1172/JCI39506
115. Chang Y, Li X, Cheng Q, Hu Y, Chen X, Hua X, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic identified HIF1A as a target for attenuating acute rejection after heart transplantation. Basic Res Cardiol. (2021) 116:64. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00904-5
116. Walmsley SR, Print C, Farahi N, Peyssonnaux C, Johnson RS, Cramer T, et al. Hypoxia-induced neutrophil survival is mediated by HIF-1α-dependent NF-κB activity. J Exp Med. (2005) 201:105–15. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040624
117. Wright HL, Lyon M, Chapman EA, Moots RJ, and Edwards SW. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid neutrophils drive inflammation through production of chemokines, reactive oxygen species, and neutrophil extracellular traps. Front Immunol. (2021) 11:584116. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584116
118. Chaudhari SM, Sluimer JC, Koch M, Theelen TL, Manthey HD, Busch M, et al. Deficiency of HIF1a in antigen-presenting cells aggravates atherosclerosis and type 1T-helper cell responses in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35:2316–25. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306171
119. Westendorf AM, Skibbe K, Adamczyk A, Buer J, Geffers R, Hansen W, et al. Hypoxia enhances immunosuppression by inhibiting CD4+ effector T cell function and promoting treg activity. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2017) 41:1271–84. doi: 10.1159/000464429
120. Hammami A, Abidin BM, Heinonen KM, and Stäger S. HIF-1a hampers dendritic cell function and Th1 generation during chronic visceral leishmaniasis. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:3500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21891-z
121. Yang M, Liu Y, Ren G, Shao Q, Gao W, Sun J, et al. Increased expression of surface CD44 in hypoxia-DCs skews helper T cells toward a Th2 polarization. Sci Rep. (2015) 1:5. doi: 10.1038/srep13674
122. Li L, Feng C, Qin J, Li D, Liu M, Han S, et al. Regulation of humoral immune response by HIF-1a-dependent metabolic reprogramming of the germinal center reaction. Cell Immunol. (2021) 367:104409. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104409
123. Koers J, Marsman C, Steuten J, Tol S, Derksen NIL, Ten Brinke A, et al. Oxygen level is a critical regulator of human B cell differentiation and IgG class switch recombination. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1082154. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1082154
124. Jain L, Bolam SM, Monk AP, Munro JT, Chen E, Tamatea J, et al. Differential effects of hypoxia versus hyperoxia or physoxia on phenotype and energy metabolism in human chondrocytes from osteoarthritic compared to macroscopically normal cartilage. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:7532. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087532
125. Fearon U, Hanlon MM, Floudas A, and Veale DJ. Cellular metabolic adaptations in rheumatoid arthritis and their therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:398–414. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00771-x
126. Kierans SJ and Taylor CT. Regulation of glycolysis by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): implications for cellular physiology. J Physiol. (2021) 599:23–37. doi: 10.1113/JP280572
127. Gan PR, Wu H, Zhu YL, Shu Y, and Wei Y. Glycolysis, a driving force of rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 132:111913. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111913
128. López-Armada MJ, Fernández-Rodríguez JA, and Blanco FJ. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis. Antioxidants. (2022) 11:1151. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061151
129. Balogh E, Veale DJ, McGarry T, Orr C, Szekanecz Z, Ng CT, et al. Oxidative stress impairs energy metabolism in primary cells and synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2018) 20:95. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1592-1
130. Chenevier-Gobeaux C, Simonneau C, Lemarechal H, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Poiraudeau S, Rannou F, et al. Hypoxia induces nitric oxide synthase in rheumatoid synoviocytes: consequences on NADPH oxidase regulation. Free Radic Res. (2012) 46:628–36. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2012.662276
131. Kim J, Kim HY, Song SY, Go SH, Sohn HS, Baik S, et al. Synergistic oxygen generation and reactive oxygen species scavenging by manganese ferrite/ceria co-decorated nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. ACS Nano. (2019) 13:3206–17. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b08785
132. Zhao R, Feng J, and He G. Hypoxia increases Nrf2-induced HO-1 expression via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2016) 21:385–96. doi: 10.2741/4395
133. Duarte TL, Talbot NP, and Drakesmith H. NRF2 and hypoxia-inducible factors: key players in the redox control of systemic iron homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2021) 35:433–52. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8148
134. Bae T, Hallis SP, and Kwak MK. Hypoxia, oxidative stress, and the interplay of HIFs and NRF2 signaling in cancer. Exp Mol Med. (2024) 56:501–14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01180-8
135. Wang LL, Lu ZJ, Luo SK, Li Y, Yang Z, and Lu HY. Unveiling the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha in osteoporosis: Implications for bone health. World J Stem Cells. (2024) 16:389–409. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.389
136. Cai L, Meng B, Jiang F, Shu WH, Wang XH, Wang MQ, et al. Novel HIF-1α Inhibitor AMSP-30m mitigates the pathogenic cellular behaviors of hypoxia-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes and alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in rats via inhibiting sonic hedgehog pathway. Inflammation. (2023) 46:2289–305. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01878-3
137. Meng B, Liu FY, Liu MM, Yu LC, Zhang WT, Zhou MY, et al. AMSP-30 m as a novel HIF-1α inhibitor attenuates the development and severity of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: Impacts on synovial apoptosis, synovial angiogenesis and sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 103:108467. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108467
138. Liang C, Li J, Lu C, Xie D, Liu J, Zhong C, et al. HIF1α inhibition facilitates Leflunomide-AHR-CRP signaling to attenuate bone erosion in CRP-aberrant rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:4579. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12163-z
139. Shin DH, Kim JH, Jung YJ, Kim KE, Jeong JM, Chun YS, et al. Preclinical evaluation of YC-1, a HIF inhibitor, for the prevention of tumor spreading. Cancer Lett. (2007) 255:107–16. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.03.026
140. Kong D, Park EJ, Stephen AG, Calvani M, Cardellina JH, Monks A, et al. Echinomycin, a small-molecule inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 DNA-binding activity. Cancer Res. (2005) 65:9047–55. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1235
141. Choi WW, Boland JL, Kalola A, and Lin J. Belzutifan (MK-6482): biology and clinical development in solid tumors. Curr Oncol Rep. (2023) 25:123–9. doi: 10.1007/s11912-022-01354-5
142. Temes E, Martín-Puig S, Acosta-Iborra B, Castellanos MC, Feijoo-Cuaresma M, Olmos G, et al. Activation of HIF-prolyl hydroxylases by R59949, an inhibitor of the diacylglycerol kinase. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:24238–44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414694200
143. Choi HJ, Song BJ, Gong YD, Gwak WJ, and Soh Y. Rapid degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by KRH102053, a new activator of prolyl hydroxylase 2. Br J Pharmacol. (2008) 154:114–25. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.70
144. Sen S and Sen S. Therapeutic effects of hyperbaric oxygen: integrated review. Med Gas Res. (2021) 11:30–3. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.310057
145. Harnanik T, Prihartono S, and Juliandhy T. Hyperbaric oxygen in animal model of rheumatoid arthritis: Analysis Of HIF-1α, ACPA and IL-17a. Infect Dis Rep. (2020) 12:8766. doi: 10.4081/idr.2020.8766
146. Dulberger A, Slade JB, Thornton JA, McNeary-Garvin A, Kelly JA, and Edmonds L. The effects of hyperbaric oxygen on MRI findings in rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot study. Undersea Hyperb Med. (2023) 50:39–43. doi: 10.22462/01.01.2023.19
147. Wang J, Yu W, Zhang Y, Chen B, and Meng Z. Mechanism of hyperbaric oxygen therapy downregulating H-type angiogenesis in subchondral bone of knee osteoarthritis through the PHD2/HIF-1α pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. (2025) 20:79. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05514-8
148. Hallak M, Inal A, Baktir MA, and Atasever A. Comparison of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the experimental model of rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2024) 51:e13906. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13906
149. Lin SS, Yuan LJ, Niu CC, Tu YK, Yang CY, and Ueng SWN. Hyperbaric oxygen inhibits the HMGB1/RAGE signaling pathway by upregulating Mir-107 expression in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. (2019) 27:1372–81. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.05.011
150. Harnanik T, Soeroso J, Suryokusumo MG, and Juliandhy T. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on T helper 17/regulatory T polarization in antigen and collagen-induced arthritis: hypoxia-inducible factor-1α as a target. Oman Med J. (2020) 35:e90. doi: 10.5001/omj.2020.08
151. Sit MT, Schmidt TW, Edmonds LD, Kelly JA, Sky KM, Thornton JA, et al. The effects of hyperbaric oxygen on rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot study. J Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 27:e462–8. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000001540
152. Zhang Y, Ma C, He L, Liao L, Guo C, Wang C, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine protects endothelial injury and antithrombosis via antioxidant and antiapoptosis in HUVECs and zebrafish. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:2232365. doi: 10.1155/2022/2232365
153. Jiang R, Zhang X, Li Y, Zhou H, Wang H, Wang F, et al. Identification of the molecular mechanisms of Salvia miltiorrhiza relevant to the treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology. Discov Med. (2020) 30:83–95. doi: 10.1079/cabicompendium.122584
154. Wu D, Xu J, Jiao W, Liu L, Yu J, Zhang M, et al. Suppression of macrophage activation by sodium danshensu via HIF-1α/STAT3/NLRP3 pathway ameliorated collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Molecules. (2023) 28:1551. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041551
155. Zhang H. Study on the intervention of geniposide on abnormal sphingolipid metabolism of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast synovial cells in hypoxic microenvironment. Anhui Univ Chin Med. (2021). doi: 10.26922/d.cnki.ganzc.2021.000121
156. Guo Q, Yang J, Chen Y, Jin X, Li Z, Wen X, et al. Salidroside improves angiogenesis-osteogenesis coupling by regulating the HIF-1α/VEGF signalling pathway in the bone environment. Eur J Pharmacol. (2020) 884:173394. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173394
157. Jin Y, Li Z, Qi L, Zhang L, Gao D, Liu H, et al. The autocrine action of salidroside on osteoclast during osteoclastogenesis via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2024) 43:9603271241269028. doi: 10.1177/09603271241269028
158. Zhang ZJ, Hou YK, Chen MW, Yu XZ, Chen SY, Yue YR, et al. A pH-responsive metal-organic framework for the co-delivery of HIF-2α siRNA and curcumin for enhanced therapy of osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:18. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01758-2
159. Bahrami A, Atkin SL, Majeed M, and Sahebkar A. Effects of curcumin on hypoxia-inducible factor as a new therapeutic target. Pharmacol Res. (2018) 137:159–69. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.10.009
160. Zhan JP, Huang S, Meng QL, Fan W, Gu HM, Cui JK, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction reduces mitochondrial autophagy in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts in hypoxic culture by inhibiting the BNIP3-PI3K/Akt pathway. J South Med University. (2025) 45:35–42. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.05
161. Nygaard G and Firestein GS. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2020) 16:316–33. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0413-5
Keywords: hypoxic microenvironment, rheumatoid arthritis, hypoxia inducible factor, molecular mechanism, treatment strategy
Citation: Zheng QH, Zhai Y, Wang YH and Pan Z (2025) The role of hypoxic microenvironment in rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 16:1633406. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1633406
Received: 22 May 2025; Accepted: 30 July 2025;
Published: 18 August 2025.
Edited by:
Allen Jay Rosenspire, Wayne State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Jun Deng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaDavid Lawrence, New York State Department of Health, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zheng, Zhai, Wang and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhi Pan, cGFuemhpQGNjdWNtLmVkdS5jbg==; Ying-hang Wang, cGFuemhpd3loQHNvaHUuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Qiu-han Zheng
Qiu-han Zheng Ye Zhai2†
Ye Zhai2†