- 1Department of Life, Health & Environmental Sciences, University of L’Aquila, L’Aquila, Italy
- 2Center of Oral Diseases, Prevention and Translational Research - Dental Clinic, L’Aquila, Italy
- 3Department of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH, United States
- 4Unit of Internal Medicine and Nephrology, San Salvatore Hospital, Center for Hypertension and Cardiovascular Prevention, L’Aquila, Italy
- 5Department of Physical and Chemical Science, University of L’Aquila, L’Aquila, Italy
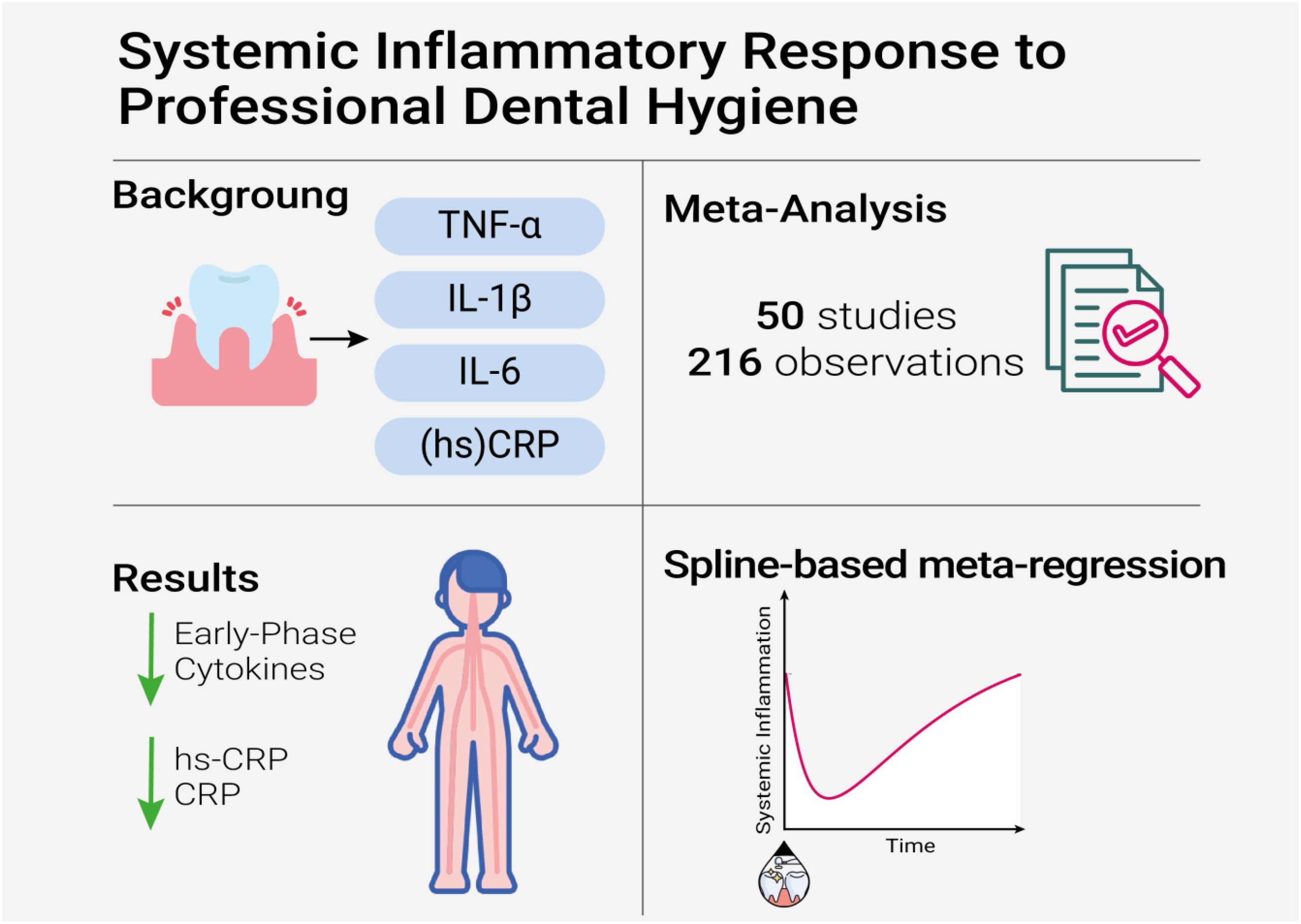
Introduction: Chronic periodontitis is linked to systemic inflammation and cardiovascular risk, yet the temporal trajectory and magnitude of systemic cytokine reduction following nonsurgical-periodontal-therapy (NSPT) remain underexplored. We conducted a meta-analysis and spline-based meta-regression to assess whether intensive NSPT, compared to standard therapy, produces sustained reductions in circulating TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP).
Methods: We systematically searched major databases for interventional studies published until January 2024 comparing intensive vs. standard NSPT on inflammatory markers. Using a custom R pipeline, standardized mean differences (SMDs), 95% confidence intervals (Cis) heterogeneity (I²) and stratified analyses by phenotype (e.g., smoking, diabetes) and time were performed. A spline-based mixed-effects meta-regression explored temporal dynamics of inflammatory reduction in the intensive group.
Results: From 216 observations (14,374 paired values), intensive NSPT led to significantly greater reductions in TNF-α (SMD –0.59, 95% CI –1.02 to –0.16; P=0.008), IL-6 (SMD –0.20, 95% CI –0.39 to –0.00; P=0.046) and hs-CRP (SMD –1.17, 95% CI –2.18 to –0.16; P=0.024) compared to standard therapy. IL-1β showed a near-significant reduction (SMD –4.14, P=0.052). Standard therapy was paradoxically associated with greater CRP reduction (SMD –0.30, P=0.001). Age, tooth count and year of publication moderated effects. Early benefits emerged within 3 months for TNF-α and 6 months for IL-1β. Although no strong nonlinear time-response was confirmed (QM = 4.23, P=0.2372),a potential rebound in cytokine suppression was suggested. The overall anti-inflammatory effect remained significant.
Discussion: Intensive NSPT reduces systemic inflammation particularly in younger, non-smoking individuals. The potential rebound in inflammatory markers underscores the need for longitudinal studies but, supports the systemic immunoregulatory effect of periodontal therapy.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO, identifier CDR42024503063.
Introduction
One of the most significant medical breakthroughs of recent years is the recognition that the immune system and inflammation are key players not only in self-directed and communicable disorders, or in defense against injury, but also in a broad range of non-communicable diseases that disproportionately affect global morbidity and mortality (1). Periodontal disease (PD) is a chronic inflammatory condition that, if not adequately treated, can progress to destruction of the supporting tissues of the teeth and alveolar bone. With more than 790 million people affected, periodontitis is the sixth most prevalent noncommunicable disease worldwide (2, 3) and a global public health problem with a huge economic impact, estimated at nearly $300 billion annually in the United States alone (4). PD is considered a multifactorial chronic inflammatory condition in which dysbiosis of the oral microbiome plays a key role (5, 6). Dysregulation of the immune system and increased levels of circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1, IL-1β, IL-6, and C-reactive protein (CRP), are detectable even in the very early stages of the disease (7) and may contribute to the establishment of a chronic, systemic, low-grade inflammatory state.
The role of periodontitis in the development of many other systemic conditions and its independent association with arterial hypertension (8), cardiovascular diseases, diabetes (9), dyslipidemia and obesity are well known, so much so that it has recently been included among the modifiable risk factors for such diseases. The pathogenetic mechanisms underlying this association are mainly related to low-grade bacteremia/endotoxemia and its inflammatory sequelae (10), the dissemination of oxidative stress-induced metabolites, and perivascular inflammation (9).
Although PD is considered a chronic and irreversible condition, meta-analytical data suggest a positive effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy (NSPT) on disease progression, with improvement of local signs of inflammation. However, the effectiveness of NSPT in mitigating systemic inflammation, expressed in terms of serum cytokines concentrations and (high-sensitivity, hs) CRP levels, remains controversial. Furthermore, any concomitant local or systemic pharmacological therapy aimed at controlling inflammation could confound the true efficacy of NSPT alone on inflammation. A 2016 meta-analysis by Akram and colleagues reported inconsistent findings regarding the efficacy of NSPT in reducing serum cytokines (11), while other authors found a benefit of NSPT only on serum IL-6 levels in the short term, and only among obese individuals (12).
Of note, NSPT can have a different impact on systemic markers of inflammation depending on whether the standard (supragingival) or the intensive (supra- and subgingival) treatment is performed. Therefore, we performed an updated meta-analysis and systematic review to evaluate the impact of intensive versus standard NSPT on circulating markers of inflammation in patients with periodontitis.
Methods
Protocol and registration
The protocol for this systematic review and meta-analysis is registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024503063). The study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) reporting guidelines (Supplementary Table 1).
Search strategy
The MEDLINE database was queried through January 16th, 2024 for studies that published the effects of intensive and standard NSPT on serum cytokines in adult patients with periodontitis. The following search algorithm was used in the R library “rentrez”: (“periodontal diseases”[MeSH Terms] AND (“cytokines”[MeSH Terms] OR “c reactive protein”[MeSH Terms])) AND ((fha[Filter]) AND (clinicalstudy[Filter] OR clinicaltrial[Filter] OR clinicaltrialprotocol[Filter] OR clinicaltrialphasei[Filter] OR clinicaltrialphaseii[Filter] OR clinicaltrialphaseiii[Filter] OR clinicaltrialphaseiv[Filter] OR comparativestudy[Filter] OR controlledclinicaltrial[Filter] OR dataset[Filter] OR meta-analysis[Filter] OR observationalstudy[Filter] OR pragmaticclinicaltrial[Filter] OR randomizedcontrolledtrial[Filter])). Additional manual search was performed on Embase, Scopus and Cochrane. No date or language restrictions were applied.
Eligibility criteria
Studies were selected based on the following inclusion criteria: randomized clinical trials, randomized double-blind clinical trials, comparative studies, prospective exploratory monocentric trials, randomized controlled trials, interventional controlled non-randomized clinical trials, controlled clinical trials, single-center interventional studies, randomized controlled parallel clinical trials, observational studies, prospective randomized clinical studies, and cohort studies. Eligible studies involved adult participants aged 18 years or older who had been diagnosed with periodontitis. Additionally, included studies investigated the effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy (NSPT) on serum cytokines - specifically TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 - and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) or CRP, in accordance with the following PICOS question: “In adults diagnosed with periodontitis (P), is intensive NSPT (I) more effective than standard treatment (C) in reducing serum cytokines and (hs)CRP (O), as assessed in randomized controlled trials and prospective observational studies (S)?”
Outcome variables
The primary outcomes were changes in serum cytokines levels, namely TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (expressed in mg/L). Secondary outcomes were changes in CRP and hs-CRP (expressed in mg/L). All data reported in different units of measurement in the original studies were converted to mg/L. Outcome variables were analyzed as the change from pre-treatment to each available post-treatment follow-up.
Study selection and data extraction
Study selection and data extraction were performed using a standardized data extraction Excel form.
Two reviewers (S.D.N. and M.C.) independently reviewed titles and abstracts to assess eligibility. Inter-reviewer reliability in the study selection process was determined by the Cohen κ test, assuming an acceptable threshold value of 0.81 (13, 14). Full-text articles of the potentially eligible studies were then analyzed to assess their inclusion. Disagreements regarding inclusion between reviewers were resolved by discussion and consensus.
Data were extracted by the two reviewers (S.D.N. and M.C.) independently, and inconsistencies were resolved through consensus discussions and consultation with a senior author (D.P). Extracted data included (see Supplementary Methods 2 for detailed information): 1) study identifiers and methodology; 2) participants characteristics; 3) type of treatment; 4) cytokines serum levels before and after treatments; 5) when available, serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and CRP levels before and after treatments. If a study included multiple groups, only pertinent groups were extracted. When primary outcome data were incomplete or inconsistently reported and clarification was necessary to determine study eligibility, authors were contacted for clarification, and the study was excluded if no response was received within 4 weeks. Other reasons for exclusion, including lack of data of interest and population characteristics/study methodologies different than required, are detailed in Supplementary Table 3.
Risk of bias and quality assessment
The bias assessment was conducted by two reviewers (S.D.N. and M.C.) independently using specific tools for observational or interventional studies, and inconsistencies were resolved through consensus discussions and consultation with a senior author (D.P). Specifically, the Newcastle–Ottawa quality assessment Scale (NOS) (15) was used to assess the risk of bias for case-control and cohort studies, while the Cochrane risk of bias template (Rob2.0) was used for randomized clinical trials (16). In order to perform meta-regression, both scales were converted into continuous values. After determining the score of each study, an overall estimation of plausible risk of bias was performed for each selected study. For randomized clinical trials, a low risk of bias was estimated when all of the criteria were met, a moderate risk was estimated when ≥1 criteria were partially met, and a high risk of bias was estimated when ≥1 criteria were not met. For case-control and cohort studies, the maximum score was 9, the minimum was 0. It was decided a priori that a score of 7 reflected high methodology quality (i.e., low risk of bias), a score of 5 or 6 indicated moderate quality (i.e. some concerns), and a score of 4 or less indicated a low quality (i.e., high risk of bias).
Sex as a biological variable
Participants sex was reported as assessed in the original studies, and the variable was used for stratified analyses. On this basis, sex-specific assessments of post-treatment changes in selected cytokines could be performed.
Statistical analysis
Study data were pooled for subsequent analyses in the software R. The meta-effect on serum inflammation of intensive versus standard NSPT was calculated from standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) using both common and random effect models. Due to the expected interstudy heterogeneity, the random effect model was preferred for the interpretation of findings.
We conducted stratified meta-analyses based on the type of inflammatory marker assessed (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, CRP and hs-CRP) within and between treatment types. For each marker and treatment type, further stratification was performed based on the elapsed time to assessment of change, participants sex, smoking habits, and diabetes status, provided that at least two studies were available within each stratification. For studies reporting on intensive NSPT, stratification based on additional local treatments (full-mouth disinfection, FMD; laser treatment; curcumin gel) was performed. The elapsed time to change was assessed: 1) as reported in the original studies; 2) according to predefined time spans (<4 to 6 weeks; <3 months; <6 months; ≥6 months) based on biological plausibility. The meta-effect was considered significant for P<0.05. Forest plots for each meta-analysis, generated with specific R libraries, namely “meta” (17) and “forestploter” (18), present the raw data (sample sizes, means, SDs), point estimates (displayed as blocks) and CIs (displayed as lines) for the chosen effect, heterogeneity statistic (I2), overall average effect with related statistics, and percent weight given to each study.
We also performed random-effects meta-regression with different moderators (elapsed time to assessment of change, study year, mean age, female sex ratio, smokers, number of teeth before treatment, diabetes ratio).
Heterogeneity between studies was assessed by the I2 statistic as defined by the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews, and an I2 value of 50% or greater was considered to represent a substantial heterogeneity.
Publication bias was investigated by visual detection (funnel plot assessment) and quantitative analysis (regression asymmetry test, trim-and-fill method)
A custom in-house R pipeline was developed to perform common and random-effects meta-analyses for TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, CRP, and hs-CRP. Subsequently, stratified analyses and meta-regressions were conducted for each marker.
Meta-regression analysis
To explore the temporal dynamics of inflammatory marker modulation following intensive NSPT, we conducted a meta-regression using a restricted cubic spline model. Analyses were performed using the metafor package (version 4.4-0) in R (19). Effect sizes (SMDs) and standard errors were extracted from the random-effects meta-analysis model of studies reporting inflammatory markers outcomes (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, or high-sensitivity C-reactive protein) in the intensive NSPT subgroup. The time variable was defined as the number of days between the intervention and post-intervention cytokine measurement. To allow for potential non-linear relationships between elapsed time from intensive NSPT and effect size, we applied a meta-regression with restricted cubic splines (3 degrees of freedom). This approach provides a flexible framework to model gradual changes in effect estimates over time without imposing a linearity constraint (20, 21). Predictions were generated across the observed range of timepoints (0–365 days) to derive the fitted SMD trajectory along with 95% confidence intervals. These predictions were plotted to visualize the time-dependent trend in treatment effects. All models used the DerSimonian and Laird estimator for between-study variance (τ2) (19). We verified the stability of the spline model and inspected residuals to ensure model adequacy.
All code used in the analysis has been deposited in the GitHub repository (https://github.org/pietropaolilab).
Results
Search results and description of included studies
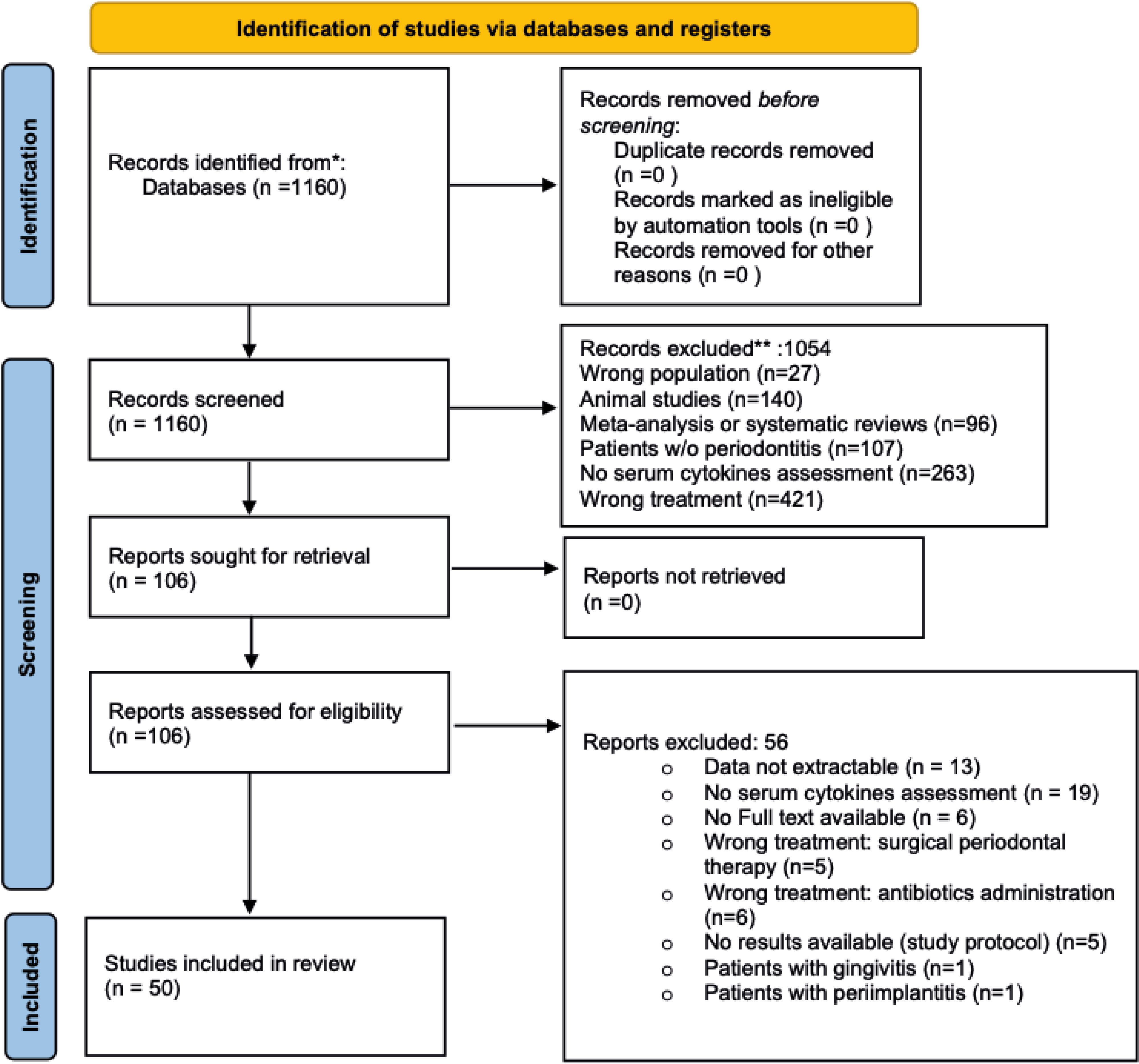
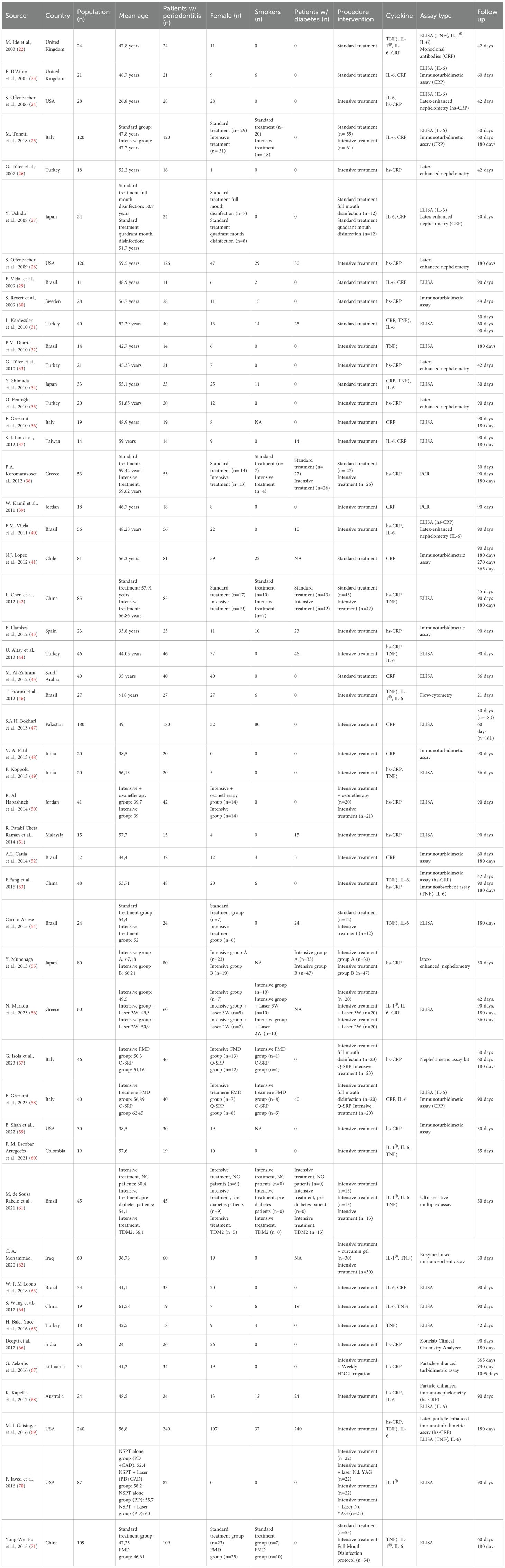
On January 16th, 2024, 1160 citations were retrieved, and 106 articles were screened for eligibility, of which 50 met our predefined inclusion criteria, for a total of 2340 patients included (45.5% women, mean age 50,47 ± 8,9 years) (see Figure 1 for data reduction). The included studies spanned a timeframe of 33 years (1990 - 2023). The descriptive characteristics of the included studies are presented in Table 1. Briefly, 498 (21,3%) participants underwent standard NSPT, while 1842 (78,3%) received intensive NSPT. One study evaluated TNF-α only, while two focused on IL-1β. One study assessed both TNF-α and IL-1β, two studies examined TNF-α and IL-6, and four studies analyzed TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 simultaneously. Furthermore, 19 studies also investigated CRP, and 21 studies evaluated hs-CRP. Diabetes and smoking status were reported by 16 and 22 studies, respectively, with 10 studies evaluating both conditions. Of participants receiving standard NSPT, 21,5% suffered from diabetes and 23% were smokers. Among those receiving intensive NSPT, 34,5% suffered from diabetes and 15% were smokers. Assessment of changes in inflammatory biomarkers occurred between 21 days and 56 days for 5 studies, 1 month for 6 studies, within 2 months for 2 studies, 6 weeks for 5 studies, within 3 months for 15 studies, within 6 months for 14 studies, and beyond 6 months for 3 studies. Most studies used the ELISA assay. Thirty studies matched for age/sex and at least one other a priori defined confounding variable, whereas twenty studies only matched for age/sex.
Quality assessment
The methodological quality of the included studies based on the Newcastle–Ottawa scale and the Cochrane Risk of Bias template (RoB 2.0) is described in Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Figure 1. Of the 50 studies analyzed, 36 were classified as having a high or unclear risk of bias, mainly due to the lack of double-blinding or issues related to the randomization methods used. However, 14 studies were identified as being at low risk of bias, with participants and/or investigators involved in outcomes assessment being blinded to the patients’ group assignment.
Description of excluded studies
56 studies did not meet the inclusion criteria and were considered ineligible. Briefly, 18 studies were excluded due to lack of cytokines assessment (72–90), while data were unavailable for 13 studies (91–103). In 11 studies, periodontal therapy involved surgical procedures or antibiotic use (104–114), and in two studies, patients presented with gingivitis or peri-implantitis (115, 116). Lastly, 11 of the 56 excluded studies were either study protocols or lacked full-text availability (117–126). For detailed information see Supplementary Table 3.
Comparative effects of interventions for the primary outcome
A total of 216 observations from 64 observations in the standard treatment group and 152 observations in the intensive treatment group were included in the meta-analysis, comprising 14,374 paired pre- and post-treatment data points.
Standard treatment
In the standard treatment subgroup (k = 64), the pooled SMD between post- and pre-treatment cytokine levels was statistically significant. Under the common-effect model, the SMD was –0.2573 (95% CI: –0.3199 to –0.1946; z = –8.05; p < 0.0001), indicating a small but consistent reduction in inflammatory markers following standard periodontal therapy. The random-effects model yielded a slightly larger effect size (SMD = –0.3192; 95% CI: –0.4621 to –0.1764; z = –4.38; p < 0.0001). Between-study heterogeneity was substantial (I² = 78.8%, 95% CI: 73.2% to 83.1%; τ² = 0.2443), suggesting variability in treatment effects across studies (Figure 2A).
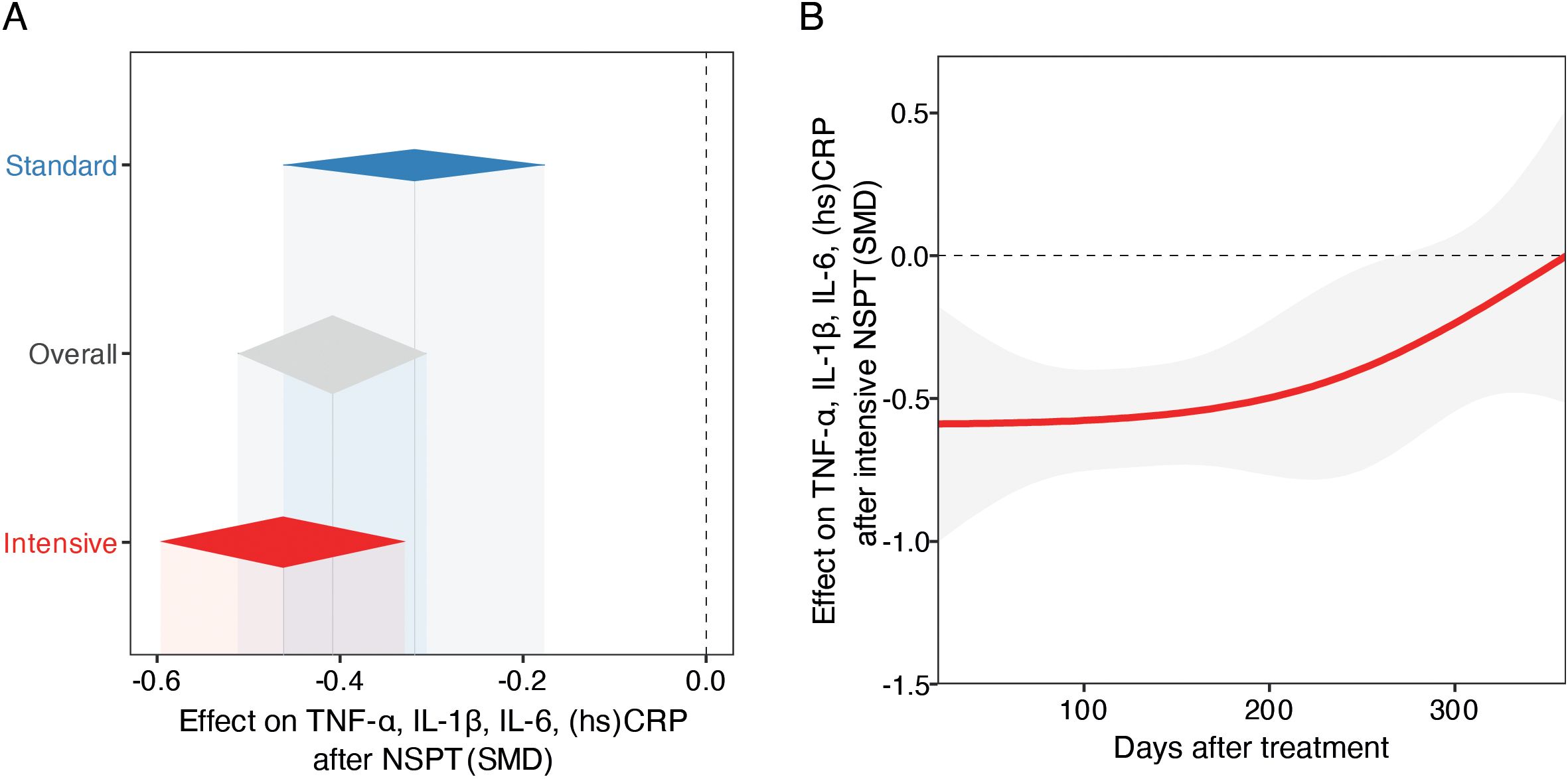
Figure 2. Meta-analysis of periodontal therapy effects on systemic inflammation and temporal treatment dynamics. (A) Forest plot of pooled SMDs and 95% CIs for early-phase inflammatory markers level changes following standard or intensive NSPT, using random-effects models. Diamonds represent pooled SMDs; the dashed vertical line indicates no effect (SMD = 0). (B) Temporal trend in cytokine reduction post-intensive NSPT, modeled with mixed-effects meta-regression using restricted cubic splines. The red line shows estimated SMD change over time; the shaded area indicates 95% CI. The analysis suggests an early anti-inflammatory response, with potential attenuation or rebound over time.
Intensive treatment
The intensive treatment subgroup (k = 152) demonstrated a more pronounced reduction in cytokine levels. The common-effect model estimated an SMD of –0.2575 (95% CI: –0.2980 to –0.2170; z = –12.46; p < 0.0001), while the random-effects model showed a larger effect size of –0.4623 (95% CI: –0.5962 to –0.3283; z = –6.76; p < 0.0001). This heterogeneity may reflect differences in the biological roles and regulatory dynamics of the inflammatory markers investigated, as well as potential batch effects related to clinical procedures or sample processing (Figure 2A).
Subgroup comparison
A stratified meta-analysis comparing standard and intensive treatments was conducted (k = 216). The overall random-effects model yielded an SMD of –0.4090 (95% CI: –0.5120 to –0.3060; z = –7.78; p < 0.0001), with substantial heterogeneity (I² = 88.2%). Subgroup analysis revealed a non-significant difference in effect size between the two treatment modalities (Q = 2.05, df = 1, p = 0.1523), although the point estimate favored the intensive treatment. The test for subgroup differences under the fixed-effect model was similarly non-significant (Q = 0.00, p = 0.9958), suggesting that, while both approaches are associated with reductions in systemic inflammatory markers, the superiority of intensive therapy remains inconclusive (Figure 2A).
Temporal dynamics of the overall anti-inflammatory effect of NSPT
To further explore whether the time elapsed between treatment and follow-up assessment influenced the magnitude of effect in the intensive group, we conducted a mixed-effects meta-regression using restricted cubic splines (df = 3). This model, based on 152 observations, showed high residual heterogeneity (τ² = 0.6085, I² = 90.1%) and did not significantly reduce unexplained variance (R² = 0.0%). The overall test for the spline terms was not statistically significant (QM = 4.23, df = 3, p = 0.2372), indicating no strong evidence for a nonlinear relationship between elapsed time and treatment effect. Nonetheless, one spline term reached nominal statistical significance (estimate = 0.5835, p = 0.048), suggesting a possible late-phase attenuation of effect or rebound, although the clinical relevance remains to be confirmed. The intercept remained significantly negative (–0.5889, p = 0.0053), consistent with an overall reduction in inflammatory markers post-treatment. These findings suggest that while periodontal treatment exerts a measurable anti-inflammatory effect, its temporal dynamics across the first months post-intervention are not clearly delineated by the current evidence base (Figure 2B).
Effect on single inflammatory markers
Results of the meta-analyses indicated a significant post-treatment reduction in serum levels of TNFα (random effect SMD -0.59, 95% CI -1.02 to -0.16; P=0.008) in favor of the intensive NSPT group (Figure 3). A similar trend was observed for IL-1β (random effect SMD -4.14, 95% CI -8.31 to -0.04; P=0.052) (Figure 3). In addition, we found a significant post-treatment reduction in serum levels of IL-6 following both the intensive (random effect SMD -0.20, 95% CI -0.39 to -0.00; P=0.046) and the standard (random effect SMD -0.27, 95% CI -0.44 to -0-09; P=0.004) NSPT (Figure 3). Heterogeneity among the included studies was substantial in the intensive group (I² = 81%, τ² = 0.2995, P < 0.01), whereas was moderate (I² = 43%, τ² = 0.0567, P = 0.03) in the standard group.
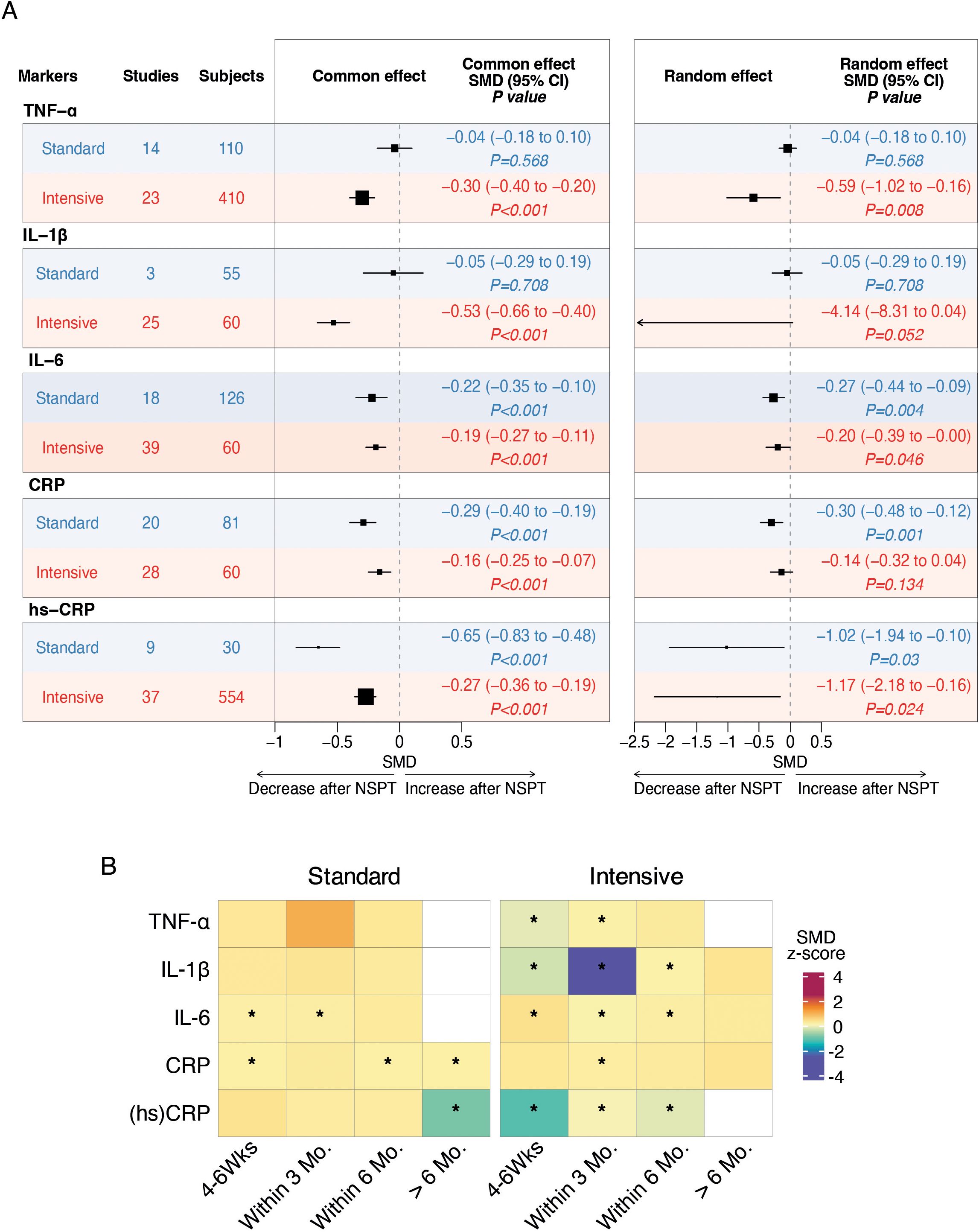
Figure 3. Forest plots and heatmaps summarizing the effects of standard and intensive nonsurgical periodontal therapy on systemic inflammatory markers. (A) Forest plots of meta-analyses evaluating the impact of standard and intensive treatment on serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, CRP, and high-sensitivity CRP. Pooled standardized mean differences with 95% confidence intervals are shown for post-treatment changes, stratified by treatment intensity. Fixed-effect model results are presented on the left, and random-effects model results are shown on the right. Negative values indicate a decrease in inflammatory marker levels following treatment. The vertical dashed line represents no effect (SMD = 0). Statistical significance is indicated by P values. (B) Heatmaps showing subgroup meta-analysis results for the temporal effects of standard and intensive treatment on inflammatory markers. Each cell represents the SMD (z-score) for a specific follow-up interval (4–6 weeks, within 3 months, within 6 months, and >6 months). Color intensity reflects the magnitude and direction of change, with cooler colors indicating greater reductions. Asterisks (*) indicate statistically significant changes (P < 0.05) based on the common-effect model.
Secondary outcomes
A significant post-treatment reduction in serum levels of hs-CRP following both the intensive (random effect SMD -1.17, 95% CI -2.18 to -0.16; P=0.024) and the standard (random effect SMD -1.02, 95% CI -1.94 to -0-10; P=0.030) NSPT resulted from the meta-analysis (Figure 3A). Heterogeneity among the included studies was considerable in both groups: in the intensive group (I² = 94%, τ² = 0.6291, P < 0.01) and in the standard group (I² = 94%, τ² = 1.9142, P < 0.01).
As to CRP levels, a significant post-treatment reduction was found in favor of the standard NSPT (random effect SMD -0.30, 95% CI -0.48 to -0.12; P=0.001) (Figure 3A).
Heterogeneity among the included studies was moderate in the intensive group (I² = 68%, τ² = 0.1590, P < 0.01), and similarly moderate in the standard group (I² = 58%, τ² = 0.0879, P < 0.01). Temporal subgroup analysis revealed that reductions in inflammatory markers varied across follow-up intervals. In particular, significant short-term reductions (within 6 months) were consistently observed for IL-6, CRP, and hs-CRP in both treatment strategies. For intensive treatment, IL-1β and TNF-α also showed significant reductions within the first 3 months, highlighting a potential early anti-inflammatory benefit (Figure 3B).
Meta-regression
A meta-regression was performed with different moderators (i.e., elapsed time to assessment of change, study year, mean age, female sex ratio, number of smokers, number of teeth before treatment, diabetes ratio).
TNFα. Within the intensive NSPT group, meta-regression indicated that only mean age and study year had a significant effect on SMD (R2: 37.74, Slope: 0.097, P=0.004; and R2: 17.10, Slope: −0.144, P=0.045, respectively), with younger individuals showing greater decrease, and more recent studies capturing larger reductions, in TNFα levels (Supplementary File 1).
IL-1β. Within the intensive NSPT group, meta-regression showed only a borderline effect of smoke on SMD (R2: 24.56, Slope: 0.976, P=0.049) (Supplementary File 1).
IL-6. Meta-regression indicated that the number of teeth before treatment had a significant effect on SMD in individuals receiving intensive NSPT (R2: 100, Slope: 0.156, P=0.001), indicating larger decrease in IL-6 with lower number of teeth (Supplementary File 1), while mean age affected the outcome in the standard treatment group (R2: 100, Slope: -0.007, P=0.013), with older individuals showing greater reduction in IL-6 (Supplementary File 1).
Hs-CRP. Within the intensive NSPT group, meta-regression indicated that only study year had a significant effect on SMD (R2: 88.37, Slope: −0.302, P=0.000), with more recent studies capturing larger reductions in hs-CRP levels (Supplementary File 1). As to the standard treated participants, younger age (P=0.0), longer elapsed time to assessment (P=0.0), more recent study year (P=0.0), greater number of teeth (P=0.0), higher female sex ratio (P=0.048), lower diabetes ratio (P=0.005) and lower number of smokers in the studies (P=0.002) significantly impacted on larger reductions in hs-CRP levels (Supplementary File 1).
CRP. Meta-regression indicated no effect of the examined moderators on SMD in the standard NSPT group (Supplementary File 1).
Stratified analyses
Stratified analyses were conducted for each outcome within the relevant treatment group(s), provided that at least two studies were available within each stratification, as specified in the methods.
Elapsed time to change assessment
TNFα. Significant reductions in TNFα levels in the intensive NSPT group occurred as early as within 3 months of treatment and lost significance thereafter. No significant changes in TNFα levels were detected following standard NSPT at any timepoint (Supplementary File 1).
IL-1β. Reductions in IL-1β levels with intensive NSPT were no longer appreciated after 6 months following treatment. Stratification was not possible for standard NSPT (Supplementary File 1).
IL-6. Irrespective of treatment group, significant reductions in IL-6 occurred between 6 weeks to 3 months after treatment (Supplementary File 1). Interestingly, a trend to an early rise in IL-6 was observed 4 to 6 weeks following intensive NSPT.
Hs-CRP. Significant reductions in hs-CRP levels occurred between 6 weeks to 3 months of treatment in the intensive NSPT group, and after 6 months in the standard treatment group (Supplementary File 1).
CRP. Reductions in CRP levels were more evident between 3 to 6 months, especially in the standard treatment group (Supplementary File 1).
Single sex studies
IL-1β. Among intensive-treated participants, male-specific studies showed significant post-treatment reductions in IL-1β levels (Supplementary File 1). Only one study assessing IL-1β changes following intensive NSPT was female-specific, and the effect was neutral.
No sex-specific studies were conducted on standard NSPT (Supplementary File 1).
IL-6. Based on the findings from two female-specific studies, post-treatment increases in IL-6 levels were observed in intensive-treated females (Supplementary File 1). No male-specific studies assessing IL-6 changes were available.
Hs-CRP. Among intensive-treated participants, female-specific studies uniquely showed post-treatment increases in hs-CRP levels (Supplementary File 1). No male-specific studies assessing hs-CRP changes were available. No sex-specific studies were conducted on hs-CRP changes following standard NSPT.
Smoking habits
TNFα and IL-1β. Based on the findings from intensive NSPT, post-treatment reductions in TNFα and IL-1β were particularly evident in non-smokers (Supplementary File 1) Only one study assessing TNFα and IL-1β changes after standard NSPT was conducted in non-smokers.
IL-6. Post-treatment reductions in IL-6 were particularly evident among smokers, irrespective of treatment modality (Supplementary File 1).
Hs-CRP and CRP. Within the intensive NSPT group, reductions in hs-CRP and CRP levels were more evident among smokers (Supplementary File 1); among standard-treated individuals, they were more pronounced in non-smokers (Supplementary File 1).
Diabetes status
TNFα and IL-1β. Based on the findings from intensive NSPT, post-treatment reductions in TNFα were particularly evident in non-diabetic individuals (Supplementary File 1). Only one study assessing IL-1β changes was conducted on diabetic individuals.
IL-6. Within the standard NSPT group, reductions in IL-6 levels were observed in both diabetic and non-diabetic participants (Supplementary File 1).
Hs-CRP and CRP. Reductions in hs-CRP and CRP levels were observed in standard-treated non-diabetic participants (Supplementary File 1).
Full mouth disinfection (intensive NSPT group)
All the examined inflammatory markers, except for CRP, were significantly reduced with FMD (Supplementary Files 1). No changes were observed with laser treatments and curcumin gel use (data not shown).
Discussion
This meta-analysis provides evidence on the effectiveness of NSPT in modulating systemic inflammation. Intensive NSPT demonstrated a more pronounced effect than the standard NSPT, with no strong evidence of a temporal relationship between treatment and anti-inflammatory effect. Specifically, intensive NSPT proved more effective in reducing key inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-1β and hs-CRP, while standard treatment showed favorable outcomes in the reduction of IL-6 and hs-CRP. Meta-regression analyses indicate that individual factors such as age, smoking habits, residual dentition, and the presence of comorbidities like diabetes significantly influence therapeutic outcomes.
Our meta-analysis particularly focused on specific cytokines and acute phase proteins involved in acute systemic inflammation. Among these, TNF-α plays a central role in the inflammatory cascade: it acts upstream by stimulating the production of downstream mediators such as IL-1β, IL-6 and CRP and, in synergy with IL-1β, contributes to the acute phases of the inflammatory response (127). The clinical relevance of IL-1β is further supported by therapeutic strategies targeting it. Inhibition of the inflammasome pathway involving IL-1β has been associated with reduced cardiovascular events in the CANTOS trial, underscoring its critical role in regulating systemic inflammation (128, 129).
Consistently, chronic periodontitis is associated with elevated levels of systemic inflammatory markers and an increase in circulating neutrophils. The early and intense activation of these pathways contributes both to local tissue destruction and to the systemic spread of inflammation, supporting the hypothesis that periodontitis may represent a chronic and often underdiagnosed infectious condition associated with systemic diseases (130, 131).
Based on this premise, our findings reinforce the hypothesis that periodontal therapy may have measurable systemic effects. In particular, improving oral health through NSPT appears not only as a local intervention but also as a potentially effective complementary strategy for managing chronic systemic inflammatory conditions. This interpretation aligns with the contemporary view of periodontitis as a chronic immunoinflammatory disease not confined to the oral cavity, but capable of significantly influencing systemic homeostasis (132).
Non-surgical periodontal approaches have also shown favorable effects on blood pressure profiles in hypertensive patients, with evidence indicating that a 30% reduction in gingival bleeding following NSPT is potentially associated with a decrease of approximately 11 mmHg in systolic blood pressure (133). This improvement is thought to result from a reduction in the oral biofilm burden, leading to decreased circulating levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, CRP) and subsequent stabilization of systemic inflammation. Indeed, a recent meta-analysis proposed NSPT as a potential non-pharmacological intervention for blood pressure control, following the cardiovascular benefits observed in both hypertensive and pre-hypertensive individuals (134).
Similarly, periodontal therapy has been shown to improve glycemic control, significantly reducing HbA1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes, thus confirming the bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes (135). In line with this, our meta-analysis observed a reduction in IL-6 levels in both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals undergoing standard treatment. However, the reduction in TNF-α and hs-CRP/CRP was more pronounced in non-diabetic patients treated with intensive and standard therapy, respectively, suggesting that the patient’s metabolic status may influence the extent of the systemic inflammatory response to periodontal therapy.
Smoking also emerged as a determining factor in terms of response to NSPT: non-smokers experienced greater reductions in TNF-α and IL-1β following intensive treatment, while smokers showed a more significant reduction in IL-6, regardless of the therapeutic approach. These differences may be attributed to the immunomodulatory effects of smoking: some studies (136, 137) have shown that substances found in tobacco, such as nicotine, catechol, and hydroquinone, inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α; others have reported increased systemic levels of IL-6 and CRP in female smokers (138, 139). These findings suggest that baseline inflammatory profiles, differing between smokers and non-smokers, may variably modulate cytokine responses to periodontal therapy, thus contributing to the heterogeneity in clinical outcomes.
Stratified time analyses further revealed a distinct kinetic profile in the systemic inflammatory response based on treatment intensity. Intensive NSPT led to a rapid and marked reduction of TNF-α, IL-6, and hs-CRP, with the lowest levels observed within the first three months after treatment. The observed reduction in IL-1β occurred within six months after treatment but was not sustained in the long term. Altogether, there findings suggest a time-dependent modulation of early inflammatory cytokines. In contrast, standard therapy showed a more gradual effect, with noticeable reductions in hs-CRP only after six months and significant CRP decreases between three and six months. These findings highlight the importance of the temporal component in the efficacy of periodontal therapy: while intensive treatment yields rapid biochemical responses, standard treatment proves equally effective in the long-term modulation of systemic inflammatory markers. Although the pooled comparison between treatment modalities did not reveal statistical significance for all markers, stratified analyses uncovered clinically meaningful distinctions in the timing and magnitude of the inflammatory response. Accordingly, the efficacy of periodontal therapy may depend not only on intensity, but also on individual patient characteristics. Such findings underscore the importance of moving toward personalized therapeutic strategies in periodontology, tailored to the patient’s systemic condition and risk factors.
Some sex-specific trends emerged in the modulation of inflammatory markers following periodontal treatment, with preliminary indications of more favorable responses in women. However, due to limited number of sex-specific studies these findings must be interpreted with caution. As such, the current evidence remains insufficient to support firm conclusions regarding sex-based differences in the systemic response to NSPT. Nonetheless, these preliminary observations point a potential role of sexual dimorphism in the inflammatory response, which should be further explored through well-powered, sex-stratified studies. This need is further supported by growing evidence of immunological dimorphism between sexes (140). Women generally exhibit stronger innate and adaptive immune responses compared to men, as evidenced by elevated expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, increased activation of inflammatory T cells, and a heightened overall inflammatory state (141). In addition, we have recently shown a female-specific association between active periodontal inflammation and metabolic syndrome, a cluster of metabolic risk factors underpinned by low-grade systemic inflammation, with higher CRP levels unique to women with both conditions (142), which is relevant in the perspective of gender and precision medicine.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis specifically evaluating the effect of NSPT on circulating inflammatory cytokines and their temporal dynamics. However, our study is not without limitations. Firstly, the reduced number of sex-specific studies limits the possibility of drawing any definite conclusions on sex-related differences in the inflammatory response, and this topic deserves investigation in future, dedicated research. While this meta-analysis aimed to distinguish between intensive and standard NSPT, we acknowledge the variability across studies in terms of instrumentation, number and type of sessions (e.g., FMD vs. quadrant-based scaling and root planning) and the use of adjunctive procedures represents a limitation. Notably, only a minority of studies explicitly reported using FMD or Q-SRP protocols, limiting the possibility of formal meta-regression on these variables. In addition, many of the included studies exhibited moderate-high risk of bias, particularly due to limitations in study design and reporting. This, combined with high heterogeneity and possible publication bias, warrants caution in interpreting the results. Most importantly, the duration of follow-up in the included studies was generally limited to 6-months. Future trials should therefore prioritize extended follow-up to clarify the durability of NSPT’s systemic anti-inflammatory effects. While our analysis revealed a rebound effect a few months after treatment, the long-term trajectory of that effect remains unknown. Finally, even though the majority of the included studies employed ELISA assays, variability in the specific testing methods used introduces a source of potential heterogeneity across the findings. These limitations highlight the urgent need for future high-quality randomized controlled trials that adopt standardized NSPT protocols, include comprehensive procedural descriptions, and account for relevant patient characteristics. Furthermore, extended follow-up durations and integrated evaluations of both periodontal and systemic outcomes will be essential to clarify the long-term impact of NSPT on systemic inflammation and support its role as a component of broader interdisciplinary care.
Conclusion
In summary, our findings support the notion that NSPT can have a significant impact on the systemic inflammatory burden, with potentially important implications for the management of conditions such as diabetes and other chronic inflammation-related disorders. However, the variability in clinical response based on individual factors such as age, sex, diabetes status, and smoking underscore the need for personalized therapeutic approaches to optimize the benefits of periodontal treatment in specific and high-risk populations.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
MC: Data curation, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. SN: Data curation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. SA: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Validation. EO: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft. RP: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Methodology, Data curation, Software, Investigation, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. DP: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Software, Visualization, Investigation, Data curation, Validation, Methodology, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the PROMOTE-BP grant from the Eklund Foundation (2022) awarded to RP and DP, the NIH/ORWH (3R01DK042191-30S1, administrative supplement for Research on Sex/Gender Differences) awarded to DP and RP, and the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation (Grant #882725, Clinical Research Investigator-Initiated Award (CRIA) – Senior Research Award (SRA)) also awarded to DP and RP.
Conflict of interest
Only DP received honoraria from Colgate-Palmolive, which are reported here solely for the sake of transparency.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used only to improve the readability and clarity of the text; no sections of the manuscript were generated by AI.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1634622/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Furman D, Campisi J, Verdin E, Carrera-Bastos P, Targ S, Franceschi C, et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat Med. (2019) 25:1822–32. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0675-0
2. Tonetti MS, Greenwell H, and Kornman KS. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J Periodontol. (2018) 89:S159–72. doi: 10.1002/JPER.18-0006
3. GBD 2017 Oral Disorders Collaborators, Bernabe E, Marcenes W, Hernandez CR, Bailey J, Abreu LG, et al. Global, regional, and national levels and trends in burden of oral conditions from 1990 to 2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease 2017 study. J Dental Res. (2020) 99:362–73. doi: 10.1177/0022034520908533
4. Listl S, Galloway J, Mossey PA, and Marcenes W. Global economic impact of dental diseases. J Dental Res. (2015) 94:1355–61. doi: 10.1177/0022034515602879
5. Santonocito S, Ferlito S, Polizzi A, Ronsivalle V, Sclafani R, Valletta A, et al. Therapeutic and metagenomic potential of the biomolecular therapies against periodontitis and the oral microbiome: current evidence and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:13708. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213708
6. Pan W, Wang Q, and Chen Q. The cytokine network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int J Oral Sci. (2019) 11:30. doi: 10.1038/s41368-019-0064-z
7. Priyamvara A, Dey AK, Bandyopadhyay D, Katikineni V, Zaghlol R, Basyal B, et al. Periodontal inflammation and the risk of cardiovascular disease. Curr Atheroscl Rep. (2020) 22:28. doi: 10.1007/s11883-020-00848-6
8. Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur Heart J. (2018) 39:3021–104. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339
9. Herrera D, Sanz M, Shapira L, Brotons C, Chapple I, Frese T, et al. Periodontal diseases and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and respiratory diseases: Summary of the consensus report by the European Federation of Periodontology and WONCA Europe. Eur J Gen Practice. (2024) 30:2320120. doi: 10.1080/13814788.2024.2320120
10. Viafara-García SM, Morantes SJ, Chacon-Quintero Y, Castillo DM, Lafaurie GI, and Buitrago DM. Repeated Porphyromonas gingivalis W83 exposure leads to release pro-inflammatory cytokynes and angiotensin II in coronary artery endothelial cells. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:19379. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54259-y
11. Akram Z, Safii SH, Vaithilingam RD, Baharuddin NA, Javed F, and Vohra F. Efficacy of non-surgical periodontal therapy in the management of chronic periodontitis among obese and non-obese patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. (2016) 20:903–14. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1793-4
12. Zhang Y, Jia R, Zhang Y, Sun X, Mei Y, Zou R, et al. Effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on cytokines/adipocytokines levels among periodontitis patients with or without obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. (2023) 23:717. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03383-3
13. Landis JR and Koch GG. An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics. (1977) 1:363–74.
14. Landis JR and Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. (1977) 1:159–74.
15. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
16. Higgins JP, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, and Sterne JA. Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons. (2019). p. 205–28.
17. Schwarzer G, Carpenter JR, and Rücker G. Meta-analysis with binary outcomes. In: InMeta-analysis with R. Springer international publishing, Cham (2015). p. 55–83.
18. Available online at: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/forestploter/vignettes/forestploter-intro.html (Accessed October 29, 2024).
19. Viechtbauer W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Software. (2010) 36:1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v036.i03
20. Thompson SG and Higgins JP. How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Stat Med. (2002) 21:1559–73. doi: 10.1002/sim.1187
21. Gasparrini A. Modeling exposure–lag–response associations with distributed lag non-linear models. Stat Med. (2014) 33:881–99. doi: 10.1002/sim.5963
22. Ide M, McPartlin D, Coward PY, Crook M, Lumb P, and Wilson RF. Effect of treatment of chronic periodontitis on levels of serum markers of acute-phase inflammatory and vascular responses. J Clin Periodontol. (2003) 30:334–40. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.2003.00282.x
23. D’aiuto F, Nibali L, Parkar M, Suvan J, and Tonetti MS. Short-term effects of intensive periodontal therapy on serum inflammatory markers and cholesterol. J Dental Res. (2005) 84:269–73. doi: 10.1177/154405910508400312
24. Offenbacher S, Lin D, Strauss R, McKaig R, Irving J, Barros SP, et al. Effects of periodontal therapy during pregnancy on periodontal status, biologic parameters, and pregnancy outcomes: a pilot study. J Periodontol. (2006) 77:2011–24. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.060047
25. Tonetti MS, D’Aiuto F, Nibali L, Donald A, Storry C, Parkar M, et al. Treatment of periodontitis and endothelial function. New Engl J Med. (2007) 356:911–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa063186
26. Tüter G, Kurtiş B, Serdar M, Aykan T, Okyay K, Yücel A, et al. Effects of scaling and root planing and sub-antimicrobial dose doxycycline on oral and systemic biomarkers of disease in patients with both chronic periodontitis and coronary artery disease. J Clin Periodontol. (2007) 34:673–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2007.01104.x
27. Ushida Y, Koshy G, Kawashima Y, Kiji M, Umeda M, Nitta H, et al. Changes in serum interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and thrombomodulin levels under periodontal ultrasonic debridement. J Clin Periodontol. (2008) 35:969–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01316.x
28. Offenbacher S, Beck JD, Moss K, Mendoza L, Paquette DW, Barrow DA, et al. Results from the Periodontitis and Vascular Events (PAVE) Study: a pilot multicentered, randomized, controlled trial to study effects of periodontal therapy in a secondary prevention model of cardiovascular disease. J Periodontol. (2009) 80:190–201. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.080007
29. Vidal F, Figueredo CM, Cordovil I, and Fischer RG. Periodontal therapy reduces plasma levels of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and fibrinogen in patients with severe periodontitis and refractory arterial hypertension. J Periodontol. (2009) 80:786–91. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.080471
30. Renvert S, Lindahl C, Roos-Jansåker AM, and Lessem J. Short-term effects of an anti-inflammatory treatment on clinical parameters and serum levels of C-reactive protein and proinflammatory cytokines in subjects with periodontitis. J Periodontol. (2009) 80:892–900. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.080552
31. Kardeşler L, Buduneli N, Çetinkalp Ş, and Kinane DF. Adipokines and inflammatory mediators after initial periodontal treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic periodontitis. J periodontology. (2010) 81:24–33. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090267
32. Duarte PM, da Rocha M, Sampaio E, Mestnik MJ, Feres M, Figueiredo LC, et al. Serum levels of cytokines in subjects with generalized chronic and aggressive periodontitis before and after non-surgical periodontal therapy: a pilot study. J Periodontol. (2010) 81:1056–63. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090732
33. Tüter G, Serdar M, Kurtiş B, Walker SG, Atak A, Toyman U, et al. Effects of scaling and root planing and subantimicrobial dose doxycycline on gingival crevicular fluid levels of matrix metalloproteinase-8,-13 and serum levels of HsCRP in patients with chronic periodontitis. J Periodontol. (2010) 81:1132–9. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090694
34. Shimada Y, Komatsu Y, Ikezawa-Suzuki I, Tai H, Sugita N, and Yoshie H. The effect of periodontal treatment on serum leptin, interleukin-6, and C-reactive protein. J Periodontol. (2010) 81:1118–23. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090741
35. Fentoğlu Ö, Sözen T, Öz SG, Kale B, Sönmez Y, Öztürk Tonguç M, et al. Short-term effects of periodontal therapy as an adjunct to anti-lipemic treatment. Oral Diseases. (2010) 16:648–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2010.01668.x
36. Graziani F, Cei S, La Ferla F, Vano M, Gabriele M, and Tonetti M. Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on the glomerular filtration rate of the kidney: an exploratory trial. J Clin Periodontol. (2010) 37:638–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01578.x
37. Lin SJ, Tu YK, Tsai SC, Lai SM, and Lu HK. Non-surgical periodontal therapy with and without subgingival minocycline administration in patients with poorly controlled type II diabetes: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral investigations. (2012) 16:599–609. doi: 10.1007/s00784-011-0535-x
38. Koromantzos PA, Makrilakis K, Dereka X, Offenbacher S, Katsilambros N, Vrotsos IA, et al. Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on C-reactive protein, oxidative stress, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and MMP-2 levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled study. J Periodontol. (2012) 83:3–10. doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.110148
39. Kamil W, Al Habashneh R, Khader Y, Al Bayati L, and Taani D. Effects of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on C-reactive protein and serum lipids in Jordanian adults with advanced periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. (2011) 46:616–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2011.01380.x
40. Vilela EM, Bastos JA, Fernandes N, Ferreira AP, Chaoubah A, and Bastos MG. Treatment of chronic periodontitis decreases serum prohepcidin levels in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clinics (Sao Paulo). (2011) 66:657–62. doi: 10.1590/s1807-59322011000400022
41. López NJ, Quintero A, Casanova PA, Ibieta CI, Baelum V, and López R. Effects of periodontal therapy on systemic markers of inflammation in patients with metabolic syndrome: a controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. (2012) 83:267–78. doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.110227
42. Chen L, Luo G, Xuan D, Wei B, Liu F, Li J, et al. Effects of non-surgical periodontal treatment on clinical response, serum inflammatory parameters, and metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized study. J Periodontol. (2012) 83:435–43. doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.110327
43. Llambés F, Silvestre FJ, Hernández-Mijares A, Guiha R, Bautista D, and Caffesse R. Efect of periodontal disease and non surgical periodontal treatment on C-reactive protein. Evaluation of type 1 diabetic patients. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. (2012) 17:e562. doi: 10.4317/medoral.17793
44. Altay U, Gürgan CA, and Ağbaht K. Changes in inflammatory and metabolic parameters after periodontal treatment in patients with and without obesity. J Periodontol. (2013) 84:13–23. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.110646
45. Al-Zahrani MS and Alghamdi HS. Effect of periodontal treatment on serum C-reactive protein level in obese and normal-weight women affected with chronic periodontitis. Saudi Med J. (2012) Mar; 33(3):309–14.
46. Fiorini T, Susin C, da Rocha JM, Weidlich P, Vianna P, Moreira CH, et al. Effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on serum and gingival crevicular fluid cytokine levels during pregnancy and postpartum. J Periodontal Res. (2013) 48:126–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2012.01513.x
47. Bokhari SA, Khan AA, Butt AK, Azhar M, Hanif M, Izhar M, et al. Non-surgical periodontal therapy reduces coronary heart disease risk markers: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol. (2012) 39:1065–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01942.x
48. Patil VA and Desai MH. Effect of periodontal therapy on serum C-reactive protein levels in patients with gingivitis and chronic periodontitis: a clinicobiochemical study. J Contemp Dental Practice. (2013) 14:233–7. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1305
49. Koppolu P, Durvasula S, Palaparthy R, Rao M, Sagar V, Reddy SK, et al. Estimate of CRP and TNF-alpha level before and after periodontal therapy in cardiovascular disease patients. Pan Afr Med J. (2013) 15:92. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2013.15.92.2326
50. Al Habashneh R, Alsalman W, and Khader Y. Ozone as an adjunct to conventional nonsurgical therapy in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontal Res. (2015) 50:37–43. doi: 10.1111/jre.12177
51. Raman RP, Taiyeb-Ali TB, Chan SP, Chinna K, and Vaithilingam RD. Effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy verses oral hygiene instructions on type 2 diabetes subjects with chronic periodontitis: a randomised clinical trial. BMC Oral Health. (2014) 14:79. doi: 10.1186/1472-6831-14-79
52. Caúla AL, Lira-Junior R, Tinoco EM, and Fischer RG. The effect of periodontal therapy on cardiovascular risk markers: a 6-month randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. (2014) 41:875–82. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12290
53. Fang F, Wu B, Qu Q, Gao J, Yan W, Huang X, et al. The clinical response and systemic effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy in end-stage renal disease patients: a 6-month randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin periodontology. (2015) 42:537–46. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12411
54. Artese HP, Longo PL, Gomes GH, Mayer MP, and Romito GA. Supragingival biofilm control and systemic inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Braz Oral Res. (2015) 29:1–7. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107BOR-2015.vol29.0071
55. Munenaga Y, Yamashina T, Tanaka J, Nishimura F, and Hiroshima Study Group. Improvement of glycated hemoglobin in Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes by resolution of periodontal inflammation using adjunct topical antibiotics: results from the Hiroshima Study. Diabetes Res Clin Practice. (2013) 100:53–60. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.01.028
56. Markou N, Pepelassi E, Madianos P, Simopoulou M, and Karoussis IK. Systemic inflammatory markers following adjunctive Nd: YAG (1064 nm) laser irradiation to step 2 of periodontal therapy: a 12-month, randomized, controlled trial. Clin Oral Investigations. (2023) 27:6925–35. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05309-3
57. Isola G, Tartaglia GM, Santonocito S, Chaurasia A, Marya A, and Lo Giudice A. Growth differentiation factor-15 and circulating biomarkers as predictors of periodontal treatment effects in patients with periodontitis: a randomized-controlled clinical trial. BMC Oral Health. (2023) 23:582. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03237-y
58. Graziani F, Gennai S, Marruganti C, Peric M, Ghiadoni L, Marhl U, et al. Acute-phase response following one-stage full-mouth versus quadrant non-surgical periodontal treatment in subjects with comorbid type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. (2023) 50:487–99. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13760
59. Shah B, Shah M, Geisinger M, Saleh MH, Meghil M, and Wang HL. Effect of non-surgical therapy on plasma C-reactive protein levels in patients with periodontitis: a single arm prospective clinical trial. J periodontology. (2023) 94:336–43. doi: 10.1002/JPER.22-0231
60. Escobar Arregocés FM, Del Hierro Rada M, Sáenz Martinez MJ, Hernández Meza FJ, Roa NS, Velosa-Porras J, et al. Systemic inflammatory response to non-surgical treatment in hypertensive patients with periodontal infection. Medicine (Baltimore). (2021) 100:e24951. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024951
61. Rabelo MS, Gomes GH, Foz AM, Stadler AF, Cutler CW, Susin C, et al. Short-term effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on local and systemic cytokine levels: role of hyperglycemia. Cytokine. (2021) 138:155360. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155360
62. Mohammad CA. Efficacy of curcumin gel on zinc, magnesium, copper, IL-1β, and TNF-α in chronic periodontitis patients. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:8850926. doi: 10.1155/2020/8850926
63. Lobao WJ, Carvalho RC, Leite SA, Rodrigues VP, Batista JE, Gomes-Filho IS, et al. Relationship between periodontal outcomes and serum biomarkers changes after non-surgical periodontal therapy. Anais da Academia Bras Ciências. (2019) 91:e20170652. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201920170652
64. Wang S, Liu J, Zhang J, Lin J, Yang S, Yao J, et al. Glycemic control and adipokines after periodontal therapy in patients with Type 2 diabetes and chronic periodontitis. Braz Oral Res. (2017) 31:e90. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2017.vol31.0090
65. Yuce HB, Gokturk O, Turkal HA, Inanir A, Benli I, and Demir O. Assessment of local and systemic 25-hydroxy-vitamin D, RANKL, OPG, and TNF levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. J Oral science. (2017) 59:397–404. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.16-0677
66. Deepti, Tewari S, Narula SC, Singhal SR, and Sharma RK. Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy along with myo-inositol on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and chronic periodontitis: A randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol. (2017) 88:999–1011. doi: 10.1902/jop.2017.170121
67. Žekonis G, Žekonis J, Gleiznys A, Noreikienė V, Balnytė I, Šadzevičienė R, et al. Effect of supragingival irrigation with aerosolized 0.5% hydrogen peroxide on clinical periodontal parameters, markers of systemic inflammation, and morphology of gingival tissues in patients with periodontitis. Med Sci Monit. (2016) 22:3713–21. doi: 10.12659/msm.900338
68. Kapellas K, Mejia G, Bartold PM, Skilton MR, Maple-Brown LJ, Slade GD, et al. Periodontal therapy and glycaemic control among individuals with type 2 diabetes: reflections from the PerioCardio study. Int J Dent Hyg. (2017) 15:e42–51. doi: 10.1111/idh.12234
69. Geisinger ML, Michalowicz BS, Hou W, Schoenfeld E, Gelato M, Engebretson SP, et al. Systemic inflammatory biomarkers and their association with periodontal and diabetes-related factors in the diabetes and periodontal therapy trial, a randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol. (2016) 87:900–13. doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.150727
70. Javed F, Kellesarian SV, Al-Kheraif AA, Ranna V, Qadri T, Yunker M, et al. Effect of Nd: YAG laser-assisted non-surgical periodontal therapy on clinical periodontal and serum biomarkers in patients with and without coronary artery disease: a short-term pilot study. Lasers Surg Med. (2016) 48:929–35. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22483
71. Fu YW, Li XX, Xu HZ, Gong YQ, and Yang Y. Effects of periodontal therapy on serum lipid profile and proinflammatory cytokines in patients with hyperlipidemia: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Investig. (2016) 20:1263–9. doi: 10.1007/s00784-015-1621-2
72. Kolbe MF, Ribeiro FV, Luchesi VH, Casarin RC, Sallum EA, Nociti FH Jr., et al. Photodynamic therapy during supportive periodontal care: clinical, microbiologic, immunoinflammatory, and patient-centered performance in a split-mouth randomized clinical trial. J Periodontol. (2014) 85:e277–86. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.130559
73. Aljateeli M, Koticha T, Bashutski J, Sugai JV, Braun TM, Giannobile WV, et al. Surgical periodontal therapy with and without initial scaling and root planing in the management of chronic periodontitis: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. (2014) 41:693–700. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12259
74. Üstün K, Erciyas K, Sezer U, Şenyurt SZ, Gündoğar H, Üstün Ö, et al. Clinical and biochemical effects of 810 nm diode laser as an adjunct to periodontal therapy: a randomized split-mouth clinical trial. Photomed Laser Surg. (2014) 32:61–6. doi: 10.1089/pho.2013.3506
75. Luchesi VH, Pimentel SP, Kolbe MF, Ribeiro FV, Casarin RC, Nociti FH Jr., et al. Photodynamic therapy in the treatment of class II furcation: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. (2013) 40:781–8. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12121
76. Müller Campanile VS, Giannopoulou C, Campanile G, Cancela JA, and Mombelli A. Single or repeated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy as adjunct to ultrasonic debridement in residual periodontal pockets: clinical, microbiological, and local biological effects. Lasers Med Sci. (2015) 30:27–34. doi: 10.1007/s10103-013-1337-y
77. Arora N, Avula H, and Avula JK. The adjunctive use of systemic antioxidant therapy (lycopene) in nonsurgical treatment of chronic periodontitis: a short-term evaluation. Quintessence Int. (2013) 44(6):395–405. doi: 10.3290/j.qi.a29188
78. Pirie M, Linden G, and Irwin C. Intrapregnancy non-surgical periodontal treatment and pregnancy outcome: a randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol. (2013) 84:1391–400. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.120572
79. Nibali L, Pelekos G, D’Aiuto F, Chaudhary N, Habeeb R, Ready D, et al. Influence of IL-6 haplotypes on clinical and inflammatory response in aggressive periodontitis. Clin Oral Investig. (2013) 17:1235–42. doi: 10.1007/s00784-012-0804-3
80. Santos VR, Ribeiro FV, Lima JA, Miranda TS, Feres M, and Bastos MF. Duarte PM. Partial-and full-mouth scaling and root planing in type 2 diabetic subjects: a 12-mo follow-up of clinical parameters and levels of cytokines and osteoclastogenesis-related factors. J Periodontal Res. (2012) 47:45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2011.01403.x
81. Ishikado A, Uesaki S, Suido H, Nomura Y, Sumikawa K, Maeda M, et al. Human trial of liposomal lactoferrin supplementation for periodontal disease. Biol Pharm Bulletin. (2010) 33:1758–62. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1758
82. Lee MK, Ide M, Coward PY, and Wilson RF. Effect of ultrasonic debridement using a chlorhexidine irrigant on circulating levels of lipopolysaccharides and interleukin-6. J Clin Periodontol. (2008) 35:415–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01221.x
83. Yamaoka M, Uematsu T, Shiba T, Matsuura T, Ono Y, Ishizuka M, et al. Effect of inorganic polyphosphate in periodontitis in the elderly. Gerodontology. (2008) 25:10–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-2358.2007.00185.x
84. Avradopoulos V, Wilder RS, Chichester S, and Offenbacher S. Clinical and inflammatory evaluation of Perioscopy on patients with chronic periodontitis. J Dent Hyg. (2004) 78(1):30–8.
85. Jentsch HF, Knöfler GU, Purschwitz RE, and Eick S. Periodontal dressing as an adjunct after scaling and root planing–A useful preventive tool? Oral Health Prev Dent. (2016) 14(2):101–9. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a35612
86. Ertugrul AS, Tekin Y, and Talmac AC. Comparing the efficiency of Er, Cr: YSGG laser and diode laser on human β-defensin-1 and IL-1β levels during the treatment of generalized aggressive periodontitis and chronic periodontitis. J Cosmetic Laser Ther. (2017) 19:409–17. doi: 10.1080/14764172.2017.1334923
87. Lecio G, Ribeiro FV, Pimentel SP, Reis AA, da Silva RV, Nociti-Jr F, et al. Novel 20% doxycycline-loaded PLGA nanospheres as adjunctive therapy in chronic periodontitis in type-2 diabetics: randomized clinical, immune and microbiological trial. Clin Oral Investig. (2020) 24:1269–79. doi: 10.1007/s00784-019-03005-9
88. Talmac AC, Yayli NZ, Calisir M, and Ertugrul AS. Comparing the efficiency of Er, Cr: YSGG laser and diode laser for the treatment of generalized aggressive periodontitis. Irish J Med Sci. (2022) 191:1331–9. doi: 10.1007/s11845-021-02705-0
89. Kaur M, Sharma RK, Tewari S, Arora R, Tanwar N, and Sangwan A. Effect of antibiotics as an adjuvant to subgingival instrumentation on systemic inflammation in patients with periodontitis: a randomized clinical trial. Quintessence Int. (2023) 54(6):460–71. doi: 10.3290/j.qi.b3942249
90. Cosgarea R, Tristiu R, Dumitru RB, Arweiler NB, Rednic S, Sirbu CI, et al. Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on periodontal laboratory and clinical data as well as on disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Oral Investig. (2019) 23:141–51. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2420-3
91. Kaur M, Geisinger ML, Geurs NC, Griffin R, Vassilopoulos PJ, Vermeulen L, et al. Effect of intensive oral hygiene regimen during pregnancy on periodontal health, cytokine levels, and pregnancy outcomes: a pilot study. J Periodontol. (2014) 85:1684–92. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.140248
92. Leite AC, Carneiro VM, and Guimarães MD. Efeitos da terapia periodontal sobre proteína c-reativa e hdl no soro de indivíduos com periodontite. Braz J Cardiovasc Surgery. (2014) 29:69–77. doi: 10.5935/1678-9741.20140013
93. Gonzales JR, Harnack L, Schmitt-Corsitto G, Boedeker RH, Chakraborty T, Domann E, et al. A novel approach to the use of subgingival controlled-release chlorhexidine delivery in chronic periodontitis: A randomized clinical trial. J Periodontol. (2011) 82:1131–9. doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.100287
94. Payne JB, Golub LM, Stoner JA, Lee HM, Reinhardt RA, Sorsa T, et al. The effect of subantimicrobial-dose–doxycycline periodontal therapy on serum biomarkers of systemic inflammation: a randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Am Dental Assoc. (2011) 142:262–73. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2011.0165
95. Michalowicz BS, Novak MJ, Hodges JS, DiAngelis A, Buchanan W, Papapanou PN, et al. Serum inflammatory mediators in pregnancy: changes after periodontal treatment and association with pregnancy outcomes. J Periodontol. (2009) 80:1731–41. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090236
96. D’Aiuto F, Parkar M, and Tonetti MS. Acute effects of periodontal therapy on bio-markers of vascular health. J Clin Periodontol. (2007) 34:124–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2006.01037.x
97. D’Aiuto F, Parkar M, Andreou G, Brett PM, Ready D, and Tonetti MS. Periodontitis and atherogenesis: causal association or simple coincidence? J Clin Periodontol. (2004) 31:402–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2004.00580.x
98. Al-Mubarak S, Ciancio S, Aljada A, Mohanty P, Mohanty P, Ross C, et al. Comparative evaluation of adjunctive oral irrigation in diabetics. J Clin Periodontol. (2002) 29:295–300. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.2002.290404.x
99. Pham TA, Nguyen PA, Tran TT, and Nguyen VT. Nonsurgical periodontal treatment improved the type 2 diabetes mellitus status in smokers: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Practice. (2022) 194:110150. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110150
100. Milanesi FC, Greggianin BF, Dos Santos GO, Toniazzo MP, Weidlich P, Gerchman F, et al. Effect of periodontal treatment on glycated haemoglobin and metabolic syndrome parameters: A randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. (2023) 50:11–21. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13717
101. Alyousef AA and Divakar DD. Chemically modified tetracyclines an emerging host modulator in chronic periodontitis patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Microbial Pathogenesis. (2017) :110:279–84. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.07.002
102. Bozoglan A, Ertugrul AS, Taspınar M, and Yuzbasioglu B. Determining the relationship between atherosclerosis and periodontopathogenic microorganisms in chronic periodontitis patients. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica. (2017) 75:233–42. doi: 10.1080/00016357.2017.1280739
103. Giannopoulou C, Cionca N, Almaghlouth A, Cancela J, Courvoisier DS, and Mombelli A. Systemic biomarkers in 2-phase antibiotic periodontal treatment: a randomized clinical trial. J Dental Res. (2016) 95:349–55. doi: 10.1177/0022034515618949
104. Bazyar H, Gholinezhad H, Moradi L, Salehi P, Abadi F, Ravanbakhsh M, et al. The effects of melatonin supplementation in adjunct with non-surgical periodontal therapy on periodontal status, serum melatonin and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with chronic periodontitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Inflammopharmacology. (2019) 27:67–76. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0539-0
105. Zhang J, Zhang AM, Zhang ZM, Jia JL, Sui XX, Yu LR, et al. Efficacy of combined orthodontic-periodontic treatment for patients with periodontitis and its effect on inflammatory cytokines: A comparative study. Am J Orthodontics Dentofacial Orthopedics. (2017) 152:494–500. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.01.028
106. Kharaeva ZF, Zhanimova LR, Mustafaev MS, De Luca C, Mayer W, Chung Sheun Thai J, et al. Effects of standardised fermented papaya gel on clinical symptoms, inflammatory cytokines, and nitric oxide metabolites in patients with chronic periodontitis: An open randomised clinical study. Mediators Inflammation. (2016) 2016:9379840. doi: 10.1155/2016/9379840
107. Izuora KE, Ezeanolue EE, Neubauer MF, Gewelber CL, Allenback GL, Shan G, et al. Changes in inflammatory and bone turnover markers after periodontal disease treatment in patients with diabetes. Am J Med Sci. (2016) 351:589–94. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2016.02.004
108. Shaddox LM, Gonçalves PF, Vovk A, Allin N, Huang H, Hou W, et al. LPS-induced inflammatory response after therapy of aggressive periodontitis. J Dental Res. (2013) 92:702–8. doi: 10.1177/0022034513495242
109. Eickholz P, Siegelin Y, Scharf S, Schacher B, Oremek GM, Sauer-Eppel H, et al. Non-surgical periodontal therapy decreases serum elastase levels in aggressive but not in chronic periodontitis. J Clin periodontology. (2013) 40:327–33. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12076
110. Wehmeyer MM, Kshirsagar AV, Barros SP, Beck JD, Moss KL, Preisser JS, et al. A randomized controlled trial of intensive periodontal therapy on metabolic and inflammatory markers in patients with ESRD: results of an exploratory study. Am J Kidney Diseases. (2013) 61:450–8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.10.021
111. Sun WL, Chen LL, Zhang SZ, Wu YM, Ren YZ, and Qin GM. Inflammatory cytokines, adiponectin, insulin resistance and metabolic control after periodontal intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic periodontitis. Internal Med. (2011) 50:1569–74. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.50.5166
112. Sun WL, Chen LL, Zhang SZ, Ren YZ, and Qin GM. Changes of adiponectin and inflammatory cytokines after periodontal intervention in type 2 diabetes patients with periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. (2010) 55:970–4. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2010.08.001
113. Joseph R, Narayan V, Krishnan R, and Melemadathil S. Non-surgical periodontal therapy improves serum levels of C-reactive protein and edematous states in female patients with idiopathic edema. J Periodontol. (2011) 82:201–9. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.100258
114. O’Connell PA, Taba M Jr, Nomizo A, Foss Freitas MC, Suaid FA, Uyemura SA, et al. Effects of periodontal therapy on glycemic control and inflammatory markers. J Periodontol. (2008) 79:774–83. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.070250
115. Elsadek MF. Effectiveness of two photosensitizer-mediated photodynamic therapy for treating moderate peri-implant infections in type-II diabetes mellitus patients: A randomized clinical trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2023) :43:103643. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2023.103643
116. Woźniewicz M, Nowaczyk PM, Kurhańska-Flisykowska A, Wyganowska-Świątkowska M, Lasik-Kurdyś M, Walkowiak J, et al. Consumption of cranberry functional beverage reduces gingival index and plaque index in patients with gingivitis. Nutr Res. (2018) 58:36–45. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.06.011
117. Maheshwari S, Chahal GS, Grover V, Rathi M, Sharma R, and Jain A. Impact of periodontal treatment on inflammatory oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease subjects: An interventional clinical trial. Am J Dent. (2023) 36:15–20.
118. King S, Church L, Garde S, Chow CK, Akhter R, and Eberhard J. Targeting the reduction of inflammatory risk associated with cardiovascular disease by treating periodontitis either alone or in combination with a systemic anti-inflammatory agent: protocol for a pilot, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e063148. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-063148
119. Hasan F, Ikram R, Simjee SU, Iftakhar K, Asadullah K, and Usman M. The effects of aspirin gel and mouthwash on levels of salivary biomarkers PGE2, TNF-α and nitric oxide in patients with periodontal diseases. Pak J Pharm Sci. (2019) 32:2019–3.
120. Trivedi R, Fares G, Nunez VB, Campbell R, Clement M, Burleson J, et al. Novel PAradigm to improve Inflammatory burden in end stage Renal disease (rePAIR): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2018) 19:370. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2760-y
121. Jiang H, Xiong X, Su Y, Zhang Y, Wu H, Jiang Z, et al. A randomized controlled trial of pre-conception treatment for periodontal disease to improve periodontal status during pregnancy and birth outcomes. BMC pregnancy childbirth. (2013) 13:228. doi: 10.1186/1471-2393-13-228
122. Saffi MA, Furtado MV, Montenegro MM, Ribeiro IW, Kampits C, Rabelo-Silva ER, et al. The effect of periodontal therapy on C-reactive protein, endothelial function, lipids and proinflammatory biomarkers in patients with stable coronary artery disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2013) 14:283. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-283
123. Bezerra JP, Shaddox LM, de Mendonca AC, Bastos MF, de Miranda TS, Santos VR, et al. Local levels of biomarkers after surgical and nonsurgical debridement of residual pockets and nonresidual sites in diabetic patients: a 12-month follow-up. Gen Dent. (2015) 63:58–64.
124. Izuora K, Ezeanolue E, Schlauch K, Neubauer M, Gewelber C, and Umpierrez G. Impact of periodontal disease on outcomes in diabetes. Contemp Clin trials. (2015) 41:93–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2015.01.011
125. IIe S. Pathogenetic substantiation of using peptidases in the treatment of patients with generalized periodontitis. Fiziolohichnyi Zhurnal (Kiev Ukraine: 1994). (2013) 59:85–91. doi: 10.15407/fz59.02.085
126. Shetty S, Bose A, Sridharan S, Satyanarayana A, and Rahul A. A clinico-biochemical evaluation of the role of a herbal (Ayurvedic) immunomodulator in chronic periodontal disease: a pilot study. Oral Health Dent Man. (2013) 12:95–104.
127. Feghali CA and Wright TM. Cytokines in acute and chronic inflammation. Front Biosci. (1997) 2:d12–26. doi: 10.2741/a171
128. Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, et al. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. New Engl J Med. (2017) 377:1119–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707914
129. Biasucci LM, Pedicino D, and Liuzzo G. Promises and challenges of targeting inflammation to treat cardiovascular disease: the post-CANTOS era. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:2164–7. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz586
130. Pani P, Tsilioni I, McGlennen R, Brown CA, Hawley CE, Theoharides TC, et al. IL-1B (3954) polymorphism and red complex bacteria increase IL-1β (GCF) levels in periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. (2021) 56:501–11. doi: 10.1111/jre.12850
131. Loos BG, Craandijk J, Hoek FJ, Dillen PM, and van der Velden U. Elevation of systemic markers related to cardiovascular diseases in the peripheral blood of periodontitis patients. J Periodontol. (2000) 71:1528–34. doi: 10.1902/jop.2000.71.10.1528
132. Villoria GE, Fischer RG, Tinoco EM, Meyle J, and Loos BG. Periodontal disease: A systemic condition. Periodontol 2000. (2024) 96:7–19. doi: 10.1111/prd.12616
133. Del Pinto R, Landi L, Grassi G, Sforza NM, Cairo F, Citterio F, et al. Hypertension and periodontitis: a joint report by the Italian Society of Hypertension (SIIA) and the Italian Society of Periodontology and Implantology (SIdP). High Blood Pressure Cardiovasc Prev. (2021) 28:427–38. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00466-6
134. Sharma S, Sridhar S, McIntosh A, Messow CM, Aguilera EM, Del Pinto R, et al. Periodontal therapy and treatment of hypertension-alternative to the pharmacological approach. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 166:105511. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105511
135. Simpson TC, Clarkson JE, Worthington HV, MacDonald L, Weldon JC, Needleman I, et al. Treatment of periodontitis for glycaemic control in people with diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Systematic Rev. (2022) 4(4):CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub4
136. Daloee MH, Avan A, Mirhafez SR, Kavousi E, Hasanian-Mehr M, Darroudi S, et al. Impact of cigarette smoking on serum pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors. Am J men’s Health. (2017) 11:1169–73. doi: 10.1177/1557988315601724
137. Ouyang Y, Virasch N, Hao P, Aubrey MT, Mukerjee N, Bierer BE, et al. Suppression of human IL-1β, IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α production by cigarette smoke extracts. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2000) 106:280–7. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.107751
138. Bermudez EA, Rifai N, Buring JE, Manson JE, and Ridker PM. Relation between markers of systemic vascular inflammation and smoking in women. Am J Cardiol. (2002) 89:1117–9. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(02)02284-1
139. Sunyer J, Forastiere F, Pekkanen J, Plana E, Kolz M, Pistelli R, et al. Interaction between smoking and the interleukin-6 gene affects systemic levels of inflammatory biomarkers. Nicotine Tobacco Res. (2009) 11:1347–53. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntp144
140. Del Pinto R, Ferri C, Giannoni M, Cominelli F, Pizarro TT, and Pietropaoli D. Meta-analysis of oral microbiome reveals sex-based diversity in biofilms during periodontitis. JCI Insight. (2024) 9:e171311. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.171311
141. Klein SL and Flanagan KL. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:626–38. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.90
Keywords: periodontitis, inflammation, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, C-reactive protein, cytokines, meta-analysis
Citation: Cardisciani M, Di Nicolantonio S, Altamura S, Ortu E, Del Pinto R and Pietropaoli D (2025) Temporal dynamics of early inflammatory markers after professional dental cleaning: a meta-analysis and spline-based meta-regression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and (hs)CRP. Front. Immunol. 16:1634622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1634622
Received: 24 May 2025; Accepted: 13 August 2025;
Published: 28 August 2025.
Edited by:
Chun-Teh Lee, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, United StatesReviewed by:
Mohammad Kashif, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH), United StatesYiping Wei, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, China
Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi, University of Baghdad, Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Cardisciani, Di Nicolantonio, Altamura, Ortu, Del Pinto and Pietropaoli. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Davide Pietropaoli, ZGF2aWRlLnBpZXRyb3Bhb2xpQHVuaXZhcS5pdA==; Rita Del Pinto, cml0YS5kZWxwaW50b0B1bml2YXEuaXQ=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Martina Cardisciani
Martina Cardisciani Sara Di Nicolantonio
Sara Di Nicolantonio Serena Altamura1,2
Serena Altamura1,2 Eleonora Ortu
Eleonora Ortu Rita Del Pinto
Rita Del Pinto Davide Pietropaoli
Davide Pietropaoli