- First Affiliated Hospital, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Cancer treatment-induced thrombocytopenia (CTIT) is a common adverse effect in malignant tumor patients, significantly increasing the risk of bleeding and negatively impacting treatment efficacy and quality of life. Current treatment options for CTIT primarily include platelet transfusion, recombinant human interleukin-11 (rhIL-11), recombinant human thrombopoietin (rhTPO) and thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RAs). However, these methods have their limitations; for instance, platelet transfusions may cause adverse reactions, and the efficacy and safety of rhTPO and TPO-RAs remain controversial. This review aims to summarize the current treatment landscape for CTIT and explore new therapeutic advancement, including the potential role of traditional Chinese medicine, in order to provide more effective treatment strategies for clinical practice.
1 Introduction
CTIT is defined as a reduction in platelet count that occurs as a consequence of anti-tumor therapies, significantly increasing the risk of bleeding and negatively impacting treatment efficacy and quality of life. The definition of CTIT refers to platelets in peripheral blood (PLT) counts below 100×109/L caused by antitumor drug therapy and includes CIT,ICIIT and targeted therapy-induced thrombocytopenia (TTIT). Research has shown that CTIT can affect up to 21.8% of patients undergoing antitumor therapy, particularly in hematological malignancies and solid tumors treated with myelosuppressive drugs (1). This condition is clinically significant as it can lead to a range of complications, including increased risk of bleeding, delays in treatment, and a potential decrease in overall treatment efficacy. The incidence of CTIT varies depending on the type of cancer, the specific treatment regimen employed, and individual patient factors (2). Understanding CTIT is crucial for oncologists and healthcare providers, as its management can profoundly impact patient outcomes and quality of life.
The mechanisms behind CTIT are multifaceted and often involve direct bone marrow suppression due to cytotoxic agents, immune-mediated mechanisms, or the effects of the tumor microenvironment (3).Certain cancers, such as hematological malignancies, are more inclined to causing CTIT because of their inherent effects on blood cell production. Additionally, certain chemotherapy regimens used can exacerbate the situation of thrombocytopenia. For instance, regimens that include agents known for their myelosuppressive properties are more likely to result in significant drops in platelet count (4). In the context of cancer treatment, comprehensive summary of clinical prevalent therapeutic approaches to mitigate this adverse effect is crucial for enhancing our understanding and management of this unfavorable condition.
As such, the relationship between tumor type, treatment strategy, and the occurrence of CTIT is a critical area of research that seeks to optimize treatment protocols and minimize adverse effects. The impact of CTIT on patient care is significant, affecting not only the current treatment plan but also increase the need for frequent monitoring (5). In severe cases, patients may require platelet transfusions, which can complicate treatment regimens and increase healthcare costs (6). Therefore, addressing CTIT is essential not only for improving treatment efficacy but also for enhancing the overall well-being of patients undergoing anti-cancer therapy. This review aims to explore the mechanisms, implications, and management strategies associated with CTIT, providing a comprehensive overview for clinicians and researchers.
2 Diagnosis, clinical manifestations and epidemiology of CTIT
2.1 Laboratory tests and diagnostic criteria for CTIT
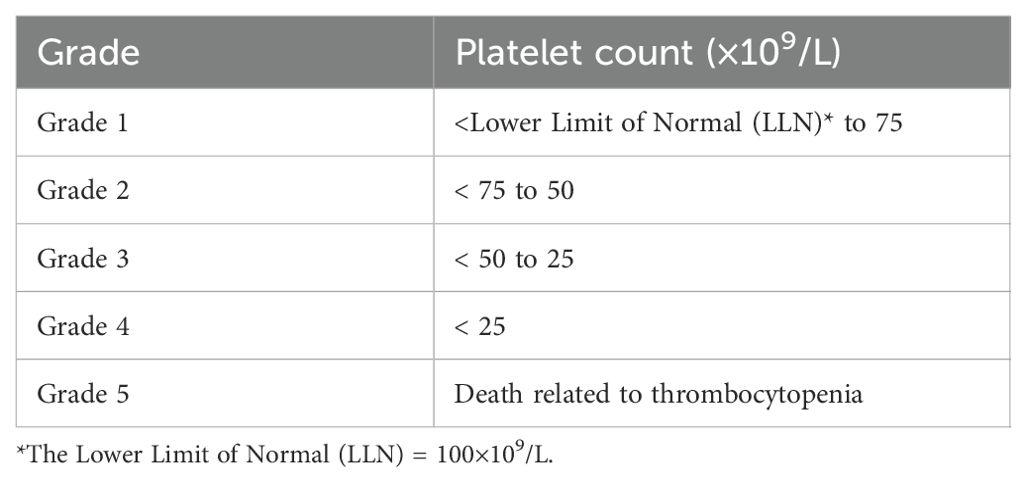
The clinical diagnosis for CTIT is indispensable to include a definite history of using a certain anti-tumor drug that may cause thrombocytopenia and the symptoms of thrombocytopenia gradually decrease or disappear after stopping the drug. Besides, other causes of thrombocytopenia have been excluded, such as aplastic anemia, acute leukemia, radiation sickness, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, bone marrow invasion by tumors, and hyperactive spleen function (7).The diagnosis of thrombocytopenia is primarily established through laboratory testing, which includes a complete blood count (CBC) that reveals the platelet count. A platelet count below 150,000 platelets per microliter is generally considered thrombocytopenia. Non-chemotherapy-related thrombocytopenia is generally diagnosed when the platelet count falls below 100 × 109/L, which differs from the criteria for grade 1 CTIT. The grading criteria for CTIT is shown in Table 1. Further laboratory investigations may include peripheral blood smears to assess platelet morphology and the presence of any atypical cells, as well as specific tests to determine the underlying cause, such as bone marrow biopsy, immunological assays for autoimmune conditions, and viral serologic tests for infections like HIV or hepatitis (8, 9). Diagnostic criteria vary depending on the suspected etiology; for example, in ITP, the diagnosis may be supported by the exclusion of other causes of thrombocytopenia and the presence of specific clinical signs (10). Overall, a comprehensive approach combining clinical evaluation and targeted laboratory tests is essential for accurate diagnosis and management.
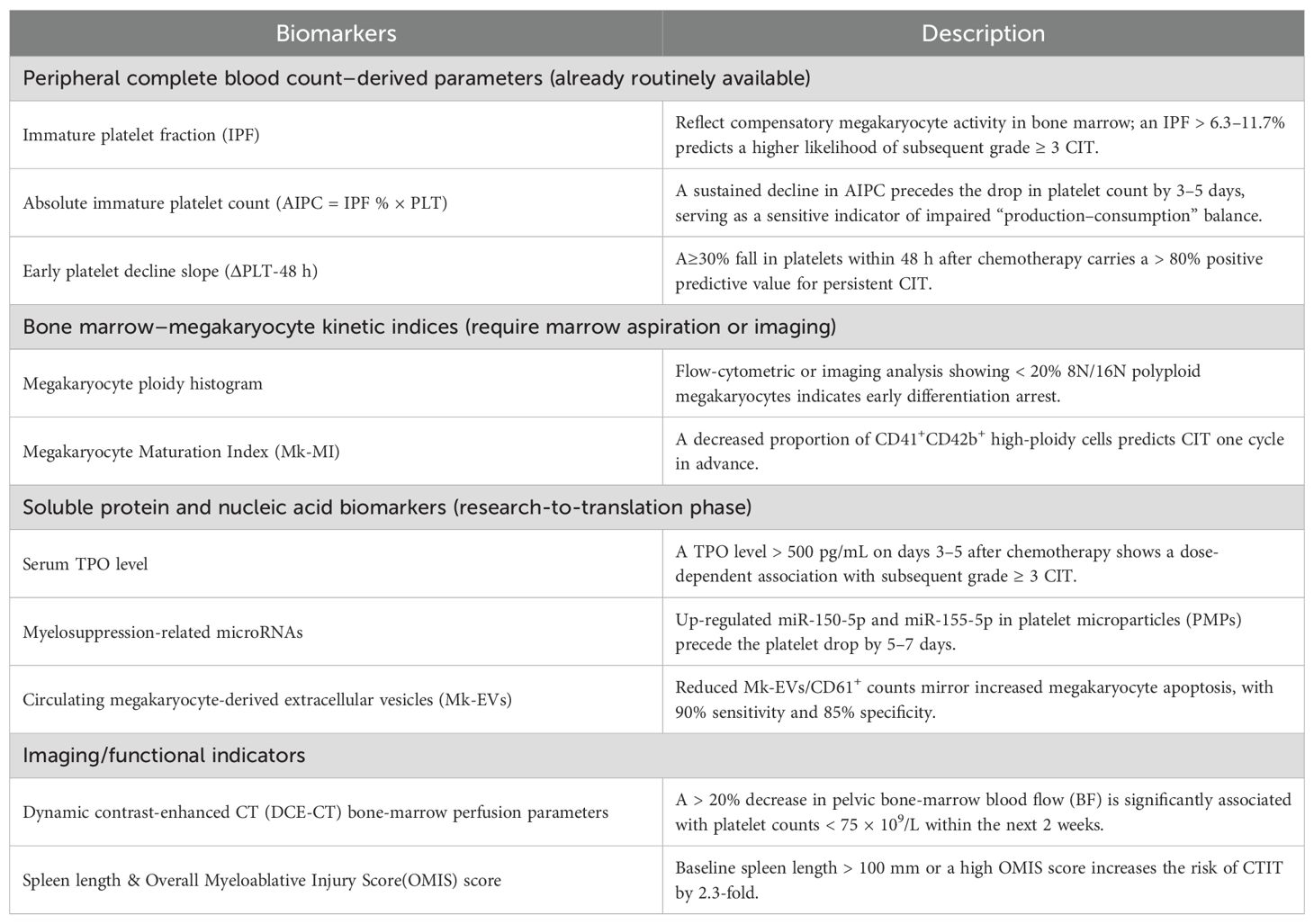
Early-detection biomarkers for CTIT can be grouped into four categories and is shown in Table 2: peripheral complete blood count–derived parameters, bone marrow–megakaryocyte kinetic indices, soluble protein/nucleic acid biomarkers, and imaging/functional indicators (11, 12). All of these can provide an early warning before the absolute platelet count falls below the critical threshold.
2.2 The epidemiology of CIT
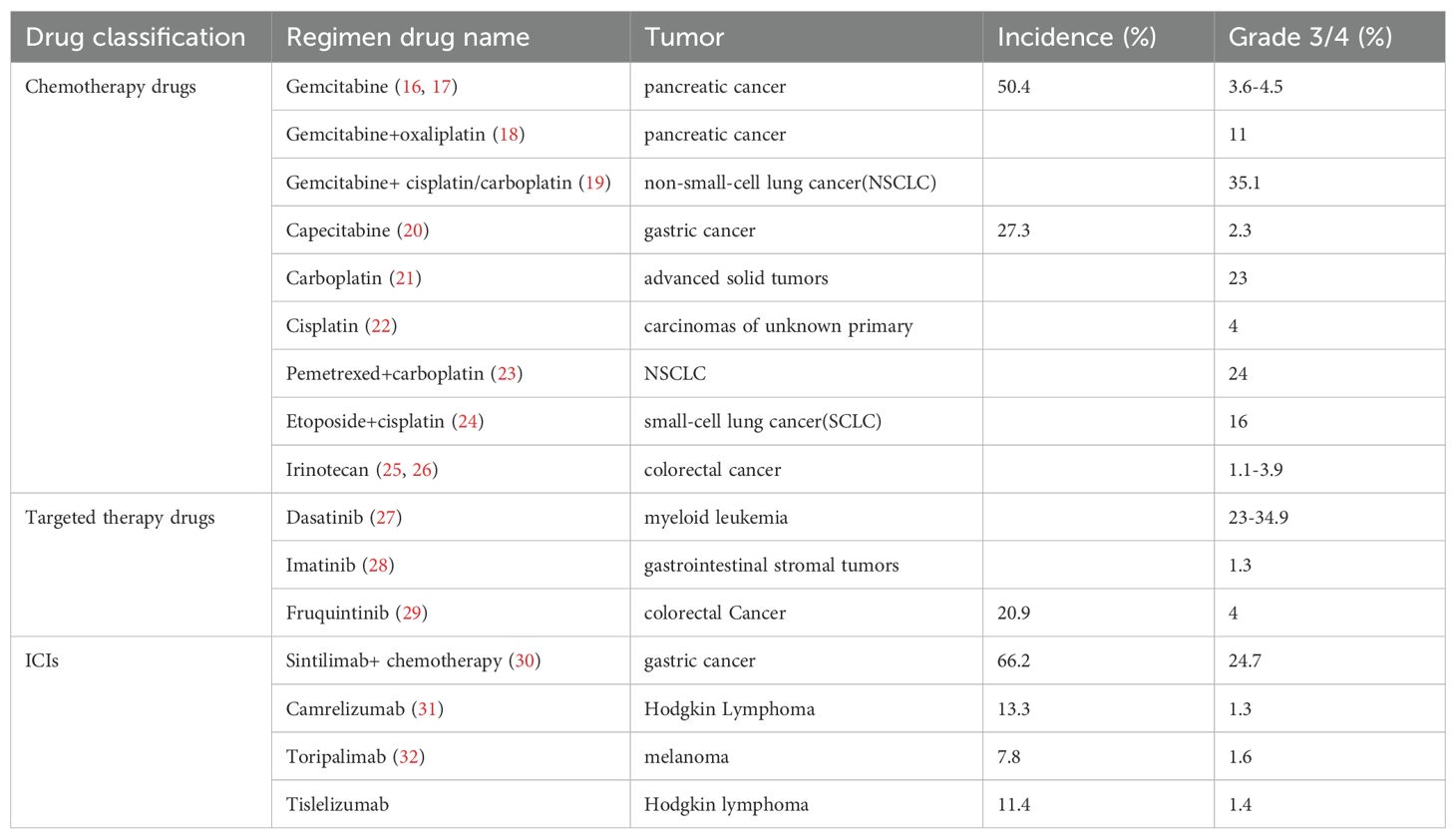
CIT’s prevalence varies significantly depending on the types of cancer and the specific chemotherapy regimens employed. CIT was most commonly observed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (25%), ovarian cancer (24%), and colorectal cancer (18%) (2). Studies have shown that CIT can affect up to 50% of patients undergoing certain chemotherapy protocols, particularly in hematological malignancies and solid tumors treated with myelosuppressive drugs (13). A clinical study in the United States enrolled adult patients with solid tumors and hematological malignancies receiving chemotherapy to investigate the risk of thrombocytopenia in chemotherapy regimens. The overall incidence of CIT was 13%, grade 3 thrombocytopenia (PLT: 25-50×109/L) and grade 4 thrombocytopenia (PLT: < 25 × 109/L) was 4% and 2%,respectively. The incidence of thrombocytopenia varies by tumor type and chemotherapy regimen, with grade 3 thrombocytopenia occurring in approximately 4% of patients with solid tumors and 16% of patients with hematologic malignancies (14). Thrombocytopenia prevention can ensure that chemotherapy goes smoothly as planned and is beneficial to the long-term survival of patients. In a systematic review and meta-analysis which included 125 clinical trials and 20,128 patients, the incidence of ICIIT was 1.16%,82 patients occurred ICIIT-related deaths (15). The incidence of thrombocytopenia caused by chemotherapy drugs, targeted therapy drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) is listed in Table 3.
2.3 Clinical symptoms of thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia present with a variety of clinical symptoms that are often indicative of its severity and underlying causes, not only characterized by reduced platelet count. Patients may experience easy bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts and spontaneous bleeding, such as petechiae or purpura on the skin. In more severe cases, patients might present with significant hemorrhage, including gastrointestinal bleeding or intracranial hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening. The clinical manifestations can vary depending on the etiology of the thrombocytopenia. For instance, in cases of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), patients may exhibit more pronounced skin manifestations, while those with thrombocytopenia due to bone marrow suppression may show signs of anemia or leukopenia as well (4, 33). Additionally, patients with underlying conditions such as liver disease may present with coagulopathy, further complicating the clinical characterization. In addition to causing bleeding in skins and internal organs, CIT may also lead to a delay in subsequent chemotherapy cycles, dose reduction, treatment interruption, and a decrease in relative dose intensity (delivered dose intensity/standard dose intensity), thereby affecting therapeutic efficacy (34). Understanding these manifestations is crucial for timely diagnosis and management, as they can significantly affect patient outcomes. The median time to the first drop in platelet count is 1–2 weeks after chemotherapy; with certain agents, CIT may appear beyond 2 weeks (14). ICIIT typically occurs within 12 weeks after drug initiation, with a median onset of approximately 41 days (35, 36); however, it can arise at any time, even after treatment has been discontinued.
2.4 Influencing factors of CTIT
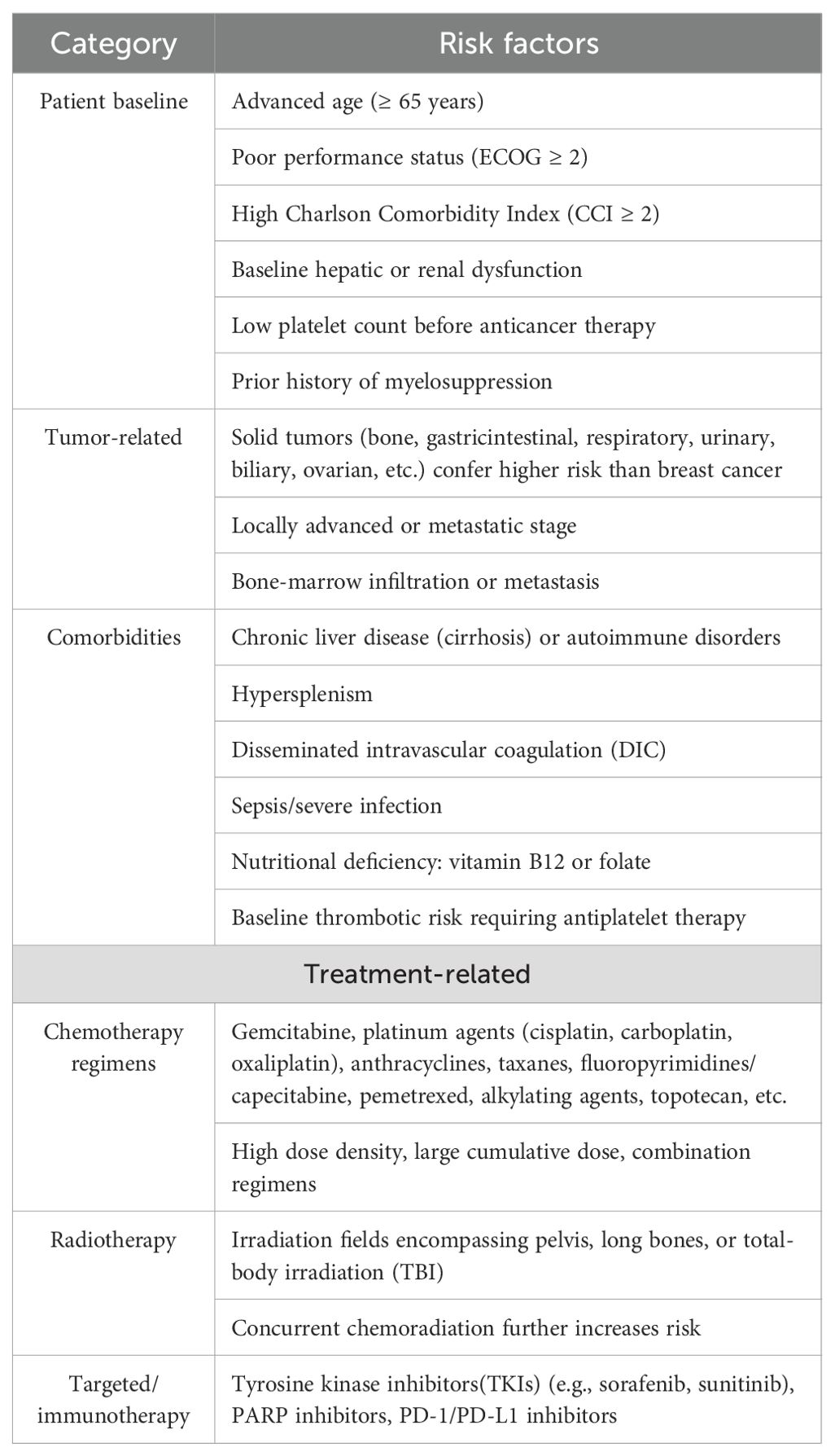
CTIT is characterized by decreased platelet count due to the cytotoxic effects of anti-tumor drugs, understanding the multifactorial causes of CTIT is essential for effective management and prevention strategies. The risk factors for CTIT are listed in Table 4 and can be grouped into four dimensions—patient baseline, tumor, treatment, and comorbidities. All key points are derived from high-quality cohort studies published in 2024 and the most recent expert consensus (37).
A multivariable model regression analyses exhibited three predictive variables for CIT which includes high ferritin, estimated glomerular filtration rate(eGFR)<60ml/min/1.73m2 and body mass index (BMI)<23kg/m2,and the model owned good predictive accuracy (38). Among a comprehensive analysis of various clinical and laboratory indicators, tumor site, treatment line, AST levels, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine were identified as important factors that influenced the occurrence of CIT (39). In a retrospective study, serum potassium ion, serum lactate dehydrogenase, platelet count, red blood cell count, and estimated glomerular filtration rate were predictors of serious CIT (40). One study also reported that chemotherapy, bone or brain metastasis were risk factors for thrombocytopenia during radiotherapy (41). Renal function is an important factor affecting chemotherapy-related thrombocytopenia (38), and patients with inadequate renal function have a greater degree of thrombocytopenia and poorer tumor treatment outcomes. The reason is that improved renal function leads to enhanced elimination of chemotherapy drugs, thereby reducing the adverse effects on megakaryocytes.
3 The mechanisms of anti-tumor drugs induced thrombocytopenia
3.1 CIT
The occurrence of CIT is multifactorial, involving various mechanisms that disrupt normal hematopoiesis and platelet production (7). Chemotherapy drugs are known to not only target cancer cells but also exert a significant inhibitory effect on bone marrow hematopoiesis (42). The cytotoxic effects of chemotherapeutic agents can lead to reduction in the number of megakaryocytes, the precursor cells that give rise to platelets. Additionally, the bone marrow microenvironment may be altered by chemotherapy, leading to further impairment of hematopoietic function and exacerbating thrombocytopenia (43). Chemotherapy drugs can cause drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia, platelet antibodies can be detected in the blood of patients, resulting in increased destruction of platelets. Previous studies have reported that repeated use of oxaliplatin can induce and sustain immune responses, leading to immune thrombocytopenia (44–47). Oxaliplatin can cause injury to the hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells, disrupting the sinusoidal barrier and subsequently leading to collagen deposition and veno-occlusive fibrosis. This damage increases intrahepatic vascular resistance and causes portal hypertension. Thrombocytopenia in this context is moderate but prolonged, typically appearing after about 18 weeks of treatment (46, 48). Due to splenomegaly, there is an increase in the sequestration and destruction of platelets within the spleen (49).
Thrombocytopenia was observed in 7%–25% of patients treated with a carboplatin-based regimens, which occurred more frequently than those receiving cisplatin-based regimens (50). When gemcitabine is used as a single-agent chemotherapy, the incidence of thrombocytopenia is approximately 3.4% to 12%. This incidence is significantly higher when used in combination chemotherapy regimens(such as gemcitabine/carboplatin) (51–54). Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare but severe complication in the treatment of gemcitabine characterized by hemolysis, thrombocytopenia, renal insufficiency and neurological symptoms with an incidence of 0.015% to 1.4% (55). Anthracycline drugs exert their antitumor effects by intercalating into the DNA double helix, thereby inhibiting the synthesis of DNA and RNA. However, this mechanism also exerts toxicity on normal hematopoietic cells, particularly on megakaryocytes in the bone marrow, leading to a reduction in platelet production (56). During the metabolic process in the body, anthracycline drugs generate free radicals, which lead to oxidative stress and subsequently damage hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow and platelets (57). The incidence of grade 3 thrombocytopenia during bortezomib treatment for relapsed, refractory myeloma is relatively high, which is approximately 14.5% (58).
3.2 ICIIT
ICIs have become a breakthrough in cancer treatment. For patients with NSCLC, ICIs are generally safer and better tolerated compared to cytotoxic drugs. However, their immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are increasingly receiving concern in clinical practice, especially the hematological irAEs (haem-irAEs), which are infrequent but can be life-threatening (59). The incidence rate of immune-related thrombocytopenia (irTCP) is 1.16%, with 82 cases of death related to ICIIT (0.45%) (15, 60). When used alone, the incidence of thrombocytopenia with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors is only 0.2%, but when combined with other treatments, the incidence can significantly increase to 6% to 6.8% (61–63). Consequently, ITP has emerged as the most prevalent haem-irAE in immunotherapy. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is a common method for treating primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). In the treatment of ITP, IVIG can temporarily block the destructive effects of antibodies on platelets, thereby increasing the number of platelets. The interval between treatments depends on the platelet count and the condition of the disease, usually once a week (63). In addition, IVIG is also used in other irTCP conditions, such as ICIIT, and can rapidly increase platelet count to a safe level, especially in emergency situations (64).
A retrospective study launched by Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center reviewed patients treated with ICIs between January 2011 and June 2017. The results indicated that out of 1038 patients treated with ICIs, 89 (8.6%) developed grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia, and 18 (20%) were attributed to ICIs after manual review and exclusion of other causes (accounting for 1.73% of the entire cohort). Thrombocytopenia and leucopaenia occurred earlier than the other hem-irAEs among ICI-treated cases such as autoimmune hemolytic anemia, with a median time of 40 days, and the onset of haem-irAEs was earlier in patients treated with combination therapy than monotherapy (65). The incidence of irTCP seemed to be lowest among patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy (p = 0.059). Patients who developed grade 3 or higher irTCP had poorer overall survival (66). In previous case reports related to ICIIT, corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, and TPO-RAs were administered, with 5 cases showing improvement and 3 cases resulting in death (67). A retrospective study of 2,360 melanoma patients treated with ICIs showed that less than 1% of patients experienced thrombocytopenia, with the majority of these patients’ platelet count returning to normal on their own (68).
The number of reported ITP cases is the most common in nivolumab and pembrolizumab in a systematic review study, there were 125 cases of ITP reported with pembrolizumab and 160 cases reported with nivolumab,338 cases totaled for all drugs. Higher incidence of ITP cases associated with PD-1 inhibitors nivolumab and pembrolizumab in comparison with oxaliplatin was noticed, but similar reporting with the PD-L1 inhibitors atezolizumab, avelumab,and durvalumab. In the literature review, melanoma (35%) and non-small-cell lung cancer (39%) were identified as the predominant types of cancer reported ICIIT in the case studies (69).
Some mechanisms at the cellular level have been proposed in irTCP caused by anti-tumor immune therapy (65, 70) and is shown in Figure 1. ICIs such as PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors can cause immune system activation and exhausted CD4+ helper T cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are reactivated (36). These activated T cells can secrete cytokines (such as IFN-γ, TNF-α, etc.) that lead to changes in the bone marrow microenvironment, thereby damaging hematopoietic stem cells and megakaryocytes (71). Cytokine storm induced by immunotherapy is a systemic inflammatory response that can be triggered by various causes, including infection, autoimmune diseases and adverse reaction to cancer immunotherapy (72).In the process of immunotherapy, cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is especially conscious of when using ICIs and immune cell therapies and relevant to adverse reaction to cancer immunotherapy (73). Cytokines manifest over-activating of the immune system which increases the incidence of irAEs after initiating ICI and serves as prediction of platelet count decrease (74). ICIs may induce or increase the production of specific anti-platelet antibodies, which can bind to platelets, marking them for phagocytosis and destruction by macrophages (75, 76). When patients have platelet antibodies in their bodies, the transfused platelets may be rapidly destroyed, leading to ineffective transfusion. The detection of platelet glycoprotein-specific auto-antibodies is a test with high specificity for antibody-mediated immune thrombocytopenia, which can differentiate between immune and non-immune thrombocytopenia.
Moreover, activated T cells secrete a large number of serum cytokines, such as IL-23 and IL-17,which can lead to reduced platelet production and increased platelet destruction. In immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), the levels of IL-23 and IL-17 are elevated (77). IL-17 plays a particularly important role in the production of inflammatory cytokines and the infiltration of white blood cells and can promote inflammatory responses of the immune system (78). IL-17 can inhibit the differentiation and maturation of megakaryocytes mediated by TPO, and affect platelet production and function, thereby further exacerbating the pathological process of ITP (79, 80). IL-23 can lead to reduced platelet production in ITP patients through the differentiation and proliferation of Th17 cells (81). Conversely, interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine that plays an important role in immune responses, inflammatory reactions, hematopoiesis, and metabolic regulation (82). IL-6 can act synergistically with other cytokines to promote the growth of early bone marrow stem cells and enhance the differentiation of blood cells, including the production of platelets. IL-6 is a strong inducer of acute-phase proteins, which can induce hepatocytes to synthesize acute-phase proteins at the transcriptional level, including thrombopoietin (TPO), thereby indirectly affecting platelet production (83). The signaling pathways activated by IL-6 can affect the activation state and function of platelets, including platelet aggregation and adhesion.
Platelets expressing PD-L1 on their surface are direct target cells for ICIs. A study revealed that PD-L1 was transferred to platelets from tumor cells after co-incubated with various NSCLC cell lines, platelet PD-L1 (pPD-L1) was correlated with tumor stage, metastasis and overall survival (84). Platelets with high PD-L1 stimulated by atezolizumab mark improved immune surveillance and prevent T cell-mediated immune suppression (85).
3.3 TTIT
Targeted therapy has emerged as a revolutionary approach in oncology, focusing on specific molecular targets associated with cancer. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which indiscriminately affects rapidly dividing cells, targeted therapies aim to interfere with particular pathways critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation. Targeted therapies are designed to attack specific cancer cells, can inadvertently affect normal hematopoiesis, leading to adverse effects such as thrombocytopenia. For instance, the introduction of drugs targeting specific oncogenic pathways has been associated with varying degrees of hematological toxicity, including platelet depletion. Recent studies have highlighted the intricate relationship between novel targeted therapies and thrombocytopenia. Furthermore, the mechanisms underlying this relationship often involve the disruption of megakaryocyte function or direct toxicity to bone marrow, which is crucial for platelet production. In particular, therapies for metastatic breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer have shown a correlation with significant drops in platelet levels, necessitating careful monitoring of blood counts during treatment (86).
Thrombocytopenia is a common adverse effect associated with various targeted therapies, including PARP inhibitors, EGFR inhibitors, and CDK4/6 inhibitors. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials involving PARP inhibitors indicated a significant increase in the risk of thrombocytopenia, with an incidence rate of 2.54 (RR, 2.54; 95% CI, 1.87-3.45; p < 0.00001) compared to control groups. Notably, the risk of high-grade thrombocytopenia (grade ≥3) was also elevated (RR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.83-4.16; p < 0.00001) (87). In the context of EGFR inhibitors, studies have shown that agents like cetuximab and erlotinib can lead to thrombocytopenia, particularly in patients with pre-existing conditions or those receiving concomitant therapies (88). Meanwhile, CDK4/6 inhibitors, such as palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib, have been associated with varying degrees of hematologic toxicity, including thrombocytopenia, with palbociclib showing a higher incidence compared to the others (89, 90). A systematic review indicated that 51.1% of patients receiving CDK4/6 inhibitors experienced hematological toxicity, with thrombocytopenia being reported in 2.1% of cases (91). These findings highlight the prevalence of thrombocytopenia as a significant concern in patients undergoing targeted therapy, necessitating vigilant monitoring and management strategies.
Poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors are a class of anti-cancer drugs that target PARP and play an important role in the treatment of hereditary cancers with the same “rogue gene,” such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer (92–95). PARP1 is expressed in the megakaryocytic lineage and is involved in regulating the differentiation of bone marrow cells. PARP inhibitors affect the proliferation and maturation of megakaryocytes by inhibiting PARP1, thereby reducing the production of platelets (96). Inhibitors (e.g.,niraparib, olaparib) trap PARP1 at DNA damage sites, block repair pathways and trigger the accumulation of DNA breaks, thereby suppress the differentiation and maturation of CD34+ bone-marrow progenitors into megakaryocytes, reducing the formation of polyploid megakaryocytes and markedly decrease proplatelet formation and platelet release (97). Thrombocytopenia usually occurs in the first month of treatment and gradually shows a trend of recovery in the second or third month, with most cases being mild to moderate, that is, grades 1 to 2 (95). The combination of targeted therapies with chemotherapy has further implications for the risk of thrombocytopenia. Studies have demonstrated that the concurrent use of PARP inhibitors with chemotherapy regimens can exacerbate the incidence of hematological toxicities, including thrombocytopenia. Despite potential responsiveness, patients receiving PARP inhibitors alongside chemotherapy experienced a significant higher rate of grade 3 thrombocytopenia compared to those receiving chemotherapy or PARP inhibitors alone (98). This synergistic effect may be attributed to the myelosuppressive nature of both treatment modalities, which can lead to compounded risks of cytopenia. Moreover, the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in combination with endocrine therapy has been shown to improve progression-free survival but also results in a higher incidence of adverse events, including thrombocytopenia (99, 100). Therefore, understanding the incidence of thrombocytopenia associated with these targeted therapies, especially in combination with chemotherapy, is crucial for optimizing treatment regimens and improving patient outcomes.
The incidence of thrombocytopenia associated with ADCs, particularly trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) and trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), has been a focus of recent clinical studies. For instance, a systematic review revealed that T-DM1 was linked to a higher incidence of thrombocytopenia, with reported rates of grade 3 or higher thrombocytopenia reaching approximately 28.1% in TKIs treatment failed breast cancer patients (101). Furthermore, a retrospective cohort study highlighted that patients of Asian ancestry experienced a significantly higher incidence of dose adjustments due to thrombocytopenia when treated with T-DM1 or T-DXd, suggesting potential genetic predispositions that warrant further investigation (102). In clinical practice, the management of thrombocytopenia in patients receiving ADCs often necessitates dose modifications or supportive therapies, such as TPO-RAs, to mitigate treatment interruptions and enhance patient safety (88).
The mechanism by which PARP inhibitors induce thrombocytopenia primarily involves their impact on megakaryocyte differentiation and function. Research indicates that the inhibition of PARP activity can disrupt the signaling pathways essential for megakaryocyte maturation, leading to impaired platelet production. This effect is particularly pronounced in patients with pre-existing low platelet count or those undergoing combination therapies that exacerbate myelosuppression (103). Additionally, ADCs, which deliver cytotoxic agents directly to tumor cells, can inadvertently affect normal hematopoietic cells, including megakaryocytes, resulting in diminished platelet output (104). By delivering cytotoxic agents directly to cancer cells, ADCs can inadvertently affect normal hematopoietic cells, including megakaryocytes. The cytotoxic payload can lead to cell death in these progenitor cells, resulting in reduced platelet production. Additionally, the immune response elicited by ADCs can further contribute to thrombocytopenia through mechanisms such as increased phagocytosis of platelets by activated macrophages (105). The interplay between these therapies and the immune system also plays a crucial role. For example, in ITP, the presence of auto-antibodies against platelets can lead to their premature destruction, a complication that may be exacerbated by certain cancer therapies. Furthermore, the activation of immune pathways by these drugs can lead to an increase in macrophage-mediated clearance of platelets, thereby contributing to thrombocytopenia (106, 107). Moreover, the role of the tumor microenvironment in modulating these effects cannot be overlooked. Tumors can secrete various cytokines that influence hematopoiesis and megakaryocyte function, potentially exacerbating the thrombocytopenic effects of both PARP inhibitors and ADCs (108).
4 Current status of traditional treatment methods
4.1 Indications and limitations of platelet transfusion
Platelet transfusion remains a critical intervention for managing thrombocytopenia, particularly in patients undergoing chemotherapy, those with hematological malignancies, or individuals with severe bleeding disorders. The primary indications for platelet transfusion include active bleeding, planned surgical procedures, and prophylaxis against bleeding in patients with severely low platelet count (109). Platelet transfusion can effectively reduce the risk of bleeding and mortality, which is the fastest and most effective way to treat severe thrombocytopenia, but it also has risks and complications. For instance, patients may have an allergic or febrile reaction to platelet products. Platelet transfusions may exacerbate thrombosis and should be approached with caution. Platelet transfusions can lead to alloimmunization, where the recipient develops antibodies against donor platelets, resulting in transfusion rejection. This condition complicates further injection and may necessitate the use of HLA-matched platelets, which are not always available (110, 111). Additionally, the risk of transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) and other adverse reactions further complicates the use of platelet transfusions. Transfusions of components containing platelet antibodies may trigger acute and severe thrombocytopenia with transfusion reactions and bleeding (112). Recent studies indicate that the effectiveness of platelet transfusions can be influenced by various factors, including the storage conditions of platelets and the presence of underlying conditions in the recipient, such as sepsis or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).The activity of platelets is greatly affected by temperature, and the optimum storage temperature is 22°C ± 2°C.The shelf life of platelets at room temperature is only 3–7 days. Maintaining an adequate supply of platelets requires a lot of resources, and platelets stored at room temperature are prone to bacterial contamination, which may lead to infection and even sepsis (113).
4.2 Application and effects of interleukin-11
Interleukin-11 (IL-11) has emerged as a therapeutic cytokine in the treatment landscape for various hematological disease conditions. Its application primarily revolves around its ability to stimulate megakaryocyte and platelet production, making it a potential effective agent for thrombocytopenia. This cytokine has been shown to enhance platelet recovery in patients suffering from CIT, thereby reducing the incidence of severe thrombocytopenia and its associated complications. Research has demonstrated that rhIL-11 can effectively shorten the duration of thrombocytopenia and increase platelet count, making it a valuable option in the therapeutic arsenal against CIT (114).
4.2.1 Mechanisms of rhIL-11
RhIL-11 is a cytokine that plays a significant role in various biological processes, particularly in hematopoiesis and immune regulation. It is primarily known for its ability to stimulate thrombopoiesis, which is the production of platelets from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. The therapeutic application of rhIL-11 has been particularly highlighted in the context of CIT, where it aids in the recovery of platelet count in patients undergoing cancer treatments that adversely affect bone marrow function. The mechanism by which rhIL-11 exerts its effects involves the activation of specific signaling pathways that promote megakaryocyte proliferation and maturation, ultimately leading to increased platelet production.Additionally,rhIL-11 has been implicated in other physiological processes such as inflammation and tissue repair, showing its multifaceted role in human health (115).
4.2.2 Biological characteristics of rhIL-11
Interleukin-11 (IL-11) is secreted by human bone marrow stromal cells and interstitial cells, which can directly stimulate the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells and megakaryocyte progenitors. The biological characteristics of rhIL-11 are crucial for understanding its therapeutic potential. RhIL-11 is a glycoprotein that belongs to the IL-6 cytokine family, exhibiting structural and functional similarities with other interleukins. It is produced in recombinant form primarily using Escherichia coli, which poses challenges in terms of expression levels and the formation of inclusion bodies (116). Recent technical advance has enabled the efficient production of tag-free rhIL-11,enhancing its biological activity and structural integrity. The purified rhIL-11 demonstrates a compact and ordered structure, which is essential for its biological function. In vitro studies have shown that rhIL-11 can stimulate the proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells, indicating its role in enhancing platelet production and supporting the recovery of patients with thrombocytopenia (117). It enhances the maturation of these cells and promotes the shedding of platelets into the circulation. Moreover, rhIL-11 has been shown to modulate the immune response, further emphasizing its importance in therapeutic applications (118).
4.2.3 Application of rhIL-11 in tumor treatment
RhIL-11 has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent in the management of CIT, a common complication in cancer treatment. Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of rhIL-11 in enhancing platelet count and mitigating adverse effects associated with low platelet levels. A systematic review involving ten randomized controlled trials indicated that rhIL-11 significantly reduced the recovery time of platelet count and decreases the volume of platelet transfusion required in patients with acute leukemia undergoing chemotherapy (114). Furthermore, real-world studies have corroborated these findings, showing that rhIL-11 treatment can provide comparable results in platelet recovery when compared to rhTPO, albeit with lower associated treatment costs (119). In solid tumors, rhIL-11 has been demonstrated to improve platelet count effectively, thus facilitating the continuation of chemotherapy regimens without significant delays or interruption. Studies have also indicated that rhIL-11 not only enhances platelet recovery but also reduces the incidence of bleeding complications associated with low platelet count (120, 121).
4.2.4 Adverse reactions and safety management of rhIL-11
RrhIL-11 is known as a therapeutic agent in treating conditions such as ITP and CIT. However, its use is associated with several adverse reactions that needs attention. Clinical studies have indicated that rhIL-11 can lead to significant cardiovascular effects, including elevated serum brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels, which may indicate heart strain or failure. Furthermore, patients receiving rhIL-11 have reported instances of edema and weight gain, alongside fluctuations in blood pressure, which necessitates careful monitoring during treatment (122). In hepatocyte cell lines,rhIL-11 also induces secretion of acute phase proteins (ferritin, fibrinogen,C-reactive protein, haptoglobin, and hemopexin) in vitro. In consideration of rhIL-11’s anti-inflammatory effects and protection from epithelial damage,rhIL-11 treatment may ameliorate systemic inflammatory diseases and stimulate epithelial wound healing (123).
4.3 RhTPO in the treatment of thrombocytopenia in anti-cancer therapy
4.3.1 Pharmacological effects of rhTPO
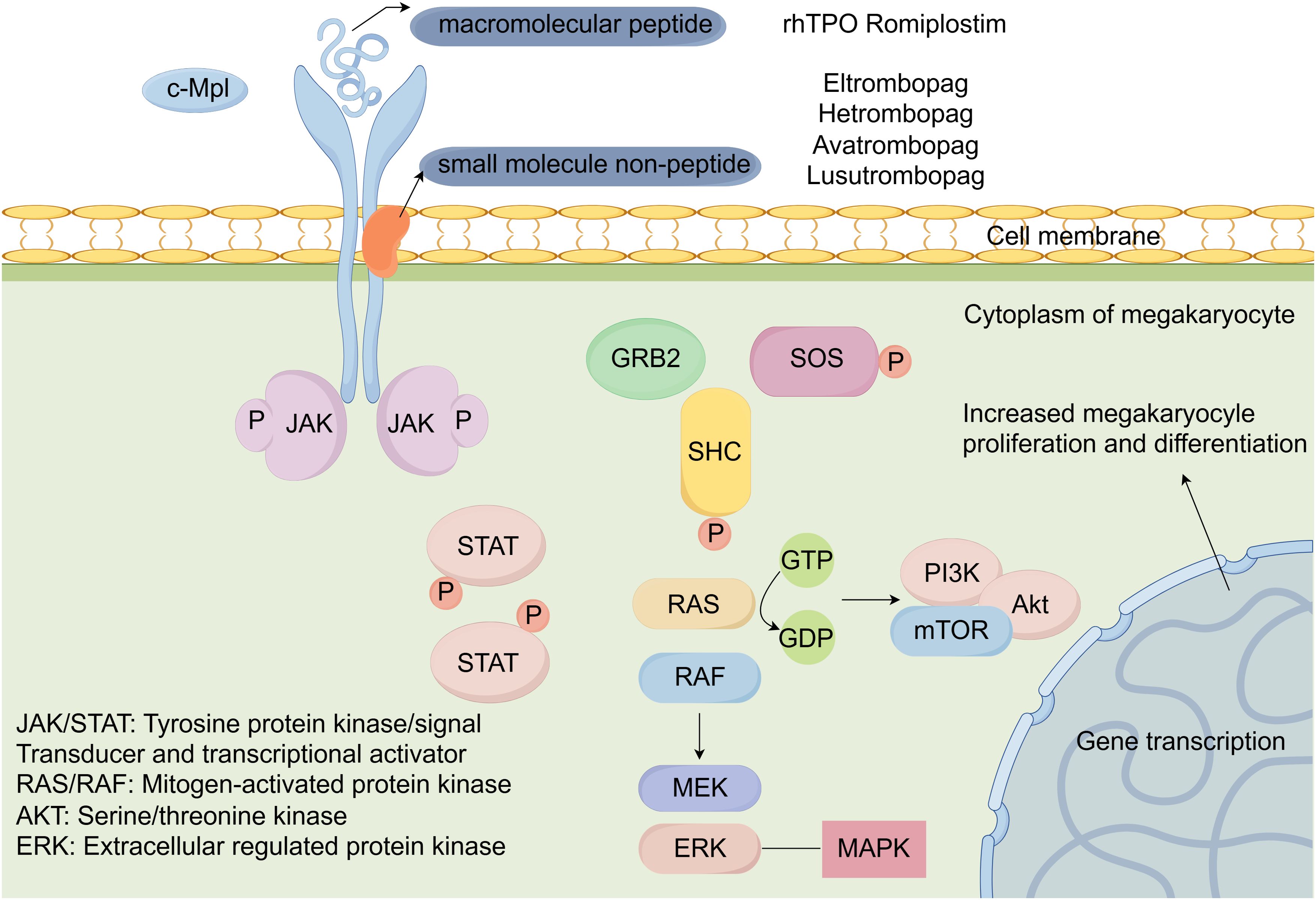
Thrombopoietin (TPO) is the most important regulator of megakaryocyte proliferation, differentiation, maturation, and platelet production. It can act on primitive hematopoietic stem cells and cooperate with erythropoietin (EPO) and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and has been demonstrated to stimulate the recovery of platelet levels and promote the reconstitution of hematopoietic function (124). RhTPO is a critical biological drug widely utilized in the treatment of various types of thrombocytopenia. Its pharmacological effects are primarily attributed to its ability to stimulate megakaryocyte proliferation and enhance platelet production in the bone marrow by binding to the thrombopoietin receptor, which activates intracellular signaling pathways critical for hematopoiesis. The downstream signaling cascades including the Janus tyrosine Kinase and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway, Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt (PI3K/Akt) pathway, and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. These pathways collectively promote the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of megakaryocyte progenitor cells in the bone marrow (33, 125). By promoting the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells into megakaryocytes, rhTPO plays a pivotal role in increasing platelet count, thereby mitigating the risks associated with low platelet levels, such as bleeding and improves treatment tolerability.
4.3.2 Clinical research on the application of rhTPO in tumor treatment
In a phase I and II clinical trial, the addition of rhTPO to chemotherapy regimen demonstrated a marked restoration of platelet count and a sustained platelet recovery response (126). The role of rhTPO in patients receiving cytarabine has been investigated and prophylactic administration of thrombopoietin reduced the incidence and duration of thrombocytopenia and platelet transfusion rate, indicating the beneficial use of rhTPO before intensive chemotherapy (127). Professor Vadhan-Raj earlier proposed the importance of early application of rhTPO to alleviate early thrombocytopenia caused by chemotherapy (128). Subsequently, several clinical studies evaluating rhTPO’s efficacy in the treatment of CIT were also conducted (127, 129, 130). The results suggest that prophylactic use of rhTPO can reduce the degree and duration of thrombocytopenia and promote early platelet recovery in patients with solid tumors after chemotherapy without causing serious adverse effects. A multi-center cross-sectional study indicated that rhTPO was frequently used among patients experiencing thrombocytopenia due to targeted therapies and immunotherapy, with outcomes showing comparable platelet recovery rates across different thrombopoietic agents (131).
4.4 Thrombopoietin receptor agonist serves as a promising therapy in thrombocytopenia
TPO plays a vital role in the regulation of platelet production and is primarily produced by liver and works on the thrombopoietin receptor (TPO-R), which is expressed on megakaryocytes and hematopoietic stem cells. Cellular mechanisms of activation of TPO-RAs are shown in Figure 2. TPO activates JAK/STAT and Ras/MAPK signaling pathways by binding to the surface receptor and induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a variety of proteins, including JAK2 and STAT5 proteins, thereby activating megakaryocytes and promoting their proliferation and differentiation into platelets (132). This process is essential for maintaining normal platelet count, which is crucial for hemostasis and the prevention of bleeding disorders. In the context of cancer treatment, the disruption of this process can ultimately lead to CTIT (133). Thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonists have emerged as a novel therapeutic approach to mitigate this adverse effect, playing vital pharmacological roles in enhancing platelet count. These agents mimic the action of endogenous TPO by stimulating the TPO-R, thereby being increasingly recognized as a crucial component of supportive care in cancer treatment.
A network meta-analysis indirectly evaluated the effects of five TPO-RAs in treating ITP. The analysis included 20 RCTs with data from 2,207 patients. All TPO-RAs significantly improved platelet response and reduced the incidence of bleeding events. compared to placebo. Avatrombopag and lusutrombopag showed the best platelet increase response, while avatrombopag having a non-significant advantage over lusutrombopag. Lusutrombopag had the lowest risk of bleeding compared to placebo, followed by eltrombopag, romiplostim, and avatrombopag. Romiplostim had the lowest rate of severe adverse events, followed by avatrombopag, eltrombopag, and lusutrombopag (134).
4.4.1 Eltrombopag
Eltrombopag is a non-peptide thrombopoietin receptor agonist that plays a crucial role in stimulating platelet production in patients with thrombocytopenia. By binding to the thrombopoietin receptor (MPL), eltrombopag mimics the action of endogenous thrombopoietin, resulting in increased megakaryocyte maturation and subsequent release of platelets into the bloodstream (135). This mechanism is beneficial for treating thrombocytopenia associated with various conditions, including ITP, aplastic anemia, and CIT. Recent studies have also indicated that eltrombopag may exert additional effects beyond mere stimulation of megakaryopoiesis. For instance, it has been shown to possess immunomodulatory properties, potentially influencing T-cell responses and reducing inflammatory cytokines, which can contribute to its therapeutic efficacy in various hematological disorders (136, 137).
In a phase 2 clinical trial, it involved patients with solid tumors including non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and others, and was conducted to compare the efficacy of eltrombopag with placebo. The results showed that the mean time for platelets to recover from nadir was 8 days in the eltrombopag group and 15 days in the placebo group. Patients in the eltrombopag treatment group had fewer platelet count below 100×109/L, fewer doses modification, and fewer adverse events (138). A real-world observational study compared eltrombopag with rhTPO and found that both agents had comparable efficacy and safety in terms of increased platelet count, prolonged platelet response time, reduced bleeding events, and reduced need for platelet transfusions in lymphoma patients experiencing severe thrombocytopenia following chemotherapy (139). However, it should be noted that the higher the highest platelet count after eltrombopag treatment, the greater the likelihood of side effects. The reported incidence of treatment-related adverse events has been relatively low, with studies indicating that only 12-14% of patients experience mild and transient adverse reactions, including headache (21.6%), asthenia (13.7%), hepatotoxicity (11.8%), and thrombosis (5.9%) (139, 140).
4.4.2 Hetrombopag
Hetrombopag is developed through structural modifications of eltrombopag, which are designed to enhance its potency while reducing toxicity. On 16 June 2021,Hetrombopag was first approved in China for treating adult patients with primary ITP who had shown poor response to prior treatments like glucocorticoids and immunoglobulins and was conditionally approved for the treatment of severe aplastic anemia (SAA) in patients refractory to immunosuppressive therapy. Hetrombopag stimulates intracellular thrombopoietin signaling pathways (including STAT3, STAT5, ERK1/2 and AKT) and promotes megakaryocyte proliferation and differentiation in proportion to concentration (141).
Results from recent clinical trials have shown promising efficacy for hetrombopag (142–144), with significant improvements noted in enhanced responses in patients with specific cancer types, underscoring the drug’s potential as a valuable therapeutic option, particularly in oncology. For instance, hetrombopag significantly improved the condition of low platelet count after chemotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors in a randomized, placebo-controlled phase II study. The response rate of the comparative groups was 60.7% (17/28) versus 12.9% (4/31) respectively. Most commonly observed adverse events were decreased neutrophil counts and anemia (145). Hetrombopag showed synergistic effect in stimulating platelet production when in combination with rhTPO, necessitating an effective management of thrombocytopenia. The proportion of recovery patients was higher than rhTPO alone, there was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the two groups which involved bleeding, platelet transfusion, elevated liver enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia, fever, fatigue, diarrhea (146). In consistence with this clinical advantage, hetrombopag combined with rhTPO generated proliferation-promoting effect and anti-apoptotic effect in TPOR-expressing cells through stimulation of STAT, PI3K and ERK signaling pathways (141).
4.4.3 Romiplostim
Romiplostim is produced in Escherichia coli by recombinant DNA technology a recombinant fusion protein containing two identical single-chain subunits, each of which is covalently linked by a Fc domain of human immunoglobulin IgG1 and a short peptide with high affinity for the TPO-R consisting of 14 amino acids (147, 148). Romiplostim has no sequence homology to endogenous TPO and stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocytes through the binding and activation of TPO-R and stimulation of C-Mannosylation of thrombopoietin(c-Mpl),JAK2-STAT5,PI3K/Akt, MEK/ERK, and p38 downstream signaling pathways, thereby producing pharmacological efficacy (147). Romiplostim is prevented from being cleared by the renal route when bound to the c-Mpl receptor. Preclinical study indicated that romiplostim not only increased platelet count but also had immunomodulatory effects by lowering anti-platelet antibody levels (149, 150). Romiplostim is also considered an alternative treatment option for patients who respond negative to rhIL-1 or rhTPO.
Soff et al. (151) reported a randomized controlled prospective trial comparing the efficacy of romiplostim and observation in patients with CIT from solid tumors. The therapeutic regimen was altered because romiplostim significantly increased the proportion of patients with platelet recovery within 3 weeks of treatment compared to the observation group (93% vs 12.5%). All patients in the observation group were subsequently crossed over to the romiplostim treatment group and continued to receive romiplostim prophylaxis for CTIT during subsequent chemotherapy and a similar response rate was observed. Al-Samkari et al. (152) performed a multi-center study including 173 patients across four US centers, with a focus on assessing the effectiveness and safety of romiplostim, as well as identifying predictors of non-response. The study found that 71% of solid tumor patients achieved a romiplostim response (defined as a median platelet count≥75×10^9/L and ≥30×10^9/L above baseline while on treatment),the median platelet count on romiplostim was significantly higher than baseline (116×10^9/L vs. 60×10^9/L; p<0.001) and 79% of solid tumor patients avoided chemotherapy dose reductions or treatment delays, and 89% avoided platelet transfusions. Bone marrow (BM) invasion by tumor, prior pelvic irradiation, and prior exposure to temozolomide were identified as significant predictors of romiplostim non-response. Patients with these predictors had lower response rates (23%, 20%, and 46% respectively).Weekly romiplostim dosing was superior to intracycle dosing in terms of higher response rates (81% vs. 63%) and fewer chemotherapy dose reductions/treatment delays (IRR 3.00, P = 0.010) and bleeding events (IRR 4.84, P = 0.029).In patients with non-myeloid hematologic malignancies(lymphoma and myeloma), the response rate was lower (10%), with only 35% achieving a platelet count ≥100×10^9/L. The median platelet count improved from 21×10^9/L at baseline to 46×10^9/L on romiplostim.
Refractory CTIT is generally defined as: platelet count remains <50 × 109/L or cannot be sustained ≥50 × 109/L after an adequate dose and duration (≥4–6 weeks) of TPO-RA therapy (romiplostim or eltrombopag); or ongoing reliance on platelet transfusions for support (43, 153). Real-world data show that romiplostim non-responders have a chemotherapy relative dose intensity (RDI) below 60% within six months and a 25% reduction in overall survival (OS) (152). Tailored escalation of TPO-RAs or combination strategies coupled with investigations into stem-cell or megakaryocyte replacement therapies constitutes the central management paradigm.30–40% of patients achieve a secondary response by switching TPO-RAs (154). Combining low-dose decitabine (3-day cycles) or low-dose cyclosporine A (1–2 mg/kg) can overcome immune barriers (155).
4.4.4 Lusutrombopag
Lusutrombopag is a small-molecule thrombopoietin receptor agonist(TPO-RA) that has gained attention for its potential use in managing thrombocytopenia, including CTIT. Lusutrombopag has a high affinity for the TPO receptor and is designed to specifically target this receptor without cross-reactivity to other receptors, minimizing off-target effects. Lusutrombopag activates downstream signaling pathways, such as the JAK2-STAT pathway. Lusutrombopag is primarily metabolized in the liver through enzymatic processes. The metabolites are then excreted through both renal and biliary pathways (156, 157). Lusutrombopag has received marketing authorization in Japan, the United States, and Europe for thrombocytopenia associated with chronic liver disease and platelet elevation therapy prior to elective invasive surgery or diagnostic procedures.
Sato et al. (157) reported the efficacy of lusutrombopag in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent both radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization. The patients’ platelet count increased to 98 × 109/L after 5 consecutive days of lusutrombopag treatment. After lusutrombopag usage within 7 days after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, the platelet count reached more than 50 × 109/L. Ishikawa et al. (158) reported the efficacy and safety of retreatment with lusutrombopag before multiple planned radiofrequency ablation in 8 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and thrombocytopenia. The results of the study showed that repeated use of lusutrombopag did not reduce its effect on increasing platelet count. The drug significantly reducing the need for chemotherapy dose reductions, treatment delays, and platelet transfusions. Lusutrombopag has demonstrated a favorable safety profile in clinical trials. Common side effects are generally mild and may include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and diarrhea. Serious adverse events, such as thromboembolic events, have been reported at low rates, but they need to be carefully monitored, especially in high risk populations (159).
4.4.5 Avatrombopag
Avatrombopag is an orally bioavailable small molecule TPO-RA. Avatrombopag does not compete with TPO for binding to the TPO receptor and has an additive effect with TPO on platelet production. Avatrombopag is primarily metabolized through the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system, with CYP2C9 and CYP3A being the main isoenzymes involved. Avatrombopag is > 96% bound to human plasma proteins and has extensive distribution according to in vitro data (160). It is the third TPO-RA approved for the treatment of ITP and the first approved for the treatment of perioperative thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease. Avatrombopag provides an alternative to blood transfusion in these patients. Unlike eltrombopag, the use of avatrombopag does not require a 4-hour window of caloric restriction and does not have the associated problems of hepatotoxicity in patients with ITP or portal vein thrombosis in patients with chronic liver disease (161).
Results of a phase 3 randomized controlled trial of the efficacy and safety of avatrombopag in CIT have been published for better understanding the benefits of avatrombopag in clinical setting (162). This international, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, phase 3 study enrolled 122 patients aged 18 years or older with ovarian, bladder, or lung cancer receiving chemotherapy and experiencing severe thrombocytopenia (platelet count <50 × 109 cells/L). Patients were randomized into 2:1 to receive either avatrombopag 60 mg or placebo orally daily for 5 days before and after chemotherapy. Only 69.5% of patients treated with avatrombopag met the primary endpoint of avoiding platelet transfusion, reducing the dose of chemotherapeutic agents, and delaying administration, compared with 72.5% of patients treated with placebo. However, avatrombopag increased the lowest platelet count compared to placebo (51×109cells/L vs. 29.1×109 cells/L).Avatrombopag was safe and well-tolerated, with no increased incidence of thromboembolic events. The study suggests that further investigation of avatrombopag in patients with more persistent CIT might be required to confirm its ability to increase platelet count.
Recently, the potential benefits of combining TPO receptor agonists with platelet transfusion in managing CIT have been reported (163). The study retrospectively collected clinical data from 120 patients with malignant tumors who developed thrombocytopenia following chemotherapy. Patients were randomly divided into three groups: Group A received avatrombopag, Group B received autologous platelet transfusion, and Group C received a combination of both treatments. The study found that Group C (combination treatment) achieved the highest effective rate of 97.50%,significantly higher than Group A (avatrombopag alone) at 80.00% and Group B (autologous platelet transfusion alone) at 77.50% (P < 0.05). The time for platelet count recovery was significantly shorter in Group C. Group C had significantly higher levels of PF4, TPO, and vWF compared to Groups A and B (P < 0.05). Post-treatment levels of APTT and PT decreased in all groups, with Group C showing significantly lower APTT compared to Groups A and B (P < 0.05). In conclusion, the combined therapy resulted in faster platelet recovery, higher platelet count, and improved coagulation function indicators.
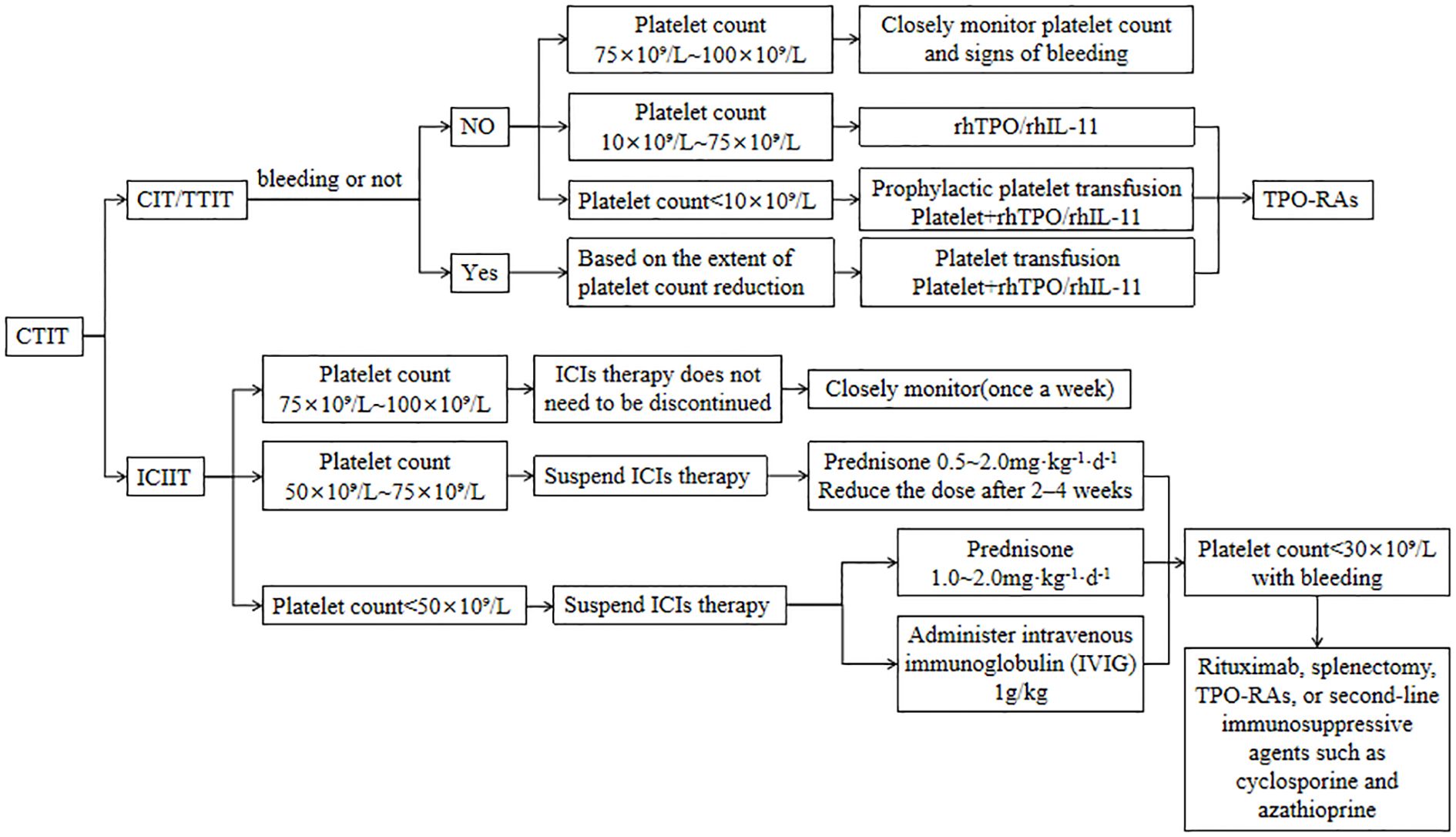
CTIT management should first clarify the etiology, assess bleeding risk, and then tailor the therapeutic strategy according to the underlying cause and CTIT severity; the main interventions are platelet transfusion and administration of thrombopoietic growth factors. While administering thrombopoietic agents, closely monitor for adverse reactions, promptly manage any events that occur, and thereby maximize treatment safety and efficacy. Grade 3–4 thrombocytopenia warrants immediate treatment discontinuation, whereas patients on long-term antineoplastic therapy who develop grade 1–2 thrombocytopenia without bleeding can continue the original regimen under close monitoring. Therapeutic algorithm for CTIT is shown in Figure 3.
4.5 Application of caffeic acid tablets in CTIT
Caffeic acid tablets, an emerging therapeutic agent, primarily composed of caffeic acid which was originally found in coffee extracts and structurally belongs to hydroxycinnamic acid compounds (164). Caffeic acid have been shown to promote megakaryocyte maturation and enhance platelet production. As an antioxidant, caffeic acid effectively neutralizes free radicals, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage, which is a contributing factor in various chronic diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular disorders (165–167). In vitro studies demonstrated that the combination of caffeic acid and hydroxydaunorubicin (DOX) exhibits a significant inhibitory effect on lung cancer cells. Caffeic acid modulates the proliferation of lung cancer cells via the MAPK signaling pathway (165).
A total of 35 publications with 2533 patients were included in a meta-analysis study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of caffeic acid tablets (CFA). The study showed that CFA significantly increased platelet counts compared to the control group. CFA demonstrated better clinical efficacy in treating thrombocytopenia, with complete remission defined as PLT≥100× 10^9/L and partial remission as 50×10^9/L < PLT < 100×10^9/L.CFA also significantly increased white blood cell counts, neutrophil counts and reduced the incidence of grade III and IV myelosuppression (167). In hepatocellular carcinoma cells, caffeic acid inhibited the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MM-9) which induces tumor invasiveness and metastases (168). Caffeic acid predominantly suppresses the growth of estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancer cells (169).
4.6 Traditional Chinese medicine
The application of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of cancer is gradually gaining attention, especially in terms of modulating immune responses, improving patients’ quality of life, and reducing side effects (170). The therapeutic mechanisms of TCM are primarily reflected in its multi-component and multi-target characteristics, which sharply contrast with the single-target drug design in modern medicine. TCM can be used as an adjuvant therapy to enhance the efficacy of conventional cancer treatments (170). Chemotherapy often causes severe side effects, including nausea, vomiting, myelosuppression, and organ dysfunction. TCM can help alleviate these adverse reactions (171, 172). For instance, a systematic review and meta-analysis involving 22 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 1834 postoperative breast cancer patients revealed that TCM combined with chemotherapy significantly improved therapeutic efficacy, immune function, and reduced adverse reactions such as leukopenia and thrombocytopenia (173). While some RCTs suggest benefits, evidence remains preliminary due to methodological heterogeneity and lack of large-scale trials. A study found that combining Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) with capecitabine-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer (CRC) is more effective than capecitabine alone. The combination therapy enhances tumor response rates and reduced the risks of thrombocytopenia (174). Moreover, a network meta-analysis highlighted the efficacy of various TCM injections, such as Aidi and Compound Kushen injections, in improving treatment responses and reducing adverse effects when used in conjunction with chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients (175).
5 Discussion
In summary, CTIT is a prevalent adverse effect of anti-tumor therapies that significantly impacts treatment efficacy and patients’ quality of life. The treatment and clinical research of CTIT has emerged as a significant concern in the realm of oncology. Platelet transfusion is the basic treatment for CIT, and the widespread use of rhIL-11 and rhTPO has significantly reduced the number of patients with chemotherapy restrictions, thus greatly reducing the need for platelet transfusion. While rhIL-11 has been approved by the FDA for use in CIT, its use has been limited due to its side effect, and manufacturers have stopped offering the drug. However, rhTPO, which is not associated with cross-reactive antibodies, completed its development in China and has become a routine component of supportive care for cancer patients. Compared with other TPO-RAs, rhTPO has lower efficacy and more complications, but with the increase of clinical trial data, TPO-RAs have become a reliable choice for the treatment of CTIT.
This review aims to explore the etiology of CTIT, its implications on patient outcomes, and the current treatment and preventive measures available. By synthesizing existing literature, we seek to provide clinicians with comprehensive management strategies to mitigate bleeding risks and enhance patients’ therapeutic effect during cancer treatment. In addition, by integrating genomic, proteomic, and metabolic insights into the development of personalized treatment protocols, we can better predict and manage the risks associated with cancer therapies. It is important to emphasize personalized treatment strategies and preventive measures tailored to each patient’s biological characteristics, genetic profile, and drug response.
Author contributions
XZ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. XS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. SS: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. QS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MC: Validation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Resources, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ten Berg MJ, van den Bemt PM, Shantakumar S, Bennett D, Voest EE, Huisman A, et al. Thrombocytopenia in adult cancer patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy: results from a retrospective hospital-based cohort study. Drug Saf. (2011) 34:1151–60. doi: 10.2165/11594310-000000000-00000
2. Wu Y, Aravind S, Ranganathan G, Martin A, and Nalysnyk L. Anemia and thrombocytopenia in patients undergoing chemotherapy for solid tumors: a descriptive study of a large outpatient oncology practice database, 2000-2007. Clin Ther. (2009) 31:2416–32. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.11.020
3. Machlus KR and Italiano JE Jr. The incredible journey: From megakaryocyte development to platelet formation. J Cell Biol. (2013) 201:785–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201304054
4. Weycker D, Hatfield M, Grossman A, Hanau A, Lonshteyn A, Sharma A, et al. Risk and consequences of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in US clinical practice. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:151. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5354-5
5. Mishra K, Jandial A, Sandal R, Meshram A, Lad D, Prakash G, et al. Bleeding risk assessment in immune thrombocytopenia. Ann Hematol. (2023) 102:3007–14. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05466-1
6. Benjamin RJ and Anderson KC. What is the proper threshold for platelet transfusion in patients with chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2002) 42:163–71. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(01)00182-2
7. Danese E, Montagnana M, Favaloro EJ, and Lippi G. Drug-induced thrombocytopenia: mechanisms and laboratory diagnostics. Semin Thromb Hemost. (2020) 46:264–74. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1697930
8. Christensen RD, Bahr TM, Davenport P, Sola-Visner MC, Kelley WE, Ilstrup SJ, et al. Neonatal thrombocytopenia: factors associated with the platelet count increment following platelet transfusion. J Pediatr. (2023) 263:113666. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2023.113666
9. Nishimura F, Ushijima T, Hamada S, Miyamura S, Oniki K, Saruwatari J, et al. Factors associated with thrombocytopenia in patients treated with pegfilgrastim. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 61:255–61. doi: 10.5414/CP204367
10. Hidiatov O, Zlamal J, Aidery P, Bakchoul T, et al. Acquired immune thrombocytopenia: An update on aspects of diagnosis and management relevant for intensive care medicine. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. (2020) 145:747–53. doi: 10.1055/a-0962-6361
11. Allegra A, Cicero N, Mirabile G, Giorgianni CM, Gangemi S, et al. Novel biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring of immune thrombocytopenia. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4438. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054438
12. Ferrara R, Zemmour C, Reichert T, Ouk D, Niccoli P, Maniry-Quellier J, et al. Predictive factors for persistent thrombocytopenia after peptide receptor radioligand therapy in enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2025) 16:1568243. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1568243
13. Degliuomini MD, Armstrong K, Mauguen A, Slotkin EK, Roberts SS, Dunkel IJ, et al. Chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in pediatric oncology: Scope of the problem and opportunities for intervention. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2022) 69:e29776. doi: 10.1002/pbc.29776
14. Shaw JL, Nielson CM, Park JK, Marongiu A, Soff GA, et al. The incidence of thrombocytopenia in adult patients receiving chemotherapy for solid tumors or hematologic Malignancies. Eur J Haematol. (2021) 106:662–72. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13595
15. Wang Y, Zhou S, Yang F, Qi X, Wang X, Guan X, et al. Treatment-related adverse events of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in clinical trials: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. (2019) 5:1008–19. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0393
16. Conroy T, Hammel P, Hebbar M, Ben Abdelghani M, Wei AC, Raoul JL, et al. FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:2395–406. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809775
17. Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. (2011) 364:1817–25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1011923
18. Poplin E, Feng Y, Berlin J, Rothenberg ML, Hochster H, Mitchell E, et al. randomized study of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin versus gemcitabine (fixed-dose rate infusion) compared with gemcitabine (30-minute infusion) in patients with pancreatic carcinoma E6201: a trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. (2009) 27:3778–85. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.9007
19. Ohe Y, Ohashi Y, Kubota K, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Negoro S, et al. Randomized phase III study of cisplatin plus irinotecan versus carboplatin plus paclitaxel, cisplatin plus gemcitabine, and cisplatin plus vinorelbine for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Four-Arm Cooperative Study in Japan. Ann Oncol. (2007) 18:317–23. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdl377
20. Lee JL, Kang YK, Kang HJ, Lee KH, Zang DY, Ryoo BY, et al. A randomised multicentre phase II trial of capecitabine vs S-1 as first-line treatment in elderly patients with metastatic or recurrent unresectable gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. (2008) 99:584–90. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604536
21. Budd GT, Ganapathi R, Adelstein DJ, Pelley R, Olencki T, Petrus J, et al. Randomized trial of carboplatin plus amifostine versus carboplatin alone in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer. (1997) 80:1134–40.
22. Gross-Goupil M, Fourcade A, Blot E, Penel N, Négrier S, Culine S, et al. Cisplatin alone or combined with gemcitabine in carcinomas of unknown primary: results of the randomised GEFCAPI 02 trial. Eur J Cancer. (2012) 48:721–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.01.011
23. Grønberg BH, Bremnes RM, Fløtten O, Amundsen T, Brunsvig PF, Hjelde HH, et al. Phase III study by the Norwegian lung cancer study group: pemetrexed plus carboplatin compared with gemcitabine plus carboplatin as first-line chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2009) 27:3217–24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.9114
24. Okamoto H, Watanabe K, Kunikane H, Yokoyama A, Kudoh S, Asakawa T, et al. Randomised phase III trial of carboplatin plus etoposide vs split doses of cisplatin plus etoposide in elderly or poor-risk patients with extensive disease small-cell lung cancer: JCOG 9702. Br J Cancer. (2007) 97:162–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603810
25. Fuchs CS, Moore MR, Harker GH, Villa L, Rinaldi DR, Hecht JR, et al. Phase III comparison of two irinotecan dosing regimens in second-line therapy of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2003) 21:807–14. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.08.058
26. Rothenberg ML, Cox JV, DeVore RF, Hainsworth JD, Pazdur R, Rivkin SE, et al. A multicenter, phase II trial of weekly irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with previously treated colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. (1999) 85:786–95.
27. Shah NP, Guilhot F, Cortes JE, Schiffer CA, le Coutre P, Brümmendorf TH, et al. Long-term outcome with dasatinib after imatinib failure in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: follow-up of a phase 3 study. Blood. (2014) 123:2317–24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-532341
28. Verweij J, Casali PG, Zalcberg J, LeCesne A, Reichardt P, Blay JY, et al. Progression-free survival in gastrointestinal stromal tumours with high-dose imatinib: randomised trial. Lancet. (2004) 364:1127–34. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17098-0
29. Li J, Qin S, Xu RH, Shen L, Xu J, Bai Y, et al. Effect of fruquintinib vs placebo on overall survival in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: the FRESCO randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2018) 319:2486–96. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.7855
30. Xu J, Jiang H, Pan Y, Gu K, Cang S, Han L, et al. Sintilimab plus chemotherapy for unresectable gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: the ORIENT-16 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2023) 330:2064–74. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.19918
31. Song Y, Wu J, Chen X, Lin T, Cao J, Liu Y, et al. A single-arm, multicenter, phase II study of camrelizumab in relapsed or refractory classical hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:7363–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1680
32. Tang B, Chi Z, Chen Y, Liu X, Wu D, Chen J, et al. Safety, efficacy, and biomarker analysis of toripalimab in previously treated advanced melanoma: results of the POLARIS-01 multicenter phase II trial. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:4250–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3922
33. Kuter DJ and Begley CG. Recombinant human thrombopoietin: basic biology and evaluation of clinical studies. Blood. (2002) 100:3457–69. doi: 10.1182/blood.V100.10.3457
34. Denduluri N, Patt DA, Wang Y, Bhor M, Li X, Favret AM, et al. Dose delays, dose reductions, and relative dose intensity in patients with cancer who received adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy in community oncology practices. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2015) 13:1383–93. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2015.0166
35. Delanoy N, Michot JM, Comont T, Kramkimel N, Lazarovici J, Dupont R, et al. Haematological immune-related adverse events induced by anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy: a descriptive observational study. Lancet Haematol. (2019) 6:e48–57. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30175-3
36. Kroll MH, Rojas-Hernandez C, and Yee C. Hematologic complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Blood. (2022) 139:3594–604. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009016
37. Adelborg K, Veres K, Horváth-Puhó E, Clouser M, Saad H, Sørensen HT, et al. Risk and adverse clinical outcomes of thrombocytopenia among patients with solid tumors-a Danish population-based cohort study. Br J Cancer. (2024) 130:1485–92. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02630-w
38. Razzaghdoust A, Mofid B, and Zangeneh. M. Predicting chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in cancer patients with solid tumors or lymphoma. J Oncol Pharm Pract. (2020) 26:587–94. doi: 10.1177/1078155219861423
39. Zhou S, Song B, Li C, Tang W, Zhang X, Jin X, et al. The predictive model for risk of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia based on antineoplastic drugs for solid tumors in eastern China. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:3185. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27824-9
40. Zhang LL, Chen X, Huang YY, Liang CX, Qiang MY, Cai ZC, et al. Incidence, consequences, and predictors of serious chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:14084–93. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6062
41. Mac M, Lamborn K, Khan W, Varghese A, Graef L, Knox S, et al. Radiotherapy-associated neutropenia and thrombocytopenia: analysis of risk factors and development of a predictive model. Blood. (1997) 89:2303–10. doi: 10.1182/blood.V89.7.2303
42. Wang R, Hu X, Wang J, Zhou L, Hong Y, Zhang Y, et al. Proanthocyanidin A1 promotes the production of platelets to ameliorate chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia through activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Phytomedicine. (2022) 95:153880. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153880
43. Gao A, Zhang L, and Zhong. D. Chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia: literature review. Discov Oncol. (2023) 14:10. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00616-3
44. Stack A, Khanal R, and Denlinger. CS. Oxaliplatin-induced immune thrombocytopenia: A case report and literature review. Clin Colorectal Cancer. (2021) 20:e1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2020.07.007
45. Ghazanfar H, Nawaz I, and Ali. N. Oxaliplatin-induced thrombocytopenia: A case report and review of pathophysiology of various speculative mechanisms. Cureus. (2020) 12:e9929. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9929
46. Jardim DL, Rodrigues CA, Novis YAS, Rocha VG, Hoff PM, et al. Oxaliplatin-related thrombocytopenia. Ann Oncol. (2012) 23:1937–42. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds074
47. Beg MS, Komrokji RS, Ahmed K, Safa MM, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced immune mediated thrombocytopenia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2008) 62:925–7. doi: 10.1007/s00280-007-0675-5
48. Soubrane O, Brouquet A, Zalinski S, Terris B, Brézault C, Mallet V, et al. Predicting high grade lesions of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome related to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases: correlation with post-hepatectomy outcome. Ann Surg. (2010) 251:454–60. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181c79403
49. Overman MJ, Maru DM, Charnsangavej C, Loyer EM, Wang H, Pathak P, et al. Oxaliplatin-mediated increase in spleen size as a biomarker for the development of hepatic sinusoidal injury. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:2549–55. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.5701
50. Griesinger F, Korol EE, Kayaniyil S, Varol N, Ebner T, Goring SM, et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line carboplatin-versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. (2019) 135:196–204. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.07.010
51. De La Fouchardière C, Malka D, Cropet C, Chabaud S, Raimbourg J, Botsen D, et al. Gemcitabine and paclitaxel versus gemcitabine alone after 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A randomized phase III PRODIGE 65-UCGI 36-GEMPAX UNICANCER study. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:1055–66. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00795
52. Ioka T, Kanai M, Kobayashi S, Sakai D, Eguchi H, Baba H, et al. Randomized phase III study of gemcitabine, cisplatin plus S-1 versus gemcitabine, cisplatin for advanced biliary tract cancer (KHBO1401- MITSUBA). J Hepatobil Pancreat Sci. (2023) 30:102–10. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.1219
53. Ozaka M, Matsumura Y, Ishii H, Omuro Y, Itoi T, Mouri H, et al. Randomized phase II study of gemcitabine and S-1 combination versus gemcitabine alone in the treatment of unresectable advanced pancreatic cancer (Japan Clinical Cancer Research Organization PC-01 study). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2012) 69:1197–204. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-1822-1
54. Choi J H, Oh S Y, Kwon H C, Kim J H, Lee J H, Lee S, et al. Gemcitabine versus gemcitabine combined with cisplatin treatment locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: a retrospective analysis. Cancer Res Treat. (2008) 40:22–6. doi: 10.4143/crt.2008.40.1.22
55. Zupancic M, Shah PC, and Shah-Khan. F. Gemcitabine-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Lancet Oncol. (2007) 8:634–41. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70203-6
56. Mattioli R, Ilari A, Colotti B, Mosca L, Fazi F, Colotti G, et al. Doxorubicin and other anthracyclines in cancers: Activity, chemoresistance and its overcoming. Mol Aspects Med. (2023) 93:101205. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2023.101205
57. Fabiani I, Aimo A, Grigoratos C, Castiglione V, Gentile F, Saccaro LF, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation: determinants of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and possible therapeutic targets. Heart Fail Rev. (2021) 26:881–90. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-10063-9
58. Richardson PG, Barlogie B, Berenson J, Singhal S, Jagannath S, Irwin D, et al. A phase 2 study of bortezomib in relapsed, refractory myeloma. N Engl J Med. (2003) 348:2609–17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030288
59. Tang SQ, Tang LL, Mao YP, Li WF, Chen L, Zhang Y, et al. The pattern of time to onset and resolution of immune-related adverse events caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer: A pooled analysis of 23 clinical trials and 8,436 patients. Cancer Res Treat. (2021) 53:339–54. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.790
60. Sun X, Roudi R, Dai T, Chen S, Fan B, Li H, et al. Immune-related adverse events associated with programmed cell death protein-1 and programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer: a PRISMA systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:558. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5701-6
61. Nishijima TF, Shachar SS, Nyrop KA, and Muss HB. Safety and tolerability of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors compared with chemotherapy in patients with advanced cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncologist. (2017) 22:470–9. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0419
62. Zhou X, Yao Z, Bai H, Duan J, Wang Z, Wang X, et al. Treatment-related adverse events of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitor-based combination therapies in clinical trials: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:1265–74. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00333-8
63. Bai Y, Wang X, Dai X, Ma Q, and Hu H. Immune-related adverse events in small-cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a comprehensive analysis from the FDA adverse event reporting system. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1398667. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1398667
64. Cooper N and Ghanima W. Immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:945–55. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1810479
65. Kramer R, Zaremba A, Moreira A, Ugurel S, Johnson DB, Hassel JC, et al. Hematological immune related adverse events after treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 147:170–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.01.013
66. Haddad TC, Zhao S, Li M, Patel SH, Johns A, Grogan M, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related thrombocytopenia: incidence, risk factors and effect on survival. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2022) 71:1157–65. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03068-2
67. Cai J, Yang G, Zhang X, Liu L, and Yan M. Immune thrombocytopenia induced by sintilimab in lung cancer: A case report and literature review. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. (2023) 26:717–20. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419
68. Shiuan E, Beckermann KE, Ozgun A, Kelly C, McKean M, McQuade J, et al. Thrombocytopenia in patients with melanoma receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. J Immunother Cancer. (2017) 5:8. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0210-0
69. Moore DC, Elmes JB, Arnall JR, Strassel SA, and Patel JN. PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-induced immune thrombocytopenia: A pharmacovigilance study and systematic review. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 129:111606. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111606
70. Appelbaum L, Sosna J, Nissenbaum Y, Benshtein A, and Goldberg SN. Electromagnetic navigation system for CT-guided biopsy of small lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2011) 196:1194–200. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.5151
71. Wang M, Zhai X, Li J, Guan J, Xu S, Li Y, et al. The role of cytokines in predicting the response and adverse events related to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:670391. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.670391
72. Liu LL, Skribek M, Harmenberg U, and Gerling M. Systemic inflammatory syndromes as life-threatening side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors: case report and systematic review of the literature. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e005841. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005841
73. Kang JH, Bluestone JA, and Young. Predicting A. and preventing immune checkpoint inhibitor toxicity: targeting cytokines. Trends Immunol. (2021) 42:293–311. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.02.006
74. Chennamadhavuni A, Abushahin L, Jin N, Presley CJ, and Manne A. Risk factors and biomarkers for immune-related adverse events: A practical guide to identifying high-risk patients and rechallenging immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:779691. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.779691
75. Jotatsu T, Oda K, Yamaguchi Y, Noguchi S, Kawanami T, Kido T, et al. Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia and hypothyroidism in a lung cancer patient treated with nivolumab. Immunotherapy. (2018) 10:85–91. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0100
76. Karakas Y, Yuce D, and Kılıckap. S. Immune thrombocytopenia induced by nivolumab in a metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patient. Oncol Res Treat. (2017) 40:621–2. doi: 10.1159/000477968
77. Ismail AM, Higazi AM, Nomeir HM, and Farag NM. IL-23/Th17 pathway and IL-17A gene polymorphism in Egyptian children with immune thrombocbytopenic purpura. Ital J Pediatr. (2021) 47:178. doi: 10.1186/s13052-021-01131-3
78. Hassan T, Zakaria M, Diaa A, Abdalla A, Ahmed A, Abdelmonem DM, et al. Contribution of T helper 17 cells and interleukin-17 to the pathogenesis of primary immune thrombocytopenia in Egyptian children. Eur J Pediatr. (2023) 182:5673–9. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05242-3
79. Li Y, Lai J, Ran M, Yi T, Zhou L, Luo J, et al. Alnustone promotes megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet production via the interleukin-17A/interleukin-17A receptor/Src/RAC1/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. (2024) 971:176548. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176548
80. Wang M, Liu W, Xu Y, Wang H, Guo X, Ding X, et al. Predicting bleeding risk in a Chinese immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) population: development and assessment of a new predictive nomogram. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:15337. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72275-1
81. Li Q, Yang M, Xia R, Xia L, and Zhang L. Elevated expression of IL-12 and IL-23 in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Platelets. (2015) 26:453–8. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2014.934217
82. Bass AR, Abdel-Wahab NA, Reid PD, Sparks JA, Calabrese C, Jannat-Khah DP, et al. Comparative safety and effectiveness of TNF inhibitors, IL6 inhibitors and methotrexate for the treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:920–6. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-223885
83. Johnson DE, O’Keefe RA, and Grandis JR. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:234–48. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.8
84. Hinterleitner C, Strähle J, Malenke E, Hinterleitner M, Henning M, Seehawer M, et al. Platelet PD-L1 reflects collective intratumoral PD-L1 expression and predicts immunotherapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:7005. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27303-7
85. Colarusso C, Falanga A, Terlizzi M, De Rosa I, Somma P, Sommella EM, et al. High levels of PD-L1 on platelets of NSCLC patients contributes to the pharmacological activity of Atezolizumab. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115709. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115709
86. Harris MA, Savas PS, Virassamy B, O’Malley MMR, Kay J, Mueller SN, et al. Towards targeting the breast cancer immune microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. (2024) 24:554–77. doi: 10.1038/s41568-024-00714-6
87. Wang C and Li J. Haematologic toxicities with PARP inhibitors in cancer patients: an up-to-date meta-analysis of 29 randomized controlled trials. J Clin Pharm Ther. (2021) 46:571–84. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13349
88. Rainone M, Kasparian S, Nguyen T, Talwar N, Yuan Y, Mei M, et al. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists for thrombocytopenia secondary to HER2-targeted antibody drug conjugates. Oncologist. (2023) 28:e843–6. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad185
89. Pu D, Wu Y, Xu D, Shi G, Chen H, Feng D, et al. The adverse events of CDK4/6 inhibitors for HR+/HER2- breast cancer: an umbrella review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1269922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1269922
90. Martins V, Jesus M, Pereira L, Monteiro C, Duarte AP, Morgado M, et al. Hematological events potentially associated with CDK4/6 inhibitors: an analysis from the european spontaneous adverse event reporting system. Pharm (Basel). (2023) 16:1340. doi: 10.3390/ph16101340
91. Andrikopoulou A, Fiste O, Apostolidou K, Skafida E, Markellos C, Liontos M, et al. CDK4/6 inhibitors and arthralgia: A single institution experience. Med Sci (Basel). (2021) 9:42. doi: 10.3390/medsci9020042
92. Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, Tutt P, Wu P, Mergui-Roelvink MM, et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N Engl J Med. (2009) 361:123–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0900212
93. de Bono JS, Mehra N, Scagliotti GV, Castro E, Dorff T, Stirling A, et al. Talazoparib monotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with DNA repair alterations (TALAPRO-1): an open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:1250–64. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00376-4
94. Bowling GC, Swargaloganathan P, Heintz C, Madan RA, Eldhose B, Dobi A, et al. Hematological toxicities with PARP inhibitors in prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of phase II/III randomized controlled trials. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:4904. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194904
95. González-Martín A, Pothuri B, Vergote I, DePont Christensen R, Graybill W, Mirza MR, et al. Niraparib in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:2391–402. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910962
96. Bruin MAC, Sonke GS, Beijnen JH, and Huitema ADR. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of PARP inhibitors in oncology. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2022) 61:1649–75. doi: 10.1007/s40262-022-01167-6
97. Guo T, Yuan Y, Ma Z, Zou Y, Tang M, Guo Z, et al. Discovery and pharmacological evaluation of potent and highly selective PARP1 inhibitors. J Med Chem. (2025) 68:13491–515. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c00185
98. Bhamidipati DB, Haro-Silerio JI, Yap TA, and Ngoi N. PARP inhibitors: enhancing efficacy through rational combinations. Br J Cancer. (2023) 129:904–16. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02326-7
99. Lin W, Zeng Y, Weng L, Yang J, and Zhuang W. Comparative analysis of adverse events associated with CDK4/6 inhibitors based on FDA’s adverse event reporting system: a case control pharmacovigilance study. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. (2024) 25:47. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00770-6
100. Do KT, Kochupurakkal B, Kelland S, de Jonge A, Hedglin J, Powers A, et al. Phase 1 combination study of the CHK1 inhibitor prexasertib and the PARP inhibitor olaparib in high-grade serous ovarian cancer and other solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:4710–6. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1279
101. Ji C, Li F, Yuan Y, Zhang H, Bian L, Zhang S, et al. Novel anti-HER2 antibody-drug conjugates versus T-DM1 for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer after tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment. Oncologist. (2023) 28:e859–66. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad127
102. Rainone M, Behrendt CE, Kasparian S, Nguyen T, Sedrak MS, Lavasani SL, et al. HER2-targeted antibody-drug conjugates for breast cancer: ancestry and dose adjustment for thrombocytopenia. Breast Cancer. (2023) 30:796–801. doi: 10.1007/s12282-023-01473-2
103. Zhou JX, Feng LJ, and Zhang X. Risk of severe hematologic toxicities in cancer patients treated with PARP inhibitors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2017) 11:3009–17. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S147726
104. Nguyen TD, Bordeau BM, and Balthasar JP. Mechanisms of ADC toxicity and strategies to increase ADC tolerability. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:713 doi: 10.3390/cancers15030713
105. Zhao H, Gulesserian S, Ganesan SK, Ou J, Morrison K, Zeng Z, et al. Inhibition of megakaryocyte differentiation by antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) is mediated by macropinocytosis: implications for ADC-induced thrombocytopenia. Mol Cancer Ther. (2017) 16:1877–86. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0710
106. Marini I and Bakchoul T. Pathophysiology of autoimmune thrombocytopenia: current insight with a focus on thrombopoiesis. Hamostaseologie. (2019) 39:227–37. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1678732
107. Fujii Y, Taniguchi M, Nagaya S, Ueda Y, Hashizume C, Watanabe K, et al. A novel mechanism of thrombocytopenia by PS exposure through TMEM16F in sphingomyelin synthase 1 deficiency. Blood Adv. (2021) 5:4265–77. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002922
108. Kinneer K, Wortmann P, Cooper ZA, Dickinson NJ, Masterson L, Cailleau T, et al. Design and preclinical evaluation of a novel B7-H4-directed antibody-drug conjugate, AZD8205, alone and in combination with the PARP1-selective inhibitor AZD5305. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:1086–101. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2630
109. Schiffer CA, Bohlke K, Delaney M, Hume H, Magdalinski AJ, McCullough JJ, et al. Platelet transfusion for patients with cancer: american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:283–99. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.1734
110. Panch SR, Guo L, and Vassallo. R. Platelet transfusion refractoriness due to HLA alloimmunization: Evolving paradigms in mechanisms and management. Blood Rev. (2023) 62:101135. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2023.101135
111. Couvidou A, Rojas-Jiménez G, Dupuis A, and Maître B. Anti-HLA Class I alloantibodies in platelet transfusion refractoriness: From mechanisms and determinants to therapeutic prospects. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1125367. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1125367
112. Semple JW, Rebetz J, and Kapur R. Transfusion-associated circulatory overload and transfusion-related acute lung injury. Blood. (2019) 133:1840–53. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-10-860809
113. Kogler V J, Miles J A, Özpolat T, Bailey S L, Byrne D A, Bawcom-Randall M, et al. Platelet dysfunction reversal with cold-stored vs room temperature-stored platelet transfusions. Blood. (2024) 143:2073–88. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023022593
114. Liu Z, Wang Y, Yan J, Liu J, Chen B, Zhang L, et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human interleukin-11 in the treatment of acute leukaemia patients with chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eval Clin Pract. (2020) 26:262–71. doi: 10.1111/jep.13152
115. Kespohl B, Schumertl T, Bertrand J, Lokau J, and Garbers C. The cytokine interleukin-11 crucially links bone formation, remodeling and resorption. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2021) 60:18–27. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.04.002
116. Neben T Y, Loebelenz J, Hayes L, McCarthy K, Stoudemire J, Schaub R, et al. Recombinant human interleukin-11 stimulates megakaryocytopoiesis and increases peripheral platelets in normal and splenectomized mice. Blood. (1993) 81:901–8.
117. Weich N S, Wang A, Fitzgerald M, Neben T Y, Donaldson D, Giannotti J, et al. Recombinant human interleukin-11 directly promotes megakaryocytopoiesis in vitro. Blood. (1997) 90:3893–902.
118. Cook SA and Schafer S. Hiding in plain sight: interleukin-11 emerges as a master regulator of fibrosis, tissue integrity, and stromal inflammation. Annu Rev Med. (2020) 71:263–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-041818-011649
119. Gong FM, Liu FY, Ma X, Ma ST, Xiao HT, Jiang G, et al. Effectiveness and economic evaluation of rhTPO and rhIL-11 in the treatment of cancer therapy induced thrombocytopenia based on real-world research. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1288964. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1288964
120. Isaacs C, Robert NJ, Bailey FA, Schuster MW, Overmoyer B, Graham M, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled study of recombinant human interleukin-11 to prevent chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with breast cancer receiving dose-intensive cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin. J Clin Oncol. (1997) 15:3368–77. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.11.3368
121. Gordon MS, McCaskill-Stevens WJ, Battiato LA, Loewy J, Loesch D, Breeden E, et al. A phase I trial of recombinant human interleukin-11 (neumega rhIL-11 growth factor) in women with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy. Blood. (1996) 87:3615–24. doi: 10.1182/blood.V87.9.3615.bloodjournal8793615
122. Sweeney M, O’Fee K, Villanueva-Hayes C, Rahman E, Lee M, Tam CN, et al. Interleukin 11 therapy causes acute left ventricular dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res. (2024) 120:2220–35. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvae224
123. Schwertschlag US, Trepicchio WL, Dykstra KH, Keith JC, Turner KJ, Dorner AJ, et al. Hematopoietic, immunomodulatory and epithelial effects of interleukin-11. Leukemia. (1999) 13:1307–15. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401514
124. Kuter. DJ. Thrombopoietin and thrombopoietin mimetics in the treatment of thrombocytopenia. Annu Rev Med. (2009) 60:193–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.60.042307.181154
125. Vadhan-Raj S, Verschraegen CF, Bueso-Ramos CB, Broxmeyer HE, Kudelká AP, Freedman RS, et al. Recombinant human thrombopoietin attenuates carboplatin-induced severe thrombocytopenia and the need for platelet transfusions in patients with gynecologic cancer. Ann Intern Med. (2000) 132:364–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-132-5-200003070-00005
126. Vadhan-Raj S, Murray LJ, Bueso-Ramos CB, Patel S, Reddy SP, Hoots WK, et al. Stimulation of megakaryocyte and platelet production by a single dose of recombinant human thrombopoietin in patients with cancer. Ann Intern Med. (1997) 126:673–81. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-9-199705010-00001
127. Wang Z, Fang X, Huang H, Hong H, Li X, Guo C, et al. Recombinant human thrombopoietin (rh-TPO) for the prevention of severe thrombocytopenia induced by high-dose cytarabine: a prospective, randomized, self-controlled study. Leuk Lymph. (2018) 59:2821–8. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1459605
128. Vadhan-Raj S, Patel S, Bueso-Ramos CB, Folloder J, Papadopolous N, Burgess A, et al. Importance of predosing of recombinant human thrombopoietin to reduce chemotherapy-induced early thrombocytopenia. J Clin Oncol. (2003) 21:3158–67. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.08.003
129. Bai CM, Zou XY, Zhao YQ, Han SM, Shan YD, et al. The clinical study of recombinant human thrombopoietin in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced severe thrombocytopenia. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2004) 84:397–400. doi: 10.3760/j:issn:0376-2491.2004.05.013
130. Mei H, Xu M, Yuan G, Zhu F, Guo J, Huang R, et al. A multicentre double-blind, double-dummy, randomised study of recombinant human thrombopoietin versus eltrombopag in the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia in Chinese adult patients. Br J Haematol. (2021) 195:781–9. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17808
131. Chen M, Li L, Xia Q, Chen X, Liao Z, Wang C, et al. A real-world observation on thrombopoietic agents for patients with cancer treatment-induced thrombocytopenia in China: A multicenter, cross-sectional study. Cancer. (2024) 130:1524–38. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35292
132. Imbach P and Crowther M. Thrombopoietin-receptor agonists for primary immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. (2011) 365:734–41. doi: 10.1056/NEJMct1014202
133. Shin J, Kim MJ, Quan X, Kim JW, Lee S, Park S, et al. Thrombopoietin receptor agonist antibody for treating chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia. BMC Cancer. (2023) 23:490. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10975-3
134. Deng J, Hu H, Huang F, Huang C, Huang Q, Wang L, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of thrombopoietin receptor agonists in adults with thrombocytopenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.704093
135. Kuter DJ. The structure, function, and clinical use of the thrombopoietin receptor agonist avatrombopag. Blood Rev. (2022) 53:100909. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2021.100909
136. Lozano ML, Segú-Vergés C, Coma M, Álvarez-Román MT, González-Porras JR, Gutiérrez L, et al. Elucidating the mechanism of action of the attributed immunomodulatory role of eltrombopag in primary immune thrombocytopenia: an in silico approach. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:6907. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136907
137. Guan Y, Hasipek M, Jiang D, Tiwari AD, Grabowski DR, Pagliuca S, et al. Eltrombopag inhibits TET dioxygenase to contribute to hematopoietic stem cell expansion in aplastic anemia. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:e149856. doi: 10.1172/JCI149856
138. Winer ES, Safran H, Karaszewska B, Bauer S, Khan D, Doerfel S, et al. Eltrombopag for thrombocytopenia in patients with advanced solid tumors receiving gemcitabine-based chemotherapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Int J Hematol. (2017) 106:765–76. doi: 10.1007/s12185-017-2319-9
139. Zhu Q, Yang S, Zeng W, Li M, Guan Z, Zhou L, et al. A real-world observation of eltrombopag and recombinant human thrombopoietin (rhTPO) in lymphoma patients with chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia. Front Oncol. (2021) 11. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.701539
140. Çekdemir D, Güvenş S, Özdemirkîran F, Eser A, Toptaş T, Özkocaman V, et al. A multi-center study on the efficacy of eltrombopag in management of refractory chronic immune thrombocytopenia: A real-life experience. Turk J Haematol. (2019) 36:230–7. doi: 10.4274/tjh.galenos.2019.2018.0307
141. Xie C, Zhao H, Bao X, Fu H, and Lou L. Pharmacological characterization of hetrombopag, a novel orally active human thrombopoietin receptor agonist. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 22:5367–77. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13809
142. Mei H, Liu X, Li Y, Zhou H, Feng Y, Gao G, et al. A multicenter, randomized phase III trial of hetrombopag: a novel thrombopoietin receptor agonist for the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:37. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01047-9
143. Yang W, Zhao X, Liu X, Xiong Y, Fan H, Zhang L, et al. Hetrombopag plus porcine ATG and cyclosporine for the treatment of aplastic anaemia: early outcomes of a prospective pilot study. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2023) 12:16. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00377-3
144. Wang Z, Chen L, Zhang F, Lu H, Chen X, Wen A, et al. First-in-patient study of hetrombopag in patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. (2020) 18:3053–60. doi: 10.1111/jth.15078
145. Qin S, Wang Y, Yao J, Liu Y, Yi T, Pan Y, et al. Hetrombopag for the management of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with advanced solid tumors: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II study. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2024) 16:17588359241260985. doi: 10.1177/17588359241260985
146. Xia X, Zhou H, Zhang H, Deng W, Li R, Huang Q, et al. Hetrombopag plus recombinant human thrombopoietin for chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with solid tumors. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. (2023) 7:102231. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.102231
147. Bussel JB, Soff G, Balduzzi A, Cooper N, Lawrence T, Semple JW, et al. A Review of Romiplostim Mechanism of Action and Clinical Applicability. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2021) 15:2243–68. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S299591
148. Frampton JE and Lyseng-Williamson KA. Romiplostim. Drugs. (2009) 69:307–17. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969030-00006
149. Kapur R, Aslam R, Speck ER, Rebetz JM, Semple JW, et al. Thrombopoietin receptor agonist (TPO-RA) treatment raises platelet counts and reduces anti-platelet antibody levels in mice with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Platelets. (2020) 31:399–402. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2019.1624709
150. Bao W, Bussel JB, Heck S, He W, Karpoff M, Boulad N, et al. Improved regulatory T-cell activity in patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia treated with thrombopoietic agents. Blood. (2010) 116:4639–45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-281717
151. Soff GA, Miao Y, Bendheim G, Batista J, Mones JV, Parameswaran R, et al. Romiplostim treatment of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia. J Clin Oncol. (2019) 37:2892–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01931
152. Al-Samkari H, Parnes AD, Goodarzi K, Weitzman JI, Connors JM, Kuter DJ, et al. A multicenter study of romiplostim for chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in solid tumors and hematologic Malignancies. Haematologica. (2021) 106:1148–57. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2020.251900
153. Soff GA, Al-Samkari H, Leader A, Eisen M, Saad H, et al. Romiplostim in chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia: A review of the literature. Cancer Med. (2024) 13:e7429. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7429
154. González-Porras JR, Godeau B, and Carpenedo M. Switching thrombopoietin receptor agonist treatments in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Ther Adv Hematol. (2019) 10:2040620719837906. doi: 10.1177/2040620719837906
155. Jiang Y, Xu Y, Wu H, He M, Jiang H, Xu X, et al. Refractory immune thrombocytopenia treated with low-dose decitabine combined with recombinant human thrombopoietin or eltrombopag: Two case reports. Med (Baltimore). (2025) 104:e41449. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041449
156. Kim ES. Lusutrombopag: first global approval. Drugs. (2016) 76:155–8. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0525-4
157. Hidaka H, Kurosaki M, Tanaka H, Kudo M, Abiru S, Igura T, et al. Lusutrombopag reduces need for platelet transfusion in patients with thrombocytopenia undergoing invasive procedures. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 17:1192–200. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.047
158. Ishikawa T, Okoshi M, Tomiyoshi K, Kojima Y, Horigome R, Imai M, et al. Efficacy and safety of repeated use of lusutrombopag prior to radiofrequency ablation in patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma and thrombocytopenia. Hepatol Res. (2019) 49:590–3. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13305
159. Alkhouri N, Imawari M, Izumi N, Osaki Y, Ochiai T, Kano T, et al. Lusutrombopag is safe and efficacious for treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 18:2600–2608.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.032
160. Fukushima-Shintani M, Suzuki K, Iwatsuki Y, Abe M, Sugasawa K, Hirayama F, et al. AKR-501 (YM477) a novel orally-active thrombopoietin receptor agonist. Eur J Haematol. (2009) 82:247–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.2008.01198.x
161. Markham A. Avatrombopag: A review in thrombocytopenia. Drugs. (2021) 81:1905–13. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01613-y
162. Al-Samkari H, Kolb-Sielecki J, Safina SZ, Xue X, Jamieson BD, et al. Avatrombopag for chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with non-haematological Malignancies: an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. (2022) 9:e179–89. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(22)00001-1
163. Hu H, Lei D, and Liang Y. Observation on the efficacy of TPO receptor agonists and platelet transfusion in chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in Malignant tumors. World J Surg Oncol. (2025) 23:13. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03659-8
164. Zhao X, Liu Z, Liu H, Guo J, Long S, et al. Hybrid molecules based on caffeic acid as potential therapeutics: A focused review. Eur J Med Chem. (2022) 243:114745. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114745
165. Bai X, Li S, Liu X, An H, Kang X, Guo S, et al. Caffeic acid, an active ingredient in coffee, combines with DOX for multitarget combination therapy of lung cancer. J Agric Food Chem. (2022) 70:8326–37. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03009
166. Goyal A, Singh VD, Solanki K, and Verma A. Revealing the curative possibilities: A comprehensive exploration of caffeic acid. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. (2024). doi: 10.2174/0113892010309341240517071344
167. Yu H, Chen R, Zhou Z, Liu R, and Wen J. Efficacy and safety of caffeic acid tablets in the treatment of thrombocytopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e35353. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035353
168. Chung TW, Moon SK, Chang YC, Ko JH, Lee YC, Cho G, et al. Novel and therapeutic effect of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma cells: complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by dual mechanism. FASEB J. (2004) 18:1670–81. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2126com
169. Rosendahl AH, Perks CM, Zeng L, Markkula A, Simonsson M, Rose C, et al. Caffeine and caffeic acid inhibit growth and modify estrogen receptor and insulin-like growth factor I receptor levels in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2015) 21:1877–87. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1748
170. Mok TS, Yeo W, Johnson PJ, Hui P, Ho WM, Lam KC, et al. A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized study of Chinese herbal medicine as complementary therapy for reduction of chemotherapy-induced toxicity. Ann Oncol. (2007) 18:768–74. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdl465
171. Chan YT, Cheung F, Zhang C, Fu B, Tan HY, Norimoto H, et al. Ancient chinese medicine herbal formula huanglian jiedu decoction as a neoadjuvant treatment of chemotherapy by improving diarrhea and tumor response. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:252. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00252
172. Li R, Zhang T, Yan SH, Yan YZ, Ding YC, Wang YS, et al. Chinese medicine combined with adjuvant chemotherapy for improving myelosuppression in colorectal cancer patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Chin J Integr Med. (2024) 30:643–52. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3558-7
173. Zhang Y, Lou Y, Wang J, Yu C, Shen W, et al. Research status and molecular mechanism of the traditional chinese medicine and antitumor therapy combined strategy based on tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:609705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.609705
174. Jiang HZ, Jiang YL, Yang B, Long FX, Yang Z, Tang DX, et al. Traditional Chinese medicines and capecitabine-based chemotherapy for colorectal cancer treatment: A meta-analysis. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:236–55. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4896
Keywords: CTIT, chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT), immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia (ICIIT), TPO-RAs, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)
Citation: Zhao X, Shan X, Sui S, Song Q, Cheng M and Zhao Y (2025) Cancer treatment-induced thrombocytopenia: diagnosis, mechanisms and management. Front. Immunol. 16:1634688. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1634688
Received: 25 May 2025; Accepted: 03 September 2025;
Published: 23 September 2025.
Edited by:
Eleni Gavriilaki, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceReviewed by:
Xiaobin Shang, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, ChinaChiranjeevi Sainatham, University of Florida Health, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Shan, Sui, Song, Cheng and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Zhao, emhhb3lpMDQxMUAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xutong Zhao
Xutong Zhao Xiu Shan†
Xiu Shan† Yi Zhao
Yi Zhao