- Department of Oncology, The Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most prevalent form of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 85% of all cases, and is associated with a poor prognosis. Despite significant advancements in treatment modalities, therapeutic efficacy remains suboptimal, underscoring the urgent need for novel strategies. In recent years, increasing attention has been directed toward the pivotal role of gut microbiota-host interactions in the treatment of NSCLC. This review systematically examines the influence of current NSCLC therapies on gut microbiota and metabolism, explores the relationship between the microbiome and therapeutic response, and highlights the critical functions of probiotics, microbial metabolites, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), and dietary interventions in NSCLC management. By elucidating the mechanisms through which gut microbiota and their metabolites modulate treatment efficacy, we investigate the potential of exogenous interventions targeting the gut ecosystem to enhance therapeutic outcomes and mitigate adverse effects. Modulating the intestinal microbiota represents a promising clinical avenue and offers a new frontier for the development of future NSCLC treatment strategies.
1 Introduction
The human microbiome comprises a diverse and dynamic community of microorganisms—including bacteria, fungi, viruses—their genetic material, and metabolic byproducts. The resident microbiota is an essential component of host health and homeostasis (1). Most microbiome research to date has focused on bacterial populations, which constitute a major proportion of these resident microbes (2). In the gut, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria dominate the bacterial composition (3–5). The gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in regulating host immunity and metabolism through the production of numerous metabolites that function as signaling molecules and metabolic substrates, linking dysbiosis with inflammation and tumorigenesis (6–8).
The cross-link between gut microbiota and lung cancer is a complex multifactorial relationship (5). Studies have shown that in patients with lung cancer, the abundance of Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Spirochaetes increases in both pulmonary and intestinal microbiomes, while Firmicutes are significantly reduced (4, 9). Research on both gut and respiratory tract microbiota has revealed notable dysregulation in NSCLC, which is further associated with distant metastasis (DM) (10). The pathogenic contribution of the gut microbiome and its specific metabolites to NSCLC lies in their modulation of chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation (11). A study combining serum metabolomics and fecal microbiome profiling identified potential biomarkers in patients with early-stage NSCLC. The metabolomic analysis revealed elevated levels of sphingolipids (e.g. D-erythrosphingosine 1-phosphate, palmitoylsphingomyelin), fatty acyls (e.g., Avocadyne 1-acetate, 12(S)-HETE, 20-carboxyleukotriene B4, thromboxane B3, 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α, decanoic acid, tetracosanoic acid), and glycerophospholipids in these patients (12).
Substantial progress has been made in NSCLC treatment in recent years, particularly in early screening, minimally invasive procedures, radiotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. These advances have significantly improved patient survival rates (13). However, several challenges persist, including the emergence of drug resistance, treatment-associated toxicity, high costs, underrepresentation of minority groups in clinical trials, and limited access to diagnostic and therapeutic resources. These issues highlight the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies to expand treatment options (14). Manipulating the gut microbiota has emerged as a promising strategy to enhance NSCLC treatment efficacy. Microbiome modulation may augment immunotherapeutic responses, mitigate adverse treatment effects such as microbial dysbiosis, and serve as a predictive biomarker for personalized therapy and disease prevention (15).
This review provides a comprehensive overview of how various NSCLC treatment modalities influence the gut microbiota and its metabolic profile. It further emphasizes the mechanisms and potential of microbiota-targeted interventions in improving clinical outcomes. Understanding the intricate relationship between gut flora, its metabolites, and NSCLC treatment holds substantial theoretical and clinical relevance, offering new insights into disease pathogenesis and therapeutic innovation.
2 Alterations in gut microbiota and metabolism induced by standard NSCLC treatments
Intestinal microbiota not only directly participates in the regulation of host tumor immunity but also indirectly influences tumor progression and therapeutic outcomes through the production of metabolic products. Within the gut microbiome, metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids disrupt the intestinal barrier, thereby affecting both innate and adaptive immunity, which triggers and exacerbates systemic immune dysregulation. Chronic inflammation, immune imbalance, and the activation of cancer-associated signaling pathways by specific bacterial strains are considered key mechanisms underlying the ecological imbalance and the immunosuppressive microenvironment (16). In patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the evolution and composition of the gut microbiota are closely linked to the efficacy and adverse effects of treatments such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy, with microbial changes playing a crucial role in predicting both therapeutic outcomes and treatment-related side effects (17, 18).
2.1 Chemotherapy
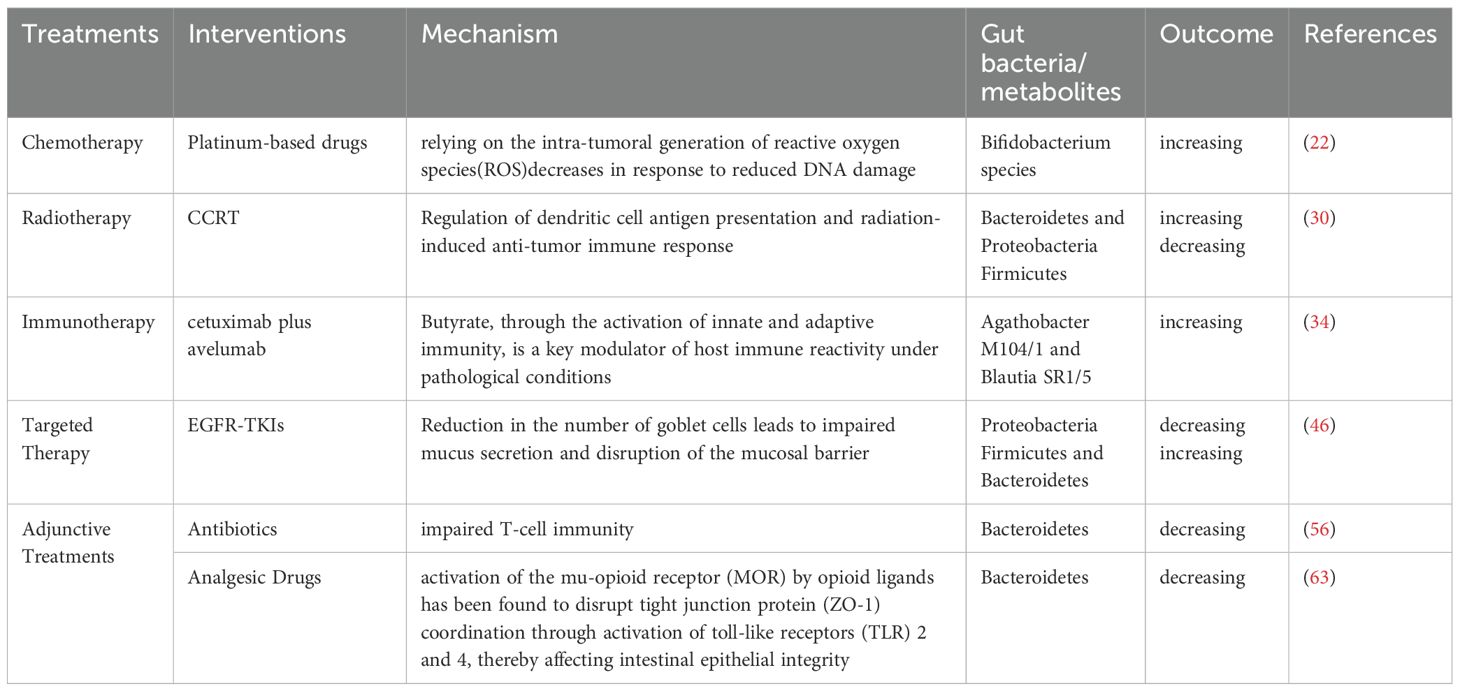
Chemotherapeutic agents are known to alter the composition of the gut microbiota, and several studies have confirmed significant shifts in specific microbial populations during NSCLC chemotherapy (19–23). Platinum-based drugs exert antitumor effects by inhibiting DNA replication and targeting cellular membranes and mitochondria, forming intra-strand platinum-DNA adducts that lead to double-strand breaks (DSBs) (24). These agents may exert their tumor-suppressive effects through microbiota-dependent pathways, with their efficacy partly relying on the intra-tumoral generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which decreases in response to reduced DNA damage. Particularly, an increase in Bifidobacterium species has been observed during platinum-based treatment of NSCLC (Table 1, Figure 1) (25). Pemetrexed, a multitargeted antifolate, inhibits several folate pathway enzymes—thymidylate synthase, dihydrofolate reductase, and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase—which are involved in purine and pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis for DNA and RNA production (26–28). In mouse models, pemetrexed treatment altered the gut microbiota, significantly increasing the relative abundance of Enterococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, and Streptococcaceae (19). Paclitaxel was found to decrease the overall abundance of gut microbiota in lung cancer-bearing mice, with a significant disruption in the Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio (p < 0.01) (29).
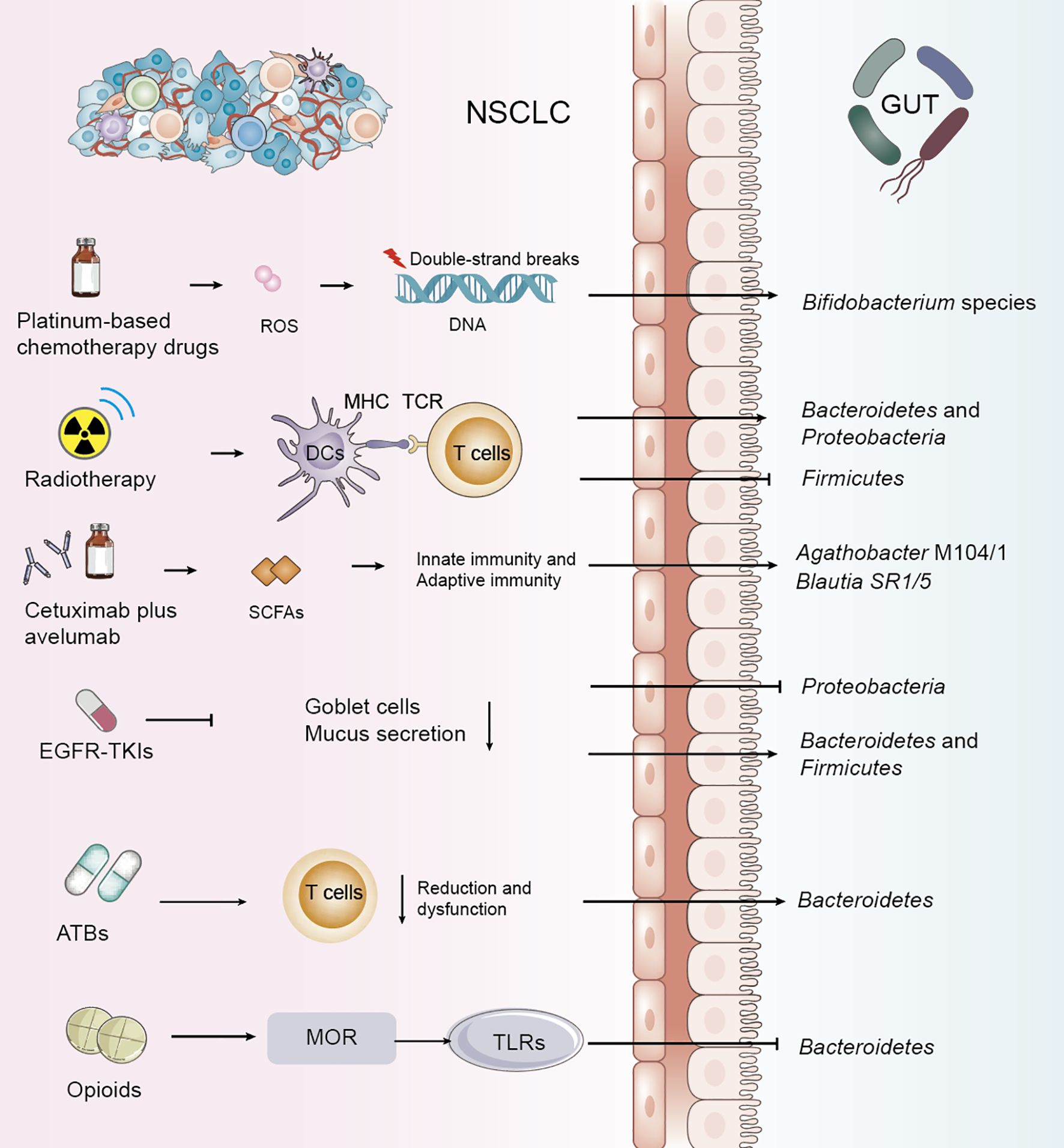
Figure 1. Impact of NSCLC treatments and adjunctive therapies on gut microbiota and metabolism. Common treatment modalities for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), exert direct or indirect effects on the gut microbiota. These alterations highlight the dynamic and reciprocal relationship between NSCLC therapies and gut microbiota composition.
2.2 Radiotherapy
For patients with locally advanced NSCLC, concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) is a standard treatment. Recent studies have shown that alpha diversity of gut microbiota is significantly associated with therapeutic response, indicating that dysbiosis is a key environmental factor affecting prognosis. One study explored dynamic changes in gut microbiota and their predictive value for progression-free survival (PFS) following CCRT in NSCLC patients. It was observed that the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria increased, while Firmicutes decreased after treatment. Patients with longer PFS demonstrated significantly greater diversity in fungi, archaea, and viruses compared to those with shorter PFS. Key metabolic pathways affected included fatty acid metabolism, arginine biosynthesis, lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis, and ascorbate and aldarate metabolism (Table 1, Figure 1) (30, 31).
2.3 Immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors
2.3.1 Immunotherapy
Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) signaling plays a role in maintaining gut mucosal tolerance. However, the direct link between host microbiota and tumor PD-L1 expression remains unclear (32). Treatment of NSCLC with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), including anti–PD-1/PD-L1 and anti–CTLA-4 agents, induces significant shifts in gut microbiota and metabolic profiles. Metagenomic sequencing has revealed correlations between microbial characteristics and clinical features such as PFS and PD-L1 expression levels (33). One study characterized the microbiome from bronchoscopic tumor biopsies of NSCLC patients undergoing ICIs therapy using 16S rRNA sequencing, revealing high levels of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria (29) The phase II CAVE-LUNG clinical trial examined the effects of cetuximab plus avelumab in chemotherapy-refractory NSCLC patients and identified increased expression of Agathobacter M104/1 and Blautia SR1/5 after treatment (P=0.016 and P=0.0008, respectively) (Table 1, Figure 1) (34). One study analyzing gut microbiota in NSCLC patients receiving atezolizumab-based immunotherapy found that microbial composition and diversity changed over the course of treatment, aiding the development of predictive biomarkers and microbiota-based biotherapeutics. Genera such as Clostridium, Lachnospiraceae, and Ruminococcaceae have been identified as potential biomarkers of therapeutic response (35). The therapeutic efficacy of ICIs is markedly enhanced in patients demonstrating durable clinical benefit as well as in those with tumors expressing PD-L1, with numerous studies underscoring this correlation (36).
2.3.2 irAEs
The complex interplay among the tumor microenvironment, gut microbiota, host factors, and responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), as well as the development of ICI-related immune-related adverse events (irAEs), remains largely unknown. Emerging evidence suggests that the gut microbiota may play a critical role in modulating tumor responses to ICIs (37). ICIs exert their therapeutic effect by activating T cells, a process frequently accompanied by autoimmune phenomena collectively termed “immune-related adverse events (irAEs).” These irAEs exhibit pleiotropic manifestations that can affect virtually any organ system, including the skin, colon, endocrine glands, joints, heart, and lungs. Importantly, the gut microbiota has been proposed as a potential biomarker for predicting irAEs. A recent study integrating gut microbiota metabolites, molecular modeling, and species-level variation identified signatures that shaped long-term therapeutic efficacy and adverse outcomes in lung cancer survivors. Patients who developed irAEs exhibited reduced abundance of Roseburia faecis, Roseburia intestinalis, Bacteroides stercoris, Lactobacillus mucosae, and Akkermansia muciniphila (38). These findings suggest that the gut microbiome may serve both as a risk factor and a protective factor for irAEs. Notably, checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis remains the most frequently reported irAE (39).
The gut microbiota has also been demonstrated to play a pivotal role in shaping the tumor immune microenvironment, thereby influencing the efficacy of ICIs (40). Alterations in gut microbial composition and function are associated with an increased risk of irAEs, and predictive models of such risks have been developed. For example, advanced machine learning approaches have been employed to identify gut microbial signatures capable of predicting irAE occurrence (39). A random forest classifier constructed from 14 microbial features exhibited strong discriminatory power between irAE and non-irAE groups. Functional analyses revealed that the gut microbiota of non-irAE patients was characterized by increased menaquinone biosynthesis, accompanied by upregulation of the rate-limiting enzymes menH and menC. Targeted metabolomic profiling further confirmed significantly higher serum menaquinone levels in non-irAE patients compared to those who developed irAEs (41). Collectively, these findings highlight the dual role of gut microbiota in shaping both therapeutic efficacy and toxicity of ICIs. Future research integrating metagenomic, metabolomic, and functional analyses will be critical to unravel the mechanistic underpinnings of these associations and to enable the development of microbiome-based biomarkers and therapeutic strategies for optimizing NSCLC treatment outcomes.
2.4 Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy using tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has become a cornerstone in NSCLC treatment alongside chemo- and radiotherapy (42). Studies examining the gastrointestinal microbiome in patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-wild-type versus EGFR-mutant NSCLC revealed a predominance of Proteobacteria, implicating its role in disease mechanisms (43). In EGFR-mutant patients treated with EGFR-TKIs, lower levels of Proteobacteria and higher levels of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes were observed (44). Despite the efficacy of second-generation TKIs such as afatinib, clinical trials have reported grade ≥3 diarrhea in over 25% of patients, with about 15% discontinuing treatment due to severe diarrhea, compromising therapeutic outcomes (45). Mouse models have shown significant increases in Peptostreptococcus, Staphylococcus, Escherichia-Shigella, and Akkermansia following afatinib treatment (Table 1, Figure 1) (46). A study investigating the gut microbiota profile in fecal samples from a lung-specific conditional EGFR mutant transgenic mouse model of lung tumorigenesis demonstrated that Lactobacillus, a genus of bacteria known for producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), may serve as a predictive factor for tumor initiation and progression in EGFR mutation-induced lung adenocarcinoma models (47).
3 Effects of adjunctive treatments on gut microbiota and metabolic alterations
3.1 Antibiotics
Antibiotics have a significant impact on gut microbiome health, often leading to dysbiosis or the proliferation of harmful flora that can undermine the effectiveness of therapies such as immunotherapy for NSCLC. Antibiotic use has been associated with poor responses to combination therapies, including immunotherapy (48–54). Analysis of bacterial phyla has shown that antibiotic treatment for up to 4 weeks prior to immunotherapy increases the abundance of Bacteroidetes. Systemic use of antibiotics has been linked to an increased Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio, correlating with poorer immunotherapy outcomes (55). Broad-spectrum antibiotic-associated gut microbiome dysbiosis, occurring in patients treated with long-term antibiotics, leads to impaired T-cell immunity (Table 1, Figure 1) (56). A study sequencing 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) from 69 fecal samples of advanced NSCLC patients prior to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy revealed that antibiotic use was significantly associated with a decrease in gut microbiota diversity (57). An analysis of bacterial diversity and differential abundance of fecal samples from NSCLC patients treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies showed that feces from patients not treated with antibiotics were enriched in Clostridium perfringens, especially within the Rumatococcaceae, UCG13, Clostridium spp., and Agathrobacterium spp. families. In contrast, feces from patients who received antibiotics were enriched in Hungatella (48). Plasma citrulline, a marker of intestinal barrier function, decreases early in NSCLC patients treated with nab-paclitaxel following antibiotic use, affecting citrulline metabolism and, consequently, intestinal microbiome metabolism (58). Vancomycin preferentially targets Gram-positive bacteria, including butyrate-producing species, reducing short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) concentrations in fecal and tissue samples. Vancomycin also eliminates two major families of SCFA-producing Clostridia: Ruminococcaceae and Eubacteriaceae (59). However, further studies are required to determine whether antibiotic use directly alters intestinal flora and metabolism, and to explore the mechanisms by which antibiotic use may reduce the efficacy of NSCLC treatments by modulating intestinal flora and metabolism.
3.2 Analgesic drugs
The gut microbiome plays an important role in modulating visceral pain, and recent evidence suggests that it may also be involved in various types of chronic pain, such as inflammatory pain, headaches, neuropathic pain, and opioid tolerance (60). Morphine and other opioids disrupt the gut barrier, alter gut flora and metabolism, and impair function by inhibiting mucus and bicarbonate secretion, disrupting muscle coordination, and increasing the risk of bacterial translocation (61). Long-term morphine use has been shown to significantly alter the gut microbiome, promoting the growth of Gram-positive pathogens while reducing biliary isolates (62). Additionally, activation of the mu-opioid receptor (MOR) by opioid ligands has been found to disrupt tight junction protein (ZO-1) coordination through activation of toll-like receptors (TLR) 2 and 4, thereby affecting intestinal epithelial integrity (Table 1, Figure 1) (63). Therefore, the rational use of analgesic drugs is also critical in the treatment of NSCLC, and it has been shown that analgesic drugs alter the gut microbiota, which in turn is detrimental to the treatment of NSCLC.
3.3 Traditional Chinese medicine as adjunctive treatment
The fundamental theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for treating NSCLC focuses on restoring balance through the principles of ‘strengthening the body’ and ‘eliminating evils’ when the body’s immunity is weak, and the tumor’s growth is overly strong. “Strengthening the body” refers to enhancing the body’s anti-cancer immunity, while “eliminating evil” directly inhibits the growth, proliferation, invasion, and migration of tumor cells. The clinical manifestations of NSCLC are often characterized by lung qi and lung yin deficiency. TCM’s core therapeutic paradigm for lung cancer revolves around the concepts of ‘lung qi deficiency’ and ‘qi-yin deficiency’, with an emphasis on “supporting the positive and curtailing the negative” (4, 64). It has been investigated that combination therapy with monoclonal antibodies remodeled the composition of the gut microbiota and increased the number of SCFAs-producing bacteria Muribaculum to sensitize the antitumor effects of anti-PD-1 therapy and restore the microbial composition of fecal samples from those who did not respond to anti-PD-1 therapy (65). Polysaccharides derived from Spirulina have been shown to increase the abundance of Lactobacillus, Allobaculum, Alloprevotella, and Olsenella, while reducing Bacteroides and Acinetobacter levels. These effects may be linked to the inhibition of lung cancer in mice (66). Fuzi-Li zhong pill (FLP) is a well-validated TCM formula that has long been used in China for gastrointestinal disease and adjunctive therapy for depression (67). Lateralis Radix Praeparata (Fuzi), a traditional Chinese herb, is known for its relatively low toxicity and has been found to improve gut dysbiosis in NSCLC, decreasing the abundance of Proteobacteria while increasing that of Firmicutes (68, 69). Si junzi Decoction (SJZD) is a traditional Chinese medicine formula widely used in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Despite its proven effectiveness, the precise mechanisms by which SJZD operates remain incompletely understood (70). A study evaluating the efficacy of SJZD on quality of life, hematological parameters, and modulation of gut flora in post-surgical NSCLC patients demonstrated that SJZD had a favorable effect on increasing microbial abundance and diversity, promoting probiotic microorganisms, and modulating microbial functions (71).
4 Beneficial intervention strategies for improving NSCLC treatment outcomes
4.1 Probiotic supplementation
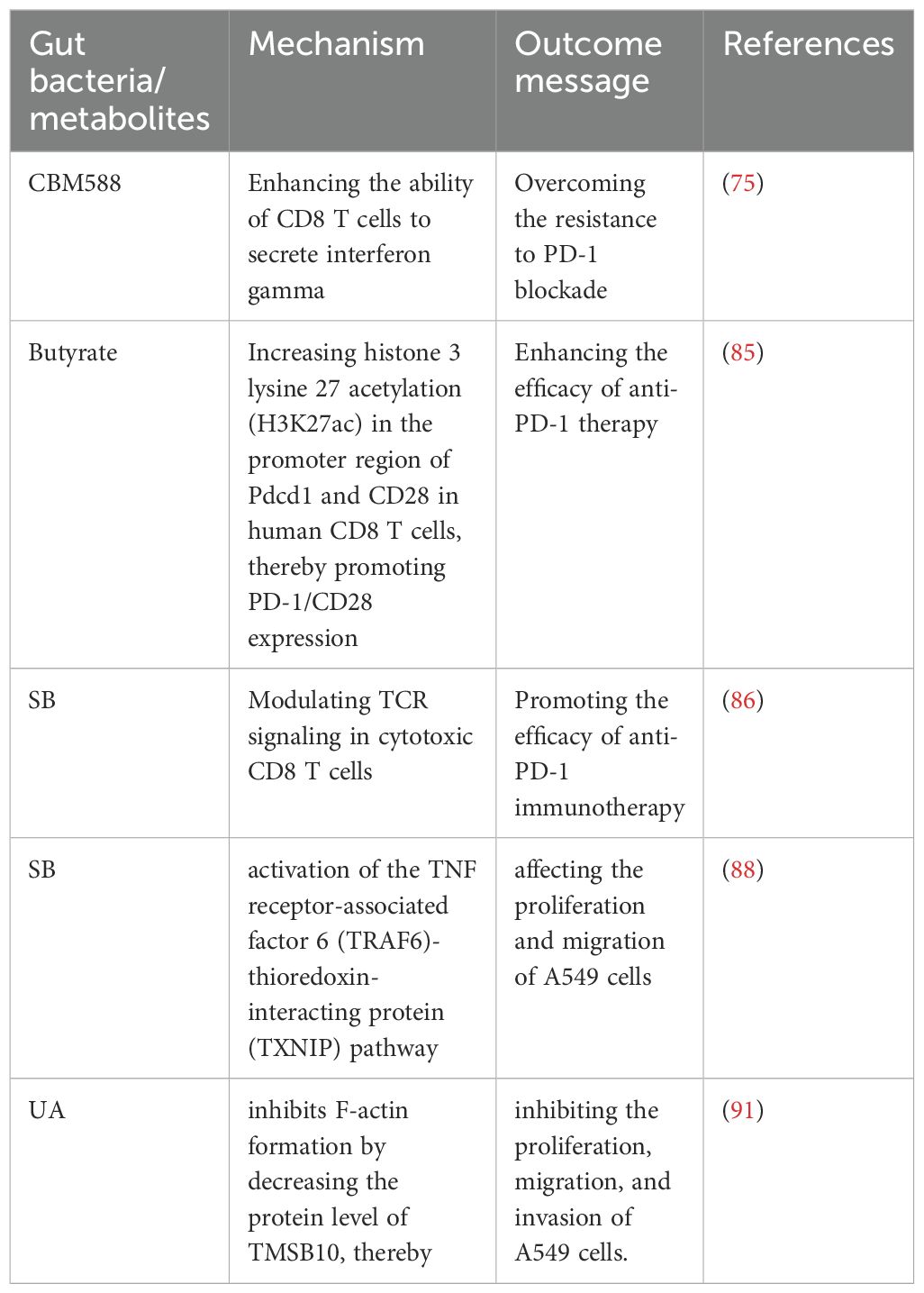
Probiotics have previously been shown to alter gut microbiota composition, thereby influencing cancer treatment outcomes. A study on the anticancer potential of probiotics suggests that gut probiotics exert tumor-suppressive effects through the gut-lung axis microecological regulation (72). Probiotics have been positively associated with overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in NSCLC patients treated with ICIs (73). Further research has shown that probiotics did not affect PFS but identified two dynamic types of gut flora during immunotherapy: one type exhibited the lowest relative abundance at the response time point, while the other showed the highest abundance at the response time point (74). Specific changes in intestinal flora, such as those induced by Clostridium butyricum, have been found to influence clinical outcomes in non-squamous NSCLC (NS-NSCLC) patients receiving bevacizumab combined with platinum chemotherapy, significantly reducing adverse events in patients (21). Clostridium butyricum MIYAIRI 588 (CBM588) has been shown to potentiate the efficacy of PD-1 blockade in NSCLC by modulating gut microbiota diversity and immune responses. CBM588 supplementation enhanced IL-10 secretion by lamina propria monocytes, improved intestinal homeostasis, and facilitated CD8+ T-cell activation, thereby helping to overcome resistance to immunotherapy (Table 2, Figure 2) (75, 76).
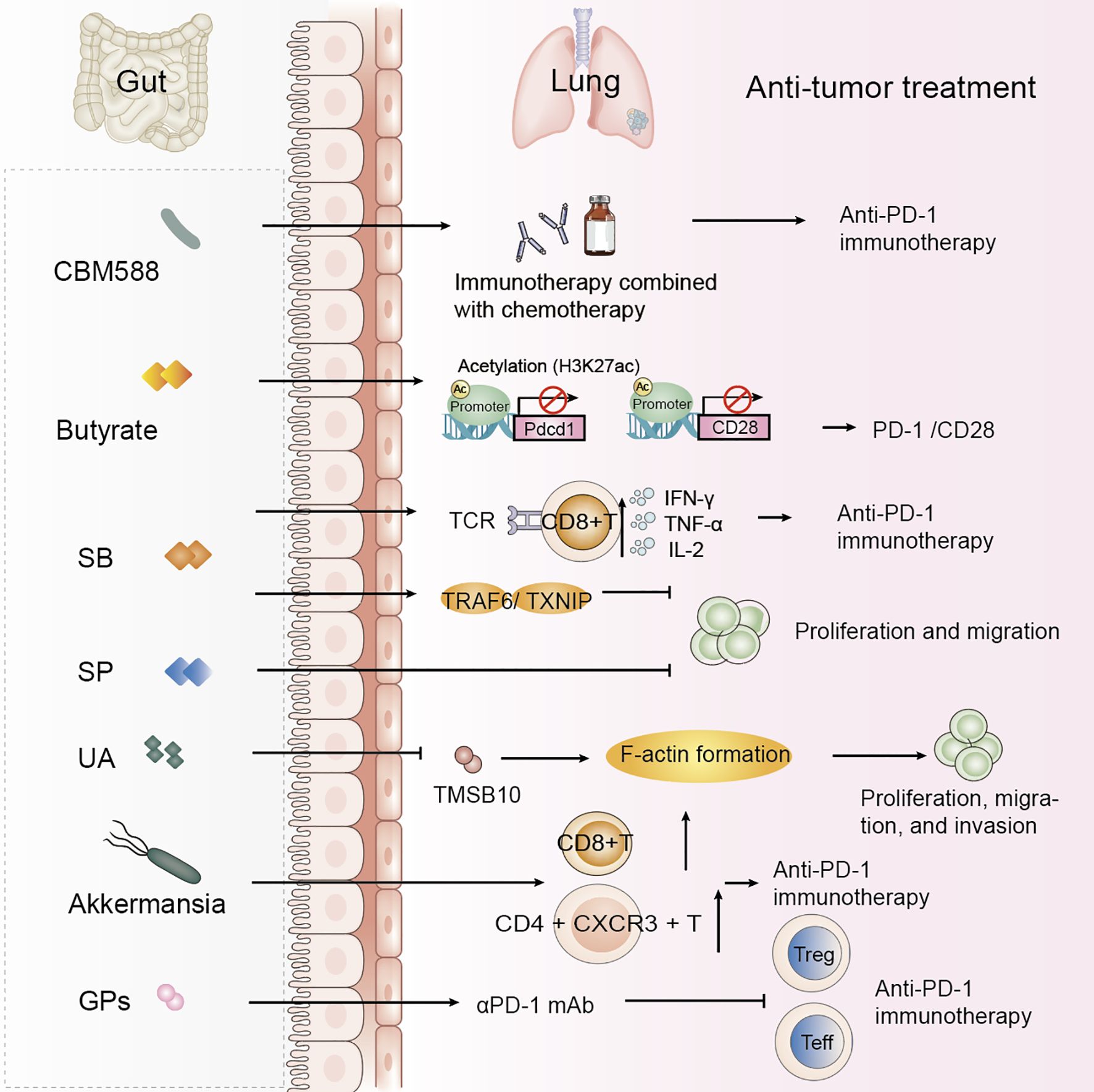
Figure 2. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites and probiotics improve NSCLC treatment efficacy. Specific gut microbiota and their metabolites modulate host immune responses and impact the efficacy of anti-tumor therapies in NSCLC. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of microbiota-derived interventions in improving therapeutic outcomes in NSCLC. SB, Sodium butyrate; SP, Sodium propionate; UA, Urolithin A; GPs, Ginseng polysaccharides.
Live biotherapeutic products (LBPs), as defined by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), are biological agents intended for disease prevention, treatment, or cure (77). Recently, LBPs designed to modulate the gut microbiota, such as Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, have shown potential therapeutic benefits, including in colorectal cancer [NCT03072641]. Of particular relevance to NSCLC, CJRB-101—an LBP containing Catenibacterium mitsuokai—has shown antitumor activity in humanized NSCLC mouse models when combined with pembrolizumab. Mechanistically, CJRB-101 reprograms M2 macrophages into M1 macrophages co-expressing CXCL9 and CXCL10, thereby enhancing CD8+ T-cell activation and augmenting antitumor immune responses (78).
4.2 Supplementation with metabolites
Characterizing the microbiota and metabolomic profiles of patients provides opportunities to target microbiota-derived metabolites that modulate the tumor microenvironment (TME) (79). These metabolites can influence NSCLC progression and shape the antitumor activity of host immune cells. For example, the gut microbiota generates short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which not only exert direct antitumor effects but also enhance immune system function (80).
4.2.1 SCFAs
In immunotherapy for NSCLC patients, specific intestinal flora can enhance T-cell responses and activate anti-tumor immune mechanisms through metabolites to improve therapeutic efficacy (81, 82). Studies have demonstrated that the diversity of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) is closely associated with the efficacy of immunotherapy (83). Metagenomic analyses reveal significant differences in metabolic pathways, with favorable responders exhibiting enhanced SCFA production. In murine models, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and SCFA supplementation improved therapeutic outcomes by promoting effector T-cell activity within tumors (84).
Serum butyrate levels were positively correlated with the expression of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) on circulating CD8 T cells and Vγ9 Vδ2 (Vδ2) T cells from NSCLC patients. Butyrate increased histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) in the promoter region of Pdcd1 and CD28 in human CD8 T cells, thereby promoting PD-1/CD28 expression and enhancing the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy (Table 2, Figure 2) (85). A study found a significant positive correlation between Streptococcus and CD8 T cell abundance, with the gut metabolite butyrate promoting the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by modulating TCR signaling in cytotoxic CD8 T cells (Table 2) (86). Butyrate supplementation also promotes the expression of anti-tumor cytokines in cytotoxic CD8 T cells through the T cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway (Figure 2) (87). Another study highlighted the potential of sodium butyrate in inhibiting lung cancer cell growth, triggering apoptosis, inducing cell cycle arrest, and modulating the immune response through activation of peripheral blood CD4+ T cells while selectively inducing IFN-γ-R1 in peripheral blood NK cells and inhibiting CD8+ T cells and NK cells. Sodium butyrate’s mechanism of action in the tumor microenvironment and its effects on the immune system offer valuable insights into its potential as an adjuvant therapy for NSCLC (83). In mice, sodium butyrate was shown to affect the proliferation and migration of A549 cells through the activation of the TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6)-thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) pathway, suggesting that sodium butyrate has an effective therapeutic effect on lung adenocarcinoma (Table 2) (88). Sodium propionate (SP) also inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (11). Lower concentrations of circulating SCFAs in lung cancer patients may affect the host immune response (89). A study establishing associations between the gut microbiome and its metabolites, and SCFAs in NSCLC patients in early and brain metastatic stages suggests that specific forms of the gut microbiome and SCFAs may be of value in the treatment of NSCLC (90).
4.2.2 Other metabolites
Urolithin A (UA), a natural compound produced by the gut microbiota through the metabolism of the polyphenols ellagitannin (ET) and ellagic acid (EA), has been found to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in NSCLC cell lines. UA inhibits F-actin formation by decreasing the protein level of TMSB10, thereby inhibiting the proliferation, migration, and invasion of A549 cells. Contributing to the treatment of NSCLC (Table 2, Figure 2) (91). Baicalin is a metabolite that modulates the gut microbiota, exerting its effects through the regulation of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Baicalin enhances the PD-1 (CD8+ T cell/Treg) balance and mitigates resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy (92).
The tryptophan–kynurenine (Trp–Kyn) metabolic axis, primarily regulated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO), exerts a profound influence on dendritic cell antigen presentation and T-cell priming through tryptophan depletion and kynurenine accumulation. This metabolic reprogramming fosters an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that promotes immune tolerance and facilitates tumor immune evasion (93, 94). Among the major metabolic pathways implicated in NSCLC immunomodulation—including short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) and bile acid metabolism—the Trp–Kyn axis demonstrates the most direct mechanistic linkage to impaired antigen presentation and reduced T-cell activation. Moreover, tumor genotypes such as EGFR and KEAP1 mutations may further modulate IDO1/TDO activity, influencing immune resistance and responsiveness to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) (95). Consequently, targeting the Trp–Kyn pathway represents a promising strategy to enhance the efficacy of ICIs and overcome immune escape in NSCLC (96).
4.3 Fecal microbiota transplantation
To date, microbiome-metabolite (ME) research in oncology has primarily focused on the impact of gut microbiota composition on the efficacy of ICIs. Variations in the relative abundance of individual microbial strains and overall microbial diversity in patients undergoing ICI therapy appear to correlate with treatment outcomes (97). FMT has potential therapeutic benefits, particularly in converting non-responders to NSCLC treatment into responders. Fecal transplantation from anti-PD-1-responsive patients to non-responsive NSCLC patients increased treatment response rates without increasing toxicity (43, 57, 98). Akkermansia muciniphila (Akk) has been associated with the clinical benefits of ICIs in NSCLC patients, and the relative abundance of Akk may serve as a reliable biomarker for predicting good or poor prognosis in patients receiving PD-1 blockade immunotherapy, refining patient stratification in future studies (99). Akk enrichment modulation enhances immune responses through fecal microbiota transplantation in patients benefiting from immune checkpoint blockade (100). In animal experiments, the relative abundance of Akk predicted clinical response to PD-1 blockade in NSCLC patients. Mice receiving FMT, negative for Fusobacterium tachyzoites, exhibited tumor resistance to PD-1 blockade (15). RNA later preserved stool samples were collected from 65 pre-treatment (baseline) and post-treatment stage III/IV NSCLC patients treated with ICI and classified as responders or non-responders according to RECIST criteria. Mixed and individual responder and non-responder microbiota were transplanted into a gnotobiotic mouse model of lung cancer and treated with ICI, while patient fecal samples were subjected to 16S rDNA and RNA sequencing, which demonstrated that responding patients had a different microbial community structure (P=0.004) and a different bacterial transcriptome (PC2=0.03) at baseline. Taxa significantly enriched in responders included amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) belonging to the genera Rumococcus, Akkermansia muciniphila, and E. faecalis. Transplantation of mixed and individual responding microbiota into gnotobiotic mice reduced tumor growth compared to non-responding colonized mice after ICI use (P=0.023, P=0.019, P=0.008, respectively), showing an increased tumor CD8 + IFN γ + T-cells and CD4+ CXCR3+T-cells phenotype after ICI treatment. Responding mice were enriched with ASV belonging to the genera Mycobacterium, Blautia, Akkermannia and E. faecalis (101). However, many FMT studies have reported only limited methodological descriptions, details of mouse cohorts, and statistical methods. One study performed human-to-germ-free mouse FMT using fecal samples from NSCLC patients with pathological response or no response after neoadjuvant ICI treatment, which produced greater anti-tumor responses in R-FMT mice in combination with anti-PD-L1 therapy compared to NR-FMT, detailed study of the mouse microbiota after FMT using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing, and use of models for the biological variables were classified and corrected, revealing that the most abundant taxa were shared between human inoculum and mice, although low abundance human taxa were more variable in post-FMT colonized mice. Multiple Clostridium spp. were also associated with tumor outcome in individual anti-PD-L1-treated R-FMT mice (102).
Research on Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) would benefit from well-designed large-scale studies that incorporate extensive metadata and standardized bio-sample collection. Such efforts are crucial to minimize noise in downstream multi-omics analyses and to ensure robust long-term follow-up to address potential safety concerns. The results of these studies could guide targeted experimental designs to explore the underlying mechanisms of FMT clinical outcomes and may ultimately lead to the personalized matching of donor and recipient characteristics to achieve optimal therapeutic success (103). Although FMT may be a promising therapeutic option, the risk of bacterial translocation (including antibiotic-resistant bacteria) and sepsis in patients remains a significant safety concern, and studies have been conducted that discuss sepsis due to FMT (104–106). The most feasible translational approach from whole-stool FMT toward safer and standardized microbiome-based therapies involves progressive refinement from complex donor-derived consortia to defined microbial communities and, ultimately, purified microbial metabolites with validated bioactivity (107, 108). Microbial ecosystem therapy (MET), comprising selected, well-characterized commensal strains, represents a key intermediate strategy that maintains ecological functionality while improving safety and reproducibility (109, 110). Preserving therapeutic efficacy along this continuum requires retention of crucial host–microbe interactions that regulate immune homeostasis (111). Therefore, future microbiota-targeted interventions should emphasize context-dependent functionality to achieve both safety and sustained immunotherapeutic benefit in NSCLC treatment.
4.4 Dietary interventions
Castalagin is a polyphenol that enhances resistance to PD-1. In their study, Messaoudene et al. reported that oral supplementation with polyphenol-rich berry camu-camu (CC; Myrciaria dubia) altered the gut microbial composition, leading to antitumor activity and a stronger anti-PD-1 response. Castalagin improved the CD8+/FOXP3+CD4+ ratio in the tumor microenvironment. Moreover, castalagin induced metabolic changes, resulting in an increase level of taurine-conjugated bile acids. Ruminococcus-rich NSCLC responders were found to be able to metabolize castalagin (112, 113). Patients should be advised to minimize animal meat intake and increase plant intake where possible, aiming for 30 plants per week. High fiber intake (>30 g/day) is thought to increase the chances of response to immunotherapy in NSCLC (114). Methionine regulates tumor immunity by modulating the activity of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), so the tumor immune response can be improved by controlling dietary methionine intake (115). Ginseng polysaccharides (GPs) are one of the most abundant constituents of ginseng, and GPs increase the antitumor response to αPD-1 mAb by inhibiting the metabolite kynurenine/tryptophan ratio, which contributes to the suppression of regulatory T-cells and the induction of Teff cells following combination therapy, enhancing the antitumor effects of immunotherapy (116). Specific diets directly or indirectly alter the intestinal flora and metabolism of NSCLC patients and increase the clinical efficacy of NSCLC.
In recent years, relevant clinical trials have been conducted around simulated fasting diets, high-fiber diets, nutritional supplements and other related trials, which have either maximized the therapeutic efficacy of NSCLC treatments or maximized the benefits for patients (117).
5 Role of gut microbiota and metabolites in NSCLC treatment and prognosis
5.1 Baseline microbiome as a predictive biomarker
As previously discussed, immunotherapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of NSCLC. Numerous studies have collected plasma and stool samples from patient cohorts prior to initiating immunotherapy, performing metabolomic and microbiome analyses (118, 119). The results obtained after enrichment are referred to as baseline microbiome characteristics. From a metagenomic perspective, enrichment of Akkermansia may be indicative of favorable prognosis in patients undergoing PD-1 blockade immunotherapy, offering potential for improved patient stratification in future studies (99). Akkermansia muciniphila, a mucin-degrading commensal bacterium, exemplifies the context-dependent functionality of microbiota-based interventions. Under conditions of adequate mucin renewal and minimal antibiotic disturbance, it reinforces gut barrier integrity and immune regulation (120, 121). However, in states of mucin depletion, chronic inflammation, or dysbiosis, its activity may shift from protective to deleterious, aggravating intestinal damage and immune dysregulation (122). These findings underscore the necessity of designing microbial consortia and derived metabolites that maintain host–microbe symbiosis and ensure both safety and therapeutic efficacy in diseases such as NSCLC (120, 122).
Additionally, metabolomic analyses suggest that patients enriched with baseline short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) may derive long-term benefits from immunotherapy (90). The close link between microbiota and metabolites at baseline not only provides novel insights for clinical stratification but also opens new avenues for clinical translation (86). For instance, some studies have demonstrated SCFA enrichment via metabolomic profiling and verified the presence of microbiota producing SCFAs as a baseline marker for therapeutic efficacy. In parallel, other studies have enriched baseline microbiota and subsequently identified corresponding metabolites, confirming the therapeutic benefits of these metabolites at baseline enrichment (92).
In summary, baseline microbiome and metabolite characteristics have been explored in existing research, and many clinical trials have since emerged, contributing to this growing field.
5.2 Gut microbiota and metabolites in NSCLC clinical trials
Numerous clinical trials have focused on the role of gut microbiota and metabolites in various treatment modalities for NSCLC, examining their impact on treatment efficacy and prognosis. These studies underscore the importance of analyzing dynamic changes in the gut microbiota throughout the course of treatment, with specific microbial and metabolic alterations observed after a certain duration of therapy. By exploring the modulation of specific microbiota, these studies suggest that manipulating the microbiome could enhance NSCLC treatment outcomes. Such findings are poised to drive major breakthroughs in future NSCLC therapies.
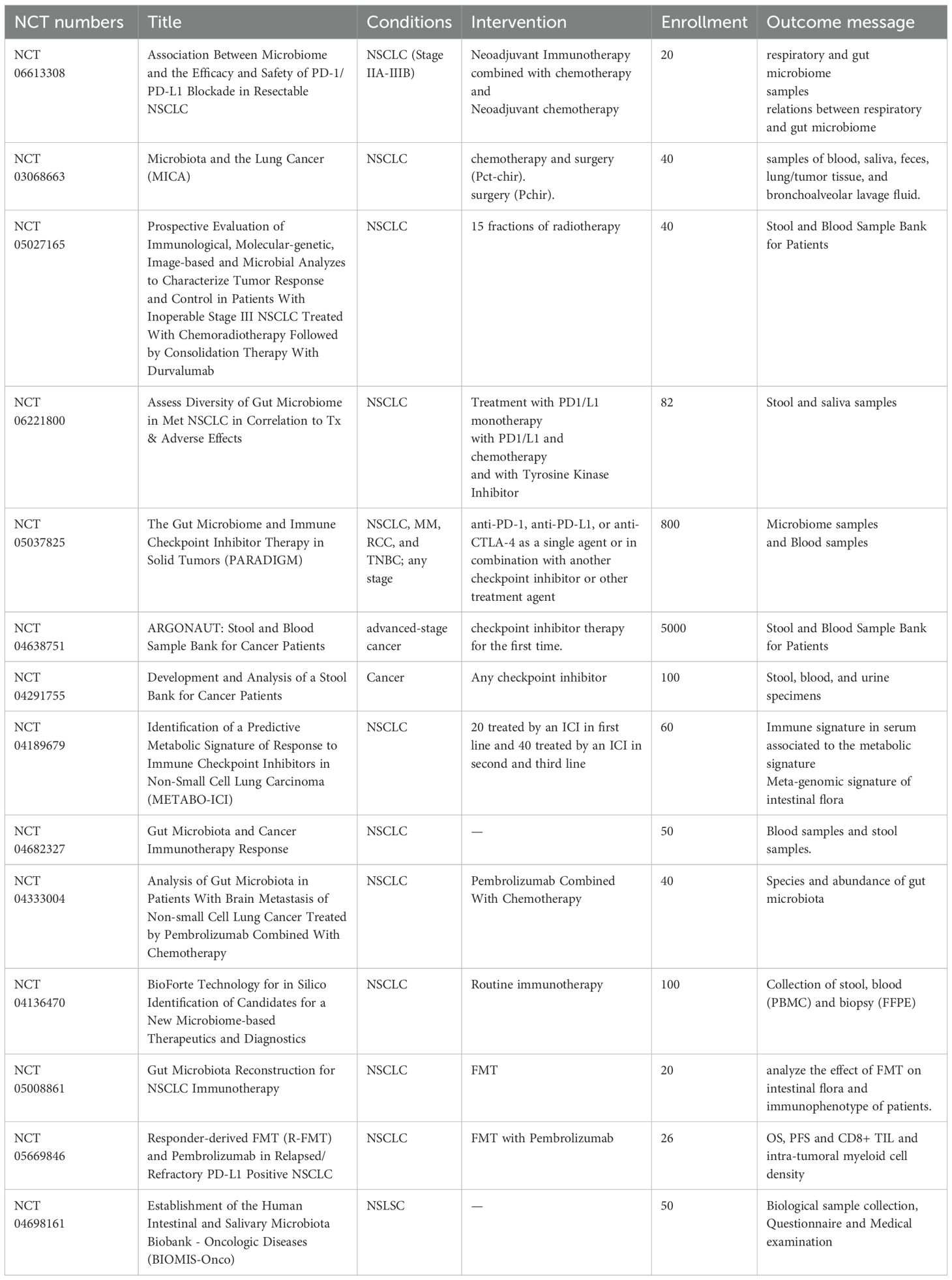
[NCT03068663] A study grouped 40 patients with NSCLC, 20 patients were treated with surgery only, while the other half also received chemotherapy. The main aim was to explore changes in the lung, upper respiratory tract and intestinal microbiota and potentially find an association between the flora and the prognosis of patients treated. [NCT06221800] Another study was conducted to collect data on the dynamics of the gut microbiome of 82 subjects with advanced/metastatic NSCLC (NSCLC) during treatment with NSCLC. The subjects were classified into 3 groups: anti-PD-1 monotherapy, anti-PD-1 combination chemotherapy and TKIs. therapy, anti-PD-1 combination chemotherapy therapy and TKIs therapy and analyzed the diversity and composition of the gut microbiome of the subjects during the treatment of NSCLC to provide reference for the efficacy of NSCLC treatment [NCT05669846]. Suitable patients will be identified at progression on PD-1 monotherapy or PD-1-containing regimens and patients will undergo a 35-day screening assessment. Following enrolment, patients will be serum matched to suitable donors and patients will receive R-FMT (induction) via colonoscopy on C1D1 and C3D1. R-FMT (maintenance) by sigmoidoscopy on C4D1 will be repeated every 9 weeks. All patients will receive an additional 200mg of pembrolizumab every 3 weeks and patients will be treated until disease progression or intolerance of toxicity or completion of 2 years of treatment (Table 3, Figure 3).
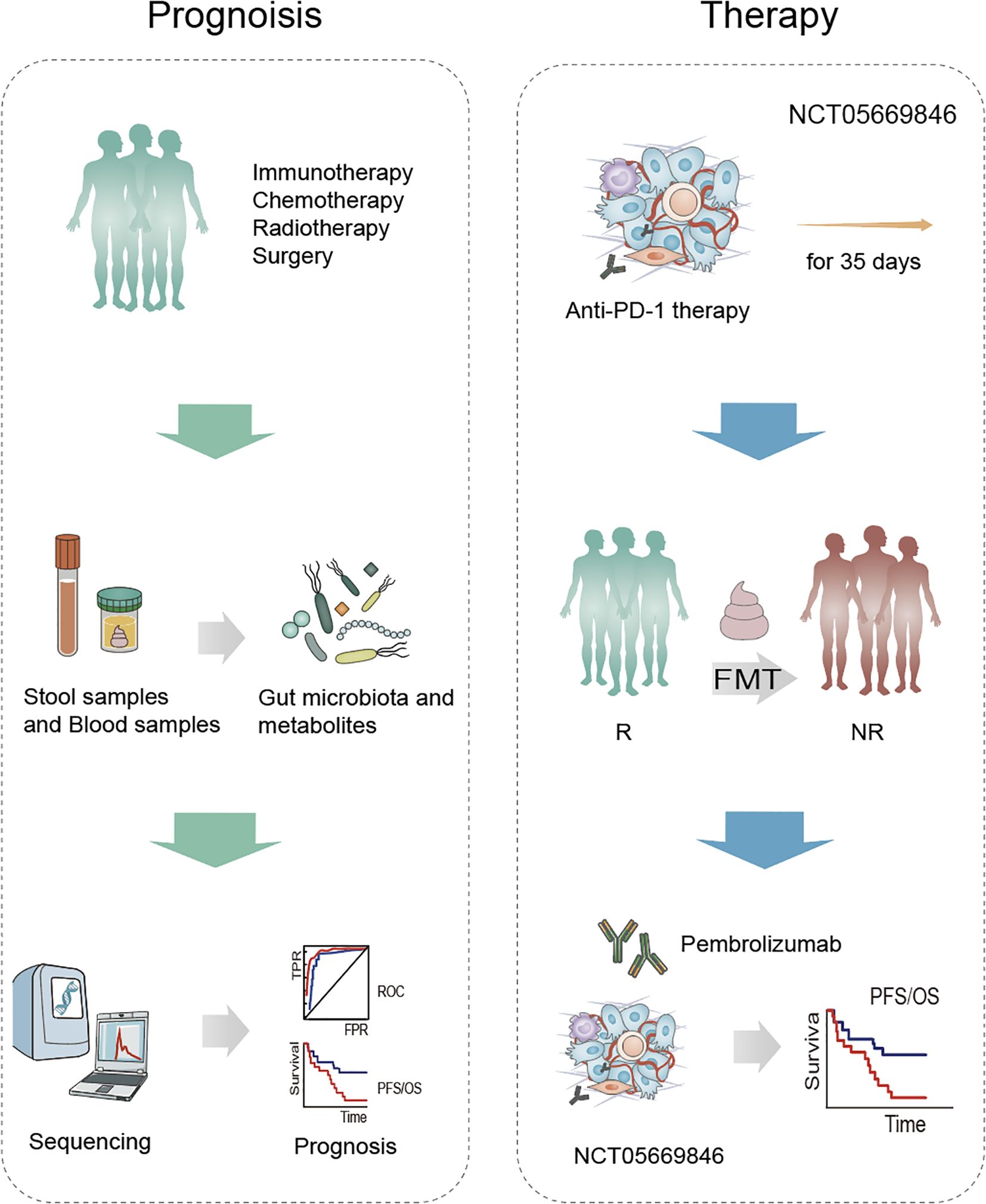
Figure 3. Microbiota-based strategies in the prognosis and treatment of NSCLC. Patients undergoing standard treatment modalities—such as immunotherapy, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery—provide stool and blood samples, from which gut microbiota and metabolites are analyzed. Subsequent sequencing and computational analysis identify microbial and metabolic biomarkers associated with treatment response and survival outcomes. As part of the clinical trial NCT05669846, patients receive anti-PD-1 therapy for 35 days. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is used to transfer gut microbes from responders (R) to non-responders (NR), followed by pembrolizumab treatment. This strategy aims to improve immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) efficacy and enhance progression-free and overall survival.
These clinical trials involve large cohorts and feature robust experimental design, with open results providing valuable insights into the relationship between gut microbiota, treatment efficacy, and patient outcomes. For further details and updates, clinicaltrials.gov is a useful resource.
6 Conclusion and future directions
As the importance of gut microbiota in disease development and treatment continues to be unveiled, increasing attention is being directed toward the role of gut microbiota and its metabolites in NSCLC therapy (123). NSCLC patients who achieve long-term survival exhibit distinct gut microbiota compositions. Patients with favorable prognoses typically possess a more diverse and abundant gut microbiome, and this diversity is closely linked to the activation of antitumor immune responses. For instance, high abundances of Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and certain lactobacilli are associated with improved immune responses and prolonged survival in NSCLC patients (18, 74). Conversely, a high abundance of Proteobacteria is associated with reduced efficacy of immunotherapy, and Helicobacter pylori seropositivity correlates with poorer survival in NSCLC patients receiving anti-PD-1 therapy (124).
Exogenous interventions hold promise in elucidating the complex mechanisms by which gut microbiota influence NSCLC treatment outcomes. First, drugs can induce dysbiosis by altering gut barrier function, thus affecting the efficacy of cancer treatments cancer therapy research (125, 126). Furthermore, preliminary studies on probiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), and specific engineered strains have demonstrated potential to enhance the response to immunotherapy in NSCLC patients (127). FMT, by reintroducing beneficial gut microbiota, offers hope for treating NSCLC patients who are resistant to conventional therapies. Despite the challenges in standardizing FMT protocols, and the inherent individual variability in microbiome composition and response to interventions, the ethical considerations surrounding microbiome-based therapies require significant advancements. The intervention of gut microbiota remains in the research phase, necessitating further clinical trials to validate its efficacy (128). As such, exploring how to manipulate gut microbiota composition to achieve more efficient and less toxic treatment strategies remains a crucial direction in cancer treatment research.
The relationship between gut microbiota and treatment outcomes is multifactorial and complex. Current research primarily focuses on macro-level microbiome composition, lacking in-depth investigation into specific microbial populations and their metabolites. To date, accurately tracking dynamic changes in the microbiome remains challenging, and a deeper understanding of the mechanisms by which specific microbes influence therapy is needed. This review primarily focuses on metagenomic sequencing, metabolomic profiling, and 16S rRNA sequencing to explore the specific roles of gut microbiota in NSCLC treatment. Future research should integrate finer techniques, such as single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomics, to establish connections from the disease and immune microenvironment perspective (129, 130). Ultimately, gut microbiota intervention is expected to become a routine component of NSCLC treatment, providing new therapeutic avenues for cancer immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. With advancements in technology and the progression of clinical trials, we are optimistic that gut microbiota will become a crucial factor in NSCLC treatment, driving cancer therapy towards more personalized and precision-based approaches.
Author contributions
J-MJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. C-GL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. DZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. JC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82203056), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2023-BS-167), the Science and Technology Talent Innovation Support Plan of Dalian (2022RQ091), and the “1+X” Program for Clinical Competency Enhancement – Clinical Research Incubation Project of the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University (2022LCYJYB01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Van Hul M, Cani PD, Petitfils C, De Vos WM, Tilg H, El-Omar EM, et al. What defines a healthy gut microbiome? Gut. (2024) 73:1893–908. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-333378
2. Hill JH and Round JL. Intestinal fungal-host interactions in promoting and maintaining health. Cell Host Microbe. (2024) 32:1668–80. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.09.010
3. Song P, Yang D, Wang H, Cui X, Si X, Zhang X, et al. Relationship between intestinal flora structure and metabolite analysis and immunotherapy efficacy in Chinese nsclc patients. Thorac Cancer. (2020) 11:1621–32. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13442
4. Wang X, Hou L, Cui M, Liu J, Wang M, Xie J, et al. The traditional chinese medicine and non-small cell lung cancer: from a gut microbiome perspective. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1151557. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1151557
5. Boesch M, Baty F, Albrich WC, Flatz L, Rodriguez R, Rothschild SI, et al. Local tumor microbial signatures and response to checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology. (2021) 10:1988403. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1988403
6. Nagasaka M, Sexton R, Alhasan R, Rahman S, Azmi AS, Sukari A, et al. Gut microbiome and response to checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer-a review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2020) 145:102841. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.102841
7. Vernocchi P, Gili T, Conte F, Del Chierico F, Conta G, Miccheli A, et al. Network analysis of gut microbiome and metabolome to discover microbiota-linked biomarkers in patients affected by non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228730
8. Lopes S, Pabst L, Dory A, Klotz M, Gourieux B, Michel B, et al. Do proton pump inhibitors alter the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients? A meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1070076. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1070076
9. Zhou Y, Liu Z, and Chen T. Gut microbiota: A promising milestone in enhancing the efficacy of pd1/pd-L1 blockade therapy. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:847350. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.847350
10. Zhang C, Wang J, Sun Z, Cao Y, Mu Z, Ji X, et al. Commensal microbiota contributes to predicting the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Sci. (2021) 112:3005–17. doi: 10.1111/cas.14979
11. Qian X, Zhang HY, Li QL, Ma GJ, Chen Z, Ji XM, et al. Integrated microbiome, metabolome, and proteome analysis identifies a novel interplay among commensal bacteria, metabolites and candidate targets in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12:e947. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.947
12. Ni B, Kong X, Yan Y, Fu B, Zhou F, Xu S, et al. Combined analysis of gut microbiome and serum metabolomics reveals novel biomarkers in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1091825. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1091825
13. Hendriks LEL, Remon J, Faivre-Finn C, Garassino MC, Heymach JV, Kerr KM, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2024) 10:71. doi: 10.1038/s41572-024-00551-9
14. Riely GJ, Wood DE, Ettinger DS, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, nccn clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2024) 22:249–74. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2204.0023
15. Souza VGP, Forder A, Pewarchuk ME, Telkar N, De Araujo RP, Stewart GL, et al. The complex role of the microbiome in non-small cell lung cancer development and progression. Cells. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/cells12242801
16. Bum Lee J, Huang Y, Oya Y, Nutzinger J Y L E A, and Sooi K. Modulating the gut microbiome in non-small cell lung cancer: challenges and opportunities. Lung Cancer. (2024) 194:107862. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2024.107862
17. Zhang H and Xu Z. Gut-lung axis: role of the gut microbiota in non-small cell lung cancer immunotherapy. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1257515. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1257515
18. Yuan H, Gui R, Wang Z, Fang F, and Zhao H. Gut microbiota: A novel and potential target for radioimmunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1128774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1128774
19. Pensec C, Gillaizeau F, Guenot D, Bessard A, Carton T, Leuillet S, et al. Impact of pemetrexed chemotherapy on the gut microbiota and intestinal inflammation of patient-lung-derived tumor xenograft (Pdx) mouse models. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:9094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65792-6
20. Bredin P and Naidoo J. The gut microbiome, immune check point inhibition and immune-related adverse events in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2022) 41:347–66. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10039-1
21. Cong J, Zhang C, Zhou S, Zhu J, and Liang C. A pilot study: favorable effects of clostridium butyricum on intestinal microbiota for adjuvant therapy of lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153599
22. Hopkins AM, Kichenadasse G, Mckinnon RA, Abuhelwa AY, Logan JM, Badaoui S, et al. Efficacy of first-line atezolizumab combination therapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving proton pump inhibitors: post hoc analysis of impower150. Br J Cancer. (2022) 126:42–7. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01606-4
23. Viaud S, Saccheri F, Mignot G, Yamazaki T, Daillère R, Hannani D, et al. The intestinal microbiota modulates the anticancer immune effects of cyclophosphamide. Science. (2013) 342:971–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1240537
24. Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Michels J, Brenner C, Szabadkai G, Harel-Bellan A, et al. Systems biology of cisplatin resistance: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. (2014) 5:e1257. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.428
25. Lee SH, Cho SY, Yoon Y, Park C, Sohn J, Jeong JJ, et al. Bifidobacterium bifidum strains synergize with immune checkpoint inhibitors to reduce tumour burden in mice. Nat Microbiol. (2021) 6:277–88. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-00831-6
26. Adjei AA. Pharmacology and mechanism of action of pemetrexed. Clin Lung Cancer. (2004) 5 Suppl 2:S51–55. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2004.s.003
27. Tomasini P, Barlesi F, Mascaux C, and Greillier L. Pemetrexed for advanced stage nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer: latest evidence about its extended use and outcomes. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2016) 8:198–208. doi: 10.1177/1758834016644155
28. Molina JR and Adjei AA. The role of pemetrexed (Alimta, ly231514) in lung cancer therapy. Clin Lung Cancer. (2003) 5:21–7. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2003.n.017
29. Georgiou K, Marinov B, Farooqi AA, and Gazouli M. Gut microbiota in lung cancer: where do we stand? Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910429
30. Xi Y, Liu F, Qiu B, Li Y, Xie X, Guo J, et al. Analysis of gut microbiota signature and microbe-disease progression associations in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:892401. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.892401
31. Qiu B, Xi Y, Liu F, Li Y, Xie X, Guo J, et al. Gut microbiome is associated with the response to chemoradiotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2023) 115:407–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.07.032
32. Chulkina M, Beswick EJ, and Pinchuk IV. Role of pd-L1 in gut mucosa tolerance and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239165
33. Dora D, Ligeti B, Kovacs T, Revisnyei P, Galffy G, Dulka E, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with anti-pd1 immunotherapy show distinct microbial signatures and metabolic pathways according to progression-free survival and pd-L1 status. Oncoimmunology. (2023) 12:2204746. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2204746
34. Martini G, Ciardiello D, Dallio M, Famiglietti V, Esposito L, Corte CMD, et al. Gut microbiota correlates with antitumor activity in patients with mcrc and nsclc treated with cetuximab plus avelumab. Int J Cancer. (2022) 151:473–80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34033
35. Morita A, Ichihara E, Inoue K, Fujiwara K, Yokoyama T, Harada D, et al. Impacts of probiotics on the efficacies of immune checkpoint inhibitors with or without chemotherapy for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. (2024) 154:1607–15. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34842
36. Liu X, Tang H, Zhou Q, Zeng Y, Lu B, Chen D, et al. Gut microbiota composition in patients with advanced Malignancies experiencing immune-related adverse events. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1109281. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1109281
37. Poto R, Troiani T, Criscuolo G, Marone G, Ciardiello F, Tocchetti CG, et al. Holistic approach to immune checkpoint inhibitor-related adverse events. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:804597. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.804597
38. Liu F, Xiang Z, Chen Y, Lu G, Wang J, Yao J, et al. Time course of visual attention in rats by atomic magnetometer. PloS One. (2024) 19:e0312589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312589
39. Zhang M, Liu J, and Xia Q. Role of gut microbiome in cancer immunotherapy: from predictive biomarker to therapeutic target. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2023) 12:84. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00442-x
40. Gao YQ, Tan YJ, and Fang JY. Roles of the gut microbiota in immune-related adverse events: mechanisms and therapeutic intervention. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2025) 22:499–516. doi: 10.1038/s41571-025-01026-w
41. Hu M, Lin X, Sun T, Shao X, Huang X, Du W, et al. Gut microbiome for predicting immune checkpoint blockade-associated adverse events. Genome Med. (2024) 16:16. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01285-9
42. Melosky B. Review of egfr Tkis in metastatic nsclc, including ongoing trials. Front Oncol. (2014) 4:244. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00244
43. Saifon W, Sensorn I, Trachu N, Oranratnachai S, Charoenyingwattana A, Runcharoen C, et al. Gastrointestinal microbiota profile and clinical correlations in advanced egfr-wt and egfr-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:963. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10050-3
44. Park K, Wan-Teck Lim D, Okamoto I, and Yang JC. First-line afatinib for the treatment of egfr mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ‘Real-world’ Clinical setting. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2019) 11:1758835919836374. doi: 10.1177/1758835919836374
45. Arrieta O, De La Torre-Vallejo M, López-Macías D, Orta D, Turcott J, Macedo-Pérez EO, et al. Nutritional status, body surface, and low lean body mass/body mass index are related to dose reduction and severe gastrointestinal toxicity induced by afatinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist. (2015) 20:967–74. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0058
46. Zhang L, Hu A, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu Y, Xu L, et al. Medication adjustment of afatinib and combination therapy with sitagliptin for alleviating afatinib-induced diarrhea in rats. Neoplasia. (2023) 43:100922. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2023.100922
47. Kim DS, Kim EH, Kim JY, Kim DH, Choi YJ, Jeong J, et al. The profile of gut microbiota in carcinogenesis driven by mutant egfr in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat. (2025) 2025. doi: 10.4143/crt.2024.1177
48. Hakozaki T, Richard C, Elkrief A, Hosomi Y, Benlaïfaoui M, Mimpen I, et al. The gut microbiome associates with immune checkpoint inhibition outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. (2020) 8:1243–50. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-20-0196
49. Shah H and Ng TL. A narrative review from gut to lungs: non-small cell lung cancer and the gastrointestinal microbiome. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2023) 12:909–26. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-595
50. Castelo-Branco L, Morgan G, Prelaj A, Scheffler M, Canhão H, Van Meerbeeck JP, et al. Challenges and knowledge gaps with immune checkpoint inhibitors monotherapy in the management of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A survey of oncologist perceptions. ESMO Open. (2023) 8:100764. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100764
51. Tinsley N, Zhou C, Tan G, Rack S, Lorigan P, Blackhall F, et al. Cumulative antibiotic use significantly decreases efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced cancer. Oncologist. (2020) 25:55–63. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0160
52. Ochi N, Ichihara E, Takigawa N, Harada D, Inoue K, Shibayama T, et al. The effects of antibiotics on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer differ based on pd-L1 expression. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 149:73–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.02.040
53. Galli G, Triulzi T, Proto C, Signorelli D, Imbimbo M, Poggi M, et al. Association between antibiotic-immunotherapy exposure ratio and outcome in metastatic non small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2019) 132:72–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.04.008
54. Wu Q, Liu J, Wu S, and Xie X. The impact of antibiotics on efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in Malignancies: A study based on 44 cohorts. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 92:107303. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107303
55. Grenda A, Iwan E, Krawczyk P, Frąk M, Chmielewska I, Bomba A, et al. Attempting to identify bacterial allies in immunotherapy of nsclc patients. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246250
56. Xu K, Cai J, Xing J, Li X, Wu B, Zhu Z, et al. Broad-spectrum antibiotics associated gut microbiome disturbance impairs T cell immunity and promotes lung cancer metastasis: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:1182. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10307-x
57. Zhang F, Ferrero M, Dong N, D'auria G, Reyes-Prieto M, Herreros-Pomares A, et al. Analysis of the gut microbiota: an emerging source of biomarkers for immune checkpoint blockade therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. . Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112514
58. Ouaknine Krief J, Helly De Tauriers P, Dumenil C, Neveux N, Dumoulin J, Giraud V, et al. Role of antibiotic use, plasma citrulline and blood microbiome in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:176. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0658-1
59. Uribe-Herranz M, Rafail S, Beghi S, Gil-De-Gómez L, Verginadis I, Bittinger K, et al. Gut microbiota modulate dendritic cell antigen presentation and radiotherapy-induced antitumor immune response. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:466–79. doi: 10.1172/JCI124332
60. Guo R, Chen LH, Xing C, and Liu T. Pain regulation by gut microbiota: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Br J Anaesth. (2019) 123:637–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2019.07.026
61. Banerjee S, Sindberg G, Wang F, Meng J, Sharma U, Zhang L, et al. Opioid-induced gut microbial disruption and bile dysregulation leads to gut barrier compromise and sustained systemic inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. (2016) 9:1418–28. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.9
62. Plein LM and Rittner HL. Opioids and the immune system - friend or foe. Br J Pharmacol. (2018) 175:2717–25. doi: 10.1111/bph.13750
63. Wang F and Roy S. Gut homeostasis, microbial dysbiosis, and opioids. Toxicol Pathol. (2017) 45:150–6. doi: 10.1177/0192623316679898
64. Li L, Zhong H, Wang Y, Pan Z, Xu S, Li S, et al. Exploring the relationship between intestinal microbiota and immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: insights from the “Lung and large intestine stand in exterior-interior relationship” Theory. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2024) 14:1341032. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1341032
65. David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature. (2014) 505:559–63. doi: 10.1038/nature12820
66. Lu Y, Peng B, Lin Y, Lin Q, Xia X, Zhong S, et al. Spirulina polysaccharide induces the metabolic shifts and gut microbiota change of lung cancer in mice. Curr Res Food Sci. (2022) 5:1313–9. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.08.010
67. Zhao F, Piao J, Song J, Geng Z, Chen H, Cheng Z, et al. Traditional chinese herbal formula, fuzi-lizhong pill, produces antidepressant-like effects in chronic restraint stress mice through systemic pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 338:119011. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119011
68. Zhang W, Ding M, Feng Y, Cai S, Luo Z, Shan J, et al. Modulation of cellular metabolism and alleviation of bacterial dysbiosis by aconiti lateralis radix praeparata in non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Phytomedicine. (2024) 126:155099. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155099
69. Ding H, Liu Y, Wang S, Mei Y, Li L, Xiong A, et al. Metabolomics as an emerging tool for the pharmacological and toxicological studies on aconitum alkaloids. Chin J Nat Med. (2025) 23:182–90. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(25)60822-3
70. Yang L, Fang Z, Zhu J, Li X, Yang B, Liu H, et al. The potential of sijunzi decoction in the fight against gastrointestinal disorders: A review. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1464498. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1464498
71. He Y, Qi A, Gu Y, Zhang C, Wang Y, Yang W, et al. Clinical efficacy and gut microbiota regulating-related effect of si-jun-zi decoction in postoperative non-small cell lung cancer patients: A prospective observational study. Integr Cancer Ther. (2024) 23:15347354241237973. doi: 10.1177/15347354241237973
72. Xia Q, Chen G, Ren Y, Zheng T, Shen C, Li M, et al. Investigating efficacy of “Microbiota modulation of the gut-lung axis” Combined with chemotherapy in patients with advanced nsclc: study protocol for a multicenter, prospective, double blind, placebo controlled, randomized trial. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:721. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08448-6
73. Wan L, Wu C, Wu Q, Luo S, Liu J, Xie X, et al. Impact of probiotics use on clinical outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitors therapy in cancer patients. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:1841–9. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4994
74. Luo WC, Mei SQ, Huang ZJ, Chen ZH, Zhang YC, Yang MY, et al. Correlation of distribution characteristics and dynamic changes of gut microbiota with the efficacy of immunotherapy in egfr-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:326. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05135-5
75. Tomita Y, Ikeda T, Sakata S, Saruwatari K, Sato R, Iyama S, et al. Association of probiotic clostridium butyricum therapy with survival and response to immune checkpoint blockade in patients with lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. (2020) 8:1236–42. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-20-0051
76. Paz Del Socorro T, Oka K, Boulard O, Takahashi M, Poulin LF, Hayashi A, et al. The biotherapeutic clostridium butyricum miyairi 588 strain potentiates enterotropism of rorγt(+)Treg and pd-1 blockade efficacy. Gut Microbes. (2024) 16:2315631. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2315631
77. Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, et al. Expert consensus document: the international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics (Isapp) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 14:491–502. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75
78. Hibberd AA, Lyra A, Ouwehand AC, Rolny P, Lindegren H, Cedgård L, et al. Intestinal microbiota is altered in patients with colon cancer and modified by probiotic intervention. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. (2017) 4:e000145. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2017-000145
79. Oh B, Boyle F, Pavlakis N, Clarke S, Eade T, Hruby G, et al. The gut microbiome and cancer immunotherapy: can we use the gut microbiome as a predictive biomarker for clinical response in cancer immunotherapy? Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194824
80. Mann ER, Lam YK, and Uhlig HH. Short-chain fatty acids: linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2024) 24:577–95. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01014-8
81. Moratiel-Pellitero A, Zapata-García M, Gascón-Ruiz M, Sesma A, Quílez E, Ramirez-Labrada A, et al. Biomarkers of immunotherapy response in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: microbiota composition, short-chain fatty acids, and intestinal permeability. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16061144
82. Thome CD, Tausche P, Hohenberger K, Yang Z, Krammer S, Trufa DI, et al. Short-chain fatty acids induced lung tumor cell death and increased peripheral blood cd4+ T cells in nsclc and control patients ex vivo. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1328263. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1328263
83. Ren S, Feng L, Liu H, Mao Y, and Yu Z. Gut microbiome affects the response to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. (2024) 15:1149–63. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15303
84. Yang Y, Ye M, Song Y, Xing W, Zhao X, Li Y, et al. Gut microbiota and scfas improve the treatment efficacy of chemotherapy and immunotherapy in nsclc. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. (2025) 11:146. doi: 10.1038/s41522-025-00785-9
85. Zhu X, Li K, Liu G, Wu R, Zhang Y, Wang S, et al. Microbial metabolite butyrate promotes anti-pd-1 antitumor efficacy by modulating T cell receptor signaling of cytotoxic cd8 T cell. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2249143. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2249143
86. Tomita Y, Sakata S, Imamura K, Iyama S, Jodai T, Saruwatari K, et al. Association of clostridium butyricum therapy using the live bacterial product cbm588 with the survival of patients with lung cancer receiving chemoimmunotherapy combinations. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010047
87. Bredin P and Naidoo J. Correction to: the gut microbiome, immune check point inhibition and immune−Related adverse events in non−Small cell lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2024) 43:865. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10062-2
88. Xiao X, Xu Y, and Chen H. Sodium butyrate-activated traf6-txnip pathway affects A549 cells proliferation and migration. Cancer Med. (2020) 9:3477–88. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2564
89. Shaikh FY, Gills JJ, and Sears CL. Impact of the microbiome on checkpoint inhibitor treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma. EBioMedicine. (2019) 48:642–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.076
90. Jiang H, Zeng W, Zhang X, Li Y, Wang Y, Peng A, et al. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastasis: from alteration to potential microbial markers and drug targets. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1211855. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1211855
91. Li M, Cui H, Deng H, Deng Y, Yin S, Li T, et al. Urolithin a promotes the degradation of tmsb10 to deformation F-actin in non-small-cell lung cancer. Phytomedicine. (2024) 135:156109. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156109
92. Yu Z, Xiaojia L, Wei Z, Jian Z, Aiting W, Jing W, et al. Baicalin circumvents anti-pd-1 resistance by regulating the gut microbiota metabolite short-chain fatty acids. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 199:107033. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.107033
93. Platten M, Nollen EA, Röhrig UF, Fallarino F, and Opitz CA. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2019) 18:379–401. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0016-5
94. Badawy AA. Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism: regulatory and functional aspects. Int J Tryptophan Res. (2017) 10:1178646917691938. doi: 10.1177/1178646917691938
95. Liu JB, Chen D, Bao TT, Fan FT, and Yu C. The anticancer effects of atractylenolide iii associate with the downregulation of jak3/stat3-dependent ido expression. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:1505. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01505
96. Yin Z, Sun B, Cheng L, Xu X, Wang S, Wei S, et al. Investigating the correlation between ido1/pd-L1 expression or co-expression and egfr/kras gene mutations in advanced nsclc. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:28985. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14768-5
97. Jamal R, Messaoudene M, De Figuieredo M, and Routy B. Future indications and clinical management for fecal microbiota transplantation (Fmt) in immuno-oncology. Semin Immunol. (2023) 67:101754. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101754
98. Thompson NA, Stewart GD, Welsh SJ, Doherty GJ, Robinson MJ, Neville BA, et al. The mitre trial protocol: A study to evaluate the microbiome as a biomarker of efficacy and toxicity in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:99. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09156-x
99. Derosa L, Routy B, Thomas AM, Iebba V, Zalcman G, Friard S, et al. Intestinal akkermansia muciniphila predicts clinical response to pd-1 blockade in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Med. (2022) 28:315–24. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01655-5
100. Attili I, Tarantino P, Passaro A, Stati V, Curigliano G, De Marinis F, et al. Strategies to overcome resistance to immune checkpoint blockade in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2021) 154:151–60. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.02.035
101. Newsome RC, Gharaibeh RZ, Pierce CM, Da Silva WV, Paul S, Hogue SR, et al. Interaction of bacterial genera associated with therapeutic response to immune checkpoint pd-1 blockade in a United States cohort. Genome Med. (2022) 14:35. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01037-7
102. Shaikh FY, Gills JJ, Mohammad F, White JR, Stevens CM, Ding H, et al. Murine fecal microbiota transfer models selectively colonize human microbes and reveal transcriptional programs associated with response to neoadjuvant checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2022) 71:2405–20. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03169-6
103. Yadegar A, Bar-Yoseph H, Monaghan TM, Pakpour S, Severino A, Kuijper EJ, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation: current challenges and future landscapes. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2024) 37:e0006022. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00060-22
104. Mcquade JL, Daniel CR, Helmink BA, and Wargo JA. Modulating the microbiome to improve therapeutic response in cancer. Lancet Oncol. (2019) 20:e77–91. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30952-5
105. Wardill HR, Secombe KR, Bryant RV, Hazenberg MD, and Costello SP. Adjunctive fecal microbiota transplantation in supportive oncology: emerging indications and considerations in immunocompromised patients. EBioMedicine. (2019) 44:730–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.070
106. Jimenez M, Langer R, and Traverso G. Microbial therapeutics: new opportunities for drug delivery. J Exp Med. (2019) 216:1005–9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190609
107. Oliveira RA and Pamer EG. Assembling symbiotic bacterial species into live therapeutic consortia that reconstitute microbiome functions. Cell Host Microbe. (2023) 31:472–84. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.03.002
108. Bayer G, Ganobis CM, Allen-Vercoe E, and Philpott DJ. Defined gut microbial communities: promising tools to understand and combat disease. Microbes Infect. (2021) 23:104816. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2021.104816
109. Duttagupta S, Hakozaki T, Routy B, and Messaoudene M. The gut microbiome from a biomarker to a novel therapeutic strategy for immunotherapy response in patients with lung cancer. Curr Oncol. (2023) 30:9406–27. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30110681
110. Wu S, Zhou Y, Dai L, Yang A, and Qiao J. Assembly of functional microbial ecosystems: from molecular circuits to communities. FEMS Microbiol Rev. (2024) 48. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuae026
111. Jiang Y, Wu R, Zhang W, Xin F, and Jiang M. Construction of stable microbial consortia for effective biochemical synthesis. Trends Biotechnol. (2023) 41:1430–41. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.05.008
112. Messaoudene M, Pidgeon R, Richard C, Ponce M, Diop K, Benlaifaoui M, et al. A natural polyphenol exerts antitumor activity and circumvents anti-pd-1 resistance through effects on the gut microbiota. Cancer Discov. (2022) 12:1070–87. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0808
113. Chen HM, Sun L, Pan PY, Wang LH, and Chen SH. Nutrient supplements from selected botanicals mediated immune modulation of the tumor microenvironment and antitumor mechanism. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2021) 70:3435–49. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02927-2
114. Lee KA, Shaw HM, Bataille V, Nathan P, and Spector TD. Role of the gut microbiome for cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: dietary and treatment implications. Eur J Cancer. (2020) 138:149–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.07.026
115. Fang L, Hao Y, Yu H, Gu X, Peng Q, Zhuo H, et al. Methionine restriction promotes cgas activation and chromatin untethering through demethylation to enhance antitumor immunity. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41:1118–1133.e1112. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.05.005
116. Huang J, Liu D, Wang Y, Liu L, Li J, Yuan J, et al. Ginseng polysaccharides alter the gut microbiota and kynurenine/tryptophan ratio, potentiating the antitumour effect of antiprogrammed cell death 1/programmed cell death ligand 1 (Anti-pd-1/pd-L1) immunotherapy. Gut. (2022) 71:734–45. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321031
117. Xin Y, Liu CG, Zang D, and Chen J. Gut microbiota and dietary intervention: affecting immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1343450. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343450
118. Gunjur A, Shao Y, Rozday T, Klein O, Mu A, Haak BW, et al. A gut microbial signature for combination immune checkpoint blockade across cancer types. Nat Med. (2024) 30:797–809. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02823-z
119. Lo Russo G, Prelaj A, Dolezal J, Beninato T, Agnelli L, Triulzi T, et al. People (Ntc03447678), a phase ii trial to test pembrolizumab as first-line treatment in patients with advanced nsclc with pd-L1 <50%: A multiomics analysis. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-006833
120. Tingler AM and Engevik MA. Breaking down barriers: is intestinal mucus degradation by akkermansia muciniphila beneficial or harmful? Infect Immun. (2025) 93:e0050324. doi: 10.1128/iai.00503-24
121. Mruk-Mazurkiewicz H, Kulaszyńska M, Czarnecka W, Podkówka A, Ekstedt N, Zawodny P, et al. Insights into the mechanisms of action of akkermansia muciniphila in the treatment of non-communicable diseases. Nutrients. (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/nu16111695
122. Liu Y, Li Z, Lee SC, Chen S, and Li F. Akkermansia muciniphila: promises and pitfallsfor next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Arch Microbiol. (2025) 207:76. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04263-w
123. Chen M, Ma L, Yu H, Huang S, Zhang J, Gong J, et al. Jk5g postbiotics attenuate immune-related adverse events in nsclc patients by regulating gut microbiota: A randomized controlled trial in China. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1155592. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1155592
124. Oster P, Vaillant L, Riva E, Mcmillan B, Begka C, Truntzer C, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection has a detrimental impact on the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies. Gut. (2022) 71:457–66. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323392
125. Niu C, Hu XL, Yuan ZW, Xiao Y, Ji P, Wei YM, et al. Pulsatilla decoction improves dss-induced colitis via modulation of fecal-bacteria-related short-chain fatty acids and intestinal barrier integrity. J Ethnopharmacol. (2023) 300:115741. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115741
126. Pinato DJ, Gramenitskaya D, Altmann DM, Boyton RJ, Mullish BH, Marchesi JR, et al. Antibiotic therapy and outcome from immune-checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:287. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0775-x
127. Takada K, Buti S, Bersanelli M, Shimokawa M, Takamori S, Matsubara T, et al. Antibiotic-dependent effect of probiotics in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with pd-1 checkpoint blockade. Eur J Cancer. (2022) 172:199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.06.002
128. Křížová L, Benešová I, Špaček J, Petruželka L, and Vočka M. Fecal microbiota transplantation - new possibility to influence the results of therapy of cancer patients. Klin Onkol. (2022) 35:436–40. doi: 10.48095/ccko2022436
129. Chen F, Yang J, Guo Y, Su D, Sheng Y, Wu Y, et al. Integrating bulk and single-cell rna sequencing data reveals the relationship between intratumor microbiome signature and host metabolic heterogeneity in breast cancer. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1140995. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1140995
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), gut microbiota, metabolites, treatment, prognosis
Citation: Jiao J-M, Liu C-G, Zang D and Chen J (2025) Gut microbiota and metabolites: emerging prospects in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 16:1638942. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1638942
Received: 31 May 2025; Accepted: 22 October 2025;
Published: 05 November 2025.
Edited by:
Siming Li, Peking University, ChinaReviewed by:
David Dora, Semmelweis University, HungaryMarian De Leon, University of the Philippines Los Baños, Philippines
Copyright © 2025 Jiao, Liu, Zang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun Chen, Y2hlbmp1bl9kbXVAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jing-Mian Jiao†
Jing-Mian Jiao† Jun Chen
Jun Chen