- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 3Breast and Thyroid Surgery, Jilin Province People’s Hospital, Changchun, China
- 4The Affiliated Hospital to Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
Metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a major chronic liver disease increasingly linked to endocrine and immunometabolic dysregulation. Hypothyroidism, both overt and subclinical, has emerged as a significant endocrine risk factor for MAFLD. Extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, a hallmark of fibrosis, represents a crucial but underexplored mediator in this process. This review highlights how altered thyroid hormone (TH) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) signaling promote ECM remodeling through metabolic, inflammatory, and fibrogenic pathways, with emphasis on hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and immune reshaping. We further summarize ECM-derived biomarkers and emerging therapeutic strategies, including THRβ agonists and ECM-targeted approaches.
1 Introduction
Metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) affects nearly one in four individuals globally and constitutes a major contributor to liver-related morbidity and mortality (1). Thyroid dysfunction, particularly hypothyroidism, is increasingly recognized as a comorbidity that may exacerbate hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis (2). Epidemiological and meta-analytic studies indicate that even subclinical hypothyroidism is associated with higher MAFLD prevalence, greater disease severity, and increased fibrosis risk, particularly among obese and postmenopausal populations (3–6). Elevated TSH levels correlate with hepatic steatosis, advanced fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma risk (7, 8). Despite these associations, the mechanistic links between hypothyroidism and MAFLD remain incompletely defined. Emerging evidence implicates extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling as a central mediator bridging endocrine dysfunction and hepatic injury (9). The ECM not only provides structural support but also modulates cell signaling, thereby influencing hepatocyte survival, insulin sensitivity, and immune homeostasis (10, 11). In MAFLD, aberrant ECM remodeling is characterized by excessive fibrillar collagen deposition, increased tissue stiffness, and dysregulated turnover of matrix-associated proteins and glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronan, as well as receptors such as RHAMM, CD44, and integrins (12, 13). These alterations promote fibrosis and metabolic dysregulation by modifying the hepatocyte microenvironment and regulating growth factor and cytokine signaling (14–17).
In this review, we synthesize clinical and experimental evidence to delineate the role of ECM remodeling in hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD. We focus on endocrine regulation of ECM dynamics, the crosstalk among hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), immune cells, and the fibrotic niche, and integrin-mediated mechanotransduction pathways linking matrix stiffness to pro-fibrotic gene expression (18). Finally, we discuss ECM-derived biomarkers and potential therapeutic strategies, including thyroid hormone receptor β (THRβ) agonists and integrin inhibitors, emphasizing ECM remodeling as both a mechanistic and therapeutic nexus in hypothyroidism-driven MAFLD.
2 Thyroid dysfunction and MAFLD: pathophysiological links
MAFLD, previously referred to as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a redefined entity that encompasses hepatic steatosis in conjunction with metabolic dysregulation—such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or other metabolic risk factors (19, 20). This updated terminology more accurately reflects the disease’s underlying pathophysiology and emphasizes its close relationship with metabolic dysfunction. Therefore, the term MAFLD is adopted throughout this article (21). In hypothyroid states, triglyceride metabolism is markedly impaired, leading to hepatic triglyceride accumulation and elevated levels of circulating free fatty acids (8). When the liver’s metabolic capacity for primary energy substrates, including carbohydrates and fatty acids is exceeded, toxic lipid intermediates accumulate, inducing hepatocellular stress, injury, and death (22). These pathophysiological events contribute to hepatic insulin resistance (IR), altered gut microbiota composition, and a range of deleterious cellular responses, including mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, oxidative stress, and excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The sustained presence of these insults drives chronic hepatic inflammation and ultimately promotes MAFLD progression (23, 24).
2.1 Thyroid hormones and receptors in MAFLD: metabolic and fibrotic regulation
Building upon the mechanistic links between hypothyroidism and MAFLD, this section highlights the roles of THs and their nuclear receptors in regulating hepatic metabolism and fibrogenesis. Triiodothyronine (T3), the active form of TH, enhances lipolysis and promotes weight loss, whereas reduced T3 levels are associated with impaired lipid degradation, decreased cholesterol clearance, and increased adiposity (25). These metabolic effects are primarily mediated by thyroid hormone receptors (THRs), ligand-dependent nuclear transcription factors. In contrast, thyroxine (T4) binds THRs with approximately tenfold lower affinity, and its direct biological effects remain less well defined. The two main THR isoforms, THRα and THRβ, are encoded by separate genes. THRα is predominantly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle, and HSC, while THRβ is highly expressed in hepatocytes and also found in the brain, kidney, and retina (26). Functional inactivation of THRα has been shown to enhance fibrogenic activity in HSCs (27). THRβ signaling plays a liver-specific role in regulating key metabolic pathways, including de novo lipogenesis, fatty acid β-oxidation, mitophagy, and cholesterol homeostasis. These processes collectively contribute to reductions in circulating low-density lipoprotein (LDL), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), and lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)]. While T3 and T4 primarily act on hepatocytes to regulate lipid metabolism, THRα expression in HSCs suggests that excessive TH levels may activate these cells, potentially contributing to fibrogenesis in hyperthyroid states (28).
Growing evidence from clinical and experimental studies has established a significant association between hypothyroidism—both overt and subclinical—and the development and progression of MAFLD in both adult and pediatric populations (3, 29). Furthermore, hypothyroid states have been linked to greater risk and severity of liver fibrosis in MAFLD (30–33). In THR-deficient mouse models, spontaneous hepatic collagen accumulation and upregulation of fibrotic gene expression have been observed, highlighting the essential regulatory role of TH in fibrogenesis. Mechanistically, TH have been shown to suppress hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting SMAD2/3 phosphorylation within the TGF-β signaling pathway, thereby downregulating fibrosis-associated gene expression (27). Recent studies also implicate TSH in the pathogenesis of metabolic liver diseases (34). THs are critical regulators of organogenesis, cellular differentiation, and systemic metabolic homeostasis. Disruption of TH and TSH signaling has been associated with a range of liver disorders, including alcoholic liver disease, MAFLD, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In experimental models of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)–induced liver injury, exogenous TH administration reduced the expression of key fibrogenic genes such as Col1a1 and Col1a2 (35).
Preclinical and clinical studies collectively support a protective role of thyroid hormones in liver homeostasis, underscoring the therapeutic potential of TH analogs in MAFLD management (36). Administration of T3 or synthetic TH analogs has demonstrated efficacy in attenuating hepatic steatosis and HCC development in rodent models exposed to high-fat diets or hepatocarcinogenic agents (4, 37–41). Additionally, TSH signaling has been shown to modulate hepatic lipid metabolism through its receptor on hepatocytes. Specifically, TSH induces hepatic steatosis by activating sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) pathways, inhibits bile acid synthesis by suppressing the SREBP2–hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF4)–CYP7A1 axis, and attenuates cholesterol biosynthesis via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)–dependent phosphorylation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) (42). Together, these findings establish TSH as an independent regulator of hepatic lipid and cholesterol homeostasis.
2.2 Pathogenic mechanisms underlying hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD
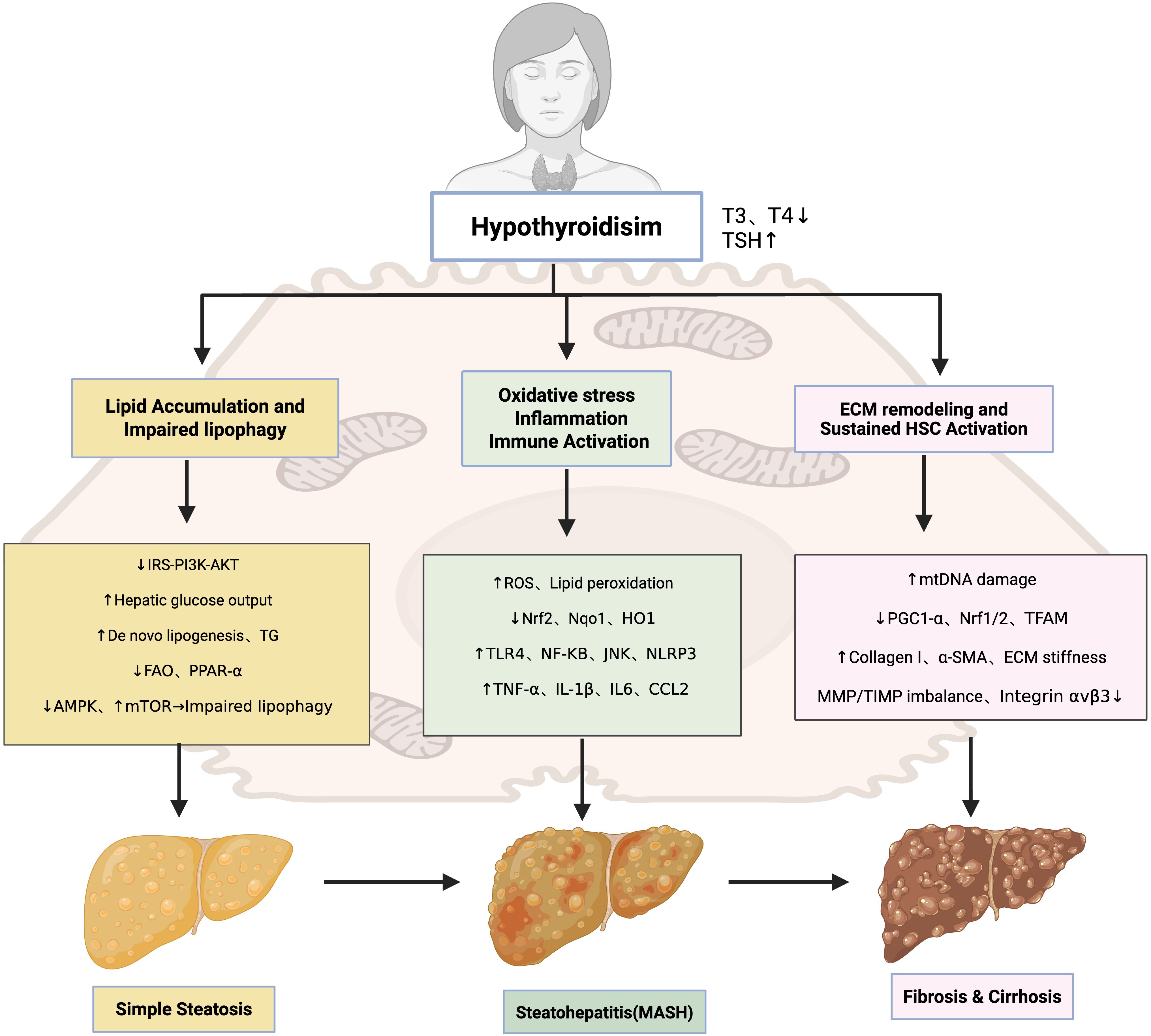
2.2.1 Simple steatosis: lipid accumulation and impaired lipophagy
Hypothyroidism promotes hepatic lipid accumulation through impaired lipid catabolism, enhanced de novo lipogenesis, and defective autophagic clearance of lipid droplets. In hypothyroid states, insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-mediated PI3K(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase)/Akt(protein kinase B) signaling is attenuated, reducing insulin sensitivity and increasing hepatic glucose output (43–47). Decreased IRS2 expression and diminished Akt phosphorylation, observed in both hypothyroidism and NASH, directly link TH deficiency to hepatic insulin resistance (48, 49). Elevated circulating TSH exacerbates this process by activating toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways, which inhibit IRS tyrosine phosphorylation and enhance serine phosphorylation, thereby aggravating insulin resistance (50, 51). However, these hypothyroidism-specific mechanisms remain less firmly established in clinical settings, as most supporting evidence derives from animal models and cross-sectional studies rather than longitudinal cohorts. Epidemiological studies support the association between hypothyroidism and insulin resistance, but evidence directly connecting this axis to ECM remodeling in MAFLD patients is currently insufficient.
In parallel, hypothyroidism disrupts systemic lipid metabolism by suppressing lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity, impairing cholesterol efflux, and reducing triglyceride clearance (52, 53). These defects lead to elevated LDL-C(low-density lipoprotein cholesterol), total cholesterol, and intrahepatic triglyceride accumulation, reinforcing steatosis and lipotoxicity (54–56). Thyroid hormones also regulate hepatic autophagy, a key pathway for lipid degradation (lipophagy). Under physiological conditions, T3 activates AMPK and inhibits mTOR to sustain autophagic flux, inducing ULK1, Beclin-1, and LC3 transcription, while stimulating lysosomal biogenesis via TFEB(transcription factor EB) (57–59). Preclinical studies show that in hypothyroidism, reduced T3 availability suppresses AMPK activity, disinhibits mTOR, and diminishes autophagic flux, leading to impaired lipophagy and mitophagy (50, 60, 61). Current understanding of autophagy impairment largely relies on preclinical models, and direct evidence substantiating similar alterations in human hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD is still insufficient. These defects accelerate lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and hepatocellular injury. Moreover, reduced Dio1(deiodinase type 1) expression in advanced MAFLD further exacerbates intrahepatic T3 deficiency, intensifying autophagy impairment (51, 62). Collectively, these mechanisms illustrate how hypothyroidism predisposes the liver to steatosis and metabolic dysfunction.
2.2.2 Steatohepatitis (MASH): oxidative stress, inflammation, and immune activation
The progression from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis is critically mediated by oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative stress, largely derived from mitochondrial β-oxidation, induces hepatocellular injury and ECM remodeling (63). Patients with hypothyroidism display elevated markers of oxidative damage, and TSH directly stimulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (64). In MAFLD, oxidative imbalance is characterized by lipid peroxidation, depletion of polyunsaturated fatty acids, and dysregulation of SREBP-1c(sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c) and PPAR-α(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha), alongside reduced nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2(Nrf2) activity and diminished expression of detoxifying enzymes such as Nqo1 and HO1 (65–67). Preclinical studies demonstrate that hypothyroidism suppresses Nrf2 signaling, thereby amplifying oxidative injury and accelerating disease progression (68, 69). Under physiological conditions, T3 activates AMPK, the unfolded protein response (UPR), and autophagy to mitigate oxidative stress; these cytoprotective mechanisms are blunted in hypothyroidism (70, 71). Nevertheless, most evidence comes from animal studies and small-scale clinical observations, while large-scale prospective cohort validation is lacking. Large prospective cohorts and mechanistic human investigations are therefore required to validate this link.
In parallel, hypothyroidism reshapes the hepatic immune microenvironment. Elevated TNF-α and IL-1β, together with reduced adiponectin, promote NF-κB–dependent transcription of proinflammatory genes (72–75). Lipotoxic hepatocyte injury releases damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that activate Kupffer cells and recruit monocytes, which secrete cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, CCL2) to amplify inflammation and stimulate hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) via TGF-β1 and PDGF (76–78). DAMPs and ROS also trigger NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Kupffer cells and recruited macrophages, leading to caspase-1–dependent cleavage of pro–IL-1β and pro–IL-18 into their active forms, thereby amplifying the inflammatory cascade. Activated HSCs perpetuate immune infiltration through chemokines such as CCL2, CCL5, IL-8, and CXCL12 (79), while neutrophils exacerbate hepatocellular damage by releasing myeloperoxidase (MPO) and ROS (80). Elevated TSH further augments TLR4/NF-κB signaling, reinforcing a vicious cycle between inflammation and insulin resistance (73, 81, 82). Together, these mechanisms converge to promote hepatocellular injury, immune cell infiltration, and HSC activation—hallmarks of MASH. But the specific contribution of hypothyroidism to these inflammatory pathways is supported mainly by experimental and associative data, with limited longitudinal clinical validation.
2.2.3 Fibrosis and cirrhosis: ECM remodeling and sustained HSC activation
In advanced stages of MAFLD, hypothyroidism accelerates fibrosis progression through both direct and indirect mechanisms. Thyroid hormone (TH) deficiency compromises mitochondrial function, resulting in ATP depletion, membrane depolarization, and excessive ROS production (81, 82). Concomitant mitochondrial DNA damage, defective mitophagy, and reduced oxidative phosphorylation further exacerbate steatosis and drive fibrogenesis (70, 71, 83).
Under physiological conditions, triiodothyronine (T3) maintains mitochondrial integrity by inducing PGC1-α, Nrf1/Nrf2, and TFAM to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and fatty acid oxidation, while also activating AMPK signaling via integrin αvβ3 (84, 85). Loss of these protective pathways in hypothyroidism enhances oxidative stress and promotes fibrotic remodeling. Although mitochondrial impairment is consistently observed in both hypothyroidism and MAFLD, direct evidence linking thyroid dysfunction to ECM remodeling through mitochondrial pathways remains limited, and current understanding is based primarily on preclinical studies.
TH deficiency also exerts a direct influence on hepatic stellate cell (HSC) biology. TH receptor α (THRα), expressed on HSCs, mediates antifibrotic signaling, and its loss favors persistent HSC activation. This state is characterized by increased collagen I and α-SMA expression, as well as disruption of the MMP/TIMP balance, culminating in pathological ECM accumulation. Activated HSCs further engage mechanotransduction pathways, particularly integrin-mediated signaling, which amplify matrix stiffness and reinforce the fibrotic cascade.
Collectively, hypothyroidism facilitates the transition from steatohepatitis to fibrosis and cirrhosis by impairing mitochondrial homeostasis, suppressing antifibrotic THRα signaling in HSCs, and driving maladaptive ECM remodeling. These interconnected mechanisms are summarized in Figure 1, which illustrates the stepwise contribution of hypothyroidism to MAFLD progression.
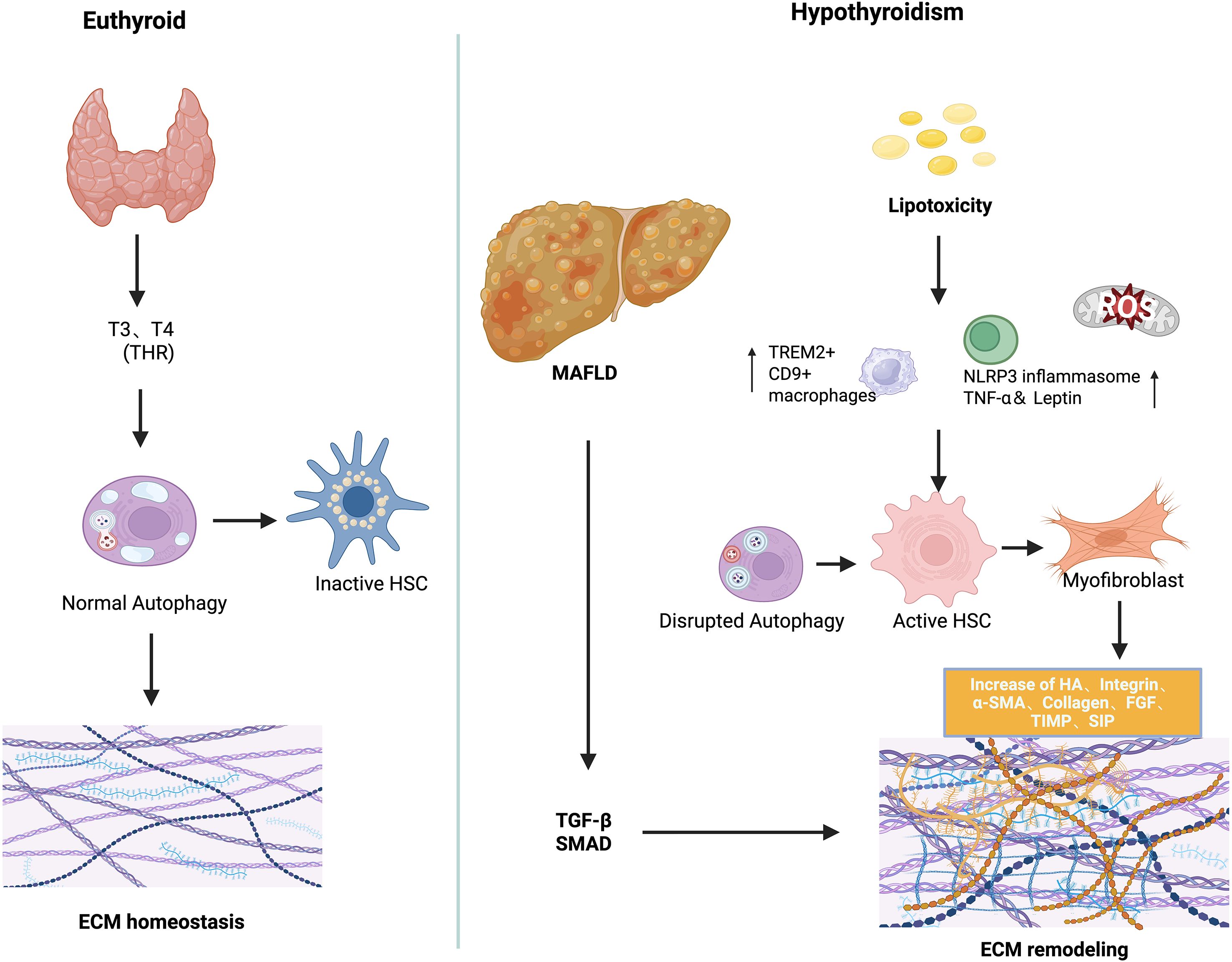
3 ECM remodeling in hypothyroidism–MAFLD crosstalk
Emerging evidence implicates hypothyroidism in the pathogenesis of MAFLD through dysregulated ECM remodeling (27). THs, particularly T3, play a crucial role in modulating HSC activation and fibrogenic signaling (81, 86–88). While general MAFLD studies provide insights into ECM dynamics, recent hypothyroidism-specific models demonstrate direct effects of thyroid hormone deficiency on ECM composition and stiffness. Under physiological conditions, hepatic ECM functions not only as a structural scaffold but also as a dynamic regulator of intercellular signaling, influencing lipid metabolism, immune homeostasis, and fibrogenesis (89). In hypothyroid states, excessive ECM synthesis—exacerbated by chronic inflammation—drives the progression from steatosis to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and ultimately hepatic failure. Sphingolipid accumulation within the ECM microenvironment, particularly ceramide-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), plays a pivotal role in immune activation and fibrotic transformation (90). Elevated palmitate levels promote ceramide and S1P production, which binds to S1PR1–4 on macrophages, triggering HSC activation and differentiation into myofibroblast-like cells (91, 92). Experimental autoimmune thyroiditis (EAT) models have demonstrated that pharmacological blockade of S1P signaling ameliorates thyroid inflammation and reduces TSH levels, underscoring a bidirectional crosstalk between thyroid dysfunction and liver inflammation via ECM pathways (93). In hypothyroid states, reduced TH signaling impairs ECM turnover by increasing fibrillar collagen deposition, enhancing matrix stiffness, and attenuating matrix degradation, all of which accelerate hepatic fibrogenesis (27, 94, 95). Experimental hypothyroid models, including T3/T4 withdrawal and TH receptor (TRα/β) knockout mice, show spontaneous hepatic collagen accumulation and elevated expression of pro-fibrotic genes, confirming that TH deficiency alone can drive ECM remodeling. Through TRα expressed in HSCs, TH facilitates the reversion of activated myofibroblasts to a quiescent phenotype, promotes apoptotic clearance, and inhibits fibrogenic gene expression (27, 96). Consistent with these findings, experimental models demonstrate that T3 supplementation alleviates liver fibrosis by restoring mitochondrial biogenesis, enhancing β-oxidation of fatty acids, and normalizing autophagic flux. T3 supplementation in hypothyroid animal models attenuates TGF-β-induced fibrosis by reducing SMAD2 phosphorylation and transcriptional activity, restores mitochondrial biogenesis, enhances β-oxidation, and normalizes autophagic flux (11). Similarly, Alonso-Merino observed spontaneous hepatic collagen accumulation in TR-deficient mice, while T3 treatment ameliorated carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced fibrosis, reinforcing the anti-fibrotic role of THs. In addition, T3 suppresses the expansion of TREM2+, CD9+ pro-fibrotic macrophages and inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome, reducing hepatic inflammation (97). TH also upregulate matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity, promoting ECM degradation and tissue remodeling (98). In contrast, thyroxine (T4) may elicit pro-fibrotic effects through non-genomic signaling via integrin αvβ3, activating Rho-dependent pathways that induce α-SMA and p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) expression in HSCs (99). These context-dependent actions underscore the complexity of TH-mediated ECM regulation in liver fibrosis (28). Oxidative stress induced hepatocellular injury represents another potential mechanism linking thyroid dysfunction to liver fibrosis. Hypothyroidism may exacerbate this injury by disrupting systemic adipokine profiles—including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), Adiponectin, and leptin—thereby amplifying hepatic inflammation and fibrogenesis (100, 101). Beyond hormonal deficiency alone, the immunopathological characteristics of certain thyroid disorders may further exacerbate liver injury. In particular, autoimmune thyroid diseases—such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis—have been increasingly associated with hepatic fibrogenesis. This association is hypothesized to arise from persistent systemic inflammation and dysregulated adipokine signaling intrinsic to autoimmune processes, which may synergistically promote hepatic inflammation and ECM accumulation in the context of thyroid hormone dysregulation (102, 103). RHAMM, a HA-binding receptor of the ECM, has emerged as a critical mediator of thyroid-liver crosstalk through its regulation of ECM remodeling (52). Our preclinical studies demonstrate that genetic ablation of RHAMM attenuates obesity-induced TSH elevation, mitigates hepatic oxidative stress, and modulates key metabolic signaling pathways in male mice. These findings indicate that RHAMM not only orchestrates ECM–cell interactions but also contributes to thyroid dysfunction and hepatic inflammation in hypothyroid states, potentially via modulation of antioxidant defense mechanisms such as Nqo1 (68). Although further validation in clinical settings is required, targeting RHAMM as an ECM receptor may represent a promising therapeutic strategy for obesity-related metabolic disorders, particularly those characterized by hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD (104). Collectively, these findings support a multifaceted role for TH in maintaining ECM homeostasis, and their dysregulation in hypothyroidism provides a mechanistic link to MAFLD development. At present, most evidence regarding ECM remodeling derives from studies in general MAFLD or hepatic fibrosis. Direct investigations under hypothyroid conditions are limited, with only a few studies using EAT models or TR-deficient mice suggesting a potential link between hypothyroidism and ECM alterations. The mechanism of ECM remodeling was shown in Figure 2.
3.1 Clinical evidence and disease heterogeneity
Thyroid dysfunction, particularly hypothyroidism, has emerged as a significant contributor to the development and progression of MAFLD (105). Obesity is frequently associated with abnormal fluctuations in TSH and TH levels—an endocrine imbalance strongly linked to various metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance (58, 106). Clinical studies have demonstrated a positive correlation between TSH levels and visceral fat area, and hypothyroidism (both subclinical and overt) is more prevalent among obese individuals (107). In overt hypothyroidism, elevated TSH and reduced free T4 or T3 concentrations are frequently accompanied by the accumulation of lipotoxic intermediates and activation of pro-fibrotic pathways. Mechanistically, these effects are mediated in part through TSH receptor signaling in hepatocytes and HSCs, which promotes inflammatory and fibrogenic responses (108).
ECM remodeling is a pathological hallmark of hepatic fibrogenesis in MAFLD and plays a central role in linking thyroid dysfunction to progressive liver injury (109). In hypothyroid states, chronic metabolic stress enhances activation of HSC—the principal ECM-producing cells—leading to increased deposition of type I collagen and other matrix proteins (27). This process is further amplified by reduced activity of MMP and elevated expression of tissue inhibitors of TIMP, which collectively impair ECM degradation and perpetuate fibrotic remodeling (17, 110). HA, a major ECM component, is elevated in both hypothyroidism and advanced liver fibrosis and has emerged as a potential noninvasive biomarker of disease severity (111). Moreover, recent studies have shown that TSH receptor activation in preadipocyte-derived fibroblasts can directly stimulate HA synthesis (112). Given HA’s dual role as a matrix component and fibrosis biomarker, targeting its production may offer therapeutic value (113).
The heterogeneity of hypothyroidism significantly influences these ECM alterations and the clinical course of MAFLD. Clinical and preclinical data suggest that overt hypothyroidism exerts more pronounced effects on hepatic ECM composition and fibrotic signaling compared with subclinical forms, while autoimmune etiologies may further amplify inflammatory and fibrogenic responses (2, 114, 115). Coexisting metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes, further modulate ECM remodeling by promoting insulin resistance, lipid dysregulation, and low-grade inflammation (14, 116). In addition, sex-specific factors, particularly postmenopausal status in women, appear to affect ECM dynamics and MAFLD susceptibility, likely through estrogen-mediated regulation of hepatic metabolism and fibrogenic pathways (117, 118). Collectively, these findings underscore the importance of considering disease heterogeneity—including hypothyroidism subtype, autoimmune status, metabolic comorbidities, and sex differences-when evaluating ECM remodeling and MAFLD progression. Accounting for these variables in both clinical and preclinical studies may improve risk stratification, biomarker discovery, and the development of ECM-targeted therapeutic strategies.
From a therapeutic standpoint, several strategies aimed at restoring hepatic thyroid hormone action and correcting ECM dysregulation are under investigation. These include enhancing intracellular TH availability via modulation of transporters such as monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8) and deiodinases (e.g., DIO1), as well as directly targeting ECM remodeling through upregulation of MMP activity, inhibition of HA synthesis, and blockade of integrin-mediated signaling pathways (119–121). Together, these findings underscore the clinical relevance of thyroid–ECM interactions in MAFLD and support the development of precision therapies for patients with comorbid thyroid dysfunction and liver fibrosis.
3.2 Pathological consequences
3.2.1 Systemic fibrogenic amplification driven by ECM remodeling
Fibrotic diseases are a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, histopathologically characterized by persistent ECM accumulation, especially of type I collagen (122). While traditionally considered organ-specific, fibrosis is increasingly recognized as a systemic pathology involving the liver, heart, lungs, and kidneys. Hypothyroidism has emerged as a key systemic amplifier of fibrotic remodeling, particularly in the context of MAFLD (2, 123). Shared fibrogenic pathways—including the TGF-β–HA/CD44–STAT3 axis—are activated across multiple organs in hypothyroid states (27). For instance, CD44 blockade reduces STAT3 activation and collagen production in atrial fibroblasts, HSCs, and pulmonary fibroblasts, underscoring a conserved ECM-mediated profibrotic mechanism (124). Hypothyroidism-induced metabolic and oxidative stress disrupts the homeostatic regulation of ECM turnover by MMP and their inhibitor (TIMP), promoting pathological cross-linking, stiffness, and matrix accumulatio (125). Lysyl oxidase (LOX)–mediated collagen cross-linking further increases ECM rigidity, which in turn activates integrin–FAK–YAP/TAZ and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways, and promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and fibrogenesis (126). Additionally, fibrotic ECM suppresses antifibrotic miRNAs (e.g.,miR-29), perpetuating collagen synthesis (127). In the liver, impaired thyroid hormone signaling sustains HSC activation and α-SMA+ myofibroblast transformation, leading to excessive deposition of fibrillar collagens and matrix stiffening (128). This biomechanical stress alters hepatocyte polarity, suppresses regeneration, and induces apoptosis. These local hepatic alterations—when coupled with systemic inflammation, dysregulated adipokines (e.g., leptin, adiponectin), and circulating profibrotic cytokines (e.g., TGF-β, IL-13)—amplify fibrotic signaling across distant organs (123, 129). Thus, liver-derived ECM remodeling not only drives hepatic fibrosis but also acts as a nexus linking hypothyroidism to multi-organ fibrogenic progression.
3.2.2 Disruption of ECM–cell communication
While systemic fibrosis reflects the macroscopic outcome of ECM dysregulation, the disruption of cell–matrix communication constitutes a pivotal microscopic mechanism that initiates and sustains tissue pathology (130). In hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD, aberrant ECM remodeling alters not only matrix composition but also its biomechanical properties, particularly stiffness. The accumulation of cross-linked collagens and fibronectin enhances tissue rigidity, which disrupts hepatocyte–matrix interactions. This mechanical stress impairs hepatocyte polarity, reduces regenerative capacity, and induces premature senescence or apoptosis (131). These biomechanical cues are sensed through integrins and focal adhesion complexes, activating downstream pathways such as FAK, RhoA/ROCK, and YAP/TAZ, which maintain HSC in a persistently activated state (132). Moreover, impaired ECM turnover due to MMP/TIMP imbalance further exacerbates matrix accumulation, forming a feed-forward loop (133). As a result, the ECM transitions from a supportive scaffold to a pathological regulator of hepatic injury and fibrogenesis.
3.2.3 Immune rewiring and chronic inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a key pathological consequence of dysregulated ECM remodeling in hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD and serves as a major driver of hepatic fibrogenesis. This inflammatory response originates from hepatocellular injury and is perpetuated by the sustained activation of fibrotic signaling cascades (134). Macrophages are central to this process, orchestrating immune responses via cytokine secretion, phagocytosis of pathogens, apoptotic cells, and ECM debris, and facilitating tissue remodeling by releasing proteolytic enzymes and their inhibitors (135). In addition, macrophages interact with other immune and stromal cells—activating lymphocytes through antigen presentation and modulating fibroblast proliferation or apoptosis—thereby shaping the balance between repair and fibrosis (136). In hypothyroid conditions, ECM remodeling is significantly altered. Accumulation of glycosaminoglycans, particularly HA, aberrantly activates cell surface receptors such as CD44 and RHAMM (137). Persistent stimulation of these receptors amplifies pro-inflammatory signaling, promoting macrophage and T cell recruitment and sustaining hepatic inflammation (138). Fragmented ECM components like fibronectin and biglycan further act as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), engaging TLR2/4 on macrophages and enhancing cytokine release (139). Concurrently, TH deficiency impairs mitochondrial function and antioxidant defenses, disrupting immune-metabolic homeostasis (140). These alterations drive M1 polarization of hepatic macrophages via NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thereby reinforcing chronic inflammation (140, 141). Macrophage-derived MMPs and proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12) further activate fibroblasts and pericytes, promoting ECM deposition (142). These interconnected events form a self-perpetuating feedback loop. Inflammatory mediators such as TGF-β stimulate HSCs via Smad and YAP/TAZ pathways, maintaining their activated, fibrogenic state. Meanwhile, increased ECM stiffness sustains mechanotransduction signaling in fibroblasts, reinforcing the cycle of immune activation, ECM remodeling, and fibrosis in hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD (143).
3.2.4 Metabolic imbalance
In hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD, aberrant ECM remodeling plays a central role in disrupting hepatic metabolic homeostasis. The excessive accumulation of stiff, cross-linked ECM components impairs hepatocyte–matrix interactions and alters integrin-mediated mechanotransduction, thereby attenuating insulin signaling pathways (144). This mechanical dysfunction results in impaired PI3K-Akt activation and reduced translocation of glucose transporter GLUT2, ultimately leading to decreased hepatic glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis. Concurrently, fibrotic ECM deposition restricts the diffusion of oxygen and nutrients within hepatic lobules, generating localized hypoxia. This hypoxic environment inhibits mitochondrial β-oxidation via downregulation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α (CPT1α), while promoting de novo lipogenesis through stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and activation of SREBP-1c (145). Systemic hypothyroidism further exacerbates these metabolic disturbances by lowering circulating thyroid hormone levels and suppressing basal metabolic rate (146). Mechanistically, reduced expression of peroxisome PGC-1α and mitochondrial TFAM—key regulators of mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative phosphorylation—compromises hepatic energy production and adaptability (147). Moreover, ECM-induced architectural remodeling may impair hepatic insulin clearance, a process that normally extracts approximately 50% of circulating insulin during the liver’s first pass (148, 149). Similar to conditions observed in cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis, reduced insulin clearance in fibrotic livers contributes to systemic hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance (145). Collectively, these ECM-mediated alterations converge to promote hepatic metabolic inflexibility, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of mitochondrial dysfunction, IR, and lipid accumulation. This pathogenic loop accelerates the progression of hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD.
3.2.5 ECM stiffening and hepatocarcinogenesis
In hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD, progressive ECM remodeling contributes not only to hepatic fibrogenesis but also to the initiation and progression of HCC (145). Excessive deposition of stiff, cross-linked ECM components including type I/III collagen, fibronectin, and HA alters the biomechanical properties of the hepatic microenvironment. This pathological stiffening disrupts hepatocyte polarity, promotes EMT, and facilitates malignant transformation. In hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD, persistent ECM remodeling not only underlies hepatic fibrogenesis but also functions as a mechanical and biochemical driver of hepatocarcinogenesis (150). Mechanistically, increased ECM stiffness activates integrin-mediated mechanotransduction pathways, notably the focal adhesion kinase (FAK), RhoA/ROCK, and YAP/TAZ signaling cascades (18, 151). These pathways converge on nuclear transcriptional programs that drive cell proliferation, inhibit apoptosis, and enhance stemness traits, ultimately predisposing hepatocytes to oncogenic reprogramming (152). Moreover, integrin-ECM interactions stimulate downstream PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling, further enhancing hepatocyte survival, migration, and proliferative potential. Although certain integrin subtypes (e.g., β1-integrin) may exert context-dependent tumor-suppressive effects via p21/p27-mediated growth arrest, the prevailing outcome in fibrotic livers is a tumor-permissive microenvironment (153). Non-fibrillar ECM components such as laminin further contribute by modulating growth factor receptor activity and amplifying oncogenic signaling (150). Progressive liver fibrosis also enhances HSC and portal fibroblast activation through matrix rigidity, creating a positive feedback loop of fibrogenesis and oncogenesis (154). In vitro studies show that stiff collagen matrices impair hepatocyte differentiation and promote proliferation and chemoresistance via β1-integrin–mediated activation of FAK, ERK, Akt, and STAT3 pathways (155). Moreover, fibrotic vascular remodeling induces tissue hypoxia, stabilizing HIF-1α, which drives vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent angiogenesis and metabolic reprogramming toward aerobic glycolysis—hallmarks of tumor progression. Paradoxically, MMP, despite their degradative role, may also promote tumorigenesis by releasing sequestered growth factors and generating ROS via Rac1 signaling, thereby contributing to genomic instability (156). Clinically, patients with hypothyroidism and advanced hepatic fibrosis exhibit elevated liver stiffness values on elastography, which are strongly associated with increased HCC risk (97). These findings support a mechanistic link between thyroid dysfunction, fibrotic ECM remodeling, and hepatic carcinogenesis, positioning ECM stiffness as a critical pathogenic nexus in the transition from MAFLD to HCC (157).
4 Therapeutic strategies targeting ECM remodeling in MAFLD
Alterations in the composition of the ECM represent a key driver in the pathogenesis of MAFLD. Excessive production of ECM components, coupled with chronic inflammation, promotes the progression from steatosis to hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis, and ultimately liver failure (90). Consequently, targeting the molecular mediators that govern ECM deposition and fibrogenesis has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy. Recent advances have identified a diverse array of pharmacological agents capable of modulating ECM dynamics either directly, through inhibition of fibrogenic pathways and matrix-producing cells, or indirectly, by addressing the metabolic and inflammatory disturbances that drive ECM dysregulation and fibrotic progression.
Although MAFLD provides a broader and more inclusive diagnostic framework, current pharmacological strategies are largely based on evidence from NASH and liver fibrosis trials, which remain applicable in the context of progressive MAFLD. But their translation into routine practice necessitates rigorous evaluation of safety, durability of efficacy, and patient heterogeneity-factors that remain insufficiently addressed to date (20).
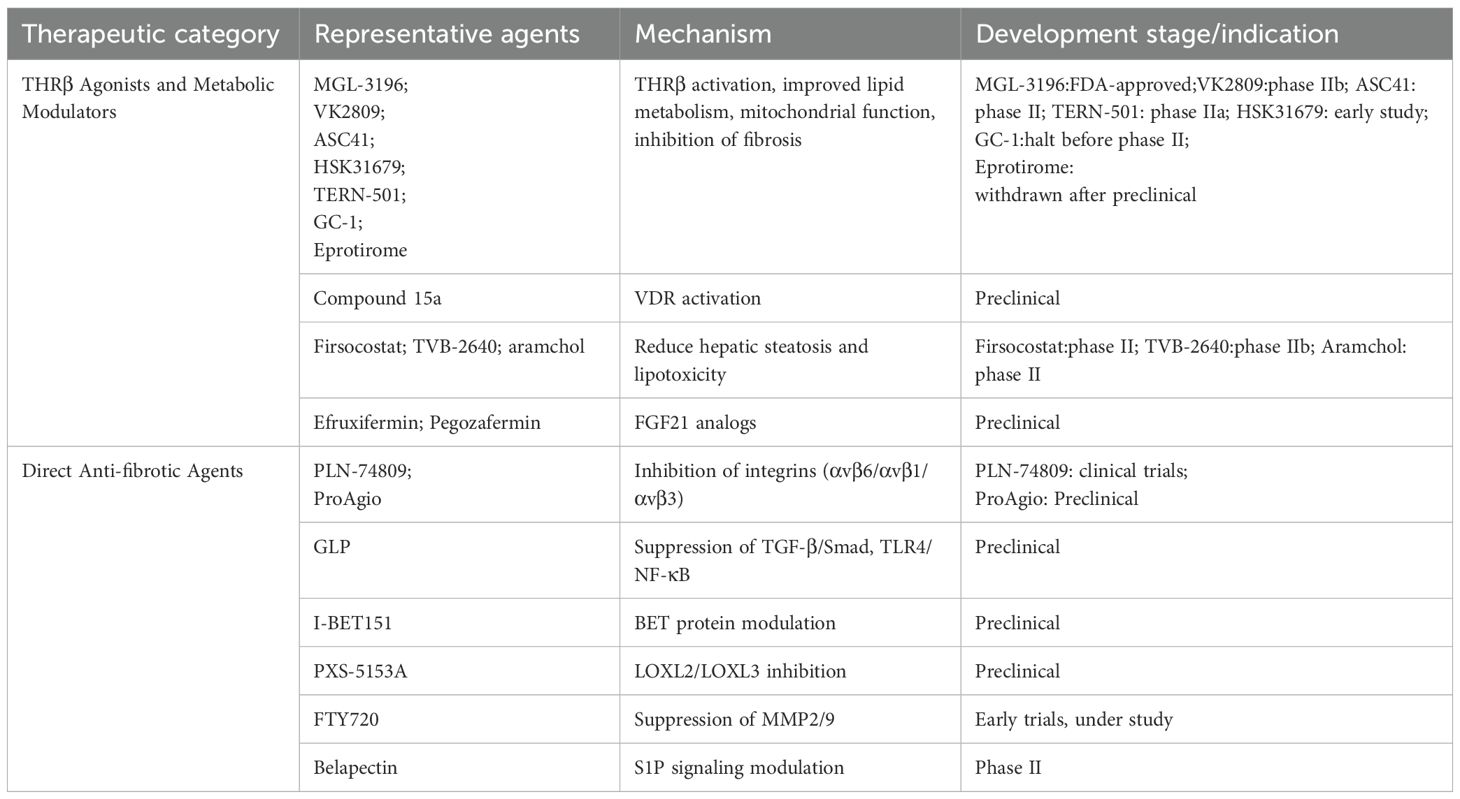
4.1 Liver-selective THRβ agonists for metabolic and fibrotic correction
Emerging pharmacological strategies have increasingly targeted THR signaling, particularly in the treatment of NASH and progressive MAFLD (158, 159). Experimental models have demonstrated that THR activation mitigates chemically induced liver fibrosis by reducing collagen deposition and α-SMA expression (96). Among THR isoforms, the β-subtype (THRβ)—predominantly expressed in hepatocytes—plays a central role in regulating mitochondrial bioenergetics, lipid metabolism, cholesterol homeostasis, and fatty acid oxidation (160). Liver-selective THRβ agonists have thus emerged as promising agents capable of reversing hepatic steatosis and attenuating fibrosis. The design of isoform- and hepatocyte-specific THRβ modulators offers a mechanistic basis for liver-targeted antifibrotic therapies, aiming to optimize efficacy while minimizing systemic adverse effects (8).
In clinical studies, Resmetirom (MGL-3196), the first THRβ agonist approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for patients with NASH and moderate to advanced fibrosis (F2–F3), has demonstrated favorable efficacy and safety profiles in late-stage clinical trials (161, 162). Similarly, VK2809 has shown significant reductions in hepatic fat content and was well tolerated in phase IIb trials (161). Several additional THRβ agonists are undergoing clinical evaluation, including ASC41 (phase II, China) (163, 164), HSK31679 (early study) (162), TERN-501 (165) (phase IIa), Sobetirome (GC-1, half before phase II) (164, 166), Eprotirome, Sobetirome, exhibited lipid-lowering effects in phase I trials under both single and multiple dosing regimens; however, its development was discontinued due to elevated liver enzyme levels, and no phase II trials were initiated (167). Eprotirome advanced to phase III for dyslipidemia but was withdrawn after preclinical studies revealed unexpected toxicities in animal models (168). These agents selectively activate THRβ in hepatocytes, hereby enhancing lipid metabolism, reducing hepatic steatosis, and suppressing inflammatory responses. Their demonstrated efficacy and relatively well-characterized safety profiles emphasize their potential as targeted therapies for MAFLD and NASH. However, long-term safety data, cost-effectiveness analyses, and the refinement of patient stratification strategies remain essential considerations prior to broader clinical implementation (8). In parallel, vitamin D receptor (VDR) agonists represent an additional nuclear receptor-based strategy with antifibrotic potential. These agents attenuate SMAD3 transcriptional activity, thereby reducing fibrogenic gene expression (96, 169). The selective VDR agonist compound 15a has been shown to suppress collagen deposition and fibrosis-related gene expression in murine models of hepatic fibrosis, without inducing hypercalcemia—a common side effect observed with Calcipotriol or 1,25(OH)2D3 (170). Beyond nuclear receptor-based strategies, other metabolic modulators also contribute to antifibrotic outcomes by mitigating hepatic steatosis and lipotoxicity, upstream drivers of fibrosis. Small molecule inhibitors targeting key enzymes of lipid synthesis—including firsocostat (Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase inhibitor), TVB-2640 (Fatty Acid Synthase inhibitor), and aramchol (Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1inhibitor) have shown efficacy in reducing hepatic fat accumulation and indirectly attenuating HSC activation. Furthermore, FGF21 analogues such as efruxifermin and pegozafermin improve insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles while suppressing fibrogenic pathways (171).
4.2 Direct anti-fibrotic agents targeting ECM remodeling
Targeting integrin-mediated activation of TGF-β has emerged as a promising antifibrotic approach within the broader strategy of ECM remodeling (172). Preclinical studies have demonstrated that inhibition of αv-containing integrins effectively attenuates fibrogenesis in models of NASH-related liver fibrosis (173). Among these, PLN-74809—a dual αvβ6/αvβ1 integrin inhibitor—has advanced to clinical trials in patients with liver fibrosis, with ongoing evaluation also in pulmonary fibrosis (174). Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide (GLP), a 25 kDa water-soluble extract from sporoderm-removed spores, has demonstrated antifibrotic activity in CCl4-induced mouse models and TGF-β1-stimulated HSC-T6 cells. GLP attenuates HSC activation, collagen deposition, and α-SMA expression by suppressing TGF-β/Smad and TLR4/NF-κB signaling, modulating ECM–receptor interactions via downregulation of integrins (e.g., ITGA6, ITGA8), and influencing apoptosis and cell cycle regulators. While these findings suggest GLP as a promising ECM-targeted natural compound, its antifibrotic potential remains to be validated in clinical settings (175). ProAgio, a protein-based agent that targets a novel site on integrin αvβ3, induces selective apoptosis in activated HSC and capillarized liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. This results in reduced collagen crosslinking, restoration of sinusoidal architecture, and decreased intrahepatic angiogenesis, thereby reversing hepatic fibrosis and improving portal pressure and liver function (176). The hyaluronidase PH20 degrades HA, disrupting HA–CD44–TGF-β/SMAD2/3 signaling and demonstrating antifibrotic potential beyond its current ophthalmic applications (177). Although HA is a widely used serum biomarker of fibrosis, its specificity is limited, as it can be confounded by inflammation and other pathological conditions (178). Likewise, inhibitors targeting integrins remain at the stage of early clinical trials, with significant barriers to routine clinical translation. A critical evaluation of these biomarkers and therapeutic strategies highlights both their promise and their current limitations. Although these findings highlight integrin inhibitors as a viable class of ECM-targeted therapeutics, the majority of candidates remain at the preclinical or early clinical stage, and unresolved issues-including off-target toxicity, uncertainties in dose optimization, and limitations in delivery strategies pose substantial barriers to successful clinical translation (174).
I-BET151, a selective bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) inhibitor, suppresses HSC activation and ECM deposition by modulating pro-fibrotic gene transcription. Despite encouraging preclinical efficacy, no clinical trials have yet been initiated in liver fibrosis, highlighting the gap between mechanistic promise and translational feasibility (179). Similarly, inhibitors of lysyl oxidase-like enzymes (LOXL2/LOXL3), such as PXS-5153A, reduce collagen crosslinking and liver stiffness in preclinical settings (180). S1P signaling has been implicated in lipid-induced macrophage activation and HSC transdifferentiation. The S1P receptor modulator FTY720 mitigates hepatic injury, triglyceride accumulation, and fibrogenesis in murine MAFLD models by suppressing MMP2 and MMP9 expression and activity (181–183). However, its immunomodulatory properties and potential cardiovascular toxicity have constrained clinical development, highlighting the challenges of translating promising preclinical findings into safe and effective patient therapies (179, 183).
Galectin-3 inhibitors, such as belapectin, constitute another emerging class of antifibrotic agents that disrupt myofibroblast activation and collagen matrix organization. Although early-phase clinical trials have yielded variable outcomes, ongoing investigations continue to refine patient stratification strategies and evaluate combination regimens to enhance therapeutic efficacy (184). Preclinical studies indicate that T3 exerts antifibrotic effects by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. In hypothyroid states, the lack of T3-mediated inhibition may result in a relative increase in TGF-β/Smad activity, thereby promoting ECM accumulation and fibrosis (96, 185, 186). Thyroid dysfunction can amplify HA-CD44 signaling and collagen crosslinking, as evidenced by studies showing that hyaluronic acid promotes COX-2 expression in orbital fibroblasts from patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy via CD44-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling (187). In this context, PH20, I-BET151, and PXS-5153A may indirectly counteract thyroid-related fibrosis by degrading ECM, inhibiting profibrotic signaling, or reducing collagen crosslinking. S1P receptor modulators and galectin-3 inhibitors could mitigate inflammation and hepatic stellate cell activation (188, 189), processes known to be exacerbated by hypothyroidism, further highlighting potential therapeutic avenues for hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD. In this context, antifibrotic agents may represent a promising strategy for hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD, as they could counteract enhanced fibrogenic signaling while also exerting direct effects on ECM remodeling. While these agents remain largely preclinical, their mechanistic alignment with thyroid-driven fibrosis strengthens their potential utility in hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD. Collectively, these findings underscore both the therapeutic potential and the uncertainties associated with translating single-agent antifibrotic therapies into routine clinical practice.
Table 1 Summary of emerging therapeutic agents targeting ECM remodeling and associated pathways in metabolic MAFLD. Therapeutics are classified according to their primary mechanism of action, including antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, lipid-modulatory effects. Development stages are based on current clinical or preclinical evidence.
5 Conclusion and perspectives
The intricate crosstalk between hypothyroidism and MAFLD is increasingly recognized as a multifactorial process involving endocrine dysfunction, metabolic dysregulation, and sustained ECM remodeling. This review underscores the pivotal role of TH signaling in modulating hepatic ECM dynamics and illustrates how ECM remodeling, in turn, amplifies fibrogenesis, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance, thereby accelerating MAFLD progression under hypothyroid conditions. The clinical and mechanistic evidence presented herein supports the concept that ECM remodeling functions not only as a downstream consequence but also as an active driver of disease synergy. Despite notable advances, several critical knowledge gaps remain. In particular, the temporal sequence and causal relationships among TH deficiency, ECM dysregulation, and hepatic injury require further elucidation through longitudinal studies and integrated multi-omics approaches (190). Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that immune–ECM interactions, the adipose–liver–thyroid axis, and gut microbiota may represent key modulators of this pathological interplay and merit deeper investigation (191, 192). From a translational perspective, targeting ECM components and associated signaling pathways—such as TGF-β, CD44/RHAMM, and THR modulators—represents a promising therapeutic avenue. However, future strategies must account for ECM heterogeneity (193), sex-specific responses, and the bidirectional dynamics of thyroid–liver axis regulation (194). Ultimately, interdisciplinary approaches bridging endocrinology, hepatology, and matrix biology will be essential for advancing precision diagnostics and tailored antifibrotic therapies in hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD.
Author contributions
TW: Writing – original draft. JYZ: Writing – review & editing. BZ: Writing – original draft. LD: Writing – original draft. JBZ: Writing – original draft. YY: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Li Y, Dai C, Ruan Y, Yang H, Zeng H, Huang R, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease from clinical to pathological characteristics: a multi-center cross-sectional study in real world. Postgraduate Med J. (2024) 100:319–26. doi: 10.1093/postmj/qgae007
2. Rahadini AAD and Rahadina A. Association between hypothyroidism and liver fibrosis risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Hepatol. (2022) 8:188–94. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2022.118594
3. Pagadala MR, Zein CO, Dasarathy S, Yerian LM, Lopez R, and McCullough AJ. Prevalence of hypothyroidism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. (2012) 57:528–34. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-2006-2
4. Liangpunsakul S and Chalasani N. Is hypothyroidism a risk factor for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis? J Clin Gastroenterol. (2003) 37:340–3.
5. Baumgartner C, da Costa BR, Collet TH, Feller M, Floriani C, Bauer DC, et al. Thyroid function within the normal range, subclinical hypothyroidism, and the risk of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. (2017) 136:2100–16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028753
6. Mantovani A, Nascimbeni F, Lonardo A, Zoppini G, Bonora E, Mantzoros CS, et al. Association between primary hypothyroidism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid. (2018) 28:1270–84. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0257
7. Das K and Chainy GB. Modulation of rat liver mitochondrial antioxidant defence system by thyroid hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2001) 1537:1–13. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4439(01)00048-5
8. Hatziagelaki E, Paschou SA, Schön M, Psaltopoulou T, and Roden M. NAFLD and thyroid function: pathophysiological and therapeutic considerations. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 33:755–68. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2022.08.001
9. Yue W, Zhang H, Gao Y, Ding J, Xue R, Dong C, et al. Procollagen-lysine 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 2 promotes collagen cross-linking and ECM stiffening to induce liver fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167205. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167205
10. Arriazu E, Ruiz de Galarreta M, Cubero FJ, Varela-Rey M, Pérez de Obanos MP, Leung TM, et al. Extracellular matrix and liver disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2014) 21:1078–97. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5697
11. Zhou J, Tripathi M, Ho JP, Widjaja AA, Shekeran SG, Camat MD, et al. Thyroid hormone decreases hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in a dietary mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Thyroid. (2022) 32:725–38. doi: 10.1089/thy.2021.0621
12. Rozario T and DeSimone DW. The extracellular matrix in development and morphogenesis: a dynamic view. Dev Biol. (2010) 341:126–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.10.026
13. Karamanos NK, Theocharis AD, Piperigkou Z, Manou D, Passi A, Skandalis SS, et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. (2021) 288:6850–912. doi: 10.1111/febs.15776
14. Musale V, Wasserman DH, and Kang L. Extracellular matrix remodelling in obesity and metabolic disorders. Life Metab. (2023) 2(4):load021. doi: 10.1093/lifemeta/load021
15. Higashi T, Friedman SL, and Hoshida Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Advanced Drug delivery Rev. (2017) 121:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.05.007
16. Munsterman ID, Kendall TJ, Khelil N, Popa M, Lomme R, Drenth JP, et al. Extracellular matrix components indicate remodelling activity in different fibrosis stages of human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Histopathology. (2018) 73:612–21. doi: 10.1111/his.13665
17. Bonnans C, Chou J, and Werb Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2014) 15:786–801. doi: 10.1038/nrm3904
18. Wang Z, Wang W, Luo Q, and Song G. High matrix stiffness accelerates migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the integrin β1-Plectin-F-actin axis. BMC Biol. (2025) 23:8. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02113-1
19. Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J, Sanyal A, Neuschwander-Tetri B, Tiribelli C, et al. MAFLD: a consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:1999–2014. e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312
20. Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J hepatology. (2020) 73:202–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039
21. Mantovani A, Csermely A, Bilson J, Borella N, Enrico S, Pecoraro B, et al. Association between primary hypothyroidism and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: an updated meta-analysis. Gut. (2024) 73:1554–61. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-332491
22. Zhao J, Hu Y, and Peng J. Targeting programmed cell death in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): a promising new therapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2021) 26:17. doi: 10.1186/s11658-021-00254-z
23. Powell EE, Wong VW-S, and Rinella M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet. (2021) 397:2212–24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32511-3
24. Mitsuhashi T, Tennyson GE, and Nikodem VM. Alternative splicing generates messages encoding rat c-erbA proteins that do not bind thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (1988) 85:5804–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5804
25. Pihlajamaki J, Boes T, Kim E-Y, Dearie F, Kim BW, Schroeder J, et al. Thyroid hormone-related regulation of gene expression in human fatty liver. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2009) 94:3521–9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-0212
26. Senese R, Cioffi F, de Lange P, Goglia F, and Lanni A. Thyroid: biological actions of ‘nonclassical’thyroid hormones. J Endocrinol. (2014) 221:R1–12. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0573
27. Manka P, Coombes JD, Sydor S, Swiderska-Syn MK, Best J, Gauthier K, et al. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha modulates fibrogenesis in hepatic stellate cells. Liver Int. (2024) 44:125–38. doi: 10.1111/liv.15759
28. Zvibel I, Atias D, Phillips A, Halpern Z, and Oren R. Thyroid hormones induce activation of rat hepatic stellate cells through increased expression of p75 neurotrophin receptor and direct activation of Rho. Lab Invest. (2010) 90:674–84. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.48
29. Loosen SH, Demir M, Kostev K, Luedde T, and Roderburg C. Incidences of hypothyroidism and autoimmune thyroiditis are increased in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 33:e1008–e12. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002136
30. Manka P, Bechmann L, Best J, Sydor S, Claridge LC, Coombes JD, et al. Low free triiodothyronine is associated with advanced fibrosis in patients at high risk for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. (2019) 64:2351–8. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05687-3
31. Bano A, Chaker L, Plompen EP, Hofman A, Dehghan A, Franco OH, et al. Thyroid function and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the rotterdam study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 101:3204–11. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1300
32. Kim D, Kim W, Joo SK, Bae JM, Kim JH, and Ahmed A. Subclinical hypothyroidism and low-normal thyroid function are associated with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 16:123–31.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.08.014
33. Martínez-Escudé A, Pera G, Rodríguez L, Arteaga I, Expósito-Martínez C, Torán-Monserrat P, et al. Risk of liver fibrosis according to TSH levels in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Med. (2021) 10(7):1350. doi: 10.3390/jcm10071350
34. Mullur R, Liu Y-Y, and Brent GA. Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiol Rev. (2014) 94:355–82. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2013
35. Ding N, Ruth TY, Subramaniam N, Sherman MH, Wilson C, Rao R, et al. A vitamin D receptor/SMAD genomic circuit gates hepatic fibrotic response. Cell. (2013) 153:601–13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.028
36. Chi H-C, Tsai C-Y, Tsai M-M, Yeh C-T, and Lin K-H. Molecular functions and clinical impact of thyroid hormone-triggered autophagy in liver-related diseases. J Biomed Science. (2019) 26:24. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0517-x
37. Perra A, Simbula G, Simbula M, Pibiri M, Kowalik MA, Sulas P, et al. Thyroid hormone (T3) and TRβ agonist GC-1 inhibit/reverse nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats. FASEB J. (2008) 22:2981–9. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-108464
38. Cable EE, Finn PD, Stebbins JW, Hou J, Ito BR, van Poelje PD, et al. Reduction of hepatic steatosis in rats and mice after treatment with a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor agonist. Hepatology. (2009) 49:407–17. doi: 10.1002/hep.22572
39. Mollica MP, Lionetti L, Moreno M, Lombardi A, De Lange P, Antonelli A, et al. 3, 5-diiodo-l-thyronine, by modulating mitochondrial functions, reverses hepatic fat accumulation in rats fed a high-fat diet. J hepatology. (2009) 51:363–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.023
40. Chi H-C, Chen S-L, Tsai C-Y, Chuang W-Y, Huang Y-H, Tsai M-M, et al. Thyroid hormone suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis via DAPK2 and SQSTM1-dependent selective autophagy. Autophagy. (2016) 12:2271–85. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1230583
41. Chi H-C, Chen S, Lin S, Tsai C, Chuang W, Lin Y, et al. Thyroid hormone protects hepatocytes from HBx-induced carcinogenesis by enhancing mitochondrial turnover. Oncogene. (2017) 36:5274–84. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.136
42. Yan F, Wang Q, Lu M, Chen W, Song Y, Jing F, et al. Thyrotropin increases hepatic triglyceride content through upregulation of SREBP-1c activity. J Hepatology. (2014) 61:1358–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.06.037
43. Li Y, Zheng M, Limbara S, Zhang S, Yu Y, Yu L, et al. Effects of the pituitary-targeted gland axes on hepatic lipid homeostasis in endocrine-associated fatty liver disease-A concept worth revisiting. J Clin Trans Hepatology. (2024) 12:416–27. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00421
44. Xu H, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Ping J, Shou Q, Chen F, et al. Metformin improves hepatic IRS2/PI3K/Akt signaling in insulin-resistant rats of NASH and cirrhosis. J Endocrinol. (2016) 229:133–44. doi: 10.1530/JOE-15-0409
45. Bo T, Gao L, Yao Z, Shao S, Wang X, Proud CG, et al. Hepatic selective insulin resistance at the intersection of insulin signaling and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:947–68. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.04.006
46. Saini V. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes. (2010) 1:68–75. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v1.i3.68
47. Zhou Q, Zhang LY, Dai MF, Li Z, Zou CC, and Liu H. Thyroid-stimulating hormone induces insulin resistance in adipocytes via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrine Connections. (2024) 13:e230302. doi: 10.1530/EC-23-0302
48. Mansouri A, Gattolliat C-H, and Asselah T. Mitochondrial dysfunction and signaling in chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. (2018) 155:629–47. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.06.083
49. Sinha RA, Singh BK, and Yen PM. Direct effects of thyroid hormones on hepatic lipid metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinology. (2018) 14:259–69. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2018.10
50. Videla LA and Valenzuela R. Perspectives in liver redox imbalance: toxicological and pharmacological aspects underlying iron overloading, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and thyroid hormone action. Biofactors. (2022) 48:400–15. doi: 10.1002/biof.1797
51. Bruinstroop E, Zhou J, Tripathi M, Yau WW, Boelen A, Singh BK, et al. Early induction of hepatic deiodinase type 1 inhibits hepatosteatosis during NAFLD progression. Mol Metab. (2021) 53:101266. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101266
52. Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Neculae E, Costea CF, Ciocoiu M, Hurjui LL, et al. Hypothyroidism-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (HIN): mechanisms and emerging therapeutic options. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5927. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165927
53. Tan K, Shiu S, and Kung A. Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity in hyper-and hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1998) 83:140–3. doi: 10.1210/jc.83.1.140
54. Jonklaas J. Hypothyroidism, lipids, and lipidomics. Endocrine. (2024) 84:293–300. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03420-9
55. Duntas LH. Thyroid disease and lipids. Thyroid. (2002) 12:287–93. doi: 10.1089/10507250252949405
56. Mavromati M and Jornayvaz FR. Hypothyroidism-associated dyslipidemia: potential molecular mechanisms leading to NAFLD. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(23):12797. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312797
57. Sinha RA, Singh BK, and Yen PM. Reciprocal crosstalk between autophagic and endocrine signaling in metabolic homeostasis. Endocr Rev. (2017) 38:69–102. doi: 10.1210/er.2016-1103
58. Sinha RA, You S-H, Zhou J, Siddique MM, Bay B-H, Zhu X, et al. Thyroid hormone stimulates hepatic lipid catabolism via activation of autophagy. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:2428–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI60580
59. Paquette MA, Atlas E, Wade MG, and Yauk CL. Thyroid hormone response element half-site organization and its effect on thyroid hormone mediated transcription. PloS One. (2014) 9:e101155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101155
60. Kizivat T, Maric I, Mudri D, Curcic IB, Primorac D, and Smolic M. Hypothyroidism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathophysiological associations and therapeutic implications. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2020) 8:347–53. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00027
61. Byrnes K, Blessinger S, Bailey NT, Scaife R, Liu G, and Khambu B. Therapeutic regulation of autophagy in hepatic metabolism. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:33–49. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.021
62. Zhou J, Sinha RA, and Yen PM. The roles of autophagy and thyroid hormone in the pathogenesis and treatment of NAFLD. Hepatoma Res. (2021) 7:72. doi: 10.20517/2394-5079.2021.82
63. Messarah M, Boumendjel A, Chouabia A, Klibet F, Abdennour C, Boulakoud MS, et al. Influence of thyroid dysfunction on liver lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in experimental rats. Exp Toxicologic Pathology. (2010) 62:301–10. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2009.04.009
64. Dardano A, Ghiadoni L, Plantinga Y, Caraccio N, Bemi A, Duranti E, et al. Recombinant human thyrotropin reduces endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients monitored for differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2006) 91:4175–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0440
65. Videla LA. Oxidative stress signaling underlying liver disease and hepatoprotective mechanisms. World J hepatology. (2009) 1:72. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v1.i1.72
66. Xu D, Xu M, Jeong S, Qian Y, Wu H, Xia Q, et al. The role of nrf2 in liver disease: novel molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:1428. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01428
67. Carpenter EL, Becker AL, and Indra AK. NRF2 and key transcriptional targets in melanoma redox manipulation. Cancers. (2022) 14:1531. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061531
68. Thanas C, Ziros PG, Chartoumpekis DV, Renaud CO, and Sykiotis GP. The keap1/nrf2 signaling pathway in the thyroid-2020 update. Antioxidants (Basel). (2020) 9(11):1082. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111082
69. Sies H. Oxidative stress: Concept and some practical aspects. Antioxidants. (2020) 9:852. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090852
70. Gariani K and Jornayvaz FR. Pathophysiology of NASH in endocrine diseases. Endocrine connections. (2021) 10:R52–65. doi: 10.1530/EC-20-0490
71. Lugari S, Mantovani A, Nascimbeni F, and Lonardo A. Hypothyroidism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease–a chance association? Hormone Mol Biol Clin Invest. (2020) 41:20180047. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2018-0047
72. Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Corrado A, Di Domenicantonio A, and Fallahi P. Autoimmune thyroid disorders. Autoimmun Rev. (2015) 14:174–80. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.10.016
73. Cai J, Zhang XJ, and Li H. The role of innate immune cells in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. (2019) 70:1026–37. doi: 10.1002/hep.30506
74. Ajuwon KM and Spurlock ME. Adiponectin inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation and IL-6 production and increases PPARgamma2 expression in adipocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2005) 288:R1220–5. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00397.2004
75. Ajuwon KM and Spurlock ME. Adiponectin inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB activation and IL-6 production and increases PPARγ2 expression in adipocytes. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. (2005) 288:R1220–R5. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00397.2004
76. Pierantonelli I and Svegliati-Baroni G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: basic pathogenetic mechanisms in the progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation. (2019) 103:e1–e13. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002480
77. Marra F and Svegliati-Baroni G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J hepatology. (2018) 68:280–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.014
78. Wiering L, Subramanian P, and Hammerich L. Hepatic stellate cells: dictating outcome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 15:1277–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.02.010
79. Carter JK and Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cell-immune interactions in NASH. Front Endocrinology. (2022) 13:867940. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.867940
80. Pulli B, Ali M, Iwamoto Y, Zeller MW, Schob S, Linnoila JJ, et al. Myeloperoxidase–hepatocyte–stellate cell cross talk promotes hepatocyte injury and fibrosis in experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Antioxidants Redox Signaling. (2015) 23:1255–69. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6108
81. Baskol G, Atmaca H, Tanriverdi F, Baskol M, Kocer D, and Bayram F. Oxidative stress and enzymatic antioxidant status in patients with hypothyroidism before and after treatment. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. (2007) 115:522–6. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-981457
82. Ramanathan R, Patwa SA, Ali AH, and Ibdah JA. Thyroid hormone and mitochondrial dysfunction: therapeutic implications for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Cells. (2023) 12:2806. doi: 10.3390/cells12242806
83. Li Z, Li Y, Zhang HX, Guo JR, Lam CWK, Wang CY, et al. Mitochondria-mediated pathogenesis and therapeutics for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2019) 63:1900043. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900043
84. Weitzel JM and Iwen KA. Coordination of mitochondrial biogenesis by thyroid hormone. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2011) 342:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.05.009
85. Cheng S-Y, Leonard JL, and Davis PJ. Molecular aspects of thyroid hormone actions. Endocrine Rev. (2010) 31:139–70. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0007
86. Gionfra F, De Vito P, Pallottini V, Lin H-Y, Davis PJ, Pedersen JZ, et al. The role of thyroid hormones in hepatocyte proliferation and liver cancer. Front Endocrinology. (2019) 10:532. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00532
87. Manka P, Coombes J, Bechmann L, Dollé L, Swiderska-Syn M, Briones-Orta M, et al. Thyroid hormone receptor regulates hepatic stellate cell activation. J Hepatology. (2017) 66:S582. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(17)31587-8
88. Öztürk Ü, Vural P, Özderya A, Karadağ B, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, and Uysal M. Oxidative stress parameters in serum and low density lipoproteins of Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients with subclinical and overt hypothyroidism. Int Immunopharmacol. (2012) 14:349–52. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2012.08.010
89. Ortiz C, Schierwagen R, Schaefer L, Klein S, Trepat X, and Trebicka J. Extracellular matrix remodeling in chronic liver disease. Curr Tissue Microenviron Rep. (2021) 2:41–52. doi: 10.1007/s43152-021-00030-3
90. Kołakowski A, Dziemitko S, Chmielecka A, Żywno H, Bzdęga W, Charytoniuk T, et al. Molecular advances in MAFLD-A link between sphingolipids and extracellular matrix in development and progression to fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(19):11380. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911380
91. Al Fadel F, Fayyaz S, Japtok L, and Kleuser B. Involvement of sphingosine 1-phosphate in palmitate-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2016) 40:1637–45. doi: 10.1159/000453213
92. Jin J, Lu Z, Li Y, Ru JH, Lopes-Virella MF, and Huang Y. LPS and palmitate synergistically stimulate sphingosine kinase 1 and increase sphingosine 1 phosphate in RAW264. 7 macrophages. J leukocyte Biol. (2018) 104:843–53. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3A0517-188RRR
93. Flores J, Rito Y, Torres G, Jung H, Treviño-Frenk I, and Corona T. Hypothyroidism in multiple sclerosis patient during fingolimod treatment. J Neurological Sci. (2015) 348:272–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.11.008
94. Bataller R and Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. (2005) 115:209–18. doi: 10.1172/JCI24282
95. Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. (2008) 134:1655–69. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.003
96. Alonso-Merino E, Martín Orozco R, Ruíz-Llorente L, Martínez-Iglesias OA, Velasco-Martín JP, Montero-Pedrazuela A, et al. Thyroid hormones inhibit TGF-β signaling and attenuate fibrotic responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2016) 113:E3451–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506113113
97. He W, Huang C, Wang L, Su W, Wang S, Huang P, et al. The correlation between triiodothyronine and the severity of liver fibrosis. BMC Endocr Disord. (2022) 22:313. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01228-8
98. Roy SG, Mishra S, Ghosh G, and Bandyopadhyay A. Thyroid hormone induces myocardial matrix degradation by activating matrix metalloproteinase-1. Matrix Biol. (2007) 26:269–79. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2006.12.005
99. Bergh JJ, Lin H-Y, Lansing L, Mohamed SN, Davis FB, Mousa S, et al. Integrin αVβ3 contains a cell surface receptor site for thyroid hormone that is linked to activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and induction of angiogenesis. Endocrinology. (2005) 146:2864–71. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0102
100. Musso G, Gambino R, Durazzo M, Biroli G, Carello M, Fagà E, et al. Adipokines in NASH: postprandial lipid metabolism as a link between adiponectin and liver disease. Hepatology. (2005) 42:1175–83. doi: 10.1002/hep.20896
101. Utzschneider KM and Kahn SE. Review: The role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2006) 91:4753–61. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0587
102. Yao Z, Gao X, Liu M, Chen Z, Yang N, Jia YM, et al. Diffuse myocardial injuries are present in subclinical hypothyroidism: A clinical study using myocardial T1-mapping quantification. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:4999. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22970-x
103. Chen YY, Shu XR, Su ZZ, Lin RJ, Zhang HF, Yuan WL, et al. A low-normal free triiodothyronine level is associated with adverse prognosis in euthyroid patients with heart failure receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy. Int Heart J. (2017) 58:908–14. doi: 10.1536/ihj.16-477
104. Chu Y, Yang S, and Chen X. Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Ther. (2025) 269:108844. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108844
105. Shantha GP, Kumar AA, Jeyachandran V, Rajamanickam D, Rajkumar K, Salim S, et al. Association between primary hypothyroidism and metabolic syndrome and the role of C reactive protein: a cross-sectional study from South India. Thyroid Res. (2009) 2:2. doi: 10.1186/1756-6614-2-2
106. Fuchs CD, Claudel T, and Trauner M. Role of metabolic lipases and lipolytic metabolites in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2014) 25:576–85. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.08.001
107. Taylor PN, Albrecht D, Scholz A, Gutierrez-Buey G, Lazarus JH, Dayan CM, et al. Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2018) 14:301–16. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2018.18
108. Petta S, Targher G, Romeo S, Pajvani UB, Zheng MH, Aghemo A, et al. The first MASH drug therapy on the horizon: Current perspectives of resmetirom. Liver Int. (2024) 44:1526–36. doi: 10.1111/liv.15930
109. Karsdal MA, Manon-Jensen T, Genovese F, Kristensen JH, Nielsen MJ, Sand JM, et al. Novel insights into the function and dynamics of extracellular matrix in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2015) 308:G807–30. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00447.2014
110. Baiocchini A, Montaldo C, Conigliaro A, Grimaldi A, Correani V, Mura F, et al. Extracellular matrix molecular remodeling in human liver fibrosis evolution. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0151736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151736
111. Zhang L, Bowen T, Paddon C, Webber J, Giles P, Steadman R, et al. Thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) activation increases hyaluronan (HA) production in preadipocyte-fibroblasts; explanation for HA accumulation in thyroid dysfunction? In: Endocrine Abstracts. Bristol, UK: Bioscientifica (2009).
112. Kim J and Seki E. Hyaluronan in liver fibrosis: basic mechanisms, clinical implications, and therapeutic targets. Hepatol Commun. (2023) 7(4):e0083. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000083
113. Grandoch M, Flögel U, Virtue S, Maier JK, Jelenik T, Kohlmorgen C, et al. 4-Methylumbelliferone improves the thermogenic capacity of brown adipose tissue. Nat Metab. (2019) 1:546–59. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0055-6
114. Pourseyedi N, Arefhosseini S, Tutunchi H, and Ebrahimi-Mameghani M. Evidence on the link between hypothyroidism and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an updated systematic review. BMC Endocrine Disord. (2025) 25:154. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01977-2
115. Marschner RA, Arenhardt F, Ribeiro RT, and Wajner SM. Influence of altered thyroid hormone mechanisms in the progression of metabolic dysfunction associated with fatty liver disease (MAFLD): A systematic review. Metabolites. (2022) 12:675. doi: 10.3390/metabo12080675
116. Lonardo A, Mantovani A, Lugari S, and Targher G. NAFLD in some common endocrine diseases: prevalence, pathophysiology, and principles of diagnosis and management. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:2841. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112841
117. Кolesnikova O, Vovk K, and Titarenko A. The impact of endothelial dysfunction on the course of metabolically associated liver disease in combination with subclinical hypothyroidism. Med Res Archives. (2024) 12(8). doi: 10.18103/mra.v12i8.5335
118. Klair JS, Yang JD, Abdelmalek MF, Guy CD, Gill RM, Yates K, et al. A longer duration of estrogen deficiency increases fibrosis risk among postmenopausal women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. (2016) 64:85–91. doi: 10.1002/hep.28514
119. Wirth EK, Puengel T, Spranger J, and Tacke F. Thyroid hormones as a disease modifier and therapeutic target in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 17:425–34. doi: 10.1080/17446651.2022.2110864
120. Moskovich D, Finkelshtein Y, Alfandari A, Rosemarin A, Lifschytz T, Weisz A, et al. Targeting the DIO3 enzyme using first-in-class inhibitors effectively suppresses tumor growth: a new paradigm in ovarian cancer treatment. Oncogene. (2021) 40:6248–57. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02020-z
121. Köhrle J and Frädrich C. Deiodinases control local cellular and systemic thyroid hormone availability. Free Radical Biol Med. (2022) 193:59–79. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.09.024
122. Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP, and Fallowfield JA. Liver fibrosis and repair: immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:181–94. doi: 10.1038/nri3623
123. Bano A, Chaker L, Muka T, Mattace-Raso FU, Bally L, Franco OH, et al. Thyroid function and the risk of fibrosis of the liver, heart, and lung in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid. (2020) 30:806–20. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0572
124. Wang F, Wang S, Zhang C, Tian X, Zhou Y, Xuan W, et al. Noncanonical JAK1/STAT3 interactions with TGF-β modulate myofibroblast transdifferentiation and fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2022) 323:L698–l714. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00428.2021
125. Barry-Hamilton V, Spangler R, Marshall D, McCauley S, Rodriguez HM, Oyasu M, et al. Allosteric inhibition of lysyl oxidase–like-2 impedes the development of a pathologic microenvironment. Nat Med. (2010) 16:1009–17. doi: 10.1038/nm.2208
126. Deng Z, Fear MW, Choi YS, Wood FM, Allahham A, Mutsaers SE, et al. The extracellular matrix and mechanotransduction in pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2020) 126:105802. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105802
127. Liu F, Lagares D, Choi KM, Stopfer L, Marinković A, Vrbanac V, et al. Mechanosignaling through YAP and TAZ drives fibroblast activation and fibrosis. Am J Physiology-Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2015) 308:L344–L57. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00300.2014
128. Du T, Huang Y, Lv Y, and Yuan G. Liver fibrotic burden across the spectrum of hypothyroidism. J Gastroenterol. (2025) 60:315–27. doi: 10.1007/s00535-024-02184-x
129. Conrad N, Judge A, Tran J, Mohseni H, Hedgecott D, Crespillo AP, et al. Temporal trends and patterns in heart failure incidence: a population-based study of 4 million individuals. Lancet. (2018) 391:572–80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32520-5
130. Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, and Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. (2010) 141:52–67. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.015
131. Wells RG. The role of matrix stiffness in regulating cell behavior. Hepatology. (2008) 47:1394–400. doi: 10.1002/hep.22193
132. Moreira RK. Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2007) 131:1728–34. doi: 10.5858/2007-131-1728-HSCALF
133. Lachowski D, Cortes E, Rice A, Pinato D, Rombouts K, and del Rio Hernandez A. Matrix stiffness modulates the activity of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in hepatic stellate cells to perpetuate fibrosis. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:7299. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43759-6
134. Iozzo RV and Schaefer L. Proteoglycan form and function: A comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix Biol. (2015) 42:11–55. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.02.003
135. Sun Z, Li L, Yan Z, Zhang L, Zang G, Qian Y, et al. Circadian rhythm disorders elevate macrophages cytokines release and promote multiple tissues/organs dysfunction in mice. Physiol behavior. (2022) 249:113772. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2022.113772
136. Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Pastore M, Gitto S, and Marra F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying liver fibrosis regression. Cells. (2021) 10:2759. doi: 10.3390/cells10102759
137. Smith TJ, Horwitz AL, and Refetoff S. The effect of thyroid hormone on glycosaminoglycan accumulation in human skin fibroblasts. Endocrinology. (1981) 108:2397–9. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-6-2397
138. Misra S, Hascall VC, Markwald RR, and Ghatak S. Interactions between hyaluronan and its receptors (CD44, RHAMM) regulate the activities of inflammation and cancer. Front Immunol. (2015) 6 - 2015. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00201
139. Fei D, Meng X, Yu W, Yang S, Song N, Cao Y, et al. Fibronectin (FN) cooperated with TLR2/TLR4 receptor to promote innate immune responses of macrophages via binding to integrin β1. Virulence. (2018) 9:1588–600. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1528841
140. Gan C, Cai Q, Tang C, and Gao J. Inflammasomes and pyroptosis of liver cells in liver fibrosis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13 - 2022. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.896473
141. Vargas R and Videla LA. Thyroid hormone suppresses ischemia-reperfusion-induced liver NLRP3 inflammasome activation: Role of AMP-activated protein kinase. Immunol Lett. (2017) 184:92–7. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.01.007
142. Smigiel KS and Parks WC. Macrophages, wound healing, and fibrosis: recent insights. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2018) 20:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0725-5
143. Manmadhan S and Ehmer U. Hippo signaling in the liver - A long and ever-expanding story. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2019) 7:33. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00033
144. Williams AS, Kang L, and Wasserman DH. The extracellular matrix and insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2015) 26:357–66. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.05.006
145. Guo T, Wantono C, Tan Y, Deng F, Duan T, and Liu D. Regulators, functions, and mechanotransduction pathways of matrix stiffness in hepatic disease. Front Physiol. (2023) 14 - 2023. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1098129
146. Ritter MJ, Amano I, and Hollenberg AN. Thyroid hormone signaling and the liver. Hepatology. (2020) 72:742–52. doi: 10.1002/hep.31296
147. Irrcher I, Adhihetty PJ, Sheehan T, Joseph AM, and Hood DA. PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha expression during thyroid hormone- and contractile activity-induced mitochondrial adaptations. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2003) 284:C1669–77. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00409.2002
148. Duckworth WC, Bennett RG, and Hamel FG. Insulin degradation: progress and potential. Endocrine Rev. (1998) 19:608–24. doi: 10.1210/edrv.19.5.0349
149. Duckworth WC, Runyan KR, Wright RK, Halban PA, and Solomon SS. Insulin degradation by hepatocytes in primary culture. Endocrinology. (1981) 108:1142–7. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-4-1142
150. Zhang DY and Friedman SL. Fibrosis-dependent mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2012) 56:769–75. doi: 10.1002/hep.25670
151. Delgado ME, Cárdenas BI, Farran N, and Fernandez M. Metabolic reprogramming of liver fibrosis. Cells. (2021) 10(12):3604. doi: 10.3390/cells10123604
152. Dong Y, Zheng Q, Wang Z, Lin X, You Y, Wu S, et al. Higher matrix stiffness as an independent initiator triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition and facilitates HCC metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. (2019) 12:112. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0795-5
153. Wu Y, Zuo J, Ji G, Saiyin H, Liu X, Yin F, et al. Proapoptotic function of integrin beta(3) in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:60–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1028
154. Li Z, Dranoff JA, Chan EP, Uemura M, Sévigny J, and Wells RG. Transforming growth factor-beta and substrate stiffness regulate portal fibroblast activation in culture. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2007) 46:1246–56. doi: 10.1002/hep.21792
155. Schrader J, Gordon-Walker TT, Aucott RL, van Deemter M, Quaas A, Walsh S, et al. Matrix stiffness modulates proliferation, chemotherapeutic response, and dormancy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2011) 53:1192–205. doi: 10.1002/hep.24108
156. Choi SS, Sicklick JK, Ma Q, Yang L, Huang J, Qi Y, et al. Sustained activation of Rac1 in hepatic stellate cells promotes liver injury and fibrosis in mice. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2006) 44:1267–77. doi: 10.1002/hep.21375
157. Fan H, Li L, Liu Z, Zhang P, Wu S, Han X, et al. Low thyroid function is associated with an increased risk of advanced fibrosis in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:3. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02612-3
158. Kelly MJ, Pietranico-Cole S, Larigan JD, Haynes N-E, Reynolds CH, Scott N, et al. Discovery of 2-[3, 5-dichloro-4-(5-isopropyl-6-oxo-1, 6-dihydropyridazin-3-yloxy) phenyl]-3, 5-dioxo-2, 3, 4, 5-tetrahydro [1, 2, 4] triazine-6-carbonitrile (MGL-3196), a highly selective thyroid hormone receptor β agonist in clinical trials for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Washington, DC, USA: ACS Publications (2014).
159. Taub R, Chiang E, Chabot-Blanchet M, Kelly MJ, Reeves RA, Guertin MC, et al. Lipid lowering in healthy volunteers treated with multiple doses of MGL-3196, a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor-β agonist. Atherosclerosis. (2013) 230:373–80. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.07.056
160. Puengel T and Tacke F. Cell type-specific actions of thyroid hormones in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Liver Int. (2024) 44:275–8. doi: 10.1111/liv.15783
161. Harrison SA, Bedossa P, Guy CD, Schattenberg JM, Loomba R, Taub R, et al. A phase 3, randomized, controlled trial of resmetirom in NASH with liver fibrosis. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:497–509. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309000
162. Xue F and Wei L. THR-β Agonist for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis treatment: challenges of a promising drug. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2024) 12:755–7. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00100
163. He H and Wu JJ. A Phase I, single-dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of ASC43F, a fixed-dose combination oral tablet of ASC41, a thyroid hormone receptor Beta agonist, and ASC42, a farnesoid X receptor agonist in healthy subjects. In: HEPATOLOGY. WILEY 111 RIVER ST, HOBOKEN 07030-5774, NJ USA (2022).
164. Prikhodko VA, Bezborodkina NN, and Okovityi SV. Pharmacotherapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: emerging targets and drug candidates. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:274. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020274
165. Noureddin M. MASH clinical trials and drugs pipeline: An impending Tsunami. Hepatology. (2024) 10:1097. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000860
166. Cho SW. Selective agonists of thyroid hormone receptor beta: promising tools for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocrinol Metab. (2024) 39:285–7. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.203
167. Chiellini G, Apriletti JW, Al Yoshihara H, Baxter JD, Ribeiro RC, and Scanlan TS. A high-affinity subtype-selective agonist ligand for the thyroid hormone receptor. Chem Biol. (1998) 5:299–306. doi: 10.1016/S1074-5521(98)90168-5
168. Boyer SH, Jiang H, Jacintho JD, Reddy MV, Li H, Li W, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a series of liver-selective phosphonic acid thyroid hormone receptor agonists and their prodrugs. J medicinal Chem. (2008) 51:7075–93. doi: 10.1021/jm800824d
169. Ito I, Waku T, Aoki M, Abe R, Nagai Y, Watanabe T, et al. A nonclassical vitamin D receptor pathway suppresses renal fibrosis. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:4579–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI67804
170. Wang C, Wang B, Xue L, Kang Z, Hou S, Du J, et al. Design, synthesis, and antifibrosis activity in liver of nonsecosteroidal vitamin D receptor agonists with phenyl-pyrrolyl pentane skeleton. J Medicinal Chem. (2018) 61:10573–87. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01165
171. Bhopale KK and Srinivasan MP. Therapeutics for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Livers. (2023) 3:597–617. doi: 10.3390/livers3040040
172. Parola M and Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH: from pathophysiology towards diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Mol Aspects Med. (2024) 95:101231. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2023.101231
173. Henderson NC, Arnold TD, Katamura Y, Giacomini MM, Rodriguez JD, McCarty JH, et al. Targeting of αv integrin identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in several organs. Nat Med. (2013) 19:1617–24. doi: 10.1038/nm.3282
174. Rahman SR, Roper JA, Grove JI, Aithal GP, Pun KT, and Bennett AJ. Integrins as a drug target in liver fibrosis. Liver Int. (2022) 42:507–21. doi: 10.1111/liv.15157
175. Chen C, Chen J, Wang Y, Fang L, Guo C, Sang T, et al. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide inhibits HSC activation and liver fibrosis via targeting inflammation, apoptosis, cell cycle, and ECM-receptor interaction mediated by TGF-β/Smad signaling. Phytomedicine. (2023) 110:154626. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154626
176. Mishra F, Yuan Y, Yang JJ, Li B, Chan P, and Liu Z. Depletion of activated hepatic stellate cells and capillarized liver sinusoidal endothelial cells using a rationally designed protein for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and alcoholic hepatitis treatment. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:7447. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137447
177. Ma R, Ren H, Xu B, Cheng Y, Gan L, Zhang R, et al. PH20 inhibits TGFβ1-induced differentiation of perimysial orbital fibroblasts via hyaluronan-CD44 pathway in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Science. (2019) 60:1431–41. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-26268
178. Neuman MG, Cohen LB, and Nanau RM. Hyaluronic acid as a non-invasive biomarker of liver fibrosis. Clin Biochem. (2016) 49:302–15. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.07.019
179. Middleton SA, Rajpal N, Cutler L, Mander P, Rioja I, Prinjha RK, et al. BET inhibition improves NASH and liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:17257. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35653-4
180. Schilter H, Findlay AD, Perryman L, Yow TT, Moses J, Zahoor A, et al. The lysyl oxidase like 2/3 enzymatic inhibitor, PXS-5153A, reduces crosslinks and ameliorates fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:1759–70. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14074
181. Kalhori V, Magnusson M, Asghar MY, Pulli I, and Törnquist K. FTY720 (Fingolimod) attenuates basal and sphingosine-1-phosphate-evoked thyroid cancer cell invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer. (2016) 23:457–68. doi: 10.1530/ERC-16-0050
182. Mauer AS, Hirsova P, Maiers JL, Shah VH, and Malhi H. Inhibition of sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling ameliorates murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiology-Gastrointestinal Liver Physiol. (2017) 312:G300–G13. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00222.2016
183. Rohrbach TD, Asgharpour A, Maczis MA, Montefusco D, Cowart LA, Bedossa P, et al. FTY720/fingolimod decreases hepatic steatosis and expression of fatty acid synthase in diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. J Lipid Res. (2019) 60:1311–22. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M093799
184. Torre P, Motta BM, Sciorio R, Masarone M, and Persico M. Inflammation and fibrogenesis in MAFLD: role of the hepatic immune system. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:781567. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.781567
185. Ma S, Wang Y, Fan S, Jiang W, Sun M, Jing M, et al. TSH-stimulated hepatocyte exosomes modulate liver-adipose triglyceride accumulation via the TGF-β1/ATGL axis in mice. Lipids Health Disease. (2025) 24:81. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02509-6
186. Fabregat I, Moreno-Càceres J, Sánchez A, Dooley S, Dewidar B, Giannelli G, et al. TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J. (2016) 283:2219–32. doi: 10.1111/febs.13665
187. Lim HS, Back KO, Kim HJ, Choi YH, Park YM, and Kook KH. Hyaluronic acid induces COX-2 expression via CD44 in orbital fibroblasts from patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2014) 55:7441–50. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14873
188. Liao C-Y, Barrow F, Venkatesan N, Nakao Y, Mauer AS, Fredrickson G, et al. Modulating sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor signaling skews intrahepatic leukocytes and attenuates murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14 - 2023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130184
189. Jiang JX, Chen X, Hsu DK, Baghy K, Serizawa N, Scott F, et al. Galectin-3 modulates phagocytosis-induced stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis in vivo. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2012) 302:G439–46. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00257.2011
190. Ma X, Huang T, Chen X, Li Q, Liao M, Fu L, et al. Molecular mechanisms in liver repair and regeneration: from physiology to therapeutics. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2025) 10:63. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02104-8
191. Yan M, Man S, Sun B, Ma L, Guo L, Huang L, et al. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: the implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2023) 8:443. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01673-4
192. Peiseler M, Schwabe R, Hampe J, Kubes P, Heikenwälder M, and Tacke F. Immune mechanisms linking metabolic injury to inflammation and fibrosis in fatty liver disease – novel insights into cellular communication circuits. J Hepatology. (2022) 77:1136–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.012
193. Subramanian P, Hampe J, Tacke F, and Chavakis T. Fibrogenic pathways in metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:6996. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136996
Keywords: hypothyroidism, MAFLD, ECM remodeling, HSC, TH signaling, liver fibrosis
Citation: Wang T, Duan L, Zhao B, Zhang J, Yu Y and Zhao J (2025) ECM remodeling in hypothyroidism-associated MAFLD: mechanisms, clinical relevance, and therapeutic targets. Front. Immunol. 16:1639196. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1639196
Received: 01 June 2025; Accepted: 17 September 2025;
Published: 03 October 2025.
Edited by:
Haibo Dong, University of North Carolina at Greensboro, United StatesReviewed by:
Dawit Tadese, Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR), EthiopiaJi Sun, China Medical University, China
Xiaoliang Gao, Fourth Military Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Duan, Zhao, Zhang, Yu and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongjiang Yu, MzQ1NTMyMTEyQHFxLmNvbQ==; Jinyue Zhao, OTczOTQ1NDFAcXEuY29t
 Tianzhen Wang1
Tianzhen Wang1 Liyun Duan
Liyun Duan Jinyue Zhao
Jinyue Zhao