- 1Department of tuberculosis, Anhui Chest Hospital, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 2Department of Infection Disease, Qinghai Center for Disease Prevention and Control, Xining, China
- 3Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 4Department of Public Health, Medical College, Qinghai University, Xining, China
Objectives: The WNT signaling pathway plays important roles in the pathophysiology of pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB). This study aimed to assess the association of the DNA methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes and PTB susceptibility, and determine whether the methylation levels might serve as valuable biomarkers for PTB diagnosis.
Methods: We collected blood samples from 98 PTB patients and 96 normal controls, and extracted DNA samples. The methylation levels of promoter region in WNT signaling pathway genes (SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, WIF-1, DKK-1, LRP5, LRP6) were detected by MethylTarget technique.
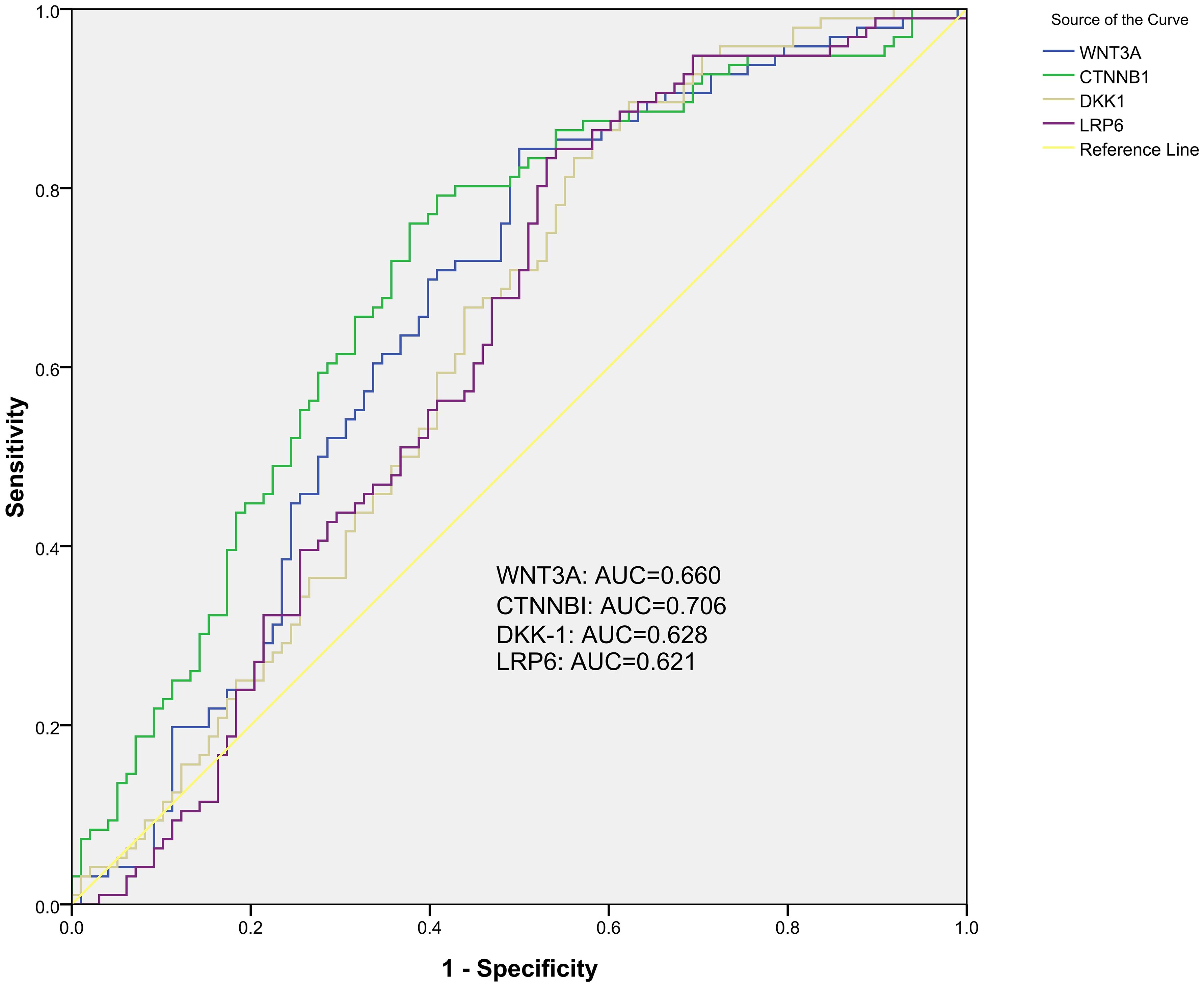
Results: We found that the methylation levels of SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 genes were significantly decreased in the peripheral blood of PTB patients when compared to normal controls, while WIF-1, LRP5 genes methylation levels showed no significant difference between PTB patients and controls. In PTB patients, the increased SFRP1 methylation level was significantly correlated with drug-induced liver injury, pulmonary infection, and the decreased WNT3A, CTNNB1 methylation levels were respectively significantly associated with drug resistance, fever. For diagnosing PTB, the CTNNB1 methylation level demonstrated a relatively higher diagnostic value, achieving an AUC of 0.706. Subsequently, the AUC of WNT3A, DKK-1, LRP6 was 0.660, 0.628, 0.621. The diagnostic value was slightly enhanced when CTNNB1 combined with WNT3A, DKK-1, LRP6, with an AUC of 0.710.
Conclusion: The methylation levels of SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 genes were significantly decreased in PTB patients, and single gene or multiple genes methylation panels might serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers for PTB.
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is a common and severe infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), and it is regarded as a major global public health concern. Pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) is the most common type. According to latest Global Tuberculosis Report, there are about 10.8 million new TB cases worldwide in 2023, and approximately 1.25 million people died from this disease (1). At present, only about 5-10% population infected with MTB would eventually develop active TB (2). Individual susceptibility varies might be related to multiple factors, such as nutritional status, immune function and genetic background (3, 4). Many genetic association studies had already identified some candidate genes related to TB susceptibility (5, 6). However, this only explained part of the genetic causes of TB, and the potential roles of other genetic mechanisms (epigenetic modifications, etc.) in TB needed to be further explored.
As the most common form of epigenetic modification, the dynamic regulation of DNA methylation modulated the immune response of MTB, thereby influencing the susceptibility and development of PTB (7, 8). Our previous study found higher methylation levels of B7-H4 and BTLA genes in PTB patients (9). CpG sites in genome usually exhibited abnormal methylation modifications during early stages of disease, which had led to increasing emphasis on DNA methylation in the field of disease diagnosis. Moreover, DNA methylation biomarker had greater stability and could be detected in blood when compared with other biomarkers (10, 11). Hence, it was of great significance to search for methylation biomarkers that could be used for the early diagnosis of PTB.
Molecular pathways that regulate immune responses are a major focus of research in the study regarding PTB pathogenesis, including WNT pathways (12, 13). Recent evidences indicated that WNT signaling pathway was a crucial transduction cascade reaction that regulated the host’s immune response to microbial pathogens infection, and exerted significant pathogenic roles in the development of PTB (14). This study also found that the mRNA levels of several WNT related genes (CTNNB1, SFRP1, WNT3A) in patients with PTB were significantly elevated (14). Wu et al. demonstrated that activation of the Wnt/β−catenin signaling pathway induced apoptosis in macrophages infected with MTB and enhanced the production of TNF−α and IL−6 (15). In addition, genetic variations in WNT signaling pathway genes were also associated with susceptibility to PTB in many studies (14, 16).
Abnormal methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes had been found to be associated with the pathogenesis of various diseases. Our recent study found that multiple variants in WNT signaling pathway genes (SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, WIF-1, DKK-1, LRP5, LRP6) were linked to some clinical characteristics of PTB patients (16). Therefore, we hypothesized that the methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes might also be associated with the development of PTB. In this study, we detected and compared the WNT signaling pathway genes methylation levels in the peripheral blood of PTB patients and controls, and analyzed whether the abnormal methylation levels could serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis of PTB.
Materials and methods
Study participants
In this case-control study, the patients with PTB were selected from Anhui Chest Hospital between January 2023 and February 2024, while the age- and gender-matched healthy volunteers were included from the health examine center in the same area as control group. PTB patients were diagnosed based on the Diagnosis for PTB (WS 288-2017) and the Classification of TB (WS 196-2017) from the Health Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. For PTB patients, the diagnostic criteria mainly included: (1) positive pathogen diagnosis (bacterial culture, sputum smear examination, GeneXpert MTB/RIF test); (2) positive immunological diagnosis (interferon-γ release assay); (3) typical clinical manifestations and imaging examination. The exclusion criteria of PTB patients in this study comprised HIV positive, pneumonia, immune deficiency, and other infectious diseases. Controls group were required to had no TB-related symptoms, no history of infectious diseases, and a negative interferon-γ release assay result.
The design and implementation of this study were in line with the principles of the Helsinki Declaration and approved by the Ethics Committee of Anhui Chest Hospital. After obtaining informed consent, we collected demographic characteristics and peripheral blood samples from all study subjects, as well as the clinical data of PTB patients, including fever, drug resistance, drug-induced liver injury (DILI), pulmonary infection, total bilirubin (TBIL), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), etc.
DNA extraction and bisulfite treatment
Approximately 3 mL of peripheral blood was collected from study subjects, and genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes using the Flexi Gene-DNA kit (Quona Company, Valencia, California) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, the extracted DNA sample was quantified using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer. Finally, the DNA sample was subjected to bisulfite conversion using the EZ DNA Methylation Gold kit (Zymo Research, Orange, CA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Methylation detecting
The promoter regions of WNT related genes (SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, WIF-1, DKK-1, LRP5, LRP6) were subjected to target region methylation sequencing using MethylTarget, and this was carried out with the assistance of the Shanghai GeneCowin Biotechnology. The CpG islands in the promoter region of these genes were sequenced with the Illumina HiSeq (Illumina), and the primers were designed to amplify the specific target fragments from the bisulfite-converted DNA (Supplementary Table S1).
Two sequential polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifications were conducted, and the main instruments, reagents used in this experiment were listed in Supplementary Table S2. The initial amplification employed specific primers to enrich bisulfite-converted target fragments from DNA sample under optimized conditions. The cycle conditions of PCR reactions were set as follows: 95°C for 2 min, 11 cycles at 94°C for 20 sec and 63°C for 40 sec, 72°C for 1 min, 24 cycles at 94°C for 20 sec and 65°C for 30 sec and 72°C for 1 min, 72°C for 2 min. Subsequently, index PCR was conducted to pool all enriched products, amplifying them with indexed primers to append platform-compatible tag sequences (Illumina HiSeq compatible). The PCR products were size-separated using agarose gel electrophoresis and purified by TIANGENG Gel Extraction Kit, and subjected to high-throughput paired-end sequencing (2 × 150 bp) on the Illumina HiSeq platform to generate FastQ files. At this stage, the cycle conditions of PCR reactions were set as follows: 95°C for 30 sec, 11 cycles at 98°C for 10 sec and 65°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 30 sec, 72°C for 5 min. The methylation level of certain specific fragment was obtained by calculating the mean methylation levels of all CpG sites on this fragment.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Plasma was isolated from peripheral blood by centrifugation at 3000 r.p.m. for 10 min and stored at -80°C until further analysis. The levels of SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK−1, and LRP6 genes were measured using ELISA kits (Fine Biotech Co., Ltd., China) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The genes expression levels were expressed in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL).
Statistical analysis
The methylation levels were expressed as median value and interquartile range, and Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the methylation levels between two different groups. The correlation between the methylation levels and laboratory data, expression levels was evaluated through Spearman’s rank correlation analysis. The diagnostic value of WNT signaling pathway gene methylation levels as biomarkers for PTB was evaluated through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and the area under the curve (AUC). The sensitivity, specificity, and cutoff values from ROC analysis was also calculated. All statistical analyses were conducted by SPSS statistics 26.0, and P value was less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Differences in WNT signaling pathway genes methylation levels between PTB and controls
This study enrolled a total of 194 subjects, comprising 98 PTB patients and 96 normal controls. The PTB patients had a mean age of 43.52 ± 17.59 years, with 45 females and 53 males. The control group exhibited a mean age of 43.44 ± 4.53 years, with 44 females and 52 males. We found that there was no statistically significant difference in the distribution of age and gender between these two groups.
As shown in Supplementary Table S3, this study first analyzed the methylation levels of multiple detected specific target fragments of WNT signaling pathway genes between PTB patients and controls. In comparison to controls, PTB patients had significant decrease in the methylation levels of SFRP1_1, SFRP1_2, WNT3A_1, WNT3A_2, CTNNB1_1, CTNNB1_2, DKK-1_1, DKK-1_2, LRP6_2 (P = 0.015, P = 0.022, P = 0.002, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P = 0.018, P = 0.002, P = 0.003, respectively), and exhibited elevated methylation of LRP6_1 (P = 0.002). No significant differences were observed in the WIF-1_1, WIF-1_2, LRP5_1, LRP5_2, LRP6_3 methylation levels (P > 0.05).
Since each gene might contain more target fragments, the mean methylation level of all CpG sites on the detected specific fragments was calculated as the methylation level of each gene. Hence, we conducted further investigations to assess the association between the WNT signaling pathway genes methylation levels and the patients with PTB. The results were shown in Figure 1, and found that PTB patients exhibited decreased methylation levels of SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 (P = 0.042, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P = 0.002, P = 0.003, respectively). In contrast, the WIF-1, LRP5 methylation levels in PTB patients showed no statistically significant difference compared to that in normal controls.
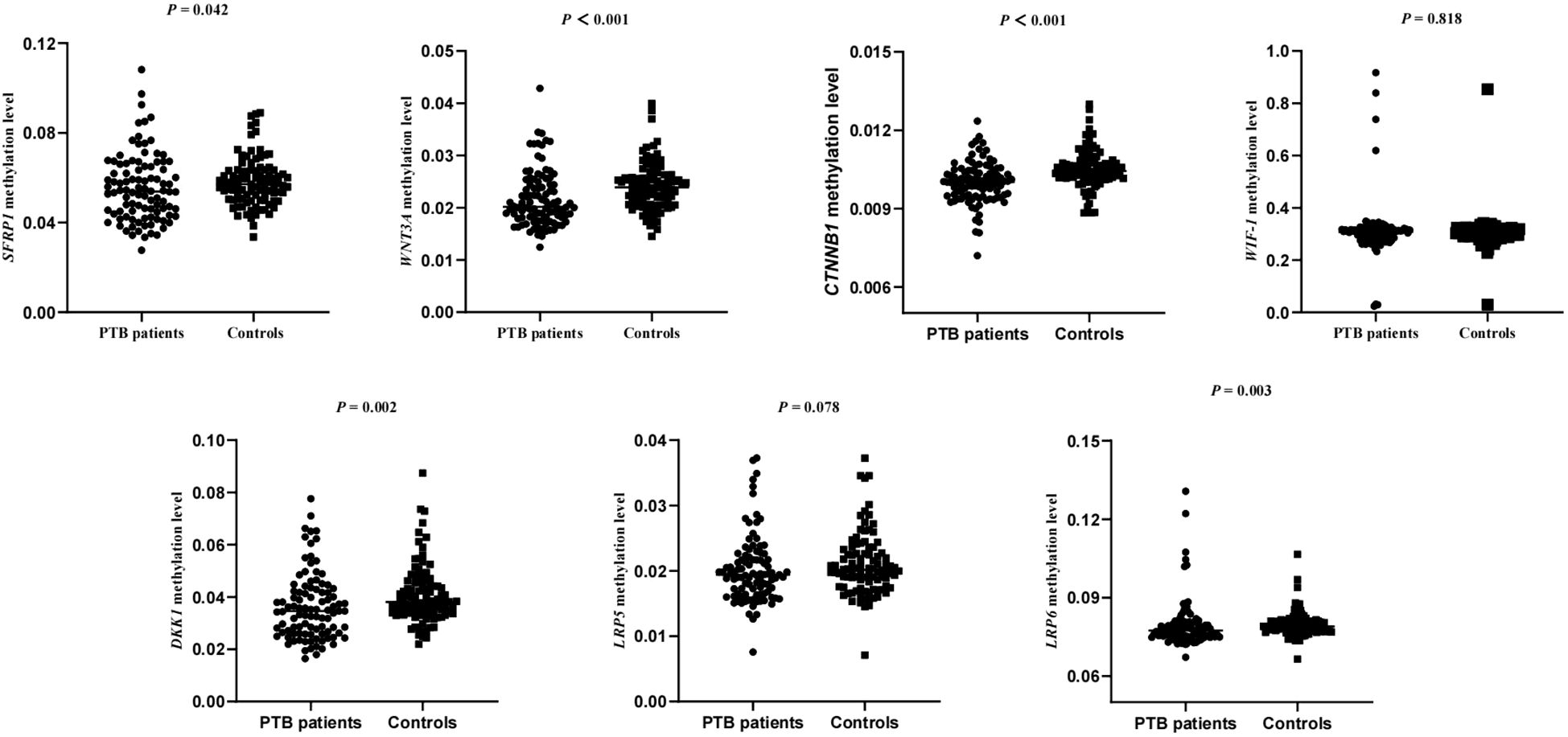
Figure 1. The methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes in PTB patients and normal controls.
The relationship between the methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes and gender in PTB patients was also analyzed. The results showed that the methylation levels of WIF1 and DKK-1 in male PTB patients were significantly lower than those in female patients, although no statistically significant differences were observed for the other genes (Supplementary Table S4).
Correlation of WNT signaling pathway genes methylation levels with common clinical manifestations among PTB patients
Considering several common clinical features of PTB patients, such as fever, drug resistance, liver damage, and it was necessary to determine whether these genes methylation levels affect the occurrence of the clinical manifestations. Hence, we assessed the possible relationship between SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 methylation levels and several clinical manifestations among PTB patients. As illustrated in Table 1, the results suggested that PTB patients with DILI, pulmonary infection respectively exhibited significantly increased SFRP1 methylation level than that in those patients without DILI, pulmonary infection (P = 0.001, P = 0.026). Moreover, the decreased WNT3A, CTNNB1 methylation levels were respectively significantly associated with drug resistance, fever in PTB patients (P = 0.012, P = 0.011). However, the DKK-1, LRP6 methylation levels were not related to above clinical features of PTB patients.
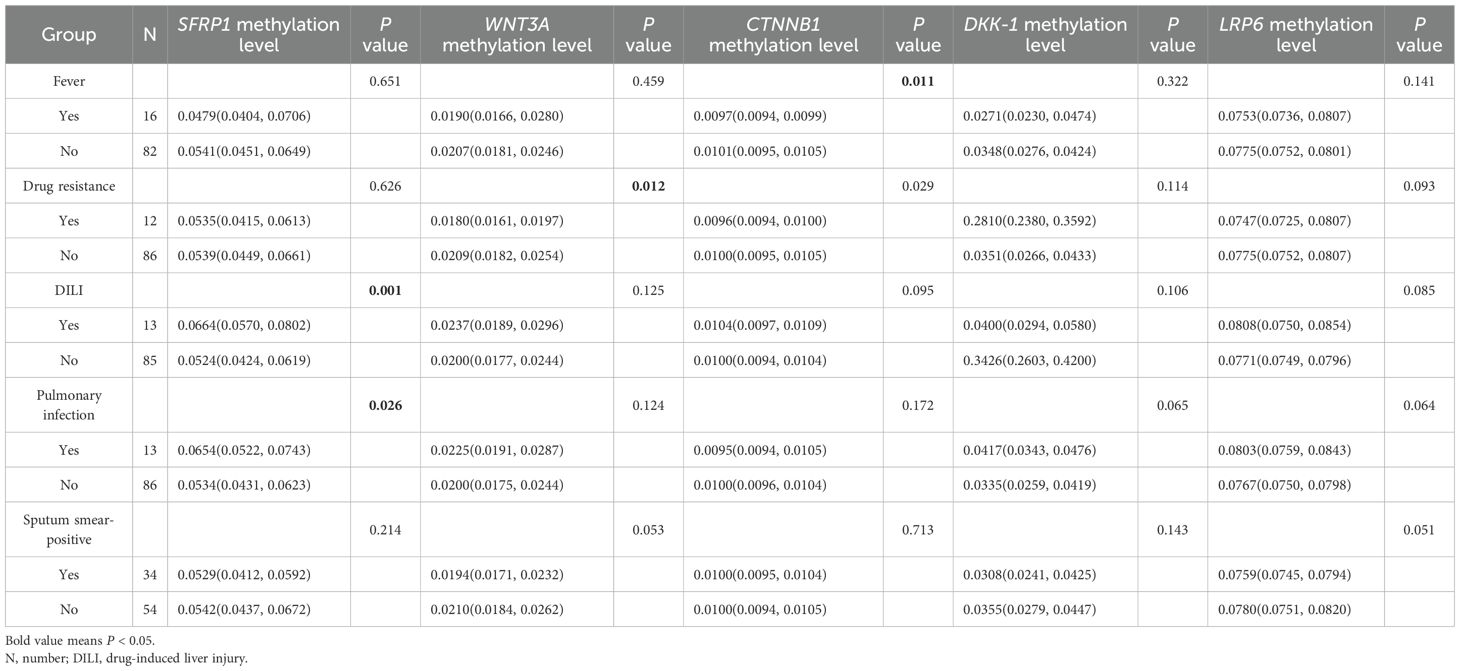
Table 1. Association between the methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes and clinical characteristics among PTB patients.
This study also evaluated the correlation between the methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes and several laboratory indicators of PTB patients, such as ESR, TBIL, ALT, and AST, while no correlation reached statistical significance (Table 2).
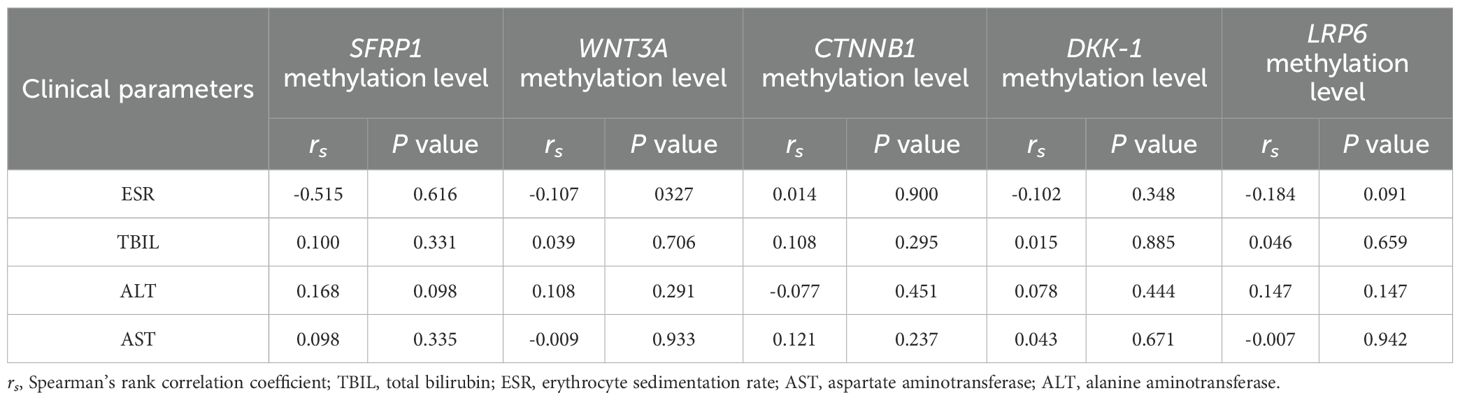
Table 2. The correlation between the methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes and ESR, TBIL, ALT, AST among PTB patients.
Diagnostic value of WNT signaling pathway genes methylation level as biomarkers for PTB
To assessed the potential value of the five WNT signaling pathway genes as diagnostic biomarkers for PTB, the ROC curve analysis was performed. For discriminating PTB patients from normal controls, ROC curve analysis indicated that WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 methylation levels might be used as diagnostic biomarkers. The AUC of CTNNB1, WNT3A, DKK-1, LRP6 was 0.706 (95% CI: 0.632, 0.780), 0.660 (95% CI: 0.582, 0.738), 0.628 (95% CI: 0.548, 0.707), 0.621 (95% CI: 0.541, 0.701), and CTNNB1 methylation level seemed to had relatively higher diagnostic value (Figure 2). The sensitivity, specificity of above diagnostic biomarkers were shown in Supplementary Table S5.
This study also further explored the comprehensive diagnostic value of these genes methylation levels for PTB, and identified three combined diagnostic models worthy of attention, including WNT3A+CTNNB1+DKK-1+LRP6, WNT3A+CTNNB1+DKK-1, WNT3A+CTNNB1. The AUC of these diagnostic models was 0.710 (95% CI: 0.637, 0.783), 0.709 (95% CI: 0.636, 0.782), 0.709 (95% CI: 0.636, 0.782) (Figure 3). The sensitivity, specificity of above diagnostic biomarkers were shown in Supplementary Table S4.
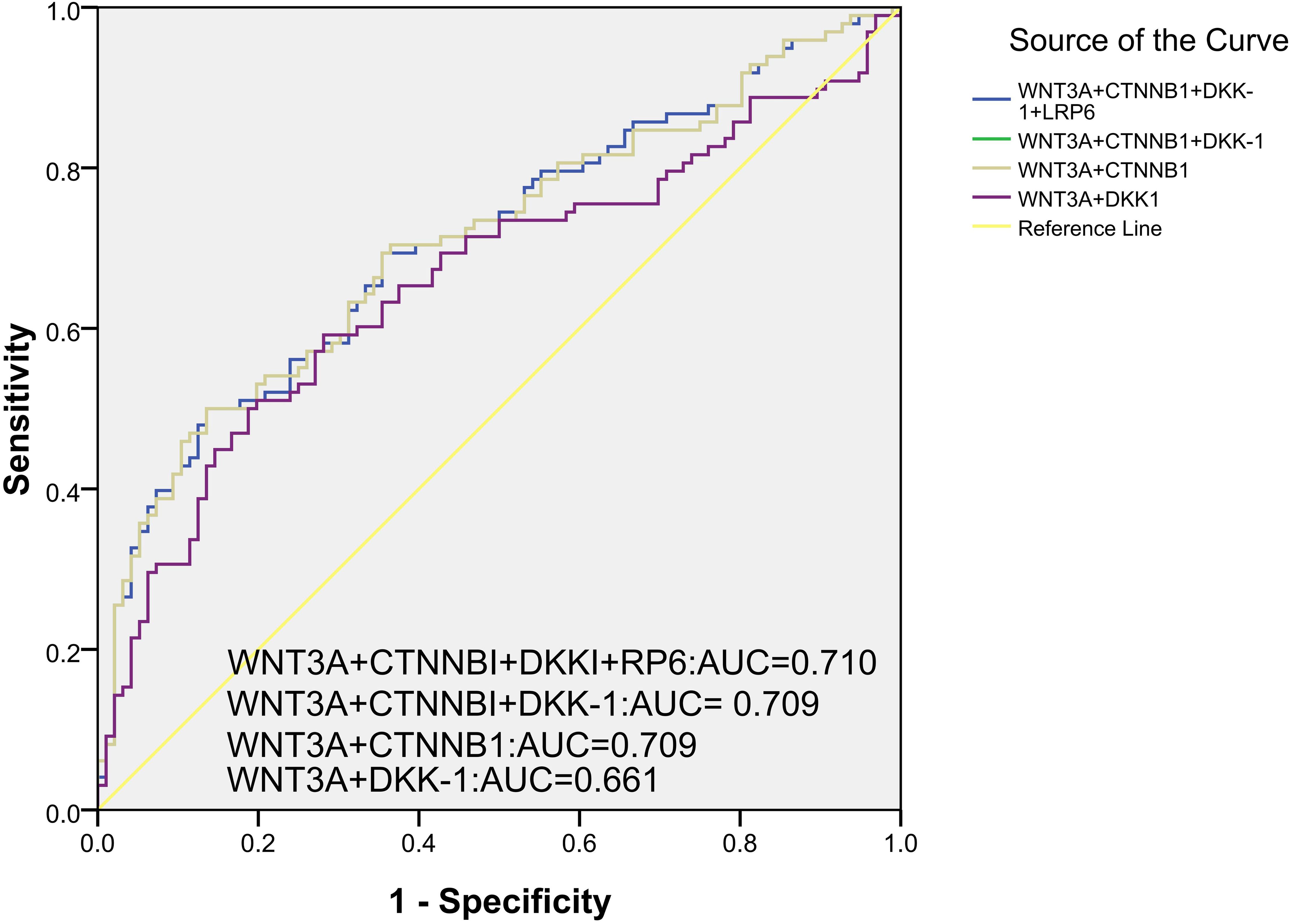
Figure 3. The combined diagnostic value of multiple gene methylation levels in PTB with ROC curve and AUC.
Associations between DNA methylation haplotypes and PTB patients
For every specific target fragment of these genes, this study also identified multiple DNA methylation haplotypes, and further analyzed the relationship between the frequency of these methylation haplotypes and PTB patients. Compared with normal controls, the frequencies of five DNA methylation haplotypes (one methylation haplotypes in CTNNB1_1, CTNNB1_2, DKK-1_1, DKK-1_2, LRP6_1) were significantly increased in PTB patients, while the the frequencies of fifteen DNA methylation haplotypes (one methylation haplotypes in DKK-1_1, LRP6_2, LRP6_3, WNT3A_2, two methylation haplotypes in CTNNB1_2, DKK-1_2, LRP6_1, three methylation haplotypes in CTNNB1_1) were significantly lower. The abnormal DNA methylation haplotypes were summarized in Supplementary Table S6.
Associations between WNT signaling pathway genes expression level and PTB patients
We assessed the SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK−1, and LRP6 genes expression levels in 44 PTB patients and 44 controls. The results showed that the expression level of DKK−1 was significantly higher in PTB patients than in controls, while no other significant differences was found (P < 0.001) (Figure 4). The possible associations between SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK−1, and LRP6 genes methylation levels and their respective expression among PTB patients were also evaluated. The results found that the methylation levels of these five genes were not correlated with their respective expression levels in PTB patients (Supplementary Table S7).
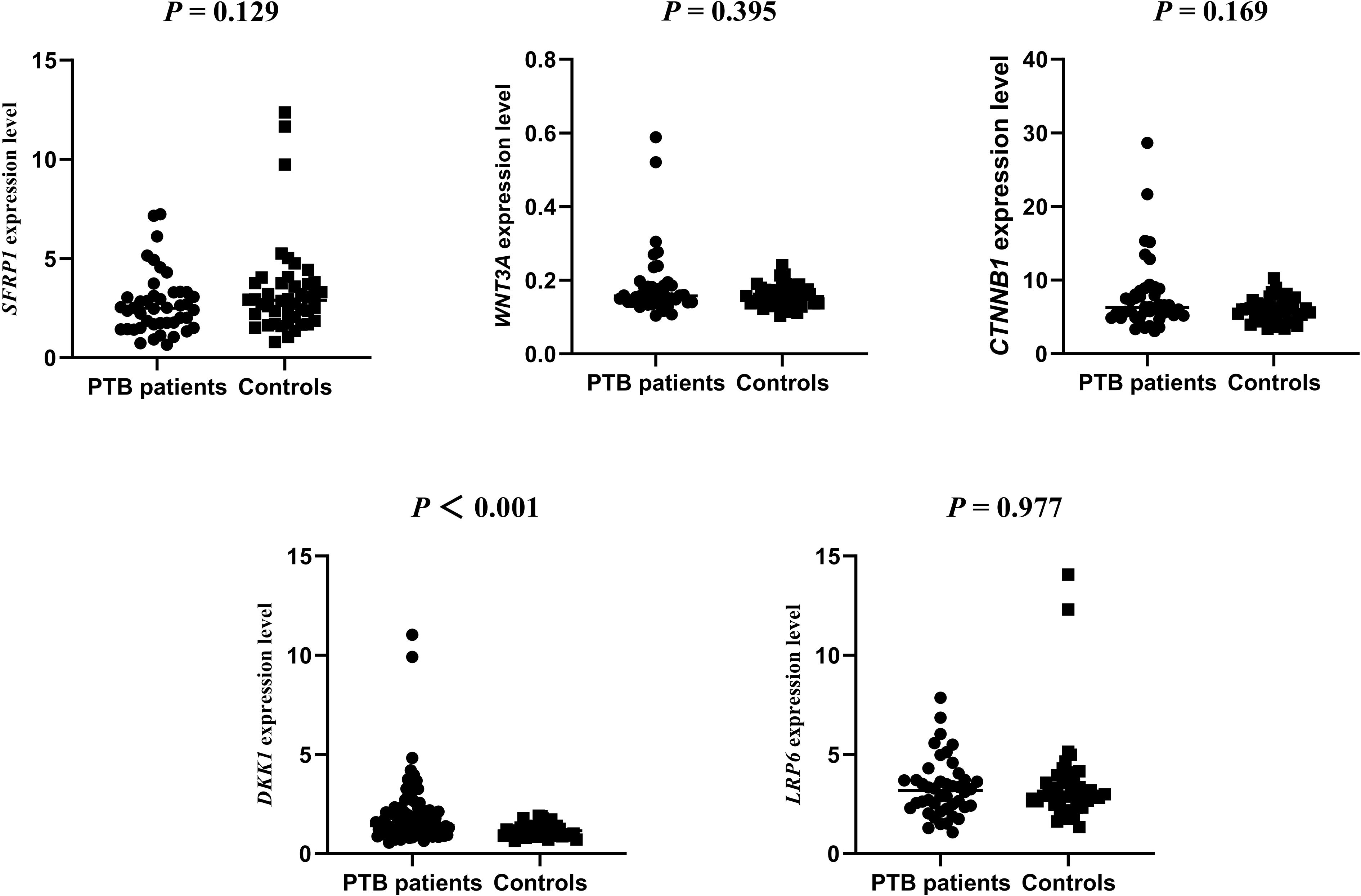
Figure 4. The expression levels of SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 genes in PTB patients and normal controls.
Discussion
In recent years, although the incidence of PTB has shown a downward trend and progress was made in PTB diagnosis, more than one-third of TB cases still fail to receive timely and effective identification. Epigenetic modifications represented a critical mechanism for regulating gene expression, and relevant studies had shown that DNA methylation not only played a significant role on the development of various diseases, including autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and cancers (17–19), but also could offer a new avenue for the early diagnosis of these diseases. For instance, the DNA methylation status of SHOX2/PTGER4 in plasma were proved to be valuable biomarkers for diagnosing lung cancer (20), and had been practically applied in clinical settings. In regard to infectious diseases, Zhang et al. identified several specific DNA methylation markers in TSPAN4 gene from peripheral blood samples, holding promise for enhancing the diagnostic accuracy of PTB (21). Our latest research also indicated that the ERAP2 methylation level was significantly higher in PTB patients when compared to controls, while the ERAP1 methylation level was decreased (22). However, there was no research exploring the WNT related genes methylation in PTB. To our knowledge, this study was the first to detect the methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes in the peripheral blood of PTB patients. The SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 genes methylation levels were significantly decreased in PTB patients, suggesting that the methylation of WNT related genes might be related to the pathogenesis of PTB, as well as served as possible biomarkers for diagnosing PTB.
The WNT signaling pathway mediated immune regulatory function during pathogen infection and inflammation, and triggered pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory responses according to the cellular and cytokine environment (23, 24). Current evidences indicated that WNT signaling pathway played crucial roles in connecting innate and adaptive immunity to combat MTB infection, and its activation could limit the pro-inflammatory response after MTB infection (25). As a core component of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, β-catenin exerted the key role in the CD4+T cells from PTB patients and mice (26). The BATF2 had also been found to regulate the number and function of macrophages by targeting TTC23 through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway during MTB infection (27). Therefore, the functions of WNT signaling pathway influenced the pathogenesis of PTB. Notably, genetic variations in multiple genes in WNT signaling pathway also affected the susceptibility and clinical manifestations of PTB. Our previous research revealed that WIF-1 rs3782499, DKK-1 GA haplotype were significantly related to PTB susceptibility, and WNT3A rs3121310, CTNNB1 rs2293303, LRP5 rs556442, LRP6 rs10743980 polymorphisms were respectively associated with DILI, sputum smear-positive, fever (16). Furthermore, the methylation status of multiple genes related to WNT pathway was also involved in the development process of various diseases (28, 29). The study by Zou et al. suggested that DKK‐1 hypermethylation might be associated with the pathological bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) (28). Here, we found the methylation levels of WNT related genes (SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6) were significantly reduced in PTB patients when compared to controls. During the onset and treatment process of PTB, patients usually exhibited some specific clinical features, such as drug resistance, liver damage, positive sputum smear, which significantly affected the treatment strategies. This study also stratified the patients based on their clinical features and further analyzed the relationship between WNT genes methylation levels and these clinical manifestations. Our results suggested that higher level of SFRP1 was associated with DILI, pulmonary infection, and decreased levels of WNT3A, CTNNB1 were respectively associated with drug resistance, fever among PTB patients. Above findings demonstrated that the abnormal methylation status of these genes might be involved in PTB process and providing new insights into the pathogenesis of PTB. Furthermore, the abnormal methylation levels of WNT related genes could also be related to the occurrence of certain clinical manifestations of patients with PTB, offering a valuable direction for reducing the occurrence of clinical manifestations.
Previous studies had suggested that WNT signaling pathway genes methylation levels could be considered as potential clinical biomarkers in human diseases (30, 31). Boughanem et al. established the promoter methylation level of SFRP2 gene as a valuable prognostic candidate for colorectal cancer when evaluated in peripheral blood, while as an indicator for treatment in tumors (30). Moreover, the serum DKK-1 methylation level could be regarded as a potential biomarker for evaluating the radiographic progression of AS (28). In this study, we searched for DNA methylation markers suitable for PTB diagnosis in WNT signaling pathway genes. Our results found that CTNNB1 methylation level might serve as a valuable diagnostic indicator, with an AUC of 0.706. Then, we further constructed a combined diagnostic indicator incorporating the methylation levels of four genes (CTNNB1, WNT3A, DKK-1, LRP6), which yielded an AUC of 0.710. In another study, Zhang et al. validated several methylated positions in TSPAN4 gene using pyrosequencing to serve as biomarkers for PTB diagnosis, achieving an AUC of 0.83 (21). In comparison, the methylation detection of WNT-related genes had certain potential for clinical diagnosis but could not yet support independent clinical application at the current AUC values. Moreover, methylation detection was relatively more cost-effective than pathogen detection and immunological detection. Therefore, further research with a larger sample size was needed to verify and improve the accuracy of methylation detection in PTB diagnosis. Generally, DNA methylation haplotype analysis also provided a new perspective for studying the direction of methylation changes (32). In this study, we finally identified 5 elevated and 15 decreased DNA methylation haplotypes in PTB patients, which were distributed across 8 specific target fragments, including CTNNB1_1, CTNNB1_2, DKK-1_1, DKK-1_2, WNT3A_2, LRP6_1, LRP6_2, LRP6_3. The changes in these methylation haplotypes discovered in this study might indicate inflammation-related alterations in PTB, highlighting the need for functional experiments to further investigate the roles of methylation changes in PTB.
Although our study presented some meaningful findings, it is also necessary to acknowledge several limitations. First, the sample size of this study might be relatively small, which affect the stability of our results. Second, this was a single-center cross-sectional study lacking an independent validation cohort. Third, we were unable to fully adjust for several important confounding factors, including drug exposure and underlying comorbidities. Therefore, future prospective, multi-center studies with larger sample sizes were needed to validate and extend these findings, thus facilitating the development of a more accurate early diagnostic model for PTB.
In conclusion, our study showed that the methylation levels of SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK-1, LRP6 genes in WNT signaling pathway were significantly decreased in PTB patients, and SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1 methylation levels were associated with some clinical characteristics, such as DILI, pulmonary infection, drug resistance, etc. Moreover, the abnormal methylation levels of WNT signaling pathway genes might be used as possible biomarkers for the diagnosis of PTB.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. The data presented in the study are deposited in the dbSNP (1063448).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Anhui Chest Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
HW: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Project administration. CW: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Methodology. QH: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YX: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation. YH: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. LX: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YL: Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YX: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Project administration, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Qinghai province highend innovative talents thousand talents program (No. 2020-12).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1639997/full#supplementary-material.
References
1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report. (2024). https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports (Accessed May 20, 2025).
2. Aravindan PP. Host genetics and berculosis: theory of genetic polymorphism and tuberculosis. Lung India. (2019) 36:244–52. doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_146_15
3. Fu H, Sun W, Xu Y, and Zhang H. Advances in cytokine gene polymorphisms in tuberculosis. mSphere. (2025) 10:e0094424. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00944-24
4. Gupta M, Srikrishna G, Klein SL, and Bishai WR. Genetic and hormonal mechanisms underlying sex-specific immune responses in tuberculosis. Trends Immunol. (2022) 43:640–56. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2022.06.004
5. Zhang TP, Li R, Wang LJ, Huang Q, and Li HM. Roles of the m6A methyltransferases METTL3, METTL14, and WTAP in pulmonary tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:992628. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.992628
6. Brenner EP and Sreevatsan S. Global-scale GWAS associates a subset of SNPs with animal-adapted variants in M. tuberculosis complex. BMC Med Genomics. (2023) 16:260. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01695-5
7. Wang M, Kong W, He B, Li Z, Song H, Shi P, et al. Vitamin D and the promoter methylation of its metabolic pathway genes in association with the risk and prognosis of tuberculosis. Clin Epigenetics. (2018) 10:118. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0552-6
8. Chen YC, Fang YT, Wu CC, Chao TY, Wang YH, Tseng CC, et al. Increased autophagy activity regulated by LC3B gene promoter DNA methylation is associated with progression to active pulmonary tuberculosis disease. Respir Res. (2025) 26:86. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03149-1
9. Cai XQ, Huang Q, and Zhang TP. The methylation in B7-H4 and BTLA genes are associated with the risk of pulmonary tuberculosis. Immunotargets Ther. (2023) 12:149–63. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S434403
10. Papanicolau-Sengos A and Aldape K. DNA methylation profiling: an emerging paradigm for cancer diagnosis. Annu Rev Pathol. (2022) 17:295–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-042220-022304
11. Shi Y, Chang C, Xu L, Jiang P, Wei K, Zhao J, et al. Circulating DNA methylation level of CXCR5 correlates with inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2023) 11:e902. doi: 10.1002/iid3.902
12. Harling K, Adankwah E, Güler A, Afum-Adjei Awuah A, Adu-Amoah L, Mayatepek E, et al. Constitutive STAT3 phosphorylation and IL-6/IL-10 co-expression are associated with impaired T-cell function in tuberculosis patients. Cell Mol Immunol. (2019) 16:275–87. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2018.5
13. Sun J, Zhang Q, Yang G, Li Y, Fu Y, Zheng Y, et al. The licorice flavonoid isoliquiritigenin attenuates Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced inflammation through Notch1/NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 294:115368. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115368
14. Hu X, Zhou J, Chen X, Zhou Y, Song X, Cai B, et al. Pathway analyses identify novel variants in the WNT signaling pathway associated with tuberculosis in chinese population. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:28530. doi: 10.1038/srep28530
15. Wu X, Deng G, Hao X, Li Y, Zeng J, Ma C, et al. A caspase-dependent pathway is involved in wnt/b-catenin signaling promoted apoptosis in bacillus calmette-guerin infected RAW264.7 macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. (2014) 15:5045–62. doi: 10.3390/ijms15035045
16. Huang Q, Wang CC, Liu YG, Zhao CM, Zhang TP, Liu Y, et al. Clinical relevance of genetic polymorphisms in WNT signaling pathway (SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, WIF-1, DKK-1, LRP5, LRP6) on pulmonary tuberculosis in a Chinese population. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1011700. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1011700
17. Bagni G, Biancalana E, Chiara E, Costanzo I, Malandrino D, Lastraioli E, et al. Epigenetics in autoimmune diseases: Unraveling the hidden regulators of immune dysregulation. Autoimmun Rev. (2025) 24:103784. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2025.103784
18. Pulliero A, Cassatella G, Astuni P, Khalid Z, Fiordoro S, and Izzotti A. The role of microRNA expression and DNA methylation in HPV-related cervical cancer: A systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:12714. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312714
19. Qin Y, Li T, An P, Ren Z, Xi J, and Tang B. Important role of DNA methylation hints at significant potential in tuberculosis. Arch Microbiol. (2024) 206:177. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03888-7
20. Weiss G, Schlegel A, Kottwitz D, König T, and Tetzner R. Validation of the SHOX2/PTGER4 DNA methylation marker panel for plasma-based discrimination between patients with Malignant and nonmalignant lung disease. J Thorac Oncol. (2017) 12:77–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.08.123
21. Zhang J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Chen L, Mo W, Yang Q, et al. Exploring TSPAN4 promoter methylation as a diagnostic biomarker for tuberculosis. Front Genet. (2024) 15:1380828. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1380828
22. Su SH, Cai XQ, Li YH, Xu AH, Huang Q, Niu H, et al. The important roles of ERAP1, ERAP2 genes polymorphisms and their DNA methylation levels in pulmonary tuberculosis. BMC Infect Dis. (2025) 25:178. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10452-1
23. Wadey KS, Somos A, Leyden G, Blythe H, Chan J, Hutchinson L, et al. Pro-inflammatory role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in endothelial dysfunction. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 9:1059124. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1059124
24. Kuncewitch M, Yang WL, Molmenti E, Nicastro J, Coppa GF, and Wang P. Wnt agonist attenuates liver injury and improves survival after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. Shock. (2013) 39:3–10. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3182764fe8
25. Brandenburg J and Reiling N. The wnt blows: on the functional role of wnt signaling in mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and beyond. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:635. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00635
26. Xiong K, Niu J, Zheng R, Liu Z, Song Y, Wang L, et al. The role of β-catenin in th1 immune response against tuberculosis and profiles of expression in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:6625855. doi: 10.1155/2021/6625855
27. Zhou J, Xiong KL, Wang HX, Sun WW, Ke H, Zhang SJ, et al. BATF2/SINHCAF regulates the quantity and function of macrophages infected with Mycobacterium Tuberculosis via regulation of TTC23 through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 288:138639. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138639
28. Zou YC, Wang ZJ, Shao LC, Xia ZH, Lan YF, Yu ZH, et al. DNA methylation of DKK-1 may correlate with pathological bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2023) 11:e911. doi: 10.1002/iid3.911
29. Tompa M, Kajtar B, Galik B, Gyenesei A, and Kalman B. DNA methylation and protein expression of Wnt pathway markers in progressive glioblastoma. Pathol Res Pract. (2021) 222:153429. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153429
30. Boughanem H, Pilo J, García-Flores LA, Arranz I, Ramos-Fernández M, Ortega-Castan M, et al. Identification of epigenetic silencing of the SFRP2 gene in colorectal cancer as a clinical biomarker and molecular significance. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:509. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05329-x
31. Kafle A, Suttiprapa S, Muhammad M, Tenorio JCB, Mahato RK, Sahimin N, et al. Epigenetic biomarkers and the wnt/β-catenin pathway in opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma: A scoping review on therapeutic opportunities. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2024) 18:e0012477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012477
Keywords: pulmonary tuberculosis, DNA methylation, WNT signaling pathway genes, tuberculosis, epigenetics
Citation: Wang H, Wang C-C, Huang Q, Xiao Y, Han Y, Xie L, Liu Y and Xiong Y-J (2025) Diagnostic potential of WNT signaling gene methylation in pulmonary tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 16:1639997. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1639997
Received: 03 June 2025; Accepted: 20 October 2025;
Published: 18 November 2025.
Edited by:
Shibali Das, Washington University in St. Louis, United StatesReviewed by:
Hao Zhang, Washington University in St. Louis, United StatesMohammed A. Alfahdawi, Al Maaref University College, Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Huang, Xiao, Han, Xie, Liu and Xiong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Liu, eWFubGl1QHFodS5lZHUuY24=; Yan-Jun Xiong, Njc0NTM5MzdAcXEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Hua Wang1†
Hua Wang1† Chao-Cai Wang
Chao-Cai Wang Qian Huang
Qian Huang Yan Liu
Yan Liu